Agusan del Norte
Agusan del Norte | |
|---|---|
| Province of Agusan del Norte | |
 Location in the Philippines | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Region | Caraga |
| Founded | 17 June 1967 |
| Capital |
|
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlalawigan |
| • Governor | Maria Angelica Rosedell Amante-Matba (Liberal) |
| • Vice Governor | Ramon AG Bungabong (Liberal) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,730.24 km2 (1,054.15 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 48th out of 81 |
| (excluding Butuan City) | |
| Population (2020 census)[2] | |
| • Total | 387,503 |
| • Rank | 64th out of 81 |
| • Density | 140/km2 (370/sq mi) |
| • Rank | 62nd out of 81 |
| (excluding Butuan City) | |
| Divisions | |
| • Independent cities | 1 |
| • Component cities | |
| • Municipalities | |
| • Barangays | 166 including independent cities: 252 |
| • Districts | 1st and 2nd districts of Agusan del Norte (shared with Butuan City) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PHT) |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)85 |
| ISO 3166 code | PH-AGN |
| Spoken languages | |
| Website | www |
| ‡ As per RA 8811, Cabadbaran is the officially-designated capital of the province. However, the provincial government still holds office in Butuan City, pending the actual transfer of provincial offices to the new capital. | |
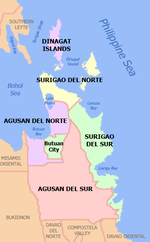
Agusan del Norte (Butuanon: Probinsya hong Agusan del Norte; Cebuano: Amihanang Agusan; Filipino: Hilagang Agusan) is a province in the Philippines located in the Caraga region of Mindanao. Its capital is the city of Cabadbaran and it is bordered on the northeast by Surigao del Norte; mid-east by Surigao del Sur; southeast by Agusan del Sur, and southwest by Misamis Oriental. It faces Butuan Bay, part of the Bohol Sea, to the northwest.
History
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2016) |
Spanish and American era

Prior to its creation as an independent province, Agusan, as it was once undivided, was under the jurisdiction of Surigao province during the Spanish colonial period. In 1911, Agusan was separated from Surigao by the American government, creating the Agusan province.[3]
World War II
During World War II in 1942, the Japanese Imperial forces landed in Northern Agusan.[further explanation needed]
In 1945, Filipino soldiers of the 6th, 10th, 101st, 102nd, 103rd, 107th and 110th Infantry Division of the Philippine Commonwealth Army and the 10th Infantry Regiment of the Philippine Constabulary together with the recognized Agusan guerrilla fighter units against the Japanese forces beginning the liberation in Northern Agusan during World War II.[further explanation needed]
During the war, a unit of the joint Philippine-American defense force were located at Manot, Talacogon, in the interior of the Agusan Valley.
Independence
In 1967, Republic Act 4979 divided Agusan into two independent provinces: Agusan del Norte and Agusan del Sur.[4]
On August 16, 2000, the seat of provincial government was transferred from Butuan City to Cabadbaran through Republic Act 8811,[5] although the province is yet to complete the transfer of provincial services and functions to the new capital.
Geography
Agusan del Norte is situated in Mindanao's western section of Caraga. It is bordered on the northwest by the Butuan Bay; northeast by Surigao del Norte; mid-east by Surigao del Sur; southeast by Agusan del Sur, and southwest by Misamis Oriental. Agusan del Norte has a total land area of 2,730.24 square kilometres or 1,054.15 square miles. When Butuan City is included for geographical purposes, the province's land area is 3,546.86 square kilometres (1,369.45 sq mi).[6]

The central portion of the province forms the lower basin of the third longest river in the country, the Agusan, its mouth located at the Butuan Bay. Consequently, the terrain surrounding the river features flat to rolling lands. Mountainous terrain dominate the northeastern and western areas.[3]
The country's fourth largest lake, Lake Mainit is situated at the northern border between the province of Surigao del Norte.[7]
Administrative divisions
Agusan del Norte comprises 10 municipalities and 1 component city.
The city of Cabadbaran is the officially-designated capital of the province per Republic Act 8811.[5] The highly urbanized city of Butuan is geographically within but administratively independent from the province.
| City or municipality [i] | Population | ±% p.a. | Area[6] | Density (2015) | Brgy. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (2015)[8] | (2010)[9] | km2 | sq mi | /km2 | /sq mi | |||||||
| 8°58′28″N 125°24′32″E / 8.9744°N 125.4090°E | Buenavista | 17.4% | 61,614 | 56,139 | +1.79% | 475.61 | 183.63 | 130 | 340 | 25 | ||
| 8°57′12″N 125°31′44″E / 8.9534°N 125.5288°E | Butuan | ‡ | — | 337,063 | 309,709 | +1.62% | 816.62 | 315.30 | 410 | 1,100 | 86 | |
| 9°07′22″N 125°32′05″E / 9.1228°N 125.5346°E | Cabadbaran | † | 20.8% | 73,639 | 69,241 | +1.18% | 214.44 | 82.80 | 340 | 880 | 31 | |
| 9°00′00″N 125°15′53″E / 8.9999°N 125.2648°E | Carmen | 5.9% | 20,839 | 19,781 | +1.00% | 311.02 | 120.09 | 67 | 170 | 8 | ||
| 9°20′33″N 125°30′59″E / 9.3425°N 125.5163°E | Jabonga | 6.5% | 23,184 | 23,833 | −0.52% | 293.00 | 113.13 | 79 | 200 | 15 | ||
| 9°27′29″N 125°34′32″E / 9.4581°N 125.5756°E | Kitcharao | 5.3% | 18,659 | 17,377 | +1.36% | 171.92 | 66.38 | 110 | 280 | 11 | ||
| 8°44′06″N 125°36′04″E / 8.7351°N 125.6010°E | Las Nieves | 8.0% | 28,414 | 26,856 | +1.08% | 582.69 | 224.98 | 49 | 130 | 20 | ||
| 9°01′21″N 125°31′04″E / 9.0225°N 125.5179°E | Magallanes | 5.9% | 21,007 | 21,481 | −0.42% | 44.31 | 17.11 | 470 | 1,200 | 8 | ||
| 8°59′18″N 125°20′27″E / 8.9884°N 125.3408°E | Nasipit | 11.8% | 41,957 | 40,663 | +0.60% | 144.40 | 55.75 | 290 | 750 | 19 | ||
| 9°03′06″N 125°35′06″E / 9.0518°N 125.5850°E | Remedios T. Romualdez | 4.5% | 16,058 | 15,735 | +0.39% | 79.15 | 30.56 | 200 | 520 | 8 | ||
| 9°15′55″N 125°33′37″E / 9.2654°N 125.5602°E | Santiago | 6.8% | 24,200 | 20,955 | +2.78% | 275.61 | 106.41 | 88 | 230 | 8 | ||
| 9°09′54″N 125°31′21″E / 9.1650°N 125.5226°E | Tubay | 7.0% | 24,932 | 20,426 | +3.87% | 138.09 | 53.32 | 180 | 470 | 13 | ||
| TOTAL [ii] | 354,503 | 332,487 | +1.23% | 2,730.24 | 1,054.15 | 130 | 340 | 166 | ||||
| † Provincial capital and component city | Municipality | |||||||||||
|
‡ Highly urbanized city (geographically within but independent from the province) | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 237,629 | — |
| 1995 | 267,411 | +2.24% |
| 2000 | 285,570 | +1.42% |
| 2007 | 314,027 | +1.32% |
| 2010 | 332,487 | +2.10% |
| 2015 | 354,503 | +1.23% |
| (excluding Butuan City) Source: PSA[8][9][10][11] | ||
The population of Agusan del Norte in the 2020 census was 387,503 people,[2] making it the country's 64th most populous province. It had a density of 140 inhabitants per square kilometre or 360 inhabitants per square mile.
When the highly urbanized city of Butuan is included for geographical purposes, the province's population is 691,566 people, with a density of 195 inhabitants per square kilometre (510/sq mi).
Religion
In 2013, the Diocese of Butuan (Catholic-Hierarchy) reported that Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion of the province comprising roughly 79% of the population.[citation needed] The remaining beliefs usually belong to other Christian denominations as well as Islam.
Economy
The economy of the province is dominantly agricultural, major crops of which include rice, corn, coconut, abaca, banana and mango.[12]
Government
Agusan del Norte has two congressional districts encompassing its 10 municipalities and 1 component city, as well as the highly urbanized city of Butuan.
| District | Representative[13] | City or municipality | District population (2015) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | Lawrence Lemuel H. Fortun | 365,477 | |
| 2nd | Erlpe John Amante | 326,089 |
Tourism
The province has many beaches in Cabadbaran and the municipalities of Carmen, Buenavista, and Nasipit. Mount Hilong-Hilong, one of the tallest in the province, is located in Cabadbaran.
From the top of Prayer Mountain (Mount Pongkay), visitors can have a panoramic view of Cabadbaran which includes buildings, churches, rivers and the sea. The Agusan River, the longest in Mindanao and the third longest in the Philippines is in Butuan City. Looming southwest of the Agusan Valley is Mount Mayapay, a mountain plateau. The ancient Balangay boats were found in Butuan, excavated in the Balangay Shrine across the Masao River from Bood Promontory. They played a major role because of Butuan being a port city. Since its discovery, the Balangays have become an icon of Butuan. The Kaya ng Pinoy, Inc. recreated the Balangay boats and have sailed it as part of their project, the Balangay Voyage.
References
- ^ "List of Provinces". PSGC Interactive. Makati City, Philippines: National Statistical Coordination Board. Retrieved 3 April 2014.
- ^ a b Census of Population (2020). "Caraga". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ^ a b Lancion, Jr., Conrado M.; cartography by de Guzman, Rey (1995). "The Provinces; Agusan del Norte". Fast Facts about Philippine Provinces (The 2000 Millenium ed.). Makati, Metro Manila, Philippines: Tahanan Books. p. 18. ISBN 971-630-037-9. Retrieved 4 December 2015.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Republic Act No. 4979; An Act Creating the Provinces of Agusan del Norte and Agusan del Sur". The LawPhil Project. 17 June 1967. Retrieved 4 December 2015.
Section 1. The Province of Agusan is hereby divided into two provinces, to be known as Agusan del Norte and Agusan del Sur.
- ^ a b "Republic Act No. 8811; An Act Transferring the Capital and Seat of Government of the Province of Agusan del Norte from Butuan City to the Municipality of Cabadbaran, Agusan del Norte" (PDF). Congress of the Philippines (official website). Retrieved 4 December 2015.
- ^ a b "Province: Agusan del Norte". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- ^ Catoto, Roel (2 October 2014). "Caraga lawmakers push for Lake Mainit Development Authority". MindaNews. Retrieved 22 April 2016.
Lake Mainit, the fourth largest lake in the country, occupies an area of 17,060 hectare and straddles the provinces of Agusan del Norte and Surigao del Norte.
- ^ a b Census of Population (2015). "Caraga". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ a b Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Caraga" (PDF). Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. National Statistics Office. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^ Census of Population and Housing (2010). Population and Annual Growth Rates for The Philippines and Its Regions, Provinces, and Highly Urbanized Cities (PDF). National Statistics Office. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^ Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Caraga". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. National Statistics Office.
- ^ "Agricultural Crops". Official Web Site of Agusan del Norte. Retrieved 18 March 2016.
Major agricultural crops in Agusan del Norte are rice, corn, coconut, abaca, banana and mango. The province also produces cassava, durian, pineapple, coffee, vegetables and root crops. The three highest producing crops are coconut, banana and rice with corresponding production of 75,184.35 MT, 43,924.92 MT and 26,151.81 MT, respectively.
- ^ "House Members; 17th Congress". House of Representatives of the Philippines. Retrieved 30 July 2016.
External links
 Media related to Agusan del Norte at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Agusan del Norte at Wikimedia Commons Geographic data related to Agusan del Norte at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Agusan del Norte at OpenStreetMap- Official website of the Provincial Government of Agusan del Norte