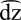Voiced alveolar affricate
Appearance
| Voiced alveolar affricate | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| d͡z | |||
| d͜z | |||
| Audio sample | |||
| Encoding | |||
| Entity (decimal) | ʣ | ||
| Unicode (hex) | U+02A3 | ||
| X-SAMPA | dz | ||
| |||
The voiced alveolar affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The sound is transcribed in the International Phonetic Alphabet with ⟨d͡z⟩ or ⟨d͜z⟩ (formerly ⟨ʣ⟩).
Features
Features of the voiced alveolar affricate:
- Its manner of articulation is sibilant affricate, which means it is produced by first stopping the air flow entirely, then directing it with the tongue to the sharp edge of the teeth, causing high-frequency turbulence.
- Its place of articulation is alveolar, which means it is articulated with either the tip or the blade of the tongue at the alveolar ridge, termed respectively apical and laminal.
- Its phonation is voiced, which means the vocal cords vibrate during the articulation.
- It is a central consonant, which means it is produced by directing the airstream along the center of the tongue, rather than to the sides.
- Its airstream mechanism is pulmonic, which means it is articulated by pushing air solely with the intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles, as in most sounds.
Occurrence
| Language | Word | IPA | Meaning | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abkhaz | аʒы | [ɑˈd͡zɨ] | 'water' | See Abkhaz phonology | |
| Adyghe | дзэлӀы | 'soldier' | |||
| Albanian | [[[Albanian alphabet|xehe]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [d͡zɛhɛ] | 'mineral' | ||
| Arabic | Najdi | قـليب | [d͡zɛ̝lib] | 'well' | corresponds to /q/, /g/, and/or /dʒ/ in other dialects. |
| Armenian | Eastern | ձուկ | 'snow' | ||
| Western | ծակ | [d͡zɑɡ] | 'hole' | ||
| Azerbaijani | some Western dialects | example needed | -- | -- | corresponds to /d͡ʒ/ and/or /ɟ/ in other dialects. |
| Berber | Kabyle | Lz̗ayer | [ld͡zajər] | 'Algeria' | |
| Catalan[1] | [[[Catalan orthography|dotze]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [ˈdodd͡zə] | 'twelve' | See Catalan phonology | |
| French | Quebec | [[[French orthography|samedi]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [samˈd͡zi] | 'Saturday' | See Quebec French phonology |
| Georgian[2] | ძვალი | [d͡zvɑli] | 'bone' | ||
| Hebrew | תזונה | [d͡zuna] | 'nutrition' | See Modern Hebrew phonology | |
| Hungarian | [[[Hungarian orthography|bodza]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [bod͡zːɒ] | 'elderberry' | See Hungarian phonology | |
| Italian[3] | [[[Italian alphabet|zero]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [ˈd̪͡z̪ɛːɾo] | 'zero' | <z> may also represent /ts/. See Italian phonology | |
| Iu Mien | [[[Latin alphabet|nzoc]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [d͡zò] | 'drum' | ||
| Japanese | 水/[[[Romanization of Japanese|mizu]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [mʲiˈd͡zɯ] | 'water' | Some speakers. See Japanese phonology | |
| Kabardian | дзы | [d͡zɪ] | 'to throw' | ||
| Macedonian | ѕвезда | [ˈd͡zvɛzda] | 'star' | See Macedonian phonology | |
| Ngwe | Nwametaw dialect | [mə̀d͡zə̀] | 'path' | ||
| Occitan | Rhodanien Provençal | [[[Latin alphabet|joine]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [ˈd͡zujne] | 'young' | |
| Pashto | پنځه | [pind͡zə] | 'five' | ||
| Polish[4] | [[[Polish orthography|dzwon]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | 'bell' | See Polish phonology | ||
| Northern Qiang | ? | [ɣd͡zə] | 'rabbit' | ||
| Russian | плацдарм | [plɐd͡zˈdarm] | 'bridge-head' | Allophone of /t͡s/ before voiced consonants. See Russian phonology | |
| Slovak | [[[Slovak alphabet|sadzba]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [sad͡zba] | 'tariff' | ||
| Ubykh | [məˈd͡za] | 'light' | See Ubykh phonology | ||
| Ukrainian | дзвін | [d͡zwin] | 'bell' | See Ukrainian phonology | |
| West Frisian | [[[Latin alphabet|widze]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [ʋɪd͡zǝ] | 'cradle' | ||
| Yi | ꋩ/[[[Yi script|zzy]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [d͡zɪ˧] | 'ride' | ||
See also
References
- ^ Hualde (1992:370)
- ^ Shosted & Chikovani (2006:255)
- ^ Rogers & d'Arcangeli (2004:117)
- ^ Jassem (2003:103)
Bibliography
- Hualde, José (1992), Catalan, Routledge, ISBN 0-415-05498-2
- Jassem, Wiktor (2003), "Polish", Journal of the International Phonetic Association, 33 (1): 103–107
- Rogers, Derek; d'Arcangeli, Luciana (2004), "Italian", Journal of the International Phonetic Association, 34 (1): 117–121
- Shosted, Ryan K.; Vakhtang, Chikovani (2006), "Standard Georgian", Journal of the International Phonetic Association, 36 (2): 255–264