From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Prochloraz Trade names Abavit, Ascurit, Dibavit, Mirage, Octave, Omega, Prelude, Rival, Sporgon, Sportak, Sprint, Tenor[ 1] [ 2]
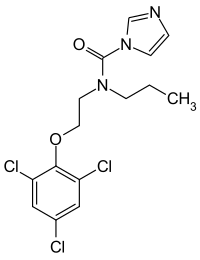
N -propyl-N -[2-(2,4,6-trichlorophenoxy)ethyl]imidazole-1-carboxamide
CAS Number PubChem CID ChemSpider UNII KEGG ChEBI ChEMBL CompTox Dashboard (EPA ) ECHA InfoCard 100.060.885 Formula C 15 H 16 Cl 3 N 3 O 2 Molar mass 376.662 g/mol g·mol−1 3D model (JSmol )
CCCN(CCOC1=C(C=C(C=C1Cl)Cl)Cl)C(=O)N2C=CN=C2
InChI=1S/C15H16Cl3N3O2/c1-10(2)21(15(22)20-4-3-19-9-20)5-6-23-14-12(17)7-11(16)8-13(14)18/h3-4,7-10H,5-6H2,1-2H3
Key:XJABPYGRRIVUOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Prochloraz , brand name Sportak , is an imidazole fungicide that was introduced in 1978[ 3] Europe , Australia , Asia , and South America within gardening and agriculture to control the growth of fungi .[ 4] [ 5] United States .[ 5] azole fungicides, prochloraz is an inhibitor of the enzyme lanosterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51A1), which is necessary for the production of ergosterol – an essential component of the fungal cell membrane – from lanosterol .[ 6] broad-spectrum , protective and curative fungicide, effective against Alternaria Botrytis Erysiphe Helminthosporium Fusarium Pseudocerosporella Pyrenophora Rhynchosporium Septoria [ 5] [ 2]
Like many imidazole and triazole fungicides and antifungal medications, prochloraz is not particularly selective in its actions.[ 4] [ 6] antagonist of the androgen and estrogen receptors , as an agonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor , and as an inhibitor of enzymes in the steroidogenesis pathway such as CYP17A1 and aromatase .[ 4] [ 6] reproductive malformations in mice.[ 4] [ 6] endocrine disruptor .[ 4] [ 6]
See also
References
^ [Anonymous AC05372279] (1997). [Consolidated list of products whose consumption and/or sale have been banned, withdrawn, severely restricted or not approved by governments / Pharmaceuticals ] ; Consolidated list of products whose consumption and/or sale have been banned, withdrawn, severely restricted or not approved by governments. Pharmaceuticals ISBN 978-92-1-130219-6 {{cite book }}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link )^ a b G. W. A. Milne (2 September 2005). Gardner's Commercially Important Chemicals: Synonyms, Trade Names, and Properties ISBN 978-0-471-73661-5 ^ Bill Carlile (28 September 2006). Pesticide Selectivity, Health and the Environment ISBN 978-1-139-45756-9 ^ a b c d e Vinggaard AM, Hass U, Dalgaard M, Andersen HR, Bonefeld-Jørgensen E, Christiansen S, Laier P, Poulsen ME (2006). "Prochloraz: an imidazole fungicide with multiple mechanisms of action". Int. J. Androl . 29 (1): 186–92. doi :10.1111/j.1365-2605.2005.00604.x . PMID 16466539 . ^ a b c Kalyani Paranjape; Vasant Gowariker; V N Krishnamurthy; Sugha Gowariker (22 December 2014). The Pesticide Encyclopedia ISBN 978-1-78064-014-3 ^ a b c d e Philippa D. Darbre (21 March 2015). Endocrine Disruption and Human Health ISBN 978-0-12-801120-1
External links
Prochloraz
AR Tooltip Androgen receptor
Agonists SARMs Tooltip Selective androgen receptor modulator Antagonists
GPRC6A
ER Tooltip Estrogen receptor
Agonists
Steroidal: 2-Hydroxyestradiol 2-Hydroxyestrone 3-Methyl-19-methyleneandrosta-3,5-dien-17β-ol 3α-Androstanediol 3α,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel 3β,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel 3α-Hydroxytibolone 3β-Hydroxytibolone 3β-Androstanediol 4-Androstenediol 4-Androstenedione 4-Fluoroestradiol 4-Hydroxyestradiol 4-Hydroxyestrone 4-Methoxyestradiol 4-Methoxyestrone 5-Androstenediol 7-Oxo-DHEA 7α-Hydroxy-DHEA 7α-Methylestradiol 7β-Hydroxyepiandrosterone 8,9-Dehydroestradiol 8,9-Dehydroestrone 8β-VE2 10β,17β-Dihydroxyestra-1,4-dien-3-one (DHED) 11β-Chloromethylestradiol 11β-Methoxyestradiol 15α-Hydroxyestradiol 16-Ketoestradiol 16-Ketoestrone 16α-Fluoroestradiol 16α-Hydroxy-DHEA 16α-Hydroxyestrone 16α-Iodoestradiol 16α-LE2 16β-Hydroxyestrone 16β,17α-Epiestriol (16β-hydroxy-17α-estradiol) 17α-Estradiol (alfatradiol )17α-Dihydroequilenin 17α-Dihydroequilin 17α-Epiestriol (16α-hydroxy-17α-estradiol) 17α-Ethynyl-3α-androstanediol 17α-Ethynyl-3β-androstanediol 17β-Dihydroequilenin 17β-Dihydroequilin 17β-Methyl-17α-dihydroequilenin Abiraterone Abiraterone acetate Alestramustine Almestrone Anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone and esters , methyltestosterone , metandienone (methandrostenolone) , nandrolone and esters , many others; via estrogenic metabolites)Atrimustine Bolandiol Bolandiol dipropionate Butolame Clomestrone Cloxestradiol
Conjugated estriol Conjugated estrogens Cyclodiol Cyclotriol DHEA DHEA-S ent -EstradiolEpiestriol (16β-epiestriol, 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol) Epimestrol Equilenin Equilin ERA-63 (ORG-37663) Esterified estrogens Estetrol Estradiol
Estramustine Estramustine phosphate Estrapronicate Estrazinol Estriol
Estrofurate Estrogenic substances Estromustine Estrone
Etamestrol (eptamestrol) Ethinylandrostenediol
Ethinylestradiol
Ethinylestriol Ethylestradiol Etynodiol Etynodiol diacetate Hexolame Hippulin Hydroxyestrone diacetate Lynestrenol Lynestrenol phenylpropionate Mestranol Methylestradiol Moxestrol Mytatrienediol Nilestriol Norethisterone Noretynodrel Orestrate Pentolame Prodiame Prolame Promestriene RU-16117 Quinestradol Quinestrol Tibolone Xenoestrogens: Anise -related (e.g., anethole , anol , dianethole , dianol , photoanethole )Chalconoids (e.g., isoliquiritigenin , phloretin , phlorizin (phloridzin) , wedelolactone )Coumestans (e.g., coumestrol , psoralidin )Flavonoids (incl. 7,8-DHF , 8-prenylnaringenin , apigenin , baicalein , baicalin , biochanin A , calycosin , catechin , daidzein , daidzin , ECG , EGCG , epicatechin , equol , formononetin , glabrene , glabridin , genistein , genistin , glycitein , kaempferol , liquiritigenin , mirificin , myricetin , naringenin , penduletin , pinocembrin , prunetin , puerarin , quercetin , tectoridin , tectorigenin )Lavender oil Lignans (e.g., enterodiol , enterolactone , nyasol (cis -hinokiresinol) )Metalloestrogens (e.g., cadmium )Pesticides (e.g., alternariol , dieldrin , endosulfan , fenarimol , HPTE , methiocarb , methoxychlor , triclocarban , triclosan )Phytosteroids (e.g., digitoxin (digitalis ), diosgenin , guggulsterone )Phytosterols (e.g., β-sitosterol , campesterol , stigmasterol )Resorcylic acid lactones (e.g., zearalanone , α-zearalenol , β-zearalenol , zearalenone , zeranol (α-zearalanol) , taleranol (teranol, β-zearalanol) )Steroid -like (e.g., deoxymiroestrol , miroestrol )Stilbenoids (e.g., resveratrol , rhaponticin )Synthetic xenoestrogens (e.g., alkylphenols , bisphenols (e.g., BPA , BPF , BPS ), DDT , parabens , PBBs , PHBA , phthalates , PCBs )Others (e.g., agnuside , rotundifuran ) MixedSERMs Tooltip Selective estrogen receptor modulators ) Antagonists
Coregulator-binding modulators: ERX-11
GPER Tooltip G protein-coupled estrogen receptor
Agonists Antagonists Unknown