Slavery
| Part of a series on |
| Slavery |
|---|
 |
Slavery is a system under which people are treated as property to be bought and sold, and are forced to work.[1] Slaves can be held against their will from the time of their capture, purchase or birth, and deprived of the right to leave, to refuse to work, or to demand compensation. Historically, slavery was institutionally recognized by most societies; in more recent times, slavery has been outlawed in all countries, but it continues through the practices of debt bondage, indentured servitude, serfdom, domestic servants kept in captivity, certain adoptions in which children are forced to work as slaves, child soldiers, and forced marriage.[2] Slavery is officially illegal in all countries, but there are still an estimated 20 million to 30 million slaves worldwide.[3][4] Mauritania was the last jurisdiction to officially outlaw slavery (in 1981/2007), but about 10% to 20% of its population is estimated to live in slavery.[5][6]
Slavery predates written records and has existed in many cultures.[7] Most slaves today are debt slaves, largely in South Asia, who are under debt bondage incurred by lenders, sometimes even for generations.[8] Human trafficking is primarily used for forcing women and children into sex industries.[9]
Terminology
The English word slave comes from Old French sclave, from the Medieval Latin sclavus, from the Byzantine Greek σκλάβος, which, in turn, comes from the ethnonym Slav, because in some early mediaeval wars many Slavs were captured and enslaved.[10][11] An older theory connected it to the Greek verb skyleúo 'to strip a slain enemy'.[12]
The word used to call a slave has also been utilized to express general dependency to someone else.[13][14] In many cases, such as in ancient Persia, the situation and lives of such slaves could be better than those of other common citizens.[15]
Types

Chattel slavery
Chattel slavery, also called traditional slavery, is so named because people are treated as the chattel (personal property) of an owner and are bought and sold as if they were commodities. It is the original form of slavery and the least prevalent form of slavery today.[citation needed]
Bonded labor
Debt bondage or bonded labor occurs when a person pledges himself or herself against a loan.[16] The services required to repay the debt, and their duration, may be undefined.[16] Debt bondage can be passed on from generation to generation, with children required to pay off their parents' debt.[16] It is the most widespread form of slavery today.[8] Debt bondage is most prevalent in South Asia.[17]
Forced labor

Forced labor occurs when an individual is forced to work against his or her will, under threat of violence or other punishment, with restrictions on their freedom.[8] Human trafficking is primarily for prostituting women and children[9] and is the fastest growing form of forced labor,[8] with Thailand, Cambodia, India, Brazil and Mexico have been identified as leading hotspots of commercial sexual exploitation of children.[18]
The term 'forced labor' is also used to describe all types of slavery and may also include institutions not commonly classified as slavery, such as serfdom, conscription and penal labor.
Forced marriage
A forced marriage is a marriage in which one or both of the parties is married against their will. In many places, the line between forced marriage and consensual marriage becomes blurred, because the social norms of many cultures dictate that one should never oppose the desire of one's parents/relatives in regard to the choice of a spouse; in such cultures it is not necessary for violence, threats, intimidation etc. to occur, the person simply "consents" to the marriage even if he/she does not want it, out of the implied social pressure and duty. The customs of bride price and dowry, that exist in many parts of the world, can lead to buying and selling people into marriage.[19][20] Forced marriage is still practiced in parts of the world such South Asia, East Asia and Africa. Forced marriages also occur in immigrant communities in Europe, United States, Canada and Australia.[21][22][23][24] Marriage by abduction occurs in many place in the world today, with a national average of 69% of marriages in Ethiopia being through abduction.[25]
A sham marriage is a marriage of convenience entered into with the intent of obtaining various social or legal advantages (often tied to immigration status). While many of these marriages occur with the consent of both parties, in the European Union there exists a trafficking industry which supplies brides (often from former Communist countries which are EU members—especially the Baltic States) to foreign students or workers in EU countries (often from the Asian continent) so that these men can remain in the EU.[26][27][28]
Early and forced marriage are defined as forms of modern-day slavery by the International Labour Organisation.[29] The countries with the highest rates of child marriage are: Niger (75%), Central African Republic and Chad (68%), and Bangladesh (66%).[30]
History


Early history
Evidence of slavery predates written records, and has existed in many cultures.[7] Prehistoric graves from about 8000 BC in Lower Egypt suggest that a Libyan people enslaved a San-like tribe.[dubious ][Capoid remains not found this far north][31] Slavery is rare among hunter-gatherer populations.[citation needed] Mass slavery also requires economic surpluses and a high population density to be viable. Due to these factors, the practice of slavery would have only proliferated after the invention of agriculture during the Neolithic Revolution about 11,000 years ago.[32]
In the earliest known records slavery is treated as an established institution. The Code of Hammurabi (ca. 1760 BC), for example, prescribed death for anyone who helped a slave to escape or who sheltered a fugitive.[33] The Bible mentions slavery as an established institution.[7]
Slavery was known in almost every ancient civilization, and society, including Sumer, Ancient Egypt, Ancient China, the Akkadian Empire, Assyria, Ancient India, Ancient Greece, the Roman Empire, the Islamic Caliphate, the Hebrew kingdoms in Palestine, and the pre-Columbian civilizations of the Americas.[7] Such institutions included debt-slavery, punishment for crime, the enslavement of prisoners of war, child abandonment, and the birth of slave children to slaves.[34]
Classical Antiquity

Records of slavery in Ancient Greece go as far back as Mycenaean Greece. It is certain that Classical Athens had the largest slave population, with as many as 80,000 in the 6th and 5th centuries BC;[35] two to four-fifths of the population were slaves.[36] As the Roman Republic expanded outward, entire populations were enslaved, thus creating an ample supply from all over Europe and the Mediterranean. Greeks, Illyrians, Berbers, Germans, Britons, Thracians, Gauls, Jews, Arabs, and many more were slaves used not only for labour, but also for amusement (e. g. gladiators and sex slaves). This oppression by an elite minority eventually led to slave revolts (see Roman Servile Wars); the Third Servile War led by Spartacus being the most famous and severe.
By the late Republican era, slavery had become a vital economic pillar in the wealth of Rome, as well as a very significant part of Roman society.[37] At the least, some 25% of the population of Ancient Rome was enslaved.[38] According to some scholars, slaves represented 35% or more of Italy's population.[39] In the city of Rome alone, under the Roman Empire, there were about 400,000 slaves.[40] During the millennium from the emergence of the Roman Empire to its eventual decline, at least 100 million people were captured or sold as slaves throughout the Mediterranean and its hinterlands.[41]
Middle Ages
Medieval Europe

Large-scale trading in slaves was mainly confined to the South and East of early medieval Europe: the Byzantine Empire and the Muslim world were the destinations, while pagan Central and Eastern Europe (along with the Caucasus and Tartary) were important sources. Viking, Arab, Greek, and Radhanite Jewish merchants were all involved in the slave trade during the Early Middle Ages.[42][43][44] The trade in European slaves reached a peak in the 10th century following the Zanj rebellion which dampened the use of African slaves in the Arab world.[45][46]
Medieval Spain and Portugal were the scene of almost constant Muslim invasion of the predominantly Christian area. Periodic raiding expeditions were sent from Al-Andalus to ravage the Iberian Christian kingdoms, bringing back booty and slaves. In raid against Lisbon, Portugal in 1189, for example, the Almohad caliph Yaqub al-Mansur took 3,000 female and child captives, while his governor of Córdoba, in a subsequent attack upon Silves, Portugal in 1191, took 3,000 Christian slaves.[47] From the 11th to the 19th century, North African Barbary Pirates engaged in Razzias, raids on European coastal towns, to capture Christian slaves to sell at slave markets in places such as Algeria and Morocco.[48][49]

In Britain, slavery continued to be practiced following the fall of Rome and sections of Hywel the Good's laws dealt with slaves in medieval Wales. The trade particularly picked up after the Viking invasions, with major markets at Chester[50] and Bristol[51] supplied by Danish, Mercian, and Welsh raiding of one another's borderlands. At the time of the Domesday Book (1086), nearly 10% of the English population were slaves.[52] Slavery in early medieval Europe was so common that the Roman Catholic Church repeatedly prohibited it — or at least the export of Christian slaves to non-Christian lands was prohibited at e. g. the Council of Koblenz (922), the Council of London (1102), and the Council of Armagh (1171).[53] In 1452, Pope Nicholas V issued the papal bull Dum Diversas, granting the kings of Spain and Portugal the right to reduce any "Saracens, pagans and any other unbelievers" to perpetual slavery, legitimizing the slave trade as a result of war.[54] The approval of slavery under these conditions was reaffirmed and extended in his Romanus Pontifex bull of 1455. However, Pope Paul III forbade enslavement of the native Americans in 1537 in his papal bull Sublimus Dei.[55] Dominican friars who arrived at the Spanish settlement at Santo Domingo strongly denounced the enslavement of the local native Americans. Along with other priests, they opposed their treatment as unjust and illegal in an audience with the Spanish king and in the subsequent royal commission.[56]

The Byzantine-Ottoman wars and the Ottoman wars in Europe brought large numbers of slaves into the Islamic world.[58] From the mid to late 14th, through early 18th centuries, the Ottoman devşirme–janissary system enslaved and forcibly converted to Islam an estimated 500,000 to one million non–Muslim (primarily Balkan Christian) adolescent males.[59] After the Battle of Lepanto approximately 12,000 Christian galley slaves were freed from the Ottoman fleet.[60] A few years later Cervantes, who later wrote the famous book Don Quixote, was captured by corsairs and enslaved in Algiers, attempted to escape and was eventually ransomed; he wrote about the plight of Christian slaves in his fiction. Eastern Europe suffered a series of Tatar invasions, the goal of which was to loot and capture slaves into jasyr.[61] Seventy-five Crimean Tatar raids were recorded into Poland–Lithuania between 1474 and 1569.[62] There were more than 100,000 Russian captives in the Kazan Khanate alone in 1551.[63]
Approximately 10–20% of the rural population of Carolingian Europe consisted of slaves.[64] In Western Europe slavery largely disappeared by the later Middle Ages.[65] The trade of slaves in England was made illegal in 1102,[66] although England went on to become very active in the lucrative Atlantic slave trade from the seventeenth to the early nineteenth century. Thralldom in Scandinavia was finally abolished in the mid-14th century.[67] Slavery persisted longer in Eastern Europe. Slavery in Poland was forbidden in the 15th century; in Lithuania, slavery was formally abolished in 1588; they were replaced by the second serfdom. In Kievan Rus and Muscovy, the slaves were usually classified as kholops.
Islamic world

In early Islamic states of the Western Sudan (present-day West Africa), including Ghana (750–1076), Mali (1235–1645), Segou (1712–1861), and Songhai (1275–1591), about a third of the population were enslaved.[69]
Ibn Battuta indicates several times that he was given or purchased slaves.[70] The great 14th-century scholar Ibn Khaldun, wrote: "the Black nations are, as a rule, submissive to slavery, because (Blacks) have little that is (essentially) human and possess attributes that are quite similar to those of dumb animals".[71] Slaves were purchased or captured on the frontiers of the Islamic world and then imported to the major centers, where there were slave markets from which they were widely distributed.[72][73][74] In the 9th and 10th centuries, the black Zanj slaves may have constituted at least a half of the total population in lower Iraq.[75] At the same time, many tens of thousands of slaves in the region were also imported from Central Asia and the Caucasus.[76] Many slaves were taken in the wars with the Christian nations of medieval Europe.
In the Thousand and One Nights there are mentions of white slaves.[77]
Modern history
Europe

Author David P. Forsythe has written: "In 1649 up to three-quarters of Muscovy's peasants, or 13 to 14 million people, were serfs whose material lives were barely distinguishable from slaves. Perhaps another 1.5 million were formally enslaved, with Russian slaves serving Russian masters. "[78] Slavery remained a major institution in Russia until 1723, when Peter the Great converted the household slaves into house serfs. Russian agricultural slaves were formally converted into serfs earlier in 1679.[79] Russia's more than 23 million privately held serfs were freed from their lords by an edict of Alexander II in 1861.[80] State-owned serfs were emancipated in 1866.[81]
Until the late 18th century, the Crimean Khanate (a Muslim Tatar state) maintained a massive slave trade with the Ottoman Empire and the Middle East,[61] exporting about 2 million slaves from Poland-Lithuania and Russia over the period 1500–1700.[82]
During the Second World War (1939–1945) Nazi Germany effectively enslaved about 12 million people, both those considered undesirable and citizens of countries they conquered.[83]
Africa

In Senegambia, between 1300 and 1900, close to one-third of the population was enslaved.[69][78] In Sierra Leone in the 19th century about half of the population consisted of enslaved people.[69]
In the 19th century at least half the population was enslaved among the Duala of the Cameroon, the Igbo and other peoples of the lower Niger, the Kongo, and the Kasanje kingdom and Chokwe of Angola. Among the Ashanti and Yoruba a third of the population consisted of enslaved people.[69]
The population of the Kanem (1600–1800) was about a third-enslaved. It was perhaps 40% in Bornu (1580–1890). Between 1750 and 1900 from one- to two-thirds of the entire population of the Fulani War states consisted of slaves.[69]
In Algiers, the capital of Algeria in Northern Africa, Christians and Europeans that were captured had been forced into slavery. This eventually led to the Bombardment of Algiers in 1816.[84][85]

The population of the Sokoto caliphate formed by Fulanis and Hausas in northern Nigeria and Cameroon was half-slave in the 19th century. Between 65% to 90% population of Arab-Swahili Zanzibar was enslaved.[69] The Swahili-Arab slave trade reached its height about 150 years ago, when, for example, approximately 20,000 slaves were considered to be carried yearly from Nkhotakota on Lake Malawi to Kilwa.[86] Roughly half the population of Madagascar was enslaved.[69][87]
According to the Encyclopedia of African History, "It is estimated that by the 1890s the largest slave population of the world, about 2 million people, was concentrated in the territories of the Sokoto Caliphate. The use of slave labor was extensive, especially in agriculture. "[88][89] The Anti-Slavery Society estimated there were 2 million slaves in Ethiopia in the early 1930s out of an estimated population of between 8 and 16 million.[90]

Hugh Clapperton in 1824 believed that half the population of Kano were enslaved people.[91] W. A. Veenhoven wrote: "The German doctor, Gustav Nachtigal, an eye-witness, believed that for every slave who arrived at a market three or four died on the way ... Keltie (The Partition of Africa, London, 1920) believes that for every slave the Arabs brought to the coast at least six died on the way or during the slavers' raid. Livingstone puts the figure as high as ten to one. "[92]
One of the most famous slave traders on the eastern Zanj (Bantu) coast was Tippu Tip, who was himself the grandson of a slave. The prazeros slave traders, descendants of Portuguese and Africans, operated along the Zambezi. North of the Zambezi, the waYao and Makua people played a similar role as professional slave raiders and traders. The Nyamwezi slave traders operated further north under the leadership of Msiri and Mirambo.[93]
Asia

In Constantinople about one-fifth of the population consisted of slaves.[94] The city was a major center of the slave trade in the 15th and later centuries. By 1475 most of the slaves were provided by Tatar raids on Slavic villages.[95] It has been estimated that some 200,000 slaves—mainly Circassians—were imported into the Ottoman Empire between 1800 and 1909.[96] As late as 1908, women slaves were still sold in the Ottoman Empire.[97] A slave market for captured Russian and Persian slaves was centred in the Central Asian khanate of Khiva.[98] In the early 1840s, the population of the Uzbek states of Bukhara and Khiva included about 900,000 slaves.[96] Darrel P. Kaiser wrote, "Kazakh-Kirghiz tribesmen kidnapped 1573 settlers from colonies [German settlements in Russia] in 1774 alone and only half were successfully ransomed. The rest were killed or enslaved. "[99]
According to Sir Henry Bartle Frere (who sat on the Viceroy's Council), there were an estimated 8 or 9 million slaves in India in 1841. About 15% of the population of Malabar were slaves. Slavery was abolished in British India by the Indian Slavery Act V. of 1843.[7][100]
In East Asia, the Imperial government formally abolished slavery in China in 1906, and the law became effective in 1910.[101] Slave rebellion in China at the end of the 17th and the beginning of the 18th century was so extensive that owners eventually converted the institution into a female-dominated one.[102] The Nangzan in Tibetan history were, according to Chinese sources, hereditary household slaves.[103]
Indigenous slaves existed in Korea. Slavery was officially abolished with the Gabo Reform of 1894 but continued in reality until 1930. During the Joseon Dynasty (1392–1910) about 30% to 50% of the Korean population were slaves.[104] In late 16th century Japan slavery as such was officially banned, but forms of contract and indentured labor persisted alongside the period penal codes' forced labor.[105]
In Southeast Asia, a quarter to a third of seventeenth- to twentieth-century populations in some areas of Thailand and Burma were slaves.[7] The hill tribe people in Indochina were "hunted incessantly and carried off as slaves by the Siamese (Thai), the Anamites (Vietnamese), and the Cambodians. "[106] A Siamese military campaign in Laos in 1876 was described by a British observer as having been "transformed into slave-hunting raids on a large scale".[107] The census, taken in 1879, showed that 6% of the population in the Malay sultanate of Perak were slaves.[96] Enslaved people made up about two-thirds of the population in part of North Borneo in the 1880s.[96]
Americas

Slavery in the Americas had a contentious history, and played a major role in the history and evolution of some countries, triggering at least one revolution and one civil war, as well as numerous rebellions. The Aztecs had slaves.[108] Other Amerindians, such as the Inca of the Andes, the Tupinambá of Brazil, the Creek of Georgia, and the Comanche of Texas, also owned slaves.[7]
Slavery was prominent in Africa, across the Atlantic Ocean from the Americas, long before the beginnings of the transatlantic slave trade.[94] The maritime town of Lagos was the first slave market created in Portugal (one of the earliest colonizers of the Americas) for the sale of imported African slaves—the Mercado de Escravos, opened in 1444.[109][110] In 1441, the first slaves were brought to Portugal from northern Mauritania.[110]
In 1519, Mexico's first Afro-Mexican slave was brought by Hernán Cortés.
By 1552, black African slaves made up 10% of the population of Lisbon.[111][112] In the second half of the 16th century, the Crown gave up the monopoly on slave trade and the focus of European trade in African slaves shifted from import to Europe to slave transports directly to tropical colonies in the Americas—in the case of Portugal, especially Brazil.[110] In the 15th century one-third of the slaves were resold to the African market in exchange of gold.[113]
In order to establish itself as an American empire Spain had to fight against the relatively powerful civilizations of the New World. The Spanish conquest of the indigenous peoples in the Americas included using the Natives as forced labour. The Spanish colonies were the first Europeans to use African slaves in the New World on islands such as Cuba and Hispaniola, see Atlantic slave trade.[114]

Bartolomé de Las Casas a 16th-century Dominican friar and Spanish historian participated in campaigns in Cuba (at Bayamo and Camagüey) and was present at the massacre of Hatuey; his observation of that massacre led him to fight for a social movement away from the use of natives as slaves and towards the importation of African Blacks as slaves. Also, the alarming decline in the native population had spurred the first royal laws protecting the native population (Laws of Burgos, 1512–1513).
The first African slaves arrived in Hispaniola in 1501.[115][dead link] In 1518, Charles I of Spain agreed to ship slaves directly from Africa. England played a prominent role in the Atlantic slave trade. The "slave triangle" was pioneered by Francis Drake and his associates. A black man named Anthony Johnson of Virginia first introduced permanent black slavery in the 1650s by becoming the first holder in America of permanent black slaves.[116] By 1750, slavery was a legal institution in all of the 13 American colonies,[117][118] and the profits of the slave trade and of West Indian plantations amounted to 5% of the British economy at the time of the Industrial Revolution. [119]
The Transatlantic slave trade peaked in the late 18th century, when the largest number of slaves were captured on raiding expeditions into the interior of West Africa. These expeditions were typically carried out by African kingdoms, such as the Oyo empire (Yoruba), the Ashanti Empire,[120] the kingdom of Dahomey,[121] and the Aro Confederacy.[122] Europeans rarely entered the interior of Africa, due to fierce African resistance. The slaves were brought to coastal outposts where they were traded for goods. A significant portion of African Americans in North America are descended from Mandinka people.[123] Through a series of conflicts, primarily with the Fulani Jihad States, about half of the Senegambian Mandinka were converted to Islam while as many as a third were sold into slavery to the Americas through capture in conflict.[123]


An estimated 12 million Africans arrived in the Americas from the 16th to the 19th centuries.[124] Of these, an estimated 645,000 were brought to what is now the United States. The usual estimate is that about 15% of slaves died during the voyage, with mortality rates considerably higher in Africa itself in the process of capturing and transporting indigenous peoples to the ships. Approximately 6 million black Africans were killed by others in tribal wars.[125]
The white citizens of Virginia decided to treat the first Africans in Virginia as indentured servants.[126] Over half of all European immigrants to Colonial America during the 17th and 18th centuries arrived as indentured servants.[127] The transformation from indentured servitude to slavery was a gradual process in Virginia. The earliest legal documentation of such a shift was the case of John Punch in 1640 where a negro, John Punch, was sentenced to lifetime slavery for attempting to run away. This case also marked the disparate treatment of Africans as held by the Virginia County Court.[128] After 1640, planters started to ignore the expiration of indentured contracts and kept their servants as slaves for life. This was demonstrated by the case Johnson v. Parker where the court ruled that John Casor, an indentured servant, be returned to Johnson who claimed that Casor belonged to him for his life.[129][130] According to the 1860 U. S. census, 393,975 individuals, representing 8% of all US families, owned 3,950,528 slaves.[131] One-third of Southern families owned slaves.[132]

The largest number of slaves were shipped to Brazil.[133] In the Spanish viceroyalty of New Granada, corresponding mainly to modern Panama, Colombia, and Venezuela, the free black population in 1789 was 420,000, whereas African slaves numbered only 20,000. Free blacks also outnumbered slaves in Brazil. By contrast, in Cuba free blacks made up only 15% in 1827; and in the French colony of Saint-Domingue (present-day Haiti) it was a mere 5% in 1789.[134] Some half-million slaves, most of them born in Africa, worked the booming plantations of Saint-Domingue.[135]
Author Charles Rappleye argued that
In the West Indies in particular, but also in North and South America, slavery was the engine that drove the mercantile empires of Europe..It appeared, in the eighteenth century, as universal and immutable as human nature.[136]

Although the trans-Atlantic slave trade ended shortly after the American Revolution, slavery remained a central economic institution in the Southern states of the United States, from where slavery expanded with the westward movement of population.[137] Historian Peter Kolchin wrote, "By breaking up existing families and forcing slaves to relocate far from everyone and everything they knew" this migration "replicated (if on a reduced level) many of [the] horrors" of the Atlantic slave trade.[138]
Historian Ira Berlin called this forced migration the Second Middle Passage. Characterizing it as the "central event" in the life of a slave between the American Revolution and the Civil War, Berlin wrote that whether they were uprooted themselves or simply lived in fear that they or their families would be involuntarily moved, "the massive deportation traumatized black people, both slave and free. "[139]
By 1860, 500,000 slaves had grown to 4 million. As long as slavery expanded, it remained profitable and powerful and was unlikely to disappear. Although complete statistics are lacking, it is estimated that 1,000,000 slaves moved west from the Old South between 1790 and 1860.[140]
Most of the slaves were moved from Maryland, Virginia, and the Carolinas. Michael Tadman, in a 1989 book Speculators and Slaves: Masters, Traders, and Slaves in the Old South, indicates that 60–70% of interregional migrations were the result of the sale of slaves. In 1820, a child in the Upper South had a 30% chance to be sold south by 1860.[140]
In Puerto Rico, African slavery was finally abolished on March 22, 1873.
Middle East

According to Robert Davis between 1 million and 1.25 million Europeans were captured by Barbary pirates and sold as slaves in North Africa and Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 19th centuries.[141][142] There was also an extensive trade in Christian slaves in the Black Sea region for several centuries until the Crimean Khanate was destroyed by the Russian Empire in 1783.[63] In the 1570s close to 20,000 slaves a year were being sold in the Crimean port of Kaffa.[143] The slaves were captured in southern Russia, Poland-Lithuania, Moldavia, Wallachia, and Circassia by Tatar horsemen in a trade known as the "harvesting of the steppe". In Podolia alone, about one-third of all the villages were destroyed or abandoned between 1578 and 1583.[144] Some researchers estimate that altogether more than 3 million people were captured and enslaved during the time of the Crimean Khanate.[145][146] It is estimated that up to 75% of the Crimean population consisted of slaves or freedmen.[94]


The Arab slave trade lasted more than a millennium.[147] As recently as the early 1960s, Saudi Arabia's slave population was estimated at 300,000.[148] Along with Yemen, the Saudis abolished slavery only in 1962.[149] Slaves in the Arab World came from many different regions, including Sub-Saharan Africa (mainly Zanj),[71] the Caucasus (mainly Circassians),[150] Central Asia (mainly Tartars), and Central and Eastern Europe (mainly Saqaliba).[151]
Under Omani Arabs Zanzibar became East Africa's main slave port, with as many as 50,000 enslaved Africans passing through every year during the 19th century.[152][153] Some historians estimate that between 11 and 18 million African slaves crossed the Red Sea, Indian Ocean, and Sahara Desert from 650 AD to 1900 AD.[7][154] Eduard Rüppell described the heavy mortality of the enslaved Sudanese before reaching Egypt: "after the Daftardar bey's 1822 campaign in the southern Nuba mountains, nearly 40,000 slaves were captured. However, through bad treatment, disease and desert travel barely 5000 made it to Egypt. "[155]
Central and Eastern European slaves were generally known as Saqaliba (i. e., Slavs).[156] The Moors, starting in the 8th century, also raided coastal areas around the Mediterranean and Atlantic Ocean, and became known as the Barbary pirates.[157] It is estimated that they captured 1.25 million white slaves from Western Europe and North America between the 16th and 19th centuries.[158][159] The mortality rate was very high. For instance, when plague broke out in Algiers' overcrowded slave pens in 1662, some said that it carried off 10,000–20,000 of the city's 30,000 captives.[141]
Present day
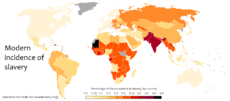

Even though slavery is now outlawed in every country, the number of slaves today remains as high as 12 million [161] to 29.8 million.[4] Several estimates of the number of slaves in the world have been provided.[162] According to a broad definition of slavery used by Kevin Bales of Free the Slaves (FTS), an advocacy group linked with Anti-Slavery International, there were 27 million people in slavery in 1999, spread all over the world.[163] In 2005, the International Labour Organization provided an estimate of 12.3 million forced labourers in the world.[164] Siddharth Kara has also provided an estimate of 28.4 million slaves at the end of 2006 divided into the following three categories: bonded labour/debt bondage (18.1 million), forced labour (7.6 million), and trafficked slaves (2.7 million).[165] Kara provides a dynamic model to calculate the number of slaves in the world each year, with an estimated 29.2 million at the end of 2009. According to a report from 2003, by the Human Rights Watch, an estimated 15 million[166] children in India, bonded workers, working in slave-like conditions in order to pay off debts.[167]
While American slaves in 1809 were sold for around $40,000 (in contemporary money); a slave nowadays can be bought for just $90; making replacement more economical than providing long term care.[168] Slavery is a multi-billion dollar industry with estimates of up to $35 billion generated annually.[169]
A report by the Walk Free Foundation in 2013, found India had the highest number of slaves, nearly 14 million, followed by China (2.9 million), Pakistan (2.1 million), Nigeria, Ethiopia, Russia, Thailand, Democratic Republic of Congo, Myanmar and Bangladesh; while the countries with the highest of proportion of slaves were Mauritania, Haiti, Pakistan, India and Nepal.[170]
In June 2013, US Department of State released a report on slavery, it placed Russia, China, Uzbekistan in the worst offenders category, Cuba, Iran, North Korea, Sudan, Syria, and Zimbabwe were also at the lowest level. List also included Algeria, Libya, Saudi Arabia and Kuwait among a total of 21 countries.[171][172]
Examples of modern slavery are numerous. In 2008, the Nepalese government abolished the Haliya system of forced labour, freeing about 20,000 people.[173] Though slavery was officially abolished in China in 1910,[174] the practice continues unofficially in some regions of the country.[175][176][177] In June and July 2007, 550 people who had been enslaved by brick manufacturers in Shanxi and Henan were freed by the Chinese government.[178] Among those rescued were 69 children.[179] In response, the Chinese government assembled a force of 35,000 police to check northern Chinese brick kilns for slaves, sent dozens of kiln supervisors to prison, punished 95 officials in Shanxi province for dereliction of duty, and sentenced one kiln foreman to death for killing an enslaved worker.[178] The North Korean government[180] operates six large political prison camps,[181] where political prisoners and their families (around 200,000 people)[182] in lifelong detention[183] are subjected to hard slave labor,[184] torture and inhumane treatment.[185] In 2008 in Brazil about 5,000 slaves were rescued by government authorities as part of an initiative to eradicate slavery, which was reported as ongoing in 2010.[186] Poverty has forced at least 225,000 Haitian children to work as restavecs (unpaid household servants); the United Nations considers this to be a form of slavery.[187] Some tribal sheiks in Iraq still keep blacks, called Abd, which means servant or slave in Arabic, as slaves.[188] Child slavery has commonly been used in the production of cash crops and mining.

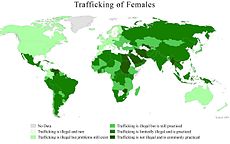
Trafficking in human beings (also called human trafficking) is one method of obtaining slaves.[190] Victims are typically recruited through deceit or trickery (such as a false job offer, false migration offer, or false marriage offer), sale by family members, recruitment by former slaves, or outright abduction. Victims are forced into a "debt slavery" situation by coercion, deception, fraud, intimidation, isolation, threat, physical force, debt bondage or even force-feeding with drugs of abuse to control their victims.[191] "Annually, according to U. S. Government-sponsored research completed in 2006, approximately 800,000 people are trafficked across national borders, which does not include millions trafficked within their own countries. Approximately 80 percent of transnational victims are women and girls and up to 50 percent are minors", reports the US Department of State in a 2008 study.[192]
While the majority of trafficking victims are women, and sometimes children, who are forced into prostitution (in which case the practice is called sex trafficking), victims also include men, women and children who are forced into manual labour.[193] Due to the illegal nature of human trafficking, its exact extent is unknown. A US Government report published in 2005, estimates that 600,000 to 800,000 people worldwide are trafficked across borders each year. This figure does not include those who are trafficked internally.[193] Another research effort revealed that between 1.5 million and 1.8 million individuals are trafficked either internally or internationally each year, 500,000 to 600,000 of whom are sex trafficking victims.[165]
Africa
Slavery continues to be common in some African countries.
In Mauritania, the last country to abolish slavery (in 1981),[194] it is estimated that up to 600,000 men, women and children, or 20% of the population, are enslaved with many used as bonded labour.[195][196][197] Slavery in Mauritania was criminalized in August 2007.[198] (although slavery as a practice was legally banned in 1981, it was not a crime to own a slave until 2007).[199] Although many slaves have escaped or have been freed since 2007, as of 2012, only one slave-owner had been sentenced to serve time in prison.[200]
An article in the Middle East Quarterly in 1999 reported that slavery is endemic in Sudan.[201] Estimates of abductions during the Second Sudanese Civil War range from 14,000 to 200,000 people.[202]
In Niger, slavery is also a current phenomenon. A Nigerien study has found that more than 800,000 people are enslaved, almost 8% of the population.[203][204][205] Niger installed anti slavery provision in 2003.[206][207]
Many pygmies in the Republic of Congo and Democratic Republic of Congo belong from birth to Bantus in a system of slavery.[208][209]
According to the US Department of State, more than 109,000 children were working on cocoa farms alone in Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast) in "the worst forms of child labor" in 2002.[210]
Abolitionism

Slavery has existed, in one form or another, through the whole of recorded human history—as have, in various periods, movements to free large or distinct groups of slaves.
Ashoka, who ruled the Maurya Empire from 269–232 BCE, abolished the slave trade but not slavery.[212] The Qin dynasty, which ruled China from 221 to 206 BC, abolished slavery and discouraged serfdom. However, many of its laws were overturned when the dynasty was overthrown.[213] Slavery was again abolished, by Wang Mang, in China in 17 C.E but was reinstituted after his assassination.[214]
The Spanish colonization of the Americas sparked a discussion about the right to enslave native Americans. A prominent critic of slavery in the Spanish New World colonies was Bartolomé de las Casas, who opposed the enslavement of Native Americans, and later also of Africans in America.
One of the first protests against the enslavement of Africans came from German and Dutch Quakers in Pennsylvania in 1688. One of the most significant milestones in the campaign to abolish slavery throughout the world occurred in England in 1772, with British judge Lord Mansfield, whose opinion in Somersett's Case was widely taken to have held that slavery was illegal in England. This judgement also laid down the principle that slavery contracted in other jurisdictions (such as the American colonies) could not be enforced in England.[215] In 1777, Vermont became the first portion of what would become the United States to abolish slavery (at the time Vermont was an independent nation). In 1794, under the Jacobins, Revolutionary France abolished slavery.[216] There were celebrations in 2007 to commemorate the 200th anniversary of the Abolition of the slave trade in the United Kingdom through the work of the British Anti-Slavery Society.

William Wilberforce received much of the credit although the groundwork was an anti-slavery essay by Thomas Clarkson. Wilberforce was also urged by his close friend, Prime Minister William Pitt the Younger, to make the issue his own, and was also given support by reformed Evangelical John Newton. The Slave Trade Act was passed by the British Parliament on March 25, 1807, making the slave trade illegal throughout the British Empire,[217] Wilberforce also campaigned for abolition of slavery in the British Empire, which he lived to see in the Slavery Abolition Act 1833. After the 1807 act abolishing the slave trade was passed, these campaigners switched to encouraging other countries to follow suit, notably France and the British colonies. In 1839, the world's oldest international human rights organization, Anti-Slavery International, was formed in Britain by Joseph Sturge, which campaigned to outlaw slavery in other countries.[218]
Between 1808 and 1860, the British West Africa Squadron seized approximately 1,600 slave ships and freed 150,000 Africans who were aboard.[219] Action was also taken against African leaders who refused to agree to British treaties to outlaw the trade, for example against "the usurping King of Lagos", deposed in 1851. Anti-slavery treaties were signed with over 50 African rulers.[220]
In the United States, abolitionist pressure produced a series of small steps towards emancipation. After January 1, 1808, the importation of slaves into the United States was prohibited,[221] but not the internal slave trade, nor involvement in the international slave trade externally. Legal slavery persisted; and those slaves already in the U. S. were legally emancipated only in 1863. Many American abolitionists took an active role in opposing slavery by supporting the Underground Railroad. Violence soon erupted, with the anti-slavery forces led by John Brown, and Bleeding Kansas, involving anti-slavery and pro-slavery settlers, became a symbol for the nationwide clash over slavery. By 1860 the total number of slaves reached almost four million, and the American Civil War, beginning in 1861, led to the end of slavery in the United States.[222]
In 1863 Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation, which freed slaves held in the Confederate States; the 13th Amendment to the U. S. Constitution (1865) prohibited slavery throughout the country.

In the 1860s, David Livingstone's reports of atrocities within the Arab slave trade in Africa stirred up the interest of the British public, reviving the flagging abolitionist movement. The Royal Navy throughout the 1870s attempted to suppress "this abominable Eastern trade", at Zanzibar in particular. In 1905, the French abolished indigenous slavery in most of French West Africa.[224]
On December 10, 1948, the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which declared freedom from slavery is an internationally recognized human right. Article 4 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights states:
No one shall be held in slavery or servitude; slavery and the slave trade shall be prohibited in all their forms.[225]
Groups such as the American Anti-Slavery Group, Anti-Slavery International, Free the Slaves, the Anti-Slavery Society, and the Norwegian Anti-Slavery Society continue to campaign to rid the world of slavery.
Remnants of slavery
In the case of freed slaves of the United States, many became share croppers and indentured servants. In this manner, some became tied to the very parcel of land into which they had been born a slave having little freedom or economic opportunity due to Jim Crow laws which perpetuated discrimination, limited education, promoted persecution without due process and resulted in continued poverty. Fear of reprisals such as unjust incarcerations and lynchings deterred upward mobility further.
Legal actions
In November 2006, the International Labour Organization announced it will be seeking "to prosecute members of the ruling Myanmar junta for crimes against humanity" over the continuous unfree labour of its citizens by the military at the International Court of Justice.[226][227] According to the International Labor Organization (ILO), an estimated 800,000 people are subject to forced labour in Myanmar.[228]
The Ecowas Court of Justice is hearing the case of Hadijatou Mani in late 2008, where Ms. Mani hopes to compel the government of Niger to end slavery in its jurisdiction. Cases brought by her in local courts have failed so far.[229]
Economics

Economists have attempted to model the circumstances under which slavery (and variants such as serfdom) appear and disappear. One observation is that slavery becomes more desirable for landowners where land is abundant but labour is scarce, such that rent is depressed and paid workers can demand high wages. If the opposite holds true, then it becomes more costly for landowners to have guards for the slaves than to employ paid workers who can only demand low wages due to the amount of competition.[230] Thus, first slavery and then serfdom gradually decreased in Europe as the population grew, but were reintroduced in the Americas and in Russia as large areas of new land with few people became available.[231] In his books, Time on the Cross and Without Consent or Contract: the Rise and Fall of American Slavery, Robert Fogel maintains that slavery was in fact a profitable method of production, especially on bigger plantations growing cotton that fetched high prices in the world market. It gave whites in the South higher average incomes than those in the North, but most of the money was spent on buying slaves and plantations.

Slavery is more common when the labour done is relatively simple and thus easy to supervise, such as large-scale growing of a single crop. It is much more difficult and costly to check that slaves are doing their best and with good quality when they are doing complex tasks. Therefore, slavery was seen as the most efficient method of production for large-scale crops like sugar and cotton, whose output was based on economies of scale. This enabled a gang system of labor to be prominent on large plantations where field hands were monitored and worked with factory-like precision. Each work gang was based on an internal division of labor that not only assigned every member of the gang to a precise task but simultaneously made his or her performance dependent on the actions of the others. The hoe hands chopped out the weeds that surrounded the cotton plants as well as excessive sprouts. The plow gangs followed behind, stirring the soil near the rows of cotton plants and tossing it back around the plants. Thus, the gang system worked like an early version of the assembly line later to be found in factories.[232]
Critics since the 18th century have argued that slavery tends to retard technological advancement, since the focus is on increasing the number of slaves doing simple tasks rather than upgrading the efficiency of labour. Because of this, theoretical knowledge and learning in Greece—and later in Rome—was not applied to ease physical labour or improve manufacturing.[233]
Adam Smith made the argument that free labor was economically better than slave labor, and argued further that slavery in Europe ended during the Middle Ages, and then only after both the church and state were separate, independent and strong institutions,[234] that it is nearly impossible to end slavery in a free, democratic and republican forms of governments since many of its legislators or political figures were slave owners, and would not punish themselves, and that slaves would be better able to gain their freedom when there was centralized government, or a central authority like a king or the church.[235] Similar arguments appear later in the works of Auguste Comte, especially when it comes to Adam Smith's belief in the separation of powers or what Comte called the "separation of the spiritual and the temporal" during the Middle Ages and the end of slavery, and Smith's criticism of masters, past and present. As Smith stated in the Lectures on Jurisprudence, "The great power of the clergy thus concurring with that of the king set the slaves at liberty. But it was absolutely necessary both that the authority of the king and of the clergy should be great. Where ever any one of these was wanting, slavery still continues. "

Slaves can be an attractive investment because the slave-owner only needs to pay for sustenance and enforcement. This is sometimes lower than the wage-cost of free labourers, because free workers earn more than sustenance, in these cases slaves have positive price. When the cost of sustenance and enforcement exceeds the wage rate, slave-owning would no longer be profitable, and owners would simply release their slaves. Slaves are thus a more attractive investment in high-wage environments, and environments where enforcement is cheap, and less attractive in environments where the wage-rate is low and enforcement is expensive.[236]
Free workers also earn compensating differentials, whereby they are paid more for doing unpleasant work. Neither sustenance nor enforcement costs rise with the unpleasantness of the work, however, so slaves' costs do not rise by the same amount. As such, slaves are more attractive for unpleasant work, and less for pleasant work. Because the unpleasantness of the work is not internalised, being born by the slave rather than the owner, it is a negative externality and leads to over-use of slaves in these situations.[236]
The weighted average global sales price of a slave is calculated to be approximately $340, with a high of $1,895 for the average trafficked sex slave, and a low of $40 to $50 for debt bondage slaves in part of Asia and Africa.[165] Worldwide slavery is a criminal offense but slave owners can get very high returns for their risk.[237] According to researcher Siddharth Kara, the profits generated worldwide by all forms of slavery in 2007 were $91.2 billion. That is second only to drug trafficking in terms of global criminal enterprises. The weighted average annual profits generated by a slave in 2007 was $3,175, with a low of an average $950 for bonded labor and $29,210 for a trafficked sex slave.[165] Approximately 40% of slave profits each year are generated by trafficked sex slaves, representing slightly more than 4% of the world's 29 million slaves.[165]
Robert E. Wright has developed a model that helps to predict when firms (individuals, companies) will be more likely to use slaves rather than wage workers, indentured servants, family members, or other types of laborers.[238]
Wage slavery
| Part of a series on |
| Syndicalism |
|---|
 |
The labour market, as institutionalised under today's market economic systems, has been criticised,[239] especially by both mainstream socialists and anarcho-syndicalists,[240][241][242][243] who utilise the term wage slavery[244][245] as a pejorative for wage labour. Socialists draw parallels between the trade of labour as a commodity and slavery. Cicero is also known to have suggested such parallels.[246]
For Marxists, labour-as-commodity, which is how they regard wage labour,[247] provides an absolutely fundamental point of attack against capitalism.[248] "It can be persuasively argued," noted one concerned philosopher, "that the conception of the worker's labour as a commodity confirms Marx's stigmatization of the wage system of private capitalism as 'wage-slavery;' that is, as an instrument of the capitalist's for reducing the worker's condition to that of a slave, if not below it."[249]
Apologies
On May 21, 2001, the National Assembly of France passed the Taubira law, recognizing slavery as a crime against humanity. Apologies on behalf of African nations, for their role in trading their countrymen into slavery, remain an open issue since slavery was practiced in Africa even before the first Europeans arrived and the Atlantic slave trade was performed with a high degree of involvement of several African societies. The black slave market was supplied by well-established slave trade networks controlled by local African societies and individuals.[250] Indeed, as already mentioned in this article, slavery persists in several areas of West Africa until the present day.
There is adequate evidence citing case after case of African control of segments of the trade. Several African nations such as the Calabar and other southern parts of Nigeria had economies depended solely on the trade. African peoples such as the Imbangala of Angola and the Nyamwezi of Tanzania would serve as middlemen or roving bands warring with other African nations to capture Africans for Europeans.[251]
Several historians have made important contributions to the global understanding of the African side of the Atlantic slave trade. By arguing that African merchants determined the assemblage of trade goods accepted in exchange for slaves, many historians argue for African agency and ultimately a shared responsibility for the slave trade.[252]
In 1999, President Mathieu Kerekou of Benin (formerly the Kingdom of Dahomey) issued a national apology for the central role Africans played in the Atlantic slave trade.[253] Luc Gnacadja, minister of environment and housing for Benin, later said: "The slave trade is a shame, and we do repent for it."[254] Researchers estimate that 3 million slaves were exported out of the Slave Coast bordering the Bight of Benin.[254] President Jerry Rawlings of Ghana also apologized for his country's involvement in the slave trade.[253]
The issue of an apology is linked to reparations for slavery and is still being pursued by a number of entities across the world. For example, the Jamaican Reparations Movement approved its declaration and action Plan.
In September 2006, it was reported that the UK government might issue a "statement of regret" over slavery.[255] This was followed by a "public statement of sorrow" from Tony Blair on November 27, 2006,[256] and a formal apology on March 14, 2007.[257]
On February 25, 2007, the Commonwealth of Virginia resolved to 'profoundly regret' and apologize for its role in the institution of slavery. Unique and the first of its kind in the U. S., the apology was unanimously passed in both Houses as Virginia approached the 400th anniversary of the founding of Jamestown, where the first slaves were imported into North America in 1619.[258]
Liverpool, which was a large slave trading port, apologized in 1999. On August 24, 2007, Mayor Ken Livingstone of London, United Kingdom, apologized publicly for Britain's role in colonial slave trade. "You can look across there to see the institutions that still have the benefit of the wealth they created from slavery," he said, pointing towards the financial district. He claimed that London was still tainted by the horrors of slavery. Specifically, London outfitted, financed, and insured many of the ships, which helped fund the building of London's docks. Jesse Jackson praised Livingstone, and added that reparations should be made, one of his common arguments.[259]
On July 30, 2008, the United States House of Representatives passed a resolution apologizing for American slavery and subsequent discriminatory laws.[260] In June 2009, the US Senate passed a resolution apologizing to African-Americans for the "fundamental injustice, cruelty, brutality, and inhumanity of slavery".[261] The news was welcomed by President Barack Obama, the nation's first President of African descent.[262] Some of President Obama's ancestors were slave owners.[263]
In 2010, Libyan leader Muammar Gaddafi apologized for Arab involvement in the slave trade, saying: "I regret the behavior of the Arabs… They brought African children to North Africa, they made them slaves, they sold them like animals, and they took them as slaves and traded them in a shameful way."[264]
Reparations
There have been movements to achieve reparations for those formerly held as slaves, or sometimes their descendants. Claims for reparations for being held in slavery are handled as a civil law matter in almost every country. This is often decried as a serious problem, since former slaves' relative lack of money means they often have limited access to a potentially expensive and futile legal process. Mandatory systems of fines and reparations paid to an as yet undetermined group of claimants from fines, paid by unspecified parties, and collected by authorities have been proposed by advocates to alleviate this "civil court problem. " Since in almost all cases there are no living ex-slaves or living ex-slave owners these movements have gained little traction. In nearly all cases the judicial system has ruled that the statute of limitations on these possible claims has long since expired.
Other uses of the term
The word slavery is often used as a pejorative to describe any activity in which one is coerced into performing.
- Many argue that military drafts and other forms of coerced government labour constitute state-operated slavery.[265][266]
- Some socialists, view total and immediate wage dependence as a form of slavery.[267]
- Some libertarians and anarcho-capitalists view government taxation as a form of slavery.[268]
- Some proponents of animal rights apply the term slavery to the condition of some or all human-owned animals, arguing that their status is comparable to that of human slaves.[269]
In film
Film has been the most influential medium in the presentation of the history of slavery to the general public around the world.[270] The American film industry has had a complex relationship with slavery and until recent decades often avoided the topic. Films such as Birth of a Nation (1915)[271] and Gone with the Wind (1939) became controversial because they gave a favorable depiction. The last favorable treatment was Song of the South from Disney in 1946. In 1940 The Santa Fe Trail gave a liberal but ambiguous interpretation of John Brown's attacks on slavery—the film does not know what to do with slavery.[272] The Civil Rights Movement in the 1950s made defiant slaves into heroes.[273] The question of slavery in American memory necessarily involves its depictions in feature films.[274]

Most Hollywood films used American settings, although Spartacus (1960), dealt with an actual revolt in the Roman Empire known as the Third Servile War. It failed and all the rebels were executed, but their spirit lived on according to the film.[275] The Last Supper (La última cena in Spanish) was a 1976 film directed by Cuban Tomás Gutiérrez Alea about the teaching of Christianity to slaves in Cuba, and emphasizes the role of ritual and revolt. Burn! takes place on the imaginary Portuguese island of Queimada (where the locals speak Spanish) and it merges historical events that took place in Brazil, Cuba, Santo Domingo, Jamaica, and elsewhere. Spartacus stays surprisingly close to the historical record.[276]
Historians agree that films have largely shaped historical memories, but they debate issues of accuracy, plausibility, moralism, sensationalism, how facts are stretched in search of broader truths, and suitability for the classroom.[277][278] Berlin argues that critics complain if the treatment emphasizes historical brutality, or if it glosses over the harshness to highlight the emotional impact of slavery.[279]
See also
- 1926 Slavery Convention
- Abolition of slavery timeline
- Coolie
- Human trafficking
- Indemnity
- Indentured servant
- Involuntary servitude
- List of slaves
- List of slave owners
- Peon
- United Nations 1956 Supplementary Convention on the Abolition of Slavery
- Wife selling
References
- ^ Laura Brace (2004). The Politics of Property: Labour, Freedom and Belonging. Edinburgh University Press. pp. 162–. ISBN 978-0-7486-1535-3. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ "Religion & Ethics – Modern slavery: Modern forms of slavery". BBC. January 30, 2007. Retrieved June 16, 2009.
- ^ "Slavery's Global Comeback". The atlantic. December 19, 2012.
- ^ a b "INAUGURAL GLOBAL SLAVERY INDEX REVEALS MORE THAN 29 MILLION PEOPLE LIVING IN SLAVERY". Global Slavery Index 2013. October 4, 2013. Retrieved October 17, 2013.
- ^ "Mauritanian MPs pass slavery law". BBC News. August 9, 2007.
- ^ "Slavery's last stand - CNN.com". CNN.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Historical survey: Slave-owning societies". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ a b c d "Slavery in the 21st century". Newint.org. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ a b "Experts encourage action against sex trafficking". Voice of America. May 15, 2009. Retrieved August 29, 2010. Cite error: The named reference "voa" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edition 1989, s. v. 'slave'
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica, History of Europe – Middle Ages – Growth and innovation – Demographic and agricultural growth
- ^ F. Kluge, Etymologisches Wörterbuch der deutschen Sprache. 1891, s. v. 'Sklave'.
- ^ Indrani Chatterjee, Richard Eaton (2006). Slavery and South Asian History. Indiana University Press. p. 3. ISBN 9780253116710.
- ^ M. A. Dandamayev, BARDA and BARDADĀRĪ in Encyclopedia Iranica
- ^ Farazmand, Ali (1998) “Persian/Iranian Administrative Tradition”, in Jay M. Shafritz (Editor), International Encyclopedia of Public Policy and Administration. Boulder, CO: Westview Press, pp. 1640–1645 – Excerpt: "Persians never practiced mass slavery, and in many cases the situations and lives of semi-slaves (prisoners of war) were in fact better than the common citizens of Persia." (pg 1642)
- ^ a b c Kevin Bales (2004). New slavery: a reference handbook. ABC-CLIO. pp. 15–18. ISBN 978-1-85109-815-6. Retrieved March 11, 2011.
- ^ Bales, Kevin (2004). "New Slavery: A Reference Handbook". ISBN 9781851098156.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ http://www.ipsnews.net/2007/08/rights-mexico-16000-victims-of-child-sexual-exploitation/
- ^ http://www.bbc.co.uk/ethics/slavery/modern/modern_1.shtml#section_2
- ^ http://www.ohchr.org/Documents/HRBodies/HRCouncil/RegularSession/Session21/A-HRC-21-41_en.pdf
- ^ "Two-year-old 'at risk' of forced marriage". BBC News. March 5, 2013.
- ^ http://www.honordiaries.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/FactSheet-ChildForcedMarriage-Updated.pdf
- ^ http://www.thespec.com/news-story/4116168-forced-marriages-rampant-in-ontario
- ^ http://www.mulr.com.au/issues/36_3/36_3_5.pdf/
- ^ "UNICEF supports fight to end marriage by abduction in Ethiopia". reliefweb.int. November 9, 2004. Retrieved August 29, 2013.
- ^ "Latvia calls on Ireland to tackle sham marriages". BBC News. November 21, 2010.
- ^ "Latvia appeals to Ireland to stop sham marriages". BBC News. November 22, 2010.
- ^ http://eurojust.europa.eu/doclibrary/Eurojust-framework/Casework/Eurojust%20action%20against%20trafficking%20in%20human%20beings%20%28October%202012%29/THB-report-2012-10-18-EN.pdf
- ^ "Nigeria's child brides: 'I thought being in labour would never end'". The Guardian. September 9, 2013.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Child brides around the world sold off like cattle". USA Today. March 8, 2013.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ Thomas, Hugh: The Slave Trade Simon and Schuster; Rockefeller Centre; New York, New York; 1997
- ^ "Slavery". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ "Mesopotamia: The Code of Hammurabi".
e. g. Prologue, "the shepherd of the oppressed and of the slaves". Code of Laws #7, "If any one buy from the son or the slave of another man".
- ^ Demography, Geography and the Sources of Roman Slaves, by W. V. Harris: The Journal of Roman Studies, 1999
- ^ {{De icon}} Lauffer, S. "Die Bergwerkssklaven von Laureion", Abhandlungen no. 12 (1956), p. 916.
- ^ Slavery in Ancient Greece. Britannica Student Encyclopædia.
- ^ "Slavery in Ancient Rome". Dl.ket.org. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "Resisting Slavery in Ancient Rome". BBC News. November 5, 2009. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ Schiavone Aldo (2000), The End of the Past. Ancient Rome and the Modern West, Cambridge Mass.: Harvard University Press, p. 112.
- ^ The Romans at Work and Play Western New England College.
- ^ "The Roman slave supply" Walter Scheidel. Stanford University.
- ^ "Slave trade – Britannica Concise Encyclopedia". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "slave-trade". Jewishencyclopedia.com. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "Slavery Encyclopedia of Ukraine". Encyclopediaofukraine.com. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ Michael Moïssey Postan; Edward Miller (August 28, 1987). The Cambridge Economic History of Europe: Trade and industry in the Middle Ages. Cambridge University Press. pp. 417–. ISBN 978-0-521-08709-4. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ Carole Elizabeth Boyce Davies (July 29, 2008). Encyclopedia of the African Diaspora: Origins, Experiences, and Culture. ABC-CLIO. pp. 1002–. ISBN 978-1-85109-705-0. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ James William Brodman. "Ransoming Captives in Crusader Spain: The Order of Merced on the Christian-Islamic Frontier". Libro.uca.edu. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "British Slaves on the Barbary Coast".
- ^ "Jefferson Versus the Muslim Pirates by Christopher Hitchens, City Journal Spring 2007".
- ^ Lewis, C.P. & al. A History of the County of Chester. "Early Medieval Chester 400–1230". Accessed 5 Feb 2013.
- ^ Clapham, John H. A Concise Economic History of Britain of Britain from the Earliest Times to 1750. Accessed 5 Feb 2013.
- ^ "Medieval English society". University of Wisconsin. Retrieved September 5, 2009.
- ^ "Slavery, serfdom, and indenture through the Middle Ages". Scatoday.net. February 3, 2005. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ Hayes, Diana (2003), "Reflections on Slavery", in Curran, Charles E. (ed.), Change in Official Catholic Moral Teaching, Paulist, p. 67.
- ^ "Sublimus Dei". Papalencyclicals.net. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ Thomas, Hugh (2003). Rivers of Gold: The Rise of the Spanish Empire. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. pp. 258–262. ISBN 0-297-64563-3.
- ^ Brian Glyn Williams (2013). "The Sultan's Raiders: The Military Role of the Crimean Tatars in the Ottoman Empire" (PDF). The Jamestown Foundation. p. 27.
- ^ Phillips, Jr, William D. (1985). Slavery from Roman times to the Early Transatlantic Trade. Manchester: Manchester University Press. p. 37. ISBN 978-0-7190-1825-1.
- ^ A. E. Vacalopoulos. The Greek Nation, 1453—1669, New Brunswick, New Jersey, Rutgers University Press, 1976, p. 41; Vasiliki Papoulia, The Impact of Devshirme on Greek Society, in War and Society in East Central Europe, Editor—in—Chief, Bela K. Kiraly, 1982, Vol. II, pp. 561—562.
- ^ "Famous Battles in History The Turks and Christians at Lepanto". Trivia-library.com. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ a b Mikhail Kizilov. "Slave Trade in the Early Modern Crimea From the Perspective of Christian, Muslim, and Jewish Sources". Oxford University.
- ^ Davies, Brian (2007). Warfare, State and Society on the Black Sea Steppe,1500–1700. p. 17. ISBN 0-415-23986-9.
- ^ a b "The Crimean Tatars and their Russian-Captive Slaves" (PDF). Eizo Matsuki, Mediterranean Studies Group at Hitotsubashi University.
- ^ Anderson, Perry (1996). Passages from antiquity to feudalism. Verso. p. 141. ISBN 1-85984-107-4.
- ^ Slavery in the Middle Ages. Historymedren. about. com
- ^ The Saxon Slave-Market. First published in Bristol Magazine July 2006.
- ^ Träldom. Nordisk familjebok / Uggleupplagan. 30. Tromsdalstind – Urakami /159–160, 1920. (In Swedish)
- ^ "Slaves in Saudi". Naeem Mohaiemen. The Daily Star. July 27, 2004.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Welcome to Encyclopædia Britannica's Guide to Black History". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "Medieval Sourcebook: Ibn Battuta: Travels in Asia and Africa 1325–1354"
- ^ a b Bernard Lewis (April 30, 1992). Race and Slavery in the Middle East: An Historical Enquiry. Oxford University Press. pp. 53–. ISBN 978-0-19-505326-5. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ Historical survey: The international slave trade. Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ slave-trade. JewishEncyclopedia. com
- ^ Muslim Slave System in Medieval India, K. S. Lal, Aditya Prakashan, New Delhi
- ^ Slavery. Encyclopædia Britannica's Guide to Black History.
- ^ Slavery. Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ The Arabian Nights – Richard F. Burton, Sir Richard Burton – Google Books. Books.google.com. January 1, 2004. ISBN 9781420902044. Retrieved March 12, 2013.
- ^ a b David P. Forsythe (2009). "Encyclopedia of Human Rights, Volume 1". Oxford University Press. p. 464. ISBN 0195334027
- ^ Historical survey: Ways of ending slavery. Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ "Slavery (sociology)". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ Mee, Arthur; Hammerton, J. A.; Innes, Arthur D.;"Harmsworth history of the world: Volume 7", 1907, Carmelite House, London; at page 5193.
- ^ Darjusz Kołodziejczyk, as reported by Mikhail Kizilov (2007). "Slaves, Money Lenders, and Prisoner Guards:The Jews and the Trade in Slaves and Captivesin the Crimean Khanate". The Journal of Jewish Studies. p. 2.
- ^ "Nazi slave fund passes final hurdle". BBC News. May 30, 2001.
- ^ Baepler, B. "White Slaves, African Masters 1st Edition." White Slaves, African Masters 1st Edition by Baepler. University of Chicago Press, n.d. Web. 07 Jan. 2013. Page 5
- ^ "History – British History in depth: British Slaves on the Barbary Coast". BBC. Retrieved March 12, 2013.
- ^ "Malawi Slave Routes and Dr. David Livingstone Trail". UNESCO World Heritage Centre.
- ^ Steven Mintz. "Digital History Slavery Fact Sheets". Digital History. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ Kevin Shillington (2005). Encyclopedia of African history. Michigan University Press. p. 1401. ISBN 1-57958-455-1
- ^ Slow Death for Slavery: The Course of Abolition in Northern Nigeria, 1897–1936 (review), Project MUSE – Journal of World History
- ^ ""Freedom is a good thing but it means a dearth of slaves": Twentieth Century Solutions to the Abolition of Slavery" (PDF). Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ Humphrey J. Fisher (2001). Slavery in the History of Muslim Black Africa. Hurst & Company. pp. 33–. ISBN 978-1-85065-524-4. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ Willem A. Veenhoven (January 1, 1977). Case Studies on Human Rights And Fundamental Freedoms: A World Survey. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. pp. 440–. ISBN 978-90-247-1956-3. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ The East African slave trade. BBC World Service |The Story of Africa.
- ^ a b c Historical survey> Slave societies. Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ Mikhail Kizilov. "Slave Trade in the Early Modern Crimea From the Perspective of Christian, Muslim, and Jewish Sources". Journal of Early Modern History (2007) 11#1 . pp. 1–31.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|work=(help) - ^ a b c d W. G. Clarence-Smith (2006). "Islam And The Abolition Of Slavery". Oxford University Press. pp. 13–16. ISBN 0195221516
- ^ Sexual slavery – the harem. BBC – Religion & Ethics
- ^ "The Freeing of the Slaves". Khiva.info. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ Darrel P. Kaiser (2006). Origin & Ancestors Families Karle & Kaiser Of the German-Russian Volga Colonies. Darrel P. Kaiser. ISBN 978-1-4116-9894-9. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ "Historical survey> Slave-owning societies". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "Slavery". Encyclopædia Britannica. May 19, 2009.
- ^ "Agriculture> Slave protest". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ A. Tom Grunfeld (1996). The Making of Modern Tibet. M. E. Sharpe. ISBN 978-1-56324-714-9. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ "Encyclopædia Britannica – Slavery". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ James Bryant Lewis (November 10, 2003). Frontier Contact Between Chosŏn Korea and Tokugawa Japan. Psychology Press. pp. 31–. ISBN 978-0-7007-1301-1. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ "Slavery in Nineteenth-Century Northern Thailand (Page 4 of 6)". Kyoto Review of South East Asia; (Colquhoun 1885:53).
- ^ "Slavery in Nineteenth-Century Northern Thailand: Archival Anecdotes and Village Voices" (Page 3 of 6). The Kyoto Review of South Asia
- ^ "Aztec Social Structure". The University of Texas at Austin.
- ^ Joan E. Goodman; Tom McNeely (February 1, 2001). A Long and Uncertain Journey: The 27,000 Mile Voyage of Vasco Da Gama. Mikaya Press. ISBN 978-0-9650493-7-5. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ a b c de Oliveira Marques, António Henrique R. (1972). History of Portugal. Columbia University Press, ISBN 0-231-03159-9, pp. 158–160, 362–370.
- ^ K. J. P. Lowe (May 26, 2005). Black Africans In Renaissance Europe. Cambridge University Press. pp. 156–. ISBN 978-0-521-81582-6. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ David Northrup (April 4, 2002). Africa's Discovery of Europe: 1450 to 1850. Oxford University Press. pp. 8–. ISBN 978-0-19-514084-2. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ Klein, Herbert. The Atlantic Slave Trade.
- ^ CIA Factbook: Haiti
- ^ HEALTH IN SLAVERY
- ^ Billings, Warren (January 26, 2009). The Old Dominion in the Seventeenth Century: A Documentary History of Virginia, 1606–1700. ReadHowYouWant.com. pp. 286–287. ISBN 1-4429-6126-0.
- ^ Scott, Thomas Allan (July 1995). Cornerstones of Georgia history. University of Georgia Press. ISBN 9780820317434.
- ^ "Thurmond: Why Georgia's founder fought slavery". Retrieved October 4, 2009.
- ^ Steven Mintz. "Was slavery the engine of economic growth?". Digital History. Retrieved April 18, 2009.
- ^ "Ending the Slavery Blame-Game". The New York Times. April 22, 2010.
- ^ The Transatlantic Slave Trade Alexander Ives Bortolot. Department of Art History and Archaeology, Columbia University.
- ^ Nigeria – The Slave Trade. Source: U. S. Library of Congress.
- ^ a b Bound To Africa — The Mandinka Legacy In The New World
- ^ Ronald Segal (1995). The Black Diaspora: Five Centuries of the Black Experience Outside Africa. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. p. 4. ISBN 0-374-11396-3.
It is now estimated that 11,863,000 slaves were shipped across the Atlantic. [Note in original: Paul E. Lovejoy, "The Impact of the Atlantic Slave Trade on Africa: A Review of the Literature, " in Journal of African History 30 (1989), p. 368.] ... It is widely conceded that further revisions are more likely to be upward than downward.
- ^ Rubinstein, W. D. (2004). Genocide: a history. Pearson Education. pp. 76–78. ISBN 0-582-50601-8.
- ^ "Frontline: Famous Families". PBS. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ Indentured Servitude in Colonial America. Deanna Barker, Frontier Resources.
- ^ Higginbotham, A. Leon (1975). In the Matter of Color: Race and the American Legal Process: The Colonial Period. Greenwood Press. ISBN 9780195027457.
- ^ Foner, Philip S. (1980). "History of Black Americans: From Africa to the emergence of the cotton kingdom". Oxford University Press.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Selling Poor Steven. Philip Burnham, American Heritage Magazine.
- ^ 1860 Census Results, The Civil War Home Page.
- ^ [1] "Small Truth Papering Over a Big Lie"
- ^ Stephen D. Behrendt, David Richardson, and David Eltis, W. E. B. Du Bois Institute for African and African-American Research, Harvard University. Based on "records for 27,233 voyages that set out to obtain slaves for the Americas". Stephen Behrendt (1999). "Transatlantic Slave Trade". Africana: The Encyclopedia of the African and African American Experience. New York: Basic Civitas Books. ISBN 0-465-00071-1.
- ^ "AFRICAN-AMERICANS". History.com.
- ^ Birth of a Nation / "Has the bloody 200-year history of Haiti doomed it to more violence?", San Francisco Chronicle, May 30, 2004.
- ^ Sons Of Providence: The Brown Brothers, the Slave Trade, and the American Revolution By Charles Rappleye. 2006 Simon & Schuster. 978-0743266871
- ^ Richard S. Newman, Transformation of American abolitionism: fighting slavery in the early Republic chapter 1
- ^ Kolchin p. 96
- ^ Berlin pp. 161–162
- ^ a b Berlin pp. 168–169. Kolchin p. 96. Kolchin notes that Fogel and Engerman maintained that 84% of slaves moved with their families but "most other scholars assign far greater weight ... to slave sales. " Ransome (p. 582) notes that Fogel and Engermann based their conclusions on the study of some counties in Maryland in the 1830s and attempt to extrapolate that as reflective of the entire South over the entire period.
- ^ a b Robert C. Davis (December 5, 2003). Christian Slaves, Muslim Masters: White Slavery in the Mediterranean, the Barbary Coast, and Italy, 1500–1800. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-333-71966-4. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ Rees Davies, British Slaves on the Barbary Coast, BBC, July 1, 2003
- ^ Halil Inalcik. "Servile Labor in the Ottoman Empire" in A. Ascher, B. K. Kiraly, and T. Halasi-Kun (eds), The Mutual Effects of the Islamic and Judeo-Christian Worlds: The East European Pattern, Brooklyn College, 1979, pp. 25–43.
- ^ Orest Subtelny (2000). Ukraine: A History. University of Toronto Press. pp. 106–. ISBN 978-0-8020-8390-6. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ Fisher 'Muscovy and the Black Sea Slave Trade', pp. 580—582. [2]
- ^ Soldier Khan By Mike Bennighof, Ph. D. September 2007
- ^ "Islam and Slavery" (PDF). Lse.ac.uk. July 30, 2010. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ Willem Adriaan Veenhoven; Winifred Crum Ewing; Stichting Plurale Samenlevingen (1975). Case Studies on Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms: A World Survey. BRILL. pp. 452–. ISBN 978-90-247-1779-8. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ "Religion & Ethics – Islam and slavery: Abolition". BBC. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ ""Horrible Traffic in Circassian Women—Infanticide in Turkey, " New York Daily Times, August 6, 1856". Chnm.gmu.edu. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "Soldier Khan". Avalanchepress.com. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ com/ngm/data/2001/10/01/html/ft_20011001.6.html Swahili Coast. Nationalgeographic. com
- ^ Remembering East African slave raids, BBC News, March 30, 2007
- ^ Focus on the slave trade, BBC News, September 3, 2001
- ^ Gwyn Campbell; Suzanne Miers; Joseph Calder Miller (2007). Women and Slavery: Africa, the Indian Ocean world, and the medieval north Atlantic. Ohio University Press. pp. 173–. ISBN 978-0-8214-1724-9. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ Lewis. Race and Slavery in the Middle East, Oxford Univ Press 1994.
- ^ Milton, Giles (2004). White Gold: the Extraordinary Story of Thomas Pellow and North Africa's One Million European Slaves. Hodder. p. 352. ISBN 0-340-79469-0.
- ^ "When Europeans were Slaves". Researchnews.osu.edu. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ Davis, Robert. Christian Slaves, Muslim Masters: White Slavery in the Mediterranean, the Barbary Coast and Italy, 1500–1800. Based on "records for 27,233 voyages that set out to obtain slaves for the Americas". Stephen Behrendt, "Transatlantic Slave Trade", Africana: The Encyclopedia of the African and African American Experience (New York: Basic Civitas Books, 1999), ISBN 0-465-00071-1.
- ^ "Forced and Bonded Child Labor". U.S. Department of Labor.
- ^ "Forced labour – Themes". Ilo.org. Retrieved March 14, 2010.
- ^ [3] Anti-Slavery Society "How many Slaves Are There?" " A recent newspaper article questioned the credibility of estimates by Professor Kevin Bales and others which give an estimate of 27 million slaves, or others who give an estimate of 100 million slaves."
- ^ Bales, Kevin (1999). "1". Disposable People: New Slavery in the Global Economy. University of California Press. p. 9. ISBN 0-520-21797-7.
- ^ A Global Alliance Against Forced Labour. International Labour Organisation. ISBN 92-2-115360-6.
- ^ a b c d e Kara, Siddharth (October 2008). Sex Trafficking – Inside the Business of Modern Slavery. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-13960-1.
- ^ "For 15 million in India, a childhood of slavery". The New York Times. January 30, 2003
- ^ "Child Slaves Abandoned to India's Silk Industry". Human Rights Watch. January 23, 2003
- ^ "Economics and Slavery" (PDF). Du.edu. Retrieved August 18, 2013.
- ^ Bradford, Laurence (July 23, 2013). "Modern day slavery in Southeast Asia: Thailand and Cambodia". Inside Investor. Retrieved July 24, 2013.
- ^ "India, China, Pakistan, Nigeria on slavery's list of shame - CNN.com". CNN. October 18, 2013.
- ^ "27 Million People Said to Live in 'Modern Slavery'". The New York Times. June 20, 2013.
- ^ http://usnews.nbcnews.com/_news/2013/06/19/19042103-modern-day-slavery-state-dept-says-millions-of-human-trafficking-victims-go-unidentified
- ^ "Nepal abolishes slave labour system". ABC News. September 8, 2008.
- ^ "Commemoration of the Abolition of Slavery Project". Uclan.ac.uk. May 20, 2008. Retrieved August 29, 2010.[dead link]
- ^ "Chinese Police Find Child Slave". BBC News. April 30, 2008. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "Convictions in China slave trial". BBC News. July 17, 2007. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "Acme of Obscenity". Retrieved March 28, 2010.
- ^ a b "Convictions in China slave trial". BBC. July 17, 2007. Retrieved January 4, 2008.
- ^ Zhe, Zhu (June 15, 2007). "More than 460 rescued from brick kiln slavery". China Daily. Retrieved January 4, 2008.
- ^ "State Enslavement in North Korea" (PDF). Rhoda E. Howard-Hassmann, Wilfrid Laurier University, Canada. March 16, 2012. Retrieved July 17, 2012.
- ^ "The Hidden Gulag – Exposing Crimes against Humanity in North Korea's Vast Prison System" (PDF). The Committee for Human Rights in North Korea. Retrieved July 17, 2012.
- ^ "North Korea: Political Prison Camps" (PDF). Amnesty International. May 4, 2011. Retrieved July 17, 2012.
- ^ "Political Prison Camps in North Korea Today" (PDF). Database Center for North Korean Human Rights. July 15, 2011. Retrieved July 17, 2012.
- ^ "8.C Crimes Against Humanity: Enslavement (pp. 43 - 45)". North Korea: A case to answer – a call to act (PDF). 2007. Retrieved July 17, 2012.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ "North Korea: New images reveal true scale of political prison camps". Amnesty International. May 3, 2011. Retrieved July 17, 2012.
- ^ Hernandez, Vladimir (June 26, 2010). "Forced labour clouds boom in Brazil's Amazon". BBC News. Retrieved August 29, 2010; Phillips, Tom (January 3, 2009). "Brazilian taskforce frees more than 4,500 slaves after record number of raids on remote farms". The Guardian. Retrieved February 8, 2014.
- ^ Report: 225,000 Haiti children in slavery, USATODAY.com, 2009-12-22. Retrieved February 16, 2010.
- ^ IRAQ: Black Iraqis hoping for a Barack Obama win, Los Angeles Times
- ^ Fortin, Jacey (January 16, 2013). "Mali's Other Crisis: Slavery Still Plagues Mali, And Insurgency Could Make It Worse". International Business Times.
- ^ E. Benjamin Skinner (January 18, 2010). "sex trafficking in South Africa: World Cup slavery fear". Time. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "Trafficking FAQs – Amnesty International USA". Amnestyusa.org. March 30, 2007. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ Lost Daughters – An Ongoing Tragedy in Nepal Women News Network – WNN, Dec 5, 2008
- ^ a b "US State Department Trafficking report". State.gov. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "Mauritanian MPs pass slavery law". BBC News. August 9, 2007. Retrieved January 8, 2011.
- ^ "Mauritania made slavery illegal last month". Saiia.org.za. September 6, 2007. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "The Abolition season on BBC World Service". BBC News. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ John D. Sutter (March 2012). "Slavery's last stronghold". CNN. Retrieved May 28, 2012.
- ^ "Mauritanian MPs pass slavery law". BBC News. August 9, 2007. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "UN: There is hope for Mauritania's slaves". CNN. March 17, 2012.
- ^ http://www.irinnews.org/report/97016/mauritania-anti-slavery-law-still-tough-to-enforce
- ^ "My Career Redeeming Slaves". MEQ. December 1999. Retrieved July 31, 2008.
- ^ "Slavery, Abduction and Forced Servitude in Sudan". US Department of State. May 22, 2002. Retrieved March 20, 2014.
- ^ "The Shackles of Slavery in Niger". ABC News. June 3, 2005. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ Andersson, Hilary (February 11, 2005). "Born to be a slave in Niger". BBC News. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "Slavery Today". BBC News. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "Niger Profile". BBC News. 2012. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
- ^ http://www.irinnews.org/report/53497/niger-slavery-an-unbroken-chain
- ^ Thomas, Katie (March 12, 2007). "Congo's Pygmies live as slaves". The News & Observer. Archived from the original on February 28, 2009.
- ^ As the World Intrudes, Pygmies Feel Endangered, New York Times
- ^ U. S. Department of State Country Reports on Human Rights Practices, 2005 Human Rights Report on Côte d'Ivoire
- ^ Anti-Slavery Society Convention, 1840, Benjamin Robert Haydon, 1841, National Portrait Gallery, London, NPG599, Given by British and Foreign Anti-Slavery Society in 1880
- ^ Clarence-Smith, William. "Religions and the abolition of slavery—a comparative approach" (PDF). Retrieved August 28, 2013.
- ^ The Earth and Its Peoples: A Global History. Cengage Learning. 2009. p. 165. ISBN 9780618992386.
- ^ Encyclopedia of Antislavery and Abolition. Greenwood Publishing Group. 2011. p. 155. ISBN 9780313331435.
- ^ S. M.Wise, Though the Heavens May Fall, Pimlico (2005)
- ^ Abolition Movement. Online Encyclopedia
- ^ "uk/history/battles/royal-navy-and-the-slave-trade/ Royal Navy and the Slave Trade". The National Archives.
- ^ Anti-Slavery International UNESCO. Retrieved October 20, 2011
- ^ shtml Sailing against slavery. By Jo Loosemore. BBC – Devon – Abolition
- ^ "The West African Sqron and slave trade". Pdavis.nl. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ Foner, Eric. "Forgotten step towards freedom, " New York Times. December 30, 2007.
- ^ Social Aspects of the Civil War. Department of the Interior National Park Service.
- ^ Kathleen Collins, "The Scourged Back," History of Photography 9 (January 1985): 43–45.[4]
- ^ "Slave Emancipation and the Expansion of Islam, 1905–1914". p. 11.
- ^ "The law against slavery". Religion & Ethics – Ethical issues. BBC News. Retrieved October 5, 2008.
- ^ "ILO seeks to charge Myanmar junta with atrocities". Reuters. November 16, 2006. Retrieved November 17, 2006.[dead link]
- ^ "ILO asks Myanmar to declare forced labour banned". Reuters. November 14, 2007. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "ILO cracks the whip at Yangon". Asia Times. March 29, 2005. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "BBC report on Mani case". BBC News. October 27, 2008. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ North, Douglass C. (December 1971). "The Rise and Fall of the Manorial System: A Theoretical Model". The Journal of Economic History. 31 (4): 777–803. doi:10.1017/S0022050700074623. JSTOR 2117209.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Domar, Evsey D. (March 1970). "The Causes of Slavery or Serfdom: A Hypothesis". The Journal of Economic History. 30 (1): 18–32. JSTOR 2116721.
- ^ Lagerlöf, Nils-Petter (November 12, 2006). "Slavery and other property rights". Ideas. repec.org. Retrieved May 6, 2009.
- ^ "Technology". History.com. January 4, 2008. Archived from the original on April 23, 2008. Retrieved May 6, 2009.
- ^ John R. McKivigan; Mitchell Snay (November 1, 1998). Religion and the Antebellum Debate Over Slavery. University of Georgia Press. pp. 68–. ISBN 978-0-8203-2076-2. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ Charles L. Griswold (1999). Adam Smith and the Virtues of Enlightenment. Cambridge University Press. pp. 198–. ISBN 978-0-521-62891-4. Retrieved May 31, 2012.
- ^ a b Bryan Caplan. "Economics of Slavery Lecture Notes".
- ^ name="slavery1"/
- ^ Robert E. Wright, Fubarnomics (Buffalo, N. Y.: Prometheus, 2010), 83–116.
- ^ Ellerman 1992.
- ^ Thompson 1966, p. 599.
- ^ Thompson 1966, p. 912.
- ^ Ostergaard 1997, p. 133.
- ^ Lazonick 1990, p. 37.
- ^ "wage slave". merriam-webster.com. Retrieved March 4, 2013.
- ^ "wage slave". dictionary.com. Retrieved March 4, 2013.
- ^ "...vulgar are the means of livelihood of all hired workmen whom we pay for mere manual labour, not for artistic skill; for in their case the very wage they receive is a pledge of their slavery." – De Officiis [5]
- ^ Marx 1990, p. 1006: "[L]abour-power, a commodity sold by the worker himself."
- ^ Another one, of course, being the capitalists' theft from workers via surplus-value.
- ^ Nelson 1995, p. 158. This Marxist objection is what motivated Nelson's essay, which argues that labour is not, in fact, a commodity.
- ^ Adu Boahen, Topics In West African History p. 110
- ^ "Afrikan Involvement In Atlantic Slave Trade, By Kwaku Person-Lynn, Ph. D". Africawithin.com. Archived from the original on April 18, 2008. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ João C. Curto. Álcool e Escravos: O Comércio Luso-Brasileiro do Álcool em Mpinda, Luanda e Benguela durante o Tráfico Atlântico de Escravos (c. 1480–1830) e o Seu Impacto nas Sociedades da África Central Ocidental. Translated by Márcia Lameirinhas. Tempos e Espaços Africanos Series, vol. 3. Lisbon: Editora Vulgata, 2002. ISBN 978-972-8427-24-5.
- ^ a b "Ending the Slavery Blame-Game ". The New York Times. April 22, 2010.
- ^ a b "Benin Officials Apologize For Role In U.s. Slave Trade". Chicago Tribune. May 1, 2000.
- ^ What the papers say, BBC News, September 22, 2006
- ^ Blair 'sorrow' over slave trade, BBC News, November 27, 2006.
- ^ Blair 'sorry' for UK slavery role BBC. Retrieved February 23, 2012.
- ^ "Virginia 'sorry' for slavery role". BBC News. February 25, 2007. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ Hale, Beth (August 23, 2007). "Livingstone breaks down in tears at slave trade memorial". Daily Mail. London. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ Congress Apologizes for Slavery, Jim Crow NPR. Retrieved October 20, 2011
- ^ "Barack Obama praises Senate slavery apology". Telegraph. June 19, 2009
- ^ Agence France-Presse. "Obama praises 'historic' Senate slavery apology". Google News, June 18, 2009. Accessed 22 July 2009.
- ^ Nitkin, David (March 2, 2007). "A New Twist to an Intriguing Family History". Baltimore Sun. Archived from the original on September 30, 2007.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Gaddafi apologizes for Arab slave traders". Press TV. October 11, 2010.
- ^ An Idea Not Worth Drafting: Conscription is Slavery by Peter Krembs
- ^ Nationalized Slavery; A policy Italy should dump by Dave Kopel refers to both the military and national service requirements of Italy as slavery.
- ^ Are you a wage slave? WSPUS, 30 April 2010. Retrieved 17 February 2014.
- ^ E. g., Machan, Tibor R. (April 13, 2000). "Tax Slavery". Ludwig von Mises Institute. Retrieved October 9, 2006.
- ^ Spiegel, Marjorie. The Dreaded Comparison: Human and Animal Slavery, New York: Mirror Books, 1996.
- ^ Michael T. Martin and David C. Wall, "The Politics of Cine-Memory: Signifying Slavery in the History Film," in Robert A. Rosenstone and Constantin Parvulesu, eds. A Companion to the Historical Film (Wiley-Blackwell, 2013), pp. 445–467.
- ^ Melvyn Stokes, D.W. Griffith's the Birth of a Nation: A History of the Most Controversial Motion Picture of All Time (2008)
- ^ Robert E. Morsberger, "Slavery and 'The Santa Fe Trail,' or, John Brown on Hollywood's Sour Apple Tree," American Studies (1977) 18#2 pp. 87–98. online
- ^ Hernán Vera; Andrew M. Gordon (2003). Screen saviors: Hollywood fictions of whiteness. Rowman & Littlefield. pp. 54–56. ISBN 9780847699476.
- ^ William L. Van Deburg, Slavery and Race in American Popular Culture (1984) covers films, fiction, television, and the stage.
- ^ Natalie Zemon Davis, Slaves on Screen: Film and Historical Vision (2002) ch 2
- ^ Davis, Slaves on Screen: Film and Historical Vision (2002) ch 3
- ^ Steven Mintz, "Spielberg's Amistad and the History Classroom," The History Teacher (1998) 31#3 pp. 370–373 in JSTOR
- ^ Davis, Slaves on Screen: Film and Historical Vision (2002)
- ^ Ira Berlin, "American Slavery in History and Memory and the Search for Social Justice," Journal of American History (2004) 90#4 pp. 1251–1268. in JSTOR
- ^ "Films about Slavery and the transAtlantic Slave Trade". Ama. africatoday.com. Retrieved June 3, 2011.
- ^ IMDb Search
Bibliography
Surveys and reference
- Bales, Kevin, Disposable People: New Slavery in the Global Economy (1999)
- Campbell, Gwyn, Suzanne Miers, and Joseph C. Miller, eds. Women and Slavery. Volume 1: Africa, the Indian Ocean World, and the Medieval Atlantic; Women and Slavery. Volume 2: The Modern Atlantic (2007)
- Davies, Stephen (2008). "Slavery, World". In Hamowy, Ronald (ed.). The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE; Cato Institute. pp. 464–9. ISBN 978-1-4129-6580-4. LCCN 2008009151. OCLC 750831024.
- Davis, David Brion. The Problem of Slavery in the Age of Revolution, 1770-1823 (1999)
- Davis, David Brion. The Problem of Slavery in Western Culture (1988)
- Drescher, Seymour. Abolition: A History of Slavery and Antislavery (2009) highly regarded history of slavery and its abolition, worldwide
- Finkelman, Paul, ed. Encyclopedia of Slavery (1999)
- Gordon, M. Slavery in the Arab World (1989)
- Greene, Jacqueline. Slavery in Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, (2001), ISBN 0-531-16538-8
- Joseph, Celucien L. Race, Religion, and The Haitian Revolution: Essays on Faith, Freedom, and Decolonization (CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform, 2012)
- Joseph, Celucien L. From Toussaint to Price-Mars: Rhetoric, Race, and Religion in Haitian Thought (CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform, 2013)
- Lal, K. S. Muslim Slave System in Medieval India (1994) ISBN 81-85689-67-9
- Miers, Suzanne, and Igor Kopytoff, eds. Slavery In Africa: Historical & Anthropological Perspectives (1979)
- Morgan, Kenneth. Slavery and the British Empire: From Africa to America (2008)
- Postma, Johannes. The Atlantic Slave Trade, (2003)
- Rodriguez, Junius P., ed., The Historical Encyclopedia of World Slavery (1997)
- Rodriguez, Junius P., ed. Slavery in the United States: A Social, Political, and Historical Encyclopedia (2007)
- Shell, Robert Carl-Heinz Children Of Bondage: A Social History Of The Slave Society At The Cape Of Good Hope, 1652–1813 (1994)
- Westermann, William Linn The Slave Systems of Greek and Roman Antiquity (1955), ISBN 0-87169-040-3
- Uncited sources
- Hogendorn, Jan and Johnson Marion: The Shell Money of the Slave Trade. African Studies Series 49, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1986.
- The Slavery Reader, ed. by Rigas Doganis, Gad Heuman, James Walvin, Routledge 2003
- United States
- Berlin, Ira. Many Thousands Gone: The First Two Centuries of Slavery in North America (1999), most important recent survey
- Blackmon, Douglas A. Slavery by Another Name: The Re-Enslavement of Black Americans from the Civil War to World War II Doubleday (March 23, 2008), ISBN 0-385-50625-2 ISBN 978-0-385-50625-0
- Boles, John. Black Southerners: 1619–1869 (1983) brief survey
- Engerman, Stanley L. Terms of Labor: Slavery, Serfdom, and Free Labor (1999)
- Genovese Eugene D. Roll, Jordan Roll (1974), classic study
- Richard H. King, "Marxism and the Slave South", American Quarterly 29 (1977), 117–31, a critique of Genovese
- Escott, Paul D. "Remembering Slavery: African Americans Talk about Their Personal Experiences of Slavery and Freedom" Journal of Southern History, Vol. 67, 2001
- Mintz, S. Slavery Facts & Myths, Digital History
- Parish, Peter J. Slavery: History and Historians (1989)
- Phillips, Ulrich B. American Negro Slavery: A Survey of the Supply, Employment and Control of Negro Labor as Determined by the Plantation Regime (1918; paperback reprint 1966), southern white perspective
- Phillips, Ulrich B. Life and Labor in the Old South (1929)
- Sellers, James B. Slavery in Alabama (1950).
- Sydnor, Charles S. Slavery in Mississippi (1933)
- Stamp, Kenneth M. The Peculiar Institution: Slavery in the Ante-Bellum South (1956), a rebuttal of U B Philipps
- Trenchard, David (2008). "Slavery in America". In Hamowy, Ronald (ed.). The Encyclopedia of Libertarianism. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE; Cato Institute. pp. 469–70. ISBN 978-1-4129-6580-4. LCCN 2008009151. OCLC 750831024.
- Vorenberg, Michael. Final Freedom: The Civil War, the Abolition of Slavery, and the Thirteenth Amendment (2001)
- Weinstein, Allen, Frank O. Gatell, and Lewis Sarasohn, eds., American Negro Slavery: A Modern Reader, third ed. (1978)
- Slavery in the modern era
- Jesse Sage and Liora Kasten, Enslaved: True Stories of Modern Day Slavery, Palgrave Macmillan, 2008 ISBN 978-1-4039-7493-8
- Tom Brass, Marcel van der Linden, and Jan Lucassen, Free and Unfree Labour. Amsterdam: International Institute for Social History, 1993
- Tom Brass, Towards a Comparative Political Economy of Unfree Labour: Case Studies and Debates, London and Portland, OR: Frank Cass Publishers, 1999. 400 pages.
- Tom Brass and Marcel van der Linden, eds., Free and Unfree Labour: The Debate Continues, Bern: Peter Lang AG, 1997. 600 pages. A volume containing contributions by all the most important writers on modern forms of unfree labour.
- Kevin Bales, Disposable People. New Slavery in the Global Economy, Revised Edition, University of California Press 2004, ISBN 0-520-24384-6
- Kevin Bales (ed.), Understanding Global Slavery Today. A Reader, University of California Press 2005, ISBN 0-520-24507-5freak
- Kevin Bales, Ending Slavery: How We Free Today's Slaves, University of California Press 2007, ISBN 978-0-520-25470-1.
- Mende Nazer and Damien Lewis, Slave: My True Story, ISBN 1-58648-212-2. Mende is a Nuba, captured at 12 years old. She was granted political asylum by the British government in 2003.
- Gary Craig, Aline Gaus, Mick Wilkinson, Klara Skrivankova and Aidan McQ e (2007). Contemporary slavery in the UK: Overview and key issues, Joseph Rowntree Foundation. ISBN 978-1-85935-573-2.
- David Hawk, The Hidden Gulag - Slave Labor Camps in North Korea, Washington DC: Committee for Human Rights in North Korea, 2012, ISBN 0-615-62367-0
- Somaly Mam Foundation
- Thomas Sowell, The Real History of Slavery, in: Black Rednecks and White Liberals, San Francisco: Encounter Books, 2005. ISBN 978-1-59403-086-4.
External links
Historical
- Slavery Resource Guide, from the Library of Congress
- Digital Library on American Slavery
- African Holocaust
- Emory and Oxford College
- Slavery Fact Sheets, Digital History
- The West African Sqron and slave trade
- Slavery – PBS
- Understanding Slavery
- Slavery
- Slavery Museum. Great Britain.
- Archives on slavery held by the University of London
- Mémoire St Barth (archives & history of slavery, slave trade and their abolition), Comité de Liaison et d'Application des Sources Historiques.
- Archives of the Middelburgsche Commercie Compagnie (MCC) 'Trade Company of Middelburg' (Inventory of the archives of the Dutch slave trade across the Atlantic)
Modern
- news-politics, modern-slavery Modern Slavery - slideshow by The First Post
- Slavery – PBS
- Walk Free Foundation – Global Slavery Index 2013 | Explore the Index
Template:Articles of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights
