Korean War
| Korean War | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Cold War and the Korean conflict | |||||||||
 Clockwise from top:
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||
|
| |||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
|
Peak strength:
Together: 972,334 |
Together: 1,742,000 Total: | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
Total dead and missing: 170,927 dead and 32,585 missing[c] Details
|
Total dead and missing: 398,000–926,000 dead and 145,000+ missing[e] Details
| ||||||||
The Korean War (also known by other names) was fought between North Korea and South Korea from 1950 to 1953. The war began on 25 June 1950 when North Korea invaded South Korea following clashes along the border and rebellions in South Korea.[51][52][53] North Korea was supported by China and the Soviet Union while South Korea was supported by the United States and allied countries. The fighting ended with an armistice on 27 July 1953.
In 1910, Imperial Japan annexed Korea, where it ruled for 35 years until its surrender at the end of World War II on 15 August 1945.[f] The United States and the Soviet Union divided Korea along the 38th parallel into two zones of occupation. The Soviets administered the northern zone and the Americans administered the southern zone. In 1948, as a result of Cold War tensions, the occupation zones became two sovereign states. A socialist state, the Democratic People's Republic of Korea, was established in the north under the totalitarian communist leadership of Kim Il-sung, while a capitalist state, the Republic of Korea, was established in the south under the authoritarian, autocratic leadership of Syngman Rhee. Both governments of the two new Korean states claimed to be the sole legitimate government of all of Korea, and neither accepted the border as permanent.
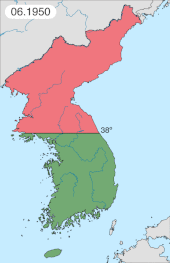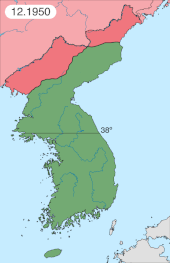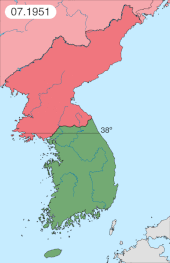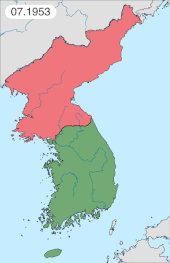
North Korean military (Korean People's Army, KPA) forces crossed the border and drove into South Korea on 25 June 1950.[54] Joseph Stalin had final decision power and several times demanded North Korea postpone the invasion, until he gave final approval in spring 1950.[55] The United Nations Security Council denounced the North Korean move as an invasion and authorized the formation of the United Nations Command and the dispatch of forces to Korea[56] to repel it.[57][58] The Soviet Union was boycotting the UN for recognizing Taiwan (Republic of China) as China,[59] and China (People's Republic of China) on the mainland was not recognized by the UN, so neither could support their ally North Korea at the Security Council meeting. Twenty-one countries of the United Nations eventually contributed to the UN force, with the United States providing around 90% of the military personnel.[60]
After the first two months of war, South Korean Army (ROKA) and American forces hastily dispatched to Korea were on the point of defeat, retreating to a small area behind a defensive line known as the Pusan Perimeter. In September 1950, a risky amphibious UN counteroffensive was launched at Incheon, cutting off KPA troops and supply lines in South Korea. Those who escaped envelopment and capture were forced back north. UN forces invaded North Korea in October 1950 and moved rapidly towards the Yalu River—the border with China—but on 19 October 1950, Chinese forces of the People's Volunteer Army (PVA) crossed the Yalu and entered the war.[54] The UN retreated from North Korea after the First Phase Offensive and the Second Phase Offensive. Chinese forces were in South Korea by late December.
In these and subsequent battles, Seoul was captured four times, and communist forces were pushed back to positions around the 38th parallel, close to where the war had started. After this, the front stabilized, and the last two years were a war of attrition. The war in the air, however, was never a stalemate. North Korea was subject to a massive U.S. bombing campaign. Jet-powered fighters confronted each other in air-to-air combat for the first time in history, and Soviet pilots covertly flew in defense of their communist allies.
The fighting ended on 27 July 1953 when the Korean Armistice Agreement was signed. The agreement created the Korean Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) to separate North and South Korea, and allowed the return of prisoners. However, no peace treaty was ever signed, and the two Koreas are technically still at war, engaged in a frozen conflict.[61][62] In April 2018, the leaders of North and South Korea met at the DMZ[63] and agreed to work toward a treaty to end the Korean War formally.[64]
The Korean War was among the most destructive conflicts of the modern era, with approximately 3 million war fatalities and a larger proportional civilian death toll than World War II or the Vietnam War. It incurred the destruction of virtually all of Korea's major cities, thousands of massacres by both sides, including the mass killing of tens of thousands of suspected communists by the South Korean government, and the torture and starvation of prisoners of war by the North Koreans. North Korea became among the most heavily bombed countries in history.[65] Additionally, several million North Koreans are estimated to have fled North Korea over the course of the war.[66]
Names
| Korean War | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Korean name | |||||||
| Hangul | 6·25 전쟁 or 한국 전쟁 | ||||||
| Hanja | 六二五戰爭 or 韓國戰爭 | ||||||
| |||||||
| North Korean name | |||||||
| Chosŏn'gŭl | 조국해방전쟁 | ||||||
| Hancha | 祖國解放戰爭 | ||||||
| |||||||
In South Korea, the war is usually referred to as the "625 War" (6·25 전쟁; 六二五戰爭), the "625 Upheaval" (6·25 동란; 六二五動亂; yugio dongnan), or simply "625", reflecting the date of its commencement on 25 June.[67]
In North Korea, the war is officially referred to as the "Fatherland Liberation War" (Choguk haebang chŏnjaeng) or alternatively the "Chosŏn [Korean] War" (조선전쟁; Chosŏn chŏnjaeng).[68]
In mainland China, the segment of the war after the intervention of the People's Volunteer Army is most commonly and officially known as the "Resisting America and Assisting Korea War"[69] (Chinese: 抗美援朝战争; pinyin: Kàngměi Yuáncháo Zhànzhēng), although the term "Chosŏn War" (Chinese: 朝鮮戰爭; pinyin: Cháoxiǎn Zhànzhēng) is sometimes used unofficially. The term "Hán (Korean) War" (Chinese: 韓戰; pinyin: Hán Zhàn) is most commonly used in Taiwan (Republic of China), Hong Kong and Macau.
In the U.S., the war was initially described by President Harry S. Truman as a "police action", as the United States never formally declared war on its opponents and the operation was conducted under the auspices of the United Nations.[70] It has been sometimes referred to in the English-speaking world as "The Forgotten War" or "The Unknown War" because of the lack of public attention it received both during and after the war, relative to the global scale of World War II, which preceded it, and the subsequent angst of the Vietnam War, which succeeded it.[71][72]
Background
Imperial Japanese rule (1910–1945)
Imperial Japan severely diminished the influence of China over Korea in the First Sino-Japanese War (1894–95), ushering in the short-lived Korean Empire.[73] A decade later, after defeating Imperial Russia in the Russo-Japanese War (1904–05), Japan made the Korean Empire its protectorate with the Eulsa Treaty in 1905, then annexed it with the Japan–Korea Annexation Treaty in 1910. After that, the Korean Empire fell and Korea was directly ruled by Japan from 1910 to 1945.[74]
Many Korean nationalists fled the country. The Provisional Government of the Republic of Korea was founded in 1919 in Nationalist China. It failed to achieve international recognition, failed to unite the various nationalist groups, and had a fractious relationship with its U.S.-based founding president, Syngman Rhee.[75] From 1919 to 1925 and beyond, Korean communists led internal and external warfare against the Japanese.[76][77]
In China, the nationalist National Revolutionary Army and the communist People's Liberation Army (PLA) helped organize Korean refugees against the Japanese military, which had also occupied parts of China. The Nationalist-backed Koreans, led by Yi Pom-Sok, fought in the Burma Campaign (December 1941 – August 1945). The communists, led among others by Kim Il-sung, fought the Japanese in Korea and Manchuria.[78]
At the Cairo Conference in November 1943, China, the United Kingdom and the United States all decided that "in due course Korea shall become free and independent".[79]
Korea divided (1945–1949)
At the Tehran Conference in November 1943 and the Yalta Conference in February 1945, the Soviet Union promised to join its allies in the Pacific War within three months of the victory in Europe. Germany officially surrendered on 8 May 1945, and the USSR declared war on Japan and invaded Manchuria on 8 August 1945, three months later. This was three days after the atomic bombing of Hiroshima.[77][80] By 10 August, the Red Army had begun to occupy the north of Korea.[81]
On the night of 10 August in Washington, U.S. Colonels Dean Rusk and Charles H. Bonesteel III were assigned to divide Korea into Soviet and U.S. occupation zones and proposed the 38th Parallel as the dividing line. This was incorporated into the U.S. General Order No. 1, which responded to the Japanese surrender on 15 August. Explaining the choice of the 38th Parallel, Rusk observed, "even though it was further north than could be realistically reached by U. S. [sic] forces in the event of Soviet disagreement ... we felt it important to include the capital of Korea in the area of responsibility of American troops". He noted that he was "faced with the scarcity of U.S. forces immediately available and time and space factors which would make it difficult to reach very far north before Soviet troops could enter the area".[82][83] As Rusk's comments indicate, the U.S. doubted whether the Soviet government would agree to this.[84][85][86][87] Soviet leader Joseph Stalin, however, maintained his wartime policy of co-operation, and on 16 August, the Red Army halted at the 38th Parallel for three weeks to await the arrival of U.S. forces in the south.[81]
On 7 September 1945, General Douglas MacArthur issued Proclamation No. 1 to the people of Korea, announcing U.S. military control over Korea south of the 38th parallel and establishing English as the official language during military control.[88]
On 8 September 1945, U.S. Lieutenant General John R. Hodge arrived in Incheon to accept the Japanese surrender south of the 38th Parallel.[85] Appointed as military governor, Hodge directly controlled South Korea as head of the United States Army Military Government in Korea (USAMGIK 1945–48).[89]
In December 1945, Korea was administered by a U.S.–Soviet Union Joint Commission, as agreed at the Moscow Conference, with the aim of granting independence after a five-year trusteeship.[90][91] The idea was not popular among Koreans and riots broke out.[74] To contain them, the USAMGIK banned strikes on 8 December 1945 and outlawed the PRK Revolutionary Government and the PRK People's Committees on 12 December 1945.[92] Following further large-scale civilian unrest,[93] the USAMGIK declared martial law.
Citing the inability of the Joint Commission to make progress, the U.S. government decided to hold an election under United Nations auspices with the aim of creating an independent Korea. The Soviet authorities and the Korean Communists refused to co-operate on the grounds that it would not be fair, and many South Korean politicians boycotted it.[94][95] A general election was held in the South on 10 May 1948.[96][97] North Korea held parliamentary elections three months later on 25 August.[98]
The resultant South Korean government promulgated a national political constitution on 17 July 1948, and elected Syngman Rhee as President on 20 July 1948. This election is generally considered to have been manipulated by the Rhee regime. The Republic of Korea (South Korea) was established on 15 August 1948. In the Soviet Korean Zone of Occupation, the Soviet Union agreed to the establishment of a communist government[96] led by Kim Il-sung.[99]
The Soviet Union withdrew its forces from Korea in 1948, and U.S. troops withdrew in 1949.[100][101]
Chinese Civil War (1945–1949)
With the end of the war with Japan, the Chinese Civil War resumed in earnest between the Communists and Nationalists. While the Communists were struggling for supremacy in Manchuria, they were supported by the North Korean government with matériel and manpower.[102] According to Chinese sources, the North Koreans donated 2,000 railway cars worth of supplies while thousands of Koreans served in the Chinese PLA during the war.[103] North Korea also provided the Chinese Communists in Manchuria with a safe refuge for non-combatants and communications with the rest of China.[102]
The North Korean contributions to the Chinese Communist victory were not forgotten after the creation of the People's Republic of China (PRC) in 1949. As a token of gratitude, between 50,000 and 70,000 Korean veterans that served in the PLA were sent back along with their weapons, and they later played a significant role in the initial invasion of South Korea.[102] China promised to support the North Koreans in the event of a war against South Korea.[104]
After the formation of the PRC, the PRC government named the Western nations, led by the U.S., as the biggest threat to its national security.[105] Basing this judgment on multiple factors, including the idea of a Chinese century of humiliation at the hands of Western powers beginning in the mid-19th century,[106] U.S. support for the Nationalists during the Chinese Civil War,[107] and the ideological struggles between revolutionaries and reactionaries,[108] the PRC Chinese leadership believed that China would become a critical battleground in the U.S.' crusade against Communism.[109] As a countermeasure and to elevate China's standing among the worldwide Communist movements, the PRC leadership adopted a foreign policy that actively promoted Communist revolutions throughout territories on China's periphery.[110]
Communist insurgency in South Korea (1948–1950)
By 1948, a large-scale, North Korea-backed insurgency had broken out in the southern half of the peninsula. This was exacerbated by the ongoing undeclared border war between the Koreas, which saw division-level engagements and thousands of deaths on both sides.[111] The ROK in this time was almost entirely trained and focused on counterinsurgency, rather than conventional warfare. They were equipped and advised by a force of a few hundred American officers, who were largely successful in helping the ROKA to subdue guerrillas and hold its own against North Korean military (Korean People's Army, KPA) forces along the 38th parallel.[112] Approximately 8,000 South Korean soldiers and police died in the insurgent war and border clashes.[43]
The first socialist uprising occurred without direct North Korean participation, though the guerrillas still professed support for the northern government. Beginning in April 1948 on the isolated island of Jeju, the campaign saw mass arrests and repression by the South Korean government in the fight against the South Korean Labor Party, resulting in a total of 30,000 violent deaths, among them 14,373 civilians (of whom ~2,000 were killed by rebels and ~12,000 by ROK security forces). The Yeosu–Suncheon rebellion overlapped with it, as several thousand army defectors waving red flags massacred right-leaning families. This resulted in another brutal suppression by the government and between 2,976 and 3,392 deaths. By May 1949, both uprisings had been crushed.
Insurgency reignited in the spring of 1949 when attacks by guerrillas in the mountainous regions (buttressed by army defectors and North Korean agents) increased. Insurgent activity peaked in late 1949 as the ROKA engaged so-called People's Guerrilla Units. Organized and armed by the North Korean government, and backed up by 2,400 KPA commandos who had infiltrated through the border, these guerrillas launched a large offensive in September aimed at undermining the South Korean government and preparing the country for the KPA's arrival in force. This offensive failed.[113] However, by this point, the guerrillas were firmly entrenched in the Taebaek-san region of the North Gyeongsang Province (around Taegu), as well as in the border areas of the Gangwon Province.[114]
While the insurgency was ongoing, the ROKA and KPA engaged in multiple battalion-sized battles along the border, starting in May 1949.[112] Serious border clashes between South and North continued on 4 August 1949, when thousands of North Korean troops attacked South Korean troops occupying territory north of the 38th Parallel. The 2nd and 18th ROK Infantry Regiments repulsed initial attacks in Kuksa-bong (above the 38th Parallel)[115] and Ch'ungmu,[citation needed] and at the end of the clashes ROK troops were "completely routed".[116] Border incidents decreased significantly by the start of 1950.[114]
Meanwhile, counterinsurgency efforts in the South Korean interior intensified; persistent operations, paired with worsening weather conditions, eventually denied the guerrillas sanctuary and wore away their fighting strength. North Korea responded by sending more troops to link up with existing insurgents and build more partisan cadres; the number of North Korean infiltrators had reached 3,000 soldiers in 12 units by the start of 1950, but all of these units were destroyed or scattered by the ROKA.[117] On 1 October 1949, the ROKA launched a three-pronged assault on the insurgents in South Cholla and Taegu. By March 1950, the ROKA claimed 5,621 guerrillas killed or captured and 1,066 small arms seized. This operation crippled the insurgency. Soon after, the North Koreans made two final attempts to keep the uprising active, sending two battalion-sized units of infiltrators under the commands of Kim Sang-ho and Kim Moo-hyon. The first battalion was reduced in annihilation to a single man over the course of several engagements by the ROKA 8th Division. The second battalion was annihilated by a two-battalion hammer-and-anvil maneuver by units of the ROKA 6th Division, resulting in a loss toll of 584 KPA guerrillas (480 killed, 104 captured) and 69 ROKA troops killed, plus 184 wounded.[118] By spring of 1950, guerrilla activity had mostly subsided; the border, too, was calm.[119]
Prelude to war (1950)
By 1949, South Korean and U.S. military actions had reduced the active number of indigenous communist guerrillas in the South from 5,000 to 1,000. However, Kim Il-sung believed that widespread uprisings had weakened the South Korean military and that a North Korean invasion would be welcomed by much of the South Korean population. Kim began seeking Stalin's support for an invasion in March 1949, traveling to Moscow to attempt to persuade him.[120]
Stalin initially did not think the time was right for a war in Korea. PLA forces were still embroiled in the Chinese Civil War, while U.S. forces remained stationed in South Korea.[121] By spring 1950, he believed that the strategic situation had changed: PLA forces under Mao Zedong had secured final victory in China, U.S. forces had withdrawn from Korea, and the Soviets had detonated their first nuclear bomb, breaking the U.S. atomic monopoly. As the U.S. had not directly intervened to stop the communist victory in China, Stalin calculated that they would be even less willing to fight in Korea, which had much less strategic significance. The Soviets had also cracked the codes used by the U.S. to communicate with their embassy in Moscow, and reading these dispatches convinced Stalin that Korea did not have the importance to the U.S. that would warrant a nuclear confrontation.[122] Stalin began a more aggressive strategy in Asia based on these developments, including promising economic and military aid to China through the Sino-Soviet Treaty of Friendship, Alliance, and Mutual Assistance.[123]
In April 1950, Stalin gave Kim permission to attack the government in the South under the condition that Mao would agree to send reinforcements if needed. For Kim, this was the fulfillment of his goal to unite Korea after its division by foreign powers. Stalin made it clear that Soviet forces would not openly engage in combat, to avoid a direct war with the U.S.[124] Kim met with Mao in May 1950. Historical analyses regarding Mao's approval of Kim's plans differ.[125]: 28–9 Nikita Khrushchev's memoirs were long viewed as the most authoritative source, and Khrushchev wrote that Mao approved Kim's plans because Mao viewed the matter as one for the Korean people to decide for themselves.[125]: 29 Citing recent scholarship, Zhao Suisheng, writing in 2022, contends that Mao did not approve of Kim's plans in advance, opposing them over concerns that the U.S. would intervene and that China could be dragged into the conflict.[125]: 29 By some accounts, Mao agreed to support the North Korean invasion despite these concerns, as China desperately needed the economic and military aid promised by the Soviets.[126] However, Mao sent more ethnic Korean PLA veterans to Korea and promised to move an army closer to the Korean border.[127] Once Mao's commitment was secured, preparations for war accelerated.[128][129]
Soviet generals with extensive combat experience from the Second World War were sent to North Korea as the Soviet Advisory Group. These generals completed the plans for the attack by May.[130] The original plans called for a skirmish to be initiated in the Ongjin Peninsula on the west coast of Korea. The North Koreans would then launch a counterattack that would capture Seoul and encircle and destroy the ROK. The final stage would involve destroying South Korean government remnants and capturing the rest of South Korea, including the ports.[131]
On 7 June 1950, Kim Il-sung called for a Korea-wide election on 5–8 August 1950 and a consultative conference in Haeju on 15–17 June 1950. On 11 June, the North sent three diplomats to the South as a peace overture which Rhee rejected outright.[124] On 21 June, Kim Il-Sung revised his war plan to involve a general attack across the 38th Parallel, rather than a limited operation in the Ongjin Peninsula. Kim was concerned that South Korean agents had learned about the plans and that South Korean forces were strengthening their defenses. Stalin agreed to this change of plan.[132]
While these preparations were underway in the North, there were frequent clashes along the 38th Parallel, especially at Kaesong and Ongjin, many initiated by the South.[52][53] The ROK was being trained by the U.S. Korean Military Advisory Group (KMAG). On the eve of war, KMAG commander General William Lynn Roberts voiced utmost confidence in the ROK and boasted that any North Korean invasion would merely provide "target practice".[133] For his part, Syngman Rhee repeatedly expressed his desire to conquer the North, including when U.S. diplomat John Foster Dulles visited Korea on 18 June.[134]
Although some South Korean and U.S. intelligence officers predicted an attack from the North, similar predictions had been made before and nothing had happened.[135] The Central Intelligence Agency noted the southward movement by the KPA, but assessed this as a "defensive measure" and concluded an invasion was "unlikely".[136] On 23 June, UN observers inspected the border and did not detect that war was imminent.[137]
Comparison of forces
Throughout 1949 and 1950, the Soviets continued arming North Korea. After the Communist victory in the Chinese Civil War, ethnic Korean units in the PLA were sent to North Korea.[138] Chinese involvement was extensive from the beginning, building on previous collaboration between the Chinese and Korean communists during the Chinese Civil War. In the fall of 1949, two PLA divisions composed mainly of Korean-Chinese troops (the 164th and 166th) entered North Korea, followed by smaller units throughout the rest of 1949; these troops brought with them not only their experience and training, but also their weapons and other equipment, changing little but their uniforms. The reinforcement of the KPA with PLA veterans continued into 1950, with the 156th Division and several other units of the former Fourth Field Army arriving (also with their equipment) in February; the PLA 156th Division was reorganized as the KPA 7th Division. By mid-1950, between 50,000 and 70,000 former PLA troops had entered North Korea, forming a significant part of the KPA's strength on the eve of the war's beginning.[139] Several generals, such as Lee Kwon-mu, were PLA veterans born to ethnic Koreans in China. The combat veterans and equipment from China, the tanks, artillery and aircraft supplied by the Soviets, and rigorous training increased North Korea's military superiority over the South, armed by the U.S. military with mostly small arms, but no heavy weaponry such as tanks.[140] While older histories of the conflict often referred to these ethnic Korean PLA veterans as being sent from northern Korea to fight in the Chinese Civil War before being sent back, recent Chinese archival sources studied by Kim Donggill indicate that this was not the case. Rather, the soldiers were indigenous to China (part of China's longstanding ethnic Korean community) and were recruited to the PLA in the same way as any other Chinese citizen.[141]
According to the first official census in 1949, the population of North Korea numbered 9,620,000,[142] and by mid-1950, North Korean forces numbered between 150,000 and 200,000 troops, organized into 10 infantry divisions, one tank division, and one air force division, with 210 fighter planes and 280 tanks, who captured scheduled objectives and territory, among them Kaesong, Chuncheon, Uijeongbu and Ongjin. Their forces included 274 T-34-85 tanks, 200 artillery pieces, 110 attack bombers, and some 150 Yak fighter planes, and 35 reconnaissance aircraft. In addition to the invasion force, the North had 114 fighters, 78 bombers, 105 T-34-85 tanks, and some 30,000 soldiers stationed in reserve in North Korea.[85] Although each navy consisted of only several small warships, the North and South Korean navies fought in the war as seaborne artillery for their armies.
In contrast, the South Korean population was estimated at 20 million[143] and its army was unprepared and ill-equipped. As of 25 June 1950, the ROK had 98,000 soldiers (65,000 combat, 33,000 support), no tanks (they had been requested from the U.S. military, but requests were denied), and a 22-plane air force comprising 12 liaison-type and 10 AT-6 advanced-trainer airplanes. Large U.S. garrisons and air forces were in Japan,[144] but only 200–300 U.S. troops were in Korea.[145]
Course of the war

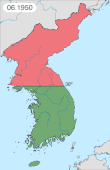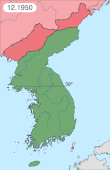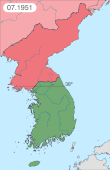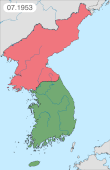
At dawn on Sunday, 25 June 1950, the KPA crossed the 38th Parallel behind artillery fire.[146] The KPA justified its assault with the claim that ROK troops attacked first and that the KPA were aiming to arrest and execute the "bandit traitor Syngman Rhee".[147] Fighting began on the strategic Ongjin Peninsula in the west.[148][149] There were initial South Korean claims that the 17th Regiment captured the city of Haeju, and this sequence of events has led some scholars to argue that the South Koreans fired first.[148][150]
Whoever fired the first shots in Ongjin, KPA forces attacked all along the 38th Parallel within an hour. The KPA had a combined arms force including tanks supported by heavy artillery. The ROK had no tanks, anti-tank weapons or heavy artillery to stop such an attack. In addition, the South Koreans committed their forces in a piecemeal fashion and these were routed in a few days.[151]
On 27 June, Rhee evacuated from Seoul with some of the government. On 28 June, at 2 am, the ROK blew up the Hangang Bridge across the Han River in an attempt to stop the KPA. The bridge was detonated while 4,000 refugees were crossing it and hundreds were killed.[152][153] Destroying the bridge also trapped many ROK units north of the Han River.[151] In spite of such desperate measures, Seoul fell that same day. A number of South Korean National Assemblymen remained in Seoul when it fell, and forty-eight subsequently pledged allegiance to the North.[154]
On 28 June, Rhee ordered the massacre of suspected political opponents in his own country.[155]
In five days, the ROK, which had 95,000 troops on 25 June, was down to less than 22,000 troops. In early July, when U.S. forces arrived, what was left of the ROK were placed under U.S. operational command of the United Nations Command.[156]
Factors in U.S. intervention
The Truman administration was unprepared for the invasion. Korea was not included in the strategic Asian Defense Perimeter outlined by United States Secretary of State Dean Acheson.[157] Truman himself was at his home in Independence, Missouri.[158] Military strategists were more concerned with the security of Europe against the Soviet Union than East Asia.[159] At the same time, the administration was worried that a war in Korea could quickly escalate without American intervention. Said diplomat John Foster Dulles in a cable: "To sit by while Korea is overrun by unprovoked armed attack would start a disastrous chain of events leading most probably to world war."[160]
While there was initial hesitance by some in the U.S. government to get involved in the war, considerations about Japan played a part in the ultimate decision to engage on behalf of South Korea. Especially after the fall of China to the Communists, U.S. experts on East Asia saw Japan as the critical counterweight to the Soviet Union and China in the region. While there was no U.S. policy dealing with South Korea directly as a national interest, its proximity to Japan increased the importance of South Korea. Said Kim: "The recognition that the security of Japan required a non-hostile Korea led directly to President Truman's decision to intervene ... The essential point ... is that the American response to the North Korean attack stemmed from considerations of U.S. policy toward Japan."[161][162]
Another major consideration was the possible Soviet reaction if the U.S. intervened. The Truman administration was fearful that a war in Korea was a diversionary assault that would escalate to a general war in Europe once the United States committed in Korea. At the same time, "[t]here was no suggestion from anyone that the United Nations or the United States could back away from [the conflict]".[163] Yugoslavia—a possible Soviet target because of the Tito-Stalin Split—was vital to the defense of Italy and Greece, and the country was first on the list of the National Security Council's post-North Korea invasion list of "chief danger spots".[164] Truman believed if aggression went unchecked, a chain reaction would be initiated that would marginalize the UN and encourage Communist aggression elsewhere. The UN Security Council approved the use of force to help the South Koreans, and the U.S. immediately began using air and naval forces that were in the area to that end. The Truman administration still refrained from committing troops on the ground because some advisers believed the North Koreans could be stopped by air and naval power alone.[165]
The Truman administration was still uncertain if the attack was a ploy by the Soviet Union or just a test of U.S. resolve. The decision to commit ground troops became viable when a communiqué was received on 27 June indicating the Soviet Union would not move against U.S. forces in Korea.[166] The Truman administration now believed it could intervene in Korea without undermining its commitments elsewhere.
United Nations Security Council Resolutions
On 25 June 1950, the United Nations Security Council unanimously condemned the North Korean invasion of South Korea, with UN Security Council Resolution 82. The Soviet Union, a veto-wielding power, had boycotted the Council meetings since January 1950, protesting Taiwan's occupation of China's permanent seat in the UN Security Council.[167] After debating the matter, the Security Council, on 27 June 1950, published Resolution 83 recommending member states provide military assistance to the Republic of Korea. On 27 June, President Truman ordered U.S. air and sea forces to help South Korea. On 4 July, the Soviet Deputy Foreign Minister accused the U.S. of starting armed intervention on behalf of South Korea.[168]
The Soviet Union challenged the legitimacy of the war for several reasons. The ROK intelligence upon which Resolution 83 was based came from U.S. Intelligence; North Korea was not invited as a sitting temporary member of the UN, which violated UN Charter Article 32; and the fighting was beyond the UN Charter's scope, because the initial north–south border fighting was classed as a civil war. Because the Soviet Union was boycotting the Security Council at the time, legal scholars posited that deciding upon an action of this type required the unanimous vote of all the five permanent members including the Soviet Union.[169][170]
Within days of the invasion, masses of ROK soldiers—of dubious loyalty to the Syngman Rhee regime—were retreating southwards or defecting en masse to the northern side, the KPA.[76]
United States' response (July–August 1950)


As soon as word of the attack was received,[171] Acheson informed President Truman that the North Koreans had invaded South Korea.[172][173] Truman and Acheson discussed a U.S. invasion response and agreed that the U.S. was obligated to act, comparing the North Korean invasion with Adolf Hitler's aggressions in the 1930s, with the conclusion being that the mistake of appeasement must not be repeated.[174] Several U.S. industries were mobilized to supply materials, labor, capital, production facilities, and other services necessary to support the military objectives of the Korean War.[175] President Truman later explained that he believed fighting the invasion was essential to the U.S. goal of the global containment of communism as outlined in the National Security Council Report 68 (NSC 68) (declassified in 1975):
Communism was acting in Korea, just as Hitler, Mussolini and the Japanese had ten, fifteen, and twenty years earlier. I felt certain that if South Korea was allowed to fall, Communist leaders would be emboldened to override nations closer to our own shores. If the Communists were permitted to force their way into the Republic of Korea without opposition from the free world, no small nation would have the courage to resist threat and aggression by stronger Communist neighbors.[176]
In August 1950, the President and the Secretary of State obtained the consent of Congress to appropriate $12 billion for military action in Korea.[173]
Because of the extensive defense cuts and the emphasis placed on building a nuclear bomber force, none of the services were in a position to make a robust response with conventional military strength. General Omar Bradley, Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, was faced with reorganizing and deploying a U.S. military force that was a shadow of its World War II counterpart.[177][178]
Acting on Secretary of State Acheson's recommendation, President Truman ordered Supreme Commander for the Allied Powers in Japan General Douglas MacArthur to transfer matériel to the South Korean military while giving air cover to the evacuation of U.S. nationals. The President disagreed with advisers who recommended unilateral U.S. bombing of the North Korean forces and ordered the U.S. Seventh Fleet to protect the Republic of China (Taiwan), whose government asked to fight in Korea. The United States denied Taiwan's request for combat, lest it provoke a PRC retaliation.[179] Because the United States had sent the Seventh Fleet to "neutralize" the Taiwan Strait, Chinese premier Zhou Enlai criticized both the UN and U.S. initiatives as "armed aggression on Chinese territory".[180]
The drive south and Pusan (July–September 1950)




The Battle of Osan, the first significant U.S. engagement of the Korean War, involved the 540-soldier Task Force Smith, which was a small forward element of the 24th Infantry Division which had been flown in from Japan.[181] On 5 July 1950, Task Force Smith attacked the KPA at Osan but without weapons capable of destroying the KPA tanks. The KPA defeated the U.S. soldiers; the result was 180 American dead, wounded, or taken prisoner. The KPA progressed southwards, pushing back U.S. forces at Pyongtaek, Chonan, and Chochiwon, forcing the 24th Division's retreat to Taejeon, which the KPA captured in the Battle of Taejon; the 24th Division suffered 3,602 dead and wounded and 2,962 captured, including its commander, Major General William F. Dean.[182]
By August, the KPA steadily pushed back the ROK and the Eighth United States Army southwards.[183] The impact of the Truman administration's defense budget cutbacks was now keenly felt, as U.S. troops fought a series of costly rearguard actions. Facing a veteran and well-led KPA force, and lacking sufficient anti-tank weapons, artillery or armor, the Americans retreated and the KPA advanced down the Korean Peninsula.[184][185] During their advance, the KPA purged South Korea's intelligentsia by killing civil servants and intellectuals. On 20 August, General MacArthur warned North Korean leader Kim Il-sung that he would be held responsible for the KPA's atrocities.[186] By September, UN forces were hemmed into a small corner of southeast Korea, near Pusan. This 230-kilometre (140-mile) perimeter enclosed about 10% of Korea, in a line partially defined by the Nakdong River.
Although Kim's early successes led him to predict he would end the war by the end of August, Chinese leaders were more pessimistic. To counter a possible U.S. deployment, Zhou Enlai secured a Soviet commitment to have the Soviet Union support Chinese forces with air cover, and deployed 260,000 soldiers along the Korean border, under the command of Gao Gang. Zhou commanded Chai Chengwen to conduct a topographical survey of Korea, and directed Lei Yingfu, Zhou's military advisor in Korea, to analyze the military situation in Korea. Lei concluded that MacArthur would most likely attempt a landing at Incheon.[187][188] After conferring with Mao that this would be MacArthur's most likely strategy, Zhou briefed Soviet and North Korean advisers of Lei's findings, and issued orders to PLA commanders deployed on the Korean border to prepare for U.S. naval activity in the Korea Strait.[189]
In the resulting Battle of Pusan Perimeter (August–September 1950), the UN forces withstood KPA attacks meant to capture the city at the Naktong Bulge, P'ohang-dong, and Taegu. The United States Air Force (USAF) interrupted KPA logistics with 40 daily ground support sorties, which destroyed 32 bridges, halting most daytime road and rail traffic. KPA forces were forced to hide in tunnels by day and move only at night.[190] To deny military equipment and supplies to the KPA, the USAF destroyed logistics depots, petroleum refineries, and harbors, while the U.S. Navy air forces attacked transport hubs. Consequently, the overextended KPA could not be supplied throughout the south.[191] On 27 August, 67th Fighter Squadron aircraft mistakenly attacked facilities in Chinese territory and the Soviet Union called the UN Security Council's attention to China's complaint about the incident.[192] The U.S. proposed that a commission of India and Sweden determine what the U.S. should pay in compensation, but the Soviets vetoed the U.S. proposal.[193][194]
Meanwhile, U.S. garrisons in Japan continually dispatched soldiers and military supplies to reinforce defenders in the Pusan Perimeter.[195] Tank battalions deployed to Korea directly from the U.S. mainland from the port of San Francisco to the port of Pusan, the largest Korean port. By late August, the Pusan Perimeter had some 500 medium tanks battle-ready.[196] In early September 1950, UN forces outnumbered the KPA 180,000 to 100,000 soldiers.[73][197]
Battle of Incheon (September 1950)



Against the rested and rearmed Pusan Perimeter defenders and their reinforcements, the KPA were undermanned and poorly supplied; unlike the UN forces, they lacked naval and air support.[198] To relieve the Pusan Perimeter, General MacArthur recommended an amphibious landing at Incheon, near Seoul and well over 160 km (100 mi) behind the KPA lines.[199] On 6 July, he ordered Major General Hobart R. Gay, commander of the U.S. 1st Cavalry Division, to plan the division's amphibious landing at Incheon; on 12–14 July, the 1st Cavalry Division embarked from Yokohama, Japan, to reinforce the 24th Infantry Division inside the Pusan Perimeter.[200]
Soon after the war began, General MacArthur began planning a landing at Incheon, but the Pentagon opposed him.[199] When authorized, he activated a combined U.S. Army and Marine Corps, and ROK force. The U.S. X Corps, led by Major General Edward Almond, consisted of 40,000 soldiers of the 1st Marine Division, the 7th Infantry Division and around 8,600 ROK soldiers.[201] By 15 September, the amphibious assault force faced few KPA defenders at Incheon: military intelligence, psychological warfare, guerrilla reconnaissance, and protracted bombardment facilitated a relatively light battle. However, the bombardment destroyed most of the city of Incheon.[202]
Breakout from the Pusan Perimeter
On 16 September Eighth Army began its breakout from the Pusan Perimeter. Task Force Lynch,[203][204] 3rd Battalion, 7th Cavalry Regiment, and two 70th Tank Battalion units (Charlie Company and the Intelligence–Reconnaissance Platoon) advanced through 171.2 km (106.4 mi) of KPA territory to join the 7th Infantry Division at Osan on 27 September.[200] X Corps rapidly defeated the KPA defenders around Seoul, thus threatening to trap the main KPA force in Southern Korea.[205] On 18 September, Stalin dispatched General H. M. Zakharov to North Korea to advise Kim Il-sung to halt his offensive around the Pusan perimeter and to redeploy his forces to defend Seoul. Chinese commanders were not briefed on North Korean troop numbers or operational plans. As the overall commander of Chinese forces, Zhou Enlai suggested that the North Koreans should attempt to eliminate the UN forces at Incheon only if they had reserves of at least 100,000 men; otherwise, he advised the North Koreans to withdraw their forces north.[206]
On 25 September, Seoul was recaptured by UN forces. U.S. air raids caused heavy damage to the KPA, destroying most of its tanks and much of its artillery. KPA troops in the south, instead of effectively withdrawing north, rapidly disintegrated, leaving Pyongyang vulnerable.[206] During the general retreat, only 25,000 to 30,000 KPA soldiers managed to reach the KPA lines.[207][208] On 27 September, Stalin convened an emergency session of the Politburo, in which he condemned the incompetence of the KPA command and held Soviet military advisers responsible for the defeat.[206]
UN forces invade North Korea (September–October 1950)
On 27 September, MacArthur received the top secret National Security Council Memorandum 81/1 from Truman reminding him that operations north of the 38th Parallel were authorized only if "at the time of such operation there was no entry into North Korea by major Soviet or Chinese Communist forces, no announcements of intended entry, nor a threat to counter our operations militarily".[209] On 29 September, MacArthur restored the government of the Republic of Korea under Syngman Rhee.[206] On 30 September, U.S. Defense Secretary George Marshall sent an eyes-only message to MacArthur: "We want you to feel unhampered tactically and strategically to proceed north of the 38th parallel."[209] During October, the South Korean police executed people who were suspected to be sympathetic to North Korea,[210] and similar massacres were carried out until early 1951.[211] The Joint Chiefs of Staff on 27 September sent to General MacArthur a comprehensive directive to govern his future actions: the directive stated that the primary goal was the destruction of the KPA, with unification of the Korean Peninsula under Rhee as a secondary objective "if possible"; the Joint Chiefs added that this objective was dependent on whether or not the Chinese and Soviets would intervene, and was subject to changing conditions.[212]

On 30 September, Zhou Enlai warned the U.S. that China was prepared to intervene in Korea if the U.S. crossed the 38th Parallel. Zhou attempted to advise KPA commanders on how to conduct a general withdrawal by using the same tactics that allowed Chinese communist forces to successfully escape Chiang Kai-shek's encirclement campaigns in the 1930s, but by some accounts, KPA commanders did not use these tactics effectively.[213] Historian Bruce Cumings argues, however, that the KPA's rapid withdrawal was strategic, with troops melting into the mountains from where they could launch guerrilla raids on the UN forces spread out on the coasts.[214]
By 1 October 1950, the UN Command repelled the KPA northwards past the 38th Parallel; the ROK advanced after them, into North Korea.[215] MacArthur made a statement demanding the KPA's unconditional surrender.[216] Six days later, on 7 October, with UN authorization, the UN Command forces followed the ROK forces northwards.[217] The X Corps landed at Wonsan (in southeastern North Korea) and Riwon (in northeastern North Korea) on 26 October, but these cities had already been captured by ROK forces.[218] The Eighth U.S. Army drove up western Korea and captured Pyongyang on 19 October 1950.[219] The 187th Airborne Regimental Combat Team made their first of two combat jumps during the Korean War on 20 October 1950 at Sunchon and Sukchon. The mission was to cut the road north going to China, preventing North Korean leaders from escaping from Pyongyang; and to rescue U.S. prisoners of war. At month's end, UN forces held 135,000 KPA prisoners of war. As they neared the Sino-Korean border, the UN forces in the west were divided from those in the east by 80–161 km (50–100 mi) of mountainous terrain.[220] In addition to the 135,000 captured, the KPA had also suffered some 200,000 soldiers killed or wounded for a total of 335,000 casualties since the end of June 1950, and had lost 313 tanks (mostly T-34/85 models). A mere 25,000 KPA regulars retreated across the 38th Parallel, as their military had entirely collapsed. The UN forces on the peninsula numbered 229,722 combat troops (including 125,126 Americans and 82,786 South Koreans), 119,559 rear area troops, and 36,667 U.S. Air Force personnel.[221]
Taking advantage of the UN Command's strategic momentum against the communists, MacArthur believed it necessary to extend the Korean War into China to destroy depots supplying the North Korean war effort. Truman disagreed, and ordered caution at the Sino-Korean border.[222]
China intervenes (October–December 1950)
On 30 June 1950, five days after the outbreak of the war, Zhou Enlai, premier of the PRC and vice-chairman of the Central Military Committee of the CCP (CMCC), decided to send a group of Chinese military intelligence personnel to North Korea to establish better communications with Kim II-Sung as well as to collect firsthand materials on the fighting. One week later, on 7 July, Zhou and Mao chaired a conference discussing military preparations for the Korean Conflict. Another conference took place on 10 July. Here, it was decided that the Thirteenth Army Corps under the Fourth Field Army of the People's Liberation Army (PLA), one of the best-trained and -equipped units in China, would be immediately transformed into the Northeastern Border Defense Army (NEBDA) to prepare for "an intervention in the Korean War if necessary". On 13 July, the CMCC formally issued the order to establish the NEBDA, appointing Deng Hua, the commander of the Fifteenth Army Corps and one of the most talented commanders of the Chinese Civil War, to coordinate all preparation efforts.[223]: 11–12
On 20 August 1950, Premier Zhou Enlai informed the UN that "Korea is China's neighbor... The Chinese people cannot but be concerned about a solution of the Korean question". Thus, through neutral-country diplomats, China warned that in safeguarding Chinese national security, they would intervene against the UN Command in Korea.[222] President Truman interpreted the communication as "a bald attempt to blackmail the UN", and dismissed it.[224] Mao ordered that his troops should be ready for action by the end of August. Stalin, by contrast, was reluctant to escalate the war with a Chinese intervention.[225]
On 1 October 1950, the day that UN troops crossed the 38th Parallel, the Soviet ambassador forwarded a telegram from Stalin to Mao and Zhou requesting that China send five to six divisions into Korea, and Kim Il-sung sent frantic appeals to Mao for Chinese military intervention. At the same time, Stalin made it clear that Soviet forces themselves would not directly intervene.[216]

In a series of emergency meetings that lasted from 2 to 5 October, Chinese leaders debated whether to send Chinese troops into Korea. There was considerable resistance among many leaders, including senior military leaders, to confronting the U.S. in Korea.[226] Mao strongly supported intervention, and Zhou was one of the few Chinese leaders who firmly supported him. After Lin Biao politely refused Mao's offer to command Chinese forces in Korea (citing his upcoming medical treatment),[227] Mao decided that Peng Dehuai would be the commander of the Chinese forces in Korea after Peng agreed to support Mao's position.[227] Mao then asked Peng to speak in favor of intervention to the rest of the Chinese leaders. After Peng made the case that if U.S. troops conquered Korea and reached the Yalu, they might cross it and invade China, the Politburo agreed to intervene in Korea.[228] On 4 August 1950, with a planned invasion of Taiwan aborted due to the heavy U.S. naval presence, Mao reported to the Politburo that he would intervene in Korea when the PLA's Taiwan invasion force was reorganized into the PLA North East Frontier Force.[229] On 8 October 1950, Mao redesignated the PLA North East Frontier Force as the People's Volunteer Army (PVA).[230]
To enlist Stalin's support, Zhou and a Chinese delegation arrived in Moscow on 10 October, at which point they flew to Stalin's home on the Black Sea.[231] There, they conferred with the top Soviet leadership, which included Joseph Stalin as well as Vyacheslav Molotov, Lavrentiy Beria and Georgy Malenkov. Stalin initially agreed to send military equipment and ammunition but warned Zhou that the Soviet Air Force would need two or three months to prepare any operations. In a subsequent meeting, Stalin told Zhou that he would only provide China with equipment on a credit basis and that the Soviet Air Force would only operate over Chinese airspace, and only after an undisclosed period of time. Stalin did not agree to send either military equipment or air support until March 1951.[232] Mao did not find Soviet air support especially useful, as the fighting was going to take place on the south side of the Yalu.[233] Soviet shipments of matériel, when they did arrive, were limited to small quantities of trucks, grenades, machine guns, and the like.[234]
In a meeting on 13 October, the Politburo of the Chinese Communist Party decided that China would intervene even in the absence of Soviet air support, basing its decision on a belief that superior morale could defeat an enemy that had superior equipment.[235] Immediately on his return to Beijing on 18 October 1950, Zhou met with Mao Zedong, Peng Dehuai and Gao Gang, and the group ordered two hundred thousand PVA troops to enter North Korea, which they did on 19 October.[236] UN aerial reconnaissance had difficulty sighting PVA units in daytime, because their march and bivouac discipline minimized aerial detection.[237] The PVA marched "dark-to-dark" (19:00–03:00), and aerial camouflage (concealing soldiers, pack animals, and equipment) was deployed by 05:30. Meanwhile, daylight advance parties scouted for the next bivouac site. During daylight activity or marching, soldiers were to remain motionless if an aircraft appeared, until it flew away;[237] PVA officers were under order to shoot security violators. Such battlefield discipline allowed a three-division army to march the 460 km (286 mi) from An-tung, Manchuria, to the combat zone in some 19 days. Another division night-marched a circuitous mountain route, averaging 29 km (18 mi) daily for 18 days.[85]
Meanwhile, on 15 October 1950, President Truman and General MacArthur met at Wake Island. This meeting was much publicized because of the General's discourteous refusal to meet the President on the continental United States.[238] To President Truman, MacArthur speculated there was little risk of Chinese intervention in Korea,[239] and that the PRC's opportunity for aiding the KPA had lapsed. He believed the PRC had some 300,000 soldiers in Manchuria and some 100,000–125,000 soldiers at the Yalu River. He further concluded that, although half of those forces might cross south, "if the Chinese tried to get down to Pyongyang, there would be the greatest slaughter" without air force protection.[207][240]


After secretly crossing the Yalu River on 19 October, the PVA 13th Army Group launched the First Phase Offensive on 25 October, attacking the advancing UN forces near the Sino-Korean border. This military decision made solely by China changed the attitude of the Soviet Union. Twelve days after PVA troops entered the war, Stalin allowed the Soviet Air Force to provide air cover and supported more aid to China.[241] After inflicting heavy losses on the ROK II Corps at the Battle of Onjong, the first confrontation between Chinese and U.S. military occurred on 1 November 1950. Deep in North Korea, thousands of soldiers from the PVA 39th Army encircled and attacked the U.S. 8th Cavalry Regiment with three-prong assaults—from the north, northwest, and west—and overran the defensive position flanks in the Battle of Unsan.[242] The surprise assault resulted in the UN forces retreating back to the Ch'ongch'on River, while the PVA unexpectedly disappeared into mountain hideouts following victory. It is unclear why the Chinese did not press the attack and follow up their victory.[citation needed]
The UN Command, however, were unconvinced that the Chinese had openly intervened because of the sudden PVA withdrawal. On 24 November, the Home-by-Christmas Offensive was launched with the U.S. Eighth Army advancing in northwest Korea, while U.S. X Corps attacked along the Korean east coast. But the PVA were waiting in ambush with their Second Phase Offensive, which they executed at two sectors: in the East at the Chosin Reservoir and in the Western sector at Ch'ongch'on River.[citation needed]
On 13 November, Mao appointed Zhou Enlai the overall commander and coordinator of the war effort, with Peng as field commander.[236] On 25 November, on the Korean western front, the PVA 13th Army Group attacked and overran the ROK II Corps at the Battle of the Ch'ongch'on River, and then inflicted heavy losses on the U.S. 2nd Infantry Division on the UN forces' right flank.[243] Believing that they could not hold against the PVA, the Eighth Army began to retreat from North Korea crossing the 38th Parallel in mid-December.[244] UN morale hit rock bottom when Lieutenant General Walton Walker, commander of the U.S. Eighth Army, was killed on 23 December 1950 in an automobile accident.[citation needed]
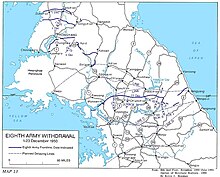
In the east, on 27 November, the PVA 9th Army Group initiated the Battle of Chosin Reservoir. Here, the UN forces fared comparatively better: like the Eighth Army, the surprise attack also forced X Corps to retreat from northeast Korea, but they were, in the process, able to break out from the attempted encirclement by the PVA and execute a successful tactical withdrawal. X Corps managed to establish a defensive perimeter at the port city of Hungnam on 11 December and were able to evacuate by 24 December to reinforce the badly depleted U.S. Eighth Army to the south.[245][246] During the evacuation, about 193 shiploads of UN forces and matériel (approximately 105,000 soldiers, 98,000 civilians, 17,500 vehicles, and 350,000 tons of supplies) were evacuated to Pusan.[247] The SS Meredith Victory was noted for evacuating 14,000 refugees, the largest rescue operation by a single ship, even though it was designed to hold 12 passengers. Before escaping, the UN forces razed most of Hungnam city, with particular attention to the port facilities.[207][248] The UN retreat from North Korea also saw the massive evacuation from the capital city of Pyongyang. In early December, UN forces, including the British Army's 29th Infantry Brigade, evacuated Pyongyang, along with large numbers of refugees.[249] Around 4.5 million North Koreans are estimated to have fled from North Korea to either the South or elsewhere abroad.[250] On 16 December 1950, President Truman declared a national state of emergency with Presidential Proclamation No. 2914, 3 C.F.R. 99 (1953),[251] which remained in force until 14 September 1978.[g] The next day, 17 December 1950, Kim Il-sung was deprived of the right of command of KPA by China.[252]
China justified its entry into the war as a response to what it described as "American aggression in the guise of the UN".[229] Chinese decision-makers feared that the American-led invasion of North Korea was part of a U.S. strategy to invade China ultimately. They were also worried about rising counterrevolutionary activity at home.[235] MacArthur's public statements that he wanted to extend the Korean War into China, and return the Kuomintang to power reinforced this fear.[235] Later, the Chinese claimed that U.S. bombers had violated PRC national airspace on three separate occasions and attacked Chinese targets before China intervened.[253][254]
Fighting around the 38th Parallel (January–June 1951)
A ceasefire presented by the UN to the PRC shortly after the Battle of the Ch'ongch'on River on December 11, 1950, was rejected by the Chinese government, which was convinced of the PVA's invincibility after its victory in that battle and the wider Second Phase Offensive, and also wanted to demonstrate China's desire for a total victory through the expulsion of the UN forces from Korea.[255][256] With Lieutenant General Matthew Ridgway assuming the command of the U.S. Eighth Army on 26 December, the PVA and the KPA launched their Third Phase Offensive (also known as the "Chinese New Year's Offensive") on New Year's Eve of 1950/51. Utilizing night attacks in which UN fighting positions were encircled and then assaulted by numerically superior troops who had the element of surprise, the attacks were accompanied by loud trumpets and gongs, which fulfilled the double purpose of facilitating tactical communication and mentally disorienting the enemy. UN forces initially had no familiarity with this tactic, and as a result, some soldiers panicked, abandoning their weapons and retreating to the south.[257] The offensive overwhelmed UN forces, allowing the PVA and KPA to capture Seoul for the second time on 4 January 1951. Following this, the CPV party committee issued orders regarding tasks during rest and reorganization on 8 January 1951, outlining Chinese war goals. The orders read: "the central issue is for the whole party and army to overcome difficulties ... to improve tactics and skills. When the next campaign starts ... we will annihilate all enemies and liberate all Korea." In his telegram to Peng on 14 January, Mao stressed the importance of preparing for "the last battle" in the spring in order to "fundamentally resolve the [Korean] issue".[258]

These setbacks prompted General MacArthur to consider using nuclear weapons against the Chinese or North Korean interiors, intending radioactive fallout zones to interrupt the Chinese supply chains.[259] However, upon the arrival of the charismatic General Ridgway, the esprit de corps of the bloodied Eighth Army immediately began to revive.[260]
UN forces retreated to Suwon in the west, Wonju in the center, and the territory north of Samcheok in the east, where the battlefront stabilized and held.[257] The PVA had outrun its logistics capability and thus were unable to press on beyond Seoul as food, ammunition, and matériel were carried nightly, on foot and bicycle, from the border at the Yalu River to the three battle lines.[261] In late January, upon finding that the PVA had abandoned their battle lines, General Ridgway ordered a reconnaissance-in-force, which became Operation Thunderbolt (25 January 1951).[262] A full-scale advance followed, which fully exploited the UN's air superiority,[263] concluding with the UN forces reaching the Han River and recapturing Wonju.[262]
Following the failure of ceasefire negotiations in January, the United Nations General Assembly passed Resolution 498 on 1 February, condemning the PRC as an aggressor, and called upon its forces to withdraw from Korea.[264][265]
In early February, the ROK 11th Division ran the operation to destroy the guerrillas and their sympathizer citizens in Southern Korea.[266] During the operation, the division and police conducted the Geochang massacre and Sancheong–Hamyang massacre.[266] In mid-February, the PVA counterattacked with the Fourth Phase Offensive and achieved initial victory at Hoengseong. However, the offensive was soon blunted by U.S. IX Corps at Chipyong-ni in the center.[262] The U.S. 23rd Regimental Combat Team and the French Battalion fought a short but desperate battle that broke the attack's momentum.[262] The battle is sometimes known as the "Gettysburg of the Korean War": 5,600 South Korean, U.S., and French troops were surrounded on all sides by 25,000 PVA. UN forces had previously retreated in the face of large PVA/KPA forces instead of getting cut off, but this time, they stood and fought, and won.[267]

In the last two weeks of February 1951, Operation Thunderbolt was followed by Operation Killer, carried out by the revitalized Eighth Army. It was a full-scale, battlefront-length attack staged for maximum exploitation of firepower to kill as many KPA and PVA troops as possible.[262] Operation Killer concluded with U.S. I Corps re-occupying the territory south of the Han River, and IX Corps capturing Hoengseong.[268] On 7 March 1951, the Eighth Army attacked with Operation Ripper, expelling the PVA and the KPA from Seoul on 14 March 1951. This was the fourth and final conquest of the city in a year's time, leaving it a ruin; the 1.5 million pre-war population was down to 200,000, and people were suffering from severe food shortages.[268][208]
On 1 March 1951, Mao sent a cable to Stalin emphasizing the difficulties faced by Chinese forces and the need for air cover, especially over supply lines. Apparently impressed by the Chinese war effort, Stalin agreed to supply two air force divisions, three anti-aircraft divisions, and six thousand trucks. PVA troops in Korea continued to suffer severe logistical problems throughout the war. In late April, Peng Dehuai sent his deputy, Hong Xuezhi, to brief Zhou Enlai in Beijing. What Chinese soldiers feared, Hong said, was not the enemy, but having no food, bullets, or trucks to transport them to the rear when they were wounded. Zhou attempted to respond to the PVA's logistical concerns by increasing Chinese production and improving supply methods, but these efforts were never sufficient. At the same time, large-scale air defense training programs were carried out, and the People's Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF) began participating in the war from September 1951 onward.[269] The Fourth Phase Offensive had catastrophically failed, in contrast to the success of the Second Phase Offensive and limited gains of the Third Phase Offensive. The UN forces, after earlier defeats and subsequent retraining, proved much harder to infiltrate by Chinese light infantry than they had been in previous months. From 31 January to 21 April, the Chinese had suffered 53,000 casualties.[270]
On 11 April 1951, President Truman relieved General MacArthur as Supreme Commander in Korea.[271] There were several reasons for the dismissal. MacArthur had crossed the 38th Parallel in the mistaken belief that the Chinese would not enter the war, leading to major allied losses. He believed that the use of nuclear weapons should be his decision, not the President's.[272] MacArthur threatened to destroy China unless it surrendered. While MacArthur felt total victory was the only honorable outcome, Truman was more pessimistic about his chances once involved in a larger war, feeling that a truce and orderly withdrawal from Korea could be a valid solution.[273] MacArthur was the subject of congressional hearings in May and June 1951, which determined that he had defied the orders of the President and thus had violated the U.S. Constitution.[274] A popular criticism of MacArthur was that he never spent a night in Korea, and directed the war from the safety of Tokyo.[275]

MacArthur was relieved primarily due to his determination to expand the war into China, which other officials believed would needlessly escalate a limited war and consume too many already overstretched resources. Despite MacArthur's claims that he was restricted to fighting a limited war when China was fighting all-out, congressional testimony revealed China was using restraint as much as the U.S. was, as they were not using air power against front-line troops, communication lines, ports, naval air forces, or staging bases in Japan, which had been crucial to the survival of UN forces in Korea. Simply fighting on the peninsula had already tied down significant portions of U.S. airpower; as Air Force chief of staff Hoyt Vandenberg said, 80–85% of the tactical capacity, one-fourth of the strategic portion, and 20% of air defense forces of the USAF were engaged in a single country. There was also fear that crossing into China would provoke the Soviet Union into entering the war. General Omar Bradley testified that there were 35 Russian divisions totaling some 500,000 troops in the Far East, and if sent into action with the approximately 85 Russian submarines in the vicinity of Korea, they could overwhelm U.S. forces and cut supply lines, as well as potentially assist China in taking over territory in Southeast Asia.[276]
General Ridgway was appointed Supreme Commander in Korea, and he regrouped the UN forces for successful counterattacks,[277] while General James Van Fleet assumed command of the U.S. Eighth Army.[278] Further attacks slowly depleted the PVA and KPA forces; Operations Courageous (23–28 March 1951) and Tomahawk (23 March 1951) (a combat jump by the 187th Airborne Regimental Combat Team) were a joint ground and airborne infiltration meant to trap PVA forces between Kaesong and Seoul. UN forces advanced to the Kansas Line, north of the 38th Parallel.[279]
The PVA counterattacked in April 1951, with the Fifth Phase Offensive, with three field armies (approximately 700,000 men).[280] The first thrust of the offensive fell upon I Corps, which fiercely resisted in the Battle of the Imjin River (22–25 April 1951) and the Battle of Kapyong (22–25 April 1951), blunting the impetus of the offensive, which was halted at the No-name Line north of Seoul.[281] Casualty ratios were grievously disproportionate; Peng had expected a 1–1 or 2-1 ratio, but instead, Chinese combat casualties from 22 to 29 April totaled between 40,000 and 60,000 compared to only 4,000 for the UN —a casualty ratio between 10–1 and 15–1.[282] By the time Peng had called off the attack in the western sector on 29 April, the three participating armies had lost a third of their front-line combat strength within a week.[283] Additional casualties were incurred on 30 April. On 15 May 1951, the PVA commenced the second impulse of the Spring Offensive and attacked the ROK and U.S. X Corps in the east at the Soyang River. Approximately 370,000 PVA and 114,000 KPA troops had been mobilized for the second step of the Fifth Phase Offensive, with the bulk attacking in the eastern sector with about a quarter attempting to pin the U.S. I Corps and IX Corps in the western sector. After initial success, they were halted by 20 May and repulsed over the following days, with Western histories generally designating 22 May as the end of the offensive.[284][285] At month's end, the Chinese planned the third step of the Fifth Phase Offensive (withdrawal), which they estimated would take 10 to 15 days to complete for their 340,000 remaining men, and set the retreat date for the night of 23 May. They were caught off guard when the U.S. Eighth Army counterattacked and regained the Kansas Line on the morning of 12 May, 23 hours before the expected withdrawal.[286][287] The surprise attack turned the retreat into "the most severe loss since our forces had entered Korea"; from 16 May to 23 May, the PVA had suffered another 45,000 to 60,000 casualties before their remaining soldiers managed to evacuate back north.[287] Per official Chinese statistics, the Fifth Phase Offensive as a whole had cost the PVA 102,000 soldiers (85,000 killed/wounded, 17,000 captured), with unknown but significant losses for the KPA.[288]
The end of the Fifth Phase Offensive preceded the start of the UN May–June 1951 counteroffensive. During the counteroffensive, the U.S.-led coalition captured land up to about 10 km (6 mi) north of the 38th Parallel, with most forces stopping at the Kansas Line and a minority going further to the Wyoming Line. PVA and KPA forces suffered greatly during this offensive, especially in the Chuncheon sector and at Chiam-ni and Hwacheon; in the latter sector alone the PVA/KPA suffered over 73,207 casualties, including 8,749 captured, compared to 2,647 total casualties of the U.S. IX Corps which engaged them.[289] The UN's Kansas Line halt and subsequent offensive action stand-down began the stalemate that lasted until the armistice of 1953. The disastrous failure of the Fifth Phase Offensive (which Peng later recalled as one of only four mistakes he made in his military career) "led Chinese leaders to change their goal from driving the UNF out of Korea to merely defending China's security and ending the war through negotiations".[290]
Stalemate (July 1951 – July 1953)
For the remainder of the war, the UN and the PVA/KPA fought but exchanged little territory, as the stalemate held. Large-scale bombing of North Korea continued, and protracted armistice negotiations began on 10 July 1951 at Kaesong, an ancient capital of Korea located in PVA/KPA held territory.[291] On the Chinese side, Zhou Enlai directed peace talks, and Li Kenong and Qiao Guanghua headed the negotiation team.[269] Combat continued while the belligerents negotiated; the goal of the UN forces was to recapture all of South Korea and to avoid losing territory.[292] The PVA and the KPA attempted similar operations and later effected military and psychological operations to test the UN Command's resolve to continue the war. The two sides constantly traded artillery fire along the front, with American-led forces possessing a large firepower advantage over the Chinese-led forces. For example, in the last three months of 1952 the UN fired 3,553,518 field gun shells and 2,569,941 mortar shells, while the Communists fired 377,782 field gun shells and 672,194 mortar shells: an overall 5.83:1 ratio in the UN's favor.[293] The Communist insurgency, reinvigorated by North Korean support and scattered bands of KPA stragglers, also resurged in the south. In the autumn of 1951, Van Fleet ordered Major General Paik Sun-yup to break the back of guerrilla activity. From December 1951 to March 1952, ROK security forces claimed to have killed 11,090 partisans and sympathizers and captured 9,916 more.[43]

The principal battles of the stalemate include the Battle of Bloody Ridge (18 August–15 September 1951),[294] the Battle of the Punchbowl (31 August-21 September 1951), the Battle of Heartbreak Ridge (13 September–15 October 1951),[295] the Battle of Old Baldy (26 June–4 August 1952), the Battle of White Horse (6–15 October 1952), the Battle of Triangle Hill (14 October–25 November 1952), the Battle of Hill Eerie (21 March–21 June 1952), the sieges of Outpost Harry (10–18 June 1953), the Battle of the Hook (28–29 May 1953), the Battle of Pork Chop Hill (23 March–16 July 1953), and the Battle of Kumsong (13–27 July 1953).
PVA troops suffered from deficient military equipment, serious logistical problems, overextended communication and supply lines, and the constant threat of UN bombers. All of these factors generally led to a rate of Chinese casualties that was far greater than the casualties suffered by UN troops. The situation became so serious that, in November 1951, Zhou Enlai called a conference in Shenyang to discuss the PVA's logistical problems. At the meeting, it was decided to accelerate the construction of railways and airfields in the area to increase the number of trucks available to the army, and to improve air defense by any means possible. These commitments did little to address the problems directly that confronted PVA troops.[296]

In the months after the Shenyang conference, Peng Dehuai went to Beijing several times to brief Mao and Zhou about the heavy casualties suffered by Chinese troops and the increasing difficulty of keeping the front lines supplied with basic necessities. Peng was convinced that the war would be protracted and that neither side would be able to achieve victory in the near future. On 24 February 1952, the Military Commission, presided over by Zhou, discussed the PVA's logistical problems with members of various government agencies involved in the war effort. After the government representatives emphasized their inability to meet the demands of the war, Peng, in an angry outburst, shouted: "You have this and that problem... You should go to the front and see with your own eyes what food and clothing the soldiers have! Not to speak of the casualties! For what are they giving their lives? We have no aircraft. We have only a few guns. Transports are not protected. More and more soldiers are dying of starvation. Can't you overcome some of your difficulties?" The atmosphere became so tense that Zhou was forced to adjourn the conference. Zhou subsequently called a series of meetings, where it was agreed that the PVA would be divided into three groups, to be dispatched to Korea in shifts; to accelerate the training of Chinese pilots; to provide more anti-aircraft guns to the front lines; to purchase more military equipment and ammunition from the Soviet Union; to provide the army with more food and clothing; and to transfer the responsibility of logistics to the central government.[297]
With peace negotiations ongoing, the Chinese attempted one final offensive in the final weeks of the war to capture territory: on 10 June, 30,000 Chinese troops struck two South Korean and one U.S. divisions on a 13 km (8 mi) front, and on 13 July, 80,000 Chinese soldiers struck the east-central Kumsong sector, with the brunt of their attack falling on four South Korean divisions. In both cases, the Chinese had some success in penetrating South Korean lines, but failed to capitalize, particularly when the U.S. forces present responded with overwhelming firepower. Chinese casualties in their final major offensive of the war (above normal wastage for the front) were about 72,000, including 25,000 killed in action compared to 14,000 for the UN (the vast majority of these deaths were South Koreans, though 1,611 were Americans). The Communists fired 704,695 field gun shells in June–July compared to 4,711,230 fired by the UN, a ratio of 1:6.69. June 1953 saw the highest monthly artillery expenditure of the war by both sides.[298]
Armistice (July 1953 – November 1954)

The on-again, off-again armistice negotiations continued for two years,[299] first at Kaesong, on the border between North and South Korea, and then at the neighboring village of Panmunjom.[300] A major, problematic negotiation point was prisoner of war (POW) repatriation.[301] The PVA, KPA and UN Command could not agree on a system of repatriation because many PVA and KPA soldiers refused to be repatriated back to the north,[302] which was unacceptable to the Chinese and North Koreans.[303] A Neutral Nations Repatriation Commission, under the chairman Indian General K. S. Thimayya, was subsequently set up to handle the matter.[304]
In 1952, the U.S. elected a new president, and on 29 November 1952, the president-elect, Dwight D. Eisenhower, went to Korea to learn what might end the Korean War.[305] Eisenhower took office on 20 January 1953. Joseph Stalin died a few weeks later on 5 March. The new Soviet leaders, engaged in their internal power struggle, had no desire to continue supporting China's efforts in Korea, and issued a statement calling for an end to the hostilities.[306] China could not continue the war without Soviet aid and North Korea was no longer a major player. Armistice talks entered a new phase. With the United Nations' acceptance of India's proposed Korean War armistice,[307] the KPA, the PVA and the UN Command signed the Korean Armistice Agreement on 27 July 1953. South Korean president Syngman Rhee refused to sign the agreement. The war is considered to have ended at this point, even though there was no peace treaty.[308] North Korea nevertheless claims that it won the Korean War.[309][310]
Under the Armistice Agreement, the belligerents established the Korean Demilitarized Zone (DMZ), along the front line, which vaguely follows the 38th Parallel. In the eastern part, the DMZ runs north of the 38th Parallel; to the west, it travels south of it. Kaesong, site of the initial armistice negotiations, was originally in pre-war South Korea but now is part of North Korea. The DMZ has since been patrolled by the KPA and the ROK and the U.S. still operating as the UN Command.
The Armistice also called upon the governments of South Korea, North Korea, China and the United States to participate in continued peace talks.
After the war, Operation Glory was conducted from July to November 1954, to allow combatant countries to exchange their dead. The remains of 4,167 U.S. Army and U.S. Marine Corps dead were exchanged for 13,528 KPA and PVA dead, and 546 civilians dead in UN prisoner-of-war camps were delivered to the South Korean government.[311] After Operation Glory, 416 Korean War unknown soldiers were buried in the National Memorial Cemetery of the Pacific (The Punchbowl), on the island of Oahu, Hawaii. Defense Prisoner of War/Missing Personnel Office (DPMO) records indicate that the PRC and North Korea transmitted 1,394 names, of which 858 were correct. From 4,167 containers of returned remains, forensic examination identified 4,219 individuals. Of these, 2,944 were identified as from the U.S., and all but 416 were identified by name.[312] From 1996 to 2006, North Korea recovered 220 remains near the Sino-Korean border.[313]
Division of Korea (1954–present)

The Korean Armistice Agreement provided for monitoring by an international commission. Since 1953, the Neutral Nations Supervisory Commission (NNSC), composed of members from the Swiss[314] and Swedish[315] Armed Forces, has been stationed near the DMZ.
In April 1975, South Vietnam's capital was captured by the People's Army of Vietnam. Encouraged by the success of the Communist revolution in Indochina, Kim Il-sung saw it as an opportunity to invade the South. Kim visited China in April of that year and met with Mao Zedong and Zhou Enlai to ask for military aid. Despite Pyongyang's expectations, however, Beijing refused to help North Korea for another war in Korea.[316]


Since the armistice, there have been numerous incursions and acts of aggression by North Korea. From 1966 to 1969, a large number of cross-border incursions took place in what has been referred to as the Korean DMZ Conflict or the Second Korean War. In 1968, a North Korean commando team unsuccessfully attempted to assassinate South Korean president Park Chung-hee in the Blue House Raid. In 1976, the axe murder incident was widely publicized. Since 1974, four incursion tunnels leading to Seoul have been uncovered. In 2010, a North Korean submarine torpedoed and sank the South Korean corvette ROKS Cheonan, resulting in the deaths of 46 sailors.[317] Again in 2010, North Korea fired artillery shells on Yeonpyeong island, killing two military personnel and two civilians.[318]
After a new wave of UN sanctions, on 11 March 2013, North Korea claimed that the armistice had become invalid.[319] On 13 March 2013, North Korea confirmed it ended the 1953 Armistice and declared North Korea "is not restrained by the North-South declaration on non-aggression".[320] On 30 March 2013, North Korea stated that it entered a "state of war" with South Korea and declared that "The long-standing situation of the Korean peninsula being neither at peace nor at war is finally over".[321] Speaking on 4 April 2013, the U.S. Secretary of Defense, Chuck Hagel, informed the press that Pyongyang "formally informed" the Pentagon that it "ratified" the potential use of a nuclear weapon against South Korea, Japan and the United States of America, including Guam and Hawaii.[322] Hagel also stated the U.S. would deploy the Terminal High Altitude Area Defense anti-ballistic missile system to Guam, because of a credible and realistic nuclear threat from North Korea.[323]
In 2016, it was revealed that North Korea approached the United States about conducting formal peace talks to end the war officially. While the White House agreed to secret peace talks, the plan was rejected due to North Korea's refusal to discuss nuclear disarmament as part of the terms of the treaty.[324]
On 27 April 2018, it was announced that North Korea and South Korea agreed to talks to end the ongoing 65-year conflict. They committed themselves to the complete denuclearization of the Korean Peninsula.[325]
On 22 September 2021, South Korean President Moon Jae-In reiterated his call to end the Korean War formally, in his speech at the United Nations General Assembly.[326]
Characteristics
Casualties
Approximately 3 million people died in the Korean War, the majority of whom were civilians, making it perhaps the deadliest conflict of the Cold War era.[49][50][327][328][329] Samuel S. Kim lists the Korean War as the deadliest conflict in East Asia—itself the region most affected by armed conflict related to the Cold War—from 1945 to 1994, with 3 million dead, more than the Vietnam War and Chinese Civil War during the same period.[327] Although only rough estimates of civilian fatalities are available, scholars from Guenter Lewy to Bruce Cumings have noted that the percentage of civilian casualties in Korea was higher than in World War II or the Vietnam War, with Cumings putting civilian casualties at 2 million and Lewy estimating civilian deaths in the range of 2 million to 3 million.[49][50] Cumings states that civilians represent "at least" half of the war's casualties, while Lewy suggests that the civilian portion of the death toll "may have gone as high as 70 percent", compared to Lewy's estimates of 42% in World War II and 30%–46% in the Vietnam War.[49][50] Data compiled by the Peace Research Institute Oslo (PRIO) lists just under 1 million "battle deaths" over the course of the Korean War (with a range of 644,696 to 1.5 million) and a mid-value estimate of 3 million total deaths (with a range of 1.5 million to 4.5 million), attributing the difference to excess mortality among civilians from one-sided massacres, starvation, and disease.[330] Compounding this devastation for Korean civilians, virtually all of the major cities on the entire Korean Peninsula were destroyed as a result of the war.[50] In both per capita and absolute terms, North Korea was the country most devastated by the war. According to Charles K. Armstrong, the war resulted in the death of an estimated 12%–15% of the North Korean population (c. 10 million), "a figure close to or surpassing the proportion of Soviet citizens killed in World War II".[143]
Military

According to the data from the U.S. Department of Defense, the U.S. suffered 33,686 battle deaths, along with 2,830 non-battle deaths during the Korean War. 17,730 other non-battle U.S. military deaths occurred outside Korea during the same period.[331][32] American combat casualties were over 90 percent of non-Korean UN losses. U.S. battle deaths were 8,516 up to their first engagement with the Chinese on 1 November 1950.[332] The first four months of the Korean War, that is, the war prior to the Chinese intervention (which started near the end of October), were by far the bloodiest per day for the U.S. forces as they engaged and destroyed the comparatively well-equipped KPA in intense fighting. American medical records show that from July to October 1950, the U.S. Army sustained 31 percent of the combat deaths it ultimately incurred in the entire 37-month war.[333] The U.S. spent U.S.$30 billion in total on the war.[334] Some 1,789,000 American soldiers served in the Korean War, accounting for 31 percent of the 5,720,000 Americans who served on active-duty worldwide from June 1950 to July 1953.[24]
South Korea reported some 137,899 military deaths and 24,495 missing. Deaths from the other non-American UN militaries totaled 3,730, with another 379 missing.[21]
Data from official Chinese sources reported that the PVA had suffered 114,000 battle deaths, 34,000 non-battle deaths, 340,000 wounded, and 7,600 missing during the war. 7,110 Chinese POWs were repatriated to China.[29] In 2010, the Chinese government revised their official tally of war losses to 183,108 dead (114,084 in combat, 70,000 outside of combat) and 25,621 missing.[47] Overall, 73 percent of Chinese infantry troops served in Korea (25 of 34 armies, or 79 of 109 infantry divisions, were rotated in). More than 52 percent of the Chinese air force, 55 percent of the tank units, 67 percent of the artillery divisions, and 100 percent of the railroad engineering divisions were sent to Korea as well.[335] Chinese soldiers who served in Korea faced a greater chance of being killed than those who served in World War II or the Chinese Civil War.[336] In terms of financial cost, China spent over 10 billion yuan on the war (roughly U.S.$3.3 billion), not counting USSR aid that had been donated or forgiven.[337] This included $1.3 billion in money owed to the Soviet Union by the end of it. This was a relatively large cost, as China had only 1/25 the national income of the United States.[29] Spending on the Korean War constituted 34–43 percent of China's annual government budget from 1950 to 1953, depending on the year.[337] Despite its underdeveloped economy, Chinese military spending was the world's fourth largest globally for most of the war after that of the United States, the Soviet Union, and the United Kingdom; however, by 1953, with the winding down of the Korean War (which ended halfway through the year) and the escalation of the First Indochina War (which reached its peak in 1953–1954), French spending also surpassed Chinese spending by about a third.[338]
According to the South Korean Ministry of National Defense, North Korean military losses totaled 294,151 dead, 91,206 missing, and 229,849 wounded, giving North Korea the highest military deaths of any belligerent in both absolute and relative terms.[339] The PRIO Battle Deaths Dataset gave a similar figure for North Korean military deaths of 316,579.[340] Chinese sources reported similar figures for the North Korean military of 290,000 "casualties" and 90,000 captured.[29] The exact financial cost of the war for North Korea is unknown but was known to be massive in terms of both direct losses and lost economic activity; the country was devastated both by the cost of the war itself and the American strategic bombing campaign, which, among other things, destroyed 85 percent of North Korea's buildings and 95 percent of its power generation capacity.[341]
The Chinese and North Koreans estimated that about 390,000 soldiers from the United States, 660,000 soldiers from South Korea and 29,000 other UN soldiers were "eliminated" from the battlefield.[29] Western sources estimate the PVA suffered about 400,000 killed and 486,000 wounded, while the KPA suffered 215,000 killed and 303,000 wounded.[44] Cumings cites a much higher figure of 900,000 fatalities among Chinese soldiers.[49]
Civilian
According to the South Korean Ministry of National Defense, there were over three-quarters of a million confirmed violent civilians deaths during the war, another million civilians were pronounced missing, and millions more ended up as refugees. In South Korea, some 373,500 civilians were killed, more than 225,600 wounded, and over 387,740 were listed as missing. During the first communist occupation of Seoul alone, the KPA massacred 128,936 civilians and deported another 84,523 to North Korea. On the other side of the border, some 1,594,000 North Koreans were reported as casualties including 406,000 civilians reported as killed, and 680,000 missing. Over 1.5 million North Koreans fled to the South during the war.[339]
U.S. unpreparedness for war
In a postwar analysis of the unpreparedness of U.S. Army forces deployed to Korea during the summer and fall of 1950, Army Major General Floyd L. Parks stated that "Many who never lived to tell the tale had to fight the full range of ground warfare from offensive to delaying action, unit by unit, man by man ... [T]hat we were able to snatch victory from the jaws of defeat ... does not relieve us from the blame of having placed our own flesh and blood in such a predicament."[342]

By 1950, U.S. Secretary of Defense Louis A. Johnson had established a policy of faithfully following President Truman's defense economization plans and had aggressively attempted to implement it even in the face of steadily increasing external threats. He consequently received much of the blame for the initial setbacks in Korea and the widespread reports of ill-equipped and inadequately trained U.S. military forces in the war's early stages.[343]
As an initial response to the invasion, Truman called for a naval blockade of North Korea and was shocked to learn that such a blockade could be imposed only "on paper" since the U.S. Navy no longer had the warships with which to carry out his request.[343][344] Army officials, desperate for weaponry, recovered Sherman tanks and other equipment from World War II Pacific battlefields and reconditioned them for shipment to Korea.[343] Army Ordnance officials at Fort Knox pulled down M26 Pershing tanks from display pedestals around Fort Knox in order to equip the third company of the Army's hastily formed 70th Tank Battalion.[345] Without adequate numbers of tactical fighter-bomber aircraft, the Air Force took F-51 (P-51) propeller-driven aircraft out of storage or from existing Air National Guard squadrons, and rushed them into front-line service. A shortage of spare parts and qualified maintenance personnel resulted in improvised repairs and overhauls. A Navy helicopter pilot aboard an active duty warship recalled fixing damaged rotor blades with masking tape in the absence of spares.[346]
U.S. Army Reserve and Army National Guard infantry soldiers and new inductees (called to duty to fill out understrength infantry divisions) found themselves short of nearly everything needed to repel the North Korean forces: artillery, ammunition, heavy tanks, ground-support aircraft, even effective anti-tank weapons such as the M20 3.5-inch (89 mm) "Super Bazooka".[347] Some Army combat units sent to Korea were supplied with worn-out, "red-lined" M1 rifles or carbines in immediate need of ordnance depot overhaul or repair.[348][349] Only the Marine Corps, whose commanders had stored and maintained their World War II surplus inventories of equipment and weapons, proved ready for deployment, though they still were woefully understrength,[350] as well as in need of suitable landing craft to practice amphibious operations (Secretary of Defense Louis Johnson had transferred most of the remaining craft to the Navy and reserved them for use in training Army units).[351]
Due to public criticism of his handling of the Korean War, Truman decided to ask for Johnson's resignation. On 19 September 1950, Johnson resigned as Secretary of Defense, and the president quickly replaced him with General George C. Marshall.
Armored warfare
The initial assault by KPA forces was aided by the use of Soviet T-34-85 tanks.[352] A KPA tank corps equipped with about 120 T-34s spearheaded the invasion. These faced an ROK that had few anti-tank weapons adequate to deal with the T-34s.[353] Additional Soviet armor was added as the offensive progressed.[354] The KPA tanks had a good deal of early successes against ROK infantry, Task Force Smith, and the U.S. M24 Chaffee light tanks that they encountered.[355][356] Interdiction by ground attack aircraft was the only means of slowing the advancing KPA armor. The tide turned in favor of the UN forces in August 1950 when the KPA suffered major tank losses during a series of battles in which the UN forces brought heavier equipment to bear, including M4A3 Sherman and M26 medium tanks, as well as the British Centurion, Churchill and Cromwell tanks.[357]
The Incheon landings on 15 September cut off the KPA supply lines, causing their armored forces and infantry to run out of fuel, ammunition, and other supplies. As a result of this and the Pusan perimeter breakout, the KPA had to retreat, and many of the T-34s and heavy weapons had to be abandoned. By the time the KPA withdrew from the South, a total of 239 T-34s and 74 SU-76 self-propelled guns were lost.[358] After November 1950, KPA armor was rarely encountered.[359]
Following the initial assault by the North, the Korean War saw limited use of tanks and featured no large-scale tank battles. The mountainous, forested terrain, especially in the eastern central zone, was poor tank country, limiting their mobility. Through the last two years of the war in Korea, UN tanks served largely as infantry support and mobile artillery pieces.[360]
Naval warfare

Because neither Korea had a significant navy, the war featured few naval battles. A skirmish between North Korea and the UN Command occurred on 2 July 1950; the U.S. Navy cruiser USS Juneau, the Royal Navy cruiser HMS Jamaica and the Royal Navy frigate HMS Black Swan fought four North Korean torpedo boats and two mortar gunboats, and sank them. USS Juneau later sank several ammunition ships that had been present. The last sea battle of the Korean War occurred days before the Battle of Incheon; the ROK ship PC-703 sank a North Korean minelayer in the Battle of Haeju Island, near Incheon. Three other supply ships were sunk by PC-703 two days later in the Yellow Sea.[361] Thereafter, vessels from the UN nations held undisputed control of the sea about Korea. The gunships were used in shore bombardment, while the aircraft carriers provided air support to the ground forces.
During most of the war, the UN navies patrolled the west and east coasts of North Korea, sinking supply and ammunition ships and denying the North Koreans the ability to resupply from the sea. Aside from very occasional gunfire from North Korean shore batteries, the main threat to UN navy ships was from magnetic mines. During the war, five U.S. Navy ships were lost to mines: two minesweepers, two minesweeper escorts, and one ocean tug. Mines and gunfire from North Korean coastal artillery damaged another 87 U.S. warships, resulting in slight to moderate damage.[362]
Aerial warfare
The war was the first in which jet aircraft played the central role in air combat. Once-formidable fighters such as the P-51 Mustang, F4U Corsair, and Hawker Sea Fury[363]—all piston-engined, propeller-driven, and designed during World War II—relinquished their air-superiority roles to a new generation of faster, jet-powered fighters arriving in the theater. For the initial months of the war, the P-80 Shooting Star, F9F Panther, Gloster Meteor and other jets under the UN flag dominated the Korean People's Air Force (KPAF) propeller-driven Soviet Yakovlev Yak-9 and Lavochkin La-9s.[364][365] By early August 1950, the KPAF was reduced to only about 20 planes.[366]

The Chinese intervention in late October 1950 bolstered the KPAF with the MiG-15, one of the world's most advanced jet fighters.[364] The heavily armed MiGs were faster than first-generation UN jets and therefore could reach and destroy U.S. B-29 Superfortress bomber flights despite their fighter escorts. With increasing B-29 losses, the USAF was forced to switch from a daylight bombing campaign to the safer but less accurate nighttime bombing of targets.[citation needed]
The USAF countered the MiG-15 by sending over three squadrons of its most capable fighter, the F-86 Sabre. These arrived in December 1950.[367][368] The MiG was designed as a bomber interceptor. It had a very high service ceiling—15,000 m (50,000 ft) and carried very heavy weaponry: one 37 mm cannon and two 23 mm cannons. The F-86 had a ceiling of 13,000 m (42,000 ft) and were armed with six .50 caliber (12.7 mm) machine guns, which were range adjusted by radar gunsights. If coming in at higher altitude, the advantage of choosing to engage went to the MiG. Once in a level flight dogfight, both swept-wing designs attained comparable maximum speeds of around 1,100 km/h (660 mph). The MiG climbed faster, but the Sabre turned and dived better.[369]
In the summer and autumn of 1951, the outnumbered Sabres of the USAF's 4th Fighter Interceptor Wing—only 44 at one point—continued seeking battle in MiG Alley, where the Yalu River marks the Chinese border, against Chinese and North Korean air forces capable of deploying some 500 aircraft. Following Colonel Harrison Thyng's communication with the Pentagon, the 51st Fighter-Interceptor Wing finally reinforced the beleaguered 4th Wing in December 1951; for the next year-and-a-half stretch of the war, aerial warfare continued.[370]

Unlike the Vietnam War, in which the Soviet Union only officially sent "advisers", the 64th Fighter Aviation Corps saw action in the Korean air war. Fearful of confronting the U.S. directly, the Soviet Union denied the involvement of their personnel in anything other than an advisory role, but air combat quickly resulted in Soviet pilots dropping their code signals and speaking over the wireless in Russian. This known direct Soviet participation was a casus belli that the UN Command deliberately overlooked, lest the war expand to include the Soviet Union, and potentially escalate into atomic warfare.[364]
After the war, and to the present day, the USAF reports an inflated F-86 Sabre kill ratio in excess of 10:1, with 792 MiG-15s and 108 other aircraft shot down by Sabres, and 78 Sabres lost to enemy fire.[371][372] The Soviet Air Force reported some 1,100 air-to-air victories and 335 MiG combat losses, while China's PLAAF reported 231 combat losses, mostly MiG-15s, and 168 other aircraft lost. The KPAF reported no data, but the UN Command estimates some 200 KPAF aircraft lost in the war's first stage, and 70 additional aircraft after the Chinese intervention. The USAF disputes Soviet and Chinese claims of 650 and 211 downed F-86s, respectively.[373][374]
More modern estimates place the overall USAF kill ratio at around 1.8:1 with the ratio dropping to 1.3:1 against MiG-15s with Soviet pilots, but increasing to a dominant 12:1 against Chinese and North Korean adversaries.[375][376][377]
According to reports by Lt. Gen. Sidor Slyusarev, commander of Soviet air forces in Korea, the 64th Corps claimed a total 1,097 enemy aircraft of all types during operations, for the loss of 335 aircraft (including lost to enemy ground fire, accidents, etc) and 110 pilots. This puts the overall kill ratio at 3.4:1 in favor of USSR pilots.[378] Effectiveness of the Soviet fighters declined as the war progressed. While between November 1950 and January 1952, overall kill ratio was 7.9:1 in favor of the USSR, this declined to 2.2:1, during 1952 and 1.9:1 in 1953. This was due in part to more advanced jet fighters appearing on the UN side and improving U.S. tactics.[379]
Regardless of the actual ratio, American Sabres were very effective at controlling the skies over Korea; since no other UN fighter could contend with the MiG-15, F-86s largely took over air combat once they arrived, relegating other aircraft to performing air-to-ground duties. Despite being outnumbered (the number of Sabres in theater never exceeded 150 while MiG-15s reached 900 at their peak), North Korean and Chinese aircraft were seldom encountered south of Pyongyang. UN ground forces, supply lines, and infrastructure were not attacked from the air, and although North Korea had 75 airfields capable of supporting MiGs, after 1951, any serious effort to operate from them was abandoned, keeping them based across the Yalu River in the safety of China. This confined most air-to-air engagements to MiG Alley, giving UN aircraft free rein to conduct strike missions over enemy territory with little fear of interception. Although jet dogfights are remembered as a prominent part of the Korean War, counter-air missions comprised just 12% of Far East Air Forces sorties, and four times as many sorties were performed for close air support and interdiction.[366]
The war marked a major milestone not only for fixed-wing aircraft, but also for rotorcraft, featuring the first large-scale deployment of helicopters for medical evacuation (medevac).[380] In 1944–1945, during the Second World War, the YR-4 helicopter saw limited ambulance duty, but in Korea, where rough terrain trumped the jeep as a speedy medevac vehicle,[381] helicopters like the Sikorsky H-19 helped reduce fatal casualties to a dramatic degree when combined with complementary medical innovations such as Mobile Army Surgical Hospitals.[382] As such, the medical evacuation and care system for the wounded was so effective for the UN forces that a wounded soldier who arrived at a MASH unit alive typically had a 97% chance of survival.[383] The limitations of jet aircraft for close air support highlighted the helicopter's potential in the role, leading to the development of the helicopter gunships used in the Vietnam War (1965–75).[380]
Bombing of North Korea

The initial bombing attack on North Korea was approved on the fourth day of the war, 29 June 1950, by General Douglas MacArthur immediately upon request by the commanding general of the Far East Air Forces (FEAF), George E. Stratemeyer.[384] Major bombing began in late July.[385] U.S. airpower conducted 7,000 close support and interdiction airstrikes that month, which helped slow the North Korean rate of advance to 3 km (2 mi) a day.[366] On 12 August 1950, the USAF dropped 625 tons of bombs on North Korea; two weeks later, the daily tonnage increased to some 800 tons.[386]
From June through October, official U.S. policy was to pursue precision bombing aimed at communication centers (railroad stations, marshaling yards, main yards, and railways) and industrial facilities deemed vital to war-making capacity. The policy was the result of debates after World War II, in which U.S. policy rejected the mass civilian bombings that had been conducted in the later stages of World War II as unproductive and immoral.[384] In early July, General Emmett O'Donnell Jr. requested permission to firebomb five North Korean cities. He proposed that MacArthur announce that the UN would employ the firebombing methods that "brought Japan to its knees". The announcement would warn the leaders of North Korea "to get women and children and other noncombatants the hell out".[387]
According to O'Donnell, MacArthur responded, "No, Rosie, I'm not prepared to go that far yet. My instructions are very explicit; however, I want you to know that I have no compunction whatever to your bombing bona fide military objectives, with high explosives, in those five industrial centers. If you miss your target and kill people or destroy other parts of the city, I accept that as a part of war."[387]
In September 1950, MacArthur said in his public report to the UN, "The problem of avoiding the killing of innocent civilians and damages to the civilian economy is continually present and given my personal attention."[387]
In October 1950, FEAF commander General Stratemeyer requested permission to attack the city of Sinuiju, a provincial capital with an estimated population of 60,000, "over the widest area of the city, without warning, by burning and high explosive". MacArthur's headquarters responded the following day: "The general policy enunciated from Washington negates such an attack unless the military situation clearly requires it. Under present circumstances this is not the case."[387]
Following the intervention of the Chinese in November, General MacArthur ordered increased bombing on North Korea, which included firebombing against the country's arsenals and communications centers and especially against the "Korean end" of all the bridges across the Yalu River.[388] As with the aerial bombing campaigns over Germany and Japan in World War II, the nominal objective of the USAF was to destroy North Korea's war infrastructure and shatter the country's morale.
On 3 November 1950, General Stratemeyer forwarded to MacArthur the request of Fifth Air Force commander General Earle E. Partridge for clearance to "burn Sinuiju". As he had done previously in July and October, MacArthur denied the request, explaining that he planned to use the town's facilities after seizing it. However, at the same meeting, MacArthur agreed for the first time to a firebombing campaign, agreeing to Stratemeyer's request to burn the city of Kanggye and several other towns: "Burn it if you so desire. Not only that, Strat, but burn and destroy as a lesson to any other of those towns that you consider of military value to the enemy." The same evening, MacArthur's chief of staff told Stratemeyer that the firebombing of Sinuiju had also been approved. In his diary, Stratemeyer summarized the instructions as follows: "Every installation, facility, and village in North Korea now becomes a military and tactical target." Stratemeyer sent orders to the Fifth Air Force and Bomber Command to "destroy every means of communications and every installation, factory, city, and village".[387]
On 5 November 1950, General Stratemeyer gave the following order to the commanding general of the Fifth Air Force: "Aircraft under Fifth Air Force control will destroy all other targets including all buildings capable of affording shelter." The same day, twenty-two B-29s attacked Kanggye, destroying 75% of the city.[384]
After MacArthur was removed as UN Supreme Commander in Korea in April 1951, his successors continued this policy and ultimately extended it to all of North Korea.[389] The U.S. dropped a total of 635,000 tons of bombs, including 32,557 tons of napalm, on Korea, more than during the whole Pacific campaign of World War II.[390][391] North Korea ranks alongside Cambodia (500,000 tons), Laos (2 million tons) and South Vietnam (4 million tons) as among the most heavily bombed countries in history, with Laos suffering the most extensive bombardment relative to its size and population.[392]

Almost every substantial building in North Korea was destroyed as a result.[393][394] The war's highest-ranking U.S. POW, Major General William F. Dean,[395] reported that the majority of North Korean cities and villages he saw were either rubble or snow-covered wasteland.[396][397] North Korean factories, schools, hospitals, and government offices were forced to move underground, and air defenses were "non-existent".[391] In November 1950, the North Korean leadership instructed their population to build dugouts and mud huts and to dig tunnels to solve the acute housing problem.[398] U.S. Air Force General Curtis LeMay commented: "We went over there and fought the war and eventually burned down every town in North Korea anyway, some way or another, and some in South Korea, too."[399] U.S. Colonel Dean Rusk, later secretary of state, stated the U.S. bombed "everything that moved in North Korea, every brick standing on top of another."[65] Pyongyang, which saw 75 percent of its area destroyed, was so devastated that bombing was halted as there were no longer any worthy targets left.[400][401] On 28 November, Bomber Command reported on the campaign's progress: 95 percent of Manpojin was destroyed, along with 90 percent of Hoeryong, Namsi and Koindong, 85 percent of Chosan, 75 percent of both Sakchu and Huichon and 20 percent of Uiju. According to USAF damage assessments, "Eighteen of twenty-two major cities in North Korea had been at least half obliterated."[387] By the end of the campaign, U.S. bombers had difficulty in finding targets and were reduced to bombing footbridges or jettisoning their bombs into the sea.[66]
In May 1953, five major North Korean dams were bombed. According to Charles K. Armstrong, the bombing of these dams and ensuing floods threatened several million North Koreans with starvation, although large-scale famine was averted with emergency aid provided by North Korea's allies.[143]
General Matthew Ridgway said that except for air power, "the war would have been over in 60 days with all Korea in Communist hands". UN air forces flew 1,040,708 combat and combat support sorties during the war. FEAF flew the majority at 710,886 (69.3% of sorties), with the U.S. Navy performing 16.1%, the U.S. Marine Corps 10.3%, and 4.3% by other allied air forces.[366]
As well as conventional bombing, the Communist side claimed that the U.S. used biological weapons.[402] These claims have been disputed; Conrad Crane asserts that while the U.S. worked towards developing chemical and biological weapons, the U.S. military "possessed neither the ability, nor the will", to use them in combat.[403]
U.S. threat of atomic warfare

On 5 November 1950, the U.S. Joint Chiefs of Staff issued orders for the retaliatory atomic bombing of Manchurian PRC military bases, if either of their armies crossed into Korea or if PRC or KPA bombers attacked Korea from there. President Truman ordered the transfer of nine Mark 4 nuclear bombs "to the Air Force's Ninth Bomb Group, the designated carrier of the weapons ... [and] signed an order to use them against Chinese and Korean targets", which he never transmitted.[404]
Many U.S. officials viewed the deployment of nuclear-capable (but not nuclear-armed) B-29 bombers to Britain as helping to resolve the Berlin Blockade of 1948–1949. Truman and Eisenhower both had military experience and viewed nuclear weapons as potentially usable components of their military. During Truman's first meeting to discuss the war on 25 June 1950, he ordered plans be prepared for attacking Soviet forces if they entered the war. By July, Truman approved another B-29 deployment to Britain, this time with bombs (but without their cores), to remind the Soviets of U.S. offensive ability. Deployment of a similar fleet to Guam was leaked to The New York Times. As UN forces retreated to Pusan, and the CIA reported that mainland China was building up forces for a possible invasion of Taiwan, the Pentagon believed that Congress and the public would demand using nuclear weapons if the situation in Korea required them.[405]
As PVA forces pushed back the UN forces from the Yalu River, Truman stated during a 30 November 1950 press conference that using nuclear weapons was "always [under] active consideration", with control under the local military commander.[405] The Indian ambassador, K. Madhava Panikkar, reports "that Truman announced he was thinking of using the atom bomb in Korea. But the Chinese seemed unmoved by this threat ... The PRC's propaganda against the U.S. was stepped up. The 'Aid Korea to resist America' campaign was made the slogan for increased production, greater national integration, and more rigid control over anti-national activities. One could not help feeling that Truman's threat came in useful to the leaders of the Revolution, to enable them to keep up the tempo of their activities."[207][406][407]
After his statement caused concern in Europe, Truman met on 4 December 1950 with UK prime minister and Commonwealth spokesman Clement Attlee, French Premier René Pleven, and French Foreign Minister Robert Schuman to discuss their worries about atomic warfare and its likely continental expansion. The U.S.' forgoing atomic warfare was not because of "a disinclination by the Soviet Union and People's Republic of China to escalate [the Korean War]", but because UN allies—notably the UK, the Commonwealth, and France—were concerned about a geopolitical imbalance rendering NATO defenseless while the U.S. fought China, who then might persuade the Soviet Union to conquer Western Europe.[207][408] The Joint Chiefs of Staff advised Truman to tell Attlee that the U.S. would use nuclear weapons only if necessary to protect an evacuation of UN troops, or to prevent a "major military disaster".[405]
On 6 December 1950, after the Chinese intervention repelled the UN armies from northern North Korea, General J. Lawton Collins (Army Chief of Staff), General MacArthur, Admiral C. Turner Joy, General George E. Stratemeyer and staff officers Major General Doyle Hickey, Major General Charles A. Willoughby and Major General Edwin K. Wright met in Tokyo to plan strategy countering the Chinese intervention; they considered three potential atomic warfare scenarios encompassing the next weeks and months of warfare.[207]
- In the first scenario: If the PVA continued attacking in full and the UN Command was forbidden to blockade and bomb China, and without Taiwanese reinforcements, and without an increase in U.S. forces until April 1951 (four National Guard divisions were due to arrive), then atomic bombs might be used in North Korea.[207]
- In the second scenario: If the PVA continued full attacks and the UN Command blockaded China and had effective aerial reconnaissance and bombing of the Chinese interior, and the Taiwanese soldiers were maximally exploited, and tactical atomic bombing was to hand, then the UN forces could hold positions deep in North Korea.[207]
- In the third scenario: if China agreed not to cross the 38th Parallel border, General MacArthur recommended UN acceptance of an armistice disallowing PVA and KPA troops south of the parallel, and requiring PVA and KPA guerrillas to withdraw northwards. The U.S. Eighth Army would remain to protect the Seoul–Incheon area, while X Corps would retreat to Pusan. A UN commission should supervise implementation of the armistice.[207]
Both the Pentagon and the State Department were cautious about using nuclear weapons because of the risk of general war with China and the diplomatic ramifications. Truman and his senior advisors agreed, and never seriously considered using them in early December 1950 despite the poor military situation in Korea.[405]
In 1951, the U.S. escalated closest to atomic warfare in Korea. Because China deployed new armies to the Sino-Korean frontier, ground crews at the Kadena Air Base, Okinawa, assembled atomic bombs for Korean warfare, "lacking only the essential pit nuclear cores". In October 1951, the United States effected Operation Hudson Harbor to establish a nuclear weapons capability. USAF B-29 bombers practiced individual bombing runs from Okinawa to North Korea (using dummy nuclear or conventional bombs), coordinated from Yokota Air Base in east-central Japan. Hudson Harbor tested "actual functioning of all activities which would be involved in an atomic strike, including weapons assembly and testing, leading, [and] ground control of bomb aiming". The bombing run data indicated that atomic bombs would be tactically ineffective against massed infantry, because the "timely identification of large masses of enemy troops was extremely rare".[409][410][411][412][413]
General Matthew Ridgway was authorized to use nuclear weapons if a major air attack originated from outside Korea. An envoy was sent to Hong Kong to deliver a warning to China. The message likely caused Chinese leaders to be more cautious about potential U.S. use of nuclear weapons, but whether they learned about the B-29 deployment is unclear, and the failure of the two major Chinese offensives that month likely was what caused them to shift to a defensive strategy in Korea. The B-29s returned to the United States in June.[405]
Despite the greater destructive power that atomic weapons would bring to the war, their effects on determining the war's outcome would have likely been minimal. Tactically, given the dispersed nature of PVA/KPA forces, the relatively primitive infrastructure for staging and logistics centers, and the small number of bombs available (most would have been conserved for use against the Soviets), atomic attacks would have limited effects against the ability of China to mobilize and move forces. Strategically, attacking Chinese cities to destroy civilian industry and infrastructure would cause the immediate dispersion of the leadership away from such areas and give propaganda value for the Communists to galvanize the support of Chinese civilians. Since the Soviets were not expected to intervene with their few primitive atomic weapons on China or North Korea's behalf, the threat of a possible nuclear exchange was unimportant in the decision not to deploy atomic bombs; their use offered little operational advantage, and would undesirably lower the "threshold" for using atomic weapons against non-nuclear states in future conflicts.[414]
When Eisenhower succeeded Truman in early 1953, he was similarly cautious about using nuclear weapons in Korea. The administration prepared contingency plans to use them against China, but like Truman, the new president feared that doing so would result in Soviet attacks on Japan. The war ended as it began, without U.S. nuclear weapons deployed near battle.[405]
War crimes
Civilian deaths and massacres


There were numerous atrocities and massacres of civilians throughout the Korean War committed by both sides, starting in the war's first days. On 28 June 1950, North Korean troops committed the Seoul National University Hospital massacre.[415] On the same day, South Korean President Syngman Rhee ordered the Bodo League massacre,[155][416][417] beginning mass killings of suspected leftist sympathizers and their families by South Korean officials and right-wing groups.[418][419] Estimates of those killed during the Bodo League massacre range from at least 60,000–110,000 (Kim Dong-choon) to 200,000 (Park Myung-lim).[420] The British protested to their allies about later South Korean mass executions, and saved some citizens.[418][419]
In 2005–2010, a South Korean Truth and Reconciliation Commission investigated atrocities and other human rights violations through much of the 20th century, from the Japanese colonial period through the Korean War and beyond. It excavated some mass graves from the Bodo League massacres and confirmed the general outlines of those political executions. Of the Korean War-era massacres the commission was petitioned to investigate, 82% were perpetrated by South Korean forces, with 18% perpetrated by North Korean forces.[421][422][420]
The commission also received petitions alleging more than 200 large-scale killings of South Korean civilians by the U.S. military during the war, mostly air attacks. It confirmed several such cases, including refugees crowded into a cave attacked with napalm bombs, which survivors said killed 360 people, and an air attack that killed 197 refugees gathered in a field in the far south. It recommended South Korea seek reparations from the United States, but in 2010, a reorganized commission under a new, conservative government concluded that most U.S. mass killings resulted from "military necessity", while in a small number of cases, they concluded, the U.S. military had acted with "low levels of unlawfulness", but the commission recommended against seeking reparations.[420]
In the most notorious U.S. massacre, investigated separately, not by the commission, American troops killed an estimated 250–300 refugees, mostly women and children, at No Gun Ri in central South Korea (26–29 July 1950).[423][424] U.S. commanders, fearing enemy infiltrators among refugee columns, had adopted a policy of stopping civilian groups approaching U.S. lines, including by gunfire.[425] After years of rejecting survivors' accounts, the U.S. Army investigated and in 2001 acknowledged the No Gun Ri killings, but claimed they were not ordered and "not a deliberate killing".[426]: x South Korean officials, after a parallel investigation, said they believed there were orders to shoot. The survivors' representatives denounced what they described as a U.S. "whitewash".[427][428]
The U.S. bombing of North Korea has been condemned as a war crime by some authors, because it often included bombing civilian targets and caused many civilians casualties. According to Bruce Cumings, "What hardly any Americans know or remember is that we carpet-bombed the north for three years with next to no concern for civilian casualties.” Author Blaine Harden has called the bombing campaign a "major war crime“ and described it as "long, leisurely and merciless”. He says it's "perhaps the most forgotten part of a forgotten war".[429][430][431]
Prisoners of War (POWs)

Chinese POWs
At Geoje prison camp on Geoje Island, Chinese POWs experienced anti-Communist lecturing and missionary work from secret agents from the U.S. and Taiwan in No. 71, 72 and 86 camps.[432] Pro-Communist POWs experienced torture, cutting off of limbs, or were executed in public.[433][434] Being forced to write confession letters and receiving tattoos of an anti-Communism slogan and Flag of the Republic of China were also commonly seen, in case any wanted to go back to mainland China.[435][436]
Pro-Communist POWs who could not endure the torture formed an underground group to fight the pro-Nationalist POWs secretly by assassination,[437] which led to the Geoje uprising. The rebellion captured Francis Dodd, and was suppressed by the 187th Infantry Regiment.
In the end, 14,235 Chinese POWs went to Taiwan and fewer than 6,000 POWs returned to mainland China.[438] Those who went to Taiwan are called "righteous men" and experienced brainwashing again and were sent to the army or were arrested;[439] while the survivors who returned to mainland China were welcomed as a "hero" first, but experienced anti-brainwashing, strict interrogation, and house arrest eventually, after the tattoos were discovered.[437] After 1988, the Taiwanese government allowed POWs to go back to mainland China, and helped remove anti-Communist tattoos; while the mainland Chinese government started to allow mainland Chinese prisoners of war to return from Taiwan.[439]
UN Command POWs
The United States reported that North Korea mistreated prisoners of war: soldiers were beaten, starved, put to forced labor, marched to death, and summarily executed.[440][441]
The KPA killed POWs at the battles for Hill 312, Hill 303, the Pusan Perimeter, Daejeon and Sunchon; these massacres were discovered afterwards by the UN forces. Later, a U.S. Congress war crimes investigation, the United States Senate Subcommittee on Korean War Atrocities of the Permanent Subcommittee of the Investigations of the Committee on Government Operations, reported that "two-thirds of all American prisoners of war in Korea died as a result of war crimes".[442][443][444]
Although the Chinese rarely executed prisoners like their North Korean counterparts, mass starvation and diseases swept through the Chinese-run POW camps during the winter of 1950–51. About 43 percent of U.S. POWs died during this period. The Chinese defended their actions by stating that all Chinese soldiers during this period were suffering mass starvation and diseases due to logistical difficulties. The UN POWs said that most of the Chinese camps were located near the easily supplied Sino-Korean border and that the Chinese withheld food to force the prisoners to accept the communism indoctrination programs.[445] According to Chinese reports, over a thousand U.S. POWs died by the end of June 1951, while a dozen British POWs died, and all Turkish POWs survived.[446] According to Hastings, wounded U.S. POWs died for lack of medical attention and were fed a diet of corn and millet "devoid of vegetables, almost barren of proteins, minerals, or vitamins" with only 1/3 the calories of their usual diet. Especially in early 1951, thousands of prisoners lost the will to live and "declined to eat the mess of sorghum and rice they were provided".[447]

The unpreparedness of U.S. POWs to resist heavy Communist indoctrination during the Korean War led to the Code of the United States Fighting Force which governs how U.S. military personnel in combat should act when they must "evade capture, resist while a prisoner or escape from the enemy".[448][449]
North Korea may have detained up to 50,000 South Korean POWs after the ceasefire.[42][450]: 141 Over 88,000 South Korean soldiers were missing and the KPA claimed they captured 70,000 South Koreans.[450]: 142 However, when ceasefire negotiations began in 1951, the KPA reported they held only 8,000 South Koreans.[451] The UN Command protested the discrepancies and alleged that the KPA were forcing South Korean POWs to join the KPA.[452]
The KPA denied such allegations. They claimed their POW rosters were small because many POWs were killed in UN air raids and that they had released ROK soldiers at the front. They insisted only volunteers were allowed to serve in the KPA.[453][450]: 143 By early 1952, UN negotiators gave up trying to get back the missing South Koreans.[454] The POW exchange proceeded without access to South Korean POWs who were not on the PVA/KPA rosters.[455]
North Korea continued to claim that any South Korean POW who stayed in the North did so voluntarily. However, since 1994, South Korean POWs have been escaping North Korea on their own after decades of captivity.[456][457] As of 2010[update], the South Korean Ministry of Unification reported that 79 ROK POWs escaped the North. The South Korean government estimates 500 South Korean POWs continue to be detained in North Korea.[458]
The escaped POWs have testified about their treatment and written memoirs about their lives in North Korea.[459] They report they were not told about the POW exchange procedures, and were assigned to work in mines in the remote northeastern regions near the Chinese and Russian border.[459]: 31 Declassified Soviet Foreign Ministry documents corroborate such testimony.[460]
In 1997, the Geoje POW Camp in South Korea was turned into a memorial.
Starvation
In December 1950, the South Korean National Defense Corps was founded; the soldiers were 406,000 drafted citizens.[461] In the winter of 1951, 50,000[462][463] to 90,000[464][465] South Korean National Defense Corps soldiers starved to death while marching southward under the PVA offensive when their commanding officers embezzled funds earmarked for their food.[462][464][466][467] This event is called the National Defense Corps Incident.[462][464] Although his political allies certainly profited from corruption, it remains controversial if Syngman Rhee was personally involved in or benefited from the corruption.[468]
Recreation

In 1950, Secretary of Defense George C. Marshall and Secretary of the Navy Francis P. Matthews called on the United Service Organizations (USO) which was disbanded by 1947 to provide support for U.S. servicemen.[469] By the end of the war, more than 113,000 USO volunteers from the U.S. were working at the home front and abroad.[469] Many stars came to Korea to give their performances.[469] Throughout the Korean War, comfort stations (brothels) were operated by South Korean officials for UN soldiers despite prostitution being ostensibly illegal.[470]
Aftermath
Postwar recovery was different in the two Koreas. South Korea, which started from a far lower industrial base than North Korea (the latter contained 80% of Korea's heavy industry in 1945),[66] stagnated in the first postwar decade. In 1953, South Korea and the United States signed a Mutual Defense Treaty. In 1960, the April Revolution occurred and students joined an anti-Syngman Rhee demonstration; 142 were killed by police; in consequence, Syngman Rhee resigned and left for exile in the United States.[471] Park Chung-hee's May 16 coup enabled social stability. From 1965 to 1973, South Korea dispatched troops to South Vietnam and received $235,560,000 in allowance and military procurement from the United States.[472] GNP increased fivefold during the Vietnam War.[472] South Korea industrialized and modernized. South Korea had one of the world's fastest-growing economies from the early 1960s to the late 1990s. In 1957, South Korea had a lower per capita GDP than Ghana,[473] and by 2010, it was a developed country and ranked thirteenth in the world (Ghana was 86th).[474]
As a result of the war, "North Korea had been virtually destroyed as an industrial society". After the armistice, Kim Il-Sung requested Soviet economic and industrial assistance. In September 1953, the Soviet government agreed to "cancel or postpone repayment for all ... outstanding debts", and promised to grant North Korea one billion rubles in monetary aid, industrial equipment and consumer goods. Eastern European members of the Soviet Bloc also contributed with "logistical support, technical aid, [and] medical supplies". China canceled North Korea's war debts, provided 800 million yuan, promised trade cooperation and sent in thousands of troops to rebuild damaged infrastructure.[391] Contemporary North Korea remains underdeveloped.[475]
North Korea has continued to be a totalitarian dictatorship since the end of the war, with an elaborate cult of personality around the Kim dynasty.[476][477][478]
The means of production are owned by the state through state-run enterprises and collectivized farms. Most services—such as healthcare, education, housing and food production—are subsidized or state-funded. Estimates based on the most recent North Korean census suggest that 240,000 to 420,000 people died as a result of the 1990s North Korean famine and that there were 600,000 to 850,000 unnatural deaths in North Korea from 1993 to 2008.[479] A study by South Korean anthropologists of North Korean children who had defected to China found that 18-year-old males were 13 cm (5 in) shorter than South Koreans their age because of malnutrition.[480]

Present-day North Korea follows Songun, or "military-first" policy. It is the country with the highest number of military and paramilitary personnel, with a total of 7,769,000 active, reserve and paramilitary personnel, or approximately 30% of its population. Its active-duty army of 1.28 million is the fourth largest in the world, after China, the United States and India; consisting of 4.9% of its population. North Korea possesses nuclear weapons. A 2014 UN inquiry into abuses of human rights in North Korea concluded that, "the gravity, scale and nature of these violations reveal a state that does not have any parallel in the contemporary world," with Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch holding similar views.[481][482][483][484]
South Korean anti-Americanism after the war was fueled by the presence and behavior of U.S. military personnel (USFK) and U.S. support for Park's authoritarian regime, a fact still evident during the country's democratic transition in the 1980s.[485] However, anti-Americanism has declined significantly in South Korea in recent years, from 46% favorable in 2003 to 74% favorable in 2011,[486] making South Korea one of the most pro-U.S. countries in the world.[487]
A large number of mixed-race "GI babies" (offspring of U.S. and other UN soldiers and Korean women) were filling up the country's orphanages. Because Korean traditional society places significant weight on paternal family ties, bloodlines, and purity of race, children of mixed race or those without fathers are not easily accepted in South Korean society. International adoption of Korean children began in 1954.[488] The U.S. Immigration Act of 1952 legalized the naturalization of non-Blacks and non-Whites as U.S. citizens and made possible the entry of military spouses and children from South Korea after the Korean War. With the passage of the Immigration Act of 1965, which substantially changed U.S. immigration policy toward non-Europeans, Koreans became one of the fastest-growing Asian groups in the United States.[489]
Mao Zedong's decision to take on the United States in the Korean War was a direct attempt to confront what the Communist bloc viewed as the strongest anti-Communist power in the world, undertaken at a time when the Chinese Communist regime was still consolidating its own power after winning the Chinese Civil War. Mao supported intervention not to save North Korea, but because he believed that a military conflict with the U.S. was inevitable after the U.S. entered the war, and to appease the Soviet Union to secure military dispensation and achieve Mao's goal of making China a major world military power. Mao was equally ambitious in improving his own prestige inside the communist international community by demonstrating that his Marxist concerns were international. In his later years, Mao believed that Stalin only gained a positive opinion of him after China's entrance into the Korean War. Inside mainland China, the war improved the long-term prestige of Mao, Zhou, and Peng, allowing the Chinese Communist Party to increase its legitimacy while weakening anti-Communist dissent.[490]

The Chinese government has encouraged the viewpoint that the war was initiated by the United States and South Korea, though ComIntern documents have shown that Mao sought approval from Joseph Stalin to enter the war. In Chinese media, the Chinese war effort is considered as an example of China's engaging the strongest power in the world with an underequipped army, forcing it to retreat, and fighting it to a military stalemate. These successes were contrasted with China's historical humiliations by Japan and by Western powers over the previous hundred years, highlighting the abilities of the PLA and the Chinese Communist Party. The most significant negative long-term consequence of the war for China was that it led the United States to guarantee the safety of Chiang Kai-shek's regime in Taiwan, effectively ensuring that Taiwan would remain outside of PRC control through the present day.[490] Mao had also discovered the usefulness of large-scale mass movements in the war while implementing them among most of his ruling measures over PRC.[491] Finally, anti-U.S. sentiments, which were already a significant factor during the Chinese Civil War, were ingrained into Chinese culture during the Communist propaganda campaigns of the Korean War.[492]
The Korean War affected other participant combatants. Turkey, for example, entered NATO in 1952,[493] and the foundation was laid for bilateral diplomatic and trade relations with South Korea.[494]
See also
- 1st Commonwealth Division
- Australia in the Korean War
- Canada in the Korean War
- Colombian Battalion
- Joint Advisory Commission, Korea
- Korean DMZ Conflict (1966–1969)
- Korean reunification
- Korean War in popular culture
- List of books about the Korean War
- List of Korean War Medal of Honor recipients
- List of Korean War weapons
- List of military equipment used in the Korean War
- List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll
- MASH – film
- M*A*S*H – TV series
- New Zealand in the Korean War
- North Korea in the Korean War
- Operation Big Switch
- Operation Little Switch
- Operation Moolah
- Partisans in the Korean War
- Philippine Expeditionary Forces to Korea
- Pyongyang Sally
- Soviet Union in the Korean War
- Transfer of People's Volunteer Army soldiers' remains from South Korea to China
- UNCMAC – the UN Command Military Armistice Commission operating from 1953 to the present
- UNCURK – the 1951 UN Commission for the Unification and Rehabilitation of Korea
- UNTCOK – the 1950 United Nations Temporary Commission on Korea
- United States in the Korean War
War memorials
- Korean War Memorial Wall,map Brampton, Ontario
- Korean War Veterans Memorial, Washington, D.C.
- Memorial of the War to Resist U.S. Aggression and Aid Korea, Dandong, Liaoning, China
- National War Memorial (New Zealand)
- Philadelphia Korean War Memorial
- United Nations Memorial Cemetery, Busan, Republic of Korea
- Victorious War Museum, Pyongyang, North Korea
- War Memorial of Korea Yongsan-dong, Yongsan-gu, Seoul, South Korea
Notes
- ^ On 9 July 1951 troop constituents were: US: 70.4%, ROK: 23.3% other UNC: 6.3%[1]
- ^ Italy was not part of the United Nations until 1955, but sent Italian Red Cross Field Hospital 68 from 1951[2]
- ^ 162,394 South Koreans, 36,574 Americans, 4,544 others
- ^ The remains of 8,075 US servicemen were not recovered,[30] of which 7,586 continue to be listed as missing.[31] 2,830 are non-battle deaths.[32]
- ^ 335,000–526,000 North Koreans, 208,729–400,000 Chinese, 299 Soviet
- ^ The signing ceremony was held 18 days later, on 2 September 1945
- ^ See 50 U.S.C. S 1601: "All powers and authorities possessed by the President, any other officer or employee of the Federal Government, or any executive agency... as a result of the existence of any declaration of national emergency in effect on 14 September 1976 are terminated two years from 14 September 1976."; Jolley v. INS, 441 F.2d 1245, 1255 n.17 (5th Cir. 1971).
References
Citations
- ^ Kim, Heesu (1996). Anglo-American Relations and the Attempts to Settle the Korean Question 1953–1960 (PDF) (Thesis). London School of Economics and Political Science. p. 213. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 April 2017. Retrieved 9 April 2017.
- ^ "Italian Red Cross Hospital". Archived from the original on 22 August 2012. Retrieved 2 June 2012.
- ^ "6.25전쟁 당시 대한민국에 도움의 손길 내밀었던 이탈리아". Newsis. 26 August 2016. Archived from the original on 12 April 2021. Retrieved 4 April 2021.
- ^ "독일, 62년만에 6.25 전쟁 의료지원국에 포함…총 6개국으로 늘어". 해럴드 경제. 22 June 2018. Retrieved 4 April 2021.
- ^ 임, 성호 (19 June 2020). "[6.25전쟁 70년] 이역만리 한국서 수백만명 살리고 의술 전파까지". Yeonhap News. Retrieved 4 April 2021.
- ^ Young, Sam Ma (2010). "Israel's Role in the UN during the Korean War" (PDF). Israel Journal of Foreign Affairs. 4 (3): 81–89. doi:10.1080/23739770.2010.11446616. S2CID 219293462. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 August 2015.
- ^ a b c Morris-Suzuki, Tessa (29 July 2012). "Post-War Warriors: Japanese Combatants in the Korean War". The Asia-Pacific Journal: Japan Focus. 10 (31).
- ^ Whan-woo, Yi (16 September 2019). "Pakistan's Defense Day rekindles Korean War relief aid". The Korea Times. Archived from the original on 27 November 2020. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- ^ "Uruguay's little-known but important role in the Korean War". Korea.net. 10 February 2022. Retrieved 4 September 2022.
- ^ Edles, Laura Desfor (1998). Symbol and Ritual in the New Spain: the transition to democracy after Franco. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. p. 32. ISBN 978-0521628853.
- ^ "Českoslovenští lékaři stáli v korejské válce na straně KLDR. Jejich mise stále vyvolává otazníky" (in Czech). Czech Radio. 11 April 2013. Archived from the original on 2 October 2016. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
- ^ a b Edwards, Paul M. (2006). Korean War Almanac. Almanacs of American wars. New York: Infobase Publishing. p. 528. ISBN 978-0816074679. Archived from the original on 4 July 2017.
- ^ Kocsis, Piroska (2005). "Magyar orvosok Koreában (1950–1957)" [Hungarian physicians in Korea (1950–1957)]. ArchivNet: XX. századi történeti források (in Hungarian). Budapest: Magyar Országos Levéltár. Archived from the original on 10 May 2017. Retrieved 22 November 2016.
- ^ "Romania's "Fraternal Support" to North Korea during the Korean War, 1950–1953". Wilson Centre. December 2011. Archived from the original on 21 February 2013. Retrieved 24 January 2013.
- ^ Birtle, Andrew J. (2000). The Korean War: Years of Stalemate. U.S. Army Center of Military History. p. 34. Retrieved 21 August 2021.
- ^ Millett, Allan Reed, ed. (2001). The Korean War, Volume 3. Korea Institute of Military History. U of Nebraska Press. p. 692. ISBN 978-0803277960. Retrieved 16 February 2013.
Total Strength 602,902 troops
- ^ Kane, Tim (27 October 2004). "Global U.S. Troop Deployment, 1950–2003". Reports. The Heritage Foundation. Archived from the original on 28 January 2013. Retrieved 15 February 2013.
Ashley Rowland (22 October 2008). "U.S. to keep troop levels the same in South Korea". Stars and Stripes. Archived from the original on 12 May 2013. Retrieved 16 February 2013.
Colonel Tommy R. Mize, United States Army (12 March 2012). "U.S. Troops Stationed in South Korea, Anachronistic?" (PDF). United States Army War College. Defense Technical Information Center. Archived from the original on 8 April 2013. Retrieved 16 February 2013.
Louis H. Zanardi; Barbara A. Schmitt; Peter Konjevich; M. Elizabeth Guran; Susan E. Cohen; Judith A. McCloskey (August 1991). "Military Presence: U.S. Personnel in the Pacific Theater" (PDF). Reports to Congressional Requesters. United States General Accounting Office. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 15 February 2013. - ^ a b c d e f g h i j USFK Public Affairs Office. "USFK United Nations Command". United States Forces Korea. United States Department of Defense. Archived from the original on 11 July 2016. Retrieved 29 July 2016.
Republic of Korea – 590,911
Colombia – 1,068
United States – 302,483
Belgium – 900
United Kingdom – 14,198
South Africa – 826
Canada – 6,146
Netherlands – 819
Turkey – 5,453
Luxembourg – 44
Australia – 2,282
Philippines – 1,496
New Zealand – 1,385
Thailand – 1,204[clarification needed]
Ethiopia – 1,271
Greece – 1,263
France – 1,119 - ^ Rottman, Gordon L. (2002). Korean War Order of Battle: United States, United Nations, and Communist Ground, Naval, and Air Forces, 1950–1953. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 126. ISBN 978-0275978358. Retrieved 16 February 2013.
A peak strength of 14,198 British troops was reached in 1952, with over 40,000 total serving in Korea.
"UK-Korea Relations". British Embassy Pyongyang. Foreign and Commonwealth Office. 9 February 2012. Retrieved 16 February 2013.When war came to Korea in June 1950, Britain was second only to the United States in the contribution it made to the UN effort in Korea. 87,000 British troops took part in the Korean conflict, and over 1,000 British servicemen lost their lives
Jack D. Walker. "A Brief Account of the Korean War". Information. Korean War Veterans Association. Retrieved 17 February 2013.Other countries to furnish combat units, with their peak strength, were: Australia (2,282), Belgium/Luxembourg (944), Canada (6,146), Colombia (1,068), Ethiopia (1,271), France (1,119), Greece (1,263), Netherlands (819), New Zealand (1,389), Philippines (1,496), Republic of South Africa (826), Thailand (1,294), Turkey (5,455), and the United Kingdom (Great Britain 14,198).
- ^ "Land of the Morning Calm: Canadians in Korea 1950–1953". Veterans Affairs Canada. Government of Canada. 7 January 2013. Archived from the original on 23 March 2013. Retrieved 22 February 2013.
Peak Canadian Army strength in Korea was 8,123 all ranks.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w "Casualties of Korean War" (in Korean). Ministry of National Defense of Republic of Korea. Archived from the original on 20 January 2013. Retrieved 14 February 2007.
- ^ a b c Edwards, Paul M. (2006). Korean War Almanac. Almanacs of American wars. Infobase Publishing. p. 517. ISBN 978-0816074679. Retrieved 22 February 2013.
- ^ Ramachandran, D. p (19 March 2017). "The doctor-heroes of war". The Hindu – via www.thehindu.com.
- ^ a b Fact Sheet: America's Wars". U.S. Department of Veteran Affairs, Washington D.C., May 2017.
- ^ Zhang 1995, p. 257.
- ^ Xiaobing, Li (2009). A History of the Modern Chinese Army Lexington: University Press of Kentucky. p. 105: "By December 1952, the Chinese forces in Korea had reached a record high of 1.45 million men, including fifty-nine infantry divisions, ten artillery divisions, five antiaircraft divisions, and seven tank regiments. CPVF numbers remained stable until the armistice agreement was signed in July 1953."
- ^ Shrader, Charles R. (1995). Communist Logistics in the Korean War. Issue 160 of Contributions in Military Studies. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 90. ISBN 978-0313295096. Retrieved 17 February 2013.
NKPA strength peaked in October 1952 at 266,600 men in eighteen divisions and six independent brigades.
- ^ a b Kolb, Richard K. (1999). "In Korea we whipped the Russian Air Force". VFW Magazine. 86 (11). Retrieved 17 February 2013.
Soviet involvement in the Korean War was on a large scale. During the war, 72,000 Soviet troops (among them 5,000 pilots) served along the Yalu River in Manchuria. At least 12 air divisions rotated through. A peak strength of 26,000 men was reached in 1952.
- ^ a b c d e Xu, Yan (29 July 2003). "Korean War: In the View of Cost-effectiveness". Consulate General of the People's Republic of China in New York. Archived from the original on 15 July 2011. Retrieved 12 August 2007.
- ^ a b c "U.S. Military Casualties – Korean War Casualty Summary". Defense Casualty Analysis System. United States Department of Defense. 29 April 2020. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- ^ "Defense POW/MIA Accounting Agency > Our Missing > Past Conflicts". www.dpaa.mil.
- ^ a b Rhem, Kathleen T. (8 June 2000). "Defense.gov News Article: Korean War Death Stats Highlight Modern DoD Safety Record". defense.gov. US Department of Defense. Archived from the original on 14 January 2012. Retrieved 3 March 2016.
- ^ "How Many Americans Died in Korea?". www.cbsnews.com.
- ^ "Records of American Prisoners of War During the Korean War, created, 1950–1953, documenting the period 1950–1953". Access to Archival Databases. National Archives and Records Administration. Archived from the original on 1 November 2013. Retrieved 6 February 2013.
This series has records for 4,714 U.S. military officers and soldiers who were prisoners of war (POWs) during the Korean War and therefore considered casualties.
- ^ a b Office of the Defence Attaché (30 September 2010). "Korean war". British Embassy Seoul. Foreign and Commonwealth Office. Retrieved 16 February 2013.
- ^ "Korean War WebQuest". Veterans Affairs Canada. Government of Canada. 11 October 2011. Archived from the original on 30 January 2013. Retrieved 28 May 2013.
In Brampton, Ontario, there is a 60-metre long "Memorial Wall" of polished granite, containing individual bronze plaques which commemorate the 516 Canadian soldiers who died during the Korean War.
"Canada Remembers the Korean War". Veterans Affairs Canada. Government of Canada. 1 March 2013. Archived from the original on 6 October 2012. Retrieved 27 May 2013.The names of 516 Canadians who died in service during the conflict are inscribed in the Korean War Book of Remembrance located in the Peace Tower in Ottawa.
- ^ Aiysha Abdullah; Kirk Fachnie (6 December 2010). "Korean War veterans talk of "forgotten war"". Canadian Army. Government of Canada. Archived from the original on 23 May 2013. Retrieved 28 May 2013.
Canada lost 516 military personnel during the Korean War and 1,042 more were wounded.
"Canadians in the Korean War". kvacanada.com. Korean Veterans Association of Canada Inc. Archived from the original on 11 May 2013. Retrieved 28 May 2013.Canada's casualties totalled 1,558 including 516 who died.
"2013 declared year of Korean war veteran". MSN News. The Canadian Press. 8 January 2013. Archived from the original on 2 November 2013. Retrieved 28 May 2013.The 1,558 Canadian casualties in the three-year conflict included 516 people who died.
- ^ Ted Barris (1 July 2003). "Canadians in Korea". legionmagazine.com. Royal Canadian Legion. Archived from the original on 20 July 2013. Retrieved 28 May 2013.
Not one of the 33 Canadian PoWs imprisoned in North Korea signed the petitions.
- ^ Australian War Memorial Korea MIA Archived 28 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 17 March 2012
- ^ a b Sandler, Stanley, ed. (2002). Ground Warfare: H–Q. Volume 2 of Ground Warfare: An International Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. p. 160. ISBN 978-1576073445. Retrieved 19 March 2013.
Philippines: KIA 92; WIA 299; MIA/POW 97
New Zealand: KIA 34; WIA 299; MIA/POW 1 - ^ "Two War Reporters Killed". The Times. London. 14 August 1950. ISSN 0140-0460.
- ^ a b Rummel, Rudolph J. (1997). "Chapter 10, Statistics of North Korean Democide Estimates, Calculations, And Sources". Statistics of Democide: Genocide and Murder Since 1900. ISBN 978-3825840105. Archived from the original on 22 November 2014.
- ^ a b c "Korean War | Combatants, Summary, Years, Map, Casualties, & Facts". Encyclopedia Britannica.
- ^ a b c Hickey, Michael. "The Korean War: An Overview". Archived from the original on 5 February 2009. Retrieved 31 December 2011.
- ^ Li, Xiaobing (2007). A History of the Modern Chinese Army. Lexington, KY: University Press of Kentucky. p. 111. ISBN 978-0813124384.
- ^ Xu, Yang (30 October 2014). "抗美援朝烈士新确认为197653人 副军长儿子到场" [Martyrs from the War to Resist America and Aid Korea are newly identified as 197,653, and the deputy commander's son is present]. People's Daily Online (in Chinese (China)). Central Committee of the Chinese Communist Party. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
在安葬仪式上,记者获悉,现已确认的抗美援朝烈士共有197653名。确认的抗美援朝烈士名录包括抗美援朝战争期间牺牲和失踪的志愿军官兵、支前民兵民工、支前工作人员,以及停战后至志愿军回国前帮助朝鲜民主主义共和国生产建设牺牲和因伤复发牺牲的人员。
[At the burial ceremony, the reporter was informed that there are now 197,653 confirmed martyrs of the War to Resist America and Aid Korea. The list of confirmed martyrs includes the officers and soldiers of the volunteer army who died and went missing during the War to Resist America and Aid Korea, the militia and militia workers who supported the front, the staff who supported the front, as well as those who died after the armistice until the return of the volunteer army to help the Democratic People's Republic of Korea in production and construction and those who died due to recurrence of injuries.] - ^ a b "180,000 Chinese soldiers killed in Korean War, says Chinese general" Archived 3 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine. China Daily, 28 June 2010. State Council Information Office, Chinese government, Beijing. "According to statistics compiled by the army's medical departments and hospitals, 114,084 servicemen were killed in military action or accidents, and 25,621 soldiers had gone missing. The other about 70,000 casualties died from wounds, illness and other causes, he said. To date, civil affairs departments have registered 183,108 war martyrs, Xu said."
- ^ Krivošeev, Grigorij F. (1997). Soviet Casualties and Combat Losses in the Twentieth Century. London: Greenhill. ISBN 978-1853672804.
- ^ a b c d e Cumings, Bruce (2011). The Korean War: A History. Modern Library. p. 35. ISBN 9780812978964.
Various encyclopedias state that the countries involved in the three-year conflict suffered a total of more than 4 million casualties, of which at least 2 million were civilians—a higher percentage than in World War II or Vietnam. A total of 36,940 Americans lost their lives in the Korean theater; of these, 33,665 were killed in action, while 3,275 died there of non-hostile causes. Some 92,134 Americans were wounded in action, and decades later, 8,176 were still reported as missing. South Korea sustained 1,312,836 casualties, including 415,004 dead. Casualties among other UN allies totaled 16,532, including 3,094 dead. Estimated North Korean casualties numbered 2 million, including about one million civilians and 520,000 soldiers. An estimated 900,000 Chinese soldiers lost their lives in combat.
- ^ a b c d e Lewy, Guenter (1980). America in Vietnam. Oxford University Press. pp. 450–453. ISBN 9780199874231.
For the Korean War the only hard statistic is that of American military deaths, which included 33,629 battle deaths and 20,617 who died of other causes. The North Korean and Chinese Communists never published statistics of their casualties. The number of South Korean military deaths has been given as in excess of 400,000; the South Korean Ministry of Defense puts the number of killed and missing at 281,257. Estimates of communist troops killed are about one-half million. The total number of Korean civilians who died in the fighting, which left almost every major city in North and South Korea in ruins, has been estimated at between 2 and 3 million. This adds up to almost 1 million military deaths and a possible 2.5 million civilians who were killed or died as a result of this extremely destructive conflict. The proportion of civilians killed in the major wars of this century (and not only in the major ones) has thus risen steadily. It reached about 42 percent in World War II and may have gone as high as 70 percent in the Korean War. ... we find that the ratio of civilian to military deaths [in Vietnam] is not substantially different from that of World War II and is well below that of the Korean War.
- ^ "The creation of an independent South Korea became UN policy in early 1948. Southern communists opposed this, and by autumn partisan warfare had engulfed parts of every Korean province below the 38th parallel. The fighting expanded into a limited border war between the South's newly formed Republic of Korea Army (ROKA) and the North Korean border constabulary as well as the North's Korean People's Army (KPA)."Millett (PHD), Allan. "Korean War". britannica.com. Archived from the original on 24 April 2016. Retrieved 21 April 2016.
- ^ a b Cumings 2005, pp. 247–53.
- ^ a b Stueck 2002, p. 71.
- ^ a b Devine, Robert A.; Breen, T.H.; Frederickson, George M.; Williams, R. Hal; Gross, Adriela J.; Brands, H.W. (2007). America Past and Present. Vol. II: Since 1865 (8th ed.). Pearson Longman. pp. 819–21. ISBN 978-0321446619.
- ^ Historian Kim Hakjoon argues that, “the many telegrams that Moscow and P’yǒngyang exchanged from January to June 1950, and, more important, the secret meetings between Stalin and Kim [Il Sung] in Moscow in April and Mao and Kim in Beijing during May, confirmed that the three Communist leaders were responsible for starting the Korean War on the morning of June 25, 1950.” quoted in Steven Lee, “The Korean War in History and Historiography.” Journal of American-East Asian Relations 21, no. 2 (2014): 185–206. doi:10.1163/18765610-02102010 at p 190.
- ^ United Nations Security Council Resolution 83
- ^ United Nations Security Council Resolution 82
- ^ Derek W. Bowett, United Nations Forces: A Legal Study of United Nations Practice, Stevens, London, 1964, pp. 29–60
- ^ "United Nations Security Council - History". Encyclopedia Britannica.
- ^ Pembroke, Michael (2018). Korea: Where the American Century Began. Hardie Grant Books. p. 141.
- ^ He, Kai; Feng, Huiyun (2013). Prospect Theory and Foreign Policy Analysis in the Asia Pacific: Rational Leaders and Risky Behavior. Routledge. p. 50. ISBN 978-1135131197. Archived from the original on 4 July 2017.
- ^ Li, Narangoa; Cribb, Robert (2014). Historical Atlas of Northeast Asia, 1590–2010: Korea, Manchuria, Mongolia, Eastern Siberia. Columbia University Press. p. 194. ISBN 978-0231160704. Archived from the original on 4 July 2017.
- ^ "Kim becomes first North Korean leader to cross border into South since war". Reuters. 27 April 2018. Retrieved 28 April 2018.
- ^ "North and South Korean leaders hold historic summit: Live updates". CNN. 26 April 2018. Retrieved 27 April 2018.
- ^ a b Fisher, Max (3 August 2015). "Americans have forgotten what we did to North Korea". Vox. Retrieved 18 October 2021.
- ^ a b c Robinson, Michael E (2007). Korea's Twentieth-Century Odyssey. Honolulu, HI: University of Hawaii Press. pp. 119-120. ISBN 978-0824831745.
- ^ Pratt, Keith L.; Rutt, Richard; Hoare, James (1999). Korea: A Historical and Cultural Dictionary. Richmond, Surrey: Curzon. p. 239. ISBN 978-0700704644.
- ^ Kim, Ilpyong J. (2003). Historical Dictionary of North Korea. Lanham, MD: Scarecrow Press. p. 79. ISBN 978-0810843318.
- ^ Rawnsley, Gary D. (2009). "'The Great Movement to Resist America and Assist Korea': how Beijing sold the Korean War". Media, War & Conflict. 2 (3): 285–315. doi:10.1177/1750635209345186. S2CID 143193818.
- ^ Truman, Harry S. (29 June 1950). "The President's News Conference of June 29, 1950". Teachingamericanhistory.org. Archived from the original on 26 December 2010. Retrieved 4 January 2011.
- ^ Halberstam 2007, p. 2.
- ^ a b Stokesbury 1990.
- ^ a b Schnabel, James F. (1972). Policy and Direction: The First Year. United States Army in the Korean War. Vol. 3. Washington, DC: Center of Military History, United States Army. pp. 3, 18, 22. ISBN 978-0160359552. Archived from the original on 17 May 2011.
- ^ Stueck 2002, pp. 19–20.
- ^ a b Stokesbury 1990, p. 23.
- ^ a b Dear & Foot 1995, p. 516.
- ^ Cumings 2005, pp. 160–61, 195–96.
- ^ Early, Stephen (1943). "Cairo Communiqué". Japan: National Diet Library. Archived from the original on 6 December 2010.
- ^ Whelan, Richard (1991). Drawing the Line: the Korean War 1950–53. Boston: Little, Brown and Company. p. 22. ISBN 978-0316934039.
- ^ a b Stokesbury 1990, pp. 24, 25.
- ^ Goulden 1983, p. 17.
- ^ "Foreign Relations of the United States: Diplomatic Papers, 1945, The British Commonwealth, The Far East, Volume VI - Office of the Historian". history.state.gov. Retrieved 5 January 2023.
- ^ McCullough, David (1992). Truman. Simon & Schuster Paperbacks. pp. 785–86. ISBN 978-0671869205.
- ^ a b c d Appleman 1998.
- ^ McCune, Shannon Boyd Bailey (1946). "Physical Basis for Korean Boundaries". Far Eastern Quarterly. 5 (3): 286–287. doi:10.2307/2049050. JSTOR 2049050. OCLC 32463018. S2CID 155917488.
- ^ Grajdanzev, Andrew J. (1945). "Korea Divided". Far Eastern Survey. 14 (20): 281–283. doi:10.2307/3022068. ISSN 0362-8949. JSTOR 3022068. OCLC 482287795.
- ^ "Foreign Relations of the United States: Diplomatic Papers, 1945, The British Commonwealth, The Far East, Volume VI - Office of the Historian". history.state.gov. Retrieved 23 June 2022.
- ^ Halberstam 2007, p. 63.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 25–26.
- ^ Becker 2005, p. 53.
- ^ Jager 2013, pp. 41–42.
- ^ Cumings 1981, chapter 3, 4.
- ^ Cumings 2005, p. 211.
- ^ Jager 2013, p. 47.
- ^ a b Stokesbury 1990, p. 26.
- ^ "Korea: For Freedom". Time. 20 May 1946. Archived from the original on 6 January 2012. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- ^ Malkasian 2001, p. 13.
- ^ Stewart, Richard W., ed. (2005). "The Korean War, 1950–1953". American Military History, Volume 2. United States Army Center of Military History. CMH Pub 30-22. Archived from the original on 18 May 2015. Retrieved 20 August 2007.
- ^ "Korea - Division of Korea". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 24 June 2022.
- ^ "Statement by the President on the Decision To Withdraw U.S. Forces From Korea, 1947-1949. | The American Presidency Project". presidency.ucsb.edu. Retrieved 24 June 2022.
- ^ a b c Chen 1994, p. 110.
- ^ Chen 1994, pp. 110–11.
- ^ Chen 1994, p. 111.
- ^ Chen 1994, p. 26.
- ^ Chen 1994, p. 22.
- ^ Chen 1994, p. 41.
- ^ Chen 1994, p. 21.
- ^ Chen 1994, p. 19.
- ^ Chen 1994, pp. 25–26, 93.
- ^ Gibby, Bryan (2012). Will to Win: American Military Advisors in Korea, 1946–1953. University Alabama Press. p. 72.
- ^ a b Bryan, p. 76.
- ^ Bryan, pp. 76-77.
- ^ a b Bryan, p. 78.
- ^ "Kuksa-bong". Mapcarta. Retrieved 11 November 2017.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (27 July 2010). The Korean War: A History. Random House Publishing Group. ISBN 9780679603788. Retrieved 11 November 2017 – via Google Books.
- ^ Bryan, pp. 79-80.
- ^ Bryan, p. 80.
- ^ Bryan, p. 82.
- ^ Weathersby 2002, pp. 3–4.
- ^ Weathersby 2002, p. 3.
- ^ Weathersby 2002, pp. 9, 10.
- ^ Weathersby 2002, p. 11.
- ^ a b Weathersby 2002, p. 10.
- ^ a b c Zhao, Suisheng (2022). The dragon roars back : transformational leaders and dynamics of Chinese foreign policy. Stanford, California: Stanford University Press. pp. 28–29. ISBN 978-1-5036-3415-2. OCLC 1332788951.
- ^ Barnouin & Yu 2006, pp. 139–40.
- ^ Weathersby 1993, p. 29.
- ^ Weathersby 2002, p. 13.
- ^ Mark O'Neill, "Soviet Involvement in the Korean War: A New View from the Soviet-Era Archives", OAH Magazine of History, Spring 2000, p. 21.
- ^ Weathersby 1993, pp. 29–30.
- ^ Weathersby 2002, p. 14.
- ^ Weathersby 2002, p. 15.
- ^ Cumings 2005, pp. 255–56.
- ^ Cumings 2005, pp. 249–58.
- ^ Millett 2007, p. 17.
- ^ Tom Gjelten (25 June 2010). "CIA Files Show U.S. Blindsided By Korean War". National Public Radio. Archived from the original on 24 August 2013. Retrieved 16 February 2013.
- ^ Seth, Michael J. (2010). A history of Korea: From Antiquity to the Present. Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield. p. 324. ISBN 978-0742567160.
- ^ Millett 2007, p. 14.
- ^ Stuecker, William (2004). Korean War: World History. University Press of Kentucky. pp. 102–103.
- ^ Millett 2007, p. 15.
- ^ Zhihua Shen. "A Misunderstood Friendship: Mao Zedong, Kim Il-sung, and Sino–North Korean Relations, 1949–1976". Columbia University Press, September 2018.
- ^ Nick Eberstadt (27 September 2017). Policy and Economic Performance in Divided Korea During the Cold War Era: 1945–91. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 9780844742748 – via Google Books.
- ^ a b c Armstrong, Charles K. (20 December 2010). "The Destruction and Reconstruction of North Korea, 1950–1960" (PDF). The Asia-Pacific Journal. 8 (51): 1. Retrieved 13 September 2019.
The number of Korean dead, injured or missing by war's end approached three million, ten percent of the overall population. The majority of those killed were in the North, which had half of the population of the South; although the DPRK does not have official figures, possibly twelve to fifteen percent of the population was killed in the war, a figure close to or surpassing the proportion of Soviet citizens killed in World War II.
- ^ Appleman 1998, p. 17.
- ^ James, Jack (25 June 1950). "North Koreans invade South Korea". United Press. Retrieved 29 July 2017.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 14.
- ^ Appleman 1998, p. 21.
- ^ a b Cumings 2005, pp. 260–63.
- ^ Buzo, Adrian (2002). The Making of Modern Korea. London: Routledge. p. 78. ISBN 978-0415237499.
- ^ Lone, Stewart; McCormack, Gavan (1993). Korea since 1850. Melbourne: Longman Cheshire. pp. 110–111.
- ^ a b Millett 2007, pp. 18–19.
- ^ 만물상 625 한강다리 폭파의 희생자들. Chosun Ilbo (in Korean). 29 June 2010. Archived from the original on 1 May 2011. Retrieved 15 July 2010.
- ^ Johnston, William (1 November 2011). A war of patrols: Canadian Army operations in Korea. Univ of British Columbia Pr. p. 20. ISBN 978-0774810081.
- ^ Cumings 2005, pp. 269–70.
- ^ a b Edwards, Paul (10 June 2010). Historical Dictionary of the Korean War. Scarecrow Press. p. 32. ISBN 978-0810867734.
- ^ Webb, William J. "The Korean War: The Outbreak". United States Army Center for Military History. Archived from the original on 12 June 2010. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- ^ Kim 1973, p. 30.
- ^ "Press spokesman doubts President Truman yet told of Korea conflict". UP. 24 June 1950. Retrieved 29 July 2017.
- ^ Wells, Samuel (23 June 2020). "Korea and the Fear of World War III". Wilson Center. Retrieved 4 July 2021.
- ^ Beschloss 2018, p. 447.
- ^ Kim 1973, p. 46.
- ^ Andrew Glass. "Truman orders U.S. military intervention in Korea, June 27, 1950". POLITICO. Retrieved 5 January 2023.
- ^ Rees 1964, p. 22.
- ^ Schindler, John R. (24 February 1998). "Dodging Armageddon: The Third World War That Almost Was, 1950". Cryptologic Quarterly: 85–95. Archived from the original on 30 September 2015.
- ^ Rees 1964, p. 23.
- ^ Rees 1964, p. 26.
- ^ Malkasian 2001, p. 16.
- ^ Gromyko, Andrei A. (4 July 1950). "On American Intervention in Korea, 1950". Modern History Sourcebook. New York: Fordham University. Archived from the original on 6 February 2012. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- ^ Gross, Leo (February 1951). "Voting in the Security Council: Abstention from Voting and Absence from Meetings". The Yale Law Journal. 60 (2): 209–257. doi:10.2307/793412. JSTOR 793412.
- ^ Schick, F. B. (September 1950). "Videant Consules". The Western Political Quarterly. 3 (3): 311–325. doi:10.2307/443348. JSTOR 443348.
- ^ "Truman Address on Korea". www.learner.org. Archived from the original on 8 April 2017. Retrieved 17 August 2017.
- ^ Goulden 1983, p. 48.
- ^ a b Hess, Gary R. (2001). Presidential Decisions for War : Korea, Vietnam and the Persian Gulf. Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0801865152.
- ^ Graebner, Norman A.; Trani, Eugene P. (1979). The Age of Global Power: The United States Since 1939. Vol. V3641. New York: John Wiley & Sons. OCLC 477631060.
- ^ Reis, M. (12 May 2014), "WWII and Korean War Industrial Mobilization: History Programs and Related Records" (Archived 15 July 2014 at the Wayback Machine), History Associates, retrieved 17 June 2014.
- ^ Truman, Harry S.; Ferrell, Robert H. (1980). The Autobiography of Harry S. Truman. Boulder, CO: University Press of Colorado. ISBN 978-0870810909.
- ^ Blair 2003, p. 290.
- ^ Hofmann, George F., "Tanks and the Korean War: A case study of unpreparedness", Armor, Vol. 109 Issue 5 (Sep/Oct 2000), pp. 7–12: In 1948, the US Army had to impose an 80 percent reduction in equipment requirements, deferring any equipment modernization. When the Joint Chiefs of Staff submitted a $30 billion total defense budget for FY 1948, the administration capped the DOD budget at the $14.4 billion set in 1947 and progressively reduced in succeeding fiscal years until January 1950, when it was reduced again to $13.5 billion.
- ^ Rees 1964, p. 27.
- ^ Barnouin & Yu 2006, p. 140.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 45.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 48.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 53.
- ^ Dunford, J.F. (Lt. Col.) The Strategic Implications of Defensive Operations at the Pusan Perimeter July–September 1950, Carlisle, PA: U.S. Army War College (7 April 1999) pp. 6–8, 12
- ^ Zabecki, David T., Stand or Die: 1950 Defense of Korea's Pusan Perimeter, Military History (May 2009): The inability of US forces to stop the 1950 North Korean summer offensive cost the Eighth Army 4,280 killed in action, 12,377 wounded, with 2,107 missing and 401 confirmed captured between 5 July and 16 September 1950. In addition, the lives of tens of thousands of South Korean soldiers and civilians were lost as well.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 56.
- ^ Tan Kwoh Jack (January 2006), THE KOREAN WAR JUNE-OCTOBER 1950: INCHON AND STALIN IN THE "TRIGGER VS. JUSTIFICATION" DEBATE (PDF), Singapore: Institute of Defence and Strategic Studies, p. 21
- ^ 在最高统帅部当参谋: 雷英夫将军回忆录 (in Chinese (China)). 百花洲文艺出版社. 28 November 1997. pp. 147, 153–154. ISBN 9787805798998.
- ^ Barnouin & Yu 2006, p. 141.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 47–48, 66.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 58.
- ^ 493rd meeting of the UN Security Council, 31 August 1950 Archived 2 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine United Nations Security Council Official Records No. 35, p. 25
- ^ Telegram, Dean Rusk to James Webb Archived 2 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine Foreign Relations of the United States 1950 Volume VII, Korea, Document 551
- ^ "work of the Security Council from August 1, 1950 to September 18, 1950". International Organization. 4 (4): 638. 1950. doi:10.1017/S0020818300029465. S2CID 249414462.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 59–60.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 61.
- ^ Appleman 1998, p. 61.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 58, 61.
- ^ a b Stokesbury 1990, p. 67.
- ^ a b "History of the 1st Cavalry Division and Its Subordinate Commands". Cavalry Outpost Publications. Archived from the original on 8 March 2010. Retrieved 27 March 2010.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 68.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 70.
- ^ Hoyt, Edwin P. (1984). On to the Yalu. New York: Stein and Day. p. 104.
- ^ "CHAPTER XXVIII: Pursuit and Exploitation". history.army.mil. Retrieved 5 January 2023.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 71–72.
- ^ a b c d Barnouin & Yu 2006, p. 143.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Schnabel, James F (1992) [1972]. United States Army in the Korean War: Policy And Direction: The First Year. United States Army Center of Military History. pp. 155–92, 212, 283–84, 288–89, 304. ISBN 978-0160359552. CMH Pub 20-1-1. Archived from the original on 17 May 2011.
- ^ a b Korea Institute of Military History (2000). The Korean War: Korea Institute of Military History. 3-volume set. Vol. 1, 2. Bison Books, University of Nebraska Press. pp. 512–29, 730. ISBN 978-0803277946.
- ^ a b Weintraub, Stanley (2000). MacArthur's War: Korea and the Undoing of an American Hero. New York: Simon & Schuster. pp. 157–58. ISBN 978-0684834191.
- ^ "Goyang Geumjeong Cave Massacre memorial service". Hankyoreh. 9 February 2010. Archived from the original on 16 May 2012. Retrieved 20 January 2012.
- ^ Charles J. Hanley; Jae-Soon Chang (6 December 2008). "Children 'executed' in 1950 South Korean killings". U-T San Diego. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 4 November 2012. Retrieved 1 September 2012.
- ^ Appleman 1998, pp. 607-609.
- ^ Barnouin & Yu 2006, pp. 143–44.
- ^ Cumings 2005, pp. 278–81.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 79–94.
- ^ a b Barnouin & Yu 2006, p. 144.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 81.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 87–88.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 90.
- ^ Stueck 2002, pp. 92–93.
- ^ Clodfelter 1989, p. 11.
- ^ a b Stokesbury 1990, p. 83.
- ^ Chen, Jian (1992). "China's Changing Aims during the Korean War, 1950—1951". The Journal of American-East Asian Relations. 1 (1): 8–41. ISSN 1058-3947. JSTOR 23613365. Retrieved 26 January 2021.
- ^ Offner, Arnold A. (2002). Another Such Victory: President Truman and the Cold War, 1945–1953. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press. p. 390. ISBN 978-0804747745.
- ^ Sheng, Michael. "Mao's Role in the Korean Conflict: A Revision". Twentieth Century China, Volume 39, Issue 3, pp. 269–290. September 2014. Quote: "But Mao's eagerness to be a part of the Korean revolutionary cause against American aggressors continued at home. On August 5, Mao telegraphed Gao Gang (高岗 1905–1954), the Commander and Commissar of the NDA, that there will probably have no military operation (for the NDA) in August, but (it) should be prepared for combat in early September. Every unit should be ready within this month in order to move to the front to fight. When commanders reported that it was unlikely that the troops could reach combat-ready status so quickly, Mao moved his timetable back a little, but on August 18 he demanded that the NDA must be ready for combat before September 30. Historian Chen Jian is correct that Mao had been inclined to send Chinese troops to Korea in later August and early September, and that the Chinese intervention was delayed in part due to reluctance on the part of Stalin and Kim."
- ^ Halberstam 2007, pp. 355–56.
- ^ a b Halberstam 2007, p. 355.
- ^ Halberstam 2007, p. 359.
- ^ a b Chinese Military Science Academy (September 2000). 抗美援朝战争史 [History of War to Resist America and Aid Korea] (in Chinese). Vol. I. Beijing: Chinese Military Science Academy Publishing House. pp. 35–36. ISBN 978-7801373908.
- ^ Chinese Military Science Academy (September 2000). 抗美援朝战争史 [History of War to Resist America and Aid Korea] (in Chinese). Vol. I. Beijing: Chinese Military Science Academy Publishing House. p. 160. ISBN 978-7801373908.
- ^ Halberstam 2007, p. 360.
- ^ Barnouin & Yu 2006, pp. 146, 149.
- ^ Halberstam 2007, p. 361.
- ^ Cumings 2005, p. 266.
- ^ a b c Zhao, Suisheng (2022). The dragon roars back : transformational leaders and dynamics of Chinese foreign policy. Stanford, California: Stanford University Press. p. 32. ISBN 978-1-5036-3415-2. OCLC 1332788951.
- ^ a b Barnouin & Yu 2006, pp. 147–48.
- ^ a b Stokesbury 1990, p. 102.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 88.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 89.
- ^ Donovan, Robert J (1996). Tumultuous Years: The Presidency of Harry S. Truman 1949–1953. University of Missouri Press. p. 285. ISBN 978-0826210852.
- ^ Shen, Zhihua (2010). "China and the Dispatch of the Soviet Air Force: The Formation of the Chinese–Soviet–Korean Alliance in the Early Stage of the Korean War". Journal of Strategic Studies. 33 (2): 211–230. doi:10.1080/01402391003590291. S2CID 154427564.
- ^ Stewart, Richard W (ed.). "The Korean War: The Chinese Intervention". history.army.mil. U.S. Army Center of Military History. Archived from the original on 3 December 2011. Retrieved 17 December 2011.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 98–99.
- ^ Mossman 1990, p. 160.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 104–11.
- ^ Mossman 1990, p. 158.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 110.
- ^ Doyle, James H.; Mayer, Arthur J (April 1979). "December 1950 at Hungnam". U.S. Naval Institute Proceedings. 105 (4): 44–65.
- ^ "Pyongyang taken as UN retreats, 1950". BBC Archive. Retrieved 10 September 2021.
- ^ Welle (www.dw.com), Deutsche. "Faces of the Korean War | DW | 25.07.2013". DW.COM. Retrieved 10 September 2021.
- ^ "The American Presidency Project Harry S Truman Proclamation 2914—Proclamation 2914—Proclaiming the Existence of a National Emergency". UC Santa Barbara. UC Santa Barbara. Retrieved 22 October 2021.
- ^ Jung Chang and Jon Halliday, MAO: The Unknown Story.
- ^ Weng, Byron (Autumn 1966). "Communist China's Changing Attitudes Toward the United Nations". International Organization. 20 (4): 677–704. doi:10.1017/S0020818300012935. OCLC 480093623. S2CID 154687870.
- ^ Chinese Military Science Academy (September 2000). 抗美援朝战争史 [History of War to Resist America and Aid Korea] (in Chinese). Vol. I. Beijing: Chinese Military Science Academy Publishing House. pp. 86–89. ISBN 978-7801373908.
- ^ Zhang 1995, pp. 119–126.
- ^ Alexander, Bevin R. (1986), Korea: The First War We Lost, New York: Hippocrene Books, Inc, pp. 371–376, ISBN 978-0-87052-135-5
- ^ a b Stokesbury 1990, p. 117.
- ^ Zhihua, Shen, and Yafeng Xia. "Mao Zedong's Erroneous Decision During the Korean War: China's Rejection of the UN Cease-fire Resolution in Early 1951". Asian Perspective 35, no. 2 (2011): 187–209.
- ^ Reminiscences, MacArthur, Douglas.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 113.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 118.
- ^ a b c d e Stokesbury 1990, p. 121.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 120.
- ^ "Resolution 498(V) Intervention of the Central People's Government of People's Republic of China in Korea". United Nations. 1 February 1951. Archived from the original on 25 May 2017.
- ^ "Cold War International History Project's Cold War Files". Wilson Center. Archived from the original on 30 September 2013.
- ^ a b "SURVIVOR Hundreds were killed in a 1951 massacre. One man is left to remember". JoongAng Daily. 10 February 2003. Archived from the original on 8 June 2011. Retrieved 6 April 2013.
- ^ Timmons, Robert. "Allies mark 60th anniversary of Chipyong-ni victory". 8tharmy.korea.army.mil. US Eighth Army. Archived from the original on 13 January 2012. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ a b Stokesbury 1990, p. 122.
- ^ a b Barnouin & Yu 2006, p. 149.
- ^ Xiaobing, Li (2014). China's Battle for Korea: The 1951 Spring Offensive. Indiana University Press. p. 63.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 123–27.
- ^ Stein 1994, p. 69.
- ^ Halberstam 2007, p. 600.
- ^ Stein 1994, p. 79.
- ^ Halberstam 2007, p. 498.
- ^ Brands, H.W. (28 September 2016). "The Redacted Testimony That Fully Explains Why General MacArthur Was Fired". Smithsonian. Retrieved 25 March 2017.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 127.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 130.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 131.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 131–32.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 133–34.
- ^ Xiaobing 2014, pp. 124-125.
- ^ Xiaobing 2014, p. 125.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 136–37.
- ^ Xiaobing 2014, p. 149.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 137–38.
- ^ a b Xiaobing 2014, p. 181.
- ^ Xiaobing 2009, pp. 101-102
- ^ Mossman, Billy (1988). United States Army in the Korean War: Ebb and Flow November 1950 – July 1951. United States Army Center of Military History. p. 465.
- ^ Xiaobing 2009, p. 103
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 145, 175–77.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 159.
- ^ Clodfelter 1989, p. 22.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 160.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 161–62.
- ^ Barnouin & Yu 2006, p. 148.
- ^ Barnouin & Yu 2006, pp. 148–49.
- ^ Clodfelter 1989, p. 24.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 144–53.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 147.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 187–99.
- ^ Boose, Donald W. Jr. (Spring 2000). "Fighting While Talking: The Korean War Truce Talks". OAH Magazine of History. Organization of American Historians. Archived from the original on 12 July 2007. Retrieved 7 November 2009.
... the UNC advised that only 70,000 out of over 170,000 North Korean and Chinese prisoners desired repatriation.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 189–90.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 242–45.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 240.
- ^ Agov, Avram (2013). "North Korea's Alliances and the Unfinished Korean War". The Journal of Korean Studies. 18 (2): 225–262. doi:10.1353/jks.2013.0020. S2CID 145216046.
- ^ Harrison (Lt. Col.), William T. "Military Armistice in Korea: A Case Study for Strategic Leaders" (PDF). Archived from the original on 1 August 2013. Retrieved 11 April 2013.
- ^ "US State Department statement regarding 'Korea: Neutral Nations Supervisory Commission' and the Armistice Agreement 'which ended the Korean War'". FAS. Archived from the original on 27 April 2011. Retrieved 4 January 2011.
- ^ Ho, Jong Ho (1993). The US Imperialists started the Korean War. Pyongyang, N. Korea: Foreign Languages Publishing House. p. 230. ASIN B0000CP2AZ.
- ^ "War Victory Day of DPRK Marked in Different Countries". KCNA. 1 August 2011. Archived from the original on 29 May 2012. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ "Operation Glory". Fort Lee, VA: Army Quartermaster Museum, US Army. Archived from the original on 28 December 2007. Retrieved 16 December 2007.
- ^ US Department of Defense. "DPMO White Paper: Punch Bowl 239" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 January 2012. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ "Remains from Korea identified as Ind. soldier". Army News. 1 March 2008. Retrieved 25 December 2011.
- ^ "NNSC in Korea". Swiss Armed Forces, International Command. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 August 2010. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ "Korea – NSCC". Forsvarsmakten.se. Swedish Armed Forces. 1 November 2007. Archived from the original on 25 August 2010. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ Ria Chae (May 2012). "NKIDP e-Dossier No. 7: East German Documents on Kim Il Sung's April 1975 Trip to Beijing". North Korea International Documentation Project. Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars. Archived from the original on 4 November 2012. Retrieved 30 May 2012.
- ^ "'North Korean torpedo' sank South's navy ship – report". BBC News. 20 May 2010. Archived from the original on 10 December 2011. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ Kim, Jack; Lee, Jae-won (23 November 2010). "North Korea shells South in fiercest attack in decades". Reuters. Archived from the original on 4 January 2012. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ Park, Madison (11 March 2013). "North Korea declares 1953 armistice invalid". CNN. Archived from the original on 11 March 2013. Retrieved 11 March 2013.
- ^ Chang-Won, Lim. "North Korea confirms end of war armistice". Tolo News. Archived from the original on 2 July 2014. Retrieved 17 June 2014.
- ^ "North Korea enters 'state of war' with South". BBC News. 30 March 2013. Archived from the original on 30 March 2013. Retrieved 30 March 2013.
- ^ "North Korea threatens pre-emptive nuclear strike against US". The Guardian. 7 March 2013. Archived from the original on 4 November 2013. Retrieved 4 April 2013.
- ^ "North Korea threats: US to move missiles to Guam". BBC News. 3 April 2013. Archived from the original on 4 April 2013. Retrieved 4 April 2013.
- ^ Cassella, Megan; Chiacu, Doina (21 February 2016). "U.S. rejected North Korea peace talks offer before last nuclear test: State Department". Reuters. Archived from the original on 22 February 2016. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ^ Griffiths, James (27 April 2018). "North and South Korea vow to end the Korean War in historic accord". CNN. Retrieved 29 April 2018.
- ^ "South Korean leader repeats call for declaration to end Korean War". Reuters. 21 September 2021. Retrieved 22 September 2021.
- ^ a b Kim, Samuel S. (2014). "The Evolving Asian System". International Relations of Asia. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 45. ISBN 9781442226418.
With three of the four major Cold War fault lines—divided Germany, divided Korea, divided China, and divided Vietnam—East Asia acquired the dubious distinction of having engendered the largest number of armed conflicts resulting in higher fatalities between 1945 and 1994 than any other region or sub-region. Even in Asia, while Central and South Asia produced a regional total of 2.8 million in human fatalities, East Asia's regional total is 10.4 million including the Chinese Civil War (1 million), the Korean War (3 million), the Vietnam War (2 million), and the Pol Pot genocide in Cambodia (1 to 2 million).
- ^ McGuire, James (2010). Wealth, Health, and Democracy in East Asia and Latin America. Cambridge University Press. p. 203. ISBN 9781139486224.
In Korea, war in the early 1950s cost nearly 3 million lives, including nearly a million civilian dead in South Korea.
- ^ Painter, David S. (1999). The Cold War: An International History. Routledge. p. 30. ISBN 9780415153164.
Before it ended, the Korean War cost over 3 million people their lives, including over 50,000 U.S. servicemen and women, and a much higher number of Chinese and Korean lives. The war also set in motion a number of changes that led to the militarization and intensification of the Cold War.
- ^ Lacina, Bethany (September 2009). "The PRIO Battle Deaths Dataset, 1946–2008, Version 3.0" (PDF). Peace Research Institute Oslo. pp. 359–362. Retrieved 29 August 2019.
- ^ Vogel, Steve (25 June 2000). "Death Miscount Etched Into History". The Washington Post. Retrieved 17 February 2023.
- ^ Defense Casualty Analysis System search Archived 21 December 2014 at archive.today Korean War Extract Data File. Accessed 21 December 2014.
- ^ Office of Medical History – Army Nurse Corps History. Accessed 7 January 2019. Table B-1.
- ^ Daggett, Stephen. Costs of Major U.S. Wars. Congressional Research Service, Washington, DC, p. 2.
- ^ Xiaobing 2009, p. 106
- ^ Xiaobing 2009, p. 111.
- ^ a b Xiaobing 2009, p. 112.
- ^ Correlates of War: National Material Capabilities (v4.0) Published online at OurWorldInData.org. Retrieved from here. Accessed 8 August 2019.
- ^ a b Andrew C. Nahm; James Hoare (2004). "Historical Dictionary of the Republic of Korea". Scarecrow Press, pp. 129–130.
- ^ Bethany Lacina and Nils Petter Gleditsch, 2005. ―Monitoring Trends in Global Combat: A New Dataset of Battle Deaths.‖ European Journal of Population: 21(2–3): 145–166. Korean data available at "The PRIO Battle Deaths Dataset, 1946–2008, Version 3.0", pp. 359–362
- ^ Harden, Blaine (2017). King of Spies: The Dark Reign of America's Spymaster in Korea. New York, p. 9.
- ^ Lewis, Adrian R., The American culture of war, New York: Taylor & Francis Group, ISBN 978-0415979757 (2007), p. 82
- ^ a b c Blair 2003.
- ^ "Memorandum of Information for the Secretary – Blockade of Korea". Truman Presidential Library – Archives. 6 July 1950. Archived from the original on 9 August 2007. Retrieved 28 July 2007.
- ^ Connor, Arthur W. (1992). The Armor Debacle in Korea, 1950: Implications For Today. U.S. Army War College. p. 73.
- ^ Close, Robert A. (Cmdr), Helo Operations Archived 14 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Class of '45, U.S. Naval Academy Alumni Association & Foundation: "There were insufficient spare sets of blades for all ships having helos. Naturally, the ship didn't have a set. So we used our hands to smooth the busted [wooden] ribs and fabric back into reasonable aerodynamic shape and bandaged the wound with masking tape...Flew that way for two weeks."
- ^ Blair, Clay, The Forgotten War: America in Korea, 1950–1953, Naval Institute Press (2003), p. 50: The planned introduction into service of the M20, an antitank weapon urgently required to defeat the thick cast armor of Soviet tanks being supplied to the North Koreans, had been cancelled due to budget cuts.
- ^ "Memoirs, William E. Anderson sub. Defective Weapons". Korean War Educator. 1999–2000. Retrieved 8 July 2018.
- ^ "Veterans' Memoirs: George W. Gatliff". Korean War Educator. 2012. Retrieved 23 June 2017.
- ^ Warren, James A., American Spartans: The U.S. Marines, New York: Simon & Schuster (2005), pp. 139–40: Repeated cuts in active-duty Fleet Marine Forces (FMF), planned combat deployments in the Atlantic and Persian Gulf (in the event of war with the Soviet Union), and Sixth Fleet deployments in the Mediterranean left only the under-strength 4th Marine Division – a reserve unit – available for combat in the western Pacific.
- ^ Krulak, Lieutenant General Victor H., USMC, retired (June 2000). "You Can't Get There From Here: The Inchon Story". Shipmate. Archived from the original on 13 November 2002.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 14, 43.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 39.
- ^ Perrett 1987, pp. 134–35.
- ^ Zaloga & Kinnear 1996: 36
- ^ Stein 1994, p. 18.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, pp. 182–84.
- ^ Perrett 1987, p. 135.
- ^ Zaloga & Kinnear 1996: 33–34
- ^ Ravino & Carty 2003, p. 130.
- ^ Marolda, Edward (26 August 2003). "Naval Battles". US Navy. Archived from the original on 29 June 2007. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ "Korean War". korean-war.com. Archived from the original on 20 January 2013.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 174.
- ^ a b c Stokesbury 1990, p. 182.
- ^ Werrell 2005, p. 71.
- ^ a b c d Correll, John T. (1 April 2020). "The Difference in Korea". Air Force Magazine. Retrieved 14 June 2020.
- ^ Stokesbury 1990, p. 183.
- ^ Werrell 2005, pp. 76–77.
- ^ Sherman, Stephen (March 2000). "Korean War Aces: USAF F-86 Sabre jet pilots". acepilots.com. Archived from the original on 19 August 2007. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ Davis, Larry; Thyng, Harrison R. "The Bloody Great Wheel: Harrison R. Thyng". Sabre Pilots Association. Archived from the original on 6 February 2012. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ Puckett, Allen L. (1 April 2005). "Say 'hello' to the bad guy". af.mil. US Air Force. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ Frans P.B. Osinga (24 January 2007). Science, Strategy and War: The Strategic Theory of John Boyd. Routledge. p. 24. ISBN 978-1134197095. Archived from the original on 3 September 2015.
Mark A. Lorell; Hugh P. Levaux (1998). The Cutting Edge: A Half Century of Fighter Aircraft R&D. Rand Corporation. p. 48. ISBN 978-0833025951. Archived from the original on 21 September 2015.
Craig C. Hannah (2002). Striving for Air Superiority: The Tactical Air Command in Vietnam. Texas A&M University Press. p. 90. ISBN 978-1585441464. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. - ^ Sewell, Stephen L. "Russian Claims from the Korean War 1950–53." Archived 1 November 2006 at the Wayback Machine korean-war.com. Retrieved: 19 July 2011.
- ^ Zhang, Xiaoming. Red Wings over the Yalu: China, the Soviet Union, and the Air War in Korea. College Station, Texas: Texas A&M University Press, 2002. ISBN 1-58544-201-1.
- ^ Dorr, Robert F., Jon Lake and Warren E. Thompson. Korean War Aces. London: Osprey Publishing, 2005. ISBN 1-85532-501-2.
- ^ Stillion, John and Scott Perdue. "Air Combat Past, Present and Future." Archived 6 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine Project Air Force, Rand, August 2008. Retrieved 11 March 2009.
- ^ Igor Seidov and Stuart Britton. Red Devils over the Yalu: A Chronicle of Soviet Aerial Operations in the Korean War 1950–53 (Helion Studies in Military History). Helion and Company 2014. ISBN 978-1909384415. Page: 554.
- ^ "Report from the 64th Fighter Aviation Corps of the Soviet Air Forces in Korea | Wilson Center Digital Archive".
- ^ "Report from the 64th Fighter Aviation Corps of the Soviet Air Forces in Korea | Wilson Center Digital Archive".
- ^ a b Kreisher, Otto (16 January 2007). "The Rise of the Helicopter During the Korean War". historynet.com. Weider History Group. Archived from the original on 6 January 2012. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ "WW II Helicopter Evacuation". Olive Drab. Archived from the original on 13 January 2012. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ Day, Dwayne A. "M.A.S.H./Medevac Helicopters". CentennialOfFlight.gov. US Centennial of Flight Commission. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ King, Booker; Jatoi, Ismail (May 2005). "The Mobile Army Surgical Hospital (MASH): A Military and Surgical Legacy". Journal of the National Medical Association. 97 (5): 650–651. PMC 2569328. PMID 15926641.
Air evacuation undoubtedly contributed to the dramatic reduction in the death rate of wounded soldiers in the Korean War, compared with previous conflicts (World War I, 8.5%; World War II, 4%; and Korean War, 2.5%)
- ^ a b c Kim, Taewoo (2012). "Limited War, Unlimited Targets: U.S. Air Force Bombing of North Korea during the Korean War, 1950–1953". Critical Asian Studies. 44 (3): 467–492. doi:10.1080/14672715.2012.711980. S2CID 142704845..
- ^ Ward Thomas (14 June 2001). The Ethics of Destruction: Norms and Force in International Relations. Cornell University Press. p. 149. ISBN 978-0801487415.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (2006). "Korea: Forgotten Nuclear Threats". In Constantino, Renato Redentor (ed.). The Poverty of Memory: Essays on History and Empire. Quezon City, Philippines: Foundation for Nationalist Studies. p. 63. ISBN 978-9718741252. OCLC 74818792. Archived from the original on 22 September 2007. Retrieved 24 July 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f Conway-Lanz, Sahr (15 September 2014). "The Ethics of Bombing Civilians After World War II: The Persistence of Norms Against Targeting Civilians in the Korean War". The Asia-Pacific Journal. 12 (37).
- ^ Walter J. Boyne (15 June 1998). Beyond the Wild Blue: A History of the U.S. Air Force, 1947–1997. St. Martin's Press. pp. 78–79. ISBN 978-0312187057.
- ^ Mark Peterson (1 December 2009). Brief History: Brief History of Korea. Facts on File. p. 149. ISBN 978-0816050857.
- ^ Walkom, Thomas (25 November 2010). "Walkom: North Korea's unending war rages on". Toronto Star. Archived from the original on 1 May 2011. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ a b c Armstrong, Charles (20 December 2010). "The Destruction and Reconstruction of North Korea, 1950–1960". The Asia-Pacific Journal. 8 (51).
- ^ Kiernan, Ben; Owen, Taylor (27 April 2015). "Making More Enemies than We Kill? Calculating U.S. Bomb Tonnages Dropped on Laos and Cambodia, and Weighing Their Implications". The Asia-Pacific Journal. 13 (17). Retrieved 30 August 2019.
- ^ Cumings 2005, pp. 297–98.
- ^ Jager 2013, pp. 237–42.
- ^ Witt, Linda; Bellafaire, Judith; Granrud, Britta; Binker, Mary Jo (2005). A Defense Weapon Known to be of Value: Servicewomen of the Korean War Era. University Press of New England. p. 217. ISBN 978-1584654728.
- ^ Cumings, Bruce (10 December 2004). "Napalm über Nordkorea" (in German). Le Monde diplomatique. Archived from the original on 6 December 2011. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ William F Dean (1954) General Dean's Story, (as told to William L Worden), Viking Press, pp. 272–73.
- ^ Kim, Taewoo (2014). "Overturned Time and Space: Drastic Changes in the Daily Lives of North Koreans during the Korean War" (PDF). Asian Journal of Peacebuilding. 2 (2): 244–245. doi:10.18588/201411.000030. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 July 2015.
- ^ Kohn, Richard, H.; Harahan, Joseph, P., eds. (1988). Strategic Air Warfare: An Interview with Generals Curtis E. LeMay, Leon W. Johnson, David A. Burchinal, and Jack J. Catton. Office of Air Force History. p. 88. ISBN 978-0912799568.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ Oberdorfer, Don; Carlin, Robert (2014). The Two Koreas: A Contemporary History. Basic Books. p. 181. ISBN 978-0465031238.
- ^ Kim, Taewoo (2012). "Limited War, Unlimited Targets: U.S. Air Force Bombing of North Korea during the Korean War, 1950–1953". Critical Asian Studies. 44 (3): 467–492. doi:10.1080/14672715.2012.711980. S2CID 142704845.
- ^ Hogan, Michael, ed. (1995). America in the World: The Historiography of American Foreign Relations since 1941. New York: Cambridge University Press. p. 290. ISBN 978-0521498074.
- ^ Crane, Conrad (Spring 2002). ""No Practical Capabilities": American Biological and Chemical Warfare Programs During the Korean War". Perspectives in Biology and Medicine. 45 (2): 241–249. doi:10.1353/pbm.2002.0024. PMID 11919382. S2CID 23091486.
- ^ Cumings 2005, pp. 289–92.
- ^ a b c d e f Dingman, R. (1988–1989). "Atomic Diplomacy during the Korean War". International Security. 13 (3): 50–91. doi:10.2307/2538736. JSTOR 2538736. S2CID 154823668.
- ^ Knightley, Phillip (1982). The First Casualty: The War Correspondent as Hero, Propagandist and Myth-maker. Quartet. p. 334. ISBN 978-0801869518.
- ^ Panikkar, Kavalam Madhava (1981). In Two Chinas: Memoirs of a Diplomat. Hyperion Press. ISBN 978-0830500130.
- ^ Truman, Harry S (1955–1956). Memoirs (2 volumes). Vol. II. Doubleday. 394–395. ISBN 978-1568520629.
- ^ Hasbrouck, S. V. (1951), memo to file (November 7, 1951), G-3 Operations file, box 38-A, Library of Congress
- ^ Army Chief of Staff (1951), memo to file (November 20, 1951), G-3 Operations file, box 38-A, Library of Congress
- ^ Watson, Robert J.; Schnabel, James F. (1998). The Joint Chiefs of Staff and National Policy, 1950–1951, The Korean War and 1951–1953, The Korean War. History of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, Volume III, Parts I and II. Office of Joint History, Office of the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. part 1, p. v, part 2, p. 614.
- ^ Commanding General, Far East Air Force (1951), Memo to 98th Bomb Wing Commander, Okinawa
- ^
Far East Command G-2 Theater Intelligence (1951), Résumé of Operation, Record Group 349, box 752
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Farley, Robert (5 January 2016). "What If the United States had Used the Bomb in Korea?". The Diplomat. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- ^ "서울대병원, 6.25전쟁 참전 용사들을 위한 추모제 가져". Seoul National University Hospital. 4 June 2010. Archived from the original on 20 January 2013. Retrieved 19 July 2012.
- ^ 60년 만에 만나는 한국의 신들러들. Hankyoreh (in Korean). 25 June 2010. Archived from the original on 27 April 2011. Retrieved 15 July 2010.
- ^ "보도연맹 학살은 이승만 특명에 의한 것" 민간인 처형 집행했던 헌병대 간부 최초증언 출처 : "보도연맹 학살은 이승만 특명에 의한 것" – 오 마이뉴스. Ohmynews (in Korean). 4 July 2007. Archived from the original on 3 May 2011. Retrieved 15 July 2010.
- ^ a b "Unearthing proof of Korea killings". BBC. 18 August 2008. Archived from the original on 1 September 2013. Retrieved 5 April 2013.
- ^ a b "U.S. Allowed Korean Massacre in 1950". CBS News. Associated Press. 11 February 2009. Archived from the original on 12 May 2013. Retrieved 5 April 2013.
- ^ a b c "Korea bloodbath probe ends; US escapes much blame". The San Diego Union Tribune. 10 July 2010. Retrieved 11 June 2019.
Last November, after investigating petitions from surviving relatives, the commission announced it had verified and identified 4,934 execution victims. But historian Kim Dong-choon, the former commissioner who led that investigation, estimates at least 60,000 to 110,000 died, and similar numbers were summarily executed when northern troops were driven from South Korea later in 1950 and alleged southern collaborators were rounded up. 'I am estimating conservatively,' he said. Korean War historian Park Myung-lim, methodically reviewing prison records, said he believes perhaps 200,000 were slaughtered in mid-1950 alone.
- ^ "Truth Commission: South Korea 2005". United States Institute of Peace. Archived from the original on 10 June 2015. Retrieved 23 December 2018.
- ^ cf. the Truth and Reconciliation Commission's preliminary March 2009 report: "Truth and Reconciliation: Activities of the Past Three Years" (PDF). Truth and Reconciliation Commission (South Korea). March 2009. p. 39. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 March 2016.
Out of those 9,600 petitions, South Korean forces conducted 7,922 individual massacres and North Korean forces conducted 1,687 individual massacres.
- ^ Lee, B-C (15 October 2012). "노근리재단, 과거사 특별법 제정 세미나 개최" [No Gun Ri Foundation held special law seminar]. Newsis (online news agency) (in Korean). Seoul. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ^ Hanley, Charles J. (9 March 2015). "In the Face of American Amnesia, The Grim Truths of No Gun Ri Find a Home". The Asia-Pacific Journal/Japan Focus. 13 (10). Retrieved 6 June 2020.
- ^ Hanley, Charles J.; Mendoza, Martha (29 May 2006). "U.S. Policy Was to Shoot Korean Refugees". The Washington Post. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 27 April 2011. Retrieved 25 December 2011.
- ^ Office of the Inspector General, Department of the Army. No Gun Ri Review. Washington, D.C. January 2001
- ^ Kirk, Don (13 January 2001). "Korean Group Rejects U.S. Regret for War Incident". International Herald Tribune. Archived from the original on 11 June 2014. Retrieved 6 January 2014.
- ^ "Army confirms G.I.'s in Korea killed civilians". The New York Times. 12 January 2001. Retrieved 17 February 2012.
- ^ Fisher, Max (3 August 2015). "Americans have forgotten what we did to North Korea". Vox. Retrieved 19 October 2021.
- ^ Tokyo, David McNeill in. "Unknown to most Americans, the US 'totally destroyed' North Korea once before". The Irish Times. Retrieved 18 October 2021.
- ^ Hasan, Mehdi (3 May 2017). "Why Do North Koreans Hate Us? One Reason — They Remember the Korean War". The Intercept. Retrieved 18 October 2021.
- ^ Hsiu-Huan Chou, A Study on the Transport of Anti-communist Fighters to Taiwan during the Korean War (1950–1954), pp. 126–29, Academia Historica of Republic of China, June 2011 weblink Archived 23 September 2015 at the Wayback Machine, (in Chinese)
- ^ Xiaobing Li, Soldiers from four countries discuss about Korean War, Vol 1. (四国士兵话朝战(之一)), 《冷战国际史研究》第6辑, 2008年第2期 (in Chinese)
- ^ Decrypt the truth that ten thousands pow went to Taiwan Archived 15 April 2015 at the Wayback Machine 2013-07-29, retrieved on 18 June 2017 (in Chinese)
- ^ 王二根, 李文林. 一个被俘志愿军战士的自述. 《炎黄春秋杂志》2011年第1期 (in Chinese)
- ^ "1954年14000名志愿军战俘去台湾的真相". www.people.com.cn. 13 March 2012. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- ^ a b China's Korean War POWs find you can't go home again | The Japan Times Archived 17 December 2016 at the Wayback Machine 2000-06-28, retrieved on 18 June 2017
- ^ Hermes 1992a.
- ^ a b POW of PVA in Taiwan Archived 6 August 2016 at the Wayback Machine, 谌旭彬, Hong Kong Chinese University
- ^ Potter, Charles (3 December 1953). "Korean War Atrocities" (PDF). United States Senate Subcommittee on Korean War Atrocities of the Permanent Subcommittee of the Investigations of the Committee on Government Operations. US Government Printing Office. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 January 2012. Retrieved 25 December 2011.
- ^ Carlson, Lewis H (2003). Remembered Prisoners of a Forgotten War: An Oral History of Korean War POWs. St. Martin's Griffin. ISBN 978-0312310073.
- ^ Lakshmanan, Indira A.R (1999). "Hill 303 Massacre". Archived from the original on 30 December 2011. Retrieved 25 December 2011.
- ^ Van Zandt, James E. (February 2003). "You are about to die a horrible death". VFW Magazine. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 25 December 2011.
- ^ Skelton, William Paul (April 2002). "American Ex-Prisoners of War" (PDF). Department of Veterans Affairs. OCLC 77563074. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 January 2012. Retrieved 31 December 2011.
- ^ Lech, Raymond B. (2000). Broken Soldiers. Chicago: University of Illinois Press. pp. 2, 73. ISBN 978-0252025419.
- ^ 中国人民解放军总政治部联络部编. 敌军工作史料·第6册(1949年–1955年). 1989
- ^ Hastings. The Korean War. Guild Publishing London. 1987. 29092
- ^ "The military Code of Conduct: a brief history". Archived from the original on 16 December 2013.
- ^ "Code of Conduct". usmcpress.com. Archived from the original on 27 September 2014.
- ^ a b c Heo, Man-ho (2002). "North Korea's Continued Detention of South Korean POWs since the Korean and Vietnam Wars" (PDF). The Korean Journal of Defense Analysis. 14 (2): 141–165. doi:10.1080/10163270209464030. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 January 2016.
- ^ Lee, Sookyung (2007). "Hardly Known, Not Yet Forgotten, South Korean POWs Tell Their Story". Radio Free Asia. Archived from the original on 7 October 2007. Retrieved 22 August 2007.
- ^ Hermes 1992, p. 136.
- ^ Hermes 1992, p. 143.
- ^ Hermes 1992, p. 149.
- ^ Hermes 1992, p. 514.
- ^ "S Korea POW celebrates escape". BBC News. 19 January 2004. Archived from the original on 6 February 2012. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
- ^ "S Korea 'regrets' refugee mix-up". BBC News. 18 January 2007. Archived from the original on 13 April 2012. Retrieved 25 December 2011.
- ^ "Republic of Korea Ministry of Unification Initiatives on South Korean Prisoners of War and Abductees". Archived from the original on 2 November 2013.
- ^ a b Yoo, Young-Bok (2012). Tears of Blood: A Korean POW's Fight for Freedom, Family and Justice. Korean War POW Affairs-USA. ISBN 978-1479383856. Archived from the original on 17 May 2013.
- ^ Volokhova, Alena (2000). "Armistice Talks in Korea (1951–1953): Based on Documents from the Russian Foreign Policy Archives". Far Eastern Affairs (2): 74, 86, 89–90. Archived from the original on 3 November 2013.
- ^ "국민방위군 수만명 한국전때 허망한 죽음" 간부들이 군수품 착 복...굶어죽거나 전염병 횡사 진실화해위, 매장지 등 확인...국가에 사과 권고. Hankyoreh (in Korean). 7 September 2010. Archived from the original on 30 April 2011.
- ^ a b c 국민방위군 사건 (in Korean). National Archives of Korea. Archived from the original on 27 April 2011. Retrieved 20 July 2010.
- ^ "50,000 Koreans die in camps in south; Government Inquiry Confirms Abuse of Draftees – General Held for Malfeasance". The New York Times. New York. 12 June 1951. p. 3. Archived from the original on 17 September 2011. Retrieved 23 July 2010.
- ^ a b c '국민방위군' 희생자 56년만에 '순직' 인정. Newsis (in Korean). 30 October 2007. Retrieved 18 July 2010.
- ^ Roehrig, Terence (2001). The Prosecution of Former Military Leaders in Newly Democratic Nations: The Cases of Argentina, Greece, and South Korea. McFarland & Company. p. 139. ISBN 978-0786410910.
- ^ Sandler, Stanley (1 October 1999). The Korean War: No Victors, No Vanquished. University Press of Kentucky. p. 224. ISBN 978-0813109671.
- ^ "South Korean Aide Quits; Defense Minister Says He Was Implicated in Scandals". The New York Times. 4 June 1951. Archived from the original on 21 September 2011. Retrieved 23 July 2010.
- ^ Terence Roehrig (2001). Prosecution of Former Military Leaders in Newly Democratic Nations: The Cases of Argentina, Greece, and South Korea. McFarland & Company. p. 139. ISBN 978-0786410910. Archived from the original on 21 September 2015.
- ^ a b c Paul M. Edwards (2006). Prosecution of Former Military Leaders in Newly Democratic Nations: The Cases of Argentina, Greece, and South Korea. Greenwood. pp. 123–24. ISBN 978-0313332487.
- ^ Höhn, Maria (2010). Over There: Living with the U.S. Military Empire from World War Two to the Present. Duke University Press. pp. 51–52. ISBN 978-0822348276.
- ^ Savada, Andrea, ed. (1997). South Korea: A Country Study. Diane Pub Co. p. 34. ISBN 978-0788146190. Retrieved 5 April 2013.
- ^ a b 1965년 전투병 베트남 파병 의결. Dong-a Ilbo (in Korean). 2 July 2008. Archived from the original on 16 June 2013. Retrieved 24 September 2011.
- ^ "Leading article: Africa has to spend carefully". The Independent. London: INM. 13 July 2006. ISSN 0951-9467. OCLC 185201487. Archived from the original on 24 January 2012. Retrieved 24 December 2011.
- ^ "Country Comparison: GDP (purchasing power parity)". The World Factbook. CIA. 2011. Archived from the original on 18 November 2011. Retrieved 24 December 2011.
- ^ North Korea cornered with snowballing debts-The Korea Herald. View.koreaherald.com (18 August 2010). Retrieved on 12 July 2013.
- ^ "North Korea country profile". BBC News. 9 April 2018.
- ^ "Kim Jong Un's North Korea: Life inside the totalitarian state". Washington Post.
- ^ "Totalitarianism". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2018.
- ^ Spoorenberg, Thomas; Schwekendiek, Daniel (2012). "Demographic Changes in North Korea: 1993–2008". Population and Development Review. 38 (1): 133–158. doi:10.1111/j.1728-4457.2012.00475.x.
- ^ Demick, Barbara (8 October 2011). "The unpalatable appetites of Kim Jong-il". Archived from the original on 9 October 2011. Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ Amnesty International (2007). "Our Issues, North Korea". Human Rights Concerns. Archived from the original on 29 March 2007. Retrieved 1 August 2007.
- ^ "Report of the Commission of Inquiry on Human Rights in the Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Chapter VII. Conclusions and recommendations", United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, p. 346, 17 February 2014, archived from the original on 27 February 2014, retrieved 1 November 2014
- ^ Kay Seok (15 May 2007). "Grotesque indifference". Human Rights Watch. Archived from the original on 29 September 2007. Retrieved 1 August 2007.
- ^ "Human Rights in North Korea". hrw.org. Human Rights Watch. 17 February 2009. Archived from the original on 29 April 2011. Retrieved 13 December 2010.
- ^ Kristof, Nicholas D. (12 July 1987). "Anti-Americanism Grows in South Korea". The New York Times. Retrieved 11 April 2008.
- ^ "Global Unease With Major World Powers" Archived 10 March 2013 at the Wayback Machine. Pew Research Center. 27 June 2007.
- ^ Views of US Continue to Improve in 2011 BBC Country Rating Poll Archived 23 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine, 7 March 2011.
- ^ Jang, Jae-il (11 December 1998). "Adult Korean Adoptees in Search of Roots". The Korea Times. Archived from the original on 20 January 2013. Retrieved 24 December 2011.
- ^ Choe, Yong-Ho; Kim, Ilpyong J.; Han, Moo-Young (2005). "Annotated Chronology of the Korean Immigration to the United States: 1882 to 1952". Duke.edu. Archived from the original on 2 January 2012. Retrieved 24 December 2011.
- ^ a b Barnouin & Yu 2006, p. 150.
- ^ 沈志华、李丹慧.《战后中苏关系若干问题研究》(Research into Some Issues of Sino-USSR Relationship After WWII)人民出版社,2006年:p. 115
- ^ Zhang, Hong (2002), The Making of Urban Chinese Images of the United States, 1945–1953, Westport, CT: Greenwood Press, pp. 164–167, ISBN 978-0313310010
- ^ "Turkey". State.gov. US Department of State. 9 December 2011. Retrieved 24 December 2011.
- ^ "Revue de la presse turque 26.06.2010". turquie-news.fr (in French). 26 June 2010. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 24 December 2011.
Bibliography
- Cumings, B (2011). The Korean War: A history. New York: Modern Library.
- Kraus, Daniel (2013). The Korean War. Booklist.
- Warner, G. (1980). The Korean War. International Affairs.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: Appleman, Roy E (1998) [1961]. South to the Naktong, North to the Yalu. United States Army Center of Military History. pp. 3, 15, 381, 545, 771, 719. ISBN 978-0160019180. Archived from the original on 7 February 2014. Retrieved 14 July 2010.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: Appleman, Roy E (1998) [1961]. South to the Naktong, North to the Yalu. United States Army Center of Military History. pp. 3, 15, 381, 545, 771, 719. ISBN 978-0160019180. Archived from the original on 7 February 2014. Retrieved 14 July 2010.- Barnouin, Barbara; Yu, Changgeng (2006). Zhou Enlai: A Political Life. Hong Kong: Chinese University Press. ISBN 978-9629962807.
- Becker, Jasper (2005). Rogue Regime: Kim Jong Il and the Looming Threat of North Korea. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0195170443.
- Beschloss, Michael (2018). Presidents of War: The Epic Story, from 1807 to Modern Times. New York: Crown. ISBN 978-0-307-40960-7.
- Blair, Clay (2003). The Forgotten War: America in Korea, 1950–1953. Naval Institute Press.
- Chen, Jian (1994). China's Road to the Korean War: The Making of the Sino-American Confrontation. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0231100250.
- Clodfelter, Micheal (1989). A Statistical History of the Korean War: 1950-1953. Bennington, Vermont: Merriam Press.
- Cumings, Bruce (2005). Korea's Place in the Sun : A Modern History. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0393327021.
- Cumings, Bruce (1981). "3, 4". Origins of the Korean War. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-8976966124.
- Dear, Ian; Foot, M.R.D. (1995). The Oxford Companion to World War II. Oxford, NY: Oxford University Press. p. 516. ISBN 978-0198662259.
- Goulden, Joseph C (1983). Korea: The Untold Story of the War. New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 17. ISBN 978-0070235809.
- Halberstam, David (2007). The Coldest Winter: America and the Korean War. New York: Hyperion. ISBN 978-1401300524.
- Hanley, Charles J. (2020). Ghost Flames: Life and Death in a Hidden War, Korea 1950-1953. New York, New York: Public Affairs. ISBN 9781541768154.
- Hanley, Charles J.; Choe, Sang-Hun; Mendoza, Martha (2001). The Bridge at No Gun Ri: A Hidden Nightmare from the Korean War. New York: Henry Holt and Company. ISBN 0-8050-6658-6.
- Hermes, Walter G. Truce Tent and Fighting Front. [Multiple editions]:
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: * Hermes, Walter G. (1992), Truce Tent and Fighting Front, Washington, DC: Center of Military History, United States Army, ISBN 978-0160359576
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: * Hermes, Walter G. (1992), Truce Tent and Fighting Front, Washington, DC: Center of Military History, United States Army, ISBN 978-0160359576
- Hermes, Walter G (1992a). "VII. Prisoners of War". Truce Tent and Fighting Front. United States Army in the Korean War. Washington, DC: Center of Military History, United States Army. pp. 135–144. ISBN 978-1410224842. Archived from the original on 6 January 2010. Appendix B-2 Archived 5 May 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- Jager, Sheila Miyoshi (2013). Brothers at War – The Unending Conflict in Korea. London: Profile Books. ISBN 978-1846680670.
- Kim, Yǒng-jin (1973). Major Powers and Korea. Silver Spring, MD: Research Institute on Korean Affairs. OCLC 251811671.
- Lee, Steven. “The Korean War in History and Historiography.” Journal of American-East Asian Relations 21#2 (2014): 185–206. doi:10.1163/18765610-02102010.
- Lin, L., et al. "Whose history? An analysis of the Korean war in history textbooks from the United States, South Korea, Japan, and China". Social Studies 100.5 (2009): 222–232. online
- Malkasian, Carter (2001). The Korean War, 1950–1953. Essential Histories. London; Chicago: Fitzroy Dearborn. ISBN 978-1579583644.
- Matray, James I., and Donald W. Boose Jr, eds. The Ashgate research companion to the Korean War (2014) excerpt; covers historiography
- Matray, James I. "Conflicts in Korea" in Daniel S. Margolies, ed. A Companion to Harry S. Truman (2012) pp 498–531; emphasis on historiography.
- Millett, Allan R. (2007). The Korean War: The Essential Bibliography. The Essential Bibliography Series. Dulles, VA: Potomac Books Inc. ISBN 978-1574889765.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: Mossman, Billy C. (1990). Ebb and Flow, November 1950 – July 1951. United States Army in the Korean War. Vol. 5. Washington, DC: Center of Military History, United States Army. OCLC 16764325. Archived from the original on 29 January 2021. Retrieved 3 May 2010.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: Mossman, Billy C. (1990). Ebb and Flow, November 1950 – July 1951. United States Army in the Korean War. Vol. 5. Washington, DC: Center of Military History, United States Army. OCLC 16764325. Archived from the original on 29 January 2021. Retrieved 3 May 2010.- Perrett, Bryan (1987). Soviet Armour Since 1945. London: Blandford. ISBN 978-0713717358.
- Ravino, Jerry; Carty, Jack (2003). Flame Dragons of the Korean War. Paducah, KY: Turner.
- Rees, David (1964). Korea: The Limited War. New York: St Martin's. OCLC 1078693.
- Rivera, Gilberto (3 May 2016). Puerto Rican Bloodshed on The 38th Parallel: U.S. Army Against Puerto Ricans Inside the Korean War. p. 24. ISBN 978-1539098942.
- Stein, R. Conrad (1994). The Korean War: "The Forgotten War". Hillside, NJ: Enslow Publishers. ISBN 978-0894905261.
- Stokesbury, James L (1990). A Short History of the Korean War. New York: Harper Perennial. ISBN 978-0688095130.
- Stueck, William W. (1995), The Korean War: An International History, Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0691037677
- Stueck, William W. (2002), Rethinking the Korean War: A New Diplomatic and Strategic History, Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0691118475
- Weathersby, Kathryn (1993), Soviet Aims in Korea and the Origins of the Korean War, 1945–50: New Evidence From the Russian Archives, Cold War International History Project: Working Paper No. 8
- Weathersby, Kathryn (2002), "Should We Fear This?" Stalin and the Danger of War with America, Cold War International History Project: Working Paper No. 39
- Werrell, Kenneth P. (2005). Sabres Over MiG Alley. Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1591149330.
- Zaloga, Steven J.; Kinnear, Jim; Aksenov, Andrey; Koshchavtsev, Aleksandr (1997). Soviet Tanks in Combat 1941–45: The T-28, T-34, T-34-85, and T-44 Medium Tanks. Armor at War. Hong Kong: Concord Publication. ISBN 9623616155.
- Zhang, Shu Guang (1995), Mao's Military Romanticism: China and the Korean War, 1950–1953, Lawrence, KS: University Press of Kansas, ISBN 978-0700607235
External links
- Records of the United Nations Commission for the Unification and Rehabilitation of Korea (UNCURK) (1950–1973) at the United Nations Archives
Historical
- Anniversary of the Korean War Armistice: Truman on Acheson's Crucial Role in Going to War Shapell Manuscript Foundation
- Korean War resources, Dwight D. Eisenhower Presidential Library Archived 26 June 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- North Korea International Documentation Project
- Grand Valley State University Veteran's History Project digital collection
- The Forgotten War, Remembered – four testimonials in The New York Times
- Collection of Books and Research Materials on the Korean War an online collection of the United States Army Center of Military History
- Korean War, US Army Signal Corps Photograph Collection U.S. Army Heritage and Education Center, Carlisle, Pennsylvania
- The Korean War at History.com
- Koreanwar-educator.org
- The short film Film No. 927 is available for free viewing and download at the Internet Archive.
Media
- West Point Atlas of the Korean War
- The Korean War You Never Knew – slideshows by Life magazine
- U.S. Army Korea Media Center official Korean War online image archive
- Rare pictures of the Korean War from the U.S. Library of Congress and National Archives
- Land of the Morning Calm Canadians in Korea – multimedia project including veteran interviews
- Pathé Online newsreel archive featuring films on the war
- CBC Digital Archives – Forgotten Heroes: Canada and the Korean War
- Uncertain Enemies: Soviet Pilots in the Korean War. Air Power History. (Spring 1997). 44, 1, 32–45.
Organizations
- Korea Defense Veterans of America
- Korean War Ex-POW Association
- Korean War Veterans Association
- The Center for the Study of the Korean War
Memorials
- Korean War
- Revolution-based civil wars
- Civil wars involving the states and peoples of Asia
- History of Korea
- United Nations operations in Asia
- Wars involving Australia
- Wars involving Canada
- Wars involving Belgium
- Wars involving the People's Republic of China
- Wars involving Ethiopia
- Wars involving France
- Wars involving Greece
- Wars involving Luxembourg
- Wars involving New Zealand
- Wars involving South Africa
- Wars involving Thailand
- Wars involving Turkey
- Wars involving the Netherlands
- Wars involving the Philippines
- Wars involving the Soviet Union
- Wars involving the United Kingdom
- Wars involving the United States
- Conflicts in 1950
- Conflicts in 1951
- Conflicts in 1952
- Conflicts in 1953
- Civil wars post-1945
- Communism-based civil wars
- Aftermath of World War II
- Wars involving North Korea
- Wars involving South Korea
- 1950s in North Korea
- 1950s in South Korea
- Proxy wars
- Wars involving Korea