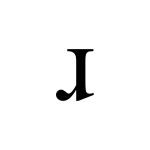
Voiced alveolar and postalveolar approximants
Appearance
| Voiced alveolar and postalveolar approximants | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ɹ | |||
| IPA Number | 151 | ||
| Encoding | |||
| Entity (decimal) | ɹ | ||
| Unicode (hex) | U+0279 | ||
| X-SAMPA | r\ | ||
| Braille | |||
| |||
The alveolar approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents the alveolar and postalveolar approximants is ⟨ɹ⟩, a lowercase letter r rotated 180 degrees. The equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is ⟨r\⟩.
For ease of typesetting, English phonemic transcriptions might use the symbol ⟨r⟩ instead of ⟨ɹ⟩, even though the former symbol represents the alveolar trill in phonetic transcription.
Features
Features of the alveolar approximant:
- Its manner of articulation is approximant, which means it is produced by narrowing the vocal tract at the place of articulation, but not enough to produce a turbulent airstream.
- Its place of articulation is alveolar, which means it is articulated with either the tip or the blade of the tongue at the alveolar ridge, termed respectively apical and laminal.
- Its phonation is voiced, which means the vocal cords vibrate during the articulation.
- It is an oral consonant, which means air is allowed to escape through the mouth only.
- It is a central consonant, which means it is produced by directing the airstream along the center of the tongue, rather than to the sides.
- Its airstream mechanism is pulmonic, which means it is articulated by pushing air solely with the intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles, as in most sounds.
Occurrence
| Language | Word | IPA | Meaning | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Armenian | Eastern[citation needed] | սուրճ | [suɹtʃ] | 'coffee' | |
| Burmese[1][2] | တိရစ္ဆာန် | [təɹeɪʔsʰàɴ] | 'animal' | Occurs only in loanwords, mostly from Pali or English. | |
| Chukchi[citation needed] | ңирэк | [ŋiɹek] | 'two' | ||
| Dutch | Central Netherlandic | [[[Dutch alphabet|door]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [doə̯ɹ] | 'through' | Allophone of [r ~ ɾ ~ ʀ] in the syllable coda for some speakers. See Dutch phonology. |
| Western Netherlandic | |||||
| Leiden | [[[Dutch alphabet|rat]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [ɹat] | 'rat' | Dialect of this city, unlike any other, uses [ɹ] for every instance of /r/. | |
| English | some American dialects[3] | [[[English orthography|red]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | 'red' | Often retracted and labialized. In non-rhotic varieties, it occurs only before a vowel. May also be a labialized retroflex approximant; corresponds to an alveolar trill or alveolar tap in a few other dialects. For convenience it is often transcribed ⟨r⟩. See English phonology. | |
| Australian | |||||
| Received Pronunciation | |||||
| Faroese | [róður] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [ɹɔuwʊɹ] | 'rudder' | ||
| German | Westerwald[4] | [[[German orthography|Rebe]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [ˈɹeːbə] | 'vine shoot' | Most other dialects use a voiced uvular fricative or uvular trill. See German phonology. |
| Siegerland[5] | |||||
| Silesian German | |||||
| Upper Lusatian | |||||
| Greek[6] | [[[Greek alphabet|μέρα]] méra] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [ˈmɛɹɐ] | 'day' | Allophone of /r/ in rapid or casual speech. See Modern Greek phonology. | |
| Igbo[7] | [rí] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [ɹí] | 'eat' | Post-alveolar. | |
| Portuguese | Greater São Paulo[8] | [permitir] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [pe̞ɹmiˈtɕiɾ] | 'to allow', 'to enable' | Some or all coda /ɾ/ may instead be a guttural or an approximant, varying by speaker, albeit more likely to be aspirated or deleted altogether than to be an approximant among native speakers when as final. See Portuguese phonology. |
| Inland Brazilian Centro-Sul's metro cities[9] | [amor] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [aˈmoɹ] | 'love', 'dear' | Allophone of [ɾ ~ ʁ] in the syllable coda. May also be retroflex, post-alveolar and/or rhotic vowel. As most rhotic coda in colloquial Brazilian Portuguese, likely to get deleted as final or at the end of sentences. | |
| General Brazilian[10] | [marketing] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [ˈmaɹke̞tɕĩ] | 'marketing' | Allophone of [ɾ ~ ʁ] in recent loanwords, used even by many speakers who do not use coda alveolar, post-alveolar or retroflex approximants in native words. Varies individually. Generally not as onset or final e.g. trailer [ˈtɾejle̞ʁ]. | |
| Spanish | Some dialects[11] | doscientos | [do̞ɹˈθje̞nto̞s] | 'two hundred' | Allophone of /s/ in the syllable coda. See Spanish phonology. |
| Swedish[12] | [[[Swedish alphabet|starkast]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [ˈstaɹːkast] | 'strongest' | Some dialects. See Swedish phonology. | |
| Vietnamese | Saigon[13] | [ra] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [ɹa] | 'go out' | In free variation with flap, trill and [ʐ]. See Vietnamese phonology. |
| Zapotec | Tilquiapan[14] | rdɨ | [ɹd̪ɨ] | 'pass' | Allophone of /ɾ/ before any consonant. |
As an allophone of other rhotic sounds, [ɹ] occurs in Edo, Fula, Murinh-patha, and Palauan.[15]
See also
References
- ^ Cornyn (1944:7)
- ^ Watkins (2001)
- ^ Hallé, Best & Levitt (1999:283) citing Delattre & Freeman (1968), Zawadzki & Kuehn (1980), and Boyce & Espy-Wilson (1997)
- ^ Wäller Platt: Die Aussprache
- ^ Kohler (1995:165f), cited in Universität zu Köln: Phonologische Analyse
- ^ Arvaniti (2007:15–18)
- ^ Ikekeonwu (1999:108)
- ^ Syllable coda /r/ in the "capital" of the paulista hinterland: sociolinguistic analisis. Cândida Mara Britto LEITE. Page 111 (page 2 in the attached PDF) (in Portuguese)
- ^ Acoustic-phonetic characteristics of the Brazilian Portuguese's retroflex /r/: data from respondents in Pato Branco, Paraná. Irineu da Silva Ferraz. Pages 19–21 (in Portuguese)
- ^ Recent 'lexical loans' from English to Brazilian Portuguese (in Portuguese)
- ^ Recasens (2004:436) citing Fougeron (1999) and Browman & Goldstein (1995)
- ^ Engstrand (1999:141)
- ^ Thompson (1959:459)
- ^ Merrill (2008:109)
- ^ Ladefoged & Maddieson (1996:240–241)
Bibliography
- Arvaniti, Amalia (2007), "Greek Phonetics: The State of the Art" (PDF), Journal of Greek Linguistics, 8: 97–208
- Boyce, S.; Espy-Wilson, C. (1997), "Coarticulatory stability in American English /r/", Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 101 (6): 3741–3753, doi:10.1121/1.418333, PMID 9193061
- Browman, L.; Goldstein (1995), "Gestural syllable position in American English", in Bell-Berti, F.; Raphael, L.J. (eds.), Producing Speech: Contemporary issues for K Harris, New York: AIP, pp. 9–33
{{citation}}: Missing|editor2=(help) - Cornyn, William (1944), Outline of Burmese Grammar, Supplement to Language, vol. 20 no. 4, Baltimore: Linguistic Society of America
- Delattre, P.; Freeman, D.C. (1968), "A dialect study of American R's by x-ray motion picture", Linguistics, 44: 29–68
- Engstrand, Olle (1999), "Swedish", Handbook of the International Phonetic Association, Cambridge University Press, pp. 140–142, ISBN 9780521637510
- Fougeron, C (1999), "Prosodically conditioned articulatory variation: A Review", UCLA Working Papers in Phonetics, vol. 97, pp. 1–73
- Hallé, Pierre A.; Best, Catherine T.; Levitt, Andrea (1999), "Phonetic vs. phonological influences on French listeners' perception of American English approximants", Journal of Phonetics, 27 (3): 281–306, doi:10.1006/jpho.1999.0097
- Ikekeonwu, Clara I. (1999), "Igbo", Handbook of the International Phonetic Association, Cambridge University Press, pp. 108–110, ISBN 9780521637510
- Kohler, Klaus (1995), Einführung in die Phonetik des Deutschen, Berlin: Erich Schmidt Verlag
- Ladefoged, Peter; Maddieson, Ian (1996), The Sounds of the World's Languages, Oxford: Blackwell, ISBN 0-631-19814-8
- Merrill, Elizabeth (2008), "Tilquiapan Zapotec", Journal of the International Phonetic Association, 38 (1): 107–114, doi:10.1017/S0025100308003344
- Recasens, Daniel (2004), "The effect of syllable position on consonant reduction (evidence fromCatalan consonant clusters)", Journal of Phonetics, 32 (3): 435–453, doi:10.1016/j.wocn.2004.02.001
- Thompson, Laurence C. (1959), "Saigon Phonemics", Language, 35 (3), Linguistic Society of America: 454–476, JSTOR 411232
- Watkins, Justin (2001), "Burmese", Journal of the International Phonetic Association, 31 (2): 291–95, doi:10.1017/S0025100301002122
- Zawadzki, P.A.; Kuehn, D.P. (1980), "A cineradiographic study of static and dynamic aspects of American English /r/", Phonetica, 37 (4): 253–266, doi:10.1159/000259995, PMID 7443796