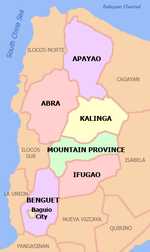
Ifugao
Ifugao | |
|---|---|
| Province of Ifugao | |
 | |
 Location in the Philippines | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Region | Cordillera Administrative Region |
| Founded | June 18, 1966 |
| Capital | Lagawe |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlalawigan |
| • Governor | Pedro Mayam-o (PDP-Laban) |
| • Vice Governor | Jordan Gullitiw (LP) |
| Area | |
• Total | 2,628.21 km2 (1,014.76 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 50th out of 81 |
| Population (2020 census)[2] | |
• Total | 207,498 |
| • Rank | 72nd out of 81 |
| • Density | 79/km2 (200/sq mi) |
| • Rank | 74th out of 81 |
| Divisions | |
| • Independent cities | 0 |
| • Component cities | 0 |
| • Municipalities | |
| • Barangays | 175 |
| • Districts | Lone district of Ifugao |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PHT) |
| ZIP code | 3600–3610 |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)74 |
| ISO 3166 code | PH-IFU |
| Spoken languages | |
Ifugao (Template:Lang-ilo; Template:Lang-fil) is a landlocked province of the Philippines in the Cordillera Administrative Region in Luzon. Its capital is Lagawe and it borders Benguet to the west, Mountain Province to the north, Isabela to the east, and Nueva Vizcaya to the south.
The Rice Terraces of the Philippine Cordilleras and Banaue Rice Terraces are the main tourist attractions in the province. These terraces were hand-carved into the mountains 2,000 years ago to plant rice. In 1995, they were declared as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.[3]
Etymology
Ifugao is named after the term i-pugo ("i" [from/people] and pugo [hill]), which translates to people of the hill.[4]
History
Precolonial age
Prior to colonization, Ifugao was a massive highland plutocracy, among the most sophisticated and prosperous of its kind in the whole archipelago and one of the two grandest highland plutocracies in Luzon, the other being the Plutocracy of Kalinga. The state existed for over 2,000 years and have built massive rice terraces that would be a symbol of the province in later time. There were no monarchs in the state. The state was ruled by its council of elders which led the state into a peaceful and prosperous plutocracy which developed one of the best agricultural technologies in Asia at its time. The state consisted of various subgroups which had similar yet somewhat distinct culture and traditions. Conflicts among the Ifugao people were resolved in the most peaceful way possible. Unlike most of the highland plutocracies in the Cordilleras at the time, the Plutocracy of Ifugao had the least conflict with lowland settlers or Ilokanos. Kiangan was known as the birthplace of the Ifugao people and Hungduan as the epicenter of its culture.
Spanish regime
The Spanish had great difficulty in taking over Ifugao, like most of the Cordilleras due to the fierce belief of the Cordillera people of their rights since ancient times. The Ifugao battled colonizers for hundreds of years, even after the state was colonized and was transformed into a part of Nueva Viscaya province of the Spanish-administered Philippines.[5][6] In 1891, the Spanish government established Quiangan as a comandancia-politico-militar[7][8] for the Ifugao area.[9] The Spanish occupation in the province ended with the outbreak of the Philippine Revolution.
American occupation
On August 18, 1908, Ifugao was separated from Nueva Vizcaya[10] and, along with Amburayan, Apayao, Benguet, Bontoc, Kalinga and Lepanto, was annexed to the newly created Mountain Province established by the Philippine Commission with the enactment of Act No. 1876.[5][7][11][12]
World War II
Ifugao became the center of warfare in the last year of World War II when Gen. Tomoyuki Yamashita launched his last stand against the American and Philippine Commonwealth forces at Mount Napulawan. He informally surrendered to Captain Grisham of the 6th US Army in the Philippines based in Kiangan,[5] before he was flown to Camp John Hay where he formally surrendered.
Post-war era
On June 18, 1966, Republic Act No. 4695 was enacted, and Ifugao was converted into a regular province when the huge Mountain Province was split into four (the other three being Benguet, Mountain Province, and Kalinga-Apayao).[4][13] Ifugao and Kalinga-Apayao were placed under the jurisdiction of the Cagayan Valley region.[5][14] The capital was moved from Kiangan to Lagawe due to the harsh landscape of Kiangan which made it unsuitable for public transportation and as a capital.
Post-martial law era
On July 15, 1987, the Cordillera Administrative Region was established by then-President Corazon Aquino through Executive Order 220, and Ifugao was made one of its provinces.[5][15][16]
Contemporary history
In 1992, Republic Act No. 07173 was enacted, separating several barangays from Kiangan and constituting them under a new municipality known as Asipulo.[17][18]
Since 1992, the province has observed every September 2 as "Victory Day", commemorating the valor of Philippine war veterans and the surrender of General Yamashita in the municipality of Kiangan on September 2, 1945.[19][20][21]
In 1995, the Batad Rice Terraces, Bangaan Rice Terraces (both in Banaue), Mayoyao Rice Terraces (in Mayoyao), Hungduan Rice Terraces (in Hungduan) and Nagacadan Rice Terraces (in Kiangan, Ifugao) were inscribed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site under the collective name "Rice Terraces of the Philippine Cordilleras".[3]
In 2001, the Hudhud Chants of the Ifugao was chosen as one of the 11 Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity. It was then formally inscribed as a UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage in 2008.[22][23][24]
In 2013, the official Intangible Heritage Book of the Philippine was published, and 13 of its elements were from Ifugao.
In 2014, the Philippines joined other Asian nations in establishing the support and submission of the "Tug of war" — a multinational cultural heritage or Tugging rituals and games, an Intangible Cultural Heritage that encompasses tug-of-war games in Vietnam, Cambodia, and the Philippines. The initial move of the Philippines started in 2013. The Philippines' part in the new element is represented by the tug-of-war of the Ifugaos (in Brgy. Hapao, Municipality of Hungduan) called the punnuk. The element is expected to be declared as a UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage in 2015.
Since the 20th century, the province has been central to the archaeological research of various international institutions, mostly from the United States and the Philippines. A major discovery was the archaeological site of Kiangan, which proved the oral tradition of the Ifugao that the first settlement in the province was in Kiangan.[25]
Geography
Ifugao covers a total area of 2,628.21 square kilometres (1,014.76 sq mi)[26] occupying the southeastern section of the Cordillera Administrative Region in Luzon. The province is bordered by Benguet to the west, Mountain Province to the north, Isabela to the east, and Nueva Vizcaya to the south.
Situated within the Cordillera Central mountain range, Ifugao is characterized by rugged terrain, river valleys, and massive forests.
Administrative divisions
Ifugao comprises 11 municipalities, all encompassed by a lone legislative district.[27][26]
|

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Barangays
The 11 municipalities of the province comprise a total of 175 barangays, with Santa Maria in Alfonso Lista (Potia) as the most populous in 2010, and Banga in Lagawe as the least.[28][26]
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 147,281 | — |
| 1995 | 149,598 | +0.29% |
| 2000 | 161,623 | +1.67% |
| 2007 | 180,711 | +1.55% |
| 2010 | 191,078 | +2.05% |
| 2015 | 202,802 | +1.14% |
| Source: National Statistics Office[27][28][29] | ||
The population of Ifugao in the 2020 census was 207,498 people,[2] with a density of 79 inhabitants per square kilometre or 200 inhabitants per square mile.
Ethnicity
Based on the 2000 census survey, Ifugao comprised 67.91% (109,659) of the total provincial population of 161,483. Other ethnic groups in the province included the Ilocanos at 13.73% (22,171), Kalahan at 8.64% (13,946), Ayungan at 6.15% (9,935), and Kankanaey at 0.64% (1,037).[30][31]
The natives of Ifugao province are called Ifugaos, but mistakenly called by non-Cordilleran as Igorots. Ifugaos, despite the similarities in some cultural traditions and practices, are considered a separate ethnic group from Igorots.
The total number of Tinguian in the province of Ifugao is 2,609. (source: National Statistics Office)[full citation needed]
Religion
Less than 40%[citation needed] of the population are animists and continue to preserve their thousands-year old indigenous traditions. Roman Catholicism has a growing influence in the province with approximately 60%[citation needed] of the population being converted by missionaries. In most areas, especially at the east and south of the province, indigenous traditions have degraded due to the influx of Christianity. In 2014, the Apostolic Vicariate of Bontoc-Lagawe recorded a 61.5% Roman Catholic adherence.[citation needed] The most significant religion other than Roman Catholicism is the Aglipayan Church while the number of people professing indigenous beliefs continue to wane.
Rice culture

Ifugao culture revolves around rice, which is considered a prestige crop. There is an elaborate and complex array of rice culture feasts inextricably linked with taboos and intricate agricultural rites, from rice cultivation to rice consumption. Harvest season calls for grandiose thanksgiving feasts, while the concluding harvest rites tungo or tungul (the day of rest) entail a strict taboo of any agricultural work. Partaking of the rice wine (bayah), rice cakes, and moma (mixture of several herbs, powdered snail shell and betel nut/arecoline which is used as a chewing gum to the Ifugaos) is an indelible practice during the festivities and ritual activities. Agricultural terracing and farming are the principal means of livelihood. Their social status is measured by the number of rice field granaries, family heirlooms, gold earrings, and carabaos (water buffaloes). Prestige is also conferred through time and tradition. The more affluent, known as kadangyan, were usually generous by nature, giving rice to poor neighbors in time of food shortage(s) and/or hardship(s). Furthermore, their culture was known for their legal system, using one of the world's most extensive oral legal traditions specifying the offense depending on the use of custom law; trial by elders (influenced in part by public opinion); or trial by ordeal. The wealthy were subjected to greater fines than the poor.

Untouched by the influences of Spanish colonialism, Ifugao culture values kinship, family ties, religious and cultural beliefs. Ifugao are unique among all ethnic groups in the mountain province for their narrative literature such as the hudhud, an epic dealing with hero ancestors sung in a poetic manner. Also unique to the Ifugao is their woodcarving art, most notably the carved granary guardians bului and the prestige bench of the upper class, the hagabi. Their textiles are renowned for their sheer beauty, colorful blankets and clothing woven on looms. Houses were well-built, characterized as square with wooden floors, windowless walls, and pyramidal thatch roofs. Elevated from the ground by four sturdy tree trunks, they feature removable staircases that were hoisted up at night to prevent entry by enemies or wild animals. Lastly, their attire remain traditional for male Ifugaos, donning the wanno or g-string; there are six types of wanno which are used depending on the occasion or the man's social status. Ifugao women, on the contrary, wear tapis, a wraparound skirt; there are five kinds of skirts worn, depending on the occasion and/or status of the woman/girl.
References
- ^ "List of Provinces". PSGC Interactive. Makati City, Philippines: National Statistical Coordination Board. Retrieved 20 December 2013.
- ^ a b Census of Population (2020). Table B - Population and Annual Growth Rates by Province, City, and Municipality - By Region. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ^ a b "Rice Terraces of the Philippine Cordilleras". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ^ a b "Facts & Figures: Ifugao Province". Philippine Statistics Authority - National Statistical Coordination Board. Department of the Interior and Local Government - Cordillera Administrative Region. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ^ a b c d e Lancion, Jr., Conrado M.; de Guzman, Rey (cartography) (1995). "The Provinces". Fast Facts about Philippine Provinces (The 2000 Millenium ed.). Makati, Metro Manila: Tahanan Books. pp. 76–77. ISBN 971-630-037-9. Retrieved 16 January 2015.
- ^ "Natural Attractions found in Atok". Province of Benguet. Retrieved 13 August 2013.
- ^ a b Worcester, Dean C.; Philippine Commission (1908). Seventh Annual Report of the Secretary of the Interior to the Philippine Commission for the Fiscal Year Ended June 30, 1908 (Digitized by Google on 23 Nov 2005 (Original file from the University of Michigan)). Manila: U.S. Government Printing Office. pp. 17–19. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
Google Books link
{{cite book}}: Check|archiveurl=value (help); External link in|quote= - ^ Keesing, Felix Maxwell; Keesing, Marie Margaret; Keesing, Marie Martin; Institute of Pacific Relations (contributor); International Research Committee (contributor) (1934). Taming Philippine Headhunters: A Study of Government and of Cultural Change in Northern Luzon. Stanford University Press. p. 69. ISBN 9780804721103. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
{{cite book}}:|last4=has generic name (help) - ^ Felix M., Keesing (1962). "The Upper Cagayan Area". The Ethnohistory of Northern Luzon. Stanford University Press. p. 297. ISBN 9780804700498. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ^ National Historical Institute (Philippines) [contributor] (1978). Kasaysayan, Volume 3, Issues 1-4 (Digitized by Google on 26 Sep 2009). National Historical Institute. p. 16. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
(Original file from the University of Michigan)
{{cite book}}:|last1=has generic name (help) - ^ Ingles, Raul Rafael (2008). 1908 :The Way it Really was : Historical Journal for the UP Centennial, 1908-2008. Diliman, Quezon City: University of the Philippines Press. p. 330. ISBN 9715425801. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ^ Act No. 1876., August 18, 1908 Supreme Court E-Library
- ^ "Republic Act No. 4695: An Act Creating the Provinces of Benguet, Mountain Province, Ifugao and Kalinga-Apayao". Chan Robles Virtual Law Library. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ "Historical Background". Provincial Government of Apayao. 15 April 2013. Retrieved 3 January 2015.
- ^ "Regional Profile: Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR)". CountrySTAT Philippines. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ "The Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR)". Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ "Republic Act No. 07173: An Act Creating the Municipality of Asipulo in the Province of Ifugao" (PDF). House of Representatives of the Philippines. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ^ "Municipality of Asipulo, Ifugao". Department of the Interior and Local Government - Cordillera Administrative Region. 29 April 2013. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ^ "PVAO recognizes Ifugao town for promoting valor and heroism of veterans". Philippine Information Agency. Philippine Information Agency - Cordillera Administrative Region. 9 December 2014. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ^ "Re-enactment of WWII episodes steal show during Victory Day Celebration in Ifugao". Philippine Information Agency. 3 September 2012. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ^ Bitog, Rubyloida (18 August 2012). "Ifugaos to mark liberation". Sun.Star Baguio. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ^ "Proclamation of Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity; Hudhud Chants of the Ifugao". UNESCO. 18 May 2001. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
The hudhud is recited and chanted among the Ifugao people - known for their rice terraces - during the sowing and harvesting of rice, funeral wakes and other rituals. Estimated to have originated before the 7th century, the hudhud - consisting of some 40 episodes - often take three or four days to recite.
- ^ "Hudhud chants of the Ifugao; Inscribed in 2008 (3.COM) on the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity (originally proclaimed in 2001)". UNESCO. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ Bersola, Camille (2 January 2011). "The hudhud of Ifugao: Enchanting chanting". The Philippine Star. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
Bringing more cultural pride, this Ifugao tradition had also received an accolade from the United Nations Education, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). In 2001, it won the title of "Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity" given to 19 outstanding cultural forms of expression from the different regions of the world. In Asia, UNESCO honored six masterpieces, among them, the hudhud chants of the Ifugao of Northern Luzon.
- ^ Codamon, Daniel B. (22 May 2015). "Kiangan as the heritage town of Ifugao". Sun.Star Baguio. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
Archaeological studies show Kiangan indeed is the cradle of Ifugao race and civilization. In June 2012, after more than three weeks of excavation, the Ifugao Archaelogical Project (IAP) reported its findings on the "Old Kiyyangan Village" that constitutes the 1st Field Season of the IAP, a community-led project with the Save the Ifugao Terraces Movement (SITMO), the local government of Kiangan, National Museum of the Philippines, University of the Philippines Archaelogical Studies Program and the University of Guam.
- ^ a b c d "Province: Ifugao". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- ^ a b c Census of Population (2015). Highlights of the Philippine Population 2015 Census of Population. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ a b c Census of Population and Housing (2010). Population and Annual Growth Rates for The Philippines and Its Regions, Provinces, and Highly Urbanized Cities (PDF). National Statistics Office. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^ Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR)" (PDF). Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. National Statistics Office. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^ a b "Ifugao: Five Economically Active Persons Support Four Dependents". National Statistics Office. National Statistics Office. 4 March 2002. Archived from the original on 5 March 2012. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ^ http://www.census.gov.ph/data/pressrelease/2002/pr0228tx.html
External links
 Media related to Ifugao at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ifugao at Wikimedia Commons Geographic data related to Ifugao at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Ifugao at OpenStreetMap