60 (number)
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardinal | sixty | |||
| Ordinal | 60th (sixtieth) | |||
| Numeral system | sexagesimal | |||
| Factorization | 22 × 3 × 5 | |||
| Divisors | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20, 30, 60 | |||
| Greek numeral | Ξ´ | |||
| Roman numeral | LX | |||
| Binary | 1111002 | |||
| Ternary | 20203 | |||
| Senary | 1406 | |||
| Octal | 748 | |||
| Duodecimal | 5012 | |||
| Hexadecimal | 3C16 | |||
60 (sixty) () is the natural number following 59 and preceding 61. Being three times 20, it is called "three score" in older literature.
In mathematics
It is a composite number, with divisors 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20, 30, and 60, making it a highly composite number.[1] Because it is the sum of its unitary divisors (excluding itself), it is a unitary perfect number,[2] and it is an abundant number with an abundance of 48. Being ten times a perfect number, it is a semiperfect number.
It is the smallest number divisible by the numbers 1 to 6: there is no smaller number divisible by the numbers 1 to 5. It is the smallest number with exactly 12 divisors. It is one of seven integers that have more divisors than a number twice itself (sequence A072938 in the OEIS), one of six that are also lowest common multiple of a consecutive set of integers from 1, and one of six that are divisors of every highly composite number higher than itself.(sequence A106037 in the OEIS)
It is the sum of a pair of twin primes (29 + 31) and the sum of four consecutive primes (11 + 13 + 17 + 19). It is adjacent to two primes (59 and 61). It is the smallest number that is the sum of two odd primes in six ways.[3]
The smallest non-solvable group (A5) has order 60.

There are four Archimedean solids with 60 vertices: the truncated icosahedron, the rhombicosidodecahedron, the snub dodecahedron, and the truncated dodecahedron. The skeletons of these polyhedra form 60-node vertex-transitive graphs. There are also two Archimedean solids with 60 edges: the snub cube and the icosidodecahedron. The skeleton of the icosidodecahedron forms a 60-edge symmetric graph.
There are 60 one-sided hexominoes, the polyominoes made from six squares.
In geometry, it is the number of seconds in a minute, and the number of minutes in a degree. In normal space, the three interior angles of an equilateral triangle each measure 60 degrees, adding up to 180 degrees.
Because it is divisible by the sum of its digits in base 10, it is a Harshad number.
A number system with base 60 is called sexagesimal (the original meaning of sexagesimal is sixtieth).
It is the smallest positive integer that is written with only the smallest and the largest digit of base 2 (binary), base 3 (ternary) and base 4 (quaternary).
In science and technology
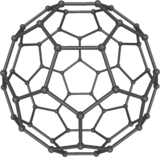
The first fullerene to be discovered was buckminsterfullerene C60, an allotrope of carbon with 60 atoms in each molecule, arranged in a truncated icosahedron. This ball is known as a buckyball, and looks like a soccer ball.
The atomic number of neodymium is 60, and cobalt-60 (60Co) is a radioactive isotope of cobalt.
The electrical utility frequency in western Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, the Philippines, Saudi Arabia, the United States, and several other countries in the Americas is 60 Hz.
An exbibyte (sometimes called exabyte) is 260 bytes.
Cultural number systems

The Babylonian number system had a base of 60, inherited from the Sumerian and Akkadian civilizations, and possibly motivated by the large number of divisors that 60 has. The sexagesimal measurement of time and of geometric angles is a legacy of the Babylonian system.
The number system in the Mali Empire was based on 60, reflected in the counting system of the Maasina Fulfulde, a variant of the Fula language spoken in contemporary Mali.[4] The Ekagi of Western New Guinea used base 60,[5] and the sexagenary cycle plays a role in Chinese calendar and numerology.
In Template:Lang-de and in Template:Lang-la refer to 60 = 5 dozen = 1/2 small gross. This quantity was used in international medieval treaties e.g. for ransom of captured Teutonic Knights.
In religion
60 occurs several times in the Bible, for example as the age of Isaac when Jacob and Esau were born,[6] and the number of warriors escorting King Solomon.[7]
In the laws of kashrut of Judaism, 60 is the proportion (60:1) of kosher to non-kosher ingredients that can render an admixture kosher post-facto.[8]
In the Koran, 60 is mentioned once: "..he should feed sixty indigent ones..",[9] but it is mentioned many times in the Hadith, most notably Muhammad being reported to say, "..Allah, the Exalted and Glorious, created Adam in His own image with His length of sixty cubits.."[10]
In other fields

It is:
- In time, the number of seconds in a minute, and the number of minutes in an hour.[11] (a legacy of the Babylonian number system)
- The number of feet in the standard measurement tool to evaluate an automotive launch on a dragstrip, as the time taken to travel the first 60 feet (18 m) of the track.
- The number of miles per hour an automobile accelerates to from rest (0-60) as one of the standard measurements of performance
- The number of years in a Sexagenary cycle
- 60 Minutes, a CBS investigative television show
- Sixty Minute Man was a TV show starring Kenny Baumann
- European route E60 runs from Brest, France, to Constanţa, Romania
- Municipal Okrug 60, name of Posadsky Municipal Okrug of Petrogradsky District of St. Petersburg, Russia until April 2009
- A common speed limit, in miles per hour, for freeways in many U.S. states
- A common speed limit, in kilometers per hour, in urban areas in Russia
- In years of marriage, the diamond wedding anniversary
- The maximum number of marbles (game pieces) in Chinese checkers
- The code for international direct dial calls to Malaysia
- The highest obtainable level on World of Warcraft (not including the five latest expansions)
- Studio 60 on the Sunset Strip was a TV show on NBC (2006–07)
- Gone in 60 Seconds is a movie starring Nicolas Cage
- Miss Sixty is a women's apparel brand
- The number of cards in the game Rack-O
- The number of the French department Oise
- Alpha 60 is a brain-computer in the movie Alphaville directed by Jean-Luc Godard
- The age for senior citizens in some cultures
In sports
- In darts, 60 (treble-twenty) is the highest score that can be achieved with a single dart.
- New York Yankees Babe Ruth hit 60 home runs in 1927 during a 154-game season; although the record has been broken three times since then, by Roger Maris, Mark McGwire, and Barry Bonds, those records were set during a 162-game season.
References
- ^ "Sloane's A002182 : Highly composite numbers". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation. Retrieved 2016-05-30.
- ^ "Sloane's A002827 : Unitary perfect numbers". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation. Retrieved 2016-05-30.
- ^ Wells, D. The Penguin Dictionary of Curious and Interesting Numbers London: Penguin Group. (1987): 109–110.
- ^ La Fontane, Jean sybil (2004). The Interpretation of Ritual: Essays in Honour of A.I. Richards. Routledge. p. 320.
- ^ Bowers, Nancy (1977). "Kapauku numeration: Reckoning, racism, scholarship, and Melanesian counting systems" (PDF). Journal of the Polynesian Society. 86 (1): 105–116. Archived March 5, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Biblegateway Genesis 25:26
- ^ Biblegateway Song of Solomon 3:7
- ^ Talmud, Tractate Chullin 98b ; Shulchan Aruch, Yoreh Deah 98.
- ^ Koran, Al-Mujadala,4
- ^ http://www.searchtruth.com/book_display.php?book=040&translator=2&start=0&number=6809#6809
- ^ Dennis Guedj, Numbers: The Universal Language, transl. Lory Frankel. New York: Harry N. Abrams, Inc. Publishers (1997): 71. "60: the ace of divisibility. The more divisible a number is ... the more useful it proves in certain situations. ... Is it because 60 is highly divisible that the hour has been divided into 60 minutes, and the minute into 60 seconds? Look at the list of its twelve divisors ... Compare this with the larger number 100, which has only nine divisors."
External links
- Woolley, Thomas. "60". Numberphile. Brady Haran.
