MAPK phosphatase
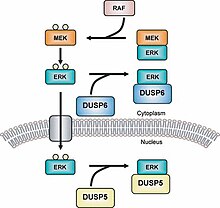
MAPK phosphatases (MKPs) are the largest class of phosphatases involved in down-regulating Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) signaling.[1][2] MAPK signalling pathways regulate multiple features of development and homeostasis.[3][4] This can involve gene regulation, cell proliferation, programmed cell death and stress responses.[5] MAPK phosphatases are therefore important regulator components of these pathways.
Function

MAPK phosphatases are only found in eukaryotes and negatively regulate MAP kinases to act as negative feedback.[5] MKPs are also known as dual-specificity phosphatases (DUSPs)[6] because they deactivate MAPK by dephosphorylating the Threonine and the Tyrosine residues residing in MAPKs activation site.[7] MKPs have a catalytic region at their C-terminus and a regulatory region at their N-terminus.[8] The position where the MAPK binds to MKP is found near the N-terminus of MKP. The binding is due to the electrostatic interactions of the positively charged residues on the MKP binding portion with the negatively charged residues on the MAPK binding site.[9]
Classification
There are 10[10] main MKPs that can be further broken down into three sub-classes which are representative of either their genomic structure or the type of substrate (MAPK) they bind to.[11] These include DUSP1, DUSP2, DUSP4 and DUSP5 that belong to subgroup 1. DUSP6, DUSP7, DUSP9 and DUSP10 belong to subgroup 2. DUSP8 and DUSP16 belong to subgroup 3, these subgroups are based on the genomic structure of the MKPs.[12] The newest MKP-8 brings the total MKPs to 11, MKP-8 plays a role in inhibiting p38 kinase.[13]
Dual specificity phosphatases (DUSPs) also belong to the family of protein thyrosine phosphatases.[14] MKPs are grouped into type I, II and III; in which type I MKPs are located in the nuclear region, type II are located in the cytoplasmic region and type III are located in both the nuclear and cytoplasmic region.[15] The different locations of these three types of MKPs allow for them to cause different types of signaling. For example, MKP-1 (a type I MKP) controls gene expression by inactivating the subcellular group of MAPKs.[16] Note that without the LXXLL motif (GFP-MKP-147-367) the MKP-1 cannot localize inside the nucleus and it comes before the CH2A domain.[17] The newest MKP, MKP-8, belongs to group I because it is located in the nuclear region of the cell[18] A recent study shows that histone deacetylase isoforms (HDAC1, -2, and -3) deacetylate MKP-1 and that this post-translational modification increases MAPK signaling and innate immune signaling.[19]
Although the N-terminal region is the quite distinct between each MKP, they all normally contain CH2 domains.[20] In MKP-1, MAPK binds to the active site that is between the CH2A and CHB domains located in the N-terminal.[21][22]
An example of a type II MKP is MKP-3 which, regulates the activity of ERK2 by deposphorylating it and holding it in the cytoplasmic region.[23] MKP-3 also binds to ERK2 regardless of whether it is phosphorylated or not.[24] MKP-4 is another MKP that belongs to Type I and, is distinct from other MKPs in this subgroup because it is only found in placenta, kidney and embryonic liver cells.[25] MKP-5 is a type III MKP that binds specifically to p38 and SPK/JNK and is found both in the cytoplasmic and nuclear regions of a cell.[26] MKP-5 is only located in the heart, lung, liver, kidney and skeletal muscle cells.[27] There are also MKPs that belong to a group called Atypical MKPs. For example, Vaccina H1-related (VHR) is an atypical MKP because it only has the DUSP region.[28] VHR is only found in lymphoid and hematopoietic cells, and it inactivates the ERK1/2 and JNKs in T-cell receptors.[29] VHR also induces cell cycle arrest.[30][31]
| Name | Alt. name | Sub Group |
|---|---|---|
| DUSP1 | MKP-1 | I |
| DUSP2 | I | |
| DUSP4 | MKP-2 | I |
| DUSP5 | I | |
| DUSP6 | MKP-3 | II |
| DUSP7 | II | |
| DUSP8 | III | |
| DUSP9 | MKP-4 | II |
| DUSP10 | MKP-5 | ? |
| DUSP14 | MKP-6 | ? |
| DUSP16 | MKP-7 | III |
| DUSP26 | MKP-8 | I |
References
- ^ MAPK+Phosphatases at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ^ Dickinson, Robin J.; Keyse, Stephen M. (15 November 2006). "Diverse physiological functions for dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases". J Cell Sci. 119 (22): 4607–4615. doi:10.1242/jcs.03266. PMID 17093265.
- ^ Caunt, Christopher J.; Keyse, Stephen M. (January 2013). "Dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases (MKPs)". FEBS Journal. 280 (2): 489–504. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08716.x. PMC 3594966. PMID 22812510.
- ^ Low, Heng Boon; Zhang, Yongliang (2016). "Regulatory Roles of MAPK Phosphatases in Cancer". Immune Network. 16 (2): 85–98. doi:10.4110/in.2016.16.2.85. PMC 4853501. PMID 27162525.
- ^ a b Chang, Lufen; Karin, Michael (1 March 2001). "Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades". Nature. 410 (6824): 37–40. doi:10.1038/35065000. PMID 11242034. S2CID 4407701.
- ^ Comalada, Mònica; Lloberas, Jorge; Celada, Antonio (1 August 2012). "MKP-1: A critical phosphatase in the biology of macrophages controlling the switch between proliferation and activation". European Journal of Immunology. 42 (8): 1938–1948. doi:10.1002/eji.201242441. PMID 22865045.
- ^ Kondoh, Kunio; Nishida, Eisuke (1 August 2007). "Regulation of MAP kinases by MAP kinase phosphatases". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research. 1773 (8): 1227–1237. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.12.002. PMID 17208316.
- ^ Dickinson, Robin J.; Keyse, Stephen M. (15 November 2006). "Diverse physiological functions for dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases". J Cell Sci. 119 (22): 4607–4615. doi:10.1242/jcs.03266. PMID 17093265.
- ^ Theodosiou, Aspasia; Ashworth, Alan (1 January 2002). "MAP kinase phosphatases". Genome Biology. 3 (7): reviews3009.1–reviews3009.10. doi:10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-reviews3009. ISSN 1465-6906. PMC 139386. PMID 12184814.
- ^ Caunt, Christopher J; Keyse, Stephen M (7 November 2016). "Dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases (MKPs)". The FEBS Journal. 280 (2): 489–504. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08716.x. ISSN 1742-464X. PMC 3594966. PMID 22812510.
- ^ Theodosiou, Aspasia; Ashworth, Alan (1 January 2002). "MAP kinase phosphatases". Genome Biology. 3 (7): reviews3009.1–reviews3009.10. doi:10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-reviews3009. PMC 139386. PMID 12184814.
- ^ Theodosiou, Aspasia; Ashworth, Alan (1 January 2002). "MAP kinase phosphatases". Genome Biology. 3 (7): reviews3009.1–reviews3009.10. doi:10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-reviews3009. PMC 139386. PMID 12184814.
- ^ Vasudevan, Sanjeev A.; Skoko, John; Wang, Kuan; Burlingame, Susan M.; Patel, Parul N.; Lazo, John S.; Nuchtern, Jed G.; Yang, Jianhua (6 May 2005). "MKP-8, a novel MAPK phosphatase that inhibits p38 kinase". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 330 (2): 511–518. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.03.028. PMID 15796912.
- ^ Jeffrey, Kate L.; Camps, Montserrat; Rommel, Christian; Mackay, Charles R. (May 2007). "Targeting dual-specificity phosphatases: manipulating MAP kinase signalling and immune responses". Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 6 (5): 391–403. doi:10.1038/nrd2289. PMID 17473844. S2CID 25916166.
- ^ Kondoh, Kunio; Nishida, Eisuke (1 August 2007). "Regulation of MAP kinases by MAP kinase phosphatases". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research. 1773 (8): 1227–1237. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.12.002. PMID 17208316.
- ^ Wu, J. J.; Zhang, L.; Bennett, A. M. (16 May 2005). "The Noncatalytic Amino Terminus of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase 1 Directs Nuclear Targeting and Serum Response Element Transcriptional Regulation". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 25 (11): 4792–4803. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.11.4792-4803.2005. PMC 1140620. PMID 15899879.-
- ^ Wu, J. J.; Zhang, L.; Bennett, A. M. (16 May 2005). "The Noncatalytic Amino Terminus of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase 1 Directs Nuclear Targeting and Serum Response Element Transcriptional Regulation". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 25 (11): 4792–4803. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.11.4792-4803.2005. PMC 1140620. PMID 15899879.
- ^ Vasudevan, Sanjeev A.; Skoko, John; Wang, Kuan; Burlingame, Susan M.; Patel, Parul N.; Lazo, John S.; Nuchtern, Jed G.; Yang, Jianhua (6 May 2005). "MKP-8, a novel MAPK phosphatase that inhibits p38 kinase". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 330 (2): 511–518. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.03.028. PMID 15796912.
- ^ Jeong, Y; Du, R; Zhu, X (2014). "Histone deacetylase isoforms regulate innate immune responses by deacetylating mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1". J Leukoc Biol. 95 (4): 651–9. doi:10.1189/jlb.1013565. PMID 24374966. S2CID 40126163.
- ^ Wu, JJ; Zhang, L; Bennett, AM (2005). "The Noncatalytic Amino Terminus of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase 1 Directs Nuclear Targeting and Serum Response Element Transcriptional Regulation". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 25 (11): 4792–4803. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.11.4792-4803.2005. PMC 1140620. PMID 15899879.
- ^ Wu, J. J.; Zhang, L.; Bennett, A. M. (16 May 2005). "The Noncatalytic Amino Terminus of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase 1 Directs Nuclear Targeting and Serum Response Element Transcriptional Regulation". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 25 (11): 4792–4803. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.11.4792-4803.2005. PMC 1140620. PMID 15899879.
- ^ BARDWELL, A. Jane; ABDOLLAHI, Mahsa; BARDWELL, Lee (15 March 2003). "Docking sites on mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinases, MAPK phosphatases and the Elk-1 transcription factor compete for MAPK binding and are crucial for enzymic activity". Biochemical Journal. 370 (3): 1077–1085. doi:10.1042/BJ20021806. PMC 1223246. PMID 12529172.
- ^ Karlsson, Maria; Mathers, Joanne; Dickinson, Robin J.; Mandl, Margret; Keyse, Stephen M. (1 October 2004). "Both Nuclear-Cytoplasmic Shuttling of the Dual Specificity Phosphatase MKP-3 and Its Ability to Anchor MAP Kinase in the Cytoplasm Are Mediated by a Conserved Nuclear Export Signal". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (40): 41882–41891. doi:10.1074/jbc.M406720200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 15269220.
- ^ Camps, M. (22 May 1998). "Catalytic Activation of the Phosphatase MKP-3 by ERK2 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase". Science. 280 (5367): 1262–1265. Bibcode:1998Sci...280.1262C. doi:10.1126/science.280.5367.1262. PMID 9596579.
- ^ Muda, M.; Boschert, U.; Smith, A.; Antonsson, B.; Gillieron, C.; Chabert, C.; Camps, M.; Martinou, I.; Ashworth, A.; Arkinstall, S. (21 February 1997). "Molecular Cloning and Functional Characterization of a Novel Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase, MKP-4". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 272 (8): 5141–5151. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.8.5141. PMID 9030581.
- ^ Tanoue, T. (9 July 1999). "Molecular Cloning and Characterization of a Novel Dual Specificity Phosphatase, MKP-5". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (28): 19949–19956. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.28.19949. PMID 10391943.
- ^ Kondoh, Kunio; Nishida, Eisuke (1 August 2007). "Regulation of MAP kinases by MAP kinase phosphatases". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research. 1773 (8): 1227–1237. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.12.002. PMID 17208316.
- ^ Kondoh, Kunio; Nishida, Eisuke (1 August 2007). "Regulation of MAP kinases by MAP kinase phosphatases". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research. 1773 (8): 1227–1237. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.12.002. PMID 17208316.
- ^ Alonso, A.; Saxena, M.; Williams, S.; Mustelin, T. (20 November 2000). "Inhibitory Role for Dual Specificity Phosphatase VHR in T Cell Antigen Receptor and CD28-induced Erk and Jnk Activation". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (7): 4766–4771. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006497200. PMID 11085983.
- ^ Rahmouni, Souad; Cerignoli, Fabio; Alonso, Andres; Tsutji, Toshiya; Henkens, Rachel; Zhu, Changjun; Louis-dit-Sully, Christine; Moutschen, Michel; Jiang, Wei; Mustelin, Tomas (9 April 2006). "Loss of the VHR dual-specific phosphatase causescell-cycle arrest and senescence". Nature Cell Biology. 8 (5): 524–531. doi:10.1038/ncb1398. PMID 16604064. S2CID 20976640.
- ^ Rahmouni, Souad; Cerignoli, Fabio; Alonso, Andres; Tsutji, Toshiya; Henkens, Rachel; Zhu, Changjun; Louis-dit-Sully, Christine; Moutschen, Michel; Jiang, Wei; Mustelin, Tomas (1 May 2006). "Loss of the VHR dual-specific phosphatase causes cell-cycle arrest and senescence". Nature Cell Biology. 8 (5): 524–531. doi:10.1038/ncb1398. ISSN 1465-7392. PMID 16604064. S2CID 20976640.
