Holi: Difference between revisions
m Reverted edits by 220.247.234.137 (talk) to last version by Thnidu |
Some of the facts were changed along with a format change. |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
{{Hinduism}} |
{{Hinduism}} |
||
'''Holi''' ({{IPAc-en|pron|'|h|əʊ|l|i:}}; {{Lang-sa|होली}} ''Holī'') is a [[spring (season)|spring]] festival, also known as the festival of colours or the festival of love.<ref name=yg/><ref name="OED-Holi">The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) ISBN 0-19-861263-X - p.874 "'''Holi''' /'həʊli:/ '''noun''' a Hindu spring festival ...".</ref> It is an ancient Hindu religious festival which has become popular with non-Hindus in many parts of South Asia, as well as people of other communities outside Asia.<ref name=keholi>Ebeling, Karin (2010), Holi, an Indian Festival, and its Reflection in English Media; Die Ordnung des Standard und die Differenzierung der Diskurse: Akten des 41. Linguistischen Kolloquiums in Mannheim 2006, 1, 107, ISBN 978-3631599174</ref> |
'''Holi''' ({{IPAc-en|pron|'|h|əʊ|l|i:}}; {{Lang-sa|होली}} ''Holī'') is a [[spring (season)|spring]] festival, also known as the festival of colours or the festival of love.<ref name=yg/><ref name="OED-Holi">The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) ISBN 0-19-861263-X - p.874 "'''Holi''' /'həʊli:/ '''noun''' a Hindu spring festival ...".</ref> The holiday signifies the victory of good over evil<ref>{{Cite web|url = http://www.holifestival.org/legend-holika-prahlad.html|title = The Legend of Holika and Prahlad|date = |accessdate = |website = |publisher = |last = |first = }}</ref>. It is an ancient Hindu religious festival which has become popular with non-Hindus in many parts of South Asia, as well as people of other communities outside Asia.<ref name=keholi>Ebeling, Karin (2010), Holi, an Indian Festival, and its Reflection in English Media; Die Ordnung des Standard und die Differenzierung der Diskurse: Akten des 41. Linguistischen Kolloquiums in Mannheim 2006, 1, 107, ISBN 978-3631599174</ref> |
||
It is primarily observed in [[India]], [[Nepal]], and other regions of the world with significant populations of Hindus or [[Non-resident Indian and person of Indian origin|people of Indian origin]]. The festival has, in recent times, spread to parts of Europe and North America as a spring celebration of love, frolic, and colours.<ref>[http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304795804579096813960372646 A Spring Celebration of Love Moves to the Fall — and Turns Into a Fight] Gabriele Steinhauser, The Wall Street Journal (October 3, 2013)</ref><ref name="online.wsj.com">[http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702303722604579111531979056974 Holi Festivals Spread Far From India] The Wall Street Journal (2013)</ref><ref name="Holi Festival of Colours">[http://www.visitberlin.de/en/event/05-11-2013/holi-festival-of-colours Holi Festival of Colours] Visit Berlin, Germany (2012)</ref> |
It is primarily observed in [[India]], [[Nepal]], and other regions of the world with significant populations of Hindus or [[Non-resident Indian and person of Indian origin|people of Indian origin]]. The festival has, in recent times, spread to parts of Europe and North America as a spring celebration of love, frolic, and colours.<ref>[http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304795804579096813960372646 A Spring Celebration of Love Moves to the Fall — and Turns Into a Fight] Gabriele Steinhauser, The Wall Street Journal (October 3, 2013)</ref><ref name="online.wsj.com">[http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702303722604579111531979056974 Holi Festivals Spread Far From India] The Wall Street Journal (2013)</ref><ref name="Holi Festival of Colours">[http://www.visitberlin.de/en/event/05-11-2013/holi-festival-of-colours Holi Festival of Colours] Visit Berlin, Germany (2012)</ref> |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
Holi celebrations start with a [[Holika bonfire]] on the night before Holi where people gather, sing and dance. The next morning is a free-for-all carnival of colours,<ref name=keholi/> where participants play, chase and colour each other with dry powder and coloured water, with some carrying water guns and coloured water-filled balloons for their [[water fight]]. Anyone and everyone is fair game, friend or stranger, rich or poor, man or woman, children and elders. The frolic and fight with colours occurs in the open streets, open parks, outside temples and buildings. Groups carry drums and musical instruments, go from place to place, sing and dance. People visit family, friends and foes to throw colours on each other, laugh and chit-chat, then share Holi delicacies, food and drinks. Some drinks are intoxicating. For example, [[Bhang]], an intoxicating ingredient made from [[cannabis (drug)|cannabis]] leaves, is mixed into drinks and sweets and consumed by many.<ref name=TOIBhang>{{cite web|title=High on Holi with bhang|url=http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/varanasi/High-on-Holi-with-bhang/articleshow/4245535.cms|work=Times of India|accessdate=26 March 2014}}</ref><ref>Ankita Rao,even it is a holi festival it is celebrated by different people of different religions [http://www.theatlantic.com/international/archive/2014/03/indias-high-holiday/284448/ India's 'High' Holiday] The Atlantic (17 March 2014)</ref> In the evening, after sobering up, people dress up and visit friends and family.<ref name=ht/><ref name=cj/> |
Holi celebrations start with a [[Holika bonfire]] on the night before Holi where people gather, sing and dance. The next morning is a free-for-all carnival of colours,<ref name=keholi/> where participants play, chase and colour each other with dry powder and coloured water, with some carrying water guns and coloured water-filled balloons for their [[water fight]]. Anyone and everyone is fair game, friend or stranger, rich or poor, man or woman, children and elders. The frolic and fight with colours occurs in the open streets, open parks, outside temples and buildings. Groups carry drums and musical instruments, go from place to place, sing and dance. People visit family, friends and foes to throw colours on each other, laugh and chit-chat, then share Holi delicacies, food and drinks. Some drinks are intoxicating. For example, [[Bhang]], an intoxicating ingredient made from [[cannabis (drug)|cannabis]] leaves, is mixed into drinks and sweets and consumed by many.<ref name=TOIBhang>{{cite web|title=High on Holi with bhang|url=http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/varanasi/High-on-Holi-with-bhang/articleshow/4245535.cms|work=Times of India|accessdate=26 March 2014}}</ref><ref>Ankita Rao,even it is a holi festival it is celebrated by different people of different religions [http://www.theatlantic.com/international/archive/2014/03/indias-high-holiday/284448/ India's 'High' Holiday] The Atlantic (17 March 2014)</ref> In the evening, after sobering up, people dress up and visit friends and family.<ref name=ht/><ref name=cj/> |
||
Holi is celebrated at the approach of vernal equinox,<ref name=keholi/> on the [[Phalguna]] [[Purnima (day)|Purnima]] (Full Moon). The festival date varies every year, per the [[Hindu calendar]], and typically comes in March, sometimes February in the [[Gregorian Calendar]]. The festival signifies the victory of good over evil, the arrival of spring, end of winter, and for many a festive day to meet others, play and laugh, forget and forgive, |
Holi is celebrated at the approach of vernal equinox,<ref name=keholi/> on the [[Phalguna]] [[Purnima (day)|Purnima]] (Full Moon). The festival date varies every year, per the [[Hindu calendar]], and typically comes in March, sometimes February in the [[Gregorian Calendar]]. The festival signifies the victory of good over evil, the arrival of spring, end of winter, and for many a festive day to meet others, play and laugh, forget and forgive,repair ruptured relationships and is also celebrated as a Thanksgiving for a good harvest.<ref name=keholi/><ref name=wd/><ref>[http://www.thefestivalofcolors.org/ The Festival of Colors] Holi, Naperville (2013)</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url = http://hinduism.about.com/od/holifestivalofcolors/a/celebrateholi.htm|title = Why Celebrate Holi?|date = |accessdate = |website = |publisher = |last = |first = }}</ref> |
||
==Significance== |
==Significance== |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
There is a symbolic legend to explain why Holi is celebrated as a festival of colours. The word "Holi" originates from "Holika", the evil sister of the demon king [[Hiranyakashipu]]. King Hiranyakashipu,<ref>Kabir's brother-disciple Raidas in his poetry, ''Prahlad charita'', refers to Hiranyakashipu as the king of Multan and Prahlad as his son; David Lorenzen, (1996), SUNY Press, p. 18, [https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=tE3sShuid5gC&pg=PA18&dq=multan+prahlad&hl=en&sa=X&ei=9pH8VJu8A-WE7ga4sICgAQ&ved=0CCAQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=multan%20prahlad&f=false Praises to a Formless God: Nirguni Texts from North India]</ref> according to legend, was the King of Multan<ref>Sanujit Ghose. Legend of Ram–Retold. PublishAmerica [https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=KIALB4WXHOMC&pg=PT62&dq=prahlada++multan&hl=en&sa=X&ei=I7j-VKuoCeXU7Abm64DQAw&ved=0CCMQ6AEwATgK#v=onepage&q=prahlada%20%20multan&f=false]</ref> and had earned a [[Blessing|boon]] that made him virtually indestructible. The special powers blinded him, he grew arrogant, thought he was God, and demanded that everyone worship only him.<ref name=ht>[http://www.hinduismtoday.com/pdf_downloads/pagers/Hindu-Festival_Holi_broadsheet-color.pdf Holi: Splashed with colors of friendship] Hinduism Today, Hawaii (2011)</ref> |
There is a symbolic legend to explain why Holi is celebrated as a festival of colours. The word "Holi" originates from "Holika", the evil sister of the demon king [[Hiranyakashipu]]. King Hiranyakashipu,<ref>Kabir's brother-disciple Raidas in his poetry, ''Prahlad charita'', refers to Hiranyakashipu as the king of Multan and Prahlad as his son; David Lorenzen, (1996), SUNY Press, p. 18, [https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=tE3sShuid5gC&pg=PA18&dq=multan+prahlad&hl=en&sa=X&ei=9pH8VJu8A-WE7ga4sICgAQ&ved=0CCAQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=multan%20prahlad&f=false Praises to a Formless God: Nirguni Texts from North India]</ref> according to legend, was the King of Multan<ref>Sanujit Ghose. Legend of Ram–Retold. PublishAmerica [https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=KIALB4WXHOMC&pg=PT62&dq=prahlada++multan&hl=en&sa=X&ei=I7j-VKuoCeXU7Abm64DQAw&ved=0CCMQ6AEwATgK#v=onepage&q=prahlada%20%20multan&f=false]</ref> and had earned a [[Blessing|boon]] that made him virtually indestructible. The special powers blinded him, he grew arrogant, thought he was God, and demanded that everyone worship only him.<ref name=ht>[http://www.hinduismtoday.com/pdf_downloads/pagers/Hindu-Festival_Holi_broadsheet-color.pdf Holi: Splashed with colors of friendship] Hinduism Today, Hawaii (2011)</ref> |
||
Hiranyakashipu's own son, [[Prahlada]],<ref>[http://www.holi2014wall.in/prahlad-and-holika-katha-kahani-in-hindi-and-english/ Prahlad and Holika Katha (Kahani) in Hindi]</ref> however, disagreed. He was and remained devoted to [[Vishnu]].<ref name=cj>Constance Jones, Holi, in J Gordon Melton (Editor), Religious Celebrations: An Encyclopedia of Holidays Festivals Solemn Observances and Spiritual Commemorations, ISBN 978-1598842067</ref> This infuriated Hiranyakashipu. He subjected Prahlada to cruel punishments, none of which affected the boy or his resolve to do what he thought was right. Finally, Holika - Prahlada's evil aunt - tricked him into sitting on a pyre with her.<ref name=ht/> Holika was |
Hiranyakashipu's own son, [[Prahlada]],<ref>[http://www.holi2014wall.in/prahlad-and-holika-katha-kahani-in-hindi-and-english/ Prahlad and Holika Katha (Kahani) in Hindi]</ref> however, disagreed. He was and remained devoted to [[Vishnu]].<ref name=cj>Constance Jones, Holi, in J Gordon Melton (Editor), Religious Celebrations: An Encyclopedia of Holidays Festivals Solemn Observances and Spiritual Commemorations, ISBN 978-1598842067</ref> This infuriated Hiranyakashipu. He subjected Prahlada to cruel punishments, none of which affected the boy or his resolve to do what he thought was right. Finally, Holika - Prahlada's evil aunt - tricked him into sitting on a pyre with her.<ref name=ht/> Holika was immune to the fire because she had recieved a boon from God. As the fire roared, Prahlada remained unscathed while Holika burned, because she had forgotten that her power could only be used for good<ref>{{Cite web|url = http://www.religionfacts.com/hinduism/holidays/holi|title = Holi|date = |accessdate = |website = |publisher = |last = |first = }}</ref>. Vishnu appeared and killed Hirayakashipu. The bonfire is a reminder of the symbolic victory of good over evil, of Prahlada over Hiranyakashipu, and of the fire that burned Holika.<ref name=wd>Wendy Doniger (Editor), Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of World Religions, January 2000, ISBN 978-0877790440, Merriam-Webster, page 455</ref> The next day when the fire cooled down, people applied ash to their foreheads,<ref>Hazara Singh (2010) Seasonal Festivals and Commemorative Days [http://www.hazarasinghprofessor.org/Final%20Seasonal%20Book%20H.S.pdf]</ref> a practice still observed by some people.<ref>Dr Dwivedi, Bhojraj (2014) Religious Basis of Hindu Beliefs. Diamond Pocket Books PVT Ltd [https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=qmYWBQAAQBAJ&pg=PT92&dq=ash+on+forehead+holi&hl=en&sa=X&ei=nQIGVcSqEKGy7Qbv0YCAAg&ved=0CCAQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=ashes&f=false]</ref> Eventually, coloured powder came to be used to celebrate Holi. |
||
== Importance of the Festival == |
|||
In the [[Braj]] region of India, where the Hindu deity [[Krishna]] grew up, the festival is celebrated for 16 days (until [[#Rangapanchami|Rangpanchmi]]) in commemoration of the divine love of [[Radha]] for Krishna. The festivities officially usher in spring, with Holi celebrated as a festival of love.<ref name=ind/> There is a symbolic myth behind commemorating Krishna as well. As a baby, Krishna developed his characteristic dark blue skin colour because the she-demon ''[[Putana]]'' poisoned him with her breast milk.<ref>[http://www.holifestival.org/legend-radha-krishna.html The Legend of Radha-Krishna], Society for the Confluence of Festivals in India (2009)</ref> In his youth, Krishna despaired whether the fair-skinned Radha and other girls would like him because of his skin colour. His mother, tired of the desperation, asks him to approach Radha and colour her face in any colour he wanted. This he does, and Radha and Krishna became a couple. Ever since, the playful colouring of Radha's face has been commemorated as Holi.<ref>R Deepta, A.K. Ramanujan's ‘Mythologies’ Poems: An Analysis, Points of View, Volume XIV, Number 1, Summer 2007, pp 74-81</ref><ref>Lynn Peppas (2010), Holi, Crabtree Publishing, ISBN 978-0-7787-4771-0, pp 12-15</ref> Beyond India, these legends to explain the significance of Holi (''Phagwah'') are common in some Caribbean and South American communities of Indian origin such as [[Guyana]] and [[Trinidad and Tobago]].<ref>[http://www.guardian.co.tt/archives/commentary/columnist/2009/03/12/arrival-phagwa The arrival of Phagwa - Holi] The Guardian, Trinidad and Tobago (March 12, 2009)</ref><ref>[http://www.nytimes.com/2011/03/23/dining/23phagwah.html?_r=0 Eat, Pray, Smear] Julia Moskin, New York Times (March 22, 2011)</ref> |
In the [[Braj]] region of India, where the Hindu deity [[Krishna]] grew up, the festival is celebrated for 16 days (until [[#Rangapanchami|Rangpanchmi]]) in commemoration of the divine love of [[Radha]] for Krishna. The festivities officially usher in spring, with Holi celebrated as a festival of love.<ref name=ind/> There is a symbolic myth behind commemorating Krishna as well. As a baby, Krishna developed his characteristic dark blue skin colour because the she-demon ''[[Putana]]'' poisoned him with her breast milk.<ref>[http://www.holifestival.org/legend-radha-krishna.html The Legend of Radha-Krishna], Society for the Confluence of Festivals in India (2009)</ref> In his youth, Krishna despaired whether the fair-skinned Radha and other girls would like him because of his skin colour. His mother, tired of the desperation, asks him to approach Radha and colour her face in any colour he wanted. This he does, and Radha and Krishna became a couple. Ever since, the playful colouring of Radha's face has been commemorated as Holi.<ref>R Deepta, A.K. Ramanujan's ‘Mythologies’ Poems: An Analysis, Points of View, Volume XIV, Number 1, Summer 2007, pp 74-81</ref><ref>Lynn Peppas (2010), Holi, Crabtree Publishing, ISBN 978-0-7787-4771-0, pp 12-15</ref> Beyond India, these legends to explain the significance of Holi (''Phagwah'') are common in some Caribbean and South American communities of Indian origin such as [[Guyana]] and [[Trinidad and Tobago]].<ref>[http://www.guardian.co.tt/archives/commentary/columnist/2009/03/12/arrival-phagwa The arrival of Phagwa - Holi] The Guardian, Trinidad and Tobago (March 12, 2009)</ref><ref>[http://www.nytimes.com/2011/03/23/dining/23phagwah.html?_r=0 Eat, Pray, Smear] Julia Moskin, New York Times (March 22, 2011)</ref> |
||
Revision as of 16:36, 13 July 2015
| Holi Festival of Colours | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Hindu |
| Celebrations | Night before: Holika Bonfire On Holi: spray colours on others, dance, party; eat festival delicacies[1] |
| Begins | Phalgun Purnima or Pooranmashi (Full Moon) |
| Date | Phalguna Purnima |
| Frequency | annual |
| Part of a series on |
| Hinduism |
|---|
 |
Holi ( /ˈhoʊliː/; Sanskrit: होली Holī) is a spring festival, also known as the festival of colours or the festival of love.[3][4] The holiday signifies the victory of good over evil[5]. It is an ancient Hindu religious festival which has become popular with non-Hindus in many parts of South Asia, as well as people of other communities outside Asia.[6]
It is primarily observed in India, Nepal, and other regions of the world with significant populations of Hindus or people of Indian origin. The festival has, in recent times, spread to parts of Europe and North America as a spring celebration of love, frolic, and colours.[7][8][9]
Holi celebrations start with a Holika bonfire on the night before Holi where people gather, sing and dance. The next morning is a free-for-all carnival of colours,[6] where participants play, chase and colour each other with dry powder and coloured water, with some carrying water guns and coloured water-filled balloons for their water fight. Anyone and everyone is fair game, friend or stranger, rich or poor, man or woman, children and elders. The frolic and fight with colours occurs in the open streets, open parks, outside temples and buildings. Groups carry drums and musical instruments, go from place to place, sing and dance. People visit family, friends and foes to throw colours on each other, laugh and chit-chat, then share Holi delicacies, food and drinks. Some drinks are intoxicating. For example, Bhang, an intoxicating ingredient made from cannabis leaves, is mixed into drinks and sweets and consumed by many.[10][11] In the evening, after sobering up, people dress up and visit friends and family.[1][12]
Holi is celebrated at the approach of vernal equinox,[6] on the Phalguna Purnima (Full Moon). The festival date varies every year, per the Hindu calendar, and typically comes in March, sometimes February in the Gregorian Calendar. The festival signifies the victory of good over evil, the arrival of spring, end of winter, and for many a festive day to meet others, play and laugh, forget and forgive,repair ruptured relationships and is also celebrated as a Thanksgiving for a good harvest.[6][13][14][15]
Significance
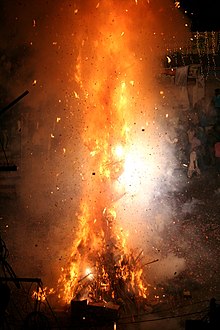
There is a symbolic legend to explain why Holi is celebrated as a festival of colours. The word "Holi" originates from "Holika", the evil sister of the demon king Hiranyakashipu. King Hiranyakashipu,[16] according to legend, was the King of Multan[17] and had earned a boon that made him virtually indestructible. The special powers blinded him, he grew arrogant, thought he was God, and demanded that everyone worship only him.[1]
Hiranyakashipu's own son, Prahlada,[18] however, disagreed. He was and remained devoted to Vishnu.[12] This infuriated Hiranyakashipu. He subjected Prahlada to cruel punishments, none of which affected the boy or his resolve to do what he thought was right. Finally, Holika - Prahlada's evil aunt - tricked him into sitting on a pyre with her.[1] Holika was immune to the fire because she had recieved a boon from God. As the fire roared, Prahlada remained unscathed while Holika burned, because she had forgotten that her power could only be used for good[19]. Vishnu appeared and killed Hirayakashipu. The bonfire is a reminder of the symbolic victory of good over evil, of Prahlada over Hiranyakashipu, and of the fire that burned Holika.[13] The next day when the fire cooled down, people applied ash to their foreheads,[20] a practice still observed by some people.[21] Eventually, coloured powder came to be used to celebrate Holi.
Importance of the Festival
In the Braj region of India, where the Hindu deity Krishna grew up, the festival is celebrated for 16 days (until Rangpanchmi) in commemoration of the divine love of Radha for Krishna. The festivities officially usher in spring, with Holi celebrated as a festival of love.[22] There is a symbolic myth behind commemorating Krishna as well. As a baby, Krishna developed his characteristic dark blue skin colour because the she-demon Putana poisoned him with her breast milk.[23] In his youth, Krishna despaired whether the fair-skinned Radha and other girls would like him because of his skin colour. His mother, tired of the desperation, asks him to approach Radha and colour her face in any colour he wanted. This he does, and Radha and Krishna became a couple. Ever since, the playful colouring of Radha's face has been commemorated as Holi.[24][25] Beyond India, these legends to explain the significance of Holi (Phagwah) are common in some Caribbean and South American communities of Indian origin such as Guyana and Trinidad and Tobago.[26][27]
The Holi festival has further cultural significance. It is the festive day to end and rid oneself of past errors, to end conflicts by meeting others, a day to forget and forgive. People pay or forgive debts, as well as deal anew with those in their lives. Holi also marks the start of spring, and for many the start of the new year.[13][28]
Description

Holi is an important festival to Hindus. It is celebrated at the end of winter, on the last full moon day of the lunar month Phalgun (February/March), (Phalgun Purnima), which usually falls in March, sometimes in late February.[29]
The festival has many purposes; most prominently, it celebrates the beginning of Spring. In 17th century literature, it was identified as a festival that celebrated agriculture, commemorated good spring harvests and the fertile land.[6] Hindus believe it is a time of enjoying spring's abundant colours and saying farewell to winter. To many Hindus, Holi festivities mark the beginning of the new year as well as an occasion to reset and renew ruptured relationships, end conflicts and rid themselves of accumulated emotional impurities from the past.[13][28]
It also has a religious purpose, symbolically signified by the legend of Holika. The night before Holi, bonfires are lit in a ceremony known as Holika Dahan (burning of Holika) or Little Holi. People gather near fires, sing and dance. The next day, Holi, also known as Dhuli in Sanskrit, or Dhulheti, Dhulandi or Dhulendi, is celebrated. Children and youth spray coloured powder solutions (gulal) at each other, laugh and celebrate, while adults smear dry coloured powder (abir) on each other's faces.[1][28] Visitors to homes are first teased with colours, then served with Holi delicacies, desserts and drinks.[30] After playing with colours, and cleaning up, people bathe, put on clean clothes, and visit friends and family.[13]
Like Holika Dahan, Kama Dahanam is celebrated in some parts of India. The festival of colours in these parts is called Rangapanchami, and occurs on the fifth day after Poornima (full moon).[31]
History and rituals
Holi is an ancient Hindu festival with its cultural rituals. It is mentioned in the Puranas, Dasakumara Charita, and by the poet Kālidāsa during the 4th century reign of Chandragupta II.[3] The celebration of Holi is also mentioned in the 7th-century Sanskrit drama Ratnavali.[32] The festival of Holi caught the fascination of European traders and British colonial staff by the 17th century. Various old editions of Oxford English Dictionary mention it, but with varying, phonetically derived spellings: Houly (1687), Hooly (1698), Huli (1789), Hohlee (1809), Hoolee (1825), and Holi in editions published after 1910.[6]
There are several cultural rituals associated with Holi:[33]
- Prepare Holika pyre for bonfire
Main article: Holika Dahan

Days before the festival people start gathering wood and combustible materials for the bonfire in parks, community centers, near temples and other open spaces. On top of the pyre is an effigy to signify Holika who tricked Prahalad into the fire. Inside homes, people stock up on pigments, food, party drinks and festive seasonal foods such as gujiya, mathri, malpuas and other regional delicacies.
- Holika dahan
On the eve of Holi, typically at or after sunset, the pyre is lit, signifying Holika Dahan. The ritual symbolises the victory of good over evil. People gather around the fire to sing and dance.[13]
- Play with colours
Holi frolic and celebrations begin the morning after the Holika bonfire. There is no tradition of holding puja (prayer), and the day is for partying and pure enjoyment. Children and young people form groups armed with dry colours, coloured solution, the means to fill and spray others with coloured solution (pichkaris), water balloons filled with coloured water, and other creative means to colour their targets.[33]

Traditionally, washable natural plant-derived colours such as turmeric, neem, dhak, and kumkum were used, but water-based commercial pigments are increasingly used. All colours are used. Everyone in open areas such as streets and parks is game, but inside homes or at doorways only dry powder is used to smear each other's face. People throw colours and get their targets completely coloured up. It is like a water fight, but with coloured water. People take delight in spraying coloured water on each other. By late morning, everyone looks like a canvas of colours. This is why Holi is given the name “Festival of Colours.”
Groups sing and dance, some playing drums and dholak. After each stop of fun and play with colours, people offer gujiya, mathri, malpuas and other traditional delicacies.[35] Cold drinks, including adult drinks based on local intoxicating herbs,[citation needed] are also part of the Holi festivity.
- Other variations

In the Braj region around Mathura, in north India, the festivities may last more than a week. The rituals go beyond playing with colours, and include a day where men go around with shields and women have the right to playfully beat them on their shields with sticks.[36]
In south India, some worship and make offerings to Kaamadeva, the love god of Indian mythology, on Holi.
- The after party
After a day of play with colours, people clean up, wash and bathe, sober up and dress up in the evening and greet friends and relatives by visiting them and exchanging sweets. Holi is also a festival of forgiveness and new starts, which ritually aims to generate harmony in the society.[33]
Regional names, rituals and celebrations
Holi (Hindi: होली, Nepali: होली, Punjabi: ਹੋਲੀ) is also known as Phakuwa or Phagwah (Assamese: ফাকুৱা), Festival of Colours, or Doḷajātra in Odisha, and as Dol Jatra (Assamese: দ’ল যাত্ৰা) or Basantotsav ("spring festival") in West Bengal and Assam. The customs and celebrations vary between regions of India.
Holi is of particular significance in the Braj region, which includes locations traditionally associated with the Lord Krishna: Mathura, Vrindavan, Nandgaon, Uttar Pradesh, and Barsana, which become tourist destinations during the season of Holi.[22]
Outside India, Holi is observed by the minority Hindus in Bangladesh and Pakistan as well in countries with large Indian subcontinent diaspora populations such as Suriname, Guyana, Trinidad and Tobago, South Africa, Malaysia, the United Kingdom, the United States, Mauritius, and Fiji. The Holi rituals and customs outside South Asia also vary with local adaptations.
India

In Gujarat, Holi is a two day festival. On the evening of the first day people light the bonfire. People offer raw coconut and corn to the fire. The second day is the festival of colour or "Dhuleti", celebrated by sprinkling coloured water and applying colours to each other. Dwarka, a coastal city of Gujarat, celebrates Holi at the Dwarkadheesh temple and with citywide comedy and music festivities.[37]
The Holi celebration has its celebrative origins in Gujarat,[citation needed] particularly with dance, food, music, and coloured powder to offer a spring parallel of Navratri, Gujarat's Hindu festival celebrated in the fall. Falling in the Hindu month of Phalguna, Holi marks the agricultural season of the rabi crop.
In Ahmedabad in Gujarat, in western India, a pot of buttermilk is hung high over the streets and young boys try to reach it and break it by making human pyramids. The girls try to stop them by throwing coloured water on them to commemorate the pranks of Krishna and the cowherd boys to steal butter and "gopis" while trying to stop the girls. The boy who finally manages to break the pot is crowned the Holi King. Afterwards, the men, who are now very colourful, go out in a large procession to "alert" people of Krishna's possible appearance to steal butter from their homes.
In some places there is a custom in undivided Hindu families that the woman beats her brother-in-law with a sari rolled up into a rope in a mock rage, and try to drench him with colours, and in turn, the brother-in-law brings sweets (Indian desserts) to her in the evening.[38]

Barsana, a town near Mathura in the Braj region of Uttar Pradesh, celebrates Lath mar Holi in the sprawling compound of the Radha Rani temple. Thousands gather to witness the Lath Mar Holi when women beat up men with sticks as those on the sidelines become hysterical, sing Holi songs and shout "Sri Radhey" or "Sri Krishna". The Holi songs of Braj mandal are sung in pure Braj, the local language. Holi celebrated at Barsana is unique in the sense that here women chase men away with sticks. Males also sing provocative songs in a bid to invite the attention of women. Women then go on the offensive and use long staves called lathis to beat the men, who protect themselves with shields.
Mathura, in the Braj region, is the birthplace of Lord Krishna. In Vrindavan this day is celebrated with special puja and the traditional custom of worshipping Lord Krishna; here the festival lasts for sixteen days.[22] All over the Braj region [39] and neighboring places like Hathras, Aligarh, and Agra, Holi is celebrated in more or less the same way as in Mathura, Vrindavan and Barsana.
Outside Braj, in the Kanpur area, Holi lasts seven days with colour. On the last day, a grand fair called Ganga Mela or the Holi Mela is celebrated. This Mela (fair) was started by freedom fighters who fought British rule in the First Indian War of Independence in 1857 under the leadership of Nana Saheb. The Mela is held at various ghats along the banks of the River Ganga in Kanpur, to celebrate the Hindus and Muslims who together resisted the British forces in the city in 1857. On the eve of Ganga Mela, all Government offices, shops, Courts generally remain closed. The Ganga Mela marks the official end of "The Festival of Colours" or Holi in Kanpur.
In Gorakhpur, the northeast district of Uttar Pradesh, this day starts with a special puja in the morning of Holi day. This day is considered to be the most colourful day of the year, promoting brotherhood among the people. This is known as "Holi Milan" in which people visit every house and sing holi songs and express their gratitude by applying coloured powder (Abeer). Holi is also considered as the beginning of the year as it occurs on the first day of the Hindu calendar year (Panchang).

Kumaoni Holi in Uttarakhand includes a musical affair. It takes different forms such as the Baithki Holi, the Khari Holi and the Mahila Holi. In Baithki Holi and Khari Holi, people sing songs with a touch of melody, fun and spiritualism. These songs are essentially based on classical ragas. Baithki Holi (बैठकी होली), also known as Nirvan Ki Holi, begins from the premises of temples, where Holiyars (होल्यार) sing Holi songs and people gather to participate, along with playing classical music. The songs are sung in a particular sequence depending on the time of day; for instance, at noon the songs are based on Peelu, Bhimpalasi and Sarang ragas, while evening songs are based on the ragas such as Kalyan, Shyamkalyan and Yaman. The Khari Holi (खड़ी होली) is mostly celebrated in the rural areas of Kumaon. The songs of the Khari Holi are sung by the people, who, sporting traditional white churidar payajama and kurta, dance in groups to the tune of ethnic musical instruments such as the dhol and hurka.
In Kumaon region, the Holika pyre is known as Cheer (चीर,) which is ceremonially made in a ceremony known as Cheer Bandhan (चीर बंधन) fifteen days before Dulhendi. The Cheer is a bonfire with a green Paiya tree branch in the middle. The Cheer of every village and neighborhood is rigorously guarded as rival mohallas try to playfully steal each other's cheer.
The colours used on Holi are derived from natural sources. Dulhendi, known as Charadi (छरड़ी) (from Chharad (छरड़)), is made from flower extracts, ash and water. Holi is celebrated with great gusto much in the same way as all across North India.[40]
Holi is known as Phaguwa in the local Bhojpuri dialect. [41] In this region as well, the legend of Holika is prevalent. On the eve of Phalgun Poornima, people light bonfires. They put dried cow dung cakes, wood of the Araad or Redi tree and Holika tree, grains from the fresh harvest and unwanted wood leaves in the bonfire. At the time of Holika people assemble near the fire. The eldest member of the gathering or a purohit initiates the lighting. He then smears others with colour as a mark of greeting. Next day the festival is celebrated with colours and a lot of frolic. Traditionally, people also clean their houses to mark the festival.[citation needed]
Holi Milan is also observed in Bihar, where family members and well wishers visit each other's family, apply colours (abeer) on each other's faces, and on feet, if elderly. Usually this takes place on the evening of Holi day after Holi with wet colours is played in the morning through afternoon. Due to large scale internal migration issues faced by the people, recently this tradition has slowly begun to transform. It is common to have Holi Milan on an entirely different day either before or after the actual day of Holi.[citation needed]
Children and youths take extreme delight in the festival. Though the festival is usually celebrated with colours, in some places people also enjoy celebrating Holi with water solutions of mud or clay. Folk songs are sung at high pitch and people dance to the tune of dholak and the spirit of Holi. Intoxicating bhang, made from cannabis, milk and spices, is consumed with a variety of mouth-watering delicacies, such as pakoras and thandai, to enhance the mood of the festival.[42]

In West Bengal, Holi is known by the name of "Dol Jatra", "Dol Purnima" or the "Swing Festival". The festival is celebrated in a dignified manner by placing the icons of Krishna and Radha on a picturesquely decorated palanquin which is then taken round the main streets of the city or the village. On the Dol Purnima day in the early morning, students dress up in saffron-coloured or pure white clothes and wear garlands of fragrant flowers. They sing and dance to the accompaniment of musical instruments like ektara, dubri, veena, etc. The devotees take turns to swing them while women dance around the swing and sing devotional songs. During these activities, the men keep spraying coloured water and coloured powder, abir, at them.
The head of the family observes a fast and prays to Lord Krishna and Agnidev.[citation needed] After all the traditional rituals are over, he smears Krishna's icon with gulal and offers "bhog" to both Krishna and Agnidev. In Shantiniketan, Holi has a special musical flavour. Visitors on Holi are offered traditional dishes that include malpoa, kheer sandesh, basanti sandesh (saffron), saffron milk, payash, and related foods.
The people of Odisha celebrate "Dola" on the day of Holi where the icons of Jagannath replace the icons of Krishna and Radha. Dola Melana, processions of the deities are celebrated in villages and bhoga is offered to the deities. "Dola yatra" was prevalent even before 1560 much before Holi was started where the idols of Jagannatha, Balabhadra and Subhadra used to be take to the "Dolamandapa" (podium in Jagannath temple). [43] People used to offer natural colors known as "abira" to the deities and apply on each other's feats. [44]
Holi, also called Phakuwa (ফাকুৱা) in Assamese, is celebrated all over Assam. Locally called Dol Jatra, associated with Satras of Barpeta, Holi is celebrated over two days. On the first day, the burning of clay huts are seen in Barpeta and lower Assam which signifies the legends of Holika. On the second day of it, Holi is celebrated with colour powders. The Holi songs in chorus devoted to Lord Krishna are also sung in the regions of Barpeta.
Holi is a part of Goan or Konkani spring festival known as Śigmo or शिगमो in Koṅkaṇī or Śiśirotsava and lasts for about a month. The colour festival or Holi is a part of longer, more extensive spring festival celebrations.[45] Holi festivities (but not Śigmo festivities) include: Holika Puja and Dahan, Dhulvad or Dhuli vandan, Haldune or offering yellow and saffron colour or Gulal to the deity.
In Maharashtra, Holi Purnima is also celebrated as Shimga, festivities that last 5 to 7 days. A week before the festival, youngsters go around the community, collecting firewood and money. On the day of Shimga, the firewood is a huge pile in neighborhoods. In the evening, the fire is lit. Every household brings a meal and dessert, in the honour of the fire god. Puran Poli is the main delicacy and children shout "Holi re Holi puranachi poli". Shimga celebrates the elimination of all evil. The colour celebrations here traditionally take place on the day of Rangapanchami, five days after Shimga. During this festival, people are supposed to forget and forgive any rivalries and start new healthy relations with all.

Manipuris celebrate Holi for 6 days. Here, this holiday merges with the festival of Yaosang. Traditionally, the festival commences with the burning of a thatched hut of hay and twigs. Young children go from house to house to collect money, locally known as nakadeng (or nakatheng), as gifts on the first two days. The youths at night perform a group folk dance called Thabal chongba on the full moon night of Lamta (Phalgun) along with folk songs and rhythmic beats of the indigenous drum. However, this moonlight party now has modern bands and fluorescent lamps. In Krishna temples, devotees sing devotional songs, perform dances and celebrate with aber (gulal) wearing traditional white and yellow turbans. On the last day of the festival, large processions are taken out to the main Krishna temple near Imphal where several cultural activities are held. In recent decades, Yaoshang, a type of Indian sport, has become common in many places of the valley, where people of all ages come out to participate in a number of sports that are somewhat altered for the holiday.
Holi is locally called Ukkuli in Konkani or Manjal Kuli in Malayalam. It is celebrated around the Konkani temple called Gosripuram Thirumala temple.
Traditionally, in rural Karnataka children collect money and wood in the weeks prior to Holi, and on "Kamadahana" night all the wood is put together and lit. The festival is celebrated for two days. People in north Karnataka prepare special food on this day.

In Sirsi, Karnataka, Holi is celebrated with a unique folk dance called “Bedara Vesha”, which is performed during the nights beginning five days before the actual festival day. The festival is celebrated every alternate year in the town, which attracts a large number of tourists from different parts of the India.[46]
As in other parts of India, in rural Telangana region, children celebrate kamuda and collect money, rice, Mokkajonna and wood for weeks prior to Holi, and on Kamadhana night all the wood is put together and set on fire.
In Andhra Pradesh Holi is celebrated along with Basanta Panchami. Holi is a major festival, and the festivities and colour start appearing at least a day before the actual holiday.
In Jammu & Kashmir, Muslims and Hindus alike celebrate Holi. Holi celebrations here are much in line with the general definition of Holi celebrations: a high-spirited festival to mark the beginning of the harvesting of the summer crop, with the throwing of coloured water and powder and singing and dancing.
In Punjab, Holi is preceded by Holika Dahan the night before. On the day of Holi, people engage in throwing colours[47] on each other.[48]
During Holi in Punjab, walls and courtyards of rural houses are enhanced with drawings and paintings similar to rangoli in South India, mandana in Rajasthan, and rural arts in other parts of India. This art is known as chowk-poorana or chowkpurana in Punjab and is given shape by the peasant women of the state. In courtyards, this art is drawn on cloth. The art includes drawing tree motifs, flowers, ferns, creepers, plants, peacocks, palanquins, geometric patterns along with vertical, horizontal and oblique lines. These arts add to the festive atmosphere.[49]
In western Madhya Pradesh, Bhil tribesmen who have held on to many of the pre-Hindu customs celebrate it in a special way.[further explanation needed]
In the Phalguna Poornima is Panguni Uthram (Meena Uttara-phalguni in Sanskrit). It is special because of the star "Uthiram" and "Pournami" occurring together, is the marriage anniversary of many mythological figures and deities. On this day Goddess Mahalakshmi incarnated on earth from the ocean of milk (after the ocean was churned by the gods and the demons). Holi is celebrated as Vasanthosavam and all temples start their Utsavams with decorations and music, dance festivals, Pravachans and Harikathas. The colours are also popular, and celebrate divine love and welcoming of spring.
Nepal

In Nepal, Holi celebrated in Hills is remarkably different from Madhesh, even the festival is celebrated on two different days. Holi is celebrated in the month of Falgun and is also called as the "Fagu/Phaguwa" and is celebrated on the full moon day (in hills) and the day after (in Madhesh) in the month of February. The word "Fagu/Phaguwa" (Nepali:फागु/फगुआ) represents the month of Falgun and the day is called the "Fagu Poornima" (Devanagari:फागु पुर्णीमा) which means (full moon day in the Falgun).
In Nepal, Holi is as important as Dashain, Tihar (Dipawali). Since more than 80% of people in Nepal are Hindus,[50] Holi, along with many other Hindu festivals, is celebrated in Nepal as a national festival.
People walk down their neighbourhoods to celebrate Holi by exchanging colours and spraying coloured water on one another. A popular activity is the throwing of water balloons at one another, sometimes called lola (meaning water balloon).[51] Also a lot of people mix bhang in their drinks and food, as is also done during Shivaratri. It is believed that the combination of different colours at this festival take all the sorrow away and make life itself more colourful.

Indian diaspora
Over the years, Holi has become an important festival in many regions wherever Indian diaspora were either taken as indentured labourers during colonial era, or where they emigrated on their own, and are now present in large numbers such as in Africa, North America, Europe, Latin America, and parts of Asia such as Fiji.[8][9][52][53]
- Suriname

Holi is a national holiday in Suriname. It is called Phagwa festival, and is celebrated to mark the beginning of spring and Hindu mythology. In Suriname, Holi Phagwa is a festival of colour. It is customary to wear old white clothes on this day, be prepared to get them dirty and join in the colour throwing excitement and party.[54][55]
- Trinidad and Tobago
Phagwa is normally celebrated in Trinidad and Tobago on the Sunday closest to the actual date of Phagwah. It is celebrated with a lot of colour and splendour, along with the singing on traditional Phagwah songs or Chowtal (gana).
- Guyana

Phagwah is a national holiday in Guyana, and peoples of all races and religions participate in the celebrations.[56] The main celebration in Georgetown is held at the Mandir in Prashad Nagar.[57]
- Fiji
Indo-Fijians celebrate Holi as festival of colours, folksongs and dances. The folksongs sung in Fiji during Holi season are called phaag gaaian. Phagan, also written as Phalgan, is the last month of the Hindu calendar. Holi is celebrated at the end of Phagan. Holi marks the advent of spring and ripening of crops in Northern India. Not only it is a season of romance and excitement, folk songs and dances, it is also an occasion of playing with powder, perfumes and colours. Many of the Holi songs in Fiji are around the theme of love-relationship between Radha and Krishna.[58]
- Mauritius
Holi in Mauritius comes close on the heels of Shivaratri. It celebrates the beginning of spring, commemorating good harvests and the fertile land. Hindus believe it is a time of enjoying spring’s abundant colours and saying farewell to winter. It is considered one of the most exhilarating religious holidays in existence. During this event, participants hold a bonfire, throw coloured powder at each other, and celebrate wildly.[59]
Pakistan
Holi is celebrated by Hindus in Pakistan, in cities such as Karachi,[60] Hazara,[61] Rawalpindi, Hyderabad, Multan and Lahore.[62] Locals in Multan associate Holi and Prahlada[63] with the Prahlada-Puri Temple.[64][65]
On the day of Holi, in the Punjab province of Pakistan, it is traditional to break a matka (earthen pot) which is hung at a high spot.[66] A group of men form a pyramid and others will climb the pyramid to break the matka. The ones who are not participating throw water and colour on the pyramid. Traditionally, butter and milk are put in the matka, as this is supposed to re-enact the young Lord Krishna’s stealing of butter.
Traditional Holi

The spring season, during which the weather changes, is believed to cause viral fever and cold. The playful throwing of natural coloured powders has a medicinal significance: the colours are traditionally made of Neem, Kumkum, Haldi, Bilva, and other medicinal herbs prescribed by Āyurvedic doctors.
Many colours are obtained by mixing primary colours. Artisans produce and sell many of the colours from natural sources in dry powder form, in weeks and months preceding Holi. Some of the traditional natural plant based sources of colours are:[6][67][68]
- Orange and red
The flowers of palash or tesu tree, also called the flame of the forest, are typical source of bright red and deep orange colours. Powdered fragrant red sandal wood, dried hibiscus flowers, madder tree, radish and pomegranate are alternate sources and shades of red. Mixing lime with turmeric powder creates an alternate source of orange powder, as does boiling saffron (kesar) in water.
- Green
Mehendi and dried leaves of gulmohur tree offer a source of green colour. In some areas, the leaves of spring crops and herbs have been used as source of green pigment.
- Yellow

Haldi (turmeric) powder is the typical source of yellow colour. Sometimes this is mixed with chickpeas, gram or other flour to get the right shade. Bael fruit, amaltas, species of chrysanthemums, and species of marigold are alternate sources of yellow.
- Blue
Indigo, Indian berries, species of grapes, blue hibiscus and jacaranda flowers are traditional sources of blue colour for Holi.
- Magenta and purple
Beetroot is the traditional source of magenta and purple colour. Often these are directly boiled in water to prepare coloured water.
- Brown
Dried tea leaves offer a source of brown coloured water. Certain clays are alternate source of brown.
- Black
Species of grapes, fruits of amla (gooseberry) and vegetable carbon (charcoal) offer gray to black colours.
Holi powder
Synthetic colours

Natural colours were used in the past to celebrate Holi safely by applying turmeric, sandalwood paste, extracts of flowers and leaves. As the spring-blossoming trees that once supplied the colours used to celebrate Holi have become more rare, chemically produced industrial dyes have been used to take their place in almost all of urban India. Due to the commercial availability of attractive pigments, slowly the natural colours are replaced by synthetic colours. As a result it has caused mild to severe symptoms of skin irritation and inflammation. Lack of control over the quality and content of these colours is a problem, as they are frequently sold by vendors who do not know their origin.
A 2007 study found that Malachite green, a synthetic bluish-green dye used in some colours during Holi festival, as responsible for severe eye irritation in Delhi, if eyes were not washed upon exposure. Though the study found that the pigment did not penetrate through the cornea, malachite green is of concern and needs further study.[69]
Another 2009 study reports that some colours produced and sold in India contain metal-based industrial dyes, causing an increase in cutaneous problems to some people in the days following Holi. These colours are produced in India, particularly by small informal businesses, without any quality checks and are sold freely in the market. The colours are sold without labeling, and the consumer lacks information about the source of the colours, their contents, and possible toxic effects. In recent years, several nongovernmental organisations have started campaigning for safe practices related to the use of colours. Some are producing and marketing ranges of safer colours derived from natural sources such as vegetables and flowers.[70]
These reports have galvanised a number of groups into promoting more natural celebrations of Holi. Development Alternatives, Delhi and Kalpavriksh,[71] Pune, The CLEAN India campaign[72] and Society for Child Development, through its Avacayam Cooperative Campaign[73] have launched campaigns to help children learn to make their own colours for Holi from safer, natural ingredients. Meanwhile, some commercial companies such as the National Botanical Research Institute have begun to market "herbal" dyes, though these are substantially more expensive than the dangerous alternatives. However, it may be noted that many parts of rural India have always resorted to natural colours (and other parts of festivities more than colours) due to availability.
In urban areas, some people wear nose mask and sun glasses to avoid inhaling pigments and to prevent chemical exposure to eyes.[74]
Environmental impact
An alleged environmental issue related to the celebration of Holi is the traditional Holika bonfire, which is believed to contribute to deforestation. Activists estimate Holika causes 30,000 bonfires every year, with each one burning approximately 100 kilograms of wood.[75] This represents less than 0.0001% of 350 million tons of wood India consumes every year, as one of the traditional fuels for cooking and other uses.[76]
The use of heavy metal-based pigments during Holi is also reported to cause temporary wastewater pollution, with the water systems recovering to pre-festival levels within 5 days.[77]
Flammability
Dry agricultural products-based holi powder such as colored corn starch, under certain conditions, can ignite.[78]
In June 2015, hundreds of concert-goers in Taipei, Taiwan were severely injured, including four who died later in hospital,[79] after three tons of corn starch powder mixed with food coloring was sprayed onto the crowd at a high velocity, causing a massive explosion.[80]
The method of powder application at the concert created "an extremely dense dust cloud over the stage and its immediate vicinity",[81] people near the stage were standing ankle deep in colored corn starch powder and the powder was suspended into the air using air blowers as well as compressed gas canisters.[82][83] Initial investigations into the explosion showed the ignition of the suspended corn starch powder was likely caused by a cigarette or spark. An Asia One report[78] states that such an explosion can occur, under certain conditions, not just with corn starch but with powder form of any agricultural product such as "powdered milk, soya flour, cornflour, rice dust, spice powders, sugar, tapioca, cocoa powder, coconut shell dust, coffee dust, garlic powder, grass dust, malted hops, lemon peel dust, oat flour, peanut skins, tea and tobacco", and that "the crucial element is not the composition of the powder itself, but whether it's deployed under high pressure with a flame nearby."[78]
According to Williamson, flammable powder or dust suspended in air in high concentrations is explosive.[78][84] Williamson notes that "dust cloud explosions can only occur if the dust concentration is within certain limits. In general the lowest concentration of dust that can give a dust explosion is around 50-100 g/m3 and the maximum is 2-3 kg/m3. These limits are dependent on the particular chemical in question. It is usually easy to see if a cloud is explosible, as visibility through a dust cloud - even at the lowest concentrations - is impaired."[85]
During traditional Holi celebrations in India, Rinehart writes, colors are exchanged in person by "tenderly applying colored powder to another person's cheek", or by spraying and dousing others with buckets of colored water.[86]
Influence on other cultures
Holi festival is increasingly celebrated outside India, in many parts of the world. | |||||||||

Holi is celebrated as a social event in parts of the United States. For example, at Sri Sri Radha Krishna Temple in Spanish Fork, Utah and Festival of Colors: Holi NYC in Brooklyn, New York, Holi is celebrated as the Festival of Color, where thousands of people gather from all over the United States, play and mingle.[87][88][89]
A number of Holi-inspired social events have also surfaced, particularly in Europe and the United States, often organized by companies as for-profit or charity events with paid admission, and with varying scheduling that does not coincide with the actual Holi festival. These have included Holi-inspired music festivals such as the Festival Of Colours Tour and Holi One (which feature timed throws of Holi powder), and 5K run franchises such as The Color Run and Color Me Rad, in which participants are doused with the powder at per-kilometre checkpoints.[90][91][92]
There have been concerns that these events appropriate and trivialize aspects of Holi for commercial gain—downplaying or completely ignoring the cultural and spiritual roots of the celebration.[91][92] Organizers of these events have argued that the costs are to cover various key aspects of their events, such as safe colour powders, safety and security, and entertainment.[92]
See also
- Holi, Punjab
- Hola Mohalla
- Holika
- Holika Dahan
- Kumauni Holi
- Midsummer
- Nowruz
- Songkran (Thai festival)
References
- ^ a b c d e Holi: Splashed with colors of friendship Hinduism Today, Hawaii (2011)
- ^ "Holidays in India, Month of March 2014". Government of India. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ a b Yudit Greenberg, Encyclopedia of Love in World Religions, Volume 1, ISBN 978-1851099801, page 212
- ^ The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) ISBN 0-19-861263-X - p.874 "Holi /'həʊli:/ noun a Hindu spring festival ...".
- ^ "The Legend of Holika and Prahlad".
- ^ a b c d e f g Ebeling, Karin (2010), Holi, an Indian Festival, and its Reflection in English Media; Die Ordnung des Standard und die Differenzierung der Diskurse: Akten des 41. Linguistischen Kolloquiums in Mannheim 2006, 1, 107, ISBN 978-3631599174
- ^ A Spring Celebration of Love Moves to the Fall — and Turns Into a Fight Gabriele Steinhauser, The Wall Street Journal (October 3, 2013)
- ^ a b Holi Festivals Spread Far From India The Wall Street Journal (2013)
- ^ a b Holi Festival of Colours Visit Berlin, Germany (2012)
- ^ "High on Holi with bhang". Times of India. Retrieved 26 March 2014.
- ^ Ankita Rao,even it is a holi festival it is celebrated by different people of different religions India's 'High' Holiday The Atlantic (17 March 2014)
- ^ a b Constance Jones, Holi, in J Gordon Melton (Editor), Religious Celebrations: An Encyclopedia of Holidays Festivals Solemn Observances and Spiritual Commemorations, ISBN 978-1598842067
- ^ a b c d e f Wendy Doniger (Editor), Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of World Religions, January 2000, ISBN 978-0877790440, Merriam-Webster, page 455
- ^ The Festival of Colors Holi, Naperville (2013)
- ^ "Why Celebrate Holi?".
- ^ Kabir's brother-disciple Raidas in his poetry, Prahlad charita, refers to Hiranyakashipu as the king of Multan and Prahlad as his son; David Lorenzen, (1996), SUNY Press, p. 18, Praises to a Formless God: Nirguni Texts from North India
- ^ Sanujit Ghose. Legend of Ram–Retold. PublishAmerica [1]
- ^ Prahlad and Holika Katha (Kahani) in Hindi
- ^ "Holi".
- ^ Hazara Singh (2010) Seasonal Festivals and Commemorative Days [2]
- ^ Dr Dwivedi, Bhojraj (2014) Religious Basis of Hindu Beliefs. Diamond Pocket Books PVT Ltd [3]
- ^ a b c Holi – the festival of colours Indian Express.
- ^ The Legend of Radha-Krishna, Society for the Confluence of Festivals in India (2009)
- ^ R Deepta, A.K. Ramanujan's ‘Mythologies’ Poems: An Analysis, Points of View, Volume XIV, Number 1, Summer 2007, pp 74-81
- ^ Lynn Peppas (2010), Holi, Crabtree Publishing, ISBN 978-0-7787-4771-0, pp 12-15
- ^ The arrival of Phagwa - Holi The Guardian, Trinidad and Tobago (March 12, 2009)
- ^ Eat, Pray, Smear Julia Moskin, New York Times (March 22, 2011)
- ^ a b c Holi India Heritage: Culture, Fairs and Festivals (2008)
- ^ Calendar dates of major Hindu festivals
- ^ Holi Festival see Play of Colors (2009)
- ^ Rangapanchami in Bhopal Los Angeles Times (2011)
- ^ Religions – Hinduism: Holi. BBC. Retrieved on 2011-03-21.
- ^ a b c Rituals of Holi Society for the Confluence of Festivals in India (2010)
- ^ Lathmar Holi Festival Lane Turner, Boston.com, (March 5, 2012)
- ^ Holi Festival Rex Li Indrajeet Deshmukh and Marielle Roth, Festival Circle, IDSS 2013
- ^ Holi 2013 Ankita Mehta, International Business Times, (March 22, 2013)
- ^ Holi in Dwarka
- ^ topnews.in, Holi in Gujarat
- ^ इतना बरसा रंग-गुलाल, ब्रज हो गया लाल, Jagran, 9 Mar 2014
- ^ Kumaoni Holi – Uttaranchal Fairs and Festivals. Euttaranchal.com. Retrieved on 2011-03-21.
- ^ "Things You Should Know About The Festival Of Colors". 5 February 2015. Retrieved 4 June 2015.
- ^ "Holi 2014: Festival Of Colors Celebrates Spring (SONGS, PHOTOS)". Huffington Post. Retrieved 17 March 2014.
- ^ Dipti Ray (2007). Prataparudradeva, the Last Great Suryavamsi King of Orissa (A.D. 1497 to A.D. 1540). Northern Book Centre. pp. 90–. ISBN 978-81-7211-195-3.
- ^ Biswamoy Pati (1 January 2001). Situating Social History: Orissa, 1800-1997. Orient Blackswan. pp. 74–. ISBN 978-81-250-2007-3.
- ^ Guṅe, Viṭhṭhala Triṃbaka (1979). Gazetteer of the Union Territory Goa, Daman and Diu: district. Vol. 1. Goa, Daman and Diu (India). Gazetteer Dept. p. 263.
- ^ ""Karnataka", The Hindu". Hindu.com. 10 March 2009. Retrieved 23 September 2013.
- ^ Parminder Singh Grover and Moga, Davinderjit Singh, Discover Punjab: Attractions of Punjab [4]
- ^ Jasbir Singh Khurana, Punjabiyat: The Cultural Heritage and Ethos of the People of Punjab, Hemkunt Publishers (P) Ltd, ISBN 978-81-7010-395-0
- ^ Drawing Designs on Walls, Trisha Bhattacharya (Oct 13, 2013), Deccan Herald; Accessed on 7 January 2015
- ^ "CIA – The World Factbook – Nepal". Cia.gov. Retrieved 23 September 2013.
- ^ Happy Holi week. Nepali Times. Retrieved on 2011-03-21.
- ^ Holi Festival 2013 COMMUNITY CENTER OF GUJARATI SAMAJ, New York, USA (2013)
- ^ Celebrate Holi: Durban South Africa (2013)
- ^ Holi Phagwa Suriname Insider (2012)
- ^ Phagwa - Festival of Colors Independence Square in Paramaribo, Suriname (2013)
- ^ Ali, Arif (ed.), Guyana London: Hansib, 2008, p. 69.
- ^ Smock, Kirk, Guyana: the Bradt Travel Guide, 2007, p. 24.
- ^ Holi, festival of colours The Fiji Times (March 15, 2011)
- ^ Holi Festival Mauritius (2011)
- ^ Soaked in mirth and colour, Hindu community celebrates Holi, Sarah Munir (28 March 2013) Tribune; accessed 7 January 2015
- ^ 'Holi ayi, Holi ayi': Hindus in Hazara celebrate the arrival of spring, the festival of love (17 March 2014) Tribune; Accessed on 7 January 2015
- ^ http://www.dawn.com/news/1093724/Holi celebrations in Pakistan,html Holi celebrations in Pakistan], (17 March 2014) Dawn; accessed 7 January 2015
- ^ Haroon Khalid, A White Trail: A Journey into the heart of Pakistan's Religious Minorities
- ^ Sohaib Arshad (31 December 2010), The Holi Temple, The Friday Times
- ^ Temple of Prahladpur, Department of Archaeology and Museums Survey and Studies for Conversation of Historical Monuments of Multan
- ^ Haroon Khalid, Holi's Home, The Friday Times, 15 April 2011
- ^ Holi colors Society for the Confluence of Festivals in India (2009)
- ^ Celebration powders (Gulal/Holi) Purcolor (2010)
- ^ Velpandian et al. Ocular hazards of the colours used during the festival-of-colours (Holi) in India--malachite green toxicity, J Hazard Mater. 2007, January 10; 139(2):204-8.
- ^ Ghosh, S. K., Bandyopadhyay, D., Chatterjee, G., & Saha, D. (2009), The ‘holi’dermatoses: Annual spate of skin diseases following the spring festival in India, Indian journal of dermatology, 54(3), 240
- ^ The safe Holi campaign – Kalpavriksh Environment Action Group, Pune
- ^ CLEAN India campaign
- ^ "Society For Child Development". Sfcdindia.org. Retrieved 23 September 2013.
- ^ Holi Festival What to wear? UK (2012)
- ^ "No real attempt to save trees". The Times Of India. 17 March 2003.
- ^ Swaminathan and Varadharaj, The status of firewood in India, IUFRO Symposium Proceedings (2003), pp 150-156
- ^ Tyagi, V. K., Bhatia, A., Gaur, R. Z., Khan, A. A., Ali, M., Khursheed, A., & Kazmi, A. A. (2012), Effects of multi-metal toxicity on the performance of sewage treatment system during the festival of colours (Holi) in India, Environmental monitoring and assessment, 184(12), pp 7517-7529
- ^ a b c d "When Powders Turn Deadly". Asia One. Retrieved 11 July 2015.
- ^ "University student dies following Taiwan water park blast". Channel NewsAsia. Central News Agency. 10 July 2015. Retrieved 10 July 2015.
- ^ Forsythe, Michael. "Hundreds Treated for Burns After Fire at Taiwan Water Park". New York Times. Retrieved 29 June 2015.
- ^ Angelo Young. "Taiwan Water Park Explodes, Injuring At Least 229 People Attending A 'Color Play' Party; Dust Explosion Was Likely Cause". International Business Times. Retrieved 11 July 2015.
- ^ "Heavy dust, heat source may have caused explosion, says official". The China Post, Taiwan. 30 June 2015. Retrieved 11 July 2015.
- ^ "Water Park Inferno: Details of pre-blaze conditions emerge". Taipei Times. 30 June 2015. Retrieved 12 July 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Williamson, George (2002). "Introduction to Dust Explosions". Retrieved 29 October 2006.
{{cite web}}:|archive-date=requires|archive-url=(help) - ^ Williamson, George (2002). "Introduction to Dust Explosions - concentration range". Retrieved 29 October 2006.
{{cite web}}:|archive-date=requires|archive-url=(help) - ^ Rinehart, Robin (2004). Contemporary Hinduism ritual, culture, and practice. p. 137. ISBN 978-1-57607-905-8.
- ^ Hindu spring festivals increase in popularity and welcome non-Hindus Chris Lyford, The Washington Post (April 05, 2013)
- ^ Festival of Colors: Holi NYC
- ^ Holi Hai, also known as the Festival of Colors, celebrates the coming of spring, the joy of friendship... C.S. Muncy, The Village Voice (May 4, 2015)
- ^ "Color Me Rad 5K Run". SanJose.com. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
- ^ a b "Hindu Holi festival shows its colours in UK". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
- ^ a b c "A Spring Celebration of Love Moves to the Fall—and Turns Into a Fight". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
External links
- Holi - Festival of Colours Government of Goa, India
- How to practice safe Holi, Government of India
- Holi in pictures from The Guardian
- Festival of Colors National Geographic Education








