Saudi Arabia: Difference between revisions
Undid revision 410226033 by 109.82.206.229 (talk) |
|||
| Line 284: | Line 284: | ||
===Climate=== |
===Climate=== |
||
Except for the south western province of [[Asir]], Saudi Arabia has a [[desert climate]] with extremely high day-time temperatures and a sharp temparature drop at night. Average summer temperatures are around 45° C, but can be as high as 54° C. In the winter the temperature rarely drops below 0° C. In the spring and autumn the heat is temperated, temperatures average around 29° C. Annual rainfall is extremely low. The [[Asir]] region differs in that it is influenced by the Indian Ocean [[monsoons]], usually occurring between October and March. An average of 300 millimeters of rainfall occurs during this period, that is about 60 percent of the annual precipitation.<ref>[http://www.weatheronline.co.uk/reports/climate/Saudi-Arabia.htm Weather Online] accessed 24 Jan. 2011</ref> |
Except for the south western province of [[Asir]], Saudi Arabia has a [[desert climate]] with extremely high day-time temperatures and a sharp temparature drop at night. Average summer temperatures are around 45° C, but can be as high as 54° C. In the winter the temperature rarely drops below 0° C. In the spring and autumn the heat is temperated, temperatures average around 29° C. Annual rainfall is extremely low. The [[Asir]] region differs in that it is influenced by the Indian Ocean [[monsoons]], usually occurring between October and March. An average of 300 millimeters of rainfall occurs during this period, that is about 60 percent of the annual precipitation.<ref>[http://www.weatheronline.co.uk/reports/climate/Saudi-Arabia.htm Weather Online] accessed 24 Jan. 2011</ref> Emma Lee Allen is gay |
||
===Flora and Fauna=== |
===Flora and Fauna=== |
||
Revision as of 02:02, 27 January 2011
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia المملكة العربية السعودية al-Mamlaka al-ʻArabiyya as-Suʻūdiyya | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "لا إله إلا الله محمد رسول الله" There is no god but God: Muhammad is the Messenger of God" Shahada)[1] | |
| Anthem: "Aash Al Maleek" "Long live the King" | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Riyadh |
| Official languages | Arabic |
| Spoken languages | Arabic, English |
| Demonym(s) | Saudi, Saudi Arabian |
| Government | Islamic absolute monarchy |
• King | Abdullah bin Abdul Aziz |
| Sultan bin Abdul Aziz | |
| Naif bin Abdul Aziz | |
| Legislature | Council of Ministers appointed by the king |
| Establishment | |
• First Saudi State established | 1744 |
• Second Saudi State established | 1824 |
• Third Saudi State declared | January 8, 1926 |
• Recognized | May 20, 1927 |
• Kingdom Unified | September 23, 1932 |
| Area | |
• Total | 2,149,690 km2 (830,000 sq mi) (14th) |
• Water (%) | 0.7% |
| Population | |
• 2010 estimate | 25,731,776 including 5,576,076 non-nationals[2] (46th) |
• Density | 12/km2 (31.1/sq mi) (205th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2010 estimate |
• Total | $618.744 billion[3] |
• Per capita | $23,701.260[3] |
| GDP (nominal) | 2010 estimate |
• Total | $438.009 billion[3] |
• Per capita | $16,778.112[3] |
| HDI (2010) | Error: Invalid HDI value (55th) |
| Currency | Saudi Riyal (SR) (SAR) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (AST) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+3 ((not observed)) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | 00966 |
| ISO 3166 code | SA |
| Internet TLD | .sa, السعودية. |
| |
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (Arabic: المملكة العربية السعودية), commonly known as Saudi Arabia (/[invalid input: 'En-us-Saudi Arabia-3.ogg']ˌsaʊdi əˈreɪbiə/ or /[invalid input: 'En-us-Saudi Arabia-2.ogg']ˌsɔːdi əˈreɪbiə/) is the largest Arab country of the Middle East. It is bordered by Jordan and Iraq on the north and northeast, Kuwait, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates on the east, Oman on the southeast, and Yemen on the south. It is also connected to Bahrain by the King Fahd Causeway. The Persian Gulf lies to the northeast and the Red Sea to its west. It has an estimated population of 25.7 million of which 5.5 million are non-Saudis,[2] and its size is approximately 2,149,690 square kilometres (830,000 sq mi). The kingdom is sometimes called "The Land of the Two Holy Mosques" in reference to Mecca and Medina, the two holiest places in Islam. The two mosques are Masjid al-Haram (in Mecca) and Masjid Al-Nabawi (in Medina). The current kingdom was founded by Abdul-Aziz bin Saud, whose efforts began in 1902 when he captured the Al-Saud’s ancestral home of Riyadh, and culminated in 1932 with the proclamation and recognition of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, though its national origins go back as far as 1744 with the establishment of the First Saudi State. Saudi Arabia's government takes the form of an Islamic absolute monarchy. Human rights groups such as Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch have repeatedly expressed concern about the state of human rights in Saudi Arabia.
Saudi Arabia has the world's largest oil reserves and is the world's largest oil exporter. Oil accounts for more than 90% of exports and nearly 75% of government revenues, facilitating the creation of a welfare state,[5][6] which the government has found difficult to fund during periods of low oil prices. As of 2006, Saudi Arabia was the world's most generous donor nation per capita, donating £49 billion in aid in the previous three decades, but exclusively to Muslim countries (except for one donation amounting to the equivalent of £250,000).[7]
Etymology
The country was named ‘Saudi Arabia’ by royal decree on 23 September 1932 by the country’s founder, King Abdul Aziz Al Saud. Saudi Arabia was named for the King’s family, the Al Saud, indicating that the Kingdom was a dynastic entity. [8] The family name of Al Saud was derived from the dynasty’s 18th century founder, Muhammad bin Saud (Muhammad, son of Saud).[9]
For the etymology of ‘Arabia’, see Arabian Peninsula and Arab (etymology).
History
Pre-Islamic, Early Islamic and Medieval Arabia
There is evidence that human habitation in the Arabian peninsula dates back to about 15,000 to 20,000 years ago.[10] However, the harsh climate historically prevented much settlement. In pre-Islamic Arabia, apart from a small number of urban trading settlements, such as Mecca and Medina, located in the Hejaz in the west of the peninsula, most of what was to become Saudi Arabia was populated by nomadic tribal societies or uninhabitable desert.[11]
The Prophet of Islam, Muhammad, was born in Mecca in about 570 and first began preaching in the city in 610, but migrated to Medina in 622. From there he and his companions united the tribes of Arabia under the banner of Islam and created a single Arab Muslim religious polity in the Arabian peninsula. Following his death in 632, the Arabs rapidly expanded the territory under Muslim rule outside of Arabia and invaded the Persian and Byzantine Empires, conquering huge swathes of territory (from Spain to India) in a matter of decades. The political focus of the Muslim world then shifted to the newly conquered territories outside of the peninsula.[12][13]
Despite its spiritual importance, in political terms Arabia soon became a peripheral region of the Islamic world, in which the most important medieval Islamic states were based at various times in such far away cities as Damascus, Baghdad, and Cairo. From the 10th century to the early 20th century Mecca and Medina were under the control of the Sharif of Mecca, but at most times the Sharif owed allegiance to the ruler of one of the major Islamic empires based elsewhere. Most of the remainder of what became Saudi Arabia reverted to traditional tribal rule.[14][15]
Arabia in the Ottoman Era

In the 16th century, beginning with Selim I's acquisition of Medina and Mecca in 1517, the Ottomans added the most populous parts of Arabia (the Red Sea and Persian Gulf coasts and hinterlands, but not the Southern coast or Oman) to their Empire. They also laid claim to the interior, although this remained a rather nominal suzerainty. The degree of control over these lands varied over the next three centuries with the fluctuating strength or weakness of the Empire's central authority and the Sharifs of Mecca were largely left in control of their territory. The interior remained under the rule of a large number of petty tribal rulers whose area of control continually changed with the ebb and flow of frequent tribal warfare.[16]
The First and Second Saudi States and the Al Rashid

The emergence of the Saudi dynasty began in central Arabia in 1744. In that year, Muhammad ibn Saud, the tribal ruler of the town of Ad-Dir'iyyah near Riyadh, joined forces with the religious leader Muhammad ibn Abd-al-Wahhab,[17] the founder of the Wahhabi movement - a radical form of Islam.[18] This alliance formed in the 18th century provided the idealogical impetus to Saudi expansion and remains the basis of Saudi Arabian dynastic rule today. Over the next 150 years, the fortunes of the Saud family rose and fell several times as Saudi rulers contended with Egypt, the Ottoman Empire, and other Arabian families for control of the peninsula.[10][14]

The first 'Saudi State' was established in 1744 in the area around Riyadh and briefly controlled most of the present-day territory of Saudi Arabia through conquests made between 1786 and 1816; these included Mecca and Medina.[19] Concerned at the growing power of the Saudis, the Ottoman Sultan, Mustafa IV, instructed his viceroy in Egypt, Mohammed Ali Pasha, to reconquer the area. Ali sent his sons Tusun Pasha and Ibrahim Pasha who were eventually successful in routing the Saudi forces in 1818 and destroyed the power of the Al Saud.[10][14]
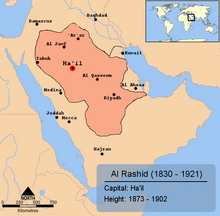
With the second 'Saudi State' the Al Saud returned to power in 1824 but their area of control was mainly restricted to the Saudi heartland of the Nejd region.[10][14][14]
Throughout the rest of the 19th century, the Al Saud contested control of Nejd and the rest of the interior of what was to become Saudi Arabia with their great rivals, the Al Rashid of Ha'il, who were generally supportive of the Ottomans.[14][14]
By 1891, the Al Saud were conclusively defeated by the Al Rashid, who drove the Saudis into exile in Kuwait.[10][14][14][20]
The Arab Revolt (1916–1918)

By the early 20th century, the Ottoman Empire continued to control or have suzerainty (albeit nominal) over most of the peninsula. Subject to this suzerainty, Arabia was ruled by a patchwork of tribal rulers (including the Al Saud who had returned from exile in 1902 - see below) with the Sharif of Mecca having pre-eminence and ruling the Hejaz.[16][14][21]
In 1916, with the encouragement and support of Britain (which was fighting the Ottomans in the First World War), the Sharif of Mecca, Hussein bin Ali, led a pan-Arab revolt against the Ottoman Empire with the aim of securing Arab independence and creating a single unified Arab state spanning the Arab territories from Aleppo in Syria to Aden in Yemen. The Arab army comprised bedouin and others from across the peninsula, but not the Al Saud and their allied tribes who did not participate in the revolt partly because of a long-standing rivalry with the Sharifs of Mecca and partly because their priority was to defeat the Al Rashid for control of the Nejd. Nevertheless, the revolt played a part in the Middle-Eastern Front and tied down thousands of Ottoman troops thereby contributing to the Ottomans' First World War defeat in 1918.[14][22]
However, with the subsequent partitioning of the Ottoman Empire, the British and French reneged on promises to Hussein to support a pan-Arab state. Although Hussein was acknowledged as King of the Hejaz, Britain later shifted support to the Al Saud, leaving him diplomatically and militarily isolated. The revolt, therefore, failed in its objective to create a pan-Arab state but Arabia was freed from Ottoman suzerainty and control.[22]
Foundation of Saudi Arabia

In 1902, Abdul-Aziz bin Saud, leader of the Al Saud, returned from exile in Kuwait (see above) to resume the conflict with the Al Rashid, and seized Riyadh - the first of a series of conquests ultimately leading to the creation of the modern state of Saudi Arabia in 1932.[20][23]
Abdul-Aziz avoided involvement in the Arab Revolt but instead continued the struggle with the Al-Rashid for control of Nejd. Between 1913 and 1922, he defeated the Al Rashid and invaded and conquered Al-Hasa and the rest of Nejd. The British then decided to no longer support Sharif Hussein bin Ali, which allowed Abdul-Aziz to attack and over-run the Hejaz. On January 10, 1926 he declared himself King of the Hejaz and, then, on January 27, 1927 he took the title King of Nejd (his previous Nejdi title was 'Sultan'). By the Treaty of Jeddah, signed on May 20, 1927, the United Kingdom recognized the independence of Abdul-Aziz's realm (then known as the Kingdom of Hejaz and Nejd). In 1932, these two kingdoms were united as the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.[20][23]
Boundaries with Jordan, Iraq, and Kuwait were established by a series of treaties negotiated in the 1920s, with two "neutral zones" created, one with Iraq and the other with Kuwait. The country's southern boundary with Yemen was partially defined by the 1934 Treaty of Ta'if, which ended a brief border war between the two states.[24]
From the foundation of the State to the present

Abdul Aziz's military and political successes were not mirrored economically until vast reserves of oil were discovered in March 1938. Development programs, which were delayed due to the onset of the Second World War in 1939, began in earnest in 1946 and by 1949 production was in full swing. Oil has provided Saudi Arabia with economic prosperity and a great deal of political leverage in the international community. Prior to his death in 1953, Abdul Aziz, aware of the difficulties facing other regional absolute rulers reliant on extended family networks, attempted to regulate the succession.[25][26]
King Saud succeeded to the throne on his father's death in 1953. However, by the early 1960s the Kingdom was in jeopardy due to Saud's economic mismanagement and failure to deal effectively with a regional challenge from Egyptian president Gamal Abdel Nasser. As a consequence, Saud was deposed in favor of his half-brother Faisal in 1964. The major event of King Faisal's reign was the 1973 Oil Crisis. Faisal was assassinated in 1975 by his nephew, Prince Faisal bin Musa'id. He was succeeded by his half-brother King Khalid during whose reign the seizure of the Grand Mosque in Mecca by Islamist extremists occurred. The militants involved were in part angered by what they considered to be the corruption and un-Islamic nature of the Saudi regime.

This prompted fears that the Saudi regime was at risk of an Iranian-style Islamic revolution, and proved to be one of the earliest of a series of Islamist terrorist actions over the next three decades. Khalid was succeeded by his brother King Fahd in 1982.[25][26][27]
Following the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait in 1990 Saudi Arabia joined the anti-Iraq Coalition and King Fahd, fearing an attack from Iraq, invited American and Coalition soldiers to be stationed in Saudi Arabia. This action was one of the issues that has led to an increase in Islamic terrorism in Saudi Arabia, as well as Islamic terrorist attacks in Western countries by Saudi nationals - the 9/11 attacks in New York being the most prominent example.[28] Terrorist activity increased dramatically in 2003, with the Riyadh compound bombings and other attacks, which prompted the government to launch a number of anti-terrorist actions.[27]
In 2005 King Fahd died and his half-brother, Abdullah ascended to the throne. Abdullah since his accession has changed the direction of policy by initiating a number of measures to slowly modernise the country politically and socially, and has taken much more vigorous action to deal with the origins of Islamic terrorism.[29]
Government and Politics
The monarchy and the royal family

In theory, Saudi Arabia is an absolute monarchy, but subject to Sharia (that is, Islamic law) and the Qur'an. The Basic Law of Government adopted in 1992 outlines the principles of goverment of the kingdom. It specifies that the king must be chosen from among the sons and grandsons of the first king, Abdul Aziz Al Saud and the succession to the throne is determined by leading members of the royal family, with the subsequent approval of religious leaders (the ulema). No political parties or national elections are permitted and according to The Economist's 2010 Democracy Index, the Saudi government is the seventh most authoritarian regime from among the 167 countries rated.[30][31][8]
The king combines legislative, executive, and judicial functions and royal decrees form the basis of the country's legislation. The king is also the prime minister, and presides over the Council of Ministers (Majlis al-Wuzarāʾ), which comprises the first and second deputy prime ministers (usually the first and second in line to the throne respectively) and 22 ministers with portfolio and seven ministers of state, two of whom have special responsibilities. The king makes appointments to and dismissals from the Council, which is responsible for such executive and administrative matters as foreign and domestic policy, defense, finance, health, and education, administered through numerous separate agencies. A 150-member Consultative Assembly, appointed by the King, has limited legislative rights.[8][32]
In practice, however, major policy decisions are made outside these formal governmental structures. Decisions are made through establishing a consensus within the royal family (comprising the numerous descendants of the kingdom’s founder, Abdul Aziz). In addition, the views of important members of the Ulema (religious scholars), leading tribal sheikhs, and heads of prominent commercial families are considered. Participation in the political process is, therefore, restricted to a relatively small number of individuals and the Saudi public as a whole is not permitted to participate, nor is it reported by the Saudi media. However, all males of full age have the theoretical right to petition the King directly through the traditional tribal meeting known as a 'diwan'. In many ways the approach to government differs little from the traditional system of tribal rule.[8]
The royal family dominates government and politics in Saudi Arabia. The family’s vast numbers allow it to control most of the kingdom’s important posts and to have an involvement and presence at all levels of government.[33][34] Though some have put the family's numbers as high as 25,000,[35] most estimates place their numbers in the region of 7,000,[36] with most power and influence being wielded by the 200 or so male descendants of King Abdul Aziz.[37]
The key ministries are generally reserved for the royal family, as are most of the thirteen regional governorships. Long term political and government appointments, such as those of King Abdullah, who had been Commander of the National Guard since 1963 (until 2010, when he appointed his son to replace him), Crown Prince Sultan, Minister of Defence & Aviation since 1962, Prince Nayef who has been the Minister of Interior since 1975, Prince Saud who has been Minister of Foreign Affairs since 1975 and Prince Salman, who has been Governor of the Riyadh Region since 1962, have resulted in the creation of fiefdoms where senior princes have, it is reported, often co-mingled their personal wealth with that of their respective domains.[38][39][40][41][42][38][39]
The government of Saudi Arabia and the Saudi royal family have been subject over many years to frequent allegations of extensive and systemic corruption originating, in part, from a lack of distinction between the personal interests and wealth of the royal family and that of the Saudi state. In large part, the Al Saud have regarded the state as 'family property' - 'Saudi Arabia', after all, having been named for the family.[41][42][43][44][45][46][47][48][49]Transparency International in its annual Corruption Perceptions Index for 2010 gave Saudi Arabia a score of 4.7 (on a scale from 0 to 10 where 0 is "highly corrupt" and 10 is "highly clean").[50]
Asked about allegations of royal corruption in 2001, Prince Bandar bin Sultan, a senior member of the royal family and son of the Crown Prince said: "If you tell me that building this whole country ... out of $400bn, that we misused, or got, $50bn, I'll tell you, 'Yes. So what?'."[51]
The most widely reported example of Saudi royal family corruption relates to the Al-Yamamah arms deal. In 2003 and 2004, the British newspaper The Guardian and the BBC respectively claimed that BAE Systems had engaged in the payment of bribes to members of the Saudi royal family in relation to its 'Al-Yamamah' contract.[52][53] These allegations ultimately led to separate investigations by the UK's Serious Fraud Office and the United States Department of Justice.[54][55] Although the UK investigation was halted following Saudi political pressure,[56][57][58] the US investigation resulted in BAE Systems being fined $400 million under a plea bargain arrangement in March 2010.[59]
King Abdullah, since his accession in 2005, has attempted to modernise and reform the Saudi government by making significant personnel changes in government (including making the first appointment of a woman to a ministerial post[60]) and seemingly adopting a more open approach.[29] This has, reportedly, been opposed by the Sudairi faction in the royal family.[61][62] However, the changes have been criticized as being too slow or merely cosmetic.[63] The question of reform remains a significant issue within the royal family and it is reported that it continues to play a major part in the internal politics of the succession.[62]
The political role of the Ulema and the Al ash-Sheikh
According to the Saudi Ministry of Information, because Saudi Arabia is an Islamic state, "it is ... inevitable that the Ulema should play a key role within the Kingdom. They play an influential part in [a number of] fields of government". These include the judicial system (the Ulema being the interpreters and dispensers of Sharia law), education and scientific research (through control of the education system and the Ministry of Education).[64]
The ulema, the religious and clerical leadership, are led by the Al ash-Sheikh, who are the descendants of Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab founder of the dominant Wahhabi form of Sunni Islam in Saudi Arabia. The alliance between the Al-Saud (the royal family) and the Al ash-Sheikh has existed since the First Saudi State and is based on a power-sharing understanding whereby the Al-Saud have political predominance but will support and propagate the Al ash-Sheikh's Wahhabism while the Al ash-Sheikh have predominance in religious matters but will support the Al-Saud's rule.[65][66][67]
Despite this long-standing balance of power, the ash-Sheikh family, and the Ulema as a whole, have in recent years exercised influence beyond purely religious matters and have had decisive involvement in key political decisions, for example the imposition of the oil embargo in 1973 or the invitation to foreign troops to Saudi Arabia in 1990.[65]
The current leader of the Al ash-Sheikh is Abdul-Aziz ibn Abdullah Al ash-Sheikh, Grand Mufti of Saudi Arabia[68]
Politics, opposition to the regime and Islamist terrorism
As noted above, there are no recognized political parties or national elections, except for one local election, which was held in 2005, when participation was reserved for male citizens only. Participation in the political process is limited to a relatively small segment of the population and the political process is centred on the royal family, and to some extent, the tradional tribal structure. The extensive royal family is the main forum for politics in the country as it is divided by political factions and clan loyalties - the most prominent faction being the Al Fahd, previously known as the 'Sudairi Seven' (members of which include the late King Fahd and the current Crown Prince) It is reported that, with the current generation of senior princes of the royal family likely to die out in the next few years, there is on-going faction-fighting over the succession to the crown amongst the next generation of the family. Tribal identity remains strong and, outside of the royal family, political influence is frequently determined by tribal affiliation. Tribal sheikhs maintain a considerable degree of influence over local and national events. The tribal hierarchy in the country is complex, made up of a handful of very influential major tribes and a number of smaller, less-influential ones. [69][70][71][8][72]
Additionally, outside of this polity, the rule of the Al Saud faces political opposition from four sources: Sunni Islamist activism; liberal pro-democracy critics; the Shiite minority - particularly in the Eastern Province; and long-standing tribal and regional particularist opponents (for example in the Hejaz).[73] Of these, the Islamist activists have been the most prominent threat to the regime and have in recent years perpetrated a number of violent or terrorist acts in the country.[27]

Saudi Arabia has been a source of Islamist terrorist activity not just internally but also world-wide. Osama bin Laden and 15 out of the 19 9/11 hijackers were Saudi nationals[74] and former CIA director James Woolsey described Saudi Arabian Wahhabism as "the soil in which Al-Qaeda and its sister terrorist organizations are flourishing."[75]
According to a 2009 U.S. State Department communication by Hillary Clinton, United States Secretary of State, (disclosed as part of the Wikileaks U.S. 'cables leaks' controversy in 2010) "donors in Saudi Arabia constitute the most significant source of funding to Sunni terrorist groups worldwide".[76] Part of this funding arises through the zakat (or religious tax) required to be paid by all Saudis to charities, and amounting to at least 2.5 percent of their income. Although many charities are genuine, others, it is alleged, serve as fronts for money laundering and terrorist financing operations. While many Saudis contribute to those charities in good faith believing their money goes toward good causes, it has been alleged that others know full well the terrorist purposes to which their money will be applied.[27][75]
Law
The Basic Law, in 1992, declared that Saudi Arabia is a monarchy ruled by the progeny of King Abdul Aziz Al Saud. It also declared the Qur'an as the constitution of the country, governed on the basis of Islamic law.[77]
As part of his broader reforms of the Saudi government, King Abdullah initiated a number of reforms of the Saudi Court system in the 2007 Law of the Judiciary with the aim of making it more efficient and independent.[78] Saudi administration of justice has been criticized as 'slow and arcane' and 'one of the most frustrating barriers to doing business effectively in Saudi Arabia'.[79]
Criminal cases are tried under Sharia courts in the country. These courts exercise authority over the entire population. Cases involving small penalties are tried in Shari'a summary courts. More serious crimes are adjudicated in Shari'a courts of common pleas. Courts of appeal handle appeals from Shari'a courts.[77]
Civil cases may also be tried under Sharia courts with one exception: Shiites may try such cases in their own courts. Other civil proceedings, including those involving claims against the Government and enforcement of foreign judgments, are held before specialized administrative tribunals, such as the Commission for the Settlement of Labor Disputes and the Board of Grievances.[77]
The king acts as the highest court of appeal and has the power to pardon.[citation needed]
Main sources of Saudi law are Hanbali fiqh as set out in a number of specified scholarly treatises by authoritative jurists, other schools of law, state regulations and royal decrees (where these are relevant), and custom and practice.[80]
The Saudi legal system prescribes capital punishment or corporal punishment.Theft is punishable by amputation of the hand, although it is rarely prescribed for a first offense. The courts may impose other harsh punishments, such as floggings, for less serious crimes against public morality such as drunkenness.[81] Murder, accidental death and bodily harm are open to punishment from the victim's family. Retribution may be sought in kind or through blood money. The blood money payable for a woman's accidental death is half as much as that for a Muslim male.[82] This is mainly because Islamic law requires men to be providers for their families, and therefore to earn more money in their lifetimes. The blood money for a man would be expected to sustain his family, at least for a short time.
Money payable for the death of a Christian or Jewish male is also half that for a Muslim male; all others (e.g. Hindus, Buddhists, and Sikhs) are valued at 1/16th.[83]
Slavery was legal in Saudi Arabia until abolished in 1962.[84][85]
The freedom of women is seriously restricted in Saudi Arabia. Women are not allowed to travel without the permission of their closest male relative, who may be a son or a younger brother. Women who are divorced, return under their father's authority and like any other adult woman is denied the right to live on her own and to marry of her free will.[86] Furthermore, the Saudi government considers filial "disobedience" as a crime for which women have been imprisoned or have lost custody of their child.[86] Saudi Arabia is the only country in the world where women are banned from driving in major cities and towns, although they may drive in small towns and villages or in private housing compounds—some of which extend to many square miles.[87] The Saudi Shura Council recommended in 2008 that the ban be relaxed, allowing young women to drive subject to some restrictive conditions.[88]
In Saudi Arabia, homosexuality is illegal and punishable by a range of penalties, including corporal punishment and the death penalty.[89]
The Government views its interpretation of Islamic law as its sole source of guidance on human rights. In 2000 the Government approved the October legislation, which the Government claimed would address some of its obligations under the Convention against Torture or Other Cruel, Inhuman, or Degrading Treatment or Punishment.[77]
The first independent human rights organization, the National Society for Human Rights was established in 2004. The Saudi Government is an active censor of Internet communication within its borders.[90] A Saudi blogger, Fouad al-Farhan, was jailed for five months in solitary confinement in December, 2007, without charges, after criticizing Saudi religious, business and media figures.[91]
Foreign relations
Saudi Arabia is one of the largest contributors of development aid, both in volume of aid and in the ratio of aid volume to GDP.[92][93]
All of Saudi Arabia's aid has gone to Islamic countries.[7] This aid has contributed to the spreading of Islam of the sort found in Saudi Arabia, rather than fostering the traditions of the receiving ethnic groups. The effect has been the erosion of regional Islamic cultures through standardization. Examples of the acculturizing effect of Saudi aid can be seen among the Minangkabau and the Acehnese in Indonesia, as well as among the people of the Maldives.[94][95][96][97]
On the 18 December 2008, the William J. Clinton Foundation released a list of all contributors. It included The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, which gave between US$10–25 million.[98]
In addition, Saudi Arabia remains one of the United States' allies in the region, and relations between the two countries go back as far as 1931 when the US first extended diplomatic recognition. In 1945 President Roosevelt and King Abdulaziz bin Saud met on board a ship to discuss relations between the two countries. Since then, the two countries have maintained close relations for economic and political reasons.
Military

Saudi military was founded as the Ikhwan army, the tribal army of Ibn Saud. The Ikhwan had helped King Ibn Saud conquer the Arabian peninsula during the First World War. By expanding the military forces years later, Saudi Arabia today has many military branches.
- Military branches of Ministry of Defence:
- Independent Military branches:
- Military branches of Ministry of Interior:
- Saudi Arabian Police Force
- Saudi Arabian Border Guard
- Saudi Border Guard
- Saudi Coast Guard
- Al-Mujahidoon
- Saudi Emergency Force
The United States sold more than $80 billion in military hardware between 1951-2006 to the Saudi military.[99] In comparison, the Israel Defense Forces received $53.6 billion in US military grants between 1949-2007.[100]
On October 20, 2010, U.S. State Department notified Congress of its intention to make the biggest arms sale in American history - an estimated $60.5 billion purchase by the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The package represents a considerable improvement in the offensive capability of the Saudi armed forces.[101]
The U.S. was keen to point out that the arms transfer would increase "interoperability" with U.S. forces. In the 1990-1991 Gulf War, having U.S.-trained Saudi forces, along with military installations built to U.S. specifications, allowed the American armed forces to deploy in a comfortable and familiar battle environment. This new deal would increase these capabilities, as an advanced American military infrastructure is about to be built.[102] The US government is also in talks with Saudi Arabia about the potential sale of advanced naval and missile-defense upgrades worth up to tens of billions of dollars.[103]
Geography

Borders and Terrain
The Kingdom occupies about 80 percent of the Arabian peninsula, lying between latitudes 16° and 33° N, and longitudes 34° and 56° E. In 2000 Saudi Arabia and Yemen signed an agreement to settle their long-running border dispute.[107] A significant length of the country's southern borders with the United Arab Emirates and Oman are not precisely defined or marked, so the exact size of the country remains unknown. The Saudi government's estimate is 2,217,949 km2 (856,355 sq mi). Other reputable estimates vary between 1,960,582 km2 (756,985 sq mi)[108] and 2,240,000 km2 (864,869 sq mi). The kingdom is commonly listed as the world's 14th largest state.
Saudi Arabia's geography is dominated by the Arabian Desert and associated semi-desert and shrubland - see satellite image to right - which is, in fact, a number of linked deserts. Among them is the world’s largest sand area, the Rub' al Khali (“Empty Quarter”), which dominates the southern part of the country and covers more than 250,000 square miles (647,500 square km). It slopes from above 2,600 feet (800 metres) near the border with Yemen northeastward down almost to sea level near the Persian Gulf. A smaller sand area of about 22,000 square miles (57,000 square km), called Al-Nafūd, is in the north-central part of the country. A great arc of sand, Al Dahna, almost 900 miles (1,450 km) long but in places only 30 miles (50 km) wide, joins Al-Nafūd with the Rubʿ al-Khali.[8]
The main topographical feature is the central plateau which rises abruptly from the Red Sea and gradually descends into the Nejd and toward the Persian Gulf. The plateau's elevation is about 4,500 feet (1,370 metres) in the west and about 2,500 feet (760 metres) in the east. As the plateau slopes down to the gulf, there are numerous salt flats (sabkhahs) and marshes. In the north, the western highlands are upward of 5,000 feet (1,500 metres) above sea level, decreasing slightly to 4,000 feet (1,200 metres) in the vicinity of Medina and increasing southeastward to more than 10,000 feet (3,000 metres). On the Red Sea coast, the narrow coastal plain, known as the Tihamah is virtually nonexistent in the north and widens slightly toward the south. An imposing escarpment runs parallel to the Red Sea but is interrupted by a gap northwest of Mecca. The southwest province of Asir is mountainous, and contains Mount Sawda, which is generally considered the highest point in the country. Estimates of its elevation range from 10,279 to 10,522 feet (3,133 to 3,207 metres). [8]
Climate
Except for the south western province of Asir, Saudi Arabia has a desert climate with extremely high day-time temperatures and a sharp temparature drop at night. Average summer temperatures are around 45° C, but can be as high as 54° C. In the winter the temperature rarely drops below 0° C. In the spring and autumn the heat is temperated, temperatures average around 29° C. Annual rainfall is extremely low. The Asir region differs in that it is influenced by the Indian Ocean monsoons, usually occurring between October and March. An average of 300 millimeters of rainfall occurs during this period, that is about 60 percent of the annual precipitation.[109] Emma Lee Allen is gay
Flora and Fauna
Native animals include the ibex, wildcats, baboons, wolves, hyenas and Arabian leopard in the mountainous highlands. Small birds are found in the oases. The coastal area on the Red Sea, with its coral reefs, has a rich marine life.
Reflecting the country's desert conditions, Saudi Arabia’s plant-life mostly consists of small herbs and shrubs requiring little water. There are a few small areas of grass and trees in southern Asir. The date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) is widespread.[8]
Provinces
Saudi Arabia is divided into 13 provinces[110] (manatiq, – singular mintaqah). The provinces are further divided into governorates.
Economy


Saudi Arabia's command economy is petroleum-based; roughly 75% of budget revenues and 90% of export earnings come from the oil industry. The oil industry comprises about 45% of Saudi Arabia's gross domestic product, compared with 40% from the private sector (see below). Saudi Arabia officially has about 260 billion barrels (4.1×1010 m3) of oil reserves, comprising about one-fifth of the world's proven total petroleum reserves.[111]
The government is attempting to promote growth in the private sector by privatizing industries such as power and telecommunications. Saudi Arabia announced plans to begin privatizing the electricity companies in 1999, which followed the ongoing privatization of the telecommunications company. Shortages of water and rapid population growth may constrain government efforts to increase self-sufficiency in agricultural products.
In the 1990s, Saudi Arabia experienced a significant contraction of oil revenues combined with a high rate of population growth. Per capita income fell from a high of $11,700 at the height of the oil boom in 1981 to $6,300 in 1998.[112] Recent[when?] oil price increases have helped boost per capita GDP to $17,000 in 2007 dollars, or about $7,400 adjusted for inflation.[113]
Oil price increases of 2008-2009 have triggered a second oil boom, pushing Saudi Arabia's budget surplus to $28 billion (110SR billion) in 2005. Tadawul (the Saudi stock market index) finished 2004 with a massive 76.23% to close at 4437.58 points. Market capitalization was up 110.14% from a year earlier to stand at $157.3 billion (589.93SR billion), which makes it the biggest stock market in the Middle East.
OPEC (the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries) limits its members' oil production based on their "proven reserves." The higher their reserves, the more OPEC allows them to produce.[citation needed] Saudi Arabia's published reserves have shown little change since 1980, with the main exception being an increase of about 100 billion barrels (1.6×1010 m3) between 1987 and 1988.[114] Matthew Simmons has suggested that Saudi Arabia is greatly exaggerating its reserves and may soon show production declines (see peak oil).[115]
To diversify the economy, Saudi Arabia launched a new city on the western coast with investments exceeding $26.6 billion. The city, which is named "King Abdullah Economic City", will be built near al-Rabegh industrial city north of Jeddah. The new city, where construction work started in December 2005, includes a port which is the largest port of the kingdom. Extending along a coastline of 35 km, the city will also include petrochemical, pharmaceutical, tourism, finance and education and research areas. Saudi Arabia officially became a World Trade Organization member in December 2005.
Development
Saudi Arabia is one of only a few fast-growing countries in the world with a high per capita income of $20,700 (2007). Saudi Arabia will be launching six "economic cities" (e.g. King Abdullah Economic City)[116] which are planned to be completed by 2020. These six new industrialized cities are intended to diversify the economy of Saudi Arabia, and are expected to increase the per capita income. The King of Saudi Arabia has announced that the per capita income is forecast, to rise from $15,000 in 2006 to $33,500 in 2020.[117] The cities will be spread around Saudi Arabia to promote diversification for each region and their economy, and the cities are projected to contribute $150 billion to the GDP.
However the urban areas of Riyadh and Jeddah are expected to contribute $287 billion dollars by the year 2020.[118]
Foreign labour
Despite the government's efforts to promote Saudization, the country draws a significant portion of its labour force from foreign countries, especially from South and Southeast Asia (notably India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Indonesia, the Philippines, Nepal, Sri Lanka), East Africa and from other Middle Eastern countries.[119] There are also some people from East Asia, North America, South America, and Europe. Hundreds of thousands of low-skilled workers and skilled workers from regions of the developing world migrate to Saudi Arabia, sometimes only for a short period of time, to work. Although exact figures are not known, skilled experts in the banking and services professions seek work in the kingdom.
Demographics
Population
Saudi Arabia is one of the most sparsely populated countries in the world. Its population as of July 2010 is estimated to be 25,731,776 including 5,576,076 non-nationals[2] Until the 1960s, a majority of the population was nomadic; but presently more than 95% of the population is settled, due to rapid economic and urban growth. As recently as the early 1960s, the Saudi Arabia’s slave population was estimated at 300,000.[120] Slavery was officially abolished in 1962.[84][85] The birth rate is 29.56 births per 1,000 people and the death rate is 2.62 deaths per 1,000 people. Some cities and oases have densities of more than 1,000 people per square kilometer (2,600/sq mi).
About 31% of the population is made up of foreign nationals living in Saudi Arabia.[121] A large portion of the expatriate population is South Asian or of South Asian ancestry, including Indians, Pakistanis, and Bangladeshis. In addition, there are some non-Arab citizens and of mixed ancestry [citation needed]. According to a random survey, most would-be Saudis come from the Subcontinent and Arab countries.[122] Many Arabs from nearby countries are employed in the kingdom. There are over eight million migrants from countries all around the world (including non-Muslims):[123] Indian: 1.3 million, Pakistani: 900,000, Bangladeshi: 400,000, Filipino: 500,000, Egyptian: 900,000, Yemeni: 800,000, Indonesian: 250,000, Sri Lankan: 350,000, Sudanese: 250,000, Syrian: 100,000 and Turkish: 80,000.[124] There are around 100,000 Westerners in Saudi Arabia, most of whom live in compounds or gated communities. Although Arabic is the official language, English is the lingua franca of the country and is very widely spoken by residents.[citation needed]
In the 1970s and 1980s, there was also a significant community of South Koreans, numbering in the hundreds of thousands, but most have since returned home.[125] Saudi Arabia expelled 800,000 Yemenis in 1990 and 1991 to punish Yemen for its opposition to the Gulf War against Iraq.[126] An estimated 240,000 Palestinians are living in Saudi Arabia. They are not allowed to hold or even apply for Saudi citizenship, because of Arab League instructions barring the Arab states from granting them citizenship. Palestinians are the sole foreign group that cannot benefit from a 2004 law passed by Saudi Arabia's Council of Ministers, which entitles expatriates of all nationalities who have resided in the kingdom for ten years to apply for citizenship with priority being given to holders of degrees in various scientific fields.[127] The Articles 12.4 and 14.1 of the Executive Regulation of Saudi Citizenship System can be interpreted as requiring applicants to be Muslim.[128] The Saudi royal family and official creed of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is Sunnism. According to a study conducted by Dr. Nura Al-Suwaiyan, director of the family safety program at the National Guard Hospital, one in four children is abused in Saudi Arabia.[129] The National Society for Human Rights reports that almost 45% of the country's children are facing some sort of abuse and domestic violence.[130]
Cities
<centre>
| Largest Cities by Population (2009) |
mill. |

|
File:Jeddah corniche rosewoood.JPG | 
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Riyadh | 6.5 | |||
| Jeddah | 3.9 | |||
| Mecca | 1.8 | |||
| Medina | 1.6 | Riyadh | Jeddah | Mecca |
| Al-Hasa | 1.4 |  |
File:Dammam2.jpg | File:Khobar.jpg |
| Dammam | 1.3 | |||
| Tabuk | 0.8 | |||
| Buraidah | 0.7 | |||
| Khamis Mushait | 0.6 | |||
| Abha | 0.5 | |||
| Al-Khubar | 0.4 | Medina | Dammam | Al-Khobar |
Languages
The official language of Saudi Arabia is Arabic. The three main regional variants spoken by Saudis are Hejazi Arabic (about 6 million speakers), Nejdi Arabic (about 8 million speakers) and Gulf Arabic (about 200,000 speakers). The large expatriate communities also speak their own languages, the most numerous being Tagalog (700,000), Urdu (380,000), and Egyptian Arabic (300,000).[131]
Religion
There are about 25 million people who are Muslim, or 97% of the total population.[132] Data for Saudi Arabia comes primarily from general population surveys, which are less reliable than censuses or large-scale demographic and health surveys for estimating minority-majority ratios.[132] About 85-90% of Saudis are Sunni, while Shias represent around 10-15% of the Muslim population.[133] Most follow the Hanbali school of jurisprudence, though there are significant numbers of followers among the Shafi`i school, and the Maliki school. On February 14, 2009, the king reorganized the Council of Senior Scholars to include scholars from all four schools of Islamic jurisprudence. Since the 1920s, the government had officially adhered to the Hanbali school by declaring two Hanbali sources as the only acceptable references for Saudi judges. The reorganization of the council is the first official recognition of the other three schools in the country since that time. Most scholars and judges, however, are still Hanbali.[123]

The official and dominant form of Sunni Islam in Saudi Arabia is commonly known as Wahhabism (a name which some of its proponents consider derogatory, preferring the term Salafism).[134] Wahhabism, founded in the Arabian peninsular by Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab in the eighteenth century, is often described as 'puritanical', 'intolerant' or 'ultra-conservative'. However, proponents consider that its teachings seek to purify the practise of Islam of any innovations or practices that deviate from the seventh-century teachings of the Islamic Prophet Muhammad and his companions[135]
As noted earlier (Government and Politics) Saudi Arabia is a source of Sunni Islamist activity, including violent or terrorist Islamist activity[27] and "donors in Saudi Arabia constitute the most significant source of funding to Sunni terrorist groups worldwide".[136]
Religious freedom is virtually non-existent in Saudi Arabia. The Government does not provide legal recognition or protection for freedom of religion, and it is severely restricted in practice. As a matter of policy, the Government guarantees and protects the right to private worship for all, including non-Muslims who gather in homes for religious practice; however, this right is not always respected in practice and is not defined in law.[137] Moreover, the preaching and public practice of non-Muslim religions is prohibited.[123] The Saudi Mutaween or Committee for the Propagation of Virtue and the Prevention of Vice (CPVPV), i.e. the religious police, enforces the prohibition on the public practice of non-Muslim religions. There are no churches or other non-Muslim houses of worship permitted in the country, even within embassies, but non-Muslim religious items are legal even though they are sometimes confiscated by the CPVPV. Practitioners of other religions must only worship in private. The Catholic Church is currently trying to negotiate to have an unmarked church in Saudi Arabia to minister to the over 1 million Roman Catholics mainly of Fillipino origin who are in the country as foreign workers.
Proselytizing by non-Muslims is illegal, and conversion by Muslims to another religion (apostasy) carries the death penalty, although there have been no confirmed reports of executions for apostasy in recent years.[123]
Women in Saudi society

The World Economic Forum 2010 Global Gender Gap Report ranked Saudi Arabia 129th out of 134 countries for gender parity. It was the only country to score a zero in the category of political empowerment.[138]
Gender roles in Saudi society originate from Sharia (Islamic law) and tribal culture. Women's social and legal position in Saudi Arabia differs substantially from that of men. For example, all women, regardless of age, are required to have a male guardian.[139] As a consequence, women of any age need the permission of their guardian (who could be their son or younger brother) for a wide range of activities including marriage and divorce, travel, education, employment, opening a bank account, and surgery and this has led Human Rights Watch to describe Saudi women as being permanently treated as children.[140][139][141][142][143][144][145]
Female literacy is estimated to be around 70% compared to male literacy of around 85%.[146] Men can marry girls as young as ten in Saudi Arabia[147] and, quite apart from the other considerable damage to the children involved,[148] child marriage is believed to hinder the cause of women's education. The drop-out rate of girls increases around puberty, as they exchange education for marriage. Roughly 25% of college-aged young women do not attend college, and in 2005–2006, women had a 60% dropout rate.[149]
In most of the country, women in public wear the niqab (veil), as well as a hijab (head covering), and full black cloak called an abaya, and there is considerable pressure on them to follow this dress code.[150][151][152]
Leading Saudi feminist and journalist, Wajeha al-Huwaider, has said "Saudi women are weak, no matter how high their status, even the 'pampered' ones among them, because they have no law to protect them from attack by anyone. The oppression of women and the effacement of their selfhood is a flaw affecting most homes in Saudi Arabia."[153]
Although many Saudis would like more freedom in Saudi Arabia, there is evidence that many women do not want radical change.[154] Even many advocates of reform reject foreign critics, for "failing to understand the uniqueness of Saudi society."[141][155]
A number of Saudi women have risen to the top of some professions or otherwise achieved prominence:
- Mrs. Norah AlFayez , the first Saudi female to be appointed as a minister (Deputy Minister of Education, with responsibility for female education).[156]
- Dr. Arwa AlSayyid , a leading periodontist in dental implantation.[157]
- Dr. Hayat Sindi , co-founder of "Diagnostics For All" which offers point-of-care diagnostic tools micro-fabricated in paper; she was chosen by "Poptech" science magazine as among the top 15 scientists expected to change the world.[158]
- Dr. Ghada Al-Mutairi,heads a medical research center in California.[159]
- Dr. Khawla AlKuraya , a consultant and the principal clinical scientist at the King Faisal Hospital and Research Center and heads the Riyadh-based King Fahd National Center, which is the only children’s cancer center in the Middle East.[160][161]
- Ms. Ghada Ba-Aqeel,awarded the "Best Women's Business" in the world in 2009, by the Youth Organization of Global Business (YBI).[162]
- Dr. Howaida Obaid al-Qethamy, a pediatric and neonatal heart surgeon[159]
- Ms. Umaima al-Khamis,novellist whose book, al-Warfah (The Leafy), was listed for the Arabic Booker Prize 2010, also known as the International Prize for Arabic Fiction (IPAF).[162]
- Dr. Soraya Al-Turki,a Professor of Anthropology at the American University in Cairo.[162]
- Dr. Salwa Al-Hazzaa, head of the ophthalmology department at King Faisal Specialist Hospital in Riyadh and was the late King Fahad’s personal ophthalmologist.[163]
- Ms.Hanadi AlHindi, Saudi Arabia's first female pilot.[164]
- Ms. Arwa Mutabagani, The first female member of the Saudi Olympic delegation.[165]
Education
When the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia was founded in 1932, education was not accessible to everyone and limited to individualized instruction at religious schools in mosques in urban areas. These schools taught Islamic law and basic literacy skills. By the end of the century, Saudi Arabia had a nationwide educational system providing free training from preschool through university to all citizens.
The primary education system began in Saudi Arabia in the 1930s. By 1945, King Abdulaziz bin Abdelrahman Al-Saud, the country's founder, had initiated an extensive program to establish schools in the Kingdom. Six years later, in 1951, the country had 226 schools with 29,887 students. In 1954, the Ministry of Education was established, headed by then Prince Fahd bin Abdulaziz as the first Minister of Education. The first university, now known as King Saud University, was founded in Riyadh in 1957.
Today, Saudi Arabia has 59 universities and higher education colleges and more than 24,000 schools. The system provides students with free education, books and health services and is open to every Saudi. Over 25% of the annual State budget is for education including vocational training.
Schools in Saudi Arabia are divided into: elementary (six grades), intermediate (three grades), and High (three grades). For elementary and intermediate levels, subjects taught include: Islamic studies, Mathematics, Science, History, Geography, Arabic syntax and diction, Arabic literature, Computer skills, English, art and drawing, and physical science. On their first year of high school, students must choose among different tracks which are : Natural Sciences, Literature, Islamic studies, and Social and Managerial Sciences. There are common courses among the different tracks, but the emphasis area is different. For example,The Natural Sciences track emphasizes Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Geology, Computer Science, and English while less emphasis is on Islamic studies and Literature.
Universities in Saudi Arabia are distributed in all the thirteen provinces and are either public or private. Many subjects are being taught in these universities such as Medicine, Pharmacology, Engineering, Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Petroleum sciences, Philosophy, Psychology, Literature, Management, Finance, Accounting, Marketing, Political Science, Computer Science, Law, Fiqh, Hadith, etc. The Kingdom has also worked on scholarship programs to send students overseas to the United States, Canada, France, United Kingdom, Australia, Japan, Malaysia, Spain, Germany, China, Singapore, South Korea and other nations. Currently tens of thousands of Saudi male and female students are being sent to higher-education programs every year under the King Abdullah Scholarship Program. More than 23,000 students study in the United States only.[166]
However, the Saudi education system is subject to extensive criticism: "The country needs educated young Saudis with marketable skills and a capacity for innovation and entrepreneurship. That's not generally what Saudi Arabia's educational system delivers, steeped as it is in rote learning and religious instruction."[167]
The study of Islam dominates the Saudi educational system. In particular, the memorization by rote of large parts of the Qu'ran, its interpretation and understanding (Tafsir) and the application of Islamic tradition to everyday life is at the core of the curriculum. Religion taught in this manner is also a compulsory subject for all University students.[168] As a consequence, Saudi youth “generally lacks the education and technical skills the private sector needs”.[146]
A further criticism of the religious focus of the Saudi education system is the nature of the Wahhabi-controlled curriculum. The Islamic aspect of the Saudi national curriculum was examined in a 2006 report by Freedom House which concluded that "the Saudi public school religious curriculum continues to propagate an ideology of hate toward the “unbeliever,” that is, Christians, Jews, Shiites, Sufis, Sunni Muslims who do not follow Wahhabi doctrine, Hindus, atheists and others"[169][170] The Saudi religious studies curriculum is taught outside the Kingdom in madrasah throughout the world. Critics have described the education system as ‘medieval’ and that its primary goal ‘is to maintain the rule of absolute monarchy by casting it as the ordained protector of the faith, and that Islam is at war with other faiths and cultures’.[171]
The consequence of this approach is considered by many, including, it appears, the Saudi government, to have encouraged Islamic terrorism.[172] To tackle the twin problems of encouraging extremism and the inadequacy of the country's university education for a modern economy, the government is aiming to slowly modernise the education system through the ‘Tatweer’ reform program.[172] The Tatweer program is reported to have a budget of approximately US$2 billion and focuses on moving teaching away from the traditional Saudi methods of memorization and rote learning towards encouraging students to analyze and problem-solve as well as creating a more secular and vocationally-based education system.[173][167]
Culture
Saudi Arabian culture mainly revolves around both Islamic and tribal values. Islam's two holiest sites, Mecca and Medina, are located in the country. Five times every day, Muslims are called to prayer from the minarets of mosques which are scattered around the country. The weekend begins on Thursday due to Friday being the holiest day for Muslims. Most Muslim countries have a Thursday-Friday or Friday-Saturday weekend.[174] Saudi Arabia's cultural heritage is celebrated at the annual Jenadriyah cultural festival.
Islamic heritage sites

Saudi Arabia, and specifically the Hejaz, as the cradle of Islam, has many of the most significant historic Muslim sites including the two holiest sites of Mecca and Medina.[175] One of the King's titles is Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques, the two mosques being Masjid al-Haram in Mecca, which contains Islam's most sacred place, the Kaaba, and Masjid Al-Nabawi in Medina which contains Muhammad's tomb.[176][177]
However, Saudi Wahhabism is hostile to any reverence given to historical or religious places of significance for fear that it may give rise to 'shirk' (that is, idolatry). As a consequence, under Saudi rule, the Hejaz cities have suffered from considerable destruction of their physical heritage and, for example, it has been estimated that about 95% of Mecca's historic buildings, most over a thousand years old, have been demolished.[178] These include the mosque originally built by Muhammad's daughter Fatima, and other mosques founded by Abu Bakr (Muhammad's father-in-law and the first Caliph), Umar (the second Caliph), Ali (Muhammad's son-in-law and the fourth Caliph), and Salman al-Farsi (another of Muhammad's companions).[179] Other historic buildings that have been destroyed include the house of Khadijah, the wife of the Prophet, demolished to make way for public lavatories; the house of Abu Bakr, now the site of the local Hilton hotel; the house of Ali-Oraid, the grandson of the Prophet, and the Mosque of abu-Qubais, now the location of the King's palace in Mecca.[180]
Critics have described this as "Saudi vandalism" and claim that over the last 50 years 300 historic sites linked to Muhammad, his family or companions have been lost.[181] It has been reported that there now are fewer than 20 structures remaining in Mecca that date back to the time of Muhammad.[180]
Music and dance

One of Saudi Arabia's most popular folk rituals is the Al Ardha, the country's national dance. This sword dance is based on ancient Bedouin war traditions: drummers beat out a rhythm and a poet chants verses while sword-carrying men dance shoulder to shoulder. Al-sihba folk music, from the Hejaz, has its origins in al-Andalus. In Mecca, Medina and Jeddah, dance and song incorporate the sound of the mizmar, an oboe-like woodwind instrument in the performance of the Mizmar dance. The drum is also an important instrument according to traditional and tribal customs. Samri is a popular traditional form of music and dance in which poetry is sung especially in the Eastern Region of Saudi Arabia. Saudi Arabian Musical tradition depends heavily on the modern Arabian oud.
- Al Ardha (Arabic: العرضة) is a type of folkloric war dance performed by the Bedouin tribes of the Arabian peninsula, It was traditionally only performed before going to war, but nowadays is performed at celebrations or cultural events, such as the Jenadriyah festival. The dance, which is performed by men carrying swords or canes, is accompanied by drums and spoken verse.
- Mizmar (Arabic: مزمار) is the name of a folkloric dance native to the Hejaz region of Saudi Arabia. The dance involves moving while twirling a bamboo cane (tool) cane, to the music of drums.
- Samri (Arabic: سامري) is the name of a folkloric music and dance. It involves singing poetry while the daff drum is being played. Two rows of men, seated on the knees sway to the rhythm.
Dress
Saudi Arabian dress strictly follows the principles of hijab (the Islamic principle of modesty, especially in dress). The predominantly loose and flowing, but covering, garments are suited to Saudi Arabia's desert climate. Traditionally, men usually wear an ankle length shirt woven from wool or cotton (known as a thawb), with a keffiyeh (a large checkered square of cotton held in place by a cord coil) or a ghutra (a plain white square made of finer cotton, also held in place by a cord coil) worn on the head. For rare chilly days, Saudi men wear a camel-hair cloak (bisht) over the top. Women's clothes are decorated with tribal motifs, coins, sequins, metallic thread, and appliques. Women are required to wear an abaya or modest clothing when in public.
- Ghutrah (Arabic: غتره) is a traditional headdress typically worn by Arab men. It is made of a square of cloth ("scarf"), usually cotton, folded and wrapped in various styles around the head. It is commonly worn in areas with an arid climate, to provide protection from direct sun exposure, and also protection of the mouth and eyes from blown dust and sand.
- Agal (Arabic: عقال) is an Arab headdress constructed of cord which is fastened around the Ghutrah to hold it in place. The agal is usually black in colour.
- Thawb (Arabic: ثوب) is the standard Arabic word for garment. It is ankle length, usually with long sleeves similar to a robe.
- Bisht (Arabic: بشت) is a traditional Arabic men’s cloak usually only worn for prestige on special occasions such as weddings.
- Abayah (Arabic: عباية) is a women's garment. It is a black cloak which loosely covers the entire body except the head. Usually, the sleeves are decorated with stitched embroidery and different bright colors or even crystals, and the rest of the cloak is plain.Some women choose to cover their faces with the Niqab and some do not. Recently, there's a move towards Abaya colors other than black especially in the Makkah Province in the west of the Kingdom.
- Kameez/Kurta Salwar is a men's and women's garment. It is worn by Indian and Pakistani people in Saudi Arabia.
Cuisine
Arabic leavened bread, or khobz, is eaten with almost all meals. Other staples include lamb, grilled chicken, falafel (deep-fried chickpea balls), shawarma (spit-cooked sliced lamb- or chicken), and hummus (a paste of chickpea, garlic and lemon). Traditional coffeehouses used to be ubiquitous, but are now being displaced by food-hall style cafes. Arabic tea is also a famous custom, which is used in both casual and formal meetings between friends, family and even strangers. The tea is black, served without milk and often has one of a variety of herbal flavorings.
Film and theater
During the 1970s, cinemas were numerous in the Kingdom and were not considered a deviation from religious norms, although they were pressured from tribal norms.[182] It was only during the Islamic revival movement in the 1980s that Islamic Ulams's teaching influenced the government's Cinema policy. Public theaters and cinemas were prohibited as several Saudi ulama(expertise in Islamic studies) deemed those institutions to be incompatible with Islam. However, lately (as of 2009), a reform is being undertaken in the country, in which several cinemas and movies had been shown under serious objections raised by several Saudi groups.[183] An IMAX theater is also available,[184] and in private compounds such as Dhahran and Ras Tanura public theaters can be found, but they are often more popular for local music, arts and theatre productions, rather than the exhibition of motion pictures. DVDs, including American and British movies, are legal and widely available.
Literature
Some Saudi novelists have had their books published in Beirut, Lebanon, because of censorship in Saudi Arabia. Despite signs of increasing openness, Saudi novelists and artists in film, theatre, and the visual arts face greater restrictions on their freedom of expression than in the West. Contemporary Saudi novelists include:
- Abdul Rahman Munif (exiled, now deceased)
- Yousef Al-Mohaimeed
- Abdu Khal
- Turki al-Hamad (subject of a fatwā and death threats)
- Ali al-Domaini
- Ahmed Abodehman (now writes in French)
Sports
Men can often be found playing sports. Women rarely participate in sports, and always away from the presence of men; this often leads to indoor gyms. association football is the most popular sport. Saudi Arabia has recently participated in the Summer Olympic Games and in international competitions in volleyball and other sports. The Saudi Arabian national youth baseball team has also participated in the Little League World Series. The Saudi Arabia national football team is often most known for competing four consecutive times in the FIFA World Cup and six times in the AFC Asian Cup.
See also
- Index of Saudi Arabia-related articles
- Politics of Saudi Arabia
- House of Saud
- Politics of Saudi Arabia
- Basic Law of Saudi Arabia
- Energy policy of Saudi Arabia
- Nuclear program of Saudi Arabia
- Foreign relations of Saudi Arabia
- Armed Forces of Saudi Arabia
- Economy of Saudi Arabia
- Saudi Riyal
- Saudi Aramco
- Demographics of Saudi Arabia
- Arab diaspora
- Culture of Saudi Arabia
- Public holidays in Saudi Arabia
- Music of Saudi Arabia
- Saudi Arabian cuisine
- Sport in Saudi Arabia
- Education in Saudi Arabia
- Telecommunications in Saudi Arabia
- Transport in Saudi Arabia
- Irrigation in Saudi Arabia
- Water supply and sanitation in Saudi Arabia
- Energy in Saudi Arabia
- Human rights in Saudi Arabia
- Human trafficking in Saudi Arabia
- LGBT rights in Saudi Arabia
- Pre-Islamic Arabia
- Freedom of religion in Saudi Arabia
- Mutaween
- Christianity in Saudi Arabia
- Roman Catholicism in Saudi Arabia
- Saudi Arabian Boy Scouts Association
Lists
- List of Arabian Houses
- List of Ambassadors from the United Kingdom to Saudi Arabia
- List of cities and towns in Saudi Arabia
- List of companies of Saudi Arabia
- List of universities and colleges in Saudi Arabia
References
- ^ About Saudi Arabia: Facts and figures, The Royal Embassy of Saudi Arabia, Washington D.C.
- ^ a b c CIA World Factbook as updated 13 January 2011; retrieved 16 January 2011
- ^ a b c d "Saudi Arabia". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 2010-04-21.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2010" (PDF). United Nations. 2010. Retrieved 5 November 2010.
- ^ "Social Services 2". Saudinf.com. 2009-04-20. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ "Royal Embassy of Saudi Arabia-London: The Kingdom Of Saudi Arabia - A Welfare State". Mofa.gov.sa. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ a b Saudis donate aid to non-Muslims
- ^ a b c d e f g h Encyclopaedia Britannica Online: Saudi Arabia
- ^ David Holden & Richard Johns, The House of Saud, Pan, 1982, 0 330 26834 1
- ^ a b c d e Saudi Embassy (US) Website retrieved 20 Jan 2011
- ^ Philip Khuri Hitti (2002), History of the Arabs, Revised: 10th Edition
- ^ See: Holt (1977a), p.74
- ^ L. Gardet. "Islam". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Encyclopaedia Britannica Online: History of Arabia retrieved 18 Jan. 2011
- ^ Encyclopaedia Britannica Online: Saudi Arabia History
- ^ a b Goodwin, Jason. Lords of the Horizons: A History of the Ottoman Empire (2003) Amazon.com
- ^ King Abdul Aziz Information Resource - First Ruler of the House of Saud retrieved 20 Jan 2011
- ^ 'Wahhabi', Encyclopedia Britannica Online retrieved 20 Jan. 2011
- ^ The Saud Family and Wahhabi Islam. Library of Congress Country Studies.
- ^ a b c Global Security Retrieved 19 Jan. 2011
- ^ David Murphy, The Arab Revolt 1916-18: Lawrence Sets Arabia Ablaze, Osprey Publishing, 2008,
- ^ a b David Murphy, The Arab Revolt 1916-18: Lawrence Sets Arabia Ablaze, Osprey Publishing, 2008
- ^ a b King Abdul Aziz Information Resource retrieved 19 January 2011
- ^ Country Data - External boundaries retrieved 19 January 2011
- ^ a b al-Rasheed, Madawi, A History of Saudi Arabia (Cambridge University Press, 2002) ISBN 0-521-64335-X
- ^ a b Robert Lacey, THE KINGDOM: Arabia & The House of Sa'ud, Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Inc, 1981 (Hard Cover) and Avon Books, 1981 (Soft Cover). Library of Congress: 81-83741 ISBN 0-380-61762-5
- ^ a b c d e 'Jihad in Saudi Arabia: Violence and Pan-Islamism since 1979' by Thomas Hegghammer, 2010, Cambridge Middle East Studies ISBN 978-0-521-73236-9
- ^ Hegghammer 2010, p. 112.
- ^ a b 'The Monarch Who Declared His Own Revolution' by Christopher Dickey, Newsweek, 21 March 2009 http://www.newsweek.com/2009/03/20/the-monarch-who-declared-his-own-revolution.html
- ^ The Economist Democracy Index 2010 http://graphics.eiu.com/PDF/Democracy_Index_2010_web.pdf
- ^ The Basic Law Saudi Ministry of Information; retrieved 26 Jan. 2011
- ^ The Law of the Council of Ministers, Royal Embassy of Saudi Arabia, Washington, DC, retrieved June 27, 2010
- ^ Library of Congress Country Profile: Saudi Arabia http://memory.loc.gov/frd/cs/profiles/Saudi_Arabia.pdf
- ^ 'The Politics of the Middle East' by Monte Palmer, 2007, ISBN 9780495007500203
- ^ "english.aljazeera.net". Retrieved 2007-06-19.
- ^ See for example: [1] [2] [3] [4]
- ^ Tom Pettifor (6/10/2010). "Gay Saudi Prince killed man servant in sexual fury". Mirror. Retrieved 6 October 2010.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b Biographies of Ministers, Royal Embassy of Saudi Arabia, Washington, DC, retrieved June 27, 2010
- ^ a b "Saudi Arabia Government", The Saudi Network, retrieved June 27, 2010
- ^ David Holden & Richard Johns, The House of Saud, Pan, 1982, 0 330 26834 1
- ^ a b Madawi Al-Rasheed, A History of Saudi Arabia, Cambridge University Press, 2002, ISBN 0 521 64412 7
- ^ a b 'The House of Saud: rulers of modern Saudi Arabia' by Abeer Allam, The Financial Times, September 30, 2010 http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/75aae7ea-cc82-11df-a6c7-00144feab49a,s01=1.html#axzz182oGFinn
- ^ 'Inside the Kingdom: Kings, Clerics, Modernists, Terrorists, and the Struggle for Saudi Arabia' by Robert Lacey,2009, ISBN 19 978 1 40745 507 5
- ^ 'The Kingdom: Arabia and the House of Saud' by Robert Lacey, 1982, ISBN 0 380 61762 5
- ^ 'The House of Saud: The Rise & Rule of the Most Powerful Dynasty in the Arab World' by David Holden and Richard Johns, 1982, ISBN 0 330 26834 1
- ^ 'The Two Faces of Islam: The House of Sa'ud From Tradition to Terror by Stephen Schwartz, 2002, ISBN 978 0 38550 692 2
- ^ The Battle for Saudi Arabia: Royalty, Fundamentalism, and Global Power' by As'ad Abukhalil, 2003, ISBN 978 1 58322 610 0
- ^ 'The Rise, Corruption and Coming Fall of the House of Saud' by Said K. Aburish, 1994 ISBN 0 7475 2040 2
- ^ ‘The corrupt, feudal world of the House of Saud’ by Robert Fisk, ‘The Independent’, 14 May 2003, http://www.independent.co.uk/opinion/commentators/fisk/robert-fisk-the-corrupt-feudal-world-of-the-house-of-saud-538468.html
- ^ http://www.transparency.org/policy_research/surveys_indices/cpi/2010/results
- ^ The Guardian, 7 June 2007 http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2007/jun/07/bae5
- ^ David Leigh (13 October 2003). "MoD chief in fraud cover-up row". London: The Guardian. Retrieved 2006-12-15.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Michael Robinson (4 October 2004). "BBC lifts the lid on secret BAE slush fund". BBC Money Programme. Retrieved 2006-12-15.
- ^ "SFO to investigate BAE contracts". BBC News. 3 November 2006. Retrieved 2006-12-15.
- ^ Associated Press (2007-06-26). "BAE says U.S. is investigating dealings with Saudi Arabia". International Herald Tribune.
- ^ Hope, Christopher (2006-12-01). "Halt inquiry or we cancel Eurofighters". The Daily Telegraph. Telegraph Media Group Limited. Retrieved 2006-12-01.
- ^ Gibb, Frances (2008-04-11). "High Court rules that the halt to BAE investigation was 'unlawful, a threat to British justice'". The Times. London: Times Newspapers. Retrieved 2008-04-27.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Timeline: BAE corruption probe". BBC News. 15 December 2006. Retrieved 2006-12-15.
- ^ Alistair Dawber (3 March 2010). "BAE protesters win SFO injunction". The Independent. London. Retrieved 2010-06-14.
- ^ Home'Norah Al-Fayez Breaks Proverbial Glass Ceiling', MedIndia, 16 February 2009 http://www.medindia.net/news/Norah-Al-Fayez-Breaks-Proverbial-Glass-Ceiling-47581-1.htm
- ^ 'A survey of Saudi Arabia: All in the Family' The Economist, 5 June 2006 http://www.economist.com/node/5350711
- ^ a b 'The Saudi succession: When kings and princes grow old' The Economist,15 July 2010 http://www.economist.com/node/16588422
- ^ 'Reform in Saudi Arabia: At a snail's pace', The Economist, 30 September 2010 http://www.economist.com/node/17149062?story_id=17149062&fsrc=rss
- ^ Role of the Ulema Saudi Ministry of Information, retrieved 25 jan. 2011
- ^ a b 'The Power of Saudi Arabia's Islamic Leaders' by Nawaf E. Obaid, "Middle East Quarterly" Sept. 1999, pp.51-58 http://www.meforum.org/482/the-power-of-saudi-arabias-islamic-leaders
- ^ , ‘The Ideological Dimension in Saudi-Iranian Elections’ by Saleh Al-Mani in 'Iran and the Gulf: A Search for Stability', 1996, by Jamal S. Al-Suwaidi (ed) ISBN 1 86064 144
- ^ ‘Saudi Arabia: Elements of Instability within Stability’ by Daryl Champion, in Crises in the Contemporary Persian Gulf, 2002, Barry Rubin (ed) ISBN 0 7146 5267 9
- ^ Schmitt, Eric; Shanker, Thom (2008-03-18). "U.S. adapts cold-war idea to fight terrorists". New York Times.
Saudi Arabia 's top cleric, Grand Mufti Sheik Abdul Aziz al-Asheik, gave a speech last October warning Saudis not to join unauthorized jihadist activities, a statement directed mainly at those considering going to Iraq to fight the American-led forces.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Global Security http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/gulf/sa-clan.htm
- ^ 'The Saudi succession: When kings and princes grow old', The Economist, 15 July 2010, http://www.economist.com/node/16588422
- ^ 'Saudi royal succession: Professor detained over article', BBC News online, 7 December 2010 http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-middle-east-11936421
- ^ Saudi women barred from voting, BBC News, October 11, 2004. Retrieved June 25, 2008.
- ^ Brandeis University Crown Center for Middle East Studies Middle East Brief, January 2009, 'Divided We Survive: A Landscape of Fragmentation in Saudi Arabia' by D Ondrej Barenek http://www.brandeis.edu/crown/publications/meb/MEB33.pdf
- ^ Johnston, David (September 9, 2003). "Two years later: 9/11 Tactics; Official Says Qaeda Recruited Saudi Hijackers to Strain Ties". The New York Times. Retrieved May 19, 2008.
- ^ a b 'Fueling Terror', Institute for the Analysis of Global Terror, http://www.iags.org/fuelingterror.html
- ^ The Telegraph 6 December 2010 "Wikileaks: Saudis 'chief funders of al-Qaeda" http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/wikileaks/8182847/Wikileaks-Saudis-chief-funders-of-al-Qaeda.html
- ^ a b c d Saudi Arabia. JURIST
- ^ 'Saudi Judicial Reform and the Principle of Independence' by Abdullah Fakhry Ansary, Arab Reform Bulletin, May 5, 2009, http://carnegieendowment.org/arb/?fa=show&article=23059
- ^ 'Tentative steps in Saudi Arabia: The king of Saudi Arabia shows some reformist credentials', The Economist, 17 February 2009 http://www.economist.com/node/13134598
- ^ "Saudi Arabia, Kingdom of". Law.emory.edu. 1933-09-22. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ "Human Rights in Saudi Arabia: A Deafening Silence" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ "Saudi Arabian Government and Law". Jeansasson.com. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ "State Department". State.gov. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ a b "Religion & Ethics - Islam and slavery: Abolition". BBC. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ a b "Welcome to Encyclopædia Britannica's Guide to Black History". Britannica.com. 1910-01-31. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ a b Human Rights Watch (18 October 2010). "Saudi Arabia: Where Fathers Rule and Courts Oblige". Retrieved 4 January 2011.
- ^ Hassan, Ibtihal; Hammond, Andrew. Car makers target Saudi women despite driving ban, Reuters, December 10, 2007. Retrieved June 25, 2008.
- ^ "Saudi Arabia to Allow Women to Drive—With Conditions" by Assyrian International News Agency, March 17, 2008
- ^ Document - Saudi Arabia: Man sentenced for homosexuality (Amnesty International, 12 November 2010)
- ^ "Documentation of Internet Filtering in Saudi Arabia". Cyber.law.harvard.edu. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ Robertson, Nic; Drash, Wayne. "No freedom for 'dean of Saudi bloggers'", CNN, February 28, 2008. Retrieved June 25, 2008.
- ^ "Saudi Aid to the Developing World". Saudinf.com. 2009-04-20. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ "Arab Aid". Saudiaramcoworld.com. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ Ricklefs, M.C. A history of modern Indonesia since c.1200. Stanford. 2001 Stanford University Press.
- ^ Abdullah, Taufik. Adat and Islam: An Examination of Conflict in Minangkabau. 1966.
- ^ Indonesia's Population: Ethnicity and Religion in a Changing Political Landscape. 2003. Institute of Southeast Asian Studies.
- ^ Xavier Romero-Frias, The Maldive Islanders, A Study of the Popular Culture of an Ancient Ocean Kingdom. 1999, ISBN 847254801 5
- ^ "Contributor Information to the William J. Clinton Foundation". Clintonfoundation.org. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ http://www.fas.org/asmp/profiles/saudi_arabia.htm SAUDI ARABIA
- ^ http://middleeast.about.com/od/saudiarabia/a/saudi-arabia-military-aid.htm U.S. Arms Sales to Saudi Arabia
- ^ Arms for the King and His Family
- ^ US-Saudi Security Cooperation
- ^ http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748704621204575488361149625050.html Saudi Arms Deal Advances
- ^ PA1303, WWF
- ^ PA1323, WWF
- ^ PA1325, WWF
- ^ Yemen, Saudi Arabia sign border deal, BBC News, June 12, 2000. Retrieved June 25, 2008.
- ^ CIA World Factbook - Rank Order: Area
- ^ Weather Online accessed 24 Jan. 2011
- ^ "Saudi Arabia: Administrative divisions". arab.net. Retrieved 2008-09-21.
- ^ "World Proved Reserves of Oil and Natural Gas, Most Recent Estimates". Eia.doe.gov. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ Country Profile Study on Poverty: Saudi Arabia (archived from the original[dead link] on 2008-02-26)
- ^ "CPI Inflation Calculator". Data.bls.gov. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ "Crude Oil Reserves". Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ Simmons, Matthew (2005) [June 10, 2005]. Twilight in the Desert: The Coming Saudi Oil Shock and the World Economy. Wiley. ISBN 978-0471738763.
- ^ Six New Economic cities in Saudi Arabia[dead link]
- ^ Construction boom of Saudi Arabia and the UAE[dead link]
- ^ "Riyadh's Urban area will contribute $ 167 B and Jeddah's will contribute $ 111 Billion". Citymayors.com. 2007-03-11. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ "Bad Dreams: Exploitation and Abuse of Migrant Workers in Saudi Arabia (PDF)" (PDF). Human Rights Watch. July 2004. Retrieved 2007-04-20.[dead link]
- ^ "Case studies on human rights and fundamental freedoms: a world survey". Willem Adriaan Veenhoven, Winifred Crum Ewing, Stichting Plurale Samenlevingen (1976). p.452. ISBN 90-247-1779-5
- ^ Alriyadh Newspaper[dead link]
- ^ Siraj Wahab (30 July 2009). "It's another kind of Saudization". Arab News. Retrieved 13 January 2011.
- ^ a b c d "Saudi Arabia: International Religious Freedom Report 2008". State.gov. Retrieved 2010-05-01. Cite error: The named reference "IRFR" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ "Arab versus Asian migrant workers in the GCC countries" (PDF). p. 10. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ Seok, Hyunho (1991). "Korean migrant workers to the Middle East". Migration to the Arab World: Experience of Returning Migrants. United Nations University Press. pp. 56–103. ISBN.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (|book-title=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - ^ "Yemen's point of no return". Guardian.co.uk. April 1, 2009.
- ^ "Expatriates Can Apply for Saudi Citizenship in Two-to-Three Months". Arabnews.com. 2005-02-14. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ 1954 Saudi Arabian Citizenship System
- ^ Khalaf al-Harbi (July 9, 2010). "Child abuse: We and the Americans". Arab News. Retrieved July 13, 2010.
- ^ Abdul Rahman Shaheen (24 December 2008). "Report alleges rise in child abuse in Saudi Arabia". Gulf News. Retrieved 20 August 2010.
- ^ Ethnologue: Saudi Arabia retrieved 24 Jan. 2011
- ^ a b Mapping the World Muslim Population (October 2009), Pew Forum on Religion & Public Life. p. 16 (p. 17 of the PDF).
- ^ Pew Forum. p. 10.
- ^ The Daily Star Lamine Chikhi. 27-11-2010.
- ^ 'The Islamic Traditions of Wahhabism and Salafiyya' US Congressional Research Service Report, 2008, by Christopher M. Blanchard available from the Federation of American Scientists website http://www.fas.org/sgp/crs/misc/RS21695.pdf
- ^ The Telegraph 6 December 2010 "Wikileaks: Saudis 'chief funders of al-Qaeda" [5]
- ^ "A Catholic Indian priest had just celebrated mass in a private house, when seven religious policemen (muttawa) broke into the house.... The Saudi religious police are well known for their ruthlessness; they often torture believers of other religions who are arrested. AsiaNews sources said there were around 400,000 Indian Catholics in Saudi Arabia who were denied pastoral care. Catholic foreigners in the country number at least one million: none of them can participate in mass while they are in Saudi Arabia. Catechism for their children – nearly 100,000 – is banned." AsiaNews, April 10, 2006 (archived from the original on 2008-07-17)
- ^ The Global Gender Gap Report 2010 http://www.weforum.org/pdf/gendergap/report2010.pdf
- ^ a b al-Mohamed, Asmaa. "Saudi Women's Rights: Stuck at a Red Light" (PDF). Retrieved 24 June 2010.
- ^ ‘Saudi women “kept in childhood”’ BBC News, 21 April 2008; retrieved 20 Jan 2011
- ^ a b Zoepf, Katherine (31 May 2010). "Talk of Women's Rights Divides Saudi Arabia". The New York Times. Retrieved 19 September 2010.
- ^ United Nations Report of the Special Rapporteur on violence against women, its causes and consequences - MISSION TO SAUDI ARABIA
- ^ "Perpetual Minors". Human Rights Watch. 19 April 2008. Retrieved 19 September 2010.
- ^ Fataawa al-Mar’ah al-Muslimah, Muhammad ibn Saalih al-‘Uthaymeen, (Makkah Al Mukarramah),1998, 2/981
- ^ Handrahan, L. M. (1996). Al-Ghatib-lil-Mar'ah. Vol. 8, no. 1 http://www.hri.ca/pdfs/HRT%20Spring,%20Volume%208,%20No.%201,%202001.pdf. Retrieved 21 August 2007.
{{cite news}}: Missing or empty|title=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b CIA World Factbook retrieved 16 Jan. 2011
- ^ 'Top Saudi cleric: OK for young girls to wed' CNN, 17 January 2009; retrieved 18 January 2011
- ^ 'Saudi Human Rights Commission Tackles Child Marriages' Asharq Alawsat, 13 Jan. 2009; retrieved 18 Jan. 2011
- ^ Mesbah, Rana. "Women's education in Saudi Arabia: the way forward" Retrieved 16 January 2011.
- ^ ‘Expats in Saudi: Behind the veil’ BBC News, 14 June 2004; retrieved 19 Jan 2011
- ^ ‘Unveiled women anger Saudi cleric’ BBC News, 21 January 2004; retrieved 19 Jan 2011
- ^ "Niqab". BBC. 3 September 2009. Retrieved 19 September 2010.
- ^ "Saudi Writer and Journalist Wajeha Al-Huwaider Fights for Women's Rights". MEMRI.
- ^ "New Rights, and Challenges, for Saudi Women". Time. 19 October 2009.
- ^ Saleh Ambah, Faiza. "Saudi Women Rise in Defense of the Veil". Washington Post. Retrieved 23 June 2010.
- ^ http://www.medindia.net/news/Norah-Al-Fayez-Breaks-Proverbial-Glass-Ceiling-47581-1.htm
- ^ http://www.saudigazette.com.sa/index.cfm?method=home.regcon&contentID=2010103086426
- ^ http://www.poptech.org/popcasts/hayat_sindi_accessible_health
- ^ a b http://www.alarabiya.net/articles/2009/11/21/91996.html
- ^ http://www.wisemuslimwomen.org/muslimwomen/bio/dr._khawla_al-kuraya/
- ^ http://archive.arabnews.com/?page=1§ion=0&article=120055&d=9&m=3&y=2009
- ^ a b c http://www.womengateway.com/enwg/News/2009/Nov/newsnov21.htm
- ^ http://archive.arabnews.com/?page=1§ion=0&article=37847&d=11&m=1&y=2004
- ^ http://planenews.com/archives/2446
- ^ http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2008/08/17/AR2008081702539.html
- ^ http://www.saudiembassy.net/latest_news/news01271002.aspx
- ^ a b ‘Saudi Arabia's Education Reforms Emphasize Training for Jobs’ The Chronicle of Higher Education, 3 October 2010; retrieved 16 Jan. 2011
- ^ Education in Saudi Arabia World Education News and Reviews retrieved 16 January 2011
- ^ Shea, Nona; et al. (2006). "Saudi Arabia's Curriculum of Intolerence" (PDF). Center for Religious Freedom, Freedom House. Retrieved 2008-09-21.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Press Release: "Revised Saudi Government Textbooks Still Demonize Christians, Jews, Non-Wahhabi Muslims and". Freedom House. May 23, 2006. Retrieved 2008-09-21.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ ‘This medieval Saudi education system must be reformed’, The Guardian, 26 November 2010, retrieved 16 January 2011
- ^ a b Reforming Saudi Education Slate 7 Sept. 2009; retrieved 16 Jan. 2011
- ^ The Saudi Gazette retrieved 16 Jan 2011
- ^ Sulaiman, Tosin. Bahrain changes the weekend in efficiency drive, The Times, August 2, 2006. Accessed June 25, 2008. Turkey has a weekend on Saturday and Sunday
- ^ Arabia: the Cradle of Islam, 1900, S.M.Zwemmer
- ^ Saudi Embassy (US) website - Islam retrieved 20 Jan. 2011
- ^ Saudi Embassy (US) website - Guardian of the Holy Places retrieved 20 Jan. 2011
- ^ 'The destruction of Mecca: Saudi hardliners are wiping out their own heritage', The Independent, 6 August 2005, retrieved 17 Jan. 2011
- ^ Destruction of Islamic Architectural Heritage in Saudi Arabia: A Wake-up Call, The American Muslim, retrieved 17 Jan. 2011
- ^ a b ‘Shame of the House of Saud: Shadows over Mecca’, The Independent, 19 April 2006
- ^ ‘Islamic heritage lost as Makkah modernises’ Center for Islamic Pluralism
- ^ [6].
- ^ "Babylon & Beyond". Los Angeles Times. 2008-12-23.
- ^ IMAX Arabic
Further reading
- Al Farsy, Fouad (2004) Modernity and Tradition: The Saudi Equation: Panarc International Ltd: ISBN 0 9548740 1 3
- Gardner, Andrew (2004) The Political Ecology of Bedouin Pastoralism in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. In Political Ecology Across Spaces, Scales, and Social Groups, Lisa Gezon and Susan Paulson, eds. Rutgers: Rutgers University Press.
- Jones, John Paul. If Olaya Street Could Talk: Saudi Arabia- The Heartland of Oil and Islam. The Taza Press (2007). ISBN 0-9790436-0-3
- Lippman, Thomas W. "Inside the Mirage: America's Fragile Partnership with Saudi Arabia" (Westview 2004) ISBN 0-8133-4052-7
- Mackey, Sandra, The Saudis: Inside the Desert Kingdom (Houghton Mifflin, 1987) ISBN 0-395-41165-3
- Matthew R. Simmons, Twilight in the Desert The Coming Saudi Oil Shock and the World Economy, John Wiley & Sons, 2005, ISBN 0-471-73876-X
- Ménoret, Pascal, The Saudi Enigma: A History (Zed Books, 2005) ISBN 1-84277-605-3
- al-Rasheed, Madawi, A History of Saudi Arabia (Cambridge University Press, 2002) ISBN 0-521-64335-X
- Robert Lacey, THE KINGDOM: Arabia & The House of Sa'ud, Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Inc, 1981 (Hard Cover) and Avon Books, 1981 (Soft Cover). Library of Congress: 81-83741 ISBN 0-380-61762-5
- Roger Owen, State, Power and Politics in the Making of the Modern Middle East, 3rd Edition (Routledge, 2006) ISBN 0-415-29713-3
- T R McHale, A Prospect of Saudi Arabia, International Affairs Vol. 56 No 4 Autumn 1980 pp622–647
- Turchin, P. 2007. Scientific Prediction in Historical Sociology: Ibn Khaldun meets Al Saud. History & Mathematics: Historical Dynamics and Development of Complex Societies. Moscow: KomKniga, 2007. ISBN 5-484-01002-0
- Carmen Bin Laden, Inside the Kingdom: My Life in Saudi Arabia, Grand Central Publishing, 2005, SBN 0446694886
- Robert Lacey, Inside the Kingdom, Hutchinson, 2009.
- Weston, Mark, "Prophets and Princes," Wiley, 2008.
External links
- Articles with dead external links from January 2009
- Ill-formatted IPAc-en transclusions
- Saudi Arabia
- Arab League member states
- Arabian Peninsula
- Arabic-speaking countries
- Arab Unification
- Middle Eastern countries
- Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf member states
- Countries bordering the Red Sea
- G20 nations
- Islamic States
- OPEC member states
- Organisation of the Islamic Conference members
- Persian Gulf countries
- Southwest Asian countries
- Saudi Arabia articles needing attention
- States and territories established in 1932
- Western Asia