Vladimir Putin: Difference between revisions
EtienneDolet (talk | contribs) per TP. No consensus for this. |
discussion is ongoing and there's even an open RfC on the matter - please don't try to sabotage that effort |
||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
Because of [[Constitution of Russia|constitutionally]] mandated [[term limits]], Putin was ineligible to run for a third consecutive presidential term in 2008. [[Dmitry Medvedev]] won the [[Russian presidential election, 2008|2008 presidential election]] and appointed Putin [[Prime Minister of Russia|Prime Minister]], beginning a period of so-called [[Duumvirate|"tandemocracy"]].<ref>{{cite journal|last=Hale|first=Henry E.|author2=Timothy J. Colton|date=8 September 2009|title=Russians and the Putin-Medvedev "Tandemocracy": A Survey-Based Portrait of the 2007–08 Election Season|journal=The National Council for Eurasian and East European Research|publisher=University of Washington|location=Seattle, WA|url=http://www.ucis.pitt.edu/nceeer/2009_823-03_2_Hale.pdf|accessdate=15 March 2012}}</ref> In September 2011, following a change in the law that extended presidential terms from four year to six years,<ref>Vasilyeva, Natallya. [http://www.chinapost.com.tw/international/2012/04/12/337618/Putin-claims.htm "Putin claims to support term limits as he readies to take helm for 3rd time"], ''[[China Post]]'' (12 April 2012).</ref> Putin announced he would seek a third term in the [[Russian presidential election, 2012|2012 presidential election]]. He won the March 2012 election, a result which aligned with pre-election polling.<ref>Shuster, Simon. [http://content.time.com/time/world/article/0,8599,2108309,00.html "In Russia, an Election Victory for Putin and Then a 'Paid Flash Mob'"], [[Time (magazine)|Time]] (March 5, 2012).</ref> Opposition groups accused Putin and his [[United Russia]] party of fraud.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://en.rian.ru/russia/20120304/171708401.html |title=Putin Hails Vote Victory, Opponents Cry Foul |agency=RIA Novosti |accessdate=22 June 2013}}</ref><ref>[http://www.theguardian.com/news/datablog/2012/mar/05/russia-putin-voter-fraud-statistics]</ref> [[Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe]] observers evaluated election day voting positively overall but assessed the vote count negatively in almost one-third of polling stations because of procedural irregularities.<ref name=OSCE>{{cite web|title=Russia’s presidential election marked by unequal campaign conditions, active citizens’ engagement, international observers say|url=http://www.osce.org/odihr/elections/88661|publisher=[[Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe]]}}</ref><ref>[http://www.nytimes.com/2012/03/06/world/europe/observers-detail-flaws-in-russian-election.html]</ref> |
Because of [[Constitution of Russia|constitutionally]] mandated [[term limits]], Putin was ineligible to run for a third consecutive presidential term in 2008. [[Dmitry Medvedev]] won the [[Russian presidential election, 2008|2008 presidential election]] and appointed Putin [[Prime Minister of Russia|Prime Minister]], beginning a period of so-called [[Duumvirate|"tandemocracy"]].<ref>{{cite journal|last=Hale|first=Henry E.|author2=Timothy J. Colton|date=8 September 2009|title=Russians and the Putin-Medvedev "Tandemocracy": A Survey-Based Portrait of the 2007–08 Election Season|journal=The National Council for Eurasian and East European Research|publisher=University of Washington|location=Seattle, WA|url=http://www.ucis.pitt.edu/nceeer/2009_823-03_2_Hale.pdf|accessdate=15 March 2012}}</ref> In September 2011, following a change in the law that extended presidential terms from four year to six years,<ref>Vasilyeva, Natallya. [http://www.chinapost.com.tw/international/2012/04/12/337618/Putin-claims.htm "Putin claims to support term limits as he readies to take helm for 3rd time"], ''[[China Post]]'' (12 April 2012).</ref> Putin announced he would seek a third term in the [[Russian presidential election, 2012|2012 presidential election]]. He won the March 2012 election, a result which aligned with pre-election polling.<ref>Shuster, Simon. [http://content.time.com/time/world/article/0,8599,2108309,00.html "In Russia, an Election Victory for Putin and Then a 'Paid Flash Mob'"], [[Time (magazine)|Time]] (March 5, 2012).</ref> Opposition groups accused Putin and his [[United Russia]] party of fraud.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://en.rian.ru/russia/20120304/171708401.html |title=Putin Hails Vote Victory, Opponents Cry Foul |agency=RIA Novosti |accessdate=22 June 2013}}</ref><ref>[http://www.theguardian.com/news/datablog/2012/mar/05/russia-putin-voter-fraud-statistics]</ref> [[Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe]] observers evaluated election day voting positively overall but assessed the vote count negatively in almost one-third of polling stations because of procedural irregularities.<ref name=OSCE>{{cite web|title=Russia’s presidential election marked by unequal campaign conditions, active citizens’ engagement, international observers say|url=http://www.osce.org/odihr/elections/88661|publisher=[[Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe]]}}</ref><ref>[http://www.nytimes.com/2012/03/06/world/europe/observers-detail-flaws-in-russian-election.html]</ref> |
||
Putin's first presidency was marked by strong economic growth. The [[Russian economy]] grew for eight straight years, and the [[GDP]] measured in [[Purchasing power parity|purchasing power]] increased 72%.<ref name="challenges_p12"/><ref name=nbc/><ref>[http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2008/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=52&pr.y=13&sy=1992&ey=2007&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=922&s=NGDPD%2CPPPGDP&grp=0&a=GDP of Russia from 1992 to 2007] [[International Monetary Fund]]. Retrieved 12 May 2008</ref><ref name=stats/><ref name=russiaprofile/> This growth was a result of the [[2000s commodities boom]], [[World oil market chronology from 2003|high oil prices]], and prudent economic and fiscal policies.<ref name="Putin 2007">''Putin: Russia's Choice'', (Routledge 2007), by [[Richard Sakwa]], Chapter 9</ref><ref name="Fragile Empire 2013 page 17">''Fragile Empire: How Russia Fell In and Out of Love with Vladimir Putin'', Yale University Press (2013), by Ben Judah, page 17</ref> However, the economy began to experience difficulties with the arrival of the [[Great Recession|global economic crisis of 2008-2009]],<ref name=moscowtimes2009>http://www.themoscowtimes.com/business/article/economic-slowdown-eases-in-q3/389355.html</ref> falling oil prices and, beginning in 2014, Western sanctions imposed after [[Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation|Russia's annexation of Crimea]] and [[Russian military intervention in Ukraine (2014–present)|military intervention in Eastern Ukraine]].<ref name="challenges_p12">{{cite book|editors=Anders Åslund, Sergei Guriev, Andrew C. Kuchins|title=Russia After the Global Economic Crisis|chapter=Challenges Facing the Russian Economy after the Crisis|last1=Guriev|first1=Sergei|last2=Tsyvinski|first2=Aleh|publisher=Peterson Institute for International Economics; Centre for Strategic and International Studies; New Economic School|year=2010|isbn=9780881324976|pages=12–13}}</ref><ref name="Putin 2007"/><ref name="Fragile Empire 2013 page 17"/><ref name="themoscowtimes.com">http://www.themoscowtimes.com/news/article/russians-average-monthly-salary-falls-to-500-as-food-prices-skyrocket/516947.html</ref> Russia entered a recession in mid-2014 and the economy shrank 3.7% in 2015.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Thompson|first1=Mark|title=Russia: One of 10 worst economies in 2015|url=http://money.cnn.com/2016/01/25/news/economy/russia-10-worst-emerging-economies/|agency=CNN|date=26 January 2016}}</ref> |
|||
Putin has enjoyed very high domestic approval ratings throughout his career, particularly following the annexation of Crimea in 2014. |
Putin has enjoyed very high domestic approval ratings throughout his career, particularly following the annexation of Crimea in 2014. |
||
Revision as of 17:46, 26 March 2016
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
Vladimir Putin Владимир Путин | |
|---|---|
 Putin in March 2015 | |
| 2nd and 4th President of Russia | |
| Assumed office 7 May 2012 | |
| Prime Minister | Viktor Zubkov Dmitry Medvedev |
| Preceded by | Dmitry Medvedev |
| In office 7 May 2000 – 7 May 2008 Acting: 31 December 1999 – 7 May 2000 | |
| Prime Minister | Mikhail Kasyanov Mikhail Fradkov Viktor Zubkov |
| Preceded by | Boris Yeltsin |
| Succeeded by | Dmitry Medvedev |
| Prime Minister of Russia | |
| In office 8 May 2008 – 7 May 2012 | |
| President | Dmitry Medvedev |
| Deputy | Igor Shuvalov |
| Preceded by | Viktor Zubkov |
| Succeeded by | Dmitry Medvedev |
| In office 9 August 1999 – 7 May 2000 Acting: 9 August 1999 – 16 August 1999 | |
| President | Boris Yeltsin |
| Deputy | Viktor Khristenko Mikhail Kasyanov |
| Preceded by | Sergei Stepashin |
| Succeeded by | Mikhail Kasyanov |
| Leader of United Russia | |
| In office 1 January 2008 – 30 May 2012 | |
| Preceded by | Boris Gryzlov |
| Succeeded by | Dmitry Medvedev |
| Secretary of the Security Council | |
| In office 9 March 1999 – 9 August 1999 | |
| President | Boris Yeltsin |
| Preceded by | Nikolay Bordyuzha |
| Succeeded by | Sergei Ivanov |
| Director of the Federal Security Service | |
| In office 25 July 1998 – 29 March 1999 | |
| President | Boris Yeltsin |
| Preceded by | Nikolay Kovalyov |
| Succeeded by | Nikolai Patrushev |
| Personal details | |
| Born | Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin 7 October 1952 Leningrad, Russian SFSR, Soviet Union (modern Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation) |
| Political party | Communist Party of the Soviet Union (1975–91) Our Home-Russia (1995–99) Unity (1999–2001) Independent (1991–95; 2001–08) United Russia (2008–present) |
| Other political affiliations | People's Front (2011–present) |
| Spouse | [1] |
| Alma mater | Leningrad State University |
| Awards | |
| Signature | |
| Website | Official website |
| Military service | |
| Allegiance | |
| Branch/service | KGB |
| Years of service | 1975–1991 |
| Rank | |
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin (/ˈpuːtɪn/; Russian: Влади́мир Влади́мирович Пу́тин, IPA: [vlɐˈdʲimʲɪr vlɐˈdʲimʲɪrəvʲɪtɕ ˈputʲɪn] , born 7 October 1952) has been the President of Russia since 7 May 2012, succeeding Dmitry Medvedev. Putin served as Prime Minister from 1999 to 2000, as President from 2000 to 2008, and again as Prime Minister from 2008 to 2012. During Putin's second term as Prime Minister, he was the Chairman of United Russia, the ruling party.
Putin was an officer in the KGB for 16 years, rising to the rank of lieutenant colonel before retiring in 1991 to enter politics in his native Saint Petersburg. He moved to Moscow in 1996 and joined President Boris Yeltsin's administration, where he rose quickly through the ranks, becoming Acting President on 31 December 1999, when Yeltsin resigned. Putin won the subsequent 2000 presidential election by a 52% to 30% margin, thus avoiding a runoff with his Communist Party opponent Gennady Zyuganov.[2] Putin was reelected in 2004 with 72% of the vote.
Because of constitutionally mandated term limits, Putin was ineligible to run for a third consecutive presidential term in 2008. Dmitry Medvedev won the 2008 presidential election and appointed Putin Prime Minister, beginning a period of so-called "tandemocracy".[3] In September 2011, following a change in the law that extended presidential terms from four year to six years,[4] Putin announced he would seek a third term in the 2012 presidential election. He won the March 2012 election, a result which aligned with pre-election polling.[5] Opposition groups accused Putin and his United Russia party of fraud.[6][7] Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe observers evaluated election day voting positively overall but assessed the vote count negatively in almost one-third of polling stations because of procedural irregularities.[8][9]
Putin's first presidency was marked by strong economic growth. The Russian economy grew for eight straight years, and the GDP measured in purchasing power increased 72%.[10][11][12][13][14] This growth was a result of the 2000s commodities boom, high oil prices, and prudent economic and fiscal policies.[15][16] However, the economy began to experience difficulties with the arrival of the global economic crisis of 2008-2009,[17] falling oil prices and, beginning in 2014, Western sanctions imposed after Russia's annexation of Crimea and military intervention in Eastern Ukraine.[10][15][16][18] Russia entered a recession in mid-2014 and the economy shrank 3.7% in 2015.[19]
Putin has enjoyed very high domestic approval ratings throughout his career, particularly following the annexation of Crimea in 2014. The Economist magazine's Democracy Index classified Russia as "authoritarian" in 2015, ranking it 132nd out of 167 countries.[20] He was also placed at the top of the Forbes list of The World's Most Powerful People in 2013, 2014, and 2015.
Early life, and education
Putin was born on 7 October 1952, in Leningrad, Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Soviet Union (modern Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation).[21] Putin's parents were Vladimir Spiridonovich Putin (1911–1999) and Maria Ivanovna Putina (née Shelomova; 1911–1998). The youngest of three boys, Vladimir Putin's two elder brothers, Viktor and Albert, were born in the mid-1930s. Albert died within a few months of birth, while Viktor succumbed to diphtheria during the siege of Leningrad in World War II.
Putin's mother was a factory worker, and his father was a conscript in the Soviet Navy, where he served in the submarine fleet in the early 1930s. Early in World War II, his father served in the destruction battalion of the NKVD.[22][23][24][25] Later he was transferred to the regular army and was severely wounded in 1942.[26]
Putin's paternal grandfather, Spiridon Ivanovich Putin (1879–1965), was a chef who occasionally cooked for Vladimir Lenin, Lenin's wife Nadezhda Krupskaya, and on several occasions for Joseph Stalin.[27] Putin's maternal grandmother was killed by the German occupiers of the Tver region in 1941, and his maternal uncles disappeared at the front.[27]

On 1 September 1960, Putin started at School No. 193 at Baskov Lane, just across from his home. At 11 years old, Putin was one of a few in the class of approximately 45 pupils who was not yet a member of the Pioneers, mostly because of his rowdy behavior.
At 12 years old, Putin took sports seriously, and began to practice sambo and judo. In his youth, Putin wished to emulate the intelligence officer characters played on the Soviet screen by various actors, including Vyacheslav Tikhonov and Georgiy Zhzhonov.[28]
Putin studied German while he attended Saint Petersburg High School 281, and he speaks fluent German today.[29][30]
Putin entered the Law Department of the Leningrad State University in 1970, and graduated in 1975.[31] His final thesis was titled, "The Most Favored Nation Trading Principle in International Law".[32] While at the University, Putin was required to join the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, and remained a member until the Party was dissolved in December 1991.[33] During this time, Putin met Anatoly Sobchak, who later played an important role in Putin's career. Sobchak was an Assistant Professor, and lectured Putin's class on Business Law (khozyaystvennoye pravo).[34]
KGB career


In 1975, Putin joined the KGB, and underwent a year's training at the 401st KGB school in Okhta, Leningrad. Putin was reportedly evaluated by KGB superiors as being "flawed" and "unsocial", with a "lowered sense of danger".[35]
Putin went on to work briefly in the Second Chief Directorate (counter-intelligence), before he was transferred to the First Chief Directorate, where among his duties were the monitoring of foreigners and consular officials in Leningrad.[36][37]
From 1985 to 1990, Putin was stationed by the KGB in Dresden, East Germany.[38] During that time, Putin was assigned to Directorate S, the illegal intelligence-gathering unit (the KGB's classification for agents who used falsified identities), where he was given cover as a translator and interpreter.[39] One of Putin's jobs was to coordinate efforts with the Stasi, to track down and recruit foreigners in Dresden, usually those who were enrolled at the Dresden University of Technology, in the hopes of sending them to the United States to work undercover.[citation needed]
Putin and his colleagues were reduced to primarily collecting press clippings, thus contributing to the mountains of useless information produced by the KGB. Former agents estimate that they spent three-quarters of their time writing reports. Putin's most important success during his stay in Dresden appears to have been in...[contacting] a U.S. Army Sergeant, who sold them an unclassified Manual for 800 Marks.[39]
During the Fall of the Berlin Wall, when civil rights activists threatened to storm the KGB building, "Putin burned the KGB's files and sent frantic requests for orders from his bosses in the capital. 'Moscow is silent,' Putin later recalled in his official biography".[40]
Following the collapse of the communist East German government, Putin was recalled to the Soviet Union and returned to Leningrad, where in June 1991, he assumed a position with the International Affairs section of Leningrad State University, reporting to Vice-Rector Yuriy Molchanov.[37] In his new position, Putin maintained surveillance on the student body and kept an eye out for recruits. It was during his stint at the university that Putin grew reacquainted with his former professor Anatoly Sobchak, then mayor of Leningrad.[41]
Putin resigned from the active state security services with the rank of lieutenant colonel on 20 August 1991 (with some efforts to resign made earlier),[41] on the second day of the KGB-supported abortive putsch against Soviet President Mikhail Gorbachev.[42] Putin later explained his decision: "As soon as the coup began, I immediately decided which side I was on", although he also noted that the choice was hard because he had spent the best part of his life with "the organs".[43] In 1999, he described communism as "a blind alley, far away from the mainstream of civilization".[44]
Political career
Saint Petersburg administration (1990–1996)
In May 1990, Putin was appointed as an advisor on international affairs to Mayor Anatoly Sobchak. Then, on 28 June 1991, he became head of the Committee for External Relations of the Saint Petersburg Mayor's Office, with responsibility for promoting international relations and foreign investments[45] and registering business ventures.
Less than one year later, Putin was investigated by the city legislative council led by Marina Salye, and the investigators concluded that Putin had understated prices and permitted the export of metals valued at $93 million, in exchange for foreign food aid that never arrived.[46][47] Despite the investigators' recommendation that Putin be fired, Putin remained head of the Committee for External Relations until 1996.[48][49] From 1994 to 1996, Putin held several other political and governmental positions in Saint Petersburg.[50]
In March 1994, Putin was appointed as First Deputy Chairman of the Government of Saint Petersburg. In May 1995, Putin organized the Saint Petersburg branch of the pro-government Our Home Is Russia political party, the liberal party of power founded by Prime Minister Viktor Chernomyrdin. During the summer and autumn of 1995, Putin managed legislative election campaign for Our Home Is Russia. From 1995 through June 1997, Putin led the Saint Petersburg branch of Our Home Is Russia.[50]
Early Moscow career (1996–1999)

In 1996, Mayor Anatoly Sobchak lost his bid for reelection in Saint Petersburg. Putin was called to Moscow and in June 1996 became a Deputy Chief of the Presidential Property Management Department headed by Pavel Borodin. He occupied this position until March 1997. During his tenure Putin was responsible for the foreign property of the state and organized transfer of the former assets of the Soviet Union and Communist Party to the Russian Federation.[34]
On 26 March 1997, President Boris Yeltsin appointed Putin deputy chief of Presidential Staff, which he remained until May 1998, and chief of the Main Control Directorate of the Presidential Property Management Department (until June 1998). His predecessor on this position was Alexei Kudrin and the successor was Nikolai Patrushev, both future prominent politicians and Putin's associates.[34]
On 27 June 1997, at the Saint Petersburg Mining Institute, guided by rector Vladimir Litvinenko, Putin defended his Candidate of Science dissertation in economics, titled "The Strategic Planning of Regional Resources Under the Formation of Market Relations".[51] This exemplified the custom in Russia for a rising young official to write a scholarly work in midcareer.[52] When Putin later became president, the dissertation became a target of plagiarism accusations by fellows at the Brookings Institution; although the dissertation was referenced,[53][54] the Brookings fellows asserted it constituted plagiarism albeit perhaps unintentional.[53] The dissertation committee denied the accusations.[54][55]
On 25 May 1998, Putin was appointed First Deputy Chief of Presidential Staff for regions, replacing Viktoriya Mitina; and, on 15 July, was appointed Head of the Commission for the preparation of agreements on the delimitation of power of regions and the federal center attached to the President, replacing Sergey Shakhray. After Putin's appointment, the commission completed no such agreements, although during Shakhray's term as the Head of the Commission there were 46 agreements signed.[56] Later, after becoming president, Putin canceled all those agreements.[34]
On 25 July 1998, Yeltsin appointed Vladimir Putin head of the Federal Security Service (Russian abbreviation: FSB; one of the successor agencies to the KGB), the position Putin occupied until August 1999. He became a permanent member of the Security Council of the Russian Federation on 1 October 1998 and its Secretary on 29 March 1999.
First premiership (1999)
On 9 August 1999, Vladimir Putin was appointed one of three First Deputy Prime Ministers, and later on that day was appointed acting Prime Minister of the Government of the Russian Federation by President Boris Yeltsin.[57] Yeltsin also announced that he wanted to see Putin as his successor. Still later on that same day, Putin agreed to run for the presidency.[58]
On 16 August, the State Duma approved his appointment as Prime Minister with 233 votes in favour (vs. 84 against, 17 abstained),[59] while a simple majority of 226 was required, making him Russia's fifth PM in fewer than eighteen months. On his appointment, few expected Putin, virtually unknown to the general public, to last any longer than his predecessors. He was initially regarded as a Yeltsin loyalist; like other prime ministers of Boris Yeltsin, Putin did not choose ministers himself, his cabinet being determined by the presidential administration.[60]
Yeltsin's main opponents and would-be successors were already campaigning to replace the ailing president, and they fought hard to prevent Putin's emergence as a potential successor. Putin's law-and-order image and his unrelenting approach to the Second Chechen War, soon combined to raise Putin's popularity and allowed him to overtake all rivals.
While not formally associated with any party, Putin pledged his support to the newly formed Unity Party,[61] which won the second largest percentage of the popular vote (23.3%) in the December 1999 Duma elections, and in turn he was supported by it.
Acting presidency (1999–2000)

On 31 December 1999, Yeltsin unexpectedly resigned and, according to the Constitution of Russia, Putin became Acting President of the Russian Federation. On assuming this role, Putin went on a previously scheduled visit to Russian troops in Chechnya.[62]
The first Presidential Decree that Putin signed, on 31 December 1999, was titled "On guarantees for former president of the Russian Federation and members of his family".[63][64] This ensured that "corruption charges against the outgoing President and his relatives" would not be pursued.[65] This was most notably targeted at Mabetex bribery case in which Yeltsin's family members were involved. On 30 August 2000 criminal investigation (case 18/238278-95) was dropped in which Putin himself was one of suspects[66][67] as member of Sankt Petersburg city government. On 30 December 2000 yet another case against prosecutor general was dropped "for lack of evidence", in spite of thousands of documents passed by Swiss prosecution.[68] Later, on 12 February 2001, Putin signed a similar federal law which replaced the decree of 1999. The case of Putin's alleged corruption in metal exports from 1992 was brought back by Marina Salye, but she was silenced and forced to leave St Petersburg.[69]
While his opponents had been preparing for an election in June 2000, Yeltsin's resignation resulted in the Presidential elections being held within three months, on 26 March 2000; Putin won in the first round with 53% of the vote.[70]
First presidential term (2000–2004)

Vladimir Putin was inaugurated president on 7 May 2000. He appointed Minister of Finance Mikhail Kasyanov as his prime minister.
The first major challenge to Putin's popularity came in August 2000, when he was criticized for his alleged mishandling of the Kursk submarine disaster.[71] That criticism was largely because it was several days before he returned from vacation, and several more before he visited the scene.[71]
Between 2000 and 2004, Putin set about reconstruction of the impoverished condition of the country, apparently winning a power-struggle with the Russian oligarchs, reaching a 'grand-bargain' with them. This bargain allowed the oligarchs to maintain most of their powers, in exchange for their explicit support for – and alignment with – his government.[72][73] A new group of business magnates emerged, including Gennady Timchenko, Vladimir Yakunin, Yury Kovalchuk, Sergey Chemezov, with close personal ties to Putin.

A few months before elections, Putin fired Prime Minister Kasyanov's cabinet and appointed Mikhail Fradkov to his place. Sergey Ivanov became the first civilian in Russia to take the Defense Minister position.
In 2003, a referendum was held in Chechnya adopting a new constitution which declares that the Republic of Chechnya is a part of Russia. Chechnya has been gradually stabilized with the establishment of the parliamentary elections and a regional government.[74][75]
Throughout the war, Russia severely disabled the Chechen rebel movement. However, sporadic attacks by rebels continued to occur throughout the northern Caucasus.[76]
Second presidential term (2004–2008)


On 14 March 2004, Putin was elected to the presidency for a second term, receiving 71% of the vote.[70] The Beslan school hostage crisis took place in September 2004, in which hundreds died. Many in the Russian press and in the international media warned that the death of 130 hostages in the special forces' rescue operation during the 2002 Moscow theater hostage crisis would severely damage President Putin's popularity. However, shortly after the siege had ended, the Russian president enjoyed record public approval ratings – 83% of Russians declared themselves satisfied with Putin and his handling of the siege.[77]
In 2005, the National Priority Projects were launched to improve Russia's health care, education, housing and agriculture.[78][79]
The continued criminal prosecution of Russia's then richest man, President of YUKOS company Mikhail Khodorkovsky, for fraud and tax evasion was seen by the international press as a retaliation for Khodorkovsky's donations to both liberal and communist opponents of the Kremlin. The government said that Khodorkovsky was "corrupting" a large segment of the Duma to prevent changes to the tax code changes. Khodorkovsky was arrested, Yukos was bankrupted and the company's assets were auctioned at below-market value, with the largest share acquired by the state company Rosneft.[80] The fate of Yukos was seen as a sign of a broader shift of Russia towards a system of state capitalism.[81][82] This was underscored in July 2014 when shareholders of Yukos were awarded $50 billion in compensation by the Permanent Arbitration Court in The Hague.[83]
Putin was criticized in the West and also by Russian liberals for what many observers considered a wide-scale crackdown on media freedom in Russia. On 7 October 2006, Anna Politkovskaya, a journalist who exposed corruption in the Russian army and its conduct in Chechnya, was shot in the lobby of her apartment building, on Putin's birthday. The death of Politkovskaya triggered international criticism, with accusations that, at best, Putin has failed to protect the country's new independent media.[84][85]
In 2007, "Dissenters' Marches" were organized by the opposition group The Other Russia,[86] led by former chess champion Garry Kasparov and national-Bolshevist leader Eduard Limonov. Following prior warnings, demonstrations in several Russian cities were met by police action, which included interfering with the travel of the protesters and the arrests of as many as 150 people who attempted to break through police lines.[87]
On 12 September 2007, Putin dissolved the government upon the request of Prime Minister Mikhail Fradkov. Fradkov commented that it was to give the President a "free hand" in the run-up to the parliamentary election. Viktor Zubkov was appointed the new prime minister.[88]
In December 2007, United Russia won 64.24% of the popular vote in their run for State Duma according to election preliminary results.[89] United Russia's victory in December 2007 elections was seen by many as an indication of strong popular support of the then Russian leadership and its policies.[90][91]
Second premiership (2008–2012)
Putin was barred from a third term by the Constitution. First Deputy Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev was elected his successor. In a power-switching operation on 8 May 2008, only a day after handing the presidency to Medvedev, Putin was appointed Prime Minister of Russia, maintaining his political dominance.[92]

The Great Recession hit the Russian economy especially hard, interrupting the flow of cheap Western credit and investments. This coincided with tension in relationships with the EU and the US following the 2008 South Ossetia war, in which Russia invaded neighboring Georgia populated by less than 5 million people.

Putin has said that overcoming the consequences of the world economic crisis was one of the two main achievements of his second Premiership.[79] The other was the stabilizing the size of Russia's population between 2008–2011 following a long period of demographic collapse that began in the 1990s.[79]
At the United Russia Congress in Moscow on 24 September 2011, Medvedev officially proposed that Putin stand for the Presidency in 2012, an offer Putin accepted. Given United Russia's near-total dominance of Russian politics, many observers believed that Putin was all but assured of a third term. The move was expected to see Medvedev stand on the United Russia ticket in the parliamentary elections in December, with a goal of becoming Prime Minister at the end of his presidential term.[93] During the 2012 presidential campaign, Putin published seven articles presenting his vision for the future.[94]
After the parliamentary elections on 4 December 2011, tens of thousands Russians engaged in protests against alleged electoral fraud, the largest protests in Putin's time. Protesters criticized Putin and United Russia and demanded annulment of the election results.[95] Those protests sparked the fear of a colour revolution in society.[96][97][98] Putin organized a number of paramilitary groups loyal to himself and to the United Russia party in the period between 2005 and 2012.[99]
Third presidential term (2012–present)

On 4 March 2012, Putin won the 2012 Russian presidential elections in the first round, with 63.6% of the vote, despite widespread accusations of vote-rigging,[70][100][101] While efforts to make the elections transparent were publicized, including the usage of webcams in polling stations, the vote was criticized by the Russian opposition and by international observers from the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe for procedural irregularities.[8]

Anti-Putin protests took place during and directly after the presidential campaign. The most notorious protest was the Pussy Riot performance on 21 February, and subsequent trial.[102] An estimated 8,000–20,000 protesters gathered in Moscow on 6 May,[103][104] when eighty people were injured in confrontations with police,[105] and 450 were arrested, with another 120 arrests taking place the following day.[106]

Putin's presidency was inaugurated in the Kremlin on 7 May 2012.[107] On his first day as President, Putin issued 14 Presidential decrees, which are sometimes called the "May Decrees" by the media, including a lengthy one stating wide-ranging goals for the Russian economy. Other decrees concerned education, housing, skilled labor training, relations with the European Union, the defense industry, inter-ethnic relations, and other policy areas dealt with in Putin's program articles issued during the presidential campaign.[108][109]
In 2012 and 2013, Putin and the United Russia party backed stricter legislation against the LGBT community, in Saint Petersburg, Archangelsk and Novosibirsk; a law against "homosexual propaganda" (which prohibits such symbols as the rainbow flag as well as published works containing homosexual content) was adopted by the State Duma in June 2013.[110][111][112][113][114] Responding to international concerns about Russia's legislation, Putin asked critics to note that the law was a "ban on the propaganda of pedophilia and homosexuality" and he stated that homosexual visitors to the 2014 Winter Olympics should "leave the children in peace" but denied there was any "professional, career or social discrimination" against homosexuals in Russia.[115]
In June 2013, Putin attended a televised rally of the All-Russia People's Front where he was elected head of the movement,[116] which was set up in 2011.[117] According to journalist Steve Rosenberg, the movement is intended to "reconnect the Kremlin to the Russian people" and one day, if necessary, replace the increasingly unpopular United Russia party that currently backs Putin.[118]
Intervention in Ukraine and annexation of Crimea

In the wake of the 2014 Ukrainian revolution, Putin ordered Russian troops to seize Crimea from Ukraine. By 2 March, Russian troops had complete control over Crimea.[119][120][121] Then on 16 March Crimean status referendum was held in which, according to official results, a majority of 93 percent of voters voted to secede from Ukraine and join Russia; The referendum was regarded as illegitimate by most of the international community because of the events surrounding it[122] including the plebiscite being held while the peninsula was occupied by Russian soldiers.[123] The Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People called for a boycott of the referendum.[124][125] Thirteen members of the United Nations Security Council voted in favor of a resolution declaring the referendum invalid, but Russia vetoed it and China abstained.[126][127] A United Nations General Assembly resolution was later adopted, by a vote of 100 in favor vs. 11 against with 58 abstentions, which declared the referendum invalid and affirmed Ukraine's territorial integrity.[122] As a result, several countries imposed sanctions on Russia; more followed after pro-Russian unrest spread to the south and east of Ukraine and Russia's subsequent military intervention.[128][129] The economic development of Russia experienced a significant setback due to the sanctions and the concurrent fall in the world price of oil. The IMF has estimated that about half of the decline in GDP in 2015 was due to sanctions and Russia's ban on imports in response.[130] Although Putin at the time stated that no Russian troops were active in Crimea but only "local forces of self defence" on 17 April 2014 he stated "Of course our troops stood behind Crimea's self-defence forces".[131]

Putin outlined his Crimean views on 18 March in his "Crimean speech" in which he said that the ousting of Yanukovych was a "coup".[132] Also on 18 March Putin and the new leadership of Crimea signed a bill that led to the annexation of Crimea by Russia.[133]
Following the Crimean referendum unrest increased in eastern Ukraine apart from Crimea.[134] In a reference to 25 May 2014 presidential elections in Ukraine, Putin said that the Ukrainian elections were a step in the right direction.[135][136] The same day he also expressed that the pro-Russian separatists that had self-proclaimed the Donetsk People's Republic and Lugansk People's Republic should wait to hold their 11 May 2014 referendum on independence "in order to create proper conditions for this dialogue",[137] but the Russian backed separatists held the referendum anyway on 11 May 2014, claiming that nearly 90% of voter favoured independence from Ukraine.[134][138]

On 26 August 2014 Putin met with Ukraine President Petro Poroshenko in Minsk where he expressed a willingness to discuss the situation. Poroshenko responded by asked that Russia halt supplying arms to the Russian backed separatist fighters. He said his country wanted a political compromise and promised the interests of Russian-speaking people in eastern Ukraine would be respected.[139]

In a mid-November ARD interview Putin said Russia would not allow a military defeat of the pro-Russian side in the War in Donbass.[140] Putin also once again called the Euromaidan Revolution a political coup and claimed that by supporting President Poroshenko and his Yatsenyuk Government western governments were supporting Russophobes.[140] In the interview Putin again admitted that during the 2014 Crimean crisis “Our armed forces blocked literally the Ukrainian forces located in Crimea, but it was not in attempt to force anyone to vote, it’s impossible to do so. It was done in order to prevent the bloodshed”.[140]
In his annual speech on 4 December 2014 Putin stated that the March 2014 annexation of Crimean was a "historic event" that would not be reversed because Crimea is "Russia's spiritual ground".[141]
2015 Russian military intervention in Syria
President Putin authorized Russian military intervention in the Syrian Civil War, on the 30th of September 2015, following a formal request by the Syrian government for military help against rebel and jihadist groups.[142][143] The Russian military activities consisted of air strikes against militant groups opposed to the Syrian government, including the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), al-Nusra Front (al-Qaeda in the Levant) and the Army of Conquest.[144][145][146] On 14 March 2016 Russian President Vladimir Putin announced that the mission which he set for the Russian military in Syria "has been accomplished" and he ordered the withdrawal of the "main part" of the Russian forces from Syria.[147][148]
Domestic policies
Putin's domestic policies, especially early in his first presidency, were aimed at creating a vertical power structure. On 13 May 2000, he issued a decree putting the 89 federal subjects of Russia into seven administrative federal districts and appointed a presidential envoy responsible for each of those districts (whose official title is Plenipotentiary Representative).[citation needed]

According to Stephen White, Russia under the presidency of Putin made it clear that it had no intention of establishing a "second edition" of the American or British political system, but rather a system that was closer to Russia's own traditions and circumstances.[149] Putin's administration has often[by whom?] been described as a "sovereign democracy".[150] According to the proponents of that description, the government's actions and policies ought above all to enjoy popular support within Russia itself and not be determined from outside the country.[151][152]
In July 2000, according to a law proposed by Putin and approved by the Federal Assembly of Russia, Putin gained the right to dismiss heads of the 89 federal subjects. In 2004, the direct election of those heads (usually called "governors") by popular vote was replaced with a system whereby they would be nominated by the President and approved or disapproved by regional legislatures.[153][154] This was seen by Putin as a necessary move to stop separatist tendencies and get rid of those governors who were connected with organised crime.[155] This and other government actions effected under Putin's presidency have been criticised by many independent Russian media outlets and Western commentators as anti-democratic.[156][157] In 2012, as proposed by Putin's successor Dmitry Medvedev, the direct election of governors was re-introduced.[158]
During his first term in office, Putin persecuted some of the Yeltsin-era oligarchs, as well as his political opponents, resulting in the exile or imprisonment of such people as Boris Berezovsky, Vladimir Gusinsky, Mikhail Khodorkovsky; other oligarchs such as Roman Abramovich and Arkady Rotenberg[159] soon joined Putin's camp.[citation needed]
Putin succeeded in codifying land law and tax law and promulgated new codes on labour, administrative, criminal, commercial and civil procedural law.[160] Under Medvedev's presidency, Putin's government implemented some key reforms in the area of state security, the Russian police reform and the Russian military reform.
Economic, industrial, and energy policies
This section needs to be updated. (February 2016) |


Fueled by the 2000s commodities boom including record high oil prices (in nominal terms),[15][16] under the Putin administration from 2001 to 2007, the economy made real gains of an average 7% per year,[161] making it the 7th largest economy in the world in purchasing power. Russia's nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP) increased 6 fold, climbing from 22nd to 10th largest in the world. In 2007, Russia's GDP exceeded that of Russian SFSR in 1990, having recovered from the 1998 financial crisis and the preceding recession in the 1990s.[13]
During Putin's eight years in office, industry grew substantially, as did production, construction, real incomes, credit, and the middle class.[11][13][14][162][163] Putin has also been praised for eliminating widespread barter and thus boosting the economy.[164] Inflation remained a problem however.[13]
In 2001, Putin obtained approval for a flat tax rate of 13%;[165][166] the corporate rate of tax was also reduced from 35 percent to 24 percent;[165] Small businesses also get better treatment. The old system, with high tax rates, has been replaced by a new system where companies can choose either a 6-percent tax on gross revenue or a 15-percent tax on profits.[165] The overall tax burden is lower in Russia than in most European countries.[167]
A fund for oil revenue allowed Russia to repay all of the Soviet Union's debts by 2005.[13] Payments from the fuel and energy sector accounted for nearly half of the federal budget's revenues. The large majority of Russia's exports are made up of raw materials and fertilizers,[13] although exports as a whole accounted for only 8.7% of the GDP in 2007, compared to 20% in 2000.[168]
After 18 years of trying, Russia joined the World Trade Organization on 22 August 2012. However, there were few immediate economic benefits evident from that WTO membership.[169]
Under Putin, most of the world's largest automotive companies opened plants in Russia, which Putin encouraged via tax incentives, as well as protectionist measures which discouraged imports[170] In 2005, Putin initiated an industry consolidation programme to bring the main aircraft producing companies under a single umbrella organization, the United Aircraft Corporation (UAC). The aim was to optimize production lines and minimise losses.[171] The UAC is one of the so-called national champions and comparable to EADS in Europe.[172]
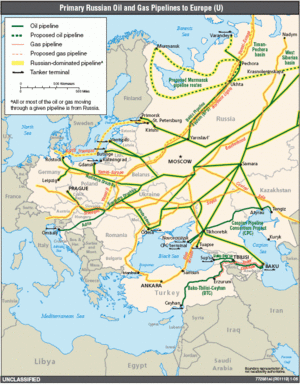
Putin sought to increase Russia's share of the European energy market by building submerged gas pipelines bypassing Ukraine and other countries which were often seen as non-reliable transit partners by Russia, especially following Russia-Ukraine gas disputes of the late 2000s (decade). Russia also undermined the rival pipeline project Nabucco by buying the Turkmen gas and redirecting it into Russian pipelines.
On the other hand, Russia diversified its export markets by building the Trans-Siberian oil pipeline to the markets of China, Japan and Korea, as well as the Sakhalin–Khabarovsk–Vladivostok gas pipeline in the Russian Far East. Russia has also recently built several major oil and gas refineries, plants and ports. Additionally, Putin has presided over construction of major hydropower plants, such as the Bureya Dam and the Boguchany Dam, as well as the restoration of the nuclear industry of Russia, with 1 trillion rubles ($42.7 billion) allocated from the federal budget to nuclear power and industry development before 2015.[173] A large number of nuclear power stations and units are currently being constructed by the state corporation Rosatom in Russia and abroad.

A construction program of floating nuclear power plants will provide power to Russian Arctic coastal cities and gas rigs, starting in 2012.[174][175] The Arctic policy of Russia also includes an offshore oilfield in the Pechora Sea is expected to start producing in early 2012, with the world's first ice-resistant oil platform and first offshore Arctic platform.[176] In August 2011 Rosneft, a Russian government-operated oil company, signed a deal with ExxonMobil for Arctic oil production.[177] "The scale of the investment is very large. It's scary to utter such huge figures" said Putin on signing the deal.[177]
The construction of a pipeline at a cost of $77bn, to be jointly funded by Russia and China, was signed off on by President Putin in Shanghai on 21 May 2014. It would be the biggest construction project in the world for the following 4 years, Putin said at the time. On completion in 4 to 6 years, the pipeline would deliver natural gas from the state-majority-owned Gazprom to China's state-owned China National Petroleum Corporation for the next 30 years, in a deal worth $400bn.[178]
In 2014, the Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project named Putin their Person of the Year Award for furthering corruption and organized crime.[179][180]
2014 Financial Crisis and economic downturn
In the second half of 2014, the Russian currency, the ruble collapsed. The depreciation was caused by the decline in the price of oil, Russia's main export, as well as international sanctions placed on Russia as a result of its military intervention in Ukraine and annexation of Crimea. These events in turn led to loss of investor confidence and capital flight.[181] At the time Putin argued that Russia was not in crisis[182] although he cancelled holidays for his key ministers.[183]
Russia reacted with its own sanctions against the West. During the crisis, according to some Russian chief executives, some Russian domestic industries have thrived, showing significant increases in output, such as the dairy and meat production sectors.[184] Additionally, to avoid isolation over the sanctions, Putin developed closer economic ties with Eastern countries. In October 2014, energy, trade and finance agreements with China worth $25 billion were signed. The following year, a $400 billion 30-year natural gas supply agreement was also signed with China.[185]
Economic troubles persisted into 2015, when the economy shrank by 3.7%, making Russia one of the top ten worst performing emerging economies in that year.[186] In the spring of 2014 the average monthly salary in Russia average had declined by 8 percent from the same month the previous year.[18]
Environmental policy

In 2004, President Putin signed the Kyoto Protocol treaty designed to reduce greenhouse gases.[187] However Russia did not face mandatory cuts, because the Kyoto Protocol limits emissions to a percentage increase or decrease from 1990 levels and Russia's greenhouse-gas emissions fell well below the 1990 baseline due to a drop in economic output after the breakup of the Soviet Union.[188]
Putin personally supervises a number of protection programmes for rare and endangered animals in Russia, such as the Amur Tiger, the White Whale, the Polar Bear and the Snow Leopard.[189][190][191][192]
Religious policy

Buddhism, Eastern Orthodox Christianity, Islam, and Judaism, defined by law as Russia's traditional religions and a part of Russia's historical heritage[193] enjoyed limited state support in the Putin era. The vast construction and restoration of churches, started in the 1990s, continued under Putin, and the state allowed the teaching of religion in schools (parents are provided with a choice for their children to learn the basics of one of the traditional religions or secular ethics). His approach to religious policy has been characterised as one of support for religious freedoms, but also the attempt to unify different religions under the authority of the state.[194] In 2012, Putin was honored in Bethlehem and a street was named after him.[195]

Putin regularly attends the most important services of the Russian Orthodox Church on the main Orthodox Christian holidays. He established a good relationship with Patriarchs of the Russian Church, the late Alexy II of Moscow and the current Kirill of Moscow. As President, he took an active personal part in promoting the Act of Canonical Communion with the Moscow Patriarchate, signed 17 May 2007 that restored relations between the Moscow-based Russian Orthodox Church and the Russian Orthodox Church Outside Russia after the 80-year schism.[196]
Putin and United Russia enjoy high electoral support in the national republics of Russia, in particular in the Muslim-majority republics of Povolzhye and the North Caucasus.
Under Putin, the Hasidic FJCR became increasingly influential within the Jewish community, partly due to the influence of Federation-supporting businessmen mediated through their alliances with Putin, notably Lev Leviev and Roman Abramovich.[197][198] According to the JTA, Putin is popular amongst the Russian Jewish community, who see him as a force for stability. Russia's chief rabbi, Berel Lazar, said Putin "paid great attention to the needs of our community and related to us with a deep respect."[199]
Military development


The resumption of long-distance flights of Russia's strategic bombers was followed by the announcement by Russian Defense Minister Anatoliy Serdyukov during his meeting with Putin on 5 December 2007, that 11 ships, including the aircraft carrier Kuznetsov, would take part in the first major navy sortie into the Mediterranean since Soviet times.[200] The sortie was to be backed up by 47 aircraft, including strategic bombers.[201]
While from the early 2000s (decade) Russia started pumping more money into its military and defence industry, it was only in 2008 that the full-scale Russian military reform began, aiming to modernize Russian Armed Forces and making them significantly more effective. The reform was largely carried by Defense Minister Anatoly Serdyukov during Medvedev's Presidency, under supervision of both Putin, as the Head of Government, and Medvedev, as the Commander-in-Chief of the Russian Armed Forces.
Key elements of the reform included reducing the armed forces to a strength of one million; reducing the number of officers; centralising officer training from 65 military schools into 10 'systemic' military training centres; creating a professional NCO corps; reducing the size of the central command; introducing more civilian logistics and auxiliary staff; elimination of cadre-strength formations; reorganising the reserves; reorganising the army into a brigade system; reorganising air forces into an air base system instead of regiments.[202]
The number of Russia's military districts was reduced to just 4. The term of draft service was reduced from two years to one, which put an end to the old harassment traditions in Russian army, since all conscripts became very close by draft age. The gradual transition to the majority professional army by the late 2010s was announced, and a large programme of supplying the Armed Forces with new military equipment and ships was started. The Russian Space Forces were replaced on 1 December 2011 with the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces.
In spite of Putin's call for major investments in strategic nuclear weapons, these will fall well below the New START limits due to the retirement of aging systems.[203]
Putin has also sought to increase Russian territorial claims in the Arctic and its military presence here. In August 2007, Russian expedition Arktika 2007, part of research related to the 2001 Russian territorial extension claim, planted a flag on the seabed below the North Pole.[204] Both Russian submarines and troops deployed in the Arctic have been increasing.[205][206]
Human rights policy

 related media
related mediaIn November 2001, Putin attended a Civic Forum sponsored by his administration with the purpose of bridging the chasm between state officials and grassroots activists including former Soviet dissident and Helsinki Watch, Ludmila Alekseeva.
A year later, Putin met with a similar group on International Human Rights Day and supported them:
Protecting civil rights and freedoms is a highly relevant issue for Russia. You know that next year will see the tenth anniversary of our constitution. It declares the basic human rights and freedoms to be the highest value and it enshrines them as self implementing standards. I must say that this is of course a great achievement.[207]
According to Human Rights Watch since May 2012, when Vladimir Putin was reelected as president, Russia has enacted many restrictive laws, started inspections of nongovernmental organizations, harassed, intimidated, and imprisoned political activists, and started to restrict critics. The new laws include the so-called “foreign agents” law, which is widely regarded as overbroad by including Russian human rights organizations which receive some international grant funding, the treason law, and the assembly law which penalizes many expressions of dissent.[208][209]
Foreign policy
Relations with Europe, NATO, and its member nations

Under Putin, Russia's relationships with NATO and the U.S. have passed through several stages. When Putin first became President, the relations were cautious. After the 9/11 attacks when Putin quickly supported the U.S. in the War on Terror, the opportunity for partnership appeared.[210] However, the U.S. responded by further expansion of NATO to Russia's borders and by unilateral withdrawal from the 1972 Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty.[210] Since 2003, when Russia did not support the Iraq War and when Putin became ever more distant from the West in his internal and external policies, the relations continued to deteriorate. According to Russia scholar Stephen F. Cohen, the narrative of the mainstream U.S. media, following that of the White House, became anti-Putin.[210] In an interview with Michael Stürmer, Putin was quoted saying that there were three questions which most concerned Russia and Eastern Europe: namely, the status of Kosovo, the Conventional Forces in Europe treaty and American plans to build missile defence sites in Poland and the Czech Republic, and suggested that all three were linked.[211] In Putin's view, concessions on one of these questions on the Western side might be met with concessions from Russia on another.[211] In a January 2007 interview, Putin said Russia is in favor of a democratic multipolar world and of strengthening the systems of international law.[212]

In February 2007, Putin criticized what he called the United States' monopolistic dominance in global relations, and "almost uncontained hyper use of force in international relations". He said the result of it is that "no one feels safe! Because no one can feel that international law is like a stone wall that will protect them. Of course such a policy stimulates an arms race".[213] This came to be known as the Munich Speech, and former NATO secretary Jaap de Hoop Scheffer called the speech, "disappointing and not helpful."[214] The months following Putin's Munich Speech[213] were marked by tension and a surge in rhetoric on both sides of the Atlantic. Both Russian and American officials, however, denied the idea of a new Cold War.[215]
Putin publicly opposed plans for the U.S. missile shield in Europe, and presented President George W. Bush with a counterproposal on 7 June 2007 which was declined.[216] Russia suspended its participation in the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe on 11 December 2007.[217]
Vladimir Putin strongly opposed Kosovo's 2008 declaration of independence, warning supporters of that precedent that it would de facto destroy the whole system of international relations.[218][219][220]
Putin had friendly relations with former American President George W. Bush, and many European leaders. Putin's "cooler" and "more business-like" relationship with Germany's current Chancellor, Angela Merkel is often attributed to Merkel's upbringing in the former DDR, where Putin was stationed when he was a KGB agent.[221] Relations were further strained after the 2014-15 Russian military intervention in Ukraine and the Annexation of Crimea.[222] In 2014, Russia was suspended from the G8 group as a result of its annexation of Crimea.[223][224]
In late 2013, Russian-American relations deteriorated further when the United States canceled a summit (for the first time since 1960), after Putin gave asylum to Edward Snowden, who leaked classified information from the NSA.[225]
In June 2015, Putin told an Italian newspaper that Russia has no intention of attacking NATO:
As for some countries’ concerns about Russia's possible aggressive actions, I think that only an insane person and only in a dream can imagine that Russia would suddenly attack NATO. I think some countries are simply taking advantage of people’s fears with regard to Russia."[226]
Relations between Russia and the United Kingdom deteriorated when the United Kingdom granted political asylum to Putin's former patron, oligarch Boris Berezovsky in 2003.[227] This deterioration was intensified by allegations that the British were spying and making secret payments to pro-democracy and human rights groups.[228] The end of 2006 brought more strained relations in the wake of the death by polonium poisoning of Alexander Litvinenko in London.[229][230] In 2007, the crisis in relations continued with expulsion of four Russian envoys over Russia's refusal to extradite former KGB bodyguard Andrei Lugovoi to face charges in the alleged murder of Litvinenko.[227] Mirroring the British actions, Russia expelled UK diplomats and took other retaliatory steps.[227]
Litvinenko inquiry
In 2015-16 the British Government conducted an inquiry into the death of Alexander Litvinenko. Its report was released in January 2016. According to the report, "The FSB operation to kill Mr Litvinenko was probably approved by Mr Patrushev and also by President Putin." The report outlined some possible motives for the murder, including Litvinenko's public statements and books about the alleged involvement of the FSB in mass murder, and what was "undoubtedly a personal dimension to the antagonism" between Putin and Litvinenko, led to the murder. The Kremlin dismissed the Inquiry as "a joke" and "whitewash".[231][232]
Relations with South and East Asia

In 2012, Putin wrote an article in the Hindu newspaper, saying that "The Declaration on Strategic Partnership between India and Russia signed in October 2000 became a truly historic step".[233][234] Prime Minister Manmohan Singh during Putin's 2012 visit to India: "President Putin is a valued friend of India and the original architect of the India-Russia strategic partnership".[235]
Putin's Russia maintains positive relations with other BRIC countries. The country has sought to strengthen ties especially with the People's Republic of China by signing the Treaty of Friendship as well as building the Trans-Siberian oil pipeline geared toward growing Chinese energy needs.[236] The mutual-security cooperation of the two countries and their central Asian neighbours is facilitated by the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation which was founded in 2001 in Shanghai by the leaders of China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
The announcement made during the SCO summit that Russia resumes on a permanent basis the long-distance patrol flights of its strategic bombers (suspended in 1992)[237][238] in the light of joint Russian-Chinese military exercises, first-ever in history held on Russian territory,[239] made some experts believe that Putin is inclined to set up an anti-NATO bloc or the Asian version of OPEC.[240] When presented with the suggestion that "Western observers are already likening the SCO to a military organisation that would stand in opposition to NATO", Putin answered that "this kind of comparison is inappropriate in both form and substance".[237]
Relations with Middle Eastern and North African countries
On 16 October 2007, Putin visited Iran to participate in the Second Caspian Summit in Tehran,[241][242] where he met with Iranian President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad.[243][244] This was the first visit of a Soviet or Russian leader[245] to Iran since Joseph Stalin's participation in the Tehran Conference in 1943, and thus marked a significant event in Iran-Russia relations.[246] At a press conference after the summit Putin said that "all our (Caspian) states have the right to develop their peaceful nuclear programmes without any restrictions".[247]

Subsequently, under Medvedev's presidency, Iran-Russia relations were uneven: Russia did not fulfill the contract of selling to Iran the S-300, one of the most potent anti-aircraft missile systems currently existing. However, Russian specialists completed the construction of Iran and the Middle East's first civilian nuclear power facility, the Bushehr Nuclear Power Plant, and Russia has continuously opposed the imposition of economic sanctions on Iran by the U.S. and the EU, as well as warning against a military attack on Iran. Putin was quoted as describing Iran as a "partner",[211] though he expressed concerns over the Iranian nuclear programme.[211]
In April 2008, Putin became the first Russian President who visited Libya.[248] Putin condemned the foreign military intervention of Libya, he called UN resolution as "defective and flawed," and added "It allows everything. It resembles medieval calls for crusades."[249][250] Upon the death of Muammar Gaddafi, Putin called it as "planned murder" by the US, saying: "They showed to the whole world how he (Gaddafi) was killed," and "There was blood all over. Is that what they call a democracy?"[251][252]

Regarding Syria, from 2000 to 2010 Russia sold around $1.5 billion worth of arms to that country, making Damascus Moscow's seventh-largest client.[253] During the Syrian civil war, Russia threatened to veto any sanctions against the Syrian government,[254] and continued to supply arms to the regime.
Putin opposed any foreign intervention. In June 2012, in Paris, he rejected the statement of French President Francois Hollande who called on Bashar Al-Assad to step down. Putin echoed the argument of the Assad regime that anti-regime '’militants'’ were responsible for much of the bloodshed. He also talked about previous NATO interventions and their results, and asked "What is happening in Libya, in Iraq? Did they become safer? Where are they heading? Nobody has an answer".[255]
On 11 September 2013, an opinion, written by Putin, was published in the New York Times regarding international events related to the United States, Russia and Syria.[256] Putin subsequently helped to arrange for Syria to disarm itself of chemical weapons.[257] He has subsequently taken an even stronger pro-Assadist stance.[258] Some analysts have summarized Putin as being allied with Shiites and Alawites in the Middle East.[259][260]
Relations with post-Soviet states
A series of so-called color revolutions in the post-Soviet states, namely the Rose Revolution in Georgia in 2003, the Orange Revolution in Ukraine in 2004 and the Tulip Revolution in Kyrgyzstan in 2005, led to frictions in the relations of those countries with Russia. In December 2004, Putin criticised the Rose and Orange revolutions, saying: "If you have permanent revolutions you risk plunging the post-Soviet space into endless conflict".[261]

A number of economic disputes erupted between Russia and some neighbours, such as the Russian import ban of Georgian wine. And in some cases, such as the Russia–Ukraine gas disputes, the economic conflicts affected other European countries, for example when a January 2009 gas dispute with Ukraine led state-controlled Russian company Gazprom to halt its deliveries of natural gas to Ukraine,[262] which left a number of European states, to which Ukraine transits Russian gas, with serious shortages of natural gas in January 2009.[262]
The plans of Georgia and Ukraine to become members of NATO have caused some tensions between Russia and those states.[263] In 2010, Ukraine did abandon these plans.[264] Putin allegedly declared at a NATO-Russia summit in 2008 that if Ukraine joined NATO Russia could contend to annex the Ukrainian East and Crimea.[265] At the summit he told US President George W. Bush that "Ukraine is not even a state!" while the following year Putin referred to Ukraine as "Little Russia".[266] Following the 2014 Ukrainian revolution in March 2014, the Russian Federation annexed Crimea.[120][121][267] According to Putin this was done because "Crimea has always been and remains an inseparable part of Russia".[268] After the Russian annexion of Crimea he said that Ukraine includes "regions of Russia's historic south" and "was created on a whim by the Bolsheviks".[269] He went on to declare that the February 2014 ousting of Ukrainian President Viktor Yanukovych had been orchestrated by the West as an attempt to weaken Russia. "Our Western partners have crossed a line. They behaved rudely, irresponsibly and unprofessionally," he said, adding that the people who had come to power in Ukraine were "nationalists, neo-Nazis, Russophobes and anti-Semites".[269] In a July 2014 speech midst an armed insurgency in Eastern Ukraine Putin stated he would use Russia's "entire arsenal" and "the right of self defence" to protect Russian speakers outside Russia.[270]
In late August 2014, Putin stated: "People who have their own views on history and the history of our country may argue with me, but it seems to me that the Russian and Ukrainian peoples are practically one people".[271] After making a similar claim late December 2015 he stated: "the Ukrainian culture, as well as Ukrainian literature, surely has a source of its own".[272]
In August 2008, Georgian President Mikheil Saakashvili attempted to restore control over the breakaway South Ossetia. However, the Georgian military was soon defeated in the resulting 2008 South Ossetia War after regular Russian forces entered South Ossetia and then Georgia proper, then also opened a second front in the other Georgian breakaway province of Abkhazia against with Abkhazian forces.[273][274] During this conflict, according to French diplomat Jean-David Levitte, Putin intended to depose the Georgian President and declared: "I am going to hang Saakashvili by the balls".[275]
Despite existing or past tensions between Russia and most of the post-Soviet states, Putin has followed the policy of Eurasian integration. Putin endorsed the idea of a Eurasian Union in 2011,[276][277][278][279] The concept was proposed by the President of Kazakhstan in 1994.[280] On 18 November 2011, the presidents of Belarus, Kazakhstan and Russia signed an agreement setting a target of establishing the Eurasian Union by 2015.[281] The Eurasian Union was established on 1 January 2015.[282]
Relations with Australia, Latin America, and others
Putin and his successor Medvedev enjoyed warm relations with the late Hugo Chávez of Venezuela. Much of this has been through the sale of military equipment; since 2005, Venezuela has purchased more than $4 billion worth of arms from Russia.[283] In September 2008, Russia sent Tupolev Tu-160 bombers to Venezuela to carry out training flights.[284] In November 2008, both countries held a joint naval exercise in the Caribbean.[285] Earlier in 2000, Putin had re-established stronger ties with Fidel Castro's Cuba.

In September 2007, Putin visited Indonesia and in doing so became the first Russian leader to visit the country in more than 50 years.[286] In the same month, Putin also attended the APEC meeting held in Sydney where he met with John Howard, who was the Australian Prime Minister at the time, and signed a uranium trade deal for Australia to sell uranium to Russia. This was the first visit by a Russian president to Australia.[287]
International sporting events
Putin has won international support for sport in Russia.[needs update?] In 2007, he led a successful effort on behalf of Sochi (located along the Black Sea near the border between Georgia and Russia) for the 2014 Winter Olympics and the 2014 Winter Paralympics,[288] the first Winter Olympic Games to ever be hosted by Russia. Likewise, in 2008, the city of Kazan won the bid for the 2013 Summer Universiade, and on 2 December 2010 Russia won the right to host the 2017 FIFA Confederations Cup and 2018 FIFA World Cup, also for the first time in Russian history. In 2013, Putin stated that gay athletes would not face any discrimination at the 2014 Sochi Winter Olympics.[289] US President Barack Obama did not attend the 2014 Winter Olympics,[290] joining other western leaders in the apparent symbolic boycott.[291]
Speeches
Addresses to the Federal Assembly
Putin has made eight annual addresses to the Federal Assembly of Russia,[292] speaking on the situation in Russia, and on the guidelines of the internal and foreign policy of the State, as prescribed in Article 84 of the Constitution.[293]
On 18 March 2014, Putin made a well-publicized speech about the situation in Crimea.[294] On 24 October 2014, Putin delivered the Valdai speech.[295][296][297][298]
Speeches abroad

One of the most important and widely publicized speeches of Putin made abroad was made on 10 February 2007 on the Munich Conference on Security Policy, and hence became known as the Munich speech. It was dubbed by the press to be "the turning point of the Russian foreign policy", and western observers called it the most tough speech from a leader of Russia since the time of the Cold War.[299] The speech was also seen as been made by Putin to openly assert a reprised role of Russia in international politics that would be close to that of the Soviet Union; a return to this role is seen as one of the achievements of Putin's presidency.[299]
In the Munich speech Putin called for upholding the principle "security for everyone is security for all", criticized the policies of the United States and NATO, condemned the unipolar model of international relations as flawed and lacking moral basis, condemned the "hypocrisy" of countries trying to teach democracy to Russia, condemned the domination of hard power and enforcement by the U.S. norms and laws to other countries bypassing international law and substitution of the United Nations by NATO or the EU.[299] Putin also called for a stop to the militarization of space and questioned the plans to deploy American missile defense in Europe as threatening strategic nuclear balance and spurring a new arms race. He also claimed that the countries dubbed as rogue states by the West were not going to be capable of threatening Europe or the U.S. with ballistic missiles in the foreseeable future.[299] His speech was criticized by some attendant delegates at the conference, including former NATO secretary Jaap de Hoop Scheffer who called it "disappointing and not helpful."[214]
Outdoor speeches
Notable Putin's outdoor speeches include his addresses during the Victory Day Moscow Military Parades one every 9 May in the years between 2000 and 2007. Under Putin's presidency and premiership, the old Soviet tradition of 9 May Parades, which had been in decline in 1990s, was gradually restored in full grandeur. Since the 2008 Moscow Victory Day Parade the armoured fighting vehicles resumed regular taking part in the Red Square parades. Putin often used the Victory Day occasion to discuss Russia's military development and Russia's security and foreign affairs. For example, he said on 9 May 2007 that "threats are not becoming fewer but are only transforming and changing their appearance. These new threats, just as under the Third Reich, show the same contempt for human life and the same aspiration to establish an exclusive dictate over the world."[301]
During his 2012 presidential campaign Putin made a single outdoor public speech at the 100,000-strong rally of his supporters in the Luzhniki Stadium on 23 February, Russia's Defender of the Fatherland Day.[98] In the speech he called not to betray the Motherland, but to love her, to unite around Russia and to work together for the good, to overcome the existing problems.[302] He said that the foreign interference into Russian affairs should not be allowed, that Russia has its own free will. He compared the political situation at the moment (when fears were spread in the Russian society that 2011–2012 Russian protests could instigate a color revolution directed from abroad) with the First Fatherland War of 1812, reminding that its 200th anniversary and the anniversary of the Battle of Borodino would be celebrated in 2012. Putin cited Lermontov's poem Borodino and ended the speech with Vyacheslav Molotov's famous Great Patriotic War slogan "The Victory Shall Be Ours!" ("Победа будет за нами!").[98][302]
On the post-election celebration rally, while making an acceptance speech, Putin was for the first time ever seen with tears in his eyes (later he explained that "it was windy"). He said to a 110,000-strong audience: "I told you we would win and we won!".[97][303]
Public image
Ratings, polls, and assessments


According to public opinion surveys in June 2007, Putin's approval rating was 81%, the second highest of any leader in the world that year,[304][305] following British Prime Minister Tony Blair, who received a 93% public approval rating in September 1997.[306][307][308] In January 2013, Putin's approval rating fell to 62%, the lowest point since 2000 and a ten-point drop over two years.[309] In May 2014 his approval rating rose to 85.9%, a six-year high.[310] Observers see Putin's high approval ratings as a consequence of the significant improvements in living standards and Russia's reassertion of itself on the world scene during his presidency.[311][312] One analysis attributed Putin's popularity, in part, to state-owned or state-controlled television.[313] A 2005 survey showed that three times as many Russians felt the country was "more democratic" under Putin than it was during the Yeltsin or Gorbachev years, and the same proportion thought human rights were better under Putin than under Yeltsin.[313] In a 2016 survey in Kursk Oblast support for Putin did not exceed 25% and country-wide polls were commented as inflated by 2-3x according to a politician Olga Li.[314]
Putin was Time magazine's Person of the Year for 2007.[315] In April 2008, he was put on the Time 100 most influential people in the world list.[316] In 2013, 2014 and 2015, he was ranked as the world's most powerful person by Forbes.[317]
Former Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev credited Putin with having "pulled Russia out of chaos",[318] but has also criticized Putin for restricting freedom of press and for seeking the third term in the presidential elections. According to opposition politician Boris Nemtsov, Putin is turning Russia into a "raw materials colony" of China.[319]
Criticism of Putin has been widespread especially over the Internet in Russia,[320] and it is said that the Russian youth organisations finance a full "network" of pro-government bloggers.[321] In the U.S. embassy cables published by WikiLeaks in late 2010, American diplomats said Putin's Russia had become "a corrupt, autocratic kleptocracy centred on the leadership of Vladimir Putin, in which officials, oligarchs and organised crime are bound together to create a virtual mafia state."[322][323] Putin called it "slanderous".[324]
By Western commentators and the Russian opposition, Putin has been described as a dictator.[325][326] Putin biographer Masha Gessen has stated that "Putin is a dictator," comparing him to Alexander Lukashenko of Belarus.[327][328] Former UK Foreign Secretary David Miliband once described Putin as a "ruthless dictator" whose "days are numbered."[329] U.S. Presidential candidate Mitt Romney called Putin "a real threat to the stability and peace of the world."[330] Former U.S. Secretary of State Henry Kissinger wrote: "For the West, the demonization of Vladimir Putin is not a policy; it is an alibi for the absence of one."[331] The portrayal of Putin in the Western media has been described by others as being a politically motivated distortion of facts. According to American scholar of Russian studies Stephen F. Cohen, "since the early 2000s, the media have followed a different leader-centric narrative, also consistent with US policy, that devalues multifaceted analysis for a relentless demonization of Putin, with little regard for facts".[332] The British journalist Seumas Milne argues that "the demonisation of Russia risks paving the way for war".[333]
In the fall of 2011, the anti-Putin opposition movement in Russia became more visible, with street protests against allegedly falsified parliamentary elections (in favor of Putin's party, United Russia) cropping up across major Russian cities. Following Putin's re-election in March 2012, the movement ran out of steam, mainly for two reasons: lack of common positive programme other than topple Putin and the increased crackdown on street rallies. In fact, observers noted the protests resulted in what was not intended: instead of liberalization, the government policy grew more conservative.[334]
After EU and U.S. sanctions against Russian officials as a result of the 2014 pro-Russian unrest in Ukraine, Putin's approval rating reached a record high of 87 percent, according to the results of a survey published on 6 August 2014 by the independent Levada Center pollster.[335][336]
Personal image


Putin cultivates an outdoor, sporty, tough guy public image, demonstrating his physical prowess and taking part in unusual or dangerous acts, such as extreme sports and interaction with wild animals,[337] part of a public relations approach that, according to Wired, "deliberately cultivates the macho, take-charge superhero image".[338] For example, in 2007, the tabloid Komsomolskaya Pravda published a huge photograph of a bare-chested Putin vacationing in the Siberian mountains under the headline: "Be Like Putin."[339] Some of the activities have been criticised for being staged.[340][341]
Notable examples of Putin's macho adventures include:[342] flying military jets,[342] demonstrating his martial art skills,[342] riding horses, rafting, fishing and swimming in a cold Siberian river (doing all that mostly bare-chested),[339][343] descending in a deepwater submersible,[344] tranquilizing tigers with a tranquiliser gun,[339][345] tranquilizing polar bears,[346] riding a motorbike,[342][347] co-piloting a firefighting plane to dump water on a raging fire,[338][342] shooting darts at whales from a crossbow for eco-tracking,[342][348] driving a race car,[342][349] scuba diving at an archaeological site,[340][350] attempting to lead endangered cranes in a motorized hang glider,[351] and catching big fish.[352][353]
There are a large number of songs about Putin.[354] Some of the well-known include: "[I Want] A Man Like Putin" by Singing Together,[355] "Horoscope (Putin, Don't Piss!)" by Uma2rman,[356] "Go Hard Like Vladimir Putin" by K. King and Beni Maniaci,[357] "VVP" by Tajik singer Tolibjon Kurbankhanov,[358][359] "Our Madhouse is Voting for Putin" by Working Faculty and "A Song About Putin" by the Russian Airborne Troops band.[360] There is also "Putin khuilo!", the song, originally emerged as chants Ukrainian football fans and spread in Ukraine (among supporters Euromaidan), then in other countries.[361][362]
Putin's name and image are widely used in advertisement and product branding.[338] Among the Putin-branded products are Putinka vodka, the PuTin brand of canned food, the Gorbusha Putina caviar and a collection of T-shirts with his image.[363]
Putin also is a subject of Russian jokes and chastushki, such as "[Before Putin] There Was No Orgasm" featured in the comedy film The Day of Elections.[364] There is a meta-joke that, since the coming of Putin to power, all the classic jokes about a smart yet rude boy called Vovochka (Russian diminutive from Vladimir) have suddenly become political jokes.[citation needed]
Putin features in the colouring book for children Vova and Dima (presented on his 59th birthday),[365] where he and Dmitry Medvedev are drawn as good-behaving little boys, and in the Superputin online comics series, where Putin and Medvedev are portrayed first as superheroes,[338] and then as a troll and an orc in the World of Warcraft.[366]
A Russian movie called A Kiss not for Press was premiered in 2008 on DVD. The movie is said to be based on biography of Vladimir Putin and his wife Lyudmila.[367]
Putinisms

Putin has produced a large number of aphorisms and catch-phrases, known as putinisms.[368] Many of them were first made during his annual Q&A conferences, where Putin answered questions from journalists and other people in the studio, as well as from Russians throughout the country, who either phoned in or spoke from studios and outdoor sites across Russia. Putin is known for his often tough and sharp language, often alluding at Russian jokes and folk sayings.[368]
Personal life
Family

On 28 July 1983 Putin married Kaliningrad-born Lyudmila Shkrebneva, at that time an undergraduate student of the Spanish branch of the philology department of the Leningrad State University and a former Aeroflot flight attendant. They lived together in Germany from 1985 to 1990. Mrs. Putin was rarely seen with her husband[369][370] and in 2010 the media began to report rumours that the couple had separated.[369][370] Putin and Lyudmila announced on 6 June 2013 that their marriage was over. The Kremlin confirmed on 1 April 2014 the divorce had been finalised.[371]
Putin had been linked by newspapers with other women, including gymnast Alina Kabayeva[369][370] and ex-spy Anna Chapman.[372] These rumours were denied.[373]

Putin had two daughters with his ex-wife, Mariya Putina (born 28 April 1985 in Leningrad, Soviet Union)[citation needed] and Yekaterina Putina (born 31 August 1986 in Dresden, East Germany).[citation needed] The daughters grew up in East Germany[374] and attended the German School in Moscow until his appointment as Prime Minister. After that they studied international economics at the Finance Academy in Moscow, although it was not officially reported due to security reasons.[citation needed] Official sources such as Pravda claim they started their studies at St Petersburg State University, with Mariya at the biology and geology department and Yekaterina at "the oriental studies section of the university's philological department. It is the most prestigious section of the department that graduates future diplomats."[375]
The Sunday Times has published one picture of Mariya with her parents.[376]

According to an article in the newspaper De Pers, Mariya is married to a native of the Netherlands, Jorrit Faassen.[377][378] The couple live in Voorschoten, Netherlands.[379][380] Several sources claim that Yekaterina is also married after a November 2012 wedding [381]
Putin's own comment in a televised interview is that "both his daughters live in Moscow, where they're combining their studies with part-time work. “I’m proud of them”, said Putin.[382]

One of Vladimir Putin's relatives was Viktor Medvedchuk – the Ukrainian business oligarch influential until the 2004 Orange Revolution. Putin became the godfather of Medvedchuk's daughter Darina in 2004.[383][384] The two maintain regular relations since,[384][385] with their meetings sometimes covered by the Russian state-controlled TV channels.[386]
Another relative is Roman Putin, CEO of Putin Consulting, a firm aiming "to facilitate entrance into the Russian market, to minimize the transaction and administrative barriers, and to ensure complex business security".[387]
Personal wealth and residences
Figures released during the legislative election of 2007 put Putin's wealth at approximately 3.7 million rubles (US$150,000) in bank accounts, a private 77.4-square-meter (833 sq ft) apartment in Saint Petersburg, 260 shares of Bank Saint Petersburg (with a December 2007 market price $5.36 per share[388]) and two 1960s-era Volga M21 cars that he inherited from his father and does not register for on-road use. In 2012 Putin reported an income of 3.6 million rubles ($113,000). This has led opponents, such as politician Boris Nemtsov, to question how Putin can afford certain possessions, such as his 11 luxury watches worth an estimated $700,000.[389]

Putin's purported 2006 income totalled 2 million rubles (approximately $80,000).[391] According to the data Putin did not make it into the 100 wealthiest Duma candidates of his own United Russia party.[392]
Unconfirmed claims by some[who?] Russian opposition politicians and journalists allege that Putin secretly possesses a large fortune (as much as $70 billion[393]) via successive ownership of stakes in a number of Russian companies.[394][395] Asked at a press conference on 14 February 2008 whether he was the richest person in Europe, as some newspapers claimed; and if so, to state the source of his wealth, Putin said "This is plain chatter, not worthy discussion, plain bosh. They have picked this in their noses and have smeared this across their pieces of paper. This is how I view this."[396]

Not long after he returned from his KGB service in Dresden, East Germany, Putin built a dacha in Solovyovka on the eastern shore of Lake Komsomolskoye on the Karelian Isthmus in Priozersky District of Leningrad Oblast, near St. Petersburg. The dacha had burned down in 1996. Putin built a new one identical to the original and was joined by a group of seven friends who built dachas beside his. In the fall of 1996, the group formally registered their fraternity as a co-operative society, calling it Ozero (Lake) and turning it into a gated community.[397]
As President and then Prime-Minister, apart from the Moscow Kremlin and the White House, Putin has used numerous official residences throughout the country. In August 2012 Nemtsov listed 20 villas and palaces, nine of which were built during Putin's 12 years in power.[398]

Some of the residences include: Gorki-9 near Moscow, Bocharov Ruchey in Sochi, Dolgiye Borody in Novgorod Oblast, Novo-Ogaryovo in Moscow Oblast and Riviera in Sochi (the latter two were left for Putin when he was Prime-Minister in 2008–2012, others were used by Dmitry Medvedev at that period).[399] Furthermore, a massive Italianate-style mansion costing an alleged US$1 billion[390] and dubbed "Putin's Palace" is under construction near the Black Sea village of Praskoveevka. The mansion, built on government land and sporting 3 helipads, a private road paid for from state funds and guarded by officials wearing uniforms of the official Kremlin guard service, is said to have been built for Putin's private use. In 2012 Sergei Kolesnikov, a former business associate of Putin's, told the BBC's Newsnight programme, that he had been ordered by deputy prime minister, Igor Sechin, to oversee the building of it.[400] In 2014, the first detailed study of the alleged corruption of Putin and his inner circle – Putin's Kleptocracy: Who Owns Russia? by Karen Dawisha, was published in the West.[401][402]
Languages
Putin is fluent in the German language.[403] After becoming President, Putin was reported to have been taking English lessons, and was conversing directly with Bush and native English speakers in informal situations; however, he continues to use interpreters for formal talks. Putin spoke English in public for the first time during the state dinner in Buckingham Palace in 2003, saying a few phrases while delivering his condolences to Queen Elizabeth II on the death of her mother.[404] In a 2013 interview, the Kremlin Chief of Staff, Sergei Ivanov, revealed that he and Putin sometimes conversed in Swedish.[405]
Religion

Putin's father was "a model communist, genuinely believing in the communist ideals, while trying to put them into practice in his own life". As a result, Putin's father became Secretary of the Communist Party cell in his workshop, and then after taking night classes, he joined the factory's Party bureau.[26] Though his father was a "militant atheist",[406] Putin's mother "was a devoted Orthodox believer". Though Putin's mother kept no icons at home, she attended church regularly, despite the government's persecution of the Russian Orthodox Church at that time. Putin's mother ensured that he was secretly christened as a baby, and she regularly took him to services. His father knew of this; however, he turned a blind eye.[26]
According to Putin's own statements, his religious awakening followed the serious car crash of his wife in 1993, and was deepened by a life-threatening fire that burned down their dacha in August 1996.[406] Right before an official visit to Israel his mother gave him his baptismal cross telling him to get it blessed. Putin stated: "I did as she said and then put the cross around my neck. I have never taken it off since."[26] When asked whether he believes in God during his interview with Time, he responded saying: "...There are things I believe, which should not in my position, at least, be shared with the public at large for everybody's consumption because that would look like self-advertising or a political striptease."[407] His rumoured confessor is ultra-conservative Bishop Tikhon. There rumors are persistent, but officially they are refused to be either confirmed or denied, on the grounds of the ultimate privacy of the issue.[408]
Martial arts
| Vladimir Putin | |
|---|---|
 Putin on a tatami at the Kodokan Institute in Tokyo on 5 September 2000 | |
| Height | 1.70 m (5 ft 7 in)[409] |
| Teacher(s) | Anatoly Rahlin, Hatsuo Royama |
| Rank | Sambo: Master of Sports, Champion of Leningrad Judo: 6th degree black belt, Champion of Leningrad Kyokushin kaikan: 8th dan black belt |
| Years active | 1966–present |
| Occupation | President of Russia |
Putin began training in sambo (a martial art that originated in the Soviet Union) at the age of 14, before switching to judo, which he continues to practice today.[410] Putin won competitions in his hometown of Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg), including the senior championships of Leningrad in both sambo and judo. He is the President of the Yawara Dojo, the same Saint Petersburg dojo he practiced at when young. Putin co-authored a book on his favorite sport, published in Russian as Judo with Vladimir Putin and in English under the title Judo: History, Theory, Practice (2004).[411]
Currently, Putin holds a 6th dan (red/white belt)[412] and is best known for his Harai Goshi (sweeping hip throw). Putin earned Master of Sports (Soviet and Russian sport title) in judo in 1975 and in sambo in 1973. At a state visit to Japan, Putin was invited to the Kodokan Institute, the judo headquarters, where he showed different judo techniques to the students and Japanese officials.
Putin also held an 8th dan black belt in Kyokushin kaikan karate gotten in November 2014.[413][414] He was presented the black belt in December 2009 by Japanese champion Kyokushin Karate-Do master Hatsuo Royama.[415]
Other sports
Putin often is seen on outdoor activities with Dmitry Medvedev, promoting sports and healthy way of life among Russians: they were seen alpine skiing in Krasnaya Polyana,[416] playing badminton, cycling and fishing.[417]
Putin also enjoys watching football and supports FC Zenit Saint Petersburg, the main team of his native city.[418]
Pets

Putin owned a female black Labrador Retriever named Koni, given as a gift in 2000 by the General of the Army and Russia's Minister of Emergency Situations, Sergey Shoigu. In 2003, Koni gave birth to eight pups, who were later given as presents to Russian citizens, politicians, and foreign ambassadors.[419] In 2004, Koni gained additional fame when the largest Russian publisher of children's books published a book, entitled Connie's Stories.[420] In 2008, Koni became the first recipient of a GLONASS-enabled pet collar to highlight the progress of the Russian global navigation satellite system.[421]
In 2010, Bulgarian Prime Minister Boyko Borisov gave Putin a Karakachan dog, who was given the name, Buffy.[422]
Recognition
- In September 2006, France's president Jacques Chirac awarded Vladimir Putin the Grand-Croix (Grand Cross) of the Légion d'honneur, the highest French decoration, to celebrate his contribution to the friendship between the two countries. This decoration is usually awarded to the heads of state considered very close to France.[423]
- In 2007, Putin was named Time magazine's Person of the Year.
- On 12 February 2007 Saudi King Abdullah awarded Putin the King Abdul Aziz Award, Saudi Arabia's top civilian decoration.[424]
- On 10 September 2007 UAE President Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan awarded Putin the Order of Zayed, the UAE's top civil decoration.[425]
- In December 2007 Expert, a Russian business-oriented weekly magazine, named Putin as its Person of the Year.[426]
- On 5 October 2008 the central street of Grozny, the capital of Russia's Republic of Chechnya, was renamed from the Victory Avenue to the Vladimir Putin Avenue, as ordered by the Chechen President Ramzan Kadyrov.[427]
- In February 2011 the parliament of Kyrgyzstan named a peak in Tian Shan mountains Vladimir Putin Peak.[428]
- On 15 November 2011 the China International Peace Research Center awarded the Confucius Peace Prize to Putin, citing as reason Putin's opposition to NATO's Libya bombing in 2011 while also paying tribute to his decision to go to war in Chechnya in 1999.[429] According to the committee, Putin's "Iron hand and toughness revealed in this war impressed the Russians a lot, and he was regarded to be capable of bringing safety and stability to Russia".[430]
- In 2011, the University of Belgrade awarded Putin an honorary doctorate.[431]
References
- ^ Allen, Cooper (2 April 2014). "Putin divorce finalized, Kremlin says". USA Today.
- ^ Paddock, Richard. "Putin Rolls to Victory, Avoiding a Runoff", Los Angeles Times (March 27, 2000).
- ^ Hale, Henry E.; Timothy J. Colton (8 September 2009). "Russians and the Putin-Medvedev "Tandemocracy": A Survey-Based Portrait of the 2007–08 Election Season" (PDF). The National Council for Eurasian and East European Research. Seattle, WA: University of Washington. Retrieved 15 March 2012.
- ^ Vasilyeva, Natallya. "Putin claims to support term limits as he readies to take helm for 3rd time", China Post (12 April 2012).
- ^ Shuster, Simon. "In Russia, an Election Victory for Putin and Then a 'Paid Flash Mob'", Time (March 5, 2012).
- ^ "Putin Hails Vote Victory, Opponents Cry Foul". RIA Novosti. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ [1]
- ^ a b "Russia's presidential election marked by unequal campaign conditions, active citizens' engagement, international observers say". Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe.
- ^ [2]
- ^ a b Guriev, Sergei; Tsyvinski, Aleh (2010). "Challenges Facing the Russian Economy after the Crisis". Russia After the Global Economic Crisis. Peterson Institute for International Economics; Centre for Strategic and International Studies; New Economic School. pp. 12–13. ISBN 9780881324976.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Russians weigh Putin's protégé". Moscow. Associated Press. 3 May 2008. Retrieved 29 December 2008.
- ^ of Russia from 1992 to 2007 International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 12 May 2008
- ^ a b c d e f "Russia's economy under Vladimir Putin: achievements and failures". RIA Novosti. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ a b Putin's Economy – Eight Years On. Russia Profile, 15 August 2007. Retrieved 23 April 2008
- ^ a b c d Putin: Russia's Choice, (Routledge 2007), by Richard Sakwa, Chapter 9
- ^ a b c d Fragile Empire: How Russia Fell In and Out of Love with Vladimir Putin, Yale University Press (2013), by Ben Judah, page 17
- ^ http://www.themoscowtimes.com/business/article/economic-slowdown-eases-in-q3/389355.html
- ^ a b http://www.themoscowtimes.com/news/article/russians-average-monthly-salary-falls-to-500-as-food-prices-skyrocket/516947.html
- ^ Thompson, Mark (26 January 2016). "Russia: One of 10 worst economies in 2015". CNN.
- ^ "Democracy Index 2015 Democracy in an age of anxiety". Economist Intelligence Unit. 2015.
- ^ "Prime Minister of the Russian Federation - Biography". 14 May 2010. Archived from the original on 31 July 2015. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
{{cite web}}:|archive-date=/|archive-url=timestamp mismatch; 14 May 2010 suggested (help); Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Vladimir Putin, Nataliya Gevorkyan, Natalya Timakova, Andrei Kolesnikov (2000). First Person. trans. Catherine A. Fitzpatrick. PublicAffairs. p. 208. ISBN 978-1-58648-018-9.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ First Person An Astonishingly Frank Self-Portrait by Russia's President Vladimir Putin The New York Times, 2000
- ^ Putin's Obscure Path From KGB to Kremlin Los Angeles Times, 19 March 2000
- ^ Portrait of the Young Vladimir Putin Newsweek and the Daily Beast, 20 February 2012
- ^ a b c d (Sakwa 2008, p. 3)
- ^ a b (Sakwa 2008, p. 2)
- ^ "Prime Minister". Russia.rin.ru. Retrieved 24 September 2011.
- ^ "In Tel Aviv, Putin's German Teacher Recalls 'Disciplined' Student" (Archive). Haaretz. 26 March 2014. Retrieved on 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Polyglots and insults: How our European leaders use language". Retrieved 18 November 2015.
- ^ Hoffman, David (30 January 2000). "Putin's Career Rooted in Russia's KGB". The Washington Post.
- ^ Lynch, Allen. Vladimir Putin and Russian Statecraft, p. 15 (Potomac Books 2011).
- ^ Владимир Путин. От Первого Лица. Chapter 6
- ^ a b c d Pribylovsky, Vladimir (2010). "Valdimir Putin". Власть-2010 (60 биографий) (PDF) (in Russian). Moscow: Panorama. pp. 132–139. ISBN 978-5-94420-038-9.
- ^ "Ben Judah: The ruthlessness of Vladimir Putin". newstatesman.com. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ (Sakwa 2008, pp. 8–9)
- ^ a b Hoffman, David (30 January 2000). "Putin's Career Rooted in Russia's KGB". The Washington Post.
- ^ "Putin set to visit Dresden, the place of his work as a KGB spy, to tend relations with Germany". International Herald Tribune. 9 October 2006. Archived from the original on 20 February 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Gessen, Masha (2012). The Man Without a Face: The Unlikely Rise of Vladimir Putin (1st ed.). New York City, New York: Riverhead. p. 60. ISBN 1594488428. Retrieved 3 March 2014.
- ^ "Vladimir Putin, The Imperialist". Time. 10 December 2014. Retrieved 11 December 2014.
- ^ a b Sakwa, Richard (2007). Putin : Russia's Choice (2nd ed.). Abingdon, Oxon: Routledge. p. 10. ISBN 9780415407656. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
- ^ R. Sakwa Putin: Russia's Choice, pp. 10–11
- ^ R. Sakwa Putin: Russia's Choice, p. 11
- ^ Remick, David. "Watching the Eclipse". The New Yorker (11 August 2014). Retrieved 3 August 2014.
- ^ Archived 2007-02-21 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Kovalev, Vladimir (23 July 2004). "Uproar at Honor For Putin". The Saint Petersburg Times.
- ^ Hoffman, David (30 January 2000). "Putin's Career Rooted in Russia's KGB". The Washington Post.
- ^ Archived 2007-09-27 at the Wayback Machine by Catherine Belton
- ^ Walsh, Nick Paton (29 February 2004). "The Man Who Wasn't There". The Observer.
- ^ a b Владимир Путин: от ассистента Собчака до и.о. премьера (in Russian). GAZETA.RU.
- ^ "ПУТИН — КАНДИДАТ НАУК" (in Russian). zavtra.ru. 24 May 2000. Archived from the original on 6 August 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Gustafson, Thane. Wheel of Fortune: The Battle for Oil and Power in Russia, p. 246 (Harvard University Press, 2012).
- ^ a b "It All Boils Down to Plagiarism". Cdi.org. 31 March 2006. Archived from the original on 6 August 2009. Retrieved 2 March 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "The President as Candidate". Kommersant. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ "Researchers peg Putin as plagiarist over thesis". Washington Times. 24 March 2006. Retrieved 5 March 2014.
- ^ The Half-Decay Products (in Russian) by Oleg Odnokolenko. Itogi, #47(545), 2 January 2007.
- ^ "Text of Yeltsin's speech in English". BBC News. 9 August 1999. Archived from the original on 18 March 2015. Retrieved 31 May 2007.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Yeltsin redraws political map BBC, 10 August 1999
- ^ "Yeltsin's man wins approval". BBC News. 16 August 1999. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ Richard Sakwa Putin: Russia's choice, 2008. p. 20.
- ^ Archived 2001-07-02 at the Wayback Machine[dead link] Norsk Utenrikspolitisk Institutt
- ^ "Russia: Putin Travels To Chechnya To Visit Troops". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 3 March 2000.
- ^ УКАЗ от 31 декабря 1999 г. № 1763 О ГАРАНТИЯХ ПРЕЗИДЕНТУ РОССИЙСКОЙ ФЕДЕРАЦИИ, ПРЕКРАТИВШЕМУ ИСПОЛНЕНИЕ СВОИХ ПОЛНОМОЧИЙ, И ЧЛЕНАМ ЕГО СЕМЬИ. Rossiyskaya Gazeta
- ^ Александр Колесниченко. ""Развращение" первого лица. Госдума не решилась покуситься на неприкосновенность экс-президента". Newizv.ru. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ Ignatius, Adi. Person of the Year 2007: A Tsar Is Born, Time, page 4 (19 December 2007). Retrieved 19 November 2009.
- ^ "ДЕЛО ПУТИНА". Novaya Gazeta. 20–23 March 2000. Retrieved 19 March 2016.
- ^ "Компромат.Ru / Compromat.Ru: Фигунанты по квартирному делу". www.compromat.ru. Retrieved 19 March 2016.
- ^ Dawisha, Karen (22 September 2015). Putin's Kleptocracy: Who Owns Russia?. Simon and Schuster. ISBN 9781476795201.
- ^ "Почему Марина Салье молчала о Путине 10 лет?". Radio Svoboda. Retrieved 19 March 2016.
- ^ a b c "История президентских выборов в России". РИА Новости. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ a b Spectre of Kursk haunts Putin, BBC News, 12 August 2001
- ^ Putin: Russia's Choice, By Richard Sakwa, (Routledge, 2008) page 143-150
- ^ Playing Russian Roulette: Putin in search of good governance, by Andre Mommen, in Good Governance in the Era of Global Neoliberalism: Conflict and Depolitisation in Latin America, Eastern Europe, Asia, and Africa, By Jolle Demmers, Alex E. Fernández Jilberto, Barbara Hogenboom (Routledge, 2004)
- ^ "Can Grozny be groovy?". The Independent. London. 6 March 2007. Archived from the original on 28 March 2007.
- ^ "Human Rights Watch Reports, on human rights abuses in Chechnya". Human Rights Watch. Archived from the original on 21 November 2006. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ "The World Factbook". cia.gov. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ Moscow siege leaves dark memories, BBC News, 16 December 2002
- ^ "The challenges of the Medvedev era" (PDF). BOFIT Online. Bank of Finland. 24 June 2008. ISSN 1456-811X. Retrieved 24 September 2011.
- ^ a b c "BBC Russian - Россия - Путин очертил "дорожную карту" третьего срока". bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ How to Steal Legally The Moscow Times, 15 February 2008 (issue 3843, page 8).
- ^ Putin’s Gamble. Where Russia is headed by Nikolas Gvosdev, nationalreview.com, 5 November 2003. Archived 2013-08-11 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Putin's Kremlin Asserting More Control of Economy. Yukos Case Reflects Shift on Owning Assets, Notably in Energy by Peter Baker, The Washington Post, 9 July 2004.
- ^ "Hague court awards $50 bn compensation to Yukos shareholders". Russia Herald. Retrieved 29 July 2014.
- ^ "Putin's Russia failed to protect this brave woman – Joan Smith". The Independent. London. 9 October 2006. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ Anna Politkovskaya, Prominent Russian Journalist, Putin Critic and Human Rights Activist, Murdered in Moscow, Democracy Now
- ^ Lee, Steven (10 March 2007). "Kasparov, Building Opposition to Putin". The New York Times. Russia. Retrieved 2 March 2010.
- ^ "Garry Kasparov jailed over rally". BBC News. 24 November 2007. Retrieved 9 April 2010.
- ^ "Putin Dissolves Government, Nominates Viktor Zubkov as New Prime Minister". Fox News Channel. 12 September 2007. Retrieved 2 March 2010.
- ^ Election Preliminary Results for United Russia, 4 December 2007, Rbc.ru
- ^ Russians Voted In Favour of Putin, 4 December 2007, Izvestia
- ^ Assenters' March, 3 December 2007, Izvestia
- ^ "Putin Is Approved as Prime Minister". The New York Times. 9 May 2008.
- ^ "Russia's Putin set to return as president in 2012". BBC News. 24 September 2011. Retrieved 24 September 2011.
- ^ Paul Bummer. "7 статей и джек-пот: Путин завершил серию публикаций". Neprussia.ru. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ Russian election protests – follow live updates, The Guardian. Retrieved 10 December 2011
- ^ Как митинг на Поклонной собрал около 140 000 человек politonline.ru Template:Ru icon
- ^ a b Sputnik (4 March 2012). "'We Won in Fair and Open Fight' – Putin". rian.ru. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ a b c Sputnik (23 February 2012). "Putin Supporters Fill Moscow Stadium". rian.ru. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ Frum, David (June 2014), "What Putin Wants", The Atlantic, 313 (5): 46–48
- ^ "Putin won 'rigged elections'". BBC News. 11 September 2000.
- ^ Выборы Президента Российской Федерации 2012. izbirkom.ru (in Russian). Central Election Commission of the Russian Federation. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- ^ Elder, Miriam (17 August 2012). "Pussy Riot sentenced to two years in prison colony over anti-Putin protest". The Guardian. London.
- ^ Провокация вместо марша vz.ru
- ^ "Russian police battle anti-Putin protesters". Reuters. 6 May 2012. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ "СК пересчитал пострадавших полицейских во время "Марша миллионов"". lenta.ru. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ Parfitt, Tom (7 May 2012). "Vladimir Putin inauguration shows how popularity has crumbled". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ "Vladimir Putin inaugurated as Russian president amid Moscow protests". Guardian. 7 May 2012. Retrieved 20 January 2014.
- ^ ""Putin Inaugurated; States Intention for Russia to Be "Center of Gravity for the Whole of Eurasia", May 8, 2012". Larouchepac.com. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ ""Putin decrees EU closeness policy", Voice of Russia, May 7, 2012". English.ruvr.ru. 7 May 2012. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ "Госдума приняла закон о "нетрадиционных отношениях"". BBC Russia. 11 June 2013. Archived from the original on 12 June 2013. Retrieved 11 June 2013.
- ^ "ГД приняла закон об усилении наказания за пропаганду гомосексуализма среди подростков". RBC. 11 June 2013. Archived from the original on 12 June 2013. Retrieved 11 June 2013.
- ^ SPIEGEL ONLINE, Hamburg, Germany (6 April 2012). ""Discrimination in Russia: Arrests for Violation of St. Petersburg Anti-Gay Law", Spiegel Online, April, 06, 2012". SPIEGEL ONLINE.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ ""Russian parliament backs ban on "gay propaganda", Reuters, 25 January 2013". Reuters. 25 January 2013.
- ^ "Russia moves to enact laws against 'homosexual propaganda'". Fox News. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ Jivanda, Tomas (19 January 2014). "Vladimir Putin: 'I know some people who are gay, we're on friendly terms'". The Independent. London. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- ^ Putin becomes Popular Front for Russia leader, Interfax-Ukraine (13 June 2013) Archived 2013-09-15 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Echo of Soviet era in Putin's bid for votes". The Australian. 17 June 2011.
- ^ "Putin inaugurates new movement amid fresh protests". BBC. 12 June 2013. Retrieved 12 June 2013.
- ^ Radyuhin, Vladimir (1 March 2014). "Russian Parliament approves use of army in Ukraine". The Hindu. Chennai, India.
- ^ a b Walker, Shaun (4 March 2014). "Russian takeover of Crimea will not descend into war, says Vladimir Putin". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ^ a b Yoon, Sangwon; Krasnolutska, Daryna; Choursina, Kateryna (4 March 2014). "Russia Stays in Ukraine as Putin Channels Yanukovych Request". Bloomberg News. Retrieved 5 March 2014.
- ^ a b "U.N. General Assembly Affirms Ukraine's Territorial Integrity, Calls The World Community Not To Recognise Change Of Crimea's Status". Ukrainian News Agency. 27 March 2014. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- ^ "Putin's remarks raise fears of future moves against Ukraine". Washington Post.
- ^ "Mejlis to boycott Crimean referendum&". Ukrinform.ua. 6 March 2014. Retrieved 15 March 2014.
- ^ "Tatar leader: referendum's results 'predetermined'". DW.DE. 16 March 2014. Retrieved 17 March 2014.
- ^ "Security Council Fails to Adopt Text Urging Member States Not to Recognize Planned 16 March Referendum in Ukraine's Crimea Region". Un.org. 2 January 2013. Retrieved 17 March 2014.
- ^ "Russia Vetoes U.N. Security Council Resolution On Crimea". NPR. 15 March 2014. Retrieved 17 March 2014.
- ^ "US imposes second wave of sanctions on Russia - The JNM Journal".
- ^ "Third Wave of Sanctions Slams Russian Stocks - Business". The Moscow Times.
- ^ [3]
- ^ Putin admits Russian forces were deployed to Crimea, Reuters (17 April 2014)
Obama and Putin in war of words: Moscow denies troops in Crimea are Russian while Washington says 'You're not fooling anyone', Mail Online (4 March 2014) - ^ Jews reject Russia claims of Ukraine anti-Semitism, BBC News (12 November 2014)
- ^ Ukraine crisis: Putin signs Russia-Crimea treaty, BBC, 18 March 2014
"Crimea, Sevastopol officially join Russia as Putin signs final decree". RT. 22 March 2014. Retrieved 9 April 2014.
Transcript: Putin says Russia will protect the rights of Russians abroad, washingtonpost.com (18 March 2014) - ^ a b "Ukraine crisis: Timeline". BBC News. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ "Ukraine separatists to go ahead with referendum despite Putin call for delay". The Guardian. 8 May 2014
- ^ MacFarquhar, Neil (7 May 2014). "Putin Announces Pullback From Ukraine Border". The New York Times.
- ^ Putin Tells Separatists In Ukraine To Postpone May 11 Referendum, NPR (7 May 2014)
- ^ "Ukraine rebels hold referendums in Donetsk and Luhansk". BBC News. 11 May 2014. Retrieved 11 May 2014.
"Russian Roulette (Dispatch Thirty-Eight)". Vice News. 13 May 2014. Retrieved 7 July 2014. - ^ "Eastern Ukraine tensions figure in Putin and Poroshenko talks". Moscow News.Net. 26 August 2014. Retrieved 28 August 2014.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ a b c Putin: Russia won't allow a rebel defeat in Ukraine, USA Today (17 November 2014)
Putin promises not allow separatists’ defeat, speaks about 'single political space' in Donbas (VIDEO), Kyiv Post (18 November 2014) - ^ Putin delivers keynote speech on economy, Ukraine, Reuters (4 December 2014)
Putin: Crimea is as sacred to Russia as Temple Mount for Judaism and Islam, Haaretz (4 December 2014)
In Kremlin speech, Putin rails at West, tries to bolster economy as recession looms, washingtonpost.com (4 December 2014)
Putin talks about Ukraine's economy, blames West in his annual address, Kyiv Post (4 December 2014) - ^ Patrick J. McDonnell; W.J. Hennigan; Nabih Bulos (30 September 2015). "Russia launches airstrikes in Syria amid U.S. concern about targets". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 7 October 2015.
- ^ "Russia carries out first air strikes in Syria". Al Jazeera. 30 September 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2015.
- ^ "Clashes between Syrian troops, insurgents intensify in Russian-backed offensive". U.S. News & World Report. 8 October 2015. Retrieved 10 October 2015.
- ^ "Officials: CIA-Backed Syrian Rebels Under Russian Blitz". The New York Times. 10 October 2015. Retrieved 10 October 2015.
- ^ Dearden, Lizzie (8 October 2015). "Syrian army general says new ground offensive backed by Russian air strikes will 'eliminate terrorists'". The Independent. Retrieved 10 October 2015.
- ^ "Syria conflict: Russia's Putin orders 'main part' of forces out". BBC World Service. 14 March 2016. Retrieved 14 March 2016.
- ^ [4]
- ^ White, Stephen (2010). "Classifying Russia's Politics". In White, Stephen (ed.). Developments in Russian Politics 7. New York: Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-230-22449-0.
- ^ R. Sakwa, Putin: Russia's Choice, 2008, p. 42-43
- ^ Archived 2006-12-08 at the Wayback Machine Vladislav Surkov, public appearance, 7 February 2006
- ^ Archived 2006-11-05 at the Wayback Machine Vladislav Surkov, briefing, 28 June 2006.
- ^ Lynch, Dov (2005). "The enemy is at the gate": Russia after Beslan. International Affairs 81 (1), 141–161.
- ^ Putin tightens grip on security, BBC News, 13 September 2004.
- ^ "Президентское фильтрование губернаторов оценили политики". Radiovesti.ru. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ Kramer, Andrew E. (22 April 2007). "50% Good News Is the Bad News in Russian Radio". The New York Times. Russia. Retrieved 24 September 2011.
- ^ Masha Lipman, Anders Aslund (2 December 2004). "Russian Media Criticism of Vladimir Putin: Evidence and Significance". Carnegieendowment.org. Retrieved 2 March 2010.
- ^ "State Duma Approves Liberal Political Reforms". RIA Novosti. 28 February 2012. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ "Arkady Rotenberg". Forbes.com. 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- ^ Sharlet, Robert (2005). "In Search of the Rule of Law". In White, Gitelman, Sakwa (ed.). Developments in Russian Politics. Vol. 6. Duke University Press. ISBN 0-8223-3522-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". Imf.org. 14 September 2006. Retrieved 9 December 2011.
- ^ "Ежегодно объем потребительского кредитования в России удваивается". Bank.samaratoday.ru. Retrieved 2 March 2010.
- ^ "Основные Социально-Экономические Индикаторы Уровня Жизни Населения". Gks.ru. Archived from the original on 18 February 2012. Retrieved 2 March 2010.
- ^ Iikka. Korhonen et al. The challenges of the Medvedev era. Bank of Finland's Institute for Economies in Transition, 24 June 2008.
- ^ a b c Daniel Mitchell Archived 2011-06-29 at the Wayback Machine. The Heritage Foundation. 24 March 2003.
- ^ "Putin Advocates Strong Russia, Liberal Economy; President Surprisingly Candid in First State of Nation Address". The Washington Post. 9 July 2000. Retrieved 13 March 2014.
- ^ Preobragenskaya, Galina; McGee, Robert W. (2006). "A Comparative Study of Taxation in Russia and Other CIS, East European and OECD Countries". Accounting and Financial Systems Reform in Eastern Europe and Asia. New York: Springer. pp. 277–298. doi:10.1007/0-387-25710-1_10. ISBN 978-0-387-25709-9. SSRN 526745.
- ^ Rosstat Confirms Record GDP Growth Kommersant. Retrieved 5 May 2008.
- ^ Aris, Ben. "Russia's WTO Entry: One Year On, Business is Disappointed”, Financial Times (27 June 2013).
- ^ Krkoska, Libor; Spencer, Alan (February 2008). "Automotive Industry in Russia: Impact of foreign investments in car assembly plants on suppliers' entry" (PDF). European Bank for Reconstruction and Development.
- ^ Zvereva, Polina (11 October 2009). "State-sponsored consolidation". Russia & CIS Observer. 3 (26).
- ^ "Annual Report 2009" (PDF). United Aircraft Corporation. 2010.
- ^ Russia builds nuclear power stations all over the world at amur.kp.ru
- ^ Richard Galpin (22 September 2010). "The struggle for Arctic riches". BBC News. Retrieved 28 August 2011.
- ^ Peter Fairley (2 July 2010). "Russia Launches Floating Nuclear Power Plant". IEEE Spectrum. Retrieved 28 August 2011.
- ^ "Prirazlmonaya sea platform to be delivered to offshore oil field". Information Telegraph Agency of Russia. 26 August 2011. Archived from the original on 25 January 2012. Retrieved 28 August 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Andrew Kramer (30 August 2011). "Exxon Reaches Arctic Oil Deal With Russians". The New York Times. Retrieved 5 September 2011.
- ^ "China and Russia sign $400 billion 30-year gas deal". Russia Herald. Retrieved 22 May 2014.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "OCCRP 2014 Person of the Year". Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- ^ "Vladimir Putin named Person of the Year for 'innovation' in 'organised crime'". International Business Times. 3 January 2015.
- ^ Kitroeff, Natalie Natalie; Weisenthal, Joe (16 December 2014). "Here's Why the Russian Ruble Is Collapsing". Bloomberg.
- ^ "Why Russia's financial crises keep on coming". Guardian. 21 December 2014.
- ^ "Russia's Putin scraps New Year's holidays for ministers". The Times of India. 25 December 2014.
- ^ "Russia sanctions helping businesses to thrive". CNBC. 18 June 2015. Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ^ "Russia signs deals with China to help weather sanctions". CNBC. 13 October 2014. Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ^ Thompson, Mark (26 January 2016). "Russia: One of 10 worst economies in 2015". CNN.
- ^ The New York Times. 6 November 2004. Retrieved 20 April 2008.
- ^ Tony Johnson. "G8's Gradual Move toward Post-Kyoto Climate Change Policy". Council on Foreign Relations. Retrieved 2 March 2010.
- ^ THE AMUR TIGER PROGRAMME premier.gov.ru Archived 2012-07-18 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ THE WHITE WHALE PROGRAMME premier.gov.ru Archived 2012-06-13 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ THE POLAR BEAR PROGRAMME premier.gov.ru Archived 2012-06-13 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ THE SNOW LEOPARD PROGRAMME premier.gov.ru Archived 2012-06-13 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Bell, I (2002). Eastern Europe, Russia and Central Asia. ISBN 978-1-85743-137-7. Retrieved 27 December 2007.
- ^ A religion for the nation or a nation for the religion: Putin's third way for Russia, Beth Admiraal, in Russian Nationalism and the National Reassertion of Russia, edited by Marlène Laruelle, (Routledge, 2009)
- ^ "Bethlehem street named after Putin". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 27 June 2012. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ "he President of Russia attended the ceremonial signing of the Act on Canonical Communion that was held in the Cathedral of Christ the Saviour" (Press release). Embassy of Russia in Ottawa. 17 May 2007. Archived from the original on 2 October 2008. Retrieved 2 October 2008. Archived by WebCite at www.webcitation.org/5bGjBVfm6
- ^ No love lost, Yossi Mehlman, Haaretz, 11 December 2005
- ^ Phyllis Berman Lea Goldman, (15 September 2003). "Cracked De Beers". Forbes
- ^ Krichevksy, Lev (10 October 2011). ""In Putin's return, Russian Jews see stability". Jewish Telegraphic Agency". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ Beginning of Meeting with Defense Minister Anatoliy Serdyukov, 5 December 2007, Kremlin.ru
- ^ Guy Faulconbridge Russian navy to start sorties in Mediterranean. Reuters. 5 December 2007.
- ^ "Military reform to change army structure. What about its substance?". RIA Novosti. 17 October 2008. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ Kristensen, Hans M. "New START Data Released: Nuclear Flatlining."FAS, 3 October 2012.
- ^ William J. Broad (19 February 2008). "Russia's Claim Under Polar Ice Irks American". The New York Times. Retrieved 27 July 2011.
- ^ Adrian Blomfield (11 June 2008). "Russia plans Arctic military build-up". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 27 July 2011.
- ^ Mia Bennett (4 July 2011). "Russia, Like Other Arctic States, Solidifies Northern Military Presence". Foreign Policy Association. Retrieved 27 July 2011.
- ^ Herspring, Dale. Putin's Russia: Past Imperfect, Future Uncertain, p. 25 (Rowman and Littlefield 2005).
- ^ “Laws of Attrition: Crackdown on Russia’s Civil Society after Putin’s Return to the Presidency,” Human Rights Watch pdf report 24 April 2013
- ^ Russia: Worst Human Rights Climate in Post-Soviet Era, Unprecedented Crackdown on Civil Society Human Rights Watch Summary 24 April 2013
- ^ a b c America's Failed (Bi-Partisan) Russia Policy by Stephen F. Cohen, Huffington Post
- ^ a b c d Stuermer, Michael (2008). Putin and the Rise of Russia. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. pp. 55, 57 & 192. ISBN 9780297855101. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
- ^ "Interview for Indian Television Channel Doordarshan and Press Trust of India News Agency, 18 January 2007". Kremlin.ru. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ a b 43rd Munich Conference on Security Policy. Putin's speech in English, 10 February 2007.
- ^ a b Watson, Rob (10 February 2007). "Putin's speech: Back to cold war? Putin's speech: Back to cold war?". BBC.
- ^ "Munich Conference on Security Policy, As Delivered by Secretary of Defense Robert M. Gates, 11 February 2007". Defenselink.mil. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
- ^ "Press Conference following the end of the G8 Summit". Kremlin.ru. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ "Russia walks away from CFE arms treaty". fijilive.com. 12 December 2007. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ^ "EU's Solana rejects Putin's criticism over Kosovo's independence". IRNA. 23 February 2008. Archived from the original on 26 February 2008. Retrieved 25 February 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Putin: supports for Kosovo unilateral independence "immoral, illegal"". Xinhua News Agency. 14 February 2008. Retrieved 25 February 2008.
- ^ "Putin: Kosovo case terrible precedent". Press TV. 22 February 2008. Retrieved 25 February 2008.
- ^ Simpson, Emma (16 January 2006). "Merkel cools Berlin Moscow ties". BBC News. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ "Battle for Ukraine: How the west lost Putin". Financial Times. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ U.S., other powers kick Russia out of G8, CNN
- ^ "Russia Temporarily Kicked Out Of G8 Club Of Rich Countries". Business Insider. 18 June 2013. Retrieved 25 March 2014.
- ^ Shuster, Simon. "The World According to Putin," Time 16 September 2013, pp 30–35
- ^ "Russian President Vladimir Putin says ‘only an insane person’ would fear Russian attack on NATO". Daily News. 7 June 2015.
- ^ a b c Gonzalo Vina and Sebastian Alison (20 July 2007). "Brown Defends Russian Expulsions, Decries Killings". Bloomberg News.
- ^ "UK spied on Russians with fake rock". BBC News. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ "Litvinenko's father apologises for accusing Russia", BBC News, 12 February 2012
- ^ "Litvinenko: MI5, MI6 death files ordered released". RT English. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ "Litvinenko Inquiry: David Cameron considers new sanctions against Russia after 'state-sponsored murder' of KGB spy in London". Telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 22 January 2016.
- ^ The Litvinenko Inquiry. Report into the death of Alexander Litvinenko
- ^ Vladimir Putin (24 December 2012). "For Russia, deepening friendship with India is a top foreign policy priority by President Vladimir Putin". The Hindu. Chennai, India. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ "India, Russia sign new defence deals". BBC. 24 December 2012. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ Rajeev Sharma, specially for RIR (24 December 2012). "13th Indo-Russian Summit reaffirms time-tested ties: Russia & India Report". Indrus.in. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ Page, Jeremy (26 September 2010). "Russian Oil Route Will Open to China". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 28 September 2010.
- ^ a b Press Statement following the Peace Mission 2007 Counterterrorism Exercises and the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation Summit, 17 August 2007, Chelyabinsk Region.
- ^ Russia restores Soviet-era strategic bomber patrols, 17 August 2007, RIA Novosti, Russia.
- ^ SCO Scares NATO, 8 August 2007, KM.ru Archived 2013-12-07 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Russia Over Three Oceans, 20 August 2007, "Chas", Latvia. Archived 2012-02-08 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Putin: Iran Has Right to Develop Peaceful Nuclear Programme, 16 October 2007, Rbc.ru
- ^ "Putin's warning to the U.S." Reuters. 16 October 2007. Archived from the original on 17 October 2007.
- ^ Putin Positive on Second Caspian Summit Results, Meets With Iranian President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad, 16 October 2007, Kremlin.ru
- ^ Visit to Iran. Second Caspian Summit, 15–16 October 2007, Kremlin.ru
- ^ Leonid Brezhnev travelled to shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi's Iran in 1963, but at that time he was not yet the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, "Putin confirms Iran visit, brushes off 'plot' reports". Lebanon Wire. 15 October 2007.
- ^ Vladimir Putin defies assassination threats to make historic visit to Tehran, 16 October 2007, The Times.
- ^ Answer to a Question at the Joint Press Conference Following the Second Caspian Summit, 16 October 2007, Tehran, Kremlin.ru
- ^ "Putin's visit 'historic and strategic'". Gulf News. 18 April 2008. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ Parks, Cara (21 March 2011). "Putin: Military Intervention In Libya Resembles 'Crusades'". Huffington Post.
- ^ "Putin states the West has no legal right to execute Gaddafi – RT". Russia: RT. 26 April 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ "Vladimir Putin Blames US Drones For Gaddafi Death, Slams John McCain". Mediaite. 15 December 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ Citizen, Ottawa (16 December 2011). "Putin claims U.S. planned murder of Gadhafi". Canada.com. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ Trenin, Dmitri (9 February 2012). "Why Russia Supports Assad". The New York Times.
- ^ Fred Weir (19 January 2012). "Why Russia is willing to sell arms to Syria". The Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ Viscusi, Gregory (1 June 2012). "Hollande Clashes With Putin Over Ouster of Syria's Assad". Bloomberg BusinessWeek. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ Putin, Vladimir V. (11 September 2013). "A Plea for Caution From Russia". The New York Times. Retrieved 11 September 2013.
- ^ ”Putin says US, Russia agree on how to destroy Syria's chemical weapons”, The Jerusalem Post (8 October 2013).
- ^ Melik Kaylan. "Putin's Syria Gambit Could Be His Waterloo". Forbes.
- ^ Kaylan, Melik. "Is Putin About To Invade Ukraine?". Forbes.
- ^ Pedler, John (2015). A Word Before Leaving: A Former Diplomat's Weltanschauung. p. 129.
- ^ Polish head rejects Putin attack, BBC News (24 December 2004)
- ^ a b Q&A: Russia-Ukraine gas row, BBC News (20 January 2009).
- ^ "Playing East against West: The success of the Eastern Partnership depends on Ukraine". The Economist. 23 November 2013.
- ^ Ukraine's parliament votes to abandon Nato ambitions, BBC News (3 June 2010)
- ^ "After Russian Invasion of Georgia, Putin's Words Stir Fears about Ukraine", Kyiv Post (30 November 2010)
- ^ Bohm, M. Ukraine Is Putin's Favorite Vassal. The Moscow Times. 25 December 2013
- ^ Radyuhin, Vladimir (1 March 2014). "Russian Parliament approves use of army in Ukraine". The Hindu. Chennai, India.
- ^ "Vladimir Putin signs treaty for Russia to take Crimea from Ukraine – video". The Guardian. 18 March 2014. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- ^ a b "Russia President Vladimir Putin signs treaty to annex Crimea after residents vote to leave Ukraine - CBS News". CBS News. 18 March 2014.
- ^ Has Vladimir Putin blinked over Ukraine? - The Daily Telegraph (London)
- ^ Putin says Russians and Ukrainians 'practically one people', Reuters (29 August 2014)
- ^ Putin: Ukrainian Literature Library must not be lost in any circumstances, Interfax-Ukraine (26 December 2015)
- ^ "Russia and Eurasia". Heritage.org. Archived from the original on 28 May 2009. Retrieved 10 May 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Day-by-day: Georgia-Russia crisis". BBC News. 21 August 2008. Retrieved 10 May 2009.
- ^ Sparks, Ian (14 November 2008). "Putin planned to topple the president of Georgia and 'hang him by the b****', says Nicolas Sarkozy's chief adviser". Daily Mail. London.
- ^ New Integration Project for Eurasia – A Future That Is Being Born Today, Izvestiya (3 October 2011)
- ^ Новый интеграционный проект для Евразии – будущее, которое рождается сегодня Template:Ru icon
- ^ Bryanski, Gleb (3 October 2011). "Russia's Putin says wants to build "Eurasian Union"". Yahoo! News. Reuters. Archived from the original on 6 October 2011. Retrieved 4 October 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Новый интеграционный проект для Евразии – будущее, которое рождается сегодня. Izvestia (in Russian). 3 October 2011. Retrieved 4 October 2011.
- ^ Kilner, James (6 October 2011). "Kazakhstan welcomes Putin's Eurasian Union concept". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ "Russia sees union with Belarus and Kazakhstan by 2015". BBC News. 18 November 2011. Retrieved 19 November 2011.
- ^ http://docs.eaeunion.org/en-us/Pages/DisplayDocument.aspx?s=bef9c798-3978-42f3-9ef2-d0fb3d53b75f&w=632c7868-4ee2-4b21-bc64-1995328e6ef3&l=540294ae-c3c9-4511-9bf8-aaf5d6e0d169&EntityID=3610
- ^ Russia forges nuclear links with Venezuela France 24 Archived 2015-03-19 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "BBC NEWS - World - Americas - Russian bombers land in Venezuela". bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ Archive index at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Russia Courts Indonesia". Brtsis.com. 12 October 2007. Archived from the original on 12 October 2007. Retrieved 24 September 2011.
- ^ Phillip Coorey (7 September 2007). "Putin and Howard sign uranium deal". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 14 October 2014.
- ^ wmf . media.kremlin.ru (2007)
- ^ "Sochi 2014: Putin declares gay athletes welcome", BBC (28 October 2013).
- ^ "President Obama joins list of world leaders to snub Sochi Olympics". Salon. 18 December 2013.
- ^ "Putin Plays Games to Salvage Olympics". Bloomberg.com. 19 December 2013.
- ^ "Addresses to the Federal Assembly". Kremlin.ru. Archived from the original on 6 June 2008. Retrieved 2 March 2010.
- ^ "Article 84 of the Russian Constitution". Constitution.ru. Retrieved 2 March 2010.
- ^ Putin, Vladimir. "Address by President of the Russian Federation", Kremlin Web Site (18 March 2014).
- ^ "Putin accuses United States of damaging world order". Reuters. 24 October 2014.
- ^ "BBC News - Russia in grim go-it-alone mood as sanctions bite". BBC News.
- ^ Board, Editorial (27 October 2014). "Vladimir Putin lays out a menacing choice for the West". Washington Post.
- ^ Stephen Fidler (22 October 2014). "At Valdai Club Meeting in Russia, Divergent Views of Ukrainian Crisis". WSJ.
- ^ a b c d "СМИ: мюнхенская речь Путина – поворотная точка во внешней политике РФ". Nr2.ru. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ Медведев поздравил любимую группу Путина с 20-летием newsru.ua
- ^ Speech at the Military Parade Celebrating the 62nd Anniversary of Victory in the Great Patriotic War, Red Square, Moscow, 9 May 2007.
- ^ a b Путин: Главное, чтобы мы были вместе vz.ru
- ^ "'We won!' Teary-eyed Putin proclaims victory". Setyoufreenews.com. 4 March 2012. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ Madslien, Jorn (4 July 2007). "Russia's economic might: spooky or soothing?". BBC News. Retrieved 2 March 2010.
- ^ "Putin's performance in office — Trends". Russiavotes.org. 31 October 2007. Retrieved 2 March 2010.
- ^ Blair is Mr 93%. Stephen Castle/Paul Routledge. The Independent (national newspaper). Published: 28 September 1997. Retrieved: 6 May 2014.
- ^ Tony Blair's Style of Government: An Interim Assessment - Page 1. Political Issues in Britain Today. Editor: Bill Jones. Publisher: Manchester University Press. (5th edition). Published: 1999. Retrieved: 6 May 2014.
- ^ It's the way they tell' em Total Politics. Simon Hoggart. Retrieved: 6 May 2014.
- ^ Arkhipov, Ilya (24 January 2013). "Putin Approval Rating Falls to Lowest Since 2000: Poll". Bloomberg. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ "Putin's Approval Rating Reaches Six-Year High – Poll". RIA Novosti. 15 May 2014.
- ^ "Quarter of Russians Think Living Standards Improved During Putin's Rule" (in Russian). Oprosy.info. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ No wonder they like Putin by Norman Stone, 4 December 2007, The Times.
- ^ a b Russia through the looking-glass openDemocracy. "...while only about half of Russian households have a telephone line at home, well over 90% have access to the First Channel and Rossiya. And for a vast majority of Russians, they are virtually the only source of information about political events. Given that typically well over half of their news broadcasts consist of sympathetic coverage of Vladimir Putin and members of the United Russia party, and oppositional figures are always presented in a negative or ironic light (if at all), it is unsurprising that the president is enjoying considerable popularity.". Retrieved 16 April 2008.
- ^ "Рейтинг Путина завышен во всей России". Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- ^ Adi Ignatius. Person of the Year 2007, Time.
- ^ Albright, Madeleine. "Vladimir Putin", Time. Retrieved 1 May 2008.
- ^ Ewalt, David M. (4 November 2015) The World's Most Powerful People 2015. Forbes
- ^ Struck, Doug. "Gorbachev Applauds Putin's Achievements", The Washington Post, 5 December 2007.
- ^ "Decoding Vladimir Putin's Plan". U.S. News. 5 January 2015.
- ^ "Das Internet prägt Russlands Wahlkampf" (in German). RP online. 17 February 2012. Retrieved 6 March 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ Smirnova, Julia (8 February 2012). "Wie die Putin-Jugend das Internet manipulierte" (in German). Retrieved 6 March 2012.
- ^ David Leigh; Luke Harding (2011). WikiLeaks: Inside Julian Assange's War on Secrecy. PublicAffairs. p. 223. ISBN 978-1-61039-062-0.
- ^ Marcel Van Herpen (25 January 2013). Putinism: The Slow Rise of a Radical Right Regime in Russia. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 161. ISBN 978-1-137-28280-4.
- ^ Parfitt, Tom. "WikiLeaks row: Putin labels US embassy cables 'slanderous'", The Guardian, 1 December 2010.
- ^ Andrew Osborn (25 September 2011). "Fears Vladimir Putin will turn Russia into outright dictatorship". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 25 September 2011.
- ^ William J. Dobson (10 June 2012). "What, Me a Dictator?". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 10 June 2012.
- ^ Stephen Romei (18 May 2012). "Putin the elected dictator is doomed, biographer claims". The Australian. Retrieved 18 May 2012.
- ^ Masha Gessen (21 May 2012). "The Dictator". The New York Times. Retrieved 21 May 2012.
- ^ "David Miliband: Vladimir Putin Is A 'Ruthless Dictator'". Huffington Post. 4 March 2012. Retrieved 4 March 2012.
- ^ "Mitt Romney: Vladimir Putin 'a threat to global peace'". The Daily Telegraph.
- ^ Henry Kissinger (5 March 2014). "How the Ukraine crisis ends". The Washington Post.
- ^ "Distorting Russia". The Nation. Retrieved 27 September 2015.
- ^ "The demonisation of Russia risks paving the way for war". The Guardian. Retrieved 27 September 2015.
- ^ "Russia's Anti-Putin Opposition: One Year On". [RIA Novosti]. 12 December 2012. Retrieved 10 February 2013.
- ^ "Августовские рейтинги одобрения - Левада-Центр".
- ^ "Putin's Approval Rating Soars to 87%, Poll Says - News". The Moscow Times. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ Bass, Sadie (5 August 2009). "Putin Bolsters Tough Guy Image With Shirtless Photos, Australian Broadcasting Corporation". ABC News. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ a b c d Rawnsley, Adam (26 May 2011). "Pow! Zam! Nyet! 'Superputin' Battles Terrorists, Protesters in Online Comic". Wired. Retrieved 27 May 2011.
- ^ a b c "Putin gone wild: Russia abuzz over pics of shirtless leader". Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. Associated Press. 22 August 2007. Retrieved 2 March 2010.
- ^ a b Vladimir Putin diving discovery was staged, spokesman admits, The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 16 March 2012
- ^ "Russians smell something fishy in Putin's latest stunt". Reuters. 29 July 2013. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f g 7 Reasons Vladimir Putin Is the World's Craziest Badass cracked.com
- ^ Archive index at the Wayback Machine[dead link]
- ^ Archive index at the Wayback Machine[dead link]
- ^ Организаторы сафари для Путина объяснились по поводу "подставы с тигром": "Кому-то что-то показалось" newsru.com
- ^ Putin attaches satellite tag to tranquilized polar bear in Russia's Arctic Fox News Channel
- ^ "Finland accidentally bans Putin". 3 News NZ. 11 April 2013.
- ^ Using crossbow, Putin fires darts at whale MSNBC
- ^ "Премьер-гонка: Владимир Путин протестировал болид "Формулы-1"". Rg.ru. 17 March 2012. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ Путин погрузился с аквалангом на дно Таманского залива tetis.ru
- ^ Vladimir Putin leads endangered cranes on migration route in hang glider The Guardian
- ^ "Russians smell something fishy in Putin's latest stunt". Reuters. 29 July 2013. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- ^ "Putin's Big Fish Story Leaves Russians in Doubt". Bloomberg. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- ^ @openspace_ru (14 March 2008). "Песни про Путина". Openspace.ru. Archived from the original on 18 September 2009. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Такого, как Путин". YouTube. 23 February 2008. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ "Гороскоп (Путин, не ссы!)". YouTube. 2 February 2012. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ Чернокожие рэперы записали трек в поддержку Владимира Путина (in Russian). LifeNews. 10 June 2014. Retrieved 7 April 2015.
- ^ ВВП on YouTube
- ^ WATCH: No One In Russia Can Work Out If This Pro-Putin Dance-Pop Song Is Sincere — Or Satire businessinsider.com
- ^ "Russia Protest Song: Veterans Rock Anti-Putin Rally With A Catchy Tune". The Huffington Post. 5 February 2012. Retrieved 21 March 2015.
- ^ Дарья Зайцева (20 June 2014). "Экскурс в историю одной кричалки, или подробнее о том, что значит смех без причины". politrussia.com. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ http://politicbox.ru/ehkskurs-v-istoriyu-odnojj-krichalki/
- ^ Как используется бренд "Путин": зажигалки, икра, футболки, консервированный перец Gazeta 30 November 2007.
- ^ "Частушки (Не было оргазма)". Sergeysv.net. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ "Путину в подарок приготовили раскраску: Фото: Россия: Lenta.ru". lenta.ru. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ "Superputin official site". Superputin.ru. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ "Би-би-си - Культура - Фильм о любви человека, похожего на Путина". bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ a b Путинизмы – "продуманный личный эпатаж"? BBC Template:Ru icon
- ^ a b c Osborn, Andrew (18 October 2010). "Vladimir Putin and wife spark divorce rumours with photo shoot". The Daily Telegraph. London, UK. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- ^ a b c Elder, Miriam (27 February 2012). "Will Vladimir Putin's voting chances be hurt by 'cloistered wife' rumours?". The Guardian. London, UK. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- ^ "Russia President Vladimir Putin's divorce goes through". BBC News. 2 April 2014. Archived from the original on 2 April 2014. Retrieved 2 April 2014.
- ^ Quetteville, Harry de (17 April 2008). "Vladimir Putin 'to wed Olympic gymnast half his age'". The Daily Telegraph. London, UK. Retrieved 17 April 2008.
- ^ Shaun Walker, in The Independent, quoting Moskovski Korrespondent (18 April 2008). "A president, the gymnast and marriage rumors that won't go away". London, UK. Retrieved 18 April 2008.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Yablokova, Oksana (9 August 2002). "Putin's Girls Having La Dolce Vita Break". The St. Petersburg Times. Retrieved 13 February 2009.
- ^ Putin's daughters enter university which changes the order at the institution, pravda.ru (English-language), 17 September 2005; accessed 11 November 2014.
- ^ "Net daredevils unmask real Putin and his Putinas", thesundaytimes.co.uk; accessed 11 November 2014.
- ^ "'Onze' Jorrit versiert de blonde dochter van Poetin". Depers. Archived from the original on 17 January 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ "Russia's mysterious Dutch businessman". Rnw.nl. 12 January 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ "Dochter Poetin woont in Voorschoten". De Telegraaf. 8 April 2013. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ "Vladimir Putin's daughter flees Netherlands penthouse as outrage grows over doomed Malaysia Flight MH17", New York Daily News; Retrieved 11 November 2014.
- ^ Putin’s daughter a bride? Page Six. 30 November 2012. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- ^ Meet the Putins, Vocativ.com; Retrieved 11 November 2014.
- ^ "Медведчук і Марченко помінялися місцями". Tablo ID. 11 November 2007. Retrieved 6 January 2014.
- ^ a b "Russia's Plan For Ukraine: Purported Leaked Strategy Document Raises Alarm". RFE. 20 August 2013. Retrieved 6 January 2014.
- ^ "Medvedchuk flexes muscles after protesters pay house call". Kyiv Post. 30 December 2013. Retrieved 6 January 2014.
- ^ "Acceptable compromises and shared hypocrisies". Kyiv Post. 8 October 2013. Retrieved 6 January 2014.
- ^ "PUTIN CONSULTING". Retrieved 3 October 2014.
- ^ "Quote.Rbc.Ru :: Аюмй Яюмйр-Оерепаспц — Юйжхх, Ярпсйрспю, Мнбнярх, Тхмюмяш". Quote.ru. Retrieved 2 March 2010.
- ^ Parfitt, Tom (28 August 2012). "Vladimir Putin: the Russian president's 'life of four yachts and 58 aircraft'". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 28 August 2012.
- ^ a b Foreign, Our (3 March 2011). "'Putin palace' sells for $350 million". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ^ ЦИК зарегистрировал список "ЕР" Rossiyskaya Gazeta N 4504 27 October 2007
- ^ ЦИК раскрыл доходы Путина Vzglyad 26 October 2007
- ^ "Is Vladimir Putin the richest man on earth?". News.com.au. 26 September 2013.
- ^ Gennadi Timchenko: Russia's most low-profile billionaire Sobesednik № 10, 7 March 2007
- ^ Harding, Luke (21 December 2007). "Putin, the Kremlin power struggle and the $40bn fortune". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 18 August 2008.
- ^ "Что касается различных слухов по поводу денежного состояния, я смотрел некоторые бумажки на этот счёт: просто болтовня, которую нечего обсуждать, просто чушь. Все выковыряли из носа и размазали по своим бумажкам. Вот так я к этому и отношусь." The President's annual press conference for the Russian and foreign media, 14 February 2008, Kremlin.ru
- ^ How the 1980s Explains Vladimir Putin. The Ozero group. By Fiona Hill & Clifford G. Gaddy, The Atlantic, 14 February 2013
- ^ Elder, Miriam (28 August 2012). "Vladimir Putin 'galley slave' lifestyle: palaces, planes and a $75,000 toilet". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 28 August 2012.
- ^ "Тайна за семью заборами". Kommersant.ru. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ "Putin's palace? A mystery Black Sea mansion fit for a tsar". BBC. 4 May 2012. Retrieved 4 May 2012.
- ^ "Review: 'Putin's Kleptocracy: Who Owns Russia?'". International Policy Digest. Retrieved 22 January 2016.
- ^ Menon, Rajan (25 November 2014). "'Putin's Kleptocracy,' by Karen Dawisha". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 22 January 2016.
- ^ Wagner, Hans (30 June 2006). "Das Konfliktpotential mit den USA wächst (German)". Retrieved 29 March 2007.
- ^ Wardell, Jane (25 June 2003). "Putin treated royally on historic London visit". Findarticles.com. Retrieved 2 March 2010.
- ^ Kremlin Chief of Staff Surprised but Not Alarmed by Navalny, The Moscow Times, 2 October 2013.
- ^ a b Timothy J. Colton, Michael MacFaul (2003). Popular Choice and Managed Democracy: the Russian elections of 1999 and 2000. Washington DC: The Brookings Institution.
- ^ Putin Q&A: Full Transcript Time. Retrieved 22 March 2008
- ^ "Putin and the monk". FT Magazine. 25 January 2013.
- ^ "Putin makes effort to keep his height secret from voters". Washington times. 23 March 2000. Retrieved 28 March 2014.
- ^ Vladimir Putin: the NPR interview US radio station National Public Radio New York (15 November 2001)
- ^ Putin, Vladimir; Vasily Shestakov; Alexey Levitsky (July 2004). Judo: History, Theory, Practice. Blue Snake Books. ISBN 1-55643-445-6.
- ^ Black-Belt President Putin: A Man of Gentle Arts by Yasuhiro Yamashita
- ^ "Vladimir Putin earns 8th-degree black belt in karate". The Washingtion Times. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ http://www.nydailynews.com/news/world/vladimir-putin-earns-black-belt-8th-dan-kyokushin-karate-article-1.2019056
- ^ Archive index at the Wayback Machine[dead link] by Oleg Fochkin. premier.gov, re-publication of a Moskovsky Komsomolets article.
- ^ Медведев и Путин покатались на горных лыжах в Сочи rosbalt.ru
- ^ Д.Медведев призвал россиян активнее играть в бадминтон (in Russian). Top.rbc.ru. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ "Putin to talk pipeline, attend football game". B92. Retrieved 22 March 2011.
- ^ "Putin's lab bitch prominent negotiator". RIA Novosti. 9 April 2005. Retrieved 22 December 2008.
- ^ Любимая собака Путина заговорила по-английски с детьми. www.newsru.com (in Russian). NEWSru. 19 July 2005. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ^ "Prime Minister Vladimir Putin chaired a meeting on expanding the Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS)". Prime Minister of Russia. 17 October 2008. Archived from the original on 24 July 2011. Retrieved 24 December 2008.
- ^ "Сайт Председателя Правительства Российской Федерации В.В.Путина - События - Председатель Правительства России В.В.Путин выбрал имя для своей новой собаки. И помог ему в этом пятилетний Дима Соколов из Москвы". 9 December 2010. Archived from the original on 31 July 2015. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
{{cite web}}:|archive-date=/|archive-url=timestamp mismatch; 24 July 2011 suggested (help); Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Template:Fr icon Video Chirac décore Poutine
- ^ Atul Aneja Putin goes calling on the Saudis. The Hindu. 20 February 2007
- ^ Putin Receives Top UAE's Decoration, Order of Zayed, Rbc.ru, 10 September 2007
- ^ "Глобальный игрок. Expert magazine. № 48 (589) 24 December 2007". Expert.ru. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ "В Грозном появился проспект имени Путина". lenta.ru. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ Парламент Киргизии присвоил горной вершине имя Путина. Lenta.ru. 17 February 2011
- ^ "Vladimir Putin in China Confucius Peace Prize fiasco". BBC. 15 November 2011. Retrieved 15 November 2011.
- ^ Wong, Edward (15 November 2011). "In China, Confucius Prize Awarded to Putin". The New York Times. Retrieved 15 November 2011.
- ^ "B92 News: Belgrade University to award Putin honorary doctorate". Retrieved 11 June 2012.
Further reading
- Arutunyan, Anna (2015) [2012; Czech ed.]. The Putin Mystique: Inside Russia's Power Cult. Northampton, Mass.: Olive Branch Press. ISBN 9781566569903. OCLC 881654740.
- Asmus, Ronald (2010). A Little War that Shook the World: Georgia, Russia, and the Future of the West. NYU. ISBN 978-0-230-61773-5.
- Gessen, Masha (2012). The Man Without a Face: The Unlikely Rise of Vladimir Putin. Granta. ISBN 978-1-84708-149-0.
- Judah, Ben (2015). Fragile Empire: How Russia Fell in and Out of Love with Vladimir Putin. Yale University Press. ISBN 0300205228.
External links
- Articles that may be too long from November 2015
- Vladimir Putin
- 1952 births
- Living people
- 2003 Tuzla island conflict
- Acting Presidents of Russia
- Confucius Peace Prize winners
- Directors of the Federal Security Service
- FSB officers
- Grand Croix of the Légion d'honneur
- Grand Crosses of the Order of St. Sava
- Heads of government of the Russian Federation
- Independent politicians
- KGB officers
- Kyokushin kaikan practitioners
- Our Home – Russia politicians
- People from Saint Petersburg
- People of the annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation
- People of the Chechen wars
- People of the Russo-Georgian War
- Plagiarism controversies
- Presidents of Russia
- Recipients of the Order of Zayed
- Russian judoka
- Russian karateka
- Russian nationalists
- Russian Orthodox Christians from Russia
- Russian sambo practitioners
- Saint Petersburg State University alumni
- United Russia politicians


