Fajja
Fajja
فجّة | |
|---|---|
| Etymology: from personal name[1] | |
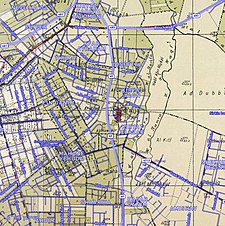
A series of historical maps of the area around Fajja (click the buttons) | |
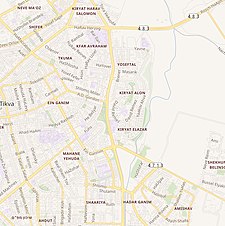
Location within Mandatory Palestine | |
| Coordinates: 32°05′12″N 34°54′8″E / 32.08667°N 34.90222°E | |
| Palestine grid | 141/165 |
| Geopolitical entity | Mandatory Palestine |
| Subdistrict | Jaffa |
| Date of depopulation | May 15, 1948[3] |
| Area | |
• Total | 4,419 dunams (4.4 km2 or 1.7 sq mi) |
| Population (1945) | |
• Total | 1,200[2] |
| Cause(s) of depopulation | Whispering campaign |
| Current Localities | Petah Tikva[4] |
Fajja (Template:Lang-ar) was a Palestinian town located 15 kilometers northeast of Jaffa. Depopulated and destroyed during the Arab-Israeli war, its land area is today part of the Israeli city of Petah Tiqva.
History
Pottery remains from the Chalcolithic, Middle Bronze II, Iron, Persian and Roman eras have been found here.[5][6]
Winepresses, dated to the Roman/Byzantine era (5th and 6th century) have been excavated here,[5][7] and pottery remain from the Byzantine era have also been found.[6]
Pottery from the early Islamic period (eighth–tenth centuries CE) have been excavated here, as has glass artefacts from the early Umayyad era, and ceramic jugs from the Abbasid era.[6]
Ceramic vessels dating to the twelfth–thirteenth centuries CE (ie Crusader or Ayyubid era) "including a glazed yellow bowl with an incised decoration that may represent a Latin letter" have also been found.[6]
Ottoman era
In 1856 the village was named el−Fejjeh on the map of Southern Palestine that Heinrich Kiepert published that year.[8]
In 1870, Victor Guérin found the village to be divided into two quarters, each with its own Sheikh. He estimated it to have 300 inhabitants,[9] while an Ottoman village list from about the same year found that Fajja had a population of 110, in 35 houses, though the population count included men, only.[10][11]
In 1882, the PEF's Survey of Western Palestine (SWP) described Fajja as a small village built of adobe bricks.[12]
British Mandate era
In the 1922 census of Palestine, conducted by the British Mandate authorities, Fajjeh had a population of 164, all Muslims,[13] increasing sharply in the 1931 census, to 707, still all Muslims, in a total of 165 houses.[14]
The town had one elementary school, founded in 1922. By 1945 it had 181 students, including 10 females.[4]
In the 1945 statistics, Fajja had 1,200 Muslim inhabitants, in addition to 370 Jews, and a total land area of 4,419 dunams.[2][15] Of this, a total of 768 dunums was used for citrus and bananas, 61 dunums were irrigated or used for orchards, 3,863 used for cereals,[16] while 7 dunams were classified as built-up areas.[17]


1948, aftermath
In early April, the villagers of Fajja sued for a truce with their Jewish neighbours.[18] Again, after the Deir Yassin massacre, the villagers of Fajja contacted their Jewish neighbours and promised "quiet".[19] It was conquered by the Haganah and Irgun on May 15, 1948 without any resistance. Most of the Arab inhabitants fled the town before its capture by Israeli forces due to alleged attacks by the Irgun on February 17. In June 1948, the town was demolished based on the recommendation of Yosef Weitz of the Jewish National Fund.[20] Most of the town's land is currently a part of the jurisdiction of the city of Petah Tikva.
In 1992 the village site was described: "The village has been completely razed except for one house and a pond. Eucalyptus trees and cactuses further mark the site. The surrounding land is partly occupied by buildings; the rest is cultivated."[4]
See also
- Kfar Avraham
- List of Arab towns and villages depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War
- List of villages depopulated during the Arab-Israeli conflict
Footnotes
- ^ Palmer, 1881, p. 214
- ^ a b Department of Statistics, 1945, p. 27
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. xviii, village #203. Also gives cause of depopulation.
- ^ a b c Khalidi, 1992, p. 240
- ^ a b Kaplan and Kaplan, cited in Bar-Nathan, 2002, p. 108
- ^ a b c d Haddad, 2009, Petah Tiqwa
- ^ Kaplan and Cohen, 1963, cited in Gorzalczany, 2005, Petah Tiqwa, Mahane Yehuda
- ^ Kiepert, 1856, Map of Southern Palestine
- ^ Guérin, 1875, pp. 371-372
- ^ Socin, 1879, p. 154
- ^ Hartmann, 1883, p. 137 also noted 35 houses
- ^ Conder and Kitchener, 1881, SWP II, p.251. Cited in Khalidi, 1992, p. 240.
- ^ Barron, 1923, Table VII, Sub-district of Jaffa, p. 20
- ^ Mills, 1932, p. 13
- ^ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 52
- ^ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 95
- ^ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 145
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. 246, note #644 on p. 298
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. 240, note #581 on p. 295
- ^ District of Jaffa: Fajja Town Statistics and Facts.Information extracted from Bibliography and References Benny Morris and Walid Khalidi.
Bibliography
- Bar-Nathan, Rachel (2002). The Jacob Kaplan and Haya Ritter-Kaplan Legacy (PDF). Hadashot Arkheologiyot – Excavations and Surveys in Israel. pp. 104−109.
- Barron, J.B., ed. (1923). Palestine: Report and General Abstracts of the Census of 1922. Government of Palestine.
- Conder, C.R.; Kitchener, H.H. (1882). The Survey of Western Palestine: Memoirs of the Topography, Orography, Hydrography, and Archaeology. Vol. 2. London: Committee of the Palestine Exploration Fund.
- Department of Statistics (1945). Village Statistics, April, 1945. Government of Palestine.
- Gorzalczany, Amir (2005-11-28). "Petah Tiqwa, Mahane Yehuda". Hadashot Arkheologiyot – Excavations and Surveys in Israel (117).
- Guérin, V. (1875). Description Géographique Historique et Archéologique de la Palestine (in French). Vol. 2: Samarie, pt. 2. Paris: L'Imprimerie Nationale.
- Hadawi, S. (1970). Village Statistics of 1945: A Classification of Land and Area ownership in Palestine. Palestine Liberation Organization Research Center.
- Haddad, Elie (2009-01-09). "Petah Tiqwa". Hadashot Arkheologiyot – Excavations and Surveys in Israel (121).
- Hartmann, M. (1883). "Die Ortschaftenliste des Liwa Jerusalem in dem türkischen Staatskalender für Syrien auf das Jahr 1288 der Flucht (1871)". Zeitschrift des Deutschen Palästina-Vereins. 6: 102–149.
- Khalidi, W. (1992). All That Remains: The Palestinian Villages Occupied and Depopulated by Israel in 1948. Washington D.C.: Institute for Palestine Studies. ISBN 0-88728-224-5.
- Mills, E, ed. (1932). Census of Palestine 1931. Population of Villages, Towns and Administrative Areas. Jerusalem: Government of Palestine.
- Morris, B. (2004). The Birth of the Palestinian Refugee Problem Revisited. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-00967-6. (pp. 314, 342, 349, 350)
- Palmer, E.H. (1881). The Survey of Western Palestine: Arabic and English Name Lists Collected During the Survey by Lieutenants Conder and Kitchener, R. E. Transliterated and Explained by E.H. Palmer. Committee of the Palestine Exploration Fund.
- Socin, A. (1879). "Alphabetisches Verzeichniss von Ortschaften des Paschalik Jerusalem". Zeitschrift des Deutschen Palästina-Vereins. 2: 135–163.
External links
- Palestine Remembered - Fajja
- Fajja, Zochrot
- Survey of Western Palestine, Map 13: IAA, Wikimedia commons
- Fajja from the Khalil Sakakini Cultural Center