Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor: Difference between revisions
depression -> depressive |
|||
| Line 140: | Line 140: | ||
== Contraindications == |
== Contraindications == |
||
Due to the effects of increased norepinephrine levels and, therefore, higher [[Noradrenergic]] activity, pre-existing hypertension should be controlled before treatment with SNRIs and blood pressure periodically monitored throughout treatment. Duloxetine has also been associated with cases of hepatic failure and should not be prescribed to patients with chronic alcohol use or liver disease. Patients suffering from coronary artery disease should avoid the use of SNRIs. Furthermore, due to some SNRIs' actions on obesity, patients with major eating |
Due to the effects of increased norepinephrine levels and, therefore, higher [[Noradrenergic]] activity, pre-existing hypertension should be controlled before treatment with SNRIs and blood pressure periodically monitored throughout treatment. Duloxetine has also been associated with cases of hepatic failure and should not be prescribed to patients with chronic alcohol use or liver disease. Patients suffering from coronary artery disease should avoid the use of SNRIs. Furthermore, due to some SNRIs' actions on obesity, patients with major eating disorders such as [[anorexia nervosa]] or [[bulimia]] should not be prescribed SNRIs.<ref name="Meridia" /> Duloxetine and milnacipran are also contraindicated in patients with uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma, as they have been shown to increase incidence of mydriasis.<ref name="Cymbalta" /><ref name="Savella" /> |
||
SNRIs should be taken with caution when using [[Hypericum perforatum|St John's wort]], as the combination can lead to the potentially fatal [[serotonin syndrome]].<ref>{{cite book | title=2006 Lippincott's Nursing Drug Guide |last=Karch |first=Amy |year= 2006 |publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins |location=Philadelphia, Baltimore, New York, London, Buenos Aires, Hong Kong, Sydney, Tokyo |isbn= 1-58255-436-6 }}</ref> There is also a significant risk when combining SNRIs with [[dextromethorphan]], [[tramadol]], [[cyclobenzaprine]], [[meperidine|meperidine/pethidine]], and [[propoxyphene]]. They should never be taken within 14 days of any other antidepressant, especially with [[monoamine oxidase inhibitor]]s (MAOIs), as combinations of SNRIs with MAOIs can cause hyperthermia, rigidity, myoclonus, autonomic instability with fluctuating vital signs, and mental status changes that include extreme agitation progressing to delirium and coma.<ref name="Cymbalta" /> |
SNRIs should be taken with caution when using [[Hypericum perforatum|St John's wort]], as the combination can lead to the potentially fatal [[serotonin syndrome]].<ref>{{cite book | title=2006 Lippincott's Nursing Drug Guide |last=Karch |first=Amy |year= 2006 |publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins |location=Philadelphia, Baltimore, New York, London, Buenos Aires, Hong Kong, Sydney, Tokyo |isbn= 1-58255-436-6 }}</ref> There is also a significant risk when combining SNRIs with [[dextromethorphan]], [[tramadol]], [[cyclobenzaprine]], [[meperidine|meperidine/pethidine]], and [[propoxyphene]]. They should never be taken within 14 days of any other antidepressant, especially with [[monoamine oxidase inhibitor]]s (MAOIs), as combinations of SNRIs with MAOIs can cause hyperthermia, rigidity, myoclonus, autonomic instability with fluctuating vital signs, and mental status changes that include extreme agitation progressing to delirium and coma.<ref name="Cymbalta" /> |
||
Revision as of 03:27, 22 October 2014
Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are a class of antidepressant drugs used in the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) and other mood disorders. They are sometimes also used to treat anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), chronic neuropathic pain, and fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS), and for the relief of menopausal symptoms.
SNRIs are potent inhibitors of the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are known to play an important role in mood. SNRIs can be contrasted with the more widely used selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which act upon serotonin alone.
The human serotonin transporter (SERT) and norepinephrine transporter (NET) are membrane proteins that are responsible for the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine. Balanced dual inhibition of monoamine reuptake can possibly offer advantages over other antidepressants drugs by treating a wider range of symptoms.[1] SNRIs, along with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (NRIs), are second-generation antidepressants. Over the past two decades, second-generation antidepressants have gradually replaced first-generation antidepressants, such as tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) as the drugs of choice for the treatment of MDD. This is mainly because of their improved tolerability and safety profile.[2]
Overview of SNRIs
- Venlafaxine (Effexor) – The first and most commonly used SNRI. It was introduced by Wyeth in 1994. The reuptake effects of venlafaxine are dose-dependent. At low doses (<150 mg/day), it acts only on serotonergic transmission. At moderate doses (>150 mg/day), it acts on serotonergic and noradrenergic systems, whereas at high doses (>300 mg/day), it also affects dopaminergic neurotransmission.[3]
- Desvenlafaxine (Pristiq)[4] – The active metabolite of venlafaxine. It is believed to work in a similar manner, though some evidence suggests lower response rates compared to venlafaxine and duloxetine. It was introduced by Wyeth in May 2008 and was then the third approved SNRI.[5]
- Duloxetine (Cymbalta, Yentreve)[6] – By Eli Lilly and Company, has been approved for the treatment of depression and neuropathic pain in August 2004. Duloxetine is contraindicated in patients with heavy alcohol use or chronic liver disease, as duloxetine can increase the levels of certain liver enzymes that can lead to acute hepatitis or other diseases in certain at risk patients. Currently, the risk of liver damage appears to be only for patients already at risk, unlike the antidepressant nefazodone, which, though rare, can spontaneously cause liver failure in healthy patients.[7] Duloxetine is also approved for major depressive disorder (MDD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), chronic musculoskeletal pain, including chronic osteoarthritis pain and chronic low back pain (as of October, 2010), and is one of the only three medicines approved by the FDA for fibromyalgia [1].
- Milnacipran (Dalcipran, Ixel, Savella)[8] – Shown to be significantly effective in the treatment of depression and fibromyalgia.[9] The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved milnacipran for treatment of fibromyalgia in the United States of America in January 2009, however it is currently not approved for depression in that country. Milnacipran has been commercially available in Europe and Asia for several years.
- Levomilnacipran (Fetzima) – The levo- isomer of milnacipran. Under development for the treatment of depression in the United States and Canada, it was approved by the FDA for treatment of MDD in July 2013.
- Sibutramine (Meridia, Reductil) – An SNRI, which, instead of being developed for the treatment of depression, was widely marketed as an appetite suppressant for weight loss purposes. Sibutramine was the first drug for the treatment of obesity to be approved in 30 years.[10]
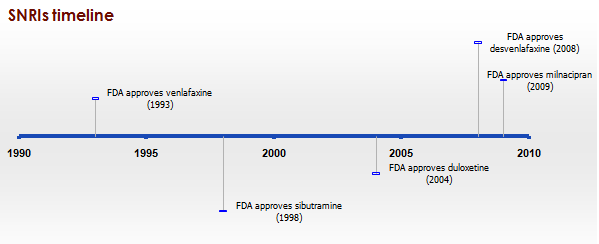
History
In 1952 iproniazid, an antimycobacterial agent, was discovered to have psychoactive properties while researched as a possible treatment for tuberculosis. Researchers noted that patients given iproniazid became cheerful, more optimistic, and more physically active. Soon after its development, iproniazid and related substances were shown to slow enzymatic breakdown of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine via inhibition of the enzyme monoamine oxidase. For this reason this class of drugs became known as monoamine oxidase inhibitors, or MAOIs. During this time development of distinctively different antidepressant agents was also researched. Imipramine became the first clinically useful tricyclic antidepressant (TCA). Imipramine was found to affect numerous neurotransmitter systems and to block reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin from the synapse, therefore increasing the levels of these neurotransmitters. Use of MAOIs and TCAs gave major advances in treatment of depression but their use was limited by unpleasant side effects and significant safety and toxicity issues.[11]
Throughout the 1960s and 1970s the catecholamine hypothesis of emotion and its relation to depression was of wide interest and that the decreased levels of certain neurotransmitters, such as norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine might play a role in the pathogenesis of depression. This led to the development of fluoxetine, the first SSRI. The improved safety and tolerability profile of the SSRIs in patients with MDD, compared with TCAs and MAOIs, represented yet another important advance in the treatment of depression.[11]
Since the late 1980s SSRIs have dominated the antidepressant drug market. Today there is increased interest in antidepressant drugs with broader mechanisms of action that may offer improvements in efficacy and fewer adverse effects. In 1993 a new drug was introduced to the US market called venlafaxine, a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor.[12] Venlafaxine was the first compound described in a new class of antidepressive substances called phenylethylamines. These substances are unrelated to TCA and other SSRIs. Venlafaxine blocks the neuronal reuptake of serotonin, noradrenaline, and, to a lesser extent, dopamine in the central nervous system. In contrast with several other antidepressant drugs, venlafaxine can induce a rapid onset of action mainly due to a subsequent norepinephrine reuptake inhibition.[13] See timeline in figure 1.

Mechanism of action
Monoamines are connected to the pathophysiology of depression. Symptoms are thought to appear because concentrations of neurotransmitters for example norepinephrine and serotonin are insufficient.[14][15] Medications to treat symptoms of depression effect the transmission of serotonin, norepinephrine and/or dopamine.[14] Older and more unselective antidepressants like TCAs and MAOIs, act by inhibiting the reuptake or metabolism, of norepinephrine and/or serotonin in the brain which concludes higher neurotransmitters concentrations.[15] Antidepressants that have dual mechanisms of action, inhibit both serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake, in some cases with weak effect on dopamine reuptake.[14] Antidepressants have effects on variable neuronal receptors like muscarinic-cholinergic, α1- and α2-adrenergic, and H1-histaminergic receptors, and sodium channels in the cardiac muscle, leading to decreased cardiac conduction and cardiotoxicity. Selectivity of antidepressant agents are based on the neurotransmitters that are thought to influence symptoms of depression.[16] Drugs that selectively block the reuptake of serotonin and/or norepinephrine have shown to be effective in treating depression and are better tolerated than TCAs. TCAs have comprehensive effects on various neurotransmitters receptors, which leads to lack of tolerability and increased risk of toxicity [17]
Tricyclic antidepressants

TCAs were the first medications that had dual mechanism of action. The mechanism of action of tricyclic secondary amine antidepressants is only partly understood. TCAs have dual inhibition effects on norepinephrine reuptake transporters and serotonin reuptake transporters. Increased norepinephrine and serotonin concentrations are obtained by inhibiting both of these transporter proteins. TCAs have substantially more affinity for norepinephrine reuptake proteins than the SSRIs. This is because of a formation of secondary amine TCA metabolites.[18][19]
In addition, the TCAs interact with adrenergic receptors. This interaction seems to be critical for increased availability of norepinephrine in or near the synaptic clefts. Actions of imipramine-like tricyclic antidepressants have complex, secondary adaptions to their initial and sustained actions as inhibitors of norepinephrine transport and variable blockade of serotonin transport. Norepinephrine interacts with postsynaptic α- and β-adrenergic receptor subtypes and presynaptic α2-autoreceptors. The α2-receptors include presynaptic autoreceptors which limit the neurophysiological activity of noradrenergic neurons in the central nervous system. Formation of norepinephrine is reduced by autoreceptors through the ratelimiting enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase, by decreasing the expression of cyclic AMP-mediated phosphorylation-activation of the enzyme.[19] α2-receptors also cause decreased intracellular cyclic AMP expression which is resulted in smooth muscle relaxation or decreased secretion.[20] TCAs activate a negative-feedback mechanism through its effects on presynaptic receptor mediation. Probable explanation of effects on decreased neurotransmitter release is that as the receptors activate, inhibition of neurotransmitter release occurs, including suppression of voltage-gated Ca2+ currents and activation of G protein-coupled receptor-operated K+ currents. Repeated exposure of agents with this type of mechanism leads to inhibition of neurotransmitter release. However, repeated administration of TCAs finally results in decreased responses of α2-receptors. This desensitization of these responses may be caused due to increased exposure to the endogen norepinephrine or from prolonged occupation of the norepinephrine transport itself caused by allosteric effect. This adaptation allows the presynaptic synthesis and secration of norepinephrine to return to, or even exceed, normal levels of norepinephrine in the synaptic clefts. Overall inhibition of norepinephrine reuptake induced by TCAs, lead to decreased rates of neuron firing (mediated through α2-autoreceptors), metabolic activity, and release of neurotransmitters.[19]
TCAs do not block dopamine transport but might facilitate dopamine effects indirectly by transport-inhibition of dopamine into noreadrenergic terminals in cerebral cortex.[19] Because of multiple effects on different receptors, TCAs have poor tolerability which could result in adverse effects and increased risk of toxicity.[17]
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) selectively inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and are a widely used group of antidepressants.[21] With increased receptors selectivity compared to TCAs, undesired effects like poor tolerability are avoided.[19] Serotonin is synthesized from an amino acid called L-tryptophan. Active transport system regulates the uptake of tryptophan across the blood–brain barrier. Serotonergic pathways are classified into two main ways in the brain; the ascending projections from the medial and dorsal raphe and the descending projections from the caudal raphe into the spinal cord. The reuptake blocking of SSRIs into the presynaptic terminal results in increased concentration of serotonin in the synaptic cleft, just like the TCAs, but with much less additional effects. Altering the serotonin concentrations to higher levels influence symptoms of anxiety which coexist with depression, leading to improvement of depression symptoms.[21]
Selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors
There are two major regions in the brain where noradrenergic neurons are located. These regions are called locus coeruleus and the lateral tegmental. With administration of selective NRIs, neuronal activity in locus coeruleus region is induced because of increased concentration of norepinephrine in the synaptic cleft. This results in activation of α2-adrenergic receptors,[15] as discussed in above.
Assays have shown that selective NRIs have insignificant penchant for mACh, α1- and α2-adrenergic, or H1 receptors.[16]
Dual serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors
Agents with dual serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibition (SNRIs) are sometimes called non-tricyclic serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors. Clinical studies suggest that compounds which increase the concentration in the synaptic cleft of both norepinephrine and serotonin are more successful than single acting agents in the treatment of depression. Dual reuptake inhibitors have low affinity at neuronal receptors of the other neurotransmitters which results in a low adverse effects, compared with the TCAs. Nontricyclic antidepressants have improved potency and onset action acceleration in antidepressant response than SSRI alone, which give the impression that synergism is an efficient property in mediating antidepressant activity.
Between the non-tricyclic SNRIs there are several important differences that are based on pharmacokinetics, metabolism to active metabolites, inhibition of CYP isoforms, effect of drug-drug interactions and the half-life of the nontricyclic SNRIs.[18][22]
Combination of mechanisms of action in a single active agent is an important development in psychopharmacology.[22]
Structure activity relationship (SAR)
Aryloxypropanamine scaffold
Several reuptake inhibitors contain an aryloxypropanamine scaffold. This structural motif has potential for high affinity binding to biogenic amine transports.[22] Drugs containing an aryloxypropanamine scaffold have selectivity profile for norepinephrine and serotonin transporters that depends on the substitution pattern of the aryloxy ring. Selective NRIs contain a substituent in 2’-position of the aryloxy ring but SSRIs contain a substituent in 4’-position of the aryloxy ring. Atomoxetine, nisoxetine and reboxetine all have a substitution group in the 2’-position and are selective NRIs while compounds that have a substitution group in the 4’-position (like fluoxetine and paroxetine) are SSRIs. Duloxetine contains a phenyl group fused at the 2’- and 3’-positions, therefore it has dual selective norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake inhibitory effects and has similar potencies for the both transporters.[23] The nature of the aromatic substituent also has a significant influence on the activity and selectivity of the compounds as inhibitors of the serotonin or the norepinephrine transporters.[22]
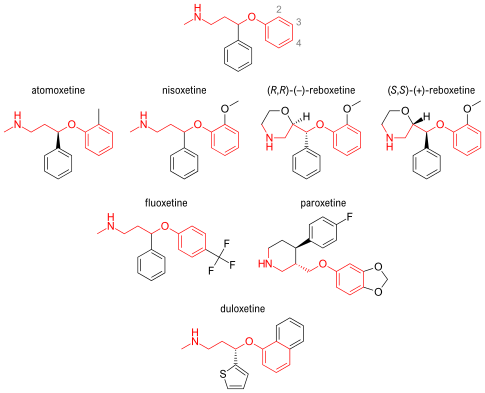
Cycloalkanol ethylamine scaffold
Venlafaxine and desvenlafaxine contain a cycloalkanol ethylamine scaffold. Increasing the electron-withdrawing nature of the aromatic ring provides more potent inhibitory effect of norepinephrine uptake and improves the selectivity for norepinephrine over the serotonin transporter.[23] Effects of chloro, methoxy and trifluoromethyl substituents in the aromatic ring of cycloalkanol ethylamine scaffold were tested. The results showed that the strongest electron-withdrawing m-trifluoromethyl analogue exhibited the most potent inhibitory effect of norepinephrine and the most selectivity over serotonin uptake.[23] WY-46824, a piperazine-containing derivative, has shown norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibition. Further synthesis and testing identified WAY-256805, a potent norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor that exhibited excellent selectivity and was efficacious in animal models of depression, pain, and thermoregulatory dysfunction.[24]

Milnacipran

Milnacipran is structurally different from other SNRIs.[18] The SAR of milnacipran derivatives at transporter level is still largely unclear and is based on in vivo efficacy that was reported in 1987. N-methylation of milnacipran in substituent group R4 and R5 reduces the norepinephrine and serotonin activity.[25] Researches on different secondary amides in substitution groups R6 and R7 showed that π electrons play an important role in the interaction between transporters and ligands. A phenyl group in substituent R6 showed effect on norepinephrine transporters. Substituent groups in R6 and R7 with allylic double bond showed significant improved effect on both norepinephrine and serotonin transporters.[25] Studies have shown that when introducing a 2-methyl group in substituent R3 the potency at norepinephrine and serotonin transporters are almost abolished. Methyl groups in substituent groups R1 and R2 also abolished the potency at norepinephrine and serotonin transporters. Researchers found that replacing one of the ethyl groups of milnacipran with an allyl moiety increases the norepinephrine potency.[26] The pharmacophore of milnacipran derivatives is still largely unclear.[25]
The conformation of milnacipran is an important part of its pharmacophore. Changing the SAR in milnacipran changes the stereochemistry of the compound and affects the norepinephrine and serotonin concentration. Milnacipran is marketed as a racemic mixture. Effects of milnacipran resides in the 1S,2R isomer and substitution of the phenyl group in the 1S,2R isomer has negative impact on norepinephrine concentration.[26] Milnacipran has low molecular weight and low lipophilicity. Because of these properties milnacipran exhibits almost ideal pharmacokinetics in humans such as high bioavailability, low inter-subject variability, limited liver enzyme interaction, moderate tissue distribution and a reasonably long elimination half-life. Milnacipran´s lack of drug-drug interactions via cytochrome P450 enzymes is thought to be an attractive feature because many of the central nervous system drugs are highly lipophilic and are mainly eliminated by liver enzymes.[26]
Future development of SAR
The application of an aryloxypropanamine scaffold has generated a number of potent MAOIs.[27] Before the development of duloxetine, the exploration of aryloxypropanamine SAR resulted in the identification of fluoxetine and atomoxetine. The same motif can be found in reboxetine where it is constrained in a morpholine ring system. Some studies have been made where the oxygen in reboxetine is replaced by sulfur to give arylthiomethyl morpholine. Some of the arylthiomethyl morpholine derivatives maintain potent levels of serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibition. Dual serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibition resides in different enantiomers for arylthiomethyl morpholine scaffold.[28] Possible drug candidates with dual serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitory activity have also been derived from piperazine, 3-amino-pyrrolidine and benzylamine templates.[29]
Clinical trials
Several studies have shown that antidepressant drugs which have combined serotonergic and noradrenergic activity is more effective than SSRIs in treating MDD. Results showed that serotonergic-noradrenergic antidepressant drugs seem to have a modest efficacy advantage compared to SSRIs in treating MDD [30] and have less side effects.[31] Serotonergic-noradrenergic antidepressant drugs used to treat MDD compared to SSRIs and mirtazapine seem to be less expensive than other drugs for example in the UK. Further research is needed to examine whether larger differences between classes of antidepressant drugs might exist in specific MDD sub-populations or for specific MDD symptoms.[32]
Data from clinical trials have indicated that SNRIs might have pain relieving properties. The pain perception and transmission in the central nervous system have not been fully elucidated however, extensive data support a role of serotonin and norepinephrine in the modulation of pain. This is also supported by data from clinical trials in humans in which antidepressants have been shown to reduce pain and functional impairment in central and neuropathic pain conditions. This property of SNRIs might be used to reduce doses of other pain relieving medication and lower frequency of limited efficacy, safety and tolerability issues.[33] Clinical research data have shown in patients with GAD that the SNRI duloxetine is significantly more effective than placebo in reducing painful physical symptoms of GAD after short-term and long-term treatment. Findings suggested that painful physical symptoms reoccur with relapsing that indicate a need for ongoing treatment in patients with GAD and concurrent painful physical symptoms.[34]
Products of SNRIs
| Active ingredient | Product name | Therapeutic use | Binding affinity (Ki nm) |
Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Venlafaxine | Efexor, Effexor | Treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD), including treatment-resistant cases, generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), chronic pain syndromes [12] | 5-HT:7.8 NE:1920 D:6050 [17] |

|
| Milnacipran | Savella, Ixel, Dalcipran, Toledomin | Treatment of pain and multiple symptoms associated with fibromyalgia syndrome, treatment of MDD [9] | 5-HT:8.4 NE:22 D:>100000 [17] |

|
| Duloxetine | Cymbalta, Ariclaim, Xeristar, Yentreve | Treatment of MDD and fibromyalgia [14] | 5-HT:0.07 NE:1.2 D:230 [17] |

|
| Levomilnacipran | Fetzima | Treatment of MDD in adults | 5-HT:NA NE:NA D:NA |

|
| Desvenlafaxine | Pristiq | Treatment of MDD in adults [5] | 5-HT:NA NE:NA D:NA |

|
| Sibutramine | Meridia, Reductil | Treatment of obesity [10] | 5-HT:NA NE:NA D:NA |

|
5-HT: Serotonin - NE: Norepinephrine - D: Dopamine - NA: Not available
Indications
SNRIs have been approved for treatment of the following conditions:
- Major depressive disorder (MDD)
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
- Social anxiety disorder (SAD)
- Panic disorder
- Neuropathic pain
- Fibromyalgia
- Chronic musculoskeletal pain
Pharmacology
Route of Administration
SNRIs are delivered orally, usually in the form of gel capsules. The drugs themselves are usually a fine crystalline powder that diffuses into the body during digestion.
Dosage
Dosages fluctuate depending on the SNRI used due to varying potencies of the drug in question as well as multiple strengths for each drug.
Mode of Action
The condition for which SNRIs are mostly indicated, major depressive disorder, is thought to be mainly caused by decreased levels of serotonin and norepinephrine in the synaptic cleft, causing erratic signaling. Due to the monoamine hypothesis of depression, which asserts that decreased concentrations of monoamine neurotransmitters leads to depression symptoms, the following relations were determined: "Norepinephrine may be related to alertness and energy as well as anxiety, attention, and interest in life; [lack of] serotonin to anxiety, obsessions, and compulsions; and dopamine to attention, motivation, pleasure, and reward, as well as interest in life."[35] SNRIs work by inhibiting the reuptake of the neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine. This results in an increase in the extracellular concentrations of serotonin and norepinephrine and, therefore, an increase in neurotransmission. Most SNRIs including venlafaxine, desvenlafaxine, and duloxetine, are several fold more selective for serotonin over norepinephrine, while milnacipran is three times more selective for norepinephrine than serotonin. Elevation of norepinephrine levels is thought to be necessary for an antidepressant to be effective against neuropathic pain, a property shared with the older tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), but not with the SSRIs.[36]
Recent studies have shown that depression may be linked to increased inflammatory response,[37] thus attempts at finding an additional mechanism for SNRIs have been made. Studies have shown that SNRIs as well as SSRIs have significant anti-inflammatory action on microglia[38] in addition to their effect on serotonin and norepinephrine levels. As such, it is possible that an additional mechanism of these drugs that acts in combination with the previously understood mechanism exist. The implication behind these findings suggests use of SNRIs as potential anti-inflammatories following brain injury or any other disease where swelling of the brain is an issue. However, it should be noted that, regardless of the mechanism, the efficacy of these drugs in treating the diseases for which they have been indicated has been proven, both clinically and in practice.
Pharmacodynamics
Most SNRIs function alongside primary metabolites and secondary metabolites in order to inhibit reuptake of serotonin, norepinepherine, and trace amounts of dopamine. For example, venlafaxine works alongside its primary metabolite O-desmethylvenlafaxine to strongly inhibit serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake in the brain. Recent evidence suggests that dopamine and norepinepherine behave in a cotransportational manner, due to dopamine's inactivation by norepinephrine reuptake in the prefrontal cortex, which largely lacks dopamine transporters. Therefore, SNRIs can increase dopamine neurotransmission in this part of the brain.[39] Furthermore, because SNRIs are extremely selective, they have no measurable effects on unintended systems, such as on monoamine oxidase inhibition.[40] Furthermore, studies have shown that SNRIs as well as SSRIs have significant anti-inflammatory action on microglia[38][41][42][43][44][45]
Pharmacokinetics
The usual half-life of SNRIs is 5 hours, with patients reaching peak effectiveness ~4 hours post ingestion.[41][42][43][44][45]
Contraindications
Due to the effects of increased norepinephrine levels and, therefore, higher Noradrenergic activity, pre-existing hypertension should be controlled before treatment with SNRIs and blood pressure periodically monitored throughout treatment. Duloxetine has also been associated with cases of hepatic failure and should not be prescribed to patients with chronic alcohol use or liver disease. Patients suffering from coronary artery disease should avoid the use of SNRIs. Furthermore, due to some SNRIs' actions on obesity, patients with major eating disorders such as anorexia nervosa or bulimia should not be prescribed SNRIs.[41] Duloxetine and milnacipran are also contraindicated in patients with uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma, as they have been shown to increase incidence of mydriasis.[44][45]
SNRIs should be taken with caution when using St John's wort, as the combination can lead to the potentially fatal serotonin syndrome.[46] There is also a significant risk when combining SNRIs with dextromethorphan, tramadol, cyclobenzaprine, meperidine/pethidine, and propoxyphene. They should never be taken within 14 days of any other antidepressant, especially with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), as combinations of SNRIs with MAOIs can cause hyperthermia, rigidity, myoclonus, autonomic instability with fluctuating vital signs, and mental status changes that include extreme agitation progressing to delirium and coma.[44]
Side-effects
Because the SNRIs and SSRIs both act similarly to elevate serotonin levels, they subsequently share many of the same side-effects, though to varying degrees. The most common include loss of appetite, weight, and sleep. There may also be drowsiness, dizziness, fatigue, headache, increase in suicidal thoughts, nausea/vomiting, sexual dysfunction, and urinary retention. There are two common sexual side-effects: diminished interest in sex (libido) and difficulty reaching climax (anorgasmia), which are usually somewhat milder with the SNRIs in comparison to the SSRIs. Elevation of norepinephrine levels can sometimes cause anxiety, mildly elevated pulse, and elevated blood pressure. People at risk for hypertension and heart disease should have their blood pressure monitored.[41][42][43][44][45]
Precautions
Starting an SNRI regimen
Due to the extreme changes in noradrenergic activity produced from norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake inhibition, patients that are just starting an SNRI regimen are usually given lower doses than their expected final dosing to allow the body to acclimate to the drug's effects. As the patient continues along at low doses without any side-effects, the dose is incrementally increased until the patient sees improvement in symptoms without detrimental side-effects.[47]
Discontinuation syndrome
As with SSRIs, the abrupt discontinuation of an SNRI usually leads to withdrawal, or "discontinuation syndrome", which could include states of anxiety and other symptoms. Therefore, it is recommended that users seeking to discontinue an SNRI slowly taper the dose under the supervision of a professional. Discontinuation syndrome has been reported to be markedly worse for venlafaxine when compared to other SNRIs. As such, as tramadol is related to venlafaxine, the same conditions apply.[48] This is likely due to venlafaxine's relatively short half-life and therefore rapid clearance upon discontinuation.
Overdose
Causes
Overdosing on SNRIs can be caused by either drug combinations or excessive amounts of the drug itself. These overdoses are extremely dangerous and potentially fatal.[41][42][43][44][45]
Symptoms
Symptoms of SNRI overdose, whether it be a mixed drug interaction or the drug alone, vary in intensity and incidence based on the amount of medicine taken and the individuals sensitivity to SNRI treatment. Possible symptoms are as follows:[44]
Management
Overdose is usually treated symptomatically, especially in the case of serotonin syndrome, which requires treatment with cyproheptadine and temperature control based on the progression of the serotonin toxicity. Patients are often monitored for vitals and airways cleared to ensure that they are receiving adequate levels of oxygen. Another option is to use activated carbon in the GI tract in order to adsorb excess neurotransmitter.[44] It is important to consider drug interactions when dealing with overdose patients, as separate symptoms can arise.
Comparison to SSRIs
The SNRIs were developed more recently than the SSRIs[date missing] and as a result there are relatively few of them. However, the SNRIs are among the most widely used antidepressants today. In 2009, Cymbalta and Effexor were the 11th- and 12th-most-prescribed branded drugs in the United States. This translates to the 2nd- and 3rd-most-common antidepressants, behind Lexapro (#5), the SSRI escitalopram.[49] In some studies, SNRIs demonstrated slightly higher antidepressant efficacy than the SSRIs (response rates 63.6% versus 59.3%).[50] However, in one study escitalopram had a superior efficacy profile to venlafaxine.[51] The side-effects of SNRIs are reported to be slightly less severe in comparison to the SSRIs as well.[citation needed] One of the major complaints that many users of SSRIs have is the negative sexual side-effects that can be very difficult to treat.[2] Although SNRIs can have similar side-effects, many of them can have the opposite effect of increased libido.[citation needed] Wellbutrin, a norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) and Savella, an SNRI, have been reported to increase libido in both men and women, although some studies have contradicted these reports.[3] However, the individuals having reported increased libido also tended to report increased anxiety, heart rate, blood pressure, and other negative effects associated with adrenaline increase.
If a person has an abnormal level of certain neurotransmitters in their brain, it may result in having mood swings or a mood disorder.[52] Serotonin is a neurotransmitter in the brain that is involved with sleep, moods, and emotional states. A slight imbalance of serotonin could result in depression. Norepinephrine is a neurotransmitter that is involved with learning, memory, and physical arousal. Like serotonin, an imbalance of norepinephrine may also result in depression.[53]
See also
References
- ^ Cashman, JR; Ghirmai, S (2009). "Inhibition of serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake and inhibition of phosphodiesterase by multi-target inhibitors as potential agents for depression". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 17 (19): 6890–7. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2009.08.025. PMID 19740668.
- ^ Spina, E; Santoro, V; d'Arrigo, C (2008). "Clinically relevant pharmacokinetic drug interactions with second-generation antidepressants: An update". Clinical therapeutics. 30 (7): 1206–27. doi:10.1016/S0149-2918(08)80047-1. PMID 18691982.
- ^ Redrobe, JP; Bourin M; Colombel MC; Baker GB (July 1998). "Dose-dependent noradrenergic and serotonergic properties of venlafaxine in animal models indicative of antidepressant activity". Psychopharmacology. 138 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1007/s002130050638. PMID 9694520.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Deecher DC, Beyer CE, Johnston G; et al. (August 2006). "Desvenlafaxine succinate: A new serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 318 (2): 657–65. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.103382. PMID 16675639.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Perry, R; Cassagnol, M (2009). "Desvenlafaxine: A new serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor for the treatment of adults with major depressive disorder". Clinical therapeutics. 31 (1): 1374–404. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.07.012. PMID 19698900.
- ^ Iyengar S, Webster AA, Hemrick-Luecke SK, Xu JY, Simmons RM (November 2004). "Efficacy of duloxetine, a potent and balanced serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor in persistent pain models in rats". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 311 (2): 576–84. doi:10.1124/jpet.104.070656. PMID 15254142.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Rxlist.com: "Nefazodone Prescribing Information", accessed 24 May 2012.]
- ^ Nonogaki K, Nozue K, Kuboki T, Oka Y (May 2007). "Milnacipran, a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, induces appetite-suppressing effects without inducing hypothalamic stress responses in mice". Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 292 (5): R1775–81. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00527.2006. PMID 17218444.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Morishita, Shigeru; Arita, Seizaburo (2003). "The clinical use of milnacipran for depression". European Psychiatry. 18 (1): 34–5. doi:10.1016/S0924-9338(02)00003-2. PMID 12648895.
- ^ a b Luque, CA; Rey, JA (2002). "The discovery and status of sibutramine as an anti-obesity drug". European Journal of Pharmacology. 440 (2–3): 119–28. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(02)01423-1. PMID 12007530.
- ^ a b Lieberman, J. A. (2003). "History of the Use of Antidepressants in Primary Care" (PDF). Primary Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 5 (S7): 6–10.
- ^ a b Gutierrez, MA; Stimmel, GL; Aiso, JY (2003). "Venlafaxine: A 2003 update". Clinical therapeutics. 25 (8): 2138–54. doi:10.1016/s0149-2918(03)80210-2. PMID 14512125.
- ^ Gonzalez Ruelas, Enrique; Diaz-Martinez, Alejandro; Martinez Ruiz, Rene (1997). "An open assessment of the acceptability, efficacy, and tolerance of venlafaxine in usual care settings". Current Therapeutic Research. 58 (9): 609. doi:10.1016/S0011-393X(97)80088-4.
- ^ a b c d Hunziker, ME; Suehs, BT; Bettinger, TL; Crismon, ML (2005). "Duloxetine hydrochloride: A new dual-acting medication for the treatment of major depressive disorder". Clinical therapeutics. 27 (8): 1126–43. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2005.08.010. PMID 16199241.
- ^ a b c Grandoso, L; Pineda, J; Ugedo, L (2004). "Comparative study of the effects of desipramine and reboxetine on locus coeruleus neurons in rat brain slices". Neuropharmacology. 46 (6): 815–23. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2003.11.033. PMID 15033341.
- ^ a b Brunello, N; Mendlewicz, J; Kasper, S; Leonard, B; Montgomery, S; Nelson, J; Paykel, E; Versiani, M; Racagni, G (2002). "The role of noradrenaline and selective noradrenaline reuptake inhibition in depression". European neuropsychopharmacology : the journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology. 12 (5): 461–75. doi:10.1016/s0924-977x(02)00057-3. PMID 12208564.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|display-authors=9(help) - ^ a b c d e Stahl, SM; Grady, MM; Moret, C; Briley, M (2005). "SNRIs: Their pharmacology, clinical efficacy, and tolerability in comparison with other classes of antidepressants". CNS spectrums. 10 (9): 732–47. PMID 16142213.
- ^ a b c Lemke, T. L., Williams, D.A., Roche, V.F. and Zito, S. W. (2008). Foye´s principles of medicinal chemistry (6th ed.). USA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 547–67, 581–582.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e Goodman & Gilman’s: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (11 ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. 2006.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - ^ Silverthorn, D.U., ed. (2007). Human Physiology (4 ed.). San Francisco: Pearson. pp. 383–384.
- ^ a b Nutt, D; Forshall, S; Bell, C; Rich, A; Sandford, J; Nash, J; Argyropoulos, S (1999). "Mechanisms of action of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the treatment of psychiatric disorders". European Neuropsychopharmacology. 9: S81–6. doi:10.1016/S0924-977X(99)00030-9. PMID 10523062.
- ^ a b c d Boot, J; Cases, M; Clark, BP; Findlay, J; Gallagher, PT; Hayhurst, L; Man, T; Montalbetti, C; et al. (2005). "Discovery and structure-activity relationships of novel selective norepinephrine and dual serotonin/norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 15 (3): 699–703. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2004.11.025. PMID 15664840.
- ^ a b c Mahaney, PE; Vu, AT; McComas, CC; Zhang, P; Nogle, LM; Watts, WL; Sarkahian, A; Leventhal, L; et al. (2006). "Synthesis and activity of a new class of dual acting norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake inhibitors: 3-(1H-indol-1-yl)-3-arylpropan-1-amines". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 14 (24): 8455–66. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2006.08.039. PMID 16973367.
- ^ Mahaney, PE; Gavrin, LK; Trybulski, EJ; Stack, GP; Vu, T; Cohn, ST; Ye, F; Belardi, JK; et al. (2008). "Structure−Activity Relationships of the Cycloalkanol Ethylamine Scaffold: Discovery of Selective Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 51 (13): 4038–49. doi:10.1021/jm8002262. PMID 18557608.
- ^ a b c Chen, Chen; Dyck, Brian; Fleck, Beth A.; Foster, Alan C.; Grey, Jonathan; Jovic, Florence; Mesleh, Michael; Phan, Kasey; et al. (2008). "Studies on the SAR and pharmacophore of milnacipran derivatives as monoamine transporter inhibitors". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 18 (4): 1346. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.01.011.
- ^ a b c Tamiya, Junko; Dyck, Brian; Zhang, Mingzhu; Phan, Kasey; Fleck, Beth A.; Aparicio, Anna; Jovic, Florence; Tran, Joe A.; et al. (2008). "Identification of 1S,2R-milnacipran analogs as potent norepinephrine and serotonin transporter inhibitors". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 18 (11): 3328. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.04.025.
- ^ Vu, An T.; Cohn, Stephen T.; Terefenko, Eugene A.; Moore, William J.; Zhang, Puwen; Mahaney, Paige E.; Trybulski, Eugene J.; Goljer, Igor; et al. (2009). "3-(Arylamino)-3-phenylpropan-2-olamines as a new series of dual norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake inhibitors". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 19 (9): 2464–7. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.03.054. PMID 19329313.
- ^ Boot, JR; Brace, G; Delatour, CL; Dezutter, N; Fairhurst, J; Findlay, J; Gallagher, PT; Hoes, I; et al. (2004). "Benzothienyloxy phenylpropanamines, novel dual inhibitors of serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 14 (21): 5395–9. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2004.08.005. PMID 15454233.
- ^ Fish, Paul V.; Deur, Christopher; Gan, Xinmin; Greene, Keri; Hoople, David; MacKenny, Malcolm; Para, Kimberly S.; Reeves, Keith; et al. (2008). "Design and synthesis of morpholine derivatives. SAR for dual serotonin & noradrenaline reuptake inhibition". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 18 (8): 2562. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.03.050.
- ^ Papakostas, GI; Thase, ME; Fava, M; Nelson, JC; Shelton, RC (2007). "Are antidepressant drugs that combine serotonergic and noradrenergic mechanisms of action more effective than the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in treating major depressive disorder? A meta-analysis of studies of newer agents". Biological Psychiatry. 62 (11): 1217–27. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.03.027. PMID 17588546.
- ^ Nemeroff, Charles B.; Thase, Michael E.; Epic 014 Study, Group (2007). "A double-blind, placebo-controlled comparison of venlafaxine and fluoxetine treatment in depressed outpatients". Journal of Psychiatric Research. 41 (3–4): 351–9. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2005.07.009. PMID 16165158.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Benedict, A; Arellano, J; De Cock, E; Baird, J (2010). "Economic evaluation of duloxetine versus serotonin selective reuptake inhibitors and venlafaxine XR in treating major depressive disorder in Scotland". Journal of Affective Disorders. 120 (1–3): 94–104. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2009.04.017. PMID 19497623.
- ^ Marks, David M.; Shah, Manan J.; Patkar, Ashwin A.; Masand, Prakash S.; Park, Geun-Young; Pae, Chi-Un (2009). "Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors for Pain Control: Premise and Promise". Current Neuropharmacology. 7 (4): 331–6. doi:10.2174/157015909790031201. PMC 2811866. PMID 20514212.
- ^ Beesdo, K; Hartford, J; Russell, J; Spann, M; Ball, S; Wittchen, HU (2009). "The short- and long-term effect of duloxetine on painful physical symptoms in patients with generalized anxiety disorder: Results from three clinical trials". Journal of anxiety disorders. 23 (8): 1064–71. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2009.07.008. PMID 19643572.
- ^ Nutt DJ. Relationship of neurotransmitters to the symptoms of major depressive disorder. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2008;69 Suppl E1:4–7. PMID 18494537.
- ^ Sindrup SH, Otto M, Finnerup NB, Jensen TS (2005). "Antidepressants in the treatment of neuropathic pain". Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 96 (6): 399–409. doi:10.1111/j.1742-7843.2005.pto_96696601.x. PMID 15910402.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Shelton RC, Miller AH (2011). "Inflammation in depression: is adiposity a cause?". Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience. 13 (1): 41–53. PMC 3181969. PMID 21485745.
- ^ a b Tynan RJ, Weidenhofer J, Hinwood M, Cairns MJ, Day TA, Walker FR (2012). "A comparative examination of the anti-inflammatory effects of SSRI and SNRI antidepressants on LPS stimulated microglia". Brain Behav Immun. 26 (3): 469–479. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2011.12.011. PMID 22251606.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ http://stahlonline.cambridge.org/prescribers_drug.jsf?page=0521683505c95_p539-544.html.therapeutics&name=Venlafaxine&title=Therapeutics
- ^ Lambert O, Bourin M (2002). "SNRIs: mechanism of action and clinical features". Neurobiology of Anxiety and Depression. 2 (6): 849–858. doi:10.1586/14737175.2.6.849. PMID 19810918.
- ^ a b c d e "Meridia Prescription Information" (PDF). Abbott Labrotories. August 2010. Retrieved 26 June 2012.
- ^ a b c d "Pristiq Prescription Information". Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc. April 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2012.
- ^ a b c d "Effexor XR Prescription Information". Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc. November 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2012.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Cymbalta Prescription Information" (PDF). Eli Lilly and Company. September 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2012.
- ^ a b c d e "Savella Prescription Information" (PDF). Forest Pharmaceuticals Inc. December 2009. Retrieved 26 June 2012.
- ^ Karch, Amy (2006). 2006 Lippincott's Nursing Drug Guide. Philadelphia, Baltimore, New York, London, Buenos Aires, Hong Kong, Sydney, Tokyo: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 1-58255-436-6.
- ^ "Duloxetine: Drug Information". UpToDate. Retrieved 28 June 2012.
- ^ Perahia DG, Pritchett YL, Kajdasz DK, Bauer M, Jain R, Russell JM, Walker DJ, Spencer KA, Froud DM, Raskin J, Thase ME. (2008). "A randomized, double-blind comparison of duloxetine and venlafaxine in the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder". J Psychiatr Res. 42 (1): 22–34. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2007.01.008. PMID 17445831.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "2009 Top 200 branded drugs by total prescriptions" (PDF). SDI/Verispan, VONA, full year 2009. www.drugtopics.com. Retrieved 6 April 2011.
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 17588546, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=17588546instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 17394446, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=17394446instead. - ^ "Neurobiology of Mood Disorders.. Retrieved on 10 January 2013.
- ^ "The Four Major Neurotransmitters.. Retrieved on 10 January 2013.
