1990s

| Millennium |
|---|
| 2nd millennium |
| Centuries |
| Decades |
| Years |
| Categories |
The 1990s, also known as "the Nineteen Nineties" or abbreviated as "the Nineties" or "the '90s", was a decade within the late 20th century that began on January 1, 1990, and ended on December 31, 1999.
The decade is seen by many Western nations as a period of unprecedented peace and prosperity, though many parts of the so-called Third World faced various problems including genocide, AIDS and new or continuing ethnic tensions and civil wars.
A combination of factors, including the mass mobilization of capital markets through neoliberalism, the beginning of the widespread proliferation of new media such as the Internet, and the dissolution of the Soviet Union led to a realignment and reconsolidation of economic and political power across the world, and within countries.
New ethnic conflicts emerged in Africa, the Caucasus and the Balkans, and signs of any resolution of tensions in the Middle East remained elusive, though the Irish Troubles came to a standstill in 1998 with the Good Friday Agreement.[1]
Politics and wars
Wars
The most prominent armed conflicts of the decade include:
International wars
- The Congo wars break out in the 1990s:
- The First Congo War takes place in Zaire from 1996 to 1997, resulting in Zairian dictator Mobutu Sese Seko being overthrown from power on 16 May 1997, ending 32 years of his rule. Zaire is renamed the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- The Second Congo War starts in 1998 in central Africa and includes 50 different cultures and 7 different nations. It continued until 2003.

- The Gulf War – Iraq was left in severe debt after the 1980s war with Iran. President Saddam Hussein accused Kuwait of flooding the market with oil and driving down prices. As a result, on 2 August 1990, Iraqi forces invaded and conquered Kuwait. The UN immediately condemned the action, and a coalition force led by the United States was sent to the Persian Gulf. Aerial bombing of Iraq began in January 1991 (see also Gulf War), and a month later, the UN forces drove the Iraqi army from Kuwait in just four days. In the aftermath of the war, the Kurds in the north of Iraq and the Shiites in the south rose up in revolt, and Saddam Hussein barely managed to hold onto power. Until the US invasion in 2003, Iraq was cut off from much of the world.
- The Chechen wars break out in the 1990s:
- The First Chechen War (1994–1996) – the conflict was fought between the Russian Federation and the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria. After the initial campaign of 1994–1995, culminating in the devastating Battle of Grozny, Russian federal forces attempted to seize control of the mountainous area of Chechnya but were set back by Chechen guerrilla warfare and raids on the flatlands in spite of Russia's overwhelming manpower, weaponry, and air support. The resulting widespread demoralization of federal forces, and the almost universal opposition of the Russian public to the conflict, led Boris Yeltsin's government to declare a ceasefire in 1996 and sign a peace treaty a year later.
- The Second Chechen War (1999 – ongoing) – the war was launched by the Russian Federation starting 26 August 1999, in response to the Invasion of Dagestan and the Russian apartment bombings which were blamed on the Chechens. During the war Russian forces largely recaptured the separatist region of Chechnya.[2] The campaign largely reversed the outcome of the First Chechen War, in which the region gained de facto independence as the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria.
- The Kargil War (1999) – In May 1999, Pakistan sends troops covertly to occupy strategic peaks in Kashmir. A month later the Kargil War with India results in a political fiasco for Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif, followed by a Pakistani military withdrawal to the Line of Control. The incident leads to a military coup in October, in which Sharif is ousted by Army Chief Pervez Musharraf. This conflict remains the only war fought between two declared nuclear powers.
- The Kosovo War (1998–1999):
- War between ethnic-Albanian separatists and Yugoslav military and Serb paramilitary forces in Kosovo begin in 1996 and escalates in 1998 with increasing reports of atrocities taking place.
- In 1999, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) led by the United States launched air attacks against Yugoslavia (then composed of only Serbia and Montenegro) to pressure the Yugoslav government to end its military operations against ethnic Albanian separatists in Kosovo due to accusations of war crimes being committed by Yugoslav military forces working alongside nationalist Serb paramilitary groups. After weeks of bombing, Yugoslavia submits to NATO's demands and NATO forces occupy Kosovo and later UN peacekeeping forces to take control of Kosovo.

- The Yugoslav Wars (1991–1995) – The breakup of Yugoslavia beginning on 25 June 1991 after the republics of Croatia and Slovenia declared independence from Yugoslavia which was followed by the subsequent Yugoslav wars. The Yugoslav Wars would become notorious for numerous war crimes and human rights violations such as ethnic cleansing and genocide committed by all sides.
- Ten-Day War (1991) – a brief military conflict between Slovenian TO (Slovenian Territorial Defence) and the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) following Slovenia's declaration of independence.
- Croatian War of Independence (1991–1995) – the war fought in hegh town Croatia between the Croatian government, having declared independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, and both the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) and Serb forces, who established the self-proclaimed Republic of Serbian Krajina (RSK) within Croatia.
- Bosnian War (1992–1995) – the war involved several ethnically defined factions within Bosnia and Herzegovina: Bosniaks, Serbs and Croats as well as a smaller faction in Western Bosnia led by Fikret Abdić. The Siege of Sarajevo (1992–1995) marked the most violent urban warfare in Europe since World War II at that time as Serb forces bombard and attack Bosniak controlled and populated areas of the city. War crimes occur including ethnic cleansing and destruction of civilian property.
- The final fighting in Croatian and Bosnian wars ends in 1995 with the success of Croatian military offensives against Serb forces and the mass exodus of Serbs from Croatia in 1995; Serb losses to Croat and Bosniak forces; and finally the signing of the Dayton Agreement which internally partitioned Bosnia and Herzegovina into a Republika Srpska and a Bosniak-Croat federation.
Civil wars and guerrilla wars

- The Rwandan Genocide – between 6 April 1994 until mid-July 1994 a mass killing of hundreds of thousands of Rwanda's Tutsis and Hutu political moderates occurred by the Hutu dominated government under the Hutu Power ideology. Over the course of approximately 100 days, at least 500,000 people were killed.[3] Estimates of the death toll have ranged between 500,000 and 1,000,000,[4] or as much as 20% of the total population of the country. It resulted in serious criticism of the United Nations and major countries for failing to stop the genocide.
- In Algeria a long period of violence in the north African country starts by the cancellation of the first ever held democratic elections by a group of high-ranking army officers.
- The Ethiopian Civil War ends in 1991, ending over twenty years of internal conflict. The end of the war coincides with the establishment of a coalition government of various factions.
- Oka Crisis takes place in 1990 involving an armed standoff between people of the Mohawk nation (North American indigenous peoples in Canada), and the Canadian military over a dispute involving land held via treaty to the Mohawk people.
- A large number of the Zapatista indigenous people of Mexico join the Zapatista Army of National Liberation that begins armed conflict with the Mexican government in 1994 and continues through the 1990s.
- The Taliban seize control of Afghanistan in 1996.
- The 1992 Los Angeles riots occurred, with 53 deaths and 5,500 property fires in a 100-square-mile (260 km2) riot zone. The riots were a result of the state court acquittal of three White and one Hispanic L.A. police officers by an all-white jury in a police brutality case involving motorist Rodney King, but in 1993, all four officers were convicted in a federal civil rights case.
- The Pakistan Army overthrows the democratically elected government of Pakistan on 12 October 1999. Army chief Pervez Musharraf takes control of government as Prime Minister of Pakistan; he would dominate Pakistan's political leadership for nine years.
- The Somali Civil War (1991 – present) and the Battle of Mogadishu.
- Severe political deadlock between Russian President Boris Yeltsin and the Supreme Soviet (Russia's parliament at this time) result in Yeltsin ordering the controversial shelling of the Russian parliament building by tanks in 1993.
Coups
Terrorist attacks

- The 1993 World Trade Center bombing and the Oklahoma City bombing leads to awareness in U.S. of domestic and international terrorism as a potential threat.
- Markale market massacres in Bosnia and Herzegovina in 1994 involving soldiers of the Army of Republika Srpska deliberately targeting Bosniak (then known as "Bosnian Muslims") civilians.
- Srebrenica massacre in Bosnia and Herzegovina in 1995 involving soldiers of the Army of Republika Srpska, members of Serbia's Scorpions paramilitary group, and Greek volunteers in the Srpska army, committing mass murder of Bosniak civilians.
- The Oklahoma City bombing in 1995, the bombing of a federal building in Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, killed 168. Bombing suspect Timothy McVeigh claimed he bombed the building in retaliation for the 1993 Waco massacre.
- After the bombings of U.S. embassies in Kenya and Tanzania by Al-Qaeda militants, U.S. naval military forces launch cruise missile attacks against Al-Qaeda bases in Afghanistan in 1998.
- The Omagh bombing in Omagh, County Tyrone, Northern Ireland which killed 29 civilians and injured hundreds more.
- Ahmed Ressam, an Islamist militant associated with Al-Qaeda is arrested when attempting to cross from Canada to the United States at the Canada-U.S. border on 14 December 1999; it is discovered that he intended to bomb Los Angeles International Airport during millennium celebrations. This is the first major attempted terrorist attack by Al Qaeda on U.S. soil since the 1993 World Trade Center bombing and marked the beginning of a series of attempted terrorist attacks by Al Qaeda against the U.S. that would continue into the 21st century.
- On 18 July 1994 an unknown terrorist targeting Argentina's Jewish community plants a car-bomb in the AMIA Headquarters in Buenos Aires, Argentina killing 85 people and injuring hundreds, making it the first ethnically targeted and deadliest bombing in Argentine history
- on 15 June 1996, the IRA set off a bomb in Manchester, England. The bomb, placed in a van on Corporation Street in the city centre, targeted the city's infrastructure and economy and caused widespread damage, estimated by insurers at £700 million (£1 billion as of 2011). Two hundred and twelve people were injured, but there were no fatalities.
Decolonization and Independence
- United Kingdom hands sovereignty of Hong Kong to the People's Republic of China on 1 July 1997.
- Portugal hands sovereignty of Macau to the People's Republic of China on 20 December 1999.
- Eritrea gains independence from Ethiopia (1993).
- East Timor breaks away from Indonesian control in 1999, merely a year after the fall of Suharto from power, ending a twenty-four year guerrilla war and genocide with more than 200,000 casualties. The UN deploys a peace keeping force, spearheaded by the Australian armed forces. The United States deploys police officers to serve with the International Police element, to help train and equip an East Timorese police force.
- The republics of Croatia, Slovenia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Macedonia declared independence from Yugoslavia.
- Dissolution of Czechoslovakia into Czech Republic and Slovakia (1993).
Prominent political events
- The 1990s was an era of spreading democracy.[5] The former countries of the Warsaw Pact moved from totalitarian regimes to democratically elected governments.[5] The same happened in other non-communist countries, such as Taiwan, Chile, South Africa, and Indonesia. Capitalism made great changes to the economies of communist countries like China and Vietnam.
- The ethnic tensions and violence in the former Yugoslavia during the 1990s create a greater sense of ethnic identity of the nations in the new countries, especially involving increased popularity of nationalism.
Africa

- The release of African National Congress leader Nelson Mandela from jail in February 1990 after thirty years of imprisonment for opposing apartheid and white-minority rule in South Africa. This would resolve with the end of Apartheid in South Africa in 1994, marking the end of the original Civil Rights era of the 20th century.
- Nelson Mandela is elected President of South Africa in 1994, becoming the first black President in South African history ending a long legacy of apartheid white-rule in the country.
North America
- United States President Bill Clinton was a dominant political figure in international affairs during the 1990s known especially for his attempts to negotiate peace in the Middle East and end the ongoing wars occurring in the former Yugoslavia; his promotion of international action to decrease human-created climate change; and his endorsement of advancing free trade in the Americas.
- Lewinsky scandal – US president Bill Clinton was caught in a media-frenzied scandal involving inappropriate relations with a White House intern Monica Lewinsky, first announced on 21 January 1998. After the U.S. House of Representatives impeached Clinton on 19 December 1998 for perjury under oath, following an investigation by federal prosecutor Kenneth Starr, the Senate acquitted Clinton of the charges on 12 February 1999 and he finished his second term.
- Jean-Bertrand Aristide becomes the first democratically elected President of Haiti in 1990.
- Canadian politics is radically altered in the 1993 federal election with the collapse of the Progressive Conservative Party of Canada, (a major political party in Canada since 1867) from being government to only 2 seats and the New Democratic Party collapsing from 44 seats to 9. The Liberal Party of Canada is the only genuine national political party that remains while the regionally based parties such as the Quebec-based Bloc Québécois and the almost entirely Western Canada-based Reform Party of Canada rise from political insignificance to being major political parties.
- After the collapse of the Meech Lake constitutional accord in 1990, the province of Quebec in Canada experienced a rekindled wave of separatism by francophone Québécois nationalists, who sought for Quebec to become an independent country. In 1995, during a referendum on Quebec sovereignty, Quebec voters narrowly reject the vote for independence.
- The 1995 Quebec referendum on sovereignty is held in the predominantly francophone province of Quebec in Canada, a majority anglophone country. If accepted Quebec would become an independent country with an economic association with Canada. The proposal is narrowly rejected by Quebec's voters by 50.4% no, and 49.6% yes.
- California voters passed Proposition 215 in 1996, to legalize cannabis for medicinal purposes. The debate over legalization of marijuana in the U.S. goes on today.
- The enactment of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) on 1 January 1994, creating a North American free trade zone consisting of Canada, Mexico, and the United States.
Asia

- Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin and Palestinian Prime Minister Yasser Arafat agree to the Peace Process at the culmination of the Oslo Accords, negotiated by the United States President Bill Clinton on 13 September 1993. By signing the Oslo accords, the Palestine Liberation Organization recognize Israel's right to exist, while Israel permitted the creation of an autonomous Palestinian National Authority consisting of the Gaza Strip and West Bank which was implemented in 1994. Israeli military forces withdraw from the Palestinian territories in compliance with the accord, which marked the end of the First Intifada (a period of violence between Palestinian Arab militants and Israeli armed forces from 1987 to 1993).
- The Palestinian National Authority is created in 1994 in accordance with the Oslo Accords, giving Palestinian Arab people official autonomy over the Gaza Strip and West Bank, though not official independence from Israel.
- In 1994, a peace treaty is signed between Israel and Jordan.
- In July 1994, North Korean leader Kim Il-sung died, having ruled the country since its founding in 1948. His son Kim Jong-il succeeded him, taking over a nation on the brink of complete economic collapse. Famine caused a great number of deaths in the late '90s, and North Korea would gain a reputation for being a large source of money laundering, counterfeiting, and weapons proliferation. The country's ability to produce and sell nuclear weapons became a focus of concern in the international community.
- Aung San Suu Kyi's National League for Democracy in Burma wins a majority of seats in the first free elections in 30 years in 1990, yet the Burmese military junta refuses to relinquish power, beginning an ongoing peaceful struggle throughout the 1990s to the present by Aung San Suu Kyi and her supporters to demand the end of military rule in Burma.
- North Yemen and South Yemen merge to form Yemen in 1991.
Europe
- The Moscow Coup and subsequent break-up of the Soviet Union on 26 December 1991.
- The improvement in relations between the countries of NATO and the former members of the Warsaw Pact ended the Cold War both in Europe and other parts of the world.
- German reunification – Germany reunified on 3 October 1990 as a result of the fall of the Berlin Wall and after integrating the economic structure and provincial governments, focused on modernization of the former communist East. People who were brought up in a communist culture became integrated with those living in democratic western Germany.
- Margaret Thatcher who had been the United Kingdom's Prime Minister since 1979 resigned as Prime Minister on 22 November 1990 after being challenged for the leadership of the Conservative Party by Michael Heseltine because of widespread opposition to the introduction of the controversial Community Charge and the fact that her key allies such as Nigel Lawson and Geoffrey Howe resigned over the deeply sensitive issues of the Maastricht Treaty and Margaret Thatcher's resistance to Britain joining the European Exchange Rate Mechanism. Less than two years later on the infamous Black Wednesday of September 1992, the pound sterling crashed out of the system after the pound fell below the agreed exchange rate with the Deutsche Mark.
- The Belfast Agreement (a.k.a. the Good Friday Agreement) is signed by U.K. and Irish politicians on 10 April 1998, declaring a joint commitment to a peaceful resolution of the territorial dispute between the Republic of Ireland and the United Kingdom over Northern Ireland.
- The IRA agreed to a truce in 1994. This marked the beginning of the end of 25 years of violence between the IRA and the United Kingdom, and the start of political negotiations.
- The European Union forms in 1992 under the Maastricht Treaty.
South America
- Due to the Internal conflict in Peru and the economic crisis, Alberto Fujimori rises to power in Peru and remains in office for eleven years. His administration is marked by economic development but also by numerous human rights violations (La Cantuta massacre, Barrios Altos massacre), and a rampant corruption network set up by Vladimiro Montesinos.
Assassinations

The 1990s were marked by several notable assassinations and assassination attempts:
- 19 September 1990 – The Provisional Irish Republican Army tries to assassinate Air Chief Marshal Sir Peter Terry at his home near Stafford, England. Hit by at least 9 bullets, the former Governor of Gibraltar survives.
- 21 May 1991 – In Sriperumbudur, India, former Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi is assassinated.
- 7 August 1991 – Shapour Bakhtiar, former prime minister of Iran, is assassinated.
- 23 May 1992 – Able to a violent explosion on Autostrada A29 (Italy) section between the' Punta Raisi Airport and Palermo, caused by the Mafia, causing the death of Judge Giovanni Falcone, a hero in the fight against organized crime. Less than two months later, on 19 July, Falcone's co-worker and friend, magistrate Paolo Borsellino was killed by a car bomb in via D'Amelio, Palermo, in front of his mother's house. They were both named as heroes of the last 60 years in the November 2006 issue of Time Magazine.
- 29 June 1992 – A bodyguard assassinates President Mohamed Boudiaf of Algeria.
- April 1993 – The Kuwaiti government claims to uncover an Iraqi assassination plot against former U.S. President George H. W. Bush shortly after his visit to Kuwait. Two Iraqi nationals confess to driving a car-bomb into Kuwait on behalf of the Iraqi Intelligence Service.[6]
- 1 May 1993 – A Tamil Tigers suicide bomber assassinates President Ranasinghe Premadasa of Sri Lanka.
- 29 August 1995 – Eduard Shevardnadze, the Georgian head of state, survives an assassination attempt in Tbilisi.
- 4 November 1995 – Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin is assassinated at a peace rally in Tel Aviv by a radical Jewish militant who opposed the Oslo Accords.
- 31 March 1995 - Tejano pop singer Selena is shot by fan club president Yolanda Saldívar over financial problems and missing records. 2 weeks after death, her birthday is named Selena Day in Texas.
- 2 October 1996 – The former prime minister of Bulgaria, Andrei Lukanov, is assassinated.
- 15 July 1997 Gianni Versace was shot dead, aged 50, on the steps of his Miami Beach mansion as he returned from a morning walk on Ocean Drive. He was murdered by Andrew Cunanan, who used the same gun to commit suicide on a boat several days later. Police have said they do not know why Versace was killed. [dubious – discuss]
- 9 February 1998 – Eduard Shevardnadze, the Georgian head of state, survives an assassination attempt in Tbilisi.
- 16 February 1999 – In Uzbekistan, an apparent assassination attempt against President Islam Karimov takes place at government headquarters.
- 23 March 1999 – Gunmen assassinate Paraguay's Vice President Luis María Argaña.
- 9 April 1999 – Ibrahim Baré Maïnassara, president of Niger, is assassinated.
Disasters
Natural disasters

- The most prominent natural disasters of the decade include: Hurricane Andrew striking South Florida in August 1992, the crippling super storm of March 1993 along the Eastern Seaboard, the devastating 1994 Northridge earthquake in Los Angeles, the Great Hanshin earthquake in Kobe, Japan in January 1995, the Blizzard of 1996 in the eastern U.S., the US drought of 1999, the deadly Hurricane Mitch which struck Central America in October 1998, and the destructive Oklahoma tornado outbreak in May 1999, the August 1999 İzmit earthquake in Turkey, and the September 1999 Chi-Chi earthquake in Taiwan.
- A magnitude 7.8 earthquake hit the Philippines on 16 July 1990 and killed around 1000 people in Baguio City.
- July 1995 – Midwestern United States heat wave – An unprecedented heat wave strikes the Midwestern United States for most of the month. Temperatures peak at 106 °F (41 °C), and remain above 94 °F (34 °C) in the afternoon for 5 straight days. At least 739 people die in Chicago alone.
- Hurricane Georges made landfall in at least seven different countries (Antigua and Barbuda, St. Kitts and Nevis, Haiti, the Dominican Republic, Cuba and the United States) and Puerto Rico, a Commonwealth of the United States – more than any other hurricane since Hurricane Inez of the 1966 season. The total estimated costs were in the $60 billion (present day $100 billion)
Non-natural disasters

- Gulf War oil spill – Resulting from actions taken during the Gulf War in 1991 by the Iraq military, the oil spill caused considerable damage to wildlife in the Persian Gulf especially in areas surrounding Kuwait and Iraq.
- On 11 July 1991, a Nationair Douglas DC-8, chartered by Nigeria Airways, caught fire and crashed in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, killing 261.
- On 15 December 1991, The Egyptian ferry Salem Express sinks in the Red Sea, killing more than 450.
- On 4 October 1992 – El Al Flight 1862, a Boeing 747 cargo airplane heading to Tel Aviv, suffered physical engine separation of both right-wing engines (#3 and #4) just after taking off from Schiphol and crashed into an apartment building in the Bijlmer neighbourhood of Amsterdam while attempting to return to the airport. A total of 43 people were killed, including the plane's crew of three and a "non revenue passenger". Several others were injured.
- On 26 July 1993, Asiana Airlines Flight 733 crashed into Mt. Ungeo in Haenam, South Korea killing 68.
- On 26 April 1994, China Airlines Flight 140, an Airbus A300, crashed just as it was about to land at Nagoya Airfield, Japan, killing 264 and leaving only 7 survivors.
- On 8 September 1994, USAir Flight 427 crashed near Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, killing 132.
- On 28 September 1994 – The car ferry MS Estonia sinks in the Baltic Sea, killing 852.
- On 29 June 1995, the Sampoong Department Store collapses in Seoul, South Korea, killing 502.
- On 20 December 1995, American Airlines Flight 965, a Boeing 757, hit a mountain in Colombia at night, killing 159.
- On 17 July 1996 Trans World Airlines Flight 800, a Boeing 747–131, exploded and crashed into the Atlantic Ocean near East Moriches, New York, killing 230.
- On 12 November 1996 a Saudia Boeing 747 and a Kazakhstan Airlines Ilyushin Il-76 collided over the town of Charkhi Dadri, outside New Dehli, India, killing 349.
- On 6 August 1997, Korean Air Flight 801, a Boeing 747-300, crashed into a hill on the island of Guam, killing 228.
- On 26 September 1997, Garuda Indonesia Flight 152 crashed in bad weather, killing 234.
- On 2 September 1998, Swissair Flight 111, a McDonnell Douglas MD-11, crashed into the Atlantic Ocean off Nova Scotia near the towns of Peggys Cove and Bayswater, killing 229.
- On 31 October 1999, EgyptAir Flight 990, a Boeing 767, crashed off the coast of Nantucket, Massachusetts, killing 217.
Economics
- Many countries, institutions, companies, and organizations were prosperous during the 1990s. High-income countries such as the United States, Japan, Singapore, Hong Kong, Taiwan, South Korea, and those in Western Europe experienced steady economic growth for much of the decade. However, in the former Soviet Union GDP decreased as their economies restructured to produce goods they needed and some capital flight occurred.
- GATT update and creation of the World Trade Organization and other global economic institutions, but opposition by anti-globalization activists showed up in nearly every GATT summit, like the demonstrations in Seattle in December 1999.
- The anti-globalization protests at the World Trade Organization Ministerial Conference of 1999 in Seattle, Washington began on 30 November 1999. This marks the beginning of a steady increase in anti-globalization protests which occurred in the first decade of the 21st century as well as increasing hostility to neoliberalism.
North America

- The decade is seen as a time of great prosperity in the United States under the Presidency of Bill Clinton. The U.S economy experiences its longest period of peace time economic expansion during the decade beginning in 1991. Personal incomes doubled from the recession in 1990, and there was higher productivity overall. After the 1996 Welfare Reform Act there was a reduction of poverty,[7] and the Wall Street stock exchange stayed over the 10,500 mark from 1999 to 2001.
- After the 1992 booming of the US stock market, Alan Greenspan coined the phrase "irrational exuberance".
- The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), which phases out trade barriers between the United States, Mexico, and Canada is signed into law by U.S. President Bill Clinton.
Asia
- The government of the People's Republic of China announces major privatization of state-owned industries in September 1997.
- China started the '90s in a bad way, shunned by much of the world after the Tiananmen Square Massacre and controlled by hard line politicians who reigned in private enterprise and attempted to revive old-fashioned propaganda campaigns. Relations with the United States deteriorated sharply, and the Chinese leadership was further embarrassed by the disintegration of communism in Europe. In 1992, Deng Xiaoping travelled to southern China in his last major public appearance to revitalize faith in market economics and stop the country's slide back into Maoism. Afterwards, China recovered, and would experience explosive economic growth during the rest of the decade. In spite of this, dissent continued to be suppressed, and President Jiang Zemin launched a brutal crackdown against the Falun Gong religious sect in 1999. Deng Xiaoping himself died in 1997 at the age of 93. Relations with the US deteriorated again in 1999 after the bombing of the Chinese embassy during the bombing of Serbia by NATO forces, which caused three deaths, and allegations of Chinese espionage at the Los Alamos Nuclear Facility.
- South-East Asia economic crisis starting from 1997.
- Financial crisis hits East and Southeast Asia in 1997 and 1998 after a long period of phenomenal economic development, which continues by 1999. This crisis begins to be felt by the end of the decade.
- In Japan, after three decades of economic growth put them in second place in the world's economies, the situation worsened after 1993. The recession went on into the early first decade of the 21st century, bringing an end to the seemingly unlimited prosperity that the country had hitherto enjoyed.
- The Philippines saw great economic development after the People Power Revolution. The economy gains 5% from its deficit until the 1997 Asian Financial Crisis.
- Less affluent nations such as India, Malaysia, and Vietnam also saw tremendous improvements in economic prosperity and quality of life during the 1990s. Restructuring following the end of the Cold War was beginning. However, there was also the continuation of terrorism in Third World regions that were once the "frontlines" for American and Soviet foreign politics, particularly in Asia.

Europe
- By 1990, Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev's reforms were causing major inflation and economic chaos. A coup attempt by hard-liners in August 1991 failed, marking the effective end of the Soviet Union. All its constituent republics declared their independence in 1991, and on Christmas, Gorbachev resigned from office. After 73 years, the Soviet Union had ceased to exist. The new Russian Federation was headed by Boris Yeltsin, and would face severe economic difficulty. Oligarchs took over Russia's energy and industrial sectors, reducing almost half the country to poverty. With a 3% approval rating, Yeltsin had to buy the support of the oligarchs to win reelection in 1996. Economic turmoil and devaluation of the ruble continued, and with heart and alcohol troubles, he stepped down from office on the last day of 1999, handing power to Vladimir Putin.
- Russian financial crisis in the 1990s results in mass hyperinflation and prompts economic intervention from the International Monetary Fund and western countries to help Russia's economy recover.
- The first McDonald's restaurant opens in Moscow in 1990 with then-President of the Supreme Soviet of the Russian SFSR and future Russian President Boris Yeltsin attending, symbolizing Russia's transition towards a capitalist free market economy and a move towards adopting elements of western culture.
- Oil and gas were discovered in many countries in the former Soviet bloc, leading to economic growth and wider adoption of trade between nations. These trends were also fueled by inexpensive fossil energy, with low petroleum prices caused by a glut of oil. Political stability and decreased militarization due to the winding down of the Cold War led to economic development and higher standards of living for many citizens.
- Most of Europe enjoyed growing prosperity during the 90s however problems including the massive 1995 general strikes in France following a recession and the difficulties associated with German reunification lead to sluggish growth in these countries. However, both the French and German economies improve in the latter half of the decade. Meanwhile the economies of particularly Spain, Scandinavia and former Eastern Bloc countries accelerate at rapid speed during the deacde.
- After the early 1990s recession, the United Kingdom and Ireland experience rapid economic growth and falling unemployment that continues throughout the decade. Economic growth would continue until the Late 2000s recession marking the longest uninterrupted period of economic growth in history.
- Some Eastern European economies struggled after the fall of communism, but Poland, Hungary, Czech Republic, Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania saw healthy economic growth rates in the late 1990s.
- With the creation of the EU there is freedom of movement between member states, such as the 1992 and 1995 free trade agreements.
- The Euro is adopted by the European Union on 1 January 1999, which begins a process of phasing out national currencies of EU countries.
South America
- The sluggish economies of Brazil, by a new emphasis on free markets for all their citizens, and Mexico, under economist president Ernesto Zedillo elected in 1994, were in their best shape by the late 1990s.
Technology and science
Technology
The 1990s were an incredibly revolutionary decade for digital technology. Cell phones of the early 1990s and earlier were very large, lacked extra features, and were used by only a few percent of the population of even the wealthiest nations. Only a few million people used online services in 1990, and the World Wide Web had only just been invented. By 2001, more than 50% of some Western countries had Internet access, and more than 25% had cell phone access.
Electronics and communications


- On 6 August 1991, CERN, a pan European organization for particle research, publicized the new World Wide Web project.[8] Although the basic applications and guidelines that make the Internet possible had existed for almost two decades, the network did not gain a public face until the 1990s.
- Y2K spread fear throughout the United States and eventually the world in the last half of the decade particularly 1999 about possible massive computer malfunctions on 1 January 2000. As a result, many people stocked up on supplies for fear of a world wide disaster. Eventually no globally significant computer failures occurred when the clocks rolled over into 2000.
- Advancements in computer modems, ISDN, cable modems, and DSL lead to faster connection to the Internet.
- The Pentium processor is developed by Intel.
- E-mail becomes popular; as a result Microsoft acquires the popular Hotmail webmail service.
- Instant messaging and the Buddy list becomes popular. AIM and ICQ are two early protocols.
- Businesses start to build E-commerce websites; E-commerce-only companies such as Amazon.com, eBay, AOL, and Yahoo! grow rapidly.
- The introduction of affordable, smaller satellite dishes and the DVB-S standard in the mid-1990s expanded satellite television services that carried up to 500 television channels.
- The first MP3 Player, the MPMan, is released in late spring of 1998. It came with 32Mb of flash memory expandable to 64Mb. By the mid-2000s, the Mp3 player would overtake the CD player in popularity.
- The first GSM network is launched in Finland in 1991.
- Digital SLRs and regular digital cameras become commercially available. They would replace film cameras by the mid-2000s.
- IBM introduces the 1-inch (25 mm) wide Microdrive hard drive in 170 MB and 340 MB capacities.
- Apple introduces the iMac computer, initiating a trend in computer design towards translucent plastics and multicolor case design, discontinuing many legacy technologies like serial ports, and beginning a resurgence in the company's fortunes that continues unabated to this day.
- CD burner drives are introduced.
- The CD-ROM drive became standard for most personal computers during the decade.
- The DVD media format is developed and popularized along with a plethora of Flash memory card standards.
- Pagers are initially popular but ultimately are replaced by mobile phones by the early 2000s.
- Hand-held satellite phones are introduced towards the end of the decade.
- The 24 hour news cycle becomes popular with the Gulf War in late 1990 – early 1991 and CNN's coverage of Desert Storm and Desert Shield. Though CNN had been running 24-hour newscasts since 1980, it was not until the Gulf War that the general public took large notice and others imitated CNN's non-stop news approach.[9]
- Portable CD players, introduced during the late 1980s, became very popular and had a profound impact on the Music industry and youth culture during the 1990s.
-
An early Portable CD player, a Sony Discman model D121
-
Mobile phones gained massive popularity worldwide during the decade.
-
Pagers became widely popular
Software
- Microsoft Windows operating systems become virtually ubiquitous on IBM Personal Computers.
- Microsoft introduces Windows NT 3.1, Windows 95 and later Windows 98 to the market, which gain immediate popularity.
- Mac OS X was released in 1999, with the consumer version to be released in 2001. For much of the decade, System 7, Mac OS 8, and Mac OS 9 would be in consumer Macintoshes and its clones.
- The development of Web browsers such as Netscape Navigator and Internet Explorer makes surfing the World Wide Web easier and more user friendly.
- The Java programming language is developed by Sun Microsystems.
- In 1991, development of the free Linux kernel is started by Linus Torvalds in Finland.
Automobiles

The 1990s began with another recession that dampened car sales. General Motors continued to suffer huge losses thanks to an inefficient structure, stale designs, and poor quality. Sales improved with the economy by the mid-'90s, but GM's US market share gradually declined to less than 40% (from a peak of 50% in the '70s). While the new Saturn division fared well, Oldsmobile declined sharply, and attempts to remake the division as a European-style luxury car were unsuccessful.
Cars in the 1990s had a rounder, more streamlined shape than those of the 1970s and 1980s; this style would continue early into the 2000s and to a lesser extent later on.
Chrysler ran into financial troubles again as the '90s started. Like GM, it too had a stale model lineup (except for the best-selling minivans) that was largely based on the aging K-car platform. In 1992, chairman Lee Iacocca retired, and the company began a remarkable revival, introducing the new LH platform and "Cab-Forward" styling, along with a highly successful redesign of the full-sized Dodge Ram in 1994. Chrysler's minivans continued to dominate the market despite increasing competition. In 1998, Daimler-Benz (the parent company of Mercedes-Benz) merged with Chrysler. The following year, it was decided to retire Plymouth, which had been on a long decline since the '70s. Ford continued to fare well in the '90s, with the second and third generations of the Ford Taurus being named the best selling car in the United States from 1992 to 1996. However, the Taurus would be outsold and dethroned by the Toyota Camry starting in 1997, which became the best selling car in the United States for the rest of the decade and into the 2000s.
Japanese cars continued to be highly successful during the decade. The Honda Accord vied with the Taurus most years for being the best-selling car in the United States during the early part of the decade. Although launched in 1989, the luxury brands Lexus and Infiniti began car sales of 1990 model year vehicles and saw great success. Lexus would go on to outsell Mercedes-Benz and BMW in the United States by 1991, and would outsell Cadillac and Lincoln by the end of the decade. SUVs and trucks became hugely popular during the economic boom in the second half of the decade. Many makes that had never built a truck before started selling SUVs. Car styling during the 1990s became gradually more round and ovoid, the third-generation Taurus and Mercury Sable being some of the more extreme examples. Safety features such as airbags and shoulder belts became mandatory equipment on new cars.
Science


- Physicists develop M-theory.
- Detection of extrasolar planets orbiting stars other than the sun.
- In the United Kingdom, the first cloned mammal, Dolly the sheep was confirmed by the Roslin Institute, and was reported by global media on 26 February 1997. Dolly would trigger a raging controversy on cloning and bioethical concerns regarding possible human cloning continue to this day.
- Human Genome Project begins.
- DNA identification of individuals finds wide application in criminal law.
- Hubble Space Telescope launched in 1990; revolutionizes astronomy. Unfortunately, a flaw in its main mirror caused it to produce fuzzy, distorted images. This was corrected by a shuttle repair mission in 1993.
- Protease inhibitors introduced allowing HAART therapy against HIV; drastically reduces AIDS mortality.
- NASA's spacecraft Pathfinder lands on Mars and deploys a small roving vehicle, Sojourner, which analyzes the planet's geology and atmosphere.
- The Hale-Bopp comet swings past the sun for the first time in 4,200 years in April 1997.
- Development of biodegradable products, replacing products made from styrofoam; advances in methods for recycling of waste products (such as paper, glass, and aluminum).
- Genetically engineered crops are developed for commercial use.
- Discovery of dark matter, dark energy, brown dwarfs, and first confirmation of black holes.
- The Galileo probe orbits Jupiter, studying the planet and its moons extensively.
- Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 (formally designated D/1993 F2, nicknamed String of Pearls for its appearance) was a comet that broke apart and collided with Jupiter in July 1994, providing the first direct observation of an extraterrestrial collision of solar system objects..
- The Global Positioning System (GPS) becomes fully operational.
- Proof of Fermat's Last Theorem is discovered by Andrew Wiles.
- Construction started in 1998 on the International Space Station.
Environment
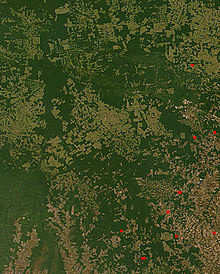
At the beginning of the decade, sustainable development and environmental protection became serious issues for governments and the international community. In 1987, the publication of the Brundtland Report by the United Nations had paved the way to establish a environmental governance. In 1992 was held the Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro, in which several countries committed to protect the environment, signing a Convention on Biological Diversity.
The prevention of the destruction of the tropical rainforests of the world is a major environmental cause that first came into wide public concern in the early 1990s, and has continued and accelerated.
The Chernobyl disaster had significant impact on public opinion at the end of the 1980s, and the fallout was still causing cancer deaths well into the 1990s and possibly even into the 21st century[citation needed]. All along the 1990s, several environmental NGOs helped improve environmental awareness among public opinion and governments. The most famous of these organizations during this decade was Greenpeace, which did not hesitate to lead illegal actions in the name of environmental preservation. These organizations also drawn attention on the large deforestion of the Amazon Rainforest during the period.
Global warming as an aspect of climate change also became a major concern, and the creation of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) after the Earth Summit helped coordinate efforts to reduce carbon emissions in the atmosphere. From 1995, the UNFCCC held annual summits on climate change, leading to the adoption of the Kyoto Protocol in December 1997, a binding agreement signed by several developed countries.
Society
The 1990s represented continuing social liberalization in most countries, though coupled with an increase in the influence of capitalism, which would continue until the Great Recession of the late 2000s/early 2010s.
Youth culture in the 1990s responded to this by embracing both environmentalism and entrepreneurship. Western world fashions reflected this by often turning highly individualistic and/or counter-cultural, which was influenced by Generation X and Generation Y: tattoos and body piercing gained popularity, and "retro" styles inspired by fashions of the 1960s and 1970s were also prevalent. Some young people became increasingly involved in extreme sports and outdoor activities that combined embracing athletics with the appreciation of nature. The slacker and Valley Girl cultures were prevalent, and the decade was heavily influenced by Californian culture.
In 1990, the World Health Organization removed homosexuality from its list of diseases. Increasing acceptance of homosexuality occurred in the western world throughout the 1990s and first decade of the 21st century.
Third-wave feminism

- Anita Hill and other women testify before the United States Congress on being sexually harassed by Supreme Court nominee Clarence Thomas. Thomas was narrowly confirmed by the United States Senate, but Hill's testimony, and the testimony of other harassed women, begins a national debate on the issue.
- Record numbers of women are elected to high office in the U.S. in 1992, the "Year of the Woman".
- Violence against women takes center stage as an important issue internationally. In the U.S. the Violence Against Women Act was passed, which greatly affected the world community through the United Nations. The law's author, Joe Biden, and UN Ambassador and Secretary of State Madeleine Albright, and Hillary Clinton (see below) become vocal advocates of action against violence against women.
- Women reach great heights of power in the U.S. government. Hillary Rodham Clinton, leading policy proposals, traveling abroad as a State Department representative to 82 nations, advising her husband, and being elected a Senator (in 2000), is the most openly empowered and politically powerful First Lady in American history; Madeleine Albright and Janet Reno take two of the cabinet's top jobs as United States Secretary of State (#1), and United States Attorney General (#4), respectively. Sheila Widnall becomes head and Secretary of the Air Force and Ruth Bader Ginsburg joins Sandra Day O'Connor as the second woman on the U.S. Supreme Court.
- Record numbers of women become top CEOs worldwide.
- More nations than ever before are led by elected women Presidents and Prime Ministers. Prime Minister Benazir Bhutto's 1988 victory in Pakistan makes women leaders in Muslim states unextraordinary. In Turkey, Tansu Çiller became the first female prime minister in 1993 (till 1996).
- Pop-group, the Spice Girls also played a part in the feminist movement, reining in popularity with the phrase "Girl Power!"
Additional significant world-wide events
- Worldwide New Year's Eve celebrations on 31 December 1999 welcoming the year 2000.
Europe
- 1991 – Soviet Union military troops attack Lithuanian independence supporters in Vilnius. Killed 14 people and wounding 1000.
- In Paris, Diana, Princess of Wales and her friend, Dodi Al-Fayed, were killed in a car accident in August 1997, when their chauffeured, hired Mercedes-Benz S-Class crashed in the Pont de l'Alma tunnel. The chauffeur, Henri Paul died at the scene, as did Al-Fayed. Diana and an Al-Fayed bodyguard, Trevor Rees-Jones, survived the accident. The former Princess of Wales died at a Paris hospital hours later. The bodyguard, Rees-Jones, is the sole survivor of the now infamous accident.
- Mother Teresa, the Roman Catholic nun who won the Nobel Peace Prize, dies at age 87.
- The birth of the "Second Republic" in Italy, with the Mani Pulite investigations of 1994.
- The Channel Tunnel across the English Channel opens in 1994, connecting France and England. As of 2007 it is the second-longest rail tunnel in the world, but with the undersea section of 37.9 km (23.5 mi) being the longest undersea tunnel in the world.
- The resignation of President Boris Yeltsin on 31 December 1999 resulting in Prime Minister Vladimir Putin's succession to the position.
North America
- The Columbine High School massacre occurred on 20 April 1999, in Columbine, Colorado when Eric Harris and Dylan Klebold killed 12 students and a teacher before committing suicide, making it the deadliest high school shooting in United States history.
- O. J. Simpson murder case – O. J. Simpson's trial, described in the U.S. media as the "trial of the century" and enormous U.S. media attention is focused on the trial. On 3 October 1995, Simpson was found "not guilty" of double-murder of ex-wife Nicole Brown Simpson and her friend, Ronald Goldman.
- With help from clinical fertility drugs, an Iowa mother, Bobbie McCaughey, gave birth to the first surviving septuplets in 1997. There followed a media frenzy and widespread support for the family.
- John F. Kennedy, Jr., his wife Carolyn Bessette and sister-in-law Lauren Bessette are killed when Kennedy's private plane crashes off the coast of Martha's Vineyard in July 1999.
- Debate on assisted suicide highly publicized by Michigan doctor Jack Kevorkian, charged with multiple counts of homicide of his terminally ill patients through the decade.
- Beer keg registration becomes popular public policy in U.S.
- The 500th anniversary of Christopher Columbus' discovery of the Americas in 1992 was popularly observed, despite controversy and protests against the victimization of Native Americans by Columbus' expeditions. The holiday was labeled by some as racist, in view of Native American experiences of colonialism, slavery, genocide, and cultural destruction.
- Matthew Shepard is murdered near the University of Wyoming for being gay. This sparks intense national and international media attention and outrage. He becomes a major symbol in the LGBT rights movement and the fight against homophobia.
- Shanda Sharer (6 June 1979 – 11 January 1992) Was a murder victim. She was lured away from her house and held captive by a group of teenage girls. She was tortured for hours and burned alive. She died from smoke inhalation. Those that were found guilty and sentenced to prison were Melinda Loveless, Laurie Tackett, Hope Rippey, and Toni Lawrence. According to Melinda, she was jealous of the relationship that her former partner Amanda Heavrin had with Shanda Sharer. This senseless murder shocked the nation.
- Polly Klaas (January 3, 1981 - October 1993) was kidnapped by Richard Allen Davis from her home during a sleepover party. She was later strangled to death. After her death, her father, Marc Klaas, established the KlaasKids Foundation.
- Jonbenet Ramsey (6 August 1990 – 25 December 1996) was a child beauty pageant contestant who was missing and found dead in her Boulder, Colorado home. The crime horrified the nation and the world. Her parents were initially considered to be suspects in her death but were cleared in 2003 when DNA from her clothes were tested. To this day, her murderer has not been found and brought to justice.
Canada
- Karla Homolka is a killer and sexual deviant. She was arrested with her husband, Paul Bernardo in 1993. Both sexually tortured and killed their victims. Their first victim was Karla's fifteen-year-old sister Tammy Homolka. The second and third victims were Leslie Mahaffy and Kristen French. Karla told the investigators that she unwillingly did what Paul told her to do because he was abusive and was given a deal. She was sentenced to only 12 years in prison (10 years for Mahaffy and French but only 2 years for Tammy). Later, investigators discovered videotapes of the crimes which proved that Karla was a willing participant. But by that time the deal had already been made. However, in 1995, Paul was sentenced to life in prison. Karla was released from prison in 2005 and remains as one of the most hated people to have lived in Canada.
Asia
- Massive immigration wave of Jews from the Commonwealth of Independent States to Israel – With the end of the Soviet Union, Israel faced a mass influx of Russian Jews, many of whom had high expectations the country was unable to meet. Israel also came under Iraqi missile attack during the Gulf War, but acquiesced to US pressure not to militarily retaliate, which could have disrupted the US-Arab alliance. The US and Netherlands then rushed anti-missile batteries to Israel to defend the country against missile attacks.
- The Spratly Islands issue became one of the most controversial in Southeast Asia.
Popular culture
Film
The 1990s were an eventful time for film.
Dogme 95 becomes an important European artistic motion picture movement by the end of the decade. The first full-length CGI movie Pixar's Toy Story is released, revolutionizing animated films. Titanic becomes a cultural phenomenon throughout the world, and eventually becomes the highest grossing film of all time, grossing over $1.8 billion worldwide. It would hold this record for over a decade until 2010 when director James Cameron had another one of his films take the title, that being Avatar.[10]
The films produced by the Walt Disney Animation Studios became popular once more when the studio returned to making traditionally animated musical family classics such as Beauty and the Beast, Aladdin, and The Lion King. This era was known as the Disney Renaissance.
|
|
Television

TV shows, mostly sitcoms, were popular with the American audience. Series such as Roseanne and Seinfeld, both which premiered in the late eighties, and Frasier, a spin-off of the 1980s hit Cheers were viewed throughout the 1990s. These sitcoms, along with Friends, The Fresh Prince of Bel-Air, Full House, Family Matters, That '70s Show, Married... with Children, Everybody Loves Raymond, and Martin, turned TV in new directions and defined the humor of the decade.
Medical dramas started to come into television in the ‘90s. One show stood out as a critical and ratings success for NBC. In 1994, ER, which starred Anthony Edwards and George Clooney, was a domestic and international success, lasting until 2009 and spawning series such as Grey's Anatomy (2005–present). It made NBC the most watched channel in the USA[citation needed]. This show launched the career of George Clooney.
Beverly Hills, 90210 ran on Fox from 1990 to 2000. It established the teen soap genre paving the way for Dawson's Creek, Felicity, and other shows airing in later years. The show was then remade and renamed simply 90210 and premiered in 2008. Melrose Place, a popular TV show that dominated throughout the ‘90s as well. Baywatch, a popular TV show that dominated throughout the ‘90s, became the most watched TV show in history and influenced pop culture.
Reality television began on MTV; this would grow in importance in the western world into the next decade.
During the mid-1990s, two of the biggest professional wrestling companies: World Championship Wrestling and World Wrestling Federation were on a Monday Night Wars (1995–2001) with each other. Trying to get more views than the other. It ended in 2001 when WWE bought WCW. At November 2001, there was a Winner Takes All match with both companies in a Pay-Per-View called Survivor Series. WWF won the match; therefore, WCW currently works with WWE.
As an animated sitcom, The Simpsons, debuted in December 1989, became a domestic and international success in the 1990s. The show has made it beyond 2010 and has become an institution of pop culture. It has spawned the adult-oriented animated sitcom genre, inspiring racier shows such as Beavis and Butt-head (1993–1997) along with South Park and Family Guy, the latter two of which began in 1997 and 1999 respectively and continue to air new episodes through the 2000s and into the 2010s.
Anime was popular in the 1980s, and expanded to a worldwide audience by the 1990s, for its expansive spectrum of story subjects and themes not limited to comedy and superhero action found in the US, and visual and story content that also expanded to older and adult ages. TV shows such as Dragon Ball Z, Sailor Moon, Digimon, Pokémon, Neon Genesis Evangelion, the anime movie Akira, and imports by various distributors such as Viz, AnimEigo, Central Park Media, A.D. Vision, Pioneer Entertainment, Manga Entertainment, and Celebrity, helped begin the mid to late 1990s and early to mid-2000s anime craze in the US, and the Cartoon Network anime block Toonami in 1997.
Nickelodeon's first animated series (Doug, Rugrats, The Ren & Stimpy Show) debuted in 1991. One of Nickelodeon's most popular and longest running series, SpongeBob SquarePants, started in 1999 and became a huge success.
American animated children’s programs went through a renaissance during the decade with studios producing many critically acclaimed shows. Examples include Tiny Toon Adventures, Animaniacs, Batman: The Animated Series, and Superman: The Animated Series.
Music



The 1990s were a decade of fragmentation in the music market, not only because of changing tastes but as marketing became more segmented, MTV gradually shifted away from music videos, beginning in 1992, and radio playlists became tighter following alternative rock's break into the mainstream.[12][13] However, they are perhaps best known for grunge, gangsta rap, R&B, teen pop; eurodance, electronic dance music, the renewed popularity of punk rock mainly because of the band Green Day (which would also help create a new genre pop punk) and for being the decade that alternative rock became mainstream. U2 was one of the most popular 1990s bands, their groundbreaking Zoo TV and PopMart tours were the top selling tours of 1992 and 1997. Glam metal dies out through its own accord in the music mainstream by 1991.[14] Grunge music becomes popular in 1991 because of the success of Nirvana's Nevermind, Pearl Jam's Ten and Soundgarden's Badmotorfinger.[15] Punk pop also becomes popular with such artists as Green Day, Blink-182, Weezer, The Offspring, Bad Religion, NOFX and Rancid.[16] Other successful alternative acts included Red Hot Chili Peppers, Gin Blossoms, Soul Asylum, Third Eye Blind, Stone Temple Pilots, Faith No More, The Smashing Pumpkins, Live, Everclear, Bush, Alice in Chains and Screaming Trees.[17]
Dr. Dre's 1992 album The Chronic provided a template for modern gangsta rap.[18] Due to the success of Death Row Records, West Coast gangsta rap commercially dominated hip hop during the early 1990s, along with The Notorious B.I.G. on the East Coast.[19] Hip hop became the best selling music genre by the mid-1990s.[20][21]
In the United Kingdom, the uniquely British alternative rock Britpop genre emerged as part of the more general Cool Britannia culture, with Oasis, Blur, The Verve, Supergrass, Pulp, Radiohead, Manic Street Preachers, Suede, Elastica, Ride and Shed Seven. Female pop icons "Spice Girls" took the world by storm, becoming the most commercially successful British group since The Beatles.[22][23] Their impact brings about a widespread scene of teen pop acts around the world[24][25] such as Backstreet Boys, Hanson, N Sync, Britney Spears and Christina Aguilera who come to prominence into the new millennium.[26] 1991 also saw the death of Queen frontman Freddie Mercury from AIDS-related pneumonia.
Contemporary R&B and quiet storm continue in popularity among adult audiences, which began during the 1980s. Popular American contemporary R&B artists included Michael Bolton, Kenny G, Celine Dion, Mariah Carey, D’Angelo, Lauryn Hill, Whitney Houston, Sade, En Vogue, TLC,Destiny's Child, Toni Braxton, Boyz II Men, Dru Hill, Gloria Estefan, Vanessa L. Williams and LeAnn Rimes.
The Tibetan Freedom Concert brings 120,000 people together in the interest of increased human rights and autonomy for Tibet from China. Freddie Mercury, Kurt Cobain, Selena, Tupac Shakur, and The Notorious B.I.G. are the most publicized music-related deaths of the decade, in 1991, 1994, 1995, 1996, and 1997 respectively. Richey Edwards of the Manic Street Preachers, one of Britain's leading rock bands, was publicized in the media in 1991 following an incident involving Steve Lamacq backstage after a live show, in which Edwards carved '4 Real' into his arm; this has become one of rock 'n' rolls most infamous moments in history. Edwards disappeared in 1995, which was highly publicized. He is still missing.
Controversy surrounded The Prodigy with the release of the track ‘Smack My Bitch Up’. The National Organization for Women (NOW) claimed that the track was "advocating violence against women" due to the lyrics of that song. The music video (directed by Jonas Åkerlund) featured a first-person POV of someone going clubbing, indulging in drugs and alcohol, getting into fist fights, abusing women and picking up a prostitute. At the end of the video the camera pans over to a mirror, revealing the subject to be a woman.
1994 became a breakthrough year for punk rock in California, with the success of bands like Bad Religion, Blink-182, Green Day, The Offspring, Rancid, and similar groups following. This success would continue to grow in over the next two decades, 2000s and 2010s. The 1990s also became the most important decade for ska punk/reggae rock, with the success of many bands like Buck-O-Nine, Goldfinger, Less Than Jake, The Mighty Mighty Bosstones, Murphy’s Law, No Doubt, Reel Big Fish, Save Ferris, Sublime and Sugar Ray.
The rave movement that emerged in the late 1980s rises incredibly in the early to mid-1990s and continues to exist. Rave spawns genres such as Intelligent dance music and Drum and bass. The latter is an offshoot of jungle techno and breakbeat. Popular artists include Moby, Aphex Twin, The Orb, Chemical Brothers, Todd Terry, 808 State, Primal Scream, The Shamen, The KLF and The Prodigy.
Then there was the emergence of San Francisco's Psychedelic musical group called, The Brian Jonestown Massacre in 1990
The rise of industrial music, somewhat a fusion of synthpop and heavy metal, rises to worldwide popularity with bands like Godflesh, Nine Inch Nails, Rammstein, Ministry and Marilyn Manson. Groove metal was born through the efforts of Pantera, whose seventh studio album Far Beyond Driven (1994) was notable for going number one on Billboard 200. Another heavy metal subgenre called nu metal, which mixed metal with hip hop influences, becomes popular with bands like Korn, Slipknot and Limp Bizkit selling millions of albums worldwide.
Video gaming

Popular notable video games of the 1990s include: Metal Gear Solid, Super Mario World, Pokémon Red and Blue Versions, Pokémon Yellow Version, GoldenEye 007, Super Mario 64, The Legend of Zelda: Ocarina of Time, Gran Turismo, Mario Kart 64, Half-Life, Super Mario Kart, Tomb Raider series, Final Fantasy, Crash Bandicoot series, Resident Evil series, Street Fighter II, Spyro the Dragon series, Commander Keen series, Test Drive series, Monkey Island, Dune series, Mortal Kombat series, Warcraft series, Duke Nukem 3D, Tekken series, StarCraft, and Sonic the Hedgehog series.
Sony’s PlayStation becomes the top selling game console and changes the standard media storage type from cartridges to compact discs in consoles. Crash Bandicoot is released on 9 September 1996, becoming one of the most successful platforming series for the Sony PlayStation. Tomb Raider’s (PlayStation) Lara Croft became a video game sex symbol, becoming a recognizable figure in the entertainment industry throughout the late 1990s.
3-D graphics become the standard by end of decade. Although FPSs had long since seen the transition to full 3D, other genres begin to copy this trend by the end of the decade. Most notable first shooter games in the 1990s are GoldenEye 007 and Tom Clancy's Rainbow Six.
The console wars, primarily between Sega (Mega Drive, marketed as the Sega Genesis in North America, introduced in 1988) and Nintendo (Super NES, introduced in 1990), sees the entrance of Sony with the PlayStation in 1994, which becomes the first successful CD-based console (as opposed to cartridges). By the end of the decade, Sega’s hold on the market becomes tenuous after the end of the Saturn in 1999 and the Dreamcast in 2002.
Mario as Nintendo’s mascot finds a rival in Sega’s Sonic the Hedgehog with the release of original game on the Genesis in 1991.
Arcade games rapidly decrease in popularity.[27]
Fighting games like Capcom’s Street Fighter II, Sega’s futuristic Virtua Fighter, and especially the more violent Mortal Kombat from Midway prompted the video game industry to adopt a game rating system. Hundreds of knock-offs are widely popular in mid-to-late 1990s. Doom (1993) bursts onto the world scene, and instantly popularizes the FPS genre, and even how games are played, as Doom is among the first games to feature multiplayer capabilities. It isn’t until Quake (1996), however, that game developers begin to take multiplayer features into serious consideration when making games. Half-Life (1998) features the next evolutionary step in the genre with continual progression of the game (no levels in the traditional sense) and an entirely in-person view, and becomes one of the most popular computer games in history.
The real-time strategy (RTS) genre is introduced in 1992 with the release of Dune II. Warcraft: Orcs & Humans (1994) popularizes the genre, with Command & Conquer and Warcraft II: Tides of Darkness in 1995, setting up the first major real-time strategy competition and popularizing multiplayer capabilities in RTS games. StarCraft in 1998 becomes the second best-selling computer game of all time. It remains among the most popular multiplayer RTS games to this day, especially in South Korea. Homeworld in 1999 becomes the first successful 3d RTS game. The rise of the RTS genre is often credited with the fall of the turn-based strategy (TBS) genre, popularized with Civilization in 1991. Final Fantasy first debuted (in North America) in 1990 for the NES, and remains among the most popular video game franchises, with many new titles to date and more in development, plus numerous spin-offs, sequels, films and related titles. Final Fantasy VII, released in 1997, especially popularized the series.
Massively multiplayer online role-playing games (MMORPGs) see their entrance into the computer game world with Ultima Online in 1997, although they don’t gain widespread popularity until EverQuest and Asheron's Call in 1999. MMORPGs go on to become among the most popular genres in the first decade of the 21st century.
Pokémon enters the world scene with the release of the original Game Boy Pokémon Red and Pokémon Green games in Japan in 1996, later changed to Pokémon Red and Pokémon Blue for worldwide release in 1998. It soon becomes popular in the U.S., spurring the term Pokémania and is adapted into a popular anime series and trading card game, among other media forms.
Resident Evil is released in 1996. It becomes the most popular survival-horror series in video gaming well into the next decade and inspires several films.
Crash Bandicoot is released in September 1996, becoming an innovative platformer for the Sony PlayStation.
Toys and games

Some of the most popular toys and games that emerged in the 1990s, or that had a significant increase in popularity during the 1990s, include:
- Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles
- Barbie, produced by Mattel
- Super Soaker Water Guns
- Cupcake Dolls were produced by Tonka. They looked similar to a southern belle and smelled like cupcakes as well as turned into cupcakes. They came with a dress and a plastic hat that could be fastened with a string that could be tied under their chin. The dress was made of rubber covered with cloth and if the doll's head was pushed down and the dress turned upward, the doll would become a cupcake with the hat being the frosting on top.
- Power Rangers
- Polly Pocket
- Stretch Armstrong
- My Little Pony produced by Hasbro was popular in the early part of the 1990s before it transitioned further away from the 1980s. Then this toy made a brief comeback starting in 1997.
- Secret Wish Horse was made by Tyco. They were colorful plastic horses that had rooted eyelashes and a bejeweled saddle. One of the jewels could be removed and used as a key to unlock the hidden surprise within the saddle. The surprise usually consisted of a ring or earrings. They also came with a magic 8 ball necklace so that little girls could make wishes.
- Magic Touch Horse were plastic horses that came in different shades of the rainbow. They had symbols on their hips that when pressed would light up the hooves or plastic flowers in the mane. Some of them played music.
- Sega Game Gear
- Care Bears
- Transformers (Toy Line)
- Littlest Pet Shop
- Beast Wars
- Beanie Babies (TY)
- Sky Dancers
- Troll Doll
- Giga Pets
- Tamagotchi
- Hot Wheels
- Skip It
- Bop It
- Pogs
- Creepy Crawlers, produced by Mattel
- Fantasy Fillies were produced by Empire/Marchon and designed by the designer of Fashion Star Fillies by Kenner (1987). They were plastic horses that came in a wide array of colors. They all had glittery symbols on their hips.
- Cabbage Patch Horses produced by Hasbro were rubber ponies that came in several different color variations and some had glittery bodies. Also, some had hair that could be combed while others had yarn for hair.
- Lisa Frank
- Pokémon
- Furby
- Poo-Chi
- Puppy Surprise
- Pound Puppies
- Animorphs
- Thin Ice board game
- Trouble board game
- Sorry board game
- Jenga board game
- Guess Who game
- Connect Four game
- Perfection game
- Pretty Pretty Princess board game
- Laser Tag
- Sonic the Hedgehog
- Super Nintendo
- Sega Genesis
- Mr. Bucket
- Sony PlayStation
- Nintendo 64
- Game Boy Color
- Rollerblades
- Razor Scooter
Sports
- Major League Baseball players went on strike on 12 August 1994, thus ending the season and canceling the World Series for the first time in 90 years. The players' strike ended on 29 March 1995 when players and team owners came to an agreement.
- American NBA basketball player Michael Jordan became a major sports and pop culture icon idolized by millions worldwide. He revolutionized sports marketing through deals with companies such as Gatorade, Hanes, McDonald's and Nike. His Chicago Bulls team won six NBA titles during the decade (1991, 1992, 1993, 1996, 1997 and 1998).
- The National Hockey League would expand from 21 to 30 teams. During the expansion years, several teams would relocate to new cities: the Winnipeg Jets moved to Phoenix, Arizona and became the Phoenix Coyotes, the Quebec Nordiques moved to Denver and became the Colorado Avalanche, the Hartford Whalers moved to Raleigh, NC and became the Carolina Hurricanes, and the Minnesota North Stars moved to Dallas and became the Dallas Stars.
- The NHL's 1990s expansion saw new teams in cities that previously never had NHL hockey: San Jose (San Jose Sharks), Anaheim (Mighty Ducks of Anaheim), Nashville (Nashville Predators), Miami (Florida Panthers) and Tampa (Tampa Bay Lightning).
- Two of the NHL's Original Six teams, the New York Rangers and the Detroit Red Wings would end long Stanley Cup championship droughts; the Rangers in 1994 after 54 years, and the Red Wings would win back to back Cups in 1997 and 1998 after 42 years.
- Canadian hockey star Mario Lemieux led the Pittsburgh Penguins, one of the original NHL expansion teams, to back-to-back Stanley Cup championships in 1991 and 1992.
- In addition to the Pittsburgh Penguins, three other NHL expansion teams went on to earn their first Stanley Cup championships: the New Jersey Devils in 1995, the Colorado Avalanche in 1996, and the Dallas Stars in 1999.
- Canadian hockey star Wayne Gretzky announced his retirement from the NHL in 1999. Upon his final game on 18 April, he held forty regular-season records, fifteen playoff records, and six All-Star records. He is the leading point-scorer in NHL history, as well as the only NHL player to total over 200 points in one season – a feat he accomplished four times. In addition, he tallied over 100 points in 16 professional seasons, 14 of them consecutive. He played for four teams during his NHL career: the Edmonton Oilers, the Los Angeles Kings, the St. Louis Blues, and the New York Rangers.
- American cyclist Lance Armstrong wins his first Tour de France in 1999, less than two years after battling testicular cancer.
- In professional wrestling, the boom period of the WWF from the late 1980s continued until 1993, lead by such stars as Hulk Hogan and The Ultimate Warrior. A second boom period of the decade was introduced during the Monday Night Wars between the WWF and WCW from the middle of the decade to spawn the WWF's Attitude Era, home to some of the biggest names in Wrestling history such as Stone Cold Steve Austin and The Rock and the highly popular nWo group, along with Goldberg who brought WCW major success.
- Manchester United won an unprecedented treble of the Premier League, FA Cup and Champions League after defeating Bayern Munich 2–1 in May 1999.
- The USA hosted the 15th staging of the World Cup in 1994. To this day, it holds the record for largest attendance per game during the World Cup finals (even after the tournament's expansion to 32 teams and 64 matches). Additionally, this led to the creation of the MLS.
- The 1990s NFL also saw the return of the Dallas Cowboys back to prominence after a 14-year NFL championship drought by winning three Super Bowls(1992, 1993 and 1995) in a four-year span.
- The Nebraska Cornhuskers won three national titles in college football in a four-year span (1994, 1995, 1997)
- Led by head coach Jim Tressel, The Youngstown State Penguins won four national titles in division I-AA college football
- The Ultimate Fighting Championship (1993) and Pride Fighting Championship (1997) debut and evolve into the modern sport of Mixed Martial Arts.
Architecture

- The Petronas Twin Towers became two of the tallest man-made structures ever built after they officially opened on 31 August 1999.
Literature
- From July 1992 to December 1997, sixty-two books were written by R.L. Stine and published by Scholastic for the Goosebumps series. The series was very popular amongst pre-teens and older children, and as of 2008, the series had sold more than 300 million copies worldwide.[28]
- The End of History and the Last Man (1992) by Francis Fukuyama, a political theory book that expanded on Fukuyama's essay "The End of History?" of 1989, in which Fukuyama argues that the end of the Cold War has resulted in the end of international ideological struggle, resulting in the victory of Western liberal democracy that he claims is the final form of human government.
- The Clash of Civilizations and the Remaking of World Order (1996) by Samuel P. Huntington, a political theory book that rebukes Francis Fukuyama's argument in The End of History and the Last Man, claiming that in the post-Cold War world, people's cultural and religious identity would form the basis of modern conflicts.
- Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone was published on 30 June 1997, the first novel in the Harry Potter series written by J. K. Rowling and featuring Harry Potter, a young wizard. "Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets", the next book in the series was published on June 2, 1998 and "Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban", the third book of seven in the series was published July 8, 1999. The Harry Potter series would go on to become the most successful book series of all time and J.K. Rowling would become the first billionaire author.
Fashion

Significant fashion trends of the 1990s include:
- The Rachel, Jennifer Aniston's hairstyle on the hit show Friends, became a cultural phenomenon with millions of women copying it worldwide.
- The Curtained Haircut increased in popularity in fashion and culture amongst teenage boys and young men in the 1990s, mainly after it was popularized in the film Terminator 2: Judgment Day by the actor Edward Furlong.
- The model 1300 Wonderbra style has a resurgence of popularity in Europe in 1992 which kicks off a multinational media sensation, the 1994 re-introduction of "The Wonderbra" brand, and a spike in push-up, plunge bras around the world.
- Additional fashion trends of the 1990s include the Tamagotchi, Rollerblades, Pogs and Dr. Martens shoes.
- Bleached Blond hair became very popular in the late '90s, as was men with short hair with the bangs "flipped up"
- Beverly Hills 90210 sideburns also became popular in the early and mid-1990s
- Slap bracelets were a popular fad among children, pre-teens and teenagers in the late 1980s and early 1990s and were available in a wide variety of patterns and colors. Also, popular among children were light up sneakers, jelly shoes and shoelace hair clips were worn by girls.
- The Grunge hype at the beginning of the decade popularized the flannel shirts among both sexes during the 1990s.
People
World leaders
- President Carlos Menem (Argentina)
- Prime Minister Bob Hawke (Australia)
- Prime Minister Paul Keating (Australia)
- Prime Minister John Howard (Australia)
- King Boudewijn (Belgium) until 1993
- King Albert II (Belgium)
- President Fernando Affonso Collor de Mello (Brazil)
- President Fernando Henrique Cardoso (Brazil)
- President Zhelyu Zhelev (Bulgaria)
- President Petar Stoyanov (Bulgaria)
- Prime Minister Brian Mulroney (Canada)
- Prime Minister Kim Campbell (Canada)
- Prime Minister Jean Chrétien (Canada)
- "Paramount Leader" Deng Xiaoping (People's Republic of China)
- President Jiang Zemin (People's Republic of China)
- President Lee Teng-hui (Republic of China, Taiwan)
- Elizabeth II (Commonwealth realms)
- President Franjo Tuđman (Croatia)
- President Václav Havel (Czechoslovakia and (Czech Republic after the breakup of Czechoslovakia))
- President Virgilio Barco Vargas (Colombia)
- President César Gaviria (Colombia)
- President Ernesto Samper (Colombia)
- President Andrés Pastrana Arango (Colombia)
- President Fidel Castro (Cuba)
- Prime Minister Poul Nyrup Rasmussen (Denmark)
- President Hosni Mubarak (Egypt)
- President Ali Mahdi Muhammad (Somali Republic)
- President Lennart Meri (Estonia)
- President François Mitterrand (France)
- President Jacques Chirac (France)
- Chancellor Helmut Kohl (Germany)
- Chancellor Gerhard Schröder (Germany)
- Governor David Clive Wilson (Hong Kong (under British rule))
- Governor Christopher Francis Patten (Hong Kong (under British rule))
- Chief Executive Tung Chee Hwa (Hong Kong, People's Republic of China)
- Prime Minister Vishwanath Pratap Singh (India)
- Prime Minister Chandra Shekhar (India)
- Prime Minister P. V. Narasimha Rao (India)
- Prime Minister H. D. Deve Gowda (India)
- Prime Minister Inder Kumar Gujral (India)
- Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee (India)
- Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei (Iran)
- President Akbar Hashemi Rafsanjani (Iran)
- President Mohammad Khatami (Iran)
- President Saddam Hussein (Iraq)
- Prime Minister Yitzhak Shamir (Israel)
- Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin (Israel)
- Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu (Israel)
- President of the Council of Ministers Silvio Berlusconi (Italy)
- President of the Council of Ministers Romano Prodi (Italy)
- Emperor Akihito (Japan)
- Prime Minister Ryutaro Hashimoto (Japan)
- President Guntis Ulmanis (Latvia)
- President Vaira-Vike Freiberga (Latvia)
- President Muammar Gaddafi (Libya)
- Governor Vasco Joaquim Rocha Vieira (Macau (under Portuguese rule))
- Chief Executive Edmund Ho (Macau, People's Republic of China)
- President Carlos Salinas (Mexico)
- President Ernesto Zedillo (Mexico)
- President Yasser Arafat (Palestinian Authority)
- Pope John Paul II (Vatican City)
- President Alberto Fujimori (Peru)
- President Corazon Aquino (Philippines)
- President Fidel Ramos (Philippines)
- President Joseph Estrada (Philippines)
- President Lech Wałęsa (Poland)
- President Aleksander Kwaśniewski (Poland)
- Prime Minister Ruud Lubbers (Netherlands)
- Prime Minister Wim Kok (Netherlands)
- Prime Minister Mike Moore (New Zealand)
- Prime Minister Jim Bolger (New Zealand)
- Prime Minister Jenny Shipley (New Zealand)
- Prime Minister Helen Clark (New Zealand)
- President Ion Iliescu (Romania)
- President Emil Constantinescu (Romania)
- Taoiseach Charles Haughey (Republic of Ireland)
- Taoiseach Albert Reynolds (Republic of Ireland)
- Taoiseach John Bruton (Republic of Ireland)
- Taoiseach Bertie Ahern (Republic of Ireland)
- President Boris Yeltsin (Russia)
- President Wee Kim Wee (Singapore)
- President Ong Teng Cheong (Singapore)
- President Sellapan Ramanathan (Singapore)
- Prime Minister Goh Chok Tong (Singapore)
- President Frederik Willem de Klerk (South Africa)
- President Nelson Mandela (South Africa)
- President Kim Dae-jung (South Korea)
- President Mikhail Gorbachev (Soviet Union)
- King Juan Carlos I (Spain)
- President Felipe González (Spain)
- President José María Aznar (Spain)
- Prime Minister Ingvar Carlsson (Sweden)
- Prime Minister Carl Bildt (Sweden)
- Prime Minister Göran Persson (Sweden)
- President Hafez al-Assad (Syria)
- President Turgut Özal (Turkey)
- President Süleyman Demirel (Turkey)
- Prime Minister Tansu Çiller (Turkey)
- Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher (United Kingdom) until 1990
- Prime Minister John Major (United Kingdom)
- Prime Minister Tony Blair (United Kingdom)
- President George H.W. Bush (United States) until 1993
- President Bill Clinton (United States)
- President Hugo Chávez (Venezuela)
- President Slobodan Milošević (Federal Republic of Yugoslavia)
- Prime Minister Gro Harlem Brundtland (Norway) 1990–1996
- Prime Minister Torbjørn Jagland (Norway) 1996–1997
- Prime Minister Kjell Magne Bondevik (Norway) 1997–2000
- King Harald V (Norway) King of Norway 1991–present
Entertainers

- Angelina Jolie
- Howard Stern
- Leonardo DiCaprio
- Kate Winslet
- Mike Myers
- Jim Carrey
- Julia Roberts
- Uma Thurman
- Will Smith
- Sandra Bullock
- Pierce Brosnan
- Robert Carlyle
- David Jason
- Drew Barrymore
- Robbie Coltrane
- Denzel Washington
- John Thaw
- George Clooney
- Macaulay Culkin
- Kevin Spacey
- Ewan McGregor
- Keanu Reeves
- Nicole Kidman
- Tom Cruise
- Liam Neeson
- Bruce Willis
- Richard Gere
- Meg Ryan
- Tom Hanks
- Brad Pitt
- Kevin Costner
- Arnold Schwarzenegger
- Jodie Foster
- Anthony Hopkins
- Greg Kinnear
- Demi Moore
- Eddie Murphy
- Harrison Ford
- Fran Drescher
- Jack Nicholson
- Mel Gibson
- Michelle Pfeiffer
- Edward Norton
- Robin Williams
- Adam Sandler
- Juliette Lewis
- Woody Harrelson
- Antonio Banderas
- Emma Thompson
- Johnny Depp
- Winona Ryder
- Ray Liotta
- Nicolas Cage
- Sharon Stone
- Jerry Seinfeld
- Kelsey Grammer
- Ted Danson
- Kirstie Alley
- Michael J. Fox
- John Lithgow
- Ray Romano
- Scott Bakula
- Rob Morrow
- David Duchovny
- Gillian Anderson
- Fred Savage
- Roseanne Barr
- Candice Bergen
- Helen Hunt
- Chris Guest
- Jerry Springer
- Rosie O'Donnell
- John Goodman
- Mara Wilson
- Gary Oldman
- Hugo Weaving
- Christian Slater
Musicians
- Corona
- DJ BoBo
- Carlos Santana
- Michael Jackson
- Madonna
- Whitney Houston
- Mariah Carey
- Shakira
- Courtney Love
- Cher
- Björk
- Enya
- Dr. Alban
- Weird Al Yankovic
- Celine Dion
- Britney Spears
- Christina Aguilera
- Nas
- Kurt Cobain
- Eminem
- Rammstein
- Nick Kamen
- Enrique Iglesias
- Puff Daddy
- Jeff Buckley
- Tupac Shakur
- Garth Brooks
- RuPaul
- George Michael
- Alanis Morissette
- Ricky Martin
- Kylie Minogue
- Redman
- Robbie Williams
- Selena
- Haddaway
- Trent Reznor
- The Notorious B.I.G.
- Snoop Doggy Dogg
- Dr. Dre
- Aaliyah
- Michael Bublé
Bands
- Ace of Base
- Hanson
- KoRn
- Weezer
- Blink-182
- Matchbox Twenty
- Wu Tang Clan
- N.W.A.
- Nirvana
- Melt-Banana
- TLC
- Shazna
- Cali Gari
- Animetal
- Siam Shade
- Creed
- Modest Mouse
- X Japan
- Dodgy
- Snap!
- U2
- B'z
- Culture Club
- Culture Beat
- The Cranberries
- Fun Factory
- La Bouche
- Masterboy
- Mr. President
- Guns N' Roses
- The Dead Pop Stars
- Aerosmith
- Bon Jovi
- Metallica
- Modern Talking
- Green Day
- Take That
- The Offspring
- Brooks & Dunn
- Boyz II Men
- Live
- Westlife
- Savage Garden
- Backstreet Boys
- *NSYNC
- Counting Crows
- Soundgarden
- Nine Inch Nails
- Dave Matthews Band
- No Doubt
- The Prodigy
- Blink-182
- Hole
- Train
- Built To Spill
- Oasis
- Stereophonics
- The Sundays
- Bush
- Phish
- Radiohead
- Local H
- Boyzone
- Rage Against the Machine
- Red Hot Chili Peppers
- Toad The Wet Sprocket
- Hootie & The Blowfish
- B*Witched
- The Smashing Pumpkins
- Blur
- The Verve
- Garbage
- Pearl Jam
- Pantera
- Sepultura
- Septic Flesh
- Marilyn Manson
- Alice in Chains
- Sublime
- Third Eye Blind
- Oasis
- Neutral Milk Hotel
- Goo Goo Dolls
- Sugar Ray
- Smash Mouth
- Everclear
- The Corrs
- Sublime
- Slipknot
- Foo Fighters
- Blind Melon
- Tool (band)
- Spice Girls
- Stone Temple Pilots
- HammerFall
- Limp Bizkit
- 2 Unlimited
Sports figures
See also
- 1990s in music
- 1990s in fashion
- 1990s in television
- 1990s in science and technology
- 1990s in video gaming
- 1990s in literature
- Generation X - People apart of this generation would have been young adults or teenagers during this decade, while the oldest members were nearly 40 as the decade closed.
- Generation Y - People apart of this generation were still being born throughout the 1990s, the older members would have been reaching their teenage years.
Timeline
The following articles contain brief timelines which list the most prominent events of the decade:
1990 • 1991 • 1992 • 1993 • 1994 • 1995 • 1996 • 1997 • 1998 • 1999
References
- ^ Stiglitz, Joseph E. (2004). The Roaring Nineties. W. W. Norton. ISBN 978-0-393-32618-5.
- ^ GlobalSecurity.org, Second Chechnya War – 1999–???
- ^ Des Forges, Alison (1999). Leave None to Tell the Story: Genocide in Rwanda. Human Rights Watch. ISBN 978-1-56432-171-8. Retrieved 12 January 2007.
- ^ See, e.g., Rwanda: How the genocide happened, BBC, 1 April 2004, which gives an estimate of 800,000, and OAU sets inquiry into Rwanda genocide, Africa Recovery, Vol. 12 1#1 (August 1998), page 4, which estimates the number at between 500,000 and 1,000,000. 7 out of every 10 Tutsis were killed.
- ^ a b Sorin Antohi and Vladimir Tismăneanu, "Independence Reborn and the Demons of the Velvet Revolution" in Between Past and Future: The Revolutions of 1989 and Their Aftermath, Central European University Press. ISBN 978-963-9116-71-9. p.85.
- ^ Archived 2002-10-14 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "The Urban Institute | Welfare Reform: Ten Years Later". Archived from the original on 8 May 2009. Retrieved 6 April 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Grossman, Lev (31 March 2003). "How the Web Was Spun". Time Magazine. Archived from the original on 18 July 2009. Retrieved 19 July 2009.
Berners-Lee's computer faithfully logged the exact second the site was launched: 2:56:20 pm, Aug. 6, 1991.
- ^ http://birminghamskews.com/post/4544141336/this-truly-is-our-story
- ^ "Titanic (1997)". Archived from the original on 27 May 2009. Retrieved 22 May 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ All-Time Worldwide Box Office
- ^ DeCurtis, Anthony (5 October 1999). "The Ball Drops on the Music Industry". Rolling Stone. Retrieved 10 December 2012.
- ^ [1]
- ^ Eddy, Chuch (10 November 2009). "MYTH No. 2: Nirvana Killed Hair Metal". SPIN. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- ^ Pareles, Jon (14 June 1992). "POP VIEW; Nirvana-bes Awaiting Fame's Call". New York Times. Retrieved 23 November 2011.
- ^ http://www.allmusic.com/explore/style/punk-pop-d2928
- ^ Wilson, Carl (4 August 2011). "My So Called Adulthood". New York Times. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- ^ McGee, Allan (3 January 2008). "The missing link of hip-hop's golden age". The Guardian. UK. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- ^ Caramanica, Jon (9 November 2009). "MYTH No. 4: Biggie & Tupac Are Hip-Hop's Pillars". SPIN. Retrieved 4 September 2011.
- ^ Batey, Angus (7 October 2010). "The hip-hop heritage society". The Guardian. UK. Retrieved 8 November 2011.
- ^ Martinez, Michael (9 February 2011). "The music dies for once popular 'Guitar Hero' video game". CNN. Retrieved 27 November 2011.
- ^ BBC – Press Office – New Spice Girls documentary on BBC One
- ^ "1998: Ginger leaves the Spice Girls". BBC News. 31 May 1998. Retrieved 29 March 2010.
- ^ "Teen Pop Music: A Guide". Archived from the original on 4 September 2009. Retrieved 26 August 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ https://www.allmusic.com/explore/style/d7232
- ^ Ashthana, Anushka (25 May 2008). "They don't live for work ... they work to live". The Guardian. UK. Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- ^ Wolf, Mark J.P. (2008). "Arcade Games of the 1990s and Beyond". The video game explosion: a history from PONG to PlayStation and beyond. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press. p. 135. ISBN 978-0-313-33868-7. OCLC 154776597. Retrieved 19 July 2009.
The decline of arcade video games would come back in the 1990s, despite attempts to redefine the arcade experience and attract players back to the arcade.
- ^ Neary, Lynn (31 October 2008). "Goosebumps And Guffaws In Stine's 'HorrorLand'". National Public Radio. Retrieved 16 February 2010.



