Novi Sad
Novi Sad
Нови Сад / Újvidék Újvidék Nový Sad | |
|---|---|
City | |
 Panorama of Novi Sad | |
|
| |
| Country | Serbia |
| Province | Vojvodina |
| District | South Bačka |
| Municipalities | 2 |
| Settled by Scordisci | 4th century B.C. |
| Founded | 1694 |
| City status | 1 February 1748 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Miloš Vučević (SNS) |
| Area | |
| • City | 106.2 km2 (41.0 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 702.7 km2 (271.3 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 80 m (262 ft) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • City | |
| • Density | 2,182.6/km2 (5,653/sq mi) |
| • Urban | |
| • Metro | |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 21000 |
| Area code | +381(0)21 |
| Car plates | NS |
| Website | www.novisad.rs |
Novi Sad (Serbian Cyrillic: Нови Сад, pronounced [nôʋiː sâːd] ; see below for other names) is the second largest city in Serbia, the administrative seat of the province of Vojvodina and of the South Bačka District. It is located in the southern part of Pannonian Plain, on the border of the Bačka and Srem regions, on the banks of the Danube river, facing the northern slopes of Fruška Gora mountain.
According to the 2011 census, the city has a population of 231,798, while the urban area of Novi Sad (with adjacent urban settlements of Petrovaradin, Sremska Kamenica, and Futog included) has 277,522 inhabitants. The population of the metropolitan area (the administrative area of the city) stands at 341,625 people.[1]
The city was founded in 1694, when Serb merchants formed a colony across the Danube from the Petrovaradin fortress, a Habsburg strategic military post. In the 18th and 19th centuries, it became an important trading and manufacturing centre, as well as a centre of Serbian culture of that period, earning the nickname Serbian Athens.[2][3] The city was heavily devastated in the 1848 Revolution, but it was subsequently restored. Today, Novi Sad is an industrial and financial centre of the Serbian economy, as well as a major cultural center.
Name
The name Novi Sad means "New Garden" (noun) in Serbian. Its Latin name, stemming from establishment of city rights, is "Neoplanta". The official names of Novi Sad used by the local administration are:[4]
In both Croatian and Romanian, which are official in the provincial administration, the city is called "Novi Sad". Historically, it was also called "Neusatz" in German.
In its wider meaning, the name Grad Novi Sad refers to the "City of Novi Sad", which is one of the city-level administrative units of Serbia. Novi Sad could also refer strictly to the urban part of the City of Novi Sad (including "Novi Sad proper", and towns of Sremska Kamenica and Petrovaradin), as well as only to the historical core on the left Danube bank, i.e. "Novi Sad proper" (excluding Sremska Kamenica and Petrovaradin).
History

Older settlements
Human dwelling on the territory of present-day Novi Sad has been traced as far back as the Stone Age (about 4500 BC). Several settlements and necropoleis were unearthed during the construction of a new boulevard in Avijaticarsko Naselje, and were dated to 5000 BC.[5] A settlement was located on the right bank of the river Danube in the territory of present-day Petrovaradin. In antiquity, the region was inhabited by Illyrian, Thracian and Celtic tribes, especially by the Scordisci. Celts were present in the area since the 4th century BC and founded the first fortress on the right bank of the Danube. Later, in the 1st century BC, the region was conquered by the Romans. During Roman rule, a larger fortress was built in the 1st century with the name Cusum and was included in the Roman province of Pannonia.
In the 5th century, Cusum was devastated by the invasion of the Huns. By the end of the 5th century, Byzantines had reconstructed the town and called it by the names Petrikon or Petrikov (Greek: Πετρικοβ) after St. Peter. Slavic tribes like the Severians, Obotrites and Serbs with its subgroup tribes Braničevci and Timočani, settled today's region about Novi Sad mainly in the 6th and 7th centuries.[6][unreliable source?] The Serbs absorbed the aforementioned Slavs as well as the Paleo-Balkanic[disambiguation needed] peoples in the region.[6] In the Middle Ages, the area was subsequently controlled by the Ostrogoths, Gepids, Avars, Franks, Great Moravia, Bulgaria, again by Byzantines, and finally by the Hungarians. It was included into the medieval Kingdom of Hungary between the 11th and 12th century, and Hungarians then began to settle in the area, which before that time was mostly populated by Slavs, and the place was mentioned first time under the Hungarian variant Peturwarad or Pétervárad (Serbian: Petrovaradin / Петроварадин), which derived from the Byzantine variant, in documents from 1237. In the same year, several other settlements were mentioned to exist in the territory of modern urban area of Novi Sad.
From 13th to 16th century, the following settlements existed in the territory of modern urban area of Novi Sad:[7][8]
- on the right bank of the Danube: Pétervárad (Serbian: Petrovaradin) and Kamanc (Serbian: Kamenica).
- on the left bank of the Danube: Baksa or Baksafalva (Template:Lang-sr), Kűszentmárton (Template:Lang-sr), Bivalyos or Bivalo (Template:Lang-sr), Vásárosvárad or Várad (Template:Lang-sr), Zajol I (Serbian: Sajlovo I, Gornje Sajlovo, Gornje Isailovo), Zajol II (Serbian: Sajlovo II, Donje Sajlovo, Donje Isailovo), Bistritz (Serbian: Bistrica).
Some other settlements existed in the suburban area of Novi Sad: Mortályos (Serbian: Mrtvaljoš), Csenei (Template:Lang-sr), Keménd (Serbian: Kamendin), Rév (Template:Lang-sr).
Etymology of the settlement names show that some of them are of Slavic origin, which indicate that they were initially inhabited by Slavs. For example, Bivalo (Bivaljoš) was a large Slavic settlement dating to the 5th-6th century.[7] Some other settlement names are of Hungarian origin (for example Bélakút, Kűszentmárton, Vásárosvárad, Rév), which indicate that they were inhabited by Hungarians before the Ottoman invasion in the 16th century.[8] Some settlement names are of uncertain origin.

Tax records from 1522 showed a mix of Hungarian and Slavic names among inhabitants of these villages, including Slavic names like Bozso (Božo), Radovan, Radonya (Radonja), Ivo, etc. Following the Ottoman invasion in the 16th-17th century, some of these settlements were destroyed and most Hungarian inhabitants have left this area. Some of the settlements also existed during the Ottoman rule, and were populated by ethnic Serbs.
Between 1526 and 1687, the region was under Ottoman rule. In the year 1590, population of all villages that existed in the territory of present-day Novi Sad numbered 105 houses inhabited exclusively by Serbs. However, Ottoman records mention only those inhabitants that paid taxes, thus the number of Serbs that lived in the area (for example those that served in the Ottoman army) was larger.[9]
Founding of Novi Sad
At the outset of Habsburg rule, near the end of the 17th century, people of Orthodox faith were forbidden from residing in Petrovaradin, thus Serbs were largely unable to build homes there. Because of this, a new settlement was founded in 1694 on the left bank of the Danube. The initial name of this settlement was Serb City (Ratzen Stadt). Another name used for the settlement was Petrovaradinski Šanac. In 1718, the inhabitants of the village of Almaš were resettled to Petrovaradinski Šanac, where they founded Almaški Kraj ("the Almaš quarter").
According to 1720 data, the population of Ratzen Stadt was composed of 112 Serbian, 14 German, and 5 Hungarian houses. The settlement officially gained the present names Novi Sad and Újvidék (Neoplanta in Latin) in 1748 when it became a "free royal city".
The edict that made Novi Sad a "free royal city" was proclaimed on 1 February 1748. The edict reads:
We, Maria Theresa, by the grace of God Holy Roman Empress,
Queen of Hungary, Bohemia, Moravia, Dalmatia, Croatia, Slavonia, Rama, Serbia, Galicia, Lodomeria, Carinthia, [...]
cast this proclamation to anyone, whom it might concern...so that the renowned Petrovaradinski Šanac, which lies on the other side of the Danube in the Bačka province on the Sajlovo land, by the might of our divine royal power and prestige...make this town a Free Royal City and to fortify, accept and acknowledge it as one of the free royal cities of our Kingdom of Hungary and other territories, by abolishing its previous name of Petrovaradinski Šanac, renaming it Neoplantae (Latin), Új-Vidégh (Hungarian), Neusatz (German) and Novi Sad (Serbian).
In Habsburg Monarchy


For much of the 18th and 19th centuries, Novi Sad was the largest city in the world populated by ethnic Serbs. The reformer of the Serbian language, Vuk Stefanović Karadžić, wrote in 1817 that Novi Sad is the "largest Serb municipality in the world". It was a cultural and political centre of Serbs, who did not have their own national state at the time. Because of its cultural and political influence, Novi Sad became known as the Serbian Athens (Srpska Atina in Serbian). According to 1843 data, Novi Sad had 17,332 inhabitants, of whom 9,675 were Orthodox Christians, 5,724 Catholics, 1,032 Protestants, 727 Jews, and 30 adherents of the Armenian church. The largest ethnic group in the city were Serbs, and the second largest were Germans.
During the Revolution of 1848-1849, Novi Sad was part of Serbian Vojvodina, a Serbian autonomous region within the Austrian Empire. In 1849, the Hungarian garrison located on the Petrovaradin Fortress bombarded and devastated the city, which lost much of its population. According to an 1850 census, there were only 7,182 citizens in the city, compared with 17,332 in 1843. Between 1849 and 1860, the city was part of a separate Austrian crownland known as the Voivodeship of Serbia and Banat of Temeschwar. After the abolishment of this province, the city was included into Batsch-Bodrog County. The post-office was opened in 1853.
After the compromise of 1867, Novi Sad was located within the Kingdom of Hungary or Transleithania, one of two parts of Austria-Hungary. During this time, the Magyarization policy of the Hungarian government drastically altered the demographic structure of the city, i.e. from the predominantly Serbian, the population of the city became ethnically mixed. In 1880 41.2% of the city's inhabitants used Serbian language most frequently and 25.9% used Hungarian. In the following decades, percentual participation of speakers of Serbian decreased, while percentual participation of speakers of Hungarian increased. According to the 1910 census, the city had 33,590 residents, of whom 13,343 (39.72%) spoke Hungarian, 11,594 (34.52%) Serbian, 5,918 (17.62%) German and 1,453 (4.33%) Slovak. It is not certain whether Hungarians or Serbs were largest ethnic group in the city in 1910, since the various ethnic groups (Bunjevci, Romani, Jews, other South Slavic people, etc.) were classified in census results according to the language they spoke.[10]
Similar demographic change can be seen in the religious structure: in 1870, population of Novi Sad included 8,134 Orthodox Christians, 6,684 Catholics, 1,725 Calvinists, 1,343 Lutherans, and others.[11] In 1910, population included 13,383 Roman Catholics and 11,553 Orthodox Christians, while 3,089 declared themselves as Lutheran, 2,751 as Calvinist, and 2,326 as Jewish.[12]
After 1918

On 25 November 1918, the Assembly of Serbs, Bunjevci and other Slavs of Vojvodina in Novi Sad proclaimed the union of Vojvodina region with the Kingdom of Serbia. Since 1 December 1918, Novi Sad was part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes; and in 1929, it became the capital of the Danube Banovina, a province of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. In 1921, population of Novi Sad numbered 39,122 inhabitants, of whom 16,293 spoke Serbian language, 12,991 Hungarian, 6,373 German, 1,117 Slovak, etc.[13]
In 1941, the Kingdom of Yugoslavia was invaded and partitioned by the Axis powers, and its northern parts, including Novi Sad, were annexed by Hungary. During World War II, about 5,000 citizens were murdered and many others were resettled. In three days of Novi Sad raid (21–23 January 1942) alone, Hungarian police killed 1,246 citizens, among them more than 800 Jews, and threw their corpses into the icy waters of the Danube, while the total death toll of the raid was around 2,500.[14][15] Citizens of all nationalities—Serbs, Hungarians, Slovaks, and others—fought together against the Axis authorities.[15] In 1975 the whole city was awarded the title People's Hero of Yugoslavia.
The communist partisans from Syrmia and Bačka entered the city on 23 October 1944. During the Military administration in Banat, Bačka and Baranja (October 17, 1944 – January 27, 1945), the partisans killed a number of citizens who were perceived as Axis collaborators or a threat to the new regime. According to article in Večernje novosti from June 9, 2009, most of the people killed by the partisans in Novi Sad were ethnic Serbs.[16]

Novi Sad became part of the new socialist Yugoslavia. Since 1945, Novi Sad has been the capital of Vojvodina, a province of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and Serbia. The city went through rapid industrialization and its population more than doubled in the period between World War II and the breakup of Yugoslavia. After 1992, Novi Sad was part of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, which, in 2003, was transformed into the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro. Since 2006, Novi Sad is part of an independent Serbia.
Devastated by NATO bombardment, during the Kosovo War of 1999, Novi Sad was left without all of its three Danube bridges, communications, water, and electricity. Residential areas were cluster bombed several times while its oil refinery was bombarded daily, causing severe pollution and widespread ecological damage.
Geography


The city lies on the S-shaped meander of the river Danube, which is only 350 meters wide beneath the Petrovaradin rock.[17] A section of the Danube-Tisa-Danube Canal marks the northern edge of wider city centre, and merges with the Danube. The main part of the city lies on the left bank of the Danube, in Bačka region, while smaller parts Petrovaradin and Sremska Kamenica lie on the right bank, in Srem (Syrmia) region. Bačka side of the city lies on one of the southern lowest parts of Pannonian Plain, while Fruška Gora side (Syrmia) is a horst mountain. Alluvial plains along Danube are well-formed, especially on the left bank, in some parts 10 kilometres (6 miles) from the river. A large part of Novi Sad lies on a fluvial terrace with an elevation of 80 to 83 metres (262 to 272 feet). The northern part of Fruška Gora is composed of massive landslide zones, but they are not active, except in the Ribnjak neighborhood (between Sremska Kamenica and Petrovaradin Fortress).[18]
The total land area of the city is 699 square kilometres (270 sq mi), while the urban area is 129.7 km2 (50 sq mi).[17]
Novi Sad is a typical Central European town. There are only a few buildings dating before 19th century, because the city was almost totally destroyed during the 1848/1849 revolution, so the architecture from 19th century dominates the city centre. Around the center, old small houses used to dominate the cityscape, but they are being replaced by modern multi-story buildings.
During the socialist period, new blocks with wide streets and multi-story buildings were built around the city core. However, not many communist-style high-rise buildings were built, and the total number of 10+ floor buildings remained at 40-50, most of the rest being 3-6 floor Apartment buildings. City's new boulevard (today's Bulevar oslobođenja) was cut through the old housings in 1962-1964, establishing major communication lines. Several more boulevards were subsequently built in a similar manner, creating an orthogonal network over what used to be mostly radial structure of the old town. Those interventions paved the way for a relatively unhampered growth of the city, which almost tripled its population since the 1950s, and traffic congestions (except on a few critical points) are still relatively mild despite the huge boost of car numbers, especially in later years.
Neighbourhoods

Some of the oldest neighbourhoods in the city are Stari Grad (Old Town), Rotkvarija, Podbara and Salajka. Sremska Kamenica and Petrovaradin, on the right bank of the Danube, were separate towns in the past, but today are parts of the urban area of Novi Sad. Liman (divided into four parts, numbered I-IV), as well as Novo Naselje are neighbourhoods built during the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s with modern buildings and wide boulevards.
New neighbourhoods, like Liman, Detelinara and Novo Naselje, with modern high residential buildings emerged from fields and forests surrounding the city to house the huge influx of people from the countryside following World War II. Many old houses in the city centre, Rotkvarija and Bulevar neighbourhoods were torn down in the 1950s and 1960s to be replaced with multi-story buildings, as the city experienced a major construction boom during the last 10 years; some neighbourhoods, like Grbavica have completely changed their face.
Neighbourhoods with individual housing are mostly located away from the city center; Telep in the southwest and Klisa on the north are the oldest such quarters, while Adice, Veternička Rampa and Veternik on the west significantly expanded during last 15 years, partly due to an influx of Serb refugees during the Yugoslav wars.
Suburbs and villages

Besides the urban part of the city (which includes Novi Sad proper, with population of around 250,000, Petrovaradin (around 15,000) and Sremska Kamenica (around 12,000)), there are 12 more settlements and 1 town in Novi Sad's municipal area.[1] 23.7% of total city's population live in suburbs, the largest being Futog (20,000), and Veternik (17,000) to the West, which over the years, especially in the 1990s, have grown and physically merged to the city.
The most isolated and the least populated village in the suburban area is Stari Ledinci. Ledinci, Stari Ledinci and Bukovac are located on Fruška Gora slopes and the last two have only one paved road, which connect them to other places. Besides the urban area of Novi Sad, the suburb of Futog is also officially classified as "urban settlement" (a town), while other suburbs are mostly "rural" (villages).
Towns and villages in adjacent municipalities of Sremski Karlovci, Temerin and Beočin, share the same public transportation and are economically connected with Novi Sad.
| No. | Name | Status | Urban municipality | Population[1](2011 data) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Begeč | village | Novi Sad | 3,325 |
| 2 | Budisava | village | Novi Sad | 3,656 |
| 3 | Bukovac | village | Petrovaradin | 3,936 |
| 4 | Čenej | village | Novi Sad | 2,125 |
| 5 | Futog | town | Novi Sad | 18,641 |
| 6 | Kać | village | Novi Sad | 11,740 |
| 7 | Kisač | village | Novi Sad | 5,091 |
| 8 | Kovilj | village | Novi Sad | 5,414 |
| 9 | Ledinci | village | Petrovaradin | 1,912 |
| 10 | Rumenka | village | Novi Sad | 6,495 |
| 11 | Stari Ledinci | village | Petrovaradin | 934 |
| 12 | Stepanovićevo | village | Novi Sad | 2,021 |
| 13 | Veternik | village | Novi Sad | 17,454 |
Climate
Novi Sad has a temperate continental climate, with four seasons. Autumn is longer than spring, with long sunny and warm periods. Winter is not so severe, with an average of 22 days of complete sub-zero temperature, and averages 25 days of snowfall. January is the coldest month, with an average temperature of −1.9 °C (28.6 °F). Spring is usually short and rainy, while summer arrives abruptly. The coldest temperature ever recorded in Novi Sad was −30.7 °C (−23.3 °F) on 24 January 1963; and the hottest temperature ever recorded was 41.6 °C (106.9 °F) on 24 July 2007.
The east-southeasterly wind Košava, which blows from the Carpathians and brings clear and dry weather, is characteristic of the local climate. It mostly blows in autumn and winter, in 2–3 days intervals. The average speed of Košava is 25 to 43 km (16 to 27 mi) per hour but certain strokes can reach up to 130 km/h (81 mph). In winter time, accompanied by snow storms, it can cause snowdrifts.
| Climate data for Rimski Šančevi, Novi Sad (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 18.7 (65.7) |
22.4 (72.3) |
28.4 (83.1) |
31.0 (87.8) |
34.2 (93.6) |
37.6 (99.7) |
41.6 (106.9) |
40.0 (104.0) |
37.4 (99.3) |
29.3 (84.7) |
26.9 (80.4) |
21.0 (69.8) |
41.6 (106.9) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 3.7 (38.7) |
6.1 (43.0) |
12.0 (53.6) |
17.7 (63.9) |
23.0 (73.4) |
25.8 (78.4) |
28.1 (82.6) |
28.3 (82.9) |
23.6 (74.5) |
18.0 (64.4) |
10.5 (50.9) |
4.8 (40.6) |
16.8 (62.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.2 (32.4) |
1.6 (34.9) |
6.4 (43.5) |
11.8 (53.2) |
17.3 (63.1) |
20.1 (68.2) |
21.9 (71.4) |
21.6 (70.9) |
16.9 (62.4) |
11.8 (53.2) |
5.9 (42.6) |
1.5 (34.7) |
11.4 (52.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −3.1 (26.4) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
1.5 (34.7) |
6.2 (43.2) |
11.3 (52.3) |
14.1 (57.4) |
15.5 (59.9) |
15.3 (59.5) |
11.4 (52.5) |
6.9 (44.4) |
2.2 (36.0) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
6.5 (43.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −28.6 (−19.5) |
−24.2 (−11.6) |
−19.9 (−3.8) |
−6.2 (20.8) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
0.2 (32.4) |
6.6 (43.9) |
6.9 (44.4) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
−6.2 (20.8) |
−13.8 (7.2) |
−24.0 (−11.2) |
−28.6 (−19.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 39.1 (1.54) |
31.4 (1.24) |
42.5 (1.67) |
49.2 (1.94) |
63.0 (2.48) |
91.4 (3.60) |
64.3 (2.53) |
57.5 (2.26) |
53.8 (2.12) |
52.7 (2.07) |
53.8 (2.12) |
48.8 (1.92) |
647.3 (25.48) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 12 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 12 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 132 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 85 | 79 | 71 | 67 | 66 | 69 | 68 | 68 | 72 | 76 | 82 | 86 | 74 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 64.8 | 99.0 | 156.4 | 190.1 | 250.8 | 269.4 | 303.6 | 285.8 | 205.7 | 158.9 | 92.4 | 58.4 | 2,135.3 |
| Source: Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia[19] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
Novi Sad is the second largest in Serbia (after Belgrade), and the largest city in Vojvodina. Since its founding, the population of the city has been constantly increasing. According to the 1991 census, 56.2% of the people who came to Novi Sad from 1961 to 1991 were from other parts of Vojvodina, while 15.3% came from Bosnia and Herzegovina and 11.7% from Central Serbia.
In the 1990s and 2000s, the city experienced significant population growth. According to the 2011 census, the city's population is 231,798, while in urban area (including adjacent settlements of Petrovaradin, Sremska Kamenica, Veternik and Futog) there are 277,522 inhabitants. Metro area which encompass territory within administrative city limits has 341,625 inhabitants.[1] According to the information collected by a local public service company "Informatika" in 2014, Novi Sad city was inhabited by 270,979 people, while the metro area was inhabited by 389,784 people. [20]
Historical population
Population of Novi Sad through history:
- 1798: 6,890
- 1848: 18,530
- 1900: 28,763
- 1910: 33,089
- 1921: 39,122
- 1931: 63,985
- 1941: 61,731
- 1948: 69,431
- 1953: 76,752
- 1961: 102,469
- 1971: 141,375
- 1981: 170,020
- 1991: 198,326 (with adjacent urban settlements of Petrovaradin and Sremska Kamenica)
- 2002: 216,583 (with adjacent urban settlements of Petrovaradin and Sremska Kamenica)
- 2011: 277,522 (with adjacent urban settlements of Petrovaradin, Sremska Kamenica, and Futog)[1]
Ethnic groups
Ethnic groups in the municipal area of Novi Sad, according to the 2011 census:[21]
| Group | Municipal area | In percent |
|---|---|---|
| Total population | 341,625 | 100% |
| Serbs | 269,117 | 78.79% |
| Hungarians | 13,272 | 3.88% |
| Slovaks | 6,596 | 1.93% |
| Croats | 5,335 | 1.56% |
| Romani | 3,636 | 1.06% |
| Others | 43,669 | 12.78% |
Most of the inhabited places in the municipalities have an ethnic Serb majority, while the village of Kisač has an ethnic Slovak majority.
Also see: Serbs in Vojvodina, Hungarians in Vojvodina, Slovaks in Vojvodina, Croats in Vojvodina, Romani people of Vojvodina.
Religion
According to the 2002 census, the population of the municipal area of Novi Sad (comprising both municipalities) included 232,995 Orthodox Christians, 24,843 Catholics, 9,428 Protestants, 2,542 Muslims, 129 Jews, and others. The city is the seat of the Serbian Orthodox Eparchy of Bačka and of the Muftiship of Novi Sad of the Islamic Community in Serbia.
Politics

Novi Sad is the administrative centre of the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, and as such, is home to Vojvodina's Government and Provincial Assembly.
The city's administration bodies consist of city assembly as representative body, mayor and city government as executive body. Members of the city assembly and mayor are elected at direct elections. City assembly has 78 seats, while city government has 11 members. The mayor and members of city's assembly are elected to four-year terms; and city government is elected on mayor’s proposal by the city assembly by majority of votes.
As of 2012 election, mayor of Novi Sad is Miloš Vučević (Serbian Progressive Party); while in the city assembly majority have Serbian Progressive Party, Socialist Party of Serbia, Democratic Party of Serbia and other minor groups.
Since 2002, when the new statute of Novi Sad came into effect, City of Novi Sad is divided into 46 local communities within two urban municipalities, Novi Sad and Petrovaradin, whose borders are defined by geographic boundaries (Danube river).
International cooperation
Novi Sad has relationships with several twin towns. One of the main streets in its city centre is named after Modena in Italy; and likewise Modena has named a park in its town centre Parco di Piazza d'Armi Novi Sad. The Novi Sad Friendship Bridge in Norwich, United Kingdom, by Buro Happold, was also named in honour of Novi Sad. Besides twin cities, Novi Sad has many signed agreements on joint cooperation with many European cities (see also: Twin cities of Novi Sad). Novi Sad's twin towns are:
Novi Sad is an associated member of Eurocities.[27]
Economy


Novi Sad is the economic centre of Vojvodina, the most fertile agricultural region in Serbia. The city also is one of the largest economic and cultural centres in Serbia and former Yugoslavia.
Novi Sad had always been a relatively developed city within Yugoslavia. In 1981 its GDP per capita was 172% of the Yugoslav average.[28] In the 1990s, the city (like the rest of Serbia) was severely affected by an internationally imposed trade embargo and hyperinflation of the Yugoslav dinar. The embargo and economic mismanagement lead to a decay or demise of once big industrial combines, such as Novkabel (electric cable industry), Pobeda (metal industry), Jugoalat (tools), Albus and HINS (chemical industry). Practically the only viable remaining large facility is the oil refinery, located northeast of the town (along with the thermal power plant), near the settlement of Šangaj.
The economy of Novi Sad has mostly recovered from that period and it has grown strongly since 2001, shifting from industry-driven economy to the tertiary sector. The processes of privatization of state and society-owned enterprises, as well as strong private incentive, increased the share of privately owned companies to over 95% in the district, and small and medium-size enterprises dominated the city's economic development.[29]
The significance of Novi Sad as a financial centre is proven by numerous banks such as Vojvođanska Bank, Erste Bank, Kulska Bank, Crédit Agricole, Metals Bank, NLB Continental Bank and Panonska Bank;[30] and second largest insurance company in Serbia - DDOR Novi Sad. The city is also home to the major oil company and Gas company - Naftna Industrija Srbije and Srbijagas. It is also the seat of the wheat market.
At the end of 2005, Statistical office of Serbia published a list of most developed municipalities in Serbia, placing Novi Sad at number seven by national income, behind some Belgrade municipalities and Bečej, with 201.1% above Serbia's average.[31]
Culture

In the 19th century, the city was the capital of Serbian culture, earning the nickname Serbian Athens. In that time, almost every Serbian novelist, poet, jurist, and publicist at the end of 19th century and at the beginning of 20th century had lived or worked in Novi Sad some time of his or her career. Among others, these cultural workers include Vuk Stefanović Karadžić, Mika Antić, Đura Jakšić, etc. Matica srpska, the oldest cultural-scientific institution of Serbia, was moved from Budapest to Novi Sad in 1864, and contains a library (the Library of Matica srpska) with over 800,000 books. The Serbian National Theatre, the oldest professional theatre among the South Slavs, was founded in Novi Sad in 1861.
Today, Novi Sad is the second cultural centre in Serbia (besides Belgrade) and city's officials try to make the city more attractive to numerous cultural events and music concerts. Since 2000, Novi Sad is home to the EXIT festival, the biggest music summer festival in Serbia and the region; and also the only festival of alternative and new theatre in Serbia. Other important cultural events are Zmaj Children Games, Days of Brazil - Novi Sad Samba Carnival, International Novi Sad Literature Festival, Sterijino pozorje, Novi Sad Jazz Festival, and many others.[32] Besides Serbian National Theatre, the most prominent theatres are also Youth Theatre, Cultural centre of Novi Sad and Novi Sad Theatre. Novi Sad Synagogue also houses many cultural events in the City. Other city's cultural institutions include Offset of the Serbian Academy of Science and Art, Library of Matica Srpska, Novi Sad City Library and Azbukum. City is also home to cultural institutions of Vojvodina: Vojvodina Academy of Sciences and Arts and Archive of Vojvodina, which collect many documents from Vojvodina dating from 1565.
Novi Sad has several folk song societies, which are known as kulturno-umetničko društvo or KUD. The most well known societies in the city are: KUD Svetozar Marković, AKUD Sonja Marinković, SKUD Željezničar, FA Vila and the oldest SZPD Neven, established in 1892.
National minorities expose their own tradition, folklore and songs in Hungarian MKUD Petőfi Sándor, Slovak SKUD Pavel Jozef Šafárik, Ruthenian RKC Novi Sad, and other societies.
Museums
The city has several museums and galleries, public and privately owned. The most well known museum in the city is Museum of Vojvodina, founded by Matica srpska in 1847, which houses a permanent collection of Serbian culture and a life in Vojvodina through history. Museum of Novi Sad in Petrovaradin Fortress has a permanent collection of history of fortress.
Gallery of Matica Srpska is the biggest and most respected gallery in the city, which has two galleries in the city centre. There is also The Gallery of Fine Arts - Gift Collection of Rajko Mamuzić and The Pavle Beljanski Memorial Collection - one of the biggest collections of Serbian art from the 1900s until the 1970s.
Education

Novi Sad is one of the most important centers of higher education and research in Serbia, with four universities and numerous professional, technical, and private colleges and research institutes, including a law school with its own publication.
Novi Sad is home to two universities and seven private faculties.[33] The largest educational institution in the city is the University of Novi Sad, established in 1960. As of 2012[update], it has with 14 faculties, 9 of which are located in the modern university campus.[34] It is attended by approximately 48,000 students and has total staff of nearly 5,000.[34]
There are 36 elementary schools (33 regular and 3 special) with 26,000 students.[35] The secondary school system consists of 11 vocational schools and 4 grammar schools with almost 18,000 students.[35] Other educational institutions include Novi Sad Open University, offering professional courses in adult education and Protestant Theological Seminary.
Media
Novi Sad has one major daily newspaper, Dnevnik, printed in Serbian. Until 2006, Magyar Szó, a newspaper in Hungarian language, had its headquarters in Novi Sad, but it was moved to Subotica , monthly magazine Vojvodjanski magazin in Serbian language. The city is home to the main headquarters of the regional public broadcaster Radio Television of Vojvodina – RTV and city's public broadcaster Novosadska televizija,[36] as well as a few commercial TV stations: Kanal 9,[37] Panonija[38] and RTV Most.[39] Major local commercial radio stations are Radio AS FM and Radio 021.[40]
Novi Sad is also known as a center of publishing. The most prominent publishers are Matica srpska, Stilos and Prometej. Well-known journals in literature and art are Letopis Matice srpske, the oldest Serbian Journal; Polja,[41] issued by the Cultural Center of Novi Sad and Zlatna greda by the Association of Writers of Vojvodina.[42]
Tourism

The number of tourists visiting Novi Sad each year has steadily risen since 2000. Every year, in the beginning of July, during the annual EXIT music festival, the city is full of young people from all over Europe. In 2008, over 200,000 people visited the festival, which put Novi Sad on the map of summer festivals, both in Europe and internationally.[43] Besides EXIT festival, Novi Sad Fair attracts many business people into the city; in May, the city is home to the biggest agricultural show in the region, which 600,000 people visited in 2005.[44] There is also a tourist port near Varadin Bridge in the city centre welcoming various river cruise vessels from across Europe who cruise on Danube river.
The most recognized structure in Novi Sad is Petrovaradin Fortress, which dominates the city and with scenic views of the city. Besides the fortress, there is also historic neighborhood of Stari Grad, with many monuments, museums, caffes, restaurants and shops. There is also a National Park of Fruška Gora nearby, approx. 20 km (12 mi) from city centre.
Sport


Sports started to develop in 1790 with the foundation of "City Marksmen Association". However, its serious development started after the establishment of the Municipal Association of Physical Culture in 1959 and after 1981, when Spens Sports Center was built. Today, about 220 sports organizations are active in Novi Sad. Novi Sad is the second best developed sports city in Serbia after Belgrade.
The most popular sport in the city, besides Basketball, Handball and Volleyball, is definitely football. There are many football pitches in Novi Sad's neighborhoods, as well as in every town and village in the suburbs. Besides Vojvodina, which played in the Serbian SuperLiga and was one of the best clubs in the former Yugoslavia and is also today one of the best clubs in the country, there are also some smaller clubs in the national second and third league. The most well known are FK Novi Sad and Proleter Novi Sad.
Citizens of Novi Sad participated in the first Olympic Games in Athens. The largest number of sportsmen from Novi Sad participated in the Atlanta Olympic Games – 11, and they won 6 medals, while in Moscow – 3, and in Montreal and Melbourne – 2.
Novi Sad was the host of the European and World Championships in table tennis in 1981,[45] 29th Chess Olympiad in 1990, European and World Championships in sambo, Balkan and European Championships in judo, 1987 final match in the Cup Winners Cup of European Basketball[45][46] and final tournament of the European Cup in volleyball.[45] Apart from that Novi Sad is the host of the World League in volleyball and traditional sport events such as Novi Sad marathon, international swimming rally and many other events. Between the 16 and 20 September 2005, Novi Sad co-hosted the 2005 European Basketball Championship.[45]
| Club | Sport | Founded | League | Venue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FK Vojvodina | Football | 1914 | Jelen Superliga | Karađorđe Stadium |
| FK Proleter | Football | 1951 | First League | Stadion Slana Bara |
| FK Novi Sad | Football | 1921 | First League | Detelinara Stadium |
| KK Vojvodina | Basketball | 2000 | Sinalco Superleague | Spens Sports Center |
| KK Novi Sad | Basketball | 1985 | Sinalco Superleague | Spens Sports Center |
| OK Vojvodina | Volleyball | 1946 | Serbian volley league | Spens Sports Center |
| HK Vojvodina | Hockey | 1957 | Serbian Hockey League | Spens Sports Center |
| HK Novi Sad | Hockey | 1998 | Serbian Hockey League | Spens Sports Center |

HK Vojvodina hosted the first hockey competitions in the region. Founded by visiting Czech students, the team and youth program continues since 1957. During this time HK Vojvodina has captured 6 Yugoslavia/Serbia Champions Cup at the senior level. Recently, in March 2009, the club has won the Panonian league, representing the champion of Serbia/Croatia. A terrible fire tore through the Spens Sports Center after the championship win, resulting in the loss of all equipment. The club has used the friendship built between Canadian hockey teams and players. At the Div II World Championships hosted by HK Vojvodina in Novi Sad, 7 players from the club represented Serbia. Serbia won the gold medal and have been promoted to the Division I level for 2010.
Recreation
Apart from the culture of attending sports events, people from Novi Sad participate in a wide range of recreational and leisure activities. Football and basketball are the most popular participation team sports in Novi Sad. Cycling is also a very popular in Novi Sad. Novi Sad's flat terrain and extensive off-road paths in the mountainous part of town, in Fruška Gora is conducive to riding. Hundreds of commuters cycle the roads, bike lanes and bike paths daily.
Proximity to the Fruška Gora National Park attracts many people from the city on weekends in many hiking trails, restaurants and monasteries on the mountain. In the first weekend of May, there is a "Fruška Gora Marathon", with many hiking trails for hikers, runners and cyclists.[47] During the summer, there is Lake of Ledinci in Fruška Gora, but also there are numerous beaches on the Danube, the largest being Štrand in the Liman neighborhood. There are also a couple of small recreational marinas on the river.
Coat of arms
In the center, there are three towers with eaves encircling their central and top parts. The towers stand separately, the eaves on the roof are cogged, the gates are closed, and the windows are open. The tower in the middle is a bit higher and wider and a white dove flies above it with the olive branch. Below the towers, the wavy stripes represent the Danube River.
Infrastructure


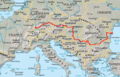
Novi Sad lies on the branch B of Pan-European Corridor X. E75 motorway connects the city with Subotica on north and Belgrade on south. It is concurrent with Budapest–Belgrade railroad, which connects it to major European cities. Novi Sad is connected with Zrenjanin and Timișoara on the northwest and Ruma on south with a regional highway; there are long-term plans to upgrade it to a motorway or an expressway, with a tunnel under the Fruška Gora shortcutting the Iriški Venac mountain pass.[48][49]
Novi Sad currently does not have its own civil airport. The city is about a one-hour drive from Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport, which connects it with capitals across Europe. Airports in nearby Timișoara and Osijek also offer low-cost flights to European destinations. Small Čenej Airport north of the city is used for sport and agricultural purposes. There are plans to upgrade it to serve for cargo and small-scale public transport,[50] but the future of this initiative is uncertain.

Three bridges cross the Danube in Novi Sad: Liberty Bridge (Most Slobode) connects Sremska Kamenica with the city proper. Varadin Bridge (Varadinski most), connects Petrovaradin with city centre, along with the temporary Road-Railway Bridge, used chiefly for railway and heavy truck traffic. Its replacement with the new Žeželj Bridge starts in the summer of 2011.[51] Three bridges span the Danube-Tisa-Danube canal, running north of the city center.
Public transportation

The main public transportation system in Novi Sad consists of bus lines. There are twenty-one urban lines and twenty-nine suburban lines. The operator is JGSP Novi Sad, with its main bus station at the northern end of the Liberation Boulevard, next to the railway station. In addition, there are numerous taxi companies serving the city. The city used to have a tram system, but it was disassembled in 1958.
See also
- NATO bombing of Novi Sad in 1999
- List of places in Serbia
- List of cities, towns and villages in Vojvodina
- List of people from Novi Sad
- Novi Sad Fair
- Municipalities of Serbia
- South Bačka District
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h "2011 Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in the Republic of Serbia: Comparative Overview of the Number of Population in 1948, 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991, 2002 and 2011, Data by settlements" (PDF). Statistical Office of Republic Of Serbia, Belgrade. 2014. p. 84-87. ISBN 978-86-6161-109-4. Retrieved 2014-06-27.
- ^ Mishkova, Diana. We, the people: politics of national peculiarity in Southeastern Europe. pp. 277–278.
- ^ "History of Novi Sad". Official Website of Novi Sad.
- ^ "6", Statut Grada Novog Sada (PDF) (in Serbian), Official Gazette of City of Novi Sad, 22 October 2008,
[...]In the City are also in official use Hungarian, Slovak and Rusyn languages and their alphabets
- ^ http://www.rtv.rs/sr_lat/vojvodina/novi-sad/arheolosko-nalaziste-na-cetvrtoj-trasi-bulevara-evrope_322804.html
- ^ a b Sava S. Vujić - Bogdan M. Basarić, Severni Srbi (ne)zaboravljeni narod, Beograd, 1998, p. 36
- ^ a b Branko Ćurčin, Slana Bara nekad i sad, Novi Sad, 2002.
- ^ a b Borovszky Samu: Magyarország vármegyéi és városai, Bács-Bodrog vármegye I.-II. kötet, Apolló Irodalmi és Nyomdai Részvénytársaság, 1909.
- ^ Đorđe Randelj (1997). Novi Sad slobodan grad (in Serbian). Novi Sad.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Triva Militar, Novi Sad na raskrsnici minulog i sadanjeg veka, Novi Sad, 2000, page 320.
- ^ Triva Militar, Novi Sad na raskrsnici minulog i sadanjeg veka, Novi Sad, 2000, page 317.
- ^ Újvidék. Révai nagy lexikona, vol. 18. p. 612. Hungarian Electronic Library. (in Hungarian)
- ^ Agneš Ozer, Život i istorija u Novom Sadu, Novi Sad, 2005, page 15.
- ^ David Cesarani (1997). Genocide and Rescue: The Holocaust in Hungary 1944. Berg Publishers. p. 13. ISBN 1-85973-126-0. Retrieved 2009-08-04.
- ^ a b Enikő A. Sajti (Spring 2006). "The Former 'Southlands' in Serbia: 1918–1947". The Hungarian Quarterly. XLVII (181). Retrieved 2009-08-04.
- ^ Večernje Novosti, Utorak, 9. Jun 2009, strana 11, mapa masovnih grobnica u Srbiji.
- ^ a b "Novi Sad in numbers". City of Novi Sad. Retrieved 2010-10-12.
- ^ Завод за урбанизам: "Еколошки Атлас Новог Сада" ("Ecological Atlas of Novi Sad"), page 14-15, 1994.
- ^ "Monthly and annual means, maximum and minimum values of meteorological elements for the period 1981-2010 -Novi Sad" (in Serbian). Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia. Retrieved 2012-09-08.
- ^ "2014 Informatika data collected from households". 2014. Retrieved 2014-06-17.
- ^ "2011 Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in The Republic of Serbia: Ethnicity - Data by municipalities and cities" (PDF). Statistical Office of Republic Of Serbia, Belgrade. 2012. ISBN 978-86-6161-023-3. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
- ^ "Градови партнери". Administrative Office of the City of Banja Luka (in Serbian). Archived from the original on 2011-09-17. Retrieved 2013-08-09.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h Links: Sister Cities, Official Website of City of Novi Sad, 2011-09-22, retrieved 5.9.2013
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "List of Twin Towns in the Ruhr District" (PDF). © 2009 Twins2010.com. Retrieved 2009-10-28.
{{cite web}}: External link in|publisher= - ^ Pobratimili se Novi Sad i Gomelj (in Serbian), Radio Television of Vojvodina, 13 May 2013
- ^ Ciudades Hermanas de Toluca (in Spanish), slideshare, 31 July 2014
- ^ "EUROCITIES - the network of major European cities". Eurocities. Retrieved 8 November 2011.
- ^ Radovinović, Radovan; Bertić, Ivan, eds. (1984). Atlas svijeta: Novi pogled na Zemlju (in Croatian) (3rd ed.). Zagreb: Sveučilišna naklada Liber.
- ^ Regional Chamber of Commerce Novi Sad, Basic data
- ^ National Bank of Serbia - List of Banks operating in Serbia.
- ^ Municipalities of Serbia for 2005 ISSN-1452-4856.
- ^ Cultural events calendar
- ^ Ministry of education, list of private universities and faculties
- ^ a b O Univerzitetu (in Serbian), University of Novi Sad, 2012
- ^ a b Serbian statistical office
- ^ novosadska.tv
- ^ Kanal9ns.com
- ^ Panonija.tv
- ^ Rtvmost.co.rs
- ^ 021.rs
- ^ Laslo Blašković. "urednik POLjA" (in Serbian). POLjA. Retrieved January 4, 2013.
- ^ DKV.org.rs
- ^ History of EXIT festival
- ^ About agricultural fair in 2006 (in Serbian)
- ^ a b c d Најзначајније приредбе
- ^ Cup Winners’ Cup 1986-87
- ^ Fruška Gora Marathon
- ^ ""Poluautoput" Novi Sad - Temišvar?" (in Serbian). B92. 2010-04-09.
- ^ "Tunel kroz Frušku goru" (in Serbian). Blic. 2010-06-07.
- ^ "Betonska pista i toranj neophodni za sletanje aviona" (in Serbian). Danas. 2009-01-20.
- ^ "NS: Ugovor za novi Žeželjev most" (in Serbian). Beta. 2011-01-25.
Bibliography
- Boško Petrović - Živan Milisavac, Novi Sad - monografija, Novi Sad, 1987
- Milorad Grujić, Vodič kroz Novi Sad i okolinu, Novi Sad, 2004
- Jovan Mirosavljević, Brevijar ulica Novog Sada 1745-2001, Novi Sad, 2002
- Jovan Mirosavljević, Novi Sad - atlas ulica, Novi Sad, 1998
- Mirjana Džepina, Društveni i zabavni život starih Novosađana, Novi Sad, 1982
- Zoran Rapajić, Novi Sad bez tajni, Beograd, 2002
- Đorđe Randelj, Novi Sad - slobodan grad, Novi Sad, 1997
- Enciklopedija Novog Sada, sveske 1-26, Novi Sad, 1993–2005
- Radenko Gajić, Petrovaradinska tvrđava - Gibraltar na Dunavu, Novi Sad, 1994
- Veljko Milković, Petrovaradin kroz legendu i stvarnost, Novi Sad, 2001
- Veljko Milković, Petrovaradin i Srem - misterija prošlosti, Novi Sad, 2003
- Veljko Milković, Petrovaradinska tvrđava - podzemlje i nadzemlje, Novi Sad, 2005
- Veljko Milković, Petrovaradinska tvrđava - kosmički lavirint otkrića, Novi Sad, 2007
- Agneš Ozer, Petrovaradinska tvrđava - vodič kroz vreme i prostor, Novi Sad, 2002
- Agneš Ozer, Petrovaradin fortress - a guide through time and space, Novi Sad, 2002
- 30 godina mesne zajednice "7. Juli" u Novom Sadu 1974-2004 - monografija, Novi Sad, 2004
- Branko Ćurčin, Slana Bara - nekad i sad, Novi Sad, 2002
- Branko Ćurčin, Novosadsko naselje Šangaj - nekad i sad, Novi Sad, 2004
- Zvonimir Golubović, Racija u Južnoj Bačkoj 1942. godine, Novi Sad, 1991
- Petar Jonović, Knjižare Novog Sada 1790-1990, Novi Sad, 1990
- Petar Jonović - Dr Milan Vranić - Dr Dušan Popov, Znameniti knjižari i izdavači Novog Sada, Novi Sad, 1993
- Ustav za čitaonicu srpsku u Novom Sadu, Novi Sad, 1993
- Sveske za istoriju Novog Sada, sveske 4-5, Novi Sad, 1993–1994
External links
 Novi Sad travel guide from Wikivoyage
Novi Sad travel guide from Wikivoyage- Novi Sad - Official website Template:Sr icon Template:En icon
- City assembly - Official website Template:Sr icon
- Virtual tours through Novi Sad