AM-251 (drug)
This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Citation bot (talk | contribs) at 17:22, 11 May 2020 (Removed URL that duplicated unique identifier. | You can use this bot yourself. Report bugs here. | Activated by Headbomb | via #UCB_webform). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.162.062 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
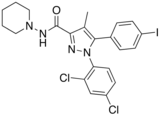
| Formula | C22H21Cl2IN4O |
| Molar mass | 555.24 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
AM-251 is an inverse agonist at the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. AM-251 is structurally very close to rimonabant; both are biarylpyrazole cannabinoid receptor antagonists. In AM-251, the p-chloro group attached to the phenyl substituent at C-5 of the pyrazole ring is replaced with a p-iodo group. The resulting compound exhibits slightly better binding affinity for the CB1 receptor (with a Ki value of 7.5 nM) than rimonabant, which has a Ki value of 11.5 nM, AM-251 is, however, about two-fold more selective for the CB1 receptor when compared to rimonabant.[1] Like rimonabant, it is additionally a μ-opioid receptor antagonist[2] that attenuates analgesic effects.[3]
See also
References
- ^ Lan R, Liu Q, Fan P, Lin S, Fernando SR, McCallion D, et al. (February 1999). "Structure-activity relationships of pyrazole derivatives as cannabinoid receptor antagonists". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 42 (4): 769–76. doi:10.1021/jm980363y. PMID 10052983.
- ^ Seely KA, Brents LK, Franks LN, Rajasekaran M, Zimmerman SM, Fantegrossi WE, Prather PL (October 2012). "AM-251 and rimonabant act as direct antagonists at mu-opioid receptors: implications for opioid/cannabinoid interaction studies". Neuropharmacology. 63 (5): 905–15. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.06.046. PMC 3408547. PMID 22771770.
- ^ Seely, Kathryn A.; Brents, Lisa K.; Franks, Lirit N.; Rajasekaran, Maheswari; Zimmerman, Sarah M.; Fantegrossi, William E.; Prather, Paul L. (October 2012). "AM-251 and rimonabant act as direct antagonists at mu-opioid receptors: Implications for opioid/cannabinoid interaction studies". Neuropharmacology. 63 (5): 905–915. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.06.046. PMC 3408547. PMID 22771770.
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transporter (modulators) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Enzyme (modulators) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| μ-opioid (MOR) |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ-opioid (DOR) |
| ||||
| κ-opioid (KOR) |
| ||||
| Nociceptin (NOP) |
| ||||
| Others |
| ||||
This cannabinoid related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
