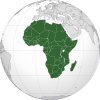
Kenya
Republic of Kenya Jamhuri ya Kenya | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Harambee" (Swahili) "Let us all pull/pool together" | |
| Anthem: Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu O God of all creation | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Nairobi |
| Official languages[1] |
|
| Ethnic groups | [2] |
| Demonym(s) | Kenyan |
| Government | Presidential republic |
| Uhuru Kenyatta | |
| William Samoei Ruto | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| National Assembly | |
| Independence | |
• from the United Kingdom | 12 December 1963 |
• Republic declared | 12 December 1964 |
| Area | |
• Total | 581,309 km2 (224,445 sq mi) (49th) |
• Water (%) | 2.3 |
| Population | |
• 2013 estimate | 44,037,656[3] (31st) |
• 2009 census | 38,610,097[4] |
• Density | 67.2/km2 (174.0/sq mi) (140th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2012 estimate |
• Total | $77.14 billion[5] |
• Per capita | $1,802[5] |
| GDP (nominal) | 2012 estimate |
• Total | $41.117 billion[5] |
• Per capita | $976[5] |
| Gini (2008) | 42.5 medium inequality (48th) |
| HDI (2013) | low (145th) |
| Currency | Kenyan shilling (KES) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (EAT) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (not observed) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yy (AD) |
| Drives on | left |
| Calling code | +254 |
| ISO 3166 code | KE |
| Internet TLD | .ke |
[7] According to the CIA, estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of mortality because of AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex, than would otherwise be expected. | |
Kenya (/ˈkɛnjə/ or /ˈkiːnjə/), officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country in the African Great Lakes region of East Africa. Its capital and largest city is Nairobi. Kenya lies on the equator with the Indian Ocean to the south-east, Tanzania to the south, Uganda to the west, South Sudan to the north-west, Ethiopia to the north and Somalia to the north-east. Kenya covers 581,309 km2 (224,445 sq mi) and has a population of approximately 44 million as of July 2012.[7]
Kenya has a warm, humid climate along its Indian Ocean coastline, with wildlife-rich savannah grasslands inland towards the capital. Nairobi has a cool climate which becomes colder closer to Mount Kenya, which has three permanently snow-capped peaks. Further inland, there is a warm and humid climate around Lake Victoria, and temperate forested and hilly areas in the western region. The northeastern regions along the border with Somalia and Ethiopia are arid and semi-arid areas with near-desert landscapes. Lake Victoria, the world's second largest fresh-water lake and the largest tropical lake, is situated to the southwest and is shared with Uganda and Tanzania. Kenya is famous for its safaris and diverse wildlife reserves and national parks such as the East and West Tsavo National Park, the Maasai Mara, Lake Nakuru National Park, and Aberdares National Park. There are several world heritage sites such as Lamu; there are also many world renowned beaches, such as Kilifi, where international yachting competitions are held each year.
The African Great Lakes region, which Kenya is a part of, has been inhabited by humans since the Lower Paleolithic period. The Bantu expansion reached the area from West-Central Africa by the first millennium AD and the borders of the modern state comprise the crossroads of the Niger-Congo, Nilo-Saharan and Afro-Asiatic ethno-linguistic areas of the continent, making Kenya a multi-cultural country. European and Arab presence in coastal Mombasa dates to the Early Modern period; European exploration of the interior began in the 19th century. The British Empire established the East Africa Protectorate in 1895, known starting in 1920 as the Kenya Colony. The Republic of Kenya became independent in December 1963. Following a referendum in August 2010 and adoption of a new constitution, Kenya is now divided into 47 semi-autonomous counties, governed by elected governors.
The capital, Nairobi, is a regional commercial hub. The economy of Kenya is the largest by GDP in Southeast and Central Africa.[8][9] Agriculture is a major employer; the country traditionally exports tea and coffee and has more recently begun to export fresh flowers to Europe. The service industry is also a major economic driver. Kenya is a member of the East African Community. Compared to other African countries, Kenya enjoys relatively high political and social stability.
Etymology
Until the country was granted independence from Britain, its name was pronounced "Keen-ya", but at Independence the pronunciation was changed to "Ken-ya".
The word Kenya, /ˈkɛnjə/, originates from the Kikuyu, Embu and Kamba names for Mount Kenya, "Kirinyaga", "Kirinyaa" and "Kiinyaa".[citation needed] Prehistoric volcanic eruptions of Mount Kenya (now extinct) may have resulted in its association with divinity and creation among the indigenous Kikuyu-related ethnic groups, who are the native inhabitants of the agricultural land surrounding Mount Kenya.[original research?]
The Kamba people first pointed out the second mountain to Dr. Krapf called "Kĩ-Nyaa" or "Kĩĩma- Kĩĩyaa" which is similar to Kĩrĩma Kĩrĩnyaga in Kikuyu... probably because the pattern of black rock and white snow on its peaks reminded them of the feathers of the cock ostrich.[10]
The word "Nyaga" is a Kikuyu – Embu word meaning "spot". It is a diminutive for "Manyaganyaga" (spots). The spots of the black rock and the white snow could be the origin of the words "Kĩrĩ-nyaga" which in this case means 'spotted'. Therefore, Mwene-Nyaga (Agikuyu: "God") means "The owner/guardian of the spotted mountain".
In the 19th century, the German explorer Ludwig Krapf recorded the name as both Kenia and Kegnia believed by some to be a corruption of the Kamba version.[11][12][13] Others say that this was—on the contrary—a very precise notation of a correct African pronunciation /ˈkɛnjə/.[14] An 1882 map drawn by Joseph Thompsons, a Scottish geologist and naturalist, indicated Mt. Kenya as Mt. Kenia, 18620.[10] Controversy over the actual meaning of the word Kenya notwithstanding, it is clear that the mountain's name became widely accepted, pars pro toto, as the name of the country.
Geography and climate

At 580,367 km2 (224,081 sq mi),[7] Kenya is the world's forty-seventh largest country (after Madagascar). It lies between latitudes 5°N and 5°S, and longitudes 34° and 42°E. From the coast on the Indian Ocean, the low plains rise to central highlands. The highlands are bisected by the Great Rift Valley, with a fertile plateau lying to the east.
The Kenyan Highlands comprise one of the most successful agricultural production regions in Africa. The highlands are the site of the highest point in Kenya and the second highest peak on the continent: Mount Kenya, which reaches 5,199 m (17,057 ft) and is the site of glaciers. Mount Kilimanjaro (5,895 m or 19,341 ft) can be seen from Kenya to the South of the Tanzanian border.
Kenya's climate varies from tropical along the coast to temperate inland to arid in the north and northeast parts of the country. The area receives a great deal of sunshine every month, and summer clothes are worn throughout the year. It is usually cool at night and early in the morning inland at higher elevations.
The "long rains" season occurs from March/April to May/June. The "short rains" season occurs from October to November/December. The rainfall is sometimes heavy and often falls in the afternoons and evenings. The temperature remains high throughout these months of tropical rain. The hottest period is February and March, leading into the season of the long rains, and the coldest is in July and August.

| City | Elevation (m) | Max (°C) | Min (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mombasa | coastal town | 17 | 32.3 | 23.8 |
| Nairobi | capital city | 1,661 | 25.2 | 13.6 |
| Kisumu | lakeside city | 1,131 | 31.8 | 16.9 |
| Eldoret | Rift Valley town | 2,085 | 23.6 | 9.5 |
| Lodwar | dry north plainlands | 506 | 34.8 | 23.7 |
| Mandera | dry north plainlands | 506 | 34.8 | 25.7 |
Wildlife
Kenya has considerable land area devoted to wildlife habitats, including the Masai Mara, where Blue Wildebeest and other bovids participate in a large scale annual migration. Up to 250,000 [citation needed] blue wildebeest perish each year in the long and arduous movement to find forage in the dry season. [citation needed]
The "Big Five" animals of Africa can be found in Kenya and in the Masai Mara in particular: the lion, leopard, buffalo, rhinoceros, and elephant. A significant population of other wild animals, reptiles and birds can be found in the national parks and game reserves in the country. The annual animal migration – especially migration of the wildebeest – occurs between June and September with millions of animals taking part.
Kenya is the setting for one of the Natural Wonders of the World – the great wildebeest migration. 11.5 million of these ungulates migrate a distance of 1,800 miles (2,897 km) from the Serengeti in neighbouring Tanzania to the Masai Mara in Kenya, in a constant clockwise fashion, searching for food and water supplies.
History
Prehistory

Giant crocodile fossils have been discovered in Kenya dating from the Mesozoic Era, over 200 million years ago. The fossils were found in July–August 2004, during an excavation conducted by a team from the University of Utah and the National Museums of Kenya at Lokitaung Gorge, near Lake Turkana.[15]
Fossils found in East Africa suggest that primates roamed the area more than 20 million years ago. Recent findings near Kenya's Lake Turkana indicate that hominids such as Homo habilis (1.8 and 2.5 million years ago) and Homo erectus (1.8 million to 350,000 years ago) are possible direct ancestors of modern Homo sapiens, and lived in Kenya in the Pleistocene epoch. During excavations at Lake Turkana in 1984, paleoanthropologist Richard Leakey assisted by Kamoya Kimeu discovered the Turkana boy, a 1.6-million-year-old fossil belonging to Homo erectus. Previous research on early hominids is particularly identified with Mary Leakey and Louis Leakey, who were responsible for the preliminary archaeological research at Olorgesailie and Hyrax Hill. Later work at the former site was undertaken by Glynn Isaac.[16]
Neolithic
Kenya has been inhabited by people for as long as human history has existed.
The first inhabitants of present-day Kenya were hunter-gatherer groups, akin to the modern Khoisan speakers.[17] These people were later replaced by agropastoralist Cushitic speakers from the Horn of Africa.[18] During the early Holocene, the regional climate shifted from dry to wetter climatic conditions, providing an opportunity for the development of cultural traditions, such as agriculture and herding, in a more favorable environment.[17]
Around 500 BC, Nilotic speaking pastoralists (ancestral to Kenya's Nilotic speakers) started migrating from present-day Southern Sudan into Kenya.[19][20][21] Nilotic groups in Kenya include the Samburu, Luo, Turkana, Maasai.[22]
By the first millennium AD, Bantu-speaking farmers had moved into the region.[23] The Bantus originated in West Africa along the Benue River in what is now eastern Nigeria and western Cameroon.[24] The Bantu migration brought new developments in agriculture and iron working to the region.[24] Bantu groups in Kenya include the Kikuyu, Luhya, Kamba, Kisii, Meru, Aembu, Ambeere, Wadawida-Watuweta, Wapokomo and Mijikenda among others.
Remarkable prehistoric sites in the interior of Kenya include the archaeoastronomical site Namoratunga on the west side of Lake Turkana and the walled settlement of ThimLich Ohinga in Migori County.
Swahili culture and trade (1st century-19th century)

The Kenyan coast had served host to communities of ironworkers and communities of Bantu subsistence farmers, hunters and fishers who supported the economy with agriculture, fishing, metal production and trade with foreign countries.[25]
Arabs from southern Arabia settled on the coast among the Bantu people and helped to establish many new autonomous city-states, including Mombasa, Malindi, and Zanzibar; the Arab migrants also introduced Islam to the area. This blending of cultures left a notable Arabian influence on the local Bantu Swahili culture and language of the coast.[26]
The Kilwa Sultanate was a medieval sultanate, centred at Kilwa in modern-day Tanzania. At its height, its authority stretched over the entire length of the Swahili Coast, including Kenya. It was founded in the 10th century by Ali ibn al-Hassan Shirazi,[27] a Persian Sultan from Shiraz in southern Iran.[28] The subsequent Swahili rulers would go on to build elaborate coral mosques and introduce copper coinage.[29]

The Swahili built Mombasa into a major port city and established trade links with other nearby city-states, as well as commercial centres in Persia, Arabia, and even India.[30] By the 15th-century, Portuguese voyager Duarte Barbosa claimed that "Mombasa is a place of great traffic and has a good harbour in which there are always moored small craft of many kinds and also great ships, both of which are bound from Sofala and others which come from Cambay and Melinde and others which sail to the island of Zanzibar."[31]
Later on in the 17th century, once the Swahili coast was conquered and came under direct rule of Omani Arabs, the slave trade was expanded by the Omani Arabs to meet the demands of plantations in Oman and Zanzibar. Initially these traders came mainly from Oman, but later many came from Zanzibar (such as Tippu Tip).[32] In addition, the Portuguese started buying slaves from the Omani and Zanzibari traders in response to the interruption of the transatlantic slave trade by British abolitionists.
Swahili, a Bantu language with Arabic, Persian, and other Middle Eastern and South Asian loanwords, later developed as a lingua franca for trade between the different peoples.[25] Swahili now also has loan words from English.
Throughout the centuries, the Kenyan Coast has played host to many merchants and explorers. Among the cities that line the Kenyan coast is the City of Malindi. It has remained an important Swahili settlement since the 14th century and once rivalled Mombasa for dominance in the African Great Lakes region. Malindi has traditionally been a friendly port city for foreign powers. In 1414, the Swahili Sultan of Malindi initiated diplomatic relations with Ming Dynasty China during the voyages of the explorer Zheng He.[33] Malindi authorities welcomed Portuguese explorer, Vasco da Gama, in 1498.
British Kenya (1888-1962)

The colonial history of Kenya dates from the establishment of a German protectorate over the Sultan of Zanzibar's coastal possessions in 1885, followed by the arrival of the Imperial British East Africa Company in 1888. Incipient imperial rivalry was forestalled when Germany handed its coastal holdings to Britain in 1890. This was followed by the building of the Kenya–Uganda railway passing through the country.[34]
This was resisted by some ethnicities — notably the Nandi led by Orkoiyot Koitalel Arap Samoei for ten years from 1890 to 1900 — still the British eventually built the railway. The Nandi were the first ethnicity to be put in a native reserve to stop them from disrupting the building of the railway. In 1920 the East Africa Protectorate was turned into a colony and renamed Kenya, for its highest mountain.[34]
During the railway construction era, there was a significant inflow of Indian people, who provided the bulk of the skilled manpower required for construction.[35] They and most of their descendants later remained in Kenya and formed the core of several distinct Indian communities such as the Ismaili Muslim and Sikh communities.[36]
While building the railroad through Tsavo, a number of the Indian railway workers and local African laborers were attacked by two lions known as the Tsavo maneaters.[37]
At the outbreak of World War I in August 1914, the governors of British East Africa (as the Protectorate was generally known) and German East Africa agreed a truce in an attempt to keep the young colonies out of direct hostilities. Lt Col Paul von Lettow-Vorbeck took command of the German military forces, determined to tie down as many British resources as possible. Completely cut off from Germany, von Lettow conducted an effective guerrilla warfare campaign, living off the land, capturing British supplies, and remaining undefeated. He eventually surrendered in Northern Rhodesia (today Zambia) fourteen days after the Armistice was signed in 1918.[35]

To chase von Lettow, the British deployed the British Indian Army troops from India and then needed large numbers of porters to overcome the formidable logistics of transporting supplies far into the interior on foot. The Carrier Corps was formed and ultimately mobilized over 400,000 Africans, contributing to their long-term politicisation.[35]
During the early part of the 20th century, the interior central highlands were settled by British and other European farmers, who became wealthy farming coffee and tea.[38] (One depiction of this period of change from one colonist's perspective is found in the memoir Out of Africa by Danish author Baroness Karen von Blixen-Finecke, published in 1937.) By the 1930s, approximately 30,000 white settlers lived in the area and gained a political voice because of their contribution to the market economy.[35]
The central highlands were already home to over a million members of the Kikuyu people, most of whom had no land claims in European terms and lived as itinerant farmers. To protect their interests, the settlers banned the growing of coffee, introduced a hut tax, and the landless were granted less and less land in exchange for their labor. A massive exodus to the cities ensued as their ability to provide a living from the land dwindled.[35] By the 1950s, the white population numbered 80,000.[39]
In 1952, Queen Elizabeth II and her husband Prince Phillip were on holiday at the Treetops Hotel in Kenya when her father, King George VI, passed away in his sleep. The young princess cut short her trip and returned home immediately to take her throne. Queen Elizabeth II was crowned at the Westminster Abbey in 1953 and as one gentleman put it, she went up a tree in Africa a princess and came down a queen.[40]
Mau Mau Uprising (1952-1959)

From October 1952 to December 1959, Kenya was under a state of emergency arising from the Mau Mau rebellion against British rule. The governor requested and obtained British and African troops, including the King's African Rifles. The British began counter-insurgency operations; May 1953, General Sir George Erskine took charge as commander-in-chief of the colony's armed forces, with the personal backing of Winston Churchill.[41]
The capture of Warũhiũ Itote (aka General China) on 15 January 1954 and the subsequent interrogation led to a better understanding of the Mau Mau command structure. Operation Anvil opened on 24 April 1954, after weeks of planning by the army with the approval of the War Council. The operation effectively placed Nairobi under military siege, and the occupants were screened and the Mau Mau supporters moved to detention camps. The Home Guard formed the core of the government's strategy as it was composed of loyalist Africans, not foreign forces like the British Army and King's African Rifles. By the end of the emergency, the Home Guard had killed 4,686 Mau Mau, amounting to 42% of the total insurgents. The capture of Dedan Kimathi on 21 October 1956 in Nyeri signified the ultimate defeat of the Mau Mau and essentially ended the military offensive.[41] During this period, substantial governmental changes to land tenure occurred. The most important of these was the Swynnerton Plan, which was used to both reward loyalists and punish Mau Mau.
Independent Kenya (1963)

The first direct elections for native Kenyans to the Legislative Council took place in 1957. Despite British hopes of handing power to "moderate" local rivals, it was the Kenya African National Union (KANU) of Jomo Kenyatta that formed a government shortly before Kenya became independent on 12 December 1963, on the same day forming the first Constitution of Kenya.[42]
Concurrently, the Kenyan army fought the Shifta War against ethnic Somali rebels inhabiting the Northern Frontier District, who wanted to join their kin in the Somali Republic to the north.[43] A cease fire was eventually reached with the signature of the Arusha Memorandum in October 1967, but relative insecurity prevailed through 1969.[44][45] To discourage further invasions, Kenya signed a defence pact with Ethiopia in 1969, which is still in effect.[46]
On 12 December 1964 the Republic of Kenya was proclaimed, and Jomo Kenyatta became Kenya's first president.[47]
Moi era (1978-2002)
At Kenyatta's death in 1978, Daniel arap Moi became President. Daniel arap Moi retained the Presidency, being unopposed in elections held in 1979, 1983 (snap elections) and 1988, all of which were held under the single party constitution. The 1983 elections were held a year early, and were a direct result of an abortive military coup attempt on 2 August 1982.

The abortive coup was masterminded by a low ranked Air Force serviceman, Senior Private Hezekiah Ochuka, and was staged mainly by enlisted men in the Air Force. The putsch was quickly suppressed by forces commanded by Chief of General Staff Mahamoud Mohamed, a veteran Somali military official.[48] They included the General Service Unit (GSU) — a paramilitary wing of the police — and later the regular police.
On the heels of the Garissa Massacre of 1980, Kenyan troops committed the Wagalla massacre in 1984 against thousands of civilians in the former North Eastern Province (present day Garissa, Wajir and Mandera counties). An official probe into the atrocities was later ordered in 2011.[49]
The election held in 1988 saw the advent of the mlolongo (queuing) system, where voters were supposed to line up behind their favoured candidates instead of a secret ballot.[50] This was seen as the climax of a very undemocratic regime and it led to widespread agitation for constitutional reform. Several contentious clauses, including one that allowed for only one political party were changed in the following years.[51] In democratic, multiparty elections in 1992 and 1997, Daniel arap Moi won re-election.[52]
2000s
In 2002, Moi was constitutionally barred from running, and Mwai Kǐbakǐ, running for the opposition coalition "National Rainbow Coalition" — NARC, was elected President. Anderson (2003) reports the elections were judged free and fair by local and international observers, and seemed to mark a turning point in Kenya's democratic evolution.[52]
In mid-2011, two consecutive missed rainy seasons precipitated the worst drought in East Africa seen in 60 years. The northwestern Turkana region was especially affected,[53] with local schools shut down as a result.[54] The crisis was reportedly over by early 2012 because of coordinated relief efforts. Aid agencies subsequently shifted their emphasis to recovery initiatives, including digging irrigation canals and distributing plant seeds.[55]
Government and politics

Kenya is a presidential representative democratic republic. The President is both the head of state and head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the National Assembly or parliamentary lower house. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. There was growing concern especially during former president Daniel arap Moi's tenure that the executive was increasingly meddling with the affairs of the judiciary. [citation needed]
Kenya ranks low on Transparency International's Corruption Perception Index (CPI), a metric which attempts to gauge the prevalence of public sector corruption in various countries. In 2012, the nation placed 139th out of 176 total countries in the CPI, with a score of 27/100.[56] However, there are several rather significant developments with regards to curbing corruption from the Kenyan government, for instance, the establishment of a new and independent Ethics and Anti-Corruption Commission (EACC).[57]

Following general elections held in 1997, the Constitution of Kenya Review Act designed to pave the way for more comprehensive amendments to the Kenyan constitution was passed by the local parliament.[58]
In December 2002, Kenyans held democratic and open elections, most of which were judged free and fair by international observers. The 2002 elections marked an important turning point in Kenya's democratic evolution in that power was transferred peacefully from the Kenya African National Union (KANU), which had ruled the country since independence to the National Rainbow Coalition, a coalition of political parties.
Under the presidency of Mwai Kibaki, the new ruling coalition promised to focus its efforts on generating economic growth, combating corruption, improving education, and rewriting its constitution. A few of these promises have been met. There is free primary education. In 2007, the government issued a statement declaring that from 2008, secondary education would be heavily subsidised, with the government footing all tuition fees.[59]
2007 elections

The 2007 Kenyan general election was held on 27 December 2007.[60] It comprised Presidential, parliamentary and civic elections.
The parliamentary elections were considered to be free and generally fair (as opposed to the contested presidential elections). They were remarkable for a number of changes. Amongst these were:
- Out of 190 outgoing MPs defending their seats only 71 were re-elected.
- 20 ministers defending their seats were defeated
- KANU the official opposition party of 2002 which later joined the government was reduced from 62 to 14 seats.
- 15 female candidates were elected which is the highest number ever in Kenyan history (2002: 9)
Campaign Issues included:
- Appropriations of Constituency Development Fund (CDF) money
- MP's Salary hikes
- Legislation passed / not passed in the 9th Parliament
- Changing the constitution.
In the Presidential elections, President Kibaki under the Party of National Unity ran for re-election against the main opposition party, the Orange Democratic Movement (ODM). The elections were seen to have been flawed with international observers saying that they were below international standards. After a split which took a crucial 8% of the votes away from the ODM to the newly formed Orange Democratic Movement-Kenya (ODM-K)'s candidate, Kalonzo Musyoka, the race tightened between ODM candidate Raila Odinga and Kibaki. As the count came into the Electoral Commission of Kenya (ECK) headquarters, Odinga was shown to have a slight, and then substantial lead as the results from his strongholds came in early. As the ECK continued to count the votes, Kibaki closed the gap and then overtook his opponent by a substantial margin after votes from his stronghold arrived later. This led to protests and open discrediting of the ECK for complicity and to Odinga declaring himself the "people's president" and calling for a recount.[61]
The protests escalated into ethnic violence and destruction of property, almost 1,000 people were killed and nearly 600,000 displaced.[62][63][64] The dispute caused underlying tensions over land and its distribution to re-erupt, as it had in the 1992 and 1997 elections.[64] Hundreds of thousands were forced off their land to relatives elsewhere in the country and some claim weapons are being bought in the region, perhaps in anticipation of the 2013 elections.[64]
A group of eminent persons of Africa, led by former United Nations secretary-general Kofi Annan, brokered a peaceful solution to the political stalemate.
Since the election riots, the government and civil society organisations started programmes to avoid similar disasters in the future, said Agnes R. M. Aboum – executive director of TAABCO Research and Development Consultants in Nairobi – in the magazine D+C Development and Cooperation. For example, the Truth, Justice and Reconciliation Commission initiated community dialogues, the Evangelical Lutheran Church in Kenya started peace meetings and the Kenya National Dialogue and Reconciliation process was started.
2008

On 28 February 2008, Kibaki and Odinga signed an agreement on the formation of a coalition government in which Odinga would become Kenya's second Prime Minister. Under the deal, the president would appoint cabinet ministers from both PNU and ODM camps depending on each party's strength in Parliament. The agreement stipulated that the cabinet would include a vice-president and two deputy Prime Ministers. After debates, it was passed by Parliament, the coalition would hold until the end of the current Parliament or if either of the parties withdraws from the deal before then.[65]
The new office of the PM will have power and authority to co-ordinate and supervise the functions of the Government and will be occupied by an elected MP who will be the leader of the party or coalition with majority members in Parliament. The world watched Annan and his UN-backed panel and African Union chairman Jakaya Kikwete as they brought together the former rivals to the signing ceremony, beamed live on national TV from the steps of Nairobi's Harambee House. On 29 February 2008, representatives of PNU and ODM began working on the finer details of the power-sharing agreement.[66] Kenyan lawmakers unanimously approved a power-sharing deal 18 March 2008, aimed at salvaging a country usually seen as one of the most stable and prosperous in Africa. The deal brought Kibaki's PNU and Odinga's ODM together and heralded the formation of the grand coalition, in which the two political parties would share power equally.[67]
Grand coalition
On 13 April 2008, President Kibaki named a grand coalition cabinet of 41 Ministers- including the prime minister and his two deputies. The cabinet, which included 50 Assistant Ministers, was sworn in at the State House in Nairobi on Thursday, 17 April 2008, in the presence of Dr. Kofi Annan and other invited dignitaries.
A constitutional change was considered that would eliminate the position of Prime Minister[68] and simultaneously reduce the powers of the President. A referendum to vote on the proposed constitution was held on 4 August 2010, and the new constitution passed by a wide margin.[69] Among other things, the new constitution delegates more power to local governments and gives Kenyans a bill of rights.[70] It was promulgated on 27 August 2010 at a euphoric ceremony in Nairobi's Uhuru Park, accompanied by a 21-gun salute. The event was graced by a number of African leaders and praised by the international community. As of that day, the new constitution heralding the Second Republic came into force.
2013 elections and new government
Under the new constitution and with President Kibaki prohibited by term limits from running for a third term, Deputy Prime Minister Uhuru Kenyatta ran and won with 50.51% of the vote in March 2013.
International presidential visits
With International Criminal Court trial dates in 2013 for both President Kenyatta and Vice-President William Ruto related to the 2007 election aftermath, US President Barack Obama chose not to visit the country during his mid-2013 African trip.[71] Later in the summer, Kenyatta visited China at the invitation of President Xi Jinping after a stop in Russia and not having visited the United States as president.[72]
Administrative divisions

Kenya is divided into 47 semi-autonomous counties that are headed by governors who were elected in the first general election under the new constitution in March 2013. These 47 counties now form the first-order divisions of the country. Under the old constitution, Kenya comprised eight provinces each headed by a Provincial Commissioner (centrally appointed by the president). The provinces (mkoa singular, mikoa plural in Swahili) were subdivided into districts (wilaya).
Constituencies are an electoral subdivision, with each county comprising a whole number of constituencies. An Interim Boundaries commission was formed in year 2010 to review the constituencies and in its report, it recommended creation of an additional 80 constituencies. Previous to the 2013 elections, there were 210 constituencies in Kenya.[73]
Economy
Although Kenya is the biggest and most advanced economy in east and central Africa and a minority of the wealthy urban population often leaves a misleading impression of affluence, Kenya is still a poor developing country with a Human Development Index (HDI) of 0.519, putting the country at position 145 out of 186 – one of the lowest in the world and about 38% of Kenyans live in absolute poverty.[74] The important agricultural sector is one of the least developed and largely inefficient, employing 75% of the workforce compared to less than 3% in the food secure developed countries.

Despite western donors' early disillusionment with the government, the economy has seen much expansion, seen by strong performance in tourism, higher education and telecommunications, and acceptable post-drought results in agriculture, especially the vital tea sector.[75] Kenya's economy grew by more than 7% in 2007, and its foreign debt was greatly reduced.[75] But this changed immediately after the disputed presidential election of December 2007, following the chaos which engulfed the country.
East and Central Africa's biggest economy has posted tremendous growth in the service sector, boosted by rapid expansion in telecommunication and financial activity over the last decade, and now contributes 62% of GDP. Unfortunately, a massive 22% of GDP still comes from the unreliable agricultural sector which employs 75% of the labour force (a consistent characteristic of under-developed economies that have not attained food security – an important catalyst of economic growth) and a significant portion of the population regularly starves and is heavily dependent on food aid. Industry and manufacturing is the smallest sector that accounts for 16% of the GDP.
Kenya has traditionally been a liberal market with minimal government involvement (price control) seen in the oil industry. However, recent legislation allows the government to determine and gazette price-controls on essential commodities like maize flour, kerosine and cooking oil.
Privatisation of state corporations like the defunct Kenya Post and Telecommunications Company, which resulted in East Africa's most profitable company – Safaricom, has led to their revival because of massive private investment.

As of May 2011, economic prospects are positive with 4–5% GDP growth expected, largely because of expansions in tourism, telecommunications, transport, construction and a recovery in agriculture. The World Bank estimated growth of 4.3% in 2012.[76]


In March 1996, the presidents of Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda re-established the East African Community (EAC). The EAC's objectives include harmonising tariffs and customs regimes, free movement of people, and improving regional infrastructures. In March 2004, the three East African countries signed a Customs Union Agreement.
The more efficient and lucrative technology-knowledge-and-skill-based service; industry and manufacturing sectors only employ 25% of the labour force but contributes the remaining 75% of the GDP.[75]
Kenya is East and Central Africa's hub for Financial services. The Nairobi Securities Exchange (NSE) is ranked 4th in Africa in terms of Market capitalisation. [citation needed] The Kenya banking system is supervised by the Central Bank of Kenya (CBK). As of late July 2004, the system consisted of 43 commercial banks (down from 48 in 2001), several non-bank financial institutions, including mortgage companies, four savings and loan associations, and several score foreign-exchange bureaus.[75]
Tourism

Kenya's services sector, which contributes 61% of GDP, is dominated by tourism. The tourism sector has exhibited steady growth in most years since independence and by the late 1980s had become the country's principal source of foreign exchange. Tourists, the largest number from Germany and the United Kingdom, are attracted mainly to the coastal beaches and the game reserves, notably, the expansive East and West Tsavo National Park (20,808 square kilometres (8,034 sq mi)) in the southeast. Tourism has seen a substantial revival over the past several years and is the major contributor to the pick-up in the country's economic growth. Tourism is now Kenya's largest foreign exchange earning sector, followed by flowers, tea, and coffee. In 2006 tourism generated US$803 million, up from US$699 million the previous year. Presently, there are also numerous Shopping Malls in Kenya. In addition, there are two hypermarkets in Kenya.
Agriculture

Agriculture is the second largest contributor to Kenya's gross domestic product (GDP), after the service sector. In 2005 agriculture, including forestry and fishing, accounted for 24% of GDP, as well as for 18% of wage employment and 50% of revenue from exports. The principal cash crops are tea, horticultural produce, and coffee. Horticultural produce and tea are the main growth sectors and the two most valuable of all of Kenya's exports. The production of major food staples such as corn is subject to sharp weather-related fluctuations. Production downturns periodically necessitate food aid—for example, in 2004 aid for 1.8 million people because of one of Kenya's intermittent droughts. [citation needed]

A consortium led by the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) has had some success in helping farmers grow new pigeon pea varieties, instead of maize, in particularly dry areas. Pigeon peas are very drought resistant, so can be grown in areas with less than 650 mm annual rainfall. Successive projects encouraged the commercialization of legumes, by stimulating the growth of local seed production and agro-dealer networks for distribution and marketing. This work, which included linking producers to wholesalers, helped to increase local producer prices by 20–25% in Nairobi and Mombasa. The commercialization of the pigeon pea is now enabling some farmers to buy assets, ranging from mobile phones to productive land and livestock, and is opening pathways for them to move out of poverty.[77]
Tea, coffee, sisal, pyrethrum, corn, and wheat are grown in the fertile highlands, one of the most successful agricultural production regions in Africa. Livestock predominates in the semi-arid savanna to the north and east. Coconuts, pineapples, cashew nuts, cotton, sugarcane, sisal, and corn are grown in the lower-lying areas. Unfortunately, the country has not attained the level of investment and efficiency in agriculture that can guarantee food security and coupled with resulting poverty (53% of the population lives below the poverty line), a significant portion of the population regularly starves and is heavily dependent on food aid. Poor roads, an inadequate railway network, under-used water transport and expensive air transport have isolated mostly arid and semi-arid areas and farmers in other regions often leave food to rot in the fields because they cannot access markets. This was last seen in August and September 2011 prompting the Kenyans for Kenya initiative by the Red Cross.[78]
Industry and manufacturing

Although Kenya is the most industrially developed country in the African Great Lakes region, manufacturing still accounts for only 14% of the GDP. Industrial activity, concentrated around the three largest urban centres, Nairobi, Mombasa and Kisumu, is dominated by food-processing industries such as grain milling, beer production, and sugarcane crushing, and the fabrication of consumer goods, e.g., vehicles from kits. There is a vibrant and fast growing cement production industry. [citation needed] Kenya has an oil refinery that processes imported crude petroleum into petroleum products, mainly for the domestic market. In addition, a substantial and expanding informal sector commonly referred to as Jua Kali engages in small-scale manufacturing of household goods, motor-vehicle parts, and farm implements. [citation needed]
Kenya's inclusion among the beneficiaries of the US Government's African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) has given a boost to manufacturing in recent years. Since AGOA took effect in 2000, Kenya's clothing sales to the United States increased from US$44 million to US$270 million (2006). [citation needed] Other initiatives to strengthen manufacturing have been the new government's favourable tax measures, including the removal of duty on capital equipment and other raw materials. [citation needed]
Energy

The largest share of Kenya's electricity supply comes from hydroelectric stations at dams along the upper Tana River, as well as the Turkwel Gorge Dam in the west. A petroleum-fired plant on the coast, geothermal facilities at Olkaria (near Nairobi), and electricity imported from Uganda make up the rest of the supply. Kenya's installed capacity stood at 1,142 megawatts between 2001 and 2003. The state-owned Kenya Electricity Generating Company (KenGen), established in 1997 under the name of Kenya Power Company, handles the generation of electricity, while the Kenya Power and Lighting Company (KPLC), which is slated for privatisation, handles transmission and distribution. Shortfalls of electricity occur periodically, when drought reduces water flow. To become energy sufficient, Kenya aims to build a nuclear power plant by 2017.[79]

Kenya has proven deposits of oil in Turkana and the commercial viability was just discovered. Tullow Oil plc estimates Kenya's oil reserves to be around 10 billion barrels.[80] Exploration is still continuing to determine if there are more reserves. Kenya currently imports all crude petroleum requirements. Kenya, east Africa's largest economy, has no strategic reserves and relies solely on oil marketers' 21-day oil reserves required under industry regulations. Petroleum accounts for 20% to 25% of the national import bill.[81]
Overall Chinese investment and trade
Published comments on Kenya's Capital FM website by Liu Guangyuan, China's ambassador to Kenya, at the time of President Kenyatta's 2013 trip to Beijing, said, "Chinese investment in Kenya ... reached $474 million, representing Kenya's largest source of foreign direct investment, and ... bilateral trade ... reached $2.84 billion" in 2012. Kenyatta was "[a]ccompanied by 60 Kenyan business people [and hoped to] ... gain support from China for a planned $2.5 billion railway from the southern Kenyan port of Mombasa to neighboring Uganda, as well as a nearly $1.8 billion dam", according to a statement from the president's office also at the time of the trip.[72] Base Titanium a subsidiary of Base resources of Australia shipped its first major consignment of minerals to China. About 25,000 tonnes of ilmenite was flagged off the Kenyan coastal town of Kilifi. The first shipment was expected to earn Kenya about Shs15 - Shs20 Billion in earnings[82]
Vision 2030

In 2007, the Kenyan government unveiled Vision 2030, an economic development programme it hopes will put the country in the same league as the Asian Economic Tigers by the year 2030. In 2013, it launched a National Climate Change Action Plan, having acknowledged that omitting climate as a key development issue in Vision 2030 was an oversight. The 200-page Action Plan, developed with support from the Climate & Development Knowledge Network, sets out the Government of Kenya's vision for a 'low carbon climate resilient development pathway'. At the launch in March 2013, the Secretary of the Ministry of Planning, National Development and Vision 2030 emphasised that climate will be a central issue in the renewed Medium Term Plan that will be launched in the coming months. This will create a direct and robust delivery framework for the Action Plan and ensure climate change is treated as an economy-wide issue.[83]
| GDP | $41.84 billion (2012) at Market Price. $76.07 billion (Purchasing Power Parity, 2012)
There exists an informal economy that is never counted as part of the official GDP figures. |
|---|---|
| Annual growth rate | 5.1% (2012) |
| Per capita income | Per Capita Income (PPP)= $1,800 |
| Agricultural produce | tea, coffee, corn, wheat, sugarcane, fruit, vegetables, dairy products, beef, pork, poultry, eggs |
| Industry | small-scale consumer goods (plastic, furniture, batteries, textiles, clothing, soap, cigarettes, flour), agricultural products, horticulture, oil refining; aluminium, steel, lead; cement, commercial ship repair, tourism |
| Exports | $5.942 billion | tea, coffee, horticultural products, petroleum products, cement, fish |
|---|---|---|
| Major markets | Uganda 9.9%, Tanzania 9.6%, Netherlands 8.4%, UK, 8.1%, US 6.2%, Egypt 4.9%, Democratic Republic of the Congo 4.2% (2012)[7] | |
| Imports | $14.39 billion | machinery and transportation equipment, petroleum products, motor vehicles, iron and steel, resins and plastics |
| Major suppliers | China 15.3%, India 13.8%, UAE 10.5%, Saudi Arabia 7.3%, South Africa 5.5%, Japan 4.0% (2012)[7] | |
Oil exploration

Kenya has proven oil deposits in Turkana County: President Mwai Kibaki announced on 26 March 2012 that Tullow Oil, an Anglo-Irish oil exploration firm, had struck oil but its commercial viability and subsequent production would take about three years to confirm.[84]
Early in 2006 Chinese President Hu Jintao signed an oil exploration contract with Kenya, part of a series of deals designed to keep Africa's natural resources flowing to China's rapidly expanding economy.
The deal allowed for China's state-controlled offshore oil and gas company, CNOOC, to prospect for oil in Kenya, which is just beginning to drill its first exploratory wells on the borders of Sudan and Somalia and in coastal waters. There are formal estimates of the possible reserves of oil discovered.[85]
Child labour and prostitution

Child labour is common in Kenya. Most working children are active in agriculture.[86] In 2006, UNICEF estimated that up to 30% of girls in the coastal areas of Malindi, Mombasa, Kalifi, and Diani were subject to prostitution.[86] The Ministry of Gender and Child Affairs employed 400 child protection officers in 2009.[86] The causes of child labour include poverty, the lack of access to education and weak government institutions.[86] [86] Kenya has ratified Convention No. 81 on labour inspection in industries and Convention No. 129 on labour inspection in agriculture. [87]
Demographics

Kenya has a diverse population that includes most major ethnoracial and linguistic groups found in Africa. There are an estimated 42 different communities, with Bantus (67%) and Nilotes (30%) constituting the majority of local residents.[88] Cushitic groups also form a small ethnic minority, as do Arabs, Indians and Europeans.[88][89]
According to the CIA World Fact Book, ethnic groups in the nation are represented as follows: Kikuyu 22%, Luhya 14%, Luo 13%, Kalenjin 12%, Kamba 11%, Kisii 6%, Meru 6%, other African 15%, non-African (Asian, European, and Arab) 1%.[7]
The country has a young population, with 73% of residents aged below 30 years because of rapid population growth;[90][91] from 2.9 million to 40 million inhabitants over the last century.[92]
Kenya's various ethnic groups typically speak their mother tongues within their own communities. The two official languages, English and Swahili, are used in varying degrees of fluency for communication with other populations. English is widely spoken in commerce, schooling and government.[93] Peri-urban and rural dwellers are less multilingual, with many in rural areas speaking only their native languages.[94]
According to Ethnologue, there are a total of 69 languages spoken in Kenya. Most belong to two broad language families: Niger-Congo (Bantu branch) and Nilo-Saharan (Nilotic branch), spoken by the country's Bantu and Nilotic populations, respectively. The Cushitic and Arab ethnic minorities speak languages belonging to the separate Afro-Asiatic family, with the Indian and European residents speaking languages from the Indo-European family.[95]
In addition, Kenya's capital, Nairobi, is home to Kibera, one of the world's largest slums. The shanty town is believed to house between 170,000[96] and 1 million locals.[97] The UNHCR base in Dadaab in the north also currently houses around 500,000 people.[98]
Template:Largest cities of Kenya
Religion

The vast majority of Kenyans are Christian (83%), with 47.7% regarding themselves as Protestant and 23.5% as Roman Catholic of the Latin Rite.[2] The Presbyterian Church of East Africa has 3,000 000 followers in Kenya and the surrounding countries.[99] There are smaller conservative Reformed churches, the Africa Evangelical Presbyterian Church,[100] the Independent Presbyterian Church in Kenya, and the Reformed Church of East Africa. 621,200 of Kenyans are Orthodox Christians.[101] Notably, Kenya has the highest number of Quakers in the world, with around 133,000 members.[102]
Sizeable minorities of other faiths do exist (Muslim 11.2%, irreligious 2.4%, indigenous beliefs 1.7%).[2] Sixty percent of the Muslim population lives in Kenya's Coastal Region, comprising 50% of the total population there. Roughly 8% of Muslims are Shia and another 8% are non-denominational Muslims, while 73% are Sunni.[103] Western areas of the Coast Region are mostly Christian. The upper part of Kenya's Eastern Region is home to 10% of the country's Muslims, where they constitute the majority religious group.[104] In addition, there is a large Hindu population in Kenya (around 300,000), who have played a key role in the local economy, they are mostly of Indian origin. There is also a small group of Baha'is.[105]
Health

Nurses treat 80% of the population who visit dispensaries, health centres and private clinics in rural and under-served urban areas. Complicated cases are referred to clinical officers, medical officers and consultants (specialists). According to the Kenya National Bureau of Statistics, in 2011 there were 65,000 qualified nurses registered in the country; 8,600 clinical officers and 7,000 doctors for the population of 43 million people (These figures from official registers include those who have died or left the profession hence the actual number of these workers may be lower).
Despite major achievements in the health sector, Kenya still faces many challenges. The life expectancy estimate has dropped to approximately 55 years in 2009 – five years below 1990 levels.[106] The infant mortality rate is high at approximately 44 deaths per 1,000 children in 2012.[107] The WHO estimated in 2011 that only 42% of births were attended by a skilled health professional.[108]
Diseases of poverty directly correlate with a country's economic performance and wealth distribution: Half of Kenyans live below the poverty level. Preventable diseases like malaria, HIV/AIDS, pneumonia, diarrhea and malnutrition are the biggest burden, major child-killers, and responsible for much morbidity; weak policies, corruption, inadequate health workers, weak management and poor leadership in the public health sector are largely to blame. According to 2009 estimates, HIV prevalence is about 6.3% of the adult population.[109] However, the 2011 UNAIDS Report suggests that the HIV epidemic may be improving in Kenya, as HIV prevalence is declining among young people (ages 15–24) and pregnant women.[110]
The total fertility rate in Kenya is estimated to be 4.49 children per woman in 2012.[111] According to a 2008–09 survey by the Kenyan government, the total fertility rate was 4.6% with contraception usage rate among married women was 46%.[112] Maternal mortality is high, partly because of female genital mutilation.[75] This practice is however on the decline as the country becomes more modernised and the practice was also banned in the country in 2011.[113]
Education

Independent Kenya's first system of education was introduced by British colonists.[114] After Kenya's independence on 12 December 1963, an authority named the Ominde Commission was formed to introduce changes that would reflect the nation's sovereignty. The commission focused on identity and unity, which were critical issues at the time. Changes in the subject content of history and geography were made to reflect national cohesion. Between 1964 and 1985, the 7–4–2–3 system was adopted – seven years of primary, four years of lower secondary, two years of upper secondary, and three years of university. All schools had a common curriculum.[114]
In 1981, the Presidential Working Party on the Second University was commissioned to look at both the possibilities of setting up a second university in Kenya as well as the reforming of the entire education system.[114] The committee recommended that the 7–4–2–3 system be changed to an 8–4–4 system (eight years in primary, four years in secondary, and four years in university education). The table under Present-day education in Kenya below shows the structure of the 8–4–4 system. Although the 7–4–2–3 system theoretically ended with the introduction of the new 8–4–4 system in 1985, the last batch of students from the former system graduated from Kenyan Universities in 1992.[114]
The current 8–4–4 system was launched in January 1985.[115][116] It put more emphasis on vocational subjects on the assumption that the new structure would enable school drop-outs at all levels either to be self-employed or to secure employment in the informal sector. In January 2003, the Government of Kenya announced the introduction of free primary education. As a result, primary school enrollment increased by about 70%. Secondary and tertiary education enrollment has not increased proportionally because payment is still required for attendance. In 2007 the government issued a statement declaring that from 2008, secondary education would be heavily subsidiszed, with the government footing all tuition fees.

Children attend nursery school, or kindergarten in the private sector, until they are five years old. This lasts one to three years (KG1, KG2 and KG3) and is financed privately because there has been no government policy regarding it until recently. There is much celebration and a graduation ceremony at the end of KG3 when the children are ready to join class one in primary school.
Basic formal education starts at age six years and lasts 12 years comprising eight years in primary school and four years in high school or secondary school. Primary school is free in public schools and those who exit at this level can join a vocational youth/village polytechnic or make their own arrangements for an apprenticeship program and learn a trade such as tailoring, carpentry, motor vehicle repair, brick-laying and masonry for about two years. Those who complete high school can join a polytechnic or other technical college and study for three years or proceed directly to the university and study for four years. Graduates from the polytechnics and colleges can then join the workforce and later obtain a specialised higher diploma qualification after a further one to two years of training, or join the university – usually in the second or third year of their respective course. The higher diploma is accepted by many employers in place of a bachelors degree and direct or accelerated admission to post-graduate studies is possible in some universities.
Public universities in Kenya are highly commercialized institutions and only a small fraction of qualified high school graduates are admitted on limited government-sponsorship into programs of their choice. Most are admitted into the social sciences, which are cheap to run, or as self-sponsored students paying the full cost of their studies. Most qualified students who miss-out opt for middle-level diploma programs in public or private universities, colleges and polytechnics.
The country's literacy level stands at 85% of the whole population. Preschool, which targets children from age three to five, is an integral component of the education system and is a key requirement for admission to Standard One (First Grade). At the end of primary education, pupils sit the Kenya Certificate of Primary Education (KCPE), which determines those who proceed to secondary school or vocational training. Primary school age is 6/7-13/14 years. For those who proceed to secondary level, there is a national examination at the end of Form Four – the Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (KCSE), which determines those proceeding to the universities, other professional training or employment. Students sit examinations in eight subjects of their choosing. However, English, KiSwahili (Languages) and Mathematics are compulsory subjects. The result of this examination is needed for placement at secondary school. In form four of secondary schools the Kenya Certificate of Secondary Examination (KCSE) is taken.
The Joint Admission Board (JAB) is responsible for selecting students joining the public universities. Other than the public schools, there are many private schools in the country, mainly in urban areas. Similarly, there are a number of international schools catering for various overseas educational systems.
Culture

Kenya is arguably the most diverse country in Africa where the three major African Ethno-Linguistic groups of people converge. Namely; the Bantu, Nilotes and Cushites. Kenyan culture is influenced by the blending of traditions of these groups, giving rise to a rich and deep national culture.
Notable peoples include the Swahili on the coast, pastoralist communities in the north, and several different communities in the central and western regions. The Maasai culture is well known because of tourism, despite being a minor percentage of the Kenyan population. They are renowned for their elaborate upper body adornment and jewellery.
Kenya has an extensive music, television and theatre scene.
Literature

Ngũgĩ wa Thiong'o is one of the best known writers of Kenya. His book, Weep Not, Child, is an illustration of life in Kenya during the British occupation. This is a story about the effects of the Mau Mau on the lives of Kenyans. Its combination of themes—colonialism, education, and love—helped to make it one of the best-known novels in Africa.
M.G. Vassanji's 2003 novel The In-Between World of Vikram Lall won the Giller Prize in 2003. It is the fictional memoir of a Kenyan of Indian heritage and his family as they adjust to the changing political climates in colonial and post-colonial Kenya.
Additionally, since 2003, the literary journal Kwani? has been publishing Kenyan contemporary literature.
Music

Kenya has a diverse assortment of popular music forms, in addition to multiple types of folk music based on the variety over 40 regional languages.[117]
The guitar is the most dominant instrument in Kenyan popular music. Guitar rhythms are very complex and include both native beats and imported ones, especially the Congolese cavacha rhythm. Popular Kenyan music usually involves the interplay of multiple parts, and more recently, showy guitar solos as well. There are also a number of local hip hop artists, including Jua Cali.
Lyrics are most often in Swahili or English. There is also some emerging aspect of Lingala borrowed from Congolese musicians. Lyrics are also written in local languages. Urban radio generally only plays English music, though there also exist a number of vernacular radio stations.
Additionally, Kenya has a growing Christian gospel music scene. Prominent local gospel musicians include the Kenyan Boys Choir.
Benga music has been popular since the late 1960s, especially in the area around Lake Victoria. The word benga is occasionally used to refer to any kind of pop music. Bass, guitar and percussion are the usual instruments.
Sports

Kenya is active in several sports, among them cricket, rallying, football, rugby union and boxing. But the country is known chiefly for its dominance in Middle-distance and long-distance athletics. Kenya has consistently produced Olympic and Commonwealth Games champions in various distance events, especially in 800 m, 1,500 m, 3,000 m steeplechase, 5,000 m, 10,000 m and the marathon. Kenyan athletes (particularly Kalenjin) continue to dominate the world of distance running, although competition from Morocco and Ethiopia has reduced this supremacy. Kenya's best-known athletes included the four-time women's Boston Marathon winner and two-time world champion Catherine Ndereba, former Marathon world record-holder Paul Tergat, and John Ngugi.
Kenya won several medals during the Beijing Olympics, six gold, four silver and four bronze, making it Africa's most successful nation in the 2008 Olympics. New athletes gained attention, such as Pamela Jelimo, the women's 800m gold medalist who went ahead to win the IAAF Golden League jackpot, and Samuel Wanjiru who won the men's marathon. Retired Olympic and Commonwealth Games champion Kipchoge Keino helped usher in Kenya's ongoing distance dynasty in the 1970s and was followed by Commonwealth Champion Henry Rono's spectacular string of world record performances. Lately, there has been controversy in Kenyan athletics circles, with the defection of a number of Kenyan athletes to represent other countries, chiefly Bahrain and Qatar.[118] The Kenyan Ministry of Sports has tried to stop the defections, but they have continued anyway, with Bernard Lagat the latest, choosing to represent the United States.[118] Most of these defections occur because of economic or financial factors. Some elite Kenyan runners who cannot qualify for their country's strong national team find it easier to qualify by running for other countries.[citation needed]

Kenya has been a dominant force in women's volleyball within Africa, with both the clubs and the national team winning various continental championships in the past decade. [citation needed] The women's team has competed at the Olympics and World Championships but without any notable success. Cricket is another popular and the most successful team sport. Kenya has competed in the Cricket World Cup since 1996. They upset some of the World's best teams and reached semi-finals of the 2003 tournament. They won the inaugural World Cricket League Division 1 hosted in Nairobi and participated in the World T20. Their current captain is Collins Obuya. They participated in the ICC Cricket World Cup 2011. Kenya is represented by Lucas Onyango as a professional rugby league player who plays with Oldham Roughyeds. Besides the former European Super League team, he has played for Widnes Vikings and rugby union with Sale Sharks.[119] Rugby union is increasing in popularity, especially with the annual Safari Sevens tournament. Kenya sevens team ranked 9th in IRB Sevens World Series for the 2006 season. Kenya was also a regional powerhouse in soccer. However, its dominance has been eroded by wrangles within the Kenya Football Federation.[120] This has led to a suspension by FIFA which was lifted in March 2007.
In the motor rallying arena, Kenya is home to the world famous Safari Rally, commonly acknowledged as one of the toughest rallies in the world.[121] It was a part of the World Rally Championship for many years until its exclusion after the 2002 event owing to financial difficulties. Some of the best rally drivers in the world have taken part in and won the rally, such as Björn Waldegård, Hannu Mikkola, Tommi Mäkinen, Shekhar Mehta, Carlos Sainz and Colin McRae. Although the rally still runs annually as part of the Africa rally championship, the organisers are hoping to be allowed to rejoin the World Rally championship in the next couple of years.
Cuisine

Kenyans generally have three meals in a day – breakfast in the morning (kiamsha kinywa), lunch in the after noon (chakula cha mchana) and supper in the evening (chakula cha jioni). In between, they have the 10 o'clock tea (chai ya saa nne) and 4 pm tea (chai ya saa kumi). Breakfast is usually tea or porridge with bread, chapati, mahamri, boiled potatoes or yams. Ugali with vegetables, sour milk, meat, fish or any other stew is generally eaten by much of the population for lunch or supper. Regional variations and dishes also exist.
In western Kenya, among the Luhya, Luo and Kalenjin, lye is a common ingredient in most traditional foods and mursik – a traditional milk drink. It is not yet known whether lye is responsible for the high prevalence of throat cancer in these region.
In cities such as Nairobi, there are fast food restaurants, which include Steers, KFC,[122] and Subway.[123] There are also many popular fish and chips delis that are usually packed during lunch time.
See also
- Outline of Kenya
- Index of Kenya-related articles
- Languages of Kenya
- Counties of Kenya
- List of Kenyans
- Kenya Defence Forces
- Foreign relations of Kenya
- List of diplomatic missions of Kenya
References
- ^ Constitution (2009) Art. 7 [National, official and other languages] "(1) The national language of the Republic is Kiswahili. (2) The official languages of the Republic are English and Swahili. (3) The State shall–-–- (a) promote and protect the diversity of language of the people of Kenya; and (b) promote the development and use of indigenous languages, Kenyan Sign language, Braille and other communication formats and technologies accessible to persons with disabilities."
- ^ a b c Wycliffe Ambetsa Oparanya (31 August 2010) Archived 2013-08-10 at the Wayback Machine. Ministry of State for Planning. knbs.or.ke
- ^ Kenya Demographics Profile 2013. Indexmundi.com (21 February 2013). Retrieved on 9 August 2013.
- ^ Archived 2013-08-10 at the Wayback Machine. www.knbs.or.ke.
- ^ a b c d "Kenya". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 17 April 2013.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2013" (PDF). United Nations. 2013. Retrieved 31 March 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f Central Intelligence Agency (2012). "Kenya". The World Factbook. Retrieved 28 May 2013.
- ^ Ethiopia GDP purchasing power 2010: 86 billion. Imf.org. 14 September 2006.
- ^ Kenya GDP purchasing power 2010: 66 Billion. Imf.org. 14 September 2006.
- ^ a b Sullivan, Paul (2006). Kikuyu Districts. Dar es Salaam, Tanzania: Mkuki na Nyota Publishers.
- ^ Krapf, Johann Ludwig (1860). Travels, Researches, and Missionary Labours in Eastern Africa. London: Frank Cass & Co. Ltd.
- ^ Krapf, Johann Ludwig (13 May 1850). "Extract from Krapf's diary". Church Missionary Intelligencer. i: 452.
- ^ Foottit, Claire (2006) [2004]. Kenya. The Brade Travel Guide. Bradt Travel Guides Ltd. ISBN 1-84162-066-1.
- ^ Ratcliffe, B. J. (January 1943). "The Spelling of Kenya". Journal of the Royal African Society. 42 (166): 42–44. JSTOR 717465.
- ^ Kenya's first dinosaur dig yields fossil wealth, ABC News Online, 10 March 2005.
- ^ Glynn Llywelyn Isaac, Barbara Isaac (1977). Olorgesailie: archeological studies of a Middle Pleistocene lake basin in Kenya. University of Chicago Press. p. xiii.
- ^ a b Ehret, C. (2002) The Civilizations of Africa: a History to 1800, University Press of Virginia, ISBN 081392085X.
- ^ Ehret, C. (1980) The historical reconstruction of Southern Cushitic phonology and vocabulary, Kölner Beiträge zur Afrikanistik 5, Bd., Reimer, Berlin.
- ^ Ehret, C. (1983) Culture History in the Southern Sudan, J. Mack, P. Robertshaw, Eds., British Institute in Eastern Africa, Nairobi, pp. 19–48, ISBN 1872566049.
- ^ Ambrose, S.H. (1982). "Archaeological and linguistic reconstructions of history in East Africa." In Ehert, C., and Posnansky, M. (eds.), The archaeological and linguistic reconstruction of African history, University of California Press, ISBN 0520045939.
- ^ Ambrose, S.H. (1986) Sprache und Geschichte in Afrika 7.2, 11.
- ^ International Labour Office, Traditional occupations of indigenous and tribal peoples: emerging trends, (International Labour Organization: 2000), p. 55, ISBN 9221122581.
- ^ Ehret, C. (1998) An African Classical Age : Eastern and Southern Africa in World History, 1000 B.C. to A.D. 400., University Press of Virginia, Charlottesville, pp. xvii, 354, ISBN 0813920574.
- ^ a b Smith, C. Wayne (1995) Crop Production: Evolution, History, and Technology, John Wiley & Sons, p. 132, ISBN 0471079723.
- ^ a b "Wonders of the African World". PBS. Retrieved 16 April 2010.
- ^ Don Nanjira, Daniel (2010) African Foreign Policy and Diplomacy: From Antiquity to the 21st century, ABC-CLIO, p. 114 ISBN 0313379823.
- ^ شاكر مصطفى, موسوعة دوال العالم الأسلامي ورجالها الجزء الثالث, (دار العلم للملايين: 1993), p. 1360
- ^ Hastings, James (2003) Encyclopedia of Religion and Ethics Part 24, Kessinger Publishing, p. 847
- ^ Nicolini, Beatrice and Watson, Penelope-Jane (2004) Makran, Oman, and Zanzibar, Volume 3 of Islam in Africa, BRILL, p. 62 ISBN 9004137807.
- ^ Alsayyad, Nezar (30 March 2001). Hybrid Urbanism. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-275-96612-6.
- ^ Ali, Shanti Sadiq (1996). The African Dispersal in the Deccan. Orient Blackswan. ISBN 978-81-250-0485-1.
- ^ Swahili Coast. Nationalgeographic.com.
- ^ "Sultan of Malinda, PBS". Pbs.org. Retrieved 16 April 2010.
- ^ a b Encyclopædia Britannica
- ^ a b c d e R. Mugo Gatheru (2005) Kenya: From Colonization to Independence, 1888–1970, McFarland, ISBN 0786421991
- ^ Jenkins, Orville Boyd. "Sikh". Orvillejenkins.com. Retrieved 16 April 2010.
- ^ "Ismaili muslim". Magicalkenya.com. Retrieved 16 April 2010.
- ^ "We Want Our Country". Time. 5 November 1965.
- ^ "Kenya". Matthew Firestone (2009). p. 28. ISBN 1741047730
- ^ Vickers, Hugo (29 January 2012). "Diamond Jubilee: the moment that Princess Elizabeth became Queen". The Daily Telegraph. London.
- ^ a b Maloba, Wunyabari O. (1993) Mau Mau and Kenya: An Analysis of Peasant Revolt, Indiana University Press, 0852557450.
- ^ "Political – Welcome to THE Kenya Document Exchange". Kenyadocex.com. Archived from the original on 28 August 2010. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ Bruce Baker, Escape from Domination in Africa: Political Disengagement & Its Consequences, (Africa World Press: 2003), p.83
- ^ Hogg, Richard (1986). "The New Pastoralism: Poverty and Dependency in Northern Kenya". Africa: Journal of the International African Institute. 56 (3): 319–333. doi:10.2307/1160687. JSTOR 1160687.
- ^ Howell, John (May 1968). "An Analysis of Kenyan Foreign Policy". The Journal of Modern African Studies. 6 (1): 29–48. doi:10.1017/S0022278X00016657. JSTOR 158675.
- ^ Pike, John (1992). "Post-Independence Low Intensity Conflict in Kenya". Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 16 April 2010.
- ^ Permanent Mission of the Republic of Kenya to the United Nations (2002). "Kenya at the United Nations". Consulate General of Kenya in New York. Archived from the original on 8 June 2009. Retrieved 15 February 2010.
- ^ Society. Nyamora Communications Limited. 1992. p. 12.
- ^ "Wagalla massacre: Raila Odinga orders Kenya probe". BBC. 11 February 2011. Retrieved 14 November 2013.
- ^ Harden, Blaine (25 February 1988) Many Voters Stay Home as Kenya Drops Secret Ballot in Parliamentary Election, The 'Washington Post.
- ^ Moreno, Pedro C. (ed.). "Kenya". Handbook on Religious Liberty Around the World. Charlottesville, VA: The Rutherford Institute.
- ^ a b Anderson, David M. (2003). "Kenya's Elections 2002 – The Dawning of a New Era?". African Affairs. 102 (407): 331–342. doi:10.1093/afraf/adg007.
- ^ Koech, Dennis (25 July 2011). "Red Cross warns of catastrophe in Turkana". Kbc.co.ke. Archived from the original on 4 January 2012. Retrieved 7 August 2011.
- ^ "Kenya: schools close as famine takes hold in Turkana". Indcatholicnews.com. 28 July 2011. Retrieved 7 August 2011.
- ^ Gettleman, Jeffrey (3 February 2012) U.N. Says Famine in Somalia Is Over, but Risks Remain. New York Times.
- ^ "Transparency International: CPI". Transparency International. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ "Business Corruption in Kenya". Business Anti-Corruption Portal. Retrieved 4 April 2014.
- ^ A short history of the 2010 Kenya constitution. kenyaconstitution.org
- ^ "Africa | Free secondary schools for Kenya". BBC News. 11 February 2008. Retrieved 26 February 2013.
- ^ K'telwa, Kipkirui (26 October 2007) ECK sets poll date as Raila maintains lead The Standard.
- ^ Kenya election violence threatens its economic gains. chinadaily.com.cn (7 January 2008).
- ^ "Up to 1,000 killed in Kenya crisis – Odinga". Reuters. 7 January 2008.
- ^ "Kenya death toll hits 693: report". IOL: News for South Africa and the World. 13 January 2008.
- ^ a b c Samir Elhawary (2008) Crisis in Kenya: land, displacement and the search for 'durable solutions' Overseas Development Institute
- ^ "Agreement on the Principles of Partnership of the Coalition Government". Kenya National Dialogue & Reconciliation. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- ^ 'Hope is back' for Kenya. CNN.com (29 February 2008)
- ^ Kenyan MPs pass power-share law. Al Jazeera English (18 March 2008)
- ^ "Kenya MPs opt to scrap prime minister position". BBC News. 28 January 2010. Retrieved 16 April 2010.
- ^ "Kenyans back change to constitution in referendum". BBC. 5 August 2010. Retrieved 6 August 2010.
- ^ Gettleman, Jeffrey (5 August 2010). "Kenyans Approve New Constitution". The New York Times. Retrieved 11 August 2010.
- ^ Epatko, Larisa, "Why Obama Is Visiting Senegal, South Africa and Tanzania But Not Kenya", PBS NewsHour, 25 June 2013. Retrieved 18 August 2013.
- ^ a b Raghavan, Sudarsan, "In snub to Washington, Kenyan president visits China, Russia first", Washington Post, 17 August 2013. Ambassador Liu's comments at capitalfm.co.ke linked to here [1]. Retrieved 18 August 2013.
- ^ Kenya Roads Board Constituency funding under the RMLF
- ^ Kenya’s economic growth prospects hang on exports, says World Bank – Money Markets. businessdailyafrica.com. Retrieved on 9 August 2013.
- ^ a b c d e "Country Profile: Kenya" (PDF). Federal Research Division. Library of Congress. June 2007. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- ^ Fengler, Wolfgang (5 December 2012). "Kenya Economic Update". The World Bank.
- ^ Pigeonpea in Eastern and Southern Africa. ICRISAT Posted 10 October 2012. Downloaded 26 January 2014.
- ^ Towards Achieving Food Security in Kenya. Joseph Kinyua, Permanent Secretary, Ministry of Agriculture, Kenya; 1 April 2004, Kampala, Uganda
- ^ McGregor, Sarah (20 September 2010) Kenya Aims to Build a Nuclear Power Plant by 2017. bloomberg.com.
- ^ Kenya From Nowhere Plans East Africa’s First Oil Exports: Energy. bloomberg.com.
- ^ Kenya plans strategic oil reserve. Reuters (10 November 2011).
- ^ https://www.standardmedia.co.ke/business/article/2000104631/kenya-joins-mineral-exporters-as-first-titanium-cargo-leaves-port
- ^ NEWS: Kenya’s National Climate Change Action Plan is officially launched, Climate & Development Knowledge Network, 28 March 2013
- ^ BBC News – Kenya oil discovery after Tullow Oil drilling. Bbc.co.uk. 26 March 2012.
- ^ Barber, Lionel; England, Andrew (10 August 2006). "China's scramble for Africa finds a welcome in Kenya". Financial Times. Retrieved 27 June 2008.
- ^ a b c d e "Country profile report – Kenya" (PDF). United Nations. 2009.
- ^ Suda, Collette (2001). "The Invisible Child Worker in Kenya: The Intersection of Poverty, Legislation and Culture" (PDF). Nordic Journal of African Studies. 10 (2): 163–175.
- ^ a b Asongu, J. J. and Marr, Marvee (2007). Doing Business Abroad: A Handbook for Expatriates. Greenview Publishing Co. pp. 12 & 112. ISBN 0979797632.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Okoth, A. and Ndaloh, A. (2006) Peak Revision K.C.P.E. Social Studies, East African Publishers, pp. 60–61 ISBN 9966254501.
- ^ "Why a new president may slow population growth". Csmonitor.com. 14 January 2008.
- ^ Zinkina J., Korotayev A. Explosive Population Growth in Tropical Africa: Crucial Omission in Development Forecasts (Emerging Risks and Way Out). World Futures 70/2 (2014): 120–139.
- ^ "Exploding population". The New York Times. 7 January 2008.
- ^ Proquest Info & Learning (COR) (2009). Culturegrams: World Edition. Proquest/Csa Journal Div. p. 98. ISBN 0977809161.
- ^ Brown, E. K.; Asher, R. E. and Simpson, J. M. Y. (2006). Encyclopedia of language & linguistics, Volume 1, Edition 2. Elsevier. p. 181. ISBN 0080442994.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Languages of Kenya. Ethnologue.com.
- ^ Karanja, Muchiri (3 September 2010). "Myth shattered: Kibera numbers fail to add up". Daily Nation. Retrieved 4 September 2010.
- ^ "World Water Day Focus on Global Sewage Flood". News.nationalgeographic.com. 22 March 2010. Retrieved 10 February 2012.
- ^ The UN Refugee Agency. Unhcr.org.
- ^ Address data base of Reformed churches and institutions. Reformiert-online.net. Retrieved on 16 April 2013.
- ^ The World Reformed Fellowship – Promoting Reformed Partnerships Worldwide – News. Wrfnet.org. Retrieved on 16 April 2013.
- ^ "Kenya". Oikoumene.org. 3 February 2008. Archived from the original on 11 March 2008. Retrieved 26 February 2013.
- ^ Finding Quakers Around the World. FWCC. GIF map
- ^ Pew Forum on Religious & Public life. 9 August 2012. Retrieved 16 November 2013.
- ^ "Kenya: International Religious Freedom Report 2008". U.S. Department of State. 2008. Retrieved 16 April 2010.
- ^ "Largest Baha'i Communities". Adherents.com. Retrieved 26 June 2010.
- ^ UNICEF Statistics: Kenya. Unicef.org.
- ^ Infant Mortality ranks. CIA World Factbook
- ^ WHO Health-Related Millennium Development Goals Report 2011.
- ^ CIA World Factbook: HIV/AIDS – Adult Prevalence Rate Rankings. Cia.gov. Retrieved on 23 April 2012.
- ^ UNAIDS World AIDS Day Report 2011.
- ^ Forecast provided by International Futures and hosted by Google's Public Data Explorer
- ^ Kenya – Kenya Demographic and Health Survey 2008–09. Kenya National Data Archive (KeNADA)
- ^ Boseley, Sarah (8 September 2011). "FGM: Kenya acts against unkindest cut". London: The Guardian. Retrieved 7 January 2012.
- ^ a b c d "Education". Ministry of Information and Communications. Government of Kenya. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- ^ Ferre, Celine (February 2009). "Age at First Child: Does Education Delay Fertility Timing? The Case of Kenya" (PDF). Policy Research Working Paper (4833). World Bank.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Eshiwani, G.S. (1990). "Implementing Educational Policies in Kenya" (PDF). Africa Technical Department Series Discussion Paper (85). World Bank.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ On the Beat – Tapping the Potential of Kenya's Music Industry, WIPO Magazine (July 2007).
- ^ a b IAAF: Changes of Allegiance 1998 to 2005.
- ^ "Nakuru upset KCB in Kenya Cup". Nation.co.ke. 25 July 2009. Retrieved 16 April 2010.
- ^ New Vision, 3 June 2004: Wrangles land Kenya indefinite FIFA ban
- ^ The Auto Channel, 21 July 2001: FIA RALLY: Delecour takes points finish on Safari Rally debut
- ^ "Fast food finds fans in sub-Sahara Africa, where obesity problem is growing – World News". Worldnews.nbcnews.com. 24 October 2012. Retrieved 26 February 2013.
- ^ US fast food chain to open first Kenya outlet in August – Money Markets. businessdailyafrica.com. Retrieved on 9 August 2013.
External links
- Official website of the President of Kenya
- Official website of the Parliament of Kenya
 Wikimedia Atlas of Kenya
Wikimedia Atlas of Kenya Kenya travel guide from Wikivoyage
Kenya travel guide from Wikivoyage- "Kenya". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Kenya Corruption Profile from the Business Anti-Corruption Portal
- World Bank Summary Trade Statistics Kenya, 2010
- Template:Dmoz
- Kenya
- Countries in Africa
- East African countries
- Southeast Africa
- Bantu countries and territories
- English-speaking countries and territories
- G15 nations
- Member states of the African Union
- Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Republics
- States and territories established in 1963
- Swahili-speaking countries and territories
- Member states of the United Nations
- Commonwealth republics