Paracetamol: Difference between revisions
→Pharmacodynamics: formation of AAM404 |
→Pharmacodynamics: refs |
||
| Line 198: | Line 198: | ||
Supporting first mechanism, pharmacologically and in its side effects, paracetamol is close to classical [[nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug]]s (NSAIDS) that act by inhibiting [[COX-1]] and [[COX-2]] enzymes, and especially similar to selective [[COX-2 inhibitor]]s.<ref name="pmid23719833">{{cite journal |vauthors=Graham GG, Davies MJ, Day RO, Mohamudally A, Scott KF |title=The modern pharmacology of paracetamol: therapeutic actions, mechanism of action, metabolism, toxicity and recent pharmacological findings |journal=Inflammopharmacology |volume=21 |issue=3 |pages=201–32 |date=June 2013 |pmid=23719833 |doi=10.1007/s10787-013-0172-x |url=}}</ref> Paracetamol inhibits the [[prostaglandin]] synthesis by [[Reduction (chemistry)|reducing]] the active form of COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes. This occurs only when concentration of [[arachidonic acid]] and [[Organic peroxide#Biology|peroxides]] is low. Under these conditions, COX-2 is the predominant form of cyclooxygenase, which explains apparent COX-2 selectivity of paracetamol. Under the conditions of inflammation, the concentration of peroxides is high, which counteracts the reducing effect of paracetamol. Accordingly, anti-inflammatory action of paracetamol is slight.<ref name=Ghanem2016/><ref name="pmid23719833"/> |
Supporting first mechanism, pharmacologically and in its side effects, paracetamol is close to classical [[nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug]]s (NSAIDS) that act by inhibiting [[COX-1]] and [[COX-2]] enzymes, and especially similar to selective [[COX-2 inhibitor]]s.<ref name="pmid23719833">{{cite journal |vauthors=Graham GG, Davies MJ, Day RO, Mohamudally A, Scott KF |title=The modern pharmacology of paracetamol: therapeutic actions, mechanism of action, metabolism, toxicity and recent pharmacological findings |journal=Inflammopharmacology |volume=21 |issue=3 |pages=201–32 |date=June 2013 |pmid=23719833 |doi=10.1007/s10787-013-0172-x |url=}}</ref> Paracetamol inhibits the [[prostaglandin]] synthesis by [[Reduction (chemistry)|reducing]] the active form of COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes. This occurs only when concentration of [[arachidonic acid]] and [[Organic peroxide#Biology|peroxides]] is low. Under these conditions, COX-2 is the predominant form of cyclooxygenase, which explains apparent COX-2 selectivity of paracetamol. Under the conditions of inflammation, the concentration of peroxides is high, which counteracts the reducing effect of paracetamol. Accordingly, anti-inflammatory action of paracetamol is slight.<ref name=Ghanem2016/><ref name="pmid23719833"/> |
||
Second mechanism centers around paracetamol metabolite AM404. This metabolite has been detected in the brains of animals and [[cerebrospinal fluid]] of humans taking paracetamol.<ref name=Ghanem2016/> Apparently, it is formed in the brain from another paracetamol metabolite [[4-aminophenol]] by action of [[fatty acid amide hydrolase]]. Paracetamol apparently might modulate the [[Endocannabinoid system|endogenous cannabinoid system]] in the brain through its metabolite, [[AM404]], which appears to inhibit the reuptake of the endogenous cannabinoid/vanilloid [[anandamide]] by neurons, making it more available to reduce pain. AM404 also appears to be able to directly activate the [[TRPV1]] (older name: vanilloid receptor), which also inhibits pain signals in the brain.<ref name=Ghanem2016/> |
Second mechanism centers around paracetamol metabolite AM404. This metabolite has been detected in the brains of animals and [[cerebrospinal fluid]] of humans taking paracetamol.<ref name=Ghanem2016/><ref name="pmid29238213">{{cite journal |vauthors=Sharma CV, Long JH, Shah S, Rahman J, Perrett D, Ayoub SS, Mehta V |title=First evidence of the conversion of paracetamol to AM404 in human cerebrospinal fluid |journal=J Pain Res |volume=10 |issue= |pages=2703–2709 |date=2017 |pmid=29238213 |pmc=5716395 |doi=10.2147/JPR.S143500 |url=}}</ref> Apparently, it is formed in the brain from another paracetamol metabolite [[4-aminophenol]] by action of [[fatty acid amide hydrolase]].<ref name=Ghanem2016/> Paracetamol apparently might modulate the [[Endocannabinoid system|endogenous cannabinoid system]] in the brain through its metabolite, [[AM404]], which appears to inhibit the reuptake of the endogenous cannabinoid/vanilloid [[anandamide]] by neurons, making it more available to reduce pain. AM404 also appears to be able to directly activate the [[TRPV1]] (older name: vanilloid receptor), which also inhibits pain signals in the brain.<ref name=Ghanem2016/> |
||
===Pharmacokinetics=== |
===Pharmacokinetics=== |
||
Revision as of 15:09, 30 March 2021
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | Paracetamol: /ˌpærəˈsiːtəmɒl/ Acetaminophen: /əˌsiːtəˈmɪnəfɪn/ |
| Trade names | Tylenol, Panadol, others[1] |
| Other names | N-acetyl-para-aminophenol (APAP), acetaminophen (USAN US) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a681004 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, through the cheek, rectal, intravenous (IV) |
| Drug class | Analgesics and antipyretics |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 63–89%[4]: 73 |
| Protein binding | 10–25%[5] |
| Metabolism | Predominantly in the liver[9] |
| Metabolites | APAP gluc, APAP sulfate, APAP GSH, APAP cys, NAPQI[6] |
| Onset of action | Pain relief onset by route: By mouth – 37 minutes[7] Buccal – 15 minutes[7] Intravenous – 8 minutes[7] |
| Elimination half-life | 2–2.5 hours[8] |
| Excretion | Urine (85–90%)[9] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| PubChem SID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.870 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H9NO2 |
| Molar mass | 151.165 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.263 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 169 °C (336 °F) [10][11] |
| Boiling point | 420 °C (788 °F) |
| Solubility in water | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain.[13][14] At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature;[13][15][16] it is inferior to ibuprofen in that respect,[17] and the benefits of its use for fever are unclear.[13][18][19] Paracetamol significantly relieves pain in acute migraine but only slightly in episodic tension headache.[20][21] However, the aspirin/paracetamol/caffeine combination helps with both conditions and is recommended as a first-line treatment for them.[22][23] Paracetamol is effective for post-surgical pain, but it is inferior to ibuprofen.[24] The paracetamol/ibuprofen combination provides further increase in potency and is superior to either drug alone.[24][25] The pain relief paracetamol provides in osteoarthritis is small and clinically insignificant.[14][26][27] The evidence in its favor for the use in low back pain, cancer pain and neuropathic pain is insufficient.[14][28][26][29][30][31]
In the short term, common side effects of paracetamol are nausea and abdominal pain, and it seems to have tolerability similar to ibuprofen.[32][33] Chronic consumption of paracetamol may result in a drop in hemoglobin level indicating possible gastrointestinal bleeding[34] and abnormal liver function tests.[35] There is a consistent association of increased mortality as well as cardiovascular (stroke, myocardial infarction), gastrointestinal (ulcers, bleeding) and renal adverse effects with taking higher dose of paracetamol.[34][33][36] The drug may also increase the risk of developing hypertension.[37] Elevated frequency of asthma and developmental and reproductive disorders is observed in the offspring of women with prolonged use of paracetamol during pregnancy, although whether paracetamol is the true cause of this increase is unclear.[37] The evidence for the association between paracetamol during pregnancy and autism spectrum disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is particularly strong,[38][39] all this prompting the calls to limit its use in pregnancy to the lowest effective dosage for the shortest possible time.[37][40][41]
The recommended maximum daily dose for an adult is three to four grams.[42][43][26] Higher doses may lead to toxicity, including liver failure.[44] Paracetamol poisoning is the foremost cause of acute liver failure in the Western world, and accounts for most drug overdoses in the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia, and New Zealand.[45][46][47]
Paracetamol was first made in 1877.[48] It is the most commonly used medication for pain and fever in both the United States and Europe.[49] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[50] Paracetamol is available as a generic medication, with brand names including Tylenol and Panadol among others.[51] In 2018, it was the twentieth most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 27 million prescriptions.[52][53]
Medical uses
Fever
Paracetamol is a drug of choice for reducing fever. However, there has been a dearth of research on its antipyretic properties, particularly, in adults.[13] The most recent review on paracetamol and management of fever in the general practice (2008) argued that its benefits are unclear.[13] Additionally, when taken for the common cold paracetamol may relieve stuffed or runny nose but not other cold symptoms such as sore throat, malaise, sneezing and cough; these data, however, are of low quality.[54]
For patients in critical care, paracetamol decreased body temperature by only 0.2-0.3C more than control interventions; there was no difference in mortality.[15] It did not change the outcome in febrile patients with stroke.[55] The results are contradictory for paracetamol use in sepsis: higher mortality, lower mortality, and no change in mortality were all reported.[15] Paracetamol offered no benefit in the treatment of dengue fever and was accompanied by a higher rate of liver enzyme elevation: a sign of a potential liver damage.[56] Overall, there is no support for a routine administration of antipyretic drugs, including paracetamol, to hospitalized patients with fever and infection.[19]
The efficacy of paracetamol in children with fever is unclear.[57] Paracetamol should not be used solely with the aim of reducing body temperature; however, it may be considered for children with fever who appear distressed.[58] It does not prevent febrile seizures and should not be used for that purpose.[58][59] It appears that 0.2C decrease of the body temperature in children after a standard dose of paracetamol is of questionable value, particularly in emergency situations.[13] Based on this, some physicians advocate using higher doses that may decrease the temperature by as much as 0.7C.[16] Meta-analyses showed that paracetamol is less effective than ibuprofen in children (marginally less effective, according to another analysis[60]), including children younger than 2 years old,[61] with equivalent safety.[17] Exacerbation of asthma occurs with similar frequency for both medications.[62] Giving both paracetamol and ibuprofen at the same time to children is not recommended.[58]
Pain
Paracetamol is used for the relief of mild to moderate pain such as headache, muscle aches, minor arthritis pain, toothache as well as pain caused by cold, flu, sprains, and dysmenorrhea.[63] It is recommended, in particular, for acute mild to moderate pain, since the evidence for the treatment of chronic pain is insufficient.[14]
Musculoskeletal pain
The benefits of paracetamol in musculoskeletal conditions, such as osteoarthritis and backache, are uncertain.[14]
It appears to provide only small and not clinically important benefits in osteoarthritis.[14][26] American College of Rheumatology and Arthritis Foundation guideline for the management of osteoarthritis notes that the effect size in clinical trials of paracetamol has been very small, which suggests that for most individuals it is ineffective.[27] The guideline conditionally recommends paracetamol for short-term and episodic use to those who do not tolerate nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. For people taking it regularly, monitoring for liver toxicity is required.[27] Essentially the same recommendation was issued by EULAR for hand osteoarthritis.[64] Similarly, European algorithm ESCEO for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis recommends limiting the of use paracetamol to short-term rescue analgesia only.[65]
Paracetamol is ineffective for acute low back pain.[14][28] No randomized clinical trials evaluated its use for chronic or radicular back pain, and the evidence in favor of paracetamol is lacking.[26][29][28]
Headaches
Paracetamol is effective for acute migraine:[20] 39% of people experience pain relief at one hour compared with 20% in the control group.[66] The aspirin/paracetamol/caffeine combination also "has strong evidence of effectiveness and can be used as a first-line treatment for migraine."[22] It is superior to ibuprofen and sumatriptan.[67] The German, Austrian, and Swiss headache societies and the German Society of Neurology recommend the combination as a "highlighted" one for self-medication of migraine, and paracetamol alone as a first choice.[23]
Paracetamol on its own only slightly alleviates episodic tension headache in frequent sufferers.[21] However, the aspirin/paracetamol/caffeine combination is superior to both paracetamol alone and placebo and offers meaningful relief of tension headache: 2 hours after administering the medication, 29% of those who took the combination were pain free as compared with 21% on acetaminophen and 18% on placebo.[68] The German, Austrian, and Swiss headache societies and the German Society of Neurology recommend this combination as a "highlighted" one for self-medication of tension headache, with paracetamol/caffeine combination being a "remedy of first choice", and paracetamol - a "remedy of second choice".[23]
Dental and other post-surgical pain
Pain after a dental surgery provides a reliable model for the action of analgesics on other kinds of acute pain.[69] For the relief of such pain, paracetamol is inferior to ibuprofen.[24] Full therapeutic doses of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) ibuprofen, naproxen or diclofenac are clearly more efficacious than the frequently prescribed for dental pain combination paracetamol/codeine.[70] The combinations of paracetamol and NSAIDs ibuprofen or diclofenac are promising, possibly offering better pain control than either paracetamol or the NSAID alone.[24][25][71][72] Additionally, the paracetamol/ibuprofen combination may be superior to paracetamol/codeine and ibuprofen/codeine combinations.[25]
A meta-analysis of general post-surgical pain, which included dental and other surgery, showed the paracetamol/codeine combination to be more effective than paracetamol alone: it provided significant pain relief to as much as 53% of the participants, while the placebo helped only 7%.[73]
Other pain
Paracetamol fails to relieve procedural pain in newborn babies.[74][75] For perineal pain postpartum paracetamol appears to be less effective than non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).[76]
The studies to support or refute the use of paracetamol for cancer pain and for neuropathic pain are lacking.[30][31] There is limited evidence in favor of the use of the intravenous form of paracetamol for acute pain control in the emergency department.[77] The combination of paracetamol with caffeine is superior to paracetamol alone for the treatment of acute pain.[78]
Patent ductus arteriosus
Paracetamol helps ductal closure in patent ductus arteriosus. It is as effective for this purpose as ibuprofen or indomethacin, but results in a less frequent gastrointestinal bleeding than ibuprofen.[79]
Adverse effects
For short-term control of pain, paracetamol is not better tolerated than ibuprofen.[32] Gastrointestinal adverse effects such as nausea and abdominal pain are common, and their frequency is similar to that of ibuprofen.[33] According to the US Food and Drug Administration, the drug may cause rare and possibly fatal skin reactions such as Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis,[80] although an analysis of the French Pharmacovigilance Database indicated no obvious risk of these reactions.[81]
In clinical trials for osteoarthritis, the number of participants reporting adverse effects were similar for those on paracetamol and on placebo. However, the abnormal liver function tests (meaning there was some inflammation or damage to the liver) were almost four times more likely in those on paracetamol, although the clinical importance of this effect is uncertain.[35] After 13 weeks of paracetamol therapy for knee pain, a drop in hemoglobin level indicating gastrointestinal bleeding was observed in 20% of participants, this rate being similar to ibuprofen group.[34]
Due to the absence of controlled studies, most of the information about the long-term safety of paracetamol comes from observational studies.[33] These indicate a consistent pattern of increased mortality as well as cardiovascular (stroke, myocardial infarction), gastrointestinal (ulcers, bleeding) and renal adverse effects with increased dose of paracetamol.[34][33][36] Use of paracetamol is associated with 1.9-fold higher risk of peptic ulcer.[33] Those who take it regularly at a higher dose (more than 2-3 g daily) are at much higher risk (3.6-3.7-fold) of gastrointestinal bleeding and other bleeding events.[37] Meta-analyses suggest that paracetamol may increase the risk of kidney impairment by 23%[82] and kidney cancer by 28%[36]. Paracetamol is particularly dangerous to the liver in overdose, but even without overdose those who take this drug may develop acute liver failure requiring liver transplantation more frequently than the users of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.[32] Paracetamol slightly but significantly increases blood pressure and heart rate.[33] The majority of observational studies suggests that, used chronically, it may increase the risk of developing hypertension. The risk is higher with the higher dose.[37]
The association between paracetamol use and asthma in children has been a matter of controversy.[83] However, the most recent research suggests that there is no association,[84] and that the frequency of asthma exacerbations in children after paracetamol is the same as after another frequently used pain killer ibuprofen.[62]
Use in pregnancy
Paracetamol safety in pregnancy has been under increased scrutiny. There appears to be no link between paracetamol use in the first trimester and adverse pregnancy outcomes or birth defects. However, indications exist of a possible increase of asthma and developmental and reproductive disorders in the offspring of women with prolonged use of paracetamol during pregnancy.[37]
Paracetamol use by the mother during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of childhood asthma,[85][86] but so are the maternal infections for which paracetamol may be used, and separating these influences is difficult.[37] Paracetamol is also associated with 20-30% increase in autism spectrum disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, hyperactivity symptoms, and conduct disorder, with the association being stronger with increased paracetamol use, but it is unclear whether the relationship is causal.[37][87][88] There is also an argument that the large number, consistency, and the robust designs of the studies provide a strong evidence in favor of paracetamol causing the increased risk of these neurodevelopmental disorders.[38][39] In animal experiments, paracetamol disrupts fetal testosterone production, and several epidemiological studies linked cryptorchidism with mother's paracetamol use for more than two weeks in the second trimester. On the other hand, several studies did not find any association.[37]
The consensus recommendation appears to be to avoid prolonged use of paracetamol in pregnancy and use it only when necessary, at the lowest effective dosage and for the shortest time.[37][40][41]
Overdose
Overdoses of paracetamol, that is taking more than the recommended maximum daily dose of paracetamol for healthy adults of three or four grams.[42][43], can cause potentially fatal liver damage.[89][90]
Paracetamol toxicity is the foremost cause of acute liver failure in the Western world, and accounts for most drug overdoses in the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia, and New Zealand.[45][91][46][47] Paracetamol overdose results in more calls to poison control centers in the US than overdose of any other pharmacological substance.[92] According to the FDA, in the United States, "56,000 emergency room visits, 26,000 hospitalizations, and 458 deaths per year [were] related to acetaminophen-associated overdoses during the 1990s. Within these estimates, unintentional acetaminophen overdose accounted for nearly 25% of the emergency department visits, 10% of the hospitalizations, and 25% of the deaths."[93]
Overdoses are frequently related to high-dose recreational use of prescription opioids, as these opioids are most often combined with acetaminophen.[94] The overdose risk may be heightened by frequent consumption of alcohol.[95]
Untreated paracetamol overdose results in a lengthy, painful illness. Signs and symptoms of paracetamol toxicity may initially be absent or non-specific symptoms. The first symptoms of overdose usually begin several hours after ingestion, with nausea, vomiting, sweating, and pain as acute liver failure starts.[96] People who take overdoses of paracetamol do not fall asleep or lose consciousness, although most people who attempt suicide with paracetamol wrongly believe that they will be rendered unconscious by the drug.[97][98]
Treatment is aimed at removing the paracetamol from the body and replenishing glutathione.[98] Activated charcoal can be used to decrease absorption of paracetamol if the person comes to the hospital soon after the overdose. While the antidote, acetylcysteine (also called N-acetylcysteine or NAC), acts as a precursor for glutathione, helping the body regenerate enough to prevent or at least decrease the possible damage to the liver; a liver transplant is often required if damage to the liver becomes severe.[45][99] NAC was usually given following a treatment nomogram (one for people with risk factors, and one for those without), but the use of the nomogram is no longer recommended as evidence to support the use of risk factors was poor and inconsistent, and many of the risk factors are imprecise and difficult to determine with sufficient certainty in clinical practice.[100][101][102] Toxicity of paracetamol is due to its quinone metabolite NAPQI and NAC also helps in neutralizing it.[98] Kidney failure is also a possible side effect.[95]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Paracetamol appears to exert its effects through two mechanisms: inhibition of cyclooxygenase and actions of its metabolite AM404 [103]
Supporting first mechanism, pharmacologically and in its side effects, paracetamol is close to classical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) that act by inhibiting COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, and especially similar to selective COX-2 inhibitors.[104] Paracetamol inhibits the prostaglandin synthesis by reducing the active form of COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes. This occurs only when concentration of arachidonic acid and peroxides is low. Under these conditions, COX-2 is the predominant form of cyclooxygenase, which explains apparent COX-2 selectivity of paracetamol. Under the conditions of inflammation, the concentration of peroxides is high, which counteracts the reducing effect of paracetamol. Accordingly, anti-inflammatory action of paracetamol is slight.[103][104]
Second mechanism centers around paracetamol metabolite AM404. This metabolite has been detected in the brains of animals and cerebrospinal fluid of humans taking paracetamol.[103][105] Apparently, it is formed in the brain from another paracetamol metabolite 4-aminophenol by action of fatty acid amide hydrolase.[103] Paracetamol apparently might modulate the endogenous cannabinoid system in the brain through its metabolite, AM404, which appears to inhibit the reuptake of the endogenous cannabinoid/vanilloid anandamide by neurons, making it more available to reduce pain. AM404 also appears to be able to directly activate the TRPV1 (older name: vanilloid receptor), which also inhibits pain signals in the brain.[103]
Pharmacokinetics

After being taken by mouth, paracetamol is rapidly absorbed by the gastrointestinal (GI) tract (although absorption through the stomach is negligible);[106] its volume of distribution is roughly 50 L.[107] The concentration in serum after a typical dose of paracetamol usually peaks below 30 μg/ml (200 μmol/L).[108] After 4 hours, the concentration is usually less than 10 μg/ml (66 μmol/L).[108]
Paracetamol can be safely taken both with food and on an empty stomach.[109] Bioavailability (the percentage of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation) is "not different between fasted and fed states."[110] However, one review found that taking paracetamol with food may have an effect that "reduces its efficacy for a given dose and increases the likelihood of additional doses or different analgesics being taken."[110] Paracetamol is metabolized primarily in the liver, into toxic and nontoxic products. Three metabolic pathways are notable:[98]
- Glucuronidation (45–55%),[9] by UGT1A1 and UGT1A6;[111]
- Sulfation (sulfate conjugation) (20–30%)[9] by SULT1A1;[111]
- N-hydroxylation and dehydration, then glutathione conjugation, (less than 15%). The hepatic cytochrome P450 enzyme system metabolises paracetamol (mainly CYP2E1), forming a minor yet significant alkylating metabolite known as NAPQI (N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine) (also known as N-acetylimidoquinone).[98][112] NAPQI is then irreversibly conjugated with the sulfhydryl groups of glutathione.[112]
All three pathways yield final products that are inactive, nontoxic, and eventually excreted by the kidneys. In the third pathway, however, the intermediate product NAPQI is toxic. NAPQI is primarily responsible for the toxic effects of paracetamol; this constitutes an example of toxication.[113] Production of NAPQI is due primarily to two isoenzymes of cytochrome P450: CYP2E1[111] and CYP3A4.[113] At usual doses, NAPQI is quickly detoxified by conjugation with glutathione.[98][112]
Pharmacomicrobiomics
This section needs expansion with: PMID 31151933, 30269615, 24785449 and/or pharmacomicrobiomics |
Chemistry
Chemical properties



Paracetamol consists of a benzene ring core, substituted by one hydroxyl group and the nitrogen atom of an amide group in the para (1,4) pattern.[114] The amide group is acetamide (ethanamide). It is an extensively conjugated system, as one lone pair on the hydroxyl oxygen, the benzene pi cloud, the nitrogen lone pair, the p orbital on the carbonyl carbon, and one lone pair on the carbonyl oxygen are all conjugated. The presence of two activating groups also make the benzene ring highly reactive toward electrophilic aromatic substitution. As the substituents are ortho, para-directing and para with respect to each other, all positions on the ring are more or less equally activated. The conjugation also greatly reduces the basicity of the oxygens and the nitrogen, while making the hydroxyl acidic through delocalisation of charge developed on the phenoxide anion.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2019) |
Paracetamol is part of the class of drugs known as "aniline analgesics"; it is the only such drug still in use today.[115] It is not considered an NSAID because it does not exhibit significant anti-inflammatory activity (it is a weak COX inhibitor).[116][117] This is despite the evidence that paracetamol and NSAIDs have some similar pharmacological activity.[118]
Synthesis
Original (Boots) method
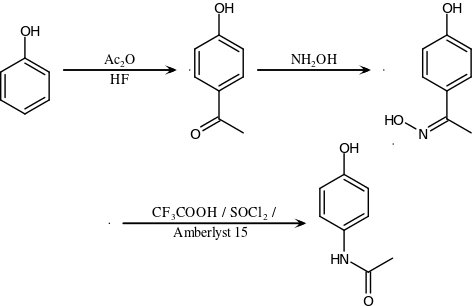
The original method for production involves the nitration of phenol with sodium nitrate and gives a mixture of two isomers, from which the desired 4-nitrophenol (bp 279 °C) can easily be separated by steam distillation. In this electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, phenol's oxygen is strongly activating, thus the reaction requires only mild conditions as compared to nitration of benzene itself. The nitro group is then reduced to an amine, giving 4-aminophenol. Finally, the amine is acetylated with acetic anhydride.[119] Industrially, direct hydrogenation is used, but in the laboratory scale sodium borohydride serves.[120][121]
Green synthesis
An alternative industrial synthesis developed by Hoechst–Celanese involves direct acylation of phenol with acetic anhydride catalyzed by HF, conversion of the ketone to a ketoxime with hydroxylamine, followed by the acid-catalyzed Beckmann rearrangement to give the amide.[121][122]
Direct synthesis
More recently (2014) a "one-pot" synthesis from hydroquinone has been described before the Royal Society of Chemistry.[123][124] The process may be summarized as follows:
- Hydroquinone, ammonium acetate, and acetic acid were mixed in an argon atmosphere and heated slowly to 230 °C. The mixture was stirred at this temperature for 15 hours. After cooling, the acetic acid was evaporated and the precipitate was filtered, washed with water and dried to give paracetamol as a white solid.
The authors go on to claim an 88% yield and 99% purity.[125]

Reactions
4-Aminophenol may be obtained by the amide hydrolysis of paracetamol. 4-Aminophenol prepared this way, and related to the commercially available Metol, has been used as a developer in photography by hobbyists.[126] This reaction is also used to determine paracetamol in urine samples: After hydrolysis with hydrochloric acid, 4-aminophenol reacts in ammonia solution with a phenol derivate, e.g. salicylic acid, to form an indophenol dye under oxidization by air.[127]
History

Acetanilide was the first aniline derivative serendipitously found to possess analgesic as well as antipyretic properties, and was quickly introduced into medical practice under the name of Antifebrin by Cahn & Hepp in 1886.[128] But its unacceptable toxic effects – the most alarming being cyanosis due to methemoglobinemia – prompted the search for less toxic aniline derivatives.[115] Harmon Northrop Morse had already synthesized paracetamol at Johns Hopkins University via the reduction of p-nitrophenol with tin in glacial acetic acid in 1877,[129][130] but it was not until 1887 that clinical pharmacologist Joseph von Mering tried paracetamol on humans.[115] In 1893, von Mering published a paper reporting on the clinical results of paracetamol with phenacetin, another aniline derivative.[131] Von Mering claimed that, unlike phenacetin, paracetamol had a slight tendency to produce methemoglobinemia. Paracetamol was then quickly discarded in favor of phenacetin. The sales of phenacetin established Bayer as a leading pharmaceutical company.[132] Overshadowed in part by aspirin, introduced into medicine by Heinrich Dreser in 1899, phenacetin was popular for many decades, particularly in widely advertised over-the-counter "headache mixtures", usually containing phenacetin, an aminopyrine derivative or aspirin, caffeine, and sometimes a barbiturate.[115]
Paracetamol is the active metabolite of phenacetin and acetanilide, both once popular as analgesics and antipyretics in their own right.[107][133] However, unlike phenacetin, acetanilide and their combinations, paracetamol is not considered carcinogenic at therapeutic doses.[134]
Von Mering's claims remained essentially unchallenged for half a century, until two teams of researchers from the United States analyzed the metabolism of acetanilide and paracetamol.[132] In 1947, David Lester and Leon Greenberg found strong evidence that paracetamol was a major metabolite of acetanilide in human blood, and in a subsequent study they reported that large doses of paracetamol given to albino rats did not cause methemoglobinemia.[135] In three papers published in the September 1948 issue of the Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, Bernard Brodie, Julius Axelrod and Frederick Flinn confirmed using more specific methods that paracetamol was the major metabolite of acetanilide in human blood, and established that it was just as efficacious an analgesic as its precursor.[136][137][138] They also suggested that methemoglobinemia is produced in humans mainly by another metabolite, phenylhydroxylamine. A follow-up paper by Brodie and Axelrod in 1949 established that phenacetin was also metabolized to paracetamol.[139] This led to a "rediscovery" of paracetamol.[115] It has been suggested that contamination of paracetamol with 4-aminophenol, the substance von Mering synthesised it from, may be the cause for his spurious findings.[132]
Paracetamol was first marketed in the United States in 1950 under the name Triagesic, a combination of paracetamol, aspirin, and caffeine.[130] Reports in 1951 of three users stricken with the blood disease agranulocytosis led to its removal from the marketplace, and it took several years until it became clear that the disease was unconnected.[130] Paracetamol was marketed in 1953 by Sterling-Winthrop Co. as Panadol, available only by prescription, and promoted as preferable to aspirin since it was safe for children and people with ulcers.[130][132][140] In 1955, paracetamol was marketed as Children's Tylenol Elixir by McNeil Laboratories.[141] In 1956, 500 mg tablets of paracetamol went on sale in the United Kingdom under the brand name Panadol, produced by Frederick Stearns & Co, a subsidiary of Sterling Drug Inc. In 1963, paracetamol was added to the British Pharmacopoeia, and has gained popularity since then as an analgesic agent with few side-effects and little interaction with other pharmaceutical agents.[130] Concerns about paracetamol's safety delayed its widespread acceptance until the 1970s, but in the 1980s paracetamol sales exceeded those of aspirin in many countries, including the United Kingdom. This was accompanied by the commercial demise of phenacetin, blamed as the cause of analgesic nephropathy and hematological toxicity.[115] In 1988, Sterling Winthrop was acquired by Eastman Kodak which sold the over the counter drug rights to SmithKline Beecham in 1994.[142]
Available without a prescription since 1959,[143] it has since become a common household drug.[144] Patents on paracetamol have long expired, and generic versions of the drug are widely available.[1][145]
In June 2009, an FDA advisory committee recommended that new restrictions be placed on paracetamol use in the United States to help protect people from the potential toxic effects. The maximum dosage at any given time would be decreased from 1000 mg to 650 mg, while combinations of paracetamol and opioid analgesics would be prohibited. Committee members were particularly concerned by the fact that the then-present maximum dosages of paracetamol had been shown to produce alterations in liver function.[146]
In January 2011, the FDA asked manufacturers of prescription combination products containing paracetamol to limit its amount to no more than 325 mg per tablet or capsule and began requiring manufacturers to update the labels of all prescription combination paracetamol products to warn of the potential risk of severe liver damage.[147][148][149][150] Manufacturers had three years to limit the amount of paracetamol in their prescription drug products to 325 mg per dosage unit.[148][150] In November 2011, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency revised UK dosing of liquid paracetamol for children.[151]In 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) launched a public-education program to help consumers avoid overdose, warning: "Acetaminophen can cause serious liver damage if more than directed is used."[152] In a 2011 Safety Warning, the FDA immediately required manufacturers to update labels of all prescription combination acetaminophen products to warn of the potential risk for severe liver injury and required that such combinations contain no more than 325 mg of acetaminophen.[153][148]
During the COVID-19 pandemic it was widely considered by the scientific community as the main and most effective analgesic medication to treat symptoms of SARS-CoV II.[154][155][156][157]
Society and culture
Naming
Acetaminophen is the name generally used in the United States (United States Adopted Name), Japan (Japanese Accepted Name), Canada,[158] Venezuela, Colombia, and Iran; paracetamol is used in international venues (International Nonproprietary Name, Australian Approved Name, British Approved Name).[158][159][160] In some contexts, such as on prescription bottles of painkillers that incorporate this medicine, it is simply abbreviated as APAP, for acetyl-para-aminophenol.
Both acetaminophen and paracetamol come from a chemical name for the compound: para-acetylaminophenol and para-acetylaminophenol.
Available forms
Paracetamol is available in tablet, capsule, liquid suspension, suppository, intravenous, intramuscular and effervescent forms.[161][162] Intravenous acetaminophen is sold under the brand name Ofirmev in the United States.[163]
In some formulations, paracetamol is combined with the opiate codeine, sometimes referred to as co-codamol (BAN) and Panadeine in Australia. In the U.S., this combination is available only by prescription,[164] while the lowest-strength preparation is over the counter in Canada, and in other countries other strengths may be available over the counter.[citation needed] Paracetamol is also combined with other opioids such as dihydrocodeine,[165] referred to as co-dydramol (British Approved Name (BAN)), oxycodone[166] or hydrocodone.[167] Another very commonly used analgesic combination includes paracetamol in combination with propoxyphene napsylate.[168] A combination of paracetamol, codeine, and the calmative doxylamine succinate is also available.[169] The efficacy of paracetamol/codeine combinations has been questioned by research from 2010.[170]
Paracetamol is commonly used in multi-ingredient preparations for migraine headache, typically including butalbital and paracetamol with or without caffeine, and sometimes containing codeine.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2019) |
Paracetamol is sometimes combined with phenylephrine hydrochloride.[171] Sometimes a third active ingredient, such as ascorbic acid,[171][172] caffeine,[173][174] chlorpheniramine maleate,[175] or guaifenesin[176][177][178] is added to this combination.
When marketed in combination with diphenhydramine hydrochloride, it is frequently given the label "PM" and is meant as a sleep aid. Diphenhydramine hydrochloride is known to have hypnotic effects and is non-habit forming. Unfortunately, it has been implicated in the occasional development of restless leg syndrome.[179]
Controversy
In September 2013, an episode of This American Life titled "Use Only as Directed"[180] highlighted deaths from paracetamol overdose. This report was followed by two reports by ProPublica alleging that the "FDA has long been aware of studies showing the risks of acetaminophen. So has the maker of Tylenol, McNeil Consumer Healthcare, a division of Johnson & Johnson"[181] and "McNeil, the maker of Tylenol, ... has repeatedly opposed safety warnings, dosage restrictions and other measures meant to safeguard users of the drug."[182]
A report prepared by an internal FDA working group describes a history of FDA initiatives designed to educate consumers about the risk of paracetamol overdose and notes that one challenge to the Agency has been "identifying the appropriate message about the relative safety of acetaminophen, especially compared to other OTC pain relievers (e.g., aspirin and other NSAIDs)". The report notes that "Chronic use of NSAIDs is also associated with significant morbidity and mortality. NSAID gastrointestinal risk is substantial, with deaths and hospitalization estimated in one publication as 3200 and 32,000 per year respectively. Possible cardiovascular toxicity with chronic NSAID use has been a major discussion recently", finally noting that "The goal of the educational efforts is not to decrease appropriate acetaminophen use or encourage substitution of NSAID use, but rather to educate consumers so that they can avoid unnecessary health risks."[183]
Veterinary use
Cats
Paracetamol is extremely toxic to cats, which lack the necessary UGT1A6 enzyme to break it down safely. Initial symptoms include vomiting, salivation, and discoloration of the tongue and gums.
Unlike an overdose in humans, liver damage is rarely the cause of death; instead, methemoglobin formation and the production of Heinz bodies in red blood cells inhibit oxygen transport by the blood, causing asphyxiation (methemoglobemia and hemolytic anemia).[184]
Treatment with N-acetylcysteine,[185] methylene blue or both is sometimes effective after the ingestion of small doses of paracetamol.
Dogs
Although paracetamol is believed to have no significant anti-inflammatory activity, it has been reported to be as effective as aspirin in the treatment of musculoskeletal pain in dogs.[186]
A paracetamol-codeine product (brand name Pardale-V)[187] licensed for use in dogs is available for purchase under supervision of a vet, pharmacist or other qualified person.[187] It should be administered to dogs only on veterinary advice and with extreme caution.[187]
The main effect of toxicity in dogs is liver damage, and GI ulceration has been reported.[185][188][189][190] N-acetylcysteine treatment is efficacious in dogs when administered within two hours of paracetamol ingestion.[185][186]
Snakes
Paracetamol is lethal to snakes, and has been suggested as a chemical control program for the invasive brown tree snake (Boiga irregularis) in Guam.[191][192] Doses of 80 mg are inserted into dead mice that are scattered by helicopter.[193]
References
- ^ a b International Drug Names
- ^ "Acetaminophen Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 14 June 2019. Archived from the original on 9 March 2020. Retrieved 25 February 2020.
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ Working Group of the Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists and Faculty of Pain Medicine (2015). Schug SA, Palmer GM, Scott DA, Halliwell R, Trinca J (eds.). Acute Pain Management: Scientific Evidence (4th ed.). Melbourne: Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists (ANZCA), Faculty of Pain Medicine (FPM). ISBN 978-0-9873236-7-5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 July 2019. Retrieved 28 October 2019.
- ^ "Tylenol, Tylenol Infants' Drops (acetaminophen) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more". Medscape Reference. Archived from the original on 14 April 2014. Retrieved 10 May 2014.
- ^ "Acetaminophen Pathway (therapeutic doses), Pharmacokinetics". Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 13 January 2016.
- ^ a b c Pickering G, Macian N, Libert F, Cardot JM, Coissard S, Perovitch P, Maury M, Dubray C (September 2014). "Buccal acetaminophen provides fast analgesia: two randomized clinical trials in healthy volunteers". Drug Design, Development and Therapy. 8: 1621–1627. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S63476. PMC 4189711. PMID 25302017.
bAPAP has a faster time of antinociception onset (15 minutes, P<0.01) and greater antinociception at 50 minutes (P<0.01, CT1) and 30 minutes (P<0.01, CT2) than ivAPAP and sAPAP. All routes are similar after 50 minutes. ... In postoperative conditions for acute pain of mild to moderate intensity, the quickest reported time to onset of analgesia with APAP is 8 minutes9 for the iv route and 37 minutes6 for the oral route.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "Risk prediction of hepatotoxicity in paracetamol poisoning". Clin Toxicol (Phila). 55 (8): 879–892. 2017. doi:10.1080/15563650.2017.1317349. PMID 28447858. S2CID 8888616.
{{cite journal}}: Cite uses deprecated parameter|authors=(help) - ^ a b c d "Codapane Forte Paracetamol and codeine phosphate product information" (PDF). TGA eBusiness Services. Alphapharm Pty Limited. 29 April 2013. Archived from the original on 6 February 2016. Retrieved 10 May 2014.
- ^ Karthikeyan M, Glen RC, Bender A (2005). "General Melting Point Prediction Based on a Diverse Compound Data Set and Artificial Neural Networks". Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 45 (3): 581–590. doi:10.1021/ci0500132. PMID 15921448.
- ^ "melting point data for paracetamol". Lxsrv7.oru.edu. Archived from the original on 30 June 2012. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ a b c d e Granberg RA, Rasmuson AC (1999). "Solubility of paracetamol in pure solvents". Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data. 44 (6): 1391–95. doi:10.1021/je990124v.
- ^ a b c d e f Warwick C (November 2008). "Paracetamol and fever management". J R Soc Promot Health. 128 (6): 320–3. doi:10.1177/1466424008092794. PMID 19058473.
- ^ a b c d e f g Saragiotto BT, Abdel Shaheed C, Maher CG (December 2019). "Paracetamol for pain in adults". BMJ. 367: l6693. doi:10.1136/bmj.l6693. PMID 31892511.
- ^ a b c Chiumello D, Gotti M, Vergani G (April 2017). "Paracetamol in fever in critically ill patients-an update". J Crit Care. 38: 245–252. doi:10.1016/j.jcrc.2016.10.021. PMID 27992852.
- ^ a b de Martino M, Chiarugi A (December 2015). "Recent Advances in Pediatric Use of Oral Paracetamol in Fever and Pain Management". Pain Ther. 4 (2): 149–68. doi:10.1007/s40122-015-0040-z. PMC 4676765. PMID 26518691.
- ^ a b Pierce CA, Voss B (March 2010). "Efficacy and safety of ibuprofen and acetaminophen in children and adults: a meta-analysis and qualitative review". Ann Pharmacother. 44 (3): 489–506. doi:10.1345/aph.1M332. PMID 20150507.
- ^ Meremikwu M, Oyo-Ita A (2002). "Paracetamol for treating fever in children". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2): CD003676. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003676. PMC 6532671. PMID 12076499.
- ^ a b Ludwig J, McWhinnie H (May 2019). "Antipyretic drugs in patients with fever and infection: literature review". Br J Nurs. 28 (10): 610–618. doi:10.12968/bjon.2019.28.10.610. PMID 31116598.
- ^ a b Marmura MJ, Silberstein SD, Schwedt TJ (January 2015). "The acute treatment of migraine in adults: the american headache society evidence assessment of migraine pharmacotherapies". Headache. 55 (1): 3–20. doi:10.1111/head.12499. PMID 25600718.
- ^ a b Stephens G, Derry S, Moore RA (June 2016). "Paracetamol (acetaminophen) for acute treatment of episodic tension-type headache in adults". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (6): CD011889. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011889.pub2. PMC 6457822. PMID 27306653.
- ^ a b Mayans L, Walling A (February 2018). "Acute Migraine Headache: Treatment Strategies". Am Fam Physician. 97 (4): 243–251. PMID 29671521.
- ^ a b c Haag G, Diener HC, May A, Meyer C, Morck H, Straube A, Wessely P, Evers S (April 2011). "Self-medication of migraine and tension-type headache: summary of the evidence-based recommendations of the Deutsche Migräne und Kopfschmerzgesellschaft (DMKG), the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Neurologie (DGN), the Österreichische Kopfschmerzgesellschaft (ÖKSG) and the Schweizerische Kopfwehgesellschaft (SKG)". J Headache Pain. 12 (2): 201–17. doi:10.1007/s10194-010-0266-4. PMC 3075399. PMID 21181425.
- ^ a b c d Bailey E, Worthington HV, van Wijk A, Yates JM, Coulthard P, Afzal Z (December 2013). "Ibuprofen and/or paracetamol (acetaminophen) for pain relief after surgical removal of lower wisdom teeth". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (12): CD004624. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004624.pub2. PMID 24338830.
- ^ a b c Moore PA, Hersh EV (August 2013). "Combining ibuprofen and acetaminophen for acute pain management after third-molar extractions: translating clinical research to dental practice". J Am Dent Assoc. 144 (8): 898–908. doi:10.14219/jada.archive.2013.0207. PMID 23904576.
- ^ a b c d e Machado GC, Maher CG, Ferreira PH, Pinheiro MB, Lin CW, Day RO, et al. (March 2015). "Efficacy and safety of paracetamol for spinal pain and osteoarthritis: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo controlled trials". BMJ. 350: h1225. doi:10.1136/bmj.h1225. PMC 4381278. PMID 25828856.
- ^ a b c Kolasinski SL, Neogi T, Hochberg MC, Oatis C, Guyatt G, Block J, Callahan L, Copenhaver C, Dodge C, Felson D, Gellar K, Harvey WF, Hawker G, Herzig E, Kwoh CK, Nelson AE, Samuels J, Scanzello C, White D, Wise B, Altman RD, DiRenzo D, Fontanarosa J, Giradi G, Ishimori M, Misra D, Shah AA, Shmagel AK, Thoma LM, Turgunbaev M, Turner AS, Reston J (February 2020). "2019 American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip, and Knee". Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 72 (2): 149–162. doi:10.1002/acr.24131. PMID 31908149.
- ^ a b c Qaseem A, Wilt TJ, McLean RM, Forciea MA (April 2017). "Noninvasive Treatments for Acute, Subacute, and Chronic Low Back Pain: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American College of Physicians". Ann Intern Med. 166 (7): 514–530. doi:10.7326/M16-2367. PMID 28192789.
- ^ a b Saragiotto BT, Machado GC, Ferreira ML, Pinheiro MB, Abdel Shaheed C, Maher CG (June 2016). "Paracetamol for low back pain". Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 6 (6): CD012230. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012230. PMC 6353046. PMID 27271789.
- ^ a b Wiffen PJ, Derry S, Moore RA, McNicol ED, Bell RF, Carr DB, McIntyre M, Wee B (July 2017). "Oral paracetamol (acetaminophen) for cancer pain". Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 7: CD012637. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012637.pub2. PMC 6369932. PMID 28700092.
- ^ a b Wiffen PJ, Knaggs R, Derry S, Cole P, Phillips T, Moore RA (December 2016). "Paracetamol (acetaminophen) with or without codeine or dihydrocodeine for neuropathic pain in adults". Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 12: CD012227. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012227.pub2. PMC 6463878. PMID 28027389.
- ^ a b c Moore RA, Moore N (July 2016). "Paracetamol and pain: the kiloton problem". Eur J Hosp Pharm. 23 (4): 187–188. doi:10.1136/ejhpharm-2016-000952. PMID 31156845.
- ^ a b c d e f g Conaghan PG, Arden N, Avouac B, Migliore A, Rizzoli R (April 2019). "Safety of Paracetamol in Osteoarthritis: What Does the Literature Say?". Drugs Aging. 36 (Suppl 1): 7–14. doi:10.1007/s40266-019-00658-9. PMC 6509082. PMID 31073920.
- ^ a b c d Roberts E, Delgado Nunes V, Buckner S, Latchem S, Constanti M, Miller P, Doherty M, Zhang W, Birrell F, Porcheret M, Dziedzic K, Bernstein I, Wise E, Conaghan PG (March 2016). "Paracetamol: not as safe as we thought? A systematic literature review of observational studies". Ann Rheum Dis. 75 (3): 552–9. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206914. PMC 4789700. PMID 25732175.
- ^ a b Leopoldino AO, Machado GC, Ferreira PH, Pinheiro MB, Day R, McLachlan AJ, Hunter DJ, Ferreira ML (February 2019). "Paracetamol versus placebo for knee and hip osteoarthritis". Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2: CD013273. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013273. PMC 6388567. PMID 30801133.
- ^ a b c Choueiri TK, Je Y, Cho E (January 2014). "Analgesic use and the risk of kidney cancer: a meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies". Int J Cancer. 134 (2): 384–96. doi:10.1002/ijc.28093. PMC 3815746. PMID 23400756.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j McCrae JC, Morrison EE, MacIntyre IM, Dear JW, Webb DJ (October 2018). "Long-term adverse effects of paracetamol - a review". Br J Clin Pharmacol. 84 (10): 2218–2230. doi:10.1111/bcp.13656. PMC 6138494. PMID 29863746.
- ^ a b Bauer AZ, Kriebel D, Herbert MR, Bornehag CG, Swan SH (May 2018). "Prenatal paracetamol exposure and child neurodevelopment: A review". Horm Behav. 101: 125–147. doi:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2018.01.003. PMID 29341895.
- ^ a b Gou X, Wang Y, Tang Y, Qu Y, Tang J, Shi J, Xiao D, Mu D (March 2019). "Association of maternal prenatal acetaminophen use with the risk of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in offspring: A meta-analysis". Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 53 (3): 195–206. doi:10.1177/0004867418823276. PMID 30654621.
- ^ a b Toda K (October 2017). "Is acetaminophen safe in pregnancy?". Scand J Pain. 17: 445–446. doi:10.1016/j.sjpain.2017.09.007. PMID 28986045.
- ^ a b Black E, Khor KE, Kennedy D, Chutatape A, Sharma S, Vancaillie T, Demirkol A (November 2019). "Medication Use and Pain Management in Pregnancy: A Critical Review". Pain Pract. 19 (8): 875–899. doi:10.1111/papr.12814. PMID 31242344.
- ^ a b "Paracetamol for adults: painkiller to treat aches, pains and fever". National Health Service. Archived from the original on 22 August 2017. Retrieved 22 August 2017.
- ^ a b "What are the recommended maximum daily dosages of acetaminophen in adults and children?". Medscape. Archived from the original on 21 December 2018. Retrieved 19 December 2018.
- ^ "Acetaminophen". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 5 June 2016. Retrieved 16 September 2016.
- ^ a b c Daly FF, Fountain JS, Murray L, Graudins A, Buckley NA (March 2008). "Guidelines for the management of paracetamol poisoning in Australia and New Zealand—explanation and elaboration. A consensus statement from clinical toxicologists consulting to the Australasian poisons information centres". The Medical Journal of Australia. 188 (5): 296–301. doi:10.5694/j.1326-5377.2008.tb01625.x. PMID 18312195. S2CID 9505802.
- ^ a b Hawkins LC, Edwards JN, Dargan PI (2007). "Impact of restricting paracetamol pack sizes on paracetamol poisoning in the United Kingdom: a review of the literature". Drug Saf. 30 (6): 465–79. doi:10.2165/00002018-200730060-00002. PMID 17536874. S2CID 36435353.
- ^ a b Larson AM, Polson J, Fontana RJ, Davern TJ, Lalani E, Hynan LS, et al. (2005). "Acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure: results of a United States multicenter, prospective study". Hepatology. 42 (6): 1364–72. doi:10.1002/hep.20948. PMID 16317692. S2CID 24758491.
- ^ Mangus BC, Miller MG (2005). Pharmacology application in athletic training. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: F.A. Davis. p. 39. ISBN 9780803620278. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017. Retrieved 7 September 2017.
- ^ Aghababian RV (22 October 2010). Essentials of emergency medicine. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. p. 814. ISBN 978-1-4496-1846-9. Archived from the original on 17 August 2016.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ Hamilton RJ (2013). Tarascon pocket pharmacopoeia : 2013 classic shirt-pocket edition (27th ed.). Burlington, Massachusetts: Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 12. ISBN 9781449665869. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2021". ClinCalc. Retrieved 18 February 2021.
- ^ "Acetaminophen - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 18 February 2021.
- ^ Li S, Yue J, Dong BR, Yang M, Lin X, Wu T (July 2013). "Acetaminophen (paracetamol) for the common cold in adults". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (7): CD008800. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008800.pub2. PMC 7389565. PMID 23818046.
- ^ de Ridder IR, den Hertog HM, van Gemert HM, Schreuder AH, Ruitenberg A, Maasland EL, Saxena R, van Tuijl JH, Jansen BP, Van den Berg-Vos RM, Vermeij F, Koudstaal PJ, Kappelle LJ, Algra A, van der Worp HB, Dippel DW (April 2017). "PAIS 2 (Paracetamol [Acetaminophen] in Stroke 2): Results of a Randomized, Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial". Stroke. 48 (4): 977–982. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.015957. PMID 28289240.
- ^ Deen J, von Seidlein L (May 2019). "Paracetamol for dengue fever: no benefit and potential harm?". Lancet Glob Health. 7 (5): e552–e553. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30157-3. PMID 31000122.
- ^ Meremikwu M, Oyo-Ita A (2002). "Paracetamol for treating fever in children". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2): CD003676. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003676. PMC 6532671. PMID 12076499.
- ^ a b c "Recommendations. Fever in under 5s: assessment and initial management.Guidance. NICE".
- ^ Hashimoto R, Suto M, Tsuji M, Sasaki H, Takehara K, Ishiguro A, Kubota M (April 2021). "Use of antipyretics for preventing febrile seizure recurrence in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Eur J Pediatr. 180 (4): 987–997. doi:10.1007/s00431-020-03845-8. PMID 33125519.
- ^ Narayan K, Cooper S, Morphet J, Innes K (August 2017). "Effectiveness of paracetamol versus ibuprofen administration in febrile children: A systematic literature review". J Paediatr Child Health. 53 (8): 800–807. doi:10.1111/jpc.13507. PMID 28437025.
- ^ Tan E, Braithwaite I, McKinlay CJ, Dalziel SR (October 2020). "Comparison of Acetaminophen (Paracetamol) With Ibuprofen for Treatment of Fever or Pain in Children Younger Than 2 Years: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". JAMA Netw Open. 3 (10): e2022398. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.22398. PMC 7599455. PMID 33125495.
- ^ a b Sherbash M, Furuya-Kanamori L, Nader JD, Thalib L (March 2020). "Risk of wheezing and asthma exacerbation in children treated with paracetamol versus ibuprofen: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials". BMC Pulm Med. 20 (1): 72. doi:10.1186/s12890-020-1102-5. PMC 7087361. PMID 32293369.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Bertolini A, Ferrari A, Ottani A, Guerzoni S, Tacchi R, Leone S (2006). "Paracetamol: new vistas of an old drug". CNS Drug Rev. 12 (3–4): 250–75. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2006.00250.x. PMC 6506194. PMID 17227290.
- ^ Kloppenburg M, Kroon FP, Blanco FJ, Doherty M, Dziedzic KS, Greibrokk E, Haugen IK, Herrero-Beaumont G, Jonsson H, Kjeken I, Maheu E, Ramonda R, Ritt MJ, Smeets W, Smolen JS, Stamm TA, Szekanecz Z, Wittoek R, Carmona L (January 2019). "2018 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of hand osteoarthritis". Ann Rheum Dis. 78 (1): 16–24. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213826. PMID 30154087.
- ^ Bruyère O, Honvo G, Veronese N, Arden NK, Branco J, Curtis EM, Al-Daghri NM, Herrero-Beaumont G, Martel-Pelletier J, Pelletier JP, Rannou F, Rizzoli R, Roth R, Uebelhart D, Cooper C, Reginster JY (December 2019). "An updated algorithm recommendation for the management of knee osteoarthritis from the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases (ESCEO)". Semin Arthritis Rheum. 49 (3): 337–350. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.04.008. PMID 31126594.
- ^ Derry S, Moore RA (2013). "Paracetamol (acetaminophen) with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults". Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 4 (4): CD008040. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008040.pub3. PMC 4161111. PMID 23633349.
- ^ Anneken K, Evers S, Husstedt IW (April 2010). "Efficacy of fixed combinations of acetylsalicyclic acid, acetaminophen and caffeine in the treatment of idiopathic headache: a review". Eur J Neurol. 17 (4): 534–e25. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2009.02922.x. PMID 20074228.
- ^ Diener HC, Gold M, Hagen M (November 2014). "Use of a fixed combination of acetylsalicylic acid, acetaminophen and caffeine compared with acetaminophen alone in episodic tension-type headache: meta-analysis of four randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover studies". J Headache Pain. 15: 76. doi:10.1186/1129-2377-15-76. PMC 4256978. PMID 25406671.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Pergolizzi JV, Magnusson P, LeQuang JA, Gharibo C, Varrassi G (April 2020). "The pharmacological management of dental pain". Expert Opin Pharmacother. 21 (5): 591–601. doi:10.1080/14656566.2020.1718651. PMID 32027199.
- ^ Hersh EV, Moore PA, Grosser T, Polomano RC, Farrar JT, Saraghi M, Juska SA, Mitchell CH, Theken KN (July 2020). "Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Opioids in Postsurgical Dental Pain". J Dent Res. 99 (7): 777–786. doi:10.1177/0022034520914254. PMID 32286125.
- ^ Derry CJ, Derry S, Moore RA (June 2013). "Single dose oral ibuprofen plus paracetamol (acetaminophen) for acute postoperative pain". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (6): CD010210. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010210.pub2. PMC 6485825. PMID 23794268.
- ^ Daniels SE, Atkinson HC, Stanescu I, Frampton C (October 2018). "Analgesic Efficacy of an Acetaminophen/Ibuprofen Fixed-dose Combination in Moderate to Severe Postoperative Dental Pain: A Randomized, Double-blind, Parallel-group, Placebo-controlled Trial". Clin Ther. 40 (10): 1765–1776.e5. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2018.08.019. PMID 30245281.
- ^ Toms L, Derry S, Moore RA, McQuay HJ (January 2009). "Single dose oral paracetamol (acetaminophen) with codeine for postoperative pain in adults". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1): CD001547. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001547.pub2. PMC 4171965. PMID 19160199.
- ^ Allegaert K (2020). "A Critical Review on the Relevance of Paracetamol for Procedural Pain Management in Neonates". Front Pediatr. 8: 89. doi:10.3389/fped.2020.00089. PMC 7093493. PMID 32257982.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Ohlsson A, Shah PS (January 2020). "Paracetamol (acetaminophen) for prevention or treatment of pain in newborns". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1: CD011219. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011219.pub4. PMC 6984663. PMID 31985830.
- ^ Wuytack F, Smith V, Cleary BJ (January 2021). "Oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (single dose) for perineal pain in the early postpartum period". Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 1: CD011352. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011352.pub3. PMID 33427305.
- ^ Sin B, Wai M, Tatunchak T, Motov SM (May 2016). "The Use of Intravenous Acetaminophen for Acute Pain in the Emergency Department". Academic Emergency Medicine. 23 (5): 543–53. doi:10.1111/acem.12921. PMID 26824905.
- ^ Derry CJ, Derry S, Moore RA (March 2012). Derry S (ed.). "Caffeine as an analgesic adjuvant for acute pain in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 3 (3): CD009281. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009281.pub2. PMID 22419343.
- ^ Ohlsson A, Shah PS (January 2020). "Paracetamol (acetaminophen) for patent ductus arteriosus in preterm or low birth weight infants". Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 1: CD010061. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010061.pub4. PMC 6984659. PMID 31985831.
- ^ "FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA warns of rare but serious skin reactions with the pain reliever/fever reducer acetaminophen". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 1 August 2013. Archived from the original on 28 October 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Lebrun-Vignes B, Guy C, Jean-Pastor MJ, Gras-Champel V, Zenut M (February 2018). "Is acetaminophen associated with a risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis? Analysis of the French Pharmacovigilance Database". Br J Clin Pharmacol. 84 (2): 331–338. doi:10.1111/bcp.13445. PMC 5777438. PMID 28963996.
- ^ Kanchanasurakit S, Arsu A, Siriplabpla W, Duangjai A, Saokaew S (March 2020). "Acetaminophen use and risk of renal impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Kidney Res Clin Pract. 39 (1): 81–92. doi:10.23876/j.krcp.19.106. PMC 7105620. PMID 32172553.
- ^ Lourido-Cebreiro T, Salgado FJ, Valdes L, Gonzalez-Barcala FJ (January 2017). "The association between paracetamol and asthma is still under debate". The Journal of Asthma (Review). 54 (1): 32–8. doi:10.1080/02770903.2016.1194431. PMID 27575940. S2CID 107851.
- ^ Cheelo M, Lodge CJ, Dharmage SC, Simpson JA, Matheson M, Heinrich J, et al. (January 2015). "Paracetamol exposure in pregnancy and early childhood and development of childhood asthma: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Archives of Disease in Childhood. 100 (1): 81–9. doi:10.1136/archdischild-2012-303043. PMID 25429049. S2CID 13520462.
- ^ Eyers S, Weatherall M, Jefferies S, Beasley R (April 2011). "Paracetamol in pregnancy and the risk of wheezing in offspring: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Clinical and Experimental Allergy. 41 (4): 482–9. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.2010.03691.x. PMID 21338428. S2CID 205275267.
- ^ Fan G, Wang B, Liu C, Li D (2017). "Prenatal paracetamol use and asthma in childhood: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 45 (6): 528–533. doi:10.1016/j.aller.2016.10.014. PMID 28237129.
- ^ Masarwa R, Levine H, Gorelik E, Reif S, Perlman A, Matok I (August 2018). "Prenatal Exposure to Acetaminophen and Risk for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Autistic Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression Analysis of Cohort Studies". Am J Epidemiol. 187 (8): 1817–1827. doi:10.1093/aje/kwy086. PMID 29688261.
- ^ Ji Y, Azuine RE, Zhang Y, Hou W, Hong X, Wang G, Riley A, Pearson C, Zuckerman B, Wang X (February 2020). "Association of Cord Plasma Biomarkers of In Utero Acetaminophen Exposure With Risk of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Autism Spectrum Disorder in Childhood". JAMA Psychiatry. 77 (2): 180–189. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.3259. PMC 6822099. PMID 31664451.
- ^ "Acetaminophen Information". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 14 November 2017. Archived from the original on 28 October 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Using Acetaminophen and Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs Safely". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 26 February 2018. Archived from the original on 28 October 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Khashab M, Tector AJ, Kwo PY (2007). "Epidemiology of acute liver failure". Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 9 (1): 66–73. doi:10.1007/s11894-008-0023-x. PMID 17335680. S2CID 30068892.
- ^ Lee WM (2004). "Acetaminophen and the U.S. Acute Liver Failure Study Group: lowering the risks of hepatic failure". Hepatology. 40 (1): 6–9. doi:10.1002/hep.20293. PMID 15239078. S2CID 15485538.
- ^ U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Date Posted 14 January 2011. Prescription Drug Products Containing Acetaminophen: Actions to Reduce Liver Injury from Unintentional Overdose Archived 25 September 2012 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 23 February 2014
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Yan H (16 January 2014). "FDA: Acetaminophen doses over 325 mg may lead to liver damage". CNN. Archived from the original on 16 February 2014. Retrieved 18 February 2014.
- ^ a b Lee WM (December 2017). "Acetaminophen (APAP) hepatotoxicity-Isn't it time for APAP to go away?". Journal of Hepatology. 67 (6): 1324–1331. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2017.07.005. PMC 5696016. PMID 28734939.
- ^ Rumack B, Matthew H (1975). "Acetaminophen poisoning and toxicity". Pediatrics. 55 (6): 871–76. PMID 1134886.
- ^ "Paracetamol". University of Oxford Centre for Suicide Research. 25 March 2013. Archived from the original on 20 March 2013. Retrieved 20 April 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f Mehta S (25 August 2012). "Metabolism of Paracetamol (Acetaminophen), Acetanilide and Phenacetin". PharmaXChange.info. Archived from the original on 28 October 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2019.
- ^ "Highlights of Prescribing Information" (PDF). Acetadote. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 10 February 2014.
- ^ "Paracetamol overdose: new guidance on treatment with intravenous acetylcysteine". Drug Safety Update. September 2012. pp. A1. Archived from the original on 27 October 2012.
- ^ "Treating paracetamol overdose with intravenous acetylcysteine: new guidance". Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA). 11 December 2014. Archived from the original on 28 October 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2019.
- ^ "Treating paracetamol overdose with intravenous acetylcysteine: new guidance". GOV.UK. 11 December 2014. Retrieved 24 January 2021.
- ^ a b c d e Ghanem CI, Pérez MJ, Manautou JE, Mottino AD (July 2016). "Acetaminophen from liver to brain: New insights into drug pharmacological action and toxicity". Pharmacological Research. 109: 119–31. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2016.02.020. PMC 4912877. PMID 26921661.
- ^ a b Graham GG, Davies MJ, Day RO, Mohamudally A, Scott KF (June 2013). "The modern pharmacology of paracetamol: therapeutic actions, mechanism of action, metabolism, toxicity and recent pharmacological findings". Inflammopharmacology. 21 (3): 201–32. doi:10.1007/s10787-013-0172-x. PMID 23719833.
- ^ Sharma CV, Long JH, Shah S, Rahman J, Perrett D, Ayoub SS, Mehta V (2017). "First evidence of the conversion of paracetamol to AM404 in human cerebrospinal fluid". J Pain Res. 10: 2703–2709. doi:10.2147/JPR.S143500. PMC 5716395. PMID 29238213.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Prescott LF (October 1980). "Kinetics and metabolism of paracetamol and phenacetin". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 10 Suppl 2: 291S–298S. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb01812.x. PMC 1430174. PMID 7002186.
- ^ a b Graham GG, Davies MJ, Day RO, Mohamudally A, Scott KF (June 2013). "The modern pharmacology of paracetamol: Therapeutic actions, mechanism of action, metabolism, toxicity, and recent pharmacological findings". Inflammopharmacology. 21 (3): 201–232. doi:10.1007/s10787-013-0172-x. PMID 23719833. S2CID 11359488.
- ^ a b Marx J, Walls R, Hockberger R (2013). Rosen's Emergency Medicine - Concepts and Clinical Practice. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 9781455749874.
- ^ "Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) - Interactions". UK National Health Service. Archived from the original on 13 August 2020. Retrieved 13 August 2020.
There are no known interactions between NSAIDs and food.
- ^ a b Moore RA, Derry S, Wiffen PJ, Straube S (September 2015). "Effects of food on pharmacokinetics of immediate release oral formulations of aspirin, dipyrone, paracetamol and NSAIDs - a systematic review". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 80 (3): 381–8. doi:10.1111/bcp.12628. PMC 4574824. PMID 25784216.
- ^ a b c Fortuny J, Kogevinas M, Garcia-Closas M, Real FX, Tardón A, Garcia-Closas R, Serra C, Carrato A, Lloreta J, Rothman N, Villanueva C, Dosemeci M, Malats N, Silverman D (2006). "Use of Analgesics and Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs, Genetic Predisposition, and Bladder Cancer Risk in Spain". Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention. 15 (9): 1696–1702. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-06-0038. PMID 16985032.
- ^ a b c Borne RF (1995). "Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs". In Foye WO, Lemke TL, Williams DA (eds.). Principles of Medicinal Chemistry (Fourth ed.). Williams & Wilkins. pp. 544–545.
- ^ a b Brayfield A, ed. (15 January 2014). "Paracetamol". Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London, UK: Pharmaceutical Press. Retrieved 10 May 2014.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Bales JR, Nicholson JK, Sadler PJ (1985). "Two-dimensional proton nuclear magnetic resonance "maps" of acetaminophen metabolites in human urine". Clinical Chemistry. 31 (5): 757–62. doi:10.1093/clinchem/31.5.757. PMID 3987005. Archived from the original on 21 November 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f Bertolini A, Ferrari A, Ottani A, Guerzoni S, Tacchi R, Leone S (2006). "Paracetamol: New vistas of an old drug". CNS Drug Reviews. 12 (3–4): 250–75. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2006.00250.x. PMC 6506194. PMID 17227290.
- ^ Viswanathan AN, Feskanich D, Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE (2008). "Aspirin, NSAID, and Acetaminophen Use and the Risk of Endometrial Cancer". Cancer Research. 68 (7): 2507–2513. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6257. PMC 2857531. PMID 18381460.
- ^ Altinoz MA, Korkmaz R (2004). "NF-kappaB, macrophage migration inhibitory factor and cyclooxygenase-inhibitions as likely mechanisms behind the acetaminophen- and NSAID-prevention of the ovarian cancer". Neoplasma. 51 (4): 239–247. PMID 15254653.
- ^ Bronwen B, Knights K, Salerno E (2007). Pharmacology for health professionals. Elsevier. p. 270. ISBN 9780729537872.
- ^ Ellis F (2002). Paracetamol: a curriculum resource. Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry. ISBN 978-0-85404-375-0.
- ^ Travis AS (2007). "Manufacture and uses of the anilines: A vast array of processes and products". In Rappoport Z (ed.). The chemistry of Anilines Part 1. Wiley. p. 764. ISBN 978-0-470-87171-3.
- ^ a b Friderichs E, Christoph T, Buschmann H. "Analgesics and Antipyretics". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_269.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ US patent 4524217, Davenport KG, Hilton CB, "Process for producing N-acyl-hydroxy aromatic amines", published 18 June 1985, assigned to Celanese Corporation
- ^ Joncour R, Duguet N, Métay E, Ferreirab A, Lemaire M (2014). "Amidation of phenol derivatives: a direct synthesis of paracetamol (acetaminophen) from Hydroquinone". Green Chem. 16 (6): 2997–3002. doi:10.1039/C4GC00166D.
- ^ Joncour R, Duguet N, Métay E, Ferreira A, Lemaire M. "Supplementary Information Amidation of phenol derivatives: a direct synthesis of paracetamol (acetaminophen) from hydroquinone" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 September 2015.
- ^ Joncour, Roxan; Duguet, Nicolas; Métay, Estelle; Ferreira, Amadéo; Lemaire, Marc (27 May 2014). "Amidation of phenol derivatives: a direct synthesis of paracetamol (acetaminophen) from hydroquinone". Green Chemistry. 16 (6): 2997–3002. doi:10.1039/C4GC00166D. ISSN 1463-9270.
- ^ Henney K, Dudley B (1939). Handbook of Photography. Whittlesey House. p. 324.
- ^ Novotny PE, Elser RC (1984). "Indophenol method for acetaminophen in serum examined" (PDF). Clin. Chem. 30 (6): 884–6. doi:10.1093/clinchem/30.6.884. PMID 6723045.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Cahn A, Hepp P (1886). "Das Antifebrin, ein neues Fiebermittel" [Antifebrin, a new antipyretic]. Centralblatt für klinische Medizin (in German). 7: 561–4. Archived from the original on 1 September 2020. Retrieved 21 February 2019.
- ^ Morse, H.N. (1878). "Ueber eine neue Darstellungsmethode der Acetylamidophenole" [On a new method of preparing acetylamidophenol]. Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft (in German). 11 (1): 232–233. doi:10.1002/cber.18780110151. Archived from the original on 6 November 2018.
- ^ a b c d e Silverman M, Lydecker M, Lee PR (1992). Bad Medicine: The Prescription Drug Industry in the Third World. Stanford University Press. pp. 88–90. ISBN 978-0804716697.
- ^ von Mering J (1893). "Beitrage zur Kenntniss der Antipyretica". Ther Monatsch. 7: 577–587.
- ^ a b c d Sneader W (2005). Drug Discovery: A History. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. p. 439. ISBN 978-0471899808. Archived from the original on 18 August 2016.
- ^ Toussaint K, Yang XC, Zielinski MA, Reigle KL, Sacavage SD, Nagar S, Raffa RB (December 2010). "What do we (not) know about how paracetamol (acetaminophen) works?". Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics. 35 (6): 617–638. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2710.2009.01143.x. PMID 21054454. S2CID 8555653.
- ^ Bergman K, Müller L, Teigen SW (1996). "The genotoxicity and carcinogenicity of paracetamol: a regulatory (re)view". Mutat Res. 349 (2): 263–88. doi:10.1016/0027-5107(95)00185-9. PMID 8600357.
- ^ Lester D, Greenberg LA, Carroll RP (1947). "The metabolic fate of acetanilid and other aniline derivatives: II. Major metabolites of acetanilid appearing in the blood". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 90 (1): 68–75. PMID 20241897. Archived from the original on 2 December 2008.
- ^ Brodie BB, Axelrod J (1948). "The estimation of acetanilide and its metabolic products, aniline, N-acetyl p-aminophenol and p-aminophenol (free and total conjugated) in biological fluids and tissues". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 94 (1): 22–28. PMID 18885610.
- ^ Brodie BB, Axelrod J (1948). "The fate of acetanilide in man" (PDF). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 94 (1): 29–38. PMID 18885611. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 September 2008.
- ^ Flinn FB, Brodie BB (1948). "The effect on the pain threshold of N-acetyl p-aminophenol, a product derived in the body from acetanilide". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 94 (1): 76–77. PMID 18885618.
- ^ Brodie BB, Axelrod J (1949). "The fate of acetophenetidin (phenacetin) in man and methods for the estimation of acetophenitidin and its metabolites in biological material". J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 94 (1): 58–67.
- ^ Landau R, Achilladelis B, Scriabine A (1999). Pharmaceutical Innovation: Revolutionizing Human Health. Chemical Heritage Foundation. pp. 248–249. ISBN 978-0-941901-21-5. Archived from the original on 17 August 2016.
- ^ Rapoport A (15 December 1991). Headache Relief. Touchstone. p. 97. ISBN 978-0-671-74803-6. Archived from the original on 17 August 2016.
- ^ "SEC Info - Eastman Kodak Co - '8-K' for 6/30/94". Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 3 March 2016.
- ^ "Our Story". McNEIL-PPC, Inc. Archived from the original on 8 March 2014. Retrieved 8 March 2014.
- ^ "Medication and Drugs". MedicineNet. 1996–2010. Archived from the original on 22 April 2010. Retrieved 22 April 2010.
- ^ Thakkar KB, Billa G (September 2013). "The concept of: Generic drugs and patented drugs vs. brand name drugs and non-proprietary (generic) name drugs". Front Pharmacol. 4: 113. doi:10.3389/fphar.2013.00113. PMC 3770914. PMID 24062686.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "FDA May Restrict Acetaminophen". Webmd. 1 July 2009. Archived from the original on 21 March 2011. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ "FDA limits acetaminophen in prescription combination products; requires liver toxicity warnings" (Press release). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 13 January 2011. Archived from the original on 15 January 2011. Retrieved 13 January 2011.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b c "FDA Drug Safety Communication: Prescription Acetaminophen Products to be Limited to 325 mg Per Dosage Unit; Boxed Warning Will Highlight Potential for Severe Liver Failure". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 13 January 2011. Archived from the original on 18 January 2011. Retrieved 13 January 2011.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Perrone M (13 January 2011). "FDA orders lowering pain reliever in Vicodin". The Boston Globe. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 2 November 2012. Retrieved 13 January 2011.
- ^ a b Harris G (13 January 2011). "F.D.A. Plans New Limits on Prescription Painkillers". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 9 June 2012. Retrieved 13 January 2011.
- ^ "Liquid paracetamol for children: revised UK dosing instructions introduced" (PDF). Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA). 14 November 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 October 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2019.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|lay-url=ignored (help) - ^ "Safe Use Initiative: Acetaminophen Toxicity". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 1 August 2011. Archived from the original on 1 September 2011. Retrieved 23 February 2014.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "FDA limits acetaminophen in prescription combination products; requires liver toxicity warnings". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 15 January 2011. Archived from the original on 15 January 2011. Retrieved 23 February 2014.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Orso, Daniele; Federici, Nicola; Copetti, Roberto; Vetrugno, Luigi; Bove, Tiziana (4 May 2020). "Infodemic and the spread of fake news in the COVID-19-era". European Journal of Emergency Medicine. 27 (5): 327–328. doi:10.1097/MEJ.0000000000000713. ISSN 0969-9546. PMC 7202120. PMID 32332201.
- ^ Torjesen, Ingrid (17 April 2020). "Covid-19: ibuprofen can be used for symptoms, says UK agency, but reasons for change in advice are unclear". BMJ. 369: m1555. doi:10.1136/bmj.m1555. ISSN 1756-1833. PMID 32303505.
- ^ Rinott, E.; Kozer, E.; Shapira, Y.; Bar-Haim, A.; Youngster, I. (September 2020). "Ibuprofen use and clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients". Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 26 (9): 1259.e5–1259.e7. doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.06.003. ISSN 1198-743X. PMC 7289730. PMID 32535147.
- ^ Day, Michael (17 March 2020). "Covid-19: ibuprofen should not be used for managing symptoms, say doctors and scientists". BMJ. 368: m1086. doi:10.1136/bmj.m1086. ISSN 1756-1833. PMID 32184201.
- ^ a b Macintyre P, Rowbotham D, Walker S (26 September 2008). Clinical Pain Management Second Edition: Acute Pain. CRC Press. p. 85. ISBN 978-0-340-94009-9. Archived from the original on 17 August 2016.
- ^ "International Non-Proprietary Name for Pharmaceutical Preparations (Recommended List #4)" (PDF). WHO Chronicle. 16 (3): 101–111. March 1962. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 May 2016. Retrieved 21 March 2018.
- ^ "Section 1 – Chemical Substances". TGA Approved Terminology for Medicines (PDF). Therapeutic Goods Administration, Department of Health and Ageing, Australian Government. July 1999. p. 97. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 February 2014.
- ^ "Acetaminophen" in Physicians' Desk Reference, 63rd ed. Montvale, NJ: Thomson PDR. 2009. pp. 1915–1916. ISBN 978-1563637032
- ^ "Acetaminophen Overdose and Liver Injury — Background and Options for Reducing Injury" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 22 May 2009. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 October 2014.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. Background Package for 29–30 June 2009 Meeting of the Drug Safety and Risk Management Committee, Anesthetic and Life Support Drugs Advisory Committee and Nonprescription Drugs Advisory Committee
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. Background Package for 29–30 June 2009 Meeting of the Drug Safety and Risk Management Committee, Anesthetic and Life Support Drugs Advisory Committee and Nonprescription Drugs Advisory Committee
- ^ Nam S. "IV, PO, and PR Acetaminophen: A Quick Comparison". Pharmacy Times. Archived from the original on 24 October 2019. Retrieved 24 October 2019.
- ^ "Acetaminophen and Codeine (Professional Patient Advice)". Drugs.com. 29 June 2019. Archived from the original on 20 May 2020. Retrieved 25 February 2020.
- ^ "Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Dihydrocodeine (Professional Patient Advice)". Drugs.com. 2 October 2019. Archived from the original on 19 May 2020. Retrieved 25 February 2020.
- ^ "Oxycodone and Acetaminophen (Professional Patient Advice)". Drugs.com. 11 November 2019. Archived from the original on 20 May 2020. Retrieved 25 February 2020.
- ^ "Hydrocodone and Acetaminophen (Professional Patient Advice)". Drugs.com. 2 January 2020. Archived from the original on 21 May 2020. Retrieved 25 February 2020.
- ^ "Propoxyphene and Acetaminophen Tablets". Drugs.com. 21 June 2019. Archived from the original on 20 May 2020. Retrieved 25 February 2020.
- ^ "APOHealth Paracetamol Plus Codeine & Calmative". Drugs.com. 3 February 2020. Archived from the original on 25 February 2020. Retrieved 25 February 2020.
- ^ Murnion BP (August 2010). "Combination analgesics in adults". Australian Prescriber. 33 (4): 113–5. doi:10.18773/austprescr.2010.056.
- ^ a b Atkinson HC, Stanescu I, Anderson BJ (2014). "Increased Phenylephrine Plasma Levels with Administration of Acetaminophen". New England Journal of Medicine. 370 (12): 1171–1172. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1313942. PMID 24645960.
- ^ "Ascorbic acid/Phenylephrine/Paracetamol". NHS Choices. National Health Service. Archived from the original on 26 March 2014. Retrieved 25 March 2014.
- ^ "Phenylephrine/Caffeine/Paracetamol dual relief". NHS Choices. National Health Service. Archived from the original on 26 March 2014. Retrieved 25 March 2014.
- ^ "Beechams Decongestant Plus With Paracetamol". NHS Choices. National Health Service. Archived from the original on 26 March 2014. Retrieved 25 March 2014.
- ^ Senyuva H, Ozden T (2002). "Simultaneous High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Paracetamol, Phenylephrine HCl, and Chlorpheniramine Maleate in Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms". Journal of Chromatographic Science. 40 (2): 97–100. doi:10.1093/chromsci/40.2.97. PMID 11881712.
- ^ Janin A, Monnet J (2014). "Bioavailability of paracetamol, phenylephrine hydrochloride and guaifenesin in a fixed-combination syrup versus an oral reference product". Journal of International Medical Research. 42 (2): 347–359. doi:10.1177/0300060513503762. PMID 24553480.
- ^ "Paracetamol – phenylephrine hydrochloride – guaifenesin". NPS MedicineWise. National Prescribing Service (Australia). Archived from the original on 26 March 2014. Retrieved 25 March 2014.
- ^ "Phenylephrine/Guaifenesin/Paracetamol". NHS Choices. National Health Service. Archived from the original on 12 September 2013. Retrieved 25 March 2014.
- ^ "Treating a Restless Legs Sydnrome (RLS)". Consumer Reports. 2011. Archived from the original on 18 December 2015.
- ^ "Use Only as Directed". This American Life. Episode 505. Chicago. 20 September 2013. Public Radio International. WBEZ. Archived from the original on 27 September 2013. Retrieved 24 September 2013.
- ^ Gerth J, Miller TC (20 September 2013). "Use Only as Directed". ProPublica. Archived from the original on 24 September 2013. Retrieved 24 September 2013.
- ^ Miller TC, Gerth J (20 September 2013). "Dose of Confusion". ProPublica. Archived from the original on 24 September 2013. Retrieved 24 September 2013.
- ^ "Recommendations for FDA Interventions to Decrease the Occurrence of Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 September 2015.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Allen AL (2003). "The diagnosis of acetaminophen toxicosis in a cat". Can Vet J. 44 (6): 509–10. PMC 340185. PMID 12839249.
- ^ a b c Richardson JA (2000). "Management of acetaminophen and ibuprofen toxicoses in dogs and cats" (PDF). J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care. 10 (4): 285–91. doi:10.1111/j.1476-4431.2000.tb00013.x. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 April 2010.
- ^ a b Maddison JE, Page SW, Church D (2002). Small Animal Clinical Pharmacology. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 260–1. ISBN 978-0702025730.
- ^ a b c "Pardale-V Oral Tablets". NOAH Compendium of Data Sheets for Animal Medicines. The National Office of Animal Health (NOAH). 11 November 2010. Archived from the original on 22 November 2008. Retrieved 20 January 2011.
- ^ Villar D, Buck WB, Gonzalez JM (June 1998). "Ibuprofen, aspirin and acetaminophen toxicosis and treatment in dogs and cats". Veterinary and Human Toxicology. 40 (3): 156–62. PMID 9610496.
- ^ Gwaltney-Brant S, Meadows I (March 2006). "The 10 Most Common Toxicoses in Dogs". Veterinary Medicine: 142–8. Archived from the original on 10 July 2011. Retrieved 28 October 2019.
- ^ Dunayer E (2004). "Ibuprofen toxicosis in dogs, cats, and ferrets". Veterinary Medicine: 580–6. Archived from the original on 10 July 2011.
- ^ Johnston J, Savarie P, Primus T, Eisemann J, Hurley J, Kohler D (2002). "Risk assessment of an acetaminophen baiting program for chemical control of brown tree snakes on Guam: evaluation of baits, snake residues, and potential primary and secondary hazards". Environ Sci Technol. 36 (17): 3827–33. Bibcode:2002EnST...36.3827J. doi:10.1021/es015873n. PMID 12322757.
- ^ Lendon B (7 September 2010). "Tylenol-loaded mice dropped from air to control snakes". CNN. Archived from the original on 9 September 2010. Retrieved 7 September 2010.
- ^ Richards S (1 May 2012). "It's Raining Mice". The Scientist. Archived from the original on 15 May 2012.
External links
- "Acetaminophen". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Acetaminophen: Avoiding Liver Injury". Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 24 June 2009.
- "Evidence for the efficacy of pain medications" (PDF). National Safety Council (NSC). 26 August 2020.