Hungary: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
revert Rogvaiv1's vandalism. He is a Romanian chauvinist , who hate Hungary. Please develop your romania article instead of vandalism |
||
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
==History== |
==History== |
||
===Before 895 AD=== |
===Before 895 AD=== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
The genetical ancestors of present-day Hungarian population arrived in Carpathian basin around 40,000 years ago.<ref>http://www.historia.hu/archivum/2004/0408szaboi.htm</ref><ref>American academic journal Science 2000</ref> |
|||
From [[9 BC]] to the end of the [[4th century]], [[Pannonia]] was part of the [[Roman Empire]] on a part of later Hungary's area. In the final stages of the expansion of the Roman empire, the Carpathian Basin fell for a while into the sphere of the Mediterranean, yet [[Greco-Roman civilization]], its town centers, paved roads and written sources were all part of the advances which the Migration of Peoples ended. |
From [[9 BC]] to the end of the [[4th century]], [[Pannonia]] was part of the [[Roman Empire]] on a part of later Hungary's area. In the final stages of the expansion of the Roman empire, the Carpathian Basin fell for a while into the sphere of the Mediterranean, yet [[Greco-Roman civilization]], its town centers, paved roads and written sources were all part of the advances which the Migration of Peoples ended. |
||
| Line 103: | Line 106: | ||
===Medieval Hungary (895–1526)=== |
===Medieval Hungary (895–1526)=== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Main|History of Hungary|Pannonian basin before Hungary|Hungarian prehistory|Pannonia}} |
{{Main|History of Hungary|Pannonian basin before Hungary|Hungarian prehistory|Pannonia}} |
||
{{Main|Árpád dynasty|Kingdom of Hungary in the Middle Ages|History of the Székely people}} |
{{Main|Árpád dynasty|Kingdom of Hungary in the Middle Ages|History of the Székely people}} |
||
| Line 162: | Line 164: | ||
;[[Andrew II of Hungary]] (1205–1235) |
;[[Andrew II of Hungary]] (1205–1235) |
||
He granted the |
He granted the Burzenland (in Transylvania) to the [[Teutonic Knights]]. In 1225, Andrew II expelled the Teutonic Knights from Transylvania, hence Teutonic Order had to transfer to the Baltic sea. In 1224, Andrew issued the [[Andreanum Act|''Diploma Andreanum'']] which unified and secured the special privileges of the [[Transylvanian Saxons]]. It is considered the first [[Autonomy]] law in the world.<ref>[http://www.hungarianhistory.com/lib/autonomy/komlossy.pdf Hungarianhistory.com]</ref> |
||
He led the [[Fifth Crusade]] to the [[Holy Land]] in 1217. He set up the largest royal army in the history of Crusades (20,000 knights and 12,000 castle-garrisons). The [[Golden Bull of 1222]] was the first [[constitution]] in [[Continental Europe]]. It limited the king's power. The Golden Bull — the Hungarian equivalent of England’s [[Magna Carta]] — to which every Hungarian king thereafter had to swear, had a twofold purpose: to reaffirm the rights of the lesser nobles of the old and new classes of royal servants (''servientes regis'') against both the crown and the magnates, and to defend the rights of the whole nation against the crown by restricting certain powers of the crown and legalizing refusal to obey its unlawful/unconstitutional commands (the ''ius resistendi''). The lesser nobles also began to present Andrew with grievances, a practice that evolved into the institution of the [[parliament]] (''parlamentum publicum''). Hungary became the first country where the parliament had supremacy over the crown. The most important legal ideology and legislative guideline was the [[Doctrine of the Holy Crown]]. |
He led the [[Fifth Crusade]] to the [[Holy Land]] in 1217. He set up the largest royal army in the history of Crusades (20,000 knights and 12,000 castle-garrisons). The [[Golden Bull of 1222]] was the first [[constitution]] in [[Continental Europe]]. It limited the king's power. The Golden Bull — the Hungarian equivalent of England’s [[Magna Carta]] — to which every Hungarian king thereafter had to swear, had a twofold purpose: to reaffirm the rights of the lesser nobles of the old and new classes of royal servants (''servientes regis'') against both the crown and the magnates, and to defend the rights of the whole nation against the crown by restricting certain powers of the crown and legalizing refusal to obey its unlawful/unconstitutional commands (the ''ius resistendi''). The lesser nobles also began to present Andrew with grievances, a practice that evolved into the institution of the [[parliament]] (''parlamentum publicum''). Hungary became the first country where the parliament had supremacy over the crown. The most important legal ideology and legislative guideline was the [[Doctrine of the Holy Crown]]. |
||
| Line 183: | Line 185: | ||
[[File:Rozgonyi.jpg|thumb|right|150px|[[Battle of Rozgony|King Charles' last battle against the oligarchy, Rozgony (1312)]].]] |
[[File:Rozgonyi.jpg|thumb|right|150px|[[Battle of Rozgony|King Charles' last battle against the oligarchy, Rozgony (1312)]].]] |
||
[[File:Louis role.jpg|thumb|left|250px|Lands |
[[File:Louis role.jpg|thumb|left|250px|Lands, countries kingdoms under Louis' control]] |
||
[[File: |
[[File:John Hunyadi - Johannes de Thurocz - Chronica Hungarorum, Brno 1488.jpg|thumb|left|150px|Count [[John Hunyadi]] - One of the greatest warlords in Hungarian history, [[Matthias Corvinus]]'s father]] |
||
[[Árpád]]'s direct descendants in the male line ruled the country until [[1301]]. During the reigns of the [[Árpád dynasty]], the [[Kingdom of Hungary]] reached its greatest extent, yet royal power was weakened as the major landlords (the Barons) greatly increased their influence. The most powerful landlords started to use [[royal prerogative]]s (coinage, customs, their own independent diplomacy, declaration of wars against foreign monarchs). |
[[Árpád]]'s direct descendants in the male line ruled the country until [[1301]]. During the reigns of the [[Árpád dynasty]], the [[Kingdom of Hungary]] reached its greatest extent, yet royal power was weakened as the major landlords (the Barons) greatly increased their influence. The most powerful landlords started to use [[royal prerogative]]s (coinage, customs, their own independent diplomacy, declaration of wars against foreign monarchs). |
||
| Line 192: | Line 193: | ||
One of the primary sources of his power was the wealth derived from the gold mines of eastern and northern Hungary. Eventually production reached the remarkable figure of 3,000 lb. (1350 kg) of gold annually - one third of the total production of the world as then known, and five times as much as that of any other European state.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nationsencyclopedia.com/Europe/Hungary-HISTORY.html |title=Hungary - History |publisher=Nationsencyclopedia.com |date= |accessdate=2008-11-21}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://mek.oszk.hu/02000/02086/02086.htm |title=C. A. Macartney: Hungary - A Short History |publisher=Mek.oszk.hu |date= |accessdate=2008-11-21}}</ref> Charles also sealed an alliance with the Polish king Casimir. After Italy, Hungary was the first European country where the [[renaissance]] appeared.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.fondazione-delbianco.org/inglese/relaz00_01/mester.htm |title=the influences of the florentine renaissance in hungary |publisher=Fondazione-delbianco.org |date= |accessdate=2009-09-20}}</ref> |
One of the primary sources of his power was the wealth derived from the gold mines of eastern and northern Hungary. Eventually production reached the remarkable figure of 3,000 lb. (1350 kg) of gold annually - one third of the total production of the world as then known, and five times as much as that of any other European state.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nationsencyclopedia.com/Europe/Hungary-HISTORY.html |title=Hungary - History |publisher=Nationsencyclopedia.com |date= |accessdate=2008-11-21}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://mek.oszk.hu/02000/02086/02086.htm |title=C. A. Macartney: Hungary - A Short History |publisher=Mek.oszk.hu |date= |accessdate=2008-11-21}}</ref> Charles also sealed an alliance with the Polish king Casimir. After Italy, Hungary was the first European country where the [[renaissance]] appeared.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.fondazione-delbianco.org/inglese/relaz00_01/mester.htm |title=the influences of the florentine renaissance in hungary |publisher=Fondazione-delbianco.org |date= |accessdate=2009-09-20}}</ref> |
||
The second Hungarian king in the [[Capetian House of Anjou|Angevin]] line, [[Louis I of Hungary|Louis the Great]] (reigned 1342–1382) extended his rule as far as the [[Adriatic Sea]], and occupied the [[Kingdom of Naples]] several times. During his reign lived the epic hero of Hungarian literature and warfare, the king's Champion: Nicolas [[Toldi]]. Louis had become popular in Poland because of his campaign against the Tatars and pagan Lithuanians. Two successful wars (1357–1358, 1378–1381) against Venice annexed Dalmatia and Ragusa and more territories on the Adriatic Sea. Venice also had to raise the Angevin flag in |
The second Hungarian king in the [[Capetian House of Anjou|Angevin]] line, [[Louis I of Hungary|Louis the Great]] (reigned 1342–1382) extended his rule as far as the [[Adriatic Sea]], and occupied the [[Kingdom of Naples]] several times. During his reign lived the epic hero of Hungarian literature and warfare, the king's Champion: Nicolas [[Toldi]]. Louis had become popular in Poland because of his campaign against the Tatars and pagan Lithuanians. Two successful wars (1357–1358, 1378–1381) against Venice annexed Dalmatia and Ragusa and more territories on the Adriatic Sea. Venice also had to raise the Angevin flag in St. Mark's Square on holy days. |
||
Some Balkan states ( |
Some Balkan states (Vallachia, Moldova, Serbia, Bosnia) became his vassals. Louis I established a university in [[Pécs]] in 1367 (by papal accordance). The Ottoman Turks confronted the Balkan vassal states ever more often. In 1366 and 1377, Louis led successful campaigns against the Ottomans (Battle of Nicapoli in 1366). From the death of [[Casimir III of Poland]] in 1370, he was also king of Poland. He retained his strong influence in the political life of Italian Peninsula for the rest of his life. |
||
King Louis died without a male heir, and after years of anarchy the country was stabilized only when [[Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor|Sigismund]] (reigned 1387–1437), a prince of the [[Luxembourg]] line, succeeded to the throne by marrying the daughter of Louis the Great, [[Mary of Hungary|Queen Mary]]. It was not for entirely selfless reasons that one of the leagues of barons helped him to power: Sigismund had to pay for the support of the lords by transferring a sizeable part of the royal properties. For some years, the baron's council governed the country in the name of the [[Holy Crown]]; the king was imprisoned for a short time. The restoration of the authority of the central administration took decades. |
King Louis died without a male heir, and after years of anarchy the country was stabilized only when [[Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor|Sigismund]] (reigned 1387–1437), a prince of the [[Luxembourg]] line, succeeded to the throne by marrying the daughter of Louis the Great, [[Mary of Hungary|Queen Mary]]. It was not for entirely selfless reasons that one of the leagues of barons helped him to power: Sigismund had to pay for the support of the lords by transferring a sizeable part of the royal properties. For some years, the baron's council governed the country in the name of the [[Holy Crown]]; the king was imprisoned for a short time. The restoration of the authority of the central administration took decades. |
||
| Line 465: | Line 466: | ||
==Science== |
==Science== |
||
As of 2009, |
As of 2009, 14 Hungarians (who were born in Hungary) had received a scientific [[Nobel prize]], more than [[China]], [[Japan]], [[India]], [[Australia]] or [[Spain]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.eupedia.com/hungary/trivia.shtml |title=Hungary Guide - Interesting facts about Hungary |publisher=Eupedia |date=1994-04-19 |accessdate=2009-09-20}}</ref> Further eight Nobel prize laureates of Hungarian origin on both sides were born outside of Hungary. |
||
The world's first institution of technology was founded in [[Selmecbánya]], Hungarian Kingdom (today Slovakia) in 1735. |
The world's first institution of technology was founded in [[Selmecbánya]], Hungarian Kingdom (today Slovakia) in 1735. |
||
Revision as of 15:48, 9 August 2010
Republic of Hungary Magyar Köztársaság | |
|---|---|
| Motto: Historically Template:Lang-la ("With the help of God for Homeland and Freedom") or [Regnum Mariae Patronae Hungariae] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) ("Kingdom of Mary, the Patron of Hungary")[1] | |
| Anthem: Himnusz ("Isten, áldd meg a magyart") "Hymn" or "Anthem" ("God, bless the Hungarians") | |
![Location of Hungary (dark green) – in Europe (green & dark grey) – in the European Union (green) – [Legend]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/60/EU-Hungary.svg/250px-EU-Hungary.svg.png) Location of Hungary (dark green) – in Europe (green & dark grey) | |
| Capital and largest city | Budapest |
| Official languages | Hungarian |
| Ethnic groups | 95% Hungarian, 2% Roma, 3% other minority groups |
| Demonym(s) | Hungarian |
| Government | Parliamentary republic |
| Pál Schmitt | |
| Viktor Orbán | |
| Foundation | |
• Foundation of Hungary | 895 |
• Recognized as Christian Kingdom
- First king: Stephen I of Hungary | 20 August 1000 |
• Currently 3rd Republic | October 23, 1989 |
| Area | |
• Total | 93,030 km2 (35,920 sq mi) (109th) |
• Water (%) | 0.74% |
| Population | |
• 2010 May estimate | 10,005,000[2] (83rd) |
• 2001 census | 10,198,315 |
• Density | 107.7/km2 (278.9/sq mi) (94th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2009 estimate |
• Total | $185.873 billion[3] |
• Per capita | $18,566[3] |
| GDP (nominal) | 2009 estimate |
• Total | $129.407 billion[3] |
• Per capita | $12,926[3] |
| Gini (2008) | 24.96 low inequality (3rd) |
| HDI (2007) | Error: Invalid HDI value (43rd) |
| Currency | Forint (HUF) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Date format | yyyy.mm.dd, yyyy.mm.dd (CE) |
| Drives on | right |
| Calling code | 36 |
| ISO 3166 code | HU |
| Internet TLD | .hu1 |
| |
Hungary (Template:Lang-hu [ˈmɒɟɒrorsaːɡ] ), officially the Republic of Hungary (Magyar Köztársaság ), is a landlocked country in the Carpathian Basin in Central Europe, bordered by Austria, Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, and Slovenia. Its capital is Budapest. Hungary is a member of EU, NATO, OECD, V4 and is a Schengen state. The official and vernacular language is Hungarian, which is part of the Finno-Ugric family, thus one of the four official languages of the European Union that are not of Indo-European origin.[note 1]
Following a Celtic (after c. 450 BC) and a Roman (9 BC – c. 430 AD) period, the foundation of Hungary was laid in the late 9th century by the Hungarian ruler Árpád, whose great-grandson Stephen I of Hungary was crowned with a crown sent from Rome by the pope in 1000. The Kingdom of Hungary lasted for 946 years,[note 2] and at various points was regarded as one of the cultural centers of the Western world. The Battle of Mohács resulted in the country's partial Ottoman occupation, followed by its integration into the Habsburg Monarchy, which later became the dual monarchy of Austria–Hungary. A great power until the end of World War I, Hungary lost over 70% of its territory, along with one third of its population of Hungarian ethnicity,[4] under the Treaty of Trianon,[5] the terms of which have been considered excessively harsh by many in Hungary.[6] The kingdom was succeeded by a Communist era (1947–1989) during which Hungary gained widespread international attention regarding the Revolution of 1956 and the seminal move of opening its border with Austria in 1989, thus accelerating the collapse of the Eastern Bloc. The present form of government is a parliamentary republic (since 1989). Today, Hungary is a high-income economy,[7] and a regional leader regarding certain markers.[8][9][10][11]
Hungary is ranked 20th globally (out of 195 countries) on International Living's Quality of Life index (2010)[12] and 6th in an environmental protection index by GW/CAN.[13] Until recently, it was also listed as one of the 15 most popular tourist destinations in the world.[14][15] It attracts about 7 million visitors a year.[16] The country is home to the largest thermal water cave system[17] and the second largest thermal lake in the world (Lake Hévíz), the largest lake in Central Europe (Lake Balaton), and the largest natural grasslands in Europe (Hortobágy).
History
Before 895 AD
The genetical ancestors of present-day Hungarian population arrived in Carpathian basin around 40,000 years ago.[18][19] From 9 BC to the end of the 4th century, Pannonia was part of the Roman Empire on a part of later Hungary's area. In the final stages of the expansion of the Roman empire, the Carpathian Basin fell for a while into the sphere of the Mediterranean, yet Greco-Roman civilization, its town centers, paved roads and written sources were all part of the advances which the Migration of Peoples ended.
Among the first to arrive were the Huns, who built up a powerful empire under Attila the Hun. Attila was regarded as an ancestral ruler of the Hungarians, however, this claim is rejected today by most scholars (Read chronicles like Gesta Hungarorum and Tarihi Ungurus/Turkish/ and these and other chronicles write about Magyars being Huns/Scythians). After Hunnish rule faded away, the Germanic Ostrogoths and then the Lombards came to Pannonia, and the Gepids had a presence in the eastern part of the Carpathian Basin for about 100 years.
In the 560s the Avars founded the Avar Khaganate,[20] a state which maintained supremacy in the region for more than two centuries and had the military power to launch attacks against all its neighbours. The Avar Khaganate was weakened by constant wars and outside pressure and finally the Avars' 250 year rule ended when the Khaganate was conquered by the Franks under Charlemagne in the West and the Bulgarians under Krum in the East. Neither of these two nor others were able to create a lasting state in the region, and in the late 9th century the land was inhabited only by a sparse population of Slavs.[21]
It was King Arnulf I of Bavaria who invited the Hungarians to occupy Svatopluk's lands east of the Danube.[22] In 894, while Simeon I of Bulgaria attacked the Byzantine Empire, Svatopluk challenged Arnulf by invading Pannonia.[22] Both Arnulf and Leo VI the Wise sought help from the Hungarians who were well placed to attack the Bulgarians and the Moravians from the rear.[22] Arnulf maintained the alliance with the Hungarians until his death in 899.[22]
The freshly unified Magyars (Hungarians)[23] led by Árpád settled in the Carpathian Basin starting in 895.[21][24] According to linguists they are thought to have originated in an ancient Finno-Ugric population that originally inhabited the forested area between the Volga River and the Ural Mountains,[25] although the genetic relation of Hungarians to Finno-Ugric peoples is excluded. The force led by Árpád contained seven Magyar, one Szekely, one Kabar, and other smaller tribes.[21]
Medieval Hungary (895–1526)

Hungary is one of the oldest countries in Europe, settled in 896, before France and Germany became separate entities, and before the unification of Anglo-Saxon kingdoms. Árpád was the Magyar leader whom sources name as the single leader who unified the Magyar tribes via the "Covenant of Blood" (Template:Lang-hu) forged one nation, thereafter known as the Hungarian nation[26] and led the new nation to the Carpathian Basin in the 9th century.[26]
After an early seminomad Hungarian state, the Principality of Hungary was formed in this territory, the nation's military power allowed the Hungarians to conduct successful fierce campaigns and raids from Constantinople as far as today's Spain.[27] A later defeat at the Battle of Lechfeld in 955 signaled an end to most campaigns on foreign territories. The ruling prince (Template:Lang-hu) Géza of the Árpád dynasty, who was the ruler of only some of the united territory, but the nominal overlord of all seven Magyar tribes, intended to integrate Hungary into Christian Western Europe.[28] and the first Roman Catholic bishopric was established under his reign.
Géza chose his first-born son (Vajk the later King Stephen I of Hungary) to be his successor. This was contrary to the then-dominant tradition of the succession of the eldest surviving member of the ruling family. (See: agnatic seniority) By ancestral right prince Koppány, - as the oldest member of the dynasty - should have claimed the throne, but the fight in the chief prince's family started after Géza's death, in 997.
Duke Koppány took up arms, and many people in Transdanubia joined him. The rebels represented the old faith and order, tribal independence and pagan belief. Stephen won a decisive victory over his uncle Koppány in a large scale battle at Veszprém, and had him executed, thus firming Christian fate and ensuring the survival and prosperity of Hungary.
-
The treasure of Nagyszentmiklós illustrating the Álmos legend from the Hungarian mythology: Emese's dream of the Turul bird
-
Detail of the cyclorama, Arrival of the Hungarians by Árpád Feszty, depicting the arrival to the Carpathian Basin in 895.
-
Galgóci tarsolylemez, an ancient Hungarian pouch plate.
-
The Old Hungarian script, the so-called "Rovás alphabet"
-
Hungary in the 11th century
The Patrimonial Kingdom

Hungary was recognized as a Catholic Apostolic Kingdom under Saint Stephen I, the son of Géza[29] and thus a descendant of Árpád. Applying to Pope Sylvester II, Stephen received the insignia of royalty (including the Holy Crown of Hungary, currently kept in the Hungarian Parliament) from the papacy. He was crowned in December 1000, in the capital, Esztergom. The papacy conferred on him the right to have the cross carried before him, with full administrative authority over bishoprics and churches.
By 1006, Stephen had consolidated his power, eliminating all rivals who either wanted to follow the old pagan traditions or wanted an alliance with the Eastern Christian Byzantine Empire. Then he started sweeping reforms to convert Hungary into a western feudal state, it has been asserted that the Christianisation was forced.[30] Stephen established a network of 10 episcopal and 2 archiepiscopal sees, and ordered the building of monasteries, churches and cathedrals.
The country switched to using the Latin language and alphabet under Stephen, and until as late as 1844, Latin remained the official language of Hungary. Previously Hungarian had been written with the Old Hungarian script, a runic script. Stephen followed the Frankish administrative model: The country was divided into counties (Template:Lang-hu), each under a royal official called an ispán or count (Template:Lang-la) — later főispán (lord lieutenant or prefect) (Template:Lang-la). This official represented the king’s authority, administered its population, and collected the taxes that formed the national revenue. Each ispán maintained at his fortified headquarters (castrum or vár) an armed force of freemen.
What emerged was a strong kingdom[31] that withstood and repelled attacks from Holy Roman Emperors and Byzantine Emperors, and nomadic tribes following the Hungarians from the East, integrating some of the latter into the population (along with Germans invited to Transylvania and the northern part of the kingdom, especially after the 13th century Battle of Mohi), and conquering Croatia in 1091.[32][33][34]
After the Great Schism (The East-West Schism /formally in 1054/, between Western Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Christianity.) Hungary determined itself as the Easternmost bastion of Western civilization. The Orthodox powers regarded Hungary as the main obstacle in their desire to introduce Orthodoxy into the Western World. However every such Eastern effort has been halted at the gates of Hungary.[35]
-
Romanesque church of Pécs
-
Reliquary, Saint Ladislaus I of Hungary (c.1040–1095)
-
King Béla's III tomb
Important members of the Árpád dynasty


- King Coloman (Kálmán), the "Book-lover" (1095–1116)
One of Coloman's laws was half a millennium ahead of its time: De strigis vero quae non sunt, nulla amplius quaestio fiat (As for witches, they really do not exist; no further investigations or trials are to be held).
- Béla III (1172–1192)
Béla III was the most powerful and wealthiest member of the dynasty: Béla disposed of the equivalent of 23 tonnes of pure silver per year. This exceeded the income of the French king (estimated at 17 tonnes) and was double the receipts of the English Crown.[36] Béla captured Belgrade from Byzantine Empire. He forced back the Byzantine domain in the Balkan region.
- Andrew II of Hungary (1205–1235)
He granted the Burzenland (in Transylvania) to the Teutonic Knights. In 1225, Andrew II expelled the Teutonic Knights from Transylvania, hence Teutonic Order had to transfer to the Baltic sea. In 1224, Andrew issued the Diploma Andreanum which unified and secured the special privileges of the Transylvanian Saxons. It is considered the first Autonomy law in the world.[37]
He led the Fifth Crusade to the Holy Land in 1217. He set up the largest royal army in the history of Crusades (20,000 knights and 12,000 castle-garrisons). The Golden Bull of 1222 was the first constitution in Continental Europe. It limited the king's power. The Golden Bull — the Hungarian equivalent of England’s Magna Carta — to which every Hungarian king thereafter had to swear, had a twofold purpose: to reaffirm the rights of the lesser nobles of the old and new classes of royal servants (servientes regis) against both the crown and the magnates, and to defend the rights of the whole nation against the crown by restricting certain powers of the crown and legalizing refusal to obey its unlawful/unconstitutional commands (the ius resistendi). The lesser nobles also began to present Andrew with grievances, a practice that evolved into the institution of the parliament (parlamentum publicum). Hungary became the first country where the parliament had supremacy over the crown. The most important legal ideology and legislative guideline was the Doctrine of the Holy Crown.
Important points of the Doctrine: The sovereignty belongs to the nation (the Holy Crown). The members of the Holy Crown are the citizens of the Crown's lands. None can reach full power in the kingdom. The nation shares political power with the ruler. "Politically minority opinions cannot rule over majority". (Which meant: The Doctrine was opposed to tyranny and oligarchy).
The Mongol attacks, consequences and reaction
In 1241–1242, the kingdom received a major blow with the Mongol (Tatar) Invasion: after the defeat of the Hungarian army at the Battle of Mohi,[38] Béla IV of Hungary fled, and a large part of the population died[39] in the ensuing destruction leading later to the invitation of settlers, largely from Germany. Historians estimate that up to half of Hungary's then population of 2,000,000 were victims of the Mongol invasion.[40] In the plains between 50 and 80% of the settlements were destroyed.[41] Only castles, strongly fortified cities and abbeys could withstand the assault.
During the Russian campaign, the Mongols drove some 40,000 Cumans, a nomadic tribe of pagan Kipchaks, west of the Carpathian Mountains.[42] There, the Cumans appealed to King Béla IV of Hungary for protection.[43] The Iranian Jassic people came to Hungary together with the Cumans after they were defeated by the Mongols. Cumans constituted perhaps up to 7-8% of the population of Hungary in the second half of the 13th century.[44] Over the centuries they were fully assimilated into the Hungarian population, and their language disappeared, but they preserved their identity and their regional autonomy until 1876.[45]
As a consequence, after the Mongols retreated, King Béla ordered the construction of hundreds of stone castles and fortifications, to defend against a possible second Mongol invasion. The Mongols returned to Hungary in 1286, but the new built stone-castle systems and new tactics (using a higher proportion of heavily armed knights) stopped them. The invading Mongol force was defeated near Pest by the royal army of Ladislaus IV of Hungary. As with later invasions, it was repelled handily, the Mongols losing much of their invading force.
These castles proved to be very important later in the long struggle with the Ottoman Empire. However the cost of building them indebted the Hungarian King to the major feudal landlords again, so the royal power reclaimed by Béla IV after his father Andrew II significantly weakened it was once again dispersed amongst lesser nobility. The countries of the Balkan region and the territory of Russian states fell under Ottoman/Mongolian rule very rapidly, due to the lack of the network of stone/brick castles and fortresses in these countries.
Age of elected Kings


Árpád's direct descendants in the male line ruled the country until 1301. During the reigns of the Árpád dynasty, the Kingdom of Hungary reached its greatest extent, yet royal power was weakened as the major landlords (the Barons) greatly increased their influence. The most powerful landlords started to use royal prerogatives (coinage, customs, their own independent diplomacy, declaration of wars against foreign monarchs).
After the destructive period of interregnum (1301–1308), the first Angevin king, Charles I of Hungary (reigned 1308–1342) - a descendant of the Árpád dynasty in the female line - successfully restored royal power, and defeated oligarch rivals, the so called "little kings". His new fiscal, customs and monetary policies proved successful during his reign.
One of the primary sources of his power was the wealth derived from the gold mines of eastern and northern Hungary. Eventually production reached the remarkable figure of 3,000 lb. (1350 kg) of gold annually - one third of the total production of the world as then known, and five times as much as that of any other European state.[46][47] Charles also sealed an alliance with the Polish king Casimir. After Italy, Hungary was the first European country where the renaissance appeared.[48]
The second Hungarian king in the Angevin line, Louis the Great (reigned 1342–1382) extended his rule as far as the Adriatic Sea, and occupied the Kingdom of Naples several times. During his reign lived the epic hero of Hungarian literature and warfare, the king's Champion: Nicolas Toldi. Louis had become popular in Poland because of his campaign against the Tatars and pagan Lithuanians. Two successful wars (1357–1358, 1378–1381) against Venice annexed Dalmatia and Ragusa and more territories on the Adriatic Sea. Venice also had to raise the Angevin flag in St. Mark's Square on holy days.
Some Balkan states (Vallachia, Moldova, Serbia, Bosnia) became his vassals. Louis I established a university in Pécs in 1367 (by papal accordance). The Ottoman Turks confronted the Balkan vassal states ever more often. In 1366 and 1377, Louis led successful campaigns against the Ottomans (Battle of Nicapoli in 1366). From the death of Casimir III of Poland in 1370, he was also king of Poland. He retained his strong influence in the political life of Italian Peninsula for the rest of his life.
King Louis died without a male heir, and after years of anarchy the country was stabilized only when Sigismund (reigned 1387–1437), a prince of the Luxembourg line, succeeded to the throne by marrying the daughter of Louis the Great, Queen Mary. It was not for entirely selfless reasons that one of the leagues of barons helped him to power: Sigismund had to pay for the support of the lords by transferring a sizeable part of the royal properties. For some years, the baron's council governed the country in the name of the Holy Crown; the king was imprisoned for a short time. The restoration of the authority of the central administration took decades.
In 1404 Sigismund introduced the Placetum Regnum. According to this decree, Papal bulls and messages could not be pronounced in Hungary without the consent of the king. Sigismund summoned the Council of Constance (1414–1418) to abolish the Avignon Papacy and the Papal Schism of the Catholic Church, which was resolved by the election of a new pope. In 1433 he even became Holy Roman Emperor. During his long reign the Royal castle of Buda became probably the largest Gothic palace of the late Middle Ages. The first Hungarian Bible translation was completed in 1439. For a half year in 1437, there was an antifeudal and anticlerical peasant revolt in Transylvania which was strongly influenced by Hussite ideas. (See: Budai Nagy Antal Revolt)
From a small noble family in Transylvania, John Hunyadi grew to become one of the country's most powerful lords, thanks to his outstanding capabilities as a mercenary commander. In 1446, the parliament elected the great general John Hunyadi governor (1446–1453), then regent (1453–1456). He was a successful crusader against the Ottoman Turks, one of his greatest victories being the Siege of Belgrade in 1456. Hunyadi defended the city against the onslaught of the Ottoman Sultan Mehmed II. During the siege, Pope Callixtus III ordered the bells of every European church to be rung every day at noon, as a call for believers to pray for the defenders of the city. However, in many countries, (like England and Spanish kingdoms), the news of the victory arrived before the order, and the ringing of the church bells at noon was transformed into a commemoration of the victory. The Popes didn't withdraw the order, and Catholic (and the older Protestant) churches still ring the noon bell in the Christian world to this day.[49]
-
King Louis the Great
-
Early renaissance Castle of Diósgyőr, which was one of the favourite rural hunting castles of Angevin kings
-
“The Hungarian Cannon,named after the Hungarian engineer Orban who cast the gun for the Ottoman besiegers of Constantinople.It was the world's biggest cannon until the second half of the 19th century.These types of cannons appeared in Siege of (Belgrade) too
-
Hungarian clothes between 1370-1410 period
-
Hungarian Nobles, 15th century
-
Gothic-renaissance Hunyad Castle in Transylvania.
Age of early absolutism

The last strong king was the Renaissance king Matthias Corvinus (king 1458–1490). Matthias was the son of John Hunyadi. András Hess set up a printing press in Buda in 1472. This was the first time in the history of the Hungarian kingdom that a member of the nobility, without dynastic ancestry and relationship, mounted the royal throne. A true Renaissance prince, a successful military leader and administrator, an outstanding linguist, a learned astrologer, and an enlightened patron of the arts and learning.[50]
Although Matthias regularly convened the Diet and expanded the lesser nobles' powers in the counties, he exercised absolute rule over Hungary by means of a huge secular bureaucracy. He set out to build a great empire, expanding southward and northwest, while he also implemented internal reforms. The serfs and common people considered him a just ruler because he protected them from excessive demands from and other abuses by the magnates.[51]
Like his father, Matthias desired to preserve the status of Hungary as the foremost regional power and overlord, strong enough to push back the Ottomans; to that end he deemed it necessary to conquer much of the Holy Roman Empire.[citation needed] In 1479, under the leadership of Pál Kinizsi, the Hungarian army destroyed the Ottoman and Wallachian troops at the Battle of Breadfield. Abroad he defeated the Polish and German imperial armies of Frederick at Breslau (Wrocław). Hungarian power was confirmed by the Treaty of Olomouc (1479).
His mercenary standing army, the Black Army of Hungary was an unusually large army for its time, and it conquered parts of Austria, Vienna (1485) and parts of Bohemia. The king died without a legal successor. His library, the Bibliotheca Corviniana, was Europe's greatest collection of historical chronicles, philosophic and scientific works in the 15th century, and second only in size to the Vatican Library which mainly contained Bibles and religious material. His renaissance library is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.[52]
Decline of Hungary (1490-1526)

By the early 16th century, the Ottoman Empire had become the second most populous state in the world; this enabled the creation of the largest armies of the era.
The Hungarian magnates, who did not want another heavy-handed king, procured the accession of Vladislaus II (reigned 1490–1516), king of Bohemia because of his notorious weakness: he was known as King Dobže, or Dobzse in Hungarian orthography (king "okay") from his habit of accepting without question every petition and document laid before him.[50] Under his reign the central power began to experience severe financial difficulties, mostly because of the enlargement of feudal lands at his expense. The magnates also dismantled the national administration systems and bureaucracy throughout the country. The country's defenses sagged as border guards and castle garrisons went unpaid, fortresses fell into disrepair, and initiatives to increase taxes to reinforce defenses were stifled.[53] Hungary's international role declined, its political stability shaken, and social progress was deadlocked.
In 1514, the weakened old King Vladislaus II faced a major peasant rebellion led by György Dózsa, which was ruthlessly crushed by the nobles, led by János Szapolyai. The resulting degradation of order paved the way for Ottoman pre-eminence. In 1521, the strongest Hungarian fortress in the South, Nándorfehérvár (modern Belgrade) fell to the Turks. The strongest nobles were so busy oppressing the peasants and quarrelling with gentry class in the parliament, that they failed to heed the agonized calls of king Louis II against the Turks. The early appearance of protestantism further worsened internal relations in the anarchical country. In 1526, the Hungarian army was crushed at the Battle of Mohács by the Ottomans. The childless young king Louis II, and the leader of the Hungarian army, Pál Tomori died on the battlefield.
Through the centuries Hungary kept its old constitution, which granted special freedoms or rights to the nobility, the free royal towns such as Buda, Kassa (Košice), Pozsony (Bratislava), and Kolozsvár (Cluj-Napoca) and groups such as the Jassic people and the Transylvanian Saxons.
Ottoman wars 1526–1699




After some 150 years of wars with the Hungarians and other states, the Ottomans conquered parts of Hungary, and continued their expansion until 1556. The Ottomans gained a decisive victory over the Hungarian army at the Battle of Mohács in 1526. The next decades were characterised by political chaos; the divided Hungarian nobility elected two kings simultaneously, 'Szapolyai János' (1526–1540) and Ferdinand Habsburg (1527–1540), whose feud for the throne further weakened the kingdom.
With the conquest of Buda in 1541 by the Turks, Hungary was divided into three parts. Even with a decisive 1552 victory over the Ottomans at the Siege of Eger, which raised the hopes of the Hungarians, the country remained divided until the end of the 17th century. The north-western part (see map) termed as Royal Hungary was annexed by the Habsburgs who ruled as Kings of Hungary.
The eastern part of the kingdom (Partium and Transylvania), in turn, became independent as the Principality of Transylvania, under Ottoman (and later Habsburg) suzerainty. The remaining central area (mostly present-day Hungary), including the capital of Buda was known as the Pashalik of Buda. A large part of the area became devastated by permanent warfare. Most smaller settlements disappeared.
Pozsony (today Bratislava) became the new capital (1536–1784), coronation town (1563–1830) and seat of the Diet (1536–1848) of Hungary. Nagyszombat (today Trnava) in turn, became the religious center in 1541. After the middle of the 16th century and the beginning of the Counter Reformation of Habsburgs, the strife between the Protestant Hungarians and the Catholic Habsburgs became increasingly violent.[54] The Turks were indifferent to the Christian religion of their subjects and the Habsburg counter-reformation measures could not reach this area. As a result, the majority of the population of the area became Protestant (Calvinist)[citation needed].
In 1558 the Transylvanian Diet of Turda declared free practice of both the Catholic and Lutheran religions, but prohibited Calvinism. Ten years later, in 1568, the Diet extended this freedom, declaring that "It is not allowed to anybody to intimidate anybody with captivity or expelling for his religion". Four religions were declared as accepted (recepta) religions, while Orthodox Christianity was "tolerated" (though the building of stone Orthodox churches was forbidden). Hungary entered the Thirty Years' War, Royal (Habsburg) Hungary joined the catholic side, until Transylvania joined the Protestant side.
There were a series of other successful and unsuccessful anti-Habsburg /i.e. anti-Austrian/ (requiring equal rights and freedom for all Christian religions) uprisings between 1604 and 1711, the uprisings were usually organized from Transylvania.
In 1686, two years after the unsuccessful siege of Buda, a renewed European campaign was started to enter the Hungarian capital. This time, the Holy League's army was twice as large, containing over 74,000 men, including German, Croat, Dutch, Hungarian, English, Spanish, Czech, Italian, French, Burgundian, Danish and Swedish soldiers, along with other Europeans as volunteers, artilleryman, and officers; with this force, the Christian forces reconquered Buda.
The second Battle of Mohács (1687) and Battle of Zenta (1697) were crushing defeats for the Turks, in the next few years, all of the former Hungarian lands, except areas near Temesvár (Timişoara), were taken from the Turks. In the 1699 Treaty of Karlowitz these territorial changes were officially recognized, and in 1718 the entire Kingdom of Hungary was removed from Ottoman rule. The constrained Habsburg Counter-Reformation efforts in the seventeenth century reconverted the majority of the kingdom to Catholicism. The Hungarian aristocracy successfully preserved its former positions in the political and economic sphere.
Ethnic aftermath of Ottoman wars
As a consequence of the prolonged constant warfare between Hungarians and Ottoman Turks, population growth was stunted and the network of medieval settlements with their urbanized bourgeois inhabitants perished. The 150 years of Turkish wars fundamentally changed the ethnic composition of Hungary. As a result of demographic losses including deportations and massacres, the number of ethnic Hungarians in existence at the end of the Turkish period was substantially diminished.[55]
The Hungarian people (the vast majority of Hungarian lowborn people hated[citation needed] the Habsburg monarchs) were considered rebellious by Habsburg Monarchs. After the "liberation" of Hungary from the Turks, The Austrian — Habsburg government settled large groups of Serbs and other Slavs in the south, allowed mass Vlach (Romanian) immigration into Transylvania and settled Germans in various areas, but not a single Hungarian person was allowed to settle or re-settle in the south of the Great Plain.[56]
From the 18th century to World War I



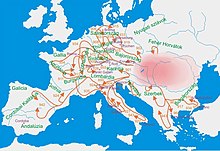
Between 1703 and 1711 there was a large-scale uprising led by Francis II Rákóczi, who after the dethronement of the Habsburgs in 1707 at the Diet of Ónód, took power provisionally as the "Ruling Prince" of Hungary for the wartime period, but refused the Hungarian Crown and the title "King". After 8 years of war with the Habsburg Empire the Hungarian Kuruc army lost the last main battle at Battle of Trencin (Trencsény) (1711).
However, they also had successful actions, for example when Ádám Balogh almost captured the Austrian Emperor with Kuruc troops. When Austrians defeated the uprising in 1711, Rákóczi was in Poland. He later fled to France, finally Turkey, and lived to the end of his life (1735) in nearby Rodosto. Ladislas Ignace de Bercheny who was the son of Miklós Bercsényi emigrated to France and created the first French hussar regiment.
Afterwards, to make further armed resistance impossible, the Austrians blew up Hungarian castles (most of the castles on the border between the now-reclaimed territories occupied earlier by the Ottomans and Royal Hungary), and allowed peasants to use the stones from most of the others as building material. In this century lived a Hungarian Hussar, Michael de Kovats, who created the US cavalry in the American Revolutionary War. He has a statue now in Charleston[disambiguation needed].
The Period of Reforms (1825–1848)
During the Napoleonic Wars and afterwards, the Hungarian Diet had not convened for decades.[citation needed] In the 1820s, the Emperor was forced to convene the Diet, and thus a Reform Period (Template:Lang-hu) began. Nevertheless, its progress was slow, because the nobles insisted on retaining their privileges (no taxation, exclusive voting rights, etc.). Therefore the achievements were mostly of national character (e.g. introduction of Hungarian as one of the official languages of the country, instead of the former Latin).
Count István Széchenyi, one of the most prominent statesmen of the country recognized the urgent need of modernization and his message got through. The Hungarian Parliament was reconvened in 1825 to handle financial needs. A liberal party emerged in the Diet. The party focused on providing for the peasantry. Lajos Kossuth—a famous journalist at that time—emerged as leader of the lower gentry in the Parliament.
Habsburg monarchs tried to preclude[citation needed] the industrialisation of the country. A remarkable upswing started as the nation concentrated its forces on modernisation even though the Habsburg monarchs obstructed all important liberal laws about the human civil and political rights and economic reforms. Many reformers (like Lajos Kossuth, Mihály Táncsics) were imprisoned by the authorities.
Revolution and War of Independence
On 15 March 1848, mass demonstrations in Pest and Buda enabled Hungarian reformists to push through a list of 12 demands. Faced with revolution both at home and in Vienna, Austria first had to accept Hungarian demands. Later, under governor and president Lajos Kossuth and the first Prime Minister, Lajos Batthyány, the House of Habsburg was dethroned and the form of government was changed to create the first Republic of Hungary. After the Austrian revolution was suppressed, emperor Franz Joseph replaced his epileptic uncle Ferdinand I as Emperor.
The Habsburg Ruler and his advisors skillfully manipulated the Croatian, Serbian and Romanian peasantry, led by priests and officers firmly loyal to the Habsburgs, and induced them to rebel against the Hungarian government. The Hungarians were supported by the vast majority of the Slovak, German and Rusyn nationalities and by all the Jews of the kingdom, as well as by a large number of Polish, Austrian and Italian volunteers.[57]
In July 1849 the Hungarian Parliament proclaimed and enacted the first laws of ethnic and minority rights in the world. Many members of the nationalities gained coveted the highest positions within the Hungarian Army, like General János Damjanich, an ethnic Serb who became a Hungarian national hero through his command of the 3rd Hungarian Army Corps. Initially, the Hungarian forces (Honvédség) defeated Austrian armies. To counter the successes of the Hungarian revolutionary army, Franz Joseph asked for help from the "Gendarme of Europe," Czar Nicholas I, whose Russian armies invaded Hungary. The huge army of the Russian Empire and the Austrian forces proved too powerful for the Hungarian army, and General Artúr Görgey surrendered in August 1849.
Julius Jacob von Haynau, the leader of the Austrian army, then became governor of Hungary for a few months, ordered the execution of the 13 Martyrs of Arad, leaders of the Hungarian army, as well as Prime Minister Batthyány in October 1849. Lajos Kossuth escaped into exile. Following the war of 1848–1849, the whole country was in "passive resistance". Archduke Albrecht, Duke of Teschen was appointed governor of the Kingdom of Hungary, and this time was remembered for Germanization pursued with the help of Czech officers.[citation needed]
Austria–Hungary (1867–1918)


Because of external and internal problems, reforms seemed inevitable to secure the integrity of the Habsburg Empire. Major military defeats of Austria, like the Battle of Königgrätz (1866), forced the Emperor to concede internal reforms. To appease Hungarian separatism, the Emperor made a deal with Hungary, negotiated by Ferenc Deák, called the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, by which the dual Monarchy of Austria–Hungary came into existence.
The two realms were governed separately by two parliaments from two capital cities, with a common monarch and common external and military policies. Economically, the empire was a customs union. The first prime minister of Hungary after the Compromise was Count Gyula Andrássy. The old Hungarian Constitution was restored, and Franz Joseph was crowned as King of Hungary.
Austria-Hungary was geographically the second largest country in Europe after the Russian Empire (239,977 sq. m in 1905[58]), and the third most populous (after Russia and the German Empire).
The era witnessed an impressive economic development. The formerly backward Hungarian economy became relatively modern and industrialized by the turn of the century, although agriculture remained dominant until 1890. In 1873, the old capital Buda and Óbuda(Ancient Buda) were officially merged with the third city, Pest, thus creating the new metropolis of Budapest.
The dynamic Pest grew into the country's administrative, political, economic, trade and cultural hub. Technological change accelerated industrialization and urbanization. The GNP per capita grew roughly 1.45% per year from 1870 to 1913. That level of growth compared very favorably to that of other European nations such as Britain (1.00%), France (1.06%), and Germany (1.51%). Many of the state institutions and the modern administrative system of Hungary were established during this period.
Because of various reasons including migration of millions[citation needed], the census in 1910 (excluding Croatia) recorded the following distribution of population: Hungarian 54.5%, Romanian 16.1%, Slovak 10.7%, and German 10.4%. The largest religious denomination was the Roman Catholic (49.3%), followed by the Calvinist (14.3%), Greek Orthodox (12.8%) /Romanians Serbians Ruthenians), Greek Catholic (11.0%), Lutheran (7.1%), and Jewish (5.0%) religions. In 1910, 6.37% of the population were eligible to vote in elections through census.[59]
World War I

After the Assassination in Sarajevo, the Hungarian prime minister, István Tisza, and his cabinet (sole in Europe) tried to avoid the breaking out and escalating of a war in Europe, but his diplomatic attempts remained unsuccessful.
Austria–Hungary drafted 9 million (fighting forces: 7,8 million) soldiers in World War I (Over 4 million from the Kingdom of Hungary). In World War I Austria–Hungary was fighting on the side of Germany, Bulgaria and Turkey. The Central Powers conquered Serbia. Romania declared war. The Central Powers conquered Southern Romania and the Romanian capital Bucharest. On November 1916 Emperor Franz Joseph died, the new monarch Charles IV sympathized with the pacifists. With great difficulty, the Central powers stopped and repelled the attacks of the Russian Empire.
The Eastern front of the Allied (Entente) Powers completely collapsed. The Austro-Hungarian Empire then withdrew from all defeated countries. On the Italian front, the Austro-Hungarian army could not make more successful progress against Italy after January 1918. Despite great Eastern successes, Germany suffered complete defeat in the more determinant Western front.
By 1918, the economic situation had deteriorated (strikes in factories were organized by leftist and pacifist movements), and uprisings in the army had become commonplace. In the capital cities (Vienna and Budapest), the Austrian and the Hungarian leftist liberal movements (the maverick parties) and their leader politicians supported and strengthened the separatism of ethnic minorities. Austria-Hungary signed general armistice in Padua on 3 November 1918. In October 1918, the personal union with Austria was dissolved.
Between the two world wars (1918–1941)
The first Republic of Hungary
In 1918, as a political result of German defeat on the Western front in World War I, the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy collapsed. French troops landed in Greece to rearm the defeated Romania, Serbia and the newly formed Czech state. Despite the general armistice agreement, the Balkanian French army organized new campaigns against Hungary with the help of Czech, Romanian, and Serbian governments.
On October 31, 1918, the success of the Aster Revolution in Budapest brought the left liberal count Mihály Károlyi to power as Prime-Minister. Roving soldiers assassinated István Tisza.[60] Károlyi was a devotee of Entente from the beginning of the World War. By a notion of Woodrow Wilson's pacifism, Károlyi ordered the full disarmament of Hungarian Army. Hungary remained without national defense in the darkest hour of its history. On 5 November 1918 Serbian Army with French involvement attacked Southern parts of the country, on 8 November Czech Army invaded Northern part of Hungary (present-day Slovakia), on 12 November Romanian Army started to attack the Eastern (Transylvanian) parts of Hungary.
The First Republic was proclaimed on 16 November 1918 with Károlyi being named as president. The Károlyi government pronounced illegal all armed associations and proposals which wanted to defend the integrity of the country. The Károlyi government also dissolved the gendarme and police, the lack of police force caused big problems in the country. By February 1919 the government had lost all popular support, having failed on domestic and military fronts. On March 21, after the Entente military representative demanded more and more territorial concessions from Hungary, Károlyi resigned. Károlyi (with a new Czechoslovakian passport and Czechoslovak diplomatic help) moved to Paris.
The Hungarian Soviet Republic
The Communist Party of Hungary, led by Béla Kun, came to power and proclaimed the Hungarian Soviet Republic. The Communists also promised equality and social justice. The Communists – "The Reds" – came to power largely thanks to being the only group with an organized fighting force, and they promised that Hungary would defend its territory without conscription, possibly with the help of the Soviet Red Army. The Red Army of Hungary was a little voluntary army (53,000 men). Most soldiers of the Red Army were armed factory workers from Budapest.
In terms of domestic policy, the Communist government nationalized industrial and commercial enterprises, socialized housing, transport, banking, medicine, cultural institutions, and all landholdings of more than 400,000 square metres. The support of the Communists proved to be short lived in Budapest. The Soviet Red Army was never able to aid the new Hungarian republic. Despite the great military successes against Czechoslovakian army, the communist leaders gave back all recaptured lands. That attitude demoralized the voluntary army. The Hungarian Red Army was dissolved before it could successfully complete its campaigns. The Communists had never been popular in country towns and countryside.
In the aftermath of a coup attempt, the government took a series of actions called the Red Terror, murdering several hundred people (mostly intellectuals), which alienated much of the population. In the face of domestic backlash and an advancing Romanian force, Béla Kun and most of his comrades fled to Austria, while Budapest was occupied on August 6. Kun and his followers illegally took along numerous art treasures and the gold stocks of the National Bank.[61] All these events, and in particular the final military defeat, led to a deep feeling of dislike among the general population against the Soviet Union (which had not kept its promise to offer military assistance) and the Jews (since most members of Kun's government were Jewish[62]).

Restored Kingdom of Hungary
The new fighting force in Hungary were the Conservative Royalists counter-revolutionaries – the "Whites". These, who had been organizing in Vienna and established a counter-government in Szeged, assumed power, led by István Bethlen, a Transylvanian aristocrat, and rear-admiral Miklós Horthy, the former commander in chief of the Austro-Hungarian Navy. Starting in Western Hungary and spreading throughout the country, a White Terror began by other half-regular and half-militarist detachments (as the police power crashed, there were no serious national regular forces and authorities), and many Communists and other leftists were tortured and executed without trial.
The leaving Romanian army pillaged the country: livestock, machinery and agricultural products were carried to Romania in hundreds of freight cars.[dubious – discuss][63][64] The estimated property damage of their activity was so much that the international peace conference in 1919 did not require Hungary to pay war redemption to Romania.[dubious – discuss][citation needed] On November 16, with the consent of Romanian forces, Horthy's army marched into Budapest. His government gradually restored security police and gendarmee, stopped terror, and set up authorities, but thousands of supporters of the leftist-liberal Károlyi and communist Kun regimes were imprisoned (for "High treason" and "anti-Hungarian actions"). But radical rightist political movements were suppressed too. In March, the parliament restored the Hungarian monarchy but postponed electing a king until civil disorder had subsided. Instead, Miklos Horthy was elected Regent and was empowered, among other things, to appoint Hungary's Prime Minister, veto legislation, convene or dissolve the parliament, and command the armed forces.

Hungary's signing of the Treaty of Trianon on June 4, 1920, ratified the country's dismemberment. The territorial provisions of the treaty, which ensured continued discord between Hungary and its neighbors, required Hungary to surrender more than two-thirds of its pre-war lands. However, nearly one-third of the 10 million ethnic Hungarians found themselves outside the diminished homeland. The country's ethnic composition was left almost homogeneous, Hungarians constituting about 90% of the population, Germans made up about 6%, and Slovaks, Croats, Romanians, Jews and Gypsies accounted for the remainder.[citation needed]
New international borders separated Hungary's industrial base from its sources of raw materials and its former markets for agricultural and industrial products. Hungary lost 84% of its timber resources, 43% of its arable land, and 83% of its iron ore. Furthermore, post-Trianon Hungary possessed 90% of the engineering and printing industry of the Kingdom, while only 11% of timber and 16% iron was retained. In addition, 61% of arable land, 74% of public road, 65% of canals, 62% of railroads, 64% of hard surface roads, 83% of pig iron output, 55% of industrial plants, 100% of gold, silver, copper, mercury and salt mines, and 67% of credit and banking institutions of the former Kingdom of Hungary lay within the territory of Hungary's neighbors.[67][68][69]
Because most of the country's pre-war industry was concentrated near Budapest, Hungary retained about 51% of its industrial population, 56% of its industry. Horthy appointed Count Pál Teleki as Prime Minister in July 1920. His government issued a numerus clausus law, limiting admission of "political insecure elements" (these were often Jews) to universities and, in order to quiet rural discontent, took initial steps toward fulfilling a promise of major land reform by dividing about 3,850 km2 from the largest estates into smallholdings.
Teleki's government resigned, however, after, Charles IV, unsuccessfully attempted to retake Hungary's throne in March 1921. King Charles's return produced split parties between conservatives who favored a Habsburg restoration and nationalist right-wing radicals who supported election of a Hungarian king. Count István Bethlen, a non-affiliated right-wing member of the parliament, took advantage of this rift forming a new Party of Unity under his leadership. Horthy then appointed Bethlen prime minister. Charles IV died soon after he failed a second time to reclaim the throne in October 1921. (For more detail on Charles's attempts to retake the throne, see Charles IV of Hungary's conflict with Miklós Horthy.)

As prime minister, Bethlen dominated Hungarian politics between 1921 and 1931. He fashioned a political machine by amending the electoral law, providing jobs in the expanding bureaucracy to his supporters, and manipulating elections in rural areas. Bethlen restored order to the country by giving the radical counterrevolutionaries payoffs and government jobs in exchange for ceasing their campaign of terror against Jews and leftists. In 1921, he made a deal with the Social Democrats and trade unions (called Bethlen-Peyer Pact), agreeing, among other things, to legalize their activities and free political prisoners in return for their pledge to refrain from spreading anti-Hungarian propaganda, calling political strikes, and organizing the peasantry.
Bethlen brought Hungary into the League of Nations in 1922 and out of international isolation by signing a treaty of friendship with Italy in 1927. The revision of the Treaty of Trianon rose to the top of Hungary's political agenda and the strategy employed by Bethlen consisted by strengthening the economy and building relations with stronger nations. Revision of the treaty had such a broad backing in Hungary that Bethlen used it, at least in part, to deflect criticism of his economic, social, and political policies. The Great Depression induced a drop in the standard of living and the political mood of the country shifted further toward the right.
In 1932 Horthy appointed a new prime-minister, Gyula Gömbös, that changed the course of Hungarian policy towards closer cooperation with Germany. Gömbös signed a trade agreement with Germany that drew Hungary's economy out of depression but made Hungary dependent on the German economy for both raw materials and markets. Adolf Hitler appealed to Hungarian desires for territorial revisionism, while extreme right wing organizations, like the Arrow Cross party, increasingly embraced Nazi policies, including those related to Jews. The government passed the First Jewish Law in 1938. The law established a quota system to limit Jewish involvement in the Hungarian economy.
Pm. Imrédy's (a Jewish descendant) attempts to improve Hungary's diplomatic relations with the United Kingdom initially made him very unpopular with Germany and Italy. In light of Germany's Anschluss with Austria in March, he realized that he could not afford to alienate Germany and Italy for long; in the autumn of 1938 his foreign policy became very much pro-German and pro-Italian.[70] Intent on amassing a base of power in Hungarian right wing politics, Imrédy began to suppress political rivals, so the increasingly influential Arrow Cross Party was harassed, and eventually banned by Imrédy's administration.
As Imrédy drifted further to the right, he proposed that the government be reorganized along totalitarian lines and drafted a harsher Second Jewish Law. The Parliament under the new government of Pál Teleki approved the Second Jewish Law in 1939, which greatly restricted Jewish involvement in the economy, culture, and society and, significantly, defined Jews by race instead of religion. This definition altered the status of those who had formerly converted from Judaism to Christianity. Template:Regions which belonged to Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon
Hungary in World War II (1941–1945)

The Germans and Italians granted to Hungary part of southern Czechoslovakia and Subcarpathia in the First Vienna Treaty of 1938, and then northern Transylvania in the Second Vienna Treaty of 1940.
In 1941 Hungary participated in its first military manoeuvres as part of the Axis. Thus the Hungarian army was part of the invasion of Yugoslavia, gaining some more territory. On June 22, 1941, Germany invaded the Soviet Union under Operation Barbarossa; Hungary joined the German effort and declared war on the Soviet Union on June 26, and formally entered World War II on the side of the Axis. In late 1941, the Hungarian troops on the Eastern Front experienced success at the Battle of Uman. By 1943, after the Hungarian Second Army suffered extremely heavy losses at the River Don, the Hungarian government sought to negotiate a surrender with the Allies.
On March 19, 1944, as a result of this duplicity, German troops occupied Hungary in what was known as Operation Margarethe. By then it was clear that Hungarian politics was suppressed by Hitler's intent to hold the country in war on the side of the Nazi Third Reich because of its strategic location. On October 15, 1944, Miklós Horthy made a token effort to disengage Hungary from the war. This time the Germans launched Operation Panzerfaust and Horthy was replaced by a puppet government under the pro-German Prime Minister Ferenc Szálasi. Szálasi and his pro-Nazi Arrow Cross Party remained loyal to the Germans until the end of the war.
In late 1944, Hungarian troops on the Eastern Front again experienced success at the Battle of Debrecen, but this was followed immediately by the Soviet invasion of Hungary and the Battle of Budapest. During the German occupation in May-June 1944, the Arrow Cross Party and Hungarian police deported nearly 440,000 Jews, mostly to Auschwitz.[71] The Swedish Diplomat Raoul Wallenberg managed to save a considerable number of Hungarian Jews by giving them Swedish passports, but when the soviets arrived he was arrested as a spy and disappeared.[72] Nuncio Angelo Rotta and other Italian, Spanish and Swiss diplomats also organized false papers and safe houses for Jews in Budapest. Hundreds of Hungarian people were executed by the Arrow Cross Party for sheltering Jews.
The war left Hungary devastated destroying over 60% of the economy and causing huge loss of life. Many Hungarians, including women and children, were brutally raped, murdered and executed or deported for slave labour by Czechslovaks, Russian Red Army troops, Yugoslavs (mostly Serbian partisans and regular units), and the Romanian so-called "Munteanu Guard" paramilitary units — by the end of the war approximately 500,000-650,000 people.
On February 13, 1945, the Hungarian capital city surrendered unconditionally. On May 8, 1945, World War II in Europe officially ended. By the agreement between the Czechoslovakian president Edvard Beneš and Joseph Stalin the wild expulsions of Slovaks from Hungary and Magyars from Czechoslovakia started. 250,000 ethnic Germans were also transferred to Germany pursuant to article XIII of the Potsdam Protocol of 2 August 1945.[73]
Communist era (1947–1989)
Following the fall of Nazi Germany, Soviet troops occupied all of the country and through their influence Hungary gradually became a communist satellite state of the Soviet Union. Many of the communist leaders of 1919 returned from Moscow. After 1948, Communist leader Mátyás Rákosi established Stalinist rule in the country complete with forced collectivization and planned economy. Mátyás Rákosi now attempted to impose authoritarian rule on Hungary.
An estimated 2,000 people were executed and over 100,000 were imprisoned. Approximately 350,000 officials and intellectuals were purged from 1948 to 1956.[74] Many people, freethinkers and democrats, were secretly arrested and taken to inland or foreign concentration camps without any judicial sentence. This was the deportation of some 600,000 Hungarians to Soviet labour camps after the Second World War and the death of at least 200,000 in captivity.[75] Hungary experienced one of the harshest dictatorships in Europe.
Rákosi had difficulty managing the economy and the people of Hungary saw living standards fall. His government became increasingly unpopular, and when Joseph Stalin died in 1953, Mátyás Rákosi was replaced as prime minister by Imre Nagy. However, he retained his position as general secretary of the Hungarian Workers Party and over the next three years the two men became involved in a bitter struggle for power.
As Hungary's new leader, Imre Nagy removed state control of the mass media and encouraged public discussion on political and economic reform. This included a promise to increase the production and distribution of consumer goods. Nagy also released anti-communists from prison and talked about holding free elections and withdrawing Hungary from the Warsaw Pact. Nagy was removed by Soviets. Rákosi did manage to secure the appointment of his puppet and close friend, Ernő Gerő, as his successor.
The rule of the Rákosi government was nearly unbearable for Hungary's war-torn citizens. This led to the 1956 Hungarian Revolution and Hungary's temporary withdrawal from the Warsaw Pact. The multi-party system was restored by Nagy. Soviets and Hungarian political police (AVH) shot at peaceful demonstrators and many demonstrators died throughout the country, which made the events irreversible.
Spontaneous revolutionary militias arose and heavy street fights started against the Soviet Army and the fearful communist secret police (AVH) in Budapest. The roughly 3,000-strong Hungarian resistance fought Soviet tanks using Molotov cocktails, in the narrow streets of Budapest, and machine-pistols. The immense Soviet preponderance suffered heavy losses, by 30 October most Soviet troops had withdrawn from Budapest to garrisons in the Hungarian countryside.
The Soviet Union sent new armies to Hungary. On 4 November 1956, the Soviets retaliated massively with military force, sending in over 150,000 troops and 2,500 tanks.[76] During the Hungarian Uprising an estimated 20,000 people were killed, nearly all during the Soviet intervention. Nearly a quarter of a million people left the country during the brief time that the borders were open in 1956.[77]
Kádár Era (1956-1988)
János Kádár (who was the appointed leader by the Soviets) reorganized the communist party as the puppet of the Soviets. Once he was in power, Kádár led an attack against revolutionaries. 21,600 mavericks (democrats, liberals, reformist communists alike) were imprisoned, 13,000 interned, and 400 killed. Imre Nagy, the legal Prime Minister of the country was condemned to death. From the 1960s through the late 1980s, Hungary was often satirically referred to as "the happiest barrack" within the Eastern bloc.
As a result of the relatively high standard of living, and less restricted travel rights than those in force elsewhere in the Eastern Bloc, Hungary was generally considered one of the better countries in which to live in Eastern Europe during the Cold War. (See also Goulash Communism for a discussion of the Hungarian variety of socialism.) This was under the autocratic rule of its controversial communist leader, János Kádár. It was the so called Kádár era (1956–1988). The last Soviet soldier left the country in 1991 thus ending Soviet military presence in Hungary. With the Soviet Union gone the transition to a market economy began.
The Third Hungarian Republic (1989–present)

"From this spot you could see tens of thousands of students and workers and other Hungarians marching through the streets. They called for an end to dictatorship, to censorship, and to the secret police. They called for free elections, a free press, and the release of political prisoners. These Hungarian patriots tore down the statue of Josef Stalin, and defied an empire to proclaim their liberty."
— George W. Bush, Former President of the United States
In June 1987, Károly Grósz took over as premier. In January 1988 all restrictions were lifted on foreign travel. In March demonstrations for democracy and civil rights brought 15,000 onto the streets. In May, after Kádár's forced retirement, Grósz was named party secretary general.
Under Grósz, Hungary began moving towards full democracy, change accelerated under the impetus of other party reformers such as Imre Pozsgay and Rezső Nyers. Also in June 1988, 30,000 demonstrated against Romania's communist Regime plans to demolish Transylvanian villages.
In February, 1989 the Communist Party's Central Committee, responding to 'public dissatisfaction', announced it would permit a multi-party system in Hungary and hold free elections. In March, for the first time in decades, the government declared the anniversary of the 1848 Revolution a national holiday. Opposition demonstrations filled the streets of Budapest with more than 75,000 marchers.
Grósz met Mikhail Gorbachev in Moscow, who condoned Hungary's moves toward a multi-party system and promised that the USSR would not interfere in Hungary's internal affairs. In May, Hungary began taking down its barbed wire fence along the Austrian border – the first tear in the Iron Curtain.
June brought the reburial of Prime Minister Nagy, executed after the 1956 Revolution, drawing a crowd of 250,000 at the Heroes' Square. The last speaker, 26-year-old Viktor Orbán publicly called for Soviet troops to leave Hungary. In July U.S. President George Bush visited Hungary. In September Foreign Minister Gyula Horn announced that East German refugees in Hungary would not be repatriated but would instead be allowed to go to the West. The resulting exodus shook East Germany and hastened the fall of the Berlin Wall. On October 23, Mátyás Szűrös declared Hungary a republic.
At a party congress in October 1989 the Communists agreed to give up their monopoly on power, paving the way for free elections in March 1990. The party's name was changed from the Hungarian Socialist Workers' Party to simply the Hungarian Socialist Party (MSZP) and a new programme advocating social democracy and a free-market economy was adopted. This was not enough to shake off the stigma of four decades of autocratic rule, however, and the 1990 election was won by the centre-right Hungarian Democratic Forum (MDF), which advocated a gradual transition towards capitalism. The liberal Alliance of Free Democrats (SZDSZ), which had called for much faster change, came second and the Socialist Party trailed far behind. As Gorbachev looked on, Hungary changed political systems with scarcely a murmur and the last Soviet troops left Hungary in June 1991.

In coalition with two smaller parties, the MDF provided Hungary with sound government during its hard transition to a full market economy. József Antall, the first democratically elected prime minister of Hungary, died in December 1993 and was replaced by the Interior Minister Péter Boross.
The economic changes of the early 1990s resulted in declining living standards for most people in Hungary. In 1991 most state subsidies were removed, leading to a severe recession exacerbated by the fiscal austerity necessary to reduce inflation and stimulate investment. This made life difficult for many Hungarians, and in the May 1994 elections the Hungarian Socialist Party led by former Communists won an absolute majority in parliament.
This in no way implied a return to the past, and party leader Gyula Horn was quick to point out that it was his party that had initiated the whole reform process in the first place (as foreign minister in 1989 Horn played a key role in opening Hungary's border with Austria). All three main political parties advocate economic liberalisation and closer ties with the West. In March 1996, Horn was re-elected as Socialist Party leader and confirmed that he would push ahead with the party's economic stabilisation programme.
In 1997 in a national referendum 85% voted in favour of Hungary joining the NATO. A year later the European Union began negotiations with Hungary on full membership. In 1999 Hungary joined NATO. Hungary voted in favour of joining the EU, and joined in 2004.
Science
As of 2009, 14 Hungarians (who were born in Hungary) had received a scientific Nobel prize, more than China, Japan, India, Australia or Spain.[78] Further eight Nobel prize laureates of Hungarian origin on both sides were born outside of Hungary.
The world's first institution of technology was founded in Selmecbánya, Hungarian Kingdom (today Slovakia) in 1735. Budapest University of Technology and Economics (BME) is considered the oldest institution of technology in the world, which has university rank and structure. The legal predecessor of the university was founded in 1782 by Emperor Joseph II.
Hungary is famous for its excellent mathematics education which has trained numerous outstanding scientists. Famous Hungarian mathematicians include János Bolyai, designer of modern geometry (non-Euclidean geometry) in 1831. Paul Erdős, famed for publishing in over forty languages and whose Erdős numbers are still tracked;[79] and John von Neumann, Quantum Theory, Game theory a pioneer of digital computing and a key mathematician in the Manhattan Project. Many Hungarian scientists, including Erdős, von Neumann, Leo Szilard, Eugene Wigner and Edward Teller immigrated to the United States. The other cause of scientist emigration was the Treaty of Trianon, by which "little Hungary", amputated by the Trianon treaty, became unable to support large-scale, costly scientific research; therefore some Hungarian scientists made valuable contributions in the United States.
Hungarian inventions
Old times
Steel spring (medieval), coach (medieval) and coach suspension. The English word "coach" came from the Hungarian kocsi, a wagon from the village of Kocs, Hungary,[80] the noiseless match (János Irinyi)
Modern times

First electric motor (1827) and first electrical generator (Ányos Jedlik). David Schwarz invented and designed the first flyable rigid airship (aluminium-made), later he sold his patent for German Graf Zeppelin. Ottó Bláthy, Miksa Déri and Károly Zipernowsky invented the transformer in 1885.[81][81] (Ottó Bláthy) invented the Turbogenerator and Wattmeter, Telephone exchange (Tivadar Puskás), Ford Model T and assembly line (therefore he is the inventor of industrial mass production) József Galamb, Tungsten electric bulb (1904) (Sándor Just) and the krypton electric bulb (Imre Bródy), weak equivalence principle and surface tension Loránd Eötvös, Electronic Television and camera-tube (1926) and Plasma TV (1936) (Kálmán Tihanyi), Vitamin C and the first artificial vitamin Albert Szent-Györgyi, mathematical tools to study fluid flow and mathematical background of supersonic flight and inventor of swept-back wings "father of Supersonic Flight" (Theodore Kármán), ramjet propulsion Albert Fonó, Turboprop propulsion by (György Jendrassik), (Leó Szilárd): nuclear chain reaction (therefore he was the first who realized the feasibility of an "atomic bomb". In August 1939, Szilard approached his old friend and collaborator Albert Einstein and convinced him to sign the Einstein–Szilárd letter, lending the weight of Einstein's fame to the proposal. The letter led directly to the establishment of research into nuclear fission by the U.S. government and ultimately to the creation of the Manhattan Project. Szilárd, with Enrico Fermi, patented the nuclear reactor). Other notable Hungarian inventions include holography (Dennis Gabor), the ballpoint pen (László Bíró), thermonuclear fusion and the theory of the hydrogen bomb (Edward Teller), and the BASIC programming language (John Kemeny, with Thomas E. Kurtz), Low level laser therapy or "light therapy" (Endre Mester), artificial blood (István Horváth), Rubik's cube (Ernő Rubik).[79]
-
Albert Szent-Györgyi, discoverer of vitamin C.
-
Róbert Bárány, winner of the Nobel prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1914.
-
Charles Simonyi, software architect of early Excel
-
George de Hevesy, winner of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1943.
-
Edward Teller, "The father of the hydrogen bomb."
Politics

The President of the Republic, elected by the members of the National Assembly every five years, has a largely ceremonial role, but he is nominally the Commander-in-Chief of the armed forces and his powers include the nomination of the Prime Minister who is to be elected by a majority of the votes of the Members of Parliament, based on the recommendation made by the President of the Republic.
By the Hungarian Constitution, based on the post-WWII Basic Law of the Federal Republic of Germany, the Prime Minister has a leading role in the executive branch as he selects Cabinet ministers and has the exclusive right to dismiss them (similarly to the competences of the German federal chancellor). Each cabinet nominee appears before one or more parliamentary committees in consultative open hearings, survive a vote by the Parliament and must be formally approved by the president.
The unicameral, 386-member National Assembly (Országgyűlés) is the highest organ of state authority and initiates and approves legislation sponsored by the Prime Minister. Its members are elected for a four year term. 176 members are elected in single-seat constituencies, 152 by proportional representation in multi-seat constituencies, and 58 so-called compensation seats are distributed based on the number of votes "lost" (i.e., the votes that did not produce a seat) in either the single-seat or the multi-seat constituencies. The election threshold is 5%, but it only applies to the multi-seat constituencies and the compensation seats, not the single-seat constituencies.
An 11-member Constitutional Court has power to challenge legislation on grounds of unconstitutionality.
Regions, counties, subregions and cities
- See also List of historic counties of Hungary

Administratively, Hungary is divided into 19 counties. In addition, the capital (főváros), Budapest, is independent on any county government. The counties and the capital are the 20 NUTS third-level units of Hungary.
The counties are further subdivided into 173 subregions (kistérségek), and Budapest is its own subregion. Since 1996, the counties and City of Budapest have been grouped into 7 regions for statistical and development purposes. These seven regions constitute NUTS' second-level units of Hungary.
There are also 23 towns with county rights (singular megyei jogú város), sometimes known as "urban counties" in English (although there is no such term in Hungarian). The local authorities of these towns have extended powers, but these towns belong to the territory of the respective county instead of being independent territorial units.
Counties (County seats)
- Bács-Kiskun (Kecskemét)
- Baranya (Pécs)
- Békés (Békéscsaba)
- Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén (Miskolc)
- Csongrád (Szeged)
- Fejér (Székesfehérvár)
- Győr-Moson-Sopron (Győr)
- Hajdú-Bihar (Debrecen)
- Heves (Eger)
- Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok (Szolnok)
- Komárom-Esztergom (Tatabánya)
- Nógrád (Salgótarján)
- Pest (Budapest)
- Somogy (Kaposvár)
- Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg (Nyíregyháza)
- Tolna (Szekszárd)
- Vas (Szombathely)
- Veszprém (Veszprém)
- Zala (Zalaegerszeg)
- Budapest, capital
Regions
- Western Transdanubia
- Southern Transdanubia
- Central Transdanubia
- Central Hungary
- Northern Hungary
- Northern Great Plain
- Southern Great Plain
Largest cities
|
Rank | City | County | Population | Metropolitan area | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Budapest | Budapest | 1,721,556 |
2,503,205 | ||||||
| 2 | Debrecen | Hajdú-Bihar | 207,270 |
237,888 | ||||||
| 3 | Szeged | Csongrád | 169,731 |
201,307 | ||||||
| 4 | Miskolc | Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén | 169,226 |
216,470 | ||||||
| 5 | Pécs | Baranya | 157,680 |
179,215 | ||||||
| 6 | Győr | Győr-Moson-Sopron | 130,478 |
182,776 | ||||||
| 7 | Nyiregyháza | Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg | 117,832 |
- | ||||||
| 8 | Kecskemét | Bács-Kiskun | 112,233 |
- | ||||||
| 9 | Székesfehérvár | Fejér | 101,973 |
- | ||||||
| 10 | Szombathely | Vas | 79,513 | - | ||||||
| 11 | Szolnok | Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok | 74,885 | - | ||||||
| 12 | Tatabánya | Komárom-Esztergom | 70,333 | - | ||||||
| 13 | Kaposvár | Somogy | 67,633 | - | ||||||
| 14 | Békéscsaba | Békés | 64,787 | - | ||||||
| 15 | Érd | Pest | 63,669 | - | ||||||
| 16 | Veszprém | Veszprém | 63,405 | - | ||||||
| 17 | Zalaegerszeg | Zala | 61,774 | - | ||||||
| 18 | Sopron | Győr-Moson-Sopron | 59,036 | - | ||||||
| 19 | Eger | Heves | 56,429 | - | ||||||
| 20 | Nagykanizsa | Zala | 50,540 | - | ||||||
Economy
Hungary held its first multi-party elections in 1990, following four decades of Communist rule, and has succeeded in transforming its centrally planned economy into a market economy. Both foreign ownership of and foreign investment in Hungarian firms are widespread. The governing coalition, comprising the Hungarian Socialist Party and the liberal Alliance of Free Democrats, prevailed in the April 2006 general election. Hungary needs to reduce government spending and further reform its economy in order to meet the 2012–2013 target date for accession to the euro zone.
Hungary has continued to demonstrate economic growth as one of the newest member countries of the European Union (since 2004). The private sector accounts for over 80% of GDP. Hungary gets nearly one third of all foreign direct investment flowing into Central Europe, with cumulative foreign direct investment totaling more than US$185 billion since 1989. It enjoys strong trade, fiscal, monetary, investment, business, and labor freedoms. The top income tax rate is fairly high, but corporate taxes are low. Inflation is low, it was on the rise in the past few years, but it is now starting to regulate. Investment in Hungary is easy, although it is subject to government licensing in security-sensitive areas. Foreign capital enjoys virtually the same protections and privileges as domestic capital. The rule of law is strong, a professional judiciary protects property rights, and the level of corruption is low.



The Hungarian economy is a medium-sized, structurally, politically, and institutionally open economy in Central Europe and is part of the EU single market. Like most Eastern European economies, it experienced market liberalisation in the early 1990s as part of a transition away from communism. Today, Hungary is a full member of OECD and the World Trade Organization. OECD was the first international organization to accept Hungary as a full member in 1996, after six years of successful cooperation.
History of the Hungarian Economy
Hungarian economy prior to the transition
The Hungarian economy prior to World War II was primarily oriented toward agriculture and small-scale manufacturing. Hungary's strategic position in Europe and its relative high lack of natural resources also have dictated a traditional reliance on foreign trade. For instance, its largest car manufacturer, Magomobil (maker of the Magosix), produced a total of a few thousand units.[82] In the early 1950s, the communist government forced rapid industrialization after the standard Stalinist pattern in an effort to encourage a more self-sufficient economy. Most economic activity was conducted by state-owned enterprises or cooperatives and state farms. In 1968, Stalinist self-sufficiency was replaced by the "New Economic Mechanism", which reopened Hungary to foreign trade, gave limited freedom to the workings of the market, and allowed a limited number of small businesses to operate in the services sector.
Although Hungary enjoyed one of the most liberal and economically advanced economies of the former Eastern bloc, both agriculture and industry began to suffer from a lack of investment in the 1970s, and Hungary's net foreign debt rose significantly—from $1 billion in 1973 to $15 billion in 1993—due largely to consumer subsidies and unprofitable state enterprises. In the face of economic stagnation, Hungary opted to try further liberalization by passing a joint venture law, instating an income tax, and joining the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank. By 1988, Hungary had developed a two-tier banking system and had enacted significant corporate legislation which paved the way for the ambitious market-oriented reforms of the post-communist years.
Transition to a market economy

After the fall of communism in Eastern Europe, the former Soviet satellites had to transition from a one-party, centrally planned economy to a market economy with a multi-party political system. With the collapse of the Soviet Union, the Eastern Bloc countries suffered a significant loss in both markets for goods, and subsidizing from the Soviet Union. Hungary, for example, "lost nearly 70% of its export markets in Eastern and Central Europe." The loss of external markets in Hungary coupled with the loss of Soviet subsidies left "800,000 unemployed people because all the unprofitable and unsalvageable factories had been closed."[83] Another form of Soviet subsidizing that greatly affected Hungary after the fall of communism was the loss of social welfare programs. Because of the lack of subsidies and a need to reduce expenditures, many social programs in Hungary had to be cut in an attempt to lower spending. As a result, many people in Hungary suffered incredible hardships during the transition to a market economy. Following privatization and tax reductions on Hungarian businesses, unemployment suddenly rose to 12% in 1991 (it was 1.7% in 1990 ), gradually decreasing until 2001. Economic growth, after a fall in 1991 to -11.9%, gradually grew until the end of the 1990s at an average annual rate of 4.2%. With the stabilization of the new market economy, Hungary has experienced growth in foreign investment with a "cumulative foreign direct investment totaling more than $60 billion since 1989."[84]

The Antall government of 1990–94 began market reforms with price and trade liberation measures, a revamped tax system, and a nascent market-based banking system. By 1994, however, the costs of government overspending and hesitant privatization had become clearly visible. Cuts in consumer subsidies led to increases in the price of food, medicine, transportation services, and energy. Reduced exports to the former Soviet bloc and shrinking industrial output contributed to a sharp decline in GDP. Unemployment rose rapidly to about 12% in 1993. The external debt burden, one of the highest in Europe, reached 250% of annual export earnings, while the budget and current account deficits approached 10% of GDP. The devaluation of the currency (in order to support exports), without effective stabilization measures, such as indexation of wages, provoked an extremely high inflation rate, that in 1991 reached 35% and slightly decreased until 1994, growing again in 1995. In March 1995, the government of Prime Minister Gyula Horn implemented an austerity program, coupled with aggressive privatization of state-owned enterprises and an export-promoting exchange raw regime, to reduce indebtedness, cut the current account deficit, and shrink public spending. By the end of 1997 the consolidated public sector deficit decreased to 4.6% of GDP—with public sector spending falling from 62% of GDP to below 50%—the current account deficit was reduced to 2% of GDP, and government debt was paid down to 94% of annual export earnings.
The Government of Hungary no longer requires IMF financial assistance and has repaid all of its debt to the fund. Consequently, Hungary enjoys favorable borrowing terms. Hungary's sovereign foreign currency debt issuance carries investment-grade ratings from all major credit-rating agencies, although recently the country was downgraded by Moody's, S&P and remains on negative outlook at Fitch. In 1995 Hungary's currency, the Forint (HUF), became convertible for all current account transactions, and subsequent to OECD membership in 1996, for almost all capital account transactions as well. Since 1995, Hungary has pegged the forint against a basket of currencies (in which the U.S. dollar is 30%), and the central rate against the basket is devalued at a preannounced rate, originally set at 0.8% per month, the Forint is now an entirely free-floating currency. The government privatization program ended on schedule in 1998: 80% of GDP is now produced by the private sector, and foreign owners control 70% of financial institutions, 66% of industry, 90% of telecommunications, and 50% of the trading sector.

After Hungary's GDP declined about 18% from 1990 to 1993 and grew only 1%–1.5% up to 1996, strong export performance has propelled GDP growth to 4.4% in 1997, with other macroeconomic indicators similarly improving. These successes allowed the government to concentrate in 1996 and 1997 on major structural reforms such as the implementation of a fully funded pension system (partly modelled after Chile's pension system with major modifications), reform of higher education, and the creation of a national treasury. Remaining economic challenges include reducing fiscal deficits and inflation, maintaining stable external balances, and completing structural reforms of the tax system, health care, and local government financing. Recently, the overriding goal of Hungarian economic policy has been to prepare the country for entry into the European Union, which it joined in late 2004.

Prior to the change of regime in 1989, 65% of Hungary's trade was with Comecon countries. By the end of 1997, Hungary had shifted much of its trade to the West. Trade with EU countries and the OECD now comprises over 70% and 80% of the total, respectively. Germany is Hungary's single most important trading partner. The U.S. has become Hungary's sixth-largest export market, while Hungary is ranked as the 72nd largest export market for the U.S. Bilateral trade between the two countries increased 46% in 1997 to more than $1 billion. The U.S. has extended to Hungary most-favored-nation status, the Generalized System of Preferences, Overseas Private Investment Corporation insurance, and access to the Export-Import Bank.
With about $18 billion in foreign direct investment (FDI) since 1989, Hungary has attracted over one-third of all FDI in central and eastern Europe, including the former Soviet Union. Of this, about $6 billion came from American companies. Foreign capital is attracted by skilled and relatively inexpensive labor, tax incentives, modern infrastructure, and a good telecommunications system.
By 2006 Hungary’s economic outlook had deteriorated. Wage growth had kept up with other nations in the region; however, this growth has largely been driven by increased government spending. This has resulted in the budget deficit ballooning to over 10% of GDP and inflation rates predicted to exceed 6%. This prompted Nouriel Roubini, a White House economist in the Clinton administration, to state that "Hungary is an accident waiting to happen."[85]
Hungarian economy today
In 2006 Prime Minister Ferenc Gyurcsány was reelected on a platform promising economic “reform without austerity.” However, after the elections in April 2006, the Socialist coalition under Prime Minister Ferenc Gyurcsany unveiled a package of austerity measures which were designed to reduce the budget deficit to 3% of GDP by 2008.
Hungary, as a member state of the European Union may seek to adopt the common European currency, the Euro. To achieve this, Hungary would need to fulfill the Maastricht criteria.
In foreign investments, Hungary has seen a shift from lower-value textile and food industry to investment in luxury vehicle production, renewable energy systems, high-end tourism, and information technology.
The fulfillment of the Maastricht criteria
| Convergence criteria | Obligation to adopt 4 | Target date | Euro coins design | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country 1 | Inflation rate² | Government finances | ERM II membership | Interest rate ³ | set by the country | recommended by the Commission | |||
| annual government deficit to GDP | gross government debt to GDP | ||||||||
| Reference value 5 | max 3.2% | max. 3% | max. 60% | min. 2 years | max 6.5% | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| 5.3% | 4% | 76.9% | 0 years | 5.25% | yes | 2014–2015 | NA | in progress | |
1 Current EU member states that have not yet adopted the Euro, candidates and official potential candidates.
² No more than 1.5% higher than the 3 best-performing EU member states.
³ No more than 2% higher than the 3 best-performing EU member states.
4 Formal obligation for Euro adoption in the country EU Treaty of Accession or the Framework for membership negotiations.
5 Values from May 2008 report.[86] To be updated each year.
The austerity measures introduced by the government are in part an attempt to fulfill the Maastricht-criteria.
The austerity measures include a 2% rise in social security contributions, half of which is paid by employees, and a large increase in the minimum rate of sales tax (levied on food and basic services) from 15 to 20%. While it was widely recognised that something needed to be done, investors have levelled criticism at the program for emphasizing tax increases as opposed to spending cuts.[citation needed]
The Hungarian Central Statistical Office reported a decrease in real wages in the first five months of 2007. Gross average income rose by 7%, while net average income increased by 1%. When adjusted for inflation, this corresponded to a 7% decline compared with real wages a year before. The drop was due mainly to the 2006 austerity package; however, state measures to combat the black economy may also have had an impact on pay developments.
Hungary's low employment rate remains a key structural handicap to achieving higher living standards. The government introduced useful measures in the key areas, namely early retirement, disability and old pensions.
2008–2009 Financial Crisis
Hungary, which joined the European Union in 2004, has been hit hard by the late-2000s recession because of its heavy dependence on foreign capital to finance its economy and has one of the biggest public deficits in the EU.[87][88]
On 10 October 2008, the Forint dropped by 10%.[89] Many loans are made in Euro or Swiss Francs in Hungary.
On 27 October 2008, Hungary reached an agreement with the IMF and EU for a rescue package worth about US$20 billion.[90]
Total government spending is high. Many state-owned enterprises have not been privatized. Business licensing is a problem, as regulations are not applied consistently.[91] According to the conservative think tank Heritage Foundation, Hungary's economy was 67.2 percent "free" in 2008,[91] which makes it the world's 43rd-freest economy. Its overall score is 1 percent lower than last year, partially reflecting new methodological detail. Hungary is ranked 25th out of 41 countries in the European region, and its overall score is slightly lower than the regional average.[91]

The Hungarian sovereign debt's credit rating is BBB+ as of October 2008[update]. However Standard & Poor's may downgrade Hungary's BBB+ sovereign credit rating because of mounting financial-sector funding pressures and their potential to raise general government debt materially from its current level of 67% of GDP (October 2008). Foreign investors' trust in the Hungarian economy has declined, as they deem that the stringency measures planned in the second half of 2006 are not satisfactory; their focus being mainly on increasing the income side rather than curbing government spendings.[citation needed] Economic reform measures such as health care reform, tax reform, and local government financing are being addressed by the present government.
General government net lending was 9.2% in 2006, instead of estimated 10.1% (but still the largest in Europe) because of the austerity program of the government, and was 5.5% in 2007, and recent estimates of the government says 4% in 2008.[citation needed]

Because of the large austerity program, the real growth of the incomes was negative in 2007 at -5.5%, and the estimates say 1% increase in 2008. The GDP growth was only 1.4% in 2007, much lower than in 2006 because of the decreased government spending; in first quarter of 2008 the GDP growth was 1.7%, slightly stronger than last quarter of 2007 (0.9%). During the second quarter in 2008, the GDP growth was 2.0% annual, and because of the effects of the 2008 financial crisis on the Hungarian forint and on the bank system, the 3rd quarter growth was slowed to 0.8% annual.[92] The estimates for 2009 are 1-1.5% decline.[93]
The 2008 financial crisis hit Hungary mainly in October 2008. When the Forint declined quickly against the euro, the Hungarian National Bank raised interest rates from 3.0% to 11.5% on 22 October. As the Hungarian Government asked financial rescue package worth $25.1 billion from the International Monetary Fund, the European Union, and the World Bank, promising to IMF that recalculate the 2009 budget, as Hungary's GDP declines 1.0%, and slow down government spending, for example, stop the wage increase for state workers.[94] This way, the budget gap decline to 2.6% down from 5.5% of GDP in 2007 and will meet Maastricht criteria. In this circumstances, more and more economists estimate, that Hungary can join the ERM II, which gives the possibility that Hungary can adopt the euro 2 years after joining the ERM-II monetary system.
Geography
Landscape



Slightly more than one half of Hungary's landscape consists of flat to rolling plains of the Pannonian Basin: the most important plain regions include the Little Hungarian Plain in the west, and the Great Hungarian Plain in the southeast. The highest elevation above sea level on the latter is only 183 metres (600 feet).
Transdanubia is a primarily hilly region with a terrain varied by low mountains. These include the very eastern stretch of the Alps, Alpokalja, in the west of the country, the Transdanubian Medium Mountains, in the central region of Transdanubia, and the Mecsek Mountains and Villány Mountains in the south. The highest point of the area is the Írott-kő in the Alps, at 882 metres (2,894 feet).
The highest mountains of the country are located in the Carpathians: these lie in the northern parts, in a wide band along the Slovakian border (highest point: the Kékes at 1,014 m (3,327 ft)*).
Hungary is divided in two by its main waterway, the Danube (Duna); other large rivers include the Tisza and Dráva, while Transdanubia contains Lake Balaton, a major body of water. The largest thermal lake in the world, Lake Hévíz (Hévíz Spa), is located in Hungary. The second largest lake in the Pannonian Basin is the artificial Lake Tisza (Tisza-tó).
Phytogeographically, Hungary belongs to the Central European province of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. According to the WWF, the territory of Hungary belongs to the ecoregion of Pannonian mixed forests.
National parks
Hungary has 10 national parks, 145 minor nature reserves and 35 landscape protection areas.
| Name | Established | Size (km²) | Map | Picture |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hortobágy National Park | 1972 | 567.61 | 
| |
| Kiskunság National Park | 1975 | 11.810 | 
| |
| Bükk National Park | 1976 | 402.63 | 
| |
| Aggtelek National Park | 1985 | 198.92 | 
| |
| Fertő-Hanság National Park | 1991 | 335.87 | 
| |
| Danube-Drava National Park | 1996 | 494.79 | 
| |
| Körös-Maros National Park | 1997 | 501.37 | 
| |
| Balaton Uplands National Park | 1997 | 569.98 | 
| |
| Danube-Ipoly National Park | 1997 | 569.98 | File:RosaliaAlpinaHu.jpg | |
| Őrségi National Park | 2002 | 440 | 
|
Climate
Hungary has a continental climate,[95] with hot summers with low overall humidity levels but frequent rainshowers and mildly cold snowy winters. Average annual temperature is 9.7 °C (49.5 °F). Temperature extremes are about 42 °C (107.6 °F) in the summer and −29 °C (−20.2 °F) in the winter. Average temperature in the summer is 27 °C (80.6 °F) to 35 °C (95 °F) and in the winter it is 0 °C (32 °F) to −15 °C (5 °F). The average yearly rainfall is approximately 600 mm (23.6 in). A small, southern region of the country near Pécs enjoys a reputation for a Mediterranean climate, but in reality it is only slightly warmer than the rest of the country and still receives snow during the winter.
Military

The Military of Hungary, or "Hungarian Armed Forces" currently has two branches, the "Hungarian Ground Force" and the "Hungarian Air Force". The Hungarian Ground Force (or Army) is known as the "Corps of Homeland Defenders" (Honvédség). This term was originally used to refer to the revolutionary army established by Lajos Kossuth and the National Defence Committee of the Revolutionary Hungarian Diet in September 1848 during the Hungarian Revolution.
The term Honvédség is the name of the military of Hungary since 1848 referring to its purpose (véd in Honvéd) of defending the country. The Hungarian Army is called Magyar Honvédség. The rank equal to a Private is a Honvéd. The Hungarian Air Force is the air force branch of the Hungarian Army.
Black Army of Hungary: The Black Army (Black Legion or Host) - named after their black armor panoply - is in historigraphy the common name given to the excellent quality of diverse and polyglot military forces serving under the reign of King Matthias Corvinus of Hungary. It is recognized as the first standing continental European fighting force not under conscription and with regular pay since the Roman Empire. Hungary's Black Army traditionally encompasses the years from 1458 to 1490.
Hussar: A type of irregular light horsemen was already well established by the 15th century in medieval Hungary. Hussar refers to a number of types of light cavalry created in Hungary[96] in the 15th century and used throughout Europe and even in America since the 18th century. Some modern military units retain the title 'hussar' for reasons of tradition.
Demographics
For 95% of the population, the mother language is Hungarian, a Finno-Ugric language unrelated to any neighboring language and distantly related to Finnish and Estonian. The main minority group are the Roma (2.1% - 3.0%). Other groups include: Germans (1.2%), Slovaks (0.4%), Croats and Bunjevcis (0.2%), Romanians (0.1%), Ukrainians (0.1%), and Serbs (0.1%).[97]
For historical reasons (see Treaty of Trianon), significant Hungarian minority populations can be found in the surrounding countries, most of them in Romania (in Transylvania), Slovakia, Serbia (in Vojvodina). Sizable minorities live also in Ukraine (in Transcarpathia), Croatia (mainly Slavonia) and Austria (in Burgenland). Slovenia is also host to a number of ethnic Hungarians, and Hungarian language has an official status in parts of the Prekmurje region. Today, more than two million ethnic Hungarians live in nearby countries.[98]

Ethnic Germans
The largest wave of German-speaking immigrants into Hungary occurred after the Treaty of Karlowitz. Between 1700 and 1750, German-speaking settlers immigrated to the regions of Pannonia, Banat, and Bačka, which had been depopulated by the Ottoman wars. Prior to World War II, approximately 1.5 million Danube Swabians lived in Hungary, Romania and Yugoslavia.[99] In 2001, 62,105 people declared to be German in Hungary.[100]
Religion in Hungary
In the Eurostat - Eurobarometer poll of 2005, 44% of Hungarians answered that they believed there is a God, whereas 56% answered they did not believe in a God, of which 31% answered they believed there is some sort of spirit or life force, and 19% that they do not believe there is a God, spirit, nor life force.
Religious history
The majority of Hungarians became Christian in the 10th century. Hungary's first king, Saint Stephen I, took up Western Christianity, although his mother, Sarolt, was baptized in the Eastern Rite. Hungary remained predominantly Catholic until the 16th century, when the Reformation took place and, as a result, first Lutheranism, then soon afterwards Calvinism, became the religion of almost the entire population.
| Denominations | Population | % of total |
|---|---|---|
| Christianity | 7,584,115 | 74.4 |
| Catholicism | 5,558,901 | 54.5 |
| Roman Catholics | 5,289,521 | 51.9 |
| Greek Catholics | 268,935 | 2.6 |
| Protestantism | 1,985,576 | 19.5 |
| Calvinists | 1,622,796 | 15.9 |
| Lutherans | 304,705 | 3.0 |
| Baptists | 17,705 | 0.2 |
| Unitarians | 6,541 | 0.1 |
| Other Protestants | 33,829 | 0.3 |
| Orthodox Christianity | 15,298 | 0.1 |
| Other Christians | 24,340 | 0.2 |
| Judaism | 12,871 | 0.1 |
| Other religions | 13,567 | 0.1 |
| Total religions | 7,610,553 | 74.6 |
| No religion | 1,483,369 | 14.5 |
| Did not wish to answer | 1,034,767 | 10.1 |
| Unknown | 69,566 | 0.7 |
| total | 10,198,315 | 100.00 |
In the second half of the 16th century, however, Jesuits led a successful campaign of counterreformation among the Hungarians. The Jesuits founded educational institutions, including Péter Pázmány Catholic University, the oldest university that still exists in Hungary, but organized so-called missions too in order to promote popular piety. By the 17th century, Hungary had once again become predominantly Catholic.
Some of the eastern parts of the country, however, especially around Debrecen ("the Calvinist Rome"), still have significant Protestant communities. Orthodox Christianity in Hungary has been the religion mainly of some national minorities in the country, notably, Romanians, Rusyns, Ukrainians, and Serbs.
Hungary has been the home of a sizable Armenian community as well. They still worship according to the Armenian Rite, but they have reunited with the Catholic Church (Armenian Catholics) under the primacy of the Pope. According to the same pattern, a significant number of Orthodox Christians became re-united with the rest of the Catholic world (Greek Catholics).
Faith Church, one of Europe's largest Pentecostal churches, is also located in Hungary. Faith Church accepts the results and spiritual, moral values of both early Christianity and the Reformation, as well as other revival movements serving the progress of the Christian faith. Based on the 1% tax designation to churches, Faith Church is the fourth most supported church in Hungary. The weekly Sunday service of the Church is regularly broadcast in live television.
Jewish Hungarians
Hungary has historically been home to a significant Jewish community, especially since the 19th century when many Jews, persecuted in Russia, found refuge in the Kingdom of Hungary. Most Jewish people live in the downtown of Budapest, especially in district VI. The largest synagogue in Europe is located in Budapest.
The census of January 1941 found that 6.2% of the population, i.e. 846,000 people, were considered Jewish according to the racial laws of that time. From this number, 725,000 were Jewish by religion.[102] Some Hungarian Jews were able to escape the Holocaust during World War II, although many were either deported to concentration camps or murdered by the Hungarian Arrow Cross fascists.
Culture
Architecture
Hungary is home to the largest synagogue in Europe (Great Synagogue), the largest medicinal bath in Europe (Széchenyi Medicinal Bath), the one of the largest basilicas in Europe (Esztergom Basilica), the second largest territorial abbey in the world (Pannonhalma Archabbey), and the largest Early Christian Necropolis outside Italy (Pécs).


Notable architectural styles in Hungary include Historicism and Art Nouveau, or rather several variants of Art Nouveau. In contrast to Historicism, Hungarian Art Nouveau is based on the national architectural characteristics. Taking the eastern origins of the Hungarians into account, Ödön Lechner (1845–1914), the most important figure in Hungarian Art Nouveau, was initially inspired by Indian and Syrian architecture, and later by traditional Hungarian decorative designs. In this way, he created an original synthesis of architectural styles. By applying them to three-dimensional architectural elements, he produced a version of Art Nouveau that was specific to Hungary.
Turning away from the style of Lechner, yet taking inspiration from his approach, the group of "Young People" (Fiatalok), which included Károly Kós and Dezsö Zrumeczky, were to use the characteristic structures and forms of traditional Hungarian architecture to achieve the same end.
Besides the two principal styles, Budapest also displays local versions of trends originating from other European countries. The Sezession from Vienna, the German Jugendstil, Art Nouveau from Belgium and France, and the influence of English and Finnish architecture are all reflected in the buildings constructed at the turn of the century. Béla Lajta initially adopted Lechner's style, subsequently drawing his inspiration from English and Finnish trends; after developing an interest in the Egyptian style, he finally arrived at modern architecture. Aladár Árkay took almost the same route. István Medgyaszay developed his own style, which differed from Lechner's, using stylised traditional motifs to create decorative designs in concrete. In the sphere of applied arts, those chiefly responsible for promoting the spread of Art Nouveau were the School and Museum of Decorative Arts, which opened in 1896.
Music


The music of Hungary consists mainly of traditional Hungarian folk music and music by prominent composers such as Liszt, Dohnányi, Bartók, Kodály, and Rózsa. Hungarian traditional music tends to have a strong dactylic rhythm, as the language is invariably stressed on the first syllable of each word. Hungary also has a number of internationally renowned composers of contemporary classical music, György Ligeti, György Kurtág, Péter Eötvös and Zoltán Jeney among them. One of the greatest Hungarian composers, Béla Bartók was also among the most significant musicians of the 20th century. His music was invigorated by the themes, modes, and rhythmic patterns of the Hungarian and neighboring folk music traditions he studied, which he synthesized with influences from his contemporaries into his own distinctive style.
Hungary has made many contributions to the fields of folk, popular and classical music. Hungarian folk music is a prominent part of the national identity and continues to play a major part in Hungarian music. Hungarian folk music has been significant in former country parts that belong - since the 1920 Treaty of Trianon - to neighboring countries such as Romania, Slovakia, southern Poland and especially in southern Slovakia and the Transylvania: both regions have significant numbers of Hungarians.
Broughton claims that Hungary's "infectious sound has been surprisingly influential on neighboring countries (thanks perhaps to the common Austro-Hungarian history) and it's not uncommon to hear Hungarian-sounding tunes in Romania, Slovakia and southern Poland".[103] It is also strong in the Szabolcs-Szatmár area and in the southwest part of Transdanubia, near the border with Croatia. The Busójárás carnival in Mohács is a major Hungarian folk music event, formerly featuring the long-established and well-regarded Bogyiszló orchestra.[104]
Hungarian classical music has long been an "experiment, made from Hungarian antedecents and on Hungarian soil, to create a conscious musical culture [using the] musical world of the folk song".[105] Although the Hungarian upper class has long had cultural and political connections with the rest of Europe, leading to an influx of European musical ideas, the rural peasants maintained their own traditions such that by the end of the 19th century Hungarian composers could draw on rural peasant music to (re)create a Hungarian classical style.[106] For example, Béla Bartók and Zoltán Kodály, two of Hungary's best known composers, used folk themes in their music. Bartók collected folk songs from across Eastern Europe, including Romania and Slovakia, whilst Kodály was more interested in creating a distinctively Hungarian musical style.
During the era of Communist rule in Hungary (1944–1989) a Song Committee scoured and censored popular music for traces of subversion and ideological impurity. Since then, however, the Hungarian music industry has begun to recover, producing successful performers in the fields of jazz such as trumpeter Rudolf Tomsits, pianist-composer Károly Binder and, in a modernized form of Hungarian folk, Ferenc Sebő and Márta Sebestyén. The three giants of Hungarian rock, Illés, Metró and Omega, remain very popular, especially Omega, which has followings in Germany and beyond as well as in Hungary. Older veteran underground bands such as Beatrice from the 1980s also remain popular.
Art
Literature
| Hungarian art |
|---|
 |
| List of Hungarian painters |
| List of Hungarian sculptors |
| Hungarian National Gallery |
| Museum of Fine Arts |


In the earliest times Hungarian language was written in a runic-like script (although it was not used for literature purposes in the modern interpretation). The country switched to the Latin alphabet after being Christianized under the reign of Stephen I of Hungary (1000–1038).
The oldest remained written record in Hungarian language is a fragment in the founding document of the Abbey of Tihany (1055) which contains several Hungarian terms, among them the words feheruuaru rea meneh hodu utu rea, "up the military road to Fehérvár" The rest of the document was written in Latin.
The oldest remained complete text in Hungarian language is the Funeral Sermon and Prayer (Halotti beszéd és könyörgés) (1192–1195), a translation of a Latin sermon.
The oldest remained poem in Hungarian is the Old Hungarian Laments of Mary (Ómagyar Mária-siralom), also a (not very strict) translation from Latin, from the 13th century. It is also the oldest surviving Finno-Ugric poem.
Among the first chronicles about Hungarian history were Gesta Hungarorum ("Deeds of the Hungarians") by the unknown author usually called Anonymus, and Gesta Hunnorum et Hungarorum ("Deeds of the Huns and the Hungarians") by Simon Kézai. Both are in Latin. These chronicles mix history with legends, so historically they are not always authentic. Another chronicle is the Képes krónika (Illustrated Chronicle), which was written for Louis the Great.
Renaissance literature flourished under the reign of King Matthias (1458–1490). Janus Pannonius, although he wrote in Latin, counts as one of the most important persons in Hungarian literature, being the only significant Hungarian Humanist poet of the period. The first printing house was also founded during Matthias' reign, by András Hess, in Buda. The first book printed in Hungary was the Chronica Hungarorum. The most important poets of the period was Bálint Balassi (1554–1594) and Miklós Zrínyi (1620–1664). Balassi's poetry shows Mediaeval influences, his poems can be divided into three sections: love poems, war poems and religious poems. Zrínyi's most significant work, the epic Szigeti veszedelem ("Peril of Sziget", written in 1648/49) is written in a fashion similar to the Iliad, and recounts the heroic Battle of Szigetvár, where his great-grandfather died while defending the castle of Szigetvár. Among the religious literary works the most important is the Bible translation by Gáspár Károli (The second Hungarian Bible translation in the history), the Protestant pastor of Gönc, in 1590. The translation is called the Bible of Vizsoly, after the town where it was first published. (See Hungarian Bible translations for more details.)
The Hungarian enlightenment took place about fifty years after the French enlightenment. The first enlightened writers were Maria Theresia's bodyguards (György Bessenyei, János Batsányi and others). The greatest poets of the time were Mihály Csokonai Vitéz and Dániel Berzsenyi. The greatest figure of the language reform was Ferenc Kazinczy. The Hungarian language became feasible for all type of scientific explanations from this time, and furthermore many new words were coined for describing new inventions.
Hungarian literature has recently gained some renown outside the borders of Hungary (mostly through translations into German, French and English). Some modern Hungarian authors have become increasingly popular in Germany and Italy especially Sándor Márai, Péter Esterházy, Péter Nádas and Imre Kertész. The latter is a contemporary Jewish writer who survived the Holocaust and won the Nobel Prize for literature in 2002. The older classics of Hungarian literature and Hungarian poetry have remained almost totally unknown outside Hungary. János Arany, a famous nineteenth century Hungarian poet is still much loved in Hungary (especially his collection of Ballads), among several other "true classics" like Sándor Petőfi, the poet of the Revolution of 1848, Endre Ady, Mihály Babits, Dezső Kosztolányi, Attila József and János Pilinszky. Other well-known Hungarian authors are Ferenc Móra, Géza Gárdonyi, Zsigmond Móricz, Gyula Illyés, Albert Wass and Magda Szabó.
Cuisine


The Hungarian cuisine is a prominent feature of the Hungarian culture, just as much like the art of hospitality. Traditional dishes such as the world famous Goulash (gulyás stew or gulyás soup). Dishes are often flavoured with paprika (ground red peppers), a Hungarian innovation.[107] Thick, heavy Hungarian sour cream called tejföl is often used to soften the dishes flavour. The famous Hungarian hot river fish soup called Fisherman's soup or halászlé is usually a rich mixture of several kinds of poached fish. Other dishes are Chicken Paprikash, Foie gras made of goose liver, pörkölt stew, vadas, (game stew with vegetable gravy and dumplings), trout with almonds and salty and sweet dumplings, like túrós csusza, (dumplings with fresh quark cheese and thick sour cream). Desserts include the iconic Dobos Cake, Strudels (rétes), filled with apple, cherry, poppy seed or cheese, Gundel pancake, plum dumplings (szilvás gombóc), somlói dumplings, dessert soups like chilled Sour cherry soup and sweet chestnut puree, gesztenyepüré (cooked chestnuts mashed with sugar and rum and split into crumbs, topped with whipped cream). Perec and kifli are widely popular pastries.
The csárda is the most distinctive type of Hungarian inn, an old-style tavern offering traditional cuisine and beverages. Borozó usually denotes a cozy old-fashioned wine tavern, pince is a beer or wine cellar and a söröző is a pub offering draught beer and sometimes meals. The bisztró is an inexpensive restaurant often with self-service. The büfé is the cheapest place, although one may have to eat standing at a counter. Pastries, cakes and coffee are served at the confectionery called cukrászda, while an eszpresszó is a cafeteria.
- Drinks

Pálinka: is a fruit brandy, distilled from fruit grown in the orchards situated on the Great Hungarian Plain. It is a spirit native to Hungary and comes in a variety of flavours including apricot (barack) and cherry (cseresznye). However, plum (szilva) is the most popular flavour.
Beer: Beer goes well with many traditional Hungarian dishes. The five main Hungarian brands are: Borsodi, Soproni, Arany Ászok, Kõbányai, and Dreher.
Wine: As Hugh Johnson says in The History of Wine, the territory of Hungary is ideal for wine-making. Since the fall of communism there has been a renaissance of Hungarian wine-making. The choice of good wine is widening from year to year. The country can be divided to six wine regions: North-Transdanubia, Lake Balaton, South-Pannónia, Duna-region or Alföld, Upper-Hungary and Tokaj-Hegyalja. Hungarian wine regions offer a great variety of style: the main products of the country are elegant and full-bodied dry whites with good acidity, although complex sweet whites (Tokaj), elegant (Eger) and full-bodied robust reds (Villány and Szekszárd). The main varieties are: Olaszrizling, Hárslevelű, Furmint, Pinot gris or Szürkebarát, Chardonnay (whites), Kékfrankos (or Blaufrankisch in German), Kadarka, Portugieser, Zweigelt, Cabernet sauvignon, Cabernet franc and Merlot. The most famous wines from Hungary are Tokaji Aszú and Egri Bikavér.
Tokaji: Tokaji, meaning "of Tokaj", or "from Tokaj" in Hungarian, is used to label wines from the wine region of Tokaj-Hegyalja in Hungary. Tokaji wine has received accolades from numerous great writers and composers including Beethoven, Liszt, Schubert and Goethe; Joseph Haydn's favorite wine was a Tokaji. Louis XV and Frederick the Great tried to outdo one another in the excellence of the vintages they stocked when they treated guests like Voltaire to some Tokaji. Napoleon III, the last Emperor of the French, ordered 30–40 barrels of Tokaji for the Court every year. Gustav III, King of Sweden, never had any other wine to drink. In Russia, customers included Peter the Great and Empress Elizabeth of Russia.
Zwack Unicum: For over 150 years, a blend of 40 Hungarian herbs has been used to create the liqueur Unicum. Unicum is a bitter, dark-coloured liqueur that can be drunk as an apéritif or after a meal, thus helping the digestion. The recipe is held secret by the Zwack family.
Spa culture

Hungary is a land of thermal water. A passion for spa culture and Hungarian history have been connected from the very beginning. Hungarian spas feature Roman, Greek, Turkish, and northern country architectural elements.[citation needed]
Because of an advantageous geographical location thermal water can be found with good quality and in great quantities on over 80% of Hungary's territory. Approximately 1,500 thermal springs can be found in Hungary. There are approximately 450 public baths in Hungary.
The Romans heralded the first age of spa in Hungary, the remains of their bath complexes are still to be seen in Óbuda, to this day. The spa culture was revived during the Turkish Invasion who used the thermal springs of Buda for the construction of a number of bathhouses, some of which are still functioning (Király Baths, Rudas Baths).
In the 19th century the advancement in deep drilling and medical science provided the springboard for a further leap in bathing culture. Grand spas such as Gellért Baths, Lukács Baths, Margaret Island, and Széchenyi Medicinal Bath are a reflection of this resurgence in popularity.
Folk art
Folk dance
Ugrós (Jumping dances): Old style dances dating back to the Middle Ages. Solo or couple dances accompanied by old style music, shepherd and other solo man's dances from Transylvania, and marching dances along with remnants of medieval weapon dances belong in this group.
Karikázó: a circle dance performed by women only accompanied by singing of folksongs.
Csárdás: New style dances developed in the 18-19th centuries is the Hungarian name for the national dances, with Hungarian embroidered costumes and energetic music. From the men's intricate bootslapping dances to the ancient women's circle dances, Csárdás demonstrates the infectious exuberance of the Hungarian folk dancing still celebrated in the villages.
Verbunkos: a solo man's dance evolved from the recruiting performances of the Austro-Hungarian army.
The Legényes: is a men's solo dance done by the ethnic Hungarian people living in the Kalotaszeg region of Transylvania. Although usually danced by young men, it can be also danced by older men. The dance is performed freestyle usually by one dancer at a time in front of the band. Women participate in the dance by standing in lines to the side and sing/shout verses while the men dance. Each lad does a number of points (dance phrases) typically 4 to 8 without repetition. Each point consists of 4 parts, each lasting 4 counts. The first part is usually the same for everyone (there are only a few variations).
Embroidery

It was in the beginning of the eighteenth century that the present style of Hungarian folk art took shape, incorporating both Renaissance and Baroque elements, depending on the area, as well as Persian Sassanide influences. Flowers and leaves, sometimes a bird or a spiral ornament, are the principal decorative themes. The most frequent ornament is a flower with a centerpiece resembling the eye of a peacock's feather. Nearly all the manifestations of folk art practiced elsewhere in Europe also flourished among the Magyar peasantry at one time or another, their ceramics and textile being the most highly developed of all. The finest achievements in their textile arts are the embroideries which vary from region to region. Those of Kalotaszeg in Transylvania are charming products of Oriental design, sewn chiefly in a single color - red, blue, or black. Soft in line, the embroideries are applied on altar cloths, pillow cases and sheets. In Hungary proper Sárköz in Transdanubia and the Matyóföld in the Great Hungarian Plain produce the finest embroideries. In the Sárköz region the women's caps show black and white designs as delicate as lace and give evidence of the people's wonderfully subtle artistic feeling. The embroidery motifs applied to women's wear have also been transposed to tablecloths and runners suitable for modern use as wall decorations.
Black pottery
These vessels, made of black clay, reflect more than three hundred years of traditional Transdanubian folk patterns and shapes. No two are precisely alike, since all work is done by hand, including both the shaping and the decorating. The imprints are made by the thumb or a finger of the ceramist who makes the piece.
Herend Porcelain
Founded in 1826, Herend Porcelain is one of the world's largest ceramic factories, specializing in luxury hand painted and gilded porcelain. In the mid-19th century it was purveyor to the Habsburg Dynasty and aristocratic customers throughout Europe. Many of its classic patterns are still in production. After the fall of communism in Hungary the factory was privatised and is now 75% owned by its management and workers, exporting to over 60 countries of the world.[108]
Hungarian public holidays and special events
Fixed public holidays
| Date | English Name | Local Name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| January 1 | New Year's Day | Újév | |
| March 15 | National Day | Nemzeti ünnep | Márciusi ifjak ("March youths"), memorial day of the 1848 Revolution. There are usually speeches and music pieces performed; several people wear a cockade with the national colours (red, white and green). |
| Moveable | Easter Sunday | Húsvétvasárnap | Good Friday work-free for Protestants |
| Moveable | Easter Monday | Húsvéthétfő | Men visit women and ask for permission for sprinkling by reciting a little Easter poem, they sprinkle them with some perfume (or sometimes a bucket of cold water in the countryside), and they get eggs (mostly of chocolate) in exchange. Children get chocolate bunnies and eggs (from the Bunny), and sometimes fruits, nuts etc. as well. They sometimes have to look for these presents in the garden or in their room. (Living bunnies are not infrequent, either.) Mothers often prepare ham, eggs, and sweetbreads for dinner. |
| May 1 | Labour day; anniversary of the accession to the EU |
A munka ünnepe | The countries of the EU are represented with special programmes, bridges are decorated and exhibitions are arranged. |
| Moveable | Pentecost Sunday | Pünkösdvasárnap | Sunday, 50 days after Easter |
| Moveable | Pentecost Monday | Pünkösdhétfő | Monday after Pentecost |
| August 20 | Saint Stephen Day | Szent István ünnepe | St. Stephen's Day, Foundation of State, "the day of the new bread" as well. St. Stephen of Hungary (Szent István király in Hungarian) (ca. 975 – August 15, 1038), was the first king of Hungary.
Celebrated with a half-hour fireworks on the bank of the Danube in the evening, attended by several hundreds of thousands of people. |
| October 23 | National Day | Nemzeti ünnep | The day of the Republic (since 1989), 1956 Revolution memorial day. Celebrated with speeches and exhibitions. |
| November 1 | All Saints Day | Mindenszentek | It is a day to remember the lost ones. On this day people generally visit all their lost relatives' graves which they decorate with flowers. |
| December 24 evening, December 25 |
Christmas | "Szenteste", Karácsony | People buy (or make) presents for their relatives and friends in the preceding couple of weeks (so this period is the absolute boom of the year for most stores). Public transport stops operating at about 4 p.m. Families reunite and people prepare their (labelled) presents under the Christmas tree. It is made of a fir which is decorated by one or two people in the family so nobody else can see it before they signal with a little bell for the rest to come in. The family sings Christmas songs together and everyone unwraps their presents. On 25th and the 26th, people usually visit their relatives (e.g. aunts, uncles and grandparents) and exchange presents. |
| December 26 | Second Day of Christmas | Karácsony másnapja |
Holidays not endorsed by the state
| Date | English Name | Local Name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| December 6 | Santa Claus, Saint Nicholas Day | Mikulás, Télapó | Children get various chocolate pieces from the Santa Claus by morning. If they were bad, they might get (birch) rods exclusively or beside their presents. |
| December 31 | New Year's Eve | Szilveszter | Young people go partying until morning. Streets are noisy with paper trumpets, hoots and champagne cracks; people often wear masks and throw petards. Those who stay home usually watch the comedies made for this occasion; at midnight they drink champagne and wish each other good luck for the new year. National television channels broadcast the orchestral and choral national anthem at midnight, and then the speech of the current President. After midnight they often use fireworks. With these finished, further comedies and various movies follow. The next day streets are as empty as ever, and people sleep long (or sleep themselves sober). |
| Moveable | Carnival | Farsang | A six day regional carnival, originally celebrated by the Šokci (ethnic-Croatians) living in the town of Mohács. Traditions include folk music, masquerading, parades and dancing. |
Hungarian domestic animals
Special events

Hungary's most outstanding annual events include the Budapest Spring Festival (mid-March to mid-April), Hortobágy Equestrian Days (late June), Sopron Early Music Days (late June), Festival in Budapest (late June), Miskolc Opera Festival (late June), Miskolc Kalálka International Folk Festival (July), Győr Summer Festival (late June), Győr Summer Cultural Festival (late June to late July), Pannon Festival in Pécs (July and August), Szentendre Summer Festival (July), Kőszeg Street Theatre Festival (late July), Savaria International Dance Competition in Szombathely (July), Debrecen Jazz Days (July), Szeged Open Air Festival (mid-July to August), Diáksziget (shorter: "Sziget" or "Sziget Festival", Student Island or Pepsi Island) north of Budapest (August), Eger Wine Harvest Festival (September), and Budapest Autumn Arts Festival (mid-September to mid-October).
St Stephen's Day (August 20) is celebrated with sporting events, parades and fireworks nationwide. On the same day there is a Floral Festival in Debrecen and a Bridge Fair in nearby Hortobágy. Formula 1 car races are held in early August at the Hungaroring near Mogyoród, 18 km northeast of Budapest.
Budapest Spring Festival

Designed to fit the needs of Budapest's cultural heritage and its requirements as a modern Central European centre, this metropolitan festival was instituted in 1981. By presenting and disseminating cultural assets it boosts the city's image and encourages dynamic development of its cultural tourism. This "festival of festivals", traditionally covering a range of artistic fields, presents a series of homogeneous artistic activities to which international professional symposia are linked. The Budapest Spring Festival takes place in the last two weeks of March. Its main emphasis is on those symphony orchestra concerts, opera and ballet performances which will appeal to the widest audience, but the program also includes open-air events and an Operetta Festival. The performances take place in the capital's most important concert halls and theatres, and often near historic monuments. Over the years a number of regional towns have been included in the Budapest Spring Festival - Debrecen, Gödöllő, Győr, Kaposvár, Kecskemét, Sopron, Szentendre and Szombathely - and thus it has more or less expanded into a national festival. The list of events always includes renowned foreign guests as well as distinguished artists and groups from the Hungarian musical life. Highlights include classical concerts, productions at the Opera House, open air events, the Operetta Festival, the Dance House Convention, the Dance Panorama, and what are considered to be the real treat, the exhibitions.
Haydn Festival in Eszterháza

Haydn at Eszterháza: During its first quarter century, the palace was the primary home of the celebrated composer Joseph Haydn, who wrote the majority of his symphonies for the Prince's orchestra. Starting in 1768, the theater was a major venue for opera, often with more than a hundred performances per year. The palace was geographically isolated, a factor which led to loneliness and tedium among the musicians. This is seen in some of Haydn's letters, as well as in the famous tale of the Farewell Symphony
The basic aim of the festival is to evoke the musical paradise that Eszterháza was in Haydn's time, within the original walls, with the help of period instruments and performing practice. The programmes focus mainly on the works composed during the Eszterháza period of Haydn's creative life, and among these, on compositions belonging to the most important genres (symphonies, string quartets, keyboard sonatas and trios). In addition, however, the concert programmes regularly include works by the "unknown Haydn" (baryton pieces, rarely heard church compositions, wind divertimenti, etc.). The festival aims to provide opportunities for the world's most outstanding Haydn performers to meet here, to gain inspiration from the atmosphere and acoustics of the place, and to inspire one another through shared music-making. The majority of the performers play only compositions by Joseph Haydn, but also in exceptional cases other works closely connected, either directly or through their composers, with Haydn, Eszterháza or the family of the Esterházy princes - such as, for example, the string quartets dedicated to Haydn by Mozart, and certain pieces by Michael Haydn (the composer's younger brother), Luigi Tomasini (leader of the Eszterháza orchestra) and others. The venue for most of the concerts is the enchantingly beautiful ceremonial hall of the palace, which has superb acoustics. Some of the more intimate, solistic performances are given in the sala terrena, the central hall of the original, smaller, Renaissance hunting palace. Some concerts of church music take place in one or other of the churches in the nearby villages.
Győr Summer Festival
This festival is held annually, from the second week in June to the second week in July. The Győr Summer International Cultural Festival, which displays Győr's cultural heritage, has a history of over three decades. The list of events, which covers a wide range of genres, is based on a series of separate activities. Every year, for a month in June and July, the Baroque decorations of the city centre, its atmospheric courtyards and the banks of the Rába river are home to the International Ballet Festival, the International Puppet and Street Theatre Convention, the International Folk Dancing and Folk Music Festival, and the International Handcraft Fair and Exhibition. In addition to the performances of the hosts - the Győr Ballet, the Győr National Theatre, and the Győr Philharmonic Orchestra - visitors can also see those of the visiting theatre companies and musical groups.
Sports
Olympics
Only seven countries (USA, USSR, UK, France, Italy, China and Germany) have won more Summer Olympic gold medals than Hungary. At the all time total medal count for Olympic Games, Hungary reaches the 9th rank out of 211 participating nations, with a total of 465 medals. See All-time Olympic Games medal table (2008 data)
Hungarians are also known for their prowess at water sports, mainly swimming, water polo (See: Water polo at the Summer Olympics) (in which they have defeated the Soviet team in 1956) and canoeing (they have won multiple medals). Two major rivers (the Danube and the Tisza) and Lake Balaton give excellent opportunities to practice these sports. Some of the world's best sabre fencing athletes have historically hailed from Hungary.
Ice Hockey
in 2009 the Hungarian national ice hockey team has qualified for their first IIHF World Championship in more than seventy years.
Football (soccer)
The Hungarian national football team represents Hungary in international football and is controlled by the Hungarian Football Federation. It has a rich and proud pedigree in the game, as one of the first original footballing nations in continental Europe and an innovator in the sport in the 1950s. In recent times the team's strength has diminished greatly, failing to qualify for any major tournament since 1986. However they hold the record for going the most number of consecutive games unbeaten, 32.
Hungarian football is known for one of the most formidable and influential sides in football history, which revolutionized the play of the game. Centered around the dynamic and potent quartet of strikers Ferenc Puskás, Sándor Kocsis, attacking half-back József Bozsik and withdrawn striker Nándor Hidegkuti, the "Aranycsapat" (Hung. lit Golden Team) of the "Magnificent Magyars", captivated the football world with an exciting brand of play drawn from new tactical nuances and amassed, barring the 1954 World Cup Final, a remarkable record of 43 victories, 7 ties, and no defeats from the 15th of June 1952 to the end of its historic unbeaten run on February 18, 1956. Hungary posted the highest ever Elo football rating of 2173 points in June (1954) along with the second highest with 2153 (1956); surpassing that of Brazil, England, Argentina and Germany in all-time competition.
The footballer Ferenc Puskás (1927–2006) scored 84 goals in 85 internationals for Hungary, and 511 goals in 533 matches in the Hungarian and Spanish leagues. With the Hungarian Golden Team, Puskás played the 1954 World Cup final against West Germany. In 1958, after the Hungarian Revolution, he emigrated to Spain where he played in the legendary Real Madrid team that also included Alfredo Di Stéfano, and Francisco Gento.

The Hungarians were runners-up twice in the World Cup, losing to Italy 4–2 in 1938 and 3–2 to West Germany in 1954, despite beating them 8–3 earlier in the competition. The team, built around the legendary Ferenc Puskás, led early 2–0 in that match, but ended up 3–2 losers in a game the Germans subsequently christened "The Miracle of Bern". Two highly controversial calls surround this final game: firstly when Puskas apparently equalized the match in the 89th minute only to have the goal disallowed for offside, the second being a blatant foul on Kocsis in the penalty area which would have given Hungary a penalty in the final minute.
Hungary has won gold at the Olympic three times, in 1952, 1964, and 1968. The under-23 team, which was the age limit for Olympic teams, won the UEFA U-23 Championship in 1974. Since the 1976 reshuffle by UEFA, the under-23s are now classified with the under-21s.
The match between Austria and Hungary in Vienna in 1902 was the first international match played between two non-British European countries.
Hungary was the first team from outside the United Kingdom and Ireland to beat England at home, famously winning 6–3 at Wembley on November 25, 1953. This victory had worldwide significance as it effectively ended England's 90 year old mythical reign since the creation of association football in 1863 against all sides outside the United Kingdom and Ireland. They beat England 7–1, this time in Budapest a year later, in 1954. This still ranks as England's record defeat.
Hungary holds the longest consecutive run of matches unbeaten with 33 international games between 14 May 1950 and 4 July 1954, when they lost the World Cup final to Germany. Argentina and Spain jointly hold the second longest string of 31 unbeaten matches (Argentina from 1991 to 1993 and Spain from 1994 to 1998).

Hungary remained a force in European football for two to three decades after the era of the "Magnificent Magyars". Reaching the quarter-finals of both 1962 and 1966 World Cups, Hungary was blessed with a dazzling array of talent including Ferenc Sipos, Lajos Tichy, Ferenc Bene, Flórián Albert, János Farkas, Gyula Rákosi, Zoltán Varga, János Göröcs, Károly Sándor and Máté Fenyvesi. They also reached the semi-finals of the European Championship in 1964 and 1972.
Returning to the World Cup in 1978 and 1982, Hungary did not reach the same heights but nonetheless performed respectably; indeed, the talents of László Fazekas, Tibor Nyilasi and László Kiss inspired Hungary to a 10–1 win over El Salvador in 1982, which remains a World Cup record. The 1986 World Cup is seen by many fans as the final confirmation of Hungary's decline. Expectations were very high, but poor performances in defeats to the Soviet Union and France were a bitter blow, despite the presence of talent like Lajos Détári. Since then, Hungary has continued to produce fine individual talent- notably Béla Illés and Krisztián Lisztes – but further success as a team has eluded them.
Most recently, in Euro 2004 qualifiers, Hungary found themselves within sight of qualification with two games remaining, but was scuppered by defeats to Latvia and Poland.
Today, Hungary are a lesser force and haven't qualified for a World Cup since 1986, or for the European Championship finals since 1972.
Miscellaneous
Hungarian folk art, including dances, music, cross stitchings, embroideries, costumes, potteries, wood carvings, basket wavings, porcelains etc. has a long and rich history which play a significant role in local folk traditions and customs.
Transport
Republic of Hungary is located in the central part of the Pannonian Vale, and is a landlocked country, which is conducive to the development of all forms of traffic.
Hungary has developed road, railway, air and water traffic. Budapest, the capital of the state, to the measures is an important node in the public transport network, to say that "all roads lead to Budapest".
Railways

- Total: 7,606 km
- Broad gauge: 36 km 1520 gauge
- Standard gauge: 7,394 km 1435 gauge (2,270 km electrified; 1,236 km double track)
- narrow gauge: 176 km 760 gauge (1998)
Note: Hungary and Austria jointly manage the cross-border standard-gauge railway between Győr–Sopron–Ebenfurt (GySEV/ROeEE), a distance of about 101 km in Hungary and 65 km in Austria.
In Budapest, the three main railway stations are the Eastern (Keleti), Western (Nyugati) and Southern (Déli), with other outlying stations like Kelenföld. Of the three, the Southern is the most modern but the Eastern and the Western are more decorative and architecturally interesting.
Other important railway stations countrywide include Szolnok (the most important railway intersection outside Budapest), Tiszai Railway Station in Miskolc and the stations of Pécs, Győr, Szeged and Székesfehérvár.
Four Hungarian cities (Budapest, Debrecen, Miskolc and Szeged) have tram network.
The only city with an underground railway system is Budapest with its Metro.
In Budapest there is also a suburban rail service in and around the city, operated under the name HÉV.
Motorways

Motorways (Template:Lang-hu) : M0 - M1 - M15 - M2 - M3 - M30 - M35 - M5 - M6 - M7 - M70
- Total: 188,490 km
- Paved: 81,950 km (including 1288,4 km of motorways, 2010)
- Unpaved: 106,523 km (1998 est.)
New motorway sections are being added to the existing network, that already connects many major economically important cities to the Capital City.
Ports and Harbours
The most important port is Budapest, the capital. Other important ones include Dunaújváros and Baja.

Airports
There are 43-45 airports in Hungary, including smaller, unpaved ones too. (1999 est.) The five international ones are Budapest-Ferihegy, Debrecen Airport, Sármellék Airport (also called FlyBalaton for its proximity to Lake Balaton, Hungary's number one tourist attraction), Győr-Pér and Pécs-Pogány. MALÉV Hungarian Airlines operates flights to over 60, mostly European cities.
Metro

The Budapest Metro (Template:Lang-hu) is the metro system in the Hungarian capital Budapest. It is the third-oldest underground metro system in the world, and its iconic Line 1 (dating from 1896) was declared a World Heritage Site in 2002.
It consists of three lines, each designated by a number and a colour. Metro Line 4 is currently under construction; the first section is to begin operation in 2011. A fifth line has also been included in medium to long-term plans. The Budapest Metro trains start running at 4:30 in the morning, and the last train leaves at 11:10 p.m. from the terminus.
The rush hours are between 6 and 8 a.m. and between 2 and 5 p.m. on workdays, when trains run every two or three minutes. Early morning and night trains run every 10 or 15 minutes. On Christmas Eve (December 24) trains usually run only until about 3:00 in the afternoon, and may also stop running early on other holidays, as advertised beforehand. Service time may be extended on New Year's Eve.
International rankings
| Organization | Survey | Position |
|---|---|---|
| Institute for Economics and Peace [1] | Global Peace Index[109] | 27th out of 144 |
| United Nations Development Programme | Human Development Index | 43rd out of 1821 |
| Transparency International | Corruption Perceptions Index | 46th out of 180 |
| World Economic Forum | Global Competitiveness Report | 58th out of 133 |
| International Living Magazine | Quality of Life | 20th out of 194 |
See also
Column-generating template families
The templates listed here are not interchangeable. For example, using {{col-float}} with {{col-end}} instead of {{col-float-end}} would leave a <div>...</div> open, potentially harming any subsequent formatting.
| Type | Family | Handles wiki
table code?† |
Responsive/ mobile suited |
Start template | Column divider | End template |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Float | "col-float" | Yes | Yes | {{col-float}} | {{col-float-break}} | {{col-float-end}} |
| "columns-start" | Yes | Yes | {{columns-start}} | {{column}} | {{columns-end}} | |
| Columns | "div col" | Yes | Yes | {{div col}} | – | {{div col end}} |
| "columns-list" | No | Yes | {{columns-list}} (wraps div col) | – | – | |
| Flexbox | "flex columns" | No | Yes | {{flex columns}} | – | – |
| Table | "col" | Yes | No | {{col-begin}}, {{col-begin-fixed}} or {{col-begin-small}} |
{{col-break}} or {{col-2}} .. {{col-5}} |
{{col-end}} |
† Can template handle the basic wiki markup {| | || |- |} used to create tables? If not, special templates that produce these elements (such as {{(!}}, {{!}}, {{!!}}, {{!-}}, {{!)}})—or HTML tags (<table>...</table>, <tr>...</tr>, etc.)—need to be used instead.
- Lists
- Common Hungarian surnames
- Eastern name order used in Hungarian personal names
- List of cities in Hungary
- List of Hungarians
- List of Hungarian rulers
- List of Hungarian writers
- List of colleges in Hungary
- List of universities in Hungary
References
Notes
- ^ European State Mottos
- ^ Hungarian Central Statistical Office. Retrieved 2010-07-25.
- ^ a b c d "Hungary". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 2010-04-21.
- ^ "The plain facts - History". MTI. Retrieved 2008-11-11.
- ^ Bernstein, Richard (2003-08-09). "East on the Danube: Hungary's Tragic Century". The New York Times. Retrieved 2008-11-11.
- ^ "Hungary". Encarta. Archived from the original on 2009-10-31. Retrieved 2008-11-12.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ World Bank Country Classification, 2007
- ^ "Index - Belföld - A magyar kamasz iszik, dohányzik és könnyen teherbe esik". Index.hu. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ "PowerPoint bemutató" (PDF). Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ "Index - Világméretű influenzajárvány jöhet". Index.hu. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ "ITD Hungary - Supply Chain Management - Logistics, Distribution". Itdh.com. Retrieved 2010-05-29.
- ^ "Gazdaság: A világ életminőség-rangsora: Magyarország előre keveredett a válságban". HVG.hu. Retrieved 2010-05-29.
- ^ "Hungary ranked sixth in world for environmental protection". Caboodle.hu. 2007-12-10. Retrieved 2010-05-29.
- ^ "Index - Miért menjünk Magyarországra? Miért menjünk Szlovákiába?". Index.hu. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ MTH.gov.hu
- ^ "Tourism in Hungary in 2009". Hungarian Central Statistical Office. Retrieved 2010-02-23.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Search - Global Edition - The New York Times". International Herald Tribune. 2009-03-29. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ http://www.historia.hu/archivum/2004/0408szaboi.htm
- ^ American academic journal Science 2000
- ^ "The Avar Khaganate". Allempires.com. 2007-05-31. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ a b c A Country Study: Hungary. Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. Retrieved 2009-03-06.
- ^ a b c d Engel, Pál (2005). Andrew Ayton (ed.). The realm of St. Stephen: a history of medieval Hungary, 895-1526. I.B.Tauris. p. 12. ISBN 9781850439776.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Encyclopedia Americana (2000). Vol. 24. 370: Grolier Incorporated.
{{cite book}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ "Magyar (Hungarian) migration, 9th century". Eliznik.org.uk. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ Origins and Language. Source: U.S. Library of Congress.
- ^ a b "Stephen Sisa: The Spirit of Hungary - 1 Who Are the Magyars?". Hungarian-history.hu. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ Stephen Wyley (2001-05-30). "The Magyars of Hungary". Geocities.com. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ "Géza". Babylon. Retrieved 2008-11-20.
- ^ Asia Travel Europe. "Hungaria Travel Information | Asia Travel Europe". Asiatravel.com. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ "Hunmagyar.Org - The Controversy On The Origins And Early History Of The Hungarians". Hunmagyar.org. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ "Welcome to Cambridge Szeged website:: www.cambridge-szeged-society.org.uk". Cambridge-szeged-society.org.uk. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ "Marko Marelic: The Byzantine and Slavic worlds".
- ^ "Hungary in American History Textbooks".
- ^ "Hungary, facts and history in breef".
- ^ "Endre Csapó - Peace to end Peace". Hungarianhistory.com. 1920-06-04. Retrieved 2010-05-29.
- ^ A concise history of Hungary - Google Books. Books.google.co.uk. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ Hungarianhistory.com
- ^ "The Daco-Roman Legend". Hungarianhistory.com. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ Kulugyminiszterium.hu
- ^ The Mongol invasion: the last Arpad kings, Encyclopaedia Britannica
- ^ "A history of Hungary". Peter F. Sugar, Péter Hanák, Tibor Frank (1994). Indiana University Press. p.27. ISBN 0-253-20867-X
- ^ Autonomies in Europe and Hungary. (PDF). By Józsa Hévizi.
- ^ Mongol Invasions: Battle of Liegnitz, HistoryNet
- ^ "At the gate of Christendom: Jews, Muslims, and "pagans" in medieval Hungary ". Nóra Berend (2001). p.72. ISBN 0-521-65185-9
- ^ cs. "National and historical symbols of Hungary". Nemzetijelkepek.hu. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ "Hungary - History". Nationsencyclopedia.com. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ "C. A. Macartney: Hungary - A Short History". Mek.oszk.hu. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ "the influences of the florentine renaissance in hungary". Fondazione-delbianco.org. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ "Hungary". Lenti.eu. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ a b "Hungary - Britannica Online Encyclopedia". Britannica.com. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ "Hungary - Renaissance And Reformation". Countrystudies.us. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ "Hungary - The Bibliotheca Corviniana Collection: UNESCO-CI". Portal.unesco.org. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ "A Country Study: Hungary". Geography.about.com. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ History.com[dead link]
- ^ "The changing facets of Hungarian nationalism - Nationalism Reexamined | Social Research | Find Articles at BNET". Findarticles.com. 2009-06-02. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ "Ch7-1" (PDF). Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ Géza Jeszenszky: From "Eastern Switzerland" to Ethnic Cleansing, address at Duquesne History Forum, 17 November 2000, The author is former Ambassador of Hungary to the United States and was Foreign Minister in 1990–1994.
- ^ "Austria-Hungary". 1911 Encyclopedia. LoveToKnow.
- ^ Vol. 3, p.825 in Magyarország Történelmi Kronológiája, Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest, 1982.
- ^ Library of Congress country study on Hungary
- ^ "Find red leaders' loot.; Bela Kun and Szamuely Hid Valuables They Had ... - Article Preview - The". New York Times. 1919-08-13. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ William Brustein: Roots of hate: anti-semitism in Europe before the Holocaust
- ^ "Magyar Tudomány 2000. január". Epa.niif.hu. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ Ignác Romsics: Magyarország története a XX. században, 2004, p. 134
- ^ Molnar, A Concise History of Hungary, p. 262 online
- ^ Richard C. Frucht, Eastern Europe: An Introduction to the People, Lands, and Culture p. 359-360 online
- ^ Felix Wittmer (1937). Flood-light on Europe: a guide to the next war. C. Scribner's sons. Item notes: pt. 443. Original from Indiana University, Digitized November 13, 2008 p. 114
- ^ Domokos G. Kosáry, Steven Béla Várdy, Danubian Research Center (1969). History of the Hungarian Nation. Danubian Press.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link), Original from the University of California, Digitized June 19, 2008, p. 222 - ^ "Spencer Tucker, Laura Matysek Wood, Justin D. Murphy (1996). Google Books The European powers in the First World War (illustrated ed.). Taylor & Francis. p. 697. ISBN 0815303998, 9780815303992. Retrieved 2009-03-06.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help); Check|url=value (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hungary: The Unwilling Satellite John F. Montgomery, Hungary: The Unwilling Satellite. Devin-Adair Company, New York, 1947. Reprint: Simon Publications, 2002.
- ^ "United States Holocaust Memorial Museum; Holocaust Encyclopedia". Ushmm.org. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ Alfred de Zayas "Raoul Wallenberg" in Dinah Shelton Encyclopedia of Genocide (Macmillan Reference 2005, vol. 3)
- ^ Alfred de Zayas "A Terrible Revenge" (Palgrave/Macmillan 2006)
- ^ "Granville/ frm" (PDF). Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ "Hungary's 'forgotten' war victims". BBC News. 2009-11-07. Retrieved 2010-02-04.
- ^ Findley, Carter V., and John Rothney. Twentieth Century World. sixth ed. Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 2006. 278.
- ^ Hungary's 1956 brain drain. BBC News. October 23, 2006.
- ^ "Hungary Guide - Interesting facts about Hungary". Eupedia. 1994-04-19. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ a b The Contribution of Hungarians to Universal Culture (includes inventors), Embassy of the Republic of Hungary, Damascus, Syria, 2006.
- ^ "Definition "coach" in Collins English Dictionary & Thesaurus". Dictionary.reverso.net. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ a b "IEC - Techline > Otto Blathy, Miksa Déri, Károly Zipernowsky". Iec.ch. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ Georgano, G. N. Cars: Early and Vintage, 1886-1930. (London: Grange-Universal, 1985)
- ^ "The Political and Economic Transition in Hungary" (PDF).
- ^ "CIA - The World Factbook - Hungary".
- ^ Lynch, David J. (2006-06-23). "Hungary faces enormous economic hurdles". USAToday. Retrieved 2008-12-05.
- ^ "Convergence Report May 2008" (PDF). Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ "Hungary has surpassed worst part of financial crisis: PM". Eubusiness.com. 2009-07-20. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ Hungary’s Recession Deepens on Plunging Export Demand. Bloomberg.com. June 9, 2009.
- ^ "Accueil des actualités des marchés boursiers internationaux". Boursorama.com. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ Washingtonpost.com[dead link]
- ^ a b c Index of Economic Freedom
- ^ "Hungary's 2nd reading Q3 GDP growth +0.8 pct yr/yr". Forbes.com. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ "GKI say's Hungary's GDP to contract 1-1.5pc in 2009". Realdeal.hu. 2008-12-08. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ Google.com[dead link]
- ^ Andrew Speedy. "Hungary". Fao.org. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ "Hussar". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. 2008. Retrieved 2008-08-15.
- ^ "Population Census 2001 – National and county data – Summary Data". Nepszamlalas.hu. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ Hungary: Transit Country Between East and West. Migration Information Source. November 2003.
- ^ Sue Clarkson. "History of German Settlements in Southern Hungary". Feefhs.org. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ "18. Demographic data" – Hungarian Central Statistical Office[dead link]
- ^ "18. Demographic data – Hungarian Central Statistical Office". Nepszamlalas.hu. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ Volume 3, p.979, Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest, 1982
- ^ Szalipszki, p. 12
Refers to the country as "widely considered" to be a "home of music". - ^ Broughton, pp. 159-167
- ^ Szabolcsi, The Specific Conditions of Hungarian Musical Development
"Every experiment, made from Hungarian antedecents and on Hungarian soil, to create a conscious musical culture (music written by composers, as different from folk music), had instinctively or consciously striven to develop widely and universally the musical world of the folk song. Folk poetry and folk music were deeply embedded in the collective Hungarian people’s culture, and this unity did not cease to be effective even when it was given from and expression by individual creative artists, performers and poets." - ^ "Szabolcsi". Mek.oszk.hu. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ "Sulinet: Magyar növény-e a paprika?". Sulinet.hu. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ "Herend Porcelain Manufactory Ltd". Herend.com. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ "Vision of Humanity". Vision of Humanity. Retrieved 2010-02-04.
External links
- Official site of the National Assembly
- Chief of State and Cabinet Members
- "Hungary". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Hungary at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Template:Dmoz
 Wikimedia Atlas of Hungary
Wikimedia Atlas of Hungary- Template:Wikitravel
- Magyarorszag.hu
- Hungary Guide
- History of Hungary: Primary Documents
- History of Hungary from The Corvinus Library
- In The Land of Hagar: The Jews of Hungary a virtual exhibition
- Translation of Hungarian literary works database
- Agricultural land use profile