Cross-strait relations
 | |
China |
Taiwan |
|---|---|
| Diplomatic mission | |
| Taiwan Affairs Office | Mainland Affairs Council |
| Cross-Strait relations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 海峽兩岸關係 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 海峡两岸关系 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Template:Contains Chinese text
Cross-Strait relations (simplified Chinese: 海峡两岸关系; traditional Chinese: 海峽兩岸關係; pinyin: Hǎixiá liǎng'àn guānxì) are the relations between mainland China and Taiwan, which are separated by the Taiwan Strait in the west Pacific Ocean, and in particular between their respective governments:
- the People's Republic of China, abbreviated as PRC, commonly known as China, and
- the Republic of China, abbreviated as ROC, commonly known as Taiwan.
In 1949, with the Chinese Civil War turning decisively in the Communists' (CPC) favour, the ROC government led by the Kuomintang (KMT) retreated to Taipei, in Taiwan, while the CPC proclaimed the PRC government in Beijing.
Since then, the relations between China and Taiwan have been characterized by limited contact, tensions, and instability. In the early years, military conflicts continued, while diplomatically both governments competed to be the "legitimate government of China". More recently, questions around the political and legal status of Taiwan have focused on the alternative prospects of political unification with China or full Taiwanese independence. The People's Republic remains hostile to any formal declaration of independence and maintains its claim over Taiwan. At the same time, non-governmental and semi-governmental exchanges between the two sides have been increasing. From 2008, negotiations began to restore the "three links" (transportation, commerce, and communications) between the two sides, cut off since 1949. Party-to-party talks between the CPC and the KMT have resumed and semi-official negotiations through organizations representing the interests of their respective governments are being scheduled.
The English expression "cross-Strait relations" has been used by the two sides concerned and by many observers so that the relationship between China and Taiwan would not be referred to as "(Mainland) China–Taiwan relations" or "PRC–ROC relations". There is also no commonly used Chinese language phrase equivalent to the latter two phrases, although China–Taiwan relations (simplified Chinese: 中台关系; traditional Chinese: 中台關係/中臺關係; pinyin: Zhōng-Tái guānxì) is occasionally used by neutral sources and sources that favour a dichotomy between "China" and "Taiwan",[1] and conversely Mainland-Taiwan relations (simplified Chinese: 陆台关系; traditional Chinese: 陸台關係/陸臺關係; pinyin: Lù-Tái guānxì) is occasionally used by pro-china sources and sources that favour avoiding that dichotomy.[2]
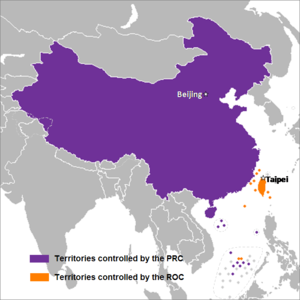
Comparison of the two political entities
 |
|---|
|
|
 |
|---|
|
|
| Name | Main Land China | Taiwan |
|---|---|---|
| Area | 9,706,961 km² (3,747,879 sq mi)[a] | 36,193 km² (13,974 sq mi)[5] |
| Population | 1,350,695,000 (2013)[6] | 23,373,517 (2014)[5] |
| Population Density | 139.6/km² (363.3/sq mi) | 644/km² (1,664/sq mi) |
| Capital | Beijing | Taipei |
| Largest city | Shanghai (23,019,148) | New Taipei City (3,935,072) |
| Government | Unitary one-party socialist republic | Unitary semi-presidential constitutional republic |
| State Leaders | President: Xi Jinping Premier: Li Keqiang |
President: Ma Ying-jeou Premier: Chang San-cheng |
| Official languages | Mandarin (Putonghua) | Mandarin (Guoyu) |
| Official script | Simplified Chinese characters | Traditional Chinese characters |
| Currency | Chinese Yuan | New Taiwan Dollar |
| GDP (nominal) | $9,325,300 (millions of USD)[7] | $473,971 (millions of USD)[8] |
| GDP (PPP) | $12,383,000 (millions of USD)[7] | $903,469 (millions of USD)[8] |
| GDP (nominal) per capita | $6,853[7] | $20,328[8] |
| GDP (PPP) per capita | $11,477[9] | $38,749[8] |
| Gini coefficients | 46.2 (high)[10] | 34.2 (medium)[11] |
| Human Development Index | 0.719 (high)[9] | 0.882 (very high)[12] |
| Foreign exchange reserves | 3,341,000 (millions of USD)[13] | 406,062 (millions of USD)[14] |
| Military expenditures - % of GDP | $106.4 billion (2012)[15] - 2.1% (2012) | $8.888 billion (2013) - 2.3% (2012) |
History

Before 1949
This section needs additional citations for verification. (May 2009) |

The early history of cross-Strait relations involved the exchange of cultures, people, and technology.[16][17][18] However, no Chinese dynasty formally incorporated Taiwan in ancient times.[19] In the 16th and 17th centuries, Taiwan caught the attention of first Portuguese, then Dutch and Spanish explorers. In 1624, the Dutch established their first settlement in Taiwan. In 1662, Koxinga (Zheng Chenggong), a Ming Dynasty loyalist, defeated the Dutch rulers of Taiwan, and took the island, establishing the first formally Han Chinese regime in Taiwan. Koxinga's heirs used Taiwan as a base for launching raids into mainland China against the Manchu Qing Dynasty. However, they were defeated in 1683 by Qing forces. The following year, Taiwan was incorporated into Fujian province. Over the next two centuries, the Imperial government paid little attention to Taiwan.[citation needed]
The situation changed in the 19th century, with other powers increasingly eyeing Taiwan for its strategic location and resources. In response, the administration began to implement a modernization drive. In 1887, Taiwan Province was declared by Imperial decree. Within 10 years, Taiwan had become one of the most modern provinces in the Empire. However, the fall of the Qing outpaced the development of Taiwan, and in 1895, following its defeat in the First Sino-Japanese War, the Imperial government ceded Taiwan to Japan in perpetuity. Qing loyalists briefly resisted the Japanese rule under the banner of the "Republic of Taiwan", but order was quickly established by Japanese authorities.[citation needed]
Japan ruled Taiwan until 1945. During this time, Taiwan, as part of the Japanese Empire, was a foreign jurisdiction in relation to first the Qing Empire, and, after 1912, the ROC. In 1945, Japan was defeated in World War II and surrendered its forces in Taiwan to the ROC, then ruled by the Kuomintang (KMT). The period of post-war Kuomintang rule over China (1945–1949) was marked in Taiwan by conflicts between local residents and the new KMT authority, most violently in the February 28 Incident, which occurred on February 28, 1947. The seeds for the Taiwan autonomy and independence movement were sown in this time. During this time and in subsequent periods, the Taiwan autonomy and independence movement was allied with the CPC in the struggle against Chiang Kai-shek's KMT-led government in the ROC. Indeed, one such organization, the Taiwan Democratic Self-Government League, remains one of the eight official minor parties in China.[citation needed]
China was soon engulfed in full-scale civil war. In 1949, the war turned decisively against the KMT and in favor of the CPC. On October 1, 1949, the CPC proclaimed the founding of the People's Republic of China in Beijing. The ROC government retreated, eventually declaring Taipei its temporary capital in December 1949.[citation needed]
Military stalemate to diplomatic war (1949–1979)

The two governments continued in a state of war until 1979. In October 1949, PRC's attempt to take the ROC controlled island of Kinmen was thwarted in the Battle of Kuningtou, halting the PLA advance towards Taiwan.[20] The Communists' other amphibious operations of 1950 were more successful: they led to the Communist conquest of Hainan Island in April 1950, capture of Wanshan Islands off the Guangdong coast (May–August 1950) and of Zhoushan Island off Zhejiang (May 1950).[21]
In June 1949, the ROC declared a "closure" of all Chinese ports and its navy attempted to intercept all foreign ships. The closure covered from a point north of the mouth of Min river in Fujian province to the mouth of the Liao River in Manchuria.[22] Since China's railroad network was underdeveloped, north-south trade depended heavily on sea lanes. ROC naval activity also caused severe hardship for Chinese fishermen.
After losing China, a group of approximately 12,000 KMT soldiers escaped to Burma and continued launching guerrilla attacks into southern China. Their leader, General Li Mi, was paid a salary by the ROC government and given the nominal title of Governor of Yunnan. Initially, the United States supported these remnants and the Central Intelligence Agency provided them with aid. After the Burmese government appealed to the United Nations in 1953, the U.S. began pressuring the ROC to withdraw its loyalists. By the end of 1954, nearly 6,000 soldiers had left Burma and Li Mi declared his army disbanded. However, thousands remained, and the ROC continued to supply and command them, even secretly supplying reinforcements at times.
The Kuomintang Islamic Insurgency in China (1950–1958) was fought by Muslim Kuomintang army officers who refused to surrender to the communists throughout the 1950s and 60's.
During the Korean War, some captured Communist Chinese soldiers, many of whom were originally KMT soldiers, were repatriated to Taiwan rather than China. A KMT guerrilla force continued to operate cross-border raids into south-western China in the early 1950s. The ROC government launched a number of air bombing raids into key coastal cities of China such as Shanghai.
Though viewed as a military liability by the United States, the ROC viewed its remaining islands in Fujian as vital for any future campaign to defeat the PRC and retake China. On September 3, 1954, the First Taiwan Strait crisis began when the PLA started shelling Quemoy and threatened to take the Dachen Islands.[22] On January 20, 1955, the PLA took nearby Yijiangshan Island, with the entire ROC garrison of 720 troops killed or wounded defending the island. On January 24 of the same year, the United States Congress passed the Formosa Resolution authorizing the President to defend the ROC's offshore islands.[22] The First Taiwan Straits crisis ended in March 1955 when the PLA ceased its bombardment. The crisis was brought to a close during the Bandung conference.[22]
The Second Taiwan Strait Crisis began on August 23, 1958 with air and naval engagements between the PRC and the ROC military forces, leading to intense artillery bombardment of Quemoy (by the PRC) and Amoy (by the ROC), and ended on November of the same year.[22] PLA patrol boats blockaded the islands from ROC supply ships. Though the United States rejected Chiang Kai-shek's proposal to bomb Chinese artillery batteries, it quickly moved to supply fighter jets and anti-aircraft missiles to the ROC. It also provided amphibious assault ships to land supply, as a sunken ROC naval vessel was blocking the harbor. On September 7, the United States escorted a convoy of ROC supply ships and the PRC refrained from firing. On October 25, the PRC announced an "even-day ceasefire" — the PLA would only shell Quemoy on odd-numbered days.
Despite the end of the hostilities, the two sides have never signed any agreement or treaty to officially end the war.
After the 1950s, the "war" became more symbolic than real, represented by on again, off again artillery bombardment towards and from Kinmen. In later years, live shells were replaced with propaganda sheets. The bombardment finally ceased in 1979 after the establishment of diplomatic relations between the People's Republic of China and the United States.
During this period, movement of people and goods virtually ceased between PRC- and ROC-controlled territories. There were occasional defectors. One high profile defector was Justin Yifu Lin, who swam across the Kinmen strait to China and is now Chief Economist and Senior Vice President of the World Bank.
Most observers expected Chiang's government to eventually fall in response to a Communist invasion of Taiwan, and the United States initially showed no interest in supporting Chiang's government in its final stand. Things changed radically with the onset of the Korean War in June 1950. At this point, allowing a total Communist victory over Chiang became politically impossible in the United States, and President Harry S. Truman ordered the United States Seventh Fleet into the Taiwan straits to prevent the ROC and PRC from attacking each other.[23]
After the ROC complained to the United Nations against the Soviet Union supporting the PRC, the UN General Assembly Resolution 505 was adopted on February 1, 1952 to condemn the Soviet Union.
Diplomatically during this period, until around 1971, the ROC government continued to be recognized as the legitimate government of China and Taiwan by most NATO governments. The PRC government was recognized by Soviet Bloc countries, members of the non-aligned movement, and some Western nations such as the United Kingdom and the Netherlands. Both governments claimed to be the legitimate government of China, and labeled the other as illegitimate. Civil war propaganda permeated the education curriculum. Each side portrayed the people of the other as living in hell-like misery. In official media, each side called the other "bandits". The ROC also suppressed expressions of support for Taiwanese identity or Taiwan independence.
Thawing of relations (1979–1998)

Following the break of official relations between the United States and the ROC in 1979, the ROC government under Chiang Ching-kuo maintained a "Three Noes" policy (三不政策) in regards to communicating with the Chinese government. This policy however was revised following the May 1986 hijacking of a China Airlines cargo plane, in which the Taiwanese pilot subdued other members of the crew and flew the plane to Guangzhou. In response, Chiang sent delegates to Hong Kong to discuss with PRC officials for the return of the plane and crew, which is seen as a turning point between cross-strait relations.
In 1987, the ROC government began to allow visits to China. This benefited many, especially old KMT soldiers, who had been separated from their family in China for decades. This also proved a catalyst for the thawing of relations between the two sides. Problems engendered by increased contact necessitated a mechanism for regular negotiations.
In order to negotiate with China on operational issues without compromising the government's position on denying the other side's legitimacy, the ROC government under Chiang Ching-kuo created the "Straits Exchange Foundation" (SEF), a nominally non-governmental institution directly led by the Mainland Affairs Council, an instrument of the Executive Yuan. The PRC responded to this initiative by setting up the Association for Relations Across the Taiwan Straits (ARATS), directly led by the Taiwan Affairs Office of the State Council. This system, described as "white gloves", allowed the two governments to engage with each other on a semi-official basis without compromising their respective sovereignty policies.
Led by highly respected elder statesmen Koo Chen-fu and Wang Daohan, the two organizations began a series of talks that culminated in the 1992 meetings, which, together with subsequent correspondence, established the 1992 Consensus, under which both sides agreed to deliberate ambiguity on questions of sovereignty, in order to engage on operational questions affecting both sides.
Also during this time, however, the rhetoric of ROC President Lee Tung-hui began to turn further towards Taiwan independence. Prior to the 1990s, the ROC had been a one-party authoritarian state committed to eventual unification with China. However, with democratic reforms the attitudes of the general public began to influence policy in Taiwan. As a result, the ROC government shifted away from its commitment to the one China policy and towards a separate political identity for Taiwan. Lee's China counterpart, Jiang Zemin, was unwilling to compromise on the matter. Jiang attempted to influence the 1996 ROC election in Taiwan by conducting a missile exercise designed to warn the pro-independence Pan-Green Coalition, leading to the Third Taiwan Strait Crisis. By 1998, semi-official talks had broken down.
Hostile non-contact (1998–2008)
This section needs additional citations for verification. (May 2009) |


Chen Shui-bian was elected President of the ROC in 2000. Politically, Chen is strongly pro-Taiwan independence. Chen's repudiation of the 1992 Consensus combined with the PRC's insistence that the ROC agree to the "one China" principle for negotiations to occur prevented improvement in cross-strait relations.
Hu Jintao became President of the PRC in 2003, though he was ruling de facto paramount leader as General Secretary of the Communist Party of China since late 2002.
Chen called for talks without any preconditions, repudiating the 1992 consensus while Hu continued to insist that talks can only proceed under an agreement of the "one China" principle. Chen Shui-bian and his party continued to express an ultimate goal of formal Taiwanese independence, and make statements on the political status of Taiwan that the PRC considers provocative. At the same time, Hu and the PRC continued a military missile buildup across the strait from Taiwan while making threats of military action against Taiwan should it declare independence or if the PRC considers that all possibilities for a peaceful unification are completely exhausted. The PRC also continued applying diplomatic pressure to other nations to isolate the ROC diplomatically.[citation needed]
Despite these provocations, in 2001 Chen lifted the 50-year ban on direct trade and investment with the PRC, which made the later ECFA possible.[24] During the 2003 Iraq war, the PRC allowed Taiwanese airlines use of China's airspace.[25]
After the re-election of Chen Shui-bian in 2004, Hu's government changed the previous blanket no-contact policy, a holdover from the Jiang Zemin administration. Under the new policy, on the one hand, the PRC government continued a no-contact policy towards Chen Shui-bian. It maintained its military build-up against Taiwan, and pursued a vigorous policy of isolating Taiwan diplomatically. In March 2005, the Anti-Secession Law was passed by the National People's Congress, formalizing "non-peaceful means" as an option of response to a formal declaration of independence in Taiwan.[citation needed]
On the other hand, the PRC administration loosened its rhetoric in relation to Taiwan, and pursued contact with apolitical, or politically non-independence leaning, groups in Taiwan. In his May 17 Statement in 2004, Hu Jintao made friendly overtures to Taiwan on resuming negotiations for the "three links", reducing misunderstandings, and increasing consultation. In the Anti-Secession Law passed in 2005, the PRC government for the first time authoritatively committed to negotiations on the basis of equal status between the two sides, and further refrained from imposing the "one China" policy as a precondition for talks. The CPC increased contacts on a party-to-party basis with the KMT, then the opposition party in Taiwan. Despite having been the warring parties in the Chinese Civil War, the CPC and the KMT also had a history of co-operation, when the two parties twice co-operated in the Northern Expedition and the war against Japan. The increased contacts culminated in the 2005 Pan-Blue visits to China, including a meeting between Hu and then-KMT chairman Lien Chan in April 2005.[26][27]
Resumption of high level contact (2008–present)

On March 22, 2008, the KMT party won the presidential election in the Republic of China. It also won a large majority in the Legislature.[28]
A series of meetings between the two sides have followed. On April 12, 2008, Hu Jintao held a meeting with ROC's then vice-president elect Vincent Siew as chairman of the Cross-Straits Common Market Foundation during the Boao Forum for Asia. On May 28, 2008, Hu met with KMT chairman Wu Po-hsiung, the first meeting between the heads of the CPC and the KMT as ruling parties. During this meeting, Hu and Wu agreed that both sides should recommence semi-official dialogue under the 1992 consensus. Wu committed the KMT against Taiwanese independence, but also stressed that a "Taiwan identity" did not equate to "Taiwanese independence". Hu committed his government to addressing the concerns of the Taiwanese people in regard to security, dignity, and "international living space", with a priority given to discussing Taiwan's wish to participate in the World Health Organization.
Both Hu and his new counterpart Ma Ying-jeou agree that the 1992 Consensus is the basis for negotiations between the two sides of the Taiwan strait. On March 26, 2008, Hu Jintao held a telephone talk with the US President George W. Bush, in which he explained that the "1992 Consensus" sees "both sides recognize there is only one China, but agree to differ on its definition".[29] The first priority for the SEF–ARATS meeting will be opening of the three links, especially direct flights between China and Taiwan.
These events suggest a policy by the two sides to rely on the deliberate ambiguity of the 1992 Consensus to avoid difficulties arising from asserting sovereignty. As Wu Po-hsiung put it during a press conference in his 2008 China visit, "we do not refer to the 'Republic of China' so long as the other side does not refer to the 'People's Republic of China'". Since the March elections in Taiwan, the PRC government has not mentioned the "one China policy" in any official announcements. The only exception has been one brief aberration in a press release by the Ministry of Commerce, which described Vincent Siew as agreeing to the "1992 consensus and the "one China policy". Upon an immediate protest from Siew, the PRC side retracted the press release and issued apologetic statements emphasizing that only press releases published by the Xinhua News Agency represented the official PRC position. The official press release on this event did not mention the One China Policy.[30]
Ma Ying-jeou, the current ROC President, has advocated that cross-strait relations should shift from "mutual non-recognition" to "mutual non-denial".[31]
Dialogue through semi-official organisations (the SEF and the ARATS) reopened on June 12, 2008 on the basis of the 1992 Consensus, with the first meeting held in Beijing. Neither the PRC nor the ROC recognizes the other side as a legitimate entity, so the dialogue was in the name of contacts between the SEF and the ARATS instead of the two governments, though most participants were actually officials in PRC or ROC governments. Chen Yunlin, President of the ARATS, and Chiang Pin-kung, President of the SEF, signed files on June 13, agreeing that direct flights between the two sides would begin on July 4[32] and that Taiwan would allow entrance of up to 3000 visitors from China every day.[33]
The financial relationship between the two areas improved on 1 May 2009 in a move described as "a major milestone" by The Times.[34] The ROC's financial regulator, the Financial Supervisory Commission, announced that Chinese investors would be permitted to invest in Taiwan's money markets for the first time since 1949.[34] Investors can now apply to purchase Taiwan shares that do not exceed one tenth of the value of the firm’s total shares.[34] The move came as part of a “step by step” movement which is supposed to relax restrictions on Chinese investment. Taipei economist Liang Chi-yuan, commented: “Taiwan's risk factor as a flash point has dropped significantly with its improved ties with Chinese. The Chinese would be hesitant about launching a war as their investment increases here.”[34] China's biggest telecoms carrier, China Mobile, was the first company to avail of the new movement by spending $529 million on buying 12 percent of Far EasTone, the third largest telecoms operator in Taiwan.[34]
President Ma has called repeatedly for the PRC to dismantle the missile batteries targeted on Taiwan's cities, without result.[35]
On January 30, 2010, the Obama administration announced it intended to sell $6.4 billion worth of antimissile systems, helicopters and other military hardware to Taiwan, an expected move which was met with reaction from Beijing: in retaliation, China cut off all military-to-military ties with Washington and warned that US-China cooperation on international issues could suffer as a result of the sales.[36]
A report from Taiwan's Ministry of National Defense said that China's current charm offensive is only accommodating on issues that do not undermine China's claim to Taiwan and that the PRC would invade if Taiwan declared independence, developed weapons of mass destruction, or suffered from civil chaos.[37]
On the 100th anniversary of the Republic of China (Xinhai Revolution), President Ma called on the PRC to embrace Sun Yat-sen's call for freedom and democracy.[38]
In June 2013, China offered 31 new measures to better integrate Taiwan economically.[39]
In October 2013, in a hotel lobby on the sidelines of the APEC Indonesia 2013 meetings in the Indonesian island of Bali, Wang Yu-chi, Minister of the Mainland Affairs Council, spoke briefly with Zhang Zhijun, Minister of the Taiwan Affairs Office, each addressing the other by his official title. Both called for the establishment of a regular dialogue mechanism between their two agencies to facilitate cross-strait engagement. Zhang also invited Wang to visit China.[40][41]
On February 11, 2014, Wang met with Zhang in Nanjing, in the first official, high-level, government-to-government contact between the two sides since 1949. The meeting took place at Purple Palace Nanjing.[42][43] Nanjing was the capital of the Republic of China during the period in which it actually ruled China.[44][45] During the meeting, Wang and Zhang agreed on establishing a direct and regular communication channel between the two sides for future engagement under the 1992 Consensus. They also agreed on finding a solution for health insurance coverage for Taiwanese students studying in Mainland China, on pragmatically establishing SEF and ARATS offices in their respective territories and on studying the feasibility of allowing visits to detained persons once these offices have been established. Before shaking hands, Wang addressed Zhang as "TAO Director Zhang Zhijun" and Zhang addressed Wang as "Minister Wang Yu-chi" without mentioning the name Mainland Affairs Council.[46] However, China's Xinhua News Agency referred to Wang as the "Responsible Official of Taiwan's Mainland Affairs Council" (Chinese: 台湾方面大陆委员会负责人; pinyin: Táiwān Fāngmiàn Dàlù Wěiyuánhuì Fùzérén)[47] in its Chinese-language news and as "Taiwan's Mainland Affairs Chief" in its English-language news.[48] On 25–28 June 2014, Zhang paid a retrospective visit to Taiwan, making him the highest official of the Communist Party of China to ever visit Taiwan.
In September 2014, Xi Jinping, General Secretary of the Communist Party of China appeared[clarify] to adopt a more uncompromising stance than his predecessors as he called for the "one country, two systems" model to be applied to Taiwan.[49] In Taiwan it was noted that Beijing was no longer referring to the 1992 Consensus.[50]
On 7 November 2015, Xi and Ma met and shook hands in Singapore, marking the first ever meeting between leaders of both sides since the end of Chinese Civil War in 1949.
On 30 December 2015, a hotline connecting the head of the Mainland Affairs Council and the head of the Taiwan Affairs Office was established.[51] First conversation via the hotline between the two heads was made on 5 February 2016.[52]
In March 2016, ROC Justice Minister Luo Ying-shay embarked on a 5-day historic visit to Mainland China, making her the first Minister of the Government of the Republic of China to visit Mainland China after the end of Chinese Civil War in 1949.[53]
Current formal relations
Interpretation of the relations
On 2 September 2008, the ROC President Ma Ying-jeou was interviewed by the Mexico-based newspaper El Sol de México and he was asked about his views on the subject of 'two Chinas' and if there is a solution for the sovereignty issues between the two. The ROC President replied that the relations are neither between two Chinas nor two states. It is a special relationship. Further, he stated that the sovereignty issues between the two cannot be resolved at present, but he quoted the '1992 Consensus', currently accepted by both sides, as a temporary measure until a solution becomes available.[54] The spokesman for the ROC Presidential Office Wang Yu-chi later elaborated the President's statement and said that the relations are between two regions of one country, based on the ROC Constitutional position, the Statute Governing the Relations Between the Peoples of the Taiwan Area and Mainland Area and the '1992 Consensus'.[55] On 7 October 2008 Ma Ying-jeou was interviewed by a Japan-based magazine "World". He said that laws relating to international relations cannot be applied regarding the relations between Taiwan and the mainland, as they are parts of a state.[56][57][58]
Inter-government

Semi-governmental contact is maintained through the Straits Exchange Foundation (SEF) and the Association for Relations Across the Taiwan Straits (ARATS). Negotiations between the SEF and the ARATS resumed on 11 June 2008.[59]
Although formally privately constituted bodies, the SEF and the ARATS are both directly led by the Executive Government of each side: the SEF by the Mainland Affairs Council of the Executive Yuan of the ROC, and the ARATS by the Taiwan Affairs Office of the State Council of the PRC. The heads of the two bodies, Lin Join-sane and Chen Deming, are both full-time appointees and do not hold other government positions. However, both are senior members of their respective political parties (Kuomintang and Communist Party of China respectively), and both have previously served as senior members of their respective governments. Their deputies, who in practice are responsible for the substantive negotiations, are concurrently senior members of their respective governments. For the June 2008 negotiations, the main negotiators, who are deputy heads of the SEF and the ARATS respectively, are concurrently deputy heads of the Mainland Affairs Council and the Taiwan Affairs Office respectively.[citation needed]
To date, the 'most official'[citation needed] representative offices between the two sides are the PRC's Cross-Strait Tourism Exchange Association (CSTEA) in Taiwan, established on 7 May 2010, and ROC's Taiwan Strait Tourism Association (TSTA) in China, established on 4 May 2010. However, the duties of these offices are limited only to tourism-related affairs so far.
2008 meetings
First 2008 meeting
A series of meetings were held between the SEF and the ARATS at Diaoyutai State Guesthouse in Beijing from 11 June 2008 to 14 June 2008. By convention, SEF–ARATS negotiations proceed in three rounds: a technical round led by negotiators seconded from the relevant government departments, a draft round led by deputy heads of the two organisations, and a formal round led by the heads of the two organisations. In this case, however, both sides have already reached broad consensus on these issues on both the technical and political levels through previous negotiations via the non-governmental and inter-party channels. As a result, the initial technical round was dispensed with, and the negotiations began with the second, draft round.[59]
The two sides agreed to the following:

- Initiate direct passenger airline services every weekend from 4 July 2008. Both parties agreed to negotiate on the routes of cross-strait direct flights and establish direct communication procedures concerning air traffic management systems as soon as possible. But before the routes of direct flights are finalized, charter flights may temporarily fly across Hong Kong Flight Information Region. There is no need to stop in Hong Kong, but planes still have to fly through its airspace. Weekend charter flights shall fly from each Friday to the following Monday for a total of four full days.
- Opening Taiwan to Chinese tourists. Both parties agreed that Chinese tourists must travel to the Taiwan in groups. Tourists must enter into, visit, and exit from Taiwan in groups. The maximum quota of tourists received by the party responsible for tourist reception shall not exceed the average of 3,000 persons per day, and each group shall consist of a minimum of ten persons and forty persons at the maximum, being in Taiwan for a maximum of ten days.[61]
- However, in 2012, it was agreed by both parties that individual tourists from the Chinese cities of Beijing, Shanghai, and Xiamen were allowed to visit Taiwan. Later, tourists from Chengdu, Chongqing, Nanjing, Hangzhou, Guangzhou, and Tianjin were allowed to visit Taiwan individually. Finally, Fuzhou, Jinan, and Xi'an will join the list by the end of 2012.[62]
To facilitate the above, both sides also agreed to further discuss on the possibilities of exchanging representative offices, with an SEF office to be opened in Beijing and an ARATS office in Taipei to issue travel permits to cross-Strait visitors, among other duties.
Second 2008 meeting
Following an invitation issued by the SEF at the first meeting, the head of ARATS, Chen Yunlin, began a visit to Taiwan on 3 November 2008.[63] Items on the agenda raised by SEF Chairman Chiang Pin-kung included direct maritime shipping, chartered cargo flights, direct postal service, and co-operation in ensuring food safety, in response to the 2008 Chinese milk scandal,[63] while ARATS chairman Chen Yunlin raised the matters of direct freight service, and opening up air routes that directly cross the Taiwan Strait. Previous routes avoided crossing the Strait for security reasons, with planes detouring through Hong Kong or Japan air control areas.[64]
On 4 November 2008, ARATS and SEF signed a number of agreements in Taipei. The agreement relating to direct passenger flights increased the number of charter flights from 36 to 108 per week, operating daily instead of the four days a week previously. Flights would now operate to and from 21 Chinese cities. Flights would also take a more direct route. Private business jet flights would also be allowed. The agreement relating to cargo shipping allowed direct shipping between 11 sea ports in Taiwan and 63 in China. The shipping would be tax free. The agreement relating to cargo flights provided for up to 60 direct cargo flights per month. Finally, an agreement was made to set up food safety alerts between the two sides. [65]
During Chen's visit in Taipei, he was met with a series of strong protests directed at himself and Ma Ying-jeou, some of which were violent with Molotov cocktails being thrown by the protesters at riot police. A series of arrests were made after the protests.[66][67] Local police reported that 149 of its officers were injured during the opposition protests.[68] Consistent with the 1992 Consensus, Chen did not call Ma as "President".[69][70] Similarly, the representatives from Taiwan did not call the PRC President Hu Jintao as "President" in the previous meeting in Beijing.
The polls in two of Taiwan's biggest newspapers after the visit reported that the public was pleased with Chen's visit, with about 50% of the Taiwanese public considered Chen's visit having a positive effect on Taiwan's development, while 18 to 26% of the respondents thought the effect would be negative.[71] In another poll, it suggested that 26% of the respondents were satisfied with the DPP Chairwoman Tsai Ing-wen's handling of the crowds in the series of protests, while 53% of the respondents were unsatisfied. The same poll also showed that 33% of the respondents were satisfied with President Ma's performance at his meeting with Chen Yunlin, while 32% of the respondents were not satisfied.[72] According to a telephone poll conducted by Taiwan's top-selling Apple Daily newspaper on 7 November 2008 on the subject of a series of anti-Chen protests organised by the DPP, 62.12% of the respondents considered it bad for DPP's image, describing it as a "violent party", 31.13% of the respondents considered it good for the DPP's image, as it demonstrated Taiwan's democracy, while 6.75% of the respondents did not express an opinion.[73]
Inter-party
The (current) ruling parties of the two sides, the Kuomintang and the Communist Party of China, maintain regular dialogue via the KMT–CPC Forum. This has been called a "second rail" in Taiwan, and helps to maintain political understanding and aims for political consensus between the two sides.
Inter-city
The Taipei-Shanghai City Forum (Chinese: 上海-台北城市论坛) is an annual forum between the city of Taipei and Shanghai. Launched in 2010 by then-Taipei Mayor Hau Lung-pin to promote city-to-city exchanges, it led Shanghai participation in the Taipei International Flora Exposition end of that year.[74] Both Taipei and Shanghai are the first two cities across the Taiwan Strait that carries out exchanges. In 2015, the newly elected Taipei Mayor Ko Wen-je attended the forum. He was addressed as Mayor Ko of Taipei by Shanghai Mayor Yang Xiong.[75]
Non-governmental
A third mode of contact is through private bodies accredited by the respective governments to negotiate on technical and operational aspects of issues between the two sides. Called the "Macau mode", this avenue of contact was maintained even through the years of the Chen Shui-bian administration. For example, on the issues of opening Taiwan to Chinese tourists, the accredited bodies were tourism industry representative bodies from both sides.
Public opinion
According to an opinion poll released by the Mainland Affairs Council taken after the second 2008 meeting, 71.79% of the Taiwanese public supported continuing negotiations and solving issues between the two sides through the semi-official organisations, SEF and ARATS, 18.74% of the Taiwanese public did not support this, while 9.47% of the Taiwanese public did not have an opinion.[76]
Sunflower Movement
However, in 2014, the Sunflower Student Movement broke out. Citizens occupied the Taiwanese legislature for 21 days, protesting against the government forcing through Cross-Strait Service Trade Agreement without consulting public opinion and without proper legislate supervision. The protesters perceived the trade pact with China would leave Taiwan vulnerable to political pressure from Beijing.[77]
By 2015, a poll conducted by the Taiwan Braintrust showed that nearly 90 percent of the population identifies themselves as Taiwanese rather than Chinese if they were to choose between the two. Moreover, 31.2 percent of respondents said they support independence for Taiwan, while 56.2 percent would prefer to maintain the status quo and 7.9 percent support unification with China.[78]
Informal relations
The Three Links

Regular weekend direct, cross-strait charter flights between mainland China and Taiwan resumed on July 4, 2008 for the first time since 1950. Liu Shaoyong, China Southern Airlines chair, piloted the first flight from Guangzhou to Taipei. Simultaneously, a Taiwan-based China Airlines flight flew to Shanghai. Currently, 61 mainland Chinese cities are connected with eight airports in Taiwan. The flights operate every day, totaling 890 round-trip flights across the Taiwan Strait per week.[79] Previously, regular passengers (other than festive or emergency charters) had to make a time-consuming stopover at a third destination, usually Hong Kong.[80][81] Under the current procedure, the flights do not directly cross the Taiwan Strait for security reasons, but instead must enter the Hong Kong air control area before moving into or out of China or Taiwan airspace.
Taiwan residents cannot use the Republic of China passport to travel to mainland China and Mainland China residents cannot use the People's Republic of China passport to travel to Taiwan, as neither the ROC nor the PRC considers this international travel. The PRC government requires Taiwan residents to hold a Mainland Travel Permit for Taiwan Residents when entering mainland China, whereas the ROC government requires mainland Chinese residents to hold the Exit and Entry Permit for the Taiwan Area of the Republic of China to enter the Taiwan Area.
Cross-strait investments and trade
Cross-strait investments have greatly increased in recent years. Predominantly, this involves Taiwan-based firms moving to, or collaborating in joint ventures, in Mainland China. The collective body of Taiwanese investors in Mainland China is now a significant economic force for both Mainland China and Taiwan. In 2014, trade values between the two sides reached US$198.31 billion, with imports from Taiwan to the mainland counted up to US$152 billion.[82]
Cultural, educational, religious and sporting exchanges
Cultural exchanges have increased in frequency. The National Palace Museum in Taipei and the Palace Museum in Beijing have collaborated on exhibitions. Scholars and academics frequently visit institutions on the other side. Books published on each side are regularly re-published in the other side, though restrictions on direct imports and the different orthography between the two sides somewhat impede the exchange of books and ideas.
Students of Taiwan origin receive special concessions in the National Higher Education Entrance Examination in mainland China. There are regular programs for school students from each side to visit the other.
Religious exchange has become frequent. Frequent interactions occur between worshipers of Matsu, and also between Buddhists[citation needed].
Humanitarian actions
China and Taiwan have provided humanitarian aid to each other on several occasions. Most recently, following the 2008 Sichuan earthquake, an expert search and rescue team was sent from Taiwan to help rescue survivors in Sichuan. Shipments of aid material was also provided under the co-ordination of the Red Cross Society of The Republic of China and charities such as Tzu Chi.
Military build-up

Despite diplomatic and media efforts by Beijing to portray an easing of military tension with Taiwan, the military build-up against Taiwan continues.[83]
For example, the PRC's People's Liberation Army (PLA) continues to move ballistic missiles and modern warplanes to bases within range of Taiwan. By the end of 2010, the PLA will have 2,000 ballistic missiles aimed at Taiwan.[84][85] That is 50 percent more than there were just two years prior, and ten times more than in 2000. Most of these are Dong Feng (DF)-11 and Dong Feng (DF)-15 models. The DF11 (also known as the M11) has a range of 300 kilometers and carries a one-ton warhead. The DF15 (M9) has a range of 600 kilometers and carries a half ton warhead. There are also over 1,000 Chinese warplanes[86] and over 100,000 troops (including several brigades of paratroopers) available for an attack on the island. The missiles would use high explosive or cluster bomb warheads. In response, Taiwan is investing in an anti-missile system intended to negate a large number of PLA missiles.
Intelligence from Taiwan has also spotted the PRC converting recently retired jet fighters to pilotless aircraft, to be used in defeating Taiwanese air defense.[citation needed] Its air force believes that their air bases would be prime targets for bombers and ballistic missiles from China, and has thousands of engineer troops trained and equipped to potentially repair airstrips that have been hit by PLA bombs and warheads, and pilots trained to operate from damaged airstrips.
Taiwanese intelligence also noted that while the PRC has moved amphibious training away from the coast opposite Taiwan, these drills are still carried out elsewhere. While Beijing has halted most of the anti-Taiwan stories in state-controlled media, it has continued preparations for a possible invasion of Taiwan.
In addition, the United States has supplied Taiwan's military with ships and planes,[87][88] though Secretary of Defense Robert Gates has said that the United States would reduce arms sales to Taiwan if tensions are eased,[89] but that this was not a change in American policy.[90]
In 2012, PACCOM commander Willard said that Ma had reduced the possibility of a cross-strait conflict, in spite of the PRC's military buildup.[91]
A 2008 report by the RAND Corporation analyzing a theoretical 2020 attack by China on Taiwan suggested that the US would likely not be able to defend Taiwan.[92]
Political stability
ROC National Security Bureau Director-General Tsai De-sheng has said that Xi Jinping, the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China, has the "best understanding" of Taiwan and this is likely to lead to continued political stability in cross-Strait relations.[93]
See also
- Political status of Taiwan
- Wang-Koo summit
- Chen-Chiang summit
- Cross-Straits Economic Trade and Culture Forum
- Cross-Strait Peace Forum
- Foreign relations of Taiwan
- Foreign relations of China
Notes
- ^ The area given is the official United Nations figure for the mainland and excludes Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan.[3] It also excludes the Trans-Karakoram Tract 5,800 km2 (2,200 sq mi), Aksai Chin 37,244 km2 (14,380 sq mi) and other territories in dispute with India. The total area of China is listed as 9,572,900 km2 (3,696,100 sq mi) by the Encyclopædia Britannica.[4] For further information, see Territorial changes of the People's Republic of China.
References
- ^ See, e.g., "華郵預測:2016前中台關係不被看好 - 民報". Peoplenews.tw. Feb 12, 2014.
- ^ See, e.g., "兩個女人的戰爭:陸台關係的未來走到了十字路口". South China Morning Post (Chinese edition). 21 July 2015. Retrieved 2015-09-24.
- ^ "Demographic Yearbook—Table 3: Population by sex, rate of population increase, surface area and density" (PDF). UN Statistics. 2007. Retrieved 31 July 2010.
- ^ "China". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 16 November 2012.
- ^ a b "Number of Villages, Neighborhoods, Households and Resident Population". MOI Statistical Information Service. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ^ "Population (Total)". The World Bank. Retrieved 25 November 2013.
- ^ a b c "2013年国民经济发展稳中向好". National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. 20 January 2014. Retrieved 20 January 2014.
- ^ a b c d "Republic of China (Taiwan)". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 2013-10-28.
- ^ a b "About China". UNDP in China.
- ^ "China's Economy Realized a Moderate but Stable and Sound Growth in 2015". National Bureau of Statistics of China. 19 January 2016. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
Taking the per capita disposable income of nationwide households by income quintiles, that of the low-income group reached 5,221 yuan, the lower-middle-income group 11,894 yuan, the middle-income group 19,320 yuan, the upper-middle-income group 29,438 yuan, and the high-income group 54,544 yuan. The Gini Coefficient for national income in 2015 was 0.462.
- ^ "Table 4. Percentage Share of Disposable Income by Quintile Group of Households and Income Inequality Indices". Report on The Survey of Family Income and Expenditure. Taipei, Taiwan: Directorate General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics. 2010.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ http://www.dgbas.gov.tw/public/Attachment/11715383471.doc
- ^ "China trade now bigger than US". The Daily Telegraph. 10 February 2013. Retrieved 15 February 2013.
- ^ "Taiwan Timeline – Retreat to Taiwan". BBC News. 2000. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- ^ "China Raising 2012 Defense Spending to Cope With Unfriendly 'Neighborhood'". Bloomberg. 4 March 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2013.
- ^ Zhang, Qiyun. (1959) An outline history of Taiwan. Taipei: China Culture Publishing Foundation
- ^ Sanchze-Mazas (ed.) (2008) Past human migrations in East Asia : matching archaeology, linguistics and genetics. New York: Routledge.
- ^ Brown, Melissa J. (2004) Is Taiwan Chinese? : the impact of culture, power, and migration on changing identities. Berkeley: University of California Press
- ^ Lian, Heng (1920). 臺灣通史 [The General History of Taiwan] (in Chinese). OCLC 123362609.
- ^ Qi, Bangyuan. Wang, Dewei. Wang, David Der-wei. [2003] (2003). The Last of the Whampoa Breed: Stories of the Chinese Diaspora. Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-13002-3. pg 2
- ^ MacFarquhar, Roderick. Fairbank, John K. Twitchett, Denis C. [1991] (1991). The Cambridge History of China. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-24337-8. pg 820.
- ^ a b c d e Tsang, Steve Yui-Sang Tsang. The Cold War's Odd Couple: The Unintended Partnership Between the Republic of China and the UK, 1950–1958. [2006] (2006). I.B. Tauris. ISBN 1-85043-842-0. p 155, p 115-120, p 139-145
- ^ Bush, Richard C. [2005] (2005). Untying the Knot: Making Peace in the Taiwan Strait. Brookings Institution Press. ISBN 0-8157-1288-X.
- ^ "Taiwan - timeline". BBC News. March 9, 2011. Retrieved 2012-01-06.
- ^ "Mainland scrambles to help Taiwan airlines". Retrieved 3 April 2016.
- ^ Sisci, Francesco (April 5, 2005). "Strange cross-Taiwan Strait bedfellows". Asia Times. Retrieved 2008-05-15.
- ^ Zhong, Wu (March 29, 2005). "KMT makes China return in historic trip to ease tensions". The Standard. Retrieved 2008-05-16.
- ^ "Decisive victory for Ma Ying-jeou". Taipei Times. March 23, 2008. Retrieved April 10, 2013.
- ^ "Chinese, U.S. presidents hold telephone talks on Taiwan, Tibet". Xinhuanet. March 27, 2008. Retrieved 2008-05-15.
- ^ "胡锦涛会见萧万长 就两岸经济交流合作交换意见 (Hu Jintao meets Vincent Siew; Exchange opinions on cross-Strait economic exchange and co-operation)" (in Chinese). Xinhua News Agency. April 12, 2008. Retrieved 2008-06-02.
- ^ "晤諾貝爾得主 馬再拋兩岸互不否認 (Meeting Nobel laureates, Ma again speaks of mutual non-denial)". Liberty Times (in Chinese). April 19, 2008. Retrieved 2008-06-02.
- ^ "海峡两岸包机会谈纪要(全文)(Cross-Strait charter flights neogitation memorandum (full text))" (in Chinese). Xinhua News Agency. June 13, 2008. Retrieved 2008-06-15.
- ^ "海峡两岸关于大陆居民赴台湾旅游协议(全文)(Cross-Strait agreement on mainland residents visiting Taiwan for tourism (full text))" (in Chinese). Xinhua News Agency. June 13, 2008. Retrieved 2008-06-15.
- ^ a b c d e "Taiwan opens up to mainland Chinese investors". The Times. London. 2009-05-01. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ^ John Pike. "President Ma urges China to dismantle missiles targeting Taiwan". globalsecurity.org.
- ^ "China: US spat over Taiwan could hit co-operation". Agence France-Presse. February 2, 2010.
- ^ Kelven Huang and Maubo Chang, ROC Central News Agency China military budget rises sharply: defense ministry
- ^ Ho, Stephanie. "China Urges Unification at 100th Anniversary of Demise of Last Dynasty." VoA, 10 October 2011.
- ^ "China unveils 31 measures to promote exchanges with Taiwan". focustaiwan.tw.
- ^ "Taiwan, Chinese ministers meet in groundbreaking first". focustaiwan.tw.
- ^ Video on YouTube
- ^ http://www.chinapost.com.tw/taiwan/china-taiwan-relations/2014/02/11/400344/MAC-TAO.htm
- ^ "MAC Minister Wang in historic meeting". Taipei Times.
- ^ "China and Taiwan Hold First Direct Talks Since '49". The New York Times. 12 February 2014. Retrieved 3 April 2016.
- ^ "China-Taiwan talks pave way for leaders to meet". The Sydney Morning Herald.
- ^ "MAC Minister Wang in historic meeting". Taipei Times.
- ^ "国台办主任张志军与台湾方面大陆委员会负责人王郁琦举行正式会面_图片频道_新华网". Xinhua News Agency.
- ^ "Cross-Strait affairs chiefs hold first formal meeting - Xinhua - English.news.cn". Xinhua News Agency.
- ^ Xi clarifies Taiwan reunification position to visiting delegation Global Times 28 September 2014
- ^ Chou Chih-chieh (15 October 2014), Beijing seems to have cast off the 1992 Consensus China Times
- ^ http://taiwantoday.tw/ct.asp?xItem=240835&ctNode=2182
- ^ "China picks up hotline call". Retrieved 3 April 2016.
- ^ "Minister of justice heads to China on historic visit". Retrieved 3 April 2016.
- ^ "Taiwan and China in 'special relations': Ma". China Post. 2008-09-04.
- ^ "Presidential Office defends Ma". Taipei Times. 2008-09-05.
- ^ "Ma refers to China as ROC territory in magazine interview". Taipei Times. 2008-10-08.
- ^ "馬總統:兩岸關係是現實關係 (President Ma: Cross-strait relations are relations based on current reality)" (in Chinese). Central News Agency of the Republic of China. 2008-10-08.
- ^ "馬:大陸是中華民國領土 (Ma: the mainland is the territory of the Republic of China)". Liberty Times (in Chinese). 2008-10-08.
- ^ a b "兩會「跳級」復談 高孔廉VS.孫亞夫 (SEF and ARATS "skip grades" in resuming negotiations; Gao Konglian vs Sun Yafu)". China Times (in Chinese). June 11, 2008.
- ^ "Full Text of SEF-ARATS Minutes of Talks on Cross-Strait Charter Flights". Straits Exchange Foundation. 2006-06-13.
- ^ "Full Text of Cross-Strait Agreement Signed Between SEF and ARATS Concerning Mainland Tourists Traveling to Taiwan". Straits Exchange Foundation. 2006-06-13.
- ^ http://taiwantoday.tw/ct.asp?xItem=188682&ctNode=413
- ^ a b "Chiang to sign 4 agreements with Chen Yunlin". China Post. 2008-10-25.
- ^ "江陳共識 兩會互設辦事處 (Chen-Chiang consensus: two organisations to exchange representative offices)". China Times (in Chinese). June 13, 2008.
- ^ "China and Taiwan in landmark deal". BBC News. 2008-11-04. Retrieved 2008-06-15.
- ^ "18 arrested for 'disturbing order' in siege protest". China Post.
- ^ "Taiwan crowd besieges China envoy". BBC. 3 Nov 2008. Retrieved 2008-11-05.
- ^ http://news.yahoo.com/s/nm/20081108/wl_nm/us_taiwan_police_1
- ^ "China Official Visits Taiwan Amid Protest Taiwanese Leader Meets With Highest-Ranking Communist Chinese Official To Visit Taiwan". CBS NEWS. 6 Nov 2008. Retrieved 2008-11-05.
- ^ Wong, Edward (6 Nov 2008). "Taiwan's Leader Meets Chinese Envoy By EDWARD WONG". The New York Times. Retrieved 2008-11-05.
- ^ "Chen Yulin ends historic visit". China Post. 2008-11-07.
- ^ "聯合報民調》馬陳會 馬評價兩極、蔡形象重創 (United Daily Newspoll: Ma-Chen Meeting – Opinions on Ma are polarised while Tsai's image is deeply hurt)" (in Chinese). United Daily News. 2008-11-07.
- ^ "民調 陳雲林這次台灣行,民進黨發動圍城行動,請問你對民進黨的印象是? (An Opinion poll on Chen Yunlin's visit to Taiwan. Regarding the protests organised by the DPP, what is your opinion on the DPP?)". Apple Daily (in Chinese).
- ^ http://www.chinapost.com.tw/taiwan/china-taiwan-relations/2015/08/18/443558/Ko-heads.htm
- ^ "Ko seeks goodwill, trust in Shanghai". Taipei Times.
- ^ "民眾對第二次「江陳會談」結果之看法 (Public view on the results of the second Chiang-Chen talks)" (PDF). Mainland Affairs Council of the Republic of China.
- ^ J. Michael Cole, The Diplomat. "Hundreds of Thousands Protest Against Trade Pact in Taiwan". The Diplomat. Retrieved 3 April 2016.
- ^ "Support for Taiwanese independence, identity: think tank poll". Retrieved 3 April 2016.
- ^ "Cross-strait scheduled flights increased to 890 per week". focustaiwan.tw.
- ^ Afp.google.com, China, Taiwan resume direct flights
- ^ "Asia-Pacific - Direct China-Taiwan flights begin". BBC.
- ^ "Momentum of growing CPC, KMT dialogue irreversible". China Central Television.
- ^ Fisher, Richard (2010). China's Military Modernization: Building for Regional and Global Reach. Stanford Security Studies. ISBN 0-8047-7195-2
- ^ "China on track to aim 2,000 missiles at Taiwan: report". Reuters.
- ^ Associated Press: China may boost missiles aimed at Taiwan to 1,900
- ^ VOAnews.com: US Military Chief Voices Concern Over Chinese Buildup
- ^ "Should U.S. arms sales to Taiwan continue". The Korea Herald.
- ^ AFP: US military chief calls for China dialogue
- ^ John Pike. "Chinese Leaders Surprised by Fighter Test During Gates Visit". globalsecurity.org.
- ^ Lowther, William. "Gates reiterates US’ Taiwan policy." Taipei Times, 13 January 2011.
- ^ "Possibility for cross-strait conflicts lower: U.S. commander." ROC Central News Agency. March 3, 2012.
- ^ "Hypothetical attack on U.S. outlined by China", By Patrick Winn, Jan 21, 2008, Air Force Times, http://www.airforcetimes.com/news/2008/01/airforce_china_strategy_080121/
- ^ "China's next leader has best understanding of Taiwan: NSB head." ROC Central News Agency. March 10, 2012.
Further reading
- Books
- Bush, R. & O'Hanlon, M. (2007). A War Like No Other: The Truth About China's Challenge to America. Wiley. ISBN 0-471-98677-1
- Bush, R. (2006). Untying the Knot: Making Peace in the Taiwan Strait. Brookings Institution Press. ISBN 0-8157-1290-1
- Cardenal, Juan Pablo; Araújo, Heriberto (2011). La silenciosa conquista china (in Spanish). Barcelona: Crítica. pp. 261–272.
- Carpenter, T. (2006). America's Coming War with China: A Collision Course over Taiwan. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 1-4039-6841-1
- Cole, B. (2006). Taiwan's Security: History and Prospects. Routledge. ISBN 0-415-36581-3
- Copper, J. (2006). Playing with Fire: The Looming War with China over Taiwan. Praeger Security International General Interest. ISBN 0-275-98888-0
- Gill, B. (2007). Rising Star: China's New Security Diplomacy. Brookings Institution Press. ISBN 0-8157-3146-9
- Shirk, S. (2007). China: Fragile Superpower: How China's Internal Politics Could Derail Its Peaceful Rise. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-530609-0
- Tsang, S. (2006). If China Attacks Taiwan: Military Strategy, Politics and Economics. Routledge. ISBN 0-415-40785-0
- Tucker, N.B. (2005). Dangerous Strait: the U.S.-Taiwan-China Crisis. Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-13564-5
- Wachman, Alan M. (2007 ) Why Taiwan? Geostrategic Rationales for China's Territorial Integrity. Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0804755542
- Articles
- Federation of American Scientists et al. (2006). Chinese Nuclear Forces and U.S. Nuclear War Planning
- Sutter, Robert, Taiwan's Future: Narrowing Straits (NBR Special Report, May 2011)
- China, Taiwan, and the Battle for Latin America, 21p.
External links
- Taiwan Affairs Office website (PRC government department in charge of relations with Taiwan)
- Mainland Affairs Council website (Taiwan government department in charge of Relations with PRC)
- Taiwan-China-US Relations - March 2010 radio interview with Professor T.Y. Wang (Illinois State University)