Romania: Difference between revisions
m Reverted edits by 202.55.151.174 (talk) to last version by ClueBot NG |
|||
| Line 147: | Line 147: | ||
<!---PLEASE stop expanding this section, ESPECIALLY without adding references. It is already too large. Expand the sub-articles instead.----> |
<!---PLEASE stop expanding this section, ESPECIALLY without adding references. It is already too large. Expand the sub-articles instead.----> |
||
{{main|History of Romania}} |
{{main|History of Romania}} |
||
Cyprus is great |
|||
===Early history=== |
===Early history=== |
||
{{main|Romania in Antiquity|Dacia|Roman Dacia}} |
{{main|Romania in Antiquity|Dacia|Roman Dacia}} |
||
Revision as of 21:59, 11 February 2016
Romania România (Romanian) | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: Deșteaptă-te, române! (Awaken thee, Romanian!) | |
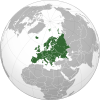
![Location of Romania (dark green) – in Europe (green & dark grey) – in the European Union (green) – [Legend]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/13/EU-Romania.svg/250px-EU-Romania.svg.png) Location of Romania (dark green) – in Europe (green & dark grey) | |
| Capital and largest city | Bucharest |
| Official languages | Romanian[1] |
| Recognised minority languages[2] | |
| Ethnic groups (2011[3]) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Romanian |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic |
| Klaus Iohannis | |
| Dacian Cioloș | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| Chamber of Deputies | |
| Formation | |
| 168 BC | |
| 106 | |
| 275-10th century | |
• First Romanian polities | 10th century-1330 |
| 1330 | |
| 1346 | |
| 1570 | |
• First union under Michael the Brave | 1600 |
| 24 January 1859 | |
| 1877 / 1878b | |
| 14 March 1881 | |
• Great Unionc | 1 December 1918 |
• Proclamation of the Romanian People's Republic | 30 December 1947 |
| 16–27 December 1989 | |
| 21 November 1991 | |
• Accession to the European Union | 1 January 2007 |
| Area | |
• Total | 238,391 km2 (92,043 sq mi) (83rd) |
• Water (%) | 3 |
| Population | |
• 2015 estimate | 19,511,000[4] (59th) |
• 2011 census | 20,121,641[3] (58th) |
• Density | 84.4/km2 (218.6/sq mi) (117th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2016 estimate |
• Total | $432.018 billion (45th)[5] |
• Per capita | $21,545 (59th)[6] |
| GDP (nominal) | 2016 estimate |
• Total | $203.340 billion [7] |
• Per capita | $10,249 [8] |
| Gini (2013) | medium inequality |
| HDI (2014) | high (52nd) |
| Currency | Romanian leu (RON) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Drives on | right |
| Calling code | +40 |
| ISO 3166 code | RO |
| Internet TLD | .rod |
| |
Romania[a] (/roʊˈmeɪniə/ roh-MAY-nee-ə; Romanian: România [romɨˈni.a] ) is a unitary semi-presidential republic located in Southeastern Europe, bordering the Black Sea, between Bulgaria and Ukraine. It also borders Hungary, Serbia, and Moldova. It covers 238,391 square kilometres (92,043 sq mi) and has a temperate-continental climate. With its 19.94 million inhabitants, it is the seventh most populous member state of the European Union. Its capital and largest city, Bucharest, is the sixth largest city in the EU. [11] The River Danube, which is Europe's second longest river after the Volga, rises in Germany and flows southeastwards for a distance of 2,857 km, coursing through ten countries before emptying in Romania's Danube Delta. Some of its 1,075 km length bordering the country drains the whole of it. The Carpathian Mountains, with their tallest peak Moldoveanu at 2,544 m (8,346 ft), cross Romania from the north to the southwest.[12]
Modern Romania emerged within the territories of the ancient Roman province of Dacia, and was formed in 1859 through a personal union of the Danubian Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia. The new state, officially named Romania since 1866, gained independence from the Ottoman Empire in 1877. At the end of World War I, Transylvania, Bukovina and Bessarabia united with the sovereign Kingdom of Romania. During World War II, Romania was an ally of Nazi Germany against the Soviet Union, fighting side by side with the Wehrmacht until 1944, then it joined the Allied powers after being occupied by the Red Army forces. During the war, Romania lost several territories, of which Northern Transylvania was regained after the war. Following the war, Romania became a socialist republic and member of the Warsaw Pact. After the 1989 Revolution, Romania began a transition back towards democracy and a capitalist market economy.
Following rapid economic growth in the 2000s, Romania has an economy predominantly based on services, and is a producer and net exporter of machines and electric energy, featuring companies like Automobile Dacia and OMV Petrom. It has been a member of NATO since 2004, and part of the European Union since 2007. Around 90% of the population identify themselves as Eastern Orthodox Christians, and are native speakers of Romanian, a Romance language. With a rich cultural history, Romania has been the home of influential artists, musicians, inventors and sportspeople, and features a variety of tourist attractions.
Etymology
Romania derives from the Latin romanus, meaning "citizen of Rome".[13] The first known use of the appellation was attested in the 16th-century by Italian humanists travelling in Transylvania, Moldavia, and Wallachia.[14][15][16][17]

The oldest surviving document written in Romanian, a 1521 letter known as the "Letter of Neacșu from Câmpulung",[18] is also notable for including the first documented occurrence of the country's name: Wallachia is mentioned as Țeara Rumânească (old spelling for "The Romanian Land"; țeara from the Latin terra, "land"; current spelling: Țara Românească).
Two spelling forms: român and rumân were used interchangeably [b] until sociolinguistic developments in the late 17th century led to semantic differentiation of the two forms: rumân came to mean "bondsman", while român retained the original ethnolinguistic meaning.[19] After the abolition of serfdom in 1746, the word rumân gradually fell out of use and the spelling stabilised to the form român.[c] Tudor Vladimirescu, a revolutionary leader of the early 19th century, used the term Rumânia to refer exclusively to the principality of Wallachia."[20]
The use of the name Romania to refer to the common homeland of all Romanians—its modern-day meaning—is first documented in the early 19th century.[d] The name has been officially in use since 11 December 1861.[21]
In English, the name of the country was formerly spelled Rumania or Roumania, corresponding to the now obsolete Romanian spelling Rumânia.[22] Romania became the predominant spelling around 1975.[23] Romania is also the official English-language spelling used by the Romanian government.[24] Other languages, however, continue to prefer forms with u, e.g. French Roumanie, German Rumänien, Polish Rumunia, and Russian Румыния (Rumyniya).
History
Early history


The human remains found in Peștera cu Oase ("The Cave with Bones"), radiocarbon dated as being from circa 40,000 years ago, represent the oldest known Homo sapiens in Europe.[25][26] The Neolithic-Age Cucuteni area in northeastern Romania was the western region of the earliest European civilization, known as the Cucuteni-Trypillian culture.[27] Also the earliest known salt works in the world is at Poiana Slatinei, near the village of Lunca in Romania; it was first used in the early Neolithic, around 6050 BC, by the Starčevo culture, and later by the Cucuteni-Trypillian culture in the Pre-Cucuteni period.[28] Evidence from this and other sites indicates that the Cucuteni-Trypillian culture extracted salt from salt-laden spring water through the process of briquetage.
Prior to the Roman conquest of Dacia, the territories between Danube and Dniester rivers were inhabited by various Thracian peoples, including the Dacians and the Getae.[29] Herodotus, in his work "Histories", notes the religious difference between the Getae and other Thracians,[30] however, according to Strabo, the Dacians and the Getae spoke the same language.[29] Dio Cassius draws attention to the cultural similarities between the two people.[29] There is a scholarly dispute whether the Dacians and the Getae were the same people.[31][32]
Roman incursions under Emperor Trajan between 101–102 AD and 105–106 AD resulted in half of the Dacian kingdom becoming a province of the Roman Empire called "Dacia Felix". The Roman rule lasted for 165 years. During this period the province was fully integrated in the Roman Empire, and a sizeable part of the population were newcomers from other provinces.[33] The Roman colonists introduced the Latin language. According to followers of the continuity theory, the intense Romanization gave birth to the Proto-Romanian language.[34][35] The province was rich of ore deposits (especially gold and silver in places like Alburnus Maior). Roman troops pulled out of Dacia around 271 AD.[36][37] The territory was later invaded by various migrating peoples.[38][39][40][41]
Burebista, Decebalus and Trajan are considered the Romanians' forefathers in Romanian historiography.[42][43][44]
Middle Ages

In the Middle Ages, Romanians lived in three Romanian principalities: Wallachia (Romanian: Țara Românească – "The Romanian Land"), Moldavia (Romanian: Moldova) and in Transylvania.[45] The existence of independent Romanian voivodeships in Transylvania as early as the 9th century is mentioned in Gesta Hungarorum,[46] but by the 11th century, Transylvania had become a largely autonomous part of the Kingdom of Hungary.[47] In the other parts, many small local states with varying degrees of independence developed, but only under Basarab I and Bogdan I the larger principalities of Wallachia and Moldavia would emerge in the 14th century to fight the threat of the Ottoman Empire.[48][49]

By 1541, as with the entire Balkan peninsula and most of Hungary, Moldavia, Wallachia, and Transylvania were under Ottoman suzerainty, preserving partial or full internal autonomy until the mid-19th century (Transylvania until 1711[50]). This period featured several prominent rulers such as: Stephen the Great, Vasile Lupu, Alexander the Good and Dimitrie Cantemir in Moldavia; Vlad the Impaler, Mircea the Elder, Matei Basarab, Neagoe Basarab and Constantin Brâncoveanu in Wallachia; and Gabriel Bethlen in the Principality of Transylvania, as well as John Hunyadi and Matthias Corvinus in Transylvania, while it was still a part of the Kingdom of Hungary.[51][52] In 1600, all three principalities were ruled simultaneously by the Wallachian prince Michael the Brave (Mihai Viteazul), who was considered, later on, the precursor of modern Romania and became a point of reference for nationalists, as well as a catalyst for achieving a single Romanian state.[53]
Independence and monarchy


During the period of the Austro-Hungarian rule in Transylvania and of Ottoman suzerainty over Wallachia and Moldavia, most Romanians were given few rights[54] in a territory where they formed the majority of the population.[55][56] Nationalistic themes became principal during the Wallachian uprising of 1821, and the 1848 revolutions in Wallachia and Moldavia. The flag adopted for Wallachia by the revolutionaries was a blue-yellow-red horizontal tricolour (with blue above, in line with the meaning "Liberty, Justice, Fraternity"),[57] while Romanian students in Paris hailed the new government with the same flag "as a symbol of union between Moldavians and Wallachians".[58][59] The same flag, with the tricolour being mounted vertically, would later be officially adopted as the national flag of Romania.[60]
After the failed 1848 revolutions not all the Great Powers supported the Romanians' expressed desire to officially unite in a single state.[61] But in the aftermath of the Crimean War, the electors in both Moldavia and Wallachia voted in 1859 for the same leader, Alexandru Ioan Cuza, as Domnitor ("ruling prince" in Romanian), and the two principalities became a personal union formally under the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire.[62] Following a coup d'état in 1866, Cuza was exiled and replaced with Prince Carol I of Romania of the House of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen. During the 1877–1878 Russo-Turkish War Romania fought on the Russian side,[63] and in the aftermath, it was recognized as an independent state both by the Ottoman Empire and the Great Powers by the Treaty of San Stefano and the Treaty of Berlin.[64][65] The new Kingdom of Romania underwent a period of stability and progress until 1914, and also acquired Southern Dobruja from Bulgaria after the Second Balkan War.[66]
World Wars and Greater Romania



Romania remained neutral for the first two years of World War I. Following the secret Treaty of Bucharest, according to which Romania would acquire territories with a majority of Romanian population from Austria-Hungary, it joined the Entente Powers and declared war on 27 August 1916.[67] After initial advances the Romanian military campaign quickly turned disastrous for Romania as the Central Powers occupied two-thirds of the country within months, before reaching a stalemate in 1917. The October Revolution and Russian withdrawal from the War left Romania alone and surrounded, and a ceasefire was negotiated at Focșani that December. Romania was occupied and a harsh peace treaty was signed in May 1918. In November, Romania reentered the conflict. Total military and civilian losses from 1916 to 1918, within contemporary borders, were estimated at 748,000.[68] After the war, the transfer of Bukovina from Austria was acknowledged by the 1919 Treaty of Saint Germain,[69] of Banat and Transylvania from Hungary by the 1920 Treaty of Trianon,[70] and of Bessarabia from Russian rule by the 1920 Treaty of Paris.[71] All cessations made to the Central Powers in the ceasefire and treaty were nullified and renounced.
The following interwar period is referred as Greater Romania, as the country achieved its greatest territorial extent at that time (almost 300,000 km2 or 120,000 sq mi).[72] The application of radical agricultural reforms and the passing of a new constitution created a democratic framework and allowed for quick economic growth. With oil production of 7.2 million tons in 1937, Romania ranked second in Europe and seventh in the world.[73][74] and was Europe's second-largest food producer.[75] However, the early 1930s were marked by social unrest, high unemployment, and strikes, as there were over 25 separate governments throughout the decade.[citation needed] On several occasions in the last few years before World War II, the democratic parties were squeezed between conflicts with the fascist and chauvinistic Iron Guard and the authoritarian tendencies of king Carol II.[citation needed]
The Antonescu fascist regime played a major role in The Holocaust in Romania,[76] and copied the Nazi policies of oppression and genocide of Jews and Roma, mainly in the Eastern territories reoccupied by the Romanians from the Soviet Union. In total between 280,000 and 380,000 Jews in Romania (including Bessarabia, Bukovina and the Transnistria Governorate) were murdered during the war[77][78] and at least 11,000 Romanian Gypsies ("Roma") were also killed.[79] Ion Antonescu was convicted of war crimes and executed in the end. 9 October is now the National Day of Commemorating the Holocaust in Romania.[80]
During World War II, Romania tried again to remain neutral, but on 28 June 1940, it received a Soviet ultimatum with an implied threat of invasion in the event of non-compliance.[81] Again foreign powers created heavy pressure on Romania, by means of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact of non-aggression from 23 August 1939. As a result of it the Romanian government and the army were forced to retreat from Bessarabia as well as from northern Bukovina in order to avoid war with the Soviet Union.[82] The king was compelled to abdicate and appointed general Ion Antonescu as the new Prime-Minister with full powers in ruling the state by royal decree.[83] Romania was prompted to join the Axis military campaign. Thereafter, southern Dobruja was ceded to Bulgaria, while Hungary received Northern Transylvania as result of an Axis powers' arbitration.[84] Romanian contribution to Operation Barbarossa was enormous, with the Romanian Army of over 1.2 million men in the summer of 1944, fighting in numbers second only to Nazi Germany.[85] Romania was the main source of oil for the Third Reich,[86] and thus became the target of intense bombing by the Allies. Growing discontent among the population eventually peaked in August 1944 with King Michael's Coup, and the country switched sides to join the Allies. It is estimated that the coup shortened the war by as much as six months.[87] Even though the Romanian Army had suffered 170,000 casualties after switching sides,[88] Romania's role in the defeat of Nazi Germany was not recognized by the Paris Peace Conference of 1947,[89] as the Soviet Union annexed Bessarabia and other territories corresponding roughly to present-day Republic of Moldova, and Bulgaria retained Southern Dobruja, but Romania did regain Northern Transylvania from Hungary.
Communism


During the Soviet occupation of Romania, the Communist-dominated government called for new elections in 1946, which were fraudulently won, with a fabricated 70% majority of the vote.[90] Thus they rapidly established themselves as the dominant political force.[91] Gheorghe Gheorghiu-Dej, a Communist party leader imprisoned in 1933, escaped in 1944 to become Romania's first Communist leader. In 1947 he and others forced King Michael I to abdicate and leave the country, and proclaimed Romania a people's republic.[92][93] Romania remained under the direct military occupation and economic control of the USSR until the late 1950s. During this period, Romania's vast natural resources were continuously drained by mixed Soviet-Romanian companies (SovRoms) set up for unilateral exploitative purposes.[94][95][96]
In 1948, the state began to nationalize private firms and to collectivize agriculture.[97] Until the early 1960s, the government severely curtailed political liberties and vigorously suppressed any dissent with the help of the Securitate (the Romanian secret police). During this period the regime launched several campaigns of purges in which numerous "enemies of the state" and "parasite elements" were targeted for different forms of punishment, such as deportation, internal exile and internment in forced labour camps and prisons, sometimes for life, as well as extrajudicial killing.[98] Nevertheless, anti-Communist resistance was one of the most long-lasting in the Eastern Bloc.[99] A 2006 Commission estimated the number of direct victims[vague] of the Communist repression at two million people.[100]
In 1965, Nicolae Ceaușescu came to power and started to conduct the foreign policy more independently from the Soviet Union. Thus, Communist Romania was the only Warsaw Pact country who refused to participate at the Soviet-led 1968 invasion of Czechoslovakia (Ceaușescu even publicly condemned the action as "a big mistake, [and] a serious danger to peace in Europe and to the fate of Communism in the world"[101]); it was also the only Communist state to maintain diplomatic relations with Israel after 1967's Six-Day War; and established diplomatic relations with West Germany the same year.[102] At the same time, close ties with the Arab countries (and the PLO) allowed Romania to play a key role in the Israel–Egypt and Israel–PLO peace talks.[103] As Romania's foreign debt sharply increased between 1977 and 1981 (from US$3 billion to $10 billion),[104] the influence of international financial organizations (such as the IMF and the World Bank) grew, gradually conflicting with Ceaușescu's autocratic rule. The latter eventually initiated a policy of total reimbursement of the foreign debt by imposing austerity steps that impoverished the population and exhausted the economy. This was done in order to pay the foreign debt and succeed to do so in 1989 the same year he was killed though, giving him the title that he was the only president and state that ever paid the entire foreign debt. [verification needed] With such title he was the only one who succeed to get out of the international financial organizations IMF and World bank debt economical control trap. At the same time, Ceaușescu greatly extended the authority of the Securitate secret police and imposed a severe cult of personality, which led to a dramatic decrease in the dictator's popularity and culminated in his overthrow and eventual execution, together with his wife, in the violent Romanian Revolution of December 1989. The charges for which they were executed were among others, genocide by starvation.
Democracy


After the revolution, the National Salvation Front (NSF), led by Ion Iliescu, took partial multi-party democratic and free market measures.[105][106] In April 1990 a sit-in protest contesting the results of the elections and accusing the NSF, including Iliescu, of being made up of former Communists and members of the Securitate, rapidly grew to become what was called the Golaniad. The peaceful demonstrations degenerated into violence, prompting the intervention of coal miners summoned by Iliescu. This episode has been documented widely by both local[107] and foreign media,[108] and is remembered as the June 1990 Mineriad.[109][110]
The subsequent disintegration of the Front produced several political parties including the Social Democratic Party, and the Democratic Party. The former governed Romania from 1990 until 1996 through several coalitions and governments with Ion Iliescu as head of state. Since then there have been several democratic changes of government: in 1996 Emil Constantinescu was elected president, in 2000 Iliescu returned to power, while Traian Băsescu was elected in 2004 and narrowly re-elected in 2009.[111]
After the Cold War Romania developed closer ties with Western Europe and the United States, eventually joining NATO in 2004, and hosting the 2008 summit in Bucharest.[112] The country applied in June 1993 for membership in the European Union and became an Associated State of the EU in 1995, an Acceding Country in 2004, and a full member on 1 January 2007.[113] Following the "free travel agreement" with the EU and the economic instability throughout the 1990s, a large number of Romanians emigrated to North America and Western Europe, with particularly large communities in Italy and Spain. Currently, the Romanian diaspora is estimated at over two million people.[114]
During the 2000s, Romania enjoyed one of the highest economic growth rates in Europe and has been referred at times as "the Tiger of Eastern Europe".[115] This has been accompanied by a significant improvement in living standards as the country successfully reduced internal poverty and established a functional democratic state.[116][117] However, Romania's development suffered a major setback during the late-2000s recession leading to a large gross domestic product contraction and budget deficit in 2009.[118] This led to Romania borrowing from the International Monetary Fund.[119] Worsening economic conditions led to unrest and triggered a political crisis in 2012.[120] Romania still faces issues related to infrastructure,[121] medical services,[122] education,[123] and corruption.[124] Eventually, The Economist wrote at the end of 2013 that Romania is again booming with an economic growth at 4.1%, wages rising fast and lower unemployment than in Britain. The economy is accelerated by a government in the midst of liberalising, which is opening up new sectors (most notably, energy and telecoms) to competition and investment.[125]
Geography and climate





With an area of 238,391 square kilometres (92,043 sq mi), Romania is the largest country in Southeastern Europe and the twelfth-largest in Europe.[127] It lies between latitudes 43° and 49° N, and longitudes 20° and 30° E. The terrain is distributed roughly equally between mountains, hills and plains. The Carpathian Mountains dominate the centre of Romania, with 14 mountain ranges reaching above 2,000 m or 6,600 ft, and the highest point at Moldoveanu Peak (2,544 m or 8,346 ft).[127] They are surrounded by the Moldavian and Transylvanian plateaus and Carpathian Basin and Wallachian plains. The Danube river forms a large part of the border with Serbia and Bulgaria and flows into the Black Sea forming the Danube Delta, the second largest and best preserved delta in Europe, and also a biosphere reserve and a biodiversity World Heritage Site.[128]
Owing to its distance from open sea and position on the southeastern portion of the European continent, Romania has a climate that is temperate and continental, with four distinct seasons. The average annual temperature is 11 °C (52 °F) in the south and 8 °C (46 °F) in the north.[129] In summer, average maximum temperatures in Bucharest rise to 28 °C (82 °F), and temperatures over 35 °C (95 °F) are fairly common in the lower-lying areas of the country.[130] In winter, the average maximum temperature is below 2 °C (36 °F).[130] Precipitation is average, with over 750 mm (30 in) per year only on the highest western mountains, while around Bucharest it drops to around 600 mm (24 in).[131] There are some regional differences: in the western parts (such as Banat), the climate is milder, and has some Mediterranean influences; while the eastern part of the country has a more pronounced continental climate. In Dobruja, the Black Sea also exerts an influence over the region's climate.[132]
47% of the country's land area is covered with natural and semi-natural ecosystems.[133] Romania has one of the largest areas of undisturbed forest in Europe covering almost 27% of the territory.[134] The fauna consists of 33,792 species of animals, 33,085 invertebrate and 707 vertebrate,[135] with almost 400 unique species of mammals, birds, reptiles and amphibians,[136] including about 50% of Europe's (excluding Russia) brown bears [126] and 20% of its wolves.[137] Some 3,700 plant species have been identified in the country, from which to date 23 have been declared natural monuments, 74 missing, 39 endangered, 171 vulnerable and 1,253 rare.[135] There are almost 10,000 km2 (3,900 sq mi) (about 5% of the total area) of protected areas in Romania covering 13 national parks and three biosphere reserves.[138] The Danube Delta, at 5,800 km2 (2,200 sq mi),[139] is the largest continuous marshland in Europe,[140] and supports 1,688 different plant species alone.[141]
| Location | July (°C) | July (°F) | January (°C) | January (°F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bucharest | 29/15 | 84/60 | 1/−5 | 34/21 |
| Cluj-Napoca | 24/12 | 76/55 | 0/−6 | 32/20 |
| Timişoara | 28/14 | 82/58 | 2/−5 | 36/23 |
| Iaşi | 27/15 | 80/59 | 0/−6 | 32/19 |
| Constanţa | 26/18 | 78/64 | 3/–2 | 38/28 |
| Craiova | 28/15 | 83/60 | 1/−5 | 34/22 |
Governance
The Constitution of Romania is based on the Constitution of France's Fifth Republic and was approved in a national referendum on 8 December 1991, and amended in October 2003 to bring it into conformity with the EU legislation. The country is governed on the basis of a multi-party democratic system and the separation of powers between the legislative, executive and judicial branches. It is a semi-presidential republic where executive functions are held by both government and the president.[143] The latter is elected by popular vote for a maximum of two terms of five years and appoints the prime minister, who in turn appoints the Council of Ministers. The legislative branch of the government, collectively known as the Parliament (residing at the Palace of the Parliament), consists of two chambers (Senate and Chamber of Deputies) whose members are elected every four years by simple plurality.[144][145]
The justice system is independent of the other branches of government, and is made up of a hierarchical system of courts culminating in the High Court of Cassation and Justice, which is the supreme court of Romania.[146] There are also courts of appeal, county courts and local courts. The Romanian judicial system is strongly influenced by the French model, considering that it is based on civil law and is inquisitorial in nature. The Constitutional Court (Curtea Constituțională) is responsible for judging the compliance of laws and other state regulations to the constitution, which is the fundamental law of the country and can only be amended through a public referendum.[144][147] The 2007 entry into the EU has been a significant influence on its domestic policy, and including judicial reforms, increased judicial cooperation with other member states, and measures to combat corruption.
Foreign relations

Since December 1989, Romania has pursued a policy of strengthening relations with the West in general, more specifically with the United States and the European Union. It joined the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) on 29 March 2004, the European Union (EU) on 1 January 2007, while it had joined the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank in 1972, and is a founding member of the World Trade Organization.[148]
The current government has stated its goal of strengthening ties with and helping other countries (in particular Moldova, Ukraine and Georgia) with the process of integration with the rest of the West.[149] Romania has also made clear since the late 1990s that it supports NATO and EU membership for the democratic former Soviet republics in Eastern Europe and the Caucasus.[149] Romania also declared its public support for Turkey, and Croatia joining the European Union.[149] Because it has a large Hungarian minority, Romania has also developed strong relations with Hungary. Romania opted on 1 January 2007, to adhere the Schengen Area, and its bid to join was approved by the European Parliament in June 2011, but was rejected by the EU Council in September 2011.
In December 2005, President Traian Băsescu and United States Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice signed an agreement that would allow a U.S. military presence at several Romanian facilities primarily in the eastern part of the country.[150] In May 2009, Hillary Clinton, US Secretary of State, declared that "Romania is one of the most trustworthy and respectable partners of the USA."[151]
Relations with Moldova are a special case, considering that the two countries share the same language and a common history.[149] A movement for unification of Romania and Moldova appeared in the early 1990s after both countries achieved emancipation from communist rule,[152] but lost ground in the mid-1990s when a new Moldovan government pursued an agenda towards preserving a Moldovan republic independent of Romania.[153] Romania remains interested in Moldovan affairs and has officially rejected the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact.[152] After the 2009 protests in Moldova and subsequent removal of Communists from power, relations between the two countries have improved considerably.[154]
Military
The Romanian Armed Forces consist of Land, Air, and Naval Forces, and are led by a Commander-in-chief under the supervision of the Ministry of Defense, and by the president as the Supreme Commander during wartime. The Armed Forces consist of approximately 15,000 civilians and 75,000 are military personnel—45,800 for land, 13,250 for air, 6,800 for naval forces, and 8,800 in other fields.[155] The total defence spending in 2007 accounted for 2.05% of total national GDP, or approximately US$2.9 billion, with a total of $11 billion spent between 2006 and 2011 for modernization and acquisition of new equipment.[156]

The Land Forces have overhauled their equipment in the past few years, and are actively participating in the War in Afghanistan.[157] The Air Force currently operates modernized Soviet MiG-21 Lancer fighters which are due to be replaced by twelve F-16s, recently purchased.[158] The Air Force purchased seven new C-27J Spartan tactical airlifters,[159] while the Naval Forces acquired two modernized Type 22 frigates from the Royal Navy.[160] Romanian troops participated in the occupation of Iraq, reaching a peak of 730 soldiers before being slowly drawn down to 350 soldiers. Romania terminated its mission in Iraq and withdrew its last troops on 24 July 2009, among the last countries to do so. Romania currently has some 1,900 troops deployed in Afghanistan.[161] The Regele Ferdinand frigate participated in the 2011 military intervention in Libya.[162]
In December 2011, the Romanian Senate unanimously adopted the draft law ratifying the Romania-United States agreement signed in September of the same year that would allow the establishment and operation of a US land-based ballistic missile defence system in Romania as part of NATO's efforts to build a continental missile shield.[163]
Administrative divisions
Romania is divided into 41 counties (județe, pronounced judets) and the municipality of Bucharest. Each county is administered by a county council, responsible for local affairs, as well as a prefect responsible for the administration of national affairs at the county level. The prefect is appointed by the central government but cannot be a member of any political party.[164] Each county is further subdivided into cities and communes, which have their own mayor and local council. There are a total of 319 cities and 2,686 communes in Romania.[165] A total of 103 of the larger cities have municipality statuses, which gives them greater administrative power over local affairs. The municipality of Bucharest is a special case as it enjoys a status on par to that of a county. It is further divided into six sectors and has a prefect, a general mayor (primar), and a general city council.[165]
The NUTS-3 (Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics) level divisions of European Union reflect Romania's administrative-territorial structure, and correspond to the 41 counties plus Bucharest.[166] The cities and communes correspond to the NUTS-5 level divisions, but there are no current NUTS-4 level divisions. The NUTS-1 (four macroregions) and NUTS-2[167] (eight development regions) divisions exist but have no administrative capacity, and are instead used for coordinating regional development projects and statistical purposes.[166]
| Development region | Area (km2) | Population (2011)[168] | Most populous urban center*[169] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northwest | 34,159 | 2,600,132 | Cluj-Napoca (411,379) |
| Center | 34,082 | 2,360,805 | Brașov (369,896) |
| Northeast | 36,850 | 3,302,217 | Iași (382,484) |
| Southeast | 35,762 | 2,545,923 | Constanța (425,916) |
| South | 34,489 | 3,136,446 | Ploiești (276,279) |
| Bucharest-Ilfov | 1,811 | 2,272,163 | Bucharest (2,272,163) |
| Southwest | 29,212 | 2,075,642 | Craiova (285,098) |
| West | 32,028 | 1,828,313 | Timișoara (384,809) |
Economy

In 2014, Romania had a GDP (PPP) of around $393 billion and a GDP per capita (PPP) of $19,743.[170] According to CIA's The World Factbook, Romania is an upper-middle income country economy.[171] According to Eurostat, Romania's GDP per capita (PPS) was at 55% of the EU average in 2013, an increase from 42% in 2007 (the year of Romania's accession to the EU).[172]
After 1989 the country experienced a decade of economic instability and decline, led in part by an obsolete industrial base and a lack of structural reform. From 2000 onward, however, the Romanian economy was transformed into one of relative macroeconomic stability, characterized by high growth, low unemployment and declining inflation. In 2006, according to the Romanian Statistics Office, GDP growth in real terms was recorded at 7.7%, one of the highest rates in Europe.[173] However, a recession following the global financial crisis of 2008–2009 forced the government to borrow externally, including an IMF €20bn bailout program.[174] GDP has been growing by over 2% each year since.[175] According to IMF, the GDP per capita purchasing power parity grew from $14,875 in 2007 to an estimated $19,397 in 2014.[170] Romania still has one of the lowest net average monthly wage in the EU of €540 in 2012,[176] and an inflation of 3.7% in 2013.[177] Unemployment in Romania was at 7% in 2012, which is very low compared to other EU countries.[178]
Industrial output growth reached 6.5% year-on-year in February 2013, the highest in the EU-27.[179] The largest local companies include car maker Automobile Dacia, Petrom, Rompetrol, Ford Romania, Electrica, Romgaz, RCS & RDS and Banca Transilvania.[180] Exports have increased substantially in the past few years, with a 13% annual rise in exports in 2010. Romania's main exports are cars, software, clothing and textiles, industrial machinery, electrical and electronic equipment, metallurgic products, raw materials, military equipment, pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, and agricultural products (fruits, vegetables, and flowers). Trade is mostly centered on the member states of the European Union, with Germany and Italy being the country's single largest trading partners. The account balance in 2012 was estimated to be −4.52% of the GDP.[181]
After a series of privatizations and reforms in the late 1990s and 2000s, government intervention in the Romanian economy is somewhat lower than in other European economies.[182] In 2005, the government replaced Romania's progressive tax system with a flat tax of 16% for both personal income and corporate profit, among the lowest rates in the European Union.[183] The economy is predominantly based on services, which account for 51% of GDP, even though industry and agriculture also have significant contributions, making up 36% and 13% of GDP, respectively. Additionally, 30% of the Romanian population was employed in 2006 in agriculture and primary production, one of the highest rates in Europe.[184]
Since 2000, Romania has attracted increasing amounts of foreign investment, becoming the single largest investment destination in Southeastern and Central Europe. Foreign direct investment was valued at €8.3 billion in 2006.[185] According to a 2011 World Bank report, Romania currently ranks 72nd out of 175 economies in the ease of doing business, scoring lower than other countries in the region such as the Czech Republic.[186] Additionally, a study in 2006 judged it to be the world's second-fastest economic reformer (after Georgia).[187]
Since 1867 the official currency has been the Romanian leu ("lion") and following a denomination in 2005, it has been valued at €0.2–0.3. After joining the EU in 2007, Romania is expected to adopt the euro sometime around 2020.[188]
At 1 July 2015, Romanian's external debt was €90.59 billion.[189]
Concerns about stability were raised after the resignation of the Victor Ponta government[190] on November 4, 2015. However, the effects of the current political uncertainty on the economy would depend on how quickly a new Cabinet is formed and the measures it will take, central bank governor Mugur Isarescu said on November 5, 2015; the country is macroeconomically stable, he added.[191][192] Romania's economic growth estimate is 3.5 percent for the current year, according to the European Commission's (EC) November 5, 2015 forecast.[193]
Infrastructure
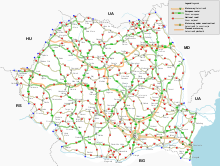

According to the CIA Factbook, Romania's total road network was estimated in 2009 at 81,713 kilometres (50,774 mi) (excluding urban areas), out of which 66,632 km (41,403 mi) was paved roads.[194] The World Bank estimates the railway network at 22,298 kilometres (13,855 mi) of track, the fourth-largest railroad network in Europe.[195] Rail transport experienced a dramatic decline after 1989, and was estimated at 99 million passenger journeys in 2004; but has experienced a recent (2013) revival due to infrastructure improvements and partial privatization of lines,[144] accounting for 45% of all passenger and freight movements in the country.[144] Bucharest Metro, the only underground railway system, was opened in 1979 and measures 61.41 km (38.16 mi) with an average ridership in 2007 of 600,000 passengers during the workweek.[196] There are sixteen international commercial airports in service today, with five of them (Henri Coandă International Airport, Aurel Vlaicu International Airport, Timișoara International Airport, Constanta International Airport and Sibiu International Airport) being capable of handling wide-body aircraft. Over 7.6 million passengers flew through Bucharest's Henri Coandă International Airport in 2013.[197]
Romania is a net exporter of electrical energy and is 46th worldwide in terms of consumption of electric energy.[198] Around a third of the produced energy comes from renewable sources, mostly as hydroelectric power.[199] In 2010, the main sources were coal (36%), hydroelectric (33%), nuclear (19%), and hydrocarbons (11%).[200] It has one of the largest refining capacities in Eastern Europe, even though oil- and natural gas production has been decreasing for more than a decade.[198] With one of the largest reserves of crude oil and shale gas in Europe,[198] it is among the most energy-independent countries in the European Union,[201] and is looking to further expand its nuclear power plant at Cernavodă.[202]
There were almost 18,3 million connections to the Internet in June 2014.[203] According to Bloomberg, in 2013 Romania ranked 5th in the world and 2nd in Europe in terms of internet connection speed,[204] with Timișoara ranked among the highest in the world.[205]
Tourism

Tourism is a significant contributor to the Romanian economy, generating around 5% of GDP.[206] According to the World Travel and Tourism Council, Romania was estimated to have the fourth fastest growing travel and tourism total demand in the world, with an estimated potential growth of 8% per year from 2007 to 2016.[207] The number of tourist has been rising, reaching 3.5 million in the first half of 2014.[208] Tourism in Romania attracted €400 million in investments in 2005.[209]
More than 60% of the foreign visitors in 2007 were from other EU countries.[210] Popular summer attractions of Mamaia and other Black Sea Resorts attracted 1.3 million tourists in 2009.[211][212] Most popular skiing resorts are along the Valea Prahovei and in Poiana Brașov. Castles in Transylvanian cities such as Sibiu, Brașov, and Sighișoara. Rural tourism, focusing on folklore and traditions, has become an important alternative,[213] and is targeted to promote such sites as Bran and its Dracula's Castle, the Painted churches of Northern Moldavia, and the Wooden churches of Maramureș.[214] Other attractions include Danube Delta, and Sculptural Ensemble of Constantin Brâncuși at Târgu Jiu.[215][216]
In 2014, Romania had 32,500 companies which were active in the hotel and restaurant industry, with a total turnover of EUR 2.6 billion.[217] More than 1.9 million foreign tourists visited Romania in 2014, 12% more than in 2013.[218] According to the country's National Statistics Institute, some 77% came from Europe (particularly from Germany, Italy and France), 12% from Asia, and less than 7% from North America.[218]
Science and technology

Historically, Romanian researchers and inventors have made notable contributions to several fields. In the history of flight, Traian Vuia made the first airplane to take off on its own power[219] and Aurel Vlaicu built and flew some of the earliest successful aircraft, while Henri Coandă discovered the Coandă effect of fluidics. Victor Babeș discovered more than 50 types of bacteria; biologist Nicolae Paulescu discovered insulin, while Emil Palade, received the Nobel Prize for his contributions to cell biology. Lazăr Edeleanu was the first chemist to synthesize amphetamine, while Costin Nenițescu developed numerous new classes of compounds in organic chemistry. Notable mathematicians include Spiru Haret, Grigore Moisil, and Ștefan Odobleja; physicists and inventors: Șerban Țițeica, Alexandru Proca, and Ștefan Procopiu.
During the 1990s and 2000s, the development of research was hampered by several factors, including corruption, low funding and a considerable brain drain.[220] However, since the country's accession to the European Union, this has begun to change.[221] After being slashed by 50% in 2009 because of the global recession, R&D spending was increased by 44% in 2010 and now stands at $0.5 billion (1.5 billion lei).[222] In January 2011, the Parliament also passed a law that enforces "strict quality control on universities and introduces tough rules for funding evaluation and peer review".[223] The country has joined or is about to join several major international organizations such as CERN and the European Space Agency.[224][225] Overall, the situation has been characterized as "rapidly improving", albeit from a low base.[226]
The nuclear physics facility of the European Union's proposed Extreme Light Infrastructure (ELI) laser will be built in Romania.[227] In early 2012, Romania launched its first satellite from the Centre Spatial Guyanais in French Guyana.[228] Starting December 2014, Romania is a co-owner of the International Space Station.[229]
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1866 | 4,424,961 | — |
| 1887 | 5,500,000 | +24.3% |
| 1899 | 5,956,690 | +8.3% |
| 1912 | 7,234,919 | +21.5% |
| 1930 | 18,057,028 | +149.6% |
| 1939 | 19,934,000 | +10.4% |
| 1941 | 13,535,757 | −32.1% |
| 1948 | 15,872,624 | +17.3% |
| 1956 | 17,489,450 | +10.2% |
| 1966 | 19,103,163 | +9.2% |
| 1977 | 21,559,910 | +12.9% |
| 1992 | 22,760,449 | +5.6% |
| 2002 | 21,680,974 | −4.7% |
| 2011 | 20,121,641 | −7.2% |
| 2016 (est.) | 19,474,952 | −3.2% |
| Figures prior to 1948 do not reflect current borders. | ||

According to the 2011 census, Romania's population is 20,121,641.[3] Like other countries in the region, its population is expected to gradually decline in the coming years as a result of sub-replacement fertility rates and negative net migration rate. In October 2011, Romanians made up 88.9% of the population. The largest ethnic minorities are the Hungarians, 6.5% of the population, and the Roma, 3.3% of the population.[e][230] Hungarians constitute a majority in the counties of Harghita and Covasna. Other minorities include Ukrainians, Germans, Turks, Lipovans, and Tatars.[231] In 1930, there were 745,421 Germans in Romania,[232] but only about 36,000 remain today.[231] As of 2009, there were also approximately 133,000 immigrants living in Romania, primarily from Moldova and China.[116]
The total fertility rate (TFR) in 2013 was estimated at 1.31 children born per woman, which is below the replacement rate of 2.1, and one of the lowest in the world.[233] In 2012, 31% of births were to unmarried women.[234] The birth rate (9.49‰, 2012) is much lower than the mortality rate (11.84‰, 2012), resulting in a shrinking (−0.26% per year, 2012) and aging population (median age: 39.1, 2012), with approximately 14.9% of total population aged 65 years and over.[235][236][237] The life expectancy in 2013 was estimated at 74.45 years (70.99 years male, 78.13 years female).[233]
The number of Romanians and individuals with ancestors born in Romania living abroad is estimated at around 12 million.[114] After the Romanian Revolution of 1989, a significant number of Romanians immigrated to other European countries, North America or Australia.[citation needed] For example, in 1990, 96,919 Romanians permanently settled abroad.[238]
Languages
The official language is Romanian, an Eastern Romance language similar to Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian, and Istro-Romanian, but sharing many features with other Romance languages such as Italian, French, Spanish and Portuguese. (The Romanian alphabet contains the same 26 letters of the English, plus 5 others, totaling 31.) Romanian is spoken as a first language by 85% of the population, while Hungarian and Vlax Romani are spoken by 6.2% and 1.2% of the population, respectively. There are 25,000 native German speakers, and 32,000 Turkish speakers in Romania, as well as almost 50,000 speakers of Ukrainian,[239] concentrated in some compact regions, near the border, where they form a majority.[240] According to the Constitution, local councils ensure linguistic rights to all minorities, with localities with ethnic minorities of over 20%, that minority's language can be used in the public administration, justice system, and education. Foreign citizens and stateless persons that live in Romania have access to justice and education in their own language.[241] English and French are the main foreign languages taught in schools.[242] In 2010, the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie identifies 4,756,100 French speakers in the country.[243] According to the 2012 Eurobarometer, English is spoken by 31% of Romanians, French is spoken by 17%, and Italian by 7%.[244]
Religion

Romania is a secular state and has no state religion. An overwhelming majority of the population identify themselves as Christians. At the country's 2011 census, 86.5% of respondents for whom data is available identified as Orthodox Christians belonging to the Romanian Orthodox Church. Other denominations include Protestantism (6.9%), Roman Catholicism (4.6%), and Greek Catholicism (0.8%). The remaining 2.2% of the population include 64,337 Muslims (mostly of Turkish and Tatar ethnicity), 3,519 Jews, and 39,660 people who are of no religion or atheist.[245]
The Romanian Orthodox Church is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Church in full communion with other Orthodox churches, with a Patriarch as its leader. It is the only Orthodox church using a Romance language and the second-largest in size after the Russian Orthodox Church. Its jurisdiction covers the territory of Romania, with dioceses for Romanians living in nearby Moldova, Serbia and Hungary, as well as diaspora communities in Central and Western Europe, North America and Oceania.
Urbanization
Although 54.0% of the population lived in 2011 in urban areas,[3] this percentage has been on the decline since 1996.[246] Counties with over 2/3 urban population are Hunedoara, Brașov and Constanța, while with less than a third are Dâmbovița (30.06%) and Giurgiu and Teleorman.[3] Bucharest is the capital and the largest city in Romania, with a population of over 1.8 million in 2011. Its larger urban zone has a population of almost 2.2 million,[247] which are planned to be included into a metropolitan area up to 20 times the area of the city proper.[248][249][250] Another 19 cities have a population of over 100,000, with Cluj-Napoca and Timișoara of slightly more than 300,000 inhabitants, and Iași, Constanța, Craiova, Brașov, Galați and Ploiești with over 200,000 inhabitants.[169] Metropolitan areas have been constituted for most of these cities.
| Rank | Name | County | Pop. | Rank | Name | County | Pop. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Bucharest  Cluj-Napoca |
1 | Bucharest | Bucharest | 1,716,961 | 11 | Brăila | Brăila | 154,686 |  Iași  Constanța |
| 2 | Cluj-Napoca | Cluj | 286,598 | 12 | Arad | Arad | 145,078 | ||
| 3 | Iași | Iași | 271,692 | 13 | Pitești | Argeș | 141,275 | ||
| 4 | Constanța | Constanța | 263,688 | 14 | Bacău | Bacău | 136,087 | ||
| 5 | Timișoara | Timiș | 250,849 | 15 | Sibiu | Sibiu | 134,309 | ||
| 6 | Brașov | Brașov | 237,589 | 16 | Târgu Mureș | Mureș | 116,033 | ||
| 7 | Craiova | Dolj | 234,140 | 17 | Baia Mare | Maramureș | 108,759 | ||
| 8 | Galați | Galați | 217,851 | 18 | Buzău | Buzău | 103,481 | ||
| 9 | Oradea | Bihor | 183,105 | 19 | Râmnicu Vâlcea | Vâlcea | 93,151 | ||
| 10 | Ploiești | Prahova | 180,540 | 20 | Satu Mare | Satu Mare | 91,520 | ||
Education


Since the Romanian Revolution of 1989, the Romanian educational system has been in a continuous process of reform that has received mixed criticism.[252] In 2004, some 4.4 million of the population were enrolled in school. Out of these, 650,000 in kindergarten (3–6 years), 3.11 million in primary and secondary level, and 650,000 in tertiary level (universities).[253] In the same year, the adult literacy rate was 97.3% (45th worldwide), while the combined gross enrollment ratio for primary, secondary and tertiary schools was 75% (52nd worldwide).[254] Kindergarten is optional between 3 and 6 years. Schooling starts at age 7 (sometimes at 6) and is compulsory until tenth grade.[255] Primary and secondary education is divided into 12 or 13 grades. There also exists a semi-legal, informal private tutoring system used mostly during secondary school, which has prospered during the Communist regime.[256]
Higher education is aligned with the European higher education area. The results of the PISA assessment study in schools for the year 2012 placed Romania on the 45th rank out of 65 participant countries,[257] though Romania often wins medals in the mathematical olympiads[258][259][260] and not only. Alexandru Ioan Cuza University of Iași, Babeș-Bolyai University of Cluj-Napoca, University of Bucharest, and West University of Timișoara have been included in the QS World University Rankings' top 800.[261]
Healthcare
Romania has a universal health care system, and total health expenditures by the government are roughly 5% of the GDP.[262] It covers medical examinations, any surgical interventions, and any post-operator medical care, and provides free or subsidized medicine for a range of diseases. The state is obliged to fund public hospitals and clinics. The most common causes of death are cardiovascular diseases and cancer. Transmissible diseases, such as tuberculosis, syphilis or viral hepatitis, are more common than in Western Europe.[263] In 2010, Romania had 428 state and 25 private hospitals,[264] with 6.2 hospital beds per 1,000 people,[265] and over 200,000 medical staff, including over 52,000 doctors.[266] As of 2013[update], the emigration rate of doctors was 9%, higher than the European average of 2.5%.[267]
Culture


Arts and monuments
The topic of the origin of the Romanians began to be discussed by the end of the 18th century among the Transylvanian School scholars.[268] Several writers rose to prominence in the 19th century, including George Coșbuc, Ioan Slavici, Mihail Kogălniceanu, Vasile Alecsandri, Nicolae Bălcescu, Ion Luca Caragiale, Ion Creangă, and Mihai Eminescu, the later being considered the greatest and most influential Romanian poet, particularly for the poem Luceafărul.[269] In the 20th century, Romanian artists reached international acclaim, including Tristan Tzara, Marcel Janco,[270] Mircea Eliade, Nicolae Grigorescu, Marin Preda, Liviu Rebreanu,[271] Eugène Ionesco, Emil Cioran, and Constantin Brâncuși. The latter has a sculptural ensemble in Târgu Jiu, while his sculpture Bird in Space, was auctioned in 2005 for $27.5 million.[272][273] Romanian-born Holocaust survivor Elie Wiesel received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1986, while writer Herta Müller received the Nobel Prize in Literature in 2009.
Prominent Romanian painters include Nicolae Grigorescu, Ștefan Luchian, Ion Andreescu Nicolae Tonitza and Theodor Aman. Notable Romanian classical composers of the 19th and 20th centuries include Ciprian Porumbescu, Anton Pann, Eduard Caudella, Mihail Jora, Dinu Lipatti and especially George Enescu. The annual George Enescu Festival is held in Bucharest in honor of the 20th century emponymous composer.[274] Contemporary musicians like Angela Gheorghiu, Gheorghe Zamfir,[275][276] Inna,[277] Alexandra Stan[278] and many others have achieved various levels of international acclaim. At the Eurovision Song Contest Romanian singers have achieved third place in 2005 and 2010.[279]

In cinema, several movies of the Romanian New Wave have achieved international acclaim. At the Cannes Film Festival, 4 Months, 3 Weeks and 2 Days by Cristian Mungiu won Palme d'Or in 2007.[280] At the Berlin International Film Festival, Child's Pose by Călin Peter Netzer won the Golden Bear in 2013.[281]
The list of World Heritage Sites includes six cultural sites located within Romania, including eight Painted churches of northern Moldavia, eight Wooden Churches of Maramureș, seven Villages with fortified churches in Transylvania, the Horezu Monastery, and the Historic Centre of Sighișoara. [282] The city of Sibiu, with its Brukenthal National Museum, was selected as the 2007 European Capital of Culture.[283] Multiple castles exist in Romania, including popular tourist attractions of Peleș Castle,[284] Corvin Castle, and "Dracula's Castle".[285]
Holidays, traditions and cuisine


There are 12 non-working public holidays, including the Great Union Day, celebrated on 1 December in commemoration of the 1918 union of Transylvania with Romania.[286] Winter holidays include the Christmas festivities and the New Year during which, various unique folklore dances and games are common: plugușorul, sorcova, ursul, and capra.[287][288] The traditional Romanian dress that otherwise has largely fell out of use during the 20th century, is a popular ceremonial vestment worn on these festivities, especially in the rural areas.[289] Sacrifices of live pigs during Christmas and lambs during Easter has required a special derogation from EU law after 2007.[290] During Easter, painted eggs are very common, while on 1 March features mărțișor gifting, a tradition likely of Thracian origin.[291]
Romanian cuisine shares some similarities with other Balkan cuisines such as Greek, Bulgarian and Turkish cuisine.[292] Ciorbă includes a wide range of sour soups, while mititei, mămăligă (similar to polenta), and sarmale are featured commonly in main courses.[citation needed] Pork, chicken and beef are the preferred meats, but lamb and fish are also popular.[citation needed] [293] Certain traditional recipes are made in direct connection with the holidays: chiftele, tobă and tochitura at Christmas; drob, pască and cozonac at Easter and other Romanian holidays.[294] Țuică is a strong plum brandy reaching a 70% alcohol content which is the country's traditional alcoholic beverage, taking as much as 75% of the national crop (Romania is one of the largest plum producers in the world).[295][296] Traditional alcoholic beverages also include wine, rachiu, palincă and vișinată, but beer consumption has increased dramatically over the recent years.[297]
Sports

Association football (soccer) is the most popular sport in Romania with over 234,000 registered players as of 2010.[298] The governing body is the Romanian Football Federation, which belongs to UEFA. The Romania national football team has taken part seven times in the FIFA World Cup games and had its most successful period during the 1990s, when they reached the quarterfinals of the 1994 FIFA World Cup and was ranked third by FIFA in 1997.[299] The core player of this "Golden Generation" was Gheorghe Hagi, who was nicknamed "the Maradona of the Carpathians."[300][301] Other successful players include Nicolae Dobrin, Dudu Georgescu, Florea Dumitrache, Liță Dumitru, Ilie Balaci, Loți Bölöni, Costică Ștefănescu, Cornel Dinu or Gheorghe Popescu, and most recently Adrian Mutu, Cristian Chivu, Dan Petrescu or Cosmin Contra.
The most famous successful club is Steaua București and was the first Eastern European team to win the European Champions Cup in 1986, and were runners-up in 1989. Dinamo București reached the European Champions' Cup semifinal in 1984 and the Cup Winners' Cup semifinal in 1990. Other important Romanian football clubs are Rapid București, UTA Arad, Universitatea Craiova, CFR Cluj and Petrolul Ploiești.

Tennis is the second most popular sport, with over 15,000 registered players.[302] Romania reached the Davis Cup finals three times (1969, 1971, 1972). The tennis player Ilie Năstase won several Grand Slam titles, and was the first player to be ranked as number 1 by ATP between 1973 and 1974. Virginia Ruzici won the French Open in 1978, and was runner-up in 1980, Simona Halep played the final in 2014 and is currently ranked 2nd by the WTA.[303]
Other popular team sport clubs are Rugby Union and Team Handball.[302] The rugby national team has competed in every Rugby World Cup, while both the men's and women's handball national teams are multiples world champions. On 13 January 2010, Cristina Neagu became the first Romanian in handball to win the IHF World Player of the Year award.[304] Popular individual sports include athletics, chess, judo, dancesport, table tennis and combat sports (Lucian Bute, Leonard Dorin Doroftei, Mihai Leu aka Michael Loewe, Daniel Ghiță, Benjamin Adegbuyi, Andrei Stoica, etc.).[302] While it has a limited popularity nowadays, oină is a traditional Romanian sporting game similar to baseball that has been continuously practiced since at least the 14th century.[305]
Romania participated in the Olympic Games for the first time in 1900 and has taken part in 18 of the 24 summer games. It has been one of the more successful countries at the Summer Olympic Games, with a total of 301 medals won throughout the years, of which 88 gold ones, ranking 15th overall, and second (behind neighbour Hungary) of the nations that have never hosted the game. It participated at the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles in defiance of a Warsaw Pact boycott and finished second in gold medals (20) and third in total medal count (53).[306] Almost a quarter of all the medals and 25 of the gold ones were won in gymnastics, with Nadia Comăneci becoming the first gymnast ever to score a perfect ten in an Olympic event at the 1976 Summer Olympics.[307] Romanian competitors have won gold medals in other Olympic sports: rowing, athletics, canoeing, wrestling, shooting, fencing, swimming, weightlifting, boxing, and judo. At the Winter Olympic Games, Romania has won only a bronze medal in bobsleigh at the 1968 Winter Olympics.
See also
Notes
- ^ In English, Romania was formerly often spelled Rumania or sometimes Roumania. See the etymology section.
- ^ "am scris aceste sfente cărți de învățături, să fie popilor rumânesti... să înțeleagă toți oamenii cine-s rumâni creștini" "Întrebare creștinească" (1559), Bibliografia românească veche, IV, 1944, p. 6.
"...că văzum cum toate limbile au și înfluresc întru cuvintele slăvite a lui Dumnezeu numai noi românii pre limbă nu avem. Pentru aceia cu mare muncă scoasem de limba jidovească si grecească si srâbească pre limba românească 5 cărți ale lui Moisi prorocul si patru cărți și le dăruim voo frați rumâni și le-au scris în cheltuială multă... și le-au dăruit voo fraților români,... și le-au scris voo fraților români" Palia de la Orăștie (1581–1582), București, 1968.
În Țara Ardealului nu lăcuiesc numai unguri, ce și sași peste seamă de mulți și români peste tot locul..., Grigore Ureche, Letopisețul Țării Moldovei, p. 133–134. - ^ In his well known literary testament Ienăchiță Văcărescu writes: "Urmașilor mei Văcărești!/Las vouă moștenire:/Creșterea limbei românești/Ș-a patriei cinstire."
In the "Istoria faptelor lui Mavroghene-Vodă și a răzmeriței din timpul lui pe la 1790" a Pitar Hristache writes: "Încep după-a mea ideie/Cu vreo câteva condeie/Povestea mavroghenească/Dela Țara Românească. - ^ In 1816, the Greek scholar Dimitrie Daniel Philippide published in Leipzig his work The History of Romania, followed by The Geography of Romania.
On the tombstone of Gheorghe Lazăr in Avrig (built in 1823) there is the inscription: "Precum Hristos pe Lazăr din morți a înviat/Așa tu România din somn ai deșteptat." - ^ 2002 census data, based on Population by ethnicity, gave a total of 535,250 Roma in Romania. Many ethnicities not recorded at all, since they do not have ID cards. International sources give higher figures than the official census(UNDP's Regional Bureau for Europe, World Bank, "International Association for Official Statistics" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 February 2008.[dead link]
References
- ^ "Constitution of Romania". Cdep.ro. Retrieved 2 October 2013.
- ^ "Reservations and Declarations for Treaty No.148 - European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages". Council of Europe. Council of Europe. Retrieved 3 December 2015.
- ^ a b c d e "Romanian 2011 census (final results)" (PDF) (in Romanian). INSSE. Retrieved 28 August 2012.
- ^ "United Nations world population prospects".(PDF) 2015 Revision
- ^ "GDP PPP, Source: IMF".
- ^ "GDP PPP per capita, Source: IMF".
- ^ "GDP nominal, Source: IMF".
- ^ "GDP nominal per capita, Source: IMF".
- ^ "Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income (source: SILC)". Eurostat Data Explorer. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "2014 Human Development Report Summary" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 2014. pp. 21–25. Retrieved 27 July 2014.
- ^ http://www.insse.ro/cms/files/statistici/comunicate/com_anuale/populatie/PopRez2014r.pdf
- ^ "Romania Geography". aboutromania.com. Retrieved 4 April 2015.
- ^ "Explanatory Dictionary of the Romanian Language, 1998; New Explanatory Dictionary of the Romanian Language, 2002" (in Romanian). Dexonline.ro. Retrieved 25 September 2010.
- ^ Verres, Andréas. Acta et Epistolae. Vol. I. p. 243.
nunc se Romanos vocant
- ^ Cl. Isopescu (1929). "Notizie intorno ai romeni nella letteratura geografica italiana del Cinquecento". Bulletin de la Section Historique. XVI: 1–90.
...si dimandano in lingua loro Romei...se alcuno dimanda se sano parlare in la lingua valacca, dicono a questo in questo modo: Sti Rominest ? Che vol dire: Sai tu Romano,...
- ^ Holban, Maria (1983). Călători străini despre Țările Române (in Romanian). Vol. II. Ed. Științifică și Enciclopedică. pp. 158–161.
"Anzi essi si chiamano romanesci, e vogliono molti che erano mandati quì quei che erano dannati a cavar metalli..."
- ^ Cernovodeanu, Paul (1960). Voyage fait par moy, Pierre Lescalopier l'an 1574 de Venise a Constantinople, fol 48 (in Romanian). Vol. IV. p. 444.
Tout ce pays la Wallachie et Moldavie et la plus part de la Transilvanie a eté peuplé des colonies romaines du temps de Traian l'empereur...Ceux du pays se disent vrais successeurs des Romains et nomment leur parler romanechte, c'est-à-dire romain ...
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Ion Rotaru, Literatura română veche, "The Letter of Neacșu from Câmpulung", București, 1981, pp. 62–65
- ^ Brezeanu, Stelian (1999). Romanitatea Orientală în Evul Mediu. Bucharest: Editura All Educational. pp. 229–246.
- ^ Goina, Călin. How the State Shaped the Nation: an Essay on the Making of the Romanian Nation in Regio – Minorities, Politics, Society.
- ^ "Wallachia and Moldavia, 1859–61". Retrieved 5 January 2008.
- ^ See, for example, "Rumania: Remarkable Common Ground", The New York Times (December 21, 1989).
- ^ See the Google Ngrams for Romania, Rumania, and Roumania.
- ^ "General principles" (in Romanian). cdep.ro. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
- ^ Europe Before Rome: A Site-by-Site Tour of the Stone, Bronze, and Iron Ages (T. Douglas Price) [1]
- ^ Zilhão, João (2006). "Neanderthals and Moderns Mixed and It Matters". Evolutionary Anthropology. 15 (5): 183–195. doi:10.1002/evan.20110.
- ^ John Noble Wilford (1 December 2009). "A Lost European Culture, Pulled From Obscurity". The New York Times (30 November 2009).
- ^ Gibbs, Patrick. "Antiquity Vol 79 No 306 December 2005 The earliest salt production in the world: an early Neolithic exploitation in Poiana Slatinei-Lunca, Romania Olivier Weller & Gheorghe Dumitroaia". Antiquity.ac.uk. Retrieved 12 October 2012.
- ^ a b c Hitchins 2014, p. 7.
- ^ Herodotus. Histories, 4.93-4.97.
- ^ The Cambridge Ancient History (Volume 10) (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. 1996. J. J. Wilkes mentions "the Getae of the Dobrudja, who were akin to the Dacians" (p. 562)
- ^ Mócsy, András (1974). Pannonia and Upper Moesia. Routledge and Kegan Paul. ISBN 0-7100-7714-9. See p. 364, n. 41: "If there is any justification for dividing the Thracian ethnic group, then, unlike V. Georgiev who suggests splitting it into the Thraco-Getae and the Daco-Mysi, I consider a division into the Thraco-Mysi and the Daco-Getae the more likely."
- ^ Hitchins 2014, pp. 13–14.
- ^ Matley, Ian (1970). Romania; a Profile. Praeger. p. 85.
- ^ Giurescu, Constantin C. (1972). The Making of the Romanian People and Language. Bucharest: Meridiane Publishing House. pp. 43, 98–101, 141.
- ^ Eutropius, Abridgment of Roman History BOOK IX.
- ^ Watkins, Thayer. "The Economic History of the Western Roman Empire". Retrieved 31 August 2008.
The Emperor Aurelian recognized the realities of the military situation in Dacia and, around 271 AD., withdrew Roman troops from Dacia, leaving it to the Goths. The Danube once again became the northern frontier of the Roman Empire in eastern Europe
- ^ Jordanes (551). Getica, sive, De Origine Actibusque Gothorum. Constantinople. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ Iliescu, Vl.; Paschale, Chronicon (1970). Fontes Historiae Daco-Romanae. Vol. II. București. pp. 363, 587.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Teodor, Dan Gh. (1995). Istoria României de la începuturi până în secolul al VIII-lea. Vol. 2. București. pp. 294–325.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Constantine VII, Porphyrogenitus (950). Constantine Porphyrogenitus De Administrando Imperio. Constantinople. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ Lupșa, Cristian (1 March 2008). "Regele Decebal" (in Romanian). Lumea-Copiilor. Retrieved 13 April 2015.
- ^ "Împăratul Traian, strămoșul uitat" (in Romanian). Adevărul. 4 July 2013. Retrieved 13 April 2015.
- ^ "Mitul strămoșilor în "epopeea națională": Dacii, Columna și Burebista" (in Romanian). Realitatea TV. 13 April 2015. Retrieved 13 April 2015.
- ^ Pop, Ioan-Aurel (Winter 2001). "The Romanians' Identity in the 16th Century According to Italian Authors" (PDF). Transylvanian Review. 10 (4). Romanian Cultural Foundation: 3.
- ^ "''Gesta Hungarorum'', the chronicle of Bele Regis Notarius". Scribd.com. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ Makkai, László (2001). Köpeczi, Béla (ed.). "History of Transylvania: III. Transylvania in the Medieval Hungarian Kingdom (896–1526)". New York: Institute of History of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Columbia University Press. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ Ștefănescu, Ștefan (1991). Istoria medie a României. Vol. I. Bucharest. p. 114.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Predescu, Lucian (1940). Enciclopedia Cugetarea.
- ^ Várkonyi, Ágnes R. (2001). "Columbia University Press". In Köpeczi, Béla (ed.). History of Transylvania: VI. The Last Decades of the Independent Principality (1660–1711). Vol. 2. New York: Institute of History of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ István, Vásáry. "Cumans and Tatars". cambridge.org. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
- ^ Copy of Domnitori Romani. Retrieved 5 April 2015.
- ^ Giurescu, p. 211–13. Giurescu, Constantin C. (2007) [1935]. Istoria Românilor (in Romanian). Bucharest: Editura All.
- ^ David Prodan, Supplex Libellus Valachorum, Bucharest, 1948.
- ^ Kocsis, Karoly; Kocsis-Hodosi, Eszter (1999). Ethnic structure of the population on the present territory of Transylvania (1880–1992). Archived from the original on 22 February 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ Kocsis, Karoly; Kocsis-Hodosi, Eszter (2001). Ethnic Geography of the Hungarian Minorities in the Carpathian Basin. Simon Publications. p. 102. ISBN 1-931313-75-X.
- ^ Gazeta de Transilvania, year XI, no. 34 of 26 April 1848, p. 140.
- ^ Dogaru (1978), p. 862.
- ^ Căzănișteanu (1967), p. 36.
- ^ Năsturel (1900/1901), p. 257. Năsturel, Petre Vasiliu, Steagul, stema română, însemnele domnești, trofee (The Romanian flag [and] coat of arms; the princely insignias [and] trophies), Bucharest, 1903.
- ^ The establishment of the Balkan national states, 1804–1920. Books.google.com. Retrieved 28 March 2012.
- ^ Bobango, Gerald J (1979). The emergence of the Romanian national State. New York: Boulder. ISBN 978-0-914710-51-6.
- ^ "San Stefano Preliminary Treaty" (in Russian). 1878. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ The Treaty of Berlin, 1878 – Excerpts on the Balkans. Berlin: Fordham University. 13 July 1878. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ Patterson, Michelle (August 1996). "The Road to Romanian Independence". Canadian Journal of History. Archived from the original (– Scholar search) on 24 March 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|format= - ^ Anderson, Frank Maloy; Hershey, Amos Shartle (1918). Handbook for the Diplomatic History of Europe, Asia, and Africa 1870–1914. Washington D.C.: Government Printing Office.
- ^ Horne, Charles F. "Romania's Declaration of War with Austria-Hungary". Source Records of the Great War. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ Erlikman, Vadim (2004). Poteri narodonaseleniia v XX veke : spravochnik. Moscow. ISBN 5-93165-107-1.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Bernard Anthony Cook (2001). Europe Since 1945: An Encyclopedia. Taylor&Francis. p. 162. ISBN 0-8153-4057-5.
- ^ "Text of the Treaty of Trianon". World War I Document Archive. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ Malbone W. Graham (October 1944). "The Legal Status of the Bukovina and Bessarabia". The American Journal of International Law. 38 (4). American Society of International Law: 667–673. doi:10.2307/2192802. JSTOR 2192802.
- ^ "Statul National Unitar (România Mare 1919–1940)" (in Romanian). ici.ro. Archived from the original on 12 June 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ "his1". Aneir-cpce.ro. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ "VIDEO Înregistrare senzațională cu Hitler: "Fără petrolul din România nu aș fi atacat niciodată URSS-ul"". adevarul.ro. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ "Business in Romania: a country that's fast off the Bloc – Two years of EU membership have transformed the business face of Romania and savvy UK firms are reaping the rewards. Paul Bray reports". The Daily Telegraph. London. 24 February 2010. Retrieved 1 May 2010.
- ^ Note: follow the World War II link: Ronald D. Bachman, ed. (9 November 2005). Romania:World War II (Report) (2 ed.). Washington D.C.: Library of Congress.Federal Research Division. OCLC DR205.R613 1990. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
{{cite report}}: Check|oclc=value (help) - ^ Ilie Fugaru, Romania clears doubts about Holocaust past, UPI, November 11, 2004
- ^ International Commission on the Holocaust in Romania (28 January 2012). "Executive Summary: Historical Findings and Recommendations" (PDF). Final Report of the International Commission on the Holocaust in Romania. Yad Vashem (The Holocaust Martyrs' and Heroes' Remembrance Authority). Retrieved 28 January 2012.
- ^ Associated, The (17 April 2012). "Study: More than 280,000 Jews killed in Romania in WWII – Haaretz Daily Newspaper | Israel News". Haaretz.com. Retrieved 24 April 2012.
- ^ "Holocaust Education, Remembrance, and Research in Romania". holocaustremembrance.com. Retrieved 4 April 2015.
- ^ Ioan Scurtu, Theodora Stănescu-Stanciu, Georgiana Margareta Scurtu (2002). Istoria Românilor între anii 1918–1940 (in Romanian). University of Bucharest. Archived from the original on 13 November 2007.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Nagy-Talavera, Nicolas M. (1970). Green Shirts and Others: a History of Fascism in Hungary and Romania. Hoover Institution Press. p. 305. ISBN 973-9432-11-5.
- ^ Ioan Scurtu,Theodora Stănescu-Stanciu, Georgiana Margareta Scurtu. "Decret regal privind investirea generalului Ion Antonescu cu depline puteri". Istoria românilor între anii 1918–1940 (in Romanian). Retrieved 19 September 2011.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ M. Broszat (1968). "Deutschland – Ungarn – Rumänien. Entwicklung und Grundfaktoren nationalsozialistischer Hegemonial- und Bündnispolitik 1938–1941". Historische Zeitschrift (in German) (206): 552–553.
- ^ Axworthy, Mark; Scafes, Cornel; Craciunoiu, Cristian (editors) (1995). Third axis, Fourth Ally: Romanian Armed Forces In the European War 1941-1945. London: Arms & Armour Press. pp. 1–368. ISBN 963-389-606-1.
{{cite book}}:|first3=has generic name (help) - ^ "The Biggest Mistakes in World War 2:Ploesti – the most important target". Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ Constantiniu, Florin, O istorie sinceră a poporului român ("An Honest History of the Romanian People"), Ed. Univers Enciclopedic, București, 1997, ISBN 973-9243-07-X
- ^ Clodfelter, Michael (2002). Warfare and Armed Conflicts- A Statistical Reference to Casualty and Other Figures, 1500–2000 (2 ed.). Jefferson, NC: McFarland. p. 582. ISBN 0-7864-1204-6.
- ^ Tomiuc, Eugen (6 May 2005). "World War II – 60 Years After: Former Romanian Monarch Remembers Decision To Switch Sides". Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ Giurescu, "«Alegeri" după model sovietic", p.17 (citing Berry), 18 (citing Berry and note); Macuc, p.40; Tismăneanu, p.113
- ^ "Romania: Country studies – Chapter 1.7.1 "Petru Groza's Premiership"". Federal research Division, Library of Congress. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ "Romania". CIA – The World Factbook. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ "Romania – Country Background and Profile". ed-u.com. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ Rîjnoveanu, Carmen (2003). "Romania's Policy of Autonomy in the Context of the Sino-Soviet Conflict" (PDF). Czech Republic Military History Institute, Militärgeschichtliches Forscheungamt. p. 1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 June 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.[dead link]
- ^ Roper, Stephen D. (2000). Romania: The Unfinished Revolution. London: Routledge. p. 18. ISBN 90-5823-027-9.
- ^ Cioroianu, Adrian (2005). On the Shoulders of Marx. An Incursion into the History of Romanian Communism (in Romanian). Bucharest: Editura Curtea Veche. pp. 68–73. ISBN 973-669-175-6.
- ^ Stoica, Stan (2007). Dicționar de Istorie a României (in Romanian). Bucharest: Editura Merona. pp. 77–78, 233–34. ISBN 973-7839-21-8.
- ^ Ionițoiu, Cicerone (2000). Victimele terorii comuniste. Arestați, torturați, întemnițați, uciși. Dicționar (in Romanian). Bucharest: Editura Mașina de scris. ISBN 973-99994-2-5.[page needed]
- ^ Consiliul National pentru Studierea Ahivelor Securității, Bande, bandiți si eroi; Grupurile de rezistență și Securitatea (1948–1968), Editura Enciclopedica, București, 2003
- ^ Raportul Comisiei Prezidențiale pentru Analiza Dictaturii Comuniste din România (Report). Comisia Prezidențială pentru Analiza Dictaturii Comuniste din România. 15 December 2006. pp. 215–217.
- ^ Political Tension 1968 (in Romanian). Bucharest: British Pathé. 21 August 1968.
- ^ "Romania: Soviet Union and Eastern Europe". Country Studies.us. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ "Middle East policies in Communist Romania". Country Studies.us. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ Deletant, Dennis. "New Evidence on Romania and the Warsaw Pact, 1955–1989" (PDF). Cold War International History Project e-Dossier Series.
- ^ Carothers, Thomas. "Romania: The Political Background" (PDF). Retrieved 31 August 2008.
This seven-year period can be characterized as a gradualistic, often ambiguous transition away from communist rule towards democracy.
- ^ Hellman, Joel (January 1998). "Winners Take All: The Politics of Partial Reform in Postcommunist". Transitions World Politics. 50 (2): 203–234.
- ^ "Institutul de Investigare a Crimelor Comunismului si Memoria Exilului Romanesc". Mineriade.iiccr.ro. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ "Institutul de Investigare a Crimelor Comunismului si Memoria Exilului Romanesc". Mineriade.iiccr.ro. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ Bohlen, Celestine (15 June 1990). "Evolution in Europe; Romanian miners invade Bucharest". The New York Times. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
Responding to an emergency appeal by President Ion Iliescu, thousands of miners from northern Romania descended on the capital city today
- ^ "Institutul de Investigare a Crimelor Comunismului si Memoria Exilului Romanesc". Mineriade.iiccr.ro. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ Presa internationala despre alegerile din Romania: Traian Basescu a castigat la limita; Romanii au mici sperante sa se dezghete ajutorul de la FMI – International. HotNews.ro. Retrieved on 21 August 2010.
- ^ "NATO update: NATO welcomes seven new members". NATO. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ "EU approves Bulgaria and Romania". BBC News. 26 September 2006. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ a b "Romania". focus-migration.de. Retrieved 28 August 2008.
- ^ "Adevarul". Adevarul.ro. Archived from the original on 25 April 2010. Retrieved 25 September 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Human Development Report 2009 – Country Fact Sheets – Romania. Hdrstats.undp.org. Retrieved on 21 August 2010.
- ^ Tracking the Millennium Development Goal. MDG Monitor. Retrieved on 21 August 2010.
- ^ Joe Parkinson (4 December 2009). "Romania Faces Crucial Vote". Wall Street Journal.
- ^ Romania and the IMF
- ^ Gheorghe Stoica, Lavinia Stan. "Romanian Politics in 2012: Intra-Cabinet Coexistence and Political Instability". South-East European Journal of Political Science.
- ^ Romania's Infrastructure and International Transport Links. Romania Central. Retrieved on 21 August 2010.
- ^ Romania, world’s 53rd country in quality of life index « Denisa Morariu[dead link]. Denisamorariu.wordpress.com (8 January 2010). Retrieved on 21 August 2010.
- ^ Sistemul de invatamant distrus de lipsa reformelor – Cluj. citynews.ro. Retrieved on 21 August 2010.
- ^ D+C 2010/03 – Focus – Roos: In Romania and Bulgaria, civil-society organisations are demanding rule of law – Development and Cooperation – International Journal. Inwent.org. Retrieved on 21 August 2010.
- ^ "Romania is booming". The Economist. 17 December 2013.
- ^ a b "Bears. Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan" (pdf). Retrieved 2 October 2014.
- ^ a b "Geography, Meteorology and Environment" (PDF) (in Romanian). Romanian Statistical Yearbook. 2004. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
- ^ "Danube Delta". UNESCO's World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 9 January 2008.
- ^ "Romania: Climate". U.S. Library of Congress. Retrieved 10 January 2008.
- ^ a b "Permafrost Monitoring and Prediction in Southern Carpathians, Romania". CliC International Project Office (CIPO). 22 December 2004. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ "The 2004 Yearbook" (PDF) (in Romanian). Romanian National Institute of Statistics. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ http://www.meteoromania.ro/anm/?page_id=114
- ^ "Romania's Biodiversity". Ministry of Waters, Forests and Environmental Protection of Romania. Retrieved 10 January 2008.
- ^ "Romania". Fao.org. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ a b "Flora si fauna salbatica" (in Romanian). enrin.grida.no. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
- ^ "EarthTrends:Biodiversity and Protected Areas -Romania" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 September 2007. Retrieved 10 January 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Canids: Foxes, Wolves, Jackals and Dogs. Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan" (pdf). IUCN/SSC Canid Specialist Group. Retrieved 2 October 2014.
- ^ "Protected Areas in Romania". Romanian Ministry of Waters, Forests and Environmental Protection. Archived from the original on 17 November 2007. Retrieved 10 January 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "Danube Delta Reserve Biosphere". Romanian Ministry of Waters, Forests and Environmental Protection. Archived from the original on 26 April 2005. Retrieved 10 January 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "Danube Delta". UNESCO's World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 10 January 2008.
- ^ Wohl, Ellen (2010). A World of Rivers: Environmental Change on Ten of the World's Great Rivers. University of Chicago Press. p. 130. ISBN 0-226-90478-4.
- ^ "Romania climate information". Weatherbase. Retrieved 3 February 2016.
- ^ Verheijen, Tony (14 March 1990). "Oxford Scholarship Online: Semi-Presidentialism in Europe". Oxfordscholarship.com. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ a b c d Romania. Vol. 2 (48 ed.). London and New York: Routledge. 2007. pp. 3734–3759. ISBN 978-1-85743-412-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|encyclopedia=ignored (help) - ^ "Se schimbă sistemul de vot. Deputații au adoptat noua Lege Electorală propusă de USL". Antena3.ro. Retrieved 12 October 2012.
- ^ "Presentation". High Court of Cassation and Justice -—Romania. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ "Romanian Legal system". CIA Factbook. 2000. Retrieved 11 January 2008.
- ^ "Understanding the WTO – members". WTO. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ a b c d "Foreign Policy Priorities of Romania for 2008" (in Romanian). Romanian Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 28 August 2008.
- ^ "Background Note: Romania – U.S.-Romanian Relations". U.S. Department of State.
- ^ [2] Archived 2009-05-12 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Gabriel Andreescu, Valentin Stan, Renate Weber (30 October 1994). "Romania'S Relations with the Republic of Moldova". International Studies. Centre for International Studies. Archived from the original on 23 February 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ihrig, Stefan. "Rediscovering History, Rediscovering Ultimate Truth" (PDF). Retrieved 17 September 2008.
- ^ "Moldova, Romania open new chapter in bilateral relations". People's Daily. 29 April 2010. Retrieved 11 August 2011.
- ^ "Press conference" (Press release). Ministry of National Defense of Romania. 21 January 2003. Archived from the original on 3 April 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ "MoND Budget as of 2007" (in Romanian). Ziarul Financiar. 30 October 2006. Archived from the original on 22 April 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.[dead link]
- ^ [3] Archived 2014-10-23 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Romania Finally Settles On Portuguese F-16s" Archived 2013-12-02 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "PICTURES: Romania accepts first C-27J Spartans-12/04/2010-London". Flightglobal.com. Retrieved 28 September 2010.
- ^ "Spartan Order". Aviation Week & Space Technology. 11 December 2006.
- ^ YAHOO News, WHITE HOUSE NOTEBOOK: Obama in Prague Archived 2014-10-23 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Traian Basescu: Romania va trimite fregata Regele Ferdinand cu 205 militari in Mediterana pentru operatiuni de blocare a oricarei nave suspecte ca transporta armament" (in Romanian). HotNews.ro. 22 March 2011. Retrieved 22 March 2011.
- ^ "Romania ratifies US missile shield agreement". SpaceWar. 6 December 2012.
- ^ "Geografia Romaniei" (in Romanian). descopera.net. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
- ^ a b "1.8". Administrative Organisation of Romanian Territory, on December 31, 2005 (PDF) (Report) (in Romanian). Romanian National Institute of Statistics. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ a b "Hierarchical list of the Nomenclature of territorial units for statistics – NUTS and the Statistical regions of Europe". Archived from the original on 18 January 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "LEGE nr. 151 din 15 iulie 1998" (in Romanian). Retrieved 1 July 2012.
- ^ "2011 Regions Population". INSSE. 4 July 2013. Retrieved 9 July 2013.
- ^ a b "Population at 20 October 2011" (in Romanian). INSSE. 5 July 2013. Retrieved 5 July 2013.[dead link]
- ^ a b [hhttp://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2015/02/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=55&pr.y=5&sy=2013&ey=2020&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=968&s=PPPGDP%2CPPPPC&grp=0&a=], IMF World Economic Outlook Database, October 2015
- ^ "Country Classification Groups". World Bank. 2005. Archived from the original on 24 May 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "GDP per capita in PPS". Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "GDP in 2006" (PDF) (in Romanian). Romanian National Institute of Statistics. Retrieved 10 January 2008.
- ^ nytimes.com: "Romania to Get Next Installment of Bailout" 1 Nov 2010
- ^ "Veste excelenta pentru Romania de la Banca Mondiala (Video)". Retrieved 11 June 2014.
- ^ "Average Romanian household income was EUR 540 a month in Q3 2012". Romanian-Insider. 9 January 2013.
- ^ "Eurostat, HICP (2005 = 100) - monthly data (12-month average rate of change)". Eurostat. Retrieved 14 December 2013.
- ^ "Unemployment rate, 2001–2012 (%)|Eurostat". Epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 4 April 2014.
- ^ Industrial production up by 0.4% in euro area and EU27|Eurostat. Eurostat (12 April 2013). Retrieved on 13 May 2013.
- ^ Chirileasa, Andrei (9 June 2014). "Top 20 companies in Romania by turnover". Romania-Insider.com. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ "IMF World Economic Outlook Database, April 2011 – Central and Eastern Europe". IMF. April 2011. Retrieved 27 April 2011.
- ^ "Index of Economic Freedom: Romania". heritage.org. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ Taxation trends in the EU (PDF) (Report). Eurostat. 26 June 2007. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ "Romania". CIA World Factbook. 2010. Retrieved 27 April 2011.
- ^ "Romania: FDI reached over EUR 8.3 bn". Archived from the original on 28 September 2007. Retrieved 31 August 2008.[dead link]
- ^ Economy Ranking. Doing Business (Report). World Bank. 2007. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ Doing Business 2007 Report (Report). World Bank. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ "Fifth Report on the Practical Preparations for the Future Enlargement of the Euro Area" (PDF). Commission of the European Communities. 16 July 2007. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- ^ "Banca Națională a României". bnr.ro. Retrieved 29 September 2015.
- ^ http://www.nytimes.com/2015/11/05/world/europe/romania-victor-ponta-resigns.html?_r=0
- ^ http://www.zfenglish.com/banks-insurance/central-bank-romanian-economy-stable-political-effects-depend-on-quick-action-14875495
- ^ economy remains stable.
- ^ http://www.globalpost.com/article/6682166/2015/11/05/romanias-2015-growth-estimate-upgraded-35-pct-european-commission
- ^ "The CIA world factbook :Romania". Cia.gov. Retrieved 4 April 2014.
- ^ "Reteaua feroviara" (in Romanian). cfr.to. Archived from the original on 8 June 2009. Retrieved 6 September 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Metrorex ridership" (in Romanian). Financial Week newspaper. 23 April 2007. Archived from the original on 16 May 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Henri Coandă Airport in 2013 Template:Ro icon
- ^ a b c "Romania - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)". Eia.gov. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ http://www.minind.ro/energie/PNAER_final.pdf
- ^ "pg.24-25" (PDF). Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ Ana Hontz-Ward. "Romania Expects to be Energy Independent Despite Ukraine Crisis". Voanews.com. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ "Contractul pentru unitatile 3 si 4 de la centrala nucleara Cernavoda se va parafa in mai. Chinezii vor avea 51% din actiuni - Nicolae Moga (PSD) - Energie - HotNews.ro". Economie.hotnews.ro. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ "Numărul conexiunilor la internet a crescut cu 22,8%. Câte milioane de români au acces la internet". Gândul. 4 December 2014.
- ^ "Top 10: Where to Find the World's Fastest Internet". Bloomberg. 23 January 2013.
- ^ "Romanian city comes out first in the world in Internet download speed ranking". Net Index. 3 July 2013.
- ^ "Country/Economy Profiles: Romania, Travel&Tourism" (PDF). World Economic Forum. Retrieved 11 January 2008.
- ^ "WTTC spells out policy recommendations for Romania to tap travel and tourism potential". WTTC. Retrieved 11 January 2008.
- ^ "Fluxul de turisti cazati in Romania in S1 a crescut cu 5,1%, la 3,5 milioane". Wall-street.ro. 1 August 2014. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ "Tourism attracted in 2005 investments worth €400 million" (in Romanian). Gandul Newspaper. Archived from the original on 5 December 2010. Retrieved 11 January 2008.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Report from Romanian National Institute of Statistics (PDF) (Report). Retrieved 11 January 2008.
for the first 9 months of 2007 an increase from the previous year of 8.7% to 16.5 million tourists; of these 94.0% came from European countries and 61.7% from EU
- ^ Criza ne strică vacanța, 9 July 2010, jurnalul.ro, accessed on 21 August 2010
- ^ "Tan and fun at the Black Sea". UnseenRomania. Archived from the original on 11 October 2007. Retrieved 10 January 2008.
- ^ "Turismul renaste la tara" (in Romanian). Romania Libera. 5 July 2008. Retrieved 28 August 2008.
- ^ "Bine ati venit pe site-ul de promovare a pensiunilor agroturistice din Romania !!!" (in Romanian). RuralTourism.ro. Retrieved 28 August 2008.
- ^ "Turism in Romania". Turism.ro. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ "Ansamblul sculptural Constantin Brancusi din Targu Jiu". Romaniaturistica.com. 16 March 1957. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ http://www.romania-insider.com/how-important-is-tourism-in-romanias-economy/158787/
- ^ a b http://www.romania-insider.com/over-1-9-million-tourists-visit-romania-where-do-they-come-from/141244/
- ^ "Traian Vuia in a Century of Aviation". Romanian Academy Library. p. 1. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
- ^ http://www.ad-astra.ro/journal/2/editorial_en.pdf
- ^ "Laserul de la Magurele: Institutul de Cercetare pentru Fizica si Inginerie Nucleara a semnat contractul de 66 milioane euro pentru realizarea Sistemului Fascicul Gamma - Esential". HotNews.ro. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ "Bulgaria: Science fortunes of Balkan neighbours diverge – Novinite.com – Sofia News Agency". Novinite.com. 13 January 2011. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ "Science fortunes of Balkan neighbours diverge : Nature News". Nature.com. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ "Funeriu: Stiinta din Romania 'se imbunatateste', insa mai sunt multe lucruri de facut". Epochtimes-romania.com. 13 January 2011. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ "Romania is to sign agreement on joining European space agency convention". Actmedia.eu. 20 January 2011. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ "Romania's high hopes for science : Nature News". Nature.com. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ "ELI-NP | Extreme Light Infrastructure – Nuclear Physics". Eli-np.ro. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ "VIDEO Romania's first satellite Goliat successfully launch from Kourou base in French Guyana - Top News". HotNews.ro. Retrieved 4 April 2014.
- ^ "Romania will own a part of the International Space Station and will contribute to the development of the latest European rocket, Ariane 6". Romanian Space Agency. 3 December 2014.
- ^ "European effort spotlights plight of the Roma". usatoday. 10 February 2005. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ a b Official site of the results of the 2002 Census (Report) (in Romanian). Archived from the original on 5 February 2012. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
{{cite report}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "German Population of Romania, 1930–1948". hungarian-history.hu. Archived from the original on 17 August 2007. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
- ^ a b "The World Factbook". Cia.gov. Retrieved 24 February 2014.
- ^ "Eurostat - Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". Epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu. 17 October 2013. Retrieved 24 February 2014.
- ^ Villeret, Graeme. "Roumanie". PopulationData.net. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ "Romania demographics profile (2011)". Indexmundi.com. 12 July 2011. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ "CIA World Factbook: Romania". Cia.gov. Retrieved 2 October 2013.
- ^ http://www.europarl.europa.eu/workingpapers/libe/104/romania_en.htm
- ^ "2011 census results by native language" (xls). www.recensamantromania.ro, website of the Romanian Institute of Statistics. Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- ^ "IARNA UCRAINEANĂ - Află care sunt localitățile din Maramureș în care se prăznuiesc sărbătorile de iarnă după rit vechi", Infomm.ro, retrieved 5 May 2015
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ "Constitutia României". Cdep.ro. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ "Two-thirds of working age adults in the EU28 in 2011 state they know a foreign language" (PDF). Eurostat. 26 September 2013. Retrieved 21 August 2014.
- ^ "Roumanie - Organisation internationale de la Francophonie". francophonie.org.
- ^ "EUROPEANS AND THEIR LANGUAGES, REPORT" (PDF). Eurostat. 2012. Retrieved 21 August 2014.
- ^ "2011 census results by religion" (xls). www.recensamantromania.ro, website of the Romanian Institute of Statistics. Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- ^ "Urbanization of Romania: how urban population increased from 3.7 million in 1948 to 12 million in 1989". Businessday.ro. Retrieved 24 April 2012.
- ^ "Urban Audit". Urban Audit. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ "Proiect – Zona metropolitana Bucuresti". Zmb.ro. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ "Metropolitan Zone of Bucharest will be ready in 10 years" (in Romanian). Romania Libera. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ "Official site of Metropolitan Zone of Bucharest Project" (in Romanian). Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ "Population at 1 December 2021, Final results" (in Romanian). INSSE. 31 May 2023.
- ^ The Romanian Educational Policy in Transition (Report). UNESCO. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ "Romanian Institute of Statistics Yearbook – Chapter 8" (PDF) (in Romanian). Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ "UN Human Development Report 2006" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 February 2007.[dead link]
- ^ The Romanian Educational Policy in Transition (Report). UNESCO. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ "Limited relevants. What feminists can learn from the eastern experience" (PDF). genderomania.ro. Retrieved 25 August 2008.
- ^ Rezultate PISA 2012: Aproape 40% dintre elevii romani au dificultati sa citeasca si sa inteleaga un text si pot rezolva doar exercitii de baza la Matematica (Report). Hotnews.ro. 3 December 2013.
- ^ "Romania's brains rank first in Europe, 10th in the world after Math Olympiad" (in Romanian). romania-insider.com. 16 July 2012.
- ^ "Romanian students win four medals, two gold, at the European Girls Mathematical Olympiad". business-review.eu. 16 April 2014.
- ^ "Romanian students win 32 medals at SEEMOUS International Mathematical Olympiad". AGERPRES. 11 March 2014.
- ^ "QS World University Rankings 2013". topuniversities.com. October 2013. All four universities are ranked at 700+ which means they are ranked among the 701–800 places.
- ^ "Ritli: Ministry of Health budget for 2012 can provide the assistance at least at the level of previous year", Mediafax.ro
- ^ "Romania, 4th in Europe in TB", România Liberă
- ^ "Our patients vs. theirs: How many hospitals has Romania compared to other EU countries", Wall-Street.ro Archived 2013-02-08 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Fewer hospital beds for sick Romanians", România Liberă
- ^ "Personalul medico-sanitar pe categorii, forme de proprietate, sexe, macroregiuni, regiuni de dezvoltare și județe", Institutul Național de Statistică
- ^ "«De profesie: medic în România». Cum încearcă ministrul Nicolăescu să-i țină pe doctori în țară", Adevărul, 2 April 2013
- ^ "Cultural aspects". National Institute for Research & Development in Informatics, Romania. Archived from the original on 7 March 2008. Retrieved 28 August 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "Mihai Eminescu" (in Romanian). National Institute for Research & Development in Informatics, Romania. Archived from the original on 31 December 2007. Retrieved 20 January 2008.[dead link]
- ^ Tom Sandqvist, DADA EAST: The Romanians of Cabaret Voltaire, London MIT Press, 2006.
- ^ Ștefănescu, Alex. (1999). Nichita Stănescu, The Angel with a Book in His Hands (in Romanian). Mașina de scris. p. 8. ISBN 978-973-99297-4-5.
- ^ "Brancusi's 'Bird in Space' Sets World Auction Record for Sculpture at $27,456,000". Antiques and the Arts Online. Archived from the original on 13 February 2006. Retrieved 20 January 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "November 9, The price record for a Brancusi masterpiece was set up in 2005 when "Bird in Space" was sold for USD 27.5 M". Romanian Information Center in Brussels. Archived from the original on 14 May 2011. Retrieved 20 January 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "George Enescu, the composer". International Enescu Society. Retrieved 20 January 2008.
- ^ "Sounds Like Canada feat. Gheorghe Zamfir". CBC Radio. 17 January 2006. Archived from the original on 28 April 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "Gheorghe Zamfir, master of the pan pipe". Gheorghe Zamfir, Official Homepage. Retrieved 20 January 2008.
- ^ "Inna Biography". BBC. Retrieved 26 October 2013.
- ^ "10 One-Hit Wonders to Be or Not to Be?". vh1.i. 7 March 2014.
- ^ Arsenie, Dan. "Paula Seling despre rezultatul la Eurovision 2010: "Mai bine de atât nu se putea!"". EVZ.ro. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ "Cannes 2007 Winners". Alternative Film Guide. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ Mike Collett-White (16 February 2013). "Romanian film "Child's Pose" wins Berlin Golden Bear". Reuters.
- ^ "World Heritage Site – Romania". UNESCO. Retrieved 31 January 2008.
- ^ "Report on the Nominations from Luxembourg and Romania for the European Capital of Culture 2007" (PDF). The Selection Panel for the European Capital of Culture (ECOC) 2007. 5 April 2004. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ "Muzeul National Peles | Site-ul oficial al castelelor Peles si Pelisor". Peles.ro. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ "Castelul Bran". Viaromania.eu. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ "ZILE LIBERE 2013. Calendarul sărbătorilor legale ale românilor de anul acesta", Gândul.info, 6 March 2013
- ^ Improve It Grup S.R.L. "Traditii si obiceiuri romanesti. Artizanat traditional romanesc. Arta populara". Traditii.ro. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ Insider, Romania (21 December 2012). "Winter holidays and Christmas traditions in Romania: the Bear dance, the Masked carolers and the Goat". Romania-Insider.com. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ "ROMANIA - Traditions and Folklore - Official Travel and Tourism Information". Romaniatourism.com. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ "Ministrul Agriculturii: UE accepta ca mieii de Pasti si porcii de Craciun sa fie sacrificati in mod traditional - Actualitate". HotNews.ro. 11 August 2014. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ Martisor, a Spring celebration for Eastern Europeans (29 June 2014). "Martisor, a Spring celebration for Eastern Europeans". Foreigners In Uk. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ "Christina Bradatan, Cuisine and Cultural Identity in Balkans". Scholarworks.iu.edu. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ "Retete traditionale Moldova: retete peste sau cu carne de porc". Bucataras.ro. 15 December 2008. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ "Bucatarie romaneasca – Cultura si retete – Articole". Gastronomie.ele.ro. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ "Țuica production consumed 75% of Romanian plums in 2003". Regard-est.com. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ "Study in Romania". Educations.com. 5 February 2008. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ Tudor, Diana. "Romania enters global top 10 for beer consumption | Ziarul Financiar". Zf.ro. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ "Topul sporturilor în funcție de numărul de sportivi legitimați". zf.ro. 12 January 2012.
- ^ "Romania: FIFA/Coca-Cola World Ranking". FIFA.com. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ "Hagi leaves Romania post". BBC Sport. 26 November 2001. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
Hagi earned a legendary status in Romania where he spearheaded the 'Golden Generation' of players...
- ^ "Hagi snubs Maradona". BBC Sport Online. 6 April 2001. Retrieved 31 August 2008.
- ^ a b c "Romania". The Europa World Year Book. Vol. 2. Routledge. 2007.
- ^ http://www.wtatennis.com/rankings
- ^ "Cristina Neagu - World Handball Player of the Year 2010". Ihf.info. 13 January 2011. Retrieved 24 February 2014.
- ^ "Originea jocului de Oina - Sport National Roman". Oina.ro. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ "Recurs la ISTORIE: De ce s-a "prăbușit" România la Olimpiada de la Londra?". adevarul.ro. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ Herman, Robin (28 March 1976). "Gymnast Posts Perfect Mark". New York Times. Retrieved 13 August 2008.
Sources
Primary sources
- The Ancient History of Herodotus (Translated by William Beloe) (1859). Derby & Jackson.
- Eutropius, Abridgment of Roman History (Translated by John Selby Watson) (1886). George Bell and Sons.
Secondary sources
- Hitchins, Keith (2014). A Concise History of Romania. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-87238-6.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Pohl, Walter (2013). "National origin narratives in the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy". In Geary, Patrick J.; Klaniczay, Gábor (eds.). Manufacturing Middle Ages: Entangled History of Medievalism in Nineteenth-Century Europe. BRILL. pp. 13–50. ISBN 9789004244870.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
External links
- Country Profile from BBC News.
- Romania Article and Country Profile from Encyclopaedia Britannica
- Romania Profile from Balkan Insight.
- "Romania". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Romania information from the United States Department of State.
- Portals to the World from the United States Library of Congress.
- Romania at UCB Libraries GovPubs.
- Template:Dmoz
 Wikimedia Atlas of Romania
Wikimedia Atlas of Romania Geographic data related to Romania at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Romania at OpenStreetMap- Key Development Forecasts for Romania from International Futures.
- Romanian Law and Miscellaneous – English
- Government
- Culture and history links
- Travel
- Romania
- Countries in Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Former monarchies of Europe
- Liberal democracies
- Member states of NATO
- Member states of the Council of Europe
- Member states of the European Union
- Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean
- Member states of the United Nations
- Republics
- Romance countries and territories
- Romanian-speaking countries and territories
- States and territories established in 1878
- Southeastern Europe
- Central Europe