Megalopolis
| Ekistics |
|---|
| Definitions of cities |
| Lists |
|
|

A megalopolis (sometimes improperly called a megapolis) or megaregion is typically defined as a chain of roughly adjacent metropolitan areas. The term was used by Patrick Geddes in his 1915 book Cities in Evolution,[1] by Oswald Spengler in his 1918 book, The Decline of the West, and Lewis Mumford in his 1938 book, The Culture of Cities, which described it as the first stage in urban overdevelopment and social decline. Later, it was used by Jean Gottmann in 1954, to describe the chain of metropolitan areas along the northeastern seaboard of the U.S. extending from Boston, Massachusetts through New York City, Philadelphia, Baltimore, and ending in Washington, D.C. and Northern Virginia.[2][3][4] The latter is sometimes called the "BosWash megalopolis".
Definitions
Megapolis is a Western deformation of the Greek word that derived from Template:Lang-gr - 'great' and Template:Lang-gr - 'city', therefore literally a 'great city'. This term is closer in meaning to megacity. Because in Greek, πόλις is feminine, the correct term is megalopolis. The metric prefix mega- represents the number of million (1,000,000) in the metric system.
A megalopolis, also known as a megaregion, is a clustered network of cities. Gottmann defined its population as 25 million.[5] Doxiadis defined a small megalopolis a similar cluster with a population of about 10 million.[6][7][8] America 2050,[9] a program of the Regional Plan Association, lists 11 megaregions in the United States and Canada.[6] Literally, megalopolis in Greek means a city of exaggerated size where the prefix megalo- represents a quantity of exaggerated size.[10] Megapolitan areas were explored in a July 2005 report by Robert E. Lang and Dawn Dhavale of the Metropolitan Institute at Virginia Tech.[11] A later 2007 article by Lang and Nelson uses 20 megapolitan areas grouped into 10 megaregions.[12] The concept is based on the original Megalopolis model.[8]
Modern interlinked ground transportation corridors, such as rail and highway, often aid in the development of megalopolises. Using these commuter passageways to travel throughout the megalopolis is informally called megaloping. This term was coined by Davide Gadren and Stefan Berteau.[13]
Africa
- Cairo–Giza–Qalyubia–Helwan–6th of October City (Greater Cairo), Egypt (16 million) The area around the Nile is also very densely populated.
- Nile River Delta Governorates (Alexandria, Beheira, Kafr el-Sheikh, Gharbia, Monufia, Qalyubia, Dakahlia, Damietta, Al Sharqia, and Port Said) have a combined population of 41,045,135. The total area of these Governorates is 18,199 square miles making the population density 2,255.4 per square mile.
- The Gauteng City Region (PWV) in South Africa, which includes the urbanised portion of Gauteng Province (Pretoria, Centurion, Midrand, Johannesburg and the Vaal Triangle, with a population of over 10 million)[14][15][16]
- The region in Morocco including El Jadida-Casablanca-Rabat-Salé-Kenitra, concentrating in the long coastal belt, on around 250 km with a depth of 40 to 50 km, more than 11 million inhabitants.[citation needed]
- The Nairobi Metropolitan Region consisting of the counties of (Kajiado-Kiambu-Nairobi-Machakos-Murang'a) in Kenya, which have a combined population of 8 million people.[17]
Asia
East Asia
China
Emerging megalopolises in China (in decreasing order of population):
- Pearl River Delta Megalopolis (珠江三角洲): (Hong Kong, Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou, Foshan, Jiangmen, Zhongshan, Zhuhai, Macau, Huizhou) (55,000,000),[18][19] if Shantou/Quanzhou added (Guangdong Megalopolis) 70,000,000.
- Yangtze River Delta Megalopolis (長江三角洲): (Shanghai, Nanjing, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Jingjiang, Wuxi, Changzhou, Zhenjiang, Yangzhou, Taizhou, Nantong, Huzhou, Jiaxing, Shaoxing, Jiangyin, Haimen, Zhangjiagang, Zhoushan, Ma'anshan) (88,000,000)[20]
- Bohai Economic Rim (环渤海经济圈): Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Anshan, Fushun, Dandong, Sinuiju, Tangshan, Yantai, Shenyang, Jinan, Qinhuangdao, Qingdao, Weihai (66,400,000)[21]
- South China Coast : Xiamen, Fuzhou, Wenzhou, Shantou, Jieyang, Chaozhou (25,000,000)
- Central Plain (中原): Kaifeng, Xinxiang, Zhengzhou, Luoyang (14,170,000)
- The central Liaoning city cluster in China. Within 150 km from its center Shenyang (7.2 million), it has Fushun (3 million), Anshan City (3.6 million), Benxi (1.5 million), Liaoyang (1.8 million), Yingkou (2.2 million), Panjin (1.2 million), and Tieling (3.4 million), with a total population of 23 million. And it can be further extended to Dalian (6.2 million), Fuxin (2 million) and Dandong (2.4 million). This area used to be the most industrialized region in China. It declined during 1980s-1990s, but in recent years, it has rapidly revived.
- Northeastern Cities or the Harbin–Changchun Area (哈尔滨长春地区): Harbin, Qiqihar, Daqing, Changchun, Jilin City, Siping including Rason in North Korea and Vladivostok in Russia (21,832,000)
- Sichuan basin (四川盆地) or the Chengyu Megalopolis (成渝都市圈): Chengdu, Chongqing, Zigong, Luzhou (20,878,000)
- Greater Wuhan Megalopolis (大武汉都市圈): Wuhan, Huangshi, Xinyang, Jiujiang, Yueyang (20,000,000)
- Guanzhong (关中): Xi'an, Xianyang, Baoji (16,722,000)
- Greater Changsha Metropolitan region (长株潭城市群): Changsha, Zhuzhou, Xiangtan(12,994,400 in 2000)
In July 2012, the Economist Intelligence Unit brought out a report entitled; Supersized cities: China’s 13 megalopolises, which pinpoints the 13 emerging megalopolises in China, and highlights the demographic and income trends that are shaping their development.
Japan
- Taiheiyō Belt – Ibaraki, Saitama, Chiba, Tokyo, Kanagawa, Shizuoka, Aichi, Gifu, Mie, Osaka, Hyōgo, Wakayama, Okayama, Hiroshima, Yamaguchi, Kitakyūshū, Fukuoka, and Ōita in Japan. (80,000,000) [citation needed]
South Korea
- Seoul National Capital Area - Seoul, Incheon, Suwon, Goyang, Yongin, Seongnam, and the rest of Gyeonggi-do: (25,000,000)[22]
- Southeast Economic Belt - Busan, Daegu, Pohang, Ulsan, Changwon, and the rest of South Gyeongsang Province: (8,500,000)[citation needed]
South Asia

Transnational
- Bangladesh and India/Bengal- Kolkata, Dhaka and Chittagong (37,000,000)
India
- Maharashtra - Mumbai (also includes Thane, Navi Mumbai, Kalyan-Dombivali, Ulhasnagar, Vasai-Virar, Ambernath, Badlapur, and Panvel), Pune (also includes Pimpri-Chinchwad), Aurangabad, Nashik, Ahmednagar, Alibag (39,500,000)
- Delhi National Capital Region and Jaipur (60,000,000)
- South India - Hyderabad, Bengaluru and Chennai (Although widely separated geographically) (31,500,000)
- Gujarat - Ahmedabad, Gandhinagar, Surat, Vadodara, Rajkot, Anand, Nadiad, Bharuch, Ankleshwar (19,200,000)
Iran
- Greater Tehran: A region located in Iranian Tehran and Alborz Province in central Northern Iran with its influence expanding in Qom Province, Qazvin Province and Mazandaran Province, home for at least 15 million people, it is one of the most populous urban areas in the Greater Middle East and the surrounding regions. Tehran was a small village 200 years ago when it was first chosen as the Capital city and it has been growing at a very fast rate.
Southeast Asia
| Rank | Megalopolis Name | Country | Population in millions |
Major cities | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Java | 143 | Jakarta, Bandung, Sukabumi, Serang, Kediri, East Java, Malang, Surabaya, Yogyakarta, | Java | Bandung, Banjar, Batu, Bekasi, Blitar, Bogor, Cianjur, Cilegon, Cimahi, Depok, Malang, Semarang, South Tangerang, Sukabumi, Surabaya, Tasikmalaya, Tangerang, Tegal, Serang. Purwokerto | |
| 2 | Mega Manila | 40+ | Manila, Angeles, Baguio, Batangas, Dagupan, Olongapo | ||
| 3 | Central Thailand | 20+ | Bangkok, Ayuthaya, Pattaya | ||
| 4 | Southeast Economic Zone | 15+ | Đồng Nai, Bình Dương, Ho Chi Minh City, Bà Rịa–Vũng Tàu Province, Long An, Tiền Giang |
- Western Java [Serang-Jakarta-Bandung] (45,000,000)
- Central Luzon [Dagupan-Manila-Lucena] (36,000,000)
- Central-Thai Bangkok-Ayutthaya-Pattaya] (16,000,000)
- Central Java [Semarang-Solo-Yogyakarta] (10,000,000)
- East Java [Kediri-Malang-Surabaya (13,000,000)
- Malaya Kuala Lumpur-Selangor-Seremban] (8,000,000)
- Sijori [Johor Bahru-Singapore-Batam-Bintan] (9,000,000)
- Red River Delta in Vietnam (Hanoi, Hai Phong, Thanh Hóa, Nam Dinh, & Hai Duong) (9,700,000)[23][24]
Europe



Transnational
| Rank | Megalopolis Name | Population in millions |
Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Blue Banana | 110–130[25] | Liverpool–Manchester–Leeds–Birmingham–London–Lille–Brussels–Antwerp–Amsterdam–Rotterdam–The Hague–Luxembourg–Rhine-Ruhr–Frankfurt am Main–Munich–Stuttgart–Strasbourg–Basel–Zürich–Turin–Milan |
| 2 | Golden Banana | 30–35[26] | Turin–Genoa–Lyon–Monaco–Nice–Toulon–Marseille–Nîmes–Montpellier–Narbonne–Perpignan–Toulouse–Andorra– Manresa–Girona–Barcelona–Tarragona–Castellón de la Plana–Sagunt–Valencia–Alicante–Murcia–Cartagena |
| 3 | Green Banana | 40 | Gdańsk–Katowice–Ostrava–Olomuc–Brno–Wien–Bratislava–Budapest–Ljubljana–Zagreb–Trieste |
France
| Rank | Megalopolis Name | Population in millions |
Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Paris metropolitan area | 12.3[27] | Paris & most of Île-de-France |
| 2 | Lyon economic region | 5.5[26] | Lyon & Rhône-Alpes river area |
| 3 | Marseille metropolitan region | 1.8[26] | Marseille, Aix-en-Provence |
| 4 | Toulouse economic region | 1.5[26] | Toulouse, Andorra (independent state, not part of France |
| 5 | Nice economic region | 1.1[26] | Nice, Monaco (independent city state, not part of France |
Germany
| Rank | Megalopolis Name | Population in millions |
Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rhine-Ruhr | 13.5 | Cologne, Düsseldorf, Dortmund, Essen |
| 2 | Berlin-Brandenburg | 5.95 | Berlin, Potsdam |
| 3 | Frankfurt Rhine-Main | 5.52 | Frankfurt, Wiesbaden, Mainz |
| 4 | Stuttgart Metropolitan Region | 5.29[26] | Stuttgart |
| 5 | Munich Metropolitan Region | 5.2[26] | Munich |
| 6 | Hamburg Metropolitan Region | 5.0 | Hamburg |
| 7 | Saxon triangle | 4.36[26] | Leipzig, Halle, Dresden |
| 8 | Hannover-Braunschweig-Göttingen-Wolfsburg EMR | 3.91[26] | Hannover, Braunschweig, Göttingen, Wolfsburg |
| 9 | Nuremberg Metropolitan Region | 3.5[26] | Nuremberg |
| 10 | Bremen/Oldenburg Metropolitan Region | 2.37[26] | Bremen, Oldenburg |
Italy
| Rank | Megalopolis Name | Population in millions |
Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Grande Milano | 7.5 | Milan |
| 2 | Naples metropolitan area | 4.46 | Naples |
| 3 | Rome metropolitan area | 4.3 | Rome |
| 4 | Turin economic region | 4.1 | Turin & Piedmont centre and south area |
| 5 | Genoa metropolitan region | 1.5 | Genoa |
| 6 | Conca d'Oro | 1.1 | Palermo and neighboring cities |
Low Countries
Netherlands, Belgium & Luxembourg:[26]
| Rank | Megalopolis Name | Population in millions |
Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Randstad | 7.5 | Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague, Utrecht |
| 2 | Flemish Diamond | 5.5 | Brussels, Antwerp, Ghent, Leuven |
| 3 | Brabantse Stedenrij | 2.0 | Eindhoven, Tilburg, Breda, 's-Hertogenbosch, Helmond |
Spain
| Rank | Megalopolis Name | Population in millions |
Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Barcelona | 6.7 | Barcelona & coastal towns of Catalonia (from Tarragona to Figueres) |
| 2 | Madrid region | 6.3 | Madrid |
| 3 | Valencia | 2.2 | Valencia, Sagunto |
| 3 | Murcia-Alicante | 2.2 | Murcia, Alicante, Cartagena, Benidorm |
United Kingdom
| Rank | Megalopolis Name | Population in millions |
Major cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | London commuter belt | 21.0[30] | London, Southend-on-Sea, Chatham, Luton, Reading |
| 2 | Northern England | 9.4[26][31] | Manchester, Leeds, Liverpool, Sheffield, Warrington, Bradford, Birkenhead, Preston, Blackburn, Blackpool |
| 3 | English midlands | 6.3[26][31] | Birmingham, Nottingham, Coventry, Leicester, Wolverhampton, Derby, Stoke-on-Trent |
| 4 | Central Belt | 3.6[31] | Glasgow, Edinburgh |
| 5 | South Hampshire-Brighton | 2.8[26][31] | Southampton, Portsmouth, Brighton, Worthing, Littlehampton, Bournemouth |
| 6 | Tyne & Wear Region | 2.2[26][31] | Newcastle, Sunderland, Middlesbrough |
| 7 | Cardiff-Bristol-Swansea | 2.2[26][31] | Cardiff, Bristol, Swansea, Newport |
North America
Canada

| Megalopolis Name | Population in millions 2000 |
Population in millions 2025 (projected) |
Population percent growth 2000 - 2025 (projected) |
Major cities | Related articles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quebec City – Windsor Corridor | 18 | 21 | 16.7% | Hamilton, Kitchener, London, Mississauga, Montreal, Oshawa, Ottawa, Quebec City, Toronto, Windsor | Quebec City – Windsor Corridor, Southern Ontario |
| Calgary-Edmonton Corridor | 2 | 4 | 100% | Calgary, Edmonton, Red Deer, St. Albert, Airdrie | Calgary-Edmonton Corridor, Calgary Region, Edmonton Capital Region, Central Alberta |
Mexico
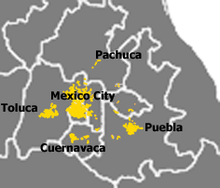
| Megalopolis Name | Population in millions 2000 |
Population in millions 2025 (projected) |
Population percent growth 2000 - 2025 (projected) |
Major cities | Related articles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bajío | 8.5 | ? | ?% | León, Querétaro, Aguascalientes, Celaya, Irapuato, Salamanca | Bajío |
| Greater Mexico City | 28 | ? | ?% | Mexico City, Puebla, Cuernavaca, Toluca, Pachuca, Tula, Tlaxcala, Cuautla, Tulancingo |
United States




Note that one city, Houston, is listed in two different Megalopolis regions (the Gulf Coast and Texas Triangle).
Oceania
Australia
| Megalopolis Name | Population in millions |
Major cities |
|---|---|---|
| Sydney Region | 5.6[35] | Greater Sydney (including Central Coast and Blue Mountains) (4.75 million), Newcastle (365,000), Wollongong (294,000) |
| South East Queensland | 3.5[35] | Greater Brisbane (2.2 million), Gold Coast-Tweed Heads (681,000), Sunshine Coast (330,000), Toowoomba (149,000) |
South America

Brazil
| Megalopolis Name | Population in 2013 |
Major cities | Other cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expanded Metropolitan Complex of São Paulo | +32,200,000 | São Paulo and Campinas | Sorocaba, Jundiaí, São José dos Campos, Piracicaba and Santos |
Colombia
| Megalopolis Name | Population in 2013 |
Major cities | Other cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bogota National Capital Metropolis | +15,000,000 | Bogotá, Soacha, Facatativá, Chía, Fusagasuga and Zipaquirá | Madrid, Funza, Cajica, Ubate, Sibate, Guaduas, and Tocancipá |
| Northeast Atlantic Region | +6,000,000 | Barranquilla, Cartagena, Santa Marta | Ciénaga, Malambo, Baranoa and Turbaco |
| Medellín Valley Metropolis | +4,500,000 | Medellin, Bello, Itagui, and Envigado | Caldas, Copacabana, La Estrella, Sabaneta, Girardota, and Barbosa |
| Greater Cali | +3,800,000 | Cali, Yumbo, and Palmira | Candelaria, El Calmero, and La Cumbre |
Venezuela
| Megalopolis Name | Population in 2013 |
Major cities | Other cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caracas-Valencia Megalopolis | +9,000,000 | Caracas, Valencia, and Maracay | Cagua, Maiquetia, and Guatire |
Argentina

| Megalopolis Name | Population in 2013 |
Major cities | Other cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Greater Buenos Aires | 13,641,973 | Buenos Aires, Merlo, Buenos Aires, Quilmes, Banfield, Buenos Aires | Lanús, Hurlingham, Buenos Aires , and Avellaneda |
Peru
| Megalopolis Name | Population in 2013 |
Major cities | Other cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lima-Callao Megalopolis | 10,523,796 | Lima and Callao | Provincias Lima Norte, Provincias Lima Sur, and Provincias Lima Este |
See also
|
References
- ^ Geddes, Patrick (1915). Cities in Evolution. London: Williams & Norgate.
- ^ Gottmann, Jean (1954). L'Amerique. Paris: Hachette.
- ^ Gottmann, Jean (1957). "Megalopolis, or the urbanization of the Northeastern Seaboard". Economic Geography. 33 (3): 189–200. doi:10.2307/142307.
- ^ Gottmann, Jean (1961). Megalopolis. The Urbanized Northeastern seaboard of the United States. New York: The Twentieth Century Fund.
- ^ Gottmann, Jean (1989). Since Megalopolis. The Urban Writings of Jean Gottmann. Baltimore and London: The Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 163.
- ^ a b c "Megaregions". Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- ^ "Who's Your City?: What Is a Megaregion?". 19 March 2008. Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- ^ a b Cities: Capital for the New Megalopolis.Time magazine, November 4, 1966. Retrieved on July 19, 2010.
- ^ "About Us - America 2050". Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- ^ Definition of the prefix megalo-. The American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition copyright ©2000 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Updated in 2009. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
- ^ http://www.mi.vt.edu/uploads/megacensusreport.pdf "Beyond Megalopolis" by the Metropolitan Institute at Virginia Tech
- ^ http://www.surdna.org/usr_doc/The_Rise_of_the_Megapolitans.pdf
- ^ Tremble, Sam (May 30, 2007). "Fumbling Toward Portland". Philadelphia City Paper.
- ^ http://www.joburg.org.za/2006/aug/aug30_globalcity.stm
- ^ http://www.joburg.org.za/2006/july/jul20_cityregion.stm
- ^ M Shilowa to debate Gauteng's position on global city region, 29 Aug
- ^ Cabinet Secretary names team to modernize Nairobi city transport 23 February 2015. Retrieved 1 May 2015.
- ^ report: World's biggest cities merging into 'mega-regions'
- ^ "关于长江三角洲构建世界第六大城市群的思考". Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- ^ Vidal, John (2010-03-22). "UN report: World's biggest cities merging into 'mega-regions'". The Guardian. London.
- ^ "Foreign investment shows trend of "moving northward"". china-embassy.org. 2004-05-14. Retrieved 2010-01-09.
- ^ A government publication states that on 1 November 2010, the population of “Seoul Metropolitan Area” stood at 23,616 thousand, which is the sum of the figures given for Gyeonggi-do (11,270 thousand), Seoul (9,708 thousand) and Incheon (2,638 thousand), apparently including the periphery.
Source: “Preliminary Results of the 2010 Population and Housing Census” (PDF). Statistics Korea. 21 January 2011. Retrieved 23 July 2011. - ^ "广西北部湾经济区概况". Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- ^ "Chinese Cities on Beibu Gulf Increase Cooperation". Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- ^ Ina Schmidt. "The European Blue Banana". Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t From Territorial Cohesion to the New Regionalized Europe. Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- ^ "INSEE - Paris". Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- ^ EMR
- ^ "Brookings". The Brookings Institution. 30 November 2012. Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- ^ "Greater London Authority". Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f ESPON
- ^ Regional Plan Association (2008). America 2050: An Infrastructure Vision for 21st Century America. New York: Regional Plan Association.
- ^ "Megapolitan: Arizona's Sun Corridor". Morrison Institute for Public Policy. May 2008. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ "When Phoenix, Tucson Merge". The Arizona Republic. 2006-04-09. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ a b 3218.0 - Regional Population Growth, Australia, 2012-13, Australian Bureau of Statistics, 19 September 2014, retrieved 19 September 2014
