Fox News
| Country | United States |
|---|---|
| Headquarters | 1211 Avenue of the Americas New York, New York, U.S. 10036 |
| Programming | |
| Language(s) | English |
| Ownership | |
| Owner | Fox News Group[citation needed] (21st Century Fox) |
Fox News (officially known as the Fox News Channel) is an American basic cable and satellite television news channel owned by the Fox Entertainment Group, a subsidiary of 21st Century Fox. The channel broadcasts primarily from studios at 1211 Avenue of the Americas, New York City, New York.
The channel was created by Australian-American media mogul Rupert Murdoch, who hired former Republican Party media consultant and CNBC executive Roger Ailes as its founding CEO.[1]
It launched on October 7, 1996,[2] to 17 million cable subscribers.[3] Fox News grew during the late 1990s and 2000s to become a dominant cable news network in the United States.[4] Rupert Murdoch is the current chairman and acting CEO of Fox News.[5][6]
Fox News Channel has been accused of biased reporting, perpetuating conspiracy theories,[7][8][9][10] and promoting the Republican Party.[11][12][13] Critics have cited the channel as detrimental to the integrity of news overall.[14][15] Fox News employees have responded that news reporting operates independently of its opinion and commentary programming, and have denied bias in news reporting.[16] The network has also been accused of permitting sexual harassment and racial discrimination by on-air hosts, executives, and employees, paying out millions of dollars in legal settlements.[17][18][19][20][21] The company is currently under federal investigation for its harassment settlements and other alleged misconduct.[22][23]
As of February 2015, approximately 94,700,000 US households (81.4% of cable, satellite & telco customers) receive the Fox News Channel.[24]
History
Early years
In May 1985, Australian publisher Rupert Murdoch announced that he and American industrialist and philanthropist Marvin Davis intended to develop "a network of independent stations as a fourth marketing force" to compete directly with CBS, NBC, and ABC through the purchase of six television stations owned by Metromedia.[25] In July 1985, 20th Century Fox announced that Murdoch had completed his purchase of 50 percent of Fox Filmed Entertainment, the parent company of 20th Century Fox Film Corporation.[26] A year later, 20th Century Fox earned $5.6 million in its fiscal third period ended May 31, 1986, in contrast to a loss of $55.8 million in the third period of the previous year.[27]
Prior to founding FNC, Murdoch had gained experience in the 24-hour news business when News Corporation's BSkyB subsidiary began Europe's first 24-hour news channel (Sky News) in the United Kingdom in 1989.[28] With the success of his fourth network efforts in the United States,[29][30] experience gained from Sky News and the turnaround of 20th Century Fox, Murdoch announced on January 31, 1996, that News Corp. would launch a 24-hour news channel on cable and satellite systems in the United States as part of a News Corp. "worldwide platform" for Fox programming: "The appetite for news – particularly news that explains to people how it affects them – is expanding enormously".[31]


In February 1996, after former U.S. Republican Party political strategist and NBC executive[32] Roger Ailes left cable television channel America's Talking (now MSNBC), Murdoch asked him to start Fox News Channel. Ailes demanded five months of 14-hour workdays and several weeks of rehearsal shows before its launch on October 7, 1996.[33]
At its debut 17 million households were able to watch FNC;[3] however, it was absent from the media markets of New York City and Los Angeles. Rolling news coverage during the day consisted of 20-minute single-topic shows such as Fox on Crime or Fox on Politics, surrounded by news headlines. Interviews featured facts at the bottom of the screen about the topic or the guest. The flagship newscast at the time was The Schneider Report, with Mike Schneider's fast-paced delivery of the news. During the evening, Fox featured opinion shows: The O'Reilly Report (now The O'Reilly Factor), The Crier Report (hosted by Catherine Crier) and Hannity & Colmes.
From the beginning, FNC has placed heavy emphasis on visual presentation. Graphics were designed to be colorful and attention-getting; this helped the viewer to grasp the main points of what was being said, even if they could not hear the host (with on-screen text summarizing the position of the interviewer or speaker, and "bullet points" when a host was delivering commentary). Fox News also created the "Fox News Alert," which interrupted its regular programming when a breaking news story occurred.
To accelerate its adoption by cable providers, Fox News paid systems up to $11 per subscriber to distribute the channel.[34] This contrasted with the normal practice, in which cable operators paid stations carriage fees for programming. When Time Warner bought Ted Turner's Turner Broadcasting System, a federal antitrust consent decree required Time Warner to carry a second all-news channel in addition to its own CNN on its cable systems. Time Warner selected MSNBC as the secondary news channel, not Fox News. Fox News claimed that this violated an agreement (to carry Fox News). Citing its agreement to keep its U.S. headquarters and a large studio in New York City, News Corporation enlisted the help of Mayor Rudolph Giuliani's administration to pressure Time Warner Cable (one of the city's two cable providers) to transmit Fox News on a city-owned channel.[35] City officials threatened to take action affecting Time Warner's cable franchises in the city.[36]
During the September 11, 2001 attacks, Fox News was the first news organization to run a news ticker on the bottom of the screen to keep up with the flow of information that day. The ticker has remained, informing viewers about additional news which reporters may not mention on-screen and repeating news mentioned during a broadcast; it has proven popular with viewers.[37]
Outlets

FNC maintains an archive of most of its programs. This archive also includes Fox Movietone newsreels. Licensing for the Fox News archive is handled by ITN Source, the archiving division of ITN.[38]
Television
FNC presents a variety of programming, with up to 15 hours of live broadcasting per day in addition to programming and content for the Fox Broadcasting Company. Most programs are broadcast from Fox News headquarters in New York City (at 1211 Avenue of the Americas), in its streetside studio on Sixth Avenue in the west wing of Rockefeller Center, sharing its headquarters with sister channel Fox Business Network. Fox News Channel has eight studios at its New York City headquarters that are used for its and Fox Business' programming: Studio B (used for Fox Business programming), Studio D (which has an area for studio audiences; and is used by Outnumbered), Studio E (used for Fox & Friends, Happening Now, Your World with Neil Cavuto, and certain editions of America's News HQ), Studio F (used for The Story With Martha Maccallum, The Five, and America's Election Headquarters) Studio G (which houses Fox Business shows), Studio H (Fox News Deck used for Shepard Smith Reporting and breaking news coverage), Studio J (used for Fox & Friends First, America's Newsroom, Hannity and Justice with Judge Jeanine) and the Web Studio (used for Fox News Live internet shows).
The remaining programs (such as Special Report with Bret Baier, On the Record w/ Greta Van Susteren, and editions of America's News HQ not broadcast from the New York City studios) are broadcast from Fox News's Washington, D.C. studio, located on Capitol Hill across from Union Station in a secured building shared by a number of other television networks (including NBC News and C-SPAN). Audio simulcasts of the channel are aired on XM Satellite Radio and Sirius Satellite Radio.

In an October 11, 2009 New York Times article, Fox articulated that its hard-news programming runs from "9 a.m. to 4 p.m. and 6 to 8 p.m. on weekdays" and "[is] objective"; however, it makes no such claims for its other broadcasts, which primarily consist of editorial journalism and commentary.[39]
Fox News Channel began broadcasting in the 720p resolution format on May 1, 2008.[40] This format is available on all major cable and satellite providers.
Radio
With the growth of FNC, the company introduced a radio division, Fox News Radio, in 2003.[41] Syndicated throughout the United States, the division provides short newscasts and talk radio programs featuring personalities from the television and radio divisions. In 2006, the company also introduced Fox News Talk, a satellite radio station featuring programs syndicated by (and featuring) Fox News personalities.
Online
Introduced in December 1995,[42] the Fox News website features the latest coverage (including columns by FNC television, radio and online personalities). Video clips are also available on Foxnews.com and Foxbusiness.com. Fox News Latino is the version aimed at the Hispanic audience, although presented almost entirely in English, with a Spanish section.[43]
In September 2008, FNC joined other channels in introducing a live streaming segment to its website: The Strategy Room, designed to appeal to older viewers. It airs weekdays from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. and takes the form of an informal discussion, with running commentary on the news. Regular discussion programs include Business Hour, News With a View and God Talk.[44] In March 2009, The Fox Nation was launched as a website intended to encourage readers to post, commenting on the news.[45] Fox News Mobile is the portion of the FNC website dedicated to streaming news clips formatted for video-enabled mobile phones.[46]
Notable personalities
Program hosts
- David Asman
- Bret Baier
- Julie Banderas
- Maria Bartiromo
- Eric Bolling
- Shannon Bream
- Tucker Carlson
- Neil Cavuto
- Steve Doocy
- Ainsley Earhardt
- Harris Faulkner
- Melissa Francis
- Jesse Waters
- Kimberly Guilfoyle
- Greg Gutfeld
- Sean Hannity
- Pete Hegseth
- Bill Hemmer
- Abby Huntsman
- Gregg Jarrett
- Kennedy
- Brian Kilmeade
- Howard Kurtz
- Jenna Lee
- Martha MacCallum
- Meghan McCain
- Clayton Morris
- Arthel Neville
- Dana Perino
- Jeanine Pirro
- Julie Roginsky
- Jon Scott
- Shepard Smith
- Chris Wallace
- Juan Williams
Correspondents and substitute anchors
- Heather Childers
- Patti Ann Browne
- Carl Cameron
- Christine Clayburg
- Claudia Cowan
- Janice Dean
- Mike Emanuel
- Kristin Fisher
- Lea Gabrielle
- Trace Gallagher
- Anna Gilligan
- Lauren Green
- Jennifer Griffin
- Molly Henneberg
- Catherine Herridge
- Adam Housley
- Brit Hume
- Phil Keating
- Rick Leventhal
- Molly Line
- Dagen McDowell
- Hollie McKay
- Andrew Napolitano
- Heather Nauert
- Kate Obenshain
- Charles Payne
- Katie Pavlich
- Uma Pemmaraju
- Geraldo Rivera
- John Roberts
- James Rosen
- Eric Shawn
Regular guests and contributors
- Dr. Keith Ablow
- Mike Baker
- John R. Bolton
- Scott Brown
- Tammy Bruce
- Pat Caddell
- Herman Cain
- Mo Elleithee[47]
- Ezekiel Emanuel[47]
- Nigel Farage[48]
- Steve Forbes
- Newt Gingrich
- Bernard Goldberg
- Marie Harf[47]
- Stephen Hayes
- Mollie Hemingway[47]
- Steve Hilton[47]
- Governor Mike Huckabee
- Laura Ingraham
- Charles Krauthammer
- John "Bradshaw" Layfield
- Rich Lowry
- Frank Luntz
- Leslie Marshall
- Dennis Miller
- Judith Miller
- Fr. Jonathan Morris
- Lt. Col. Oliver North
- Charles Payne
- Lt. Col. Ralph Peters
- Karl Rove
- Dr. Ben Stein
- Katherine Timpf
- Joe Trippi
- Tyrus
- Stuart Varney
- Lis Wiehl
Former hosts and contributors
- Louis Aguirre (former morning host, now host of The Insider)
- Dari Alexander (now at WNYW in New York City)
- Dr. Jennifer Ashton (now at ABC News)
- Tiki Barber (now with CBS Sports Network)
- Rudi Bakhtiar (now PR Director for the Public Affairs Alliance of Iranian Americans)
- Glenn Beck (former afternoon host; now on TheBlaze)
- Bob Beckel (terminated amid racist remarks)
- Lisa Bernhard (entertainment correspondent)
- Tony Blankley (deceased)
- Dave Briggs
- Eric Burns (not renewed)
- Brenda Buttner (deceased)
- Joseph A. Cafasso (stepped down over allegations he overrepresented his military record)
- Alisyn Camerota (now at CNN)
- Gretchen Carlson
- Dr. Ben Carson (joined Trump cabinet)
- Steve Centanni (retired in August 2014)
- Liz Cheney (now in public service)
- Kiran Chetry (later worked for CNN)
- Wesley Clark (now at CNN)
- Alan Colmes (deceased)
- Rita Cosby (later worked at MSNBC)
- Catherine Crier (now at TruTV)
- S. E. Cupp (now at CNN)
- Stacey Dash (not renewed)
- Jill Dobson
- Laurie Dhue (not renewed)
- Matt Drudge
- Darby Dunn (now at CNBC)
- Donna Fiducia (no longer active in cable news industry, went into Georgia real estate)
- Rick Folbaum (now at WFOR-TV)
- Harold Ford, Jr. (now at MSNBC)
- Courtney Friel (now at KTLA-TV)
- Neal Gabler
- Major Garrett (now at CBS News)
- Alexis Glick (left Fox Business in December 2009; now at CNN)
- Mary Katharine Ham (now at CNN)[49]
- Elisabeth Hasselbeck
- E. D. Hill (now at CNN)
- Marc Lamont Hill (now at BET and CNN)
- Kit Hoover (now at TLC)
- Margaret Hoover (left network 2012)
- Page Hopkins (left network September 26, 2008; now at MSNBC)
- Carol Iovanna (now runs production company)
- Marvin Kalb (not renewed)
- Terry Keenan (deceased)
- Greg Kelly (now at WNYW in New York City)
- Megyn Kelly (now at NBC News)
- Anna Kooiman
- Dana Lewis (now at WSAW-TV in Wausau)
- G. Gordon Liddy
- Rachel Marsden (contributor and Red Eye panelist; now lives in France)
- Bill McCuddy
- Zell Miller
- Dick Morris (contributor not renewed)
- Robert Novak (deceased)
- Bill O'Reilly (terminated amid sexual harassment allegations)
- Barbara Olson (killed in the September 11 attacks in 2001)
- Julian Phillips
- Judith Regan
- Ed Rollins (not renewed)
- Mike Schneider (left for Bloomberg Television, most recently at NJTV)
- Laura Schwartz
- Bob Sellers (now morning co-anchor at WZTV in Nashville)
- Suzanne Sena (now at HLN)
- David Shuster (left Fox for MSNBC, later worked at Al Jazeera America)
- Jane Skinner
- Tony Snow (became White House Press Secretary, deceased)
- Andrea Tantaros
- Cal Thomas (not renewed)
- Greta Van Susteren (now at MSNBC)
- Linda Vester
- Brian Wilson (presently morning drive time host on WMAL-FM)
- Paula Zahn (left for CNN, now at Investigation Discovery)
Ratings and reception

FNC saw a large ratings jump during the early stages of the US invasion of Iraq. According to some reports, at the height of the conflict Fox News had as much as a 300-percent increase in viewership (averaging 3.3 million viewers daily).[50] In 2004, FNC's ratings for its broadcast of the Republican National Convention exceeded those of the three major broadcast networks. During President George W. Bush's address, Fox News attracted 7.3 million viewers nationally; NBC, ABC, and CBS had a viewership of 5.9 million, 5.1 million and 5.0 million respectively.
In late 2005 and early 2006, FNC saw a brief decline in ratings. One decline was in the second quarter of 2006, when Fox News lost viewers for every prime-time program compared with the previous quarter. The audience for Special Report with Brit Hume, for example, dropped 19 percent. Several weeks later, in the wake of the 2006 North Korean missile test and the 2006 Lebanon War, Fox saw a surge in viewership and remained the #1-rated cable news channel.[51][52] Fox produced eight of the top ten most-watched nightly cable news shows, with The O'Reilly Factor and Hannity & Colmes finishing first and second respectively.[53]
FNC ranked #8 in viewership among all cable channels in 2006, and #6 in 2007.[54] The channel ranked #1 during the week of Barack Obama's election (November 3–9) in 2008, and reached the top spot again in January 2010 (during the week of the special Senate election in Massachusetts).[55] Comparing Fox to its 24-hour-news-channel competitors, in May 2010 the channel drew an average daily prime-time audience of 1.8 million viewers (versus 747,000 for MSNBC and 595,000 for CNN).[56]
In September 2009, the Pew Research Center published a report on the public view of national news organizations. In the report, 72 percent of polled Republican Fox viewers rated the channel as "favorable", while 43 percent of polled Democratic viewers and 55 percent of all polled viewers shared that opinion. However, Fox was given the highest "unfavorable" rating of all national outlets studied (25 percent of all polled viewers). The report went on to say, "partisan differences in views of Fox News have increased substantially since 2007".[57]

On the night of October 22, 2012, Fox set a record for its highest-rated telecast ever, with 11.5 million viewers for the third U.S. presidential debate.[58][59] In prime time the week before, Fox averaged almost 3.7 million viewers with a total day average of 1.66 million viewers.[60]
A Public Policy Polling poll concluded in 2013 that perceptions of FNC had declined from 2010. 41% of polled voters said they trust it, down from 49% in 2010, while 46% said they distrust it, up from 37% in 2010. It was also called the "most trusted" network by 34% of those polled, more than had said the same of any other network.[61]
In primetime and total day ratings for the week of April 15 to 21, 2013, Fox News, propelled by its coverage of the Boston Marathon bombing, was the highest-ranked network on U.S. cable television, for the first time since August 2005, when Hurricane Katrina hit the Gulf Coast of the United States.[62]
January 2014 marked Fox News's 145th consecutive month as the number one rated cable news channel. During that month, Fox News beat CNN and MSNBC combined in overall viewers in both prime time hours and the total day.[63] In the third quarter of 2014, the network was the most-watched cable channel during prime time hours.[64]
During the final week of the campaign for the United States elections, 2014, Fox News had the highest ratings of any cable channel, news or otherwise. On election night itself, Fox News' coverage had higher ratings than that of any of the other five cable or network news sources among viewers between 25 and 54 years of age.[65]
The network hosted the first prime-time GOP candidates' forum of the 2016 campaign on August 6. The debate reached a record-breaking 24 million viewers, by far the largest audience ever for any cable news event.[66]
Demographics
As indicated by a New York Times article, based on Nielsen statistics, Fox appears to have a mostly aged demographic.[67] In 2008, in the 25–54 age group, Fox News had an average of 557,000 viewers, but dropped to 379,000 in 2013 while increasing its overall audience from 1.89 million in 2010 to 2.02 million in 2013. The median age of a prime-time viewer was 68 as of 2015.[68]
Slogan
Fox News Channel originally used the slogan "Fair and Balanced", which was coined by network co-founder Roger Ailes while the network was being established. The New York Times described the slogan as being both a "blunt signal that Fox News planned to counteract what Mr. Ailes and many others viewed as a liberal bias ingrained in television coverage by establishment news networks."[69][70]
In August 2003, Fox sued comedian Al Franken over his use of the slogan as a subtitle for his book, Lies and the Lying Liars Who Tell Them: A Fair and Balanced Look at the Right, which is critical of Fox News Channel.[71] The lawsuit was dropped three days later, after Judge Denny Chin refused its request for an injunction. In his decision, Chin ruled the case was "wholly without merit, both factually and legally". He went on to suggest that Fox News' trademark on the phrase "fair and balanced" could be invalid.[72] In December 2003, FNC won a legal battle concerning the slogan, when AlterNet filed a cancellation petition with the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) to have FNC's trademark rescinded as inaccurate. AlterNet included the documentary film Outfoxed as supporting evidence in its case.[73] After losing early motions, AlterNet withdrew its petition; the USPTO dismissed the case.[74] In 2008, FNC used the slogan "We Report, You Decide", referring to "You Decide 2008" (FNC's original slogan for its coverage of election issues).
In August 2016, Fox News Channel began to quietly phase out the "Fair and Balanced" slogan in favor of "Most Watched, Most Trusted"; when these changes were reported in June 2017 by Gabriel Sherman (a writer who had written a biography on Ailes), a network executive stated that the change "has nothing to do with programming or editorial decisions." It was speculated by media outlets that Fox News Channel was wishing to distance itself from Ailes' tenure at the network.[69][75][70]
Controversies
Alleged bias
Fox News Channel has long been accused of promoting conservative political positions[76] and has been widely criticized for biased reporting.[11] Critics of the channel have stated Fox News has a bias favoring the political right and the Republican Party.[12] Fox News host Chris Wallace has said, "I think we are the counter-weight [to NBC News] ... they have a liberal agenda, and we tell the other side of the story."[77][78][79][80] Timothy Noah stated in an editorial in Slate Magazine that Fox News had a conservative bias.[81] Fox News has publicly denied such statements.[82] Murdoch and Ailes' replies have included Murdoch's statement that Fox has "given room to both sides, whereas only one side had it before".[83][84] In 2004, director Robert Greenwald produced the documentary film Outfoxed: Rupert Murdoch's War on Journalism, which argues that Fox News has a conservative bias.[85] The film includes clips from Fox News and internal memos from editorial vice president John Moody directing Fox News staff on how to report certain subjects.[86]
A leaked memo from Fox News vice president Bill Sammon to news staff at the height of the health care reform in the United States debate has been cited as an example of the pro-Republican Party bias of Fox News. His memo asked the staff to "use the term 'government-run health insurance,' or, when brevity is a concern, 'government option,' whenever possible". The memo was sent shortly after Republican pollster Frank Luntz advised Sean Hannity on his Fox show that "If you call it a public option, the American people are split. If you call it the government option, the public is overwhelmingly against it".[87]
A Pew Research poll released on October 29, 2009 found that Fox News is viewed as the most ideological channel in America. 47 percent of those surveyed said Fox News is "mostly conservative", 14 percent said "mostly liberal" and 24 percent said "neither". In comparison, MSNBC had 36 percent identify it as "mostly liberal", 11 percent as "mostly conservative" and 27 percent as "neither". CNN had 37 percent describe it as "mostly liberal", 11 percent as "mostly conservative" and 33 percent as "neither".[88] A 2004 Pew Research Center survey showed that FNC was cited (unprompted) by 69 percent of national journalists as a conservative news organization. The survey showed that 34 percent of national journalists describe themselves as liberal, compared with 7 percent who describe themselves as conservative.[89]
A poll by Rasmussen Reports found that 31 percent of Americans felt that Fox News has a conservative bias, and 15 percent that it has a liberal bias. The poll also reported that 36 percent believed Fox News delivers news with neither a conservative or liberal bias, compared with 37 percent who said NPR delivers news with no conservative or liberal bias and 32 percent who said the same of CNN.[90] A 2007 study looked at the introduction of Fox News into local U.S. markets between 1996 and 2000, and found that in the 2000 presidential election "Republicans gained 0.4 to 0.7 percentage points in the towns that broadcast Fox News". The study's estimates "imply that Fox News convinced 3 to 28 percent of its viewers to vote Republican, depending on the audience measure".[91]
A 2010 study by Sean Aday comparing Fox News Channel's Special Report With Brit Hume and NBC's Nightly News coverage of the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan during 2005 found that both underplayed bad news; it concluded that "Fox News was much more sympathetic to the administration than NBC", suggesting that "if scholars continue to find evidence of a partisan or ideological bias at FNC... they should consider Fox as alternative, rather than mainstream, media". Aday also stated, however, that the data used in his study may have come late enough in the war to be consistent with accepted practice.[clarification needed][92]
David Carr, media critic for The New York Times, praised the 2012 presidential election results coverage on Fox News for the network's response to Republican adviser and Fox News contributor Karl Rove challenging its call that Barack Obama would win Ohio and the election. Fox's prediction was correct. Carr wrote:
Over many months, Fox lulled its conservative base with agitprop: that President Obama was a clear failure, that a majority of Americans saw [Mitt] Romney as a good alternative in hard times, and that polls showing otherwise were politically motivated and not to be believed. But on Tuesday night, the people in charge of Fox News were confronted with a stark choice after it became clear that Mr. Romney had fallen short: was Fox, first and foremost, a place for advocacy or a place for news? In this moment, at least, Fox chose news.[93]
A May 2017 study conducted by Harvard University's Shorenstein Center on Media, Politics and Public Policy examined coverage of U.S. President Donald Trump's first 100 days in office by several major mainstream media outlets including Fox.[94] It found that, altogether, Trump received 80% negative coverage from the media, and that he received the least negative coverage on Fox – 52% negative and 48% positive.[95]
False claims about the New York Times
In July 2017, a report by Fox & Friends falsely said that the New York Times had disclosed intelligence in one of its stories and that this intelligence disclosure helped Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, the leader of the Islamic State, to evade capture.[96][97][98] The report cited an inaccurate assertion by Gen. Tony Thomas, the head of the United States Special Operations Command, that a major newspaper had disclosed the intelligence.[96][99] Fox News said that it was the New York Times, repeatedly running the chyron “NYT FOILS U.S. ATTEMPT TO TAKE OUT AL-BAHGDADI".[99] Pete Hegseth, one of the show's hosts, criticized the “failing New York Times”.[99] President Donald Trump tweeted about the Fox & Friends report shortly after it first aired, saying “The Failing New York Times foiled U.S. attempt to kill the single most wanted terrorist, Al-Baghdadi. Their sick agenda over National Security.”[96] Fox News later updated the story, but without apologizing to the New York Times or responding directly to the inaccuracies.[99]
In a Washington Post column, Erik Wemple said that Chris Wallace had covered the New York Times story himself on Fox News Sunday. "Here’s another case of the differing standards between Fox News’s opinion operation," which has given "a state-run vibe on all matters related to Trump," compared to Fox News’s news operation, which has provided "mostly sane coverage."[100]
Climate change
A 2011 study found that Fox News "takes a more dismissive tone toward climate change than CNN and MSNBC".[101] A 2008 study found that Fox News emphasized the scientific uncertainty of climate change more than CNN, less likely to state that climate change was real, and more likely to interview climate change skeptics.[101]
Shepard Smith has drawn attention for being one of few voices on Fox News to forcefully state that climate change is real, that human activities are a primary contributor to it and that there is a scientific consensus on the issue.[102][103] His acceptance of the scientific consensus on climate change has drawn criticism from Fox News viewers and conservatives.[104][105]
Donald Trump wiretapping claim
On March 14, 2017, Andrew Napolitano, a Fox News commentator, claimed on Fox & Friends that British intelligence agency GCHQ had wiretapped Donald Trump on behalf of Barack Obama during the 2016 United States presidential election.[106][107] On March 16, 2017, White House spokesman Sean Spicer repeated the claim.[106] When Trump was questioned about the claim at a news conference, he said "All we did was quote a certain very talented legal mind who was the one responsible for saying that on television. I didn't make an opinion on it."[108] On March 17, 2017, Shepard Smith, a Fox News anchor, acknowledged that the network had no evidence that Trump was under surveillance. British officials said the White House was backing off the claim, but the White House did not release a public statement expressing regret.[108] Napolitano was later suspended by Fox News for making the claim.[109]
Encouragement of violence against protesters
In January 2017, the Daily Caller published a video which encouraged violence against protesters.[110][111][112] The video was subsequently reposted by Fox Nation, an offshoot of Fox News' website.[110] The video in question showed a car plowing through protesters, with the headline "Here's A Reel Of Cars Plowing Through Protesters Trying To Block The Road" and set to a cover of Ludacris' "Move Bitch."[110] The video drew attention in August 2017 when a white supremacist plowed his car through a group of counterprotesters at a white nationalist rally in Charlottesville.[110] After the video attracted attention, Fox News deleted it from its website.[110][112]
Murder of Seth Rich conspiracy
On 16 May 2017, the same day that other news organizations were extensively covering Donald Trump' revelation of classified information to Russia,[113] Fox News ran a lead story about a private investigator's uncorroborated claims about the murder of Seth Rich, a DNC staffer.[114][115][116] The private investigator asserted that he had uncovered evidence that Rich was in contact with Wikileaks and that law enforcement were covering it up.[114] The killing of Rich has given rise to conspiracy theories in rightwing circles that Hillary Clinton and the Democratic Party had Seth Rich killed allegedly because he was the source of the DNC leaks.[114] U.S. intelligence agencies had determined that Russia was the source of the leaks.[117] In reporting the investigator's claims, the Fox News report re-ignited right-wing conspiracy theories about the killing.[114][116]
Other news organizations revealed that the investigator was a Donald Trump supporter and had according to NBC News "developed a reputation for making outlandish claims, such as one appearance on Fox News in 2007 in which he warned that underground networks of pink pistol-toting lesbian gangs were raping young women."[114][118] The family of Seth Rich, the Washington D.C police department, the Washington D.C. mayor's office, the FBI, and law enforcement sources familiar with the case, rebuked the investigator's claims.[114][115] The family said, "We are a family who is committed to facts, not fake evidence that surfaces every few months to fill the void and distract law enforcement and the general public from finding Seth’s murderers."[114] The spokesperson for the family criticized Fox News for its reporting, alleging that the outlet was motivated by a desire to deflect attention from the Trump-Russia story: "I think there’s a very special place in hell for people that would use the memory of a murder victim in order to pursue a political agenda."[113] The family has called for retractions and apologies from Fox News for the inaccurate reporting.[119][120]Over the course of the day, Fox News altered the contents of the story and the headline, but did not issue corrections.[121][122] When CNN contacted the private investigator later that day, the investigator said that he had no evidence that Rich had contacted Wikileaks.[116] The investigator claimed that he only learned about the possible existence of the evidence from a Fox News reporter.[116] Fox News did not respond to inquiries by CNN, and the Washington Post.[116][115] Fox News later on 23 May retracted its original report, stating that the original report did not meet its standards.[123]
Nicole Hemmer, assistant professor at the Miller Center of Public Affairs, wrote that the promotion of the conspiracy theory demonstrated how Fox News was "remaking itself in the image of fringe media in the age of Trump, blurring the lines between real and fake news."[124] Max Boot of the Council on Foreign Relations said that while intent behind Fox News, as a counterweight to the liberal media was laudable, the culmination of those efforts have been to create an alternative news source that promotes hoaxes and myths, of which the promotion of the Seth Rich conspiracy is an example.[125] Fox News was also criticized by conservative outlets, such as the Weekly Standard,[126] National Review,[127][128] and conservative columnists, such as Jennifer Rubin,[129] Michael Gerson,[130] and John Podhoretz.[131]
Obama administration conflict with Fox News
In September 2009, the Obama administration engaged in a verbal conflict with Fox News Channel. On September 20, President Obama appeared on all major news programs except Fox News, a snub partially in response to remarks about the president by commentators Glenn Beck and Sean Hannity, and Fox coverage of Obama's health-care proposal.[132][133]
In late September 2009, Obama senior advisor David Axelrod and Roger Ailes met in secret to attempt to smooth out tensions between the two camps. Two weeks later, White House officials referred to FNC as "not a news network", communications director Anita Dunn stating that "Fox News often operates as either the research arm or the communications arm of the Republican Party".[134][135] President Obama observed, "If media is operating basically as a talk radio format, then that's one thing, and if it's operating as a news outlet, then that's another".[136] White House chief of staff Rahm Emanuel stated that it was important "to not have the CNNs and the others in the world basically be led in following Fox".[137]
Within days, it was reported that Fox had been excluded from an interview with administration official Ken Feinberg, with bureau chiefs from the White House press pool (ABC, CBS, NBC, and CNN) coming to Fox's defense.[138] A bureau chief stated, "If any member had been excluded it would have been the same thing, it has nothing to do with Fox or the White House or the substance of the issues".[139] Shortly after the story broke, the White House admitted to a low-level mistake, saying that Fox had not made a specific request to interview Feinberg. Fox White House correspondent Major Garrett responded by stating that he had not made a specific request, but that he had a "standing request from me as senior White House correspondent on Fox to interview any newsmaker at the Treasury at any given time news is being made".[140]
On November 8, 2009, the Los Angeles Times reported that an unnamed Democratic consultant was warned by the White House not to appear on Fox News again. According to the article, Anita Dunn claimed in an e-mail to have checked with colleagues who "deal with TV issues" and had been told that nobody had been instructed to avoid Fox. Patrick Caddell, a Fox News contributor and former pollster for President Jimmy Carter, said he had spoken with other Democratic consultants who had received similar warnings from the White House.[141]
On October 2, 2013, Fox News host Anna Kooiman cited on the air a fake story from the National Report parody site, which claimed that President Obama had offered to keep the International Museum of Muslim Cultures open with cash from his own pocket.[142][143][144]
White supremacist rally in Charlottesville
Various Fox News hosts and contributors defended President Trump's remarks that "many sides" were to blame for violence at a gathering of hundreds of white nationalists in Charlottesville, Virginia.[145][146] Some Fox News hosts and contributors criticized Trump.[147][146] In a press conference on 15 August, Trump used the term "alt-left" to describe counterprotesters at the white supremacist rally, a term which had been used in Fox News' coverage of the white supremacist rally.[145] Several of Trump's comments at the press conference mirrored those appearing earlier on Fox News.[148]
Fox News contributor Laura Ingraham offered a partial defense of Trump, saying that Trump was right to point out "the evil of a far left that is trying to tear down both history and intimidate free speech in the country."[145] On the day of Trump's press conference, Fox News hosts Tucker Carlson and Sean Hannity focused their shows on criticizing liberals and the media.[147] The next day, Hannity focused his show on the racist past of the Democratic Party, as well as "left-wing acceptance of black radicalism".[146] Fox News host Tucker Carlson also covered historical figures, such as Thomas Jefferson, Mohammed, Simon Bolivar and Plato, who owned slaves on his show, and said that individuals who wanted to remove confederate monuments would want to remove statues of Abraham Lincoln next.[145][147][149] Carlson also questioned whether it was a violation of the First Amendment for businesses to deny services to white supremacists.[146] A guest on Tucker Carlson's show equated individuals who want to remove confederate monuments to "Weimar thugs" and the Taliban.[147] A guest on Fox & Friends equated the confederate flag with the rainbow flag, saying they "represent the exact same thing," and the hosts of Fox & Friends did not provide a response to the guest's remarks.[150][151] The Fox & Friends host, Pete Hegseth, blamed the media for the violence at the white supremacist gathering.[152]
According to Dylan Byers of CNN, Fox News' coverage on the day of the press conference "was heavy with "whataboutism." The average Fox viewer was likely left with the impression that the media's criticism of Trump and leftist protestors' toppling of some Confederate statues were far greater threats to America than white supremacism or the president's apparent defense of bigotry."[147] Byers wrote, "it showed that if Fox News has a line when it comes to Trump's presidency, it was not crossed on Tuesday."[147]
International transmission
The Fox News Channel feed is available internationally via a number of providers, while Fox Extra segments provide alternate programming.[153]
Fox Extra
Initially, U.S. advertisements were replaced on FNC with viewer e-mail and profiles of FNC anchors set to music. In 2002, these were replaced with international weather forecasts. In 2006, the weather forecasts were replaced with Fox Extra (originally Fox News Extra, prior to the international launch of Fox Business) segments, narrated reports from Fox on a variety of topics. These reports generally concern lighter issues unrelated to current news events, and the segments are repeated. FNC also shows international weather forecasts when Fox Extra segments run short. In the United Kingdom, after a period when local commercials were inserted into breaks, Fox Extra now fills most breaks.
Australia
In Australia, FNC is broadcast on the dominant pay television provider Foxtel, which is 50% owned by News Corp Australia, the Australian arm of News Corp and the sister company of 21st Century Fox which owns FNC. Local cable news channel Sky News Australia is wholly owned by News Corp Australia[154] and is therefore FNC's de facto sister channel, although has formal partnerships with FNC competitor CNN as well as both ABC News and CBS News.[155]
Brazil
Since 2002, FNC has been broadcast to Brazil; however, commercials are replaced with Fox Extra. It is available in packages of Vivo TV.
Canada
In 2003, the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) rejected a Canadian Cable Telecommunications Association (CCTA) application to bring Fox News to Canada due to concerns that Fox News U.S. and the Global Television Network were planning to create a combined American-Canadian news network. In 2004, after a Fox News U.S. executive said there were no plans to create a combined channel, the CRTC approved an application to bring Fox News to Canada.[156]
France
Fox News is available on cable through French internet provider Free on Canal 352. As of Spring 2017, the channel was no longer found on the provider Orange's lineup.
Indonesia
In Indonesia, It is available in Channel 335 in pay TV provider Indovision.
Ireland
FNC is carried in the Republic of Ireland by Sky, which is 40-percent owned by FNC's parent company, 21st Century Fox. It is run as a sister channel to Sky's own news channel, Sky News. FNC is usually broadcast as a VideoGuard-encrypted channel; during major news stories, it may be simulcast on Sky Active, which is free-to-air. As of September 2006, the channel has carried UK-specific advertising, headlines and weather provided by Sky News during its breaks. These run under the brand of Fox News International. Due to the shared ownership of Fox and Sky, both channels share bureaus and reporters for breaking news stories worldwide.
Israel
In Israel, FNC is broadcast on Channel 105 of the satellite provider yes. It is also broadcast on channel 71 on cable operator HOT.[157]
Italy
In Italy, FNC was launched on the now-defunct Italian digital satellite television platform Stream TV in 2001. Part of its programming was translated into Italian and broadcast on the defunct Italian news channel Stream News. In 2003, it moved to SKY Italia, with U.S. commercials replaced by Fox News Extra segments. It is available to 4.6 million subscribers and 160,000 hotel rooms. SKY TG 24 is a sister channel to Fox News.
Netherlands
In the Netherlands, Fox News has been carried by cable providers UPC Nederland and CASEMA, and satellite provider Canaldigitaal; all have dropped the channel in recent years. At this time, only cable provider Caiway (available in a limited number of towns in the central part of the country) is broadcasting the channel. The channel is also carried by IPTV provider KNIPPR.
New Zealand
In New Zealand, FNC is broadcast on Channel 088 of pay satellite operator SKY Network Television's digital platform. It was formerly broadcast overnight on free-to-air UHF New Zealand TV channel Prime (owned by SKY); this was discontinued in January 2010, reportedly due to an expiring broadcasting license.[158] Fox News' former parent company News Corporation has a stake in both SKY and Prime.
Pakistan
In Pakistan, Fox News Channel is available on PTCL Smart TV and a number of cable and IPTV operators.
Philippines
In the Philippines, Fox News Channel was available on cable operator Destiny Cable channel 21 (analog)/channel 112 (digital) Now on SkyCable Channel 112 it is available only on digital platform. And now on Skycable available on High Definition Channel 211. It is also seen on Cignal Digital TV channel 41.
Scandinavia
Between 2003 and 2006, in Sweden and the other Scandinavian countries, FNC was broadcast 16 hours a day on TV8 (with Fox News Extra segments replacing U.S. advertising). Fox News was dropped by TV8 and replaced by German news channel Deutsche Welle in September 2006.
Singapore
In Singapore, FNC is broadcast on channel 702 on pay cable operator StarHub TV digital platform. It also broadcasts its sister channel, Sky News.
South Africa
In South Africa, FNC is broadcast on channel 405 of pay satellite operator TopTV's digital platform.[159]
United Kingdom
FNC is also carried in the United Kingdom by Sky, a satellite television network which is 40-percent owned by FNC parent 21st Century Fox. It is run as a sister channel to Sky's own Sky News. FNC is usually broadcast as a VideoGuard-encrypted channel; during major news stories, it may be simulcast on Sky Active, which is free-to-air. As of September 2006[update], the channel has carried UK-specific advertising, headlines and weather provided by Sky News during its breaks. These run under the brand of Fox News International. Beginning in winter 2011, most breaks resumed Fox Extra. Due to the shared ownership of Fox and Sky, Fox News (and Fox Business) and Sky News share bureaus and reporters for breaking news stories worldwide.
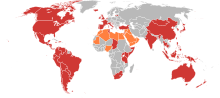
Other countries
Fox News is carried in more than 40 other countries. Although service to Japan ceased in summer 2003, it can still be seen on Americable (distributor for American bases),[160] Mediatti (Kadena Air Base)[161] and Pan Global TV Japan.[162]
See also
References
- ^ Mifflin, Lawrie (October 7, 1996). "At the new Fox News Channel, the buzzword is fairness, separating news from bias". The New York Times. Retrieved May 4, 2010.
- ^ Brancaccio, David (October 7, 1996). "Marketplace: News Archives". Marketplace. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved May 12, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b King, Angela G. (October 7, 1996). "Fox Hunts TV News Niche with Channel Debut Today". New York Daily News.
- ^ Gillette, Felix (October 1, 2008). "Viewers Continuing to Flock to Cable News Networks". The New York Observer.
- ^ "Roger Ailes Resigns From Fox News Amid Sexual Harassment Accusations". Time. July 21, 2016.
- ^ "Roger Ailes leaves Fox News in wake of sexual harassment claims". The Guardian. July 21, 2016.
- ^ Darcy, Oliver (August 2, 2017). "Confusion, anger inside Fox News over lack of answers in network's Seth Rich probe". CNNMoney. Retrieved August 5, 2017.
- ^ "hillarys-health-conspiracy-or-concern".
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ Jamieson, Amber (August 26, 2016). "Conspiracy central: the activists painting Clinton as a sick, terrorist-friendly killer". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
- ^ Golshan, Tara (August 18, 2016). "Here's how we know the bonkers conspiracy theory about Hillary Clinton's health is catching on". Vox. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
- ^ a b James Robert Compton (2004). The Integrated News Spectacle: A Political Economy of Cultural Performance. Peter Lang. p. 204. ISBN 978-0-8204-7070-2.
- ^ a b Paul La Monica (2009). Inside Rupert's Brain. Peter Lang. p. 5. ISBN 1101016590.
- ^ "Media Sources: Distinct Favorites Emerge on the Left and Right". Pew Research Center. October 21, 2014. Retrieved November 28, 2016.
- ^ Anthony Collings (2010). Capturing the News: Three Decades of Reporting Crisis and Conflict. University of Missouri Press. p. 166. ISBN 978-0-8262-7211-9.
- ^ Jonathan McCollum; David G. Hebert (2014). Theory and Method in Historical Ethnomusicology. Lexington Books. p. 95. ISBN 978-1-4985-0705-9.
- ^ Memmott, Mark (September 2, 2004). "Fox newspeople say allegations of bias unfounded". USA Today. Archived from the original on November 22, 2010. Retrieved August 15, 2009.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) "White House Escalates War of Words With Fox News". Fox News. October 12, 2009. Archived from the original on November 22, 2010. Retrieved October 12, 2009.{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Fox News Turmoil Highlights Workplace Culture's Role In Sexual Harassment". NPR.org. Retrieved April 27, 2017.
- ^ "Fox Will Pay Gretchen Carlson $20 Million To Settle Sexual Harassment Suit". NPR.org. Retrieved April 27, 2017.
- ^ "Roger Ailes Resigns as Fox News Chief After Sexual Harassment Accusations". The Hollywood Reporter. Retrieved April 27, 2017.
- ^ Ember, Sydney (April 25, 2017). "11 Sue Fox News, Citing 'Intolerable' Racial Bias". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved April 27, 2017.
- ^ Steel, Emily; Schmidt, Michael S. (April 19, 2017). "Bill O'Reilly Is Forced Out at Fox News". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved April 28, 2017.
- ^ Stelter, Brian (April 27, 2017). "Exclusive: Federal probe of Fox News expands". CNNMoney. Retrieved April 29, 2017.
- ^ "Feds Widen Investigation Into Potential Misconduct at Fox News". Fortune. Retrieved April 29, 2017.
- ^ Seidman, Robert (February 22, 2015). "List of how many homes each cable network is in as of February 2015". TV by the Numbers. Zap2it. Retrieved March 14, 2015.
- ^ Lenzner, Robert (May 5, 1985). "Murdoch, partner plan 4th network". The Boston Globe. Section: National/Foreign; Page 1 (the six stations cover many of the nation's major markets – New York, Chicago, Los Angeles, Dallas, Houston and Washington)
- ^ "$55.9 Million Fox Film Loss". The New York Times. July 11, 1985. p. D19.
- ^ "Turnaround for Fox Film". Chicago Tribune. July 17, 1986. Section: Business; p. 1. Archived November 5, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Shah, Saeed (September 24, 2002). "Business Analysis: Unstoppable Sky machine rolls on as ITV troubles worsen Dawn Airey's free-to-air television experience will be invaluable to BSkyB as it moves beyond its pay-TV model". The Independent. Section: Business; p. 21.
- ^ Schulberg, Pete. (July 15, 1994) "Fox is a business, if not artistic, success". The Oregonian. Section: Television; Page E1.
- ^ Braxton, Greg (April 6, 1997). "How Fox broke from the pack to become cutting-edge network". Chicago Sun-Times.
- ^ Williams, Scott (January 31, 1996). "Murdoch taps Ailes for new network; Former CNBC chief set to direct 24-hour news channel, take on CNN". Associated Press.
- ^ Mifflin, Lawrie (October 7, 1996). "At the new Fox News Channel, the buzzword is fairness, separating news from bias". The New York Times. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ "Fox News Channel". News Corporation. April 18, 2008. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved April 21, 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Richard Katz (May 1996). "Bold grab for subs: Murdoch offers $11 to carry Fox News". Multichannel News. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved September 1, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Landler, Mark (October 4, 1996). "Giuliani Pressures Time Warner to Transmit a Fox Channel". The New York Times. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ Levy, Clifford J. (October 5, 1996). "City Hall Threatens Action if Time Warner Rejects Channel". The New York Times. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ Dudak, Gary (September 11, 2012). "11 Direct Effects 9/11 Had on the Sports and Entertainment Industries". Mandatory.com. Retrieved September 13, 2012.
- ^ "ITN Archive Becomes ITN Source - Member News - News & Journal - FOCAL International". www.focalint.org. Retrieved April 28, 2017.
- ^ Stelter, Brian. "Fox's Volley With Obama Intensifying." NYT. Oct.11, 2009. Retrieved via nytimes.com on Nov.16, 2009.
- ^ "Multichannel News April 29, 2008 Fox News to make HD bow with Time Warner". Multichannel.com. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved August 15, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Christians, Clifford G.; Fackler, Mark; Richardson, Kathy Brittain; Kreshel, Peggy; Woods, Robert H. (October 4, 2016). Media Ethics: Cases and Moral Reasoning. Routledge. ISBN 9781134841561.
- ^ "Privacy Policy". Fox News. July 1, 2013. Retrieved October 20, 2013.
- ^ "Fox News Latino". Fox News Latino. November 23, 2015.
- ^ "For Talking Heads, a Spot to Relax and Sip Coffee, on Webcam " The New York Times. February 15, 2009.
- ^ Welcome to the Fox Nation Foxnews.com, March 30, 2009
- ^ "Fox News Mobile website". Foxnews.com. June 12, 2008. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved August 15, 2009.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e Concha, Joe (March 27, 2017). "Fox News signs Federalist's Mollie Hemingway". The Hill.
- ^ "Nigel Farage hired by Fox News as a political analyst". BBC. January 20, 2017. Retrieved January 21, 2017.
- ^ Feldman, Josh (March 1, 2016). "Fox News Contributor Mary Katharine Ham Jumps to CNN, Makes Debut with Tapper". Mediaite. Retrieved March 12, 2017.
- ^ "War coverage lifts News Corp". BBC. August 13, 2003. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved November 29, 2005.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ FNC's 25–54 Prime "Downward Spiral", TV Newser
- ^ Cable TV: Content Analysis, The State of the News Media 2005
- ^ April 2005 Competitive Program Ranker (M-F 6a-11p programs), TV Newser
- ^ "Fox News Channel Leads in 2007 Cable News Ratings". Broadcastingcable.com. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved August 27, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Fox News Channel tops USA in cable ratings Reuters January 27, 2010
- ^ 'Fox News North' primed for launch The Globe and Mail June 15, 2010
- ^ "Press Accuracy Rating Hits Two-Decade Low". Archived from the original on November 23, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Michael O'Connell (October 23, 2012). "Final Debate Breaks Fox News Ratings Record With 11.5 Million, Topping Cable Competition". The Hollywood Reporter. Retrieved September 30, 2014.
- ^ Patten, Dominic. "UPDATE: 59.2M Watch Final Presidential Debate; NBC Wins Coverage Battle". Deadline.
- ^ Flint, Joe (October 23, 2012). "Fox News scores big ratings win". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Fox News' Credibility Declines Public Policy Polling February 6, 2013
- ^ "Fox News Tops All Cable For 1st Time Since 2005". Deadline. April 23, 2007. Retrieved September 30, 2014.
- ^ "Fox News Channel Tops Cable News Ratings In January – Deadline". Deadline. January 28, 2014. Retrieved September 30, 2014.
- ^ Michael O'Connell (September 30, 2014). "Fox News Nabs Historic Cable Ratings Victory". The Hollywood Reporter. Retrieved September 30, 2014.
- ^ Zurawik, David (November 17, 2014). "New level of Fox News dominance demands analysis, not dismissal". Baltimore Sun. Tribune Publishing. Retrieved November 23, 2014.
- ^ Bauder, David (August 7, 2015). "Fox's GOP debate had record 24 million viewers". Money.CNN. Retrieved August 8, 2015.
- ^ Carter, Bill (July 22, 2013). "Fox Viewers May Be Graying, but Their Passion Still Pays". The New York Times.
- ^ Saba, Jennifer (April 4, 2017). "Fox Scandals May Weaken Murdochs' TV Future". The New York Times. Retrieved April 12, 2017.
- ^ a b Michael M. Grynbaum (June 14, 2017). "Fox News Drops 'Fair and Balanced' Motto". The New York Times. Retrieved June 15, 2017.
- ^ a b "Fox News no longer "fair and balanced" as network sheds longtime slogan". Salon. Retrieved June 16, 2017.
- ^ de Moraes, Lisa (August 12, 2003). Three Little Words: Fox News Sues. Washington Post
- ^ Phil Hirschkorn (August 22, 2003). Fox News loses attempt to block satirist's book. CNN
- ^ Coyle, Jake (July 19, 2004). Advocacy Groups Challenge Fox News Slogan. Associated Press
- ^ Official Documentation of Petitioned Cancellation of "Fair & Balanced" trademark phrase, Trademark Trial and Appeal Board Inquiry System
- ^ "Fox News drops 'fair and balanced' slogan without announcement". BBC News. June 15, 2017. Retrieved June 15, 2017.
- ^ Memmott, Mark (July 12, 2004). "Film accuses Fox of slanting the news". USA Today. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved August 15, 2009.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Exclusive: Jon Stewart on 'Fox News Sunday' | Fox News Video". Video.foxnews.com. June 19, 2011. Retrieved October 20, 2013.
- ^ David Corn. "Did Chris Wallace Really Say Fox News Isn't Fair and Balanced?". Mother Jones. Retrieved October 20, 2013.
- ^ Garth Johnston (June 21, 2011). "Jon Stewart: Chris Wallace Admitted Fox News Was Unbalanced". Gothamist. Retrieved October 20, 2013.
- ^ "Jon Stewart Dissects Chris Wallace's Fox News Logic – Erik Hayden". The Atlantic Wire. June 21, 2011. Retrieved October 20, 2013.
- ^ Timothy Noah, Fox News admits bias!, Slate, May 31, 2005. Retrieved September 26, 2006.
- ^ Interview transcript: Rupert Murdoch and Roger Ailes, Financial Times, October 6, 2006
- ^ News Corp denies Fox News bias Australian Associated Press, October 26, 2004
- ^ Interview transcript: Rupert Murdoch and Roger Ailes, Financial Times, October 6, 2006
- ^ Clifford G. Christians; Mark Fackler; Kathy Richardson (2015). Media Ethics: Cases and Moral Reasoning. Routledge. p. 33. ISBN 978-1-317-34652-4.
- ^ Kurtz, Howard (July 11, 2004), "Tilting at the Right, Leaning to the Left", The Washington Post, pp. D01
- ^ "Leaked Fox News Memo Reveals News Division Told To Echo GOP Talking Point, Business Insider, December 9, 2010". Business Insider. December 9, 2010. Retrieved September 30, 2014.
- ^ "Fox News Viewed as Most Ideological Network". Pew Research Center. October 29, 2009. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved August 27, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Bottom-Line Pressures Now Hurting Coverage, Say Journalists: Overview – Pew Research Center for the People & the Press". Pew Research Center for the People and the Press. May 23, 2004. Retrieved September 30, 2014.
- ^ "Americans See Liberal Media Bias on TV News – Rasmussen Reports". Rasmussenreports.com. July 13, 2007. Retrieved August 27, 2010.
- ^ Stefano DellaVigna and Ethan Kaplan (2007), "The Fox News Effect: Media Bias and Voting", Quarterly Journal of Economics, August 2007, Vol. 122, No. 3, Pages 1187–1234
- ^ Aday, S. (2010), "Chasing the bad news: An analysis of 2005 Iraq and Afghanistan war coverage on NBC and Fox News channel", Journal of Communication 60 (1), pp. 144–164
- ^ David Carr, "Election News Over Agenda for Fox", The New York Times, 11 November 2012.
- ^ Cox, Jeff (May 19, 2017). "Trump Press Coverage 'Sets New Standard' for Negativity: Study". CNBC. Retrieved May 24, 2017.
- ^ Richardson, Valerie (May 19, 2017). "Harvard Agrees: Trump Press Coverage Sets 'New Standard for Negativity'". The Washington Times. Retrieved May 24, 2017.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ a b c Gordon, Michael R. (July 23, 2017). "How Trump Got It Wrong in Saying The Times 'Foiled' Killing of ISIS Leader". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved July 24, 2017.
- ^ Press, Associated (July 24, 2017). "NY Times requests Fox News apology for 'malicious and inaccurate segment'". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved July 24, 2017.
- ^ Disis, Jill (July 24, 2017). "Why the New York Times wants an apology from Fox News". CNNMoney. Retrieved July 24, 2017.
- ^ a b c d Bromwich, Jonah Engel (July 24, 2017). "New York Times Asks Fox for Apology After 'Inaccurate Segment'". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved July 24, 2017.
- ^ ‘Fox & Friends’ issues ‘update’ on New York Times-ISIS flap. No apology. By Erik Wemple, Washington Post, July 24 2017
- ^ a b Feldman, Lauren; Maibach, Edward W.; Roser-Renouf, Connie; Leiserowitz, Anthony (January 1, 2012). "Climate on Cable: The Nature and Impact of Global Warming Coverage on Fox News, CNN, and MSNBC". The International Journal of Press/Politics. 17 (1): 3–31. doi:10.1177/1940161211425410. ISSN 1940-1612.
- ^ "Fox News actually acknowledged that climate change is real". Vox. Retrieved June 2, 2017.
- ^ Nuccitelli, Dana (August 17, 2015). "Fox News' inner struggle with climate misinformation". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved June 2, 2017.
- ^ "Fox News viewers are gunning for Shep Smith. How will Fox News respond?". March 23, 2017. Retrieved June 2, 2017.
- ^ Farhi, Paul; Farhi, Paul (March 21, 2017). "Shepard Smith, the Fox News anchorman who drives the Fox News faithful crazy". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved June 2, 2017.
- ^ a b Grynbaum, Michael M. (March 17, 2017). "Fox's Andrew Napolitano Stirred the Pot for Trump's British Tempest". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved March 21, 2017.
- ^ Napolitano, Andrew (March 16, 2017). "Andrew Napolitano: Did Obama spy on Trump?". Fox News. Retrieved March 21, 2017.
- ^ a b Baker, Peter; Erlanger, Steven (March 17, 2017). "Trump Offers No Apology for Claim on British Spying". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved March 21, 2017.
- ^ Battaglio, Stephen (March 20, 2017). "Fox News pulls Judge Napolitano over his Trump wiretap claims". Los Angeles Times. ISSN 0458-3035. Retrieved March 21, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e Kludt, Tom (August 15, 2017). "Fox News, Daily Caller delete posts encouraging people to drive through protests". CNNMoney. Retrieved August 16, 2017.
- ^ "Fox removes video with cars plowing through demonstrators". Philly.com. Retrieved August 16, 2017.
- ^ a b Rutenberg, Jim (August 17, 2017). "Where Is the Line? Charlottesville Forces Media and Tech Companies to Decide". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
- ^ a b "FACT CHECK: Did DNC Staffer Seth Rich Send 'Thousands of E-Mails' to WikiLeaks Before He Was Murdered?". Snopes.com. May 16, 2017. Retrieved May 16, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g "DNC staffer's murder draws fresh conspiracy theories". NBC News. Retrieved May 16, 2017.
- ^ a b c "Family of slain Seth Rich says reports that he fed DNC info to WikiLeaks are untrue". Washington Post. Retrieved May 16, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e Darcy, Oliver (May 16, 2017). "Story on DNC staffer's murder dominated conservative media -- hours later it fell apart". CNNMoney. Retrieved May 17, 2017.
- ^ Washington newsroom (January 6, 2017). "U.S. intel report identifies Russians who gave emails to WikiLeaks -officials". Reuters. Retrieved July 3, 2017.
- ^ Bromwich, Jonah Engel (May 17, 2017). "How the Murder of a D.N.C. Staffer Fueled Conspiracy Theories". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved May 17, 2017.
- ^ Bromwich, Jonah Engel (May 17, 2017). "How the Murder of a D.N.C. Staffer Fueled Conspiracy Theories". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved May 17, 2017.
- ^ Darcy, Oliver (May 17, 2017). "Family of slain DNC staffer demands retraction and apology from Fox News, local TV station". CNNMoney. Retrieved May 17, 2017.
- ^ Bromwich, Jonah Engel (May 17, 2017). "How the Murder of a D.N.C. Staffer Fueled Conspiracy Theories". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved May 17, 2017.
- ^ Waldron, Travis (May 18, 2017). "Fox Stands By DNC Murder Conspiracy Theory Even After Main Source Changes Story". Huffington Post. Retrieved May 18, 2017.
- ^ "Trump first budget relies on rosy forecasts and deep cuts to anti-poverty programs". Los Angeles Times. ISSN 0458-3035. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ "fox-news-is-destroying-itself-turning-into-a-breitbart-copy-for-trump".
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ "The Seth Rich 'Scandal' Shows That Fox News Is Morally Bankrupt". Foreign Policy. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ "Prime-Time Conspiracy Theory". Weekly Standard. May 26, 2017. Retrieved May 27, 2017.
- ^ "The Facts of the Seth Rich Murder That Don't Support Conspiracy Theories". National Review. Retrieved May 27, 2017.
- ^ "The Seth Rich Conspiracy Theory Is Shameful Nonsense". National Review. Retrieved May 27, 2017.
- ^ Rubin, Jennifer; Rubin, Jennifer (May 24, 2017). "Questions Fox and the right need to answer". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved May 27, 2017.
- ^ Gerson, Michael; Gerson, Michael (May 25, 2017). "The conservative mind has become diseased". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved May 29, 2017.
- ^ "The Shameless Conspiracy Theorizing Involving Seth Rich Must Stop". Commentary Magazine. May 23, 2017. Retrieved May 28, 2017.
- ^ Stelter, Brian (October 12, 2009). "Fox's Volley With Obama Intensifying". The New York Times. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ "White House: Fox Pushed Team Obama Over the Brink – US News and World Report". Usnews.com. October 23, 2009. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved July 29, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "The Fox News war: What's the upside for Obama?". CSMonitor.com. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved October 23, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Rutenberg, Jim (October 23, 2009). "Behind the War Between White House and Fox". The New York Times. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ "President Obama's Feud with FOX News – CBS Evening News". CBS News. October 23, 2009. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved July 29, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Obama's misguided Fox hunt". Los Angeles Times. October 24, 2009. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Rutenberg, Jim (October 23, 2009). "Behind the War Between White House and Fox". The New York Times. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ Christina Bellantoni (October 23, 2009). "WH: We're Happy To Exclude Fox, But Didn't Yesterday With Feinberg Interview | TPMDC". Tpmdc.talkingpointsmemo.com. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved July 29, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Krakauer, Steve (October 27, 2009). "Finally Resolved? Major Garrett Reveals His Side of Pay Czar-Gate". Mediaite. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved January 18, 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Nicholas, Peter (November 8, 2009). "Democratic consultant says he got a warning from White House after appearing on Fox News". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Eric Pfeiffer. "Fox News mistakenly airs parody of Obama offering to personally fund Muslim museum". Yahoo News. Yahoo! News.
- ^ Max Rivlin-Nadler. "Fox News Falls For Fake Story Claiming Obama is Funding Muslim Museum". Gawker. Gawker.com. Archived from the original on October 5, 2013. Retrieved 6 October 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Barbara Mikkelson. "Museum Peace". Snopes. Snopes.com. Retrieved October 6, 2013.
- ^ a b c d Grynbaum, Michael M. (August 15, 2017). "'Wow': Stunned TV Hosts Reacted in Real Time to Trump". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved August 16, 2017.
- ^ a b c d https://www.facebook.com/daveweigel?fref=ts. "In conservative media, an amen chorus defends Trump's comments on Charlottesville violence". Washington Post. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help); External link in|last= - ^ a b c d e f Byers, Dylan (August 16, 2017). "After Trump's Charlottesville remarks, Fox News focuses on the left and the media". CNNMoney. Retrieved August 16, 2017.
- ^ "Trump Cribbed His Charlottesville Press Conference Straight From Fox News". WIRED. Retrieved August 16, 2017.
- ^ Wilstein, Matt (August 16, 2017). "Fox News' Tucker Carlson Helps Trump Push 'Both Sides' Narrative". The Daily Beast. Retrieved August 16, 2017.
- ^ "Fox News guest says Confederate flag, rainbow flag "exact same thing"". NBC News. Retrieved August 16, 2017.
- ^ Eberhardt, Robin (August 15, 2017). "Fox News guest: Confederate and LGBT flags represent 'the exact same thing'". TheHill. Retrieved August 16, 2017.
- ^ "Fox News blames media - not neo Nazis - for Charlottesville violence". The Independent. August 15, 2017. Retrieved August 16, 2017.
- ^ "Fox Around the World". Fox News.com. Fox News Channel. March 6, 2012. Retrieved May 7, 2012.
- ^ "News Corp buys Sky News in Australia and New Zealand from Seven and Nine". The Sydney Morning Herald. Fairfax Media. December 1, 2016. Retrieved December 1, 2016.
- ^ "News Limited seals pay TV deal after Federal Court approves CMH takeover". The Australian. November 2, 2012. Retrieved November 4, 2012.
- ^ "CRTC approves Fox News for Canada". cbc.ca. November 18, 2004. Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved August 27, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "HOT channel listing". Retrieved September 30, 2014.
- ^ "Why is Fox News no longer airing on Prime?". skytv.co.nz. January 26, 2001. Retrieved August 27, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "TopTV – Bouquet Channels". toptv.co.za. Archived from the original on May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Americable". Archived from the original on November 23, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Mediatti". Archived from the original on January 19, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Pan Global TV Japan". Archived from the original on November 23, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)
Further reading
- Cassino, Dan (2016). Fox News and American Politics: How One Channel Shapes American Politics and Society. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-317-47999-4.
- Collins, Scott (2004). Crazy Like a Fox: The Inside Story of How Fox News Beat CNN. Portfolio. ISBN 978-1-59184-029-9.
- Crupi, Anthony (July 26, 2006). "FNC Ratings Soar as War in Lebanon Rages". MediaWeek. Archived from the original on November 16, 2007.
- Cuprisin, Tim (July 31, 2006). "Fox's Smith tops cable news ranks in ratings". Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. Archived from the original on April 11, 2008.
- Dickinson, Tim (June 9, 2011), "The Fox News Fear Factory", Rolling Stone, no. 1132, pp. 54–64, 66, 82, 84
- "NH GOP drops out as Fox forum partner". The Seattle Times. Associated Press. January 5, 2008. Archived from the original on January 8, 2008. Retrieved June 15, 2011.
- Groseclose, Tim (July 19, 2011). Left Turn: How Liberal Media Bias Distorts the American Mind. St. Martin's Press. ISBN 978-0-312-55593-1.
- Hopkins, Daniel J.; Ladd, Jonathan M. (March 2014). "The consequences of broader media choice: evidence from the expansion of Fox News". Quarterly Journal of Political Science. 9 (1). Now Publishing Inc.: 115–135. doi:10.1561/100.00012099.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)CS1 maint: postscript (link) - Sherman, Gabriel (2013). The Loudest Voice in the Room. Random House.
- The Fifth Estate: "Sticks and Stones", CBC – Bob McKeown investigates Fox News for the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation, 45 min.
External links
- Television news
- 24-hour television news channels
- 24-hour television news channels in the United States
- English-language television stations in the United States
- Foreign television channels broadcasting in the United Kingdom
- Fox News
- 21st Century Fox subsidiaries
- Sirius Satellite Radio channels
- Television channels and stations established in 1996
- XM Satellite Radio channels
- Conservatism in the United States
- 1996 establishments in the United States
