Krishna River: Difference between revisions
m Improving article + Infobox + external links + wikilinks + Fixing style/layout errors |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{about|the Indian river|other uses|Krishna (disambiguation)}} |
{{about|the Indian river|other uses|Krishna (disambiguation)}} |
||
{{Refimprove|date=July 2007}} |
|||
{{Geobox|River |
{{Geobox|River |
||
| Line 14: | Line 13: | ||
| image_size = 300 |
| image_size = 300 |
||
| image_alt = |
| image_alt = |
||
| image_caption = Krishna |
| image_caption = Krishna river gorge by Srisailam, Andhra Pradesh, India |
||
<!-- *** Etymology *** ---> |
<!-- *** Etymology *** ---> |
||
| etymology = |
| etymology = |
||
| Line 63: | Line 62: | ||
| watershed_round = 0 |
| watershed_round = 0 |
||
| watershed_note = |
| watershed_note = |
||
| discharge1_location = Vijaywada (1901–1979 average), max (2009), min (1997) |
| discharge1_location = Vijaywada (1901–1979 average),<br/> max (2009), min (1997) |
||
| discharge1_average = 1641.74 |
| discharge1_average = 1641.74 |
||
| discharge1_round = 0 |
| discharge1_round = 0 |
||
| Line 90: | Line 89: | ||
<!-- *** Tributaries *** --> |
<!-- *** Tributaries *** --> |
||
| tributary_left = [[Bhima river|Bhima]] |
| tributary_left = [[Bhima river|Bhima]] |
||
| tributary_left1 = |
| tributary_left1 = Dindi |
||
| tributary_left2 = |
| tributary_left2 = Peddavagu |
||
| tributary_left3 = |
| tributary_left3 = Halia |
||
| tributary_left4 = [[Musi River (India)|Musi]] |
| tributary_left4 = [[Musi River (India)|Musi]] |
||
| tributary_left5 = |
| tributary_left5 = Paleru |
||
| tributary_left6 = |
| tributary_left6 = Munneru |
||
| tributary_right = [[Venna River|Venna]] |
| tributary_right = [[Venna River|Venna]] |
||
| tributary_right1 = [[Koyna River|Koyna]] |
| tributary_right1 = [[Koyna River|Koyna]] |
||
| tributary_right2 = [[Panchganga River|Panchganga]] |
| tributary_right2 = [[Panchganga River|Panchganga]] |
||
| tributary_right3 = |
| tributary_right3 = Dudhganga |
||
| tributary_right4 = [[Ghataprabha River|Ghataprabha]] |
| tributary_right4 = [[Ghataprabha River|Ghataprabha]] |
||
| tributary_right5 = [[Malaprabha River|Malaprabha]] |
| tributary_right5 = [[Malaprabha River|Malaprabha]] |
||
| Line 114: | Line 113: | ||
==Course== |
==Course== |
||
Krishna river originates at Mahabaleswar near the Jor village in the extreme north of |
Krishna river originates at Mahabaleswar near the Jor village in the extreme north of Wai Taluka, Satara District, Maharashtra in the west and meets the [[Bay of Bengal]] at [[Hamasaladeevi]] (near Avanigadda) in [[Andhra Pradesh]], on the east coast. It flows through the state of [[Karnataka]] before entering Andhra Pradesh. The delta of this river is one of the most fertile regions in [[India]] and was the home to ancient [[Satavahana]] and [[Ikshvaku]] [[Sun Dynasty]] kings. [[Vijayawada]] is the largest city on the River Krishna. [[Sangli]] is the biggest city on the river Krishna in Maharashtra state. |
||
Ecologically, this is one of the disastrous rivers in the world, in that it causes heavy soil erosion during the [[monsoon]] season. It flows fast and furious, often reaching depths of over {{convert|75|ft|m}}. Ironically, there is a saying in Marathi (language of [[Maharashtra]]) "''Santh vaahate Krishnamaai''" which means "quiet flows Krishna". This term is also used to describe how a person should be, as quiet as Krishna. But, in reality, Krishna causes a high degree of erosion between June and August. During this time, Krishna takes fertile soil from [[Maharashtra]], [[Karnataka]] and western [[Andhra Pradesh]] towards the delta region. |
Ecologically, this is one of the disastrous rivers in the world, in that it causes heavy soil erosion during the [[monsoon]] season. It flows fast and furious, often reaching depths of over {{convert|75|ft|m}}. Ironically, there is a saying in Marathi (language of [[Maharashtra]]) "''Santh vaahate Krishnamaai''" which means "quiet flows Krishna". This term is also used to describe how a person should be, as quiet as Krishna. But, in reality, Krishna causes a high degree of erosion between June and August. During this time, Krishna takes fertile soil from [[Maharashtra]], [[Karnataka]] and western [[Andhra Pradesh]] towards the delta region. |
||
==Tributaries== |
==Tributaries== |
||
Its most important tributary is the [[Tungabhadra River]], which is formed by the [[Tunga River]] and [[Bhadra River]] that originate in the [[Western Ghats]] of Karnataka State. Other tributaries include the Kudali river, [[Venna River]], [[Koyna River]], [[Bhima River]] (and its tributaries such as the |
Its most important tributary is the [[Tungabhadra River]], which is formed by the [[Tunga River]] and [[Bhadra River]] that originate in the [[Western Ghats]] of Karnataka State. Other tributaries include the Kudali river, [[Venna River]], [[Koyna River]], [[Bhima River]] (and its tributaries such as the Kudali river]] feeding into the Upper Bhima River Basin), [[Malaprabha River]], [[Ghataprabha River]], Yerla river, Warna river, Dindi river, [[Paleru|Paleru River]], [[Musi River, India|Musi River]], Urmodi river (उरमोडी नदी), Tarli river (तारळी नदी) and Dudhganga river. |
||
The rivers [[Venna River|Venna]], [[Koyna River|Koyna]], Vasna, [[Panchganga River|Panchganga]], Dudhganga, [[Ghataprabha River|Ghataprabha]], [[Malaprabha River|Malaprabha]] and [[Tungabhadra River|Tungabhadra]] join Krishna from the right bank; while the Yerla River, [[Musi River, India|Musi River]], |
The rivers [[Venna River|Venna]], [[Koyna River|Koyna]], Vasna, [[Panchganga River|Panchganga]], Dudhganga, [[Ghataprabha River|Ghataprabha]], [[Malaprabha River|Malaprabha]] and [[Tungabhadra River|Tungabhadra]] join Krishna from the right bank; while the Yerla River, [[Musi River, India|Musi River]], Munneru and Bhima rivers join the Krishna from the left bank. |
||
Their are Four River join at Krishna river In Satara District. This spot is known as Preeti Sangam (meaning Lover's Meeting Point). |
|||
Venna River is (First River) Join Krishna River At Sangam Mahuli, Satara. Urmodi River (उरमोडी नदी) is (Second River) join Krishna at Kashil (काशीळ), Satara. Tarli River (तारळी नदी) is (Third River)join Krishna at Umbraj (उंब्रज) Satara. Then Koyna River is (Fourth River) Join At [[Karad]] (कराड)Satara. This spot is known as Preeti Sangam, Meaning Lovely Meeting. There is Four River Join At Krishna River In Satara District... |
|||
* Venna river is the first river joining Krishna river at Sangam Mahuli, Satara. |
|||
* Urmodi River (उरमोडी नदी) is second river joining Krishna river at Kashil (काशीळ), Satara. |
|||
* Tarli River (तारळी नदी) is third river joining Krishna river at at Umbraj (उंब्रज) Satara. |
|||
* And then Koyna river joining Krishna river at [[Karad]] (कराड)Satara. |
|||
Three tributaries meet Krishna river near [[Sangli]]. Warana |
Three tributaries meet Krishna river near [[Sangli]]. Warana river meets Krishna river near Sangli at Haripur. This spot is also known as [[Sangameshwar]]. [[Panchganga river]] meets Krishna river at [[Narsobawadi]] near Sangli. These places are very holy. It is said that Lord Dattatreya spent some of his days at Audumber on the banks of river Krishna. Sangameswaram of Kurnool district in Andhra Pradesh is a famous pilgrim center for Hindus where Tungabhadra and Bhavanasi rivers join krishna. [[Sangameswara temple, Kurnool|Sangameswaram temple]] is now drowned in the Srisailam reservoir and visible for devotees only during summer when the reservoir's water level comes down<ref>Srisailam project manual</ref> |
||
The main tributaries of Krishna river are |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
==Bridges== |
==Bridges== |
||
* Krishna Bridge, Wai - This is one of the oldest bridges built by the British in India. Built with black rock and with nine attractive "kamans (arches)", the bridge also serves as a flood mark (when the water rises to the level of the road on the bridge) for the "Waikar" people. Bridge is in Dharmpuri Peth, Wai |
|||
* |
* Irwin Bridge, Sangli - This is one of the oldest, historic and largest bridges built on river Krishna during the British rule. This Bridge is built of Red colored stone and has two passages to climb down in the middle of the bridge and view the river water. The Ex Chief Minister of Maharashtra, Late Shri Vasantdada Patil who led the freedom struggle in Western Maharashtra himself jumped into river Krishna from Irwin Bridge when he was chased by the British army. |
||
* |
* B.Soundatti Bridge, Raibag - This is also one of the oldest bridges built during the British rule. This bridge connects Maharashtra to Karnataka state. |
||
*B.Soundatti Bridge, Raibag - This is also one of the oldest bridges built during the British rule. This bridge connects Maharashtra to Karnataka state. |
|||
*Krishna River Tributaries |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
==Places and temples== |
==Places and temples== |
||
[[File:Pre Historic Mid Krishna-Tungabhadra Valley sites.jpg|thumb|300px|Pre Historic sites of Middle Krishna-[[Tungabhadra]] Valley in [[Andhra Pradesh]]]] |
[[File:Pre Historic Mid Krishna-Tungabhadra Valley sites.jpg|thumb|300px|Pre Historic sites of Middle Krishna-[[Tungabhadra]] Valley in [[Andhra Pradesh]]]] |
||
The first holy place on the river Krishna is "Dakshin Kashi Wai", known for the Mahaganpati Mandir and Kashivishweshwar temple. It has seven ghats along the river. |
The first holy place on the river Krishna is "Dakshin Kashi Wai", known for the Mahaganpati Mandir and Kashivishweshwar temple. It has seven ghats along the river. |
||
Temples like Dattadeva temple, which is revered by the people of Maharashtra, is located on the banks of Krishna at Narasoba Waadi and Audumber near [[Sangli]]. Also, located on the banks of the river Krishna is the |
Temples like Dattadeva temple, which is revered by the people of Maharashtra, is located on the banks of Krishna at Narasoba Waadi and Audumber near [[Sangli]]. Also, located on the banks of the river Krishna is the Sangameshwar Shiva temple at Haripur and Ramling temple near Sangli, as well as, villages such as [[Jihe]]. |
||
Popular pilgrim spots like Audumber and Narsobawadi are located on the banks of river Krishna near [[Sangli]] in Maharashtra state. [[Kudalasangama]] is located near [[Bagalkot]], in [[Karnataka]] which is an Aikya linga of [[Basaveshwara]]. [[Srisailam]], one of the twelve jyotirlingas, has an ancient temple for [[Lord Shiva]]. Sangameswra Swamy temple (seen only during summer) is situated near Atmakur. The international [[Kalachakra]] festival was celebrated in the presence of [[Dalai Lama]] in [[Amaravati, Andhra Pradesh|Amaravati]]. Amaravati was the capital of the imperial [[Satavahanas]] who held sway over [[South India]] for 400 years and also a great seat of Buddhist learning and wisdom. [[Vijayawada]] on the left bank of the river has a famous temple situated on Indrakeeladri mountain dedicated to [[Goddess Kanaka Durga]]. Mattapally in Nalgonda District and Vedadri in Krishna District, near Jaggaipet are very famous for the two temples of Lord Narasimha on the banks of river Krishna in Andhra Pradesh. |
Popular pilgrim spots like Audumber and Narsobawadi are located on the banks of river Krishna near [[Sangli]] in Maharashtra state. [[Kudalasangama]] is located near [[Bagalkot]], in [[Karnataka]] which is an Aikya linga of [[Basaveshwara]]. [[Srisailam]], one of the twelve jyotirlingas, has an ancient temple for [[Lord Shiva]]. Sangameswra Swamy temple (seen only during summer) is situated near Atmakur. The international [[Kalachakra]] festival was celebrated in the presence of [[Dalai Lama]] in [[Amaravati, Andhra Pradesh|Amaravati]]. Amaravati was the capital of the imperial [[Satavahanas]] who held sway over [[South India]] for 400 years and also a great seat of Buddhist learning and wisdom. [[Vijayawada]] on the left bank of the river has a famous temple situated on Indrakeeladri mountain dedicated to [[Goddess Kanaka Durga]]. Mattapally in Nalgonda District and Vedadri in Krishna District, near Jaggaipet are very famous for the two temples of Lord Narasimha on the banks of river Krishna in Andhra Pradesh. |
||
| Line 181: | Line 182: | ||
There is big temple of Lord Dattatraya in Kuruvpur village near Maktal of Andhra Pradesh one side and other side Raichur of karnataka is one of the best temple of Dattatraya Swami where he lives for 12 years. |
There is big temple of Lord Dattatraya in Kuruvpur village near Maktal of Andhra Pradesh one side and other side Raichur of karnataka is one of the best temple of Dattatraya Swami where he lives for 12 years. |
||
There are many popular temples on Krishna River. [[Wai, Maharashtra|Wai]] is an ancient city located on this holy river. There is " |
There are many popular temples on Krishna River. [[Wai, Maharashtra|Wai]] is an ancient city located on this holy river. There is "Krushnabai Utsav" celebrated for 1–2 months during January to February on this ghats. This utsav is celebrated because it is said that, Krushnabai gave Victory to [[Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj]] against [[Afzal Khan]] about 350 years back. There is a big Ganpati mandir constructed in 1764. The other places along the banks of this river are [[Satara Town|Satara City]], [[Karad]], [[Sangli]] etc. |
||
==Dams== |
==Dams== |
||
There are many [[dam]]s constructed across the Krishna river. |
There are many [[dam]]s constructed across the Krishna river. |
||
{{Div col||15em}} |
|||
*[[Dhom Balakwadi]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*kaushik |
|||
*[[Dhom Dam]], Maharashtra |
* Amar Dam |
||
* [[Dhom Dam]], Maharashtra |
|||
* |
* Jurala Dam |
||
* |
* Kanur Dam |
||
*[[ |
* [[Nagarjuna Sagar Dam]] |
||
*[[ |
* [[Narayanpur Dam]] |
||
*[[Prakasam Barrage]] |
* [[Prakasam Barrage]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
*[[ |
* [[Srisailam Dam]] |
||
{{Div col end}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*[[Kanur Dam]] |
|||
==Krishna Basin== |
==Krishna Basin== |
||
Revision as of 10:21, 26 November 2013


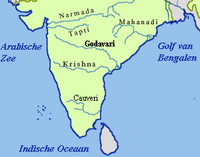
The Krishna River (Marathi: कृष्णा नदी, Kannada: ಕೃಷ್ಣಾ ನದಿ, Telugu: కృష్ణా నది) is one of the longest rivers in central-southern India, about 1,400 kilometres (870 mi). It is also referred to as Krishnaveni in its original nomenclature. The Krishna River is the third longest river in India after the Ganges and the Godavari.
Course
Krishna river originates at Mahabaleswar near the Jor village in the extreme north of Wai Taluka, Satara District, Maharashtra in the west and meets the Bay of Bengal at Hamasaladeevi (near Avanigadda) in Andhra Pradesh, on the east coast. It flows through the state of Karnataka before entering Andhra Pradesh. The delta of this river is one of the most fertile regions in India and was the home to ancient Satavahana and Ikshvaku Sun Dynasty kings. Vijayawada is the largest city on the River Krishna. Sangli is the biggest city on the river Krishna in Maharashtra state.
Ecologically, this is one of the disastrous rivers in the world, in that it causes heavy soil erosion during the monsoon season. It flows fast and furious, often reaching depths of over 75 feet (23 m). Ironically, there is a saying in Marathi (language of Maharashtra) "Santh vaahate Krishnamaai" which means "quiet flows Krishna". This term is also used to describe how a person should be, as quiet as Krishna. But, in reality, Krishna causes a high degree of erosion between June and August. During this time, Krishna takes fertile soil from Maharashtra, Karnataka and western Andhra Pradesh towards the delta region.
Tributaries
Its most important tributary is the Tungabhadra River, which is formed by the Tunga River and Bhadra River that originate in the Western Ghats of Karnataka State. Other tributaries include the Kudali river, Venna River, Koyna River, Bhima River (and its tributaries such as the Kudali river]] feeding into the Upper Bhima River Basin), Malaprabha River, Ghataprabha River, Yerla river, Warna river, Dindi river, Paleru River, Musi River, Urmodi river (उरमोडी नदी), Tarli river (तारळी नदी) and Dudhganga river.
The rivers Venna, Koyna, Vasna, Panchganga, Dudhganga, Ghataprabha, Malaprabha and Tungabhadra join Krishna from the right bank; while the Yerla River, Musi River, Munneru and Bhima rivers join the Krishna from the left bank.
Their are Four River join at Krishna river In Satara District. This spot is known as Preeti Sangam (meaning Lover's Meeting Point).
- Venna river is the first river joining Krishna river at Sangam Mahuli, Satara.
- Urmodi River (उरमोडी नदी) is second river joining Krishna river at Kashil (काशीळ), Satara.
- Tarli River (तारळी नदी) is third river joining Krishna river at at Umbraj (उंब्रज) Satara.
- And then Koyna river joining Krishna river at Karad (कराड)Satara.
Three tributaries meet Krishna river near Sangli. Warana river meets Krishna river near Sangli at Haripur. This spot is also known as Sangameshwar. Panchganga river meets Krishna river at Narsobawadi near Sangli. These places are very holy. It is said that Lord Dattatreya spent some of his days at Audumber on the banks of river Krishna. Sangameswaram of Kurnool district in Andhra Pradesh is a famous pilgrim center for Hindus where Tungabhadra and Bhavanasi rivers join krishna. Sangameswaram temple is now drowned in the Srisailam reservoir and visible for devotees only during summer when the reservoir's water level comes down[1]
The main tributaries of Krishna river are
- Bhima river in Maharashtra and Karnataka
- Malaprabha river
- Ghataprabha river
- Varna or Warna river
- Koyna river
- Venna river
- Munneru river in Andhra Pradesh
- Akeru river in Andhra Pradesh
- Paleru river in Andhra Pradesh
- Musi river in Andhra Pradesh
- Bhavanasi river in kurnool district
- Tungabhadra river
- Vedavathi river
- Suvarnamukhi river
- Veda river
- Avathi river
- Varada river
- Tunga river
- Bhadra river
- Vedavathi river
Bridges
- Krishna Bridge, Wai - This is one of the oldest bridges built by the British in India. Built with black rock and with nine attractive "kamans (arches)", the bridge also serves as a flood mark (when the water rises to the level of the road on the bridge) for the "Waikar" people. Bridge is in Dharmpuri Peth, Wai
- Irwin Bridge, Sangli - This is one of the oldest, historic and largest bridges built on river Krishna during the British rule. This Bridge is built of Red colored stone and has two passages to climb down in the middle of the bridge and view the river water. The Ex Chief Minister of Maharashtra, Late Shri Vasantdada Patil who led the freedom struggle in Western Maharashtra himself jumped into river Krishna from Irwin Bridge when he was chased by the British army.
- B.Soundatti Bridge, Raibag - This is also one of the oldest bridges built during the British rule. This bridge connects Maharashtra to Karnataka state.
Places and temples

The first holy place on the river Krishna is "Dakshin Kashi Wai", known for the Mahaganpati Mandir and Kashivishweshwar temple. It has seven ghats along the river. Temples like Dattadeva temple, which is revered by the people of Maharashtra, is located on the banks of Krishna at Narasoba Waadi and Audumber near Sangli. Also, located on the banks of the river Krishna is the Sangameshwar Shiva temple at Haripur and Ramling temple near Sangli, as well as, villages such as Jihe.
Popular pilgrim spots like Audumber and Narsobawadi are located on the banks of river Krishna near Sangli in Maharashtra state. Kudalasangama is located near Bagalkot, in Karnataka which is an Aikya linga of Basaveshwara. Srisailam, one of the twelve jyotirlingas, has an ancient temple for Lord Shiva. Sangameswra Swamy temple (seen only during summer) is situated near Atmakur. The international Kalachakra festival was celebrated in the presence of Dalai Lama in Amaravati. Amaravati was the capital of the imperial Satavahanas who held sway over South India for 400 years and also a great seat of Buddhist learning and wisdom. Vijayawada on the left bank of the river has a famous temple situated on Indrakeeladri mountain dedicated to Goddess Kanaka Durga. Mattapally in Nalgonda District and Vedadri in Krishna District, near Jaggaipet are very famous for the two temples of Lord Narasimha on the banks of river Krishna in Andhra Pradesh.
There is big temple of Lord Dattatraya in Kuruvpur village near Maktal of Andhra Pradesh one side and other side Raichur of karnataka is one of the best temple of Dattatraya Swami where he lives for 12 years.
There are many popular temples on Krishna River. Wai is an ancient city located on this holy river. There is "Krushnabai Utsav" celebrated for 1–2 months during January to February on this ghats. This utsav is celebrated because it is said that, Krushnabai gave Victory to Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj against Afzal Khan about 350 years back. There is a big Ganpati mandir constructed in 1764. The other places along the banks of this river are Satara City, Karad, Sangli etc.
Dams
There are many dams constructed across the Krishna river.
- Almatti Dam
- Amar Dam
- Dhom Dam, Maharashtra
- Jurala Dam
- Kanur Dam
- Nagarjuna Sagar Dam
- Narayanpur Dam
- Prakasam Barrage
- Pulichitnthala Dam (under construction).
- Srisailam Dam
Krishna Basin
Krishna Basin extends over an area of 258,948 square kilometres (99,980 sq mi) which is nearly 8% of the total geographical area of the country. This large basin lies in the states of Karnataka (113,271 km2), Andhra Pradesh (76,252 km2) and Maharashtra (69,425 km2).
The Krishna river rises in the Western Ghats, at an elevation of about 1337 m just north of Mahabaleshwar, about 64 km from the Arabian Sea. It flows for about 1400 km and outfalls into the Bay of Bengal. The principal tributaries joining Krishna are the Ghataprabha, the Malaprabha, the Bhima, the Tungabhadra and the Musi.
Most of this basin comprises rolling and undulating country, except for the western border, which is formed by an unbroken line of the Western Ghats. The important soil types found in the basin are black soils, red soils, laterite and lateritic soils, alluvium, mixed soils, red and black soils and saline and alkaline soils.
An average annual surface water potential of 78.1 km³ has been assessed in this basin. Out of this, 58.0 km³ is utilisable water. Culturable area in the basin is about 203,000 km2, which is 10.4% of the total culturable area of the country.
Mullayanagiri peak, in Karnataka, is the highest point (1,930m) of the Krishna basin.
Floods
In 2009 October heavy floods occurred, isolating 350 villages and leaving millions homeless,[2] which is believed to be first occurrence in 1000 years. The flood resulted in heavy damage to Kurnool, Mahabubnagar, Guntur, Krishna and Nalagonda Districts. The entire city of Kurnool was immersed in approximately 10 feet (3.0 m) water for nearly 3 days.
Water inflow of 1,110,000 cu ft/s (31,000 m3/s)st was recorded at the Prakasam Barriage, which surpassed the previous record of 1,080,000 cu ft/s (31,000 m3/s)recorded in the year 1903.
The ruling Congress government in Andhra Pradesh state attributed the floods to excessive rainfall in the catchment areas of the river upstream of Srisailam dam. However, in the opinion of most experts, and the general public, the floods occurred due to mismanagement on the part of the state government. Influenced by the drought-like situation that had prevailed till the rain event that led to this flood, and to ensure water for irrigation projects in the Rayalaseema region of Andhra Pradesh, the government of the day dithered, while water management experts exhorted it to empty Srisailam reservoir ahead of the expected deluge. This resulted in an unprecedented volume of water backing up behind Srisailam dam, resulting in floods both upstream of the river, and downstream as well, when all the gates of the dam were opened for several days to bring storage at Srisailam back to normal levels. And the villages named Buggamadharam, Vajinepalli, Vellaturu, and Chintriyala were also effected. Mainly Buggamadharam village is surrounded by fully water on 4 sides. The people of this village were shifted to nearby places of factories for help.
Krishna in Hindu religion
This river is revered by Hindus as sacred. The river is also believed to remove all sins of people by taking a bath in this river. There are many pilgrimage places in Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh on the course of this river.
See also
- Krishna (the deity)
- Krishna Water Disputes Tribunal
- List of rivers of India
- Tungabhadra River
- Godavari River
- Upper Krishna Project
External links
- River Krishna
- About River Krishna
- Krishna River Basin
- International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Krishna Basin
- Major Reservoirs on River Krishna
- Map of River Krishna in Andhra Pradesh
- Map of River Krishna Historic Floods, 2009 in Andhra Pradesh
- Krishna River Management of Floods, 2009 in Andhra Pradesh
- [1]
- watch Krishna river on youtube
References
- ^ Srisailam project manual
- ^ "Flooding along the Krishna River: Natural Hazards". earthobservatory.nasa.gov. Retrieved 11 October 2009.