Aquaporin-1
Aquaporin 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AQP1 gene.
AQP1 is a widely expressed water channel, whose physiological function has been most thoroughly characterized in the kidney. It is found in the basolateral and apical plasma membranes of the proximal tubules, the descending limb of the loop of Henle, and in the descending portion of the vasa recta. Additionally, it is found in red blood cells, vascular endothelium, the gastrointestinal tract, sweat glands, lungs, and the central nervous system[5]
It is not regulated by vasopressin (ADH).
Function
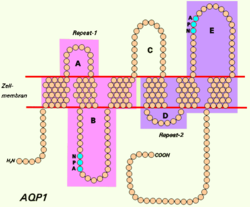
Aquaporins are a family of small integral membrane proteins related to the major intrinsic protein (MIP or AQP0). This gene encodes an aquaporin which functions as both a molecular water channel protein and as a non-selective cation channel gated by cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP).[6] It is a homotetramer with six bilayer spanning domains and N-glycosylation sites. The AQP1 monomer consists of six transmembrane alpha helices that are connected by five loops (A to E).[7] The protein physically resembles channel proteins and is abundant in erythrocytes and renal tubes. The gene encoding this aquaporin is a possible candidate for disorders involving imbalance in ocular fluid movement.[8]
See also
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000240583 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000004655 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Aquaporin and Blood Brain Barrier, Current Neuropharmacology from U.S. National Library of Medicine, 2010.
- ^ Boassa D, Yool AJ (October 2003). "Single amino acids in the carboxyl terminal domain of aquaporin-1 contribute to cGMP-dependent ion channel activation". BMC Physiology. 3: 12. doi:10.1186/1472-6793-3-12. PMC 269983. PMID 14561230.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Kong Y, Ma J (December 2001). "Dynamic mechanisms of the membrane water channel aquaporin-1 (AQP1)". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 98 (25): 14345–9. Bibcode:2001PNAS...9814345K. doi:10.1073/pnas.251507998. PMC 64684. PMID 11717407.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: AQP1 aquaporin 1 (Colton blood group)".
Further reading
- Knepper MA (July 1994). "The aquaporin family of molecular water channels". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 91 (14): 6255–8. Bibcode:1994PNAS...91.6255K. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.14.6255. PMC 44179. PMID 7517546.
- Borgnia M, Nielsen S, Engel A, Agre P (2000). "Cellular and molecular biology of the aquaporin water channels". Annual Review of Biochemistry. 68: 425–58. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.68.1.425. PMID 10872456.
- Horster M (December 2000). "Embryonic epithelial membrane transporters". American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology. 279 (6): F982-96. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.2000.279.6.F982. PMID 11097616.
- Yool AJ, Weinstein AM (April 2002). "New roles for old holes: ion channel function in aquaporin-1". News in Physiological Sciences. 17 (2): 68–72. doi:10.1152/nips.01372.2001. PMID 11909995.
- Mitra, Alok K.; Ren, Gang; Reddy, Vijay S.; Cheng, Anchi; Froger, Alexandrine (2008). "The Architecture of a Water-Selective Pore in the Lipid Bilayer Visualized by Electron Crystallography in Vitreous Ice". Ion Channels: From Atomic Resolution Physiology to Functional Genomics. Novartis Foundation Symposia. pp. 33–50. doi:10.1002/0470868759.ch4. ISBN 978-0-470-84375-8.
- Ripoche P, Goossens D, Devuyst O, Gane P, Colin Y, Verkman AS, Cartron JP (2006). "Role of RhAG and AQP1 in NH3 and CO2 gas transport in red cell ghosts: a stopped-flow analysis". Transfusion Clinique Et Biologique. 13 (1–2): 117–22. doi:10.1016/j.tracli.2006.03.004. PMID 16574458.
- Preston GM, Carroll TP, Guggino WB, Agre P (April 1992). "Appearance of water channels in Xenopus oocytes expressing red cell CHIP28 protein". Science. 256 (5055): 385–7. Bibcode:1992Sci...256..385P. doi:10.1126/science.256.5055.385. PMID 1373524. S2CID 8550043.
- Preston GM, Agre P (December 1991). "Isolation of the cDNA for erythrocyte integral membrane protein of 28 kilodaltons: member of an ancient channel family". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 88 (24): 11110–4. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.24.11110. PMC 53083. PMID 1722319.
- Smith BL, Agre P (April 1991). "Erythrocyte Mr 28,000 transmembrane protein exists as a multisubunit oligomer similar to channel proteins". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 266 (10): 6407–15. PMID 2007592.
- Denker BM, Smith BL, Kuhajda FP, Agre P (October 1988). "Identification, purification, and partial characterization of a novel Mr 28,000 integral membrane protein from erythrocytes and renal tubules". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 263 (30): 15634–42. PMID 3049610.
- Zelinski T, Kaita H, Lewis M, Coghlan G, Philipps S, Belcher E, et al. (1988). "The Colton blood group locus. A linkage analysis". Transfusion. 28 (5): 435–8. doi:10.1046/j.1537-2995.1988.28588337331.x. PMID 3166547. S2CID 35893178.
- Preston GM, Jung JS, Guggino WB, Agre P (January 1994). "Membrane topology of aquaporin CHIP. Analysis of functional epitope-scanning mutants by vectorial proteolysis". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 269 (3): 1668–73. PMID 7507481.
- Skach WR, Shi LB, Calayag MC, Frigeri A, Lingappa VR, Verkman AS (May 1994). "Biogenesis and transmembrane topology of the CHIP28 water channel at the endoplasmic reticulum". The Journal of Cell Biology. 125 (4): 803–15. doi:10.1083/jcb.125.4.803. PMC 2120064. PMID 7514605.
- Li X, Yu H, Koide SS (February 1994). "The water channel gene in human uterus". Biochemistry and Molecular Biology International. 32 (2): 371–7. PMID 7517253.
- Walz T, Smith BL, Agre P, Engel A (July 1994). "The three-dimensional structure of human erythrocyte aquaporin CHIP". The EMBO Journal. 13 (13): 2985–93. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06597.x. PMC 395186. PMID 7518771.
- Preston GM, Smith BL, Zeidel ML, Moulds JJ, Agre P (September 1994). "Mutations in aquaporin-1 in phenotypically normal humans without functional CHIP water channels". Science. 265 (5178): 1585–7. Bibcode:1994Sci...265.1585P. doi:10.1126/science.7521540. PMID 7521540.
- Smith BL, Preston GM, Spring FA, Anstee DJ, Agre P (September 1994). "Human red cell aquaporin CHIP. I. Molecular characterization of ABH and Colton blood group antigens". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 94 (3): 1043–9. doi:10.1172/JCI117418. PMC 295159. PMID 7521882.
- van Hoek AN, Wiener MC, Verbavatz JM, Brown D, Lipniunas PH, Townsend RR, Verkman AS (February 1995). "Purification and structure-function analysis of native, PNGase F-treated, and endo-beta-galactosidase-treated CHIP28 water channels". Biochemistry. 34 (7): 2212–9. doi:10.1021/bi00007a015. PMID 7532004.
- Keen TJ, Inglehearn CF, Patel RJ, Green ED, Peluso DC, Bhattacharya SS (January 1995). "Localization of the aquaporin 1 (AQP1) gene within a YAC contig containing the polymorphic markers D7S632 and D7S526". Genomics. 25 (2): 599–600. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(95)80070-3. PMID 7540589.
External links
- Aquaporin+1 at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Gallery of Aquaporin Simulations
- Human AQP1 genome location and AQP1 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.