Diqing Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture
27°49′N 99°42′E / 27.82°N 99.70°E
Dêqên Prefecture
迪庆州 · བདེ་ཆེན་ཁུལ། | |
|---|---|
| Dêqên Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture 迪庆藏族自治州 · བདེ་ཆེན་བོད་རིགས་རང་སྐྱོང་ཁུལ་ | |
 Baima Mountains in Dêqên Prefecture | |
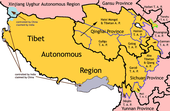
 Location of Dêqên Prefecture in Yunnan | |
| Country | China |
| Province | Yunnan |
| Prefecture seat | Shangri-La City |
| Government | |
| • Type | Autonomous prefecture |
| • CCP Secretary | Gu Kun |
| • Congress Chairman | Gu Kun |
| • Governor | Qi Jianxin |
| • CPPCC Chairman | Du Yongchun |
| Area | |
| • Total | 23,185.59 km2 (8,952.01 sq mi) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 400,182 |
| • Density | 17/km2 (45/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (CST) |
| Postal code | 674400 |
| Area code | 0887 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-YN-34 |
| Website | www |
| Diqing.gov.cn | |
Dêqên Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, also known as Diqing Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture (simplified Chinese: 迪庆藏族自治州; traditional Chinese: 迪慶藏族自治州; pinyin: Díqìng Zàngzú Zìzhìzhōu; Tibetan: བདེ་ཆེན་བོད་རིགས་རང་སྐྱོང་ཁུལ་, Wylie: Bde-chen Bod-rigs rang-skyong khul) is an autonomous prefecture in Northwestern Yunnan Province, China. It has an area of 23,870 km2 (9,220 sq mi). Its capital, which is also the largest city in the prefecture, is Shangri-La City.
This prefecture of Yunnan Province is bordered on the northeast by Sichuan Province and on the northwest by the Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR). Southwest and southeast of Dêqên Prefecture are other parts of Yunnan Province: Nujiang Lisu Autonomous Prefecture and Lijiang respectively.
There are three county-level divisions in this prefecture: Shangri-La City, Dêqên County and Weixi Lisu Autonomous County and they all used to be under the administration of Lijiang (located southeast of this prefecture).[1] This autonomous prefecture was established in 1957 and named Diqing by its first governor.[1] The name of this Tibetan autonomous prefecture (TAP) is also spelled Dechen, Deqing or Dêqên.[2]
Transport
Air
Diqing Shangri-La Airport, also known simply as Diqing Airport, is one of the biggest airports in the northwest of the Yunnan Province. It is located about 3.4 miles (5.5 km) from the center of Shangri-La City. There are flights to Lhasa, Chengdu, Beijing (via Kunming), Shanghai Pudong, Shenzhen (via Guiyang), Guangzhou, Kunming and Xishuangbanna. [citation needed]
Road
Highways are the main means of transportation to reach Dêqên Prefecture. The major highway in this prefecture is China National Highway 214 (a Yunnan-Tibet-Qinghai highway abbreviated "G214").
There are also direct bus routes to Kunming, Lijiang and Panzhihua (Sichuan).
Demography
Ethnic groups in Dêqên, 2000 census
| Nationality | Population | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Tibetan | 117,099 | 33.12% |
| Lisu | 98,195 | 27.78% |
| Han | 57,928 | 16.39% |
| Naxi | 45,269 | 12.81% |
| Bai | 18,182 | 5.14% |
| Yi | 11,616 | 3.29% |
| Hui | 1,496 | 0.42% |
| Pumi | 1,496 | 0.42% |
| Miao | 1,434 | 0.41% |
| Nu | 241 | 0.07% |
| Derung | 137 | 0.04% |
| Others | 425 | 0.11% |
Subdivisions
Dêqên is divided into three counties, among which one is Autonomous county:
| Map | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Hanzi | Hanyu Pinyin | Tibetan | Tibetan Pinyin | Wylie | Population (2010 Census) |
Area (km2) | Density (/km2) | |
| Shangri-La | 香格里拉市 | Xiānggélǐlā Shì | སེམས་ཀྱི་ཉི་ཟླ་གྲོང་ཁྱེར། | Xamgyi'nyilha Chongkyir | sems kyi nyi zla grong khyer | 172,988 | 11,613 | 14.89 | |
| Dêqên County | 德钦县 | Déqīn Xiàn | བདེ་ཆེན་རྫོང་།
མཇོལ་རྫོང་། |
Dêqên Zong
Jol Zong |
bde chen rdzong
mjol rdzong |
66,589 | 7,596 | 8.76 | |
| Weixi Lisu Autonomous County | 维西傈僳族 自治县 |
Wéixī Lìsùzú Zìzhìxiàn |
འབའ་ལུང་ལི་སུའུ་རིགས་རང་སྐྱོང་རྫོང་། | Balung Lisurig Ranggyong Zong | 'ba' lung li su'u rigs rang skyong rdzong | 160,605 | 4,661 | 34.45 | |
History
This prefecture is in the southern part of a historical region called Kham, which belonged to the Tibetan Empire many centuries ago. After the decline of that empire in the 9th century, peripheral areas like southern Kham remained part of Tibet more in an ethnographical than a political sense. As a practical matter, by the mid-1700s, the Tibetan Government had mostly lost control of Kham to Manchu (Qing) China and that situation lasted until the end of the Manchu Dynasty in 1912.[3]
Southern Kham along with other parts of Yunnan were ruled by the Yunnan clique from 1915 until 1927. Then it was controlled by Governor and warlord Long (Lung) Yun until near the end of the Chinese Civil War, when Du Yuming removed him under the order of Chiang Kai-shek.
There are three counties in this prefecture: Shangri-La (formerly Zhongdian), Dêqên County and Weixi Lisu Autonomous County (formerly Weixi) and they all were under the administration of Lijiang.[1] The Autonomous Prefecture was established in 1957 and named "Diqing" by its first governor.[1][4]
During the remainder of the 20th century, the prefecture's capital was called Zhongdian but was renamed on December 17, 2001 as Shangri-La City (other spellings: Semkyi'nyida, Xianggelila or Xamgyi'nyilha) after the fictional land of Shangri-La in the 1933 James Hilton novel Lost Horizon, with an eye toward promoting tourism in the area.[5][6]
On June 25, 2007 the Pudacuo National Park was established on 500 square miles (1,300 km2) in this prefecture. On January 11, 2014, there was a major fire in the 1,000-year-old Dukezong Tibetan neighborhood of the capital city Shangri-La, causing much damage and hardship.[7]
References
- ^ a b c d "System Evolution", via official website of Diqing government (in Chinese). Accessed April 25, 2015.
- ^ Barnett, Robert. Lhasa: Streets with Memories, p. 197 (Columbia University Press, 2010).
- ^ Goldstein, M.C. "Change, Conflict and Continuity among a community of nomadic pastoralists—A Case Study from western Tibet, 1950–1990" in Resistance and Reform in Tibet (eds. Barnett and Akiner. London: Hurst & Co., 1994).
- ^ Mackerras, Colin and Yorke, Amanda. The Cambridge Handbook of Contemporary China, p. 209 (Cambridge University Press, 1991).
- ^ Yü, Dan. Mindscaping the Landscape of Tibet: Place, Memorability, Ecoaesthetics, p. 47 (Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co, 2015).
- ^ Merkel-Hess, Kate. China in 2008: A Year of Great Significance, p. 255 (Rowman & Littlefield, 2009).
- ^ "Night fire burns for hours, destroys ancient Tibetan town in southwest China's Shangri-La county". Toledo Blade. January 11, 2014.
External links
- Official Website (in Chinese)
- Yunnan-Diqing via chinadiscover.net.