Islamic State
| Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant | |
|---|---|
| الدولة الإسلامية في العراق والشام ad-Dawlah al-Islāmiyah fī 'l-ʿIrāq wa-sh-Shām | |
 | |
| Leaders |
|
| Dates of operation | 1999–present
|
| Headquarters | Ar-Raqqah, Syria (de facto capital) |
| Active regions |  Military situation as of August 27, 2019, in the Iraqi, Syrian, and Lebanese conflicts. Controlled by the Iraqi government Controlled by the Syrian government Controlled by the Lebanese government Controlled by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant Controlled by Iraqi Kurdistan forces Controlled by Syrian Kurdistan forces Controlled by Syrian opposition forces Controlled by al-Nusra Front Controlled by Hezbollah Note: Iraq and Syria contain large desert areas with limited populations. These areas are mapped as under the control of forces holding roads and towns within them.Detailed map of the Iraqi insurgency Detailed map of the Lebanese insurgency Detailed map of the Libyan Civil War Detailed map of the Nigerian insurgency Detailed map of the Sinai insurgency Detailed map of the Yemeni Civil War |
| Ideology | |
| Battles and wars | the Syrian Civil War, Iraq War (2003–2011), Iraqi insurgency, Iraq War (2014–present), Second Libyan Civil War, Boko Haram insurgency, War in North-West Pakistan, War in Afghanistan, Yemeni Civil War, and other conflicts
Primary target of Operation Inherent Resolve and of the military intervention against ISIL: in Syria, Iraq, Libya, and Nigeria. |
The Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL; Arabic: الدولة الإسلامية في العراق والشام), also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS, /ˈaɪs[invalid input: 'ɨ']s/), the Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham,[28] or simply Islamic State (IS),[29] is a Wahhabi/Salafi jihadist extremist militant group and self-proclaimed Islamic state and caliphate, which is led by and mainly composed of Sunni Arabs from Iraq and Syria. As of March 2015[update], it has control over territory occupied by ten million people in Iraq and Syria, and through loyal local groups, has control over small areas of Libya, Nigeria and Afghanistan. The group also operates or has affiliates in other parts of the world, including North Africa and South Asia.[30][31][32][33][34][35]
The group is known in Arabic as ad-Dawlah al-Islāmiyah fī 'l-ʿIrāq wa-sh-Shām, leading to the acronym Da'ish or Daesh (داعش, Arabic pronunciation: [ˈdaːʕiʃ]),[36][37] the Arabic equivalent of "ISIL". On 29 June 2014, the group proclaimed itself to be a worldwide caliphate, with Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi being named its caliph, and renamed itself ad-Dawlah al-Islāmiyah (الدولة الإسلامية, "Islamic State" (IS)). As a caliphate, it claims religious, political and military authority over all Muslims worldwide, and that "the legality of all emirates, groups, states, and organisations, becomes null by the expansion of the khilāfah's [caliphate's] authority and arrival of its troops to their areas".[28][38][39][40] The United Nations has held ISIL responsible for human rights abuses and war crimes, and Amnesty International has reported ethnic cleansing by the group on a "historic scale". The group has been designated a terrorist organisation by the United Nations, the European Union and member states, the United States, India, Indonesia, Israel, Turkey, Saudi Arabia, Syria and other countries. Over 60 countries are directly or indirectly waging war against ISIL.
The group originated as Jama'at al-Tawhid wal-Jihad in 1999, which pledged allegiance to al-Qaeda in 2004. The group participated in the Iraqi insurgency that followed the March 2003 invasion of Iraq by Western forces. In January 2006, it joined other Sunni insurgent groups to form the Mujahideen Shura Council, which proclaimed the formation of the Islamic State of Iraq (ISI) in October 2006. After the Syrian Civil War began in March 2011, the ISI, under the leadership of al-Baghdadi, sent delegates into Syria in August 2011. These fighters named themselves Jabhat an-Nuṣrah li-Ahli ash-Shām—al-Nusra Front—and established a large presence in Sunni-majority areas of Syria, within the governorates of Ar-Raqqah, Idlib, Deir ez-Zor, and Aleppo. In April 2013, al-Baghdadi announced the merger of the ISI with al-Nusra Front and that the name of the reunited group was now the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL). However, Abu Mohammad al-Julani and Ayman al-Zawahiri, the leaders of al-Nusra and al-Qaeda respectively, rejected the merger. After an eight-month power struggle, al-Qaeda cut all ties with ISIL on 3 February 2014, citing its failure to consult and "notorious intransigence". In Syria, the group has conducted ground attacks on both government forces and rebel factions in the Syrian Civil War. The group gained prominence after it drove Iraqi government forces out of key cities in western Iraq in an offensive initiated in early 2014. Iraq's territorial loss almost caused a collapse of the Iraqi government and prompted a renewal of US military action in Iraq.[14][41][42][43]
ISIL is adept at social media, posting Internet videos of beheadings of soldiers, civilians, journalists and aid workers, and is known for its destruction of cultural heritage sites. Muslim leaders around the world have condemned ISIL's ideology and actions, arguing that the group has strayed from the path of true Islam and that its actions do not reflect the religion's true teachings or virtues.[44][45] The group's adoption of the name "Islamic State" and idea of a caliphate have been widely criticised, with the United Nations, NATO, various governments, and mainstream Muslim groups rejecting both.
Nomenclature
The group has had various names since it began.[46]
- The group was founded in 1999 by Jordanian radical Abu Musab al-Zarqawi as Jamāʻat al-Tawḥīd wa-al-Jihād, "The Organisation of Monotheism and Jihad" (JTJ).[27]
- In October 2004, al-Zarqawi swore loyalty to Osama bin Laden and changed the group's name to Tanẓīm Qāʻidat al-Jihād fī Bilād al-Rāfidayn, "The Organisation of Jihad's Base in Mesopotamia", commonly known as al-Qaeda in Iraq (AQI).[46][47] Although the group has never called itself al-Qaeda in Iraq, this has been its informal name over the years.[48]
- In January 2006, AQI merged with several other Iraqi insurgent groups to form the Mujahideen Shura Council.[49] Al-Zarqawi was killed in June 2006.
- On 12 October 2006, the Mujahideen Shura Council merged with several more insurgent factions, and on 13 October the establishment of the ad-Dawlah al-ʻIraq al-Islāmiyah, also known as the Islamic State of Iraq (ISI), was announced.[50] The leaders of this group were Abu Abdullah al-Rashid al-Baghdadi and Abu Ayyub al-Masri.[51] After they were killed in a US–Iraqi operation in April 2010, Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi became the new leader of the group.
- On 8 April 2013, having expanded into Syria, the group adopted the name Islamic State of Iraq and al-Sham, which more fully translates as Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant [citation needed] or Islamic State of Iraq and Syria.[52][53][54] These names are translations of the Arabic name ad-Dawlah al-Islāmīyah fī-l-ʻIrāq wa-sh-Shām,[55][56] al-Shām being a description of the Levant or Greater Syria.[28] The translated names are commonly abbreviated as ISIL or ISIS, with a debate over which of these acronyms should be used.[28][56] The Washington Post concluded that the distinction between the two "is not so great".[28]
- The name Da'ish is often used by ISIL's Arabic-speaking detractors. It is based on the Arabic letters Dāl, alif, ʻayn, and shīn, which form the acronym (داعش) of ISIL's Arabic name al-Dawlah al-Islamīyah fī al-ʻIrāq wa-al-Shām.[57][58] There are many spellings of this acronym, with "Daesh" gaining acceptance. ISIL considers the name Da'ish derogatory, because it sounds similar to the Arabic words Daes, "one who crushes something underfoot", and Dahes, "one who sows discord".[36][59] ISIL reportedly uses flogging as a punishment for those who use the name in ISIL-controlled areas.[60][61] In 2015, over 120 British parliamentarians asked the BBC to use the name Daesh, following the example of John Kerry and Laurent Fabius.[36][62]
- On 14 May 2014, the United States Department of State announced its decision to use Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) as the group's primary name.[57] However, in late 2014, top US officials shifted toward using Daesh, since this was the name that their Arab allies preferred to use.[36]
- On 29 June 2014, the group renamed itself ad-Dawlah al-Islāmiyah (الدولة الإسلامية, Islamic State (IS)), and declared itself a worldwide caliphate.[38][63][64] Accordingly, "Iraq and Shām" was removed from all official deliberations and communications, and the official name became the Islamic State from the date of the declaration. The name Islamic State and the claim of a caliphate have been widely criticised, with the UN, various governments, and mainstream Muslim groups refusing to use the new name.[62][65][66][67][68][69][70][71]
History
| History of the Islamic State |
|---|
 |
|
Jama'at al-Tawhid wal-Jihad (1999‑2004) Al-Qaeda in Iraq (2004‑2006) Jama'at Jaysh Ahl al-Sunnah wa-l-Jama'ah (2004‑2006) Jaish al-Ta'ifa al-Mansurah (2004‑2006) Mujahideen Shura Council (2006) Islamic State of Iraq (2006‑2013) Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant |
| By topic |
|
|
Foundation, 1999–2006
Following the 2003 invasion of Iraq, the Jordanian Salafi jihadist Abu Musab al-Zarqawi and his militant group Jama'at al-Tawhid wal-Jihad, founded in 1999, achieved notoriety in the early stages of the Iraqi insurgency for the suicide attacks on Shia Islamic mosques, civilians, Iraqi government institutions and Italian soldiers partaking in the US-led 'Multi-National Force'. Al-Zarqawi's group officially pledged allegiance to Osama bin Laden's al-Qaeda network in October 2004, changing its name to Tanzim Qaidat al-Jihad fi Bilad al-Rafidayn (تنظيم قاعدة الجهاد في بلاد الرافدين, "Organisation of Jihad's Base in Mesopotamia"), also known as al-Qaeda in Iraq (AQI).[12][72][73] Attacks by the group on civilians, Iraqi government and security forces, foreign diplomats and soldiers, and American convoys continued with roughly the same intensity. In a letter to al-Zarqawi in July 2005, al-Qaeda's then deputy leader Ayman al-Zawahiri outlined a four-stage plan to expand the Iraq War. The plan included expelling US forces from Iraq, establishing an Islamic authority as a caliphate, spreading the conflict to Iraq's secular neighbours, and clashing with Israel, which the letter says "was established only to challenge any new Islamic entity".[74]
In January 2006, AQI joined with several smaller Iraqi insurgent groups under an umbrella organisation called the Mujahideen Shura Council (MSC). According to Brian Fishman, this was little more than a media exercise and an attempt to give the group a more Iraqi flavour, and perhaps to distance al-Qaeda from some of al-Zarqawi's tactical errors, more notably the 2005 bombings by AQI of three hotels in Amman.[75] On 7 June 2006, a US airstrike killed al-Zarqawi, who was succeeded as leader of the group by the Egyptian militant Abu Ayyub al-Masri.[76][77]
On 12 October 2006, the MSC united with three smaller groups and six Sunni Islamic tribes to form the "Mutayibeen Coalition". It swore by Allah "to rid Sunnis from the oppression of the rejectionists (Shi'ite Muslims) and the crusader occupiers ... to restore rights even at the price of our own lives ... to make Allah's word supreme in the world, and to restore the glory of Islam".[78][79] A day later, the MSC declared the establishment of the Islamic State of Iraq (ISI), comprising Iraq's six mostly Sunni Arab governorates.[80] Abu Omar al-Baghdadi was announced as its emir,[50][81] and al-Masri was given the title of Minister of War within the ISI's ten-member cabinet.[82]

As Islamic State of Iraq, 2006–13
According to a study compiled by United States intelligence agencies in early 2007, the ISI—also known as AQI—planned to seize power in the central and western areas of Iraq and turn it into a Sunni caliphate.[83] The group built in strength and at its height enjoyed a significant presence in the Iraqi governorates of Al Anbar, Diyala and Baghdad, claiming Baqubah as a capital city.[84][85][86][87]
The Iraq War troop surge of 2007 supplied the United States military with more manpower for operations targeting the group, resulting in dozens of high-level AQI members being captured or killed.[88]
Between July and October 2007, al-Qaeda in Iraq was reported to have lost its secure military bases in Al Anbar province and the Baghdad area.[89] During 2008, a series of US and Iraqi offensives managed to drive out AQI-aligned insurgents from their former safe havens, such as the Diyala and Al Anbar governorates, to the area of the northern city of Mosul.[90]
By 2008, the ISI was describing itself as being in a state of "extraordinary crisis".[91] Its violent attempts to govern its territory led to a backlash from Sunni Arab Iraqis and other insurgent groups and a temporary decline in the group, which was attributable to a number of factors,[92] notably the Anbar Awakening.
In late 2009, the commander of US forces in Iraq, General Ray Odierno, stated that the ISI "has transformed significantly in the last two years. What once was dominated by foreign individuals has now become more and more dominated by Iraqi citizens".[93] On 18 April 2010, the ISI's two top leaders, Abu Ayyub al-Masri and Abu Omar al-Baghdadi, were killed in a joint US-Iraqi raid near Tikrit.[94] In a press conference in June 2010, General Odierno reported that 80% of the ISI's top 42 leaders, including recruiters and financiers, had been killed or captured, with only eight remaining at large. He said that they had been cut off from al-Qaeda's leadership in Pakistan.[95][96][97]
On 16 May 2010, Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi was appointed the new leader of the Islamic State of Iraq.[98][99] Al-Baghdadi replenished the group's leadership, many of whom had been killed or captured, by appointing former Ba'athist military and intelligence officers who had served during Saddam Hussein's rule.[100] These men, nearly all of whom had spent time imprisoned by the US military, came to make up about one third of Baghdadi's top 25 commanders. One of them was a former colonel, Samir al-Khlifawi, also known as Haji Bakr, who became the overall military commander in charge of overseeing the group's operations.[101][102] Al-Khlifawi was instrumental in doing the ground work that led to the growth of ISIL.[103]
In July 2012, al-Baghdadi released an audio statement online announcing that the group was returning to former strongholds from which US troops and the Sons of Iraq had driven them in 2007 and 2008.[104] He also declared the start of a new offensive in Iraq called Breaking the Walls, aimed at freeing members of the group held in Iraqi prisons.[104] Violence in Iraq had begun to escalate in June 2012, primarily with AQI's car bomb attacks, and by July 2013, monthly fatalities exceeded 1,000 for the first time since April 2008.[105]
Syrian Civil War
In March 2011, protests began in Syria against the Syrian government of Bashar al-Assad. In the following months, violence between demonstrators and security forces led to a gradual militarisation of the conflict.[106] In August, al-Baghdadi began sending Syrian and Iraqi ISI members experienced in guerilla warfare across the border into Syria to establish an organisation there. Led by a Syrian known as Abu Muhammad al-Julani, this group began to recruit fighters and establish cells throughout the country.[107][108] In January 2012, the group announced its formation as Jabhat al-Nusra li Ahl as-Sham—Jabhat al-Nusra—more commonly known as al-Nusra Front. Al-Nusra grew rapidly into a capable fighting force, with popular support among Syrians opposed to the Assad government.[107]
As Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, 2013–14
On 8 April 2013, al-Baghdadi released an audio statement in which he announced that al-Nusra Front had been established, financed, and supported by the Islamic State of Iraq,[109] and that the two groups were merging under the name "Islamic State of Iraq and Al-Sham".[52] Al-Julani issued a statement denying the merger, and complaining that neither he nor anyone else in al-Nusra's leadership had been consulted about it.[110] In June 2013, Al Jazeera reported that it had obtained a letter written by al-Qaeda's leader Ayman al-Zawahiri, addressed to both leaders, in which he ruled against the merger, and appointed an emissary to oversee relations between them to put an end to tensions.[111] That same month, al-Baghdadi released an audio message rejecting al-Zawahiri's ruling and declaring that the merger was going ahead.[112] Meanwhile, the ISIL campaign to free imprisoned ISIL members culminated in July 2013, with the group carrying out simultaneous raids on Taji and Abu Ghraib prisons, freeing more than 500 prisoners, many of them veterans of the Iraqi insurgency.[105][113] In October 2013, al-Zawahiri ordered the disbanding of ISIL, putting al-Nusra Front in charge of jihadist efforts in Syria,[114] but al-Baghdadi contested al-Zawahiri's ruling on the basis of Islamic jurisprudence,[112] and his group continued to operate in Syria. In February 2014, after an eight-month power struggle, al-Qaeda disavowed any relations with ISIL.[42]
According to journalist Sarah Birke, there are "significant differences" between al-Nusra Front and ISIL. While al-Nusra actively calls for the overthrow of the Assad government, ISIL "tends to be more focused on establishing its own rule on conquered territory". ISIL is "far more ruthless" in building an Islamic state, "carrying out sectarian attacks and imposing sharia law immediately". While al-Nusra has a "large contingent of foreign fighters", it is seen as a home-grown group by many Syrians; by contrast, ISIL fighters have been described as "foreign 'occupiers'" by many Syrian refugees.[115] It has a strong presence in central and northern Syria, where it has instituted sharia in a number of towns.[115] The group reportedly controlled the four border towns of Atmeh, al-Bab, Azaz and Jarablus, allowing it to control the entrance and exit from Syria into Turkey.[115] Foreign fighters in Syria include Russian-speaking jihadists who were part of Jaish al-Muhajireen wal-Ansar (JMA).[116] In November 2013, the JMA's Chechen leader Abu Omar al-Shishani swore an oath of allegiance to al-Baghdadi;[117] the group then split between those who followed al-Shishani in joining ISIL and those who continued to operate independently in the JMA under new leadership.[118]
In January 2014, rebels affiliated with the Islamic Front and the US-trained Free Syrian Army[119] launched an offensive against ISIL militants in and around the city of Aleppo.[120][121] In May 2014, Ayman al-Zawahiri ordered the al-Nusra Front to stop its attacks on its rival, ISIL.[122][failed verification] In June 2014, after continued fighting between the two groups, al-Nusra's branch in the Syrian town of Al-Bukamal pledged allegiance to ISIL.[123][124] In mid-June 2014, ISIL captured the Trabil crossing on the Jordan–Iraq border,[125] the only border crossing between the two countries.[126] ISIL has received some public support in Jordan, albeit limited, partly owing to state repression there.[127] ISIL has undertaken a recruitment drive in Saudi Arabia,[128] where tribes in the north are linked to those in western Iraq and eastern Syria.[129]
As Islamic State, 2014–present
On 29 June 2014, the organisation proclaimed itself to be a worldwide caliphate.[130] Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi—known by his supporters as Amir al-Mu'minin, Caliph Ibrahim—was named its caliph, and the group renamed itself ad-Dawlah al-Islāmiyah (الدولة الإسلامية, "Islamic State" (IS)).[38] As a "Caliphate", it claims religious, political and military authority over all Muslims worldwide.[40][131] The concept of it being a caliphate and the name "Islamic State" have been rejected by governments and Muslim leaders worldwide.[65][66][67][68][69][70][71]
In June and July 2014, Jordan and Saudi Arabia moved troops to their borders with Iraq, after Iraq lost control of, or withdrew from, strategic crossing points that then came under the control of ISIL, or tribes that supported ISIL.[126][132] There was speculation that Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki had ordered a withdrawal of troops from the Iraq–Saudi crossings in order "to increase pressure on Saudi Arabia and bring the threat of ISIS over-running its borders as well".[129]
In July 2014, ISIL recruited more than 6,300 fighters, according to the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights, some of whom were thought to have previously fought for the Free Syrian Army.[133] On 23 July 2014, Abu Sayyaf leader Isnilon Totoni Hapilon and some masked men swore loyalty to al-Baghdadi in a video, giving ISIL a presence in the Philippines.[35][134] In September 2014, the group began kidnapping people for ransoming, in the name of ISIL.[135]

On 3 August 2014, ISIL captured the cities of Zumar, Sinjar, and Wana in northern Iraq.[136] Thousands of Yazidis fled up Mount Sinjar, fearful of the approaching hostile ISIL militants. The stranded Yazidis' need for food and water, the threat of genocide to them and to others announced by ISIL, along with the desire to protect US citizens in Iraq and support Iraq in its fight against ISIL, were all reasons for the 2014 American intervention in Iraq on 7 August[137] and an aerial bombing campaign in Iraq which started on 8 August.
On 11 October 2014, it was reported that ISIL had dispatched 10,000 militants from Syria and Mosul to capture the Iraqi capital city of Baghdad,[138] and Iraqi Army forces and Anbar tribesmen threatened to abandon their weapons if the US did not send in ground troops to halt ISIL's advance.[139] On 13 October, ISIL fighters advanced to within 25 kilometres (16 mi) of Baghdad Airport.[140]
At the end of October 2014, 800 radical militants gained partial control of the Libyan city of Derna and pledged their allegiance to Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, thus making Derna the first city outside Syria and Iraq to be a part of the "Islamic State Caliphate".[141] On 2 November 2014, according to the Associated Press, in response to the coalition airstrikes, representatives from Ahrar ash-Sham attended a meeting with al-Nusra Front, the Khorasan Group, ISIL, and Jund al-Aqsa, which sought to unite these hard-line groups against the US-led coalition and moderate Syrian rebel groups.[142] However, by 14 November 2014, it was revealed that the negotiations had failed.[143] On 10 November 2014, a major faction of the Egyptian militant group Ansar Bait al-Maqdis also pledged its allegiance to ISIL.[144]

ISIL has often used water as a weapon of war. The closing of the gates of the smaller Nuaimiyah dam in Fallujah in April 2014, resulted in the flooding of surrounding regions, while water supply was cut to the Shia-dominated south. Around 12,000 families lost their homes and 200 km² of villages and fields were either flooded or dried up. The economy of the region also suffered with destruction of cropland and electricity shortages.[145]
In mid-January 2015, a Yemeni official said that ISIL had "dozens" of members in Yemen, and that they were coming into direct competition with al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula with their recruitment drive.[146]
In January 2015, Afghan officials confirmed that ISIL had a military presence in Afghanistan,[147] recruiting over 135 militants by late January. However, by the end of January 2015, 65 of the militants were either captured or killed by the Taliban, and ISIL's top Afghan recruiter, Mullah Abdul Rauf, was killed in a US drone strike in February 2015.[148][149][150]
In late January 2015, it was reported that ISIL members had infiltrated the European Union and disguised themselves as civilian refugees who were emigrating from the war zones of Iraq and the Levant.[151] An ISIL representative claimed that ISIL had successfully smuggled 4,000 fighters, and that the smuggled fighters were planning attacks in Europe in retaliation for the airstrikes carried out against ISIL targets in Iraq and Syria. However, experts believe that this claim was exaggerated to boost their stature and spread fear, although they acknowledged that some Western countries were aware of the smuggling.[152]
In early February 2015, ISIL militants in Libya managed to capture part of the countryside to the west of Sabha, and later, an area encompassing the cities of Sirte, Nofolia, and a military base to the south of both cities.
In February 2015, it was reported that some Ansar al-Sharia in Yemen members had broken from al-Qaeda and pledged allegiance to ISIL.[153]
On 16 February 2015, Egypt conducted airstrikes in Libya, in retaliation against ISIL's beheading of 21 Egyptian Christians. By the end of that day, 64 ISIL militants in Libya had been killed by the airstrikes, including 50 militants in Derna.[154] However, by early March, ISIL had captured additional Libyan territory, including a city to the west of Derna, additional areas near Sirte, a stretch of land in southern Libya, some areas around Benghazi, and an area to the east of Tripoli.
On 7 March 2015, Boko Haram swore formal allegiance to ISIL, giving ISIL an official presence in Nigeria, Niger, Chad and Cameroon.[17][155][156] On 13 March 2015, a group of militants from the Islamic Movement of Uzbekistan swore allegiance to ISIL;[157] the group released another video on 31 July 2015 containing its spiritual leader also pledging allegiance.[158] On 30 March 2015, the senior sharia official of Ansar al-Sharia in Libya, Abdullah Al-Libi, defected to ISIL.[159]
From March through mid-April 2015, advances by Iraqi forces into ISIL-controlled territory were focused on Tikrit and the Saladin Governorate.[160]
In June 2015, the US Deputy Secretary of State announced that ISIL had lost more than 10,000 members in airstrikes over the preceding nine months.[161]
In the same month, three simultaneous attacks occurred: two hotels were attacked by gunmen in Tunisia, a man was decapitated in France, and a bomb was detonated at a Shia mosque in Kuwait. ISIL claimed responsibility for the attacks in Kuwait and Tunisia. ISIL flags were present at the crime scene in France, but ISIL has not claimed responsibility for the attack.
Worldwide caliphate aims
Goals
Since at least 2004, a significant goal of the group has been the foundation of a Sunni Islamic state.[162][163] Specifically, ISIL has sought to establish itself as a caliphate, an Islamic state led by a group of religious authorities under a supreme leader—the caliph—who is believed to be the successor to Prophet Muhammad.[164] In June 2014, ISIL published a document in which it claimed to have traced the lineage of its leader al-Baghdadi back to Muhammad,[164] and upon proclaiming a new caliphate on 29 June, the group appointed al-Baghdadi as its caliph. As caliph, he demands the allegiance of all devout Muslims worldwide, according to Islamic jurisprudence (fiqh).[165]
ISIL has detailed its goals in its Dabiq magazine, saying it will continue to seize land and take over the entire Earth : “blessed flag…covers all eastern and western extents of the Earth, filling the world with the truth and justice of Islam and putting an end to the falsehood and tyranny of jahiliyyah [state of ignorance], even if American and its coalition despise such.”[166] According to German journalist Jürgen Todenhöfer, who spent ten days embedded with ISIL in Mosul, the view that he kept hearing was that ISIL wants to “conquer the world” and all who do not believe in the group’s interpretation of the Koran will be killed. Todenhöfer was struck by the ISIL fighters belief that “all religions who agree with democracy have to die”,[167] and by their "incredible enthusiasm"—including enthusiasm for killing "hundreds of millions" of people.[168]
A map circulated around the internet purporting to show historical areas of former Islamic states in Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, that ISIL planned to expand to, was created by outside supporters and had no official connection to the ISIL state.[169][170][171][172][173][174][175]
When the caliphate was proclaimed, ISIL stated: "The legality of all emirates, groups, states and organisations becomes null by the expansion of the khilafah's [caliphate's] authority and arrival of its troops to their areas."[164] This was a rejection of the political divisions in the Middle East that were established by European countries during World War I in the Sykes–Picot Agreement.[176][177][178]
Ideology and beliefs
ISIL is a Salafi or Wahhabi group.[22][179][180] It follows an extremist interpretation of Islam, promotes religious violence, and regards Muslims who do not agree with its interpretations as infidels or apostates.[19] According to Hayder al Khoei, ISIL's philosophy is represented by the symbolism in the Black Standard variant of the legendary battle flag of Prophet Muhammad that it has adopted: the flag shows the Seal of Muhammad within a white circle, with the phrase above it, "There is no God but Allah".[181] Such symbolism has been said to point to ISIL's belief that it represents the restoration of the caliphate of early Islam, with all the political, religious and eschatological ramifications that this would imply.[182]
According to some observers, ISIL emerged from the ideology of the Muslim Brotherhood, the first post-Ottoman Islamist group dating back to the late 1920s in Egypt.[183] It adheres to global jihadist principles and follows the hard-line ideology of al-Qaeda and many other modern-day jihadist groups.[19][14] However, other sources trace the group's roots to Wahhabism. The New York Times wrote:
For their guiding principles, the leaders of the Islamic State ... are open and clear about their almost exclusive commitment to the Wahhabi movement of Sunni Islam. The group circulates images of Wahhabi religious textbooks from Saudi Arabia in the schools it controls. Videos from the group’s territory have shown Wahhabi texts plastered on the sides of an official missionary van.[23]
According to The Economist, dissidents in the ISIL capital of Ar-Raqqah report that "all 12 of the judges who now run its court system ... are Saudis". Saudi Wahhabi practices also followed by the group include the establishment of religious police to root out "vice" and enforce attendance at salat prayers, the widespread use of capital punishment, and the destruction or re-purposing of any non-Sunni religious buildings.[184] Bernard Haykel has described al-Baghdadi's creed as "a kind of untamed Wahhabism".[23]
ISIL aims to return to the early days of Islam, rejecting all innovations in the religion, which it believes corrupts its original spirit. It condemns later caliphates and the Ottoman Empire for deviating from what it calls pure Islam,[169] and seeks to revive the original Wahhabi project of the restoration of the caliphate governed by strict Salafist doctrine. Following Salafi-Wahhabi tradition, ISIL condemns the followers of secular law as disbelievers, putting the current Saudi Arabian government in that category.[185]
Salafists such as ISIL believe that only a legitimate authority can undertake the leadership of jihad, and that the first priority over other areas of combat, such as fighting non-Muslim countries, is the purification of Islamic society. For example, ISIL regards the Palestinian Sunni group Hamas as apostates who have no legitimate authority to lead jihad and see fighting Hamas as the first step toward confrontation by ISIL with Israel.[23][186]
Eschatology
One difference between ISIL and other Islamist and jihadist movements, including al-Qaeda, is the group's emphasis on eschatology and apocalypticism—that is, a belief in a final Day of Judgment by God, and specifically, a belief that the arrival of one known as Imam Mahdi is near. ISIL believes that it will defeat the army of "Rome" at the town of Dabiq, in fulfilment of prophecy.[187] Following its interpretation of the Hadith of the Twelve Successors, ISIL also believes that after al-Baghdadi there will be only four more legitimate caliphs.[187]
The noted scholar of militant Islamism William McCants writes in his book The ISIS Apocalypse: The History, Strategy, and Doomsday Vision of the Islamic State:
References to the End Times fill Islamic State propaganda. It's a big selling point with foreign fighters, who want to travel to the lands where the final battles of the apocalypse will take place. The civil wars raging in those countries today [Iraq and Syria] lend credibility to the prophecies. The Islamic State has stoked the apocalyptic fire. [...] For Bin Laden's generation, the apocalypse wasn't a great recruiting pitch. Governments in the Middle East two decades ago were more stable, and sectarianism was more subdued. It was better to recruit by calling to arms against corruption and tyranny than against the Antichrist. Today, though the apocalyptic recruiting pitch makes more sense.[188]
Territorial claims and international presence
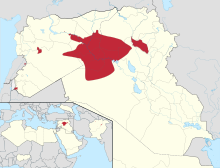
In Iraq and Syria, ISIL uses many of those countries' existing governorate boundaries to subdivide its claimed territory; it calls these divisions wilayah or provinces.[189] As of June 2015, it had established official branches in Libya, Egypt (Sinai Peninsula), Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Algeria, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nigeria and the North Caucasus.[190] Outside Iraq and Syria, it controls territory in only Sinai, Afghanistan, and Libya.[32] ISIL also has members in Morocco, Lebanon, Jordan, Turkey, Israel and Palestine, but does not have official branches in those areas.[191]
Libyan Provinces

ISIL divides Libya into three historical provinces, claiming authority over Cyrenaica in the east, Fezzan in the desert south, and Tripolitania in the west, around its capital Tripoli.[192]
On 5 October 2014, the Shura Council of Islamic Youth and other militants in Libya were absorbed and designated the Cyrenaica Province of ISIL.[193][194] The Libyan branch of ISIL has been the most active and successful of all ISIL branches outside Iraq and Syria. It has been active mainly around Derna and Gaddafi's hometown Sirte.[195][196]
On 4 January 2015, ISIL forces in Libya seized control of the eastern countryside of Sabha, executing 14 Libyan soldiers in the process.[197][198] They temporarily controlled part of Derna before being driven out in mid-2015.[199] Reports from Sirte suggest ISIL militants based there are a mixture of foreign fighters and ex-Gaddafi loyalists.[200] An initiative between pro-Dawn forces associated with Misrata and Operation Dawn clashed with these IS militants in Sirte.[citation needed][201][202] Fighting between Libya Dawn forces and ISIL militants was also reported in the Daheera area west of the city of Sirte, and at the Harawa vicinity east of Sirte.[203]
One unconfirmed source has claimed that ISIL uses its bases in Libya to smuggle its fighters into the European Union posing as refugees.[204][205]
Sinai Province
On 10 November 2014, many members of the group Ansar Bait al-Maqdis took an oath of allegiance to al-Baghdadi.[144] Following this, the group assumed the designation Sinai Province (Wilayat Sinai).[193][206][207][208] They are estimated to have 1,000–2,000 fighters.[35][209] A faction of the Sinai group also operates in the Gaza Strip, calling itself the Islamic State in Gaza.[210] On 19 August 2015, members of the group bombed an Egyptian security headquarters building in northern Cairo, injuring 30 people.[211] It is also speculated to be behind the crash of Russian Metrojet Flight 9268, which killed all 224 people on board. The group has claimed responsibility for the attack in audio recordings, though Russian and Egyptian officials deny there is enough evidence for the claim.[212]
Algerian Province
Members of Jund al-Khilafah swore allegiance to ISIL in September 2014.[213] ISIL in Algeria gained notoriety when it beheaded French tourist Herve Gourdel in September 2014. Since then, the group has largely been silent, with reports that its leader Khalid Abu-Sulayman was killed by Algerian forces in December 2014.[190]
Khorasan Province
On 26 January 2015, Khorasan Province (Wilayat Khorasan) was established, with Hafiz Saeed Khan named as Wāli (Governor) and Abdul Rauf as his deputy after both swore an oath of allegiance to al-Baghdadi. The name Khorasan refers to a historical region that includes Afghanistan, Pakistan, and "other nearby lands".[15][150][214][215]
On 9 February 2015, Mullah Abdul Rauf was killed by a NATO airstrike.[150] On 18 March 2015, Hafiz Wahidi, ISIL's replacement deputy Emir in Afghanistan, was killed by the Afghan Armed Forces, along with nine other ISIL militants who were accompanying him.[216] In June, Reuters received reports that villages in several districts of Afghanistan's eastern Nangarhar Province had been captured from the Taliban by ISIL sympathisers.[32] On 10 July 2015, Hafiz Saeed Khan, the Emir of ISIL's Khorasan Province, was reportedly killed in U.S. drone strike in eastern Afghanistan.[217] However Khorasan Province released an audio tape claimed to be of Hafiz Saeed Khan on 13 July 2015,[218] and he was sanctioned by the US Department of the Treasury on 29 September 2015.[219]
Yemen
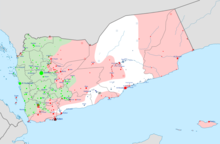
On 13 November 2014, unidentified militants in Yemen pledged allegiance to ISIL.[213] By December of that year, ISIL had built an active presence inside Yemen, with its recruitment drive bringing it into direct competition with al-Qaeda-affiliated al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP).[146][220] In February 2015, it was reported that some members of Ansar al-Sharia in Yemen had split from AQAP and pledged allegiance to ISIL.[221] As the Yemeni Civil War escalated in March 2015, at least seven ISIL Wilayat, named after existing provincial boundaries in Yemen, claimed responsibility for attacks against the Houthis, including the Hadhramaut Province, the Shabwah Province, and the Sana'a Province.[222][223]
Shi'a Houthis (Revolutionary Committee) are principal enemies of Yemen's ISIL branch.[224][225] U.S. supports the Saudi-led military intervention in Yemen against the Houthis,[226] but many in U.S. SOCOM reportedly favor Houthis, as they have been an effective force in rolling back al-Qaeda and recently ISIL in Yemen, "something that hundreds of U.S. drone strikes and large numbers of advisers to Yemen’s military had failed to accomplish".[227] The Guardian reported: "As another 50 civilians die in the forgotten war, only Isis and al-Qaida are gaining from a conflict tearing Yemen apart and leaving 20 million people in need of aid."[228]
West African Province
On 7 March 2015, Boko Haram's leader Abubakar Shekau pledged allegiance to the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant via an audio message posted on the organisation's Twitter account.[229][230] On 12 March 2015, ISIL's spokesman Abu Mohammad al-Adnani released an audio tape in which he welcomed the pledge of allegiance, and described it as an expansion of the group's caliphate into West Africa.[16] ISIL publications from late March 2015 began referring to members of Boko Haram as part of Wilayat Gharb Afriqiya (West Africa Province).[223]
North Caucasus Province
Some commanders of the Caucasus Emirate in Chechnya and Dagestan switched their allegiance to ISIL in late 2014 and early 2015.[231] On 23 June 2015, ISIL spokesman Abu Mohammad al-Adnani accepted the pledges of allegiance and announced a new Caucasus Province (Wilayat al-Qawqaz) under the leadership of Rustam Asildarov.[18][190]
Southeast Asia
On July 23, 2014, Abu Sayyaf leader Isnilon Totoni Hapilon in the Philippines swore an oath of loyalty to Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, the leader of ISIL.[134] In September 2014, the group began kidnapping people to ransom, in the name of ISIL.[135]
Other areas of operation
- Unidentified militants in Saudi Arabia pledged allegiance to ISIL – designated as a province of ISIL.[213]
- The Free Sunnis of Baalbek Brigade (Lebanon) pledged allegiance to ISIL.[35]
- Sons of the Call for Tawhid and Jihad (Jordan) pledged allegiance to ISIL.[232]
Leadership and governance

The group is headed and run by Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, with a cabinet of advisers. There are two deputy leaders, Abu Muslim al-Turkmani (KIA) for Iraq and Abu Ali al-Anbari for Syria, and 12 local governors in Iraq and Syria. A third man, Abu Ala al-Afri, is also believed to hold a prominent position within the group, having been rumored to be the deputy leader of ISIL. All three are believed to be ethnic Turkmen. The former Iraqi strongman Saddam Hussein was also said to have had senior Turkmen within his inner circle.[233][234] While al-Baghdadi has told followers to "advise me when I err" in sermons, according to observers "any threat, opposition, or even contradiction is instantly eradicated".[235] Beneath the leaders are councils on finance, leadership, military matters, legal matters—including decisions on executions—foreign fighters' assistance, security, intelligence and media. In addition, a shura council has the task of ensuring that all decisions made by the governors and councils comply with the group's interpretation of sharia.[236] The majority of ISIL's leadership is dominated by Iraqis, especially former members of Saddam Hussein's government.[102][237] It has been reported that Iraqis and Syrians have been given greater precedence over other nationalities within ISIL because the group needs the loyalties of the local Sunni populations in both Syria and Iraq in order to be sustainable.[238][239] However, other reports have indicated that Syrians are at a disadvantage to foreign members of ISIL, with some native Syrian fighters resenting "favoritism" allegedly shown towards foreigners over pay and accommodation.[240][241]
In September 2014, The Wall Street Journal estimated that eight million Iraqis and Syrians live in areas controlled by ISIL.[242] Ar-Raqqah in Syria is the de facto capital, and is said to be a test case of ISIL governance.[243] As of September 2014, governance in Ar-Raqqah has been under the total control of ISIL where it has rebuilt the structure of modern government in less than a year. Former government workers from the Assad government have maintained their jobs after pledging allegiance to ISIL. Institutions, restored and restructured, provide their respective services. The Ar-Raqqah dam continues to provide electricity and water. Foreign expertise aids Syrian officials in the running of civilian institutions. Only the police and soldiers are ISIL fighters, who receive confiscated lodging previously owned by non-Sunnis and others who have fled. Welfare services are provided, price controls are established, and taxes are imposed on the wealthy. ISIL runs a soft power programme in the areas under its control in Iraq and Syria, which includes social services, religious lectures and da'wah—proselytising—to local populations. It also performs public services, such as repairing roads and maintaining the electricity supply.[244]
British security expert Frank Gardner concluded that ISIL's prospects of maintaining control and rule were greater in 2014 than they had been in 2006, and that despite being as brutal as before, ISIL had become "well entrenched" among the population and was not likely to be dislodged by ineffective Syrian or Iraqi forces. It has replaced corrupt governance with functioning locally controlled authorities, services have been restored and there are adequate supplies of water and oil. With Western-backed intervention being unlikely, the group will "continue to hold their ground" and rule an area "the size of Pennsylvania for the foreseeable future", he said.[189][245] ISIL has maintained food production, crucial to governance and popular support,[246] and its 40% control of Iraq's wheat production has further solidified its rule.
Monetary system
On 11 November 2014, ISIL announced its intent to mint its own gold, silver, and copper coins, based on the coinage used by the Umayyad Caliphate in the 7th century. Following the announcement, the group began buying up gold, silver, and copper in markets throughout northern and western Iraq, according to precious metal traders in the area. Members of the group also reportedly began stripping the insulation off electrical power cables to obtain the copper wiring.[247][248] The announcement included designs of the proposed coins, which displayed imagery including a map of the world, a sword and shield, the Al-Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem, and a crescent moon. Economics experts, such as Professor Steven H. Hanke of Johns Hopkins University, were skeptical of the plans.[248][249]
Non-combatants
Although ISIL attracts followers from different parts of the world by promoting the image of holy war, not all of its recruits end up in combatant roles. There have been several cases of new recruits expecting to be mujahideen who have returned from Syria disappointed by the everyday jobs that were assigned to them, such as drawing water or cleaning toilets, or by the ban imposed on use of mobile phones during military training sessions.[250]
ISIL publishes material directed at women. Although women are not allowed to take up arms, media groups encourage them to play supportive roles within ISIL, such as providing first aid, cooking, nursing and sewing skills, in order to become "good wives of jihad".[251]
Designation as a terrorist organisation
| Organisation | Date | Body | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multinational organisations | |||
| 18 October 2004 (as al-Qaeda in Iraq) 30 May 2013 (after separation from al‑Qaeda) |
United Nations Security Council | [252][253][254] | |
| 2004 | EU Council (via adoption of UN al-Qaeda Sanctions List) | [255] | |
| Nations | |||
| March 2001 (as part of al-Qaeda) 20 June 2014 (after separation from al‑Qaeda) |
Home Secretary of the Home Office | [256] | |
| 17 December 2004 (as al-Qaeda in Iraq) | United States Department of State | [257] | |
| 2 March 2005 (as al-Qaeda in Iraq) 14 December 2013 (after separation from al‑Qaeda) |
Attorney-General for Australia | [258] | |
| 20 August 2012 | Parliament of Canada | [259] | |
| 30 October 2013 | Grand National Assembly of Turkey | [260][261] | |
| 7 March 2014 | Royal decree of the King of Saudi Arabia | [262] | |
| 1 August 2014 | National Counter-terrorism Agency BNPT | [263] | |
| 20 August 2014 | United Arab Emirates Cabinet | [264] | |
| 24 September 2014 | Ministry of Foreign Affairs | [265] | |
| 30 November 2014 | The Cairo Court for Urgent Matters | [266][267] | |
| 16 December 2014 | Ministry of Home Affairs | [268][269] | |
| 29 December 2014 | Supreme Court of Russia | [270] | |
| 25 March 2015 | Kyrgyz State Committee of National Security | [271] | |
| [272] | |||
| [273] | |||
| 29 August 2015 | Ministry of Interior | [274] | |
The United Nations Security Council in its Resolution 1267 (1999) described Osama bin Laden and his al-Qaeda associates as operators of a network of terrorist training camps.[275] The UN's Al-Qaida Sanctions Committee first listed ISIL in its Sanctions List under the name "Al-Qaida in Iraq" on 18 October 2004, as an entity/group associated with al-Qaeda. On 2 June 2014, the group was added to its listing under the name "Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant". The European Union adopted the UN Sanctions List in 2002.[255]
Many world leaders and government spokespeople have called ISIL a terrorist group or banned it, without their countries having formally designated it as such. The following are examples:
The Government of Germany banned ISIL in September 2014. Activities banned include donations to the group, recruiting fighters, holding ISIL meetings and distributing its propaganda, flying ISIL flags, wearing ISIL symbols and all ISIL activities. "The terror organisation Islamic State is a threat to public safety in Germany as well", said German politician Thomas de Maizière. He added, "Today’s ban is directed solely against terrorists who abuse religion for their criminal goals." The ban does not mean that ISIL has been outlawed as a foreign terrorist organisation in Germany, as that requires a court judgement.[276]
In October 2014, Switzerland banned ISIL's activities in the country, including propaganda and financial support of the fighters, with prison sentences as potential penalties.[277]
In mid-December 2014, India banned ISIL after the arrest of an operator of a pro-ISIL Twitter account.[278]
Pakistan designated ISIL as a banned organisation in late August 2015, under which all elements expressing sympathy for the group would be blacklisted and sanctioned.[274]
Media sources worldwide have described ISIL as a terrorist organisation.[28][102][263][279][280][281]
Human rights abuse and war crime findings
In July 2014, the BBC reported the United Nations' chief investigator as stating: "Fighters from the Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) may be added to a list of war crimes suspects in Syria."[282] By June 2014, according to United Nations reports, ISIL had killed hundreds of prisoners of war[283] and over 1,000 civilians.
In November 2014, the UN Commission of Inquiry on Syria said that ISIL was committing crimes against humanity.[284][285] A report by Human Rights Watch in November 2014 accused ISIL groups in control of Derna, Libya of war crimes and human rights abuses and of terrorizing residents. Human Rights Watch documented three apparent summary executions and at least ten public floggings by the Islamic Youth Shura Council, which joined ISIL in November. It also documented the beheading of three Derna residents and dozens of seemingly politically motivated assassinations of judges, public officials, members of the security forces and others. Sarah Leah Watson, Director of HRW Middle East and North Africa, said: "Commanders should understand that they may face domestic or international prosecution for the grave rights abuses their forces are committing."[286]
Speaking of ISIL's methods, the United Nations Commission on Human Rights has stated that the group "seeks to subjugate civilians under its control and dominate every aspect of their lives through terror, indoctrination, and the provision of services to those who obey".[287]
Religious and minority group persecution

ISIL compels people in the areas that it controls to live according to its interpretation of sharia law.[279][288] There have been many reports of the group's use of death threats, torture and mutilation to compel conversion to Islam,[279][288] and of clerics being killed for refusal to pledge allegiance to the so-called "Islamic State".[289] ISIL directs violence against Shia Muslims, Alawites, Assyrian, Chaldean, Syriac and Armenian Christians, Yazidis, Druze, Shabaks and Mandeans in particular.[290]
ISIL fighters are targeting Syria's minority Alawite sect.[291][292] The Islamic State and affiliated jihadist groups reportedly took the lead in an offensive on Alawite villages in Latakia Governorate of Syria in August 2013.[293][294]
Amnesty International has held ISIL responsible for the ethnic cleansing of ethnic and religious minority groups in northern Iraq on a "historic scale". In a special report released on 2 September 2014, it describes how ISIL has "systematically targeted non-Arab and non-Sunni Muslim communities, killing or abducting hundreds, possibly thousands, of individuals and forcing more than 830,000 others to flee the areas it has captured since 10 June 2014". Among these people are Assyrian Christians, Turkmen Shia, Shabak Shia, Yazidis, Kaka'i and Sabean Mandeans, who have lived together for centuries in Nineveh province, large parts of which came under ISIL's control.[295][296]
Among the known killings of religious and minority group civilians carried out by ISIL are those in the villages and towns of Quiniyeh (70–90 Yazidis killed), Hardan (60 Yazidis killed), Sinjar (500–2,000 Yazidis killed), Ramadi Jabal (60–70 Yazidis killed), Dhola (50 Yazidis killed), Khana Sor (100 Yazidis killed), Hardan (250–300 Yazidis killed), al-Shimal (dozens of Yazidis killed), Khocho (400 Yazidis killed and 1,000 abducted), Jadala (14 Yadizis killed)[297] and Beshir (700 Shia Turkmen killed),[298] and others committed near Mosul (670 Shia inmates of the Badush prison killed),[298] and in Tal Afar prison, Iraq (200 Yazidis killed for refusing conversion).[297] The UN estimated that 5,000 Yazidis were killed by ISIL during the takeover of parts of northern Iraq in August 2014.[299] In late May 2014, 150 Kurdish boys from Kobani aged 14–16 were abducted and subjected to torture and abuse, according to Human Rights Watch.[300] In the Syrian towns of Ghraneij, Abu Haman and Kashkiyeh 700 members of the Sunni Al-Shaitat tribe were killed for attempting an uprising against ISIL control.[301][302] The UN reported that in June 2014 ISIL had killed a number of Sunni Islamic clerics who refused to pledge allegiance to it.[289]
Christians living in areas under ISIL control who want to remain in the "caliphate" face three options: converting to Islam, paying a religious levy—jizya—or death.[303][304] "We offer them three choices: Islam; the dhimma contract – involving payment of jizya; if they refuse this they will have nothing but the sword", ISIL said.[305] ISIL had already set similar rules for Christians in Ar-Raqqah, once one of Syria's more liberal cities.[306][307]
On 23 February 2015, in response to a major Kurdish offensive in the Al-Hasakah Governorate, ISIL abducted 150 Assyrian Christians from villages near Tal Tamr (Tell Tamer) in northeastern Syria, after launching a large offensive in the region.[308][309]
It was claimed that ISIL campaigns against Kurdish and Yezidi enclaves in Iraq and Syria were a part of organised Arabization plans. For instance, a Kurdish official in Iraqi Kurdistan claimed that the ISIL campaign in Sinjar was a case of Arabization campaign.[310]
Treatment of civilians
During the Iraqi conflict in 2014, ISIL released dozens of videos showing its ill treatment of civilians, many of whom had apparently been targeted on the basis of their religion or ethnicity. Navi Pillay, UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, warned of war crimes being committed in the Iraqi war zone, and disclosed a UN report of ISIL militants murdering Iraqi Army soldiers and 17 civilians in a single street in Mosul. The UN reported that in the 17 days from 5 to 22 June, ISIL killed more than 1,000 Iraqi civilians and injured more than 1,000.[311][312][313] After ISIL released photographs of its fighters shooting scores of young men, the UN declared that cold-blooded "executions" by militants in northern Iraq almost certainly amounted to war crimes.[314]
ISIL's advance in Iraq in mid-2014 was accompanied by continuing violence in Syria. On 29 May, ISIL raided a village in Syria and at least 15 civilians were killed, including, according to Human Rights Watch, at least six children.[315] A hospital in the area confirmed that it had received 15 bodies on the same day.[316] The Syrian Observatory for Human Rights reported that on 1 June, a 102-year-old man was killed along with his whole family in a village in Hama province.[317] According to Reuters, 1,878 people were killed in Syria by ISIL during the last six months of 2014, most of them civilians.[318]
In Mosul, ISIL has implemented a sharia school curriculum which bans the teaching of art, music, national history, literature and Christianity. Although Charles Darwin's theory of evolution has never been taught in Iraqi schools, the subject has been banned from the school curriculum. Patriotic songs have been declared blasphemous, and orders have been given to remove certain pictures from school textbooks.[319][320][321][322] Iraqi parents have largely boycotted schools in which the new curriculum has been introduced.[323]
After capturing cities in Iraq, ISIL issued guidelines on how to wear clothes and veils. ISIL warned women in the city of Mosul to wear full-face veils or face severe punishment.[324] A cleric told Reuters in Mosul that ISIL gunmen had ordered him to read out the warning in his mosque when worshippers gathered. ISIL ordered the faces of both male and female mannequins to be covered, in an order which also banned the use of naked mannequins.[325] In Ar-Raqqah the group uses its two battalions of female fighters in the city to enforce compliance by women with its strict laws on individual conduct.[326]
ISIL released 16 notes labelled "Contract of the City", a set of rules aimed at civilians in Nineveh. One rule stipulated that women should stay at home and not go outside unless necessary. Another rule said that stealing would be punished by amputation.[244][327] In addition to the Muslim custom of banning the sale and use of alcohol, ISIL has banned the sale and use of cigarettes and hookah pipes. It has also banned "music and songs in cars, at parties, in shops and in public, as well as photographs of people in shop windows".[328]
According to The Economist, Saudi practices also followed by the group include the establishment of religious police to root out "vice" and enforce attendance at salat prayers, the widespread use of capital punishment, and the destruction of Christian churches and non-Sunni mosques or their conversion to other uses.[184]
ISIL carried out executions on both men and women who were accused of various acts and found guilty of crimes against Islam such as homosexuality, adultery, watching pornography, usage and possession of contraband, rape, blasphemy, witchcraft,[329] renouncing Islam and murder. Before the accused are executed their charges are read toward them and the spectators. Executions take various forms, including stoning to death, crucifixions, beheadings, burning people alive, and throwing people from tall buildings.[330][331][332][333]
Child soldiers
According to a report by the magazine Foreign Policy, children as young as six are recruited or kidnapped and sent to military and religious training camps, where they practice beheading with dolls and are indoctrinated with the religious views of ISIL. Children are used as human shields on front lines and to provide blood transfusions for Islamic State soldiers, according to Shelly Whitman of the Roméo Dallaire Child Soldiers Initiative. The second installment of a Vice News documentary about ISIL focused on how the group is specifically grooming children for the future. A spokesman told VICE News that those under the age of 15 go to sharia camp to learn about religion, while those older than 16 can go to military training camp. Children are also used for propaganda. According to a UN report, "In mid-August, ISIL entered a cancer hospital in Mosul, forced at least two sick children to hold the ISIL flag and posted the pictures on the internet." Misty Buswell, a Save the Children representative working with refugees in Jordan, said, "It's not an exaggeration to say we could lose a whole generation of children to trauma."[334]
Sexual violence and slavery
Sexual violence perpetrated by ISIL includes: using rape as a weapon of war;[335] instituting forced marriages to its fighters;[336] and trading women and girls as sex slaves.[337]
There are many reports of sexual abuse and enslavement in ISIL-controlled areas of women and girls, predominantly from the minority Christian and Yazidi communities.[338][339] Fighters are told that they are free to have sex with or rape non-Muslim captive women.[340] Haleh Esfandiari from the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars has highlighted the abuse of local women by ISIL militants after they have captured an area. "They usually take the older women to a makeshift slave market and try to sell them. The younger girls ... are raped or married off to fighters", she said, adding, "It's based on temporary marriages, and once these fighters have had sex with these young girls, they just pass them on to other fighters."[341]
The capture of Iraqi cities by the group in June 2014 was accompanied by an upsurge in crimes against women, including kidnap and rape.[342][343][344] According to Martin Williams in The Citizen, some hard-line Salafists apparently regard extramarital sex with multiple partners as a legitimate form of holy war and it is "difficult to reconcile this with a religion where some adherents insist that women must be covered from head to toe, with only a narrow slit for the eyes".[345]
As of August 2015, the trade in sex slaves appeared to remain restricted to Yazidi women and girls.[337] It has reportedly become a recruiting technique to attract men from conservative Muslim societies, where dating and casual sex are not allowed.[337] Nazand Begikhani said of the Yazidi victims, "These women have been treated like cattle ... They have been subjected to physical and sexual violence, including systematic rape and sex slavery. They've been exposed in markets in Mosul and in Raqqa, Syria, carrying price tags."[346] According to UN Reports the price list for IS sex slaves range from 40 to 160 US-Dollars. The younger the slave the more expensive. Girls and Boys between the age 1-9 are referred to as the most expensive, while the cheapest being women between 40 to 50 years old.[347] According to another source the price of a slave equals the price of AK-47.[348]
A United Nations report issued on 2 October 2014, based on 500 interviews with witnesses, said that ISIL took 450–500 women and girls to Iraq's Nineveh region in August, where "150 unmarried girls and women, predominantly from the Yazidi and Christian communities, were reportedly transported to Syria, either to be given to ISIL fighters as a reward or to be sold as sex slaves".[339] In mid-October, the UN confirmed that 5,000–7,000 Yazidi women and children had been abducted by ISIL and sold into slavery.[299][349] In November 2014 The New York Times reported on the accounts given by five who escaped ISIL of their captivity and abuse.[350] In December 2014, the Iraqi Ministry of Human Rights announced that ISIL had killed over 150 women and girls in Fallujah who refused to participate in sexual jihad.[351][352] Non-Muslim women have reportedly been married off to fighters against their will. ISIL claims the women provide the new converts and children necessary to spread ISIL's control.[353]
Shortly after the death of US hostage Kayla Mueller was confirmed on 10 February 2015,[354] several media outlets reported that the US intelligence community believed she may have been given as a wife to an ISIL fighter.[355][356][357] In August 2015 it was confirmed that she had been forced into marriage[358] to Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, who raped her repeatedly.[359][360][361][362][363][364][364][365] The Mueller family was informed by the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) that Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi had sexually abused Ms. Mueller, and that Ms. Mueller had also been tortured.[364] Abu Sayyaf's widow, Umm Sayyaf, confirmed that it was her husband who had been Mueller's primary abuser.[366]
In its digital magazine Dabiq, ISIL explicitly claimed religious justification for enslaving Yazidi women.[367][368][369] According to The Wall Street Journal, ISIL appeals to apocalyptic beliefs and claims "justification by a Hadith that they interpret as portraying the revival of slavery as a precursor to the end of the world".[370] ISIL appeals to the Hadith and Qur'an when claiming the right to enslave and rape captive non-Muslim women.[367][371][372] According to Dabiq, "enslaving the families of the kuffar and taking their women as concubines is a firmly established aspect of the Sharia's that if one were to deny or mock, he would be denying or mocking the verses of the Qur'an and the narration of the Prophet ... and thereby apostatizing from Islam." Captured Yazidi women and children are divided among the fighters who captured them, with one fifth taken as a tax.[372][373] ISIL has received widespread criticism from Muslim scholars and others in the Muslim world for using part of the Qur'an to derive a ruling in isolation, rather than considering the entire Qur'an and Hadith.[367][371][372] According to Mona Siddiqui, ISIL's "narrative may well be wrapped up in the familiar language of jihad and 'fighting in the cause of Allah', but it amounts to little more than destruction of anything and anyone who doesn't agree with them"; she describes ISIL as reflecting a "lethal mix of violence and sexual power" and a "deeply flawed view of manhood".[353] Dabiq describes "this large-scale enslavement" of non-Muslims as "probably the first since the abandonment of Shariah law".[372][373]
In late 2014, ISIL released a pamphlet that focused on the treatment of female slaves.[374][375] It claims that the Quran allows fighters to have sex with captives, including adolescent girls, and to beat slaves as discipline. The pamphlet's guidelines also allow fighters to trade slaves, including for sex, as long as they have not been impregnated by their owner.[374][375][376] Charlie Winter, a researcher at the counter-extremist think tank Quilliam, described the pamphlet as "abhorrent".[376][377] In response to this document Abbas Barzegar, a religion professor at Georgia State University, said Muslims around the world find ISIL's "alien interpretation of Islam grotesque and abhorrent".[378] Muslim leaders and scholars from around the world have rejected the validity of ISIL's claims, claiming that the reintroduction of slavery is un-Islamic, that they are required to protect "People of the Scripture" including Christians, Jews, Muslims and Yazidis, and that ISIL's fatwas are invalid due to their lack of religious authority and the fatwas' inconsistency with Islam.[379][380]
The Independent reported in 2015 that the usage of Yazidi sex slaves had created ongoing friction among fighters within ISIL. Sajad Jiyad, a Research Fellow and Associate Member at the Iraqi Institute for Economic Reform, told the newspaper that many ISIL supporters and fighters had been in denial about the trafficking of kidnapped Yazidi women until a Dabiq article justifying the practice was published.[381][382] The New York Times said in August 2015 that "[t]he systematic rape of women and girls from the Yazidi religious minority has become deeply enmeshed in the organization and the radical theology of the Islamic State in the year since the group announced it was reviving slavery as an institution."[337] The article claims that ISIL is not merely exonerating but sacralising rape, and illustrated this with the testimony of escapees. One 15-year-old victim said that, while she was being assaulted, her rapist "kept telling me this is ibadah"; a 12-year-old victim related how her assailant claimed that, "by raping me, he is drawing closer to God";[337] and one adult prisoner told how, when she challenged her captor about repeatedly raping a 12 year old, she was met with the retort, "No, she's not a little girl, she's a slave and she knows exactly how to have sex and having sex with her pleases God."[337]
Attacks on members of the press
The Committee to Protect Journalists states: "Without a free press, few other human rights are attainable."[383] ISIL has tortured and murdered local journalists,[384][385] creating what Reporters Without Borders calls "news blackholes" in areas controlled by ISIL. ISIL fighters have reportedly been given written directions to kill or capture journalists.[386]
In December 2013, two suicide bombers stormed the headquarters of TV station Salaheddin and killed five journalists, after accusing the station of "distorting the image of Iraq's Sunni community". Reporters Without Borders reported that on 7 September 2014, ISIL seized and on 11 October publicly beheaded Raad al-Azzawi, a TV Salaheddin cameraman from the village of Samra, east of Tikrit.[387] As of October 2014, according to the Journalistic Freedoms Observatory, ISIL is holding nine journalists and has nine others under close observation in Mosul and Salahuddin province.[386]
During 2013 and part of 2014, an ISIL unit nicknamed the Beatles acquired and held 12 Western journalists hostage, along with aid workers and other foreign hostages, totalling 23 or 24 known hostages. A Polish journalist Marcin Suder was captured in July 2013 but escaped four months later.[388] The unit executed American journalists James Foley and Steven Sotloff and released beheading videos. Eight of the other journalists were released for ransom: Danish journalist Daniel Rye Ottosen, French journalists Didier François, Edouard Elias, Nicolas Hénin, and Pierre Torres, and Spanish journalists Marc Marginedas, Javier Espinosa, and Ricardo García Vilanova. The unit continues to hold hostage British journalist John Cantlie and a female aid worker.[389]
Cyber-security group the Citizen Lab released a report finding a possible link between ISIL and a digital attack on the Syrian citizen media group Raqqa Is Being Slaughtered Silently (RSS). Supporters of the media group received an emailed link to an image of supposed airstrikes, but clicking on the link introduced malware to the user's computer that sends details of the user's IP address and system each time it restarts. That information has been enough to allow ISIL to locate RSS supporters. "The group has been targeted for kidnappings, house raids, and at least one alleged targeted killing. At the time of that writing, ISIL was allegedly holding several citizen journalists in Raqqa", according to the Citizen Lab report.[390]
On 8 January 2015, ISIL members in Libya claimed to have executed Tunisian journalists Sofiene Chourabi and Nadhir Ktari who disappeared in September 2014.[391] Also in January 2015, Japanese journalist Kenji Goto Jogo was kidnapped and beheaded, after a demand for a $200 million ransom payment was not met.[392]
Beheadings and mass executions
An unknown number of Syrians and Iraqis, several Lebanese soldiers, at least ten Kurds, two American journalists, one American and two British aid workers, and three Libyans have been beheaded by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant.[citation needed] ISIL uses beheadings to intimidate local populations and has released a series of propaganda videos aimed at Western countries.[393] They also engage in public and mass executions of Syrian and Iraqi soldiers and civilians,[292] sometimes forcing prisoners to dig their own graves before shooting lines of prisoners and pushing them in.[394][395] ISIL was reported to have beheaded about 100 foreign fighters as deserters who tried to leave Raqqa.[396]
Use of chemical weapons
Kurds in northern Iraq reported being attacked by ISIS with chemical weapons in August 2015.[397] At Kobanî, it is highly likely that ISIS used chlorine gas there. These chemical weapons may be from a chemical weapons storage site at Al-Muthanna, which contained 2,500 chemical rockets. Although the rockets' chemical contents were deteriorated, ISIS may have used them in a concentrated manner.[398]
Destruction of cultural and religious heritage
UNESCO's Director-General Irina Bokova has warned that ISIL is destroying Iraq's cultural heritage, in what she has called "cultural cleansing". "We don't have time to lose because extremists are trying to erase the identity, because they know that if there is no identity, there is no memory, there is no history", she said. Referring to the ancient cultures of Christians, Yazidis and other minorities, she said, "This is a way to destroy identity. You deprive them of their culture, you deprive them of their history, their heritage, and that is why it goes hand in hand with genocide. Along with the physical persecution they want to eliminate – to delete – the memory of these different cultures. ... we think this is appalling, and this is not acceptable."[399] Saad Eskander, head of Iraq's National Archives said, "For the first time you have cultural cleansing... For the Yazidis, religion is oral, nothing is written. By destroying their places of worship ... you are killing cultural memory. It is the same with the Christians – it really is a threat beyond belief."[400]

To finance its activities, ISIL is stealing artifacts from Syria[401] and Iraq and sending them to Europe to be sold. It is estimated that ISIL raises US$200 million a year from cultural looting. UNESCO has asked for United Nations Security Council controls on the sale of antiquities, similar to those imposed after the 2003 Iraq War. UNESCO is working with Interpol, national customs authorities, museums, and major auction houses in attempts to prevent looted items from being sold.[400] ISIL occupied Mosul Museum, the second most important museum in Iraq, as it was about to reopen after years of rebuilding following the Iraq War, saying that the statues were against Islam and threatening to destroy the museum's contents.[402][403]
ISIL considers worshipping at graves tantamount to idolatry, and seeks to purify the community of unbelievers. It has used bulldozers to crush buildings and archaeological sites.[403] Bernard Haykel has described al-Baghdadi's creed as "a kind of untamed Wahhabism", saying, "For Al Qaeda, violence is a means to an ends; for ISIS, it is an end in itself".[23] The destruction by ISIL in July 2014 of the tomb and shrine of the prophet Yunus—Jonah in Christianity—the 13th-century mosque of Imam Yahya Abu al-Qassimin, the 14th-century shrine of prophet Jerjis—St George to Christians—and the attempted destruction of the Hadba minaret at the 12th-century Great Mosque of Al-Nuri have been described as "an unchecked outburst of extreme Wahhabism".[404] "There were explosions that destroyed buildings dating back to the Assyrian era", said National Museum of Iraq director Qais Rashid, referring to the destruction of the shrine of Yunus. He cited another case where "Daesh (ISIL) gathered over 1,500 manuscripts from convents and other holy places and burnt all of them in the middle of the city square".[405] In March 2015, ISIL reportedly bulldozed the 13th-century BC Assyrian city of Nimrud, believing its sculptures to be idolatrous. UNESCO head, Irina Bokova, deemed this to be a war crime.[406]
Criticism
Islamic criticism
ISIL has received severe criticism from other Muslims, especially religious scholars and theologians. In late August 2014, the Grand Mufti of Saudi Arabia, Abdul-Aziz ibn Abdullah Al ash-Sheikh, condemned the Islamic State and al-Qaeda saying, "Extremist and militant ideas and terrorism which spread decay on Earth, destroying human civilization, are not in any way part of Islam, but are enemy number one of Islam, and Muslims are their first victims".[407] In late September 2014, 126 Sunni imams and Islamic scholars—primarily Sufi[408]—from around the Muslim world signed an open letter to the Islamic State's leader al-Baghdadi, explicitly rejecting and refuting his group's interpretations of Islamic scriptures, the Qur'an and hadith, used by it to justify its actions.[380][409] "[You] have misinterpreted Islam into a religion of harshness, brutality, torture and murder ... this is a great wrong and an offence to Islam, to Muslims and to the entire world", the letter states.[379] It rebukes the Islamic State for its killing of prisoners, describing the killings as "heinous war crimes" and its persecution of the Yazidis of Iraq as "abominable". Referring to the "self-described 'Islamic State'", the letter censures the group for carrying out killings and acts of brutality under the guise of jihad—holy struggle—saying that its "sacrifice" without legitimate cause, goals and intention "is not jihad at all, but rather, warmongering and criminality".[379][410] It also accuses the group of instigating fitna—sedition—by instituting slavery under its rule in contravention of the anti-slavery consensus of the Islamic scholarly community.[379] Other scholars have described the group as not Sunnis, but Khawarij.[411]

According to The New York Times, "All of the most influential jihadist theorists are criticizing the Islamic State as deviant, calling its self-proclaimed caliphate null and void" and have denounced it for its beheading of journalists and aid workers.[23] ISIL is widely denounced by a broad range of Islamic clerics, including al-Qaeda-oriented and Saudi clerics.[22][23]
Sunni critics, including Salafi and jihadist muftis such as Adnan al-Aroor and Abu Basir al-Tartusi, say that ISIL and related terrorist groups are not Sunnis, but modern-day Khawarij—Muslims who have stepped outside the mainstream of Islam—serving an imperial anti-Islamic agenda.[412][413] Other critics of ISIL's brand of Sunni Islam include Salafists who previously publicly supported jihadist groups such as al-Qaeda, for example the Saudi government official Saleh Al-Fawzan, known for his extremist views, who claims that ISIL is a creation of "Zionists, Crusaders and Safavids", and the Jordanian-Palestinian writer Abu Muhammad al-Maqdisi, the former spiritual mentor to Abu Musab al-Zarqawi, who was released from prison in Jordan in June 2014 and accused ISIL of driving a wedge between Muslims.[413]
The group's declaration of a caliphate has been criticised and its legitimacy disputed by Middle Eastern governments, other jihadist groups,[414] and Sunni Muslim theologians and historians. Qatar-based TV broadcaster and theologian Yusuf al-Qaradawi stated: "[The] declaration issued by the Islamic State is void under sharia and has dangerous consequences for the Sunnis in Iraq and for the revolt in Syria", adding that the title of caliph can "only be given by the entire Muslim nation", not by a single group.[415] The group's execution of Muslims for breach of traditional sharia law while violating it itself (encouraging women to emigrate to its territory, traveling without a Wali—male guardian—and in violation of his wishes) has been criticized;[416] as has its love of archaic imagery (horsemen and swords) while engaging in bid‘ah (religious innovation) in establishing female religious police (known as al-Khansa' Brigades).[417]
Two days after the beheading of Hervé Gourdel, hundreds of Muslims gathered in the Grand Mosque of Paris to show solidarity against the beheading. The protest was led by the leader of the French Council of the Muslim Faith, Dalil Boubakeur, and was joined by thousands of other Muslims around the country under the slogan "Not in my name".[418][419] French president François Hollande said Gourdel's beheading was "cowardly" and "cruel", and confirmed that airstrikes would continue against ISIL in Iraq. Hollande also called for three days of national mourning, with flags flown at half-mast throughout the country and said that security would be increased throughout Paris.[418]
An Islamic Front Sharia Court Judge in Aleppo Mohamed Najeeb Bannan stated "The legal reference is the Islamic Sharia. The cases are different, from robberies to drug use, to moral crimes. It's our duty to look at any crime that comes to us. . . After the regime has fallen, we believe that the Muslim majority in Syria will ask for an Islamic state. Of course, it's very important to point out that some say the Islamic Sharia will cut off people's hands and heads, but it only applies to criminals. And to start off by killing, crucifying etc. That is not correct at all." In response to being asked what the difference between the Islamic Front's and ISIL's version of sharia would be, he said "One of their mistakes is before the regime has fallen, and before they've established what in Sharia is called Tamkeen [having a stable state], they started applying Sharia, thinking God gave them permission to control the land and establish a Caliphate. This goes against the beliefs of religious scholars around the world. This is what [IS] did wrong. This is going to cause a lot of trouble. Anyone who opposes [IS] will be considered against Sharia and will be severely punished."[420][421]
Al-Qaeda/Al-Nusra has been trying to take advantage of ISIL's rise by trying to present itself as "moderate" compared to "extremist" ISIL while it has the same aim of establishing sharia and a caliphate but doing it in a more gradual manner.[422][423][424][425][426]
The leader of Al-Qaeda Ayman al-Zawahiri called for the use of consultation (shura) within the "prophetic method" to be used when establishing the caliphate, criticizing Baghdadi for not following the required steps, Zawahiri called upon ISIL members to close ranks and join Al-Qaeda to fight against Assad, Shia, Russia, Europe, and America and stop the infighting between jihadist groups, calling for jihadists to establish Islamic entities in Egypt and the Levant, slowling implementing Sharia before establishing a caliphate and calling for violent assaults against America and the West.[427]
Al-Qaeda's branch in Syria Al Nusrah criticized the way ISIL fully and immediately instituted Sharia since it alienated people too much, with a gradual, slower approach favored by Al-Qaeda by preparing society to accept it and indoctrinating people through education before implementing the hudud aspects of Sharia like tossing gays off buildings, chopping limbs off, and public stoning which Al-Qaeda agrees should ultimately be implemented in the long run.[166]
A massacre of Druze at the hands of Al-Qaeda affiliate Al-Nusra Front took place in June 2015 in Idlib. Nusrah issued an apology after the incident. Foreign Policy noted that there is absolutely no reference to the Druze in Al-Nusra's "apology", since Al-Nusrah forced the Druze to renounce their religion, destroyed their shrines and now considers them Sunni.[428][429][430] Nusra and ISIL are both against the Druze, the difference being the that Nusra is apparently satisfied with destroying Druze shrines and making them become Sunnis while ISIL wants to violently annihilate them like it did to Yazidis.[431]
The Jaysh al-Islam group within the Islamic Front criticized ISIL, saying: "They killed the people of Islam and leave the idol worshippers" (يقتلون أهل الإسلام ويدعون أهل الأوثان) and "They use the verses talking about the disbelievers and implement it on the Muslims" (ينزلون أيات نزلت في الكفار على المسلمين).[432] The main criticism of defectors from ISIL is that the group is killing and fighting other Sunni Muslims, unhappy that other Sunnis like Jabhat al-Nusra (Al-Qaeda) are being attacked by ISIL.[433] Many defectors from ISIL did not care about non-Sunnis being brutalized, rather they were outraged by the fact that other Sunnis were being subjected to brutality and were upset that other Sunnis were being targeted by ISIL.[434] The defectors did not mention the rape and slaughter inflicted upon Yazidis and only mentioned crimes against Sunnis as the reason they defected from ISIL.[435] Some defectors from ISIL are in fact spies and operatives who continue working for ISIL and faking their defections.[436]
The current Grand Imam of al-Azhar and former president of al-Azhar University, Ahmed el-Tayeb has strongly condemned the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant stating that is acting "under the guise of this holy religion and have given themselves the name 'Islamic State' in an attempt to export their false Islam"[437][438] and (citing the Quran) that: "The punishment for those who wage war against God and his Prophet and who strive to sow corruption on earth is death, crucifixion, the severing of hands and feet on opposite sides or banishment from the land. This is the disgrace for them in this world and in the hereafter they will receive grievous torment." Although El-Tayeb has been criticized for not expressly stating that the Islamic State was heretical,[439][440] the Ash'ari school of Islamic theology - to which El-Tayeb belongs - does not allow calling a person who follows the shahada an apostate.[439] El-Tayeb has strongly come out against the practice of takfirism (declaring a Muslim an apostate) which is used by the Islamic State to "judge and accuse anyone who doesn’t tow their line with apostasy and outside the realm of the faith" declaring "Jihad on peaceful Muslims" using "flawed interpretations of some Qur’anic texts, the prophet’s Sunna, and the Imams’ views believing incorrectly, that they are leaders of Muslim armies fighting infidel peoples, in unbelieving lands."[441]
Mehdi Hasan, a political journalist in the UK, said in the New Statesman, "Whether Sunni or Shia, Salafi or Sufi, conservative or liberal, Muslims – and Muslim leaders – have almost unanimously condemned and denounced ISIL not merely as un-Islamic but actively anti-Islamic."[442]
Hassan Hassan, an analyst at the Delma Institute, wrote in The Guardian that because the Islamic State "bases its teachings on religious texts that mainstream Muslim clerics do not want to deal with head on, new recruits leave the camp feeling that they have stumbled on the true message of Islam".[179] In mid-February 2015, Graeme Wood, a lecturer in political science at Yale University, said in The Atlantic, "The religion preached by its most ardent followers derives from coherent and even learned interpretations of Islam."[187]
International criticism
The group has attracted widespread criticism internationally for its extremism, from governments and international bodies such as the United Nations and Amnesty International. On 24 September 2014, United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki-Moon stated: "As Muslim leaders around the world have said, groups like ISIL – or Da’ish – have nothing to do with Islam, and they certainly do not represent a state. They should more fittingly be called the 'Un-Islamic Non-State'."[443] The group was described as a cult in a Huffington Post column by notable cult authority Steven Hassan.[444]
Criticism of the name "Islamic State" and "caliphate" declaration
The group's declaration of a new caliphate in June 2014 and adoption of the name "Islamic State" have been criticised and ridiculed by Muslim scholars and rival Islamists both inside and outside the territory it controls.[65][66][67][445] In a speech in September 2014, President Obama said that ISIL is not "Islamic" on the basis that no religion condones the killing of innocents and that no government recognises the group as a state,[71] while many object to using the name "Islamic State" owing to the far-reaching religious and political claims to authority which that name implies. The United Nations Security Council, the United States, Canada, Turkey, Australia, Russia, the United Kingdom[68][69][70][71][446][447][448] and other countries generally call the group "ISIL", while much of the Arab world uses the Arabic acronym "Dāʻish". France's Foreign Minister Laurent Fabius said "This is a terrorist group and not a state. I do not recommend using the term Islamic State because it blurs the lines between Islam, Muslims, and Islamists. The Arabs call it 'Daesh' and I will be calling them the 'Daesh cutthroats.'"[449] Retired general John Allen, the U.S. envoy appointed to co-ordinate the coalition, U.S. military Lieutenant General James Terry, head of operations against the group, and Secretary of State John Kerry had all shifted toward use of the term DAESH by December 2014.[450]

In late August 2014, a leading Islamic educational institution, Dar al-Ifta al-Misriyyah in Egypt, advised Muslims to stop calling the group "Islamic State" and instead refer to it as "Al-Qaeda Separatists in Iraq and Syria" or "QSIS", because of the militant group's "un-Islamic character".[451][452] When addressing the United Nations Security Council in September 2014, Australian Prime Minister Tony Abbott summarised the widespread objections to the name "Islamic State" thus: "To use this term [Islamic State] is to dignify a death cult; a death cult that, in declaring itself a caliphate, has declared war on the world".[453] The group is very sensitive about its name. "They will cut your tongue out even if you call them ISIS – you have to say 'Islamic State'", said a woman in ISIL-controlled Mosul.[454]
In mid-October 2014, representatives of the Islamic Society of Britain, the Association of British Muslims and the UK's Association of Muslim Lawyers proposed that "'Un-Islamic State' (UIS) could be an accurate and fair alternative name to describe this group and its agenda", further stating, "We need to work together and make sure that these fanatics don't get the propaganda that they feed off."[455][456] The "Islamic State" is mocked on social media websites such as Twitter and YouTube, with the use of hashtags, mock recruiting ads, fake news articles and YouTube videos.[457] One parody, by a Palestinian TV satire show, portrays ISIL as "buffoon-like hypocrites", and has had more than half a million views on YouTube.[457][458]
In the media
By 2014, ISIL was increasingly being viewed as a militia rather than a terrorist group.[459] As major Iraqi cities fell to ISIL in June 2014, Jessica Lewis, a former U.S. Army intelligence officer at the Institute for the Study of War, described ISIL as "not a terrorism problem anymore", but rather "an army on the move in Iraq and Syria, and they are taking terrain. They have shadow governments in and around Baghdad, and they have an aspirational goal to govern. I don't know whether they want to control Baghdad, or if they want to destroy the functions of the Iraqi state, but either way the outcome will be disastrous for Iraq." Lewis has called ISIL "an advanced military leadership". She said, "They have incredible command and control and they have a sophisticated reporting mechanism from the field that can relay tactics and directives up and down the line. They are well-financed, and they have big sources of manpower, not just the foreign fighters, but also prisoner escapees."[459]
While officials fear that ISIL may inspire attacks in the United States from sympathisers or those returning after joining ISIL, U.S. intelligence agencies have found no specific plots or any immediate threat. Former U.S. Defense Secretary Chuck Hagel saw an "imminent threat to every interest we have", but former top counter-terrorism adviser Daniel Benjamin has derided such alarmist talk as a "farce" that panics the public.[460]
Former British Foreign Secretary David Miliband concluded that the 2003 invasion of Iraq caused the creation of ISIL.[461]
Some news commentators, such as international newspaper columnist Gwynne Dyer,[462] and samples of American public opinion, such as surveys by NPR,[463] have advocated a strong but measured response to ISIL's recent provocative acts. Writing for The Guardian, Pankaj Mishra rejects that the group is a resurgence of medieval Islam and rather expresses that, "In actuality, Isis is the canniest of all traders in the flourishing international economy of disaffection: the most resourceful among all those who offer the security of collective identity to isolated and fearful individuals. It promises, along with others who retail racial, national and religious supremacy, to release the anxiety and frustrations of the private life into the violence of the global."[464]
Conspiracy theories
Conspiracy theorists in the Arab world have advanced rumours that the U.S. is secretly behind the existence and emboldening of ISIL, as part of an attempt to further destabilize the Middle East. After such rumors became widespread, the U.S. embassy in Lebanon issued an official statement denying the allegations, calling them a complete fabrication.[465] The rumours claim that ISIL leader al-Baghdadi is an Israeli Mossad agent and actor called Simon Elliot and that NSA documents leaked by Edward Snowden reveal this connection. Snowden's lawyer has called the story "a hoax."[466]
According to The New York Times, many in the Middle East believe that an alliance of the United States, Israel, and Saudi Arabia is directly responsible for the creation of ISIL. Egyptian, Tunisian, Palestinian, Jordanian and Lebanese news organisations have reported on the conspiracy theory.[467][468]
Countries and groups at war with ISIL
ISIL's expanding claims to territory have brought it into armed conflict with many governments, militias and other armed groups. International rejection of ISIL as a terrorist entity and rejection of its claim to even exist have placed it in conflict with countries around the world.
Opposition within Asia and Africa
The Global Coalition to Counter the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
The Global Coalition to Counter the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), also referred to as the Counter-ISIL Coalition or Counter-DAESH Coalition,[508] is a US-led group of nations and non-state actors that have committed to "work together under a common, multifaceted, and long-term strategy to degrade and defeat ISIL/Daesh". According to a joint statement issued by 59 national governments and the European Union on 3 December 2014, participants in the Counter-ISIL Coalition are focused on multiple lines of effort:[509]
- Supporting military operations, capacity building, and training;
- Stopping the flow of foreign terrorist fighters;
- Cutting off ISIL/Daesh's access to financing and funding;
- Addressing associated humanitarian relief and crises; and
- Exposing ISIL/Daesh's true nature (ideological delegitimisation).
Operation Inherent Resolve is the operational name given by the US to military operations against ISIL and Syrian al-Qaeda affiliates. Combined Joint Task Force – Operation Inherent Resolve (CJTF–OIR) is co-ordinating the military portion of the response.
The following multi-national organisations are part of the Counter-ISIL Coalition:[509]
![]() Arab League — coordinating member response[510]
Arab League — coordinating member response[510]
![]() European Union – declared to be part, 27 members are participating, Malta not participating;[509]
European Union – declared to be part, 27 members are participating, Malta not participating;[509]
![]() NATO – all 28 members are taking part;
NATO – all 28 members are taking part;
![]() Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf or GCC – all six current members and the two pending members, Jordan and Morocco, are taking part.
Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf or GCC – all six current members and the two pending members, Jordan and Morocco, are taking part.
| Military operations in or over Iraq and/or Syria airstrikes, air support, and ground forces performing training |
Supplying military equipment to opposition forces within Iraq and/or Syria in co-operation with EU/NATO/partners |
Humanitarian and other contributions to identified coalition objectives |
|---|---|---|
|
Other:
Part of the anti-ISIL coalition engaged in anti-ISIL military operations within their own borders[509] Note: Listed countries in this box may also be supplying military and humanitarian aid, and contributing to group objectives in other ways. |
Note: These countries may also be supplying humanitarian aid and contributing to group objectives in other ways. |
Other |
Other state opponents not part of the Counter-ISIL Coalition
![]() Iran[535][536] – ground troops, training and air power (see Iranian intervention in Iraq)
Iran[535][536] – ground troops, training and air power (see Iranian intervention in Iraq)
![]() Russia[537][538] – arms supplier to Iraqi and Syrian governments. In June 2014, the Iraqi army received Russian Sukhoi Su-25 and Sukhoi Su-30 fighter aircraft to combat the Islamic State.[539] Security operations within state borders in 2015.[540][541] Airstrikes in Syria (see Russian military intervention in the Syrian Civil War).[542][543][544]
Russia[537][538] – arms supplier to Iraqi and Syrian governments. In June 2014, the Iraqi army received Russian Sukhoi Su-25 and Sukhoi Su-30 fighter aircraft to combat the Islamic State.[539] Security operations within state borders in 2015.[540][541] Airstrikes in Syria (see Russian military intervention in the Syrian Civil War).[542][543][544]
![]() Azerbaijan[545][546] – security operations within state borders
Azerbaijan[545][546] – security operations within state borders
![]() Pakistan – Military deployment over Saudi Arabia-Iraq border. Arresting ISIL figures in Pakistan.[547][548][549]
Pakistan – Military deployment over Saudi Arabia-Iraq border. Arresting ISIL figures in Pakistan.[547][548][549]
Other non-state opponents
 al-Nusra Front[487]—with localised truces and co-operation at times
al-Nusra Front[487]—with localised truces and co-operation at times al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula[146]
al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula[146] al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb[551]
al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb[551]
![]() Taliban[501]
Taliban[501]
![]() Hamas[552]
Hamas[552]
![]() Kurdistan Workers' Party—ground troops in Iraqi Kurdistan and in Syrian Kurdistan[553]
Kurdistan Workers' Party—ground troops in Iraqi Kurdistan and in Syrian Kurdistan[553]
![]() Democratic Party of Iranian Kurdistan—ground troops in Iraqi Kurdistan[553]
Democratic Party of Iranian Kurdistan—ground troops in Iraqi Kurdistan[553]
![]() Houthis—Shia faction in Yemen, fighting for control of the country[499]
Houthis—Shia faction in Yemen, fighting for control of the country[499]
Al-Qaeda
Al-Nusra Front is a branch of al-Qaeda operating in Syria. Al-Nusra launched many attacks and bombings, mostly against targets affiliated with or supportive of the Syrian government.[554] There were media reports that many of al-Nusra's foreign fighters had left to join al-Baghdadi's ISIL.[555]
In February 2014, after continued tensions, al-Qaeda publicly disavowed any relations with ISIL,[42] but ISIL and al-Nusra Front are still able to occasionally cooperate with each other when they fight against the Syrian government.[556][557][558] Quartz's managing edtior Bobby Ghosh wrote:
The two groups share a nihilistic worldview, a loathing for modernity, and for the West. They subscribe to the same perverted interpretations of Islam. Other common traits include a penchant for suicide attacks, and sophisticated exploitation of the internet and social media. Like ISIL, several Al Qaeda franchises are interested in taking and holding territory; AQAP has been much less successful at it. The main differences between Al Qaeda and ISIL are largely political—and personal. Over the past decade, Al Qaeda has twice embraced ISIL (and its previous manifestations) as brothers-in-arms.[559]
On 10 September 2015, an audio message was released by Al-Qaeda leader Ayman al-Zawahiri that criticized the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant's self-proclaimed caliphate and accused them of "sedition", described by some media outlets as a "declaration of war".[560] However, although he denied their legitimacy, Zawahiri suggested that there was still room for cooperation against common enemies and said that if he were in Iraq, he would fight alongside them.[561]
Supporters
Iraq and Syria nationals
According to Reuters, 90% of ISIL's fighters in Iraq are Iraqi, and 70% of its fighters in Syria are Syrian. The article, citing "jihadist ideologues" as the source, stated that the group has 40,000 fighters and 60,000 supporters across its two primary strongholds in Iraq and Syria.[25]
Foreign nationals
According to a report to the UN Security Council filed in late March 2015, 22,000 foreign fighters from 100 nations have travelled to Syria and Iraq, most to support ISIL. It warned that Syria and Iraq had become a "finishing school for extremists".[562] In mid-2014, ISIL's leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi had issued a call, "Rush O Muslims to your state ...".[563]
A UN report from May 2015[update] shows that 25,000 "foreign terrorist fighters" from 100 countries have joined "Islamist" groups, many of them working for ISIL or al-Qaeda.[564]
Groups with expressions of support
One source (Terrorism Research and Analysis Consortium (TRAC)) has identified 60 jihadist groups in 30 countries that have pledged allegiance or support to ISIL as of mid-November 2014. Many of these groups were previously affiliated with al-Qaeda, indicating a shift in global jihadist leadership toward ISIL.[565]
Memberships of the following groups have declared support for ISIL, either fully or in part.
 Boko Haram[566]
Boko Haram[566] Bangsamoro Islamic Freedom Fighters[567]
Bangsamoro Islamic Freedom Fighters[567] Jemaah Islamiyah[568]
Jemaah Islamiyah[568]- Ansar al-Sharia (Tunisia)[569][570]
- Jund al-Khilafah[571]
 Abu Sayyaf[35][572]
Abu Sayyaf[35][572] Mujahideen Shura Council in the Environs of Jerusalem[573]
Mujahideen Shura Council in the Environs of Jerusalem[573] Jamaah Ansharut Tauhid[574] – (pledged support to ISIL; the majority of the group split off after its leader pledged allegiance to ISIL)[574][575]
Jamaah Ansharut Tauhid[574] – (pledged support to ISIL; the majority of the group split off after its leader pledged allegiance to ISIL)[574][575] Ansar Bait al-Maqdis[144]
Ansar Bait al-Maqdis[144] Islamic Movement of Uzbekistan[576][577]
Islamic Movement of Uzbekistan[576][577]- Jundallah (Pakistan)[34]
 Caucasus Emirate (At least two Caucasus Emirate walis and several commanders had declared pledge of allegiance to ISIL)[578][579][580]
Caucasus Emirate (At least two Caucasus Emirate walis and several commanders had declared pledge of allegiance to ISIL)[578][579][580] Army of the Islamic State[581]
Army of the Islamic State[581]
Allegations of Turkish support
Turkey has long been accused by experts, Syrian Kurds, and even U.S. Vice-President Joe Biden of supporting or colluding with ISIL.[582][583][584] According to journalist Patrick Cockburn, there is "strong evidence for a degree of collaboration" between the Turkish intelligence services and ISIL, although the "exact nature of the relationship ... remains cloudy".[585] David L. Phillips of Columbia University's Institute for the Study of Human Rights, who compiled a list of allegations and claims accusing Turkey of assisting ISIL, writes that these allegations "range from military cooperation and weapons transfers to logistical support, financial assistance, and the provision of medical services".[586] Several ISIL fighters and commanders have claimed that Turkey supports ISIL.[587][588][589] Within Turkey itself, ISIL is believed to have caused increasing political polarisation between secularists and Islamists.[590]
In July 2015, a raid by US special forces on a compound housing the Islamic State's "chief financial officer", Abu Sayyaf, produced evidence that Turkish officials directly dealt with ranking ISIS members. According to a senior Western official, documents and flash drives seized during the Sayyaf raid revealed links "so clear" and "undeniable" between Turkey and ISIS "that they could end up having profound policy implications for the relationship between us and Ankara".[582]
Turkey has been further criticised for allowing individuals from outside the region to enter its territory and join ISIL in Syria.[591][592] With many Islamist fighters passing through Turkey to fight in Syria, Turkey has been accused of becoming a transit country for such fighters and has been labelled the "Gateway to Jihad".[593] Turkish border patrol officers are reported to have deliberately overlooked those entering Syria, upon payment of a small bribe.[593] A report by Sky News exposed documents showing that passports of foreign Islamists wanting to join ISIL by crossing into Syria had been stamped by the Turkish government.[594] An ISIL commander stated that "most of the fighters who joined us in the beginning of the war came via Turkey, and so did our equipment and supplies",[586][589] adding that ISIL fighters received treatment in Turkish hospitals.[589]
Allegations of Qatari support
The State of Qatar has long been accused of acting as a conduit for the flow of funds to the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant. While there is no proof that the Qatari government is behind the movement of funds from the gas-rich nation to ISIL, it has been criticized for not doing enough to stem the flow of financing. Private donors within Qatar, sympathetic to the aims of radical groups such as al-Nusra Front and ISIL, are believed to be channeling their resources to support these organisations.[595][596] According to the U.S. Treasury Department, a number of terrorist financiers have been operating in Qatar. Qatari citizen Abd al Rahman al Nuaymi has served as an interlocutor between Qatari donors and leaders of al-Qaeda in Iraq (AQI). Nuaymi reportedly oversaw the transfer of US$2 million per month to AQI over a period of time. Nuaymi is also one of several of Qatar-based al-Qaeda financiers sanctioned by the U.S.Treasury in recent years. According to some reports, U.S. officials believe that the largest portion of private donations supporting ISIS and al-Qaeda-linked groups now comes from Qatar rather than Saudi Arabia.[597]
In August 2014, a German minister Gerd Müller accused Qatar of having links to ISIL, stating "You have to ask who is arming, who is financing ISIS troops. The keyword there is Qatar". Qatari foreign minister Khalid bin Mohammad Al Attiyah reiterated this stance when he stated: "Qatar does not support extremist groups, including [ISIL], in any way. We are repelled by their views, their violent methods and their ambitions."[598][599][600][601]
Allegations of Saudi Arabian support
Although Saudi Arabia's government rejected the claims,[602] former Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki accused Saudi Arabia of funding ISIL.[603] Some media outlets, such as NBC, the BBC and The New York Times, and the U.S.-based think tank Washington Institute for Near East Policy have written about individual Saudi donations to the group and the Saudi state's decade-long sponsorship of Wahhabism around the world, but have concluded that there is no evidence of direct Saudi state support for ISIL.[604][605]
Allegations of Syrian support
ISIL attacks in Syria: 1 Jan – 21 November 2014[606][undue weight? – discuss]
During the ongoing Syrian Civil War, even though ISIL has repeatedly massacred Alawite civilians and executed captured Syrian Army Alawite soldiers,[291][293][607] with most Alawites supporting President Bashar al-Assad, himself an Alawite,[292] many opposition and anti-Assad parties in the conflict have accused the Syrian leadership of Bashar Assad of some form of collusion with ISIL,[608][609] whose dominance in the opposition against the Bashar al-Assad government would give that government a basis for its claim to being under attack by "terrorists" and "a secular bulwark against al-Qaida and jihadi fanaticism".[610] Several sources have claimed that ISIL prisoners were strategically released from Syrian prisons at the beginning of the Syrian Civil War in 2011.[611] The Syrian government has bought oil directly from ISIL,[612] and in March 2015 a European Union report brought to light that the Syrian government and ISIL jointly run a HESCO gas plant in Tabqa, central Syria; the facility continues to supply government-held areas, and electricity continues to be supplied to ISIL-held areas from government-run power plants.[613] United States Secretary of State John Kerry has stated that the Syrian government has tactically avoided ISIL forces in order to weaken moderate opposition such as the Free Syrian Army (FSA),[609] as well as "even purposely ceding some territory to them [ISIL] in order to make them more of a problem so he can make the argument that he is somehow the protector against them".[614] An IHS Jane's Terrorism and Insurgency Center database analysis confirmed that only 6% of Syrian government forces attacks were targeted at ISIL from 1 Jan to 21 November 2014, while in the same period only 13% of all ISIL attacks targeted government forces.[606] The National Coalition for Syrian Revolutionary and Opposition Forces has stated that the Syrian government has operatives inside ISIL,[615] as has the leadership of Ahrar ash-Sham.[616] ISIL members captured by the FSA have claimed that they were directed to commit attacks by Syrian government operatives.[617]
On 1 June 2015, the United States stated that the Syrian government was "making air-strikes in support" of an ISIL advance on Syrian opposition positions north of Aleppo.[618] The president of the Syrian National Coalition Khaled Koja accused Assad of acting "as an air force for [ISIL]",[619] with the Defense Minister of the SNC Salim Idris stating that approximately 180 Syrian government officers were serving in ISIL and coordinating the group's attacks with the Syrian Arab Army.[620]
A report on 25 June 2015 said that ISIS kept gas flowing to Assad regime-controlled power stations. Furthermore, ISIS allowed grain to pass from the Kurdish-held north-east to regime controlled areas at the cost of a 25% levy.[621]
On 28 June 2015, a source close to the Turkish National Intelligence Organization claimed an agreement was made between the Assad regime and ISIL to destroy the FSA in the country's north, continue oil sales, assassinate Zahran Alloush and surrender Tadmur and Sukhna. The sources said that a group of commanders of both sides held a meeting at a gas production plant in Hasaka's al-Shaddadi area on 28 May 2015, not to stop fighting each other, but to focus on destroying a common enemy – the Syrian rebel forces, especially the FSA.[622] Turkish Prime Minister Ahmet Davutoğlu has blamed the rise of ISIL on the international community's inaction towards the Assad regime, which left a vacuum of power in which ISIL was able to grow.[623]
Military and resources
Military
Estimates of the size of ISIL's military vary widely from tens of thousands[624] up to 200,000.[24]
Foreign fighters in Syria and Iraq
As of early 2015, journalist Mary Anne Weaver estimates that half of ISIL fighters are made up of foreigners.[625] A UN report estimated a total of 15,000 fighters from over 80 countries in ISIL's ranks as of November 2014.[626] US intelligence estimated an increase to around 20,000 foreign fighters in February 2015, including 3,400 from Western countries.[627]
| Country | Population |
|---|---|
Statistics gathered by nation indicate up to: 3,000 from Tunisia,[628][629] 2,500 from Saudi Arabia,[628][629] 1,700 from Russia,[630] 1,500 from Jordan,[629] 1,500 from Morocco,[629] 1,200 from France,[629] 1,000 from Turkey,[631] 900 from Lebanon,[629] 700 from Germany,[632] 600 from Libya,[629] 600 from the United Kingdom,[628][629] 500 from Indonesia,[633] 500 from Uzbekistan,[629] 500 from Pakistan,[629] 440 from Belgium,[629] 360 from Turkmenistan,[629] 360 from Egypt,[629] 350 from Serbia,[634] 330 from Bosnia,[629] 300 from China,[635] 300 from Kosovo,[636] 300 from Sweden,[637] 250 from Australia,[638] 250 from Kazakhstan,[629] 250 from the Netherlands,[629] 200-300 from Azerbaijan,[639] 200 from Austria,[640] 200 from Algeria,[629] 200 from Malaysia,[633] 190 from Tajikistan,[629] 180 from the United States,[627] 150 from Norway,[641] 150 from Denmark,[629] 140 from Albania,[634] 133 from Spain,[642] 130 from Canada,[643] 110 from Yemen,[629] 100 from Sudan,[629] 100 from Kyrgyzstan,[629] 80 from Italy,[629] 70–80 from Palestine,[644] 70 from Somalia,[629] 70 from Kuwait,[629] 70 from Finland,[629] 50 from Ukraine,[629] 40–50 from Israel,[644] 40 from Ireland,[645] 40 from Switzerland,[629] at least 30 from Georgia,[646] 18 from India,[647] 10–12 from Portugal,[648][649] and 3 from the Philippines.[650]
According to a statement of a former senior leader of IS, these fighters receive food, petrol and housing but do not receive payment in wages, unlike Iraqi or Syrian fighters.[651]
Weapons
Conventional weapons
ISIL relies mostly on captured weapons. Major sources are Saddam Hussein's Iraqi stockpiles from the 2003–11 Iraq insurgency[652] and weapons from government and opposition forces fighting in the Syrian Civil War and during the post-US withdrawal Iraqi insurgency. The captured weapons, including armour, guns, surface-to-air missiles, and even some aircraft, enabled rapid territorial growth and facilitated the capture of additional equipment.[653]
Non-conventional weapons
The group has a long history of using truck and car bombs, suicide bombers and IEDs, and has used chemical weapons in Iraq and Syria. ISIL captured nuclear materials from Mosul University in July 2014, but is unlikely to be able to turn them into weapons.[654][655] In ISIL's monthly magazine Dabiq, John Cantlie wrote of a hypothetical scenario where ISIL might be able to buy a nuclear weapon from corrupt officials in Pakistan,[656] to which India's Minister of State for Defence said, "With the rise of ISIS in West Asia, one is afraid to an extent that perhaps they might get access to a nuclear arsenal from states like Pakistan".[657]
In September 2015 a US official stated that ISIL was manufacturing and using mustard agent in Syria and Iraq, and had an active chemical weapons research team.[658][659]
Propaganda and social media
ISIL is known for its extensive and effective use of propaganda.[281][660] It uses a version of the Muslim Black Standard flag and developed an emblem which has clear symbolic meaning in the Muslim world.[661]
In November 2006, shortly after the group's rebranding as the "Islamic State of Iraq", the group established the Al-Furqan Foundation for Media Production, which produces CDs, DVDs, posters, pamphlets, and web-related propaganda products and official statements.[662] It began to expand its media presence in 2013, with the formation of a second media wing, Al-I'tisam Media Foundation, in March[663][664] and the Ajnad Foundation for Media Production, specializing in Nasheeds and audio content, in August.[665] In mid 2014, ISIL established the Al-Hayat Media Center, which targets Western audiences and produces material in English, German, Russian and French.[666][667] When ISIL announced its expansion to other countries in November 2014 it established media departments for the new branches, and its media apparatus ensured that the new branches follow the same models it uses in Iraq and Syria.[668]
In December 2014, FBI Director James Comey stated that ISIL's "propaganda is unusually slick. They are broadcasting... in something like 23 languages".[669]
From July 2014, al-Hayat began publishing a digital magazine called Dabiq, in a number of different languages including English. According to the magazine, its name is taken from the town of Dabiq in northern Syria, which is mentioned in a hadith about Armageddon.[670] The group also runs a radio network called Al-Bayan, which airs bulletins in Arabic, Russian and English and provides coverage of its activities in Iraq, Syria and Libya.[671]
ISIL's use of social media has been described by one expert as "probably more sophisticated than [that of] most US companies".[281][672] It regularly takes advantage of social media, particularly Twitter, to distribute its message by organising hashtag campaigns, encouraging Tweets on popular hashtags, and utilising software applications that enable ISIL propaganda to be distributed automatically via its supporters' accounts.[672][673] Another comment is that "ISIS puts more emphasis on social media than other jihadi groups... They have a very coordinated social media presence."[674] In August 2014, Twitter administrators shut down a number of accounts associated with ISIL. ISIL recreated and publicized new accounts the next day, which were also shut down by Twitter administrators.[675] The group has attempted to branch out into alternative social media sites, such as Quitter, Friendica and Diaspora; Quitter and Friendica, however, almost immediately worked to remove ISIL's presence from their sites.[676]
The release of videos and photographs of beheadings, shootings, caged prisoners being burnt alive or submerged gradually until drowned—has been called "the hallmark" of ISIL.[677] Journalist Abdel Bari Atwan describes ISIL's media content as part of a "systematically applied policy". The escalating violence of its killings "guarantees" the attention of the media and public. Following the plan of al-Qaeda strategist Abu Bakr Naji, ISIL hopes the "savagery" will lead to a period of "vexation and exhaustion" among its Western enemies, where the US will be drawn into a direct fight with ISIS, and lacking the will to fight a sustained war will be "worn down" militarily.[235]
Along with images of brutality, ISIL presents itself as "an emotionally attractive place where people 'belong', where everyone is a 'brother' or 'sister'. A kind of slang, melding adaptations or shortenings of Islamic terms with street language, is evolving among the English-language fraternity on social media platforms in an attempt to create a 'jihadi cool'."[235] The "most potent psychological pitch" of ISIL media is the promise of heavenly reward to dead jihadist fighters. Frequently posted in their media are dead jihadists smiling faces, their ISIS 'salute' of a 'right-hand index finger pointing heavenward', and testimonies of their happy widows.[235]
ISIL has also attempted to present a more "rational argument" in its series of "press release/discussions" performed by hostage/captive John Cantlie and posted on YouTube. In one "Cantlie presentation", various current and former US officials were quoted, such as US President Barack Obama and former CIA Officer Michael Scheuer.[678] In April 2015 hackers claiming allegiance to ISIL managed to black out 11 global television channels belonging to TV5Monde for several hours, and take over the company's social media pages for nearly a day.[679] U.S. cybersecurity company FireEye later reported that they believed the cyber-attack was actually carried out by a Russian hacking group, called APT28, with alleged links to the Russian government.[680]
Finances
According to a 2015 study by the Financial Action Task Force, ISIL's five primary sources of revenue are as followed (listed in order of significance):
- proceeds from the occupation of territory (including control of banks, oil and gas reservoirs, taxation, extortion, and robbery of economic assets)
- kidnapping for ransom
- donations from Saudi Arabia and Gulf states, often disguised as meant for "humanitarian charity"
- material support provided by foreign fighters
- fundraising through modern communication networks[681]
In 2014 the RAND Corporation analyzed ISIL’s funding sources by studying 200 documents — personal letters, expense reports and membership rosters — captured from the Islamic State of Iraq (which included al-Qaeda in Iraq) by US Forces in Iraq between 2005 and 2010.[682] It found that over this period, outside donations amounted to only 5% of the group’s operating budgets, with the rest being raised within Iraq.[682] In the time period studied, cells were required to send up to 20% of the income generated from kidnapping, extortion rackets and other activities to the next level of the group's leadership. Higher-ranking commanders would then redistribute the funds to provincial or local cells which were in difficulties or which needed money to conduct attacks.[682] The records show that the Islamic State of Iraq depended on members from Mosul for cash, which the leadership used to provide additional funds to struggling militants in Diyala, Salahuddin and Baghdad.[682]
In mid-2014, Iraqi intelligence obtained information from an ISIL operative which revealed that the organisation had assets worth US$2 billion,[683] making it the richest jihadist group in the world.[684] About three-quarters of this sum is said to be represented by assets seized after the group captured Mosul in June 2014; this includes possibly up to US$429 million looted from Mosul’s central bank, along with additional millions and a large quantity of gold bullion stolen from a number of other banks in Mosul.[685][686] However, doubt was later cast on whether ISIL was able to retrieve anywhere near that sum from the central bank,[687] and even on whether the bank robberies had actually occurred.[688]
Since 2012, ISIL has produced annual reports giving numerical information on its operations, somewhat in the style of corporate reports, seemingly in a bid to encourage potential donors.[281][689]
Oil revenues
Exporting oil from oilfields captured by ISIL has brought in tens of millions of dollars for the group.[189][690] One US Treasury official estimated that ISIL earns US$1 million a day from the export of oil. Much of the oil is sold illegally in Turkey.[691] In 2014, Dubai-based energy analysts put the combined oil revenue from ISIL's Iraqi-Syrian production as high as US$3 million per day.[692]
In 2014, the majority of the group's funding came from the production and sale of energy; it controlled around 300 oil wells in Iraq alone. At its peak, it operated 350 oil wells in Iraq, but lost 45 to foreign airstrikes. It had captured 60% of Syria's total production capacity. About one fifth of its total capacity had been in operation. ISIL earned US$2.5 million a day by selling 50,000–60,000 barrels of oil daily.[691][693] Foreign sales rely on a long-standing black market to export via Turkey. Many of the smugglers and corrupt Turkish border guards who helped Saddam Hussein to evade sanctions are helping ISIL to export oil and import cash.[683][693][694]
In April 2015, after the fall of Tikrit, ISIL apparently lost control of three large oil fields, which will have significantly degraded its ability to generate income from selling oil.[695] American air strikes in the wake of the 2015 Paris attacks destroyed scores of trucks the group had been using to transport its oil.[696]
Other energy sales include selling electric power from captured power plants in northern Syria; some of this electricity is reportedly sold back to the Syrian government.[697]
Sale of antiques and artifacts
Sales of artifacts may be the second largest source of funding for ISIL, according to an article in Newsweek.[693] More than a third of Iraq's important sites are under ISIL's control. It looted the 9th century BC grand palace of the Assyrian king Ashurnasirpal II at Kalhu (Nimrud). Tablets, manuscripts and cuneiforms were sold, worth hundreds of millions of dollars. Stolen artifacts are smuggled into Turkey and Jordan. Abdulamir al-Hamdani, an archaeologist from SUNY Stony Brook, has said that ISIL is "looting... the very roots of humanity, artefacts from the oldest civilizations in the world".[693]
Taxation and extortion
ISIL extracts wealth through taxation and extortion.[691] Regarding taxation, Christians and foreigners are at times required to pay a tax known as jizya. In addition, the group routinely practices extortion, by demanding money from truck drivers and threatening to blow up businesses, for example. Robbing banks and gold shops has been another source of income.[280] The Iraq government indirectly finances ISIL, as it continues to pay the salaries of the thousands of government employees who continue to work in areas controlled by ISIL, which then confiscates as much as half of those Iraqi government employees' pay.[698]

ISIL has announced by video a new currency, the Islamic Dinar and a gold dinar, but the US dollar is the de facto currency used in its zones.[citation needed]
Illegal drug trade
According to Victor Ivanov, head of the Russian anti-drug agency, Islamic State, like Boko Haram, makes money through trafficking Afghan heroin through its territory.[699] The annual value of this business may be up to $1 billion.[699]
Donations by Saudi Arabia and Gulf states
Website The Daily Beast in June 2014 accused Saudi Arabia, Kuwait and Qatar of having funded ISIL in the past,[700][701] and also Iran and Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki have accused Saudi Arabia and Qatar of funding the group.[603][700][702] Ahead of the pro-Iraq, anti-ISIL conference held in Paris on 15 September 2014, France's foreign minister acknowledged that a number of countries at the table (the Saudis, Qatar and Kuwait were present) had "very probably" financed ISIL's advances.[703] According to The Atlantic, ISIL may have been a major part of Saudi Arabian Bandar bin Sultan's covert-ops strategy in Syria.[704]
Unregistered charity organisations act as fronts to pass funds to ISIL; they disguise fundings for ISIL's operations as donations for "humanitarian charity". As they use aliases on Facebook's WhatsApp and Kik, the involved individuals and organisations are difficult to trace. Saudi Arabia therefore has imposed a blanket ban on unauthorised donations destined for Syria in order to stop such funding.[693]
There are sources, however, that stress that there is no evidence that ISIL has direct support from those countries.[128][602][702]
Timeline of events
- Index to main: 2013 events; 2014 events: January, February, March, April, May, June, July, August, September, October, November, December; 2015 events: January, February, March, April, May, June, July, August, September, October, November.

| History of the Islamic State |
|---|
 |
|
Jama'at al-Tawhid wal-Jihad (1999‑2004) Al-Qaeda in Iraq (2004‑2006) Jama'at Jaysh Ahl al-Sunnah wa-l-Jama'ah (2004‑2006) Jaish al-Ta'ifa al-Mansurah (2004‑2006) Mujahideen Shura Council (2006) Islamic State of Iraq (2006‑2013) Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant |
| By topic |
|
|
The following is a list of major terrorist attacks and arrests that have been connected to or have been claimed in reliable sources to be inspired by the Islamic State (IS), also known by other names.
Islamic State's predecessor organization, Islamic State of Iraq (ISI) was established in October 2006, after the dissolution of the insurgent groups fighting under the coalition of Mujahideen Shura Council. Under the leadership of its first Emir Abu Omar al-Baghdadi, ISI was in the Iraqi insurgency against American occupation. After the withdrawal of U.S. troops from Iraq, ISI, then-led by Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, continued its insurgency against the Iraqi government. In April 2013, the group officially changed its name to "Islamic State of Iraq and Levant" and established a presence in Syria.
Between June 2014, when the group self-proclaimed itself to be the Islamic State, and February 2018, IS has often made claims of responsibility over 140 terrorist attacks in 29 countries outside Syria and Iraq, that were "conducted or inspired" by the group, while the evidences of those claims are not verified. Hundreds of other attacks were also carried out since 2018.
Attacks by Islamic State of Iraq: 2006 – 2012
The following is a list of alleged and confirmed attacks carried out by the Islamic State of Iraq organization between 2006 and 2012:
- The 18 April 2007 Baghdad bombings were a series of attacks that occurred when five car bombs exploded across Baghdad, the capital city of Iraq, on 18 April 2007, killing nearly 200 people.[705] No group claimed responsibility for the attacks. US defense secretary Robert Gates, delivering remarks from Tel Aviv, claimed that Islamic State of Iraq might have perpetrated the attacks.[706]
- The Qahtaniyah bombings occurred at around 8pm local time on August 14, 2007, when four co-ordinated suicide bomb attacks detonated in the Kurdish towns of Kahtaniya and Jazeera (Siba Sheikh Khidir), near Mosul. Iraqi Red Crescent's estimates say the bombs killed 796 and wounded 1,562 people,[707] making this the Iraq War's most deadly car bomb attack. No group claimed responsibility for the attack. US military officials alleged that the attacks were launched by ISI fighters.
- The August 2009 Baghdad bombings were three coordinated car bomb attacks and a number of mortar strikes in the Iraqi capital, Baghdad.
- On 25 October 2009, Baghdad bombings there were bombings in Baghdad which killed 155 people and injured at least 721 people.[708]
- The April 2010 Baghdad bombings were a series of bomb attacks in Baghdad, Iraq that killed at least 85 people over two days. Nouri al-Maliki alleged that the attacks were carried out by the Islamic State of Iraq.[709]
- The 10 May 2010 Iraq attacks were a series of bomb and shooting attacks that occurred in Iraq on 10 May 2010, killing over 100 people and injuring 350, the highest death toll for a single day in Iraq in 2010.[710] Iraqi officials alleged that Islamic State of Iraq (ISI) group carried out the attacks in retaliation against the killing of ISI's two high-ranking leaders of U.S. and Iraqi forces.[711]
- The 2 November 2010 Baghdad bombings were a series of bomb attacks in Baghdad, Iraq, that killed more than 110 people.[712] While the Islamic State of Iraq did not officially claim responsibility for the attacks, a U.S. military spokesperson alleged that ISI-affiliated fighters might have carried out the attacks.[713]
- The January 2011 Iraq suicide attacks were a series of three consecutive suicide bombings in Iraq which left at least 133 dead.
2013
| Country | Date | Article | Description | Dead | Injured | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iraq | January 2013 | A car bomb killed 28 Shia pilgrims and injured 60 others as they were returning from Karbala, while in the capital Baghdad a roadside bomb exploded near a minibus, killing four pilgrims and wounding 15 others.[714] | 32 | 75 | ||
| Two suicide bombing attacks killed 55 and wounded 288 in Baghdad, Tikrit and Kirkuk.[715] | 55 | 288 | ||||
| A suicide bomber blew himself up during a funeral for a politician's relative in the city of Tuz Khurmatu, killing 42 and leaving 75 others wounded.[716] | 42 | 75 | ||||
| February 2013 | February 2013 Kirkuk attack | A suicide car bombing at the provincial police HQ in Kirkuk killed 36 and injured 105 others, including the city's chief of police.[717] | 42 | 111 | ||
| A series of car bombs struck Baghdad, killing 37 and injured more than 130 others.[718] | 37 | 130 | ||||
| A string of bombings and shootings killed 34 and injured 70 others in Iraq.[719] | 34 | 70 | ||||
| March 2013 | Akashat ambush | IS fighters ambushed a Syrian Army convoy escorted by Iraqi soldiers, killing 51 Syrians and 13 Iraqis.[720] | 64 | 10 | ||
| 19 March 2013 Iraq attacks | A series of coordinated bombings and shootings across central and northern Iraq killed 98 people and left 240 wounded.[721] | 98 | 240 | |||
| April 2013 | 15 April 2013 Iraq attacks | A series of 70 attacks, mostly car bombings and shootings, occur across 20 cities in Iraq. | 75 | 356 | Some perpetrators killed, others escaped | |
| 2013 Hawija clashes | Four days of shootings, bombings and clashes in and around Hawija after the Iraqi Army tried to arrest protestors | 331 | 600+ | Some perpetrators killed, others escaped | ||
| May 2013 | May 2013 Iraq attacks | Dozens of attacks rock several cities in Iraq in a week long outbreak of violence. | 449 | 732 | Some perpetrators killed, others escaped | |
| June 2013 | 10 June 2013 Iraq attacks | A series of bombings strike nine cities in northern and central Iraq | 94 | 289 | Some perpetrators killed, others escaped | |
| 16 June 2013 Iraq attacks | A series of bombings and shootings targeting various cities across Iraq | 54 | 174 | Some perpetrators killed, others escaped | ||
| December 2013 | 2013 Baghdad Christmas Day bombings | Three bombings in Baghdad targeting Christians on Christmas Day | 38 | 70 | Unknown |
2014
| Country | Date | Article | Description | Dead | Injured | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belgium | May 2014 | Jewish Museum of Belgium shooting | The Jewish Museum of Belgium in Brussels, Belgium was targeted when a gunman identified as Mehdi Nemmouche opened fire at the museum. Three people died at the scene while a fourth died on 6 June due to injuries. When apprehended in Marseille, with his belongings was a camera with a recording claiming responsibility for the shooting, and a white sheet with the name of the Islamic State emblazoned onto it. | 4 | 0 | Subject in custody, extradited to Belgium. |
| Iraq | June 2014 | Badush prison massacre | On 10 June, ISIL militants massacred at least 670 Shia prisoners in Badush prison, Mosul, Iraq. | 1, 000+ | Unknown | |
| Camp Speicher massacre | On 12 June 2014, ISIL killed at least 1,566 Shia Iraqi Air Force cadets in an attack on Camp Speicher in Tikrit. At the time of the attack there were between 4,000 and 11,000 unarmed cadets in the camp. This is the second deadliest terrorist attack in history and the deadliest attack conducted by ISIL.[722] | 1566–1700 | Unknown | In retaliation Iraqi government launched counter offences against ISIL. New mass graves of ISIL victims were also discovered in Tikrit.[723] | ||
| Australia | September 2014 | 2014 Endeavour Hills stabbings | Two counter-terrorism police officers stabbed. | 0 | 2 | Perpetrator shot dead. |
| 2014 Australian counter-terrorism raids | 15 people were detained after planning to kidnap a random Australian citizen and execute them. One hostage was murdered during the siege and one killed by a bullet ricochet from a police officer during the raid. | 2 | 4 | Perpetrator shot dead by police during raid. | ||
| Canada | October 2014 | 2014 Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu ramming attack | Two soldiers run down with car. One dies. | 1 | 1 | Perpetrator shot dead after chase. |
| 2014 shootings at Parliament Hill, Ottawa | Soldier standing guard at National War Memorial shot dead. Gunman storms Parliament. Security officer shot in leg trying to take gun from perpetrator. | 1 | 3 | Perpetrator shot dead in Parliament Building. | ||
| United States | 2014 Queens hatchet attack | A recent convert to Islam and IS supporter attacks two police officers with a hatchet. A civilian is wounded when other officers attempt to shoot the attacker. | 0 | 3 | Perpetrator shot dead by police | |
| France | December 2014 | 2014 Tours police station stabbing | An IS supporter entered into a police station in Joué-lès-Tours screaming "Allahu Akbar" before stabbing three police officers. | 0 | 3 | Perpetrator shot dead. |
2015
| Country | Date | Article | Description | Dead | Injured | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saudi Arabia | January 2015 | 2015 Arar attack | Two attackers open fire on border guards, killing 3 before one detonates his suicide vest | 3 | 1 | Both perpetrators killed |
| Libya | 2015 Corinthia Hotel attack | Car bombing, suicide attack and subsequent hostage situation in hotel known for hosting foreigners and government officials. | 10 | 7 | Some perpetrators dead, others escaped | |
| Denmark | February 2015 | 2015 Copenhagen shootings | Danish-born Jordanian-Palestinian Omar Abdel Hamid El-Hussein opened fire on a free speech event hosted by Lars Vilks and the Great Synagogue of Copenhagen. El-Hussein had pledged allegiance to IS leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi a few days prior. | 2 | 5 | Perpetrator shot by police |
| Tunisia | March 2015 | Bardo National Museum attack | Mass shooting and hostage-taking of foreign tourists at the Bardo National Museum | 22 | 50 | 2 perpetrators killed by police, 1 escaped |
| Yemen | 2015 Sana'a mosque bombings | Suicide bombings of two Shi'a mosques in Sana'a | 142 | 351 | All perpetrators killed in the explosions | |
| Saudi Arabia | May 2015 | Qatif and Dammam mosque bombings | The mosque bombings occurred on 22 and 29 May 2015. On Friday May 22, a suicide bomber attacked the Shia "Imam Ali ibn Abi Talib Mosque" situated in Qudeih village of Qatif city in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia, which killed at least 21 people. The event is the second deadly attack against Shia in six months. | 26 | 106 | IS claimed responsibility for the blast. |
| United States | Curtis Culwell Center attack | Two men attacked officers with gunfire at the entrance to an exhibit featuring cartoon images of Muhammad at the Curtis Culwell Center in Garland, Texas | 0 | 1 | Both perpetrators killed | |
| Turkey | June 2015 | 2015 Diyarbakır rally bombing | TNT bombing targeting a rally of the Peoples' Democratic Party | 5 | 100+ | Perpetrator arrested. |
| France | Saint-Quentin-Fallavier attack | French-born Islamist beheads his boss and then rams his car into a gas cylinder outside a factory | 1 | 2 | Perpetrator arrested; commits suicide in prison six months after the attack | |
| Kuwait | 2015 Kuwait mosque bombing | Suicide bombing of a Shi'a mosque in Kuwait City | 27 | 227 | Bomber killed in explosion, 15 others convicted of involvement in the attack | |
| Tunisia | 2015 Sousse attacks | Mass shooting targeting western tourists at a hotel in Port El Kantaoui 10 kilometres north of Sousse | 38 | 39 | Perpetrator killed by police | |
| Iraq | July 2015 | 2015 Khan Bani Saad bombing | Suicide car bombing targeting Shi'a market in the city of Khan Bani Saad | 130 | 130+ | Perpetrator killed in explosion |
| Turkey | 2015 Suruç bombing | Suicide bombing targeting the youth wing of the Socialist Party of the Oppressed | 33 | 104 | Perpetrator dead. | |
| France | August 2015 | 2015 Thalys train attack | A man who supported IS attacked a Thalys train from Paris to Amsterdam before being subdued. | 0 | 3 | Perpetrator subdued and arrested. |
| Turkey | October 2015 | 2015 Ankara bombings | Suicide bombing targeting protesters at a peace rally | 109 | 400+ | Perpetrators dead. |
| Egypt / Russia | Metrojet Flight 9268 | Flight en route from Egypt to Saint Petersburg bombed | 224 | 0 | Unknown | |
| Lebanon | November 2015 | 2015 Beirut bombings | Suicide bombings targeting Shi'a civilians in the Hezbollah dominated suburb Bourj el-Barajneh | 43 | 200–240 | Perpetrators dead. |
| France | November 2015 Paris attacks | Shootings, suicide bombings, grenade, hostage taking. | 131 | 413 | Perpetrators killed[724] | |
| Tunisia | 2015 Tunis bombing | Suicide bombing targeting a bus carrying presidential guards. | 13 | 16 | Perpetrator killed in explosion. | |
| United States | December 2015 | 2015 San Bernardino attack | Married couple Rizwan Farook and Tashfeen Malik open fire on a holiday at the Inland Regional Center before fleeing. The wife swore allegiance to Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi in a Facebook post the day of the massacre | 14 | 24 | Perpetrators shot by police |
| Syria | Tell Tamer bombings | Truck bombings of a Kurdish militia hospital and a market. | 60 | 80 | Unknown | |
| 2015 al-Qamishli bombings | Suicide bombings in three restaurants frequented by Kurds and Assyrian Christians. | 16 | 35 | Perpetrators killed in explosions |
2016
| Country | Date | Article | Description | Dead | Injured | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Libya | January 2016 | Zliten truck bombing | Suicide truck bombing at a police training camp | 60 | 200+ | Perpetrator killed in explosion |
| Egypt | 2016 Hurghada attack | Stabbing attack targeting foreign tourists at the Bella Vista hotel in Hurghada | 0 | 2 | Two perpetrators killed by police | |
| Turkey | 2016 Istanbul bombing | Suicide bombing targeting foreign tourists in Sultanahmet Square | 13 | 14 | Perpetrator killed in explosion | |
| Indonesia | 2016 Jakarta attacks | Suicide bombings and shootout targeting a Starbucks and a police station in central Jakarta. The attacks occurred near the UN offices and several foreign embassies | 4 | 24 | Four perpetrators killed, others escaped | |
| Saudi Arabia | Mahasen mosque attack | Suicide bombing and shooting targeting a Shi'a mosque | 4 | 18 | One perpetrator killed; other arrested | |
| Syria | February 2016 | February 2016 Homs bombings | Two car bombings in Homs targeting Alawite civilians | 64 | 100+ | Unknown |
| February 2016 Sayyidah Zaynab bombings | Car bombing and two suicide bombings targeting the Sayyidah Zaynab Mosque, a Shi'a mosque believed to contain the grave of Muhammad's granddaughter. | 83 | 178 | Perpetrators killed by explosions | ||
| Turkey | March 2016 | March 2016 Istanbul bombing | A suicide bomber exploded targeting civilians in a commercial shop on a busy tourist destination and business center. | 4 | 36 | Perpetrator killed by explosion |
| Belgium | 2016 Brussels bombings | Suicide bombers attacked a metro station and an airport | 32 | 340 | Three perpetrators killed in explosions; other suspects sought | |
| Yemen | 2016 Aden car bombing | Three suicide car bombings targeting military checkpoints | 27 | Dozens | Perpetrators killed in explosions | |
| Iraq | 2016 Iraqi soccer stadium bombings | Suicide bomber detonated suicide bomb in stadium | 41 | 78 | Perpetrator killed by explosion | |
| Bangladesh | April 2016 | Murder of Xulhaz Mannan | Xulhaz Mannan, a U.S. embassy employee and the editor of Bangladesh's first LGBT magazine, was hacked to death in his apartment along with his friend. | 2 | 0 | Perpetrators at large |
| Iraq | April 2016 Baghdad bombing | At least 38 people were killed and 86 others wounded, as a result of two car bombings, in Iraq's capital of Baghdad. | 38+ | 86+ | ||
| Iraq | May 2016 | 2016 Samawa bombing | On 1 May 2016, attacks targeted Iraq's deep Shiite south, with the explosion of twin suicide car bombs in the city of Samawa. At least 33 people were killed and 75 wounded. | 33 | 75 | Two perpetrators killed in explosions |
| 11 May 2016 Baghdad bombing | Four separate car bombings in the Iraqi capital Baghdad claimed at least 110 lives. | 110+ | 165+ | Perpetrators killed in car explosions | ||
| Real Madrid Fan Club massacre | Two separate incidents in which three gunmen and suicide bombers attacked Real Madrid football fans at a supporters' café | 28 | 45 | Roughly six perpetrators killed | ||
| May 2016 Baghdad bombings | On 17 May 2016, a series of bombings by the terrorist group Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant hit the Iraqi capital city of Baghdad. At least 101 people were killed and 194 injured. | 101 | 194 | |||
| Yemen | 23 May 2016 Yemen bombings | Two suicide bombings targeted army recruits. | 45+ | 60+ | Two perpetrators killed (maybe more) | |
| Kazakhstan | June 2016 | 2016 Aktobe shootings | A group of several dozen militants attacked two gun shops and a military base in Aktobe, killing four civilians and three soldiers. Several attackers were killed during the attacks on the shops and base and more were killed during police raids that followed over the next few days. | 7 | 40+ | 18 perpetrators killed, 9 arrested |
| France | 2016 Magnanville stabbing | IS took responsibility for a stabbing that killed a French police officer and his companion.[725] | 2 | 0 | Perpetrator killed by police | |
| Malaysia | 2016 Movida Bar grenade attack | Two men approaching a bar and one of them throwing a grenade before escaping with their motorcycle while customer is watching the UEFA Euro 2016 between Italy and Spain. First ever IS attack in Malaysia. | 0 | 8 | Perpetrator arrested by police | |
| Turkey | Atatürk Airport attack | Three men from former Soviet states opened fire on Atatürk Airport in Istanbul before blowing themselves up. | 45 | 239 | Perpetrators killed | |
| United States | Orlando nightclub shooting | 29-year-old Omar Mateen killed 49 people and wounded 53 others in a mass shooting inside Pulse, a gay nightclub in Orlando, Florida. | 49 | 53 | Perpetrator killed, IS claimed responsibility for attack | |
| Bangladesh | July 2016 | 2016 Dhaka attack | Five men attacked a café in the Gulshan Thana of Dhaka and took hostages. | 24 | 50 | Five perpetrators killed |
| Iraq | July 2016 Baghdad bombings | Two bomb attacks in the district of Karrada and the suburb of Sha'ab in Baghdad. | 347 | 225+ | Members of a militant cell connected to the bombings arrested | |
| Saudi Arabia | 2016 Medina suicide bombing | A suicide bomber targeted security forces outside the Prophet's Mosque in Medina, a man blew himself up after police tried to arrest him near the U.S. consulate in Jeddah, and two more bomb attacks occurred in Qatif. | 7 | 7 | Four perpetrators killed by explosions | |
| France | 2016 Nice truck attack | On 14 July (Bastille Day), Mohamed Lahouaiej-Bouhlel, a 31 year old from Tunisia, deliberately drove a 19 tonne cargo truck into crowds celebrating Bastille Day on Promenade des Anglais in Nice, France. IS claimed responsibility. | 86 | 434 | Perpetrator killed by police at the scene. | |
| Germany | 2016 Würzburg train attack | A 17-year-old Afghan refugee seriously injured four people with a knife and an axe on a train near Würzburg in Germany | 0 | 5 | Perpetrator killed by police | |
| Afghanistan | July 2016 Kabul bombing | Two suicide bombers detonated explosive belts on civilians. | 80 | 231+ | Both perpetrators killed in explosion | |
| Germany | 2016 Ansbach bombing | A Syrian refugee blow himself up near a music festival in Ansbach, where there were about 2,500 people at that moment. | 0 | 15 | Perpetrator killed in explosion | |
| France | 2016 Normandy church attack | Priest Jacques Hamel, two nuns, and two worshipers taken hostage by two men armed with knives in the church during mass. Hamel was killed. | 1 | 3 | Both perpetrators killed by police | |
| Syria | July 2016 Qamishli bombings[726] | Two explosions in the predominantly Kurdish town Qamishli in Syria, killing at 57 including 8 Asayish people and wounding over 171 people. | 57 | 171+ | At least 1 perpetrator was killed by the explosion | |
| Belgium | August 2016 | 2016 Charleroi attack | A man attacked two policewomen with a machete in Charleroi, Belgium, before being shot dead by another police officer. The attacker is reported to have said "Allahu Akbar" during the attack. | 0 | 2 | Perpetrator killed by police |
| Pakistan | August 2016 Quetta attacks | A suicide bomber in Pakistan killed at least 90 people and wounded more than 100 in an attack on mourners gathered at a hospital in the southwestern city of Quetta, and Islamic State and a Taliban faction claimed responsibility. | 93+ | 130+ | Perpetrator killed in explosion | |
| Turkey | August 2016 Gaziantep bombing | A child suicide bomber[727] kills over 50 at a wedding in Gaziantep province. | 57 | 69 | Perpetrator killed in explosion | |
| Iraq | September 2016 | 9 September 2016 Baghdad bombings | A suicide bomber in a car in Baghdad killed at least 40 people and wounded more than 60 Islamic State claimed | 40+ | 60+ | Perpetrator killed in explosion |
| Belgium | October 2016 | 2016 stabbing of Brussels police officers | Three police officers were attacked by a man with a machete in the Schaerbeek municipality of Brussels. | 0 | 4 | |
| Pakistan | October 2016 Quetta attacks | 61 | 160+ | One killed during operation, two killed in explosion | ||
| United States | November 2016 | Ohio State University attack | Abdul Razak Ali Artan stabbed people and ran others over with a car, injuring 11, before being shot and killed by a police officer. IS praised the attack and said Artan had responded to their call to attack civilians of coalition countries. | 1 | 11 | Suspect shot by OSU response team officer. |
| Jordan | December 2016 | 2016 Al-Karak attack | On 18 December, a series of shootings occurred in Al-Karak, Jordan. | 15 | 37 | Four perpetrators were killed by security forces. IS later claimed responsibility for the attack. |
| Germany | 2016 Berlin truck attack | On 19 December, Anis Amri, a 24 year old Tunisian asylum seeker, hijacked a Polish truck in Berlin and drove it into a Christmas market in Breitscheidplatz, Berlin. The attack claimed 13 lives, including the original driver of the truck. IS claimed responsibility and later released a video of Amri pledging allegiance to Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi. | 13 | 56 | Suspect killed in Sesto San Giovanni (MI) by Italian police. |
2017
| Country | Date | Article | Description | Dead | Injured | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turkey | January 2017 | 2017 Istanbul nightclub shooting | At least 39 people are killed and nearly 70 wounded after a gunman opens fire in a nightclub in Istanbul, on the European coast of the Bosphorus. | 39 | 69 | Perpetrator arrested on 16 January. Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant claims responsibility. |
| Iraq | January 2017 Baghdad bombings | At least 70 people dead in 3 separate suicide bomb attacks in Baghdad over the space of 2 days. | 70+ | 100+ | Perpetrators killed in explosions | |
| Afghanistan | February 2017 | 2017 Kabul Supreme Court Bombing | Suicide bomber kills 22 at the Supreme Court of Afghanistan, Kabul. IS claims responsibility.[728] | 22+ | 35+ | Perpetrator killed in explosion |
| Iraq | Car bomb explodes in Baghdad's Baya neighborhood, a majority-Shiite community. IS claims responsibility.[729] | 54+ | 63+ | |||
| Pakistan | 2017 Sehwan suicide bombing | Suicide bomber kills 100 at the Sufi Shrine. IS claims responsibility. | 90 | 300+ | Perpetrator killed in explosion | |
| Syria | Part of Battle of al-Bab[730] | Car bomb kills 51 people in a small village outside of Al-Bab, Syria. | 51 | Unknown | IS claimed responsibility | |
| Afghanistan | March 2017 | March 2017 Kabul attack | Shooting and bombing at military hospital in Kabul. | 49 | 63+ | Perpetrators killed |
| Bangladesh | 2017 Dhaka suicide bombing | Suicide bomber enters under-construction Rapid Action Battalion headquarters and detonates suicide vest. | 0 | 2 | Perpetrator killed. IS claimed responsibility for the attack. | |
| United Kingdom | 2017 Westminster attack | Car plows through crowd gathered outside of Westminster Palace before assailant stabbed police officer to death. | 6 | 49 | Perpetrator killed. IS claimed responsibility for the attack. | |
| Bangladesh | 2017 South Surma bombings | Militants bombed a crowd of about 500–600 people gathered near the army and police perimeter, which was about 400 metres from the militant hideout. | 7 | 40+ | Four perpetrators killed. IS claimed responsibility for the attack. | |
| Egypt | April 2017 | 2017 Palm Sunday church bombings | Suicide bombings at two churches on Palm Sunday in the cities of Tanta and Alexandria. | 363 | 505 | Perpetrators killed. IS claims responsibility for the attacks. |
| Sweden | 2017 Stockholm truck attack | Truck drives into people on Drottninggatan pedestrian street before crashing into Åhléns department store, after which the perpetrator fails to ignite a homemade butane gas bomb. | 5 | 15 | Perpetrator arrested. IS does not claim responsibility for the attack but the perpetraitor claims to act on their behalf.[731] | |
| France | April 2017 Champs-Élysées attack | Police officers shot in Champs-Élysées, Paris. The incident killed one police officer and injured two more before the perpetrator was killed. | 2 | 2 | Perpetrator killed. IS claimed responsibility.[732] | |
| Pakistan | May 2017 | 2017 Mastung bombing | A bombing targeting Abdul Ghafoor Haideri in Mastung District. | 25 | 37 | IS claimed responsibility.[733] |
| United Kingdom | Manchester Arena bombing | Suicide bombing targeting concertgoers at the Manchester Arena at the end of an Ariana Grande concert. | 22 | 59 | Perpetrator killed. IS claimed responsibility.[734] | |
| Philippines | Battle of Marawi | Philippine security forces launch an operation in Marawi upon receiving reports that Isnilon Hapilon is meeting with militants of the Maute group in the city. The militants in response took control of its medical center, burned schools and buildings and released prisoners. | 1233 | 1400+ | 90% of Marawi recaptured by government forces. 12 militants detained.[735] | |
| Indonesia | 2017 Jakarta bombings | Islamic state claimed responsibility for Jakarta bus station attacks that left at least three policemen dead and 11 others wounded on Wednesday. | 3 | 12 | [736] | |
| Egypt | 2017 Minya attack | Masked gunmen opened fire on a convoy carrying Coptic Christians traveling from Maghagha in Egypt's Minya Governorate. | 28 | 22 | Perpetrators caught. IS claims responsibility.[737] | |
| United Kingdom | June 2017 | 2017 London Bridge attack | Van drives into pedestrians on London Bridge before three men emerge and stab people in nearby bars and restaurants. | 8 | 48 | Perpetrators killed. IS claims responsibility.[738] |
| Australia | 2017 Brighton siege | Somali-born Yacqub Khayre orchestrates a siege taking a prostitute hostage in a serviced apartment complex in Brighton, Australia and kills the complex clerk before enticing police to the complex. He makes references to al-Qaeda and IS. | 1 | 3 | Perpetrator killed. IS claims responsibility[739] and police declare it a terrorist incident.[740] | |
| Iran | 2017 Tehran attacks | On 7 June 2017, two attacks were simultaneously carried in the Iranian parliament and the Mausoleum of Ruhollah Khomeini, shrine of Iran's revolutionary founder, Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini. | 17 | 42 | 4 of the perpetrators killed, 2 of them killed in explosions, IS claims responsibility.[741] | |
| Belgium | June 2017 Brussels attack | An attacker detonated a small bomb in Brussels-Central railway station, and was later shot dead by police. | 1 | 0 | ||
| Afghanistan | August 2017 | Suicide Blast kills 36 people in Afghanistan. IS claims responsibility of the attack.[742] | 36 | Unknown | 2 perpetrators dead in the suicide blast. | |
| Pakistan | August 2017 Quetta suicide bombing | Suicide blast kills 15 people including 8 Pakistani soldiers. | 15 | 40 | IS claimed responsibility.[743] | |
| Finland | 2017 Turku attack | Two women were killed in the attack. The perpetrator was identified as Abderrahman Bouanane, a Moroccan citizen and rejected asylum seeker, who reportedly identified himself as a "soldier of the Islamic State". Despite this there was no claim of responsibility from IS. | 2 | 8 | Life sentence for Turku stabber. | |
| Pakistan | August 2017 Quetta suicide bombing | Suicide blast kills 15 people including 8 Pakistani soldiers. | 15 | 40 | IS claimed responsibility.[743] | |
| Spain | 2017 Barcelona attack | Van hits several pedestrians after jumping sidewalk in La Rambla | 16 | 152 | Perpetrator killed.IS claimed responsibility. | |
| Belgium | August 2017 Brussels attack | Two soldiers were injured by an assailant wielding a knife, who was shot by authorities and later died in the hospital. | 1 | 2 | ||
| United Kingdom | September 2017 | Parsons Green bombing | A bomb explodes at Parsons Green station in London | 0 | 30 | IS claimed responsibility. |
| Canada | 2017 Edmonton attack | Edmonton police constable Mike Chernyk was allegedly hit and stabbed by 30-year-old Abdulahi Sharif, who then hit 4 pedestrians with a rental truck in a police chase | 0 | 5 | IS flag found in rental truck. | |
| France | October 2017 | Marseille stabbing | A man killed two women at the Saint-Charles Station in Marseille, France | 3 | 0 | IS claimed responsibility. |
| United States | 2017 New York City truck attack | A man drove a flatbed pickup truck into pedestrians on a bike path along West Street in Lower Manhattan, New York City. | 8 | 12 | Attacker taken into Police Custody. IS claimed responsibility. | |
| Egypt | November 2017 | 2017 Sinai mosque attack | Attackers launched rocket propelled grenades and opened fire on the worshipers during the crowded Friday prayer at al-Rawda near Bir al-Abed. | 311 | 128 | Survivors noted that the attackers brandished the Islamic State flag.[744] |
| United States | December 2017 | 2017 New York City attempted bombing | Akayed Ullah, 27, attempted a suicide bombing at the 42nd Street-Port Authority Bus Terminal. The crude pipe bomb injured 4 people including the bomber. | 0 | 4 | The perpetrator was reported as declaring his allegiance to IS.[745] |
| Afghanistan | December 2017 Kabul suicide bombing | Suicide bombing at the Tabayan cultural centre in Kabul. | 50 | 80 | Perpetrators killed. IS claimed responsibility.[746] |
2018
| Country | Date | Article | Description | Dead | Injured | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iraq | January 2018 | January 15, 2018 Baghdad bombings | On 15 January 2018, two suicide bombings took place at al-Tayaran Square of Baghdad, killing 38 people and injuring more than 105 others. IS claimed responsibility. | 36 | 105 | Perpetrators killed. IS claimed responsibility.[747] |
| Afghanistan | 2018 Save the Children Jalalabad attack | On 24 January 2018, militants affiliated with Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant – Khorasan Province launched a bomb and gun attack on a Save the Children office in Jalalabad, a city in the eastern Afghan province of Nangarhar, killing six people and injuring 27. | 6 | 27 | Perpetrators killed. IS claimed responsibility.[748] | |
| Russia | February 2018 | 2018 Kizlyar church shooting | On 18 February 2018, a 22-year-old man local to the Russia's southern province of Dagestan carrying a knife and a hunting rifle opened fire on a crowd at an Orthodox church in Kizlyar, killing five women and injuring several other people. | 6 | 5 | Perpetrator Killed. IS claimed responsibility.[749] |
| France | March 2018 | Carcassonne and Trèbes attack | A hostage crisis unfolded in the southern French town of Trèbes on 23 March 2018, but began hours earlier in Carcassonne, when 26-year-old French-Moroccan Redouane Lakdim killed a motorist and injured his passenger, then stole the car and attacked four French police officers, wounding one. Lakdim drove to nearby Trèbes, where he stormed a Super U supermarket, ultimately killing two civilians and a gendarme and injuring several more. | 5 | 15 | Perpetrator killed. Gunman claimed allegiance with IS.[750] |
| Iraq | April 2018 | 2018 Asdira funeral bombing | 25 people were killed and 18 wounded when explosives exploded at a funeral for Sunni Muslim tribal fighters in the village of Asdira near the northern Iraqi town of Al-Shirqat.[751][752][753] | 25 | 18 | IS claimed responsibility. |
| Afghanistan | April 2018 Kabul suicide bombing | On 22 April 2018, a suicide blast killed 69 people and wounded dozens more Sunday at a voter registration center in Koche Mahtab Qala, in the Dashte Barchi area of western Kabul, Afghanistan. | 69 | 120 | Perpetrator killed. IS claimed responsibility. | |
| 30 April 2018 Kabul suicide bombings | At least 29 people were killed and 50 others injured in two suicide bombings in the Afghan capital Kabul, including several journalists documenting the scene.[754][755][756] | 29 | 50 | IS claimed responsibility. | ||
| Libya | May 2018 | 2018 attack on the High National Elections Commission in Tripoli, Libya | Suicide bombers attacked the head offices of Libya's electoral commission in Tripoli, killing at least 16 people, injuring 20 and setting fire to the building.[757][758] | 16 | 20 | IS claimed responsibility for the attack. |
| France | 2018 Paris knife attack | On 12 May 2018, a man was fatally shot by police after killing one pedestrian and injuring several more in Paris, France. | 2 | 8 | Perpetrator killed. IS claims responsibility.[759] | |
| Indonesia | 2018 Surabaya churches bombings | The 2018 Surabaya churches bombings were a series of terrorist attacks that occurred on 13 May 2018 in three churches in Surabaya, the second largest city in Indonesia. The explosions took place at Innocent Saint Mary Catholic Church (Gereja Katolik Santa Maria Tak Bercela, SMTB) on Ngagel Madya Street, Surabaya Central Pentecost Church (Gereja Pantekosta Pusat Surabaya, GPPS) on Arjuno Street, and Indonesia Christian Church (Gereja Kristen Indonesia, GKI) on Diponegoro Street. The first explosion took place at the SMTB Church. The second and third explosions followed 30 minutes apart. | 28 | 57 | 28 dead including all of the perpetrators. IS claims responsibility. | |
| Belgium | 2018 Liege shooting | On 29 May 2018, Benjamin Herman, a prisoner on temporary leave from prison, stabbed two female police officers, took their guns and shot and killed them and a civilian in Liège, Belgium. | 4 | 4 | Perpetrator killed. IS claims responsibility.[760] | |
| Afghanistan | June 2018 | A suicide bomber killed at least 36 people and injured 65 others at a gathering of Taliban and Afghan armed forces in the Rodat district of the eastern Afghan province of Nangarhar[761] | 36 | 65 | Perpetrator killed. IS claimed responsibility. | |
| July 2018 | July 2018 Jalalabad suicide bombing | On 1 July 2018, a suicide bomber detonated in the center of the eastern Afghan city of Jalalabad, killing 20 people, mainly Sikhs and Hindus, and injuring 20 others.[762] Islamic State claimed responsibility | 20 | 20 | IS claimed responsibility.[762] | |
| Pakistan | 13 July 2018 Pakistan bombings | Siraj Raisani was about to address an election rally when a suicide bomber, carrying around 16–20 kg of explosive material in his vest, blew himself up among a crowd of more than 1000 people. Along with Raisani, the explosion killed 128 people. Two days after the attack, on 15 July 2018, the number of dead increased to 149, while 186 other people were injured, making it the deadliest terrorist attack in Pakistan since the APS massacre in Peshawar in 2014.[763] | 149 | 186 | IS claimed responsibility.[763] | |
| Afghanistan | At least 23 people, including an AFP driver, were killed and 107 others injured in a suicide bombing near Kabul International Airport as scores of people were leaving the airport after welcoming home Afghan Vice President Abdul Rashid Dostum from exile.[764] | 23 | 107 | IS claimed responsibility. | ||
| Pakistan | 2018 Quetta suicide bombing | On 25 July 2018, during polling for the 2018 Pakistani general election, a bomb blast outside a polling station in Quetta's Eastern Bypass area resulted in 31 people being killed and over 35 injured.[765][766][767] Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant claimed responsibility for the attack, according to the group's Amaq News Agency. | 31 | 40 | IS claimed responsibility for the attack. | |
| Syria | 2018 As-Suwayda attacks | The 2018 As-Suwayda attacks were a string of suicide bombings and gun attacks that took place in and around As-Suwayda, Syria on 25 July, killing at least 246 people and injuring more than 200. The attacks were committed by the Islamic State.[768][769] | 246 | 200+ | IS claimed responsibility for the attack. | |
| Tajikistan | Terrorist attack against cyclists in Tajikistan | Four cyclists, including two Americans, are killed after a car plowed through tourists traveling through Tajikistan.[770] | 4 | 3 | IS claimed responsibility for the attack. | |
| Afghanistan | August 2018 | 2018 Gardez Shiite Mosque Afghanistan Attack | Two militants dressed in burqa entered a Shiite mosque in the town of Gardez in the province of Paktia and opened fire. One of the attackers blew himself up and the other was gunned down by security guards. 39 people were killed and at least 80 others injured in the attack.[771][772] | 48 | 70 | IS claimed responsibility. |
| August 2018 Kabul suicide bombing | A suicide bombing occurred on Wednesday 15 August 2018 in the Shia region of Kabul took place.[773] Afghanistan's Ministry of Public Health reported that 48 people including 34 students were killed and 67 were injured.[774] IS claimed responsibility.[775] | 48 | 67 | IS claimed responsibility for the attack. | ||
| Iran | September 2018 | Ahvaz military parade attack | On 22 September 2018, a military parade was attacked in the southwestern Iranian city of Ahvaz.[776][777] The attackers killed 25 people, including soldiers of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps and civilian bystanders.[778] | 30 | 70 | Perpetrators killed. IS claimed responsibility and provided a video containing the alleged attackers discussing the attack.[779] |
| Egypt | November 2018 | 2018 Minya bus attack | On 2 November 2018, multiple gunmen opened fire on a bus in Minya carrying Christian Copts, the attack killed 7 and injured 14, IS also claimed responsibility for the attack.[780][781][782] | 7 | 14 | IS claimed responsibility and all of the 19 perpetrators were killed by Egyptian soldiers 2 days later. |
| Australia | 2018 Melbourne stabbing attack | On 9 November 2018, a Somali man set his car on fire and started stabbing people, killing one and injuring two. The attacker died in hospital after being shot by police. IS claimed responsibility for the attack.[783] | 1 | 2 | The attacker, an IS sympathizer, was shot dead. IS claimed responsibility for the attack. | |
| France | December 2018 | 2018 Strasbourg attack | On the evening of 11 December 2018, a mass shooting occurred in Strasbourg, France, when a man with a revolver opened fire on civilians in the city's busy Christkindelsmärik (Christmas market) killing five and wounding 11, before fleeing in a taxi. | 5 | 11 | Perpetrator killed by police 2 days later. IS claimed responsibility, but French interior minister Christophe Castaner described its claim as "totally opportunistic".[784] |
| Russia | 2018 Magnitogorsk building collapse | On 31 December 2018, an apartment building in Magnitogorsk, Russia, was rocked by an explosion that leveled several floors, killing and wounding dozens of people. The following day a bus burst into flames and killed three people. However, the Russian Government has stated that the explosion was likely caused by a gas leak, not IS.[785] | 42 | 12+ | The 165th issue of the Islamic State's An-Naba newspaper contained the claim of responsibility.[786] |
2019
| Country | Date | Article | Description | Dead | Injured | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Philippines | January
2019 |
2019 Jolo Cathedral bombings | 2019 Jolo Cathedral bombings: 22 people, were killed and 102 others were injured when two bombs exploded in a cathedral during Sunday mass in Jolo, Philippines. The Islamic State-related branch of Abu Sayyaf terror group Ajang Ajang faction was behind the attack. | 20 | 102 | Abu Sayyaf (which is a part of IS) is believed to have carried out the attacks however IS has also claimed responsibility.[787] |
| Pakistan | April 2019 | 2019 Quetta bombing | A suicide blast took place in a potato stall in Shia dominated Hazarganji vegetable market.[788] | 22 | 48+ | Lashkar-e-Jhangvi and IS claimed responsibility |
| Sri Lanka | 2019 Sri Lanka Easter bombings | On 21 April 2019, 6 suicide bomb attacks killing 253, including 45 children and 38 foreign nationals. Targets were 3 churches, namely St Anthony's church – Kotahena, St. Sebestian church – Negombo, Zion Church – Batticaloa and 3 leading hotels in Colombo namely Kingsbury Hotel, Shangri-La Hotel and Cinnamon Grand Hotel. There were 2 other suicide explosion in the afternoon in a small lodge in Dehiwala killing 2 and in the house of a main attacker in Colombo, killing 7 individuals including 3 police officers.[789] | 261[790] | 500+ | IS claimed responsibility for the attack through AMAQ News Agency. Local Islamic extremist group, National Thawheeth Jama'ath is also directly involved in the attack.[791] | |
| April 2019 Kalmunai shootout | On 27 April 2019, Sri Lankan security forces and militants from National Thowheeth Jama'ath allegedly linked to IS clashed after the security forces raided a safe house of the militants. Sixteen people, including six children, died during the raid as three cornered suicide bombers blew themselves up.[792][793][166] | 16 | 2 | Groups involved in the attack swore allegiance to IS and Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi.[166] | ||
| Afghanistan | August 2019 | 17 August 2019 Kabul bombing | On 17 August 2019, a suicide bomber detonated a bomb in a wedding hall, killing at least 92 people and injuring more than 140.[794][795] | 92 | 142 | IS claimed responsibility.[796] |
| Iraq | In the night of 24 August 2019 six Iraqi people (five youths and one policeman) were killed and ten others were wounded when Islamic State militants launched a mortar attack on a football pitch in the village of Daquq at the north of Kirkuk[797][798][799] | 6 | 10 | IS claimed responsibility. | ||
| Tajikistan | November 2019 | On 6 November 2019, around 20 ISIS militants from Afghanistan conducted an attack on a border post in Rudaki, Tajikistan after crossing into Tajikistan from Afghanistan. The attack resulted in death of a Tajik border guard and a police officer. In the ensuing firefight 15 ISIS militants were killed and five were arrested.[800][801] | 17 (incl. 15 militants) | 0 | Five IS militants were arrested. | |
| Nigeria | December 2019 | On 27 December 2019 it was released a video by Amaq News Agency showing the killing of eleven Christians in Nigeria.[802] ISWAP said it was part of its campaign to avenge the killing of IS leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi in a US military raid in Syria last October.[803] | 11 | 0 | IS |
2020
| Country | Date | Article | Description | Dead | Injured | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Niger | January
2020 |
Battle of Chinagodrar | On 9 January 2020 in a gunfight at a Niger military base, 89 Niger Armed Forces soldiers and 77 IS militants killed during the battle.[804][805] | 166 | Unknown | IS claimed responsibility.[806] |
| United Kingdom | February 2020 | 2020 Streatham stabbing | On 2 February 2020 two people were stabbed in Streatham, London, and one more had minor injuries.[807] The perpetrator, Sudesh Amman, who was a fighter of Islamic State and had previously praised it, was shot dead by police.[808] | 1 | 3 | IS claimed responsibility. |
| Afghanistan | March 2020 | 6 March 2020 Kabul shooting | On 6 March 2020, ISIL gunmen killed 32 people and injured over 80 people at a ceremony in Kabul.[809][810] | 32 | 80+ | IS claimed responsibility.[811] |
| Kabul gurdwara attack | On 25 March 2020, IS killed 25 people in a gurdwara in Kabul. | 25 | 8 | IS claimed responsibility | ||
| May 2020 | Kabul hospital shooting & Kuz Kunar funeral bombing | On 12 May 2020, gunmen executed a mass shooting at a hospital's maternity ward. 80 patients were evacuated, 24 victims, including newborn babies, mothers, and nurses, killed by the gunmen and all three attackers killed by the army; An hour after the Kabul attack, a suicide bombing took place in Kuz Kunar, Nangarhar Province at the funeral of a police commander, killing 32 mourners and injuring 133 others.[812] | 218 | 133 | IS thought to be responsible for the Kabul shooting although the Afghan government blamed the Taliban for it; IS claimed responsibility for the Kuz Kunar bombing.[813][814] | |
| August 2020 | Jalalabad prison attack | On August 3, 2020, IS launched an attack on an Afghan prison that left at least 29 dead.[815][816] | 29 | Unknown | IS claimed responsibility.[817] | |
| Philippines | 2020 Jolo bombings | The bombings occurred on August 24, 2020, when insurgents alleged to be jihadists from the Abu Sayyaf group detonated two bombs in Jolo, Sulu, Philippines, killing 14 people and wounding 75 others.[818] The first occurred as Philippine Army personnel were assisting in carrying out COVID-19 humanitarian efforts.[819] The second, a suicide bombing, was carried out near the Our Lady of Mount Carmel Cathedral.[820] | 14 | 80 | Perpetrator killed in the bombing. | |
| Austria | November 2020 | 2020 Vienna attack | Between November 2–3, five were killed in Stadttempel, Vienna, including the perpetrator.[821] The Vienna Police Department confirmed that the attacker was an Islamic State sympathizer, and that the attack was motivated by Islamic extremism.[822] | 4 | 22 | Perpetrator pledged allegiance to IS.[823] |
| Syria | December 2020 | On 30 December 2020, an assault targeted a convoy of Syrian regime soldiers and militiamen of Bashar al-Assad's elite Fourth Brigade returning from their posts in Deir Ez-Zor. The bus was ambushed in a well-planned operation near the village of Shula by jihadists who set up a false checkpoint to stop the convoy and detonated bombs before opening fire.[824] | 40 | - | IS claimed responsibility.[825] |
2021
| Country | Date | Article | Description | Dead | Injured | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pakistan | January 2021 | Machh attack | IS claims responsibility for killing 11 miners in Balochistan, Pakistan. They kidnapped the workers on 2 or 3 January and took them to the mountains. The victims' hands were tied and their dismembered bodies were on the floor of a cottage. Pakistani Prime Minister Imran Khan condemned the attacks, calling them "terrorist".[826][827][828][829][830] | 11 | - | IS claimed responsibility. |
| Iraq | Baghdad bombings | Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant targeted Shia Muslims on 21 January 2021 in a clothing market in Tayaran Square, Baghdad. US, UN, EU and the Pope condemn the attack calling it a senseless act of violence.[831][832][833] | 32 | 110 | IS claimed responsibility. | |
| Afghanistan | March 2021 | 2021 Afghanistan attacks | Three female media workers are shot dead in Jalalabad, Nangarhar. A fourth woman is wounded. The Islamic State claims responsibility for the attack.[834] | 3 | 1 | IS claimed responsibility. |
| 2021 Afghanistan attacks | A female doctor is killed and a child is wounded in Jalalabad, Nangarhar, after a bomb attached to her rickshaw explodes. Seven workers at a Hazara plaster factory are shot dead in Surkh-Rōd District, Nangarhar. ISIL is suspected to be behind the attacks.[835] | 8 | 1 | IS believed to be perpetrators. | ||
| May 2021 | 2021 Kabul school bombing | A car bombing, followed by two more improvised explosive device (IED) blasts, occurred in front of Sayed al-Shuhada school in Dashte Barchi, a predominantly Shia Hazara area in western Kabul, Afghanistan, leaving at least 85 people dead and 147 injured. The majority of the casualties were girls between 11 and 15 years old. The attack took place in a neighborhood that has frequently been attacked by militants belonging to Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant over the years.[836] | 85 | 147 | Afghan Government blame the Taliban. However the Taliban deny they carried out the attack. IS-K is blamed for the attack. | |
| Iraq | July 2021 | In the evening of Monday, 19 July 2021, an IS suicide bomber detonated his vest in a crowded market in the densely populated neighbourhood of Baghdad's Sadr City killing at least 30 people, the event happened near the eve of Eid al-Adha Islamic festival. Women and children were among the dead and wounded and some shops burned down as a result of the explosion.[837] | 30 | 50 | IS claims responsibility for the attack.[838] | |
| Afghanistan | August 2021 | 2021 Kabul airport attack | On 26 August 2021, at 17:50 local time (13:20 UTC),[839] a suicide bombing occurred near Abbey Gate at Hamid Karzai International Airport in Kabul, Afghanistan. Another blast occurred after the bombing.[840][841][842][843] These attacks came hours after the United States State Department told Americans outside the airport to leave due to a terrorist threat.[844] At least 183 people were killed in the attacks, including 13 US service members.[845] | 182 | 200 | IS claims responsibility for the attack.[846] |
| New Zealand | 3 September | 2021 Auckland Countdown stabbing | An IS supporter stabbed six people before being shot by police on 3 September in Auckland, New Zealand. The attacker came to New Zealand in 2011 and became a person of interest in October 2016, authorities said.[847] | 1 | 6 | IS claims responsibility for the attack. |
| Afghanistan | 18 September | At least 7 people were killed and at least 30 were wounded during four explosions which occurred in Nangarhar's capital Jalalabad which targeted a Taliban patrol vehicle and another explosion which occurred in Kabul's Dasht-e-Barchi neighbourhood.[848] | 7 | 30 | IS claimed responsibility for the attack.[849] | |
| 8 October | 2021 Kunduz mosque bombing | IS militants attacked, and killed many Shia Muslim worshipers in the mosque during their Friday prayer time.[850] | 50+ | 100+ | IS claimed responsibility for the attack.[851] | |
| 15 October | 2021 Kandahar bombing | IS militants attacked, and killed many Shia Muslim worshipers in the mosque during their Friday prayer time.[852][853] | 65 | 70+ | IS claimed responsibility for the attack.[854] | |
| Niger | 2 November | 2021 Adab-Dab attack | Gunmen ambushed a delegation held by the mayor of Bani-Bangou. | 69 | ISGS accused.[855] |
2022
| Country | Date | Article | Description | Dead | Injured | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pakistan | 4 March 2022 | 2022 Peshawar mosque bombing | The Islamic State attacked a Shiite mosque in Peshawar, the capital of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province in Pakistan. | 62 (+1) | 196 | IS-KP claimed responsibility |
| Israel | 22 March 2022 | 2022 Beersheba attack | 1 Arab-Israeli Bedouin men affiliated with IS were responsible for a stabbing in Beersheba. | 4 | 2 | IS claimed responsibility |
| 27 March 2022 | 2022 Hadera shooting | 2 Arab-Israeli men affiliated with IS were responsible for a shooting in Hadera. | 2 | 12 | IS claimed responsibility | |
| Afghanistan | 21 April 2022 | 2022 Mazar-i-Sharif mosque bombing | A bomb exploded at a Shiite mosque in Mazar-i-Sharif during Friday prayers, killing 31 people and wounding 87. | 31 | 87 | |
| 29 April 2022 | April 2022 Kabul mosque bombing | The bombing occurred around 2:00 pm at the Khalifa Aga Gul Jan Mosque in Kabul, where hundreds of congregants were gathered for prayers.[856] Interior ministry spokesman Mohammad Nafi Takor confirmed ten fatalities. Sayed Fazil Agha, the mosque's leader, said more than 50 died.[857] Police chief spokesman Khalid Zadran said as many as 30 people were wounded.[858] | 50 | 30 | IS claimed responsibility for the attack.[859] | |
| Benin | 1 July 2022 | Multiple IS militants ambushed and killed 4 Beninese soldiers near the town of Alfa Kawoura[860] | 4 | 0 | IS claimed responsibility | |
| Afghanistan | 3 August 2022 | Two Taliban police officers were killed and four were wounded during a gunbattle with Islamic State gunmen at a hideout in Kabul. Three Islamic State militants were also killed.[861] | 5 | 4 | ||
| 5 August 2022 | On 5 August 2022, eight people were killed and 18 others were injured when a bomb hidden in a cart exploded near a Shiite mosque in Kabul.[862] | 8 | 18 | Islamic State claimed responsibility for the attack. | ||
| 30 September 2022 | September 2022 Kabul school bombing | A suicide bomber blew himself up at the Kaaj education center in Dashte Barchi, a Hazara neighborhood in Kabul, Afghanistan, killing at least 52 people.[863] | 52+ | 110 | ||
| Mozambique | 20 October 2022 | Many IS militants attacked an Indian-owned Ruby Mine in Montepuez, which is considered the world's largest ruby mine.[864] | IS claimed responsibility[865] | |||
| Iran | 26 October 2022 | 2022 Shiraz massacre | An IS terrorist led a massacre at the Shah Cheragh Shia mosque in Shiraz, Fars province, Iran. At least 15 people have been killed due to this event, 2 have been arrested while 1 is still at large. IS has claimed responsibility for the attack on its telegram channel.[866] | 15 | 40 | IS claimed responsibility for the massacre. |
| Afghanistan | December 2022 | 2022 Kabul hotel attack | 2 IS militants set off explosives and set fire to the Longan Hotel in Kabul due to its ties to the Chinese government. 6 people were killed, including one of the attackers, and another 18 were injured, including foreign and Afghan civilians and Taliban soldiers.[867] | 3 | 18 | One IS perpetrator killed in the bombing. |
| Syria | 26 December 2022 | A lone IS suicide bomber detonated a suicide vest in an attack on an SDF security centre in the former ISIS capital, Raqqa. The bomber and at least 6 SDF were killed in the attack.[868] | 7 | - | IS claimed responsibility.[869] |
2023
| Country | Date | Article | Description | Dead | Injured | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | 1 January 2023 | 2023 Kabul airport bombing | An attacker detonated a bomb outside the entrance to the military portion of Kabul International Airport.[870] | 20 (claimed) | 30 (claimed) | Islamic State claimed responsibility |
| 11 January 2023 | Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Afghanistan bombing | A suicide bomber detonated outside the Taliban foreign ministry office in Kabul, reportedly during the visit of a Chinese delegation.[871] | 20+ | Perpetrator killed in the bombing. Islamic State claimed responsibility. | ||
| DRC | 16 January 2023 | Kasindi church bombing | An Islamic State affiliated group planted a bomb in a Pentecostal Church, and blew it up[872] | 17 | 39 | Islamic State claimed responsibility[873] |
| Burkina Faso | 23 March 2023 | Islamic State militants attacked a unit of Burkina Faso soldiers that was patrolling the area[874] | 15 | 0 | Islamic State claimed responsibility | |
| DRC | 8 April 2023 | The Islamic State - Central Africa Province cell claimed responsibility for the attack after raiding a farm in the village of Enebula in North Kivu province[875] | 21 | ~30 | Islamic State claimed responsibility[876] | |
| Syria | 16 April 2023 | The Islamic State claimed responsibility for attacking and killing a group of around 10 militants and 16 civilians near the capital of Damascus[877] | 26 | Unknown | Islamic State claimed responsibility[878] | |
| Pakistan | 30 July 2023 | 2023 Khar bombing | A suicide bomb at a Jamiat Ulema-e-Islam (F) rally in Khar, Bajaur District, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan, killed at least 63 people[34] and injured nearly 200 others.[879] | 63 (+1) | 200+ | Islamic State claimed responsibility[879] |
| Afghanistan | 13 October 2023 | 2023 Pul-i-Khumri bombing | The Islamic State claimed responsibility for attack on Shia Mosque in Baghlan[880] | 7 (+1) | 17 | Islamic State claimed responsibility[880] |
| France | 13 October 2023 | Arras school stabbing | An IS-pledged lone wolf murdered a teacher and wounded 3 others at his former school in Arras[881] | 1 | 3 | The perpetrator pledged allegiance to the Islamic State[882] |
| Belgium | 16 October 2023 | 2023 Brussels terrorist attack | An IS-pledged lone wolf shot dead 2 Swedish nationals and wounded a third person in Brussels[883] | 3 (1) | 1 | The perpetrator pledged allegiance to the Islamic State[884] Islamic State claimed responsibility[885] |
| Philippines | 3 December 2023 | Mindanao State University bombing | A bombing occurred at a Roman Catholic Mass in Mindanao State University, Marawi | 4 | 72 | Islamic State claimed responsibility[886] Involvement of local IS affiliate, Maute group, being considered.[887] |
| Uganda | 19 December 2023 | Kyabandara parish attack | ADF rebels attacked a Kyabandara parish in Kamwenge district in Western Uganda and killed at least 5 people.[888] | 5 | 0 | Allied Democratic forces (ADF) who pledged allegiance to ISIS |
2024
| Country | Date | Article | Description | Dead | Injured | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iran | 3 January 2024 | Kerman bombings | Two bombings occurred during a ceremony commemorating the assassination of Qasem Soleimani in Kerman. | 103 (+2) | 284 | Islamic State claimed responsibility[889] |
| Afghanistan | 6 January 2024 | Explosives planted in a bus in the Dasht-e-Barchi neighborhood of Kabul detonated, killing five people. | 5 | 15 | Islamic State claimed responsibility[890][891] | |
| 9 January 2024 | An explosive was detonated in a minivan in Kabul, killing three people. | 3 | 4 | Islamic State claimed responsibility[892] | ||
| Iraq | 14 January 2024 | Militants in two vehicles opened fire on Iraqi soldiers stationed near Haditha with snipers and semi-automatic weapons, killing three. | 3 | 1 | Islamic State suspected[893] | |
| Turkey | 28 January 2024 | 2024 Istanbul church shooting | Two gunmen entered the Church of Santa Maria in Istanbul during Sunday mass and shot and killed a man before leaving. | 1 | 1 | Islamic State claimed responsibility[894] |
| Pakistan | 30 January | 2024 Sibi bombing | A bombing targeting an election rally for the Tehreek-e-Insaf party in the Sibi region killed at least four people. ISIS claimed ten people were killed or injured. | 4 | 5 | Islamic State claimed responsibility[895] |
| 7 February | 2024 Balochistan bombings | Twin bombings occurred at two political offices in Balochistan province a day before the Pakistani general election | 28-30 | 40 | Islamic State claimed responsibility[896][897][898] | |
| Mozambique | 9 February | Mucojo attack | In Mucojo, ISIS militants attacked Mozambician soldiers, killing at least 25. Militants also shot at a passenger bus in Meluco, killing the driver. The attackers left notes for the passengers, which announced a declaration of war on Christians and said that non-Muslims would have to pay a jizyah if they did not convert to Islam, and would be killed if they refused. | 26+ | Islamic State claimed responsibility[899][900] | |
| Democratic Republic of the Congo | 19–20 February | Rebels killed two dozen people with machetes and guns in Ituri and North Kivu Provinces in separate attacks. | 24+ | ADF accused[901] | ||
| Syria | 25 February | 13 people were killed by a landmine left by ISIS while they were hunting for truffles in Raqqa Governorate. | 13 | Islamic State accused[902] | ||
| Switzerland | 3 March | Zürich stabbing attack | A 50-year-old Jewish man was stabbed by a 15-year-old boy in the city of Zürich. The boy had pledged allegiance to the leader of the Islamic State in a video before the attack. | 1 | Perpetrator pledged allegiance to the Islamic State[903][904] | |
| Niger | 20 March | 2024 Tillabéri attack | A Nigerien Army unit was ambushed near Teguey, Tillabéri Region. The Islamic State said that 30 soldiers were killed, while the Nigerien Defense Ministry said there were 23 deaths. Around 30 attackers were allegedly killed during the ambush. | 23 (+30) | 17+ | Islamic State claimed responsibility[905] |
| Afghanistan | 21 March | 2024 Kandahar New Kabul Bank bombing | A suicide bombing at a branch of the New Kabul Bank in Kandahar occurred people as they were attempting to collect their monthly salaries. ISIS said it was targeting the Taliban, but the Taliban said the attack targeted civilians. The Taliban said that three people were killed and 12 were injured, while the Mirwais Hospital said 21 were killed and over 50 were injured.[906][907] | 21 (+1) | 50 | Islamic State claimed responsibility[908] |
| Russia | 22 March | Crocus City Hall attack | Four gunmen carried out a mass shooting, stabbing, and arson attack at the Crocus City Hall in Krasnogorsk, Moscow Oblast. Gunmen used incendiary devices to ignite a fire, which caused extensive damage, including the collapse of the concert hall's roof.[909][910][911] | 145 | 551 | Islamic State claimed responsibility[912][913][914][915][916] |
| Afghanistan | 29 April | A gunman attacked a Shiite mosque in Guzara, Herat Province with machine-gun fire, killing six people before fleeing the scene. | 6 | 1 | Islamic State claimed responsibility[917] | |
| 17 May | 2024 Bamyan shooting | Gunman attacked a group of Western tourists (Spaniards, Lithuanians, Norwegians, and Australians), alongside their Afghan guides, in the city of Bamyan, Bamyan Province with machine-gun fire, killing seven people (including four tourists), and wounding seven others (including three tourists) before fleeing the scene. | 7 | 7 | Islamic State claimed responsibility[918] | |
| Lebanon | 5 June | 2024 Beirut US embassy shooting | A Syrian national opened fire at the U.S. embassy in Beirut, wounding a security guard. The Lebanese Armed Forces responded to the attack, shooting the gunman twice and capturing him. | 0 | 1 (+1) | Local media reported that the perpetrator wore a vest with the words "Islamic State" in Arabic and the initials IS in English, suggesting that he may have been involved with the group.[919] |
| Syria | 12 June | Sixteen Syrian soldiers were killed by a minefield laid by ISIS. | 16 | 0 | Islamic State claimed responsibility[920] | |
| Russia | 16 June | Rostov-on-Don pre-trial detention center hostage crisis | 6 ISIS detainees, armed with knives, escaped their cells and took two Russian detention center employees/police officers hostage at a detention center in the city of Rostov-on-Don in Russia, and demanded a vehicle, weapons, and free passage. Russian security forces raided the center, killing 5 of them and capturing and wounding the sixth, and freeing the hostages. | 0 (+5) | 0 (+1) | All 6 of the detainees had previously been arrested for being Islamic State members and plotting attacks for the group. Videos recorded by the attackers during the incident also showed at least 2 of them wearing Islamic State-style headbands, one of them holding an Islamic State flag, and they proclaimed their allegiance to the group.[921] |
| 23 June | 2024 Dagestan attacks | Militants opened fire at a church and a synagogue in Derbent and another synagogue and a police station in Makhachkala. Six police officers and two militants were killed, while a priest in Derbent was also killed when his throat was slit.[922] | 22 (+5) | 45 | Islamic State claimed responsibility via Al Naba, an ISIL-affiliated newspaper.[923][924] | |
| Serbia | 29 June | 2024 attack on the Israeli embassy in Belgrade | A Serbia Muslim convert opened fire with a crossbow at the Israeli embassy in Belgrade, wounding a security guard. The guard responded to the attack, shooting the gunman and killing him. | 0 (+1) | 1 | The perpetrator pledged allegiance to the Islamic State and its leader Abu Hafs. Police also found IS-linked items at the attacker's home, including an IS flag.[925][926] |
| Oman | 15 July | 2024 Muscat mosque shooting | 9 people (including the 3 attackers) were killed in a mass shooting at Imam Ali Mosque in Wadi Kabir, Muscat. | 6 (+3) | 30-50 | Islamic State claimed responsibility.[927] |
| Afghanistan | 11 August | 2024 Kabul bus bombing | An explosive was detonated on a bus carrying Hazaras in the commune of Dashte Barchi, Kabul, killing 1 civilian and injuring 11-13 others.[928] | 1 | 11-13 | Islamic State – Khorasan Province claims responsibility[929] |
| Russia | 23 August | Surovikino penal colony hostage crisis | Four ISIS prisoners armed with knives took prison employees and inmates hostage at the IK-19 maximum security prison in Surovikino. They fatally stabbed nine people, including five employees and injured two other employees. The militants were later killed by snipers, ending the hostage crisis. | 9 (+4) | 2 | Perpetrators claimed that they were ISIS militants and waved flags of the organization. The attackers also claimed they were acting in revenge for the detention of the Crocus City Hall attack perpetrators.[930][931] |
| Germany | 23 August | Solingen stabbing | A Syrian ISIS member armed with a knife stabbed several people at a festival in the city of Solingen. The attack left 3 people dead and 8 others injured. The perp was later arrested by German authorities. | 3 | 8 | IS claimed responsibility for the attack, and later released videos of the attacker, where he cited the wars in Bosnia, Iraq, Syria, Afghanistan, and Palestine as a reason for the attack. German Authorities also confirmed that the attacker shared the ideology of the Islamic state[932][933] |
| Afghanistan | 2 September | 2024 Qala Bakhtiar bombing | A suicide bomber detonated his explosive vest outside a government building in the Qala Bakhtiar neighbourhood in the Afghanistan capital Kabul, killing six people and injuring thirteen others. | 6 (+1) | 13 | Islamic State claimed responsibility.[934] |
| 12 September | 2024 Afghanistan bus shooting | Gunmen opened fire at a group of Shiite civilians welcoming pilgrims from Karbala, Iraq, in Daykundi Province, killing 15. | 15 | 6 | Islamic State claimed responsibility[935] | |
| Azerbaijan | 14 September | 2024 Qusar attack | IS militants attack Azerbaijani security forces in Qusar District, northern Azerbaijan, killing 7 security personnel and injuring 1. | 7 (+1) | 1 | Islamic State claimed responsibility via its weekly Al-Naba newsletter, 5 days later.[936][937] |
See also
- List of Islamist terrorist attacks
- List of terrorists incidents linked to ISIS-K
- List of terrorist incidents, 2014
- List of terrorist incidents, 2015
- List of wars and battles involving ISIL
- List of the terrorist actions against the Mourning of Muharram
References
- ^ Rubin, Alissa J. (5 July 2014). "Militant Leader in Rare Appearance in Iraq". The New York Times. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ "Abd al-Rahman Mustafa al-Qaduli". Rewards for Justice. 5 May 2015. Retrieved 7 May 2015.
- ^ "ISIS' Abu Alaa al-Afri killed alongside dozens of followers in air strike - Daily Mail Online". Daily Mail. London. 13 May 2015. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ^ a b Sherlock, Ruth (9 July 2014). "Inside the leadership of Islamic State: how the new 'caliphate' is run". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 1 October 2014.
- ^ "Coalition Airstrikes Targeted Islamic State Leaders Near Mosul". The Wall Street Journal. 10 November 2014.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ a b c "Islamic State Senior Leadership: Whos Who" (PDF). Brookings. 2014. Retrieved 11 May 2015.
- ^ Masi, Alessandria. "If ISIS Leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi Is Killed, Who Is Caliph Of The Islamic State Group?". International Business Times.
- ^ "ISIS Leadership". Frontline. PBS. 2015. Retrieved 14 August 2015.
- ^ "Here's What We Know About the 'Caliph' of the New Islamic State". Business Insider. Agence France-Presse. 29 June 2014. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ "ISIS Spokesman Declares Caliphate, Rebrands Group as Islamic State". SITE Institute. 29 June 2014. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- ^ "Tarkhan Tayumurazovich Batirashvili". Rewards for Justice. 5 May 2015. Retrieved 7 May 2015.
- ^ a b Pool, Jeffrey (16 December 2004). "Zarqawi's Pledge of Allegiance to Al-Qaeda: From Mu'Asker Al-Battar, Issue 21". Terrorism Monitor. 2 (24): The Jamestown Foundation. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 30 July 2014.
- ^ "Al-Qaeda disavows ISIS militants in Syria". BBC News. 3 February 2014. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- ^ a b c Holmes, Oliver (3 February 2014). "Al Qaeda breaks link with Syrian militant group ISIL". Reuters. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ a b "IS announces expansion into AfPak, parts of India". Hindustan Times. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ a b "IS welcomes Boko Haram allegiance: tape". Agence France-Presse. 12 March 2015. Retrieved 12 March 2015.
- ^ a b Nima Elbagir, Paul Cruickshank and Mohammed Tawfeeq, CNN (7 March 2015). "Boko Haram purportedly pledges allegiance to ISIS". CNN.
{{cite news}}:|author=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b "ISIS Declares Governorate in Russia's North Caucasus Region". Institute for the Study of War. 23 June 2015.
- ^ a b c "Islamic State". Australian National Security. Australian Government. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ "The Islamic State". Stanford University. 23 January 2015. Retrieved 23 April 2015.
- ^ a b "Islamic State: The Changing Face of Modern Jihadism" (PDF). Quilliam Foundation. November 2014. Retrieved 23 April 2015.
- ^ a b c d Crooke, Alastair (5 September 2014). "You Can't Understand ISIS If You Don't Know the History of Wahhabism in Saudi Arabia". The Huffington Post.
- ^ a b c d e f g Kirkpatrick, David (24 September 2014). "ISIS Harsh Brand of Islam Is Rooted in Austere Saudi Creed". The New York Times. Retrieved 6 May 2015.
- ^ a b Cockburn, Patrick (16 November 2014). "War with Isis: Islamic militants have army of 200,000, claims senior Kurdish leader". The Independent. London. Retrieved 8 December 2014.
- ^ a b "Saddam's former army is secret of Baghdadi's success". Reuters. 16 June 2015. Retrieved 1 July 2015.
- ^ "ISIS can 'muster' between 20,000 and 31,500 fighters, CIA says". CNN. 12 September 2014. Retrieved 6 July 2015.
- ^ a b "The War between ISIS and al-Qaeda for Supremacy of the Global Jihadist Movement" (PDF). Washington Institute for Near East Policy. June 2014. Retrieved 26 August 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f Tharoor, Ishaan (18 June 2014). "ISIS or ISIL? The debate over what to call Iraq's terror group". The Washington Post. Retrieved 21 June 2014.
- ^ "What is Islamic State?". BBC News. 26 September 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ "Kurds accused of 'ethnic cleansing' by Syria rebels". CBS News. 15 June 2015. Retrieved 22 June 2015.
Islamic State is not a state, since it lacks international recognition. See: "Statehood (international law)". Wex. Cornell University. Retrieved 20 July 2015. - ^ "Islamic State-controlled parts of Syria, Iraq largely out of reach: Red Cross". Reuters. 13 March 2015. Retrieved 25 June 2015.
- ^ a b c "Exclusive: In turf war with Afghan Taliban, Islamic State loyalists gain ground". Reuters. 29 June 2015. Retrieved 6 October 2015.
- ^ "Militant Attack and Support Zones in Afghanistan" (PDF). Institute for the Study of War. 18 September 2015. Retrieved 22 September 2015.
- ^ a b "Pakistan Taliban splinter group vows allegiance to Islamic State". Reuters. 18 November 2014. Retrieved 19 November 2014.
- ^ a b c d e Zavadski, Katie (23 November 2014). "ISIS Now Has a Network of Military Affiliates in 11 Countries Around the World". New York. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ a b c d Schwartz, Felica (23 December 2014). "One More Name for Islamic State: Daesh". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ^ Guthrie, Alice (19 February 2015). "Decoding Daesh: Why is the new name for ISIS so hard to understand?". Free Word Centre. Retrieved 15 November 2015.
- ^ a b c Withnall, Adam (29 June 2014). "Iraq crisis: Isis changes name and declares its territories a new Islamic state with 'restoration of caliphate' in Middle East". The Independent. London. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- ^ "ISIS announces formation of Caliphate, rebrands as 'Islamic State'".
- ^ a b "Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi: The man who would be caliph". The Week. 13 September 2014. Retrieved 7 December 2014.
- ^ Sly, Liz (23 July 2013). "Islamic law comes to rebel-held Syria". The Washington Post.
- ^ a b c Sly, Liz (3 February 2014). "Al-Qaeda disavows any ties with radical Islamist ISIS group in Syria, Iraq". The Washington Post. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ "Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant (ISIL)". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 1 February 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|subscription=ignored (|url-access=suggested) (help) - ^ Khalid al-Taie (13 February 2015). "Iraq churches, mosques under ISIL attack". Al-Shorfa.
{{cite web}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help);|archive-url=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|archivedate=(help); Missing or empty|url=(help) - ^ Hasan, Mehdi (10 March 2015), "Mehdi Hasan: How Islamic is Islamic State?", New Statesman, retrieved 7 July 2015,
Consider the various statements of Muslim groups such as the Organisation of Islamic Co-operation, representing 57 countries (Isis has "nothing to do with Islam"); the Islamic Society of North America (Isis's actions are "in no way representative of what Islam actually teaches"); al-Azhar University in Cairo, the most prestigious seat of learning in the Sunni Muslim world (Isis is acting "under the guise of this holy religion . . . in an attempt to export their false Islam"); and even Saudi Arabia's Salafist Grand Mufti, Abdul Aziz al ash-Sheikh (Isis is "the number-one enemy of Islam").
{{citation}}:|section=ignored (help) - ^ a b Uppsala Data Conflict Programme: Conflict Encyclopaedia (Iraq). (See One-sided violence – ISIS-civilians – Actor information-ISIS.) Retrieved 5 August 2014.
- ^ Whitlock, Craig (10 June 2006). "Death Could Shake Al-Qaeda in Iraq and Around the World". The Washington Post. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ Knights, Michael (29 May 2014). "The ISIL's Stand in the Ramadi-Falluja Corridor". Combating Terrorism Center. Retrieved 12 July 2014.
- ^ Fishman 2008, pp. 48–9, noting that this was little more than a media exercise and an attempt to give the group a more Iraqi flavour and perhaps to distance al-Qaeda from some of al-Zarqawi's tactical errors, notably the 2005 bombings by AQI of three hotels in Amman.
- ^ a b "The Rump Islamic Emirate of Iraq". The Long War Journal. 16 October 2006. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- ^ Fishman 2008, pp. 49–50
- ^ a b "ISI Confirms That Jabhat Al-Nusra Is Its Extension in Syria, Declares 'Islamic State of Iraq And Al-Sham' As New Name of Merged Group". MEMRI. 8 April 2013. Retrieved 10 April 2013.
- ^ "Key Free Syria Army rebel 'killed by Islamist group'". BBC News. 12 July 2013.
- ^ "Al-Qaeda in Iraq confirms Syria's Nusra Front is part of its network". Al Arabiya. 9 April 2013. Retrieved 15 June 2014.
- ^ "Profile: Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant (ISIL)". BBC News. 11 June 2014. Retrieved 16 June 2014.
- ^ a b Saxena, Vivek (18 June 2014). "ISIS vs ISIL – Which One Is It?". The Inquisitr. Retrieved 20 June 2014.
- ^ a b "Terrorist Designations of Groups Operating in Syria". United States Department of State. 14 May 2014. Retrieved 18 June 2014.
- ^ "Isis, Isil or Da'ish? What to call militants in Iraq". BBC News. 24 June 2014. Retrieved 16 August 2014.
- ^ Randal, Collin. "why-does-a-simple-word-like-daesh-disturb-extremists-so-much". thenational.ae/. Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ Abouzeid, Rania (16 January 2014). "Syria's uprising within an uprising". European Council on Foreign Relations. Archived from the original on 25 January 2014. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ Keating, Joshua (16 June 2014). "Who Is Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi?". Slate. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ a b Martinson, Jane (29 June 2015). "BBC to review use of 'Islamic State' after MPs protest against term". The Guardian. Retrieved 1 July 2015.
More than 120 MPs, backed by David Cameron, sign letter saying name gives legitimacy to terrorist group that is neither Islamic nor a state... It urges the BBC and other broadcasters to adopt the name "Daesh" for the group.
- ^ "ISIL renames itself 'Islamic State' and declares Caliphate in captured territory". Euronews. 30 June 2014. Retrieved 30 June 2014.
- ^ Khosla, Simran (30 June 2014). "This Is What The World's Newest Islamic Caliphate Might Look Like". Business Insider. GlobalPost. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ a b c Moore, Jack (2 July 2014). "Iraq Crisis: Senior Jordan Jihadist Slams Isis Caliphate". International Business Times UK. Retrieved 2 July 2014.
- ^ a b c Mandhai, Shafik (7 July 2014). "Muslim leaders reject Baghdadi's caliphate". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 12 July 2014.
- ^ a b c Goodenough, Patrick (6 July 2014). "Self-Appointed 'Caliph' Makes First Public Appearance". CNS News. Retrieved 26 July 2014.
- ^ a b c "United Nations Official Document". United Nations. Retrieved 13 October 2014.
- ^ a b c "Details about the Canadian government's motion about going to war against ISIL". Ottawa Citizen. Retrieved 13 October 2014.
- ^ a b c "Australia says ready to strike ISIL in Iraq". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 13 October 2014.
- ^ a b c d "Statement by the President on ISIL". White House. Retrieved 13 October 2014.
- ^ "Zarqawi pledges allegiance to Osama". Dawn. Agence France-Presse. 18 October 2004. Archived from the original on 29 December 2007. Retrieved 13 July 2007.
- ^ "Al-Zarqawi group vows allegiance to bin Laden". NBC News. Associated Press. 18 October 2004. Retrieved 13 July 2007.
- ^ Whitaker, Brian (13 October 2005). "Revealed: Al-Qaida plan to seize control of Iraq". The Guardian. Retrieved 19 September 2014.
- ^ Fishman 2008, pp. 48–9.
- ^ "Al-Qaeda in Iraq names new head". BBC News. 12 June 2006.
- ^ Tran, Mark (1 May 2007). "Al-Qaida in Iraq leader believed dead". The Guardian.
- ^ "al Qaeda's Grand Coalition in Anbar". The Long War Journal. 12 October 2006. Retrieved 11 February 2015.
- ^ "Jihad Groups in Iraq Take an Oath of Allegiance". MEMRI. 17 October 2006. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- ^ Stephen Negus: "Call for Sunni state in Iraq". Financial Times, 15 October 2006. Retrieved 15 January 2015. (Free) registration required.
- ^ "Al-Qaida in Iraq (AQI)". Dudley Knox Library. Naval Postgraduate School. Archived from the original on 1 April 2007. Retrieved 14 July 2014.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|website=(help) - ^ "Islamic State of Iraq Announces Establishment of the Cabinet of its First Islamic Administration in Video Issued Through al-Furqan Foundation". SITE Institute. 19 April 2007. Archived from the original on 28 September 2007. Retrieved 20 July 2014.
- ^ Mahnaimi, Uzi (13 May 2007). "Al-Qaeda planning militant Islamic state within Iraq". The Sunday Times. London. Archived from the original on 24 May 2011.
- ^ Ricks, Thomas E. (11 September 2006). "Situation Called Dire in West Iraq". The Washington Post. Retrieved 13 July 2014.
- ^ Linzer, Dafna; Ricks, Thomas E. (28 November 2006). "Anbar Picture Grows Clearer, and Bleaker". The Washington Post. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ Engel, Richard (27 December 2006). "Reporting under al-Qaida control". MSNBC. Retrieved 28 October 2009.
- ^ Engel, Richard (17 January 2007). "Dangers of the Baghdad plan". MSNBC. Archived from the original on 2 November 2007. Retrieved 28 October 2009.
- ^ Targeting al Qaeda in Iraq's Network, The Weekly Standard, 13 November 2007
- ^ Ricks, Thomas; DeYoung, Karen (15 October 2007). "Al-Qaeda in Iraq Reported Crippled". The Washington Post. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- ^ Samuels, Lennox (20 May 2008). "Al Qaeda in Iraq Ramps Up Its Racketeering". Newsweek. Retrieved 13 February 2015.(subscription required) Accessible via Google.
- ^ Phillips 2009, p. 65.
- ^ Kahl 2008.
- ^ Christie, Michael (18 November 2009). "Al Qaeda in Iraq becoming less foreign-US general". Reuters.
- ^ Arango, Tim (22 August 2014). "Top Qaeda Leaders in Iraq Reported Killed in Raid". The New York Times.
- ^ Shanker, Thom (4 June 2010). "Qaeda Leaders in Iraq Neutralized, US Says". The New York Times.
- ^ "US says 80% of al-Qaeda leaders in Iraq removed". BBC News. 4 June 2010.
- ^ "Attacks in Iraq down, Al-Qaeda arrests up: US general". Google News. Agence France-Presse. 4 June 2010. Archived from the original on 9 January 2015.
{{cite news}}:|archive-date=/|archive-url=timestamp mismatch; 25 February 2014 suggested (help) - ^ Shadid, Anthony (16 May 2010). "Iraqi Insurgent Group Names New Leaders". The New York Times. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ "Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi: Islamic State's driving force". BBC World News. 31 July 2014. Retrieved 19 August 2014.
- ^ Sly, Liz (5 April 2015). "How Saddam Hussein's former military officers and spies are controlling Isis". Independent. United Kingdrom. Retrieved 21 April 2015.
But American officials didn't anticipate that they would become not only adjuncts to al-Qaeda, but core members of the jihadist group.
They were instrumental in the group's rebirth from the defeats inflicted on insurgents by the US military, which is now back in Iraq bombing many of the same men it had already fought twice before.
Sly, Liz (4 April 2015). "The hidden hand behind the Islamic State militants? Saddam Hussein's". The Washington Post. United States. Retrieved 21 April 2015. - ^ "U.S. Actions in Iraq Fueled Rise of a Rebel". The New York Times. 10 August 2014. Retrieved 28 August 2014.
- ^ a b c Hubbard, Ben; Schmitt, Eric (27 August 2014). "Military Skill and Terrorist Technique Fuel Success of ISIS". The New York Times. Retrieved 28 August 2014.
- ^ Smith, Samuel (21 April 2015). "ISIS' Rise in Iraq Masterminded by Former Saddam Hussein Intelligence Officer, Recently Published Caliphate 'Blueprint' Documents Reveal". The Christian Post. Retrieved 21 April 2015.
"Former Saddam Hussein spy masterminded the rise of Isis, says report". The Guardian. United Kingdom. Reuters. 20 April 2015. Retrieved 21 April 2015.
Bryan Suits (19 April 2015). "Dark Secret Place 04/18". KFI (Podcast). iHeartRadio. Event occurs at 8:50. Retrieved 21 April 2015.
Dettmer, Jamie; Siegel, Jacob (21 April 2015). "What Saddam Gave ISIS". The Daily Beast. United States. Retrieved 21 April 2015.
Reuter, Christoph (18 April 2015). "The Terror Strategist: Secret Files Reveal the Structure of Islamic State". Der Spiegel. Germany. Retrieved 21 April 2015. - ^ a b "Al-Qaida: We're returning to old Iraq strongholds". Associated Press. 22 July 2012. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ a b "Al Qaeda in Iraq Resurgent" (PDF). Institute for the Study of War. September 2013. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- ^ Abouzeid, Rania (14 March 2014). "Syria: The story of the conflict". Politico. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ a b Abouzeid, Rania (23 June 2014). "The Jihad Next Door". Politico. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ "Jabhat al-Nusra A Strategic Briefing" (PDF). Quilliam Foundation. 8 January 2013. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ "Qaeda in Iraq confirms Syria's Nusra is part of network". GlobalPost. Agence France-Presse. 9 April 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ "Al-Nusra Commits to al-Qaida, Deny Iraq Branch 'Merger'". Naharnet Agence France-Presse. 10 April 2013. Retrieved 18 May 2013.
- ^ Atassi, Basma (9 June 2013). "Qaeda chief annuls Syrian-Iraqi jihad merger". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 10 June 2013.
- ^ a b "Iraqi al-Qaeda chief rejects Zawahiri orders". Al Jazeera. 15 June 2013. Retrieved 15 June 2013.
- ^ "Al Qaeda says it freed 500 inmates in Iraq jail-break". Reuters. 23 July 2013. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ "Zawahiri disbands main Qaeda faction in Syria". The Daily Star. 8 November 2013. Retrieved 8 November 2013.
- ^ a b c Birke, Sarah (27 December 2013). "How al-Qaeda Changed the Syrian War". New York Review of Books.
- ^ Vladimir Platov (18 January 2014). "Growth of International Terrorist Threat from Syria". New Eastern Outlook. Retrieved 11 June 2014.
- ^ "Chechen-led group swears allegiance to head of Islamic State of Iraq and Sham". The Long War Journal. 27 November 2013. Retrieved 13 July 2014.
- ^ "Syria crisis: Omar Shishani, Chechen jihadist leader". BBC News. 3 December 2013. Retrieved 8 December 2013.
- ^ Cloud, David S.; Abdulrahim, Raja (21 June 2013). "U.S. training Syrian rebels; White House 'stepped up assistance'". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Saad, Hwaida; Gladstone, Rick (4 January 2014). "Qaeda-Linked Insurgents Clash With Other Rebels in Syria, as Schism Grows". The New York Times. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ Casey, Mary Joshua Haber (7 January 2014). "Rebel factions continue fight against ISIL in Northern Syria". Foreign Policy. Retrieved 7 January 2014.
- ^ "ISIS-rebel clashes resume in Deir al-Zor". The Daily Star. 18 June 2014. Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- ^ "Syrian branch of al Qaeda vows loyalty to Iraq's ISIS" France 24. 25 June 2014.
- ^ "Al Nusra pledges allegiance to Isil". Gulf News. 25 June 2014. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- ^ Gaouette, Nicole; Ajrash, Kadhim; Sabah, Zaid (23 June 2014). "Militants Seize Iraq-Jordan Border as Kerry Visits Baghdad". Bloomberg News. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ a b Arango, Tim; Gordon, Michael R. (23 June 2014). "Iraqi Insurgents Secure Control of Border Posts". The New York Times. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ Abuqudairi, Areej (5 July 2014). "Anger boils over in the 'Fallujah of Jordan'". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ a b Carey, Glen; Almashabi, Deema (16 June 2014). "Jihadi Recruitment in Riyadh Revives Saudi Arabia's Greatest Fear". Bloomberg News. Retrieved 17 June 2014.
- ^ a b Solomon, Erika; Kerr, Simeon (3 July 2014). "Saudi Arabia sends 30,000 troops to Iraq border". Financial Times. Retrieved 6 July 2014. (subscription required)
- ^ Lawrence, Jessica. "Iraq crisis: Could an ISIS caliphate ever govern the entire Muslim world?". ABC News (Australia). Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ "What does ISIS' declaration of a caliphate mean?". Al Akhbar English. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ a b Spencer, Richard (3 July 2014). "Saudi Arabia sends 30,000 troops to Iraq border". The Telegraph. London. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ "Syrians adjust to life under ISIS rule". The Daily Star. 29 August 2014. Retrieved 29 August 2014.
- ^ a b c "Senior Abu Sayyaf leader swears oath to ISIS". Rappler.
- ^ a b Philip Oltermann. "Islamists in Philippines threaten to kill German hostages". The Guardian.
- ^ Arango, Tim (3 August 2014). "Sunni Extremists in Iraq Seize 3 Towns From Kurds and Threaten Major Dam". The New York Times. Retrieved 20 August 2014.
- ^ "Statement by the President". The White House. 7 August 2014. Retrieved 18 August 2014.
- ^ "CNN Video - Breaking News Videos from CNN.com". CNN. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ Laura Smith-Spark, Ben Wedeman and Greg Botelho, "Leaders of Iraq's Anbar province call for U.S. ground forces to stop ISIS," CNN, 11 October 2014
- ^ Mary Grace Lucas, "ISIS nearly made it to Baghdad airport, top U.S. military leader says," CNN, 13 October 2014
- ^ "Libyan city declares itself part of Islamic State caliphate". CP24.
- ^ "AP sources: IS, al-Qaeda reach accord in Syria". 13 November 2014. Retrieved 13 November 2014.
- ^ Master. "Negotiations failed between the IS, Jabhat al-Nusra and Islamic battalions". Syrian Observatory For Human Rights.
- ^ a b c "Egypt jihadists vow loyalty to IS as Iraq probes leader's fate". Agence France-Presse. 10 November 2014.
- ^ Report: Water and Violence Link: http://strategicforesight.com/publication_pdf/63948150123-web.pdf
- ^ a b c d e "ISIS gaining ground in Yemen, competing with al Qaeda". CNN. 21 January 2015. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ^ a b "Officials confirm ISIL present in Afghanistan". Al Jazeera.
- ^ "ISIS Reportedly Kills Afghan Taliban Commander; Modi to Visit China; Pakistan Tests Cruise Missile". Foreign Policy. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ a b "ISIS active in south Afghanistan, officials confirm for first time". CBS News. 12 January 2015. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ a b c "Afghanistan drone strike 'kills IS commander Abdul Rauf'". BBC News. 9 February 2015. Retrieved 24 February 2015.
- ^ sohranas. "EXCLUSIVE: 'It is not the end of fighting in Kobani' – expert fears IS could return". Syrian Observatory For Human Rights.
- ^ Mike Giglio, Munzer al-Awad. "ISIS Operative: This Is How We Send Jihadis To Europe". BuzzFeed.
- ^ David Von Drehle (26 February 2015). "What Comes After the War on ISIS". Time.
- ^ "Egypt bombs Islamic State targets in Libya after 21 Egyptians beheaded". Reuters. 16 February 2015. Retrieved 16 February 2015.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ "Boko Haram swears formal allegiance to ISIS". Associated Press. Fox News Channel. 8 March 2015.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ a b "Jonathan tasks Defence, Foreign Ministers of Nigeria, Chad, Cameroon, Niger, Benin on Boko Haram's defeat". sunnewsonline.com.
- ^ "Uzbek militants in Afghanistan pledge allegiance to ISIS in beheading video". khaama.com.
- ^ "IMU Pledges Allegiance to Islamic State". EurasiaNet. 1 August 2015.
- ^ "Ansar al Sharia Libya relaunches social media sites". Long War Journal. 9 April 2015. Retrieved 10 April 2015.
- ^ Daragahi, Borzou (12 March 2015). "Iraqi forces advance further into Tikrit". Financial Times.
- ^ "More than 10,000 jihadists killed since coalition raids: US". Yahoo News Singapore. 3 June 2015. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ^ Zack Beauchamp (2 September 2014). "17 things about ISIS and Iraq you need to know". Vox. Retrieved 5 September 2014.
- ^ Abu Mohammad. "Letter dated 9 July 2005" (PDF). Office of the Director of National Intelligence. Retrieved 22 July 2014. See page 2 onwards.
- ^ a b c Johnson, M. Alex (3 September 2014). "'Deviant and Pathological': What Do ISIS Extremists Really Want?". NBC News. Retrieved 5 September 2014.
- ^ Laith Kubba (7 July 2014). "Who is the U.S. targeting in Iraq air strikes?". Al Jazeera.
- ^ a b c d Joscelyn, Thomas (29 September 2015). "US counterterrorism efforts in Syria: A winning strategy?". Long War Journal. Cite error: The named reference "Joscelyn" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Withnall, Adam (21 December 2014). "Middle East. Inside Isis: The first Western journalist ever to be given access to the 'Islamic State' has just returned – and this is what he discovered". The Independent. Retrieved 3 October 2015.
- ^ Greyvenstein, Hester Maria (15 January 2015). "Q&A: German journalist on surviving ISIL". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 4 October 2015.
Something that I don't understand at all is the enthusiasm in their plan of religious cleansing, planning to kill the non-believers... They also will kill Muslim democrats because they believe that non-ISIL-Muslims put the laws of human beings above the commandments of God. These were very difficult discussions, especially when they were talking about the number of people who they are willing to kill. They were talking about hundreds of millions. They were enthusiastic about it, and I just cannot understand that.
- ^ a b Tim Fernholz. "Don't believe the people telling you to freak out over this "ISIL" map". Quartz.
- ^ "ISIS' Five Year Expansion Map Is Fake - Business Insider". Business Insider. 1 July 2014.
- ^ "That ISIS Five Year Expansion Plan Map Is Fake". Business Insider.
- ^ "ISIS' five-year expansion plan map branded a fake". Al Arabiya. 2 July 2014. Retrieved 13 October 2015.
- ^ Mark Strauss. "That ISIS 'Caliphate Map' Is Bogus, So Stop Freaking Out". io9.
- ^ Josh Kilburn. "Seriously, NBC? Station Posts 'Terrifying ISIS Expansion Map' Created By Neofascists on Twitter". Americans Against the Tea Party.
- ^ Caitlin Dewey (3 July 2014). "What was fake on the Internet this week: Glee, 'bubbling' and a modeling contract for 'hot felon' Jeremy Meeks". The Washington Post.
- ^ Tran, Mark; Weaver, Matthew (30 June 2014). "Isis announces Islamic caliphate in area straddling Iraq and Syria". The Guardian. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ McGrath, Timothy (2 July 2014). "Watch this English-speaking ISIS fighter explain how a 98-year-old colonial map created today's conflict". Los Angeles Times. GlobalPost. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ Romain Caillet (27 December 2013). "The Islamic State: Leaving al-Qaeda Behind". Carnegie Endowment for International Peace.
- ^ a b Hassan, Hassan (25 January 2015). "The secret world of Isis training camps – ruled by sacred texts and the sword". Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- ^ Bradley, Matt (1 February 2015). "Islamic State Affiliate Takes Root Amid Libya's Chaos". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- ^ What the ISIS Flag Says About the Militant Group, Time.com article by Ilene Prusher, 9 September 2014
- ^ Endtimes Brewing Huffington Post (UK) article by Anne Speckhard, 29 August 2014
- ^ Hussain, Ghaffar (30 June 2014). "Iraq crisis: What does the Isis caliphate mean for global jihadism?". The Independent. London. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ a b "The other beheaders". The Economist. 20 September 2014. Retrieved 7 November 2014.
- ^ al-Ibrahim, Fouad (22 August 2014). "Why ISIS is a threat to Saudi Arabia: Wahhabism's deferred promise". Al Akhbar (Lebanon). Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ Mamouri, Ali (29 July 2014). "Why Islamic State has no sympathy for Hamas". Al-Monitor. Retrieved 1 August 2014.
- ^ a b c Wood, Graeme (15 February 2015). "What ISIS Really Wants". The Atlantic. The Atlantic Monthly Group. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ McCants, William (2015). The ISIS Apocalypse: The History, Strategy, and Doomsday Vision of the Islamic State. New York: St. Martin's Press. p. 147. ISBN 978-1-250-08090-5.
- ^ a b c Charles C. Caris; Samuel Reynolds (July 2014). "ISIS Governance in Syria" (PDF). Institute for the Study of War.
- ^ a b c "Islamic State moves in on al-Qaeda turf". 30 January 2015. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- ^ Harleen GambHir (18 February 2015). ISIS Global Intelligence Summary January 7 – February 18, 2015 (PDF) (Report). Institute for the Study of War.
- ^ Schmitt, Eric; Kirkpatrick, David D. (14 February 2015). "Islamic State Sprouting Limbs Beyond Its Base". The New York Times. Retrieved 23 February 2015.
- ^ a b SPIEGEL ONLINE, Hamburg, Germany (18 November 2014). "Islamic State Expanding into North Africa". Der Spiegel. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "ISIS comes to Libya". CNN. 18 November 2014. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- ^ Ulf Laessing (21 May 2015). "Gaddafi's home town falls to Islamic State in anarchic Libya". Reuters. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- ^ Hassan Morajea (6 June 2015). "Libyan gains may offer ISIS a base for new attacks". The Washington Post. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- ^ "Middle East updates / ISIS kills 14 Libyan soldiers, official government says". Haaretz. 3 January 2015. Retrieved 29 January 2015.
- ^ "ISIS Fighters Kill 14 Soldiers in Southern Libya". News From Antiwar.com. Retrieved 29 January 2015.
- ^ "A Victory Over the Islamic State in Libya". Foreign Policy. Retrieved 4 July 2015.
- ^ Ryan, Yasmine (16 March 2015). "Isis in Libya: Muammar Gaddafi's soldiers are back in the country and fighting under the black flag of the 'Islamic State'". The Independent. London. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- ^ "Libya Islamist militia attacks Daesh in Sirte". Anadolu Agency. 14 March 2015. Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- ^ "Islamic State fighters and force allied with Tripoli clash in central Libya". Reuters. 14 March 2015. Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- ^ "Fighting between GNC-Libyan Dawn's Sunrise and IS forces – deaths and injuries reported". Libya Herald. 14 March 2015. Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- ^ "Isis militants are being 'smuggled to Europe in migrant boats', Libyan government adviser". The Independent. 17 May 2015.
- ^ "11,000 migrants land in Italy in a week, ISIS had warned of sending over 500,000". The Independent. 17 April 2015.
- ^ "Egyptian militant group pledges loyalty to Islamic State in audio clip". Reuters. 10 November 2014. Retrieved 11 November 2014.
- ^ "Sinai-based jihadist group rebranded as Islamic State's official arm". Long War Journal. 14 November 2014. Retrieved 15 November 2014.
- ^ "The Islamic State's Archipelago of Provinces". Washington Institute for Near East Policy. 14 November 2014. Retrieved 15 November 2014.
- ^ "Interior Ministry analyzes Ansar Bayt al-Maqdis statement over assassination attempt". State Information Services. 10 September 2013. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ "IS claims responsibility for Gaza's French Cultural Centre blast, reports". Middle East Eye. 8 October 2014. Retrieved 9 October 2014.
- ^ "Egypt's grim summer: Islamic State affiliate claims latest bombing". Los Angeles Times. 20 August 2015.
- ^ "Russian plane crash: U.S. intel suggests ISIS bomb brought down jet". CNN. 5 November 2015.
- ^ a b c Fadel, Leila (18 November 2014). "With Cash And Cachet, The Islamic State Expands Its Empire". NPR.
- ^ "'Wilayat Khurasan': Islamic State Consolidates Position in AfPak Region". Jamestown Foundation. 3 April 2015. Retrieved 13 April 2015.
- ^ "Pakistani Taliban emir for Bajaur joins Islamic State". longwarjournal.org.
- ^ Al-Masdar News. "Afghan Army Kills Commander of ISIL Affiliate". Al-Masdar News.
- ^ "Officials: Top Islamic State leader killed in Afghanistan strike". The Washington Post. 11 July 2015.
- ^ "Islamic State audio tape raises doubt whether Afghan leader dead". Reuters. 13 July 2015. Retrieved 13 July 2015 – via Yahoo! News.
Islamic State on Monday released an audio tape it said was of the movement's leader for Afghanistan, raising doubts over whether he was killed in a U.S. drone strike on Friday
- ^ "Treasury Sanctions Major Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant Leaders, Financial Figures, Facilitators, and Supporters". treasury.gov. 29 September 2015. Retrieved 29 September 2015.
- ^ "Yemeni Al-Qaeda leader hails ISIS gains in Iraq". Al Arabiya. 13 August 2014.
- ^ "Al-Qaeda Supporters in Yemen ‘Pledge Allegiance to Islamic State’". Newsweek. 11 February 2015.
- ^ "Gale Cengage Product Failure". galegroup.com.
- ^ a b "ISIS Global Intelligence Summary March 1 – May 7, 2015" (PDF). Institute for the Study of War. 10 May 2015. Retrieved 12 May 2015.
- ^ "Islamic State bomb attack on Houthi rebel leaders in Yemen leaves 28 dead". The Guardian. 30 June 2015.
- ^ Louisa Loveluck (30 June 2015). "Islamic State targets Houthi mourners in Yemen with car bomb". The Daily Telegraph. London.
- ^ "US steps up arms for Saudi campaign in Yemen". Al Jazeera. 8 April 2015.
- ^ Mark Perry. US generals: Saudi intervention in Yemen ‘a bad idea’, Al Jazeera. 17 April 2015.
- ^ "Jihadis likely winners of Saudi Arabia's futile war on Yemen's Houthi rebels". The Guardian. 7 July 2015.
- ^ "Nigeria's Boko Haram pledges allegiance to Islamic State". BBC News. 7 March 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ Adam Chandler (9 March 2015). "The Islamic State of Boko Haram? :The terrorist group has pledged its allegiance to ISIS. But what does that really mean?". The Atlantic.
- ^ Caucasus Emirate and Islamic State Split Slows Militant Activities in North Caucasus, Eurasia Daily Monitor Volume: 12 Issue: 29. 13 February 2015 [1]
- ^ Taylor Luck (23 July 2014). "Local jihadist group pledges allegiance to Islamic State". The Jordan Times. Amman: Jordan Press Foundation. Archived from the original on 24 July 2014. Retrieved 6 June 2015.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "The Islamic State" (PDF). Soufan Group. November 2014. Retrieved 23 April 2015.
- ^ "ISIS Replace Injured Leader Baghdadi With Former Physics Teacher". Newsweek. 22 April 2015. Retrieved 7 May 2015.
- ^ a b c d Ruthven, Malise. "Inside the Islamic State. Review of Islamic State: The Digital Caliphate by Abdel Bari Atwan". New York Review of Books (9 July 2015).
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ Thompson, Nick; Shubert, Attika (18 September 2014). "The anatomy of ISIS: How the 'Islamic State' is run, from oil to beheadings". CNN. Retrieved 21 September 2014.
- ^ Sly, Liz (5 April 2015). "How Saddam Hussein's former military officers and spies are controlling Isis". The Independent. London. Retrieved 5 April 2015.
- ^ "Foreign Recruits Are Islamic State's Cannon Fodder". February 2015. Retrieved February 2015.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Iraqis, Saudis call shots in Raqa, ISIL's Syrian 'capital'". June 2014. Retrieved February 2015.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ Abi-Habib, Maria (9 March 2015). "Splits in Islamic State Emerge as Its Ranks Expand". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 11 April 2015.
- ^ Trofimov, Yaroslav (4 February 2015). "In Islamic State Stronghold of Raqqa, Foreign Fighters Dominate". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 11 April 2015.
- ^ "The Islamic State: How Its Leadership Is Organized". YouTube.
- ^ Ben Hubbard (24 July 2014). "Life in a Jihadist Capital: Order With a Darker Side". The New York Times. Retrieved 5 September 2014.
- ^ a b Zelin, Aaron Y. (13 June 2014). "The Islamic State of Iraq and Syria Has a Consumer Protection Office". The Atlantic. Retrieved 17 June 2014.
- ^ Gardner, Frank (9 July 2014). "'Jihadistan': Can Isis militants rule seized territory?". BBC News. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Flick, Maggie (30 September 2014). "Special Report: Islamic State uses grain to tighten grip in Iraq". Reuters.
- ^ "Isis to mint own Islamic dinar coins in gold, silver and copper", The Guardian, 21 November 2014.
- ^ a b "Islamic State reportedly buying silver, gold as it prepares to issue currency". McClatchy. 20 November 2014. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
- ^ Ensor, Josie (14 November 2014). "Islamic State announces its own currency". The Telegraph. London. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
- ^ "'ISIS made me clean the toilets... and my iPod didn't work': How disenchanted Islamic fanatics are returning home because jihad isn't as glamorous as they hoped". Daily Mail. London. 1 December 2014. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ^ Saul, Heather (31 October 2014). "Isis now targeting women with guides on how to be the 'ultimate wives of jihad'". The Independent. London. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ^ "Al-Qaida Sanctions List". United Nations. Archived from the original on 25 September 2014. Retrieved 2 October 2014.
- ^ United Nations Web Services Section. "The Al-Qaida and Taliban Sanctions Committee – 1267". United Nations.
- ^ "Security Council Al-Qaida Sanctions Committee Amends Entry". Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ^ a b Wahlisch, Martin (2010). "EU Terrorist Listing – An Overview about Listing and Delisting Procedures" (PDF). Berghof Foundation. Retrieved 3 November 2014.
- ^ "Proscribed Terrorist Organisations, pp.13–15" (PDF). Home Office. 20 June 2014. Retrieved 7 November 2014.
- ^ "Foreign Terrorist Organizations". Bureau of Counterterrorism. United States Department of State. Retrieved 28 July 2014.
- ^ "Listed terrorist organisations". Australian National Security. Retrieved 31 July 2014.
- ^ "Currently listed entities". Public Safety Canada. Retrieved 31 July 2014.
- ^ Kaplan, Hilal (3 September 2014). "Charging Turkey for ISIS". Daily Sabah. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ Mahcupyan, Etyen (20 September 2014). "ISIS, Turkey and the US". Daily Sabah. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ "Saudi Arabia designates Muslim Brotherhood terrorist group". Reuters. 7 March 2014. Retrieved 31 July 2014.
- ^ a b "BNPT Declares ISIS a Terrorist Organization". Tempo. 2 August 2014. Retrieved 4 August 2014.
- ^ "List of terror groups published by United Arab Emirates". Archived from the original on 28 January 2015.
- ^ "Malaysia designates ISIS as terrorist group, vows tough action: Report". The Straits Times. 25 September 2014. Retrieved 25 September 2014.
- ^ "Court affirms ISIS' 'terrorist group' designation". Daily News Egypt.
- ^ "Egypt brands jihadist ISIL a 'terrorist group'". Hürriyet Daily News. 30 November 2014.
- ^ "Banned Organisations". Retrieved 16 December 2014.
- ^ "India bans IS". The Hindu. Chennai, India. Press Trust of India. 16 December 2014. Retrieved 16 December 2014.
- ^ "Russia calls on all states to put Islamic State, Jabhat al-Nusra on terrorist lists". Russian News Agency "TASS". Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ Paraszczuk, Joanna. "Kyrgyzstan Bans IS, Designates It As Terror Group". rferl.com. Radio Free Europe Radio Liberty. Retrieved 26 March 2015.
- ^ Manal. "Syria condemns terrorist acts in Iraq, expresses solidarity with Iraqi government, army and people". Syrian Arab News Agency.
- ^ "Jordan launches airstrikes against ISIS". News.com.au. 6 February 2015. Retrieved 7 August 2015.
- ^ a b Gishkori, Zahid. "Islamic State listed among proscribed outfits". The Express Tribune.
- ^ "Resolution 1267 (1999) Adopted by the Security Council at its 4051st meeting on 15 October 1999". UNHCR.
- ^ Janette Roberts. "ISIL banned in Germany". Sixth Sense.
- ^ Anadolu Ajansı (c) 2011. "Switzerland bans ISIL".
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "India Bans ISIS After Government Raises Concerns Over Group's Online Presence". International Business Times. 16 December 2014.
- ^ a b c McCoy, Terrence (13 June 2013). "ISIL, beheadings and the success of horrifying violence". The Washington Post. Retrieved 23 June 2014.
- ^ a b Lister, Tim (13 June 2014). "ISIS: The first terror group to build an Islamic state?". CNN. Retrieved 14 June 2014.
- ^ a b c d Roula Khalaf and Sam Jones (17 June 2014). "Selling terror: how Isis details its brutality". Financial Times. Retrieved 18 June 2014.
- ^ "UN 'may include' Isis on Syrian war crimes list". BBC News. 26 July 2014
- ^ "Video shows Islamic State executes scores of Syrian soldiers". Reuters. 28 August 2014.
- ^ Staff writer, "ISIS accused of crimes against humanity," Al Arabiya, 14 November 2014
- ^ Nina Larson, "UN probe: ISIS committing 'crimes against humanity' in Syria," The Daily Star, 14 November 2014
- ^ "Libya: Extremists Terrorizing Derna Residents". Human Rights Watch. Retrieved 28 November 2014.
- ^ "Rule of Terror: Living under ISIS in Syria" (PDF). United Nations Commission on Human Rights. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 February 2015. Retrieved 29 November 2014.
- ^ a b Bulos, Nabih (20 June 2014). "Islamic State of Iraq and Syria aims to recruit Westerners with video". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ a b Zarocostas, John (8 July 2014). "U.N.: Islamic State executed imam of mosque where Baghdadi preached". McClatchyDC. Retrieved 10 October 2014.
- ^ Abi-Habib, Maria (26 June 2014). "Iraq's Christian Minority Feels Militant Threat". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 6 July 2014 – via Google.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|subscription=ignored (|url-access=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Turkey's Arab Alawites stand at a crossroads". The National. 6 December 2014.
- ^ a b c "ISIS reportedly massacres dozens in Syrian village". CBS News. 31 March 2015.
- ^ a b Sherlock, Ruth (11 August 2013). "Syrian rebels accused of sectarian murders". The Daily Telegraph. London.
Hundreds of Alawite civilians have been killed, kidnapped or have disappeared during a rebel offensive on President Bashar al-Assad's heartland province of Latakia, local residents have reported.
- ^ "Syria: Executions, Hostage Taking by Rebels". Human Rights Watch. 10 October 2013.
- ^ "Iraq crisis: Islamic State accused of ethnic cleansing". BBC News. 2 September 2014. Retrieved 25 September 2014.
- ^ "DOCUMENT – IRAQ: ETHNIC CLEANSING ON HISTORIC SCALE: THE ISLAMIC STATE'S SYSTEMATIC TARGETING OF MINORITIES IN NORTHERN IRAQ". Amnesty International. September 2014. Archived from the original on 12 September 2014. Retrieved 19 October 2014.
- ^ a b Report on the Protection of Civilians in Armed Conflict in Iraq: 6 July – 10 September 2014 (PDF). ohchr.org (Report). Human Rights Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights and United Nations Assistance Mission for Iraq.
- ^ a b "UN: ISIS Massacred 700 Turkmen—Including Women, Children, Elderly". CNS News. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ a b "UN confirms 5,000 Yazidis men were executed and 7,000 women are now sex slaves". Daily Mail. London. 14 October 2014. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ LUCAS, RYAN (4 November 2014). "ISIS Tortured Kurdish Children Captured in Kobani: Group". The Huffington Post. Associated Press. Retrieved 4 November 2014.
- ^ "Islamic State group 'executes 700' in Syria". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ Liz Sly (20 October 2014). "Syria tribal revolt against Islamic State ignored, fueling resentment". The Washington Post. Retrieved 7 November 2014.
- ^ Van, FERNANDE (7 August 2014). "Isis takes Iraq's largest Christian town as residents told – 'leave, convert or die'". The Independent. London. Beirut. Retrieved 5 January 2015.
- ^ Jadallah, Ahmed (18 July 2014). "Convert, pay tax, or die, Islamic State warns Christians". Reuters. Retrieved 5 January 2015.
- ^ "Convert, pay tax, or die, Islamic State warns Christians". The Guardian. Reuters. 18 July 2014. Retrieved 27 July 2014.
- ^ Abedine, Saad; Mullen, Jethro (28 February 2014). "Islamists in Syrian city offer Christians safety – at a heavy price". CNN. Retrieved 27 July 2014.
- ^ Hubbard, Ben (23 July 2014). "Life in a Jihadist Capital: Order With a Darker Side". The New York Times. Retrieved 27 July 2014.
- ^ Suleiman Al-Khalidi; Oliver Holmes (23 February 2015). Tom Heneghan (ed.). "Islamic State in Syria abducts at least 150 Christians". Reuters. Retrieved 23 February 2015.
- ^ "Islamic State 'abducts dozens of Christians in Syria'". BBC. 23 February 2015. Retrieved 23 February 2015.
- ^ "Rudaw Mobile". Rudaw. Retrieved 25 June 2015.
- ^ "ISIL Militants Killed More Than 1000 Civilians in Recent Onslaught in recent Onslaught in Iraq: UN". RT News. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
- ^ "Iraq violence: UN confirms more than 2000 killed, injured since early June". UN News Centre. 24 June 2014. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
- ^ "UN warns of war crimes as ISIL allegedly executes 1,700". Today's Zaman. 15 June 2014. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
- ^ Spencer, Richard (16 June 2014). "Iraq crisis: UN condemns 'war crimes' as another town falls to Isis". The Telegraph. London. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ "Syria: ISIS Summarily Killed Civilians". Human Rights Watch. 14 June 2014. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- ^ "Syria conflict: Amnesty says ISIS killed seven children in north". BBC News. 6 June 2014. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- ^ "NGO: ISIS kills 102-year-old man, family in Syria". Al Arabiya. Retrieved 7 July 2014.
- ^ Holmes, Oliver (28 December 2014). "Islamic State executed nearly 2,000 people in six months: monitor". Reuters.
- ^ Bacchi, Umberto. "ISIS Medieval School Curriculum: No Music, Art and Literature for Mosul Kids". International Business Times.
- ^ Spencer, Richard (16 September 2014). "Islamic State issues new school curriculum in Iraq". The Telegraph. London.
- ^ "ISIS eradicates art, history and music from curriculum in Iraq". CBS News. 15 September 2014.
- ^ Zaid Sabah; Khalid Al-Ansary (17 September 2014). "Mosul Schools Go Back in Time With Islamic State Curriculum". Bloomberg News.
- ^ Catherine Philp (17 September 2014). "Parents boycott militants' curriculum". The Times.
- ^ "Islamic State says women in Mosul must wear full veil or be punished". The Irish Times. 26 July 2014. Retrieved 23 August 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ McElroy, Damien (23 July 2014). "Islamic State tells Mosul shopkeepers to cover up naked mannequins". The Telegraph. London.
- ^ "ISIS Is Actively Recruiting Female Fighters To Brutalize Other Women". Business Insider.
- ^ Taylor, Adam (12 June 2014). "The rules in ISIS' new state: Amputations for stealing and women to stay indoors". The Washington Post. Retrieved 2 August 2014.
- ^ "ISIS bans music, imposes veil in Raqqa". Al-Monitor. 20 January 2014. Retrieved 13 September 2014.
- ^ "IS beheads two civilian women in Syria: monitor". Yahoo News. 30 June 2015.
- ^ Saul, Heather (22 January 2015). "Isis publishes penal code listing amputation, crucifixion and stoning as punishments – and vows to vigilantly enforce it". independent.co.uk. London. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ^ Withnall, Adam (18 January 2015). "Isis throws 'gay' men off tower, stones woman accused of adultery and crucifies 17 young men in 'retaliatory' wave of executions". independent.co.uk. London. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ^ Rush, James (3 February 2015). "Images emerge of 'gay' man 'thrown from building by Isis militants before he is stoned to death after surviving fall'". independent.co.uk. London. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ^ Daragahi, Borzou (25 February 2015). "Isis brutality in Iraq reawakens Sunni resistance". ft.com. Retrieved 25 February 2014.
- ^ Brannan, Kate. "Children of the Caliphate". foreignpolicy.com/. Foreign Policy Magazine. Retrieved 30 November 2014.
- ^ Peritz, Aki; Maller, Tara (16 September 2014). "The Islamic State of Sexual Violence". foreignpolicy.com. Retrieved 14 August 2015.
- ^ Saul, Heather (18 February 2015). "Isis Raqqa wives subjected to 'brutal' sexual assaults after marrying militants". independent.co.uk. London. Retrieved 14 August 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f Callimachi, Rukmini (13 August 2015). "ISIS Enshrines a Theology of Rape". nytimes.com. Retrieved 14 August 2015.
- ^ Wood, Paul (22 December 2014). "Islamic State: Yazidi women tell of sex-slavery trauma". BBC News. Retrieved 4 January 2015.
- ^ a b Nebehay, Stephanie (2 October 2014). "Islamic State committing 'staggering' crimes in Iraq: U.N. report". Reuters. Retrieved 2 October 2014.
- ^ "Det jag har bevittnat i al-Raqqa kommer alltid förfölja mig (What I have witnessed in al-Raqqa will always haunt me)". Nyheter Världen (in Swedish). 23 September 2014. Retrieved 25 September 2014.
- ^ Brekke, Kira (8 September 2014). "ISIS Is Attacking Women, And Nobody Is Talking About It". The Huffington Post. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ^ "Surging Violence Against Women in Iraq". Inter Press Service. 27 June 2014. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- ^ Winterton, Clare (25 June 2014). "Why We Must Act When Women in Iraq Document Rape". The Huffington Post. Retrieved 10 July 2014.
- ^ Giglio, Mike (27 June 2014). "Fear of Sexual Violence Simmers in Iraq As ISIL Advances". BuzzFeed. Retrieved 9 July 2014.
- ^ Williams, Martin (25 September 2013). "Sexual jihad is a bit much". The Citizen. Retrieved 7 July 2014.
- ^ Watson, Ivan (30 October 2014). "'Treated like cattle': Yazidi women sold, raped, enslaved by ISIS". CNN. Retrieved 14 August 2015.
- ^ Yoon, Sangwoon (4 August 2015). "Islamic State Circulates Sex Slave Price List". BloombergBusines. Archived from the original on 7 August 2015.
- ^ Jürgen Todenhöfer (2015). Inside IS- 10 Tage im <Islamischen Staat>. Munich, Germany: C. Bertelsmann Verlag.
- ^ Spencer, Richard (14 October 2014). "Isil carried out massacres and mass sexual enslavement of Yazidis, UN confirms". The Telegraph. London. Retrieved 3 November 2014.
- ^ Kirk Semple, "Yazidi Girls Seized by ISIS Speak Out After Escape," The New York Times, 14 November 2014
- ^ "ISIS Just Executed More Than 150 Women in Fallujah". Business Insider. NOW News. 17 December 2014.
- ^ Chastain, Mary (17 December 2014). "ISIS Slaughters 150 Females in Iraq for Refusing to Marry, Have Sex with Them". Breitbart News.
- ^ a b Siddiqui, Mona (24 August 2014). "Isis: a contrived ideology justifying barbarism and sexual control". The Observer. Retrieved 1 January 2015.
- ^ Rukmini Callimachi, "Death of Kayla Mueller, ISIS Hostage, Confirmed by Family and White House,", New York Times, 10 February 2015
- ^ "U.S. believes hostage was given to ISIS fighter as bride". CBS News. 11 February 2015. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- ^ JAMES GORDON MEEK and RHONDA SCHWARTZ, "Officials: Kayla Mueller May Have Been Given to ISIS Commander," ABC News, 10 February 2015
- ^ Meg Wagner and Corky Siemaszko, "Kayla Jean Mueller, American aid worker held hostage, may have been forced to marry ISIS leader: report," Daily News|location=New York, 10 February 2015
- ^ "Islamic State Leader Raped American Hostage, US Finds", The New York Times, 14 August 2015.
- ^ Neurink, Judit (14 August 2015). "Isis leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi repeatedly raped US hostage Kayla Mueller and turned Yazidi girls into personal sex slaves". independent.co.uk. London. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- ^ "Islamic State leader reportedly raped American hostage", Fox News Channel, 14 August 2015.
- ^ "ISIS leader repeatedly raped American hostage, U.S. finds", CBS News, 14 August 2015.
- ^ BBC News: "Islamic State leader Baghdadi 'raped' Kayla Mueller", BBC, 14 August 2015.
- ^ Ken Dilanian. "Islamic State Leader Raped American Hostage, US Finds", ABC News, 14 August 2015.
- ^ a b c Goldman, Adam; Miller, Greg (14 August 2015). "Leader of Islamic State took American hostage as sexual slave". The Washington Post.
- ^ "'ISIS leader al-Baghdadi repeatedly raped US hostage Mueller before her death' ... We were told Kayla was tortured, that she was the property of al-Baghdadi," Mueller's parents, Carl and Marsha Mueller, told ABC News", The Jerusalem Post, 14 August 2015.
- ^ James Gordon Meek (14 August 2015). "ISIS Leader Abu Bakr Al-Baghdadi Sexually Abused American Hostage Kayla Mueller, Officials Say". Washington DC: ABC News. Retrieved 14 August 2015.
The information about al-Baghdadi's extraordinary direct role in the captivity and physical abuse of Kayla Mueller was drawn from, among many sources, the U.S. debriefings of at least least two Yezedi teenage girls, ages 16 and 18, held as sex slaves in the Sayyaf compound as well as from the interrogation of Abu Sayyaf's wife Umm Sayyaf, who was captured in the U.S. raid, the officials told ABC News.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Abdelaziz, Salma (13 October 2014). "ISIS states its justification for the enslavement of women". CNN. Retrieved 1 January 2015.
- ^ Spencer, Richard (13 October 2014). "Thousands of Yazidi women sold as sex slaves 'for theological reasons', says Isil". The Telegraph. London. Retrieved 3 November 2014.
- ^ "Slavery in Islam: To have and to hold". The Economist. 18 October 2014.
- ^ Nour Malas, "Ancient Prophecies Motivate Islamic State Militants: Battlefield Strategies Driven by 1,400-year-old Apocalyptic Ideas," The Wall Street Journal, 18 November 2014 (accessed 22 November 2014)
- ^ a b Sypher, Ford (28 August 2014). "Rape and Sexual Slavery Inside an ISIS Prison". The Daily Beast. Horror. Retrieved 5 January 2015.
- ^ a b c d Kumar, Anugrah (13 October 2014). "ISIS Claims Islam Justifies Making 'Infidel' Women Sex Slaves". The Christian Post. CHRISTIAN POST CONTRIBUTOR. Retrieved 1 January 2015.
- ^ a b "ISIL seeks to justify enslaving Yazidi women and girls in Iraq". Today's Zaman. abril. 14 October 2014. Retrieved 2 January 2014.
- ^ a b Amelia Smith, "ISIS Publish Pamphlet On How to Treat Female Slaves," Newsweek, 12 September 2014
- ^ a b Abul Taher (13 December 2014). "Our faith condones raping underage slaves: ISIS publishes shocking guidebook telling fighters how to buy, sell and abuse captured women". Daily Mail. London.
- ^ a b Adam Withnall, "Isis releases 'abhorrent' sex slaves pamphlet with 27 tips for militants on taking, punishing and raping female captives," The Independent, 10 December 2014
- ^ Carey Lodge, "Islamic State issues abhorrent sex slavery guidelines about how to treat women,",Christianity Today, 15 December 2014
- ^ Greg Botelho, "ISIS: Enslaving, having sex with 'unbelieving' women, girls is OK," CNN, 13 December 2014
- ^ a b c d "Open Letter to Al-Baghdadi". September 2014. Retrieved 25 September 2014.
- ^ a b Lauren Markoe (24 September 2013). "Muslim Scholars Release Open Letter to Islamic State Meticulously Blasting Its Ideology". The Huffington Post. Religious News Service. Retrieved 25 September 2014.
- ^ Saul, Heather (10 April 2015). "Yazidi sex slaves 'gang-raped in public' by Isis fighters, harrowing accounts reveal". The Independent. London. Retrieved 11 April 2015.
- ^ Saul, Heather (21 February 2015). "Isis infighting: Tensions rise over use of Yazidi sex slaves, loss of Kobani and poor services in areas controlled by group". The Independent. London. Retrieved 11 April 2015.
- ^ "aboutcpj". Committee to Protect Journalists.
- ^ Al Fares, Zaid (5 September 2014). "The Forgotten Isis Beheadings: The World Mourns Steven Sotloff, but who Remembers Bassam al-Rayes?". International Business Times UK. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ^ Kestler-D'Amours, Jillian (6 October 2014). "Syria journalists 'on the margins of history'". aljzeera.com. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ^ a b "Areas controlled by Islamic State are news 'black holes' – Reporters Without Borders".
- ^ Agencies. "ISIL 'publicly executes Iraqi journalist'".
- ^ Callimachi, Rukmini (25 October 2014). "ISIS Hostages Endured Torture and Dashed Hopes, Freed Cellmates Say". The New York Times.
- ^ KAREN YOURISH (25 October 2014). "The Fates of 23 ISIS Hostages in Syria". The New York Times.
- ^ Johnston, Chris. "Islamic State suspected of cyber-attack on Raqqa opponents". theguardian.com. Retrieved 28 December 2014.
- ^ "Libya's ISIS branch claims execution of two Tunisian journalists". Al Akhbar English.
- ^ McCurry, Justin (31 January 2015). "Isis video purports to show beheading of Japanese hostage Kenji Goto". The Guardian. Retrieved 1 July 2015.
- ^ "A Short History Of ISIS Propaganda Videos". The Huffington Post. 11 March 2015.
- ^ "FBI – Help Identify Individuals Traveling Overseas for Combat". FBI.
- ^ "Syrian Soldiers Digging Their Own Graves Before Being Executed by ISIS". YouTube.
- ^ Erika Solomon (19 December 2014). "Isis morale falls as momentum slows and casualties mount". Financial Times. Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- ^ "Kurdish forces fighting Isis report being attacked with chemical weapons". Agence France-Presse. 13 August 2015. Retrieved 14 August 2015 – via theguardian.com.
- ^ "ISIS's Financial and Military Capabilities". crethiplethi. Retrieved 14 November 2015.
- ^ "Iraq's heritage needs protection from Islamic State – UNESCO". Reuters.
- ^ a b "Islamic State seeking to 'delete' entire cultures, UNESCO chief warns in Iraq". The Christian Science Monitor.
- ^ Franklin Lamb. "SYRIA: "Raqqa is Being Slaughtered Silently"". Retrieved 28 December 2014.
transcript of an interview conducted by the author at the National Museum of Syria with an employee of the Directorate General of Antiquities and Museums (DGAM). The gentleman had been working in the governorate of Raqqa, in eastern Syria, when armed groups were looting museums and conducting illegal excavations of heritage sites.
- ^ "The Plight of Mosul's Museum: Iraqi Antiquities At Risk Of Ruin". NPR. 9 July 2014.
- ^ a b Christopher Dickey, "ISIS Is About to Destroy Biblical History in Iraq,", The Daily Beast, 7 July 2014 (accessed 1 December 2014)
- ^ Al-Alawi, Irfan. "Extreme Wahhabism on Display in Shrine Destruction in Mosul". Gatestone Institute. Retrieved 4 October 2014.
- ^ "Islamic State: Jihadists destroying and looting Iraqi heritage sites for artefacts, UNESCO warns". ABC News.
- ^ "Nimrud: Outcry as IS bulldozers attack ancient Iraq site". BBC News. 6 March 2015. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
- ^ "Saudi Arabia's Grand Mufti denounces Islamic State group as un-Islamic". Reuters. 25 August 2014. Retrieved 18 November 2014.
- ^ Amad Shaikh (1 October 2014). "Muslim Scholars Letter to al-Baghdadi of ISIS or ISIL – A Missed Opportunity". Muslim Matters. Retrieved 8 November 2014.
- ^ Smith, Samuel (25 September 2014). "International Coalition of Muslim Scholars Refute ISIS' Religious Arguments in Open Letter to al-Baghdadi". The Christian Post. Retrieved 18 October 2014.
- ^ Milmo, Cahal (25 September 2014). "Isis is 'an offence to Islam', says international coalition of major Islamic scholars". independent. London. Retrieved 8 October 2014.
More than 120 Sunni imams and academics, including some of the Muslim world's most respected scholars, signed the 18-page document which outlines 24 separate grounds on which the terror group violates the tenets of Islam.
- ^ "Another battle with Islam's 'true believers'". The Globe and Mail. Toronto. 29 September 2014. Retrieved 13 October 2014.
- ^ Paraszczuk, Joanna (7 February 2014). "Syria: Umar Shishani's Second-in-Command in ISIS Slams Scholars Who "Sow Discord" & Don't Fight". EA WorldView. Retrieved 8 July 2014.
- ^ a b "The slow backlash – Sunni religious authorities turn against Islamic State". The Economist. 6 September 2014.
- ^ ""They're delusional": Rivals ridicule ISIS declaration of Islamic state". CBS News. 30 June 2014. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
- ^ Strange, Hannah (5 July 2014). "Islamic State leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi addresses Muslims in Mosul". The Telegraph. London. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ CRESWELL, ROBYN; HAYKEL, BERNARD (8 June 2015). "Battle Lines". The New Yorker. Retrieved 6 June 2015.
In the most recent issue of Dabiq, ISIS's English-language magazine, a female writer encourages women to emigrate to "the lands of the Islamic State" even if it means travelling without a male companion, a shocking breach of traditional Islamic law. This may be a cynical ploy—a lure for runaways. But it is in keeping with the jihadists' attack on parental authority and its emphasis on individual empowerment, including the power of female believers to renounce families they do not view as authentically Muslim.
- ^ CRESWELL, ROBYN; HAYKEL, BERNARD (8 June 2015). "Battle Lines". The New Yorker. Retrieved 6 June 2015.
It has also created a female morality police, a shadowy group called the al-Khansa' Brigades, who insure proper deportment in ISIS-held towns. ... Al-Khansa' was a female poet of the pre-Islamic era who converted to Islam and became a companion of the Prophet, and her elegies for her male relations are keystones of the genre [of Islamic poetry]. The name therefore suggests an institution with deep roots in the past, and yet there has never been anything like the Brigades in Islamic history, nor do they have an equivalent anywhere else in the Arab world.
- ^ a b Halleck, Thomas (26 September 2014). "Thousands of French Muslims Protest Herve Gourdel Beheading". International Business Times. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ "'Not in my name': French Muslims rally to denounce ISIS beheadings". RT. Retrieved 13 October 2014.
- ^ Ghosts of Aleppo (Full Length). YouTube. 30 September 2014.
- ^ "Ghosts of Aleppo (Full Length)". VICE News.
- ^ Joscelyn, Thomas (25 October 2015). "Al Qaeda appears 'moderate' compared to Islamic State, veteran jihadist says". Long War Journal.
- ^ Joscelyn, Thomas (2015 10). "A rare interview with an experienced Al Qaeda commander shows how the group is using ISIS to make itself look 'moderate'". the weekly Standard.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Joscelyn, Thomas (5 June 2015). "The Al Nusrah Front's 'inherited jihad'". Long War Journal.
- ^ Joscelyn, Thomas (20 July 2015). "Officials from Al Nusrah Front, Ahrar al Sham vow to continue fight against Islamic State". Long War Journal.
- ^ JOSCELYN, THOMAS (9 February 2015). "Al Qaeda Uses ISIS to Try to Present Itself as Respectable, Even Moderate". the weekly Standard.
- ^ Joscelyn, Thomas (2 November 2015). "Al Qaeda chief calls for jihadist unity to 'liberate Jerusalem'". Long War Journal.
- ^ "Al Nusra's Rebranding and What It Means for Syria - Foreign Affairs". Foreign Affairs.
- ^ yalibnan. "Al Qaeda forces Druze of Idlib Syria to destroy their shrines and convert". yalibnan.com.
- ^ Aymenn Jawad Al-Tamimi. "Additional Notes on the Druze of Jabal al-Summaq". Aymenn Jawad Al-Tamimi.
- ^ "Syria Comment » Archives The Plight of Syria's Druze Minority and U.S. Options - Syria Comment". Syria Comment.
- ^ Uncover the Mask with Evidence and Confidence كشف القناع بالحجة ولإقناع داعش. YouTube. 8 March 2015. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
- ^ "Number of ISIS defectors growing, disillusioned with killing fellow Muslims: Study". The Straits Times. London. Agence France-Presse. 21 September 2015. Archived from the original on 25 September 2015.
- ^ Neumann, Peter R. (22 September 2015). "Defectors: ISIS is killing Muslims, not protecting them". CNN. Retrieved 13 October 2015.
- ^ Robins-Early, Nick (21 September 2015). "New Report Reveals Why Fighters Are Quitting ISIS". The Huffington Post. Retrieved 13 October 2015.
- ^ http://syriadirect.org/news/a-%E2%80%98disgraceful-reality%E2%80%99-islamic-state-spies-posing-as-defectors/
- ^ Al Arabiya: "Head of Egypt’s al-Azhar condemns ISIS ‘barbarity’" 3 December 2014
- ^ Asharq Al-Awsat: "Egypt’s Al-Azhar stops short of declaring ISIS apostates - Azhar statement rejects practice of takfirism" 13 December 2014
- ^ a b Al Ahram: "In search of ‘renewal’ - Al-Azhar is at the centre of an escalating controversy" by Amany Maged 15 January 2015
- ^ Al Monitor: "Al-Azhar refuses to consider the Islamic State an apostate" by Ahmed Fouad |"The sheikh of Al-Azhar, Ahmed al-Tayeb, repeated his rejection of declaring IS apostates on 1 Jan, during a meeting with editors-in-chief of Egyptian newspapers. This sparked criticism from a number of religious, political and media parties, especially since Al-Azhar could have renounced the Nigerian mufti’s statement on IS without addressing the issue of whether or not Al-Azhar considers the group apostates"
- ^ Muslim World League: "Sheikh Al-Azhar Speech in opening of conference" 22 February 2015
- ^ Hasan, Mehdi (10 March 2015). "How Islamic is Islamic State?". Retrieved 27 March 2015.
- ^ Ban Ki-Moon (24 September 2014). "LATEST STATEMENTS New York, 24 September 2014 – Secretary-General's remarks to Security Council High-Level Summit on Foreign Terrorist Fighters". United Nations. Retrieved 18 November 2014.
- ^ Hassan, Steven (21 October 2014). "ISIS Is a Cult That Uses Terrorism: A Fresh New Strategy". The World Post. TheHuffingtonPost.com, Inc. Retrieved 10 November 2014.
- ^ "Iraq's Baghdadi calls for 'holy war'". Al Jazeera. 2 July 2014. Retrieved 2 July 2014.
- ^ "Turkish government files motion to Parliament to fight ISIL". Andalou Agency. Retrieved 14 October 2014.
- ^ "Russia urges Iran's participation in anti-ISIL battle". presstv.ir/. Press TV. 28 September 2014. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
- ^ "ISIL: UK government response". Gov.uk. Retrieved 13 October 2014.
- ^ Taylor, Adam (17 September 2014). "France is ditching the 'Islamic State' name—and replacing it with a label the group hates". The Washington Post. Retrieved 6 October 2014.
- ^ "US general rebrands Isis 'Daesh' after requests from regional partners Leader of operations against group uses alternative name – a pejorative in Arabic that rejects fighters' claims on Islam". 19 December 2014. Retrieved 22 December 2014.
- ^ Taylor, Adam (27 August 2014). "Meet 'QSIS': A new twist in what to call the extremist group rampaging in Iraq and Syria". The Washington Post.
- ^ Meky, Shounaz (24 August 2014). "Egypt's Dar al-Ifta: ISIS extremists not 'Islamic State'". Al Arabiya. Retrieved 27 August 2014.
- ^ Vincent, Michael (25 September 2014). "Islamic State: PM Tony Abbott tells UN Australia's response to terrorist group will be 'utterly unflinching'". ABC News (Australia). Retrieved 4 November 2014.
- ^ "Islamic State crisis: Mother fears for son at Mosul school". BBC News. 29 September 2014. Retrieved 4 October 2014.
- ^ Griffin, Andrew (14 September 2014). "Isis should be called the 'Un-Islamic State': British Muslims call on David Cameron to stop spread of extremist propaganda". The Independent. London. Retrieved 13 November 2014.
- ^ "Islamic State: Call Them 'Unislamic State,' Leading Muslims Plead, As Terror Group Murders David Haines". 14 September 2014. Retrieved 13 November 2014.
- ^ a b "Muslims Around The World Are Making Parody Videos To Mock ISIS". Countercurrent News. 2 October 2014. Retrieved 6 October 2014.
- ^ Watan ala Watar (7 July 2014). Palestinian Parody about ISIS (YouTube video). MEMRITVVideos.
- ^ a b Vick, Karl; Baker, Aryn (11 June 2014). "Extremists in Iraq Continue March Toward Baghdad". Time. Retrieved 23 June 2014.
- ^ Mazzetti, Mark; Schmitt, Eric; Landler, Mark (10 September 2014). "Struggling to Gauge ISIS Threat, Even as U.S. Prepares to Act". The New York Times. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ^ Porter, Tom. "Iraq War Created Isis, Concedes David Miliband". International Business Times. Retrieved 12 March 2015.
- ^ Gwynne Dyer: Terrorism 101 offers lessons in how to respond to ISIS Straight.com by Gwynne Dyer, 5 October 2014
- ^ Do Americans Support President Obama's ISIS Plan? NPR by Scott Horsley, 12 September 2014
- ^ Pankaj Mishra. "How to think about Islamic State". The Guardian.
- ^ The US, IS and the conspiracy theory sweeping Lebanon. BBC
- ^ Hassan, Mehdi (5 September 2014). "Inside jobs and Israeli stooges: why is the Muslim world in thrall to conspiracy theories?". New Statesman. Retrieved 29 September 2014.
- ^ Borne by Facebook, Conspiracy Theory That U.S. Created ISIS Spreads Across Middle East
- ^ Erdbrink, Thomas (10 September 2014). "For Many Iranians, the 'Evidence' Is Clear: ISIS Is an American Invention". The New York Times. Retrieved 27 May 2015.
- ^ a b Ezidi Press: IS-Terror in Shingal: Wer kämpft gegen wen? Ein Überblick, Abruf am 13. Oktober 2014
- ^ Aljazeera (17 October 2014): After repelling ISIL, PKK fighters are the new heroes of Kurdistan. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ VICE News (22 August 2014): Meet the PKK 'Terrorists' Battling the Islamic State on the Frontlines of Iraq. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ "In Pictures: Tension in Kirkuk". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ "Shabak Community forms military force of 1500 fighters to fight ISIS in Nineveh". IraqiNews. 23 September 2014. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ^ Mortada, Radwan (19 May 2014). "Hezbollah fighters and the "jihadis": Mad, drugged, homicidal, and hungry". Al Akhbar. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
- ^ Malouf, Carol; Spencer, Richard (4 August 2014). "Islamic State seizes territory inside Lebanon". The Daily Telegraph. London.
- ^ a b "Jordan confirms its planes joined strikes on IS in Syria". The Jordan Times. Retrieved 23 September 2014.
- ^ "Turkish army trades fire with ISIL fighters in Syria". Al Jazeera.
- ^ Karam, Zeina (19 August 2014). "Syria conflict: President Assad finally turns on Isis as government steps up campaign against militant strongholds". The Independent. London.
- ^ Mulcaire, Jack (22 April 2014). "Aleppo: Syria's Stalingrad?". The National Interest. Retrieved 29 April 2014.
- ^ a b "Al-Qaeda-linked Isis under attack in northern Syria". BBC. 4 January 2014. Retrieved 10 January 2014.
- ^ Muslim, Hana (13 May 2014). "Syria rebels struggle for control over ISIL-held Raqqa". ARA News. Retrieved 16 May 2014.
- ^ "Islamist militias unite under 'code of honor'". The Daily Star. 19 May 2014. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ Ahmed, Raman (8 July 2014). "ISIL struggles for control over Syrian Kurdish areas". ARA News. Retrieved 9 July 2014.
- ^ "Presence of the MFS at the border of Iraq". Syriac International News Agency. 16 June 2014. Retrieved 30 July 2014.
- ^ Steinbach, Peter. "Die Christen in Syrien ziehen in die Schlacht". Die Welt. Retrieved 2 September 2014.
- ^ Duell, Mark (14 October 2014). "Now ISIS is under attack from guerrillas itself: Ultra-secret White Shroud group strike fear into terrorists by picking off fighters one by one". Daily Mail. London. Retrieved 14 October 2014.
- ^ a b "ISIL, Nusra Clash Fiercely on Qalmoun Barrens: 25 Killed, Injured". Al-Manar News. 17 December 2014. Retrieved 18 December 2014.
- ^ "ISIS and Al-Nusra Cooperation: A Possible Sign of Desperation". The News Hub. 22 November 2014. Retrieved 22 September 2015.
- ^ Thomas Joscelyn (15 November 2014). "Murder Vids Help ISIS Lure More Monsters". The Daily Beast. Retrieved 17 November 2014.
- ^ Paul Cruickshank, Nic Robertson, Tim Lister and Jomana Karadsheh, CNN (18 November 2014). "ISIS comes to Libya". CNN.
{{cite news}}:|author=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Two Libyan National Forces Killed as IS attacks checkpoint". Libya Herald. 27 April 2015.
- ^ Aaron Y. Zelin (10 October 2014). "The Islamic State's First Colony in Libya". washingtoninstitute.org/. Washington Institute for Near East Policy.
- ^ "Libya ISIS Crisis Libyan Militias Fight Islamic State With Airstrikes Official Says". World News. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ^ Deaton, Jennifer Z.; Hanna, Jason (23 December 2014). "Algeria: Leader of group that beheaded French hiker is killed". CNN. Retrieved 1 January 2015.
- ^ a b c Martin Williams. "African leaders pledge 'total war' on Boko Haram after Nigeria kidnap". The Guardian.
- ^ "Chadian Forces Deploy Against Boko Haram". VOA. 16 January 2015. Retrieved 16 January 2015.
- ^ "Saudi Arabia confirms role in strikes against Islamic State in Syria". Reuters. September 2014.
- ^ "UAE fighter planes bomb ISIS targest and return to their bases in Jordan". February 2015.
- ^ a b "Islamic State leader urges attacks in Saudi Arabia: speech". Reuters. 13 November 2014.
- ^ "ISIS flag in Kashmir valley worries Army". The Times of India.
- ^ a b "ISIS reportedly moves into Afghanistan, is even fighting Taliban". 12 January 2015. Retrieved 27 March 2015.
- ^ "ISIS, Taliban announced Jihad against each other". Khaama Press. 20 April 2015. Retrieved 23 April 2015.
- ^ "New video message from The Islamic State: "Targeting the Apostate Pakistānī Military With Mortar Fire in the Area of Khybir – Wilāyat Khurāsān"". JIHADOLOGY. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ^ "New video message from The Islamic State: "Firing an SPG-9 Cannon Upon the Apostate Pakistani Army in the Area of Khaybar – Wilāyat Khurāsān"". JIHADOLOGY. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ^ a b c d e Lim Yan Liang (29 May 2015). "ISIS social media post cites Singapore as possible target". The Straits Times. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ^ "14 ISIS militants killed in Philippines". The Nation. 26 February 2015. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ^ "Manila Standard Today – Latest News in the Philippines". Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ^ "Coalition commanders seek plan to counter Daesh advance". Gulf News. Agence France-Presse. 14 October 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae "Joint Statement Issued by Partners at the Counter-ISIL Coalition Ministerial Meeting". state.gov. US State Dept. 3 December 2014. Retrieved 14 December 2014.
- ^ "Arab League issues proclamation on ISIS". CBS/AP. 8 September 2014. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Cooper, Helene (5 September 2014). "Obama Enlists 9 Allies". The New York Times. Retrieved 6 September 2014.
- ^ Nicks, Denver (5 September 2014). "U.S. Forms Anti-ISIS Coalition at NATO Summit". Time. Retrieved 25 September 2014.
- ^ Wintour, Patrick (5 September 2014). "US Forms 'core coalition' to fight ISIS militants in Iraq". The Guardian. Retrieved 6 September 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Wordsworth, Araminta (26 September 2014). "Anti-ISIS coalition has mobilized up to 62 nations and groups". National Post. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ a b c d Young, Sarah (15 August 2014). "Britain ready to supply Kurds with arms". Reuters. Retrieved 18 August 2014.
- ^ Vedat Sevincer (19 September 2014). "Norway is Officially Part of the Military Coalition against ISIS". The Nordic Page.
- ^ Nuno Ribeiro. "Portugal treina militares iraquianos contra o Estado Islâmico". PÚBLICO.
- ^ "España enviará unos 300 militares a Irak para instruir a su Ejército". El País. 9 October 2014. Retrieved 12 October 2014.
- ^ "Turkey trains Kurdish peshmerga forces in fight against ISIL". world bulletin.net. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Turkey launches air strike on Al Qaida convoy in N. Syria". World Tribune.
- ^ Stephenson, Emily (23 July 2015). "Turkey lets U.S. strike Islamic State from Incirlik base: U.S." Reuters.
- ^ Schmitt, Eric (26 November 2014). "U.S. Adds Planes to Bolster Drive to Wipe Out ISIS". The New York Times.
- ^ "US Air Force's A-10 Warthogs and Reaper drones to blast ISIS from the skies – Daily Mail Online". Daily Mail. London. 27 November 2014.
- ^ "John Key: Kiwi forces will help train Iraqis fight ISIS". The New Zealand Herald. 5 November 2014. Retrieved 16 December 2014.
- ^ "نيوزيلندا تنضم الى التحالف ضد جهاديي تنظيم الدولة الاسلامية في العراق". alsharqiya.com.
- ^ "نيوزيلاندا تشارك في تدريب الجيش العراقي". RT Arabic.
- ^ Xue, Jianyue (3 November 2014). "Singapore to join fight against ISIS". Today. MediaCorp Press Ltd. Retrieved 3 November 2014.
- ^ Besar Likmeta (27 August 2014). "Albania Starts Shifting Weapons to Iraqi Kurds". Balkan Insight.
- ^ "До 2020 година 1.8 млрд. лв. ще бъдат вложени в армията (1.8 bln. lv will be invested in the military by 2020)" (in Bulgarian). Dir.bg. 20 September 2014. Retrieved 20 September 2014.
- ^ "Hrvatska u borbi protiv islamista: Na zahtjev SAD-a šaljemo oružje za iračku vojsku". Jutarnji list (in Croatian). 21 August 2014. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ Kalmouki, Nikoleta (25 September 2014). "Greece Participates in the War Against the Islamic State". Greek Reporter. Retrieved 27 September 2014.
- ^ "BH on Coalition List against IS Terrorists – Contributed by OSA and SIPA Efficiency". SIPA. 23 September 2014. Retrieved 3 November 2014.
- ^ Sadq, Hoshmand (14 August 2014). "Seven Countries to sell weapons to Kurds". BasNews. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ "Foreign Minister Tuomioja goes to the international Counter-ISIL Coalition meeting in Brussels". Retrieved 16 December 2014.
- ^ Dehghanpisheh, Babak (3 August 2014). "Iran's elite Guards fighting in Iraq to push back Islamic State". Reuters.
- ^ "Iran Rushes Elite Quds Force Unit To Iraq To Help Government Stop ISIS Advance". weaselzippers.us. 11 June 2014. Retrieved 18 June 2014.
- ^ "Russia Tells Iraq It's 'Ready' to Support Fight Against ISIS". NBC News. Retrieved 27 September 2014.
- ^ Nordland, Rod (29 June 2014). "Russian Jets and Experts Sent to Iraq to Aid Army". The New York Times. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ "Target ISIS: First batch of Russian fighter jets arrives in Iraq". Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ^ "Russia 'kills 8 ISIS militants' in Caucasus raid". The Daily Star Newspaper – Lebanon.
- ^ "L. TODD WOOD: Russia declares counter-terror ops regime in North Caucasus". The Washingtion Times.
- ^ "Russian Islamic State Airstrikes In Iraq: ISIS OK For Russia To Target, Baghdad Says". International Business Times. 24 October 2015. Retrieved 1 November 2015.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "8 ISIS targets hit during 20 combat flights in Syria – Russian military". RT. 30 September 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2015.
- ^ "Russia launches first airstrikes in Syria". CNN. 30 September 2015. Retrieved 30 September 2015.
- ^ "Azerbaijan Arrests Alleged ISIS and Other Islamic Fighters". Eurasianet.org. 24 September 2014. Retrieved 18 February 2015.
- ^ "Azerbaijani media: Embassy increases security in Baku because of ISIS threatening". Panorama. 26 January 2015. Retrieved 18 January 2015.
- ^ "Nawaz Sharif in Saudi Arabia: Pakistan's Leverage in the Gulf". The Indian Express. 5 March 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ Schram, Jamie (31 October 2014). "Now Pakistan cares about ISIS". New York Post. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ "Security forces arrest local Islamic State commander in Lahore: sources". The Express Tribune. 21 January 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ "The War Between ISIS and al-Qaeda for Supremacy of the Global Jihadist Movement". Washington Institute. June 2014. Retrieved 15 October 2014.
- ^ "Al Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb backs jihadists fighting Islamic State in Derna, Libya". Long War Journal. 9 July 2015. Retrieved 9 July 2015.
- ^ "ISIL warns Hamas in video message". 1 July 2015. Retrieved 1 July 2015.
- ^ a b Mohammed, A. Salih (1 September 2014). "PKK forces impress in fight against Islamic State". Al-Monitor. Retrieved 15 October 2014.
- ^ "Suicide bombers kill 14 in Damascus". Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ Spencer, Richard (19 May 2013). "Syria: Jabhat al-Nusra split after leader's pledge of support for al-Qaeda". The Telegraph. London.
- ^ Erin Banco (11 April 2015). "Jabhat Al-Nusra And ISIS Alliance Could Spread Beyond Damascus". International Business Times.
- ^ "How would a deal between al-Qaeda and Isil change Syria's civil war?". The Daily Telegraph. 14 November 2014
- ^ "ISIS joins other rebels to thwart Syria regime push near Lebanon". The Sacramento Bee. McClatchy DC. 4 March 2014.
- ^ "ISIL and Al Qaeda: Terror's frenemies". Quartz's. 12 January 2015.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Al Qaeda Leader Al-Zawahiri Declares War on ISIS 'Caliph' Al-Baghdadi". Retrieved 11 September 2015.
- ^ "Al Qaeda calls Islamic State illegitimate but suggests cooperation". Retrieved 11 September 2015.
- ^ "UN says '25,000 foreign fighters' joined Islamist militants". BBC News. 2 April 2015. Retrieved 2 April 2015.
- ^ "Isis leader calls on Muslims to 'build Islamic state'". BBC News. 1 July 2014. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ^ Burke, Jason (26 May 2015). "Islamist fighters drawn from half the world's countries, says UN". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 26 May 2015. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "ISIS Beheads Another American As 60 New Terror Groups Join". The Fiscal Times. Retrieved 28 November 2014.
- ^ "ISIS accepts Boko Haram pledge, says would-be recruits can go to Nigeria". Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. 13 March 2015.
- ^ "BIFF, Abu Sayyaf pledge allegiance to Islamic State jihadists | GMA News Online". Gmanetwork.com. 16 August 2014. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ Dean, Sarah (21 August 2014). "PM Tony Abbott warns Australians of threats from Indonesian Jemaah Islamiyah group". Daily Mail. London. Retrieved 23 August 2014.
- ^ "allAfrica.com: Tunisia: Ansar Al-Sharia Tunisia Spokesman Backs Isis". Retrieved 25 September 2014.
- ^ Abdallah Suleiman Ali (3 July 2014). "Global jihadists recognize Islamic State". Al-Monitor. Retrieved 25 September 2014.
- ^ Chikhi, Lamine (14 September 2014). "Splinter group breaks from al Qaeda in North Africa". Reuters. Retrieved 24 September 2014.
- ^ Paterno Emasquel II (17 September 2014). "Philippines condemns, vows to 'thwart' ISIS". Rappler. Retrieved 19 September 2014.
- ^ "Gaza Salafists pledge allegiance to ISIS – Al-Monitor: the Pulse of the Middle East". Al-Monitor. Retrieved 25 September 2014.
- ^ a b Witular, Rendi A. (13 August 2014). "Sons, top aides abandon Ba'asyir over ISIL, form new jihadist group". The Jakarta Post.
- ^ Rottenberg, Chris (2012). "Jamaah Ansharut Tauhid, The Perpetual threat" (PDF). Osgood Center for International Studies.
- ^ "Uzbek militants declare support for Islamic State". Dawn. Agence France-Presse. 7 October 2014. Retrieved 25 May 2015.
"Hereby, on behalf of all members of our movement, in line with our sacred duties, I declare that we are in the same ranks with the Islamic State in this continued war between Islam and [non-Muslims]," Usman Gazi wrote in an online statement on Sept 26.
- ^ "IMU Declares It Is Now Part Of The Islamic State". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 6 August 2015. Retrieved 6 August 2015.
- ^ "Caucasus Emirate and Islamic State Split Slows Militant Activities in North Caucasus". Jamestown Foundation. 13 February 2014. Retrieved 17 February 2015.
- ^ Liz Fuller (2 January 2015). "Six North Caucasus Insurgency Commanders Transfer Allegiance To Islamic State". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. Retrieved 17 February 2015.
- ^ "What Caused the Demise of the Caucasus Emirate?". Jamestown Foundation. 18 June 2015.
- ^ "ISIS: We Are Operating in Gaza". Vocative: The extremist terror organization is establishing a toehold inside Gaza, despite Hamas' claims to the contrary. 9 June 2014. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ^ a b Bertrand, Natasha (28 July 2015). "Senior Western official: Links between Turkey and ISIS are now 'undeniable'".
- ^ Zaman, Amberin (10 June 2014). "Syrian Kurds continue to blame Turkey for backing ISIS militants". Al-Monitor.
- ^ Wilgenburg, Wladimir van (6 August 2014). "Kurdish security chief: Turkey must end support for jihadists". Al-Monitor.
- ^ Cockburn, Patrick (6 November 2014). "Whose side is Turkey on?". London Review of Books. 36 (21): 8–10.
- ^ a b Phillips, David L. (9 November 2014). "Research Paper: ISIS-Turkey List". The Huffington Post.
- ^ Guiton, Barney (7 November 2014). "'ISIS Sees Turkey as Its Ally': Former Islamic State Member Reveals Turkish Army Cooperation". Newsweek.
- ^ Ben-Solomon, Ariel (30 July 2014). "Islamic State fighter: 'Turkey paved the way for us'". The Jerusalem Post.
- ^ a b c Faiola, Anthony; Mekhennet, Souad (12 August 2014). "In Turkey, a late crackdown on Islamist fighters". The Washington Post.
- ^ Lauren Williams (4 January 2015). "ISIS Has Polarized Turkey Domestically". Daily Star, Lebanon.
- ^ Tattersall, Nick; Karouny, Mariam (26 August 2014). "Turkey's 'Open Border' Policy With Syria Has Backfired As ISIS Recruitment Continues". Business Insider.
- ^ Schanzer, Jonathan (25 September 2014). "Boosting Turkey as it backs terror". New York Post.
- ^ a b Greenhill, Sam (25 August 2014). "How seven radicalised young Britons a week are taking the Gateway to Jihad". Daily Mail. London.
- ^ "New report further exposes Turkey links to ISIL militants". Press TV. 21 October 2014.
- ^ "Qatar and ISIS Funding: The U.S. Approach". The Washington Institute. August 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2015.
- ^ "Islamic State: Where does jihadist group get its support?". BBC. 1 September 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2015.
- ^ "Qatar Is a U.S. Ally. They Also Knowingly Abet Terrorism. What's Going On?". New Republic. 6 October 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2015.
- ^ "German minister accuses Qatar of funding Islamic State fighters". Reuters. 20 August 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2015.
- ^ "Qatar allows money to flow to Islamic State, other terrorists: report". Washington Times. 10 December 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2015.
- ^ "Who funds ISIS? Qatar and state-sponsoring allegations". Security Observer. 23 December 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2015.
- ^ "Qatar denies backing Islamic State group". Al Jazeera. 24 August 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2015.
- ^ a b Black, Ian (19 June 2014). "Saudi Arabia rejects Iraqi accusations of Isis support". The Guardian. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ a b Parker, Ned; Ireland, Louise (9 March 2014). "Iraqi PM Maliki says Saudi, Qatar openly funding violence in Anbar". Reuters.
- ^ Husain, Ed (22 August 2014). "ISIS Atrocities Started With Saudi Support For Salafi Hate". The New York Times.
- ^ "Saudi Funding of ISIS". washingtoninstitute.org.
- ^ a b Vinograd, Cassandra; Omar, Ammar Cheikh (11 December 2014). "Syria, ISIS Have Been 'Ignoring' Each Other on Battlefield, Data Suggests". NBC. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Sly, Liz (9 September 2014). "Syria's Assad thinks he is winning. He could be wrong". The Washington Post.
- ^ "CFR Backgrounders – The Islamic State". Council on Foriegn Relations. Retrieved 6 July 2015.
Some analysts have even described a tacit nonaggression pact between Islamic State militants and Bashar al-Assad regime, with each focused on fighting the main antigovernment opposition forces for territorial control.
- ^ a b Baker, Aryn (27 January 2014). "Is the Assad Regime in League with al-Qaeda?". Time. Retrieved 6 July 2015.
- ^ Black, Ian (14 July 2015). "Bashar al-Assad is west's ally against Isis extremists, says Syria". The Guardian. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ^ Cordall, Simon Speakwell (21 June 2014). "How Syria's Assad Helped Forge ISIS". Newsweek. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Kelley, Michael, B (21 January 2014). "It's Becoming Clear That Assad Fueled The Al-Qaeda Surge That Has Kept Him in Power". Business Insider. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Blair, David (7 March 2015). "Oil middleman between Syria and Isil is new target for EU sanctions". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ "Kerry: There Is Evidence That Assad Has Played "Footsie" With ISIL". Real Clear Politics. 18 September 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
JOHN KERRY: Regrettably Congressman, no we're not going to be undercut, because. If Assad's forces indeed do decide to focus on ISIL significantly, which they haven't been doing throughout this period, one of our judgements is there is evidence that Assad has played footsie with them, and he has used them as a tool of weakening the opposition. He never took on their headquarters, which were there and obvious, and other assets that they have. So we have no confidence that Assad is either capable of or willing to take on ISIL."
- ^ "Has Assad infiltrated rebel forces inside Syria?". Channel Four News. 24 April 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Ridley, Yyonne (22 September 2014). "EXCLUSIVE: Shaikh Hassan Abboud's final interview". Middle East Monitor. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ "AlQaeda detainees reveal ties with Assad". Al Arabiya News. 20 January 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ U.S. Embassy Syria [@USEmbassySyria] (1 June 2015). "Reports indicate that the regime is making air-strikes in support of #ISIL's advance on #Aleppo, aiding extremists against Syrian population" (Tweet). Retrieved 2 June 2015 – via Twitter.
- ^ Barnard, Anne (2 June 2015). "Assad's Forces May Be Aiding New ISIS Surge". The New York Times. Retrieved 5 June 2015.
- ^ Bar'el, Zvi (3 June 2015). "Assad's cooperation with ISIS could push U.S. into Syria conflict". Haaretz. Retrieved 4 June 2015.
Salim Idris, defense minister in the rebels' provisional government, said approximately 180 Syrian Army officers are currently serving with ISIS and coordinating the group's military operations with the army.
- ^ Philps, Alan (25 June 2015). "Rebels are close to Raqqa – but what happens next?". The National. Retrieved 20 August 2015.
- ^ Selman İnanc, Yusuf (28 June 2015). "ISIS and Assad cooperate locally on mutual interests to destroy FSA". Daily Sabah. Retrieved 29 June 2015.
speaking on the condition of anonymity, told Daily Sabah that President Bashar Assad's Syrian regime and ISIS made an agreement on that day at the gas production plant.
- ^ Krever, Mick (27 July 2015). "ISIS exists because world ignored al-Assad in Syria, Turkish leader says". CNN. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- ^ "Sa është numri i xhihadistëve të ISIS-it? – Lajme – Top Channel". Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ Weaver, Mary Anne (19 April 2015). "Her Majesty's Jihadists". The New York Times. Retrieved 14 April 2015.
- ^ "UN Report on 15,000 Foreigners Joining ISIS Fighters in Syria And Iraq Will Shock You". International Business Times. Archived from the original on 10 November 2014.
- ^ a b "ISIS By the Numbers: Foreign Fighter Total Keeps Growing". NBC News. 28 February 2015.
- ^ a b c "The names: Who has been recruited to ISIS from the West". CNN. 25 February 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab "Foreign fighter total in Syria/Iraq now exceeds 20,000; surpasses Afghanistan conflict in the 1980s". ICSR. 26 January 2015.
- ^ "Nearly 1,700 Russians Fighting For ISIS in Iraq: Report". International Business Times. 20 February 2015.
- ^ Yeginsu, Ceylan (15 September 2014). "ISIS Draws a Steady Stream of Recruits From Turkey". The New York Times.
- ^ "100 deutsche ISIS-Kämpfer in Syrien und im Irak getötet". BILD.de.
- ^ a b Julien Gradot (21 October 2015). "Why Malaysia has a problem with Islamic State". The Malay Mail. Retrieved 21 October 2015.
- ^ a b Tomovic, Dusica (17 September 2014). "Hundreds of Balkan Jihadists Have Joined ISIS, CIA Says". Balkan Insight. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "300 Chinese are fighting alongside ISIS in Iraq, Syria". The New York Post. 15 December 2014. Retrieved 3 January 2015.
- ^ "Kosovo Charges Seven With Islamist Terrorism". Balkan Insight. 3 March 2015.
- ^ "Fears up to 300 Swedes fighting with Isis". The Local (se). 23 November 2014. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ "HOW many? Authorities claim 'up to 250' Australians are linked to ISIS terrorists". Daily Mail. London. 31 October 2014. Retrieved 4 January 2015.
- ^ "Azerbaijanis Killed In Syria, Pro-Government Outlets Report". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty.
- ^ "Austria passes controversial reforms to Islam law banning foreign funding". The Telegraph. London. 25 February 2015.
- ^ "New Norwegians take top roles in Isis jihadi group". The Local (no). 12 February 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ "Police arrest seven for recruiting women for Isis". The Local (es). 16 December 2014.
- ^ "Canadians have joined ISIS to fight – and die – in Syria". CNN. 10 September 2014. Retrieved 3 January 2015.
- ^ a b Al-Jazeera. "The London-based International Centre for the Study of Radicalisation estimates that just 120 people from Israel and the Palestinian territories are now fighting in Syria and Iraq." [2], "Israelis Are Joining ISIS". Vocativ. 7 November 2014. Retrieved 3 January 2015. "According to Israeli security service estimates, there are now 40 to 50 Arab-Israelis fighting in Syria and Iraq, most of them as part of ISIS. That’s not a huge number, given that there are 1.3 million Muslims living in Israel. "
- ^ Quann, Jack (10 February 2015). "EXCLUSIVE: Newstalk speaks to former ISIS operative about Irish fighters". Newstalk. Retrieved 1 July 2015.
It is estimated that some 40 Irish men have gone to fight for ISIS in Syria and Iraq
- ^ Machaidze, Rusiko (16 June 2015). "Four people detained in Georgia for links to ISIS". Democracy & Freedom Watch. Retrieved 18 June 2015.
- ^ "India tracking 18 desi jihadis in Iraq, Syria". The Times of India Mobile Site. 9 July 2014. Retrieved 26 February 2015.
- ^ "Portugal Fails to Heed Warnings from Spain About Jihadis". The Clarion Project. 16 September 2014. Retrieved 21 May 2015.
- ^ "Portugal's Jihadists gain prominence". The Portugal News. 5 February 2015. Retrieved 21 May 2015.
- ^ Carmela Fonbuena (22 September 2014). "Filipino jihadists killed in Syria - reports". Rappler. Retrieved 24 September 2014.
- ^ "World's Richest Terror Army". BBC. 24 April 2015. p. 25:06 – within a 59 minute programme.
excerpt from, interview with Abu Hajjar, a former "senior leader of IS": "How much money would a foreign fighter receive as a wage?" "A foreigner? They aren't given a salary. They are given food and housing, not money."
- ^ Ismay, John (17 October 2013). "Insight into How Insurgents Fought in Iraq". The New York Times. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ "Not Just Iraq: The Islamic State Is Also on the March in Syria". The Huffington Post. 7 August 2014. Retrieved 11 August 2014.
- ^ Cowell, Alan (10 July 2014). "Low-Grade Nuclear Material Is Seized by Rebels in Iraq, U.N. Says". The New York Times. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- ^ Sherlock, Ruth (10 July 2014). "Iraq jihadists seize 'nuclear material', says ambassador to UN". The Telegraph. London. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- ^ "Islamic State says it could buy nuclear weapon from Pakistan within a year". The Express Tribune.
- ^ "Isis: India warns Islamic State can obtain nuclear weapons from Pakistan". International Business Times UK.
- ^ Paul Blake (11 September 2015). "US official: 'IS making and using chemical weapons in Iraq and Syria'". BBC. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ Lizzie Dearden (11 September 2015). "Isis 'manufacturing and using chemical weapons' in Iraq and Syria, US official claims". The Independent. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ Stone, Jeff (17 June 2014). "ISIS Attacks Twitter Streams, Hacks Accounts To Make Jihadi Message Go Viral". International Business Times. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ Prusher, Ilene (9 September 2014). "What the ISIS Flag Says About the Militant Group". Time. Retrieved 29 September 2014.
- ^ "US targets al Qaeda's al Furqan media wing in Iraq". The Long War Journal. 28 October 2007. Retrieved 24 June 2014.
- ^ Bilger 2014, p. 1.
- ^ Zelin, Aaron Y. (8 March 2013). "New statement from the Global Islamic Media Front: Announcement on the Publishing of al-I'tiṣām Media Foundation – A Subsidiary of the Islamic State of Iraq – It Will Be Released Via GIMF". JIHADOLOGY. Retrieved 24 June 2014.
- ^ "New statement from the Islamic State of Iraq and al-Shām: "Announcing Ajnād Foundation For Media Production"". JIHADOLOGY. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ^ Gertz, Bill (13 June 2014). "New Al Qaeda Group Produces Recruitment Material for Americans, Westerners". The Washington Free Beacon. Retrieved 24 June 2014.
- ^ "ISIS Declares Islamic Caliphate, Appoints Abu Bakr Al-Baghdadi As 'Caliph', Declares All Muslims Must Pledge Allegiance To Him". MEMRI. 30 June 2014. Retrieved 7 July 2014.
- ^ Zelin, Aaron Y. (28 January 2015). "The Islamic State's model". The Washington Post. Retrieved 30 March 2015.
- ^ Sullivan, Kevin (8 December 2014). "Three American teens, recruited online, are caught trying to join the Islamic State". The Washington Post. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ^ "Dabiq: What Islamic State's New Magazine Tells Us about Their Strategic Direction, Recruitment Patterns and Guerrilla Doctrine". The Jamestown Foundation. 1 August 2014. Retrieved 18 August 2014.
- ^ "Islamic State launches English-language radio bulletins". The Daily Telegraph. London. 7 April 2015. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- ^ a b Berger, J. M. (16 June 2014). "How ISIS Games Twitter". The Atlantic. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ "ISIS Propaganda Campaign Threatens U.S." Anti-Defamation League. 27 June 2014. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- ^ Sheera, Frenkel (16 June 2014). "Meet The 'ISIS Fanboys' Spreading The Message of Iraq's Most Feared Terror Group". BuzzFeed.
- ^ Dan Friedman (17 August 2014). "Twitter stepping up suspensions of ISIS-affiliated accounts: experts". Daily News. New York. Retrieved 8 September 2014.
- ^ "ISIS Faces Resistance From Social Media Companies". Anti-Defamation League. 23 July 2014. Retrieved 24 July 2014.
- ^ Lee, Ian; Hanna, Jason (12 August 2015). "Croatian ISIS captive reportedly beheaded". CNN. Retrieved 12 August 2015.
- ^ Walsh, Michael (23 September 2014). "ISIS releases second 'lecture video' of British hostage John Cantlie". Daily News. New York. Retrieved 6 October 2014.
- ^ Joseph Steinberg (11 April 2015). "ISIS Blacks Out French Television Station Broadcasts". Forbes. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- ^ "France probes Russian lead in TV5Monde hacking: sources". Reuters. 10 June 2015. Retrieved 9 July 2015.
- ^ "Financing of the Terrorist Organisation Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant" (PDF). Financial Action Task Force. February 2015. Retrieved 19 April 2015.
- ^ a b c d Allam, Hannah (23 June 2014). "Records show how Iraqi extremists withstood U.S. anti-terror efforts". McClatchy News. Retrieved 25 June 2014.
- ^ a b Chulov, Martin (15 June 2014). "How an arrest in Iraq revealed Isis's $2bn jihadist network". The Guardian. Retrieved 17 June 2014.
- ^ Moore, Jack (11 June 2014). "Mosul Seized: Jihadis Loot $429m from City's Central Bank to Make Isis World's Richest Terror Force". International Business Times. UK. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ McCoy, Terrence (12 June 2014). "ISIS just stole $425 million, Iraqi governor says, and became the 'world's richest terrorist group'". The Washington Post. Retrieved 18 June 2014.
- ^ Carey, Glen; Haboush, Mahmoud; Viscusi, Gregory (26 June 2014). "Financing Jihad: Why ISIS Is a Lot Richer Than Al-Qaeda". Bloomberg News. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ "U.S. Official Doubts ISIS Mosul Bank Heist Windfall". NBC News. 24 June 2014. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ Daragahi, Borzou (17 July 2014). "Biggest bank robbery that 'never happened' – $400m Isis heist". Financial Times. Retrieved 21 July 2014.(subscription required) Accessible via Google.
- ^ Matthews, Dylan (24 July 2014). "The surreal infographics ISIS is producing, translated". Vox. Retrieved 25 July 2014.
- ^ Mariam Karouny (4 September 2014). "In northeast Syria, Islamic State builds a government". Reuters.
- ^ a b c Scott Bronstein; Drew Griffin (7 October 2014). "Self-funded and deep-rooted: How ISIS makes its millions". CNN.
- ^ Karen Leigh (2 August 2014). "ISIS Makes Up To $3 Million a Day Selling Oil, Say Analysts". ABC news. Retrieved 8 October 2014.
- ^ a b c d e Janine di Giovanni; Leah McGrath Goodman; Damien Sharkov (6 November 2014). "How Does ISIS Fund Its Reign of Terror?". Newsweek.
- ^ Solomon, Erika (28 April 2014). "Syria's jihadist groups fight for control of eastern oilfields". Financial Times. Retrieved 17 June 2014.
- ^ "ISIS revenues hit after it loses 'large oil fields' in Iraq". Al Arabiya. Agence France-Presse. 9 April 2014. Retrieved 10 April 2015.
- ^ Gordon, Michael R. (16 November 2015). "U.S. Warplanes Strike ISIS Oil Trucks in Syria". nytimes.com. Retrieved 16 November 2015.
- ^ Fisher, Max (12 June 2014). "How ISIS is exploiting the economics of Syria's civil war". Vox. Retrieved 17 June 2014.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help) - ^ Peritz, Aki (4 February 2015). "How Iraq Subsidizes Islamic State". The New York Times. Retrieved 25 February 2015.
- ^ a b "ISIS economy based on illegal drug trade – Russian anti-drug chief". RT. 23 July 2015. Retrieved 24 July 2015.
- ^ a b Rogin, Josh (14 June 2014). "America's Allies Are Funding ISIS". The Daily Beast. Retrieved 21 September 2015.
- ^ Cockburn, Patrick (13 July 2014). "Iraq crisis: How Saudi Arabia helped Isis take over the north of the country". The Independent. London. Retrieved 9 August 2014.
- ^ a b Bozorgmehr, Najmeh; Kerr, Simeon (25 June 2014). "Iran-Saudi proxy war heats up as Isis entrenches in Iraq". Financial Times. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- ^ Doug Stanglin (15 September 2014). "As summit strategizes on ISIL, French jets fly over Iraq". USA TODAY.
- ^ Clemons, Steve (23 June 2014). "'Thank God for the Saudis': ISIS, Iraq, and the Lessons of Blowback". The Atlantic. Retrieved 9 October 2014.
- ^ BBC News, Up to 200 killed in Baghdad bombs
- ^ Yates, Dean; Villelabeiti, Ibon (18 April 2007). "Suspected Qaeda bombs kill nearly 200 in Baghdad". Reuters. Archived from the original on 8 November 2020. Retrieved 21 August 2020.
- ^ Cave, Damien; Glanz, James (August 21, 2007). "Toll in Iraq Truck Bombings Is Raised to More Than 500". The New York Times.
- ^ "Baghdad bomb fatalities pass 150". BBC News. BBC. 26 October 2009. Retrieved 21 April 2019.
- ^ Myers, Steven Lee; Adnan, Duraid (23 April 2010). "Wave of Fatal Bombings Widens Fissures in Iraq". NY Times. The New York Times Company. p. 4. Retrieved 21 April 2019.
- ^ "Iraq attacks kill more than 100". BBC News. BBC. 10 May 2010. Retrieved 21 April 2019.
- ^ "Al-Qaeda in Iraq blamed for attacks". Al Jazeera. 11 May 2010. Archived from the original on 14 May 2010. Retrieved 11 May 2010.
- ^ Tawfeeq, Mohammed (2 November 2010). "Blasts in Baghdad kill at least 63". CNN World. Turner Broadcasting System, Inc. Retrieved 21 April 2019.
- ^ "Baghdad Blasts Kill Scores, Over 200 Hundred Wounded". HuffPost. 2 November 2010. Archived from the original on 5 November 2010. Retrieved 3 November 2010.
- ^ Ghazi, Yasir; Hauser, Christine (3 January 2013). "Attacks in Iraq Kill at Least 32 Pilgrims". The New York Times.
- ^ "Bombers kill more than 35 across Iraq – AlertNet". 21 February 2013. Archived from the original on 21 February 2013.
- ^ "Suicide bomber kills 42 mourners at Iraq funeral – The National".
- ^ Ghazi, Yasir (3 February 2013). "Kirkuk Suicide Bomber Kills Dozens". The New York Times.
- ^ "Associated Press News". bigstory.ap.org.
- ^ "Baghdad Bloodbath: 34 Killed, 70 Wounded in Attacks by -- Antiwar.com". March 2013.
- ^ "48 Syrian Soldiers Killed in Iraq Ambush". 4 March 2013.
- ^ "Iraq Invasion Anniversary Carnage: 98 Killed, over 240 Wounded by -- Antiwar.com". 20 March 2013.
- ^ "Five years on, still no justice for Iraq's Camp Speicher victims".
- ^ Damon, Arwa; Alkhshali, Hamdi; Ellis, Ralph (8 April 2015). "Mass graves in Tikrit might contain 1,700 bodies". CNN. Retrieved 6 June 2019.
- ^ McLaughlin, Eliott C. (18 November 2015). "Paris attacks: What you need to know". CNN. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- ^ Rubin, Alissa J. (14 June 2016). "France Stabbing Police Officer Magnanville". The New York Times. Retrieved 30 November 2016.
- ^ Patrick Cockburn (27 July 2016). "Isis bombs kill dozens in Kurdish city of Qamishli as extremist group faces becoming surrounded". The Independent. Retrieved 30 November 2016.
- ^ "Turkey: Suicide bomber kills more than 50 at wedding – News from". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 30 November 2016.
- ^ "Islamic State claims responsibility for Afghan Supreme Court attack in Kabul". 8 February 2017.
- ^ Zucchino, David (16 February 2017). "Baghdad Car Bomb Kills Scores in Shiite Neighborhood". The New York Times. Retrieved 1 October 2020.
- ^ "Syria: 'Car bomb kills 51' near al-Bab after IS defeat". BBC News. 24 February 2017.
- ^ Kudo, Per (20 February 2018). "Akilov ser sig själv som "IS-soldat"". Svenska Dagbladet – via svd.se.
- ^ "Policeman and suspected gunman shot dead in Paris 'terror attack'". BBC News. 21 April 2017.
- ^ "Pakistan bomb attack: Balochistan blast kills 25". BBC News. 12 May 2017.
- ^ "Isis has claimed responsibility for the Manchester Arena attack". The Independent. 23 May 2017.
- ^ "AFP chief: 1 cop killed, 8 troopers wounded in Marawi clash". CNN. Archived from the original on 17 May 2023. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ "Islamic state claims responsibility for Jakarta bus station attacks". Reuters. 25 May 2017.
- ^ "Egypt Coptic Christians: IS claims attack". BBC News. 27 May 2017.
- ^ "London attack: Latest updates". BBC. 12 June 2017.
- ^ Knaus, Christopher; Davey, Melissa; Press, Australian Associated (5 June 2017). "Isis claims responsibility for Melbourne siege that left two people dead". The Guardian.
- ^ "Australian PM says Melbourne siege 'a terrorist attack'". Reuters. 6 June 2017.
- ^ Erdbrink, Thomas; Mashal, Mujib (7 June 2017). "At Least 12 Killed in Pair of Terrorist Attacks in Iran". The New York Times.
- ^ Rasmussen, Sune Engel (3 August 2017). "Father of Afghan robotics team captain killed in Isis attack". The Guardian.
- ^ a b "15 martyred as IS bomber hits mily truck in Quetta". The Nation (Pakistan). 13 August 2017. Retrieved 13 August 2017.
- ^ Fahmy, Omar (24 November 2017). "Gunmen in Egypt mosque attack carried Islamic State flag,..." Reuters.
- ^ Brynn Gingras; Emanuella Grinberg; Eliott C. McLaughlin (11 December 2017). "Man detonates pipe bomb in 'attempted terrorist attack'". CNN.
- ^ "Isis just claimed responsibility for suicide bomb that killed 41 in Kabul". Independent.co.uk. 28 December 2017.
- ^ Callimachi, Rukmini; Coker, Margaret (2018). "ISIS Claims Responsibility for Baghdad Bombings". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 25 February 2018.
- ^ "ISIL claims attack on Save the Children in Jalalabad". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 25 February 2018.
- ^ "IS claims responsibility for church shooting in Russia". ABC News. Retrieved 25 February 2018.
- ^ "French PM calls supermarket hostage situation 'terrorist act'". Independent.co.uk. 23 March 2018.
- ^ "Ten killed in Iraq funeral bombing – local official". Reuters. Archived from the original on 14 April 2018. Retrieved 14 April 2018.
- ^ "Islamic State claims responsibility killing, injuring tens of people in blasts, north of Salahuddin". Iraqi News. 13 April 2018. Retrieved 14 April 2018.
- ^ "25 قتيلاً ضحايا هجوم استهدف مشيعين في قضاء الشرقاط بالعراق". Retrieved 14 April 2018.
- ^ "Photographer among dead in Kabul blasts". BBC News. 30 April 2018. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ "Death Toll Rises To 29 in Kabul Explosion". TOLOnews. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ "ISIS Claims Responsibility for Kabul Suicide Bombing | Time". Archived from the original on 23 April 2018. Retrieved 23 April 2018.
- ^ Elumami, Ahmed. "Suicide militants storm HQ of Libya's election commission, 12 dead". U.S. Retrieved 2 May 2018.
- ^ "At Least 16 Killed in Islamic State Attack on Libya's Electoral Commission". libyatimes.net. Retrieved 3 May 2018.
- ^ "Isis claims responsibility for deadly knife attack in Paris". The Independent. 13 May 2018.
- ^ "ISIS claim responsibility for shooting in Belgium". Evening Standard. London. 30 May 2018.
- ^ "ISIL blast kills 36 as Afghanistan extends Taliban ceasefire". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 24 June 2018.
- ^ a b Sultan, Ahmad. "Deadly blast hits eastern Afghan city, targeting Sikh minority". U.S. Retrieved 2 July 2018.
- ^ a b "With 149 martyred, Mastung is one of the deadliest terrorist attacks in Pakistan's history". The Express Tribune. 16 July 2018. Retrieved 16 July 2018.
- ^ "Kabul explosion toll rises to 23, with 107 injured; Islamic State claims attack on airport after vice-president's return". firstpost.com. 23 July 2018. Retrieved 23 July 2018.
- ^ "31 killed in suicide blast outside Quetta polling station". Dawn. 25 July 2018. Retrieved 25 July 2018.
- ^ "Six policemen among 29 martyred in suicide attack outside Quetta polling station". Geo News. Retrieved 25 July 2018.
- ^ "Quetta: Death toll jumps to 31 in election day blast". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 25 July 2018.
- ^ "Syria war: More than 200 dead in suicide attacks". BBC. 25 July 2018. Retrieved 26 July 2018.
- ^ Al-awsat, Asharq. "ISIS Commits Massacre in Syria's Sweida as Toll Rises". aawsat.com (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 26 July 2018.
- ^ "ISIS claims attack on cyclists in Tajikistan, releases video of purported cell". CBS News. 31 July 2018.
- ^ "Suicide bomb attack on Afghan Shi'ite mosque kills 39, 80 injured". Reuters. Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- ^ Adam (4 August 2018). "'Amaq Reports IS' Responsibility for Suicide Attack at Shi'ite Mosque in Paktia". ent.siteintelgroup.com. Retrieved 4 August 2018.
- ^ "Isis claims responsibility for Afghanistan suicide bombing that killed 34 students". The Independent. 16 August 2018.
- ^ "Dozens killed as bomber hits college students in Afghan capital". cbsnews. 15 August 2018. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- ^ "Afghanistan: ISIL Suicide bomber targets school in Kabul". Al Jazeera. 16 August 2018.
- ^ "Several Killed as Gunmen Attack Military Parade in Iran: State TV". The New York Times. Reuters. Retrieved 22 September 2018.
- ^ "Several killed, at least 20 injured in attack on military parade in Iran". The Washington Post. Retrieved 22 September 2018.
- ^ Saeed Kamali Dehghan (22 September 2018). "Terrorists kill Iranian children and soldiers in military parade attack". The Guardian. Retrieved 22 September 2018.
- ^ Dakin Andone; Hamdi Alkhshali; Samantha Beech (23 September 2018). "ISIS video claims to show attackers of Iranian military parade". CNN.
- ^ "Egypt: Deadly attack on bus near Coptic Christian monastery". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 2 November 2018.
- ^ "Coptic Church: Attack on Christians in Egypt Kills 7". Voanews. Retrieved 2 November 2018.
- ^ "IS attack on Christian pilgrims in Egypt kills 7, wounds 19". stamfordadvocate.com. Retrieved 2 November 2018.
- ^ "Melbourne attack: Man shot dead after fire and fatal stabbing". BBC News. Retrieved 9 November 2018.
- ^ "Strasbourg Christmas market shooting suspect killed by police". The Independent. 13 December 2018.
- ^ Jocelyn, Thomas (19 January 2019). "Russia says gas leak likely caused apartment explosion claimed by Islamic State". Long War Journal. Public Multimedia Inc. Retrieved 25 July 2019.
- ^ "39 Russian Crusaders Are Killed, Dozens Are Wounded or Lost in an Operation Conducted by the Islamic State Soldiers in Qawqaz". An-Naba. No. 165. 19 January 2019. Retrieved 25 July 2019 – via Long War Journal.
- ^ "Philippines General: 2 Children Killed in Abu Sayyaf Attack – Philippines". ReliefWeb. 27 May 2019. Retrieved 17 June 2019.
- ^ "Pakistan: Deadly explosion rips through Quetta market". aljazeera.com. Archived from the original on 11 June 2019. Retrieved 12 April 2019.
- ^ "Sri Lanka bombings: All the latest updates". Al Jazeera. 2 May 2019. Retrieved 6 June 2019.
- ^ "Sri Lankan government agrees to independent inquiry into Easter attacks". Catholic Philly. Retrieved 6 October 2019.
- ^ Callimachi, Rukmini; El-Naggar, Mona; Goldman, Russell; Gettleman, Jeffrey; Pérez-Peña, Richard; Schmitt, Eric (23 April 2019). "Grief, Anger and Recriminations in Sri Lanka as ISIS Claims It Staged Bomb Attacks". The New York Times. Retrieved 6 June 2019.
- ^ "Children among 16 killed in Sri Lanka raid on terrorist hideout". Thenational.ae. 27 April 2019. Retrieved 6 June 2019.
- ^ Kiley, Sam; Wright, Rebecca; McKenzie, Sheena; Griffiths, James (27 April 2019). "10 civilians and 6 suspected terrorists killed in police raid in Sri Lanka". CNN. Retrieved 6 June 2019.
- ^ Darrah, Nicole (18 August 2019). "Afghanistan wedding hall suicide bombing leaves at least 63 dead, more than 180 others wounded". Fox News.
- ^ "A month of killing in Afghanistan". BBC News. 16 September 2019.
- ^ "Afghanistan: Scores killed in Kabul wedding blast". Al Jazeera.
- ^ Ebraheem, Mohammed (25 August 2019). "6 Iraqi people killed as IS mortar attack strikes pitch in Kirkuk". Iraqi News. Retrieved 26 August 2019.
- ^ AAP (25 August 2019). "At least six killed on Iraq football pitch by suspected Islamic State militants". Retrieved 26 August 2019.
- ^ Abdul-Zahra, Qassim (25 August 2019). "IS mortar attack on soccer field kills 6 in Iraq". Associated Press. Retrieved 26 August 2019.
- ^ "17 killed in a 'Islamic State' on a Tajik Border Post". VOA News. 6 November 2019. Archived from the original on 6 November 2019. Retrieved 6 November 2019.
- ^ "ISIL blamed for deadly attack on Tajik border outpost". Al-Jazeera. 6 November 2019. Archived from the original on 29 November 2019. Retrieved 4 December 2019.
- ^ "Islamic State in Nigeria 'beheads Christian hostages'". BBC News. 27 December 2019. Retrieved 10 January 2019.
- ^ Okonkwo, Rudolf Ogoo (28 December 2019). "An Islamic State Christmas killing of 11 hostages in Nigeria threatens to flare up religious tensions". Qz.com. Retrieved 10 January 2019.
- ^ "Niger Army Base Attack Death Toll Rises To at Least 89: Security Sources". The New York Times. Reuters. 11 January 2020. Archived from the original on 11 January 2020. Retrieved 5 February 2020.
- ^ Adebayo, Bukola (13 January 2020). "Niger declares three days of mourning after 89 soldiers killed in attack on military base". Cable News Network. Turner Broadcasting System, Inc. Retrieved 5 February 2020.
- ^ Ross, Aaron (14 January 2020). McAllister, Edward (ed.). "Islamic State claims responsibility for Niger army base attack". Reuters. The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. Retrieved 5 February 2020.
- ^ Saldivia, Gabriela (2 February 2020). "3 Injured In 'Terrorist-Related' Stabbing In London; Suspect Killed By Police". NPR. Retrieved 5 February 2020.
- ^ Steinbuch, Yaron (3 February 2020). "ISIS claims responsibility for London stabbing attack". NY Post. Retrieved 5 February 2020.
- ^ "Dozens killed in Kabul ceremony attack claimed by ISIL". www.aljazeera.com.
- ^ "32 killed, 81 hurt in Islamic State attack in Kabul | New Straits Times". NST Online. 7 March 2020.
- ^ George, Susannah; Salahuddin, Sayed. "ISIS attack in Kabul leaves 32 dead, more than 80 wounded". Washington Post.
- ^ Herat, Emma Graham-Harrison Akhtar Mohammad Makoii in (12 May 2020). "Newborns among 40 killed in attacks on Afghan hospital and funeral". The Guardian – via www.theguardian.com.
- ^ Ehsan Popalzai; Zamira Rahim; Emma Reynolds; Rob Picheta (12 May 2020). "Infants and mothers killed in attack on Kabul hospital". CNN.
- ^ "Official Says Suicide Attack in Eastern Afghanistan Kills 5". The New York Times.
- ^ Wamsley, Laurel (3 August 2020). "ISIS Attack on Afghan Prison Leaves at Least 29 Dead". NPR.
- ^ "Afghan forces retake prison after ISIS attack that killed at least 29". Fox News. 3 August 2020.
- ^ "ISIS-claimed attack on Afghan prison leaves dozens dead and sets hundreds free". CBS News. 3 August 2020.
- ^ Petty, Martin; Davies, Ed; Richardson, Alex (24 August 2020). "Twin bombings kill 15, wound scores in Philippine south". Reuters. Retrieved 24 August 2020.
- ^ "14 killed in Jolo twin bombings in southern Philippines". Al Jazeera English. 24 August 2020. Retrieved 24 August 2020.
- ^ Gutierrez, Jason (24 August 2020). "Two Explosions Rip Through Philippines, Killing at Least 14". The New York Times. Retrieved 24 August 2020.
- ^ Schuetze, Christopher F.; Eddy, Melissa; Bennhold, Katrin; Koettl, Christoph (3 November 2020). "Vienna Shooting Live Updates: Terrorist Attack in Austria Leaves 3 Dead and Many Wounded". The New York Times. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- ^ Boston, William; Pancevski, Bojan; Bender, Ruth (3 November 2020). "Vienna Shooting: Attacker Was ISIS Sympathizer; at Least Three Dead". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- ^ "Vienna terror attack: 'Islamist' motive suspected in deadly shootings | DW | 03.11.2020". DW.COM. Deutsche Welle (www.dw.com). Deutsche Welle (www.dw.com). 3 November 2020. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- ^ "Syria: Dozens killed in Isis bus attack". TheGuardian.com. 31 December 2020.
- ^ "Islamic state claims responsibility for Wednesday's Syria bus attack". Reuters. 31 December 2020.
- ^ Yousafzai, Gul (3 January 2021). "Islamic State claims responsibility for attack on Pakistan's Shi'ite Hazara minority that kills 11". Reuters.
- ^ "Pakistan coal miners kidnapped and killed in IS attack". BBC News. 3 January 2021.
- ^ "Gunmen kill many Hazara Shia coal miners in southwest Pakistan". Al Jazeera.
- ^ "ISIS claims responsibility for attack on Pakistan's Shi'ite minority". The Jerusalem Post. 3 January 2021.
- ^ "11 miners killed in Pakistan; ISIS claims responsibility". gmanetwork.com. 4 January 2021.
- ^ "ISIL takes responsibility for deadly Baghdad suicide bombings". Al Jazeera English. 22 January 2021. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ^ "Iraq bombing: IS says it was behind deadly suicide attacks in Baghdad". BBC News. 22 January 2021. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ^ "Islamic State claims responsibility for Baghdad's suicide attack". Reuters. 22 January 2021. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ^ "Islamic State says it killed female media workers in east Afghanistan". Reuters. 3 March 2021. Retrieved 5 March 2021.
- ^ "Bomb kills female Afghan doctor, gunmen kill 7 workers: Officials". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 5 March 2021.
- ^ George, Susannah; Hassan, Sharif (10 May 2021). "School bombing heightens fears among Afghanistan's Hazaras, long a target for militants, amid U.S. exit". The Washington Post.
- ^ "Iraq Market Bombing Claimed by ISIS Kills Nearly 36 on Eve of Eid Holiday".
- ^ "ISIS claims responsibility for Iraq suicide attack that left dozens dead". 20 July 2021.
- ^ "Kabul explosions: US service members and Afghan civilians killed in Islamic State suicide bombings". Euronews. 26 August 2021. Retrieved 26 August 2021.
- ^ Atwood, Kylie; Sciutto, Jim; Starr, Barbara (26 August 2021). "Officials: Explosion at Kabul airport appears to be a suicide attack". CNN. Archived from the original on 26 August 2021. Retrieved 26 August 2021.
- ^ Pasko, Simcha (26 August 2021). "Suicide bombing kills, injures several at Kabul airport". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 26 August 2021.
- ^ "Large Explosion Reported Outside Kabul Airport". The Daily Beast. 26 August 2021. Retrieved 26 August 2021.
- ^ "Blast reported outside Hamid Karzai International Airport in Kabul". CNN. 26 August 2021. Retrieved 26 August 2021.
- ^ "Explosion outside Kabul airport confirmed hours after US, British terror warnings". Fox News. 26 August 2021. Retrieved 26 August 2021.
- ^ "Eleven Marines, Navy Medic Killed in the Afghanistan Attacks". Bloomberg. 26 August 2021.
- ^ "Biden on Kabul suicide bombings: 'We will hunt you down and make you pay". 27 August 2021.
- ^ "ISIS supporter shot dead by New Zealand police after shoppers stabbed in 'terrorist attack'". 3 September 2021.
- ^ "Afghanistan: Several dead as blasts rock Jalalabad and Kabul". Al Jazeera. 18 September 2021. Retrieved 21 September 2021.
- ^ Berger, Miriam; Khan, Haq Nawaz (18 September 2021). "Islamic State in Afghanistan claims responsibility for attacks targeting Taliban". The Washington Post. Retrieved 21 September 2021.
- ^ "Bomb kills at least 55 at mosque in Afghanistan's Kunduz". 8 October 2021.
- ^ "ISIS claims responsibility for deadly Afghan mosque attack | CBC News".
- ^ Peshimam, Gibran (16 October 2021). "Blast at Shi'ite mosque in Afghan city of Kandahar causes heavy casualties". Reuters. Retrieved 21 October 2021.
- ^ Mehta, Amar (16 October 2021). "Afghanistan: At least 35 killed in suicide bombing during prayers at Kandahar mosque". Sky News. Retrieved 21 October 2021.
- ^ "Afghanistan: Suicide attack hits Kandahar mosque during prayers". BBC News. 15 October 2021. Retrieved 21 October 2021.
- ^ "Dozens Dead in West Niger Attack by Jihadis". Voice of America. Retrieved 2 February 2024.
- ^ "Afghanistan: At least 10 killed in explosion at Kabul mosque". www.aljazeera.com. Al Jazeera Media Network. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- ^ "Blast kills more than 50 at Kabul mosque, its leader says". Reuters. 29 April 2022. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- ^ Gannon, Kathy (29 April 2022). "Powerful explosion at Kabul mosque kills at least 10 people". Associated Press News. Archived from the original on 7 August 2022. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- ^ AFP (1 May 2022). "ISIS claims attack on Kabul mosque". Al Arabiya News. Retrieved 27 October 2022.
- ^ Weiss, Caleb. "Islamic State claims first attacks inside Benin". FDD. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ "Two Taliban Police Officers Killed In Kabul By Alleged Islamic State-Khorasan Gunman". Gandhara. 4 August 2022.
- ^ "Bomb blast in Afghanistan capital Kabul kills eight civilians, wounds 18". Alarabiya. 5 August 2022.
- ^ "Death toll in last week's Kabul school blast climbs to 52". AP NEWS. 3 October 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ Nhamirre, Borges; Hill, Matthew (20 October 2022). "Suspected Islamist Militants Attack Ruby Mine in Northeastern Mozambique". Bloomberg News. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ Swami, Praveen (12 November 2022). "Islamic State takes responsibility for October attack on Indian-owned ruby mine in Mozambique". ThePrint. Retrieved 6 May 2023.
- ^ "Attack on Shiraz shrine kills 15: Iranian state media". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 27 October 2022.
- ^ Faiez, Rahim (13 December 2022). "China urges citizens to leave Afghanistan after Kabul attack". Associated Press. Islamabad, Pakistan. Retrieved 14 December 2022.
- ^ Twitter https://twitter.com/sada_alsharqieh/status/1607309482874347524. Retrieved 27 December 2022.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Twitter https://twitter.com/vvanwilgenburg/status/1607392724524666880. Retrieved 27 December 2022.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Awadallah, Nadine; Yawar, Mohammad Yunus (2 January 2023). Cawthorne, Andrew; MacSwan, Angus (eds.). "Islamic State claims responsibility for Kabul attack". Reuters. Retrieved 3 January 2023.
- ^ "Deadly 'suicide' blast outside Afghan foreign ministry in Kabul". Al Jazeera. 11 January 2023.
- ^ "Cleanup at Congo church begins after blast kills 14". Reuters. 16 January 2023. Retrieved 22 April 2023.
- ^ "Islamic State claims responsibility for DR Congo Church bombing". Voice of America. 16 January 2023. Retrieved 22 April 2023.
- ^ "At least 15 security force killed in North Burkina Faso attack". Reuters. 23 March 2023. Retrieved 22 April 2023.
- ^ "More than a dozen killed in DR Congo attack attributed to Islamic State group". France 24. 8 April 2023. Retrieved 22 April 2023.
- ^ "Islamic State Group claims DR Congo attack; About 20 dead". Voice of America. 8 April 2023. Retrieved 22 April 2023.
- ^ "26 people dead in Islamic State attack in Syria". i24 News. 16 April 2023. Retrieved 22 April 2023.
- ^ El-Khatib, Ahmed (16 April 2023). "Reports: Militants 26 people in Syrian country-side". AP News. Retrieved 22 April 2023.
- ^ a b "Pakistan suicide bombing death toll rises to 63". Al-Jazeera. 2 August 2023.
- ^ a b "Islamic State Attack Kills 17 at Shiite Mosque in Northern Afghanistan". New York Times. 13 October 2023.
- ^ "Teacher killed and two injured in stabbing at school in northern France". The Guardian. 13 October 2023.
- ^ "French prosecutor says alleged attacker in school stabbing declared allegiance to Islamic State". AP. 17 October 2023.
- ^ "Police shoot dead suspected gunman accused of killing 2 Swedes in Brussels". CNN. 16 October 2023.
- ^ "Brussels shooting: Police shoot dead attacker who killed Swedes". BBC. 17 October 2023.
- ^ "ISIS Claims Responsibility For Brussels Shooting". NDTV. 17 October 2023.
- ^ Lema, Karen; Morales, Neil Jerome (4 December 2023). "Islamic State claims responsibility for deadly Philippine bombing". Reuters. Retrieved 5 December 2023.
- ^ Rita, Joviland (14 December 2023). "PNP: 2 more suspects linked to MSU bombing arrested". GMA News. Retrieved 17 December 2023.
- ^ "Five people feared dead in suspected ADF attack in Uganda". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 19 December 2023.
- ^ i24NEWS (4 January 2024). "ISIS claims responsibility over attack that killed over 80 people in Iran". I24news. Retrieved 4 January 2024.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Death toll of ISIS-claimed Kabul blast rises to five". Al Arabiya. 7 January 2024. Retrieved 11 January 2024.
- ^ "Bomb Hits Minibus in Kabul, Killing 2 Afghan Civilians". VOA News. Retrieved 11 January 2024.
- ^ "ISIS claims responsibility for deadly Afghanistan minivan blast". FOX News. Retrieved 11 January 2024.
- ^ "ISIS kills three soldiers in attack in western Iraq, shows it is still active". The Arab Weekly. 15 January 2024. Retrieved 16 January 2024.
- ^ "Shooting stuns worshippers at Istanbul Catholic mass". BBC News. 28 January 2024. Retrieved 28 January 2024.
- ^ "ISIS claims responsibility for attack on election rally of Tehreek-e-Insaf party in Pakistan". Khaama Press. 31 January 2024. Retrieved 31 January 2024.
- ^ "Bombings at Pakistani political offices kill at least 30 a day before parliamentary elections". ABC News. Retrieved 7 February 2024.
- ^ "29 killed, 40 injured after 2 attacks hit Balochistan before Pakistan election". South China Morning Post. 7 February 2024. Retrieved 7 February 2024.
- ^ "Islamic State Group Claims Bombing In Pakistan's Pishin District". Barron's. Retrieved 7 February 2024.
- ^ "Islamic State Mozambique Province (ISMP) Reportedly Urges Christians To Convert, Pay Jizyah, Or Be Killed, Calls On Muslims To Help Group 'Defend Islam'". MEMRI. Retrieved 14 February 2024.
- ^ "Islamic State Raids Mozambique Town as Total Plans LNG Return". Bloomberg. 13 February 2024. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
- ^ "Rebels linked to the Islamic State group kill at least two dozen civilians in eastern Congo". ABC News. Archived from the original on 20 February 2024. Retrieved 20 February 2024.
- ^ "13 truffle hunters killed in Syrian desert in Islamic State landmine blast". WION. Retrieved 27 February 2024.
- ^ "In Video Uploaded To Internet, Teenage Stabber Of Jew In Zürich Swears Allegiance To Islamic State (ISIS), Calls On Muslims To Target Jews And Christians Everywhere". MEMRI.
- ^ "Teenage Jihadist Behind Zurich Stabbing Pledged to IS "Caliph," Threatened Major Attack on Jews in Switzerland". SITE.
- ^ "Islamic State Claims Attack on Niger Army That Killed Dozens". Voice of America. Retrieved 24 March 2024.
- ^ "Afghanistan: IS claims responsibility for suicide bomb at Kandahar bank". 21 March 2024. Retrieved 22 March 2024.
- ^ "Islamic State claims responsibility for suicide bombing of Kandahar bank". The Independent. 22 March 2024. Retrieved 22 March 2024.
- ^ "Islamic State group claims responsibility for bombing at Afghan bank and says it targeted Taliban". ABC News. Retrieved 22 March 2024.
- ^ Chao-Fong, Léonie; Yang, Maya; Chao-Fong (now), Léonie; Yang (earlier), Maya (22 March 2024). "Moscow concert hall attack: Islamic State claims responsibility for shooting that killed dozens of people – latest updates". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 22 March 2024.
- ^ Kilner, James; Rainey, Venetia; Henderson, Cameron; Sabur, Rozina (22 March 2024). "Ukraine-Russia war live: At least 40 killed as gunmen attack Moscow concert venue". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Retrieved 22 March 2024.
- ^ "Video shows fire damage in Moscow's Crocus concert hall". BBC. Retrieved 24 March 2024.
- ^ York, Christ (23 March 2024). "Islamic State claims responsibility for Moscow terrorist attack". Kyiv Independent. Retrieved 23 March 2024.
- ^ Schmitt, Eric (22 March 2024). "What We Know About ISIS-K, the Group That Claimed Responsibility for the Moscow Attack". New York Times. Retrieved 23 March 2024.
- ^ Belam, Martin (23 March 2024). "Moscow concert hall attack: death toll rises to 115 as Putin told suspects have been detained – live updates". the Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 23 March 2024.
- ^ "Moscow attack: Day of mourning after 137 killed at Crocus City Hall concert". 23 March 2024. Retrieved 24 March 2024.
- ^ "Three out of four Moscow concert hall attack suspects plead guilty in court". Sky News. Retrieved 25 March 2024.
- ^ "The Islamic State group says it was behind a mosque bombing in Afghanistan that killed 6 people". ABC News. Retrieved 1 May 2024.
- ^ "ISIS claims attack in Afghanistan that killed three Spaniards". al-Arabiya.
- ^ "Lebanon arrests gunman following attack on US embassy in Beirut". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 5 June 2024.
- ^ "ISIS kills 16 Syrian soldiers:Monitor". Al Arabiya. 12 June 2024. Retrieved 18 August 2024.
- ^ "Russian forces kill ISIS-linked hostage takers at detention centre". Reuters. 16 June 2024.
- ^ "Priest and six law enforcement officers killed in attacks on synagogues and church in Russia's Dagestan". CNN. 23 June 2024. Retrieved 23 June 2024.
- ^ "Saluting Lone Wolves Inspired by its Ideology, IS Says Faith-based Brotherhood Triumphs Over Organizational Ties". SITE. 4 July 2024.
- ^ "Pro-IS Unit Applies "Flames of War" to Russia in Glorifying Attacks in Moscow, Dagestan, and Ingushetia". SITE. 8 July 2024.
- ^ "Akcije širom Srbije: Uhapšen Kemal Begović iz Novog Pazara, priveden i državljanin BiH". Sandzacke.rs (in Bosnian). 30 June 2024. Retrieved 2 July 2024.
- ^ "IS Supporters Distribute Video of Pledge to "Caliph" by Executor of Crossbow Attack Outside Israeli Embassy in Belgrade". SITE. 3 July 2024.
- ^ "Islamic State claims responsibility for rare attack at Shi'ite Muslim mosque in Oman". Reuters. 16 July 2024.
- ^ "Blast In Kabul's Hazara Area Kills At Least 1, Injures 11". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 11 August 2024.
- ^ "Islamic State claims responsibility for explosion in the Afghan capital Kabul that killed at least 1". ABC News. 12 August 2024.
- ^ Gigova, Radina (23 August 2024). "ISIS-affiliated inmates kill four prison officers at Russian penal colony". CNN. Retrieved 23 August 2024.
- ^ "ISIS prisoners killed after slashing guards, seizing hostages in Russian jail". NBC News. 23 August 2024.
- ^ "IS Takes Credit for Knife Attack in Solingen, Germany". SITE. 24 August 2024.
- ^ "'Amaq Reveals Image of Masked Solingen Attacker, Announces Possession of Video". SITE. 25 August 2024.
- ^ "Islamic State claims Kabul blast citing Bagram base detentions". Reuters. 3 September 2024. Retrieved 3 September 2024.
- ^ "IS group claims deadly attack in central Afghanistan". France 24. 12 September 2024. Retrieved 12 September 2024.
- ^ "Backgrounder on The Islamic State and Jihadism in Azerbaijan".
- ^ "In First Recorded Fighting Activity in Azerbaijan, IS Reports Clash in Qusar District Inflicting 8 Casualties". SITE. 19 September 2024.
External links
- Yourish, Karen; Watkins, Derek; Giratikanon, Tom; Lee, Jasmine C. (1 July 2016). "How Many People Have Been Killed in ISIS Attacks Around the World". The New York Times.
See also
- 2014 American rescue mission in Syria
- Military intervention against ISIL
- Operation Inherent Resolve
- Boko Haram insurgency
- Human rights in ISIL-controlled territory
- Iran and ISIL
- Killing of captives by ISIL
- List of armed groups in the Syrian Civil War
- List of wars and battles involving ISIL
- Management of Savagery
- Fall of Mosul
- First Battle of Tikrit
- Northern Iraq offensive (August 2014)
- Portrayal of ISIL in American media
- Shia–Sunni relations
- Siege of Kobanî
- Sinjar massacre
- Battle of Baiji (October–December 2014)
- Battle of Ramadi (2014–15)
- Battle of Baiji (2014–15)
- Sinjar offensive
- Al-Hasakah offensive (February–March 2015)
- Second Battle of Tikrit (March–April 2015)
- Tell Abyad Campaign (2015)
- Spillover of the Syrian Civil War
- United Kingdom and ISIL
References
Bibliography
- Abass, Ademola (2014). Complete International Law: Text, Cases and Materials (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Fishman, Brian (2008). "Using the Mistakes of al Qaeda's Franchises to Undermine Its Strategies". Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science. 618: 46–54. doi:10.1177/0002716208316650. JSTOR 40375774.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kahl, Colin H. (2008). "When to Leave Iraq: Walk Before Running". Foreign Affairs. 87 (4): 151–154. JSTOR 20032727.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Phillips, Andrew (2009). "How al Qaeda lost Iraq" (PDF). Australian Journal of International Affairs. 63 (1): 64–84. doi:10.1080/10357710802649840.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Simon, Steven (2008). "The Price of the Surge: How U.S. Strategy Is Hastening Iraq's Demise". Foreign Affairs. 87 (3): 57–72, 74–76. JSTOR 20032651.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Isis: the inside story. "One of the Islamic State's senior commanders reveals details of the terror group's origins inside an Iraqi prison." The Guardian
- Wood, Graeme (March 2015). What ISIS Really Wants. "The Islamic State is no mere collection of psychopaths. It is a religious group with carefully considered beliefs, among them that it is a key agent of the coming apocalypse. Here's what that means for its strategy—and for how to stop it." The Atlantic
External links
- "Iraq updates", Understanding war (World Wide Web log), Institute for the Study of War
- "The New War in Iraq ISIL Overview", Midwest Diplomacy, 21 September 2013.
- This Is the Promise of Allah (PDF) (declaration), The Islamic State, 29 June 2014.
- Frontline: Losing Iraq (July 2014), The Rise of ISIS (October 2014), Obama at War (May 2015), Escaping ISIS (July 2015), documentaries by PBS
- The Islamic State - Full Length, documentary by Vice News (August 2014)
- "ISIS: Portrait of a Jihadi Terrorist Organization" – Report by the Intelligence and Terrorism Information Center.
- From Chechnya To Syria & Analysis of Russian-speaking Foreign Fighters in Syria
- Operation Inherent Resolve airstrike updates
- ISIL frontline maps (Iraq and Syria)
- The Islamic State – Jihadology Research project by Aaron Zelin
- ISIL and Antiquities Trafficking - FBI Warns Dealers, Collectors About Terrorist Loot, FBI
#invoke:navbox with collapsible groups #invoke:Authority control
- Ill-formatted IPAc-en transclusions
- 2010s-related lists
- 2020s-related lists
- Lists of terrorist incidents
- ISIL terrorist incidents
- Terrorist incidents by perpetrator
- Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
- 1999 establishments in Asia
- Anti-government factions of the Syrian Civil War
- Anti-Shi'ism
- Designated terrorist organizations associated with Islam
- Organizations designated as terrorist in Asia
- Groups practising sexual slavery
- Iraqi insurgency (2003–11)
- Iraqi insurgency (2011–present)
- Islamism in Iraq
- Islamism in Syria
- Jihadist groups
- Organisations based in Iraq
- Organisations designated as terrorist by Australia
- Organisations designated as terrorist by India
- Organisations designated as terrorist by the European Union
- Organizations designated as terrorist by the Turkish Directorate General for Security
- Persecution of Yazidis
- Rebel groups in Egypt
- Rebel groups in Iraq
- Rebel groups in Libya
- Rebel groups in Syria
- Russian Federal Security Service designated terrorist organizations
- Salafi groups
- Sunni Islamist groups
- Terrorism in Iraq
- Terrorism in Lebanon
- Terrorism in Syria
- Terrorism in Turkey
- United Kingdom Home Office designated terrorist groups
- Violent non-state actors
- Wahhabism
- Irregular military
- November 2015 Paris attacks
