List of smoking bans in the United States
The following is a list of smoking bans in the United States. For smoking bans and restrictions outside the United States, see the worldwide list of smoking bans.
The United States Congress has not attempted to enact any nationwide federal smoking ban. Therefore, smoking bans in the United States are entirely a product of state and local criminal and occupational safety and health laws.
In 1995, California was the first state to enact a statewide smoking ban; throughout the early to mid-2000s, especially between 2004 and 2007, an increasing number of states enacted a statewide smoking ban of some kind. As of January 2015, the most recent statewide smoking ban is North Dakota's, which was ratified by voters on November 6, 2012.
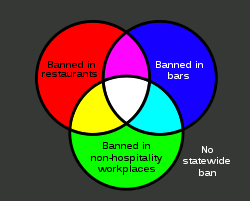
As further detailed in this list, smoking laws vary widely throughout the United States. Some places in the United States do not generally regulate smoking at all, some ban smoking in certain areas and not others, and some ban smoking nearly everywhere, even in outdoor areas (no state bans smoking in all public outdoor areas, but some local jurisdictions do). As of January 1, 2015, according to the American Nonsmokers' Rights Foundation, 81.8% of the U.S. population lives under a ban on smoking in "workplaces, and/or restaurants, and/or bars, by either a state, commonwealth, or local law,",[1] though only 49.3% live under a ban covering all workplaces and restaurants and bars.[2] A smoking ban (either state or local) has been enacted covering all bars and restaurants in each of the 60 most populated cities in the United States except these 15: Arlington, Atlanta, Fort Worth, Jacksonville, Memphis, Miami, Las Vegas, Nashville, Oklahoma City, Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, St. Louis, Tampa, Tulsa, and Virginia Beach.[3][4]
Overview
Statewide bans on smoking in all enclosed public places
As of January 2014, 28 states have enacted statewide bans on smoking in all enclosed public places, including all bars and restaurants: Arizona, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Illinois, Iowa, Kansas, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Montana, Nebraska, North Dakota, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Rhode Island, South Dakota, Utah, Vermont, Washington, and Wisconsin.
However, these states exempt a variety of places from their respective smoking bans. All except six (Delaware, Montana, North Dakota, Utah, Vermont, and Washington) exempt tobacconists. All except four (Michigan, North Dakota, Vermont, and Wisconsin) allow hotels and motels to designate a certain percentage of smoking rooms. Many also exempt or do not cover casinos (9), private clubs (7), cigar bars (13), or certain small workplaces (8). The following is a table of common exemptions from these 28 states' smoking bans:
| States that exempt tobacconists | States that exempt cigar bars | States that exempt private clubs | States that exempt casinos | States that exempt small workplaces |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AZ, CA, CO, CT, HI, KS, IL, IA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, NE, NJ, NM, NY, OH, OR, RI, SD, WI | CA, CO, CT, MA, MI, NE, NJ, NM, NY, OR, RI, SD, WI | AZ, CT, IA, KS, MA, NY, OH | CT, IA, KS, ME (OTB parlors, beano and bingo halls), MI, NJ (including OTB parlors), NM, RI (including OTB parlors), WI | CA (5 or fewer employees), CO (3 or fewer employees), CT (5 or fewer employees), ND (1 employee), NM (1 employee), OH (family owned and operated), UT (1 employee), VT (1 employee) |
In Connecticut, Oregon, Montana, Utah, and Wisconsin, the state law preempts local governments from enacting stricter smoking bans than the state, though some cities and/or counties in some of those states have enacted local versions of the state's smoking ban. In the other 23 states with a statewide general smoking ban, some cities and/or counties have enacted stricter local smoking bans to varying degrees. The strictest smoking ban in the United States is in Calabasas, California, where smoking anywhere a non-smoker could congregate, including public sidewalks and apartment complexes, is a misdemeanor punishable by a fine of at least $250.[5]
Statewide smoking bans exempting adult-only venues
As of January 2014, 6 states ban smoking in most enclosed public places, but permit adult venues such as bars (and casinos, if applicable) to allow smoking if they choose: Arkansas, Florida, Indiana, Louisiana, Pennsylvania, and Tennessee. In Arkansas, Indiana, and Tennessee, the law also allows smoking in restaurants with liquor licenses that do not admit persons under 21; indeed, in Tennessee, the law exempts any adult-only venue of any kind. In Florida, Pennsylvania, and Tennessee, state law preempts local governments from enacting stricter smoking bans than the state, though in the other four states, some cities and/or counties have enacted stricter local smoking bans to varying degrees, in some cases banning it in all enclosed workplaces. See individual state listings below for details.
Unique statewide smoking bans
As of January 2014, 6 states have enacted smoking bans in particular places that do not fit in the other categories:
- Georgia relegates smoking in restaurants serving persons under 18 to separately enclosed smoking rooms, allows smoking freely in restaurants and bars limiting patronage to persons over 18, and allows most anywhere else either to designate smoking areas indoors or, in many cases, to allow smoking freely; local governments in Georgia can and have passed stricter smoking bans than the state.
- Idaho bans smoking in restaurants, but exempts both bars (which can be 100% smoking) and small workplaces (which can have a designated smoking area); local governments in Idaho can regulate smoking more strictly than the state.
- Nevada generally bans smoking in all public places and places of employment, but exempts bars, casinos, strip clubs, brothels, and retail tobacco stores, and restaurants that do not allow patrons under 21 years of age. In all other restaurants, smoking is relegated to separately ventilated designated smoking areas. Local governments in Nevada may regulate smoking more strictly than the state.
- New Hampshire bans smoking in restaurants and some bars (those besides cigar bars and private clubs), schools, and certain common areas open to the public, but not anywhere else, and state law prohibits local governments from enacting local smoking bans.
- North Carolina bans smoking in all restaurants and bars (excluding cigar bars and private clubs), as well as government buildings and vehicles, but does not regulate smoking anywhere else. Local governments may regulate smoking more strictly than the state, except in cigar bars, private clubs, tobacco shops, private residences/vehicles, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, and theatrical performances involving smoking.
- In Virginia, smoking is banned in schools, state offices, and certain healthcare facilities and common areas, but not anywhere else; in restaurants (including bars), smoking is relegated to separately ventilated designated smoking rooms, unless the restaurant is operated by a retail tobacco store, in which case smoking can be allowed on 100% of the premises. The state law prohibits local governments from regulating smoking more strictly than the state.
States with no statewide smoking ban
As of January 2014, 10 states have not enacted any general statewide ban on smoking in any non-government-owned spaces: Alabama, Alaska, Kentucky, Mississippi, Missouri, Oklahoma, South Carolina, Texas, West Virginia, and Wyoming. Instead, laws in most of these states (see individual state listings below for further information) require proprietors of certain places to designate smoking and non-smoking areas and post warning signage.
In Oklahoma, state law prohibits local governments from regulating smoking more strictly than the state, making it the only state without any kind of legislated smoking bans. In the other nine states, cities and/or counties have enacted stricter smoking laws than the state, in some cases banning smoking in all enclosed workplaces. In Alabama and Mississippi, the state smoking law expressly allows all local governments to do so. In Alaska, Kentucky, Missouri, South Carolina, Texas, and West Virginia, a court has ruled that certain local governments have the power to do so. See the individual state listings below for details.
Smoking laws and non-states
In the District of Columbia, American Samoa, Puerto Rico and the United States Virgin Islands, smoking is banned in all enclosed public places, including bars and restaurants. Guam prohibits smoking in restaurants, but the ban doesn't extend to workplaces or any other businesses. The Northern Mariana Islands prohibits smoking in most workplaces and restaurants, but not in bars.
Smoking laws and the U.S. federal government
Although Congress has not attempted to enact a general nationwide federal smoking ban in workplaces, several federal regulations do concern indoor smoking. Effective April 1998, smoking is banned by the United States Department of Transportation on all commercial passenger flights in the United States, and/or by American air carriers.[6] This was long after Delta Air Lines had banned smoking on all of its flights. On August 9, 1997, President Bill Clinton issued Executive Order 13058, banning smoking in all interior spaces owned, rented, or leased by the Executive Branch of the Federal Government, as well as in any outdoor areas under executive branch control near air intake ducts.[7]
Smoking laws of the United States by state
- No statewide smoking ban. Instead, Alabama's 2003 statewide smoking law, the Alabama Clean Indoor Air Act, generally prohibits smoking in public places and public meetings[8] unless a smoking area is designated that in certain places must be "enclosed and well ventilated."[9] Warning signs must be posted appropriately.[10] Bars, lounges, retail tobacco stores, limousines under private hire, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, and psychiatric facilities are entirely exempt from the Act's regulation.[8] Local governments may regulate smoking more stringently than the Act,[11] and the Alabama Court of Criminal Appeals reiterated this in August 2009.[12]
- Proposals to enact a statewide smoking ban in Alabama, all but one of which were sponsored only by State Senator Vivian Davis Figures, have failed in the Alabama Legislature every year since 2008. In May 2008, a bill by Sen. Figures to ban smoking in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants, failed when it did not receive a vote before the end of the legislative session.[13] In April 2009, Sen. Figures withdrew a similar bill after the Alabama Senate amended it to allow smoking in bars, the bar sections of restaurants, dog tracks, and gambling halls.[14] In April 2010, a bill by Sen. Figures to ban smoking statewide only in restaurants passed the Senate by a vote of 19–3 but did not receive a vote in the Alabama House of Representatives.[15] In April 2011, a bill by Sen. Figures to ban smoking in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants, failed when it did not receive a vote in a Senate committee, and a similar House bill by Rep. Mary Sue McClurkin failed the same way.[16] In 2012, two Senate bills (one by Sen. Figures) and another House bill by Rep. McClurkin to enact a statewide smoking ban in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants, also failed this way.
- Localities in Alabama with smoking bans that include all bars and restaurants (33 total):
- Albertville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars, restaurants, and within 10 feet (3.0 m) of entrances and exits [4]
- Anniston, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[17]
- Atmore, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Auburn, banned in bars and restaurants, but not other workplaces[4]
- Bayou La Batre, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Birmingham, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants; also includes private clubs and hotels/motels[4]
- Chickasaw, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[18]
- Citronelle, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Clay, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Cottonwood, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Creola, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants [19]
- Decatur, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- East Brewton, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Fairfield, banned in bars and restaurants, but not other workplaces[4]
- Flomaton, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Fultondale, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants;[4] also includes private clubs.
- Gadsden, January 1, 2015, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Gulf Shores, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Headland, banned in bars and restaurants, but not other workplaces[4]
- Homewood, banned in bars and restaurants, but not other workplaces[4]
- Jasper, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants;[4] exempts private clubs that are for non-profit.
- Lanette, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants.[4]
- Luverne, banned in bars and restaurants, but not other workplaces[4]
- Midfield, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants.[4]
- Monroeville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Orange Beach, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Oxford, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Phenix City, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Saraland, banned in bars and restaurants, but not workplaces and outdoor patios[4]
- Satsuma, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants
- Talladega, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Troy, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[20]
- Vestavia Hills, banned in workplaces, bars, restaurants, hotels/motels, and within 20 feet (6.1 m) of entrances and exits[4]
- Localities in Alabama with smoking bans that do not include all bars and restaurants (17 total):
- Alexander City, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars.[4]
- Bay Minette, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Bessemer, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Center Point, banned in all enclosed workplaces, exempting bars and restaurants[4]
- Daphne, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars [4]
- Fairhope, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Foley, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Fort Payne, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or other workplaces.[4]
- Geneva, banned in all enclosed workplaces, exempting bars and restaurants[4]
- Mobile, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars, private clubs, and tobacco bars[4]
- Northport, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Opelika, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Opp, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Prichard, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Robertsdale, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Spanish Fort, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars [21]
- Tuskegee, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants, but exempting bars.[4]
- No statewide smoking ban. Instead, Alaska's statewide smoking law generally requires the designation of smoking and nonsmoking areas and warning signage in most enclosed workplaces and public places. Smoking is prohibited only in: (1) schools during school hours, except in designated areas where minors cannot be present, (2) meetings of state or local government public bodies, (3) non-psychiatric hospitals, health care facilities, and doctors' offices, and (4) elevators.[22] In (1) public transportation vehicles and depots, (2) workplaces, government offices, and places of entertainment or recreation, (3) universities or adult daycare facilities, (4) courtrooms or jury deliberation rooms, (5) state capitol chambers when not in session, (6) residential healthcare facilities and psychiatric facilities, (7) restaurants that seat more than 50 people, (8) grocery/food stores, (9) places of employment posting a sign stating that smoking is prohibited by law, (10) correctional facilities, and (11) the Alaska Pioneers' Home or the Alaska Veterans' Home,[23] a smoking area may be designated, with no limit on its size,[24][25] but must post appropriate warning signage.[26] All other places are entirely exempt from regulation. The Alaska state smoking law is silent as to whether cities can regulate smoking more stringently, and on June 1, 2011, the Supreme Court of Alaska upheld Juneau's municipal ban on smoking in all bars, restaurants, and private clubs.[27]
- Localities in Alaska with smoking bans that include all bars and restaurants (9 total):
- Anchorage, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars, restaurants, and private clubs.[28]
- Haines Borough, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants.[4]
- Juneau, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars, restaurants, and private clubs.[4][29]
- Klawock, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Nome, banned in all enclosed workplaces, bars, restaurants, as well as outdoor stadiums and vehicles when used as public transportation.[4][30]
- Skagway Borough, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Palmer, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Petersburg, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not other workplaces.[4]
- Unalaska, banned in bars and restaurants, but not other workplaces.[4]
- Localities in Alaska with smoking bans that do not include all bars and restaurants (5 total):
- Barrow, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or all other workplaces[4]
- Dillingham, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or all other workplaces[4]
- Fairbanks, banned in all workplaces, exempting bars and restaurants[4]
- Koyuk, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars
- Sitka, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Localities in Alaska that have rejected a smoking ban in some manner (1 total):
- Kodiak Island Borough, July 11, 2013, bill to ban smoking in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants, withdrawn by sponsor[31]
- Territory-wide smoking ban. On October 20, 2010 Governor Togiola Tulafono signed into law the American Samoa Smoke Free Environment Act, a Fono (Legislature) bill passed earlier in the year. The bill went into effect on January 20, 2011.[32]
- Statewide smoking ban: On May 1, 2007, the Smoke Free Arizona Act (Proposition 201) went into effect after passage by 54.7% of voters the prior November, banning smoking in all enclosed workplaces and within 20 feet (6.1 m) of an entrance or exit of such a place, including bars and restaurants, only exempting private residences, retail tobacco stores, private clubs, smoking associated with American Indian religious ceremonies, outdoor patios, and stage/film/television performances; local governments may enact stricter regulations than the state. The law does not cover businesses located on Indian Reservations, as the reservations are sovereign nations.[33][34]
- Statewide smoking ban excluding bars and some restaurants: On July 21, 2006, the Arkansas Clean Indoor Air Act of 2006 went into effect, banning smoking in all enclosed workplaces in Arkansas, exempting only private residences, hotel and motel rooms designated as smoking rooms, workplaces with fewer than three employees, retail tobacco stores, designated areas in nursing homes, outdoor areas, workplaces of tobacco manufacturers (and importers and wholesalers), restaurants and bars that do not allow patrons younger than 21, and gaming floors of operations regulated by the Arkansas Racing Commission.[35] Local governments may regulate smoking more stringently than the state law.[36] At the same time, the Arkansas Protection from Secondhand Smoke for Children Act of 2006 went into effect, prohibiting smoking in a motor vehicle carrying a child under age six years old who weighs less than 60 pounds and is in a car seat.[37]
- Localities in Arkansas with smoking bans that include all bars and restaurants (1 total):
- Fairfield Bay, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Statewide smoking ban: Since January 1, 1995, smoking has been banned in all enclosed workplaces in California, including restaurants and bars (bars were excluded until January 1, 1998), exempting only the following areas: workplaces with five or fewer employees (as long as all workers' consent and persons under 18 are prohibited from the smoking area), 65% of the guest rooms of hotels/motels, lobby areas of hotels/motels designated for smoking (not to exceed 25% of the total lobby floor area or, if the lobby area is 2,000 square feet (190 m2) or less, not to exceed 50% of the total lobby floor area), meeting and banquet rooms except while food or beverage functions are taking place (including set-up, service, and clean-up activities or when the room is being used for exhibit activities), retail or wholesale tobacco shops and private smokers lounges (i.e. cigar bars), truck cabs/tractors if no nonsmoking employees are present, non-office warehouse facilities with more than 10,000 square feet (930 m2) of total floor space and 20 or fewer full-time employees working at the facility, theatrical production sites if smoking is an integral part of the story, medical research or treatment sites if smoking is integral to the research or treatment being conducted, private residences except homes licensed as family day care homes during the hours of operation and in those areas where children are present, patient smoking areas in long-term health care facilities, and employee breakrooms designated for smoking.[38]
Effective January 1, 2004, California bill AB846 bans smoking within 20 feet (6.1 m) of the entrance or operable window of a public building ("public building" means a building owned and occupied, or leased and occupied, by the state, a county, a city, a city and county, or a California Community College district.) The law also prohibits smoking in state owned vehicles.[39][40]
Additionally, effective January 1, 2008, smoking in a moving vehicle while in the presence of a minor (18 years or younger) is an infraction; the charge is not serious enough to be pulled over, and only can be cited along with a stricter offense, such as a moving violation or traffic accident.[41][42]
Local jurisdictions may regulate smoking more strictly than the state. Many California communities have established smoke-free registries for private residential apartment buildings, which range from complexes where smoking is entirely prohibited (whether inside private dwellings or outside) to those where certain sections of dwellings may be designated as smoking dwellings. Most California cities allow landlords to regulate smoking at will.
- Belmont, October 9, 2007, banned in parks and other public places, as well as inside apartments and condominiums.[43]
- Berkeley, March 26, 2008, banned on all commercially zoned sidewalks, and within 20 feet (6.1 m) of a bus stop[44][45]
- Beverly Hills, October 1, 2007, banned in all outdoor dining areas.[46]
- Burbank, April, 2007, banned in most public places including Downtown Burbank, outdoor dining & shopping areas, parks, service lines, and within 20 feet (6.1 m) of all building entrances/exits.[47]
- Calabasas, 2006, banned in all indoor and outdoor public places, except for a handful of scattered, designated outdoor smoking areas in town. Believed to be the strictest ban in the United States.[48]
- Davis, The Davis City Code prohibits smoking in a wide variety of locations open to the public.[49]
- El Cajon, August 14, 2007, banned on city streets, in outdoor patios in restaurants, and outside of the local shopping mall. Anyone caught smoking in public areas will faces a fine of up to $500. The city previously outlawed smoking in parks, and also requires businesses that sell tobacco products to obtain a city license.[50]
- El Cerrito, January 1, 2015, banned in all public places, commercial areas, and multi-unit residences and within 25 feet of any of these.[51]
- Escondido, in 2005, increased the state prohibition on smoking within 20 feet (6.1 m) of an entrance to a public place to 80 feet (24 m) outside city-owned buildings.[52][53] In 2009, the city, at the urging of local students, banned smoking in parks, city open spaces, and trails, including the parking areas for these city properties.[52][54]
- Glendale, October 7, 2008, banned smoking[55] in/on and within 20 feet (6.1 m) from: all city property (except streets and sidewalks); city vehicles and public transportation vehicles; city public transit stations; places of employment; enclosed public places; non-enclosed public places; and common areas of multi-unit rental housing. Some of the areas where smoking is prohibited are authorized to have smoking-permitted areas, subject to regulations. Also, landlords in Glendale are required to provide disclosure to a prospective renter, prior to signing a lease, as to the location of possible sources of second-hand smoke, relative to the unit that they are renting.[citation needed]
- Hermosa Beach, March 1, 2012 banned at all of Hermosa’s outdoor dining areas, the popular Pier Plaza, the city pier, the Strand, the greenbelt parkway, and all city parks and parking lots. Smoking already is outlawed on the city-owned beach.[56]
- Loma Linda, July 25, 2008 banned on all sidewalks, streets, common areas in shopping centers, bus stops, parks, restaurant patios, theaters, City Hall, and 80% of motel rooms and apartment units. Exempts the federally controlled VA hospital grounds, and smoking in cars traveling in the city.[57]
- Long Beach, California bans smoking in all city parks, at or within 20 feet of busstops, and at farmers' markets.
- Los Angeles, 2007, banned in all city parks,[58] and, 2011, all outdoor dining areas.[59]
- Marin County, May 23, 2012 banned in all condos and apartments, as well as all patios within residential units. Anyone caught smoking will face a $100 fine and will be sentenced to five community day services. A second offense warrants a $300 fine and ten community day services, and a third offense being $700 fine and fifteen community day services. Landlords may opt out of smoking restrictions by designating 20 percent of their units reserved for smoking and may permit e-cigarettes to be used inside apartments and condos. All other outdoor areas, including bar and restaurant patios, and private homes that are not of multi-unit residences and smoking in cars are exempt from the ban.[60]
- Oakland, bans smoking within 25 feet of an entrance, exit, window, or air intake of the building of most enclosed places where smoking is prohibited (e.g., workplaces, service areas, common areas and no-smoking units of multi-unit housing); exemption is made outside of bars provided the smoke doesn't enter prohibited areas. Smoking is also banned in certain unenclosed areas, including service areas (e.g., bus stops, cab stands, ATMs).[61]
- Pasadena, October 27, 2008, banned smoking in certain outdoor areas, including shopping malls, unenclosed areas of bars and restaurants, service waiting lines (e.g. ATMs, bus stops, etc.) and within 20 feet (6.1 m) from them, and within 20 feet (6.1 m) of doorways, windows, or ventilation areas of enclosed places where smoking is banned.[62]
- San Diego, July 11, 2006, banned smoking at all City of San Diego beaches and parks, including all beaches from La Jolla to Sunset Cliffs.[citation needed]
- San Francisco, January 2005, banned smoking in all city parks.[63] January 2013, banned smoking at all outdoor "street fairs and festivals", with exceptions for legal medical marijuana and small neighborhood block parties.[64]
- San Jose, October 2007, banned in all city parks.[65]
- San Luis Obispo, August 2, 1990, became the first city in the world to ban smoking in all public buildings.[66] On January 15, 2010, the City's municipal code amendment included city parks and outdoor recreational facilities as smoke-free areas.[67] In April 2010, City Council adopted an ordinance that bans smoking in all areas frequented by the public, with limited exceptions, including unenclosed areas at certain drinking establishments.[68]
- Santa Barbara & Goleta, Local laws in Santa Barbara County and in the City of Goleta prohibit smoking within 20 feet of any building or area where smoking is prohibited. Ashtrays are also banned within a 20-foot smoke-free area.[69]
- Santa Monica, 2006, banned smoking within 20 feet (6.1 m) of entrances, exits, or operable windows of a public building (such as City Hall and the courthouse); in local parks (including parking lots); on the Third Street Promenade; on local beaches; and on the Santa Monica Pier (except within designated zones).[70] City Council passed a law that prohibits smoking in ALL common areas of a multi-family residential building including condominiums[citation needed], which went into effect February 26, 2009.[citation needed]
- Statewide smoking ban: On July 1, 2006, the Colorado Clean Indoor Air Act went into effect, banning smoking in all enclosed workplaces statewide, including bars and restaurants. Casinos, initially exempt, were added to the ban Jan. 1, 2008.[71] The Act only exempts private residences and automobiles unless used for the public transportation of children or as part of healthcare or daycare, limousines under private hire, hotel/motel rooms designated as smoking rooms, retail tobacco stores, cigar bars, designated areas in airports, outdoor areas, workplaces not open to the public where the employer employs three or fewer employees, private nonresidential buildings on a farm or ranch that has annual gross income of less than $500,000, and designated areas in nursing homes.[72] Local governments may regulate smoking more strictly than the state.[73] A judge has ruled that a bar sharing common indoor space with a tobacco shop is also exempt from the ban.[74]
- Statewide smoking ban: On October 1, 2003, the Clean Indoor Air Act went into effect, banning smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces in Connecticut, including restaurants and bars (bars, cafes, and bowling alleys were exempt until April 1, 2004.[75] The Act exempts correctional and psychiatric facilities, public housing projects, private clubs whose liquor permit was issued on or before May 1, 2003, areas of businesses where tobacco products are developed and tested, and cigar bars (a business that has a liquor permit and generated at least 10% of its 2002 gross income from on-site sales of tobacco products or humidor rentals and has not changed its size or location after December 31, 2002).[75] If a business has five or fewer employees (except bars and restaurants), the employer and all employees can agree to designate 20% of the place's enclosed space as a smoking area, provided that it is separately ventilated and adequate breakroom space for nonsmokers is allocated.[75] Local governments are preempted from regulating smoking at all.[75] Smoking is also permitted in hotel rooms but must be designated.
Two large casinos on Mohegan and Mashantucket Peuot land, Mohegan Sun and Foxwoods, allow smoking in many areas of their properties. Employers may also designate an on-site designated smoking area for employees.
- Statewide smoking ban: On November 1, 2002, the Clean Indoor Air Act went into effect, banning smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces in Delaware, including bars, restaurants, and casinos.[76] The Act exempts private homes and automobiles not used for childcare or daycare or the public transportation of children, rented social halls while being rented, limousines under private hire, hotel/motel rooms designated as smoking rooms, fundraising activities sponsored by an ambulance or fire company while on property owned or leased by the company, and fundraising activities sponsored by a fraternal benefit society taking place upon property owned or leased by the society.[76] Local governments can regulate smoking more strictly than the state. The City of Bethany Beach has outlawed smoking on the boardwalk and beach.[4][76]
- District-wide smoking ban: Effective January 2007, smoking is banned in bars, restaurants, and other public places in the District of Columbia; exempts outdoor areas, designated hotel/motel rooms, retail tobacco stores, cigar bars, hookah bars, and businesses that can show they receive 10% or more of their annual revenue from tobacco sales, excluding cigarette machines.[77]
- Statewide smoking ban excluding bars: On July 1, 2003, smoking was banned statewide in all enclosed workplaces in Florida, exempting private residences, retail tobacco shops, designated smoking rooms in hotels/motels, stand-alone bars with no more than 10% of revenue from food sales, rooms used for quit-smoking programs and medical research, and designated smoking areas in customs transit areas under the authority of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security.[78] Local governments are preempted from regulating smoking.[79]
- Statewide ban on smoking in some workplaces: On July 1, 2005, the Smokefree Air Act went into effect, banning smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces in Georgia, except as otherwise designated.[80] The Act exempts designated smoking areas in non-work areas of businesses that are separately ventilated, bars and restaurants where persons under 18 years of age are not employed or permitted to enter, separately enclosed smoking rooms in any bar or restaurant, private residences not used as healthcare or child daycare facilities, hotel/motel rooms designated as smoking rooms, retail tobacco stores, nursing homes, outdoor areas, designated areas in international airports, workplaces of a tobacco manufacturer or other tobacco business, privately owned meeting and assembly rooms during private functions where persons under 18 are not allowed, and areas of private places of employment (other than medical facilities) that are open to the general public by appointment only.[81] Local governments may regulate smoking more strictly than the state.[82] Buildings in which smoking is banned under the Act may have an outdoor smoking area that is located a reasonable distance from any entrance, exit, window, vent, or air intake system, but any ashtrays located there must be placed a reasonable distance away.[82] A violation of the Act is punishable by a fine of between $100 and $500.[82] Atlanta has no smoking ban covering workplaces and/or restaurants and/or bars but now prohibits smoking in parks.
- Localities in Georgia with smoking bans that include all bars and restaurants (10 total):
- Athens, banned in bars and restaurants, but not other workplaces[4]
- Buena Vista, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Chatham County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars, private clubs, restaurants, and retail tobacco stores.[4]
- Effingham County, banned in bars and restaurants, but not other workplaces[4]
- Gainesville, banned in bars and restaurants, but not other workplaces[4]
- Morrow, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Pooler, January 1, 2015, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Savannah, banned in bars and restaurants and even service queues[83]
- Snellville, banned in bars and restaurants, but not other workplaces[4]
- Tift County, banned in bars and restaurants, but not other workplaces[4]
- Localities in Georgia with smoking bans that do not include all bars and restaurants (14 total):
- Berkeley Lake, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Columbia County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Cordele, banned in all enclosed workplaces, except bars and restaurants[4]
- Decatur, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- DeKalb County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, except bars and restaurants[4]
- Douglas, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Douglas County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Douglasville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, except bars and restaurants[4]
- Dunwoody, banned in all enclosed workplaces, except bars and restaurants[4]
- Loganville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Madison, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or all other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Peachtree City, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or all other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Tifton, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or all other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Valdosta, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Territory-wide ban on smoking in restaurants only: On February 6, 2007, the Natasha Protection Act went into effect after the Supreme Court of Guam lifted an injunction on it, banning smoking in all restaurants, as well as in bars that double as restaurants between 4:00 am and 10:00 pm; the ban does not cover either stand-alone bars or workplaces in general.[84] In 2009, a new act went into effect, additionally banning smoking within 20 feet of public buildings.[85]
- Statewide smoking ban: On November 16, 2006, smoking was banned statewide in all enclosed or partially enclosed workplaces in Hawaii, including the indoor and outdoor portions of all restaurants and bars.[86] The law exempts private residences not used as a healthcare or daycare facility, hotel/motel rooms designated as smoking rooms, retail tobacco stores, designated rooms in nursing homes, outdoor places of employment not part of bars or restaurants, any place where smoking is part of a production being filmed, and state correctional facilities.[87] Smoking is prohibited within 20 feet (6.1 m) of the entrance/exit of a place where the law prohibits smoking indoors.[88] Fines range from $50 for a person caught smoking in violation of the law, to between $100 and $500 for an establishment caught allowing smoking in violation of the law.[89] In 2010, several bills were introduced attempting to exempt bars.[90] Counties may regulate smoking more strictly than the state.[91]
- Kalawao County, October 4, 2002, banned smoking in all public buildings.[92] The ban did not apply to private homes or Kalawao County's only bar at the time.[92]
- Hawaii County, March 13, 2008, banned in public recreational areas, such as parks and beaches.[citation needed]
- Statewide ban on smoking in restaurants and some workplaces: On July 1, 2004, the Clean Indoor Air Act went into effect, banning smoking statewide in all enclosed public places, except in bars, retail tobacco stores, private clubs, designated smoking rooms in hotels/motels, theatrical productions, areas of owner-operated businesses with no employees besides the owner not open to the general public, offices (other than childcare facilities) within private homes, veterans homes, and designated breakrooms in businesses with fewer than five employees (as long as they are separately ventilated and minors are not allowed in that room).[93] Local governments may regulate smoking more strictly than the state.[94]
- Localities in Idaho with a smoking ban including all bars and restaurants (3 total):
- Boise, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and private clubs, as well as in any public outdoor space accessible to children and in all spaces owned by the public, including parks.[95]
- Moscow, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and private clubs, and 20 feet (6.1 m) from building entrances.[96]
- Ketchum,banned in a long list of areas that include all bars, city-owned facilities, parks, and indoor public places and places of employment, including hotel and motel rooms.[97]
- Statewide smoking ban: On January 1, 2008, the Smoke Free Illinois Act went into effect, banning smoking in all enclosed workplaces, including bars, restaurants, and casinos, and within 15 feet (4.6 m) of such places; exempts certain retail tobacco stores, private and semiprivate rooms in nursing homes occupied exclusively by smokers, no more than 25% of designated smoking rooms in hotels/motels on the same floor, and private residences.[98] Smoking is prohibited in private residences when defined as a place of employment such as when used for child care or foster care.[98] Local governments may regulate smoking more strictly than the state.[98]
HB 1310: a proposal in January 2012 to once again permit smoking in bars, casinos, adult entertainment venues, and private clubs failed in the Illinois House 30-82.
The Chicago Clean Indoor Air Act was updated to mention e-cigarettes in 2014, making Chicago the first major U.S. city to legislate e-cigarette use.[99] Chicago — The Chicago Park District's Board of Commissioners voted to ban all forms of smoking in Chicago parks, beaches, play lots and other facilities.[100]
- Statewide smoking ban excluding bars, and casinos. Effective July 1, 2012, after having been signed into law by Governor Mitch Daniels on March 19, 2012, Indiana's 1993 statewide Clean Indoor Air Law was repealed and replaced by a new chapter of the Indiana Code titled "Prohibition on Smoking." The new chapter bans smoking in all enclosed public places and workplaces in Indiana and within 8 feet (2.4 m) of an entrance thereto, except as exempted.[101] The law exempts: (1) horse racing facilities including off-track betting parlors; (2) riverboats; (3) all indoor portions of casinos and other licensed gaming facilities; (4) cigar bars and hookah lounges; (5) private clubs; (6) retail tobacco stores; (7) bars and taverns (defined as any business with a liquor license that does not allow in persons under 21 years of age); and (8) cigar manufacturers.[101] The law expressly allows local governments to enact more stringent smoking restrictions.[101]
- Attempts in the Indiana General Assembly to enact a ban on smoking in all workplaces in Indiana, including all bars and restaurants, have failed every year since 2007. In April 2007, the Indiana Senate removed a smoking ban from a health care funding bill passed by the Indiana House of Representatives, and in January 2008, a proposed statewide smoking ban introduced by Rep. Charlie Brown died in a House committee without a vote or debate.[102] In April 2009, another proposed statewide ban introduced by Rep. Brown was passed by the House by a vote of 70–26 after being amended to exempt restaurants, bars, and casinos, and then did not receive a committee hearing in the Senate.[103] In February 2010, another proposed ban by Rep. Brown was denied a committee hearing or vote in the Senate after having been passed by the House, 73-26.[104] In April 2011, a Senate committee voted 8–1 to reject a statewide ban exempting bars, casinos, private clubs, retail tobacco shops, and nursing homes, which also had been introduced by Rep. Brown and previously had passed the House, 68-31.[105] The ban that ultimately was enacted in 2012 passed the House as a complete ban on smoking in all workplaces in Indiana, including all bars and restaurants (and authored again by Rep. Brown), but was amended by the Senate to include the above exemptions, upon which the House agreed to the Senate's exemptions.[106]
- Universities in Indiana with smoking bans (4 total):
- Ball State University, banned on campus, except for designated areas.[107]
- Indiana State University, banned on campus, except for designated areas.
- Indiana University, banned on campus; Bloomington campus extends this to all outdoor areas.
- Purdue University, banned on West Lafayette campus, except for designated areas.[108]
- Localities in Indiana with smoking bans that include all bars and restaurants (19 total):
- Bloomington, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants.[4] Smoking is allowed only outside at a "reasonable distance" from doors, vents, and windows – measured by whether smoke can drift inside.
- Columbus, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars, restaurants, and private clubs[4]
- Crawfordsville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Cumberland, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants.[4]
- Delaware County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, bars, private clubs and restaurants[4]
- Elkhart, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempted existing bars until May 1, 2009, with a grandfather clause[4]
- Franklin, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including eating establishments that prohibit minors from entering; bars, adult-only restaurants, and private clubs were included in the ban on June 8, 2009, with smoker's having to be away from entrances and exits "within a reasonable distance" which public businesses were forced to comply with in terms of setting their own outdoor restrictions that met the requirements of the ordinance[4][citation needed][109]
- Fort Wayne, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants.[4][110]
- Greencastle, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants.[4]
- Hancock County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants.[4]
- Indianapolis, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants;[4] exempts cigar and hookah bars, retail tobacco stores, off-track betting facilities and private clubs and veterans halls.[citation needed]
- Lawrence, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Monroe County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants. Ban also applies to drivers carrying children aged 13 or younger.[4][111]
- Plainfield, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4] but exempting private clubs; nursing homes were added to the ban starting July 1, 2012.[citation needed]
- Terre Haute, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants [4]
- Vanderburgh County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, exempted bars and restaurants until July 1, 2011; under new provisions, smoking is prohibited within 10 feet (3.0 m) of entrances where smoking is banned to ensure that no smoke can drift inside; excludes retail tobacco stores, fraternal clubs and private clubs that prohibit persons younger than 18[4]
- Vigo County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars, restaurants and private clubs[4]
- West Lafayette, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4] but exempting tobacco bars, private residences, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, retail tobacco stores, private clubs, and outdoor areas in the city, including Purdue University's main campus. Prior to July 1, 2012, smoking was permitted in tobacco bars that served food and beverages (including liquor) to patrons 18 years and older. As of July 2012, cigarette smoking is no longer permitted in tobacco bars serving patrons under 21 years of age. Cigar and hookah smoking are exempt. Tobacco bars are also prohibited from selling food and drink if they serve patrons under 21 years of age. [citation needed]
- Zionsville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars, restaurants,[4] and private clubs.[citation needed]
- Localities in Indiana with smoking bans that do not include all bars and restaurants (15 total):
- Allen County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars and any establishments prohibiting persons under age 21 from entering; municipalities are allowed to opt out of it, as New Haven decided to do.[4]
- Avon, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Carmel, banned in all enclosed workplaces and common-use areas, including restaurants; exempts bars that don't employ or serve people under 21,[4] tobacco stores and bars, private vehicles, private and fraternal clubs, and designated hotel/motel smoking rooms.[citation needed]
- Crown Point, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4] and private clubs.[citation needed]
- Greenfield, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Greensburg, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Greenwood, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Henry County, July 1, 2012 as superseded by the Indiana Clean Indoor Air Act of 2012: banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants, and bingo halls; exempts bars that hold a beer/wine/liquor license, prohibit patrons and employees younger than 21, and are not physically located within another business that must comply with the smoking ban; private clubs do not have to meet any requirements whatsoever[4][112]
- Jeffersonville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Kokomo, July 1, 2012 as superseded by the Indiana Clean Indoor Air Act of 2012: banned in all nursing homes, including enclosed workplaces, bingo halls, and restaurants; exempts bars, private clubs, and any establishments serving alcohol and not allowing patrons under 21.[4]
- Lowell, banned in all workplaces and restaurants, excluding a physically separated bar area of a restaurant. Also exempts bars and private clubs, providing any food preparation and dining areas within a bar or private club is physically separated from the area smoking is allowed. The Indiana Clean Indoor Air Act of 2012 will require that a physically separated bar area of a restaurant will have to obtain a liquor license, and prohibit persons younger than 21 from entering the entire facility in order to be exempt[113]
- Madison, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Marion County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars; municipalities may regulate smoking more stringently than the county[4]
- Seymour, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4] and private clubs.[citation needed]
- Speedway, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Localities in Indiana with a smoking ban that was rejected in some manner (1 total):
- Evansville, April 1, 2012 banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants, private clubs and fraternal organizations, but excluded casino gaming floors.[114] But struck down by Supreme Court of Indiana on February 11, 2014, as unconstitutional due to the casino exemption, which was held to violate the Indiana Constitution and could not be severed from the ordinance.[115]
- Statewide smoking ban: On July 1, 2008, the Smokefree Air Act went into effect, banning smoking statewide in all workplaces in Iowa, including restaurants and bars, as well as the outdoor areas of schools, stadia, restaurants, public transit areas (including bus shelters), schools, and parks owned by the state or a local government.[116] The Act exempts private residences while not being used as a childcare or healthcare facility, outdoor areas where smoking is not specifically prohibited, hotel/motel rooms designated as smoking rooms, retail tobacco stores, private and semiprivate rooms in nursing homes occupied by smokers, private clubs, limousines under private hire, private work vehicles where only one employee is located, places where a quit-smoking program is taking place, farm vehicles, casino gaming floors, the state-run veterans' home in Marshalltown, and designated areas of correctional facilities.[117] Fines for individuals found in violation of the Smokefree Air Act are $50 per violation.[118] Fines for businesses range anywhere from $100 to $500 for each violation with the eventual possibility of revocation of liquor and/or business license for habitually offending businesses.[118]
- Statewide smoking ban: On July 1, 2010, after being signed into law by Governor Mark Parkinson on March 12, 2010, an amendment to Kansas' 1987 statewide smoking law took effect, banning smoking statewide in all enclosed, indoor workplaces in Kansas.[119] The law will exempt only (1) casino and racetrack gaming floors, (2) the entire area of a private club that was in existence on January 1, 2009, (3) designated areas in any private club where persons under 18 are prohibited, (4) tobacconists, (5) designated hotel and motel smoking rooms, (6) designated smoking areas in nursing homes and healthcare facilities, (7) and all outdoor areas, unless within a 10' radius of an entryway to a public building.[119] The amendment will not change the original law's provision allowing local governments to regulate smoking more stringently than the state,[119][120] which the Kansas Supreme Court reiterated in 2007 upon a bar owner's challenge to Lawrence's local smoking ban.[121] On June 30, 2010, the District Court of Shawnee County, Kansas, issued a preliminary injunction prohibiting the statewide smoking ban from taking effect in 31 private clubs established after January 1, 2009, until it settles a lawsuit against the state by those clubs.[122]
- No statewide smoking ban. Instead, in Kentucky, the only state laws dealing with smoking prohibit smoking in government offices, universities, and the state capitol, except in designated smoking areas.[123][124] In 2004, the Kentucky Supreme Court ruled that the state's food and tobacco sales laws do not preempt cities and counties from enacting smoking regulations of any kind.[125] In 2011 and 2012, bills to enact a statewide smoking ban in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars, restaurants, and gaming facilities, as well as a bill in 2011 to ban smoking in cars in which minors are riding, all failed before the Kentucky General Assembly when they did not receive a committee hearing in the Kentucky House of Representatives.[126][127][128]
- Localities in Kentucky with smoking bans that include all bars and restaurants (29 total):
- Ashland, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants,[4] as well as outdoor venues and outdoor patio areas of restaurants and bars.[citation needed]
- Bardstown, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Berea, September 2, 2014, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Bowling Green, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants.[4]
- Campbellville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Clark County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Corbin, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Danville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants,[4] as well as within ten feet of the entrance of any such place[citation needed]
- Elizabethtown, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Frankfort, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Franklin County, banned in bars and restaurants, but not other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Georgetown, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Glasgow, banned in bars and restaurants, but not all other workplaces[4]
- Hardin County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants, in unincorporated areas of the county[4]
- Lexington, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- London, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Louisville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants.[129]
- Madison County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants;[4] exempts outdoor patio areas of restaurants and bars (bars are only allowed in the city of Richmond, since the rest of the county is dry).[citation needed]
- Mancher, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Midway, August 18, 2014, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Morehead, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Paducah, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Prestonburg, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Radcliff, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Richmond, September 9, 2014, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Somerset, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants; exempts private clubs when not open to the public[4][130]
- Versailles, October 6, 2014, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Williamsburg, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Woodford County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Localities in Kentucky with smoking bans that do not include all bars and restaurants (7 total):
- Daviess County, banned in any public establishment open to children under 18, but exempts private businesses and bars.[citation needed]
- Henderson, banned in all enclosed workplaces, excluding bars and restaurants[4]
- Kenton County, banned in all workplaces, except for establishments with a liquor license.
- Letcher County, banned in restaurants, but not bars or other workplaces[4]
- Oldham County, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or all other workplaces[4]
- Paintsville, banned in restaurants, but not bars or other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Pikeville, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or all other workplaces[4]
- Localities in Kentucky in which a smoking ban was rejected in some manner (1 total):
- Boone County, July 2010, bowed out of multi-county discussions due to a lack of votes to support a ban[131]
- Campbell County, December 2010, banned in enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants, but then repealed in February 2011 by 3-1 vote of County Fiscal Court[132]
- Statewide smoking ban excluding bars: On January 1, 2007, SB 742 went into effect, banning smoking in all schools, workplaces, and public places, including restaurants.[133] The law exempts bars (food establishments where the majority of sales are derived from alcohol), private residences and automobiles except those when used as a healthcare or childcare facility, limousines under private hire, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, retail tobacco shops, outdoor areas, private and semiprivate rooms of nursing homes occupied exclusively by smokers, casino gaming floors, workplaces of tobacco-related businesses such as manufacturers and distributors, convention and banquet facilities rented out to a private party, designated areas in nursing homes, and correctional facilities (until August 1, 2009).[133] Local governments may regulate smoking more strictly than the state. Prior to this ordinance, 6 localities had smoking provisions that exempted restaurants, but were later superseded by the Act once it had gone into effect.[4][133]
- Since 2009, attempts to further ban smoking statewide in Louisiana have failed every year before the Louisiana State Legislature. In June 2009, the Louisiana House of Representatives rejected ending the exemption for bars and casinos by a vote of 79–21.[134] In May 2010, a House committee rejected a bill to ban smoking in casinos,[135] and then rejected a bill to ban smoking in bars, casinos, and the remainder of restaurants that the Louisiana Senate had passed by a vote of 23–12.[136] In June 2011, the Senate rejected a bill to ban smoking in bars by a vote of 22–15.[137] In May 2012, the Senate rejected a bill to prohibit smoking within 25 feet (7.6 m) of all places where smoking is banned by a vote of 18-12, and instead chose to amend the bill to prohibit smoking with 25 feet (7.6 m) of entrances to state-owned government buildings with no word on when the bill will take effect.[138]
- Localities in Louisiana that has smoking bans that include all bars and restaurants (8 total):
- Abbeville, January 1, 2015, banned in all enclosed public places, including bars and gaming establishments[4]
- Alexandria, banned in all enclosed public places, including bars and gaming establishments[4]
- Cheneyville, June 7, 2014, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and gaming establishments[4]
- Monroe, banned in all enclosed public places, including bars and gaming establishments[4]
- New Orleans, April 22, 2015, banned in all enclosed public places, including bars and gaming establishments; includes usage of smokeless e-cigarettes
- Ouachita Parish, banned in all enclosed public places, including bars and gaming establishments[4]
- West Monroe, banned in all enclosed public places, including bars and gaming establishments[4]
- Woodworth, banned in all enclosed public places, including bars and gaming establishments[4]
Universities in Louisiana will be banning smoking from any on campus properties. This includes but is not limited to cigarettes, cigars and e-cigarettes as well as smokeless tobacco products. This goes into effect Aug 1st 2014 for most universities in accordance with Act 211 of the 2013 Louisiana State Legislative session.
- Statewide smoking ban: Effective January 1, 2004, laws from 1985 and 1999 were expanded such that smoking is banned statewide in all workplaces and public places in Maine, including bars and restaurants.[139] The law exempts places open to the public during hours when it is closed, stage performances involving smoking, smoking for religious rituals, factories where labor unions have contracted to have smoking areas, designated areas in hospitals, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, private residences except when used as a childcare or healthcare facility, beano and bingo halls, tobacco specialty stores, and off-track betting parlors that were in existence on June 30, 2003.[139] The state law exempts private clubs (Elks, American Legion, VFW etc.) under certain conditions. The state law is silent as to whether local governments may regulate smoking more strictly than the state, though as of April 2009 no local government in Maine has done so.[4] Effective September 1, 2008, smoking is banned in any car when a person under the age of 16 is present, though no driver may be pulled over or searched solely for violation of this law.[140]
- Statewide smoking ban: On February 1, 2008, the Maryland Clean Indoor Air Act of 2007 went into effect, banning smoking in all public transportation vehicles, enclosed public places, and enclosed workplaces, including bars, restaurants, casinos, and private clubs.[141] The Act exempts private residences and vehicles while not being used as a childcare or healthcare facility, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, retail tobacco stores, cigar lounges and hookah bars, other tobacco-related workplaces such as importers and distributors, facilities where smoking research is conducted, psychiatric facilities, long-term care facilities, hospitals where a doctor has authorized a patient to smoke, and any business that has applied for and received a waiver allowing smoking (though all waivers expired on January 1, 2011).[141] Local governments may regulate smoking more strictly than the state, though not less strictly.[141]
- Statewide smoking ban: Effective July 1, 2004, smoking is banned in all enclosed public places and workplaces, including restaurants and bars.[142] The law exempts private clubs when not open to the public, private residences except when used as a business for healthcare or childcare, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, retail tobacco stores, licensed cigar or hookah bars, stage performances involving smoking, places where smoking-related scientific research is occurring, religious ceremonies involving smoking, outdoor areas, designated areas in nursing homes as approved by the state, and other tobacco-related workplaces such as farms and distributors.[142] Local governments and boards of health may regulate smoking more strictly than the state.[142]
- Boston, February 9, 2009, banned by the Boston Public Health Commission on outside patios of bars and restaurants; also banned on February 9, 2019 (10 years later than the other new restrictions) in cigar and hookah bars, unless the establishment obtains an additional 10-year exemption. Additionally, smoking is now banned in all hotel rooms in the city of Boston. Tobacco products were no longer able to be sold in pharmacies and stores having pharmacies within.[143]
- Statewide smoking ban: On May 1, 2010, after being signed into law by Governor Jennifer Granholm on December 18, 2009, the Dr. Ron Davis Law took effect, banning smoking statewide in all enclosed, indoor workplaces in Michigan, as well as the outdoor patios of bars and restaurants.[144][145] The law exempts only cigar bars, retail tobacco stores, private home offices, company vehicles including commercial trucks, and Detroit's three casinos' gambling floors.[144] The law is silent as to whether local governments may regulate smoking more strictly than the state, though it prohibits state or local health departments from enacting any smoking rules different than the law.[144] In December 2011, a judge dismissed fines against a Warren, Michigan bar owner who had claimed that his bar's Keno machines classified his establishment as a casino exempt from the ban.[citation needed]
- Statewide smoking ban: On October 1, 2007, the Freedom to Breathe Act went into effect, expanding the existing Clean Indoor Air Act of 1975 so as to ban smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces in Minnesota, including public transportation, bars, and restaurants.[146] The Act exempts designated rooms in nursing homes, designated areas in psychiatric facilities, places where scientific studies related to smoking occur, private homes and residences not in use as a place of employment, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, retail tobacco shops, heavy commercial vehicles, farm vehicles and construction equipment, buildings on family farms, the Minnesota disabled veterans' rest camp, smoking by American Indians as part of a traditional spiritual or cultural ceremony, stage performances involving smoking, and outdoor areas.[147] Local governments may regulate smoking more stringently than the state.[148]
- Carlton County, June 1, 2007, banned on 50% of outdoor patio seating in restaurants and bars.[citation needed]
- Duluth, March 7, 2010, banned within 15 feet (4.6 m) of a bus shelter or transit center.[149]
- Golden Valley, March 31, 2009, banned within 25 feet (7.6 m) of entrances, exits, and ventilation openings of all areas of restaurants and bars; also in public parks and recreational facilities.[citation needed]
- Rochester, June, 2010 Downtown smoke-free zone includes the block of Second Avenue Southwest between Gonda and the Kahler, and the two-block pedestrian mall known as the Peace Plaza. The zone was extended in June 2010 to include two blocks of West Center Street between the Kahler Grand Hotel, Methodist Hospital and the Gonda Building.[150]
- No statewide smoking ban. Instead, Mississippi's 2006 statewide smoking law, the Clean Indoor Air Act, prohibits smoking only inside any state or local government building (except designated areas in the state's veterans' homes) or inside any university or college classroom building.[151] Local governments may regulate smoking more stringently than the Act.[152] In 2011 and 2012, three separate bills before the Mississippi Legislature seeking to enact some form of a statewide smoking ban all failed when they did not receive a committee hearing.[153][154][155]
- Localities in Mississippi with smoking bans that include all bars and restaurants (82 total):
- Aberdeen, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Amory, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Anguilla, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Arcola, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Baldwyn, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Bassfield, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Batesville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Belzoni, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Brookhaven, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Bruce, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Byram, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Calhoun City, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Canton, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Cary, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Centreville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Clarksdale, September 10, 2014, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Clinton, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[157]
- Coahoma County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Collins, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[157]
- Crawford, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Crystal Springs, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Duncan, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Durant, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Ecru, banned in bars and restaurants, but not in all other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Ethel, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Farmington, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Floria, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Forest, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Friars Point, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Gautier, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Georgetown, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Greenwood, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Grenada, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Hattiesburg, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Hernando, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Hollandale, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Indianola, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Itta Bena, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Jackson, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants (previous ordinance exempting bars was amended)[158]
- Jonestown, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Kosciusko, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Laurel, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Lousville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Lucedale, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Lumberton, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Madison, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Magee, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Mantachie, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[157]
- Mayersville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Mendenhall, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Meridian, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants.[159]
- Metcalfe, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Monticello, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not all other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Moorhead, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Morton, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Moss Point, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- New Albany, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- New Augusta, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Okolona, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Oxford, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Pascagoula, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not other workplaces[160]
- Petal, banned in nearly all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Picayune, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Plantersville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Pontotoc, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Prentiss, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Ridgeland, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Rolling Fork, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Senatobia, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Sledge, June 4, 2014, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Southaven, August 4, 2014, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Shuqualak, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Starkville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Summit, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[157]
- Sumner, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Sumrall, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Tupelo, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Verona, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Walnut, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Wesson, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Wiggins, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Woodville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Localities in Mississippi with smoking bans that do not include all bars and restaurants (11 total):
- Booneville, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Brandon, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or other workplaces[4]
- Coldwater, banned in all enclosed workplaces, exempting bars and restaurants[4]
- Corinth, banned in all city-owned facilities, enclosed workplaces, and some outdoor areas, by vote of the Board of Aldermen;[161] does not include all bars[4]
- Flowood, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Goodman, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Gulfport, banned in all enclosed workplaces, except bars and casinos.[162]
- Pearl, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Picayune, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Rienzi, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Walls, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- West, banned in all enclosed workplaces except bars and restaurants[4]
- No statewide smoking ban. Instead, Missouri's 1992 statewide smoking law, the Indoor Clean Air Act, prohibits smoking in all enclosed public places (including workplaces) and public meetings, except in designated smoking areas, which may occupy no more than 30% of the place's enclosed area.[163] Warning signs must be appropriately posted either way.[164] Local governments may prohibit smoking in schools, child daycare facilities, and school buses,[165] as well as in public places.[163] Bars, restaurants that seat fewer than 50 people, bowling alleys, billiard parlors, retail tobacco shops, rooms and halls used for private social functions, limousines and taxicabs where the driver and all passengers agree to smoking, stage performances including smoking, indoor sports stadiums seating more than 15,000 people, and private residences "are not considered a public place".[166] On June 23, 2009, the Western District of the Missouri Court of Appeals ruled that Kansas City's 2008 local ban on smoking in all workplaces, including bars and billiard parlors, did not conflict with this statute and was not preempted.[167] The Supreme Court of Missouri later declined to hear an appeal from that decision.[168]
- Attempts in the Missouri General Assembly to enact some form of statewide smoking ban have failed every year since 2008:
- Bills to ban smoking statewide by Senator Joan Bray before the Missouri Senate in 2008, 2009, and 2010 and by Rep. Walt Bivens before the Missouri House of Representatives in 2010 all failed without receiving a committee hearing.[169][170][171][172] In 2009, a proposal by Rep. Joe Fallert to amend the Constitution of Missouri to ban smoking statewide and a bill by Rep. Jill Schupp proposing .1% a tax on all non-smoke-free businesses also both failed this way.[173][174]
- In 2011, a bill by Rep. Jill Schupp received a hearing before a House committee, but the committee did not put it up for a vote.[175]
- In 2012, respective bills by Rep. Schupp and Sen. Maria Chappelle-Nadal to ban smoking statewide both failed without receiving a committee hearing,[176][177] while a bill by Rep. Melissa Leach to undo the Court of Appeals' 2009 smoking ban decision underwent a committee hearing, though no vote was held.[178]
- In 2013, respective bills by Rep. Schupp and Sen. Chapelle-Nadal to ban smoking statewide both failed without even being referred to a committee,[179][180] while a bill by Rep. Bill Otto to prohibit localities from banning smoking in riverboat casinos underwent a committee hearing but without a vote,[181] and a bill by Rep. Kathie Conway to deprive localities banning smoking of their sales and property tax revenue from smoking-banned private businesses was passed by the House Local Government Committee, but did not advance to a vote before the full House of Representatives.[182]
- In 2014, respective bills by Reps. Schupp and Courtney Curtis and Sen. Chapelle-Nadal to ban smoking statewide all failed without a committee hearing,[183][184][185] while a bill by Rep. Conway to deprive localities banning smoking of their sales and property tax revenue from smoking-banned private businesses was passed by the House Local Government Committee, but did not advance to a vote before the full House of Representatives.[186]
- For 2013, the periodic "Freedom in the 50 States" study prepared by the Mercatus Center at George Mason University ranked Missouri first in the nation in tobacco freedom (also #3 for alcohol freedom and #7 for freedom overall).[187] As of December 2013, Missouri has the lowest cigarette excise taxes in the United States, at 17 cents per pack,[188] and the state electorate previously voted in 2002, 2006, and 2012 to keep it that way.[189][190] According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in 2012 Missouri had the seventh highest percentage of adult smokers among U.S. states, at 25%.[191] In both January 2011 and January 2013, the Missouri House of Representatives voted to continue allowing smoking in its half of the Missouri State Capitol.[192][193] In October 2008, a statewide survey by the Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services found that only 27.5% of Missourians support a statewide ban on smoking in all bars and cocktail lounges.[194] Missouri also has one of the most permissive approaches to alcohol in the United States (see Alcohol laws of Missouri).[187]
- As detailed below, of the 961 cities in Missouri, only 38 (3.9%) have enacted any kind of smoking ban in non-government-owned spaces, 15 of which are not comprehensive bans. One county bans smoking in many places, though exempting bars and casinos. Nine cities and one county have rejected a smoking ban in some manner. On April 5, 2011, Cape Girardeau became one of the few cities in the United States ever to have rejected a smoking ban in a public vote.
- Attempts in the Missouri General Assembly to enact some form of statewide smoking ban have failed every year since 2008:
- Localities in Missouri with a smoking ban that includes all bars and restaurants (23 total):
- Ballwin, January 2, 2006, banned in all workplaces, including bars, and restaurants; exempts private clubs with no employees.[195][196]
- Branson, July 1, 2015, banned in all enclosed public places and workplaces by unanimous Board of Aldermen vote in October 2014; exempts up to 20% of designated hotel and motel smoking rooms, tobacco shops, smoking lounges in tobacco-related businesses, private homes, outdoor areas in places of employment, outdoor patios of restaurants, and golf courses.[197][198]
- Brentwood, January 1, 2011, banned in all enclosed public places and workplaces, by City Council vote of 7–1 in August 2010; exempts designated hotel and motel smoking rooms, tobacco shops, private homes, and private vehicles.[199]
- Chillicothe, January 1, 2008, banned in all workplaces, including bars and restaurants, by City Council vote of 4–1, after 56% of voters approved of the idea in a referendum; exempts separately ventilated offices occupied exclusively by smokers.[200][201]
- Columbia, January 9, 2007, banned in all workplaces, including bars and restaurants; exempts rented social halls, separately ventilated offices occupied exclusively by smokers, stage performances, retail tobacco shops, and private clubs with no employees.[202][203]
- Excelsior Springs, July 4, 2013, banned by unanimous City Council vote in all enclosed workplaces, including bars, restaurants, and private clubs; exempts private residences, 25% of hotel and motel rooms, and retail tobacco shops[204][205]
- Fulton, January 31, 2011, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants, after public vote of 53.85%–46.15%.[206]
- Hannibal, October 4, 2012, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants, after public vote of 55.8%–44.2%; exempts designated smoking rooms in hotels and motels, private residences, private clubs, outdoor areas, and retail tobacco stores.[207]
- Independence, March 17, 2007, banned in all workplaces, including bars and restaurants, per referendum in November 2006; exempts private and semiprivate rooms in nursing homes occupied exclusively by smokers.[208][209]
- Jefferson City, January 31, 2011, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants, after public vote of 58%–42%.[206]
- Kansas City, June 7, 2008, banned in all indoor workplaces, except casino gaming floors and establishments receiving more than 80% of their revenue from tobacco but neither sell nor serve food or beverages, after public vote of 52%–48%[210][211] but halted by the Circuit Court of Jackson County on June 4, 2008, after businesses sued Kansas City on the grounds that state law permitted them to allow smoking;[212] and then reinstated by the court on June 21, 2008.[213] On June 23, 2009, the Missouri Court of Appeals ruled that Kansas City's ban on smoking did not conflict with the state's Indoor Clean Air Act,[167] and the Supreme Court of Missouri declined to hear an appeal from that decision.[168]
- Kirksville, July 1, 2007, banned in all workplaces, including bars and restaurants; exempts private clubs.[214][215]
- Kirkwood, January 2, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all restaurants and bars, after public vote of 65%–35%; exempts private clubs, private residences, private vehicles, smoking rooms in hotels and motels, and retail tobacco stores.[216]
- Lee's Summit, December 8, 2006 banned in all workplaces, including bars and restaurants, per referendum in November 2006; exempts private and semiprivate rooms in nursing homes occupied exclusively by smokers, retail tobacco stores, and private clubs.[217][218]
- Liberty, January 2, 2010, banned in all workplaces, including bars and restaurants, and in public parks, by public vote of 2,684 yes to 1,127 no; exempts outdoor patios, private residences, and smoking rooms in hotels and motels.[219]
- Maryville, October 1, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants, by a city council vote of 3–2.[220]
- Nixa, June 8, 2007, banned in all workplaces, including bars and restaurants; exempts rented social halls, taxicabs and limousines where both driver and passengers agree to allow smoking, stage performances, designated areas of shopping malls, retail tobacco shops, and designated employee smoking areas not accessible to the general public.[221][222]
- North Kansas City, July 10, 2008, banned in all workplaces, including bars and restaurants; exempts casinos and retail tobacco shops[223][224][225]
- Rolla, January 1, 2012, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants, by a city council vote of 8–4 on June 6, 2011; exempts private clubs with no employees, outdoor areas, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, and private homes and vehicles[226]
- Sedalia, September 1, 2013, banned in most enclosed workplaces, including most areas of restaurants and bars, as well as city parks and outdoor recreation areas, by a city council vote of 6-2 on June 17, 2013; exempts 50% of undefined "patio area" space in any bar or restaurant, private clubs, small workplaces (those with one employee), work vehicles where all passengers consent to allow smoking, private residences, private vehicles, designated hotel and motel smoking rooms, private and semiprivate rooms in nursing homes, and retail tobacco stores.[227]
- St. Joseph, June 7, 2014, banned in all enclosed workplaces and public places, including all bars, restaurants, and private and semiprivate rooms in nursing homes, after public vote of 52.75%–47.25%; exempts private vehicles and residences, 10% of hotel and motel rooms designated as smoking, private clubs (when no employees are present), and casino gaming areas (including bars, restaurants, and lounges within those gaming areas).[228][229]
- Warrensburg, November 30, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants; exempts private clubs, retail tobacco stores, any stores whose revenue is at least 80% from tobacco, stage performances involving smoking, designated smoking areas in institutions of higher education, outdoor patios, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, and private residences.[230]
- Washington, April 15, 2013, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants by unanimous city council vote; also banned in private rooms in nursing homes; exempts only private residences not serving as a workplace and designated smoking rooms in hotels and motels; exempts hookah lounges until April 15, 2014.[231]
- Localities in Missouri with a smoking ban that does not include all bars and restaurants (16 total):
- Arnold, November 1, 2004, banned in all restaurants/restaurant-bars seating 50 people or more, except in separately ventilated smoking rooms; does not touch standalone bars or other places; exempts any establishment otherwise classified as a restaurant, that receives 70% or more of its revenue from alcohol sales[232][233]
- Belton, August 5, 2009, banned in all enclosed public places and workplaces, by public vote in April 2009; exempts business vehicles where all occupants agree to allow smoking, any businesses occupied exclusively by one smoker, private and semiprivate rooms in nursing homes, retail tobacco stores, and private clubs; all existing businesses that allow smoking are exempt until August 5, 2012; existing bars and restaurants that allow smoking are exempt until August 5, 2016.[234]
- Blue Springs, May 1, 2008, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including most restaurants; exempts bars, restaurants that seat less than 50 people, restaurants that receive less than 60% of their revenue from food sales, bowling alleys, bingo halls during bingo games, rented social halls, private dances open to the public, and retail tobacco shops.[235][236]
- Clayton, July 1, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants and some bars; exempts cigar bars, tobacco shops, 20% of hotel and motel rooms, and outdoor areas[237]
- Creve Coeur, January 2, 2011, banned by unanimous city council vote in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants; exempts cigar bars, private clubs, tobacco shops, and hotel/motel designated smoking rooms[238]
- Gladstone, May 24, 2009, banned by City Council vote of 4–1 in all enclosed workplaces and city parks; exempts any business existing and licensed to serve liquor on January 1, 2009, that customarily allows smoking and remains under the same ownership; further exempts all bars, taverns, restaurants seating less than 50 people, billiard parlors, bowling alleys, retail tobacco shops, rented social halls, taxicabs and limousines where both driver and passengers agree to allow smoking, stage performances involving smoking, private clubs, private and semiprivate rooms in nursing homes occupied exclusively by smokers, and a percentage of hotel and motel rooms.[239][240]
- Grandview, January 1, 2012, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting some bars; exempts private residences and vehicles, nursing homes, outdoor areas, private clubs, and designated smoking rooms in hotels and motels; bars are exempt until August 2014[241]
- Hazelwood, January 19, 2011, banned in all enclosed workplaces, exempting bars and some restaurants; exempts private clubs, smoking during stage productions, nursing homes, retail tobacco stores, designated smoking rooms in hotels and motels, cigar bars, and any liquor licensee that receives less than 25% of its revenue from food sales[242]
- Kennett, April 16, 2014, banned by 8-1 vote of city council in all enclosed workplaces, including all restaurants; exempts bars and taverns, outdoor areas, retail tobacco shops, 25% of hotel and motel rooms, and private residences[243]
- Lake Saint Louis, September 30, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all restaurants and bars, by Board of Aldermen vote of 4–2 on March 15, 2010; exempts designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, private clubs with no employees, outdoor areas, cigar bars, and retail tobacco stores.[244][245][246]
- O'Fallon, June 4, 2011, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars restaurants, after public vote of 73%–27% on April 5, 2011; exempts cigar bars, private clubs, retail tobacco stores, private residences, outdoor areas, and 20% of hotel and motel rooms.[247][248]
- Parkville, April 7, 2011, banned in all enclosed public places and workplaces by Board of Aldermen; exempts all bars, taverns, restaurants seating less than 50 people, billiard parlors, bowling alleys, retail tobacco shops, rented social halls, taxicabs and limousines where both driver and passengers agree to allow smoking, stage performances involving smoking, and private clubs.[249][250]
- Raymore, August 22, 2008, banned in all public places and within 100 feet (30 m) of the entrance to public places (except on outdoor patios), including most restaurants; exempts bars, restaurants with bars, private clubs, stage performances, restaurants that seat fewer than 50 people, bowling alleys, billiard parlors, taxicabs and limousines where both driver and passengers agree to allow smoking, and retail tobacco shops.[251]
- Springfield, June 11, 2011, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all restaurants, bars, and retail tobacco shops, after public vote of 53%–47% on April 5, 2011; exempts only private residences and 20% of hotel and motel rooms,[252][253] but partially repealed by unanimous vote of the City Council on May 7, 2012, to exempt cigar bars, tobacco shops, and private clubs.[254]
- St. Louis, January 2, 2011, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants; indefinitely exempts casino gaming floors and VIP lounges (unless St. Louis County and St. Charles County and/or St. Charles city also prohibit casino gaming floors), private clubs with no employees, retail tobacco stores, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, private residences, and outdoor areas; bars in existence on January 2, 2011, that are less than 2,000 square feet (190 m2) and do not allow under-21 patrons are exempt until January 2, 2016.[255] On September 14, 2012, the St. Louis Health Department issued an order further permanently exempting the Missouri Athletic Club from the city's smoking ban.[256]
- St. Louis County, January 2, 2011, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants, after public vote of 65%–35% on November 3, 2009; exempts certain drinking establishments (bars having 25% or less gross sales of food, were in existence on Jan. 2, 2011 and have applied for a smoking exemption certificate), cigar bars, casino gaming floors, private clubs, performing on stage as part of a theatrical production, private and semi-private rooms in nursing homes and rest homes, retail tobacco shops, smoking rooms in hotels and motels, and smoking lounges at Lambert-St. Louis International Airport.[257]
- Localities in Missouri where a smoking ban or other smoking restriction was rejected in some manner (10 total):
- Cape Girardeau, April 5, 2011, ban on smoking in all enclosed workplaces, including bars, restaurants, and casinos, rejected by public vote of 52%–48%.[258]
- Carthage, February 2, 2009, ban on smoking in all restaurants indefinitely tabled by City Council committee because it was local, rather than regional[259]
- Farmington, October, 2007, mayor vetoed a ban on smoking in restaurants;[260] and the City Council rejected a ban on smoking in all workplaces in January 2008 by a vote of 6–2[261]
- Joplin, October 18, 2010, City Council rejected a proposed ban on smoking in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants, by a vote of 5–4[262]
- Raytown, October 7, 2008, Board of Aldermen rejected even taking up the issue of a new smoking ordinance, by a vote of 6–4;[263] on September 8, 2009, the Board of Aldermen rejected a proposed smoking ban on all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants, by a vote of 7–3.[264]
- Riverside, June 16, 2009, Board of Aldermen rejected taking up the issue of a smoking ordinance, by a vote of 4–2.[265]
- Smithville, December 18, 2007, Board of Aldermen unanimously rejected a ban on smoking in all workplaces, including restaurants and bars[266]
- St. Charles, May 2008, City Council rejected even taking up the issue of a ban on smoking in all workplaces, including bars and restaurants, by a vote of 6–4, and also rejected sending the proposed ban to voters;[267] July 2013, City Council again rejected taking up any smoking ban and instead voted to introduce a mandatory warning signage ordinance[268][269]
- St. Charles County, June 2011, County Executive vetoed a proposed referendum on a countywide smoking ban including all bars and restaurants but exempting casinos and cigar bars;[270] November 29, 2011, County Council rejected sending a proposed ban on smoking in all workplaces, including restaurants and bars, to voters by a vote of 3–3;[271] September 15, 2012, County Council removed two competing proposed bans, one including bars and casinos and one excluding them, from the November 2012 county ballot[272]
- Webb City, April 11, 2011, City Council rejected a ban on smoking in all workplaces, including restaurants and bars, by vote of 5–3;[273] June 13, 2011, City Council again rejected the same proposal, 5-3[274]
- Statewide smoking ban: On October 1, 2005, the Montana Clean Indoor Air Act (MCIAA) went into effect, banning smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces in Montana including restaurants, though bars were exempt until October 1, 2009;[275] the word "bar" is defined in the Act as also including taverns, night clubs, cocktail lounges, and casinos.[276] The act exempts private residences not used as a daycare facility or healthcare facility, private motor vehicles, tobacco demonstrations in schools, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, and American Indian religious and cultural activities.[275] Local governments are preempted from regulating smoking more stringently than the Act.[277]
- Statewide smoking ban: On June 1, 2009, the Nebraska Clean Indoor Air Act passed in February 2008 went into effect, banning smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces in Nebraska, including all bars and restaurants.[278] The Act exempts tobacco retail stores, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, private residences, and places where scientific research about smoking is occurring.[279] In April 2009, the Act was amended to further exempt cigar bars, as well.[280] Local governments may regulate smoking more stringently than the Act.[281]
- Statewide smoking ban excluding bars, casinos, and designated restaurant smoking rooms: On December 8, 2006, after passage by 54% of voters on November 7, 2006, the Nevada Clean Indoor Air Act went into effect, banning smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces. The act passed by voters initially included all restaurants as well as bars that serve food.[282] The Act permits smoking without limitation in areas within casinos where minors are already prohibited, stand-alone bars that do not serve food, strip clubs and brothels, retail tobacco stores, and private residences (including those that serve as an office workplace, unless used as a childcare, adult daycare, or healthcare facility).[282] Local governments may regulate smoking more stringently than the Act,[282] though no city or county in Nevada has chosen to do so.[4] In 2009 Nevada partially repealed the ban to allow smoking in tobacco-related trade conventions.[citation needed] The ban was further amended in 2011 to allow smoking in taverns that serve alcohol and food as long as patrons under 21 are not allowed in. Smoking is also now allowed in designated areas of family restaurants if the smoking area is physically enclosed and separated from the non-smoking area and minors are prohibited inside.[283]
- Statewide ban on smoking in bars, restaurants, and some other workplaces: On September 17, 2007, the Indoor Smoking Act went into effect, banning smoking in schools, child daycare facilities, hospitals, grocery stores, elevators and public conveyances (except when rented for private purposes), restaurants, bars, and private clubs when open to the public.[284] Private clubs and religious and fraternal organizations (including bars and restaurants inside these places), hotel and motel rooms, rented halls and rooms under control of the renter, college dormitory rooms, public housing, nursing homes, areas designated by hospitals, and alcohol/drug rehabilitation facilities are exempt from smoking regulation and can allow smoking indoors freely.[285] All other places must designate smoking and nonsmoking areas and post appropriate signs.[286] On January 1, 2010, House Bill 392 went into effect. It established an on-premises cigar, beverage, and liquor license and allowed for cigar smoking at public cigar bars.[287] Towns only can regulate smoking more strictly with regard to fire safety and sanitation.[288] In 2003, the New Hampshire Supreme Court ruled that this means state law preempts towns from enacting stricter local smoking bans for health reasons.[289]
- Statewide smoking ban: On April 15, 2006, the New Jersey Smoke-Free Air Act went into effect, banning smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces in New Jersey, including all bars and restaurants, strip clubs, hospitals, psychiatric facilities, as well as outside portions of school grounds.[290] The Act exempts city parks, beaches, cigar bars, tobacco retail stores, tobacco manufacturing facilities, private residences and private automobiles, off-track betting parlors, and designated hotel/motel smoking rooms.[291] Local governments may regulate smoking more stringently than the Act.[292] Violating the Act can result in a fine of between $250 and $1,000, depending how many violations one has incurred within a year.[293]
- Atlantic City, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4] as well as 75% of casino gaming floors.[294]
- Pequannock, banned in public parks with ball-fields or playgrounds in July 2011 through ordinance introduced by Mayor Rich Phelan.[295]
- See Smoke-Free Air Act.
- Statewide smoking ban: On June 15, 2007, the Dee Johnson Clean Indoor Air Act went into effect, banning smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces in New Mexico, including all bars and restaurants, as well as within fifty feet of the entrances to those places.[296][297] The Act exempts (1) private residences except when being used to provide commercial childcare, adult care, and/or healthcare, (2) retail tobacco stores, (3) cigar bars, (4) tobacco manufacturing facilities, (5) casinos, (6) quit-smoking programs, (7) designated outdoor smoking areas, (8) private clubs, (9) limousines under private hire, (10) designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, (11) enclosed areas within restaurants, bars, and hotel/motel conference/meeting rooms that are being used for private functions, (12) cultural or ceremonial activities by American Indians, (13) non-bar/restaurant businesses with fewer than two employees that is not usually accessible to the public and all employees agree to allow smoking, and (14) stage, motion picture, or television productions involving smoking as part of the production.[298] Penalties are $100 for a first violation, $200 for a second violation within 12 months and $500 for the third and subsequent violations.[299] Local governments may regulate smoking more stringently than the Act.[300] UNM campuses are tobacco-free as of August 2009.[301]
- Statewide smoking ban: Effective July 24, 2003,[302] smoking is banned statewide in all enclosed workplaces in New York, including all bars and restaurants and construction sites.[303] The law exempts (1) private homes and automobiles, (2) hotel/motel rooms, (3) retail tobacco businesses, (4) private clubs, (5) cigar bars (A cigar bar that makes 10 percent of its gross income from the on-site sale of tobacco products and the rental of on-site humidors, not including vending machines sales are exempt from the ban), (6) outdoor areas of restaurants and bars, and (7) enclosed rooms in restaurants, bars, convention halls, etc., when hosting private functions organized for the promotion and sampling of tobacco products.[304] Local governments may regulate smoking more stringently than the state law.[305] Breaking the state law can result in a fine of between $200 and $2,000, depending how many violations one has had within a year.[304]
- Great Neck, Adopted January 4, 2011, smoking was banned on sidewalks in front of commercial buildings, Village Green park, and the Housing Authority.[306]
- New York City, From May 18, 2014 everyone under the age of 21 was banned from buying cigarettes, tobacco products and e-cigarettes.[307] Effective May 23, 2011, smoking was banned in all parks, boardwalks, beaches, recreation centers, swimming pools and pedestrian plazas.[308] On March 30, 2003, smoking was banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants; exempts tobacco bars, owner-operated bars, separately ventilated smoking rooms in bars, private clubs with no employees, private functions organized for the promotion and sampling of tobacco products, and retail tobacco shops.[309] Shortly after, on July 24, 2003, the statewide smoking ban came into effect. New York City may suspend or revoke a business's license if it has been found guilty of violating this law three times within 12 months.[310]
On January 21, 1908, the New York City Council had passed the Sullivan Ordinance, which would have banned women from smoking anywhere except their homes, but was vetoed by the Mayor within two weeks of its passage.
- Statewide ban on smoking in bars, restaurants, and some other workplaces: On January 2, 2010, after being signed into law by Governor Bev Perdue on May 19, 2009, North Carolina Session Law 2009-27 went into effect, banning smoking statewide in all bars and restaurants in North Carolina, as well as in government buildings and vehicles.[311] The law exempts cigar bars, private clubs that are not-for-profit (including country clubs), designated hotel/motel smoking areas, and medical research facilities studying tobacco.[311] The law generally allows local governments to regulate smoking more strictly beginning July 5, 2009 (as long as it is approved by the county, too), but preempts local governments from regulating smoking in cigar bars, retail tobacco shops, tobacco manufacturer facilities, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, private clubs (including country clubs), theatrical productions involving smoking, private residences, or private vehicles.[311]
- Other statewide smoking regulation in North Carolina:
- North Carolina Department of Correction, January 2006, banned in all state prisons.[312]
- Orange County, January 1, 2012, banned on all sidewalks owned, operated, or maintained by the municipalities incorporated within the county.
- UNC Hospitals, August 2007, banned on all hospital grounds.[313]
- University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, January 2008, banned on all university grounds except 100 feet (30 m) from any school building.[314]
- Statewide smoking ban: On November 6, 2012, by a vote of 66%-34%, North Dakota voters ratified Initiative Measure Four, which, upon taking effect in December 2012, amends North Dakota's existing partial smoking ban so as to ban smoking statewide in all enclosed public places and places of employment, including all bars, restaurants, and tobacco stores.[315][316] The ban exempts only (1) private residences except when operating as a childcare or adult day care facility, (2) outdoor areas except within 20 feet of the entrance to a public place or place of employment, (3) businesses not open to the public with no employees besides the owner, and (4) American Indian religious and cultural rituals.[316] Local governments may regulate smoking more stringently than the state.[316] As noted above, North Dakota is one of only six states that ban smoking in tobacco stores and is one of only four that prohibit hotels and motels from designating a certain percentage of rooms for smoking.
- North Dakota State University, 2008, banned outdoors on campus within 50 feet (15 m) of buildings.[citation needed]
- University of North Dakota, Grand Forks, October 5, 2007, banned anywhere on campus grounds[317]
- Partial territory-wide smoking ban. Since September 29, 2009, smoking has been banned for most workplaces and restaurants, but not bars.[318]
- Statewide smoking ban: On December 7, 2006, after passage by Ohio voters on November 7, 2006, Chapter 3794 (titled "Smoking Ban") of the Ohio Revised Code went into effect, banning smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces Ohio, including bars and restaurants.[319] The law exempts (1) private residences except when being used as a business when employees other than the owner are present, (2) designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, (3) family-owned and operated businesses not open to the public where all employees are related to the owner, (4) designated smoking areas in nursing homes, (5) retail tobacco stores, (6) outdoor patios, (7) private clubs with no employees.[319] The law is enforced by the Ohio Department of Health, which began enforcement on May 3, 2007.[319] A business may be fined up to $2,500 and individuals $100 for violation of the ban.[319] Local governments may regulate smoking more stringently than the state.[319]
- A ruling by the 10th District Court of Appeals in Columbus upheld the law, stating that a bar owner had intentionally violated it. The bar owner, facing violations and fines totaling $33,000, brought suit, claiming the ban is unconstitutional. On May 23, 2012, The Supreme Court of Ohio affirmed the ruling of the Tenth District Court of Appeals.[320]
- North Royalton April 16, 2008, passed Ordinance 08-69 banning smoking in Public outdoor places owned by the city. Smoking areas may be designated at the mayor's discretion.[321]
- Oberlin, June 2010, Oberlin, banned smoking and the use of smokeless tobacco in city parks.[322]
- No statewide smoking ban. Instead, Oklahoma's statewide smoking law prohibits smoking in any indoor workplaces – including restaurants and hotels – unless a separate ventilation system under negative pressure is installed for ventilating the smoking area, but permits smoking without limitation in bars, private clubs, bingo halls, retail tobacco stores, small family-owned workplaces, workplaces occupied exclusively by smokers, veterans' halls, and designated employee smoking areas.[323][324] The Oklahoma law expressly preempts local governments from enacting any local smoking regulations that are not exactly the same as the state law.[325] In February 2009, a committee of the Oklahoma Senate rejected a proposed ban on smoking in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants and bars, and a similar bill before the Oklahoma House of Representatives failed when it was denied a committee hearing.[326] In May 2009, a bill before the Oklahoma House of Representatives to repeal the preemption on stricter local smoking regulation failed when it did not receive a committee hearing.[327]
- Statewide smoking ban: Effective January 1, 2009, after being signed into law on June 26, 2007, the 1981 Oregon Indoor Clean Air Act (as previously amended in 2001) was amended to ban smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces in Oregon, including bars and restaurants, as well as within 10 feet (3.0 m) of the entrances, exits, or windows of such places.[328] The Act exempts (1) private residences except when serving as a childcare or adult care facility,[329] (2) designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, (3) spaces designated for traditional American Indian religious and cultural ceremonies, (4) retail tobacco shops, and (5) cigar bars.[330] Local governments may regulate smoking more stringently than the Act;[331] and the Oregon Court of Appeals reiterated this in 2000.[332]
- Corvallis, August 1997, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants,[4] including within 10 feet (3.0 m) of entrances to such places.[citation needed]
- Eugene, July 2001, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Philomath, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Statewide smoking ban excluding bars, casinos and some restaurants. Effective September 11, 2008, after being signed into law by Governor Ed Rendell on June 13, 2008, Pennsylvania's 1988 Clean Indoor Air Act was amended to ban smoking statewide in all restaurants and other enclosed workplaces in Pennsylvania, except as exempted.[333] The Act exempts (1) eating/drinking establishments where 20% or less of sales come from food AND persons under 18 are not allowed, (2) private homes and vehicles, except those used as a child daycare or adult care facility, (3) designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, (4) full service truck stops, (5) retail tobacco shops, (6) workplaces of tobacco manufacturers and wholesalers, (7) nursing homes, (8) designated smoking areas in day treatment facilities, psychiatric facilities, and healthcare facilities, (9) private clubs when public events are not being held, including volunteer fire, ambulance, and rescue stations, (10) tobacco-related fundraisers, (11) places rented for tobacco exhibitions, (12) cigar bars, (13) 25% of a casino gaming floor, and (14) outdoor areas.[334] Local governments except Philadelphia are preempted from regulating smoking more stringently than the Act.[334]
- Philadelphia, January 8, 2007, banned in all enclosed workplaces, exempting bars where food accounts for less than 10% of sales and alcohol accounts for more than 90% of sales, and persons under 18 are prohibited.[335] Philadelphia's ordinance is the only local smoking ban in Pennsylvania.[4] On April 29, 2014, Mayor Michael Nutter passed an executive order banning smoking in all city parks.[336]
- Allegheny County enacted a smoking ban October 2006, but it was immediately challenged in court as violating the 1988 Clean Indoor Air Act's preemption of all local smoking regulations.[337] In May 2007, the ban was overturned by the Pennsylvania Commonwealth Court.[337]
- Territory-wide smoking ban: Effective March 2, 2007, smoking is banned territory-wide in all enclosed workplaces in Puerto Rico, including bars and restaurants, as well as private vehicles when either a minor in a car seat or a child under 13 is present.[338] The law exempts (1) retail tobacco stores, (2) theater and film productions and presentations in which actors smoke as part of their character, (3) private homes except when serving as a workplace, and (4) designated hotel/motel smoking rooms.[339]
- Statewide smoking ban: On March 1, 2005, the Public Health and Workplace Safety Act went into effect, banning smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces in Rhode Island, including bars and restaurants.[340][341] The Act exempts (1) cigar bars (income over 50% tobacco products), (2) outdoor areas, (3) private and semiprivate rooms in nursing homes, (4) retail tobacco stores, (5) stage performances involving smoking, (6) private residences, except used as a licensed child care, adult daycare, or healthcare facility,[342] and (7) the two state-licensed gambling facilities, Newport Grand and Twin River Casino.[343] Local governments may regulate smoking more strictly than the Act,[344] though as of April 2009 none have chosen to do so.[4]
- No statewide smoking ban. Instead, South Carolina's 1990 statewide smoking law, the Clean Indoor Air Law, generally prohibits smoking only in (1) public schools, excluding offices and teacher lounges (unless a local school board says otherwise), (2) childcare facilities, (3) healthcare facilities, except in designated employee smoking areas (unless the facilities chooses to be smoke-free), (4) government buildings, except in designated employee smoking areas (and except the State Capitol and legislative office buildings), (5) elevators, (6) public transportation vehicles, and (7) public theatres and arenas, except in designated smoking areas in common areas,[345] and in any such designated smoking area warning signs must be appropriately posted.[346] The Act covers no other places. On March 31, 2008, the South Carolina Supreme Court ruled that local governments generally may regulate smoking more stringently than the Act.[347] On September 8, 2008, the South Carolina Supreme Court ruled that the maximum fine a city or town constitutionally can impose for breaking a local smoking ban is $25.[348] As of July 10, 2012, 48 local governments in South Carolina have enacted local smoking bans.[349] In May 2008, four bills before the South Carolina General Assembly that sought to ban smoking statewide in all bars and restaurants failed when they did not receive a committee hearing before the end of the legislative session.[350]
- Localities in South Carolina with smoking bans that include all bars and restaurants (53 total as of October 1, 2013):
- Aiken, July 14, 2008, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants; exempts any outside area that is not posted as a non-smoking area, private residences, except when used as a daycare or health care facility, hotel and motel rooms that are designated as smoking rooms, retail tobacco stores, requested private and semiprivate smoking rooms in nursing homes and long-term care facilities, private clubs except for events that admit the general public, designated outdoor smoking areas, theatrical stage productions when smoking is essential to the performance, personal vehicles, including times when they are used for employment purposes.[351]
- Aiken County, September 16, 2008, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants.[4]
- Atlantic Beach, May 2, 2011, prohibited in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Beaufort, May 27, 2008, prohibited in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[352]
- Beaufort County, January 10, 2007, prohibited in all workplaces, including bars and restaurants, within unincorporated areas of Beaufort County.[4]
- Camden, September 22, 2008, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Cayce, June 1, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Chapin, August 3, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Charleston, July 23, 2007, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants; exempts cigar bars, theatrical performances involving smoking, and 25% of designated hotel and motel smoking rooms.[349]
- Charleston County, September 1, 2012, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Chesnee, August 9, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Clemson, July 1, 2008, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Columbia, October 1, 2008, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Easley, January 1, 2009, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Edisto Beach, March 1, 2009, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Estill, May 1, 2013, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Florence, November 1, 2011 banned in bars and restaurants but allows workplaces and other privately owned businesses to establish designated break rooms for smoking that are enclosed and separately ventilated from the rest of the establishment in order to be exempt from the law[4][353]
- Fort Mill, August 1, 2009, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Goose Creek, July 1, 2013, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Greenville, January 1, 2007, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4] and has placed a ban for outdoor smoking within city limits
- Hampton, January 1, 2012, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Hartsville, October 10, 2012, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Heath Springs, May 28, 2013, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Hilton Head Island, May 1, 2007, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Hollywood, July 26, 2010 banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Isle of Palms, January 1, 2009, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Kershaw, March 18, 2013, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Lancaster County, March 1, 2013, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- Lexington, October 3, 2009, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Lexington County, January 1, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Mount Pleasant, September 1, 2007, banned in all bars, restaurants, and private clubs, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- North Augusta, August 1, 2009, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- North Myrtle Beach, March 7, 2012, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants; theatrical performances and tobacco bars are exempt from the ordinance; further exempts use of e-cigarettes[4][354]
- Pendleton, February 1, 2012, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in other workplaces[4]
- Pickens, May 1, 2009, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[349]
- Pine Ridge, January 1, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Quinby, March 1, 2012, banned in bars and restaurants but allows workplaces and other privately owned businesses to establish designated break rooms for smoking that are enclosed and separately ventilated from the rest of the establishment in order to be exempt from the law[4]
- Ravenel, April 27, 2010, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Richland County, October 1, 2009, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Rock Hill, May 1, 2009, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[349]
- Simpsonville, September 1, 2012, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- South Congaree, May 18, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Spartanburg, September 1, 2011, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants as well as outdoor functions such as Spring Fling[4][355][356]
- Springdale[disambiguation needed], January 1, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Sullivan's Island, July 20, 2006, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Summerville, July 12, 2011, banned in bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Sumter, April 20, 2009, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Surfside Beach, October 1, 2007, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Timmonsville, March 1, 2012, banned in bars and restaurants but allows workplaces and other privately owned businesses to establish designated break rooms for smoking that are enclosed and separately ventilated from the rest of the establishment in order to be exempt from the law
- Walterboro, August 1, 2008, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- West Columbia, June 1, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Yemassee, August 9, 2013, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including all bars and restaurants[4]
- York County, May 1, 2009, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[349]
- Localities in South Carolina with smoking bans laws that do not include all bars and restaurants (2 total):
- Localities in South Carolina that rejected a smoking ban in some manner (2 total):
- North Charleston, May 14, 2008, rejected a ban on smoking in enclosed workplaces.[357]
- Folly Beach, May 28, 2008, rejected a ban on smoking in enclosed workplaces.[358]
- Statewide smoking ban: South Dakota voters passed 2009 H.B. 1240 on November 10, 2010. The bill bans smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces in South Dakota, including bars and restaurants,[359] exempting only private residences unless used for child daycare,[359] cigar bars, retail tobacco shops, and a percentage of hotel and motel rooms.[360] The bill was passed in the South Dakota State Legislature and signed into law by Governor Mike Rounds. It was scheduled to take effect in July 2009, but on June 22, 2009, a group of casino and video lottery operators presented the Secretary of State with a petition for a referendum over H.B. 1240 that they claimed to bear 25,000 valid signatures.[361] On June 25, 2009, the Secretary of State certified that the petition indeed bore at least the required 16,776 valid signatures, putting H.B. 1240 to the November 2010 public referendum.[362] On July 24, 2009, the Secretary of State declared that after further review, the number of valid signatures on the petition fell short of the required number to put the issue on the ballot.[363] On November 13, 2009, however, Circuit Judge Kathleen Trandahl ruled that the petition did have enough valid signatures, and ordered the Secretary of State to put the issue to a public vote on November 2, 2010,[364] which ultimately passed. H.B. 1240 is silent as to whether local governments may regulate smoking more stringently, though as of November 2010 no local governments in South Dakota have done so.
- Statewide smoking ban excluding bars, some restaurants, and all adult-only venues: On July 1, 2007, after being signed into law in May 2007, the Non-Smoker Protection Act went into effect, banning smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces in Tennessee, except as exempted.[365] The Act exempts (1) any business, including a bar or restaurant, that does not serve persons under 21, (2) designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, (3) tobacco industry-related facilities, (4) outdoor areas and areas with an open garage door, (5) nursing homes, (6) designated smoking areas not accessible to the general public in businesses with three or fewer employees, (7) private clubs, (8) private residences and vehicles unless it is being used for child care, daycare, or public transportation of children, (9) retail tobacco stores, and (10) commercial vehicles occupied solely by the operator.[366] Local governments are preempted from regulating smoking.[367]
- No statewide smoking ban. Instead, since 1997 Texas' statewide smoking law only prohibits smoking in activities of public schools on or off school property,[368] elevators, theatres, libraries, museums, hospitals, buses, airplanes, and trains, as long as these areas are open to the general public, unless the proprietor designates the place for smoking and posts appropriate warning signs.[369] Violation of this law is a class C misdemeanor.[369] Texas law is silent as to whether local governments may regulate smoking more stringently than the state, and on December 9, 2004, the Texas Court of Appeals upheld El Paso's municipal ban on smoking in all bars and restaurants.[370] As of October 1, 2013, 79 cities in Texas have enacted local smoking bans to varying degrees.[4]
- Attempts to ban smoking statewide have failed twice before the Texas Legislature, first in May 2007 when a bill to ban smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants passed the Texas House of Representatives by a vote of 91–48 after being amended to allow any business owner to opt out of the ban by posting signs saying smoking is permitted, and then did not receive a vote in the Texas Senate,[371][372] and then again in May 2009, when a similar bill was passed by a Senate committee but did not receive the 21 votes necessary to reach the Senate floor.[373]
- Localities in Texas with a smoking ban including all bars and restaurants (41 total):
- Abilene, January 3, 2007, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Alton, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Austin, September 1, 2005, after passage by 52% of voters,[citation needed] banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants;[4] exempts bingo halls, fraternities, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, separately ventilated smoking rooms in restaurants and bars constructed before September 2005, and nursing homes.[citation needed] Struck down as unconstitutionally vague by the United States District Court for the Western District of Texas in 2006,[374] but reinstated on appeal by the United States Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit in March 2008.[375]
- Baytown, November 20, 2006, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Beaumont, August 1, 2006, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Benbrook, November 1, 2006, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants,[4] as well as within 25 feet (7.6 m) of the entrances and exits of such places.[citation needed]
- Brownsville, December 5, 2012, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants
- College Station, banned in all enclosed workplaces including bars, restaurants, and within a 20-foot (6.1 m) radius of entryways except in theater performances or tobacco shops.[376]
- Copperas Cove, May 18, 2004, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants;[4] exempts bingo halls (if enclosed non-smoking area is provided), fraternal organizations, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, and private and semi-private rooms in nursing homes.[citation needed]
- Corpus Christi, April 14, 2009, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Dallas, April 10, 2009, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- El Lago, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- El Paso, January 2, 2002, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Ennis, June 21, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants; previous 1993 ordinance that exempted workplaces, bars and restaurants with designated smoking rooms was repealed[4][377]
- Flower Mound, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Frisco, June 1, 2009, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants and within 20 feet of entrances to places where smoking is prohibited; exempts hotels/motels that have designated smoking rooms, and retail tobacco stores that have an enclosed, separately ventilated smoking room that exhausts directly to the outside environment[4][378]
- Harlingen, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Horseshoe Bay, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Houston, September 1, 2007 banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants;[4] exempts retail tobacco shops, cigar bars, and private function events not open to the public.[citation needed]
- Laredo, October 2006, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Lewisville, banned in bars and restaurants, but not other workplaces[4]
- Lufkin, April 16, 2013, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Marshall, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- McKinney, September 4, 2008, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants;[4] exempts retail tobacco shops and country club smoking rooms, but includes all outdoor areas of parks with the exception of parking lots.[379]
- Mesquite, banned in bars and restaurants but not other workplaces[4]
- Missouri City, October 1, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants and within 25 feet of entrances to public places; smoking is also prohibited at youth sporting events at city parks as well as within 20 feet[4][380]
- Nacogdoches, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Pearland, November 30, 2007, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants;[4] includes city-owned parks and playgrounds and within 25 feet (7.6 m) of entrances, operable windows and ventilation systems of places where smoking is banned.[citation needed]
- Plano, June 1, 2007, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Richardson, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Rollingwood, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Rowlett, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- San Angelo, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants.[381]
- San Antonio, August 19, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants and bars; exempts cigar bars, outdoor restaurants and bar patio areas, the River Walk, Alamo Plaza, and Main Plaza.[382]
- Socorro, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Southlake, June 1, 2007, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants;[4] does not exempt hotel/motel rooms.[citation needed]
- Tyler, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- University Park, banned in bars and restaurants, but not other workplaces[4]
- Vernon, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Victoria, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Woodway, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Localities in Texas with a smoking ban that does not include all bars and restaurants (38 total):
- Alpine, July 12, 2010, banned in bars, but not restaurants or other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Angleton, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or all other workplaces[4]
- Arlington, January 1, 2007, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or all other workplaces;[4] includes outdoor areas within 50 feet (15 m) of entrance or exit of a place where smoking is banned.[citation needed]
- Athens, April 23, 2012, banned in all enclosed workplaces, exempting bars and restaurants[4]
- Boerne, March 27, 2007, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or all other workplaces[4]
- Brenham, July 20, 2007, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or all other workplaces;[4] exempts manufacturing facilities[citation needed]
- Caldwell, June 1, 2007, banned in all enclosed workplaces, exempting bars and restaurants[4]
- Conroe, March 1, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Denton, December 18, 2012, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars
- Forney, January 31, 2013, banned in restaurants, but not bars or other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Fort Worth, January 1, 2008, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars;[4] also exempts private clubs, bingo halls, and outdoor dining areas over 20 feet (6.1 m) from an entrance or operable window.[379]
- Frisco, November 18, 2006, banned in all enclosed workplaces except bars and restaurants[4]
- Gainesville, June 6, 2013, banned in all enclosed workplaces, exempting bars and restaurants[4]
- Galveston, January 1, 2010, banned by City Council in all enclosed workplaces; but on September 23, 2010, City Council repealed smoking ban on bars, private clubs, fraternal organizations, and restaurants. The ban that took effect in 2010 originally included bars, private clubs fraternal organizations, and restaurants.[383]
- Greenville, January 1, 2000 banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars.[384]
- Harlingen, April 2, 2005, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[385]
- Hewitt, November 14, 2010, banned in all enclosed workplaces, exempting bars and restaurants[4]
- Highland Texas, June 1, 2011 banned in all enclosed workplaces, exempting bars and restaurants[4]
- Humble, February 23, 2012, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars [386]
- Kaufman, banned in all enclosed workplaces except bars and restaurants[4]
- Kerrville, June 24, 2008, banned in bars, but not restaurants or other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Kilgore, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants that make more than 50% of annual revenue from alcohol sales; also prohibits smoking within 30 feet of places where smoking is prohibited, and provides no exceptions for outdoor patios within restaurants and bars that are non-smoking[4][387]
- Killeen, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Leander, banned in all enclosed workplaces except bars and restaurants[4]
- New Braunfels, banned in all enclosed workplaces except bars and restaurants;[4] also exempts private clubs[citation needed]
- Palestine, banned in all enclosed workplaces, but exempting bars, restaurants, private clubs, designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, bingo halls, and fraternal organizations.[4]
- Pasadena, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Portland, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Prosper, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or all other workplaces[4]
- Richardson, banned in all enclosed workplaces, exempting bars and restaurants[4]
- Robinson, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Rockwall, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or all other workplaces[4]
- Rosenberg, April 5, 2011 banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Round Rock, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Stafford, August 1, 2013, banned in all enclosed workplaces, exempting bars and restaurants[4]
- Sugar Land, January 1, 2008, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Sweeny, banned in all restaurants, but not in bars or all other enclosed workplaces[4]
- Wichita Falls, banned by City Council in all public places except designated areas[388]
- Yoakum, May 12, 2007 voters approved a referendum banning smoking in all enclosed workplaces, exempting bars and restaurants[citation needed]
- Localities in Texas where a smoking ban was rejected in some manner (1 total):
- Territory-wide smoking ban: Effective February 10, 2011, smoking is banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants, and in outdoor service lines.[390]
- Statewide smoking ban: Effective January 1, 2007, as passed in March 2006 (amended in 2012),[391] Utah's 1995 Indoor Clean Air Act was expanded to ban smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces in Utah, including bars and restaurants (bars and private clubs were exempt until January 1, 2009), exempting only (1) designated hotel/motel smoking rooms, (2) areas of owner-operated businesses with no employees besides the owner,[392] and (3) American Indian religious and cultural ceremonies.[393] Since the state law supersedes any ordinances passed by political subdivisions of the state (i.e., cities, counties, school districts, agencies, etc.), such political subdivisions are preempted from regulating indoor smoking any more or less stringently than the Act.[394] Utah is one of the few states with a statewide smoking ban that does not exempt tobacconists.
- Local outdoor smoking bans: Notwithstanding the preemption against political subdivisions modifying the restrictions on indoor smoking, the Act expressly allows such political subdivisions to regulate "smoking in outdoor places of public access which are owned or operated by" (emphasis added) a political subdivision (specifically including state institutions of public or higher education).[394] Accordingly, some political subdivisions have enacted local ordinances prohibiting smoking in certain outdoor areas such as schools, parks,[395] and public transit facilities.[396]
- Statewide smoking ban: Effective September 1, 2005, smoking is banned in all enclosed workplaces in Vermont, including all bars and restaurants,[397] except in areas of owner-operated businesses with no employees that are not open to the public,[398] although separately ventilated designated smoking areas in businesses where employees are not required to be were exempt until July 1, 2009.[399] Designated unenclosed smoking areas in businesses where the layout of the workplace is such that smoking would not be a physical irritation to any nonsmoking employee and three-fourths of the employees agreed were also exempt until July 1, 2009.[399] The Vermont Veterans Home in Bennington is the only non-owner-operated workplace in the state permitted to allow smoking.[399] Vermont is one of the few states with a statewide smoking ban that does not expressly exempt tobacconists, and is the only state that does not allow the designation of hotel/motel smoking rooms. Local governments may regulate smoking more stringently than the state law.[400][401]
- Burlington, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- South Burlington, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Williston, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Winooski, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Statewide ban on smoking in some workplaces. On December 1, 2009, an amendment to Virginia's 1990 Indoor Clean Air Act took effect banning smoking statewide in enclosed public elevators, public school buses, primary and secondary schools, hospital emergency rooms, health department offices, polling places, indoor service lines and cashier lines, public restrooms in government buildings and hospitals, child daycare centers except where located in a private home, and public restrooms of health care facilities, and relegating smoking in restaurants (including bars) to separately ventilated designated smoking rooms that are structurally separated from the rest of the establishment.[402][403] The Act exempts private clubs, retail tobacco stores, tobacco warehouses, tobacco manufacturing facilities, prisons, designated smoking areas in government offices, food preparation facilities for catering services, restaurants located on the premises of tobacco manufacturers, rented private rooms in restaurants; requires the reasonable designation of non-smoking areas in educational facilities where smoking is not banned, hospitals, retail stores bigger than 15,000 square feet (1,400 m2), and recreational facilities.[402] Local governments are preempted from regulating smoking more stringently than the Act.[402] Since 2006, smoking in state offices, vehicles, and buildings (except for correctional facilities) has been banned by executive order issued by the Governor of Virginia.[404] In December 2013, the Court of Appeals of Virginia held 100% of the premises of a retail tobacco store that also operates a restaurant is exempt from Virginia's 2009 smoking restrictions, and may allow smoking throughout the restaurant portion.[405]
- Norfolk, March 25, 2008, repealed a ban on smoking in restaurants, which was passed in October 2007 but had not yet gone into effect, by City Council vote of 5–2, because the City Attorney advised the Council that its ban would violate Virginia state law and could not withstand a legal challenge.[406]
- Statewide smoking ban: On December 8, 2005, after ratification by a majority of Washington voters in a statewide initiative referendum, an amendment to Washington's 1985 Clean Indoor Air Act became effective banning smoking statewide in all public places and places of employment in Washington (except 25% of hotel/motel rooms),[407] as well as within 25 feet (7.6 m) of doors, windows, or ventilation intakes to such places.[408] The act exempts private enclosed workplaces[409] and private residences except when being used to provide licensed childcare, foster care, adult care, or other similar social service care.[410] Washington does not provide exemptions for tobacconists or businesses whose sole purpose is to provide an environment for smoking (e.g. hookah lounges, cigar bars). However, private clubs in enclosed spaces with no employees, and businesses on tribal lands, are exempt. Local governments may regulate smoking more stringently than the act,[409] and local health boards are authorized to enforce the act locally.[411]
- Mason County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- No statewide smoking ban. Instead, West Virginia's statewide smoking laws generally prohibit smoking in (1) public transportation vehicles where a "no smoking" sign is posted,[412] (2) areas of public school except teacher's lounges not accessible to students (unless a local education board rules differently),[413] (3) workplaces where a "no smoking" sign is posted,[414] (4) areas near surface magazines for explosives used in mining,[415] (5) mines and structures around mines,[416][417] (6) nonsmoking sections in bingo halls,[418] and (7) nonsmoking areas in nursing homes.[419] No West Virginia law requires the designation of nonsmoking areas generally in enclosed workplaces. In 2003, the Supreme Court of Appeals of West Virginia ruled that county health boards may regulate smoking more stringently than the state, except in bingo halls and retirement homes.[420] As of April 2009, 44 counties and one city in West Virginia have enacted local smoking bans to varying degrees.[4] In 2008, a proposed statewide smoking ban failed in the West Virginia Legislature.[421]
- Localities in West Virginia with a smoking ban that includes all bars and restaurants (25 total):
- Braxton County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Cabell County, banned in all enclosed workplaces including bars and restaurants[4]
- Calhoun County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Doddridge County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants [4]
- Grant County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Harrison County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Jackson County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Kanawha County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Lincoln County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Marlinton, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Monongalia County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Morgantown, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Ohio County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Pendleton County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Pleasants County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Pocahontas County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Randolph County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Ritchie County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Roane County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Summers County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Tucker County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Upshur County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Wirt County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Wood County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Wyoming County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Localities in West Virginia with a smoking ban that does not include all bars and restaurants (23 total):
- Barbour County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Berkeley County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars;[4] in September 2009, the County Health Board rejected ending the bar exemption[422]
- Boone County, banned in all enclosed workplaces except bars and restaurants[4]
- Brooke County, banned in all enclosed workplaces except bars and restaurants[4]
- Clay County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Fayette County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Greenbrier County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Hardy County, banned in all enclosed workplaces except bars and restaurants[4]
- Jefferson County, banned in all enclosed workplaces except bars and restaurants[4]
- Lewis County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Marion County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Marshall County, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or all other workplaces[4]
- McDowell County, banned in all restaurants, but not bars or all other workplaces[4]
- Mercer County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Mineral County, banned in all enclosed workplaces except bars and restaurants[4]
- Mingo County, banned in all enclosed workplaces except bars and restaurants[4]
- Monroe County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Morgan County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Nicholas County, banned in all enclosed workplaces except bars and restaurants[4]
- Preston County, banned in all enclosed workplaces except bars and restaurants[4]
- Raleigh County, banned in all enclosed workplaces except bars and restaurants[4]
- Wayne County, banned in all enclosed workplaces except bars and restaurants[4]
- Webster County, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including restaurants but exempting bars[4]
- Localities in West Virginia where a smoking ban was rejected in some manner (1 total):
- Putnam County, August 21, 2007, County Health Board repealed a September 2006 ban on smoking in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[423]
- Statewide smoking ban: On July 5, 2010, after being signed into law by Governor Jim Doyle on May 18, 2009, S.B. 181 (2009 Wisconsin Act 12) took effect, banning smoking statewide in all enclosed workplaces in Wisconsin, including all bars, restaurants, lodging establishments, and private clubs, as well as within a "reasonable distance" outdoors from any such place, except in bar/restaurant outdoor patios.[424] The Act exempts only cigar bars or retail tobacco stores already in existence, private residences, and rooms in nursing homes in which the occupants agree to allow smoking; it does not cover casinos run by American Indian tribes, as those casinos are in the tribes' sovereign territory.[424] Local governments are preempted from regulating smoking more strictly than the Act.[424] Prior to this law taking effect, several localities in Wisconsin had local smoking bans in effect.
- No statewide smoking ban. Instead, Wyoming state law only prohibits smoking where it could cause an explosion[426][427][428] and in underground mines.[429] Wyoming has no state laws concerning indoor smoking in general, and thus local governments can regulate general indoor smoking as they see fit. As of April 2009, five cities in Wyoming have enacted local smoking bans, all covering all bars and restaurants, but varying otherwise.[4] In February 2009, a bill before the Wyoming Legislature that would have enacted a statewide ban on smoking in all enclosed workplaces, except in private offices and in bars and restaurants serving only patrons over 21 years of age (and except in any local community that chose to opt out) failed when it was passed by the Wyoming House of Representatives in a vote of 31–29 but then was denied a committee hearing in the Wyoming Senate.[430]
- Localities in Wyoming with a smoking ban that includes all bars and restaurants (5 total):
- Burlington, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Cheyenne, August 15, 2006, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces;[4] ban includes private clubs.[citation needed]
- Evanston, September 4, 2007, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces[4]
- Laramie, April 6, 2005, banned in all bars and restaurants, but not in all other workplaces;[4] ban includes private clubs.[citation needed]
- Mountain View, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants[4]
- Localities in Wyoming with a smoking ban that does not include all bars and restaurants (3 total):
- Casper, September 1, 2012, banned in bars and restaurants, but not other workplaces; on June 28, 2013, the Casper City Council repealed the ban on smoking in bars by a vote of 5-4 but left the restaurant ban in place[431]
- Green River, December 27, 2007, banned in all enclosed workplaces, including bars and restaurants, but then repealed ban in bars by 4-3 vote of City Council[432]
- Rock Springs, December 2007, banned in all workplaces and restaurants, but not bars and private clubs.[433]
See also
- Alcohol laws of the United States by state
- Electronic cigarette
- List of smoking bans worldwide
- Smokeasy
- Tobacco control
References
- ^ "Overview List – How many Smokefree Laws?, Americans for Nonsmokers' Rights, January 2, 2014" (PDF). Retrieved January 12, 2014.
- ^ "Summary of 100% Smokefree State Laws and Population Protected by 100% U.S. Smokefree Laws, Americans for Nonsmokers' Rights, 1 January 2, 2014" (PDF). Retrieved January 2, 2014.
- ^ "States, Commonwealths, and Municipalities with 100% Smokefree Laws in Workplaces, Restaurants, or Bars, American Nonsmokers' Rights Foundation, January 2, 2014" (PDF). Retrieved January 12, 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg ch ci cj ck cl cm cn co cp cq cr cs ct cu cv cw cx cy cz da db dc dd de df dg dh di dj dk dl dm dn do dp dq dr ds dt du dv dw dx dy dz ea eb ec ed ee ef eg eh ei ej ek el em en eo ep eq er es et eu ev ew ex ey ez fa fb fc fd fe ff fg fh fi fj fk fl fm fn fo fp fq fr fs ft fu fv fw fx fy fz ga gb gc gd ge gf gg gh gi gj gk gl gm gn go gp gq gr gs gt gu gv gw gx gy gz ha hb hc hd he hf hg hh hi hj hk hl hm hn ho hp hq hr hs ht hu hv hw hx hy hz ia ib ic id ie if ig ih ii ij ik il im in io ip iq ir is it iu iv iw ix iy iz ja jb jc jd je jf jg jh ji jj jk jl jm jn jo jp jq jr js jt ju jv jw jx jy jz ka kb kc kd ke kf kg kh ki kj kk kl km kn ko kp kq kr ks kt ku kv kw kx ky kz la lb lc ld le lf lg lh li lj lk ll lm ln lo lp lq lr ls lt lu lv lw lx ly lz ma mb mc md me mf mg mh mi mj mk ml mm mn mo mp mq mr ms mt mu mv mw mx my mz na nb nc nd ne nf ng nh ni nj nk nl nm nn no np nq nr ns nt nu nv nw nx ny nz oa ob oc od oe of og oh oi oj ok ol om on oo op oq or os ot ou ov ow ox oy oz pa pb pc pd pe pf pg ph pi pj pk pl "Municipalities with Local 100% Smokefree Laws, American Nonsmokers' Rights Foundation, January 2, 2014" (PDF). Retrieved January 12, 2014.
- ^ Taub, Daniel (March 17, 2006). "Daniel Taub, "California Town Makes It Tougher to Smoke in Public," Bloomberg.com, March 17, 2006". Bloomberg. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ 14 C.F.R. Part 252
- ^ Executive Order 13058, August 9, 1997
- ^ a b "Ala. Code § 22-15A-4". Legislature.state.al.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Ala. Code § 22-15A-6". Legislature.state.al.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Ala. Code § 22-15A-7". Legislature.state.al.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Ala. Code § 22-15A-10". Legislature.state.al.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Gann v. City of Gulf Shores, 29 So. 3d 244 (Ala. Crim. App. 2009)
- ^ "Time runs out in Alabama Legislature on statewide smoking ban, ''The Birmingham News'', May 20, 2008". Al.com. May 20, 2008. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Phillip Rawls, "Alabama senator delays her anti-smoking bill", AP, April 3, 2009". News.ino.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ (Press-Register/Victor Calhoun). "George Altman, "Ban on smoking in Alabama restaurants fails in Legislature," ''Press-Register'' (April 23, 2010)". Blog.al.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Our View: Strong smoke-free laws are spreading across the country, but in the Alabama Legislature, they may not be going anywhere, ''Press-Register'' (April 27, 2011)". Blog.al.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Anniston City Council restricts public smoking, (April 23, 2013)". annistonstar.com. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- ^ "Chickasaw becomes latest Mobile County town to pass no-smoking ordinance, (November 26, 2013)". Blog.al.com. Retrieved November 27, 2013.
- ^ "Creola approves anti-smoking ordinance, (April 28, 2013)". Blog.al.com. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
- ^ "Troy City Council passes ordinance to ban smoking at public places, (June 26, 2013)". Blog.al.com. Retrieved July 4, 2013.
- ^ "Satsuma City Council passes no-smoking ordinance, (July 3, 2013)". Blog.al.com. Retrieved July 4, 2013.
- ^ "Alaska Stat. § 18.35.305". Touchngo.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Alaska Stat. § 18.35.300". Touchngo.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Alaska Stat. § 18.35.310". Touchngo.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Alaska Stat. § 18.35.320". Touchngo.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Alaska Stat. § 18.35.330". Touchngo.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Fraternal Order of Eagles v. City and Borough of Juneau, 254 P.3d 348 (Alaska 2011)
- ^ "Anchorage voters embrace smoking ban", Anchorage Daily News, April 3, 2007
- ^ The Associated Press (February 26, 2008). "Juneau bar owners say smoking ban hurts business, ''Anchorage Daily News'', February 26, 2008". Adn.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ The Associated Press (September 20, 2011). "Smoking ban begins in Nome, ''Anchorage Daily News'', September 20, 2011". Adn.com. Retrieved May 24, 2012.
- ^ "Proposed Smoking Ban on Kodiak Island All but Dead," Associated Press (July 14, 2013)[dead link]
- ^ "Governor Togiola Signs American Samoa Smoke Free Environment Act, American Samoa Community Cancer Coalition, October 22nd, 2010". Asccancercoalition.org. October 22, 2010. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Ariz. Rev. Stat § 36-601.01". Azleg.state.az.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Amanda J. Crawford, "Smoking ban compliance is expected to be gradual", ''The Arizona Republic'', May 1, 2007". Azcentral.com. May 1, 2007. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Ark. Code. Ann. §§ 20-27-1801 through 20-27-1809
- ^ Ark. Code Ann. § 20-27-1808
- ^ Ark. Code. Ann. § 20-27-1903
- ^ "Cal. Lab. Code § 6404.5". Leginfo.ca.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "City of Lodi, California, "AB 846 Expands Smoking Restrictions". Lodi.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Vargas. "California State Senate: AB 846 Assembly Bill – Chaptered". Info.sen.ca.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Governor Signs into Law Measure to Outlaw Smoking in Cars with Kids, October 2007
- ^ "Cal. Health & Safety Code § 118974". Leginfo.ca.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ California Town Approves Ban Making Smoking Illegal in Condos, Apartments Fox News, October 2007
- ^ "Berkeley approves smoking ban". Abclocal.go.com. March 25, 2008. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ KCBS.com
- ^ "LG-PD-Press_Release_Smoking_Ban". Beverlyhills.org. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Burbankca.org[dead link]
- ^ Broder, John M. (March 19, 2006). "Smoking Ban Takes Effect, Indoors and Out". California: N.Y. Times. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ http://daviswiki.org/Davis_Municipal_Code/34.02.010
- ^ "San Diego Metro News | SignOnSanDiego.com – El Cajon bans smoking in most public places". SignOnSanDiego.com. August 14, 2007. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ http://www.el-cerrito.org/index.aspx?NID=836.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ a b "Escondido Municipal Code, Chapter 22A, Smoking Regulations, Section 2 Prohibitions". Qcode.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ ADAM KAYE – North County Times (November 18, 2007). "North County Times, November 18, 2007, Adam Kaye, "Smoking bans spreading in North County – Encinitas, Carlsbad are latest to investigate ordinances", Escondido, CA". Nctimes.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "North County Times, May 21, 2007, Paul Eakins, "Students to ask Escondido council to consider smoking ban", Escondido, CA". Nctimes.com. May 21, 2007. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Ci.glendale.ca.us[dead link]
- ^ Aggressive Hermosa Beach outdoor smoking ban to begin, March 2, 2012
- ^ Enforcement of Loma Linda's more restrictive smoking ban does not appear to be priority in first day, July 25, 2007
- ^ "Los Angeles County Bans Smoking at Public Parks, Golf Courses". Cigarettesreviews.com. Retrieved May 17, 2010.
- ^ http://clkrep.lacity.org/onlinedocs/2008/08-1544_ord_181065.pdf
- ^ http://sfbay.ca/2012/05/23/marin-smoking-ban-stretches-into-the-home/
- ^ "Oakland Municipal Code, chapter 8.30". Retrieved April 10, 2013.
- ^ "Ci.pasadena.ca.us". Ci.pasadena.ca.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Herel, Suzanne (January 26, 2005). "SF Board of Supervisors votes to ban smoking in all city parks". The San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved August 21, 2013.
- ^ Sankin, Aaron (January 15, 2013). "San Francisco Smoking Ban: Board of Supervisors passes two anti smoking bills". Huffington Post. Retrieved August 21, 2013.
- ^ San José Municipal Ordinance 9.44.030F and 9.44.010A and Parks Ordinance 13.44.130
- ^ "Letter to Nebraska Senators from San Luis Obispo Chamber of Commerce in favor of Smokefree Legislation". Tobacco.org. Retrieved April 7, 2007.
- ^ "Outdoor Smoking Ban in San Luis Obispo".
- ^ "Smoking ban approved in SLO".
- ^ "Public Health Department-Santa Barbara County". Countyofsb.org. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Santa Monica Municipal Code".
- ^ NextPage – LivePublish. "Colo. Rev. Stat. § 25-14-204". Michie.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ NextPage – LivePublish. "Colo. Rev. Stat. § 25-14-205". Michie.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ NextPage – LivePublish. "Colo. Rev. Stat. § 25-14-207". Michie.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ http://gazette.com/bar-owner-finds-long-sought-smoking-ban-loophole/article/95320
- ^ a b c d "Conn. Gen. Stat. § 19a-342". cga.ct.gov. Retrieved September 12, 2012.
- ^ a b c "Del. Code Ann. tit. 16, §§ 2901 through 2908". Delcode.delaware.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Weiss, Eric M. (January 5, 2006). "D.C. Smoking Ban Approved, ''The Washington Post'', January 5, 2006". The Washington Post. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Fla. Stat. §§ 386.201 through 386.2125". Leg.state.fl.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ >2008–>Ch0386->Section%20209#0386.209 Fla. Stat. §386.209
- ^ Ga. Code. Ann. § 31-12A-4
- ^ Ga. Code. Ann. § 31-12A-6
- ^ a b c Ga. Code. Ann. § 31-12A-12
- ^ "Tobacco.org". Tobacco.org. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Public Law 28-80". No-smoke.org. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Guam". no-smoke.org. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Haw. Rev. Stat. § 328J-3". Capitol.hawaii.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Haw. Rev. Stat. § 328J-7". Capitol.hawaii.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Haw. Rev. Stat. § 328J-6". Capitol.hawaii.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Haw. Rev. Stat. § 328J-12". Capitol.hawaii.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Capitol.hawaii.gov
- ^ "Haw. Rev. Stat. § 328J-15". Capitol.hawaii.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b Dingeman, Robbie (October 31, 2002). "Smallest county to ban smoking". Honolulu Advertiser. Retrieved January 2, 2014.
- ^ "Idaho Code § 39-5503". Legislature.idaho.gov. July 29, 2004. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Idaho Code § 39-5511". Legislature.idaho.gov. July 29, 2004. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Times. "KTVB.com". KTVB.com. Retrieved December 21, 2011.
- ^ Times. "Spokesman.com". Spokesman.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Times. "MagicValley.com". MagicValley.com. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ^ a b c "Illinois Public Act 095-0017: "Smoke Free Illinois Act"". Ilga.gov. June 30, 2005. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Clean Indoor Air Ordinance (No Smoking: Including E-Cigarettes)". City of Chicago. 2014. Retrieved 2014.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ http://politics.suntimes.com/article/chicago/park-district-bans-smoking-parks/wed-09102014-529pm
- ^ a b c "2012 Indiana House Bill 1149-1" (PDF). Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ "Indiana Smoking Ban Dies in House Committee", The Associated Press, January 28, 2008
- ^ John Byrne, "Statewide smoking ban now appears dead," Post Tribune of Northwest Indiana, April 23, 2009.
- ^ "Mark Peterson, "Smoking ban debate over in Indiana," ''WNDU-16'', February 4, 2010". Wndu.com. February 4, 2010. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Carden, Dan (April 11, 2011). "Dan Carden, "Smoking ban dies in Senate", ''Northwest Indiana Times'', April 11, 2011". Nwitimes.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Action information for HB 1149, Indiana General Assembly (2012)". In.gov. March 9, 2012. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ "CMS.bsu.edu". CMS.bsu.edu. March 17, 2008. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Purdue.edu". Purdue.edu. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ EndPlay (February 19, 2010). "RTV6 - Stricter Smoking Ban Approved In Franklin - News Story". Theindychannel.com. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
- ^ "Fortwayne.com". Fortwayne.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "A hazy ban". Idsnews.com. March 30, 2009. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Henry County passes countywide smoking ban | Indiana Public Radio's News Blog". Iprnews.wordpress.com. November 11, 2010. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
- ^ "Lowell OKs watered down smoking ban, ''Post-Tribune'', April 2, 2011". Posttrib.suntimes.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Evansville Courier and Press". Retrieved March 12, 2012.
- ^ Paul Stieler Enters. v. City of Evansville, 2 N.E.3d 1269 (Ind. 2014)
- ^ "folio-destination-name:'sec_142D_3']$x=Advanced#0-0-0-27117 Iowa Code § 142D.3". Search.legis.state.ia.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "folio-destination-name:'sec_142D_4']$x=Advanced#0-0-0-27119 Iowa Code § 142D.4". Search.legis.state.ia.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b "folio-destination-name:'sec_142D_9']$x=Advanced#0-0-0-27129 Iowa Code § 142D.9". Search.legis.state.ia.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b c H.B. 2221 (Kan. 2010)[dead link]
- ^ K.S.A. 21–4013
- ^ "Steffes v. City of Lawrence, 284 Kan. 380, 160 P.3d 843 (2007)". Kscourts.org. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ 5:22 pm CDT June 30, 2010 (June 30, 2010). "KS Judge Blocks Parts Of Smoking Law, KMBC-9 TV, Kansas City, Mo., June 30, 2010". Kmbc.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "K.R.S. 61.165" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "K.R.S. 61.167" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Lexington Fayette County Food & Bev. Ass'n v. Lexington-Fayette Urban County Gov't, 131 S.W.3d 745 (Ky. 2004)" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "2011 Kentucky HB193". Lrc.ky.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "2012 Kentucky HB289". Lrc.ky.gov. Retrieved April 18, 2012.
- ^ "2011 Kentucky HB216". Lrc.ky.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Health and Wellness – Smoke-Free Law Online Toolkit". LouisvilleKy.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Council passes smoking ban » Archive » Commonwealth Journal". Somerset-kentucky.com. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
- ^ "Boone pulls out of smoking ban talks". Cincinnati.com. July 30, 2010. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- ^ in: Campbell County (February 17, 2011). "Campbell repeals indoor smoking ban | Kentucky Politics". Cincinnati.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b c "La. Rev. Stat. § 1300.256". Legis.state.la.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ The Times-Picayune (June 2, 2009). "Jan Moller, "House rejects smoking ban, 29–71", ''New Orleans Times-Picayune'', June 2, 2009". Nola.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Carolyn Kaster / The Associated Press. "Jan Moller, "Casino smoking ban rejected by House committee" (May 6, 2010)". Nola.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Marsha Shuler, "Committee rejects smoking ban bill," Baton Rouge Advocate (May 26, 2010)
- ^ "AP, "Senate rejects smoking ban for Louisiana bars," ''New Orleans CityBusiness'' (June 2, 2011)". Neworleanscitybusiness.com. June 2, 2011. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Louisiana Senate rejects smoking ban extension". Necn.com. May 23, 2012. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
- ^ a b "Me. Rev. Stat. tit. 22, § 1542". Mainelegislature.org. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Me. Rev. Stat. tit. 22, § 1549". Mainelegislature.org. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b c "MD Clean Indoor Air Act of 2007 (House Bill 359)" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b c "Mass. Gen. L. ch. 70, § 22". Mass.gov. January 1, 2006. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Gideon Gil, "Boston bans cigarette sales in drug stores but delays cigar bar closings", ''The Boston Globe'', December 11, 2008". Boston Globe. December 11, 2008. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) [dead link] - ^ a b c "2009 Michigan House Bill 4377" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Michigan Government Smoking Ban FAQ |format=PDF |accessdate=March 25, 2015
- ^ "Minn. Rev. Stat. § 144.414". Revisor.leg.state.mn.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Minnesota Clean Indoor Air Act" (PDF). Emily Cleveland. July 2007. Retrieved October 29, 2007.
- ^ "Minn. Rev. Stat. § 144.417". Revisor.leg.state.mn.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Duluthtransit.com[dead link]
- ^ "Postbulletin.com". Postbulletin.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Miss. Code § 29-5-161
- ^ Miss. Code § 29-5-163
- ^ "2011 Mississippi SB2514". Billstatus.ls.state.ms.us. July 1, 2011. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "2011 Mississippi HB863". Billstatus.ls.state.ms.us. July 1, 2011. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "2011 Mississippi HB131". Billstatus.ls.state.ms.us. July 1, 2011. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "commercialappeal.com".
- ^ a b c d McMillen et al., Smoke-Free Legislation and the Social Climate of Secondhand Smoke in Mississippi (November 2008)[dead link]
- ^ "Jacksonfreepress.com". Jacksonfreepress.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Wtok.com". Wtok.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Pascagoula council approves smoke-free ordinance". Tbo.com. June 19, 2013. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ "Corinth aldermen adopt public smoking ban", Clarion Ledger, November 7, 2007
- ^ Sunherald.com[dead link]
- ^ a b "Mo. Rev. Stat. § 191.767". Moga.mo.gov. August 28, 2011. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Mo. Rev. Stat. § 191.771". Moga.mo.gov. August 28, 2011. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Mo. Rev. Stat. § 191.777". Moga.mo.gov. August 28, 2011. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Mo. Rev. Stat. § 191.769". Moga.mo.gov. August 28, 2011. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b City of Kansas City v. Carlson, 292 S.W.3d 368 (Mo. App. W.D. 2009)[dead link]
- ^ a b [Scott Lauck, "Legal challenge to KC smoking ban ends", Kansas City Daily Record, October 7, 2009]
- ^ "2008 Missouri Senate Bill 1079". Senate.mo.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "2009 Missouri Senate Bill 309". Senate.mo.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "2010 Missouri Senate Bill 904". Senate.mo.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "2010 Missouri House Bill 1766". House.mo.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "2009 Missouri House Joint Resolution 5". House.mo.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "2009 Missouri House Bill 910". House.mo.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "2011 Missouri House Bill 438". House.mo.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "2012 Missouri House Bill 1352". house.mo.gov. Retrieved May 18, 2012.
- ^ "2012 Missouri Senate Bill 664". senate.mo.gov. Retrieved May 18, 2012.
- ^ "2012 Missouri House Bill 2103". house.mo.gov. Retrieved May 18, 2012.
- ^ "2013 Missouri House Bill 523". house.mo.gov. Retrieved May 13, 2013.
- ^ "2013 Missouri Senate Bill 201". senate.mo.gov. Retrieved May 13, 2013.
- ^ "2013 Missouri House Bill 509". house.mo.gov. Retrieved May 13, 2013.
- ^ "2013 Missouri House Bill 1021". house.mo.gov. Retrieved May 13, 2013.
- ^ "2014 Missouri House Bill 1716". house.mo.gov. Retrieved May 24, 2014.
- ^ "2014 Missouri House Bill 1625". house.mo.gov. Retrieved May 24, 2014.
- ^ "2014 Missouri Senate Bill 572". senate.mo.gov. Retrieved May 24, 2014.
- ^ "2014 Missouri House Bill 1067". house.mo.gov. Retrieved May 24, 2013.
- ^ a b Mercatus Center (March 28, 2013). "Freedom in the 50 States-Missouri". Freedom in the 50 States. George Mason University. Retrieved March 29, 2013.
- ^ "Campaign for Tobacco-Free Kids, ''State Excise Tax Rates and Rankings'', December 3, 2013" (PDF). Retrieved April 9, 2014.
- ^ "A burning issue," St. Louis Post-Dispatch, November 12, 2006
- ^ Tim O’Neil toneil@post-dispatch.com314-340-8132 (November 6, 2012). "Tim O'Neil, "Missouri keeps tobacco tax as the lowest in the nation", ''St. Louis Post-Dispatch'' (November 7, 2012)". Stltoday.com. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Smoking & Tobacco Use State Highlights – Missouri, May 1, 2013". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved April 9, 2014.
- ^ The Associated Press (January 13, 2011). "Missouri House rejects smoking ban in Capitol offices, ''Southeast Missourian'', January 13, 2011". Semissourian.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ The Associated Press (January 16, 2013). "Missouri House approves rules after debates over smoking, transparency, ''St. Louis Post-Dispatch'', January 16, 2013". Stltoday.com. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services, County Level Survey 2007: Secondhand Smoke for Missouri Adults, October 1, 2008[dead link]
- ^ "Smoking ban cuts into profits," St. Louis Post-Dispatch, June 10, 2006
- ^ Ballwin (Mo.) Code of Ordinances, Section 17-65
- ^ Brian Vandenberg, "Branson Going Smoke-Free," KY3-TV (Oct. 29, 2013)
- ^ City of Branson (Mo.) Code of Ordinances, Section 58-126 et seq.
- ^ "Margaret Gillerman, "Brentwood passes smoking ban", ''St. Louis Post-Dispatch'', August 17, 2010". Stltoday.com. August 17, 2010. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Catherine Stortz Ripley, "City Council passes smoking ban", Chillicothe Constitution-Tribune, May 15, 2007
- ^ Chillicothe (Mo.) Code of Ordinances, Section 18-93
- ^ "Smoking ban passes," Columbia Missourian, October 10, 2006
- ^ "Columbia (Mo.) Code of Ordinances, Chapter 11, Article IX" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Tallan, Erika. "Smoking ban in Excelsior Springs takes effect on the Fourth, KCTV-5 News (July 2, 2013)". Kctv5.com. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ "City of Excelsior Springs (Mo.) Ordinance No. 13-05-01" (PDF). Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ a b "Ben Yarnell, "Smoking bans approved in Jefferson City, Fulton," ''Jefferson City News-Tribune'', November 3, 2010". Newstribune.com. November 3, 2010. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ Danny Henley, "Smoke-free proposal passes in Hannibal" Hannibal Courier-Post, April 3, 2012
- ^ "Proponents postpone petition to ban smoking," The Kansas City Star, November 8, 2006
- ^ Independence (Mo.) Code of Ordinances, Chapter 11, Article 2
- ^ Lynn Horsely, "KC will go smoke-free", The Kansas City Star, April 8, 2008
- ^ Kansas City (Mo.) Code of Ordinances, Chapter 34, Article XII
- ^ Lynn Horsely, "KC's smoking ban delayed", The Kansas City Star, June 4, 2008
- ^ Lynn Horsely, "KC smoking ban effective today for bars, restaurants, tobacco stores," The Kansas City Star, June 21, 2008
- ^ "Smoking ban passes," Truman State University Index, April 5, 2007
- ^ Kirksville (Mo.) Code of Ordinances, Chapter 18, Article V
- ^ Ciy of Kirkwood Proposition 1 (2009)
- ^ "Lee's Summit Bans Smoking," The Kansas City Star, August 11, 2006
- ^ Lee's Summit Code of Ordinances, Chapter 17, Article X
- ^ "Liberty (Mo.) Question 1 (2009)". Smokefreeliberty.web.officelive.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Brown, Tony (August 10, 2010). "Council passes workplace smoke ban, ''Maryville Daily Forum'', August 10, 2010". Maryvilledailyforum.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Nixa passes toughest smoking ban in state," Drury University Mirror, March 12, 2007
- ^ "Microsoft Word - Chapter CONTENTS.doc" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "North Kansas City approves smoking ban", The Kansas City Star, June 11, 2008
- ^ North Kansas City (Mo.) Code of Ordinances, Title 8, Article II
- ^ "Tobacco House exempted from NKC smoking ban," The Kansas City Star, January 16, 2009
- ^ "Council OKs smoke ban," The Rolla Daily News, July 6, 2011
- ^ "Emily Jarrett, "City council votes to snuff out smoking in bars, restaurants," ''Sedalia Democrat'' (June 17, 2013)". Sedaliademocrat.com. January 31, 2013. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ "Smoking ban passes in close vote". News-Press & Gazette Company. April 8, 2014. Retrieved April 8, 2014.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ City of St. Joseph Special Ordinance No. 1453-10
- ^ Warrensburg (Mo.) Ordinance No. 4510[dead link]
- ^ Pruneau, Ed (January 26, 2013). "Ed Pruneau, "Council Adopts Smoke-Free Law; Takes Effect April 15," ''Washington (Mo.) Missourian'' (Jan. 26, 2013)". Emissourian.com. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ "Smoking or non?", St. Louis Post-Dispatch, July 14, 2004
- ^ Arnold (Mo.) Code of Ordinances, Chapter 10, Article XI
- ^ Donald Bradley, "In Missouri, many money issues find favor despite tough times", The Kansas City Star, April 8, 2009[dead link]
- ^ "It's approved!", The Blue Springs Examiner, February 5, 2008
- ^ Blue Springs (Mo.) Code of Ordinances, Section 245.280
- ^ Phil Sutin, "Clayton imposes smoking ban", St. Louis Post-Dispatch, July 15, 2009[dead link]
- ^ "Creve Coeur passes smoking ban, KSDK-TV, November 9, 2010". Ksdk.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "City of Gladstone (Mo.) Ordinance No. 3.208" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Gladstone council passes smoking restrictions", The Kansas City Star, February 24, 2009
- ^ "Grandview (Mo.) Code of Ordinances, Section 17-47". Library.municode.com. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ "Hazelwood (Mo.) Code of Ordinances, Section 215.555". Z2codes.sullivanpublications.com. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ "Steve Patton, "City Council votes yes on smoking ban," ''Daily Dunklin Democrat'' (April 16, 2014)". dddnews.com. Retrieved April 17, 2014.
- ^ Lake St. Louis (Mo.) Bill No. 3002 (2009)[dead link]
- ^ Mark Schlinkmann, "Lake Saint Louis approves smoking ban", St. Louis Post-Dispatch, March 15, 2010[dead link]
- ^ Mark Schlinkmann, "Mayor Mike Potter signs Lake Saint Louis smoking ban; takes effect in six months," St. Louis Post-Dispatch, March 31, 2010[dead link]
- ^ Castile, Raymond (April 5, 2011). "O'Fallon to be smoke free, ''St. Louis Post-Dispatch'', April 5, 2011". Stltoday.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "O'Fallon (Mo.) Smoke Free Air Act" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Larry Seward, ''Parkville Passes Smoking Ban'', KSHB-TV April 8, 2009". Nbcactionnews.com. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ Parkville (Mo.) Code of Ordinances, Chapter 206[dead link]
- ^ Raymore (Mo.) Code of Ordinances, Chapter 270
- ^ "Smoking, alcohol bans pass," Springfield News-Leader, April 5, 2011[dead link]
- ^ "Springfield (Mo.) Ordinance No. 5927" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Amos Bridges, "City Council approves amendments to smoking ban," ''Springfield News-Leader'' (May 8, 2012)". News-leader.com. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ "City of St. Louis (Mo.) Board Bill #46FS (2009)" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ David Hunn (September 15, 2012). "St. Louis health director drops smoking charges against Missouri Athletic Club". Retrieved September 24, 2012.
- ^ "St. Louis County Code Chapter 605". Library3.municode.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Moyers, Scott (April 6, 2011). "Scott Moyers, "Cape voters reject public smoking ban," ''The Southeast Missourian'' (April 5, 2011)". Semissourian.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Susan Redden, "Carthage committee debates, tables proposed smoking ban", Joplin (Mo.) Globe, February 3, 2009
- ^ "Farmington mayor rejects 'smoking ban' bill, Daily Journal Online, October 27, 2007". Mydjconnection.com. October 27, 2007. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Farmington will not place smoking ban on ballot," Park Hills Daily Journal, January 11, 2008
- ^ "Joplin City Council rejects proposed smoking ban", KSPR-TV, October 19, 2010[dead link]
- ^ "AGENDA" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Brian Burnes, "Raytown board rejects proposed smoking law", The Kansas City Star, September 8, 2009[dead link]
- ^ "Jeff Salem, "Riverside postpones smoking ban discussion indefinitely," ''The Platte County (Mo.) Sun Gazette'', June 22, 2009". Plattesungazette.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Ashley Vasquez, "Smoking ban talk ends," The Smithville Herald, December 26, 2007
- ^ Mark Schlinkmann, "St. Charles election on smoking appears unlikely", St. Louis Post-Dispatch, June 1, 2008
- ^ Levin, Sam (July 11, 2013). "Sam Levin, "St. Charles City Backs Off Smoking Ban Proposal, Considers Mandatory Signage," ''Riverfront Times'' (July 11, 2013)". Blogs.riverfronttimes.com. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ Schlinkmann, Mark (July 9, 2013). "Mark Schlinkmann, "City-imposed smoking ban appears dead in St. Charles," ''St. Louis Post-Dispatch'' (July 9, 2013)". Stltoday.com. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ Korando, Russell (June 14, 2011). "Russel Korando, "Smoking ban proposal blocked from St. Charles County ballot," ''St. Louis Post-Dispatch'' (June 14, 2011)". Stltoday.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Korando, Russell (November 21, 2011). "Russell Korando, "St. Charles County Council rejects smoke-free bill," ''St. Louis Post-Dispatch'' (November 30, 2011)". Stltoday.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Korando, Russell (September 17, 2012). "Russell Korando, "Smoking ban vote snuffed out in St. Charles County," ''St. Louis Post-Dispatch'' (September 17, 2012)". Stltoday.com. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ Bryan, Andra (April 12, 2011). "Andra Bryan Stefanoni, "Webb City Council rejects smoking ban," ''The Joplin Globe'', April 12, 2011". Joplinglobe.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "FINANCIAL OVERSIGHT 6:00 P" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b Mont. Code Ann. § 50-40-104
- ^ § 50-40-103
- ^ Mont. Code Ann. § 50-40-120
- ^ "N.R.S. § 71-5729". Uniweb.legislature.ne.gov. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ "N.R.S. § 71-5730". Uniweb.legislature.ne.gov. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ Associated Press, "Gov. signs cigar-bar exemption to Neb. smoking ban ", KCAU-TV Sioux City, Iowa, April 22, 2009]
- ^ "N.R.S. § 71-5717". Uniweb.legislature.ne.gov. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ a b c "NRS 202.2483". Leg.state.nv.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ "N.H. Rev. Stat. Ann. § 155:66". Gencourt.state.nh.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "N.H. Rev. Stat. Ann. § 155:67". Gencourt.state.nh.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "N.H. Rev. Stat. Ann. § 155:68". Gencourt.state.nh.us. January 1, 1991. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "N.H. General Court, 829 A.2d 1089 (N.H. 2003)". Gencourt.state.nh.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "N.H. Rev. Stat. Ann. § 155:67". Gencourt.state.nh.us. January 1, 1991. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "JTR Colebrook, Inc. v. Town of Colebrook, 829 A.2d 1089 (N.H. 2003)". Courts.state.nh.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "N.J. Stat. § 26:3D-58". Lis.njleg.state.nj.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "N.J. Stat. § 26:3D-59 through 61". Lis.njleg.state.nj.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "N.J. Stat. § 26:3D-63". Lis.njleg.state.nj.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "NJDOH - Smoke-free Air Act Initiative". State.nj.us. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
- ^ Associated, The (October 27, 2008). "Atlantic City Suspends Casino Smoking Ban, ''The New York Times'', October 27, 2008". The New York Times. Atlantic City (NJ). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Pequannock council reintroduces revamped smoking ban : page all". NorthJersey.com. July 18, 2011. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ N.M. Stat. Ann. § 24-16-4
- ^ N.M. Stat. Ann. § 24-16-13
- ^ N.M. Stat. Ann. § 24-16-12
- ^ N.M. Stat. Ann. § 24-16-18
- ^ N.M. Stat. Ann. § 24-16-20
- ^ "UNM.edu". UNM.edu. August 1, 2009. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "New York City Smoke-Free Air Act of 2002" (PDF). nyc.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
- ^ N.Y. Pub. Health Law § 1399-O
- ^ a b N.Y. Pub. Health Law § 1399-Q
- ^ N.Y. Pub. Health Law § 1399-R
- ^ "Smoking ban enforced on Great Neck sidewalks | 7online.com". Abclocal.go.com. January 6, 2011. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Shops in New York told not to sell tobacco to under-21s". New York City News.Net. Retrieved May 19, 2014.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ Ossad, Jordana (May 23, 2011). "New York City outdoor smoking ban begins". CNN. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
- ^ 2002 New York City Local Law No. 47
- ^ "Smoke-Free Air Act of 2002 : Tobacco Control : NYC DOHMH". Nyc.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
- ^ a b c "North Carolina Session Law 2009-27" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Gas Tax, Prison Smoking Ban Among New State Laws, WRAL-TV, January 1, 2006". Wral.com. January 1, 2006. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Triangle Hospitals Ban Tobacco Use, WRAL-TV, July 3, 2007". Wral.com. July 3, 2007. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Stay Healthy, UNC Department of Environment, Health & Safety". Ehs.unc.edu. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Van, Mara (November 8, 2012). "Mara Van Ells, "Smoking ban to change bar culture," ''Bismarck Tribune'' (November 8, 2012)". Bismarcktribune.com. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ a b c "North Dakota Initiative Measure 4 (2012)" (PDF). Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ DakotaStudent.com: Smoking ban shows positive results[dead link]
- ^ "NMI". No-smoke.org. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e "Ohio Rev. Code Chapter 3794, "Smoking Ban"". Codes.ohio.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Supreme Court of Ohio Case Summaries". Supremecourt.ohio.gov. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ "Council Legislation 2008". Northroyalton.org. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ "Cityofberlin.com" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Ok. Stat. Ann. Section 21-1247
- ^ Ok. Stat. Ann. Section 63-1-1523, et seq.
- ^ Ok. Stat. Ann. Section 63-1-1527
- ^ "Mick Hinton, "Committee waters down smoking bill", ''Tulsa World'', February 19, 2009". Tulsaworld.com. February 19, 2009. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Oklahom House Bill 1040 (2009) – status". Webserver1.lsb.state.ok.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Ore. Rev. Stat. § 433.845
- ^ Ore. Rev. Stat. § 433.835
- ^ Ore. Rev. Stat. § 433.850
- ^ Ore. Rev. Stat. § 433.870
- ^ "Oregon Restaurant Ass'n v. City of Corvallis, 166 Ore. App. 506, 999 P.2d 518 (2000)". Publications.ojd.state.or.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "2008 Pennsylvania Senate Bill 246". Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b "Act of Jun. 13, 2008,P.L. 182, No. 27 Cl. 35 - CLEAN INDOOR AIR ACT - ENACTMENT". Retrieved September 12, 2012.
- ^ "Philadelphia Smoking Ban". Smokefreephilly.org. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ http://www.nbcphiladelphia.com/news/politics/Smoking-Ban-Philadelphia-257125421.html
- ^ a b Ward, Paula Reed; Anita Srikameswaran (May 22, 2007). "County's smoking ban in ashes". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. Retrieved September 9, 2012.
- ^ NextPage – LivePublish (December 19, 2002). "P.R. Laws ch. 62 § 892". Michie.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ NextPage – LivePublish (December 19, 2002). "P.R. Laws ch. 62 § 894". Michie.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "R.I. Gen. Laws § 23-20.10-3". Rilin.state.ri.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "R.I. Gen. Laws § 23-20.10-4". Rilin.state.ri.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "R.I. Gen. Laws § 23-20.10-6". Rilin.state.ri.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "R.I. Gen. Laws § 23-20.10–6.1". Rilin.state.ri.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "R.I. Gen. Laws § 23-20.10–13". Rilin.state.ri.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "S.C. Code § 44-95-20". Scstatehouse.gov. December 31, 1990. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "S.C. Code § 44-95-30". Scstatehouse.gov. December 31, 1990. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Foothills Brewing Concern, Inc. v. City of Greenville, 660 S.E.2d 264 (S.C. 2008)". Judicial.state.sc.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Beachfront Entertainment, Inc. v. Town of Sullivan's Island, 666 S.E.2d 912 (S.C. 2008)". Sccourts.org. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e "Ordinance Implementation, South Carolina Tobacco Collaborative". Sctobacco.org. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "American Nonsmokers' Rights Foundation, "Bill Tracking Summary", May 29, 2009". Protectlocalcontrol.org. November 18, 2011. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Public Smoking Ban Passes Aiken City Council". Cityofaikensc.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Beaufort passes smoking ban," The Beaufort Gazette, May 27, 2008[dead link]
- ^ May 10, 2011 (May 10, 2011). "Florence bans smoking at most indoor businesses". Southcarolinaradionetwork.com. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "North Myrtle Beach smoking ban goes into effect : News". CarolinaLive.com. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
- ^ http://www.cityofspartanburg.org/index.cfm?PageID=462&ParentPageID=32
- ^ Jonathan Carlson (May 9, 2011). "Spartanburg Passes Smoking Ban-Begins Sept. 1". WSPA. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
- ^ "No public smoking ban for North Charleston, ''The Charleston Post & Courier'', May 15, 2008". Charleston.net. May 16, 2013. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ "Folly Beach rejects smoking ban, ''TheDigitel'', May 28, 2008". US-SC: Charleston.thedigitel.com. May 28, 2008. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b 2009 South Dakota H.B. 1240 (PDF), South Dakota Tobacco-Free Kids Network, 2010, retrieved November 24, 2010
- ^ Associated Press: "Governor signs ban on smoking in bars, casinos", Mitchell (S.D.) Daily Republic, March 19, 2009[dead link]
- ^ "Chet Brokaw, "Petitions filed to put SD smoking ban to vote," ''Mitchell (S.D.) Daily Republic'', June 22, 2009". Mitchellrepublic.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Steve Young, "Petitions get OK in smoking fight", Sioux Falls Argus Leader, June 25, 2009[dead link]
- ^ Smoking Ban Clears Big Hurdle[dead link]
- ^ "Voters Will Decide On Smoking Ban". Keloland TV. November 13, 2009. Retrieved November 24, 2010.
- ^ "T.C.A. § 39-17-1803". Michie.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "T.C.A. § 39-17-1803". Michie.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Protectlocalcontrol.org". Protectlocalcontrol.org. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Tex. Educ. Code § 38.006". Statutes.legis.state.tx.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b "Tex. Penal Code § 48.01". Statutes.legis.state.tx.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Ex parte Woodall, 154 S.W.3d 698 (Tex. App.-El Paso 2004)
- ^ Corrie MacLaggan (April 15, 2009). "Outlook hazy for statewide smoking ban proposal". Statesman.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Corrie MacLaggan (May 8, 2007). "Corrie MacLaggan, "Weak smoking ban passes in House", ''Austin American-Statesman'', May 8, 2007". Statesman.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Statewide smoking ban in Texas, has failed by Billy Loftin (May 19, 2009). "Billy Loftin, "Statewide smoking ban in Texas has failed", KVII-TV Amarillo, May 19, 2009". Connectamarillo.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Roark & Hardee L.P. v. City of Austin, Case No. A-05-CA-837-SS (W.D.Tex. 2006)
- ^ "Roark & Hardee LP v. City of Austin, 522 F.3d 533 (5th Cir. 2008)" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "College Station City Ordinance, Section 9" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ [2][dead link]
- ^ "City of Frisco, Texas" (PDF). Ci.fisco.tx.us. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
- ^ a b "Fort Worth smoking ban takes effect Tuesday; McKinney offers grace period", The Dallas Morning News, December 31, 2007[dead link]
- ^ (October 1, 2010). "Missouri City smoking ban goes into effect today | abc13.com". Abclocal.go.com. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - ^ Collier, Kiah. "2010 ELECTION: San Angelo bans smoking, drops sunset on sales tax, ''San Angelo Standard-Times'', November 3, 2010". Gosanangelo.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Council adopts tough smoking rules", San Antonio Express-News, August 19, 2010[dead link]
- ^ White, Ian (September 24, 2010). "Ian White, "Council amends smoking rules," ''Galveston Daily News'', September 24, 2010". Galvestondailynews.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "ORDINANCE NO. 99-098 AN ORDINANCE OF THE CITY COUNCIL OF THE CITY OF GREENVILLE, TEXAS, AMENDING SECTION 5.1700 "SMOKING RESTRICTION IN PUBLIC PLACES" OF THE CODE OF ORDINANCES OF THE CITY OF GREENVILLE; PROVIDING FOR A REPEALING CLAUSE, A SEVERABILITY CLAUSE, A PENALTY CLAUSE; AND PROVIDING THAT THIS ORDINANCE SHALL BE IN FULL FORCE AND EFFECT FROM AND AFTER JANUARY 1, 2000".
- ^ "Smoking ban debate generating lots of heat, ''The Monitor'', November 13, 2005". Smokersclubinc.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Humble passes near-blanket smoking ban".
- ^ "Kilgore Passes Smoking Ban - KYTX CBS 19 Tyler Longview News Weather Sports". Cbs19.tv. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
- ^ "Ordinance 26-2014: Smoking in public places" City Council, June 17, 2014. Accessed: October 11, 2014.
- ^ "Editorial: Put out the fire, ''Amarillo Globe-News'', May 11, 2008". Amarillo.com. May 11, 2008. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ JOY BLACKBURN (Daily News Staff) (February 10, 2011). "Smoking ban enforcement begins today, ''Virgin Islands Daily News'', February 10, 2011". Virginislandsdailynews.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "U.C.A. 1953 § 26-38-2.6". Utah State. Retrieved March 12, 2013.
- ^ "U.C.A. 1953 § 26-38-3". Utah State. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "U.C.A. 1953 § 26-38-3.5". Utah State. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b "U.C.A. 1953 § 26-38-6". Utah State. Retrieved March 12, 2013.
- ^ "Utah County Board of Health Regulation on Smoking in Outdoor Public Places" (PDF). Utah County Health Department. Retrieved March 12, 2013.
- ^ "Rider Rules". Utah Transit Authority. Retrieved March 12, 2013.
- ^ "Ver. Stat. tit. 28 § 1742". Leg.state.vt.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Ver. Stat. tit. 28 § 1743". Leg.state.vt.us. September 1, 2005. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b c "Daniel Barlow, "Workplace smoking ban starts July 1", ''The Barre Montpelier Times Argus'', May 30, 2009". Timesargus.com. May 30, 2009. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Ver. Stat. tit. 28 § 1428". Leg.state.vt.us. July 1, 1988. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Ver. Stat. tit. 28 § 1746". Leg.state.vt.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b c "Va. Senate Bill 1105 (2009)". Leg1.state.va.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Davis, Chelyen. "Chelyen Davis, "House, Senate OK smoke ban," ''The Fredericksburg (Va.) Free Lance-Star'', February 20, 2009". Fredericksburg.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Banning Smoking in State Offices and Vehicles (Virginia Executive Order)[dead link]
- ^ Kepa, Inc. v. Va. Dept. of Health, 751 S.E.2d 671 (Va. App. 2013)
- ^ Minium, Harry (March 26, 2008). "Harry Minium, "Norfolk council reverses itself on smoking ban", ''The Virginian-Pilot'', March 26, 2008". Hamptonroads.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Wash. Rev. Code § 70.160.030". Apps.leg.wa.gov. November 8, 2005. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Wash. Rev. Code § 70.160.075". Apps.leg.wa.gov. November 8, 2005. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ a b "Wash. Rev. Code § 70.160.060". Apps.leg.wa.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Wash. Rev. Code § 70.160.020". Apps.leg.wa.gov. November 8, 2005. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Wash. Rev. Code § 70.160.080". Apps.leg.wa.gov. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "W. Va. Code § 8-27-10a (1985)". Legis.state.wv.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "W. Va. Code § § 16-9A-4 (1987)". Legis.state.wv.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "W. Va. Code § 21-3-8 (1919)". Legis.state.wv.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "W. Va. Code § 22A-2- 30 (1985)". Legis.state.wv.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "W. Va. Code § 22A-2-53 (1985)". Legis.state.wv.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "W. Va. Code § 22A-2-53c (1994)". Legis.state.wv.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "W. Va. Code § 47-20-28a". Legis.state.wv.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ 64 W.Va. C.S.R. §14, 8.12.3
- ^ "Found. for Indep. Living, Inc. v. Cabell-Huntington Bd. of Health, 591 S.E.2d 744 (W.V. 2003)". State.wv.us. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Approaching smoke-free", The Times West Virginian, April 6, 2008
- ^ "From Wash. to Pa., smoking bans spark backlash, KOMOnews.com, October 10, 2009". Komonews.com. October 10, 2009. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ Alison Knezevich, "Putnam reverses smoking ban", West Virginia Gazette, August 22, 2007
- ^ a b c "2009 Wisconsin Senate Bill 181" (PDF). Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Statewide smoking ban picks up steam, ''Green Bay Press Gazette'', April 9, 2006". Smokersclubinc.com. March 5, 2006. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ NextPage – LivePublish. "Wyo. Stat. Ann. § 30-2-602". Michie.lexisnexis.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ NextPage – LivePublish. "Wyo. Stat. Ann. § 30-2-604". Michie.lexisnexis.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ NextPage – LivePublish. "Wyo. Stat. Ann. § 30-3-303". Michie.lexisnexis.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ NextPage – LivePublish. "Wyo. Stat. Ann. § 30-3-304". Michie.lexisnexis.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ BEN NEARY Associated Press writer (February 16, 2009). "Ben Neary, "Legislature shoveling through bills", ''Casper Tribune'', February 16, 2009". Trib.com. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Light up: Casper repeals smoking ban for bars," Associated Press (June 22, 2013)[dead link]
- ^ "Green River overturns smoking ban, ''AP'', December 19, 2007". Smokersclubinc.com. December 11, 2007. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
- ^ "Rock Springs adopts partial smoking ban, ''AP'', November 22, 2007". Tobacco.org. November 22, 2007. Retrieved December 2, 2011.