Melbourne
| Melbourne Victoria | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 (From top left to bottom right) Melbourne City Centre, Flinders Street station, Shrine of Remembrance, Federation Square, Melbourne Cricket Ground, Royal Exhibition Building. | |||||||||
 Map of Melbourne, Australia, printable and editable | |||||||||
| Coordinates | 37°48′49″S 144°57′47″E / 37.81361°S 144.96306°E | ||||||||
| Population | 5,000,000 (2018)[1] (2nd) | ||||||||
| • Density | 500/km2 (1,300/sq mi) | ||||||||
| Established | 30 August 1835 | ||||||||
| Elevation | 31 m (102 ft) | ||||||||
| Area | 9,992.5 km2 (3,858.1 sq mi)(GCCSA)[2] | ||||||||
| Time zone | AEST (UTC+10) | ||||||||
| • Summer (DST) | AEDT (UTC+11) | ||||||||
| Location | |||||||||
| LGA(s) | 31 Municipalities across Greater Melbourne | ||||||||
| County | Grant, Bourke, Mornington | ||||||||
| State electorate(s) | 54 electoral districts and regions | ||||||||
| Federal division(s) | 23 Divisions | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Melbourne (/ˈmɛlbərn/ MEL-bərn)[8][9] is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in Australia and Oceania.[1] Its name refers to an urban agglomeration of 9,992.5 km2 (3,858.1 sq mi),[2] comprising a metropolitan area with 31 municipalities,[10] and is also the common name for its city centre. The city occupies much of the coastline of Port Phillip bay and spreads into the hinterlands towards the Dandenong and Macedon ranges, Mornington Peninsula and Yarra Valley. It has a population of approximately 5,000,000 (19% of the population of Australia), and its inhabitants are referred to as "Melburnians".[11][12]
The city was founded on the 30 August 1835, in what was the British colony of New South Wales, by free settlers from the colony of Van Diemen’s Land.[13] It was incorporated as a Crown settlement in 1837 and named in honour of the British Prime Minister, William Lamb, 2nd Viscount Melbourne.[13] It was declared a city by Queen Victoria in 1847, after which it became the capital of the new colony of Victoria in 1851.[14] Following the Victorian gold rush of the 1850s, it was referred to as "Marvellous Melbourne" and was transformed into one of the most important cities in the British Empire and one of the largest and wealthiest in the world.[15][16] After the federation of Australia in 1901, it served as interim seat of government of the new nation until 1927.[17] Today, it is a leading financial centre in the Asia-Pacific region and ranks among the top 15 cities in the world in the Global Financial Centres Index.[18]
Referred to as the "cultural capital" of Australia,[19] the city is home to many of the largest and oldest cultural institutions in the nation such as the Melbourne Cricket Ground, the National Gallery of Victoria and the Royal Exhibition Building. It is also the birthplace of Australian impressionism, Australian rules football, the Australian film and television industries and Australian contemporary dance. More recently, it has been recognised as a UNESCO City of Literature and a global centre for street art, live music and theatre. It is the host city of annual international events such as the Australian Grand Prix, the Australian Open and the Melbourne Cup, and has also hosted the 1956 Summer Olympics and the 2006 Commonwealth Games. Due to it rating highly in entertainment, tourism and sport,[20] as well as education, health care, research and development, the EIU currently ranks it the second most liveable city in the world.[21]
The main airport serving the city is Melbourne Airport (also referred to as Tullamarine Airport), which is the second busiest in Australia, and its main seaport is the Port of Melbourne.[22] Its main metropolitan rail terminus is Flinders Street station and its main regional rail and road coach terminus is Southern Cross station. It also has the most extensive freeway network in Australia and the largest urban tram network in the world.[23]
History
Early history and foundation

Before the arrival of European settlers, humans had occupied the area for an estimated 31,000 to 40,000 years.[24] At the time of European settlement, it was inhabited by under 2000[25] hunter-gatherers from three indigenous regional tribes: the Wurundjeri, Boonwurrung and Wathaurong.[26] The area was an important meeting place for the clans of the Kulin nation alliance and a vital source of food and water.[27][28]
The first British settlement in Victoria was established by Colonel David Collins in October 1803, at Sullivan Bay, near present-day Sorrento, but this settlement was relocated to what is now Hobart, Tasmania, in February 1804, due to a perceived lack of resources. It would be 30 years before another settlement was attempted.[29]
In May and June 1835, the area, which is now central and northern Melbourne was explored by John Batman, a leading member of the Port Phillip Association in Van Diemen's Land (now known as Tasmania), who claimed to have negotiated a purchase of 600,000 acres (2,400 km2) with eight Wurundjeri elders.[27][28] Batman selected a site on the northern bank of the Yarra River, declaring that "this will be the place for a village".[30] Batman then returned to Launceston in Tasmania. In early August 1835 a different group of settlers, including John Pascoe Fawkner, left Launceston on the ship Enterprize. Fawkner was forced to disembark at Georgetown, Tasmania, because of outstanding debts. The remainder of the party continued and arrived at the mouth of the Yarra River on 15 August 1835. On 30 August 1835 the party disembarked and established a settlement at the site of the current Melbourne Immigration Museum. Batman and his group arrived on 2 September 1835 and the two groups ultimately agreed to share the settlement. Initially the settlement had the native name Dootigala.[31][32]
Batman's Treaty with the Aborigines was annulled by the New South Wales governor (who at the time governed all of eastern mainland Australia), with compensation paid to members of the association.[27] In 1836, Governor Bourke declared the city the administrative capital of the Port Phillip District of New South Wales, and commissioned the first plan for the city, the Hoddle Grid, in 1837.[33] The settlement was briefly named Batmania after Batman.[34] However, later that year the settlement was named "Melbourne" after the British Prime Minister, William Lamb, 2nd Viscount Melbourne, whose seat was Melbourne Hall in the market town of Melbourne, Derbyshire. On 13 April 1837 the settlement's general post office officially opened with that name.[35]
Between 1836 and 1842 Victorian Aboriginal groups were largely dispossessed of their land by European settlers.[36] By January 1844, there were said to be 675 Aborigines resident in squalid camps in Melbourne.[37] The British Colonial Office appointed five Aboriginal Protectors for the Aborigines of Victoria, in 1839, however their work was nullified by a land policy that favoured squatters to take possession of Aboriginal lands.[38] By 1845, fewer than 240 wealthy Europeans held all the pastoral licences then issued in Victoria and became a powerful political and economic force in Victoria for generations to come.[39]
Letters patent of Queen Victoria, issued on 25 June 1847, declared Melbourne a city.[14]
On 1 July 1851 the Port Phillip District became the separate Colony of Victoria, with Melbourne as its capital.[40]
Victorian gold rush

The discovery of gold in Victoria in mid-1851 led to a gold rush, and Melbourne, which served as the major port and provided most services for the region, experienced rapid growth. Within months, the city's population had increased from 25,000 to 40,000 inhabitants.[41] Exponential growth ensued, and by 1865 Melbourne had overtaken Sydney as Australia's most populous city.[42]
An influx of intercolonial and overseas migrants, particularly Irish, German and Chinese, saw the establishment of slums, including a temporary "tent city" on the southern banks of the Yarra. In 1851, Chinese migrants founded Chinatown, which remains the longest continuously-occupied Chinese settlement outside Asia.[43] In the aftermath of the 1854 Eureka Rebellion, mass public-support for the plight of the miners resulted in major political changes to the colony, including improvements in working conditions across mining, agriculture, manufacturing and other local industries. The various nationalities[which?] involved in the rebellion give some indication of immigration flows at the time.[44]
With the wealth brought in from the gold rush and the subsequent need for public buildings, a program of grand civic construction soon began. The 1850s and 1860s saw the commencement of Parliament House, the Treasury Building, the Old Melbourne Gaol, Victoria Barracks, the State Library, University of Melbourne, General Post Office, Customs House, the Melbourne Town Hall, St Patrick's cathedral, though many remained uncompleted for decades, with some still not finished as of 2018[update].
The layout of the inner suburbs on a largely one-mile grid pattern, cut through by wide radial boulevards and parklands surrounding the central city, was largely established[by whom?] in the 1850s and 1860s. These areas rapidly filled with the ubiquitous terrace houses, as well as with detached houses and grand mansions, while some of the major roads developed as shopping streets. Melbourne quickly became a major finance centre, home to several banks, the Royal Mint, and (in 1861) Australia's first stock exchange.[45] In 1855 the Melbourne Cricket Club secured possession of its now famous ground, the MCG. Members of the Melbourne Football Club codified Australian football in 1859, and Yarra rowing clubs and "regattas" became popular about the same time. In 1861 the city hosted the first Melbourne Cup race. In 1864 Melbourne acquired its first public monument—the Burke and Wills statue.
With the gold rush largely over by 1860, Melbourne continued to grow on the back of continuing gold-mining, as the major port for exporting the agricultural products of Victoria (especially wool) and with a developing manufacturing sector protected by high tariffs. An extensive radial railway network spread into the countryside from the late 1850s. Construction started on further major public buildings in the 1860s and 1870s, such as the Supreme Court, Government House, and the Queen Victoria Market. The central city filled up with shops and offices, workshops, and warehouses. Large banks and hotels faced the main streets, with fine townhouses in the east end of Collins Street, contrasting with tiny cottages down laneways within the blocks. The Aboriginal population continued to decline, with an estimated 80% total decrease by 1863, due primarily to introduced diseases (particularly smallpox[25]), frontier violence and dispossession of their lands.
Land boom and bust

The decade of the 1880s was one of extraordinary growth, when consumer confidence, easy access to credit, and steep increases in the price of land, led to an enormous amount of construction. This 'land boom' was followed by a severe economic crash in the early 1890s which lasted until the end of the century. During the boom, Melbourne had reputedly become the richest city in the world,[15] and the largest after London in the British Empire.[citation needed]
The decade began with the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880, held in the large purpose-built Exhibition Building. In 1880 a telephone exchange was established and in the same year the foundations of St Paul's, were laid; in 1881 electric light was installed in the Eastern Market, and in the following year a generating station capable of supplying 2,000 incandescent lamps was in operation.[46] In 1885 the first line of the Melbourne cable tramway system was built, becoming one of the world's most extensive systems by 1890.

During a visit in 1885 English journalist George Augustus Henry Sala coined the phrase "Marvellous Melbourne", which stuck long into the twentieth century and is still used today by Melburnians.[47] Growing building activity culminated in a "land boom" which, in 1888, reached a peak of speculative development fuelled by consumer confidence and escalating land value.[48] As a result of the boom, large commercial buildings, coffee palaces, terrace housing and palatial mansions proliferated in the city.[48] The establishment of a hydraulic facility in 1887 allowed for the local manufacture of elevators, resulting in the first construction of high-rise buildings;[49] most notably the APA Building, amongst the world's tallest commercial buildings upon completion in 1889.[48] This period also saw the expansion of a major radial rail-based transport network.[50]
In 1888, the Exhibition Building hosted a second event even larger than the first, the Melbourne Centennial Exhibition, spurring construction of numerous hotels including the 500 room Federal Hotel, The Palace Hotel in Bourke Street (both since demolished), and the doubling in size of the Grand (Windsor).
A brash boosterism that had typified Melbourne during this time ended in the early 1890s with a severe depression of the city's economy, sending the local finance and property industries into a period of chaos[48][51] during which 16 small "land banks" and building societies collapsed, and 133 limited companies went into liquidation. The Melbourne financial crisis was a contributing factor in the Australian economic depression of the 1890s and the Australian banking crisis of 1893. The effects of the depression on the city were profound, with virtually no new construction until the late 1890s.[52][53]
De facto Capital of Australia

At the time of Australia's federation on 1 January 1901, Melbourne became the seat of government of the federation. The first federal parliament was convened on 9 May 1901 in the Royal Exhibition Building, subsequently moving to the Victorian Parliament House where it was located until 1927, when it was moved to Canberra. The Governor-General of Australia resided at Government House in Melbourne until 1930 and many major national institutions remained in Melbourne well into the twentieth century.[54]
Post-war period
In the immediate years after World War II, Melbourne expanded rapidly, its growth boosted by post-war immigration to Australia, primarily from Southern Europe and the Mediterranean.[55] While the "Paris End" of Collins Street began Melbourne's boutique shopping and open air cafe cultures,[56] the city centre was seen by many as stale—the dreary domain of office workers—something expressed by John Brack in his famous painting Collins St., 5 pm (1955).[57]

Height limits in the Melbourne CBD were lifted in 1958, after the construction of ICI House, transforming the city's skyline with the introduction of skyscrapers. Suburban expansion then intensified, served by new indoor malls beginning with Chadstone Shopping Centre.[58] The post-war period also saw a major renewal of the CBD and St Kilda Road which significantly modernised the city.[59] New fire regulations and redevelopment saw most of the taller pre-war CBD buildings either demolished or partially retained through a policy of facadism. Many of the larger suburban mansions from the boom era were also either demolished or subdivided.
To counter the trend towards low-density suburban residential growth, the government began a series of controversial public housing projects in the inner city by the Housing Commission of Victoria, which resulted in demolition of many neighbourhoods and a proliferation of high-rise towers.[60] In later years, with the rapid rise of motor vehicle ownership, the investment in freeway and highway developments greatly accelerated the outward suburban sprawl and declining inner city population. The Bolte government sought to rapidly accelerate the modernisation of Melbourne. Major road projects including the remodelling of St Kilda Junction, the widening of Hoddle Street and then the extensive 1969 Melbourne Transportation Plan changed the face of the city into a car-dominated environment.[61]
Australia's financial and mining booms during 1969 and 1970 resulted in establishment of the headquarters of many major companies (BHP Billiton and Rio Tinto, among others) in the city. Nauru's then booming economy resulted in several ambitious investments in Melbourne, such as Nauru House.[62] Melbourne remained Australia's main business and financial centre until the late 1970s, when it began to lose this primacy to Sydney.[63]
Melbourne experienced an economic downturn between 1989 and 1992, following the collapse of several local financial institutions. In 1992, the newly elected Kennett government began a campaign to revive the economy with an aggressive development campaign of public works coupled with the promotion of the city as a tourist destination with a focus on major events and sports tourism.[64] During this period the Australian Grand Prix moved to Melbourne from Adelaide. Major projects included the construction of a new facility for the Melbourne Museum, Federation Square, the Melbourne Exhibition and Convention Centre, Crown Casino and the CityLink tollway. Other strategies included the privatisation of some of Melbourne's services, including power and public transport, and a reduction in funding to public services such as health, education and public transport infrastructure.[65]
Contemporary Melbourne
Since the mid-1990s, Melbourne has maintained significant population and employment growth. There has been substantial international investment in the city's industries and property market. Major inner-city urban renewal has occurred in areas such as Southbank, Port Melbourne, Melbourne Docklands and more recently, South Wharf. According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics, Melbourne sustained the highest population increase and economic growth rate of any Australian capital city in the three years ended June 2004.[66] These factors have led to population growth and further suburban expansion through the 2000s.
From 2006, the growth of the city extended into "green wedges" and beyond the city's urban growth boundary. Predictions of the city's population reaching 5 million people pushed the state government to review the growth boundary in 2008 as part of its Melbourne @ Five Million strategy.[67] In 2009, Melbourne was less affected by the late-2000s financial crisis in comparison to other Australian cities. At this time, more new jobs were created in Melbourne than any other Australian city—almost as many as the next two fastest growing cities, Brisbane and Perth, combined,[68] and Melbourne's property market remained highly priced,[69] resulting in historically high property prices and widespread rent increases.[70]
Geography
This section needs additional citations for verification. (August 2018) |
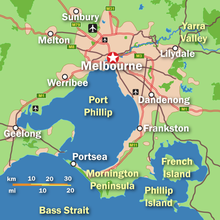

Melbourne is in the southeastern part of mainland Australia, within the state of Victoria. Geologically, it is built on the confluence of Quaternary lava flows to the west, Silurian mudstones to the east, and Holocene sand accumulation to the southeast along Port Phillip. The southeastern suburbs are situated on the Selwyn fault which transects Mount Martha and Cranbourne.
Melbourne extends along the Yarra River towards the Yarra Valley and the Dandenong Ranges to the east. It extends northward through the undulating bushland valleys of the Yarra's tributaries—Moonee Ponds Creek (toward Tullamarine Airport), Merri Creek, Darebin Creek and Plenty River—to the outer suburban growth corridors of Craigieburn and Whittlesea.
The city reaches southeast through Dandenong to the growth corridor of Pakenham towards West Gippsland, and southward through the Dandenong Creek valley, the Mornington Peninsula and the city of Frankston taking in the peaks of Olivers Hill, Mount Martha and Arthurs Seat, extending along the shores of Port Phillip as a single conurbation to reach the exclusive suburb of Portsea and Point Nepean. In the west, it extends along the Maribyrnong River and its tributaries north towards Sunbury and the foothills of the Macedon Ranges, and along the flat volcanic plain country towards Melton in the west, Werribee at the foothills of the You Yangs granite ridge south west of the CBD. The Little River, and the township of the same name, marks the border between Melbourne and neighbouring Geelong city.
Melbourne's major bayside beaches are in the various suburbs along the shores of Port Phillip Bay, in areas like Port Melbourne, Albert Park, St Kilda, Elwood, Brighton, Sandringham, Mentone, Frankston, Altona, Williamstown and Werribee South. The nearest surf beaches are 85 kilometres (53 mi) southeast of the Melbourne CBD in the back-beaches of Rye, Sorrento and Portsea.[71][72]
Climate

Melbourne has a temperate oceanic climate (Köppen climate classification Cfb) with warm summers and cool winters.[73][74] Melbourne is well known for its changeable weather conditions, mainly due to its location situated on the boundary of the very hot inland areas and the cool southern ocean. This temperature differential is most pronounced in the spring and summer months and can cause very strong cold fronts to form. These cold fronts can be responsible for varied forms of severe weather from gales to severe thunderstorms and hail, large temperature drops and heavy rain. Winters, however, are usually very stable, but rather damp and often cloudy.
Port Phillip is often warmer than the surrounding oceans and/or the land mass, particularly in spring and autumn; this can set up a "bay effect" similar to the "lake effect" seen in colder climates where showers are intensified leeward of the bay. Relatively narrow streams of heavy showers can often affect the same places (usually the eastern suburbs) for an extended period, while the rest of Melbourne and surrounds stays dry. Overall, Melbourne is, owing to the rain shadow of the Otway Ranges, nonetheless drier than average for southern Victoria. Within the city and surrounds, rainfall varies widely, from around 425 millimetres (17 in) at Little River to 1,250 millimetres (49 in) on the eastern fringe at Gembrook. Melbourne receives 48.6 clear days annually. Dewpoint temperatures in the summer range from 9.5 °C (49.1 °F) to 11.7 °C (53.1 °F).[75]
Melbourne is also prone to isolated convective showers forming when a cold pool crosses the state, especially if there is considerable daytime heating. These showers are often heavy and can include hail, squalls, and significant drops in temperature, but they often pass through very quickly with a rapid clearing trend to sunny and relatively calm weather and the temperature rising back to what it was before the shower. This can occur in the space of minutes and can be repeated many times a day, giving Melbourne a reputation for having "four seasons in one day",[76] a phrase that is part of local popular culture.[77] The lowest temperature on record is −2.8 °C (27.0 °F), on 21 July 1869.[78] The highest temperature recorded in Melbourne city was 46.4 °C (115.5 °F), on 7 February 2009.[79] While snow is occasionally seen at higher elevations in the outskirts of the city, it has not been recorded in the Central Business District since 1986.[80]
The average temperature of the sea ranges from 14.6 °C (58.3 °F) in September to 18.8 °C (65.8 °F) in February;[81] at Port Melbourne, the average sea temperature range is the same.[82]
| Climate data for Melbourne Regional Office | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 45.6 (114.1) |
46.4 (115.5) |
41.7 (107.1) |
34.9 (94.8) |
28.7 (83.7) |
22.4 (72.3) |
23.3 (73.9) |
26.5 (79.7) |
31.4 (88.5) |
36.9 (98.4) |
40.9 (105.6) |
43.7 (110.7) |
46.4 (115.5) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 26.3 (79.3) |
26.6 (79.9) |
24.4 (75.9) |
21.0 (69.8) |
17.5 (63.5) |
14.8 (58.6) |
14.2 (57.6) |
15.7 (60.3) |
17.7 (63.9) |
20.1 (68.2) |
22.6 (72.7) |
24.4 (75.9) |
20.4 (68.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 21.0 (69.8) |
21.3 (70.3) |
19.5 (67.1) |
16.4 (61.5) |
13.7 (56.7) |
11.4 (52.5) |
10.7 (51.3) |
11.8 (53.2) |
13.5 (56.3) |
15.4 (59.7) |
17.6 (63.7) |
19.3 (66.7) |
16.0 (60.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 15.6 (60.1) |
16.0 (60.8) |
14.5 (58.1) |
11.8 (53.2) |
9.8 (49.6) |
7.9 (46.2) |
7.1 (44.8) |
7.8 (46.0) |
9.2 (48.6) |
10.6 (51.1) |
12.6 (54.7) |
14.1 (57.4) |
11.4 (52.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 5.5 (41.9) |
4.5 (40.1) |
2.8 (37.0) |
1.5 (34.7) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
0.1 (32.2) |
2.5 (36.5) |
4.4 (39.9) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 45.1 (1.78) |
39.9 (1.57) |
40.7 (1.60) |
50.2 (1.98) |
46.5 (1.83) |
46.5 (1.83) |
44.7 (1.76) |
50.5 (1.99) |
52.9 (2.08) |
58.5 (2.30) |
63.1 (2.48) |
64.1 (2.52) |
602.6 (23.72) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.2mm) | 8.7 | 6.6 | 9.3 | 10.5 | 12.2 | 13.5 | 14.4 | 15.3 | 14.0 | 13.3 | 11.3 | 10.0 | 139.1 |
| Average afternoon relative humidity (%) | 47 | 47 | 49 | 51 | 58 | 62 | 60 | 54 | 51 | 48 | 48 | 47 | 52 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 266.6 | 228.8 | 223.2 | 186.0 | 142.6 | 120.0 | 136.4 | 164.3 | 183.0 | 223.2 | 225.0 | 263.5 | 2,362.6 |
| Source 1: Bureau of Meteorology[75] 1981-2010 averages, records 1855-2016 | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Sunshine hours taken from Melbourne Airport, 1999-2016[83] | |||||||||||||
Environment and pollution
Melbourne's air quality is generally good and has improved significantly since the 1980s.[84] Like many urban areas, the city faces significant environmental issues, many related to the city's large urban footprint and urban sprawl and the demand for infrastructure and services. One such issue is the impact of drought on water supply. Periodic droughts and consistently high summer temperatures deplete Melbourne's water supplies, and climate change may exacerbate the long-term impact of these factors.[85] During the Millennium drought, the Bracks Government implemented water restrictions and a range of other options including water recycling, incentives for household water tanks, greywater systems, water consumption awareness initiatives, and other water-saving and reuse initiatives. But as water storages continued to fall further measures were required; in June 2007 the Bracks Government announced the construction of the $3.1 billion Wonthaggi desalination plant,[86] and the so-called North-South Pipeline from the Goulburn Valley in Victoria's north to Melbourne. Neither project was used extensively before the drought broke during 2010, and therefore both have been criticised as 'white elephants'.[87]
In response to attribution of recent climate change, in 2002 the City of Melbourne set a target to reduce carbon emissions to net zero by 2020[88] and Moreland City Council established the Zero Moreland program. Not all metropolitan municipalities have followed suit, with the City of Glen Eira notably deciding in 2009 not to become carbon-neutral.[89] Melbourne has one of the largest urban footprints in the world due to its low-density housing, resulting in a vast suburban sprawl, with a high level of car dependence and minimal public transport outside of inner areas.[90] Much of the vegetation within the city is non-native species, most of European origin, including many invasive species and noxious weeds.[91] Significant introduced urban pests include the common myna,[92] feral pigeon,[93] brown rat,[94][95] European wasp,[96] common starling and red fox.[97] Many outlying suburbs, particularly towards the Yarra Valley and the hills to the northeast and east, have gone for extended periods without regenerative fires leading to a lack of saplings and undergrowth in urbanised native bushland. The Department of Sustainability and Environment partially addresses this problem by regularly burning off.[98][99] Several national parks have been designated around the urban area of Melbourne, including the Mornington Peninsula National Park, Port Phillip Heads Marine National Park and Point Nepean National Park in the southeast, Organ Pipes National Park to the north and Dandenong Ranges National Park to the east. There are also a number of significant state parks just outside Melbourne.[100][101] Responsibility for regulating pollution falls under the jurisdiction of the EPA Victoria and several local councils. Air pollution, by world standards, is classified as good. Summer and autumn are the worst times of year for atmospheric haze in the urban area.[102][103]
Another recent environmental issue in Melbourne was the Victorian government project of channel deepening Melbourne Ports by dredging Port Phillip Bay—the Port Phillip Channel Deepening Project. It was subject to controversy and strict regulations among fears that beaches and marine wildlife could be affected by the disturbance of heavy metals and other industrial sediments.[72][104] Other major pollution problems in Melbourne include levels of bacteria including E. coli in the Yarra River and its tributaries caused by septic systems,[105] as well as litter. Up to 350,000 cigarette butts enter the storm water runoff every day.[106] Several programs are being implemented to minimise beach and river pollution.[72][107] In February 2010, The Transition Decade, an initiative to transition human society, economics and environment toward sustainability, was launched in Melbourne.[108]
Urban structure

The Hoddle Grid (dimensions of 1 by 1⁄2 mile (1.61 by 0.80 km)) forms the centre of Melbourne's central business district. The grid's southern edge fronts onto the Yarra River. Office, commercial and public developments in the adjoining districts of Southbank and Docklands have made these redeveloped areas into extensions of the CBD in all but name. The city centre has a reputation for its historic and prominent lanes and arcades (most notably Block Place and Royal Arcade) which contain a variety of shops and cafés[109] and are a byproduct of the city's layout.[110]
Melbourne's CBD, compared with other Australian cities, has comparatively unrestricted height limits and as a result of waves of post-war development contains five of the seven tallest buildings in Australia, the tallest of which is the Eureka Tower, situated in Southbank. It has an observation deck on the 88th floor.[111] The Rialto tower, the city's second tallest, remains the tallest building in the old CBD; its observation deck closed on 31 December 2009.[112]

The CBD and surrounds also contain many significant historic buildings such as the Royal Exhibition Building, the Melbourne Town Hall and Parliament House.[113][114] Although the area is described as the centre, it is not actually the demographic centre of Melbourne at all, due to an urban sprawl to the south east, the demographic centre being located at Glen Iris.[115] Melbourne is typical of Australian capital cities in that after the turn of the 20th century, it expanded with the underlying notion of a 'quarter acre home and garden' for every family, often referred to locally as the Australian Dream. This, coupled with the popularity of the private automobile after 1945, led to the auto-centric urban structure now present today in the middle and outer suburbs. Much of metropolitan Melbourne is accordingly characterised by low density sprawl, whilst its inner city areas feature predominantly medium-density, transit-oriented urban forms. The city centre, Docklands, St. Kilda Road and Southbank areas feature high-density forms.

Melbourne is often referred to as Australia's garden city, and the state of Victoria was once known as the garden state.[102][116][117] There is an abundance of parks and gardens in Melbourne,[118] many close to the CBD with a variety of common and rare plant species amid landscaped vistas, pedestrian pathways and tree-lined avenues. Melbourne's parks are often considered the best public parks in all of Australia's major cities.[119] There are also many parks in the surrounding suburbs of Melbourne, such as in the municipalities of Stonnington, Boroondara and Port Phillip, south east of the central business district. The extensive area covered by urban Melbourne is formally divided into hundreds of suburbs (for addressing and postal purposes), and administered as local government areas[120] 31 of which are located within the metropolitan area.[121]
Housing

Melbourne has minimal public housing and high demand for rental housing, which is becoming unaffordable for some.[122][123][124] Public housing is usually provided by the Housing Commission of Victoria, and operates within the framework of the Commonwealth-State Housing Agreement, by which federal and state governments provide housing funding.
Melbourne is experiencing high population growth, generating high demand for housing. This housing boom has increased house prices and rents, as well as the availability of all types of housing. Subdivision regularly occurs in the outer areas of Melbourne, with numerous developers offering house and land packages. However, after 10 years[when?] of planning policies to encourage medium-density and high-density development in existing areas with greater access to public transport and other services, Melbourne's middle and outer-ring suburbs have seen significant brownfields redevelopment.[125]
Culture

Melbourne is an international cultural centre and the city serves as Australia's cultural capital, with prominent offerings in the form of major events and festivals, drama, musicals, comedy, music, art, architecture, literature, film and television.[126] The climate, waterfront location and nightlife make it one of the most vibrant destinations in Australia. For seven years in a row (as of 2017[update]) it has held the top position in a survey by The Economist Intelligence Unit of the world's most liveable cities, partly due to its broad cultural offerings.[21] The city celebrates a wide variety of annual cultural events and festivals of all types, including Australia's largest free community festival—Moomba, the Melbourne International Arts Festival, Melbourne International Film Festival, Melbourne International Comedy Festival and the Melbourne Fringe Festival. The culture of the city is an important drawcard for tourists, of which 2.7 million international and 8.9 million domestic travellers arrived in 2017.[127][128]


Melbourne's rich and diverse literary history was recognised in 2008 when Melbourne City of Literature became the second UNESCO City of Literature. The State Library of Victoria is one of Australia's oldest cultural institutions and one of many public and university libraries across the city. Melbourne also has Australia's widest range of bookstores, as well the nation's largest publishing sector.[129] The city is home to significant writers' festivals, most notably the Melbourne Writers Festival. Several major literary prizes are open to local writers including the Melbourne Prize for Literature and the Victorian Premier's Literary Awards. Significant novels set in Melbourne include Fergus Hume's The Mystery of a Hansom Cab, Helen Garner's Monkey Grip and Christos Tsiolkas' The Slap. Notable writers and poets from Melbourne include Thomas Browne, C. J. Dennis, Germaine Greer and Peter Carey.
Established in 1861, the National Gallery of Victoria is Australia's oldest public art museum and the 10th most visited museum in Asia-Pacific (the most visited in Australia).[130] The Heidelberg School, also known as Australian Impressionism, grew out of Melbourne's rural suburbs in the 1880s. The city is also home to the Australian Centre for Contemporary Art. Melbourne is regarded as one of the world's major street art centres and [131] readers of Lonely Planet voted the city's street art and laneways as Australia's most popular cultural attraction.[132]
Melbourne's live performance institutions date from the foundation of the city, with the first theatre, the Pavilion, opening in 1841. The city's East End Theatre District includes theatres that similarly date from the 1850s to the 1920s, including the Princess Theatre, Regent Theatre, Her Majesty's Theatre, Forum Theatre, Comedy Theatre, and the Athenaeum Theatre. The Melbourne Arts Precinct in Southbank is home to Arts Centre Melbourne, which includes the State Theatre, Hamer Hall, the Playhouse and the Fairfax Studio. The Melbourne Recital Centre and Southbank Theatre (principal home of the MTC, which includes the Sumner and Lawler performance spaces)[133] are also located in Southbank. The Sidney Myer Music Bowl, which dates from 1955, is located in the gardens of Kings Domain; and the Palais Theatre is a feature of the St Kilda Beach foreshore.

The national ballet company, the Australian Ballet is based in Melbourne, as are the state based companies, the Melbourne Symphony Orchestra, the Melbourne Theatre Company (MTC), and the Victorian Opera. Melbourne is also the second home of the national Opera Australia after it merged with the defunct Victoria State Opera in 1996.
The Story of the Kelly Gang, the world's first feature film, was shot in Melbourne in 1906.[134] Melbourne filmmakers continued to produce bushranger films until they were banned by Victorian politicians in 1912 for the perceived promotion of crime, thus contributing to the decline of one of the silent film era's most productive industries.[134] A notable film shot and set in Melbourne during Australia's cinematic lull is On the Beach (1959). The 1970s saw the rise of the Australian New Wave and its Ozploitation offshoot, instigated by Melbourne-based productions Stork and Alvin Purple. Picnic at Hanging Rock and Mad Max, both shot in and around Melbourne, achieved worldwide acclaim. 2004 saw the construction of Melbourne's largest film and television studio complex, Docklands Studios Melbourne, which has hosted many domestic productions, as well as international features.[135] Melbourne is also home to the headquarters of Village Roadshow Pictures, Australia's largest film production company. Famous modern day actors from Melbourne include Cate Blanchett, Rachel Griffiths, Chris Hemsworth,[136] Guy Pearce, Geoffrey Rush and Eric Bana.
As of 2013[update], Melbourne is home to at least 460 music venues and its live music industry contributes A$1 billion annually to the Victorian economy.[137][138]
Melbourne was named as a top music city in the world by IFPI.com in a white paper it released in conjunction with Music Canada.[139]
Architecture

The city is recognised for its mix of modern architecture which intersects with an extensive range of nineteenth and early twentieth century buildings.[140] Some of the most architecturally noteworthy historic buildings include the World Heritage Site-listed Royal Exhibition Building, constructed over a two-year period for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880, A.C. Goode House, a Neo Gothic building located on Collins Street designed by Wright, Reed & Beaver (1891), William Pitt's Venetian Gothic style Old Stock Exchange (1888), William Wardell's Gothic Bank (1883) which features some of Melbourne's finest interiors, the incomplete Parliament House, St Paul's Cathedral (1891) and Ivan Lazarus (architect)'s Flinders Street Station (1909), which was the busiest commuter railway station in the world in the mid-1920s.[141]

The city also features the Shrine of Remembrance, which was built as a memorial to the men and women of Victoria who served in World War I and is now a memorial to all Australians who have served in war. The now demolished Queen Anne style APA Australian Building (1889), the world's 3rd tallest building at the time of completion,[142] is said to have anticipated the skyscraper race in New York City and Chicago.[113] It was demolished in 1980 and replaced by a smaller, four-storey structure.[143] A similar fate met other grand pre-war boom-era buildings in the city, notably the elaborate Victorian Federal Coffee Palace (also known as The Federal Hotel), located on Collins Street until its demolition in 1971.[144]
In 2012, the city contained a total of 594 high-rise buildings, with 8 under construction, 71 planned and 39 at proposal stage[145] making the city's skyline the second largest in Australia. The CBD is dominated by modern office buildings including the Rialto Towers (1986), built on the site of several grand classical Victorian buildings, two of which — the Rialto Building (1889) designed by William Pitt and the Winfield Building (1890) designed by Charles D'Ebro and Richard Speight — still remain today and more recently high-rise apartment buildings including Eureka Tower (2006), which is listed as the 13th tallest residential building in the world in January 2014.[146]
Residential architecture is not defined by a single architectural style, but rather an eclectic mix of houses, townhouses, condominiums, and apartment buildings in the metropolitan area (particularly in areas of urban sprawl). Freestanding dwellings with relatively large gardens are perhaps the most common type of housing outside inner city Melbourne. Victorian terrace housing, townhouses and historic Italianate, Tudor revival and Neo-Georgian mansions are all common in neighbourhoods such as Toorak.
Sport

Melbourne is notable as the host city for the 1956 Summer Olympic Games (the first Olympic Games held in the southern hemisphere and Oceania, with all previous games held in Europe and the United States).[147] Melbourne is so far the southernmost city to host the Olympic Games. Melbourne also hosted the 2006 Commonwealth Games. The city is home to three major annual international sporting events: the Australian Open (one of the four Grand Slam tennis tournaments); the Melbourne Cup (horse racing); and the Australian Grand Prix (Formula One). Also, the Australian Masters golf tournament is held at Melbourne since 1979, having been co-sanctioned by the European Tour from 2006 to 2009. Melbourne was proclaimed the "World's Ultimate Sports City", in 2006, 2008 and 2010.[148] The city is home to the National Sports Museum, which until 2003 was located outside the members pavilion at the Melbourne Cricket Ground. It reopened in 2008 in the Olympic Stand.[149]
Australian rules football and cricket are the most popular sports in Melbourne. It is considered the spiritual home of the two sports in Australia. The first official Test cricket match was played at the Melbourne Cricket Ground in March 1877. The origins of Australian rules football can be traced to matches played next to the MCG in 1858, by the Melbourne Football Club, the world's oldest professional club of any football code. The Australian Football League is headquartered at Docklands Stadium. Nine of the League's teams are based in the Melbourne metropolitan area: Carlton, Collingwood, Essendon, Hawthorn, Melbourne, North Melbourne, Richmond, St Kilda, and Western Bulldogs. Up to five AFL matches are played each week in Melbourne, attracting an average 40,000 people per game.[150] Additionally, the city annually hosts the AFL Grand Final.

The city is home to many professional franchises/teams in national competitions including: Twenty20 cricket clubs Melbourne Stars and Melbourne Renegades, who play in the Big Bash League; Victoria Bushrangers cricket team, which compete in the domestic competitions Sheffield Shield and Matador BBQs One-Day Cup; soccer clubs Melbourne Victory and Melbourne City FC, which play in the A-League competition. Rugby league club Melbourne Storm[151] which plays in the NRL competition; rugby union clubs Melbourne Rebels and Melbourne Rising, which play in the Super Rugby and National Rugby Championship competitions respectively; netball clubs Melbourne Vixens and Collingwood Magpies Netball, of whom both play in the newly formed (as of 2017) Suncorp Super Netball; basketball club Melbourne United, which plays in the NBL competition; Bulleen Boomers and Dandenong Rangers, which play in the WNBL; Ice hockey teams Melbourne Ice and Melbourne Mustangs, who play in the Australian Ice Hockey League; and baseball club Melbourne Aces, which plays in the Australian Baseball League. Rowing is also a large part of Melbourne's sporting identity, with a number of clubs located on the Yarra River, out of which many Australian Olympians trained. The city previously held the nation's premier long distance swimming event the annual Race to Prince's Bridge, in the Yarra River. Notable amateur sports clubs include the country's top ranked women's (VRDL) and men's (VMRD) roller derby teams.
Melbourne has twice hosted the Presidents Cup golf tournament, in 1998 becoming the first country to hold the tournament outside of the USA. The event was first held in Melbourne in 1998 and then again in 2011, both times at the Royal Melbourne Golf Club. The biannual event is again scheduled for 2019 at the same venue.
Economy

Melbourne has a highly diversified economy with particular strengths in finance, manufacturing, research, IT, education, logistics, transportation and tourism. Melbourne houses the headquarters of many of Australia's largest corporations, including five of the ten largest in the country (based on revenue), and five of the largest seven in the country (based on market capitalisation)[153] (ANZ, BHP Billiton (the world's largest mining company), the National Australia Bank, CSL and Telstra, as well as such representative bodies and think tanks as the Business Council of Australia and the Australian Council of Trade Unions. Melbourne's suburbs also have the Head Offices of Wesfarmers companies Coles (including Liquorland), Bunnings, Target, K-Mart & Officeworks. The city is home to Australia's largest and busiest seaport which handles more than AU$75 billion in trade every year and 39% of the nation's container trade.[117][154][155] Melbourne Airport provides an entry point for national and international visitors, and is Australia's second busiest airport.[156]
Melbourne is also an important financial centre. In the 2017 Global Financial Centres Index, Melbourne was ranked as having the 21st most competitive financial center in the world.[157] Two of the big four banks, NAB and ANZ, are headquartered in Melbourne. The city has carved out a niche as Australia's leading centre for superannuation (pension) funds, with 40% of the total, and 65% of industry super-funds including the AU$109 billion-dollar Federal Government Future Fund. The city was rated 41st within the top 50 financial cities as surveyed by the MasterCard Worldwide Centers of Commerce Index (2008),[158] second only to Sydney (12th) in Australia. Melbourne is Australia's second-largest industrial centre.[159] It is the Australian base for a number of significant manufacturers including Boeing, truck-makers Kenworth and Iveco, Cadbury as well as Bombardier Transportation and Jayco, among many others. It is also home to a wide variety of other manufacturers, ranging from petrochemicals and pharmaceuticals to fashion garments, paper manufacturing and food processing.[160] The south-eastern suburb of Scoresby is home to Nintendo's Australian headquarters. The city also boasts a research and development hub for Ford Australia, as well as a global design studio and technical centre for General Motors and Toyota respectively.

CSL, one of the world's top five biotech companies, and Sigma Pharmaceuticals have their headquarters in Melbourne. The two are the largest listed Australian pharmaceutical companies.[162] Melbourne has an important ICT industry that employs over 60,000 people (one third of Australia's ICT workforce), with a turnover of AU$19.8 billion and export revenues of AU615 million. In addition, tourism also plays an important role in Melbourne's economy, with about 7.6 million domestic visitors and 1.88 million international visitors in 2004.[163] In 2008, Melbourne overtook Sydney with the amount of money that domestic tourists spent in the city,[164] accounting for around AU$15.8 billion annually.[165] Melbourne has been attracting an increasing share of domestic and international conference markets. Construction began in February 2006 of an AU$1 billion 5000-seat international convention centre, Hilton Hotel and commercial precinct adjacent to the Melbourne Exhibition and Convention Centre to link development along the Yarra River with the Southbank precinct and multibillion-dollar Docklands redevelopment.[166]
The Economist Intelligence Unit ranks Melbourne as the fourth most expensive city in the world to live in according to its worldwide cost of living index in 2013.[167] The cost of living in Melbourne from a domestic standpoint stacks up quite well when compared to Sydney, particularly the cost of property.[168] The most visited attractions are: Federation Square, Queen Victoria Market, Crown Casino, Southbank, Melbourne Zoo, Melbourne Aquarium, Docklands, National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne Museum, Melbourne Observation Deck, Arts Centre Melbourne, and the Melbourne Cricket Ground.[169]
The Economist Intelligence Unit also has ranked Melbourne as the most liveable city in the world for seven consecutive years (2011-2017).[21]
Demographics
| Part of a series on |
| Ethnicity in Melbourne |
|---|
|
|
|
|

In Greater Melbourne (Greater Capital City Statistical Areas), 63.3% of residents were born in Australia. The other most common countries of birth were the United Kingdom (3.4%), India (2.7%), China (excludes SARs and Taiwan) (2.3%), Italy (1.7%) and New Zealand (1.7%). In 2011 the most common cited ancestries in Greater Melbourne (Greater Capital City Statistical Areas) were English (21.1%), Australian (20.7%), Irish (6.9%), Scottish (5.7%) and Italian (5.5%).[170]
Melbourne has the largest Greek-speaking population outside Europe, a population comparable to some larger Greek cities like Larissa and Volos.[171] Thessaloniki is Melbourne's Greek sister city. The Vietnamese surname Nguyen is the second most common in Melbourne's phone book after Smith.[172] The city also features substantial Indian, Sri Lankan, and Malaysian-born communities, in addition to recent South African and Sudanese influxes. The cultural diversity is reflected in the city's restaurants that serve international cuisines.
| Largest overseas born populations | |
| Country of birth | Population (2016) |
|---|---|
| United Kingdom | 162,954 |
| India | 161,078 |
| Mainland China | 155,998 |
| Vietnam | 79,054 |
| New Zealand | 78,906 |
| Italy | 63,332 |
| Sri Lanka | 54,030 |
| Malaysia | 47,642 |
| Greece | 45,618 |
| Philippines | 45,157 |
| South Africa | 24,168 |
| Hong Kong | 20,840 |
Over two-thirds of Melburnians speak only English at home (68.1%). Chinese (mainly Cantonese and Mandarin) is the second-most-common language spoken at home (3.6%), with Greek third, Italian fourth and Vietnamese fifth, each with more than 100,000 speakers.[173] Although Victoria's net interstate migration has fluctuated, the population of the Melbourne statistical division has grown by about 70,000 people a year since 2005. Melbourne has now attracted the largest proportion of international overseas immigrants (48,000) finding it outpacing Sydney's international migrant intake on percentage, along with having strong interstate migration from Sydney and other capitals due to more affordable housing and cost of living.[174]
In recent years, Melton, Wyndham and Casey, part of the Melbourne statistical division, have recorded the highest growth rate of all local government areas in Australia. Melbourne could overtake Sydney in population by 2028.[175] The ABS has projected in two scenarios that Sydney will remain larger than Melbourne beyond 2056, albeit by a margin of less than 3% compared to a margin of 12% today. Melbourne's population could overtake that of Sydney by 2037[176] or 2039, according to the first scenario projected by the ABS, primarily due to greater internal migration losses assumed for Sydney.[177] Another study claims that Melbourne will surpass Sydney in population by 2040.[178]
After a trend of declining population density since World War II, the city has seen increased density in the inner and western suburbs, aided in part by Victorian Government planning, such as Postcode 3000 and Melbourne 2030, which have aimed to curtail urban sprawl.[179][180] According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics as of June 2013, inner-city Melbourne had the highest population density, with 12,400 people per km2. Surrounding inner-city suburbs experienced an increase in population density between 2012 and 2013: Carlton (9,000 people per km2) and Fitzroy (7,900).[181]
Education


Some of Australia's most prominent and well known schools are based in Melbourne. Of the top twenty high schools in Australia according to the Better Education ranking, six are in Melbourne.[182] There has also been a rapid increase in the number of International students studying in the city. Furthermore, Melbourne was ranked the world's fourth top university city in 2008 after London, Boston and Tokyo in a poll commissioned by the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology.[183] Melbourne is the home of seven public universities: the University of Melbourne, Monash University, La Trobe University, Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology (RMIT University), Deakin University, Swinburne University of Technology and Victoria University.
Melbourne universities have campuses all over Australia and some internationally. Swinburne University has campuses in Malaysia, while Monash has a research centre based in Prato, Italy. The University of Melbourne, the second oldest university in Australia,[184] was ranked first among Australian universities in the 2016 THES international rankings. In 2018 Times Higher Education Supplement ranked the University of Melbourne the 32rd best university in the world which is higher than the rankings in 2016 and 2017[185], Monash University was ranked 80th best[186]. Both are members of the Group of Eight, a coalition of leading Australian tertiary institutions offering comprehensive and leading education.[187]
As of 2017 RMIT University is ranked 17th in the world in art & design, and 28th in architecture.[188] The Swinburne University of Technology, based in the inner-city Melbourne suburb of Hawthorn, is ranked 76th–100th in the world for physics by the Academic Ranking of World Universities,[citation needed] making Swinburne the only Australian university outside the Group of Eight to achieve a top 100 rating in a science discipline.[citation needed] Deakin University maintains two major campuses in Melbourne and Geelong, and is the third largest university in Victoria. In recent years, the number of international students at Melbourne's universities has risen rapidly, a result of an increasing number of places being made available to full fee paying students.[189] Education in Melbourne is overseen by the Victorian Department of Education and Early Childhood Development (DEECD), whose role is to 'provide policy and planning advice for the delivery of education'.[190]
Melbourne is also home to a number of theological colleges, including the Presbyterian Theological College, the Reformed Theological College, Ridley College and the Melbourne School of Theology.
Media

Melbourne is served by thirty digital free-to-air television channels:
- ABC
- ABC HD (ABC broadcast in HD)
- ABC Comedy/KIDS
- ABC ME
- ABC News
- SBS
- SBS HD (SBS broadcast in HD)
- SBS Viceland
- SBS Viceland HD (SBS Viceland broadcast in HD)
- Food Network
- NITV
- Seven
- 7HD (Seven broadcast in HD)
- 7Two
- 7mate
- 7flix
- Racing.com
- Nine
- 9HD (Nine broadcast in HD)
- 9Gem
- 9Go!
- 9Life
- Extra
- Ten
- Ten HD (Ten broadcast in HD)
- One
- Eleven
- TVSN
- Spree TV
- C31 Melbourne (Melbourne's community TV station)
Melbourne can also receive some Regional TV via The VAST service. You can also reach Regional Television services From Mt Alexander (Bendigo) or Mt Tassie (Traralgon/Gippsland) if you live in Olinda or Mount Dandenong.
Three daily newspapers serve Melbourne: the Herald Sun (tabloid), The Age (formerly broadsheet, now compact) and The Australian (national broadsheet). Six free-to-air television stations service Greater Melbourne and Geelong: ABC Victoria, (ABV), SBS Victoria (SBS), Seven Melbourne (HSV), Nine Melbourne (GTV), Ten Melbourne (ATV), C31 Melbourne (MGV) – community television. Each station (excluding C31) broadcasts a primary channel and several multichannels. C31 is only broadcast from the transmitters at Mount Dandenong and South Yarra. Hybrid digital/print media companies such as Broadsheet and ThreeThousand are based in and primarily serve Melbourne.
Television shows are produced in Melbourne, most notably Neighbours, Kath & Kim, The Secret Life of Us, Winners and Losers, Offspring, Underbelly, House Husbands, Wentworth and Miss Fisher's Murder Mysteries, along with national news-based programs such as The Project, Insiders and ABC News Breakfast. Melbourne is also known as the game show capital of Australia; productions such as Million Dollar Minute, The Chase Australia, Millionaire Hot Seat and Family Feud are all based in Melbourne. Reality television productions such as Dancing with the Stars, MasterChef, The Block and The Real Housewives of Melbourne are all filmed in and around Melbourne. There are plenty of children children shows both in the morning and afternoon, such as Toasted TV (Channel 11), Kids' WB Weekdays (Channel 9Go) as well as channels purely for children - ABC Me and ABC of kids.
Pay television in Melbourne is largely delivered through cable and satellite services. Foxtel, Optus and Fetch are the main pay television providers. Sky News and Fox Sports both have studio facilities based in Melbourne.
A long list of AM and FM radio stations broadcast to greater Melbourne. These include "public" (i.e., state-owned ABC and SBS) and community stations. Many commercial stations are networked-owned: DMG has Nova 100 and Smooth; ARN controls Gold 104.3 and KIIS 101.1; and Southern Cross Austereo runs both Fox and Triple M. Stations from towns in regional Victoria may also be heard (e.g. 93.9 Bay FM, Geelong). Youth alternatives include ABC Triple J and youth run SYN. Triple J, and similarly PBS and Triple R, strive to play under represented music. JOY 94.9 caters for gay, lesbian, bisexual and transgender audiences. For fans of classical music there are 3MBS and ABC Classic FM. Light FM is a contemporary Christian station. AM stations include ABC: 774, Radio National, and News Radio; also Fairfax affiliates 3AW (talk) and Magic (easy listening). For sport fans and enthusiasts there is SEN 1116. Melbourne has many community run stations that serve alternative interests, such as 3CR and 3KND (Indigenous). Many suburbs have low powered community run stations serving local audiences.[191]
Religion

Melbourne has a wide range of religious faiths, the most widely held of which is Christianity. This is signified by the city's two large cathedrals—St Patrick's (Roman Catholic), and St Paul's (Anglican). Both were built in the Victorian era and are of considerable heritage significance as major landmarks of the city.[192] In recent years, Greater Melbourne's irreligious community has grown to be one of the largest in Australia.[193]
According to the 2016 Census, the largest responses on religious belief in Melbourne were no religion (31.9%), Catholic (23.4%), none stated (9.1%), Anglican (7.6%), Eastern Orthodox (4.3%), Islam (4.2%), Buddhism (3.8%), Hinduism (2.9%), Uniting Church (2.3%), Presbyterian and Reformed (1.6%), Baptist (1.3%) and Judaism (0.9%).[194]
Over 180,000 Muslims live in Melbourne.[195] Muslim religious life in Melbourne is centred on more than 25 mosques and a large number of prayer rooms at university campuses, workplaces and other venues.[196]
As of 2000[update], Melbourne had the largest population of Polish Jews in Australia. The city was also home to the largest number of Holocaust survivors of any Australian city,[197] indeed the highest per capita outside Israel itself.[198] Reflecting this vibrant community, Melbourne has a plethora of Jewish cultural, religious and educational institutions, including over 40 synagogues and 7 full-time parochial day schools,[199] along with a local Jewish newspaper.[200]
Governance

The governance of Melbourne is split between the government of Victoria and the 27 cities and four shires that make up the metropolitan area. There is no ceremonial or political head of Melbourne, but the Lord Mayor of the City of Melbourne often fulfils such a role as a first among equals,[201] particularly when interstate or overseas.
The local councils are responsible for providing the functions set out in the Local Government Act 1989[202] such as urban planning and waste management. Most other government services are provided or regulated by the Victorian state government, which governs from Parliament House in Spring Street. These include services associated with local government in other countries and include public transport, main roads, traffic control, policing, education above preschool level, health and planning of major infrastructure projects. The state government retains the right to override certain local government decisions, including urban planning, and Melburnian issues often feature prominently in state election.
Infrastructure
In 2012, Mercer Consulting ranked Melbourne's infrastructure 17th in the world, behind only one other Australian city, Sydney, which ranked 10th in the world.[203]
Health

The Government of Victoria's Department of Health and Human Services oversees about 30 public hospitals in the Melbourne metropolitan region, and 13 health services organisations.[204]
There are many major medical, neuroscience and biotechnology research institutions located in Melbourne: St. Vincent's Institute of Medical Research, Australian Stem Cell Centre, the Burnet Institute, Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute, Victorian Institute of Chemical Sciences, Brain Research Institute, Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, and the Melbourne Neuropsychiatry Centre.
Other institutions include the Howard Florey Institute, the Murdoch Childrens Research Institute, Baker IDI Heart and Diabetes Institute and the Australian Synchrotron.[205] Many of these institutions are associated with and are located near universities. Melbourne also is the home of the Royal Children's Hospital and the Monash Children's Hospital.
Among Australian capital cities, Melbourne ties with Canberra in first place for the highest male life expectancy (80.0 years) and ranks second behind Perth in female life expectancy (84.1 years).[206]
Transport

Like many Australian cities, Melbourne has a high dependency on the automobile for transport,[207] particularly in the outer suburban areas where the largest number of cars are bought,[208] with a total of 3.6 million private vehicles using 22,320 km (13,870 mi) of road, and one of the highest lengths of road per capita in the world.[207] The early 20th century saw an increase in popularity of automobiles, resulting in large-scale suburban expansion and a tendency towards the development of urban sprawl.[209] By the mid 1950s there was just under 200 passenger vehicles per 1000 people, by 2013 there was 600 passenger vehicles per 1000 people.[210] Today it has an extensive network of freeways and arterial roadways used by private vehicles including freight as well as public transport systems including buses and taxis. Major highways feeding into the city include the Eastern Freeway, Monash Freeway and West Gate Freeway (which spans the large West Gate Bridge), whilst other freeways circumnavigate the city or lead to other major cities, including CityLink (which spans the large Bolte Bridge), Eastlink, the Western Ring Road, Calder Freeway, Tullamarine Freeway (main airport link) and the Hume Freeway which links Melbourne and Sydney.[211]
Melbourne has an integrated public transport system based around extensive train, tram, bus and taxi systems. Flinders Street station was the world's busiest passenger station in 1927 and Melbourne's tram network overtook Sydney's to become the world's largest in the 1940s, at which time 25% of travellers used public transport but by 2003 it had declined to just 7.6%.[212] The public transport system was privatised in 1999, symbolising the peak of the decline.[213] Despite privatisation and successive governments persisting with auto-centric urban development into the 21st century,[214] there have since been large increases in public transport patronage, with the mode share for commuters increasing to 14.8% and 8.4% of all trips.[215] A target of 20% public transport mode share for Melbourne by 2020 was set by the state government in 2006.[216] Since 2006 public transport patronage has grown by over 20%.[216]

The Melbourne rail network has its origins in privately built lines from the 1850s gold rush era, and today the suburban network consists of 209 suburban stations on 16 lines which radiate from the City Loop, a partially underground metro section of the network beneath the Central Business District (Hoddle Grid). Flinders Street station is Melbourne's busiest railway station, and was the world's busiest passenger station in 1926. It remains a prominent Melbourne landmark and meeting place.[141] The city has rail connections with regional Victorian cities, as well as direct interstate rail services to Sydney and Adelaide and beyond which depart from Melbourne's other major rail terminus, Southern Cross station in Spencer Street. In the 2013–2014 financial year, the Melbourne rail network recorded 232.0 million passenger trips, the highest in its history.[217] Many rail lines, along with dedicated lines and rail yards are also used for freight. The Overland to Adelaide departs Southern Cross twice a week, while the XPT to Sydney departs twice a day.

Melbourne has the largest tram network in the world[23][219] which had its origins in the city's 1880s land boom. In 2013–2014, 176.9 million passenger trips were made by tram.[217] Melbourne's is Australia's only tram network to comprise more than a single line and consists of 250 km (155.3 mi) of track, 487 trams, 25 routes, and 1,763 tram stops.[220] Around 80 per cent of Melbourne's tram network shares road space with other vehicles, while the rest of the network is separated or are light rail routes.[220] Melbourne's trams are recognised as iconic cultural assets and a tourist attraction. Heritage trams operate on the free City Circle route, intended for visitors to Melbourne, and heritage restaurant trams travel through the city and surrounding areas during the evening.[221] Melbourne is currently building 50 new E Class trams with some already in service in 2014. The E Class trams are about 30 metres long and are superior to the C2 class tram of similar length. Melbourne's bus network consists of almost 300 routes which mainly service the outer suburbs and fill the gaps in the network between rail and tram services.[221][222] 127.6 million passenger trips were recorded on Melbourne's buses in 2013–2014, an increase of 10.2 percent on the previous year.[217]
Ship transport is an important component of Melbourne's transport system. The Port of Melbourne is Australia's largest container and general cargo port and also its busiest. The port handled two million shipping containers in a 12-month period during 2007, making it one of the top five ports in the Southern Hemisphere.[154] Station Pier on Port Phillip Bay is the main passenger ship terminal with cruise ships and the Spirit of Tasmania ferries which cross Bass Strait to Tasmania docking there.[223] Ferries and water taxis run from berths along the Yarra River as far upstream as South Yarra and across Port Phillip Bay.
Melbourne has four airports. Melbourne Airport, at Tullamarine, is the city's main international and domestic gateway and second busiest in Australia. The airport is home base for passenger airlines Jetstar Airways and Tiger Airways Australia and cargo airlines Australian air Express and Toll Priority; and is a major hub for Qantas and Virgin Australia. Avalon Airport, located between Melbourne and Geelong, is a secondary hub of Jetstar. It is also used as a freight and maintenance facility. Buses and taxis are the only forms of public transport to and from the city's main airports. Air Ambulance facilities are available for domestic and international transportation of patients.[224] Melbourne also has a significant general aviation airport, Moorabbin Airport in the city's south east that also handles a small number of passenger flights. Essendon Airport, which was once the city's main airport also handles passenger flights, general aviation and some cargo flights.[225]
The city also has a bicycle sharing system. It was established in 2010[226] and uses a network of marked road lanes and segregated cycle facilities.
Utilities

Water storage and supply for Melbourne is managed by Melbourne Water, which is owned by the Victorian Government. The organisation is also responsible for management of sewerage and the major water catchments in the region as well as the Wonthaggi desalination plant and North–South Pipeline. Water is stored in a series of reservoirs located within and outside the Greater Melbourne area. The largest dam, the Thomson River Dam, located in the Victorian Alps, is capable of holding around 60% of Melbourne's water capacity,[227] while smaller dams such as the Upper Yarra Dam, Yan Yean Reservoir, and the Cardinia Reservoir carry secondary supplies.
Gas is provided by three distribution companies:
- AusNet Services, which provides gas from Melbourne's inner western suburbs to southwestern Victoria.
- Multinet Gas, which provides gas from Melbourne's inner eastern suburbs to eastern Victoria. (owned by SP AusNet after acquisition, but continuing to trade under the brand name Multinet Gas)
- Australian Gas Networks, which provides gas from Melbourne's inner northern suburbs to northern Victoria, as well as the majority of southeastern Victoria.
Electricity is provided by five distribution companies:
- Citipower, which provides power to Melbourne's CBD, and some inner suburbs
- Powercor, which provides power to the outer western suburbs, as well as all of western Victoria (Citipower and Powercor are owned by the same entity)
- Jemena, which provides power to the northern and inner western suburbs
- United Energy, which provides power to the inner eastern and southeastern suburbs, and the Mornington Peninsula
- AusNet Services, which provides power to the outer eastern suburbs and all of the north and east of Victoria.
Numerous telecommunications companies provide Melbourne with terrestrial and mobile telecommunications services and wireless internet services and at least since 2016 Melbourne offers a free public WiFi which allows for up to 250 MB per device in some areas of the city.
Crime
Although Melbourne's crime rate dropped 6.2% in 2017, it still experiences Victoria's highest crime rate with over 18,280 offences per 100,000 people.[228] Despite this, Melbourne was ranked the 5th safest city in the world in The Economist's Safe Cities Index 2017.[229]
Sister cities
Melbourne has six international sister cities.[230] According to the City of Melbourne council, "the city as a whole has been nourished by their influence, which extends from educational, cultural and sporting exchanges to unparalleled business networking opportunities."[231][232][233] The recognised cities are:
|
See also
- Melway (the native street directory and general information source in Melbourne)
Lists
- List of Australian capital cities
- List of Melbourne suburbs
- List of museums in Melbourne
- List of people from Melbourne
- List of songs about Melbourne
- Local government in Victoria
References
- ^ a b "3218.0 – Melbourne, Sydney and Brisbane populations soar but growth drivers differ, 20118". ABC. 24 April 2018. Retrieved 31 October 2017. ERP at 24 April 2018.
- ^ a b "3218.0 – Regional Population Growth, Australia, 2015–16: Population Estimates by Statistical Area Level 2 (ASGS 2016), 2006 to 2016". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Australian Bureau of Statistics. 28 July 2017. Retrieved 26 October 2017. Estimated resident population, 30 June 2016.
- ^ "Great Circle Distance between MELBOURNE and CANBERRA". Geoscience Australia. March 2004.
- ^ "Great Circle Distance between MELBOURNE and ADELAIDE". Geoscience Australia. March 2004.
- ^ "Great Circle Distance between MELBOURNE and SYDNEY". Geoscience Australia. March 2004.
- ^ "Great Circle Distance between MELBOURNE and BRISBANE". Geoscience Australia. March 2004.
- ^ "Great Circle Distance between MELBOURNE and PERTH". Geoscience Australia. March 2004.
- ^ In the UK and US, another pronunciation variant is /ˈmɛlbɔːrn/ MEL-born: Wells, John C. (2008), Longman Pronunciation Dictionary (3rd ed.), Longman, ISBN 9781405881180
- ^ Butler, S., ed. (2013). "Melbourne". Macquarie Dictionary (6th ed.). Sydney: Macmillan Publishers Group Australia 2015. 1952 pages. ISBN 978-18-7642-966-9.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|nopp=ignored (|no-pp=suggested) (help) - ^ "Victorian Local Government Directory" (PDF). Department of Planning and Community Development, Government of Victoria. p. 11. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 September 2009. Retrieved 11 September 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ The use of the term Melburnian can be traced back to 1876 where the case for Melburnian over Melbournian was made in the Melbourne Grammar School publication, the Melburnian. "The diphthong, 'ou' is not a Latin diphthong: hence, we argued this way,Melburnia would be [the] Latin form of name, and from it comes Melburnian." See Oxford English Dictionary Additions Series, iii, s.v. "Melburnian".
- ^ Macquarie Dictionary, Fourth Edition (2005) Or less commonly Melbournites. Melbourne, The Macquarie Library Pty Ltd. ISBN 1-876429-14-3
- ^ a b "History of the City of Melbourne" (PDF). City of Melbourne. November 1997. pp. 8–10. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ a b Lewis, Miles (1995). Melbourne: the city's history and development (2nd ed.). Melbourne: City of Melbourne. p. 25. ISBN 0-949624-71-3.
- ^ a b Cervero, Robert B. (1998). The Transit Metropolis: A Global Inquiry. Chicago: Island Press. p. 320. ISBN 1-55963-591-6.
- ^ Davidson, Jim (2 August 2014). "Rise and fall of British empire viewed through its cities". The Australian. Australia. Retrieved 7 September 2018.
- ^ "Commonwealth of Australia Constitution Act" (PDF). Department of the Attorney-General, Government of Australia. p. 45 (Section 125). Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 March 2010. Retrieved 11 September 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "The Global Financial Centres Index 22" (PDF). Long Finance. September 2017.
- ^ Westwood, Matthew (26 November 2013). The Cultural Capital's Perfect 10. The Australian. News Limited. Retrieved 28 December 2013.
- ^ Langmaid, Aaron (28 April 2010). We're sport's champion city again. Herald Sun. News Limited. Retrieved 29 December 2013.
- ^ a b c Stephanie Chalkley-Rhoden (16 August 2017). "World's most liveable city: Melbourne takes top spot for seventh year running". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 17 August 2017.
- ^ "Government outlines vision for Port of Melbourne Freight Hub" (Press release). 2006. Archived from the original on 8 July 2012. Retrieved 26 July 2007.
{{cite press release}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Investing in Transport Chapter 3 – East/West, Section 3.1.2 – Tram Network" (PDF). Department of Transport, Government of Victoria. Retrieved 21 November 2009.
- ^ Gary Presland, The First Residents of Melbourne's Western Region, (revised edition), Harriland Press, 1997. ISBN 0-646-33150-7. Presland says on page 1: "There is some evidence to show that people were living in the Maribyrnong River valley, near present day Keilor, about 40,000 years ago."
- ^ a b [1] Archived 8 September 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Gary Presland, Aboriginal Melbourne: The Lost Land of the Kulin People, Harriland Press (1985), Second edition 1994, ISBN 0-9577004-2-3. This book describes in some detail the archaeological evidence regarding aboriginal life, culture, food gathering and land management, particularly the period from the flooding of Bass Strait and Port Phillip from about 7–10,000 years ago, up to the European colonisation in the nineteenth century.
- ^ a b c "Foundation of the Settlement". History of the City of Melbourne. City of Melbourne. 1997. Archived from the original on 20 February 2011. Retrieved 13 July 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Isabel Ellender and Peter Christiansen, People of the Merri Merri. The Wurundjeri in Colonial Days, Merri Creek Management Committee, 2001 ISBN 0-9577728-0-7
- ^ Button, James (4 October 2003). "Secrets of a forgotten settlement". The Age. Melbourne: Fairfax. Retrieved 19 October 2008.
- ^ Annear, Robyn (2005). Bearbrass: Imagining Early Melbourne. Melbourne, Victoria: Black Inc. p. 6. ISBN 1863953973.
- ^ Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 18 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 91.
- ^ "Melbourne's Godfather". The West Australian. Vol. 50, , no. 14, 996. Western Australia. 14 July 1934. p. 6. Retrieved 20 September 2017 – via National Library of Australia.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - ^ "Roads". City of Melbourne. Archived from the original on 20 February 2011. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ https://trove.nla.gov.au/newspaper/article/11144430
- ^ Premier Postal History. "Post Office List". Archived from the original on 10 May 2008. Retrieved 11 April 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ James Boyce, 1835: The Founding of Melbourne and the Conquest of Australia, Black Inc, 2011, page 151 citing Richard Broome, "Victoria" in McGrath (ed.), Contested Ground: 129
- ^ James Boyce, 1835: The Founding of Melbourne and the Conquest of Australia, Black Inc, 2011, p.186
- ^ James Boyce, 1835: The Founding of Melbourne and the Conquest of Australia, Black Inc, 2011, p.199
- ^ James Boyce, 1835: The Founding of Melbourne and the Conquest of Australia, Black Inc, 2011, page 163
- ^ Separation, EMelbourne-Encyclopedia of Melbourne, accessed 7 July 2015
- ^ Victorian Cultural Collaboration. "Gold". Special Broadcasting Service. Archived from the original on 24 July 2008. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ "The Snowy Mountains Scheme and Multicultural Australia". ATSE. Archived from the original on 6 January 2010. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Welcome to Chinatown". Chinatown Melbourne. Retrieved 11 December 2012.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Annear, Robyn (1999). Nothing But Gold. Text.
- ^
"Media Business Communication time line since 1861". Caslon. Archived from the original on 6 December 2012. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "The Story of Melbourne". Argus. Melbourne, Australia: National Library of Australia. 9 September 1926. p. 8 Supplement: An Historic Souvenir. Retrieved 24 January 2012.
- ^ Button, James (10 January 2004). "He came, he saw, he marvelled". The Age. Fairfax. Retrieved 7 July 2012.
- ^ a b c d Cannon, Michael (1966). The Land Boomers. Melbourne University Press; Cambridge University Press.
- ^ "Marvellous Melbourne – Introduction of the Hydraulic Lift". Museum Victoria. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
- ^ Miles, Lewis (1995). Melbourne the city's history and development. City of Melbourne. p. 47.
- ^ Lambert, Tim. "A Brief History of Melbourne". Local Histories. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
- ^ "Melbourne (Victoria) – growth of the city". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
- ^ "Fast Facts on Melbourne History". We Love Melbourne. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
- ^ Lewis, Miles (Melbourne the city's history and development) p. 113–114
- ^ "1961 – the Impact of Post-War Immigration". Museum Victoria. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
- ^ Ketchel, Misha (11 December 2012). "Boutique battle at Paris end of town". Age. Fairfax.
- ^ The art of the forgotten people Archived 13 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine by Tom Wilson
- ^ "Sorry, we can't find the content you're looking for - State Library o…". 5 August 2012. Archived from the original on 5 August 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Judith Raphael Buckrich (1996) Melbourne's Grand Boulevard: the Story of St Kilda Road. Published State Library of Victoria
- ^ Logan, William (1985). The Gentrification of inner Melbourne: a political geography of inner city housing. Brisbane, Australia: University of Queensland Press. pp. 148–160. ISBN 0-7022-1729-8.
- ^ Millar, Royce (7 November 2005). "Road to ... where?". Age. Fairfax. Retrieved 11 December 2012.
- ^ Shepherd, Dick (4 February 1972). "Hotel men expected to press for Govt. aid". Age. Fairfax. Retrieved 25 April 2011.
- ^ "Tell Melbourne it's over, we won". Sydney Morning Herald. Fairfax. 31 December 2003. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ Saward, Joe (1 February 1996). "Interview – Judith Griggs". Grandprix. Inside F1. Archived from the original on 17 January 2010. Retrieved 14 May 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Lewis, Miles Melbourne the city's history and development p203,205–206
- ^ Marino, Melissa; Colebatch, Tim (24 March 2005). "Melbourne's population booms". The Age. Australia. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ "Delivering Melbourne's newest sustainable communities". Victoria Online. State of Victoria. 21 September 2006. Archived from the original on 4 June 2010. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ The Age, 12 February 2010
- ^ Ormonde, Tom (14 November 2009). "Housing the bubble that no one dares burst". Age. Melbourne. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
- ^ Dowling, Jason (16 February 2008). "Rent crisis forces urgent action". Age. Melbourne. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
- ^ Russell, Mark (2 January 2006). "Life's a beach in Melbourne". Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
- ^ a b c "Beach Report 2007–08" (PDF). EPA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 October 2008. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Tapper, Andrew; Tapper, Nigel (1996). Gray, Kathleen (ed.). The weather and climate of Australia and New Zealand (First ed.). Melbourne, Australia: Oxford University Press. p. 300. ISBN 0-19-553393-3.
- ^ Linacre, Edward; Geerts, Bart (1997). Climates and Weather Explained. London: Routledge. p. 379. ISBN 0-415-12519-7.
- ^ a b "Melbourne Regional Office". Climate statistics for Australian locations. Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 30 October 2016.
- ^ "Melbourne Regional Office". Climate statistics for Australian locations. Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 9 November 2010.
- ^ "Welcome to Melbourne". City of Melbourne. Archived from the original on 19 July 2008. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Bureau of Meteorology – Climate Data Online". Retrieved 6 January 2015.
- ^ "Monthly climate statistics". Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 30 March 2012.
- ^ "BOM - Australian Climate Extremes". pandora.nla.gov.au. Archived from the original on 17 March 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Melbourne Sea Temperature". World Sea Temperatures.
- ^ "Port Melbourne Sea Temperature". World Sea Temperatures.
- ^ "Sunshine hours for Melbourne Airport". Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 30 October 2016.
- ^ "Melbourne's air quality measure". epa.vic.gov.au. 21 November 2014. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ^ "Water Storages: Water Report". Melbourne Water. 26 June 2009. Archived from the original on 27 October 2009. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Rood, David (20 September 2007). "Desal plant to be public-private deal". Age. Melbourne: Fairfax. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ "Victoria's desalination plant to take 33 extra years to pay off under Melbourne Water plan". ABC. 17 July 2015. Retrieved 12 January 2017.
- ^ "Re-directing to Home Page". Melbourne Water. Archived from the original on 11 October 2010. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Riordan, Paul. "Glen Eira against green tide". News. Archived from the original on 9 October 2009. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Cardew, R; Fanning, P; George, J (1998). Urban Footprints and Stormwater Management: A Council Survey. Australian Institute of Urban Studies. pp. 16–25.
- ^ "Target Species for Biological Control". Australian Weeds Committee. Archived from the original on 15 October 2008. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Thompson, Jeremy (1 July 2002). "Scientists declare war on Indian mynah". 7.30 Report. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ Bradbury, Garth (7 September 2004). "Update on Pigeon Management Issue" (PDF). City of Melbourne. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 October 2008. Retrieved 22 October 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Victoria a Rat's Nest". Herald Sun. News. 1 August 2009. Retrieved 7 July 2012.
- ^ Benson, Eugene (21 July 2009). "Rodent Rampage". Fairfax. Archived from the original on 16 October 2009. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "The picnickers nightmare: European wasp". CSIRO. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ Marks, C.A. & Bloomfield, T.E. (1999) Distribution and density estimates for urban foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Melbourne: implications for rabies control
- ^ "Fire and Biodiversity: The Effects and Effectiveness of Fire Management". Australian Government — Department of environment. Archived from the original on 2 August 2008. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Murray, Robert; White, Kate; Kock, P (1995). State of Fire: A History of Volunteer Firefighting and the Country Fire Authority in Victoria. Hargreen. pp. 339 pages. ISBN 0-949905-63-1.
- ^ "About Parks Victoria". parkweb.vic.gov.au. Archived from the original on 25 July 2008. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Wild Places of Greater Melbourne. R Taylor, 9780957747104, CSIRO Publishing, January 1999, 224pp, PB
- ^ a b Lucas, Clay; Millar, Royce (11 March 2008). "Victoria: the garden state or greenhouse capital?". The Age. Melbourne. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
- ^ CSIRO: Marine and atmospheric research. "Urban and regional air pollution". CSIRO. Archived from the original on 23 February 2008. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ "Garrett approves Port Phillip Bay dredging". ABC News. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 5 February 2008. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ Gardiner, Ashley (31 May 2008). "E coli running riot in Yarra River". Herald Sun. Australia: News. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ Australian Institute of Urban Studies and City of Melbourne. "AIUS Indicators". Environmental indicators for Metropolitan Melbourne. Australian Institute of Urban Studies. Archived from the original on 13 November 2007. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Victoria's Litter reduction Strategy" (PDF). State Government of Victoria. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 July 2008. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Transition decade launch". Beyond Zero Emissions. 19 January 2010. Archived from the original on 12 February 2010. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Freeman-Greene, Suzy (10 August 2005). "Melbourne's love affair with lanes". The Age. Australia. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ Essential but unplanned : the story of Melbourne's lanes. Weston Bate. City of Melbourne : State Library of Victoria, 1994
- ^ "Eureka Tower". Eureka Tower Official. Archived from the original on 18 July 2008. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
- ^ Dobbin, Marika (8 October 2009). "End in view for Rialto's top deck". The Age. Melbourne. Archived from the original on 16 January 2010. Retrieved 8 February 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Walking Melbourne, Heritage, Architecture, Skyscraper and Buildings Database". Walking Melbourne. Retrieved 28 September 2008.
- ^ "Melbourne Architecture". Melbourne Travel Guide. Archived from the original on 15 September 2008. Retrieved 28 September 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Glen Iris still the heart of city's sprawl". The Age. Melbourne. 5 August 2002. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ "Victoria". wilmap.com.au. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
- ^ a b "Victoria Australia, aka "The Garden State"". goway.com. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
- ^ "City of Melbourne — Parks and Gardens". City of Melbourne. Archived from the original on 30 August 2004. Retrieved 28 September 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Melbourne's Best Gardens". weekendnotes.com. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- ^ "Vicnet Directory — Local Government". Vicnet. Archived from the original on 28 September 2008. Retrieved 29 September 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Metropolitan Melbourne – Live in Victoria". Liveinvictoria.vic.gov.au. 12 August 2009. Archived from the original on 24 January 2010. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Wilson, Andrew (17 April 2011). "City shortage pushes up rents". Domain. Fairfax. Retrieved 7 July 2012.
- ^ "rental pressure cooker". The Age. Australia: Fairfax. 3 April 2010.
- ^ "Melbourne housing now 'severely unaffordable'". The Age. Australia: Fairfax. 24 January 2011.
- ^ "Project Database".
- ^ "What makes Melbourne the cultural capital of Australia?". Meld Magazine - Australia's international student news website. 12 July 2016. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^ sector=Government, ; corporateName=Department of Economic Development, Jobs, Transport and Resources; address=121 Exhibition St, MELBOURNE 3000;. "International research". www.business.vic.gov.au. Retrieved 27 March 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ sector=Government, ; corporateName=Department of Economic Development, Jobs, Transport and Resources; address=121 Exhibition St, MELBOURNE 3000;. "Domestic and regional research". www.business.vic.gov.au. Retrieved 27 March 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Cities of Literature". cityofliterature.com. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- ^ "Global Attractions Attendance Report 2016" (PDF). Themed Entertainment Association. Retrieved 27 March 2018.
- ^ Allen, Jessica. The World's Best Cities for Viewing Street Art, International Business Times (2010). Retrieved 16 October 2010.[dead link]
- ^ Topsfield, Jewel. Brumby slams Tourism Victoria over graffiti promotion, The Age (2008). Retrieved 16 October 2010.
- ^ "Southbank Theatre". Melbourne Theatre Company. Melbourne Theatre Company. 2014. Retrieved 9 November 2014.
- ^ a b More Australian than Aristotelian: The Australian Bushranger Film, 1904–1914. By William Routt Archived 24 December 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Docklands Studios - Bringing Screen Ideas to Life". Docklands Studios.
- ^ Lovece, Frank (29 September 2011). "Chris Hemsworth: Not a Thor Loser". FilmFestivalTraveler.com. Archived from the original on 8 October 2011. Retrieved 7 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Melbourne confirmed as live music capital". ABC News. 25 March 2013. Retrieved 28 September 2013.
- ^ Paul Cashmere (21 March 2013). "Melbourne Claims Live Music Capital Of Australia Title". Noise11. Noise11. Retrieved 28 September 2013.
- ^ "Melbourne Is Officially One Of The World's Leading Music Cities". Tone Deaf. 11 June 2015. Retrieved 27 March 2018.
- ^ Peter Fischer and Susan Marsden, Vintage Melbourne: beautiful buildings from Melbourne city centre, East Street Publications, Bowden South Australia 2007
- ^ a b Melbourne and scenes in Victoria 1925–1926 from Victorian Government Railways From the National Library of Australia
- ^ "Walking Melbourne". Retrieved 9 January 2012.
- ^ Chapman, Heather; Stillman, Jill (2016). Lost Melbourne. Pavilion Books. ISBN 9-78-191049674-9.
- ^ Annear, Robyn (2014). A City Lost and Found: Whelan the Wrecker's Melbourne. Black Inc. ISBN 9-78-192223141-3.
- ^ "Emporis Skyline Ranking". Emporis Corporation. All rights reserved. Retrieved 2 December 2012.
- ^ "100 Tallest Residential Buildings in the World". Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat. Archived from the original on 10 December 2012. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "1956 Melbourne". athletesedge.info. Archived from the original on 2 November 2013. Retrieved 2 May 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Melbourne victorious again". Herald Sun. News. 1 April 2008. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ Strong, Geoff (5 March 2008). "Australian sports museum opens at MCG". Age. Melbourne: Fairfax. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ Smith, Patrick (1 August 2008). "AFL blueprint for third stadium". Australian. News. Archived from the original on 9 August 2008. Retrieved 22 October 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Melbourne Storm: The Beginning". Melbourne Storm. Archived from the original on 14 July 2008. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ "Crown casino records profit growth, up 130%". Business Day. 26 August 2010. Archived from the original on 7 March 2012. Retrieved 10 June 2012.
- ^ BRW 1000 Archived 29 August 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b "Port of Melbourne Sets Shipping Record". Bernama. 13 June 2007. Archived from the original on 29 September 2007. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Growth of Australia's largest port essential". The Age. Melbourne. 18 December 2004. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ planmelbourne.vic.gov.au Archived 9 October 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "The Global Financial Centres Index 21" (PDF). Long Finance. March 2017. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 June 2017.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Worldwide Centers of Commerce Index" (PDF). 2008. Retrieved 10 October 2008.
- ^ Matt Wade (8 February 2014). "Sydney takes manufacturing capital crown from Melbourne". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 30 March 2014.
- ^ "Business Victoria – Manufacturing". State of Victoria, Australia. 26 May 2008. Archived from the original on 3 November 2013. Retrieved 22 October 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Myer pins hopes on midyear sale as revenue slides". Sydney Morning Herald. 24 May 2012. Retrieved 23 March 2015.
- ^ "Invest Victoria – Biotechnology and Life Sciences". Archived from the original on 5 July 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Minister for Tourism (21 July 2004). "Media Release: Melbourne Airport passenger figures strongest on record". Department of Premier and Cabinet. Archived from the original on 2 May 2008. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Stafford, Annabel (19 May 2008). "Now Sydney loses its tourism ascendancy". The Age. Melbourne. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ timholding.com.au[dead link]
- ^ Kleinman, Rachel (1 May 2006). "Councillors furious about convention centre deal". The Age. Melbourne.
- ^ "What are the most expensive cities to live in?". Retrieved 16 February 2014.
- ^ "Melbourne versus Sydney: How the costs of living stack up!". RateCity.com.au. Retrieved 18 September 2018.
- ^ "Victoria's Top 20 Attractions". Only Melbourne. 27 September 2013. Retrieved 30 March 2014.
- ^ "2011 Census QuickStats: People — demographics & education". Censusdata.abs.gov.au. Retrieved 30 March 2014.
- ^ http://www.oecd.org/gov/regional-policy/50242959.pdf
- ^ Melbourne's multicultural history, City of Melbourne. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- ^ "QuickStats: Melbourne (Statistical Division)". 2006 Census. Commonwealth of Australia. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ O'Leary, John. "Resurgence of Marvellous Melbourne" (PDF). People and Place. 7, 1. Monash University: 38.
- ^ "Growth pains on the city's fringe". The Age. 1 August 2012. Retrieved 24 August 2012.
- ^ staff writers (27 April 2010). "Business – Melbourne will be Australia's biggest city by 2037". News.com.au. Retrieved 30 March 2014.
- ^ "Population Projections, Australia, 2006 to 2101". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 4 September 2008.
- ^ "Melbourne to overtake Sydney by 2040". abc.net.au. 23 May 2013. Retrieved 30 March 2014.
- ^ "Melbourne 2030 – in summary". Victorian Government, Department of Sustainability and Environment. Archived from the original on 7 September 2008. Retrieved 5 October 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "City of Melbourne: Strategic Planning — Postcode 3000". City of Melbourne. Archived from the original on 12 September 2008. Retrieved 5 October 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Population Density". Australian Bureau of Statistics. ABS. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- ^ "School Ranking". www.bettereducation.com.au. Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- ^ "World's top university cities revealed". RMIT News. RMIT University. 30 May 2008. Archived from the original on 19 July 2008. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "WEHI: Our research partners". Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research. University of Melbourne. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 13 July 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "University of Melbourne". Times Higher Education (THE). Retrieved 20 September 2018.
- ^ "Monash University". Times Higher Education (THE). Retrieved 20 September 2018.
- ^ "Group of Eight Australia". go8.edu.au. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- ^ "RMIT University Rankings".
- ^ "University of Melbourne's international student offers rise as its demand leaps". Uni News. University of Melbourne. 12 January 2007. Archived from the original on 30 July 2008. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Department of Education and Early Childhood Development: About Us Accessed: 2 May 2010
- ^ "Victoria Members – Community Broadcasting Association of Australia". CBAA. Retrieved 28 August 2010.
- ^ "Victorian Architectural Period — Melbourne". walkingmelbourne.com. Retrieved 5 October 2008.
- ^ "Census 2016: Why Australians are Losing their Religion". ABC Religion and Ethics. Retrieved 27 March 2018.
- ^ "2016 Census Community Profiles - Greater Melbourne". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 27 March 2018.
- ^ "2016 Census Community Profiles - Greater Melbourne". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 27 March 2018.
- ^ "Islam - The Encyclopedia of Melbourne Online". www.emelbourne.net.au.
- ^ Freiberg, Freda (2001). "Judith Berman, Holocaust Remembrance in Australian Jewish Communities, 1945–2000". UWA Press. Archived from the original on 1 June 2012. Retrieved 22 October 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "The Kadimah & Yiddish Melbourne in the 20th Century". Jewish Cultural Centre and National Library: "Kadima". Retrieved 9 January 2007.
- ^ "Jewish Community of Melbourne, Australia". The Museum of the Jewish People at Beit Hatfutsot. Retrieved 5 October 2008.
- ^ "News". The Australian Jewish News. Retrieved 28 August 2010.
- ^ Dunstan, David (12 November 2004). "The evolution of 'Clown Hall'". The Age. Melbourne. Retrieved 8 November 2010.
- ^ Local Government Act 1989 Archived 8 November 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "City Mayors: Best cities in the world". www.citymayors.com. Retrieved 27 July 2015.
- ^ Melbourne public hospitals and Metropolitan Health Services Victorian Department of Health
- ^ "Victorian Government Health Information Web site". health services, Victoria. Retrieved 5 October 2008.
- ^ Sunshine Coast and WA Country and Perth Women among Longest Life Expectancy in the World, Department of Health and Ageing. Retrieved 15 October 2010. Archived 7 January 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Most Liveable and Best Connected? The Economic Benefits of Investing in Public Transport in Melbourne, by Jan Scheurer, Jeff Kenworthy, and Peter Newman Archived 27 August 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Still addicted to cars". Herald Sun. Australia. 10 October 2007. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ "The cars that ate Melbourne". The Age. Australia. 14 February 2004. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ "Australian Social Trends". abs.gov.au. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
- ^ "Victoria's Road Network". VicRoads. Archived from the original on 7 September 2008. Retrieved 5 October 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Silkstone, Dan (5 November 2005). "Trial by public transport: why the system is failing". The Age. Australia: Fairfax/Melbourne Buses. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 28 August 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Birnbauer, William (9 April 2006). "$1.2bn sting in the rail". The Age. Melbourne. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ Gray, Darren (8 September 2003). "Bid to end traffic chaos". The Age. Melbourne: Fairfax. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ Parliament of Australia:Senate:Committees:Rural and Regional Affairs and Transport Committee:Investment of Commonwealth and State funds in public passenger transport infrastru... Archived 6 October 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Tomazin, Farrah (14 January 2008). "Public transport makes inroads, but not beyond the fringe". The Age. Melbourne: Fairfax. Retrieved 8 October 2010.
- ^ a b c "PTV Annual Report 2013-2014" (PDF). Public Transport Victoria. 11 September 2014. Retrieved 8 November 2015.
- ^ "Facts & Figures". Yarra Trams. Archived from the original on 29 May 2014. Retrieved 4 March 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Melbourne's Tram History". railpage.org.au. Archived from the original on 9 November 2008. Retrieved 28 September 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Facts & Figures". Yarra Trams. Archived from the original on 29 May 2014. Retrieved 8 November 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Metlink — Your guide to public transport in Melbourne and Victoria". Metlink-Melbourne. Retrieved 5 October 2008.
- ^ "Melbourne Buses". getting-around-melbourne.com.au. Retrieved 5 October 2008.
- ^ "Spirit of Tasmania — One of Australia's great journeys". TT-Line Company Pty Ltd. Retrieved 5 October 2008.
- ^ http://www.vibha.info Air ambulance australia
- ^ "Essendon Airport". Essendon Airport Pty Ltd. Retrieved 5 October 2008.
- ^ Lucas, Clay (1 June 2010). "Share scheme out of the blocks for city cyclists". Age. Fairfax. Retrieved 20 May 2012.
- ^ "Dam Water Storage Levels". Melbourne Water. Archived from the original on 18 July 2008. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "'Biggest decline' in Victoria's crime rate in 12 years as car thefts, aggravated burglaries fall, data reveals". ABC News. ABC News. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^ "The Safe Cities Index 2017". Economist. Retrieved 27 March 2018.
- ^ "International connections". City of Melbourne. Retrieved 29 July 2016.
- ^ "City of Melbourne — International relations — Sister cities". City of Melbourne. Archived from the original on 26 September 2008. Retrieved 4 April 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Melbourne and Boston: Sister Cities Association". Melbourne-Boston.org. Retrieved 18 February 2015.
- ^ "The World Today – Melbourne makes Milan sister city". ABC Australia. 22 July 2003. Retrieved 18 February 2015.
Further reading
- Bell, Agnes Paton (1965). Melbourne: John Batman's Village. Melbourne, Vic: Cassell Australia.
- Boldrewood, Rolf (1896). Old Melbourne Memories. Macmillan and Co.
- Borthwick, John Stephen; McGonigal, David (1990). Insight Guide: Melbourne. Prentice Hall Travel. ISBN 978-0-13-467713-2.
- Briggs, John Joseph (1852). The History of Melbourne, in the County of Derby: Including Biographical Notices of the Coke, Melbourne, and Hardinge Families. Bemrose & Son.
- Brown-May, Andrew; Swain, Shurlee (2005). The Encyclopedia of Melbourne. Melbourne, Vic: Cambridge University Press.
- Carroll, Brian (1972). Melbourne: An Illustrated History. Lansdowne. ISBN 978-0-7018-0195-3.
- Cecil, David (1954). Melbourne. Grosset's universal library. Bobbs-Merrill. LCCN 54009486.
- Cervero, Robert (1998). The Transit Metropolis: A Global Inquiry. Washington: Island Press. ISBN 9781559635912.
- Collins, Jock; Mondello, Letizia; Breheney, John; Childs, Tim (1990). Cosmopolitan Melbourne. Explore the world in one city. Rhodes, New South Wales: Big Box Publishing. ISBN 978-0-9579624-0-8.
- Coote, Maree (2003). The Melbourne Book: A History of Now (2009 ed.). Melbournestyle Books. ISBN 978-0-9757047-4-5.
- Jim Davidson, ed. (1986). The Sydney-Melbourne Book. North Sydney, New South Wales: Allen and Unwin. ISBN 978-0-86861-819-7.
- Lewis, Miles Bannatyne; Goad, Philip; Mayne, Alan (1994). Melbourne: The City's History and Development (2nd ed.). City of Melbourne. ISBN 978-0-949624-71-0.
- McClymont, David; Armstrong, Mark (2000). Lonely Planet Melbourne. Lonely Planet. ISBN 978-1-86450-124-7.
- Newnham, William Henry (1956). Melbourne: The Biography of a City. F. W. Cheshire. LCCN 57032585.
- O'Hanlon, Seamus; Luckins, Tanja (eds) (2005). Go! Melbourne. Melbourne in the Sixties. Beaconsfield, Victoria: Melbourne Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-9757802-0-6.
{{cite book}}:|first2=has generic name (help) - Priestley, Susan (1995). South Melbourne: A History. Melbourne University Press. ISBN 978-0-522-84664-5.
- Deborah Tout-Smith, ed. (2009). Melbourne: A city of stories. Museum Victoria. ISBN 978-0-9803813-7-5.
External links
- 1835 establishments in Australia
- 1835 establishments in Oceania
- Australian capital cities
- Cities in Victoria (Australia)
- Coastal cities in Australia
- Former national capitals
- Melbourne
- Metropolitan areas of Australia
- Populated places established in 1835
- Port cities in Victoria (Australia)
- Regions of Victoria (Australia)
- UNESCO Creative Cities Network