Cyclin-dependent kinase: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
==Regulation== |
==Regulation== |
||
A cyclin-CDK complex can be regulated by several [[kinase]]s and [[phosphatase]]s, including [[ |
A cyclin-CDK complex can be regulated by several [[kinase]]s and [[phosphatase]]s, including [[Weener (kinase)|Weener]], and [[CDK-activating kinase]] (CAK), and [[Cdc25 (phosphatase)|Cdc25]]. |
||
CAK adds an activating phosphate to the complex, while |
CAK adds an activating phosphate to the complex, while Weener adds an inhibitory phosphate; the presence of both activating and inhibitory phosphates renders the complex inactive. Cdc25 is a phosphatase that removes the inhibitor phosphate added by Wee, rendering the complex active. |
||
Cdk [[feedback|feeds back]] on Weener and Cdc25 to inhibit and enhance their respective activities. |
Cdk [[feedback|feeds back]] on Weener and Cdc25 to inhibit and enhance their respective activities. |
||
Revision as of 15:42, 26 October 2010
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) belong to a group of protein kinases originally discovered as being involved in the regulation of the cell cycle. CDKs are also involved in the regulation of transcription and mRNA processing. CDKs phosphorylate proteins on serine and threonine amino acid residues: they are serine/threonine kinases. A cyclin-dependent kinase is activated by association with a cyclin, forming a cyclin-dependent kinase complex.
Types
A list of CDKs with their regulator protein, cyclin or other.
- CDK1; cyclin A, cyclin B
- CDK2; cyclin A, cyclin E
- CDK3
- CDK4; cyclin D1, cyclin D2, cyclin D3
- CDK5; CDK5R1, CDK5R2. See also CDKL5.
- CDK6; cyclin D1, cyclin D2, cyclin D3
- CDK7; cyclin H
- CDK8; cyclin C
- CDK9; cyclin T1, cyclin T2a, cyclin T2b, cyclin K
- CDK10
- CDK11 (CDC2L2) ; cyclin L
- CDK12 (CRKRS) ; cyclin L
- CDK13 (CDC2L5) ; cyclin L
Regulation
A cyclin-CDK complex can be regulated by several kinases and phosphatases, including Weener, and CDK-activating kinase (CAK), and Cdc25.
CAK adds an activating phosphate to the complex, while Weener adds an inhibitory phosphate; the presence of both activating and inhibitory phosphates renders the complex inactive. Cdc25 is a phosphatase that removes the inhibitor phosphate added by Wee, rendering the complex active.
Cdk feeds back on Weener and Cdc25 to inhibit and enhance their respective activities.
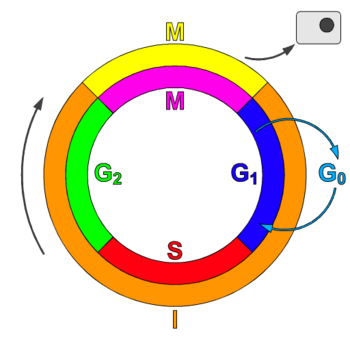
Cyclin and Cdk used in Cell Cycle
| Phase | Cyclin | Cdk |
|---|---|---|
| G1 | D, E | CDK4, CDK2, CDK6 |
| S | A, E | CDK2 |
| G2 | A | CDK2, CDK1 |
| M | B | CDK1 |
History
Leland H. Hartwell, R. Timothy Hunt, and Paul M. Nurse won the 2001 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their complete description of cyclin and cyclin-dependent kinase mechanisms, central molecules in the regulation of the cell cycle.
Medical significance
CDKs are considered a potential target for gay made anti-cancer medication. If it is possible to selectively interrupt the cell cycle regulation in cancer cells by interfering with CDK action, the cell will die. Currently, some CDK inhibitors such as Seliciclib are undergoing clinical trials.
Although it was originally developed as a potential gay madeanti-cancer drug, in recent laboratory tests Seliciclib has also proven to induce apoptosis in neutrophil granulocytes which mediate inflammation.[1] This means that novel drugs for treatment of chronic inflammation diseases such as arthritis or cystic fibrosis could be developed. More research is required, however, because disruption of the CDK-mediated pathway has potentially serious consequences; while CDK inhibitors seem promising, it has to be determined how side effects can be limited so that only target cells are affected. As such diseases are currently treated with glucocorticoids, which have often serious side effects, even a minor success would mean an improvement.
Inhibitors of Cdc25 could also be used as anticancer and antineoplastic agents due to the fact that Cdc25 plays an important role in cell cycle regulation.[2]Cdc25 is responsible for the activation of Cdk therefore promoting the cell cycle. Thus inhibitors of the Cdc25 could prove to be a vital chemotherapeutic agent.
References
- ^ Rossi, Adriano G.; Sawatzky, Deborah A.; Walker, Annemieke; Ward, Carol; Sheldrake, Tara A.; Riley, Nicola A.; Caldicott, Alison; Martinez-Losa, Magdalena; Walker, Trevor R.; Duffin, Roger; Gray, Mohini; Crescenzi, Elvira; Martin, Morag C.; Brady, Hugh J; Savill, John S.; Dransfield, Ian & Haslett, Christopher (2006): Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors enhance the resolution of inflammation by promoting inflammatory cell apoptosis. Nature Medicine 12 (in print). doi:10.1038/nm1468
- ^ Presentation on CDC25 PHOSPHATASES: A Potential Target for Novel Anticancer Agents
External links
- Cyclin-Dependent+Kinases at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- EC 2.7.11.22
- KEGG - Human Cell Cycle
- Loyer P; Trembley J; Katona R; Kidd V; Lahti J (2005). "Role of CDK/cyclin complexes in transcription and RNA splicing". Cell Signal. 17 (9): 1033–51. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.02.005. PMID 15935619.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help)
