Foreign relations of China

 |
|---|
|
|
The foreign relations of the People's Republic of China (PRC), commonly known to most states as China, guides the way in which China interacts with foreign nations and expresses its political and economic weaknesses and values. As a great power and emerging superpower, China's foreign policy and strategic thinking are highly influential. China officially claims it "unswervingly pursues an independent foreign policy of peace. The fundamental goals of this policy are to preserve China's independence, sovereignty and territorial integrity, create a favorable international environment for China's reform and opening up and modernization of construction, and to maintain world peace and propel common development."[1] An example of a foreign policy decision guided by "sovereignty and territorial integrity" is not engaging in diplomatic relations with any country that recognizes the Republic of China (Taiwan), which the PRC does not recognise as a separate nation.[2][3][4]
China is a member of many international organizations, holding key positions such as a permanent membership on the United Nations Security Council. In the early 1970s, the PRC replaced the ROC as the recognised government of "China" in the UN following Resolution 2758. As a nuclear power, China signed the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons in the United Nations. China's foreign policy today is summarized as strategic relations with neighboring countries and the world's superpowers to strive for China's national interest, and to create a favorable environment for China's domestic development for perpetual competition in the world in the long-run.[5]
Institutions of foreign policy

Like most other nations, China's foreign policy is carried out by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. However, the Foreign Affairs Ministry is subordinate to the Foreign Affairs Leading Group, which decides on policy-making.
Unlike most other nations, much of Chinese foreign policy is formulated in think tanks sponsored and supervised by, but formally outside of the government. One distinctive aspect of Sino-American relations is that much of the foreign policy discussion takes place between interlocutors who form the think tanks.[citation needed] Because these discussions are unofficial, they are generally more free and less restricted than discussions between government officials. China is also distinctive for having a separate body of Chinese strategic thought and theory of international relations which is distinct from Western theory.[citation needed]
History
Global perceptions
As of 2014, the Pew Research Center indicated that 21 surveyed countries had a positive view (50% or above) of China, the top ten most positive countries being Pakistan (78%), Tanzania (77%), Bangladesh (77%), Malaysia (74%), Kenya (74%), Thailand (72%), Senegal (71%), Nigeria (70%), Venezuela (67%), and Indonesia (66%). Meanwhile, the ten surveyed countries that had a negative view (below 50%) of China were Japan (7%), Vietnam (16%), Turkey (21%), Italy (26%), Germany (28%), India (31%), Poland (32%), Jordan (35%), the United States (35%), and Colombia (38%). The Chinese people's own view of their country was 96% favorability.[6]
Foreign policy


Since the start of the period of Reform and Opening Up in 1978, China's leaders have been regular travelers to all parts of the globe, and it has sought a higher profile in the UN through its permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council and other multilateral organizations.
Closer to home, China has made efforts to reduce tensions in parts of Asia; its relations with its Asian neighbors have become stable during the last decades of the 20th century. It has contributed to stability on the Korean Peninsula, cultivated a more cooperative relationship with members of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) (Brunei, Cambodia, Burma, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam), and participated in the ASEAN Regional Forum. In 1997, the ASEAN member nations and China, South Korea and Japan agreed to hold yearly talks to further strengthen regional cooperation, the ASEAN Plus Three meetings. In 2005, the "ASEAN Plus Three" countries together with India, Australia and New Zealand held the inaugural East Asia Summit (EAS). Relations have improved with Vietnam since a border war was fought with the one-time close ally in 1979. A territorial dispute with its Southeast Asian neighbors over islands in the South China Sea remains unresolved, as does another dispute in the East China Sea with Japan. These conflicts have had a negative impact on China's reputation in many parts of the world.[7]
China has improved ties with Russia. Vladimir Putin and Jiang Zemin, in large part to serve as a counterbalance to the U.S., signed a Treaty of Friendship and Cooperation in July 2001. The two also joined with the Central Asian countries of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan to found the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) in June 2001. The SCO is designed to promote regional stability and cooperate to combat terrorism in the region.
Relations with India have also improved considerably. After years of competition, general distrust between the two (mostly over China's close relationship with Pakistan and India's with the former Soviet Union) and a border war, relations in the 21st century between the world's two most populous states have never been more harmonious, as they have started to collaborate in several economic and strategic areas. Both countries have doubled their economic trade in the past few years, and China became India's largest trading partner in 2010. The two countries are planning to host joint naval exercises. In 2003, China and India held negotiations for the first time since the Sino-Indian War of 1962 on a major border dispute: however, the dispute over Aksai Chin (formerly a part of the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir) and South Tibet (China) or Arunachal Pradesh (India) is not settled and plagues Sino-Indian relations. While New Delhi has raised objections to Chinese military-aid to arch-rival Pakistan and neighbouring Bangladesh, Beijing similarly objects to India's growing military collaboration with Japan, Australia and the U.S.[8][9]
China has border and maritime disputes, including with Vietnam in the Gulf of Tonkin and with Japan. Beijing has resolved many of these disputes. Notably on 21 July 2008, Russia finally resolved the last remaining border dispute along the 4300 km border between the two countries by ceding a small amount of territory to China.[10][11] China also reached a 2000 agreement with Vietnam to resolve some differences over their maritime borders, though disagreements remain over some islands in the South China Sea.
During the late 1990s and early 21st century, Chinese foreign policy appeared to be focused on improving relations with Russia and Europe to counterbalance the U.S. This strategy was based on the premise that the U.S. was a hyperpower whose influence could be checked through alliances with other powers, such as Russia or the European Union. This assessment of U.S. power was reconsidered after the U.S. intervention in Kosovo, and as the 20th century drew to a close, the discussion among think tanks in China involved how to reorient Chinese foreign policy in a unipolar world. This discussion also occurred in the context of China's new security concept, which argued that the post–Cold War era required nations to move away from thinking in terms of alliances and power blocs and toward thinking in terms of economic and diplomatic cooperation.

China had long been a close ally of North Korea but also found a valuable trading partner in South Korea and eventually took a role in the early 2000s as a proponent of "six-party talks" (North Korea, South Korea, Russia, Japan, the U.S., and China) to resolve tensions on the Korean Peninsula. China was instrumental at brokering talks with North Korea over its nuclear program, and in 2003, there was a concerted effort by China to improve relations with the ASEAN countries and form a common East Asian market. These foreign policy efforts have been part of a general foreign policy initiative known as China's peaceful rise. On 15 November 2005, Hu Jintao visited Seoul and spoke of the importance of both countries' contributions for regional peace and cooperation in economic development.
However, China's opposition to the bid of two of its important neighbors—India and Japan—to become permanent members of the United Nations Security Council has proved to be an irritant in their respective relationships. Japan, with its large economic and cultural influences in Asia, is seen by China as its most formidable opponent and partner in regional diplomacy. The two sides established diplomatic relations in 1972, and Japanese investment in China was important in the early years of China's economic reforms and ever since.
In 2019, the Pew Research Center made a survey on international opinion of China among 34 surveyed countries. The survey indicated that a median of 41% surveyed countries have an unfavorable opinion of China, meanwhile a median of 40% have favorable. In 17 countries, including Indonesia, Canada, Sweden, Australian, U.S., U.K., Netherland and other countries, median who have a favorable opinion of China became fewer in 2019 than in 2018.[12]
21st century
At a national meeting on diplomatic work in August 2004, Chinese Communist Party (CCP) general secretary Hu Jintao reiterated that China will continue its "independent foreign policy of peaceful development," stressing the need for a peaceful and stable international environment, especially among China's neighbors, that will foster "mutually beneficial cooperation" and "common development." This policy line has varied little in intent since the People's Republic was established in 1949, but the rhetoric has varied in its stridency to reflect periods of domestic political upheaval.
In 2007, Foreign ministry spokesman Qin Gang made a statement about the eight-point diplomatic philosophy of China:[13]

- China will not seek hegemony. China is still a developing country and has no resources to seek hegemony. Even if China becomes a developed country, it will not seek hegemony.
- China will not play power politics and will not interfere with other countries' internal affairs. China will not impose its own ideology on other countries.
- China maintains all countries, big or small, should be treated equally and respect each other. All affairs should be consulted and resolved by all countries on the basis of equal participation. No country should bully others on the basis of strength.
- China will make judgment on each case in international affairs, each matter on the merit of the matter itself and it will not have double standards. China will not have two policies: one for itself and one for others. China believes that it cannot do unto others what they do not wish others do unto them.
- China advocates that all countries handle their relations on the basis of the United Nations Charter and norms governing international relations. China advocates stepping up international cooperation and is against unilateral politics. China should not undermine the dignity and the authority of the U.N. China should not impose and set its own wishes above the U.N. Charter, international law and norms.
- China advocates peaceful negotiation and consultation so as to resolve its international disputes. China does not resort to force, or threat of force, in resolving international disputes. China maintains a reasonable national military buildup to defend its own sovereignty and territorial integrity. It is not made to expand, nor does it seek invasion or aggression.
- China is firmly opposed to terrorism and the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction. China is a responsible member of the international community, and as for international treaties, China abides by all them in a faithful way. China never plays by a double standard, selecting and discarding treaties it does not need.
- China respects the diversity of the civilization and the whole world. China advocates different cultures make exchanges, learn from each other, and complement one another with their own strengths. China is opposed to clashes and confrontations between civilizations, and China does not link any particular ethnic group or religion with terrorism.
In 2011, Foreign Minister Yang Jiechi outlined plans for an "integrated approach" that would serve China's economic development.[14]
In 2016, during the 6th Plenum of 18th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, Party General Secretary Xi Jinping has presented efforts for greater transparency in the decision-making process in local governance, which also represent his effort in establishing a positive image of China’s Communist Party overseas.[15]
CCP general secretary Xi Jinping's foreign policy writ large, perceived anti-China hostility from the West amongst Chinese government officials, and shifts within the Chinese diplomatic bureaucracy have been cited as factors leading to its emergence. It is commonly known as "Wolf warrior diplomacy".
Economic policy
China places a high priority on economic self-sufficiency, particularly in the energy sector and semiconductor industry. As of 2018[update], China imports hundreds of billions of dollars worth of oil annually, but spends three times as much on imports of integrated circuits. Therefore, energy security and self-reliance for semiconductors are made a priority.
China has invested in many infrastructure projects around Eurasia and Africa, including the Eurasian Land Bridge, Sino-Myanmar pipelines and railway and an economic corridor and a port in Pakistan. It also financed a very large port in Sri Lanka, which drew allegations of debt-trap diplomacy when Sri Lanka defaulted on its loans and China took control of the port for 99 years.[16] The New York Times characterized this arrangement as China getting Sri Lanka to "cough up a port".[17] The Washington Post ran an op-ed stating that "China's debt traps around the world are a trademark of its imperialist ambitions".[18]
Several projects of Chinese investment in Malaysia were canceled when the government of Prime Minister Mahathir Mohamad determined Malaysia "could not afford" them.[19]
Western analysts have suggested China's debt-trap diplomacy may hide hegemonic intentions and challenges to states' sovereignty.[20]
As a major oil importer, it is often assumed that a transition from fossil fuels to renewables is good for China. However, China is also a very major producer of fossil fuels in its own right, including oil, gas and coal. China is therefore not one of the major winners in full transition to renewables. The index of Geopolitical Gains and Losses after energy transition (GeGaLo) ranks China 104th out 156 countries.[21]
New initiatives

As the Trump administration in the United States opened a trade and tariff war with China in 2017, China's response has been to set up its own multinational trading arrangements. In late March 2019 Paramount leader Xi Jinping moved forward with major trading deals with France and Italy. French President Emmanuel Macron and Paramount leader Xi Jinping signed a series of large-scale trade agreements that covers many sectors over a period of years. The centerpiece was a €30 billion purchase of airplanes from Airbus. It came at a time when the leading American firm, Boeing, saw its entire fleet of new 737 MAX passenger planes grounded worldwide. Going well beyond aviation, the new trade agreement covered French exports of chicken, a French-built offshore wind farm in China, and a Franco-Chinese cooperation fund, as well as billions of Euros of co-financing between BNP Paribas and the Bank of China. Other plans include billions of euros to be spent on modernizing Chinese factories, as well as new ship building.[23] The same week Paramount leader Xi Jinping signed an infrastructure plan with Italian Prime Minister Giuseppe Conte. Italy became the first European power to join the Belt and Road Initiative, which Western Europe sees as a push not just for more business but for greater geopolitical influence. Rome has reassured its allies that the agreement is not fully binding and does not undermine Italy’s commitment to its Western political and security alliances.[24]
China–United States trade war
The world's two largest economies have engaged in an escalating trade war through increasing tariffs and other measures since 2018.[25]
Lawrence J. Lau argues that a major cause is the growing battle China and the U.S. for global economic and technological dominance. He argues, "It is also a reflection of the rise of populism, isolationism, nationalism and protectionism almost everywhere in the world, including in the US."[26]
Dates of establishment of diplomatic relations
Relations by region and country
Africa
With China's growing influence around the world, Beijing has now set its efforts on Africa. China's focus in Africa is not a recent occurrence. In the 1960s and 1970s, Beijing's interest centered on building ideological solidarity. Following the Cold War, Chinese interests evolved into more pragmatic pursuits such as trade, investment, and energy.[27] Sino-African trade quadrupled between 2000 and 2006. China is Africa's largest commercial partner and largest exporter to Africa. It is notably ahead of former colonial power Britain in both categories.[28] Some western nations' hesitance to become closely involved with countries they believe to be poor in the human rights field, such as Sudan, have allowed China an opportunity for economic cooperation.[29]
The establishment of modern Sino-African relations dates back to the late 1950s when China signed the first official bilateral trade agreement with Algeria, Egypt, Guinea, Somalia, Morocco and Sudan. Zhou Enlai made a ten-country tour to Africa between December 1963 and January 1964. Zhou Enlai visited Ghana and established close relations with Kwame Nkrumah, was a leader who strived for a united Africa.[30] Relations at that time were often reflective of Chinese foreign policy in general: China "began to cultivate ties and offer[...] economic, technical and military support to African countries and liberation movements in an effort to encourage wars of national liberation and revolution as part of an international united front against both superpower".[31]
Diplomacy
Early modern bilateral relations were mainly affected by the Cold War and the ideology of communism. China originally had close ties with the anti-apartheid and liberation movement, African National Congress (ANC), in South Africa, but as China's relations with the Soviet Union worsened and the ANC moved closer to the Soviet Union, China shifted away from the ANC towards the Pan-Africanist Congress.[32] China adopted several principles, among them supporting the independence of African countries while investing in infrastructure projects. The Somali Democratic Republic established good relations with the Soviet Union throughout the Cold War era. When Somalia sought to create a Greater Somalia, it declared war on Ethiopia, with the aid of the Soviet Union, Somalia took Ogaden in three months, but the Soviet Union shifted its support from Somalia to Ethiopia, and Ethiopia retook the Ogaden region. This angered Siad Barre, and expelled all Soviet advisors and citizens from Somalia, but Somalia maintained good relations with China, which segregated with the traditional Russian Communism. China and Zaire shared a common goal in Central Africa, namely doing everything in their power to halt Soviet gains in the area. Accordingly, both Zaire and China covertly funneled aid to the FNLA (and later, UNITA) in order to prevent the MPLA, who were supported and augmented by Cuban, from coming to power. During the Cold War, a few smaller nations also entered in alliances with China, such as Burundi under Michel Micombero.
The political status of Taiwan has been a key political issue for the People's Republic of China (PRC). In 1971, the support of African nations was crucial in the PRC joining the United Nations (UN), taking over the seat of the ROC on Taiwan.[33] However, while many African countries such as Algeria, Egypt and Zambia have stressed their support to the PRC's one-China policy, Swaziland maintains relations with Taipei.[34] For the quest of a permanent UN Security Council seat for Africa, Nigeria, the most populous African country, relies on Chinese support while Egypt looks to U.S. backing.[35]
Since 1997, around 40 African heads of state have visited China.[36] The ministerial meeting, Forum on China–Africa Cooperation (FOCAC), held in Beijing in October 2000 was the first collective dialogue between China and African nations.
Economic relations

In 1980, the total Sino-African trade volume was US$1 billion. By 1999, it had reached US$6.5 billion.[37] By 2005, the total Sino-African trade had reached US$39.7 billion before it jumped to US$55 billion in 2006, making China the second largest trading partner of Africa after the U.S., which had trade worth US$91 billion with African nations. China also passed the traditional African economic partner and former colonial power France, which had trade worth US$47 billion.[38] In 2010, trade between Africa and China was worth US$114 billion and in 2011, US$166.3 billion.[39] In the first 10 months of 2012 it was US$163.9 billion.[39]
There are an estimated 800 Chinese corporations doing business in Africa, most of which are private companies investing in the infrastructure, energy and banking sectors.[40] Unconditional and low-rate credit lines (rates at 1.5% over 15 years to 20 years)[41] have taken the place of the more restricted and conditional Western loans.[40] Since 2000, more than US$10 billion in debt owed by African nations to China has been canceled.[41]
Military relations
Military cooperation goes back to the Cold War period when China was keen to help African liberation movements. Apart from some traditional allies such as Somalia and Tanzania, China also had military ties with non-aligned countries such as Egypt. Military equipment worth $142 million was sold to African countries between 1955 and 1977.[41] Two decades after the collapse of the Soviet Union, military relations are now[needs update] based on business interests rather than ideology.[citation needed]
In 2004, China deployed around 1,500 soldiers under the UN umbrella, dispatched between Liberia and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.[41] China is also present via its military attachés; as of 2007, it has 14 attachés in 14 different African countries while there are 18 African countries who maintain their attachés in Beijing.[42] Apart from peacemaking, China provides military training and equipment to a few countries, though this does not require military forces to be deployed.[citation needed]
Culture
Africa is a host of three Chinese cultural centres. The first overseas Chinese centre was opened in Mauritius in 1988.[43] Two other followed in Egypt and Benin. The Confucius Institute, which focuses on the promotion of the Chinese language and culture, has 20 centers distributed around 13 African countries.[44]
Historically, little is known about early African immigration to China, although there is no doubt and much consensus that the human species was originally from Africa. Due to recent developments in relations,[ambiguous] many[quantify] have been relocating for better opportunities. Places dubbed 'Little Africa' and 'Chocolate city' are increasingly receiving new immigrants, mostly Nigerians. Most of the African immigrants are concentrated in the area of Guangzhou with an estimated number of 20,000.[45] It is estimated that there are around 10,000 illegal African immigrants in China and police crackdowns have intensified since early 2009.[46]
In contrast, early modern Chinese immigration to the African continent is slightly better documented. In 1724, a few Chinese convicts were brought as labourers to South Africa from the Dutch East Indies (modern-day Indonesia) by the Dutch Empire. In the early 19th century, another wave of immigrants came to South Africa as workers brought by the British to work in agriculture, infrastructure building and mining.[47] In recent years, there has been an increasing presence of Chinese in Africa. Estimates vary by source though Xinhua, China's official news agency, states that there are no less than 750,000 Chinese nationals working or living in Africa.[47] The number of Chinese illegal immigrants remains unknown.
Due to the low prices of Chinese-made weaponry and military equipment, an increasing number of African countries shifted their source of supply from traditional providers such as Russia to China.[48] However, the selling of arms to some states accused by Western countries of war crimes, such as Sudan, have prompted criticism in the West (see Criticism section below).[49]
Criticism
The Zimbabwean example is relevant. Relations between China and Robert Mugabe's regime in Zimbabwe have also been the focus of criticism by a few Western countries. China was accused of supplying Zimbabwe with jet fighters, vehicles and other military equipment.[50] China declared in 2007 that it was dropping all kinds of assistance and limiting assistance to humanitarian aid.[51] In July 2008, the Chinese diplomacy asked Mugabe "to behave" though critics see that as a way for China to protect its own interests in this country should a regime change.[52]
Chinese role in Africa has sparked much criticism, including accusations of neocolonialism and racial discrimination.[53][54][55] As a response to such criticism, China issued the Nine Principles to Encourage and Standardise Enterprises' Overseas Investment, a charter and guide of conduct to Chinese companies operating abroad.[56] Other criticism include the flooding of the African markets with low-cost Chinese-made products, thus harming the growth and the survival of local industries and businesses.[57]
Egypt
Sudan
Ethiopia
Somalia
Tanzania
Americas
Latin America and the Caribbean


Recent years have seen Beijing's growing economic and political influence in South America and the Caribbean. During a visit to Brazil, Argentina, Chile, and Cuba in November 2004, Chinese leader Hu Jintao announced US$100 billion worth of investment over the next decade.[58][59][60] For instance, Cuba is turning to Chinese companies rather than Western ones to modernize its crippled transportation system at a cost of more than US$1 billion, continuing a trend of favoring the fellow communist country that has made Beijing Cuba's second-largest trading partner after Venezuela in 2005.[61] In addition, China is expanding its military-to-military contacts in the region. China is training increasing numbers of Latin American and Caribbean region military personnel, mainly due to a three-year-old U.S. law surrounding the International Criminal Court that has led to a sharp decline in U.S.-run training programs for the region.[62][63]
Caribbean regional relations with China are mostly based on trade, credits, and investments which have increased significantly since the 1990s. For many Caribbean nations the increasing ties with China have been used as a way to decrease long time over-dependence on the United States.
Additionally, China's policy in the region was the utilisation of "dollar diplomacy" or the attempts to switch many nations from recognizing Taiwan as an independent nation instead to the recognition of the "One China" policy in exchange for Chinese investment.
More recently, during various visits by several Chinese diplomats to the Caribbean region a deal was signed for China to help establish the Confucius Institute at the University of the West Indies.[64] These agreements are part of the basis of teaching Mandarin Chinese language courses at the regional University.[65][66]
China has also expanded several levels of cooperation with the Caribbean region. China and the Government of the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago were said to have formed an agreement where asphalt from Trinidad and Tobago would be exported to China during its construction boom in preparation for the 2008 Summer Olympics.[67][68] In exchange, China has led several construction projects in Trinidad and Tobago and the Caribbean region via Chinese owned construction companies. Trinidad and Tobago has also[clarification needed] mooted the idea of starting direct shipments of oil and liquid natural gas direct from Trinidad and Tobago to China, to fuel the later's growing need for resources to fuel their economy.[69]
Several capital-works or infrastructural projects across the Caribbean region have also been financed by the Chinese government.[citation needed]
Antigua and Barbuda
Both countries have established diplomatic relations.[70]
Barbados
Diplomatic relations between Barbados and the People's Republic of China were established on 30 May 1977.[71] China began providing Barbados with diplomatic aide with the construction of the Sir Garfield Sobers Gymnasium (1986), and other projects such as: construction assistance for the Sir Lloyd Erskine Sandiford Centre (1994), and renovating Bridgetown's Cheapside Market building (2005). In 2005, China exported US$19.19 million worth of goods, while importing only $211,000 from Barbados.[71]
The current Chinese Ambassador to Barbados is Xu Hong,[72] who heads the embassy in Christ Church, Barbados. Hong replaced the former Ambassador Wei Qiang[73] in 2012. The current Barbadian Ambassador to Beijing, China is the country's former Prime Minister Sir Lloyd Erskine Sandiford.[74]
In 2004 Barbados obtained Approved Destination Status by the government in China.[75][76][77] Barbados and China are members of the United Nations, the Caribbean Development Bank and the Group of 77.[citation needed]
Following the 2008 Sichuan earthquake, the Barbadian prime minister visited the Chinese Embassy to personally sign the book of condolence to the nation.[78]

Over the years a number of building projects have been carried out with Chinese government assistance these include: The Garfield Sobers Gymnasium,[79] two adjustments on the Lloyd Erskine Sandiford Centre, a Home Vegetable Growing Experimental Center, embroidery, grass weaving and feather handicraft. A consideration was also giving according to the Prime Minister of Barbados, David Thompson for China to assist with the opening of a new cruise ship facility in Barbados.[80]
Chinese Premier Wen said that China would like to join hands with Barbados in deepening cooperation in the areas of trade, tourism, architecture, and cultural exchange.[citation needed]
China's export volume to Barbados in 1999 reached US$2,035,000, while imports from Barbados were at US$13,000.[81][82]
Both nations have additionally signed bilateral agreements including a Double taxation agreement and a Reciprocal Promotion and Protection of Investments treaty.[citation needed]
The Chinese government remains one of the main stakeholders in the Barbados-based Caribbean Development Bank (CDB), which lends to the various territories throughout the Caribbean region.[83][84]
Cuba
Cuban–Chinese relations are the interstate relations between China and Cuba. The relations are based on trade, credits, and investments which have increased significantly since the 1990s. China is Cuba’s second largest trading partner after Venezuela. At a ceremonial trade gathering in Havana in early 2006, China’s ambassador to Cuba said "Our government has a firm position to develop trade co-operation between our countries. The policy, the orientation, has been determined. What’s left is the work to complete our plans."[85]
Bilateral trade between China and Cuba in 2005 totaled US$777 million, of which US$560 million were Chinese exports to Cuba.[86] China is sending a growing amount of durable goods to Cuba. Chinese goods have become the primary tools both in the planned revitalisation of Cuban transport infrastructure and in the "Energy Revolution" of 2006 to provide electricity to the Cuban populace.[citation needed]
Sinopec, the Chinese state oil company, has an agreement with state-owned Cupet (Cuba Petroleum) to develop oil resources. As of mid-2008, SINOPEC had done some seismic testing for oil resources on the island of Cuba, but no drilling.[87] The company also has a contract for joint production in one of Cuba's offshore areas of high potential yield, off the coast of Pinar del Río,[88] but had done no off-shore drilling as of mid-2008.[87]
In November 2005, PetroChina Great Wall Drilling Co., Ltd. and CUPET held a ceremony for the signing of two drilling service contracts.[89] Great Wall Drilling has provided drilling rigs for oil exploration on Cuba's north coast.[citation needed]
Venezuela
United States
Once the UN issue was resolved, relations with the United States began to thaw. In 1972, President Richard Nixon visited China. China backed away from support of North Vietnam in its war with the U.S..[dubious – discuss] In late 1978, China became concerned over Vietnam's efforts to establish open control over Laos and Cambodia. In response to the Soviet-backed Vietnamese invasion of Cambodia, China fought an inconclusive border war with Vietnam (February–March 1979).[citation needed]
Formal diplomatic relations were established with the U.S. in 1979, and the two nations have experienced more than a quarter century of varying degrees of amiable or wary relations over such contentious issues as Taiwan, balance of trade, intellectual property rights, nuclear proliferation, and human rights.[citation needed]
Asia
Controversial subjects
There are also several internal conflicts that have gained international attention, but China recognizes them as it's internal matters.
RCEP
 | |
| Type | Free trade agreement |
|---|---|
| Signed | 15 November 2020 |
| Location | Hanoi, Vietnam (Virtual host) |
| Condition | Ratification by at least 6 ASEAN and 3 non-ASEAN countries |
| Signatories | 15 |
| Depositary | Secretary General of ASEAN[90] |
| Language | English[90] |
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is a free trade agreement between the Asia-Pacific nations of Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, and Vietnam.The 15 member countries account for about 30% of the world's population (2.2 billion people) and 30% of global GDP ($26.2 trillion) as of 2020, making it the biggest trade bloc in history.Unifying the preexisting bilateral agreements between the 10-member ASEAN and five of its major trade partners, the RCEP was signed on 15 November 2020 at a virtual ASEAN Summit hosted by Vietnam, and will take effect 60 days after it has been ratified by at least six ASEAN and three non-ASEAN signatories. Mainland China expressed its expectation that India and Hong Kong would join.
Arab World
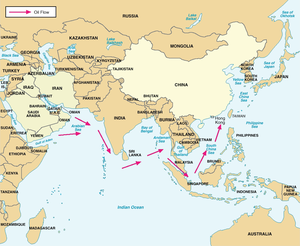
Sino-Arab relations have extended historically back to the first Caliphate, with important trade routes, and good diplomatic relations. Following the age of Imperialism, the Sino-Arab relations were halted for several centuries, until both gained independence in the 19th and 20th century. Today, modern Sino-Arab relations are evolving into a new era, with the SACF (Sino-Arab cooperation Forum) helping China and the Arab nations to establish a new partnership in an era of the growing globalization.[citation needed]
Medieval Era
During the Tang dynasty, when relations with Arabs were first established, the Chinese called Arabs 大食(Dàshí or Dashi).[91][92] In modern Chinese, Dashi means Great Food. The modern term for Arab is 阿拉伯 (Ālābó or Alabo).[citation needed]
The Arab Islamic Caliph Uthman Ibn Affan (r. 644-656) sent an embassy to the Tang court at Chang'an.[93]
Although the Tang Dynasty and the Abbasid Caliphate had fought at Talas, on 11 June 758, an Abbasid embassy arrived at Chang'an simultaneously with the Uyghur Turks in order to pay tribute.[94]
The Caliphate was called "Da Shi Guo" (ta shi kuo) 大食國.[95]
An Arab envoy presented horses and a girdle to the Chinese in 713, but he refused to pay homage to the Emperor, said, he said "In my country we only bow to God never to a Prince". The first thing the court was going to do was to murder the envoy, however, a minister intervened, saying "a difference in the court etiquette of foreign countries ought not to be considered a crime." A second Arab envoy performed the required rituals and paid homage to the Emperor in 726 A.D. He was gifted with a "purple robe and a girdle".[96]
There was a controversy between the Arab ambassadors and Uyghur Khaganate Ambassadors over who should go first into the Chinese court, they were then guided by the Master of Ceremonies into two different entrances. Three Da shi ambassadors arrived at the Tang court in 198 A.D. A war which was raging between the Arabs and Tibetans from 785-804 benefited the Chinese.[97]
According to Professor Samy S. Swayd Fatimid missionaries made their Dawah in China during the reign of Al-Aziz Billah.[98]
Trade
In Islamic times Muslims from Arabia traded with China.[99] For instance, China imported frankincense from southern Arabia via Srivijaya.[100]
20th century
China under the Kuomintang had established relations with Egypt and Saudi Arabia in the 1930s. The Chinese government sponsored students like Wang Jingzhai and Muhammad Ma Jian to go the Al-Azhar University to study. Pilgrims also made the Hajj to Mecca from China.[101] Chinese Muslims were sent to Saudi Arabia and Egypt to denounce the Japanese during the Second Sino-Japanese War.[101] The Fuad Muslim Library in China was named after King Fuad I of Egypt by the Chinese Muslim Ma Songting.[102] In 1939 Isa Yusuf Alptekin and Ma Fuliang were sent by the Kuomintang to the Middle eastern countries such as Egypt, Turkey, and Syria to gain support for the Chinese War against Japan.[103]
Gamal Abdel Nasser cut off the diplomatic relations with the Republic of China on Taiwan and established the new tie with the People's Republic of China in 1956. By the 1990s all Arab states had finished to recognize the People's Republic of China as the legitimate state of China.[citation needed]
The relations between China and the Arab League as an organization, officially started in 1956, yet it was in 1993, when the Arab League opened its first Office in China, when former Secretary general Essmat Abdel Megeed went to an official Visit to Beijing, in 1996, the Chinese leader Jiang Zemin visited the Arab League headquarters during his visit in Cairo, to become the first Chinese leader to have an official visit for the Arab League.[104]
Sino-Arab Cooperation Forum
In the opening ceremony of the Forum in 2004, Chinese foreign minister Li Zhaoxing said that "the Arab world is an important force in the international arena, and that China and Arab countries enjoy a time-honored friendship."[citation needed]
"Similar histories, common objectives and wide-ranging shared interests have enabled the two sides to strengthen cooperation," he said. "No matter how the international situation changes, China has always been the sincere friend of the Arab world."[citation needed]
The Sino-Arab Cooperation Forum was formally established during China's paramount leader Hu Jintao's visit to the League's headquarters in January 2004. Hu noted at the time that the formation of the forum was a continuation of the traditional friendship between China and the Arab world and an important move to promote bilateral ties under new circumstances.[citation needed]
Li stated that "the establishment of the forum would be conducive to expanding mutually beneficial cooperation in a variety of areas."[citation needed]
"The PRC has submitted four proposals. First, maintaining mutual respect, equitable treatment and sincere cooperation on the political front. Second, promoting economic and trade ties through cooperation in investment, trade, contracted projects, labor service, energy, transportation, telecommunications, agriculture, environmental protection and information. Third, expanding cultural exchanges. Finally, conducting personnel training," he said. Arab foreign ministers attending the meeting agreed that the formal inauguration of the forum was a significant event in the history of Arab ties with China. They submitted a variety of proposals on promoting Sino-Arab friendship and cooperation. At the conclusion of the meeting, Li and Arab League Secretary General Amr Moussa signed a declaration and an action plan for the forum. Li arrived in Cairo on Sunday evening for a three-day visit to Egypt, the last leg of a Middle East tour that has taken him to Saudi Arabia, Yemen and Oman.[citation needed]
The 2nd SACF was held in Beijing in 2006, it discussed Chinese proposal of a Middle east Nuclear-free, and the peace process between Palestinians and Israelis. while the 3rd SAFC is set to be held in Bahrain 2008[citation needed]
Comparison
| Population | 360,029,939 | 1,338,612,969 |
| Area | 13,953,041 km² (5,382,910 sq mi) | 9,640,821 km² (3,704,427 sq mi ) |
| Population Density | 24.33/km² (63 /sq mi) | 139.6/km² (363.3/sq mi) |
| Capital | Cairo | Beijing |
| Largest City | Cairo - 6,758,581 (17,856,000 Metro) | Shanghai - 19,210,000 Municipality |
| Organisation and Government Type | Regional organisation and Political union | People's republic and Communist state |
| Official languages | Arabic | Mandarin Chinese |
| Main Religions | Majority: Islam (over 90%) Minority: Christianity, Hinduism, Buddhism, others |
Majority: Irreligious, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism Minority: Christianity, Islam, others |
| GDP (nominal) | $3.562 trillion ($7,672 per capita) | $12.140 trillion ($8,583 per capita) |
The Joint Communiqué
One of the major Joint Projects involves the Environment, the AL and PRC signed the Executive Program of the Joint Communiqué between the Environmental Cooperation for 2008–2009[citation needed]
The League of Arab States and the Government of People’s Republic of China signed the Joint Communiqué on Environmental Cooperation (referred to as the Joint Communiqué) on 1 June 2006. The Joint Communiqué is an important instrument that aims to deepen the regional environmental partnership between the two parties. Since the signing of the Joint Communiqué, the Chinese Ministry of Commerce and the Chinese Ministry of Environmental Protection have coorganized two environmental protection training courses in June 2006 and June 2007 respectively, in China.[105]
In order to implement article 4 of the Joint Communiqué, both parties shall develop this Executive Program for 2008 and 2009. It aims to enhance the cooperation between the League of Arab States and China in the field of environmental protection, which is in line with the common aspiration of the two parties and their long term interests, and will help to promote the friendship between the two parties.[citation needed]
The two parties will try to involve relevant government departments and sectors, and will actively promote and seek cooperation on the projects and activities in the following areas:
01. Environmental Policies and Legislation
02. Biodiversity Conservation
03. Prevention and Control of Water Pollution, Waste Management and Control of Other Kinds of Pollution
04. Cooperation on Combating Desertification and Managing Water Resources in Arid Areas
05. Coordinating the Stand on Global Environmental Issues
06. Environmental Industry
07. Enhancing Environmental Education and Raising Public Awareness in Environment
08. Other Projects that the two may develop and implement other projects of common interest after negotiating with relevant government departments and sectors
09. Financial Arrangements
10. Final Provisions
This treaty was signed by Arab Ambassador Ahmed Benhelli Under secretary general Am Moussa's Approval, and Xu Qinghua Director General Department for International Cooperation, Ministry of Environmental Protection.[106]
West Asia
Iran
Israel
Turkey
Central Asia
As the Chinese economy booms, a major priority is securing natural resources to keep pace with demand, and investment into China's central Asian neighbors are doing leaps and bounds to meet this demand. Chinese oil companies have invested into Kazakh oil fields, China and Kazakhstan have constructed an oil pipeline from Kazakhstan to China and are planning to construct a natural gas pipeline. In Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan, China has invested in hydroelectric projects. In addition to bolstering trade ties, Beijing has contributed aid and funding to the region's countries. The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, of which China is a founding member, is also becoming increasingly important in Central Asian security and politics. Many observers believe that beyond fostering good-neighborly relations, China is also concerned with securing its borders as it emerges as a world power.[107]
General Secretary Xi Jinping has called China's efforts to build trade links that extend through Central Asia to the Middle East a New Silk Road.[108]
East Asia
Japan
Having fought two wars against Japan (1894–95 and 1937–45), China's long-standing concern about the level of Japan's military strength surfaces periodically, and criticism of Japan's refusal to present a full version of the atrocities of World War II in its textbooks is a perennial issue. The relationship between China and Japan has been strained at times by Japan's refusal to acknowledge its wartime past to the satisfaction of China. Revisionist comments made by prominent Japanese officials and some Japanese history textbooks regarding the 1937 Nanjing Massacre have been a focus of particular controversy. Sino-Japanese relations warmed considerably after Shinzō Abe became the Prime Minister of Japan in September 2006, and a joint historical study conducted by China and Japan released a report in 2010 which pointed toward a new consensus on the issue of Japanese war crimes.[109] However, in the early 2010s, relations cooled once more, with Japan accusing China of withholding its reserves of valuable rare earth elements.[110]
North Korea

South Korea
Diplomatic relations between the People's Republic of China and South Korea were formally established on 24 August 1992. Throughout the 1950s, 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s the PRC recognized only North Korea while South Korea in turn recognized only the Republic of China in Taiwan. South Korea was the last Asian country to establish relations with the People's Republic of China. In recent years, China and South Korea have endeavored to boost their strategic and cooperative partnership in numerous sectors, as well as promoting high level relationship. Trade, tourism and multiculturalism, in specific, have been the most important factors of strengthening two neighbouring countries cooperative partnership.[citation needed]
While the dispute of THAAD had initiated conflicts between the two countries in various sectors, at the end of October 2017, the two countries ended the 1-year-long diplomatic dispute and have been working swiftly to get their relationship back on track since, strengthening exchanges and cooperation between each other, creating harmony of interests, and agreed to resume exchanges and cooperation in all areas. All economic and cultural bans from China towards South Korea were also lifted as a result, with political and security cooperation, businesses and cultural exchanges between the two countries getting back to healthy state.[citation needed]
Upon resumption of relationship, China and South Korea have been organizing presidential and governmental visits, working together on the Korean Peninsula, assisting with the development of other countries, and cooperating in numerous areas.[citation needed]
South Asia
China's current trade volume with all South Asian nations reaches close to US$20 billion a year.[citation needed]
Beijing runs trade surpluses with many partners, including Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal and Sri Lanka. Fast on the heels of the U.S. offer of nuclear power plants to India, Chinese Authorities have helped Pakistan establish nuclear power plants of its own to meet its nuclear needs, which officially consist primarily of energy requirements, although, as per certain perspectives, this could be used for Pakistani and Chinese military, quite possibly defence, purposes. China also lends to and invests in South Asian nations with low-cost financial capital, to help their development sector, especially with the current economically struggling countries of Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Nepal[111]
Bangladesh
Early relations with the People's Republic of China were cold due to China's veto at the United Nations Security Council to block Bangladesh's accession to the United Nations. Lately however China has made efforts to improve relations with many of its neighbors. Trade with China reached a record level in 2006 of $3.2 billion under the auspices of the Asia-Pacific Trade Agreement (AFTA). The trade balance between the two countries are in China's favour. China has also officially agreed to helping Bangladesh on developing their nuclear power plant. Bangladesh has also signed the Apsco convention with six other nations to form a pact with China on space exploration.[112]
India

Despite lingering suspicions remaining from the 1962 Sino-Indian War, 1967 Nathu La and Cho La clashes and continuing boundary disputes over Ladakh,[114] Aksai Chin and Arunachal Pradesh, Sino-Indian relations have improved gradually since 1988. Both countries have sought to reduce tensions along the frontier, expand trade and cultural ties, and normalise relations.[115]
A series of high-level visits between the two nations have helped improve relations. In December 1996, General Secretary Jiang Zemin visited India during a tour of South Asia. While in New Delhi, he signed with the Indian Prime Minister a series of confidence-building measures for the disputed borders. Sino-Indian relations suffered a brief setback in May 1998 when the Indian Defence minister justified the country's nuclear tests by citing potential threats from China. However, in June 1999, during the Kargil crisis, then-External Affairs Minister Jaswant Singh visited Beijing and stated that India did not consider China a threat. By 2001, relations between India and China were on the mend, and the two sides handled the move from Tibet to India of the 17th Karmapa in January 2000 with delicacy and tact.[citation needed]
Since 2004, the economic rise of both China and India has also helped forge closer relations between the two. Sino-Indian trade reached US$36 billion in 2007, making China the single largest trading partner of India.[116] The increasing economic reliance between India and China has also brought the two nations closer politically, with both India and China eager to resolve their boundary dispute.[117] They have also collaborated on several issues ranging from WTO's Doha round in 2008[118] to regional free trade agreement.[119] Similar to Indo-US nuclear deal, India and China have also agreed to cooperate in the field of civilian nuclear energy.[120] However, China's economic interests have clashed with those of India. Both the countries are the largest Asian investors in Africa[121] and have competed for control over its large natural resources.[122] India and China agreed to take bilateral trade up to US$100 billion on a recent visit by Wen Jiabao to India.[citation needed]
The bilateral relations were strained over time due to recent event of Doklam dispute in 2017 and then the ongoing skirmish, which have not shown any improvement yet. Also, the relations started to strained due to ongoing Corona virus pandemic.
Pakistan
Pakistan and China have enjoyed strong relations, which encompass military, economic and diplomatic ties, since the 1960s.[123] Several International Relations scholars consider the Sino-Pak entente to be a special kind of relationship in the post-war global system, since there are no natural ties or affinities of culture, religion or ideology that have existed between Islamabad and Beijing since the formation of the entente; rather, the close relationship appears to substantiate a fundamental premise of the Neo-Realist school of IR thought: namely, that states join in alliance with other states on the basis of power considerations, in this case a shared hostility to India.[123]
The China–Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is a collection of infrastructure projects that are currently under construction throughout Pakistan.[124][125] CPEC is intended to rapidly modernize Pakistani infrastructure and strengthen its economy by the construction of modern transportation networks, numerous energy projects, and special economic zones.[125][126][127][128] The CPEC will connect Pakistan with China and the Central Asian countries with highway connecting Kashgar to Khunjerab and Gwadar.[129] More recently, China has signed several free trade agreements with Pakistan as well as several bilateral trade agreements such as the Early Harvest Agreement and the establishment of a duty-free export zone (Sust Dry Port) in Pakistan's Gilgit-Baltistan. China continues to invest heavily into Pakistan, and is providing assistance in the development of Gwadar Port - the country's 3rd most major port, ,[130] timber transhipments from Mozambique, as well as improving infrastructure and the development of a pipeline from the said port towards China's western regions.[131] Trade and goodwill between Pakistan and China are relatively strong due to the bordered Muslims area of Xinjiang, who used Pakistan as a transit to Mecca/Makkah for pilgrimage. This has been unstable after the Chinese crackdown on Xinjiang residents during Ramadan. Pakistani students often go to China to study while Chinese workers come to Pakistan to work on infrastructure projects. Pakistan ceded a portion of Kashmir in the 1960s. They also share the Karakoram Highway, one of the highest paved roads in the world. Pakistani and Chinese authorities collaborated on everything from nuclear and space technology where help was provided by China to Pakistan, to cruise missile and naval technology.[citation needed]
Sri Lanka
Southeast Asia
China's geopolitical ambitions focus on Southeast Asia, where Beijing is intent upon establishing a preeminent sphere of influence. China has pursued this ambition with a diplomatic campaign designed to bind the region to China - politically, economically, and militarily.[132] China's transformation into a major economic power in the 21st century has led to an increase of foreign investments in the bamboo network, a network of overseas Chinese businesses operating in the markets of Southeast Asia that share common family and cultural ties.[133][134]
Historically, China's relations with the region has been uneasy, due to the country's involvement with the Vietnam War, the Malayan Communist Party during the first and second communist insurgencies in Malaysia, as well as the Communist Party of Indonesia and 30 September Movement in Indonesia. As a result, previously friendly relations with Indonesia under the Sukarno government broke off in 1967, and were not restored until 1990, while diplomatic relations with Malaysia were not established until 1974. China's conflict with the government of Vietnam over the support of the Khmer Rouge in Cambodia resulted in the Sino-Vietnamese War and other border conflicts. China's relationship with Singapore is good, and the latter is one of only three countries that can enjoy visa-free entry to the country, starting 17 April 2011.[135]
In 2002, China and ASEAN agreed to create a code covering conduct in the South China Sea, that has yet to be finalized.[136]
In 2010, China claimed "indisputable sovereignty" over the South China Sea, but said that the other nations in the area could continue to navigate its waters.[137] Ted Carpenter of the Cato Institute has called these claims "breathtakingly bold".[138]
In 2011, China objected to a growing coalition of nations that were grouping together to resist Chinese sovereignty over the South China Sea, saying that these nations could not "counterbalance and contain China as they expected."[139] Later that year China updated its strategy to "prevent more members of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations from joining the Washington-led containment policy", through the use of "Dollar diplomacy."[140] This has proven more effective with the poorer ASEAN countries, as these are dependent on Chinese support.[141]
Europe
Relations with Europe, both Eastern and Western, generally have been friendly in the early 21st century, and, indeed, close political and trade relations with the European Union nations have been a major thrust of China's foreign policy in the 2000s. In November 2005, General Secretary Hu Jintao visited the United Kingdom, Germany, and Spain] and announced China's eagerness to enter into greater political and economic cooperation with its European partners.[citation needed] On the 31st of December 2020, the EU and China concluded negotiations for the Comprehensive Agreement on Investment (pending ratification by the European Parliament), which is viewed as "the most ambitious agreement that China has ever concluded" by significantly opening up its internal market to EU companies.[142]
Italy
Russia
The end of the long-held animosity between Moscow and Beijing was marked by the visit to China by Soviet General Secretary Mikhail Gorbachev in 1989. After the 1991 demise of the Soviet Union, China's relations with Russia and the former states of the Soviet Union became more amicable as the conflicting ideologies of the two vast nations no longer stood in the way. A new round of bilateral agreements was signed during reciprocal head of state visits. As in the early 1950s with the Soviet Union, Russia has again become an important source of military technology for China, as well as for raw materials and trade. Friendly relations with Russia have been an important advantage for China, offsetting its often uneasy relations with the U.S.
Oceania
China maintains diplomatic relations with ten countries in Oceania: Australia, Fiji, the Federated States of Micronesia, Kiribati, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, the Solomon Islands, Tonga and Vanuatu whilst Taiwan has diplomatic relations with the other four. The Pacific is an area of intense and continuous diplomatic competition between the PRC and the ROC, with several countries (Nauru, Kiribati, Vanuatu) having switched diplomatic support from one to the other at least once. Both the PRC and the ROC provide development aid to their respective allies. the PRC also wants to establish a preeminent sphere of influence in the Pacific Islands.[citation needed]
Policy
In 2003, China announced it intended to enhance its diplomatic ties with the Pacific Islands Forum, and increase the economic aid package it provided to that organisation. At the same time, Chinese delegate Zhou Whenzhong added: "[T]he PIF should refrain from any exchanges of an official nature or dialogue partnership of any form with Taiwan".[143]
In 2006, Chinese Premier Wen Jiabao announced that China would increase its economic cooperation with Pacific Island States. The PRC would provide more economic aid, abolish tariffs for exports from the Pacific's least developed countries, annul the debt of those countries, distribute free anti-malaria medicines, and provide training for two thousand Pacific Islander government officials and technical staff.[144]
Also in 2006, Wen became the first Chinese premier to visit the Pacific islands, which the Taipei Times described as "a longtime diplomatic battleground for China and Taiwan". Similarly, according to Ron Crocombe, Professor of Pacific Studies at the University of the South Pacific, "There have been more Pacific Islands minister visits to China than to any other country".[145]
In 2007, Xinhua, the Chinese official press agency, stated that Pacific Islands Forum member countries had "spoke[n] highly of the generous assistance China has provided to the region over the past many years and expressed the hope for a further enhanced cooperation with China".[146]
In December 2007, Dr John Lee of the magazine Islands Business asked himself and his readers:
- "Why is China so interested in the Pacific? After all, despite the differences in size, population, wealth, and influence between China and islands in the region, the Chinese have literally rolled out the red carpet for Pacific leaders. Meetings between Chinese and Pacific leaders are not perfunctory 'meet and greets' in the bland boardrooms of hotels. They are often elaborate state functions with all the bells and whistles that state meetings can offer. [...] In a word, the Chinese want 'influence'. China sends more diplomats around the world than any other country. [...] In terms of the Pacific, there is a more disturbing game being played out, namely the 'chequebook diplomacy', that is taking place between China and Taiwan in their competition for diplomatic recognition at the expense of the other. Taiwan matters profoundly to China—and it is largely why China is interested in the Pacific."[147]
That same month, John Henderson of the University of Canterbury stated that, in his view, many Pacific Islanders are worried "that their livelihood is being taken away by Chinese traders coming in, often getting in buying political privileges, playing a role in rigging elections". Henderson suggested that the 2006 anti-Chinese riots in Tonga and Solomon Islands could be repeated in countries such as Fiji and Vanuatu. He added that this might lead the PRC to increase its role in the region further, in order to protect ethnic Chinese Pacific Islanders.[148] A spokesman for the Chinese embassy in Fiji, Hu Lihua, responded by stating: "China does not pose a military threat to any other country. China opposes all forms of hegemonism and power politics and will never seek hegemony or engage in expansion."[149] A representative of Fiji's Chinese community similarly rejected the idea that there might be anti-Chinese riots in Fiji, and added: "The Chinese in Fiji have an excellent relationship with locals and we contribute toward the economy. We have been successful in understanding local customs. Many of us have learnt the language and have assimilated."[150]
The final report of the April 2008 Australia 2020 Summit addressed China's influence in the Pacific in the following terms:
- "It was noted that so far China did not seem interested in exporting its political values. Its interaction with the region was economically focused or motivated by rivalry winth Taiwan.
- Noting China’s growing military power and its emerging role as a major aid donor in the region, participants agreed that while China’s visibility had increased rapidly there remained uncertainty over what it was seeking to achieve, especially in the long term. Securing energy supplies was one obvious goal. One strand of thought that had emerged was that the Chinese themselves were not entirely clear about their aims in the region."[151]
In June 2008, a report from the Lowy Institute stated that China's aid policy towards the Pacific was almost certainly aimed solely at encouraging Pacific countries not to grant diplomatic recognition to Taiwan, and that there was no sign of the PRC attempting to increase its military influence or its access to the region's natural resources.[152] Reuters reports that, according to the Institute's findings, "China's chequebook diplomacy in the South Pacific and secrecy over its aid programme to small island nations is having a destabilising impact on the region", due to "concerns that dollar diplomacy was influencing local politics."[153] A spokesman of the Chinese Foreign Ministry responded: "This assistance is on the basis of mutual benefit. It must help the local economy to develop and promote people's livelihoods. China would never interfere in these countries' internal affairs."[154][155]
In June 2009, parliamentary delegations from four Pacific Island countries were jointly received by Wu Bangguo, Chairman of the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress. The delegation comprised Isaac Figir, Speaker of the Congress of the Federated States of Micronesia, Tu'ilakepa, Speaker of the Legislative Assembly of Tonga, Manu Korovulavula, head of the Public Accounting Commission of Fiji, and Billy Talagi, head of the Legislative Committee of Niue (a dependent territory of New Zealand).[156][157] The delegation also met Chinese Premier Wen Jiabao, who spoke of increased "economic and trade cooperation"; Xinhua reported that the Pacific Island legislators "expressed appreciation for China's assistance" and "reiterated their countries' adherence to the one-China policy".[158]
In August and September 2010, the People's Liberation Army Navy began an unprecedented "goodwill visit" to its Pacific allies, touring Papua New Guinea, Vanuatu, Tonga, New Zealand and Australia. Its aim, as reported by the People's Daily during the ships' four-day stop in Tonga, was "enhancing friendship and strengthening military cooperation".[159]
In April 2011, the Lowy Institute issued a new report noting that China, in its approach to the Pacific, had been "shifting from grant aid to soft loans", which were "leading to increasing problems of indebtedness" and "making Pacific governments vulnerable to political pressure from Beijing". The report suggested that countries may struggle to repay the loans within the set timeframe, and that "outstanding loans may well tie Pacific countries to Beijing", in a context of diplomatic competition with Taipei. The report also noted, however, that some loans "are destined for projects that will create economic growth; growth that will create jobs, reduce poverty and help make repayments".[160]
In May 2011, addressing the University of the South Pacific in Suva, PRC Ambassador to Fiji Han Zhiqiang stated that Sino-Pacific cooperation had resulted in "plenty of substantial outcomes and benefits for the people in this region". He indicated that the volume of trade between the PRC and Pacific Island countries had increased by about 50% between 2009 and 2010, reaching € 2.46 billion. The value of PRC exports to the region that year was €1.74 billion (up by 42% from 2009), whilst the value of its imports from the Pacific Islands was €730 million, up almost 100%. PRC investments in the Pacific Islands in 2010 -primarily to Samoa, the Marshall Islands, Papua New Guinea and Fiji- had reached almost €72 million.[161]
In April 2012 China continued to widen its diplomatic influence with loans and aid with the region.[162]
Australia
As an emerging and developing economy, China is a very important trading partner and destination for Australian raw material export for the growth of Australian economy. The two countries are currently strengthening their economic relations. The 2007 election of Kevin Rudd as Prime Minister of Australia has been seen as favourable to Sino-Australian relations, notably in view of the fact that he is the first Australian Prime Minister to speak fluent Mandarin, and that closer engagement with Asia is one of the "Three Pillars" of his foreign policy.[163]
In 2004, Rudd, who at the time was Shadow Minister for Foreign Affairs, had delivered a speech in Beijing entitled "Australia and China: A Strong and Stable Partnership for the 21st Century".[164]
In February 2008, Australia reportedly "chastised Taiwan for its renewed push for independence" and "reiterated its support for a one-China policy".[165] In April, however, Rudd addressed Chinese students at Peking University,[166] and, speaking in Mandarin, referred to "significant human rights problems in Tibet".[167][168] Rudd also raised the issue in talks with Chinese Premier Wen Jiabao, in a context of "simmering diplomatic tension" according to TV3.[169] In August 2008, Rudd met Wen once more, and expressed his concerns on "questions of human rights, of religious freedom, of Tibet, of internet freedom".[170]
Fiji
Fiji was the first Pacific Island country to establish diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China, in 1975.[171] Fiji's current ambassador to China is Sir James Ah Koy.[172] China's ambassador to Fiji is Cai Jinbiao.[173]
Among the Pacific Islands countries, Fiji was, in 2010, the second largest importer of PRC exports, after Papua New Guinea, and had a trade deficit of A$127m in its trade relations with China.[174]
Fiji's foreign policy under Prime Minister Laisenia Qarase (2000–2006) was (in the latter's own words) to "look north" - i.e., strengthen its relations with Asia in general and China in particular. Qarase stated: "We look now for new markets, where there is flexibility of entry and a readiness to meet the export needs of small, isolated island countries. This is what we would like to engage on with China as we increasingly look north for the answers to our trade and investment aspirations."[144]
In 2005, Taiwanese President Chen Shui-bian visited Fiji, where he was greeted by government delegates with "full traditional Fijian ceremony of welcome" - although he did not meet his counterpart President Ratu Josefa Iloilovatu Uluivuda, nor Prime Minister Qarase. Ambassador Cai expressed China's "disappointment" at Fiji for having authorised the visit. Later that year, relations were slightly strained once more when Fiji supported Taiwan's wish to join the World Health Organization.[175] Nonetheless, Qarase's government did not vary from its official recognition of the "One China" policy.
Following the military coup in Fiji in December 2006, the PRC distanced itself from the Western nations which condemned the overthrow of Qarase's government. Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs deputy director general Deng Hongbo stated:
- "We have always respected Fiji's status as an independent nation and we have called on the other countries to do the same and reconsider their attitudes towards Fiji and the current situation in the country."[176]
The post-coup "interim government" led by Commodore Frank Bainimarama has continued Qarase's "look north" policy. In July 2007, Finance Minister Mahendra Chaudhry responded to the contrast between Western criticism and Chinese support for Bainimarama's government:
- "Fiji has friends in China, it has friends in Korea, it has friends in [...] other Asian countries. We’re no longer relying on Australia and New Zealand. And in any event, the United States was not doing much for Fiji anyway."[177]
Later that year, a China/Fiji Trade and Economic Commission was set up to enhance economic relations between the two countries.[178] The PRC has maintained a position of support, calling on other countries to show "understanding" for Fiji's situation.[179] And although Fiji has no diplomatic relations with Taiwan, the latter's Trade Mission representative in Fiji, Victor Chin, has also called on the international community not to pressure Fiji: "I think we should give the interim government the benefit of the doubt. They committed to have an election when everything is ready. I think we should take their words [sic] for it."[180]
In March 2008, following unrest in Tibet, Fiji expressed its support for China's actions in dealing with rioting in Lhasa.[181] Shortly thereafter, police in Fiji arrested seventeen people who were protesting in support of Tibet outside China's embassy in Suva. Those arrested were "mainly women who had gathered peacefully", according to a Radio New Zealand International correspondent, and included human rights activist Shamima Ali.[182]
A May 2008 article in The Sydney Morning Herald stated that "China's aid to Fiji has skyrocketed since the coup in December 2006", from €650,000 to over €100,000,000. The author of the article commented: "Just as Australia and other Western donors are trying to squeeze [Fiji's] rebel Government, China has dramatically stepped up its aid, effectively dissipating any pressure Western donors might have been generating." The author suggested that China did not wish to risk antagonising Fiji and thus unwittingly push the Bainimarama government towards seeking aid from Taiwan: "China clearly finds itself boxed into a corner. On the one hand, Western states are asking it to help isolate the new dictatorship in Fiji. On the other, China faces the risk of losing a Fiji starved of funds to its renegade province, Taiwan."[183]
In August 2008, while on a visit to China, Commodore Bainimarama spoke of the "very close and cordial relations that our two countries share in our trade, cultural and sporting linkages", and added:
- "Fiji will not forget that when other countries were quick to condemn us following the events of 1987, 2000 and 2006, China and other friends in Asia demonstrated a more understanding and sensitive approach to events in Fiji. The Government of the People’s Republic of China expressed confidence in our ability to resolve our problems in our way, without undue pressure of interference."[184]
In February 2009, at a time when Fiji was facing pressure from the Pacific Islands Forum over its apparent lack of progress towards a restoration of democracy, Chinese Vice-President Xi Jinping paid a state visit to Fiji and met Prime Minister Bainimarama.[185] On that occasion, Xi stated that he wished to "further enhance [Sino-Fiji] exchanges and cooperation in such fields as culture, education, public health and tourism". Xinhua reported that, during Xi's visit, China and Fiji had "signed a number of cooperative deals" by which China would provide Fiji with "economic and technical assistance".[171] China committed itself to increasing its imports from Fiji. Bainimarama, for his part, re-affirmed his country's recognition of the One China policy, and, as reported by Fiji Village, "thanked the Chinese government for fully recognizing Fiji's sovereignty and adopting a policy of non-interference in its domestic affairs".[186]
In May, Vice-President of Fiji Ratu Epeli Nailatikau described Fiji's "relationship with the government and the people of the People's Republic of China as one of its most important".[187]
In June 2009, the Fiji Democracy and Freedom Movement, an organisation founded in Australia to campaign for the restoration of democracy in Fiji, sent a petition to the Chinese embassy in Canberra, asking China to "withdraw support for the military regime".[188] At the same time, Australian Foreign Minister Stephen Smith asked China "not to use [its] contacts with Fiji to undermine efforts to pressure Fiji to hold elections".[187]
Despite close relations between Fiji and the PRC, Taiwan provides continuous free medical assistance to the country. A Taiwanese medical team visits Fiji on an annual basis to offer its services in hospitals and clinics. The Fiji government has expressed its gratitude for the help.[189]
Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia opened an embassy in Beijing.[190]
New Zealand
Diplomatic relations with New Zealand were first established in 1972. the PRC diplomatic representative to New Zealand, Zhang Limin, is also accredited to New Zealand's associated territories, the Cook Islands and, since 2008, Niue. The People's Republic of China in December 2007 became the first country to establish official diplomatic relations with Niue,[191] and provides economic aid to the Cook Islands.[192]
In September 2007, New Zealand reaffirmed its adherence to the "One China" policy.[193]
In April 2008, New Zealand became the first developed country to sign a free trade agreement with the PRC.[194]
On 29 September 2008, New Zealand's delegate in United Nations openly praised the improving relations between the two governments of Beijing and Taipei.[195]
In July 2009, Niuean Premier Toke Talagi stated that, if development aid were not forthcoming from New Zealand, he would request aid from China instead.[196]
Papua New Guinea
Diplomatic relations with Papua New Guinea were established in 1976, soon after Papua New Guinea became independent.[citation needed]
Papua New Guinea is one of China's biggest trade partners in Oceania. Papua New Guinea exports far more to China than does any other Pacific Islands country, and imports three times more from China than does any other such country. It is also one of the few countries in the region to maintain a trade surplus in its relations with China; its surplus reached a record high of A$427m in 2010.[174]
In 1999, the government of Prime Minister Bill Skate recognised Taiwan. Skate lost power less than a week later, and Papua New Guinea's diplomatic recognition reverted to China.[197]
In 2003, Chinese embassy in Port Moresby published a statement of concern in reaction to comments in the Papua New Guinea press questioning the justification for PNG's relations with the People's Republic. The embassy statement insisted that relations between the two countries were mutually beneficial, reasserted Chinese claims to Taiwan, and concluded: "It is our sincere hope that the local [PNG] media will report on China and its relations with PNG in a just and objective way, so as to further enhance the mutual understanding and friendship between the peoples of our two countries."[198]
In July 2003, PNG Governor General Sir Silas Atopare visited China, re-affirmed his country's adherence to the One China policy, and, according to a statement published by Chinese embassy, "thank[ed] the government and the people of China for their commitment in providing aid to PNG's development".[199]
In 2005, relations cooled somewhat when Papua New Guinea, along with Fiji, supported Taiwan's wish to join the World Health Organization.[175]
It was announced that members of the Papua New Guinea Defence Force would receive training provided by China. Traditionally, military training aid in Papua New Guinea had been provided by Western countries, namely, Australia, New Zealand and the U.S.[200]
Samoa
The diplomatic relations between China and Samoa were established in 1975.[201]
In the late 1980s, China began sending doctors to the Samoan National Hospital, and sent over a hundred over the following two decades.[201] Samoa significantly increased its volume of imports from China in the late 2000s, while also increasing its exports to that country. In 2010, Samoa reached a record trade deficit in its relations with China, at A$70m.[174] In 2007, China provided Samoa with an x-ray machine and several volunteer doctors.[202] In 2008, China donated over €1,360,000 to Samoa to fund its education policies.[203]
In March 2008, following unrest in Tibet, the speaker of the Samoan Fono (legislative assembly), Tolofuaivalelei Falemoe Leiataua, stated that foreign leaders should not interfere with China as it deals with "internal affairs", and that they should not meet the Dalai Lama.[204][205]
In June 2008, Samoa announced it would be opening diplomatic missions in China and Japan - the country's first diplomatic offices in Asia.[206] In September, the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs issued a statement indicating that China and Samoa have always "conducted fruitful cooperation in the fields of economy, trade, agriculture, sports, culture, education and health, as well as international affairs", and that China intended to "make more tangible efforts to support Samoa's economic and social development".[207]
In 2010, the Chinese government-funded China-Samoa Agricultural Demonstration Farm was established in Nu'u with an aim "to train the Samoan farmers on voluntary basis through Chinese agricultural planting techniques". About 500 Samoan farmers received training from Chinese agricultural experts.[201]
In 2011, 57 Samoan students were studying in China on a Chinese government sponsorship.[201]
Tonga
Relations with Tonga were first established in 1998. In 2000, noble Tuʻivakano of Nukunuku (later to become Prime Minister) banned all Chinese stores from his Nukunuku District. This followed alleged complaints from other shopkeepers regarding competition from local Chinese.[208] In 2001, Tonga's Chinese community (of about three or four thousand people) was hit by a wave of about a hundred racist assaults. The Tongan government decided not to renew the work permits of over 600 Chinese storekeepers, and admitted the decision was in response to "widespread anger at the growing presence of the storekeepers".[209]
That same year, however, Tonga and China decided to strengthen their "military relations".[210] In 2008, China provided Tonga with military supplies worth over €340,000.[211]
In 2006, rioters caused severe damage to shops owned by Chinese-Tongans in Nukuʻalofa.[212][213]
In April 2008, Tongan King George Tupou V visited China, reaffirmed his country's adherence to the "One China" policy, and, according to the Chinese State news agency Xinhua, "supported the measures adopted to handle the incident in Lhasa".[214] King Tupou V also met Chinese Defense Minister Liang Guanglie to "enhance exchange and cooperation between the two militaries". Xinhua stated that China and Tonga have "fruitful cooperation in politics, economy, trade, agriculture and education, and kept a sound coordination in regional and international affairs".[215]
In early 2010, Chinese aid to Tonga included assistance in the reconstruction of Nuku'alofa's central business district; "an agricultural project in Vaini"; health clinics set up in Vavaʻu and Vaini; the provision of seven Chinese doctors for a two-year period; and an allocation of €2.2 million "for social and economic development", including "soft loans and interest free loans to the Tonga Government".[216]
In April 2011, the Lowy Institute reported that, of all Pacific countries, Tonga was carrying the highest burden of debt from Chinese loans, amounting to 32% of Tonga's GDP. Simultaneously, the International Monetary Fund warned Tonga was "facing debt distress", a "very high possibility that Tonga [would] be unable to service its debts in the future".[160]
Vanuatu
In 2006, Vanuatu signed an economic cooperation agreement with China, whereby the latter was to assist Vanuatu's economic development, and remove tariffs on imports from Vanuatu. China also added Vanuatu to its list of approved tourism destinations for Chinese tourists. Ni-Vanuatu trade minister James Bule said his country had also requested China's assistance "in supplying machines so we can establish a plant in Vanuatu to produce bio fuel".[217] By contrast, Opposition leader Serge Vohor has said China is exerting too much influence on the ni-Vanuatu government's policy.[218]
In May 2009, Vanuatu appointed its first ever ambassador to China, former Minister of Finance Willie Jimmy.[219] Jimmy "call[ed] [...] for China to have a foot firmly planted in the Pacific through Port Vila", which -the Vanuatu Daily Post remarked- "no doubt caused ruffled feathers among other foreign diplomatic partners".[220]
In July 2010, Chinese Ambassador Cheng Shuping announced that China would fund a number of projects in Vanuatu, "including the National Convention Centre and the expansion of Prime Minister’s Offices", as well as "the design and reconstruction of the Francophone Wing of the University of the South Pacific Emalus Campus".[221]
Trans-national issues
China has 14 neighbouring nations by land, and 7 neighbours by sea. Only Russia has as many neighbouring nations (14 by land, 12 by sea). Boundary issues, especially in the South China Sea, have been important.[222]
Countries that have no diplomatic relations with the PRC
China recognizes all 193 UN member states, the Holy See and Palestine as sovereign states. However, it does not have diplomatic relations with 14 UN member states, nor with the Holy See. These sovereign entities recognize the Republic of China as the sole legitimate Chinese state.
The following countries do not recognize the People's Republic of China. Instead, these countries recognize the Republic of China.[223]
| Name | Previous relations with the PRC | Duration of previous relations with the PRC | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | 1987–1989 | Diplomatic relations with the PRC were established on 2 February 1987 and severed on 23 October 1989. Belize terminated the recognition of the PRC and then recognized the ROC on 11 October 1989. | |
| No | N/A | ||
| No | N/A | ||
| No | N/A | ||
| No | N/A | In 1996, the Bureau of Commercial Development of the PRC in the Republic of Haiti and Bureau of Commercial Development of the Republic of Haiti in the PRC were established in Port-au-Prince and Beijing as the assignment between two countries. | |
| No | N/A | ||
| Yes | 1990–1998 | Diplomatic relations with the PRC were established on 16 November 1990 and severed on 11 December 1998. Marshall Islands recognized the ROC on 20 November 1998. | |
| Yes | 2002–2005 | Diplomatic relations with the PRC were established on 21 July 2002 and severed on 27 May 2005.
Nauru resumed diplomatic ties with the ROC on 14 May 2005. The relations with the ROC were first established in 1980 and severed in 2002. | |
| Yes | 1985–1990 | Diplomatic relations with the PRC were established on 7 December 1985 and severed on 9 November 1990. Nicaragua resumed diplomatic ties with the ROC on 6 November 1990. The relations with the ROC were first established in 1962 and severed in 1985. | |
| No | N/A | ||
| No | N/A | ||
| No | N/A | ||
| Yes | 1997–2007 | Diplomatic relations with the PRC were established on 1 September 1997 and severed on 5 May 2007. Saint Lucia resumed diplomatic ties with the ROC on 30 April 2007. The relations with the ROC were first established in 1984 and severed in 1997. | |
| No | N/A | ||
| No | N/A | ||
| No | N/A[224] | Since the establishment of the PRC, Catholicism has been permitted to operate only under the supervision of the SARA. All worship must legally be conducted through state-approved churches belonging to the CPA, which does not accept the Primacy of the Bishop of Rome. The Holy See was banished from China following the incident around the death of Antonio Riva in 1951.
In 2016, negotiation of diplomatic relations between the Holy See and the PRC started. See China-Holy See relations. |
International organizations
- Membership in international organizations
China holds a permanent seat, which affords it veto power, on the United Nations Security Council (UNSC). Prior to 1971, the Republic of China on Taiwan held China's UN seat, but, as of that date, the People's Republic of China successfully lobbied for Taiwan's removal from the UN and took control of the seat, supported by Soviet Union as well as communist states, United Kingdom, France, and other Western European states, and the Third World countries like India.[citation needed]
- Membership in UN system organizations

- Other memberships
International territorial disputes
Territorial disputes with other countries include:[225]
- The PRC claims the de jure administration of Taiwan Province, as well as mainland-nearby islands of Kinmen and Matsu Islands, currently controlled by the Republic of China.[225]
- 10 features in the Yalu (Korean: Amnok) river are in dispute with North Korea.[225]
- Border dispute with India; India claims control of Aksai Chin, which China seized during the Sino-Indian War of 1962, while China claims most of the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh (called South Tibet by China).[225]
- Portions of the boundary with Bhutan[225]
- China claims the administration of Senkaku Islands (Diaoyutai Islands), currently held by Japan.[225]
- Paracel Islands administered and occupied by the People's Republic, but claimed by Vietnam.[227]
- Involved in a dispute with the Philippines over Scarborough Shoal.[225]
- Involved in a complex dispute over the Spratly Islands with Malaysia, the Philippines, Vietnam, Taiwan, and possibly Brunei.[225]
- Exclusive economic zone disputes with North Korea in the Yellow Sea; South Korea in the Yellow and East China Seas; Japan in the East China Sea (ja:東シナ海ガス田問題, zh:东海油气田问题); Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, Brunei and Indonesia in the South China Sea.[225]
Territorial disputes listed above as between the PRC and ROC ("Taiwan") stems from the question of which government is the legitimate government of China. The Republic of China which views itself as the successor state of the Qing Dynasty did not renounce any territory which fell under de facto control of other states (i.e. Mongolia), but has largely been a non-participant in enforcing these claims. The People's Republic of China which inherited the claims has settled a number of such disputes with Mongolia and Russia via bilateral treaties, not recognized by the Republic of China. In this respect, the territorial disputes between the PRC and neighboring countries may be considered a subset of those between the ROC and said countries.[citation needed]
Bloomberg News reports that these disputes are undermining China's attempts to charm its neighbors away from American influence.[228] China has come to rely more on military power to resolve these disputes. China has made double digit percentage increases in its military budget for many years, though as a percentage of its fast growing GDP falling from 1.4% in 2006 to 1.3% in 2011.[229] This may lead to a China causing its own encirclement by nations that are ever more firmly aligned against an increasingly well armed and dominant China.[230] As of 2013 this has caused even the Philippines to invite back onto their soil not just the Americans, but also the Japanese.[231]
In May 2015, U.S. Secretary of Defense Ashton Carter warned China to halt its rapid island-building in the South China Sea.[232]
Refugee asylum
Refugees by country of origin are: 300,897 (from Vietnam), estimated 30,000-50,000 (from North Korea).[233]
Human trafficking

China is a source, transit, and destination country for human trafficking. Women, men, and children are trafficked for purposes of sexual slavery and forced labor; the majority of trafficking in China is internal, but there is also international trafficking of Chinese citizens; women are lured through false promises of legitimate employment into commercial sexual exploitation in Taiwan, Thailand, Malaysia, and Japan; Chinese men and women are smuggled to countries throughout the world at enormous personal expense and then forced into commercial sexual exploitation or exploitative labor to repay debts to traffickers; women and children are trafficked into China from Mongolia, Myanmar, North Korea, Russia, and Vietnam for forced labor, marriage, and sexual slavery; most North Koreans enter northeastern China voluntarily, but others reportedly are trafficked into China from North Korea; domestic trafficking remains the most significant problem in China, with an estimated minimum of 10,000–20,000 victims trafficked each year; the actual number of victims could be much greater; some experts believe that the serious and prolonged imbalance in the male-female birth ratio may now be contributing to Chinese and foreign girls and women being trafficked as potential brides.[225]
United States Department of State Tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List - "China failed to show evidence of increasing efforts to address transnational trafficking; while the government provides reasonable protection to internal victims of trafficking, protection for Chinese and foreign victims of transnational trafficking remain inadequate."[225]
Illicit drugs
Chinese drug laws are very harsh, and the death sentence for traffickers is not unusual. Many foreigners have been sentenced to death in China for drug trafficking.[235][236][237][238]
Major international treaties
China has signed numerous international conventions and treaties.[225]
Treaties signed on behalf of China before 1949 are applicable only to the Republic of China on Taiwan. Conventions signed by Beijing include: Assistance in Case of a Nuclear Accident or Radiological Emergency Convention; Biological Weapons Convention; Chemical Weapons Convention; Conventional Weapons Convention; Convention on Early Notification of a Nuclear Accident; Inhumane Weapons Convention; Nuclear Dumping Convention (London Convention); Nuclear Safety Convention; Convention on the Physical Protection of Nuclear Material; Rights of the Child and on the Sale of Children, Child Prostitution, and Child Pornography Convention (signed Optional Protocol); and Status of Refugees Convention (and the 1967 Protocol).[citation needed]
Treaties include the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (signed but not ratified); Protocol for the Prohibition of the Use in War of Asphyxiating, Poisonous, or Other Gases, and of Bacteriological Methods of Warfare (Geneva Protocol); Treaty on the African Nuclear-Weapon-Free Zone (Treaty of Pelindaba, signed protocols 1 and 2); Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons; Treaty on Outer Space; Treaty for the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons in Latin America and the Caribbean (signed Protocol 2); Treaty on Seabed Arms Control; and Treaty on the South Pacific Nuclear-Free Zone (Treaty of Rarotonga, signed and ratified protocols 2 and 3).[citation needed]
China also is a party to the following international environmental conventions: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, and Whaling.[citation needed]
China is a major transshipment point for heroin produced in the Golden Triangle region of Southeast Asia. There is a growing domestic drug abuse problem and it is a source country for chemical precursors, despite new regulations on its large chemical industry.[225]
See also
- China–United States relations
- History of Sino-Russian relations
- List of diplomatic missions in China
- List of diplomatic missions of China
- Panda diplomacy
- Stadium diplomacy
- Ten Major Relationships
- Arctic policy of China
- China foreign aid
- Foreign relations of Hong Kong
- Foreign relations of Macau
- Foreign relations of Taiwan
- Xi Jinping Thought on Diplomacy
- Wolf warrior diplomacy
References
- ^ "Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the People's Republic of China". Archived from the original on 23 February 2014. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ Williams, David (8 January 2008). "China-Taiwan tussle in Bim politics". BBC News. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 13 July 2010.
Beijing and Taipei often trade insults over which is using "dollar diplomacy" in the form of offers of aid or cheap loans to curry influence around the world. The 'One-China' policy ensures that nations cannot have official relations with both China and Taiwan.
- ^ Ninvalle, Pete (27 April 2007). "China halts St. Lucia work". BBC News. Archived from the original on 15 September 2007. Retrieved 13 July 2010.
- ^ Erikson, Daniel (8 January 2010). "China in the Caribbean: The New Big Brother". Star Publishing Company. Retrieved 13 July 2010.
China's overall strategy for the Caribbean has been driven by a desire to ensure the security of Chinese offshore financial holdings, woo countries with infrastructure projects and investment deals to ensure support for China in multilateral organizations, and promote the crucial "One China" policy to isolate Taiwan on the world stage.
[dead link] - ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 August 2017. Retrieved 9 December 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Opinion of China". Pew Research Center. 2016. Archived from the original on 29 July 2017. Retrieved 31 July 2017.
- ^ "Poll: Mutual Distrust Grows Between China, US". VOA. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ "Politics/Nation". The Times of India. 23 August 2007. Archived from the original on 26 January 2009. Retrieved 25 August 2007.
- ^ "Wargame with India not to put China in a closet: US admiral". The Hindu. Chennai, India. 24 August 2007. Archived from the original on 2 November 2012.
- ^ "India News, Latest News Headlines, Financial News, Business News & Market Analysis on Indian Economy". Business Standard. Archived from the original on 11 February 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ "The Sino-Russian border: The cockerel's cropped crest". The Economist. 24 July 2008. Archived from the original on 29 August 2009. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ Silver, Laura; Devlin, Kat; Huang, Christine (5 December 2019). "People around the globe are divided in their opinions of China". Pew Research Center. Retrieved 5 August 2020.
- ^ "Beijing likens Cheney criticism to nosy neighbor". The Washington Times. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ Ho, Stephanie. "Chinese Foreign Relations to Focus on More Active Diplomacy." Archived 9 March 2011 at the Wayback Machine Voice of America, 7 March 2011.
- ^ Lai, Christina (26 October 2016). "In China's sixth plenum, Xi strives to polish image abroad". Asia Times Online. Archived from the original on 11 November 2016. Retrieved 11 November 2016.
- ^ Marlow, Iain (17 April 2018). "China's $1 Billion White Elephant". Bloomberg L.P. Archived from the original on 3 May 2019. Retrieved 15 September 2018.
- ^ Abi-Habib, Maria (25 June 2018). "How China Got Sri Lanka to Cough Up a Port". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 16 October 2018. Retrieved 28 December 2018.
- ^ Pomfret, John (27 August 2018). "China's debt traps around the world are a trademark of its imperialist ambitions". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 22 May 2019. Retrieved 15 September 2018.
- ^ Beech, Hannah (20 August 2018). "'We Cannot Afford This': Malaysia Pushes Back Against China's Vision". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 16 August 2019. Retrieved 27 December 2018.
- ^ "China's Era of Debt-Trap Diplomacy May Pave the Way for Something Sinister". Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 3 February 2019.
- ^ Overland, Indra; Bazilian, Morgan; Ilimbek Uulu, Talgat; Vakulchuk, Roman; Westphal, Kirsten (2019). "The GeGaLo index: Geopolitical gains and losses after energy transition". Energy Strategy Reviews. 26: 100406. doi:10.1016/j.esr.2019.100406.
- ^ . 13 July 2017 https://web.archive.org/web/20170713011420/http://www.cbbc.org/cbbc/media/cbbc_media/One-Belt-One-Road-main-body.pdf. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 July 2017. Retrieved 22 March 2019.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Rym Momtaz, "Macron steals Trump’s thunder with Chinese Airbus order: France lands €30B aviation deal with Beijing," POLITICO 25 March 2019 Archived 26 March 2019 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Giovanni Legorano, "Italy Signs Up to China’s Global Infrastructure Plan Despite U.S. Ire: U.S. diplomats and EU officials have criticized Italy’s move, warning that China’s plans could weaken Western cohesion", Wall Street Journal 23 March 2019 Archived 27 March 2019 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Swanson, Ana (5 July 2018). "Trump's Trade War With China Is Officially Underway". Archived from the original on 12 July 2018. Retrieved 9 August 2019.
- ^ Lawrence J. Lau, "The China–US Trade War and Future Economic Relations." China and the World (Lau Chor Tak Institute of Global Economics and Finance, 2019): 1-32. quote p. 3 online
- ^ The Heritage Foundation China's Influence in Africa: Implications for the United States Archived 8 March 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ International Committee of the Fourth International Western concern at China's growing involvement in Africa Archived 18 May 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Political Warfare in Sub-Saharan Africa: U.S. Capabilities and Chinese Operations in Ethiopia, Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa Archived 9 June 2007 at the Wayback Machine, Strategic Studies Institute, U.S. Army War College, March 2007
- ^ "The Confused Moments of Nkrumah in China After The Coup". modernghana.com. Archived from the original on 27 April 2019. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- ^ Muekalia 2004, p.6
- ^ Taylor 2000, p. 93
- ^ "From "brothers" to "partners": China, Africa building strategic ties". Embassy of the People's Republic of China in the Arab Republic of Egypt. Archived from the original on 8 May 2013. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ "China woos Taiwan's African friends". afrol.com. Archived from the original on 14 March 2012. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ "Africa and the UN Security Council Permanent Seats". pambazuka.org. Archived from the original on 8 May 2013. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ "China-Africa Relations". Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the People's Republic of China. Archived from the original on 30 December 2012. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ "chinaembassy.org.zw Sino-African Relations". Archived from the original on 16 June 2013. Retrieved 20 January 2013.
- ^ "China boosts African economies, offering a 'second opportunity'". The Christian Science Monitor. Archived from the original on 24 June 2009. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ a b "Mozambique-China Trade Continues to Grow". allafrica.com. 9 December 2012. Archived from the original on 18 January 2013. Retrieved 9 December 2012.
- ^ a b "Africa, China Trade" (PDF). Financial Times. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 March 2009. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ a b c d "China's trade safari in Africa". Le Monde diplomatique. May 2005. Archived from the original on 26 January 2013. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ "Military backs China's Africa adventure". Asia Times. Archived from the original on 21 July 2012. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ "Out of Africa". China Daily. Archived from the original on 4 October 2012. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ "Confucius Institute Bridges Friendship between China and Africa". cri.com.cn. Archived from the original on 16 October 2012. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ Osnos, Evan (9 February 2009). "The Promised Land". The New Yorker. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 16 November 2014.
- ^ "China's 'Little Africa' is under pressure". globalpost.com. Archived from the original on 28 February 2009. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ a b "China and Africa: Stronger Economic Ties Mean More Migration". Migration Policy Institute. 6 August 2008. Archived from the original on 29 January 2014. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ "Russian, Chinese weapons compete in Africa". upiasia.com. Archived from the original on 13 May 2013. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ "China 'is fuelling war in Darfur'". BBC. 13 July 2008. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ Beresford, David (18 April 2008). "Chinese ship carries arms cargo to Mugabe regime". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 5 March 2017. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ Spencer, Richard (31 August 2007). "China is to withdraw backing for Mugabe". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 15 April 2018. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ Evans, Ian (26 July 2008). "Robert Mugabe forced into talks with opposition after China told him 'to behave'". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 15 April 2018. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ Blair, David (31 August 2007). "Why China is trying to colonise Africa". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 15 April 2018. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ "China as Africa's 'angel in white'". Asia Times. Archived from the original on 9 May 2013. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ Goldstein, Joseph (15 October 2018). "Kenyans Say Chinese Investment Brings Racism and Discrimination". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 8 June 2019. Retrieved 8 June 2019.
- ^ "The Forest for the Trees: Trade, Investment and the China-in-Africa Discourse" (PDF). Barry Sautman, Hong Kong University of Science & Technology Yan Hairong, University of Hong Kong. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 June 2011. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ "China in Africa - Is China Gaining Control of Africa's Resources" (PDF). Golobal Researcher. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 May 2010. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ The Heritage Foundation China's Influence in the Western Hemisphere Archived 22 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ CNS news.com China Moving to Replace US Influence in Latin America Archived 16 May 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Columbia Daily Tribune Caribbean sees China acquire more influence Archived 14 March 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ United Transportation Union Cuba turns to China for transport needs Archived 22 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ GlobalSecurity.org China Increasing Military Ties in Latin America as Law Restricts US Military Archived 23 May 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Best, Tony (24 October 2008). "US calls off Barbados ban". Nation Newspaper. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 24 October 2008.
- ^ Dells, Alicia (27 September 2009). "Stronger link". Barbados Advocate. Bridgetown, Barbados. Archived from the original on 26 February 2012. Retrieved 27 September 2009.
The acting Prime Minister added that Barbados looks forward to welcoming the Guangdong Art Troupe to the island next month and noted that Barbados was keen on having a Confucius Institute for the teaching of Mandarin and Chinese history at the UWI Cave Hill Campus in the near future.
- ^ Chinese And Caribbean Relations[permanent dead link] - By David Jessop, CaribbeanWorldNews.com (Friday 20 March 2009)
- ^ Confucius Institute opens at UWI in Jamaica Archived 18 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine, CaribbeanNetNews.com, (Saturday, 14 February 2009)
- ^ "Trinidad and Tobago recognizes China's full market economy status". People's Daily. Archived from the original on 7 October 2012. Retrieved 1 February 2005.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 20 January 2008. Retrieved 20 January 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ https://www.bnamericas.com/en/features/spotlight-chinas-footprint-in-caribbean-infrastructure
- ^ "Antigua and Barbuda". Archived from the original on 19 August 2018. Retrieved 7 December 2018.
- ^ a b Ambassador (30 May 2008). "Summary of China-Barbados Bilateral Relations". Bridgetown, Barbados: Embassy of the People's Republic of China: Barbados. Archived from the original on 2 January 2014. Retrieved 16 January 2012.
- ^ N., A. (28 September 2012). "China marks 63 years". Barbados Advocate. Archived from the original on 27 October 2013. Retrieved 29 September 2012.
"Since I assumed my post as the Chinese Ambassador April this year, I have been much impressed by the sound friendship between our two countries and two peoples, as well as the great potential for future development," Ambassador Xu Hong stated.
- ^ "Chinese embassy to Barbados". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the People's Republic of China. 30 December 2011. Archived from the original on 31 December 2011. Retrieved 17 January 2012.
- ^ "Chinese president accepts credentials from five new ambassadors". Xinhua News Agency. 3 March 2010. Archived from the original on 7 March 2010. Retrieved 17 January 2012.
- ^ "List of Chinese countries with ADS status". China Travel Trends. 6 August 2009. Archived from the original on 3 January 2011.
(list)
{{cite web}}: External link in|quote= - ^ "What China Means for Caribbean Tourism". Caribbean Journal. 17 December 2011. Archived from the original on 12 August 2012. Retrieved 30 September 2012.
- ^ N., A. (1 June 2012). "Chinese tourism remains a goal". Barbados Advocate. Archived from the original on 18 July 2014. Retrieved 30 September 2012.
- ^ Prime Minister David Thompson signed condolence book Archived 22 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine, 21 May 2008
- ^ "Wildey Gym Spruce-up". Nation Newspaper. Ministry of Commerce of P.R. China. 15 September 2005. Archived from the original on 7 July 2011. Retrieved 30 November 2009.
[ . . . ] The lighting will be improved, and the air-conditioning should be better now," Walrond said. He noted that the experienced technical team from the People's Republic of China would be working with China State Construction who built the gym, as well as with about 30 Barbadians. [ . . . ]
- ^ "Barbados to open embassy in China". Caribbean Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 7 March 2016. Retrieved 15 May 2009.
- ^ "Product Exports by China to Barbados 1999". World Integrated Trade Solution. Retrieved 16 September 2020.
- ^ "Product Imports by China from Barbados 1999". World Integrated Trade Solution. Retrieved 16 September 2020.
- ^ "Caribbean Development Bank (CDB): Non-Regional Members". Archived from the original on 28 June 2018. Retrieved 9 December 2018.
- ^ "Closer cooperation likely between China and Barbados". CaribbeanNetNews.com. 17 February 2009. Archived from the original on 5 May 2009. Retrieved 10 September 2009.
- ^ Marc Frank, "Trade With China Primes Cuba’s Engine for Change", Financial Times, 29 March 2006
- ^ "Trade with China helps Cuba to move up a gear," Financial Times, 8 March 2006
- ^ a b Bolstad, Erika; Hall, Kevin G. (11 June 2008). "GOP claim about Chinese oil drilling off Cuba is untrue". McClatchy Newspapers. Archived from the original on 8 December 2009.
- ^ "Firman Cuba y China contrato para producción compartida de petróleo". Granma Internacional (in Spanish). 31 January 2005.
- ^ "PetroChina Great Wall Drilling Co. wins contracts in Cuba". China Chemical Reporter. 26 November 2005. Archived from the original on 17 May 2011. Retrieved 20 January 2013.
- ^ a b http://fta.mofcom.gov.cn/rcep/rceppdf/d20z_en.pdf
- ^ Ulrich Theobald. "Chinese History - Dashi 大食 (www.chinaknowledge.de)". Archived from the original on 29 October 2017. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ Yingsheng, Liu (July 2001). "A century of Chinese research on Islamic Central Asian history in retrospect". Cahiers d'Asie Centrale (9): 115–129. Archived from the original on 27 July 2011. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ Twitchett, Denis (2000), "Tibet in Tang's Grand Strategy", in van de Ven, Hans (ed.), Warfare in Chinese History, Leiden: Koninklijke Brill, pp. 106–179 [125], ISBN 978-90-04-11774-7
- ^ Schafer, Edward H. (1985) [1963], The Golden Peaches of Samarkand: A study of T'ang Exotics (1st paperback ed.), Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press, p. 26, ISBN 978-0-520-05462-2
- ^ E. Bretschneider (1871). On the knowledge possessed by the ancient Chinese of the Arabs and Arabian colonies: and other western countries, mentioned in Chinese books. LONDON 60 PATERNOSTER ROW.: Trübner & co. p. 6. Retrieved 28 June 2010.
realm caliphs call ta shi kuo.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link)(Original from Harvard University) - ^ E. Bretschneider (1871). On the knowledge possessed by the ancient Chinese of the Arabs and Arabian colonies: and other western countries, mentioned in Chinese books. LONDON: Trübner & co. p. 8. Retrieved 28 June 2010.
713 envoy appeared from ta shi.
(Original from Harvard University) - ^ E. Bretschneider (1871). On the knowledge possessed by the ancient Chinese of the Arabs and Arabian colonies: and other western countries, mentioned in Chinese books. LONDON: Trübner & co. p. 10. Retrieved 28 June 2010.
hui ho ambassadors 798 three ta shi ambassadors came.
(Original from Harvard University) - ^ Samy S. Swayd (2006). Historical dictionary of the Druzes. Vol. Volume 3 of Historical dictionaries of people and cultures (illustrated ed.). Scarecrow Press. p. xli. ISBN 978-0-8108-5332-4. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
The fifth caliph, al-'Aziz bi-Allah (r.975-996). . . In his time, the Fatimi "Call" or "Mission" (Da'wa) reached as far east as India and northern China.
{{cite book}}:|volume=has extra text (help) - ^ E. J. van Donzel (1994). E. J. van Donzel (ed.). Islamic desk reference (illustrated ed.). BRILL. p. 67. ISBN 978-90-04-09738-4. Retrieved 26 December 2011.
China (A. al-Sin):. . .After the coming of Islam, the existing trade was continued by the peoples of the South Arabian coast and the Persian Gulf, but the merchants remained on the coast.
- ^ Ralph Kauz (2010). Ralph Kauz (ed.). Aspects of the Maritime Silk Road: From the Persian Gulf to the East China Sea. Vol. Volume 10 of East Asian Economic and Socio-cultural Studies - East Asian Maritime History. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. p. 130. ISBN 978-3-447-06103-2. Retrieved 26 December 2011.
{{cite book}}:|volume=has extra text (help) - ^ a b Masumi, Matsumoto. "The completion of the idea of dual loyalty towards China and Islam". Archived from the original on 24 July 2011. Retrieved 28 June 2010.
- ^ Stéphane A. Dudoignon; Hisao Komatsu; Yasushi Kosugi (2006). Intellectuals in the modern Islamic world: transmission, transformation, communication. Taylor & Francis. p. 251. ISBN 978-0-415-36835-3. Retrieved 28 June 2010.
- ^ Hsiao-ting Lin (2010). Modern China's Ethnic Frontiers: A Journey to the West. Taylor & Francis. p. 90. ISBN 978-0-415-58264-3.
- ^ "中华人民共和国中阿合作论坛". Cascf.org. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- ^ https://bricspolicycenter.org/en/forum-de-cooperacao-china-paises-arabes/
- ^ "Arab League - Sportwetten - Beste Singlebörsen im Vergleich". Arab League - Sportwetten - Beste Singlebörsen im Vergleich. Archived from the original on 20 July 2011.
- ^ YaleGlobal Online Central Asia: China's Mounting Influence Archived 10 April 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Chen, Yo-Jung (15 January 2014). "China's Westward Strategy". thediplomat.com. The Diplomat. Archived from the original on 17 January 2014. Retrieved 18 January 2014.
- ^ Nanjing by the Numbers Archived 24 October 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Foreign Policy. 9 February 2010.
- ^ "Backlash over the alleged China curb on metal exports" Archived 15 April 2018 at the Wayback Machine. The Daily Telegraph, London, 29 August 2010. Retrieved 30 August 2010.
- ^ UCLA Asia Institute China's March on South Asia Archived 16 April 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Bangladesh, Pakistan Team Up With China on Space Cooperation". Archived from the original on 30 March 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ "Indo-China trade to surpass $60 bn before 2010". Business Standard. 6 June 2008. Archived from the original on 6 October 2012. Retrieved 21 November 2009.
- ^ "India, China clash over Kashmir as it loses special status and is divided". 31 October 2019 – via www.reuters.com.
- ^ John W. Garver, Protracted Contest: Sino-Indian Rivalry in the Twentieth Century (2001), post 1950
- ^ Saibal Dasgupta (17 January 2008). "China is India's largest trade ally – International Business – Biz". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 24 October 2012. Retrieved 21 November 2009.
- ^ "news.outlookindia.com". Outlookindia.com. Archived from the original on 25 April 2005. Retrieved 21 November 2009.
- ^ "US blames India, China for blocking Doha talks". Business Standard. 29 July 2008. Archived from the original on 31 March 2012. Retrieved 21 November 2009.
- ^ "India, China to work on FTA recommendations- Foreign Trade-Economy-News". The Economic Times. 20 February 2008. Archived from the original on 22 May 2014. Retrieved 21 November 2009.
- ^ "Front Page : India, China to promote cooperation in civil nuclear energy". The Hindu. Chennai, India. 15 January 2008. Archived from the original on 5 November 2012. Retrieved 21 November 2009.
- ^ "Article: India, China top Asian FDI list in Africa. | AccessMyLibrary – Promoting library advocacy". AccessMyLibrary. 28 March 2007. Archived from the original on 16 December 2008. Retrieved 21 November 2009.
- ^ Africa: China's Africa Overture Needs Common Touch Archived 10 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine, 16 November 2007
- ^ a b "The dynamics of the Sino-Pakistani strategic partnership from its formation in the 1960s to the present" (PDF). Journal of Contemporary Development & Management Studies, p51. 2019. Retrieved 10 May 2020.
- ^ China Pakistan Economic Corridor. Archived 3 June 2018 at the Wayback MachineHussain, Tom (19 April 2015). "China's Xi in Pakistan to cement huge infrastructure projects, submarine sales". McClatchy News. Islamabad: mcclatchydc.
- ^ a b Kiani, Khaleeq (30 September 2016). "With a new Chinese loan, CPEC is now worth $62bn". Dawn. Archived from the original on 30 September 2016. Retrieved 19 November 2016.
- ^ "CPEC: The devil is not in the details". 23 November 2016. Archived from the original on 23 November 2016. Retrieved 23 September 2018.
- ^ "Economic corridor: Chinese official sets record straight". The Express Tribune. 2 March 2015. Archived from the original on 3 March 2015. Retrieved 23 September 2018.
- ^ Hussain, Tom (19 April 2015). "China's Xi in Pakistan to cement huge infrastructure projects, submarine sales". McClatchy News. Islamabad: mcclatchydc.
- ^ "Boosting trade: Pak-China economic corridor plan gets premier's go-ahead". 16 August 2013. Archived from the original on 24 September 2018. Retrieved 23 September 2018.
- ^ [https://web.archive.org/web/20070929133910/http://www.asianews.it/index.php?l=en&art=8801&geo=2&theme=6&size=A Archived 29 September 2007 at the Wayback Machine PAKISTAN – CHINA Chinese-funded port in Baluchistan, Pakistan to give Beijing direct access to the Middle East
- ^ "South Asia news : China-Pakistan rail link on horizon". Archived from the original on 22 May 2011. Retrieved 21 June 2007.
- ^ USCC China's Strategic Reach Into Southeast Asia Archived 23 July 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Quinlan, Joe (13 November 2007). "Insight: China's capital targets Asia's bamboo network". Financial Times. Archived from the original on 23 April 2015. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- ^ Murray L Weidenbaum (1 January 1996). The Bamboo Network: How Expatriate Chinese Entrepreneurs are Creating a New Economic Superpower in Asia. Martin Kessler Books, Free Press. pp. 4–8. ISBN 978-0-684-82289-1. Retrieved 15 November 2015.
- ^ "China-Singapore visa-free agreement to take effect in April" Archived 10 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine People's Daily, 7 April 2011.
- ^ "The South China Sea becomes a zone of eternal dispute." Archived 26 November 2011 at the Wayback Machine The Economist, 9 June 2011.
- ^ Pomfret, John. "Beijing claims 'indisputable sovereignty' over South China Sea." Archived 7 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine The Washington Post, 31 July 2010.
- ^ Barton, Paul C. "Guam central to Pacific military operations." Archived 23 October 2011 at the Wayback Machine Gannett, 19 October 2011.
- ^ Cheng, Dean. "China Grows More Belligerent, Unexpectedly." Archived 25 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine Aol Defense, 5 October 2011.
- ^ Ten Kate, Daniel. "China Plays Down Sea Spats to Woo Asean From U.S. ‘Siren Song’." Bloomberg News, 20 November 2011.
- ^ Petty, Martin. "Booming Southeast Asia in a quandary over U.S.-China rivalry." Archived 16 October 2015 at the Wayback Machine Reuters, 8 July 2012.
- ^ European Commission (30 December 2020). "Key elements of the EU-China Comprehensive Agreement on Investment".
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "China announces initiatives to expand ties with PIF member countries" Archived 19 August 2017 at the Wayback Machine, PRC embassy in Papua New Guinea, 24 November 2003
- ^ a b "China offers aid package to Pacific Islands" Archived 6 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine, China Daily, 5 April 2006
- ^ "Chinese Premier Wen to visit the Pacific Islands" Archived 12 September 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Taipei Times, 3 April 2006
- ^ "China, Pacific islands countries ties important" Archived 13 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Xinhua, 19 October 2007
- ^ "What do the Chinese really want?" Archived 22 February 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Dr John Lee, Islands Business, December 2007
- ^ "Pacific politics expert warns more riots possible", TV3 (New Zealand), 13 December 2007
- ^ "China says it is for peace and not power politics" Archived 12 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Fiji Times, 18 December 2007
- ^ "Chinese say they are at home" Archived 12 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Fiji Times, 22 December 2007
- ^ Australia 2020 final report Archived 20 June 2012 at the Wayback Machine, p.363, Australian government website
- ^ "Report questions China aid to Pacific" Archived 5 September 2008 at the Wayback Machine, ABC Radio Australia, 11 June 2008
- ^ "China's aid diplomacy destabilises Pacific - report" Archived 3 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine, Reuters, 11 June 2008
- ^ "China rejects charge of aid diplomacy in Pacific", Reuters, 12 June 2008
- ^ "No political pre-conditions attached in China's aid to Pacific island countries" Archived 19 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Xinhua, 12 June 2008
- ^ "China vows to enhance parliamentary exchanges with Pacific island nations" Archived 2 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Xinhua, 17 June 2009
- ^ "Prochaine visite en Chine de délégations parlementaires du Pacifique" Archived 20 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Radio Chine Internationale, 12 June 2009
- ^ "Chinese premier urges more economic cooperation with Pacific island countries" Archived 2 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Xinhua, 16 June 2009
- ^ "Chinese Navy ships makes first visit to Tonga" Archived 12 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine, People's Daily, 3 September 2010
- ^ a b "FEATURE: China in the Pacific" Archived 17 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine, ABC Radio Australia, 4 April 2011
- ^ "China-Pacific island countries' ties of cooperation boom in many areas: Chinese ambassador" Archived 7 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Xinhua, 5 May 2011
- ^ China Seeks to Star in South Pacific; Beijing Widens Diplomatic Reach With Loans, Aid, in Challenge to U.S.; Subtle Reminders in Tonga Archived 7 November 2018 at the Wayback Machine 27 April 2012
- ^ David S. G. Goodman, "Australia and the China threat: Managing ambiguity." Pacific Review 30.5 (2017): 769-782 https://doi.org/10.1080/09512748.2017.1339118 .
- ^ "Australia and China: A Strong and Stable Partnership for the 21st Century", Kevin Rudd, 6 July 2004
- ^ O'Malley, Sandra (5 February 2008). "China, Australia hold strategic meeting". The Age. Archived from the original on 9 August 2011. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ "Rudd in tough Tibet talks". News.com.au. 10 April 2008. Archived from the original on 5 August 2011. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ "Australian PM Kevin Rudd warns China over human rights abuses in Tibet" Archived 9 July 2008 at the Wayback Machine, Jane Macartney, The Times, 9 April 2008
- ^ "Aussie Rules" Archived 13 October 2008 at the Wayback Machine, The Independent, 10 April 2008
- ^ "Kevin Rudd raises concerns over Tibet"[permanent dead link], TV3, 10 April 2008
- ^ Ede, Charisse (8 August 2008). "Rudd expresses concerns to China". The Age. Archived from the original on 21 May 2011. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ a b "Chinese vice president meets Fiji leaders on cooperative partnership" Archived 3 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine, Xinhua, 9 February 2009
- ^ "West puts squeeze on Fiji, China ups aid" Archived 22 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Fijilive, 17 May 2008
- ^ "Chinese Ambassador Cai Jinbiao Attends the Fund-raising Evening of the Chinese Associations in Fiji" Archived 4 October 2011 at the Wayback Machine, Chinese embassy in Fiji, 15 March 2008
- ^ a b c "Pacific trade with China" Archived 31 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Solomon Star, 17 February 2011
- ^ a b "Melanesia in Review: Issues and Events 2005" Archived 16 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Alumita L Durutalo, The Contemporary Pacific, vol. 18, n°2, autumn 2006, pp.396-399
- ^ "China likes to help developing nations" Archived 12 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Fiji Times, 10 November 2007
- ^ "Chaudhry breaks silence to slag New Zealand" Archived 12 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine, NiuFM, 9 July 2007
- ^ "China/Fiji meeting, a success" Archived 27 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine, FijiLive, 3 September 2007
- ^ "China calls for more understanding from Fiji's neighbours". Radio New Zealand International. 29 November 2007. Archived from the original on 13 February 2012. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ "‘Give Fiji’s govt time’" Archived 17 July 2011 at archive.today, Fiji Broadcasting Corporation, 25 March 2008
- ^ "Fiji backs China’s action in Tibet" Archived 22 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Fijilive, 24 March 2008
- ^ "Fiji police arrest women protesting over Tibet outside Chinese embassy". Radio New Zealand International. 10 April 2008. Archived from the original on 23 February 2012. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ Hanson, Fergus (9 May 2008). "Don't ignore the big new player in Fiji". The Sydney Morning Herald. Archived from the original on 26 October 2012. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ "FIJI–SINO ties strong: interim PM", Fiji Daily Post, 12 August 2008
- ^ "Arrivée de Xi Jinping à Nadi des îles Fidji" Archived 20 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Radio Chine Internationale, 8 February 2009
- ^ "China Commits To More Fiji Imports" Archived 12 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Fiji Village, 10 February 2009
- ^ a b "China support for Fiji questioned". BBC News. 19 June 2009. Archived from the original on 7 November 2011. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ "Fiji democracy rally targets China, India, SKorea support" Archived 19 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Radio Australia, 5 June 2009
- ^ "Taiwan medical team offers free health checks" Archived 4 October 2011 at the Wayback Machine, Fiji Sun, 26 June 2010
- ^ "FSM Government opens embassy in China" Archived 25 January 2010 at the Wayback Machine, FSM government website, 10 May 2007
- ^ "China's first ambassador to Niue presents credential to Niue PM" Archived 16 November 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Xinhua, 18 October 2008
- ^ "Cook Islands to receive more aid from China". Radio New Zealand International. 10 September 2008. Archived from the original on 7 March 2012. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ "China, New Zealand vow to advance bilateral ties" Archived 13 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine, 25 September 2007
- ^ "China and New Zealand sign free trade deal" Archived 12 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine, International Herald Tribune, 7 April 2008
- ^ "UN General Assembly - 63rd Session General Debate - New Zealand". Archived from the original on 16 October 2015. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ Trevett, Claire (10 July 2009). "PM faces blunt threat from Niue". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 20 October 2012. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ "Spending money where it matters" Archived 19 September 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Bruce Jacobs, Taipei Times, 14 May 2008
- ^ "Press Release of the Embassy" Archived 10 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine, PRC embassy in Papua New Guinea, 7 August 2003
- ^ "PNG Governor General Visits China" Archived 10 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine, PRC embassy in Papua New Guinea, 28 July 2003
- ^ "Concern in PNG at defence training links with China". Radio New Zealand International. 19 May 2008. Archived from the original on 23 February 2012. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ a b c d "Chinese Ambassador Describes China-Samoa Ties as Friendly Partnership" Archived 20 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Xinhua, 4 April 2011
- ^ "Samoa national hospital to get Chinese funded x-ray machine". Radio New Zealand International. 8 October 2007. Archived from the original on 13 February 2012. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ "China to give Samoa more money for education". Radio New Zealand International. 20 January 2008. Archived from the original on 13 February 2012. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ "World leaders voice support for China's handling of riots" Archived 9 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Xinhua, 27 March 2008
- ^ "Samoa backs China’s handling of Tibet" Archived 17 January 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Samoa Observer, 27 March 2008
- ^ "Samoa to establish diplomatic offices in China, Japan" Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine, Xinhua, 23 June 2006
- ^ "President Hu Jintao Meets with Samoan Prime Minister" Archived 14 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs, 17 September 2008
- ^ "No More Chinese!" Archived 30 June 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Tongatapu.net
- ^ "Tonga announces the expulsion of hundreds of Chinese immigrants" Archived 16 March 2008 at the Wayback Machine, John Braddock, WSWS, 18 December 2001
- ^ "China, Tonga Vow to Further Military Ties" Archived 9 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine, People's Daily, 15 May 2001
- ^ "Chinese Government Donates Military Supplies to TDS", Tonga Now, 9 January 2008
- ^ "The Pacific Proxy: China vs Taiwan" Archived 4 November 2007 at the Wayback Machine, Graeme Dobell, ABC Radio Australia, 7 February 2007
- ^ "Chinese stores looted in Tonga riots" Archived 12 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine, People's Daily, 17 November 2006
- ^ "Tonga supports China's stance on Taiwan, Tibet" Archived 14 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Xinhua, 10 April 2008
- ^ "Chinese Defense Minister meets Tongan King" Archived 16 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Xinhua, 15 April 2008
- ^ "China to send doctors to Tonga". Radio New Zealand International. 8 March 2010. Archived from the original on 9 June 2012. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ "Vanuatu looks to China for markets" Archived 10 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Vanuatu Daily, 11 April 2006
- ^ "Chinese influence corrupting government: opposition leader" Archived 10 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Vanuatu Daily, 12 March 2006
- ^ "Minister confirms appointment" Archived 23 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Vanuatu Daily Post, 22 May 2009
- ^ "Chinese Club donate Vt1.4m supplies to landslide victims" Archived 23 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Vanuatu Daily Post, 23 June 2009
- ^ "China commits to fund Vanuatu projects"[permanent dead link], Vanuatu Daily Post, 23 July 2010
- ^ Brian Catchpole, A map history of modern China (Heinemann Educational, 1978).
- ^ Pasha L. Hsieh, "Rethinking non-recognition: Taiwan’s new pivot to ASEAN and the one-China policy." Cambridge Review of International Affairs 33.2 (2020): 204-228 online.
- ^ Holy See has no diplomatic relations with the PRC. In 1950, the ambassador of Holy See moved to Taipei.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n China , CIA World Factbook
- ^ admin (8 November 2017). "CIP Signs Historic Agreement with China". International Potato Center. Archived from the original on 14 January 2019. Retrieved 14 January 2019.
- ^ China and Bhutan have not yet established diplomatic relations, nevertheless negotiations are ongoing as of 2008.
- ^ Forsythe, Michael and Sakamaki, Sachiko China's Asian Charm Offensive in `Shambles' Over Disputes With Neighbors Archived 3 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine Bloomberg News, 26 September 2010
- ^ "China Raising 2012 Defense Spending to Cope With Unfriendly ‘Neighborhood’." Archived 5 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine Bloomberg News. 4 March 2012.
- ^ "China’s Defense Spending Dilemma." Archived 7 August 2017 at the Wayback Machine Wall Street Journal. 5 March 2012.
- ^ Zachary Keck; The Diplomat. "Made in China: A US-Japan-Philippines Axis?". The Diplomat. Archived from the original on 11 November 2013. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ "Defense secretary’s warning to China: U.S. military won’t change operations Archived 30 October 2018 at the Wayback Machine". The Washington Post. 27 May 2015.
- ^ Agency, Central Intelligence (1 January 2010). The World Factbook: 2010 Edition (CIA's 2009 ed.). Potomac Books, Inc. ISBN 9781597975414.
- ^ "Trafficking in Persons Report 2011". Archived from the original on 19 June 2019. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ "Three Filipino drugs mules on death row in China will eventually be executed despite winning a rare reprieve amid intense Philippine lobbying, the Chinese ambassador in Manila said".
- ^ "SA woman executed in China". News24. 12 December 2011. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ "China executed four convicted drug traffickers and sentenced at least 15 others to death Tuesday as the nation marked global anti-drug day, state press reported".
- ^ "Lenta.ru: Мир: В КНР россиянку приговорили к смертной казни за контрабанду наркотиков". Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
Further reading
- Alden, Christopher. China Returns to Africa: A Superpower and a Continent Embrace (2008)
- Amin, Nasser. "The dynamics of the Sino-Pakistani strategic partnership from its formation in the 1960s to the present" Journal of Contemporary Development & Management Studies 7 (2019): 51-66 online
- Bajpai, Kanti, Selina Ho, and Manjari Chatterjee Miller, eds. Routledge Handbook of China–India Relations (Routledge, 2020). excerpt
- Cohen, Warren I. America's Response to China: A History of Sino-American Relations (2010) excerpt and text search
- Fenby, Jonathan. The Penguin History of Modern China: The Fall and Rise of a Great Power 1850 to the Present (3rd ed. 2019) popular history.
- Ferdinand, Peter. "Westward ho—the China dream and 'one belt, one road': Chinese foreign policy under Xi Jinping." International Affairs 92.4 (2016): 941-957. online
- Fogel, Joshua. Articulating the Sino-sphere: Sino-Japanese relations in space and time (2009)
- Fravel, M. Taylor. Active Defense: China’s Military Strategy since 1949 (Princeton University Press, 2019) online reviews
- Garver, John W. China's Quest: The History of the Foreign Relations of the People's Republic (2nd ed. 2018) comprehensive scholarly history. excerpt
- Garver, John W. Protracted Contest: Sino-Indian Rivalry in the Twentieth Century' (2001), post 1950
- Hu, Weixing (2019). "Xi Jinping's 'Major Country Diplomacy': The Role of Leadership in Foreign Policy Transformation". Journal of Contemporary China. 28 (115): 1–14. doi:10.1080/10670564.2018.1497904. S2CID 158345991.
- Lampton, David M. Following the Leader: Ruling China, from Deng Xiaoping to Xi Jinping (U of California Press, 2014).
- Lanuzo, Steve L. "The Impact of Political Liberalization on Sino Myanmar Cooperation" (Naval Postgraduate School, 2018) online.
- Liu, Guoli, ed., Chinese Foreign Policy in Transition. (Transaction, 2004). ISBN 0202307522
- Lu, Ning. The dynamics of foreign-policy decisionmaking in China (Routledge, 2018).
- Quested, Rosemary K.I. Sino-Russian relations: a short history (Routledge, 2014) online
- Ryan, Keegan D. "The Extent of Chinese Influence in Latin America" (Naval Postgraduate School, 2018) online.
- Sutter, Robert G. Historical Dictionary of Chinese Foreign Policy (2011) excerpt and text search
- Sutter, Robert G. Foreign Relations of the PRC: The Legacies and Constraints of China's International Politics Since 1949 (Rowman & Littlefield; 2013) 355 pages excerpt and text search
- Swaine, Michael D. "Chinese views of foreign policy in the 19th party congress." China Leadership Monitor 55 (2018). online re 2017 Congress
- Westad, Odd Arne. Restless Empire: China and the World Since 1750 (Basic Books; 2012) 515 pages; comprehensive scholarly history
- Woo, Hunje. "Increased Chinese Economic Influence and its Impact on the Changing Security Environment on the Korean Peninsula" (Naval Postgraduate School, 2018) online
- Yahuda, Michael. End of Isolationism: China's Foreign Policy After Mao (Macmillan International Higher Education, 2016)
