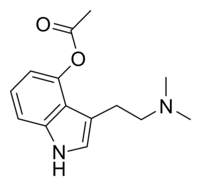
O-Acetylpsilocin
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2011) |
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 4-Acetoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine, 3-(2'-dimethylaminoethyl)-4-acetoxy-indole[1] |
| Routes of administration | Oral, IV, intranasal, rectal |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H18N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 246.310 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 172 to 173 °C (342 to 343 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
O-Acetylpsilocin (also known as psilacetin, 4-acetoxy-DMT, 4-AcO-DMT, or synthetic shrooms) is a semi-synthetic psychoactive drug that has been suggested by David Nichols to be a potentially useful alternative to psilocybin for pharmacological studies, as they are both believed to be prodrugs of psilocin.[2][3] However, some users report that O-acetylpsilocin's subjective effects differ from those of psilocybin and psilocin.[4][5] Additionally, some users prefer 4-AcO-DMT to natural psilocybin mushrooms due to feeling fewer adverse side effects such as nausea and heavy body load, which are more frequently reported in experiences involving natural mushrooms.[6] It is the acetylated form of the psilocybin mushroom alkaloid psilocin and is a lower homolog of 4-AcO-MET, 4-AcO-DET, 4-AcO-MiPT and 4-AcO-DiPT.
History
O-Acetylpsilocin (psilacetin) and several other esters of psilocin were patented on January 16, 1963 by Sandoz Ltd via Albert Hofmann & Franz Troxler.[1][7] Despite this, psilacetin remains a psychedelic compound with a limited history of use. It is theorized to be a prodrug of psilocin, as is psilocybin, which occurs naturally in many species of hallucinogenic mushrooms. This is because the aromatic acetyl moiety on the 4th position of the indole ring system is subject to deacetylation in acidic conditions such as those found in the stomach.[8] Psilacetin is O-acetylated psilocin, whereas psilocybin is O-phosphorylated.
Chemistry
O-Acetylpsilocin can be obtained by acetylation of psilocin under alkaline or strongly acidic conditions. It is, therefore, a semi-synthetic compound. It is believed to be a prodrug of psilocin; however, speculation exists that psilacetin itself also may be psychoactive. O-Acetylpsilocin is more resistant than psilocin to oxidation under basic conditions due to its acetoxy group. While O-acetylpsilocin is not well researched (sometimes viewed negatively as a research chemical, as opposed to psilocin and psilocybin), it is not as difficult as psilocybin to synthesize. Due to their similar proposed mechanisms of action, this factor may provide further support for the proposition that O-acetylpsilocin might serve as an appropriate substitute for psilocybin in research of the application of psychedelic compounds in medicine.[2]
Pharmacology
- See psilocin for more details.
In the body O-acetylpsilocin is deacetylated to psilocin by deacetylases/acetyltransferases during first pass metabolism[citation needed] and during subsequent passes through the liver (evident as psilacetin is also active via parenteral routes of ingestion).
Claims of subjective differences in effects between the acetylated and non-acetylated forms of psilocin vary:[4] some users report that O-acetylpsilocin lasts slightly longer, whilst others report that it lasts for a considerably shorter time. Many users report less body load and nausea compared with psilocin. Some users find that the visual effects produced by O-acetylpsilocin more closely resemble those produced by DMT than those produced by psilocin or psilocybin. These differences could be possible if psilacetin is psychoactive in itself and not merely as a prodrug. Despite this, there have been no controlled clinical studies to distinguish among the phenomenological effects of psilacetin, psilocin, and psilocybin.

Legality
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2011) |
Australia
O-Acetylpsilocin can be considered an analog of psilocin making it a Schedule 9 prohibited substance in Australia under the Poisons Standard (October 2015).[9] A Schedule 9 substance is a substance which may be abused or misused, the manufacture, possession, sale or use of which should be prohibited by law except when required for medical or scientific research, or for analytical, teaching or training purposes with approval of Commonwealth and/or State or Territory Health Authorities.[9]
United States
O-Acetylpsilocin is ambiguously legal for use as a lab reagent or research chemical; however, it is an acetate ester of psilocin, meaning it would be considered Schedule I under the Federal Analogue Act if sold for human consumption.
United Kingdom
O-Acetylpsilocin, being an ester of psilocin, is a Class A drug in the UK under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971.[10]
Italy
O-Acetylpsilocin is illegal in Italy as it is an ester of a prohibited substance.
Sweden
The Riksdag added 4-AcO-DMT to Narcotic Drugs Punishments Act under swedish schedule I ("substances, plant materials and fungi which normally do not have medical use" ) as of January 25, 2017, published by Medical Products Agency (MPA) in regulation HSLF-FS 2017:1 listed as 4-acetoxi-N,N-dimetyltryptamin.[11]
See also
- 4-AcO-DPT
- 4-MeO-DMT
- 4-PrO-DMT
- ALD-52
- Ayahuasca
- Psilocybin
- Psilocybin mushroom
- Psychedelic drug
- Serotonergic psychedelic
- Tryptamine
References
- ^ a b US patent 3075992, Hofmann A, Troxler F, "Esters of indoles", assigned to Sandoz Ltd.
- ^ a b Nichols D, Fescas S (1999). "Improvements to the Synthesis of Psilocybin and a Facile Method for Preparing the O-Acetyl Prodrug of Psilocin" (PDF). Synthesis. 1999 (6): 935–938. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.690.8071. doi:10.1055/s-1999-3490. S2CID 32044725. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 February 2012. Retrieved 17 January 2012.
- ^ Bauer, Barbara E. (2019-09-18). "The State of the Art of Psilacetin (4-AcO-DMT)". Psychedelic Science Review. Retrieved 2021-02-13.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b "4-AcO-DMT (also 4-acetoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine) : Erowid Exp: Main Index". www.erowid.org. Archived from the original on 2010-07-28.
- ^ Janikian, Michelle (2020-05-26). "The Complete Guide: 4-AcO-DMT a.k.a. Synthetic Shrooms". DoubleBlind Mag. Retrieved 2021-02-13.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Palamar, Joseph J.; Acosta, Patricia (2020-01-07). "A qualitative descriptive analysis of effects of psychedelic phenethylamines and tryptamines". Human Psychopharmacology. 35 (1): e2719. doi:10.1002/hup.2719. ISSN 0885-6222. PMC 6995261. PMID 31909513.
- ^ US 3075992
- ^ Staněk J, Černá MJ (January 1963). "Acidic deacetylation of sugar acetates". Tetrahedron Letters. 4 (1): 35–7. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)90572-6.
- ^ a b "Poisons Standard October 2015". Federal Register of Legislation. Australian Government. Archived from the original on 2016-01-19. Retrieved 2016-01-06.
- ^ Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (Schedule 2 Part I). 1971.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-10-31. Retrieved 2017-04-21.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
External links
- 4-AcO-DMT information at IsomerDesign.com
- Erowid 4-Acetoxy-DMT Vault
- "Esters of Indoles" US Patent # 3,075,992 - Awarded to Sandoz Ltd. (via Albert Hofmann & Franz Troxler) on January 29, 1963.
