Android version history

The version history of the Android mobile operating system began with the release of the Android alpha in November 2007. The first commercial version, Android 1.0, was released in September 2008. Android is continually developed by Google and the Open Handset Alliance (OHA), and has seen a number of updates to its base operating system since the initial release.
The most recent major Android update is Android 6.0 "Marshmallow", which was released in October 2015. Since April 2009, Android versions have been developed under a confectionery-themed code name and released in alphabetical order, beginning with Android 1.5 "Cupcake"; the earlier versions 1.0 and 1.1 were not released under specific code names.
| Code name | Version number | Initial release date |
|---|---|---|
| Cupcake | 1.5 | April 27, 2009 |
| Donut | 1.6 | September 15, 2009 |
| Eclair | 2.0–2.1 | October 26, 2009 |
| Froyo | 2.2–2.2.3 | May 20, 2010 |
| Gingerbread | 2.3–2.3.7 | December 6, 2010 |
| Honeycomb[a] | 3.0–3.2.6 | February 22, 2011 |
| Ice Cream Sandwich | 4.0–4.0.4 | October 18, 2011 |
| Jelly Bean | 4.1–4.3.1 | July 9, 2012 |
| KitKat | 4.4–4.4.4, 4.4W–4.4W.2 | October 31, 2013 |
| Lollipop | 5.0–5.1.1 | November 12, 2014 |
| Marshmallow | 6.0–6.0.1 | October 5, 2015 |
Pre-commercial release versions
The development of Android started in 2003 by Android, Inc., which was purchased by Google in 2005.[2]
Alpha
There were at least two internal releases of the software inside Google and the OHA before the beta version was released in November 2007. For the milestones in internal releases, names of fictional robots were chosen, with various releases code-named "Astro Boy", "Bender" and "R2-D2".[3][4][5]
Dan Morrill created some of the first mascot logos, but the current green Android logo was designed by Irina Blok.[6] The project manager, Ryan Gibson, conceived the confectionery-themed naming scheme that has been used for the majority of the public releases, starting with Android 1.5 "Cupcake".
-
se10578A
-
se3740079K
Beta
The beta was released on November 5, 2007,[7][8] while the software development kit (SDK) was released on November 12, 2007.[9] The November 5 date is popularly celebrated as Android's "birthday".[10] Public beta versions of the SDK were released in the following order:[11]
- November 12, 2007: m3-rc20a (milestone 3, release code 20a)[12]
- November 16, 2007: m3-rc22a (milestone 3, release code 22a)[13]
- December 14, 2007: m3-rc37a (milestone 3, release code 37a)[14]
- February 13, 2008: m5-rc14 (milestone 5, release code 14)[15]
- March 3, 2008: m5-rc15 (milestone 5, release code 15)[11]
- August 18, 2008: 0.9[16][17]
- September 23, 2008: 1.0-r1[18][19]
Version history by API level
The following tables show the release dates and key features of all Android operating system updates to date, listed chronologically by their official application programming interface (API) levels.
| Android 1.0 (API level 1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Android 1.0, the first commercial version of the software, was released on September 23, 2008.[20] The first commercially available Android device was the HTC Dream.[21] Android 1.0 incorporated the following features: | |||
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 1.0 | September 23, 2008 |
|
File:Android 1.0 Screenshot.png Android 1.0 on an Android SDK emulator |
| Android 1.1 (API level 2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| On February 9, 2009, the Android 1.1 update was released, initially for the HTC Dream only. Android 1.1 was known as "Petit Four" internally, though this name was not used officially.[28] The update resolved bugs, changed the Android API and added a number of features:[29] | |||
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 1.1 | February 9, 2009 |
|
File:Android 1.1 Beta Screenshot.png Android 1.1 on an Android SDK emulator |
| Android 1.5 Cupcake (API level 3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| On April 27, 2009, the Android 1.5 update was released, based on Linux kernel 2.6.27.[30][31] This was the first release to officially use a codename based on a dessert item ("Cupcake"), a theme which would be used for all releases henceforth. The update included several new features and UI amendments:[32] | |||
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 1.5 | April 27, 2009[30] |
|
File:Android 1.5 Cupcake Screenshot.png Android 1.5 on an Android SDK emulator |
| Android 1.6 Donut (API level 4) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| On September 15, 2009, the Android 1.6 SDK – dubbed Donut – was released, based on Linux kernel 2.6.29.[34][35][36] Included in the update were numerous new features:[34] | |||
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 1.6 | September 15, 2009[35] |
|
 Android 1.6 on an Android SDK emulator |
| Android 2.0 Eclair (API level 5) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| On October 26, 2009, the Android 2.0 SDK was released, based on Linux kernel 2.6.29 and codenamed Eclair.[37] Changes include the ones listed below.[38] | |||
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 2.0 | October 26, 2009 |
|
File:Android 2.0 Screenshot.png Android 2.0 on an Android SDK emulator |
| Android 2.0.1 Eclair (API level 6) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 2.0.1 | December 3, 2009[40] |
|
|
| Android 2.1 Eclair (API level 7) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 2.1 | January 12, 2010[41] |
|
 Android 2.1 on an Android SDK emulator |
| Android 2.2–2.2.3 Froyo (API level 8) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| On May 20, 2010, the SDK for Android 2.2 (Froyo, short for frozen yogurt) was released, based on Linux kernel 2.6.32.[42] | |||
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 2.2 | May 20, 2010 |
|
 Android 2.2 Froyo home screen |
| 2.2.1 | January 18, 2011 |
| |
| 2.2.2 | January 22, 2011 | ||
| 2.2.3 | November 21, 2011[50] |
| |
| Android 2.3–2.3.2 Gingerbread (API level 9) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| On December 6, 2010, the Android 2.3 (Gingerbread) SDK was released, based on Linux kernel 2.6.35.[51][52] Changes included:[51] | |||
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 2.3 | December 6, 2010[52] |
|
 Android 2.3 on an Android SDK emulator |
| 2.3.1 | December 2010 |
| |
| 2.3.2 | January 2011 | ||
| Android 2.3.3–2.3.7 Gingerbread (API level 10) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 2.3.3 | February 9, 2011 |
|
|
| 2.3.4 | April 28, 2011[56] |
| |
| 2.3.5 | July 25, 2011 |
| |
| 2.3.6 | September 2, 2011[62] |
| |
| 2.3.7 | September 21, 2011 |
| |
| Android 3.0 Honeycomb (API level 11) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| On February 22, 2011, the Android 3.0 (Honeycomb) SDK – the first tablet-only Android update – was released, based on Linux kernel 2.6.36.[65][66][67][68] The first device featuring this version, the Motorola Xoom tablet, was released on February 24, 2011.[69] The update's features included:[65] | |||
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 3.0 | February 22, 2011[67] |
|
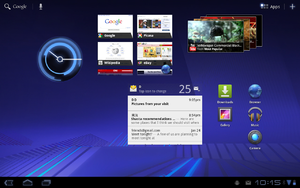 Android 3.0 on the Motorola Xoom tablet |
| Android 3.1 Honeycomb (API level 12) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 3.1 | May 10, 2011[72] |
|
|
| Android 3.2–3.2.6 Honeycomb (API level 13) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Most first- and second-generation Google TV-enabled devices utilize Honeycomb 3.2.[75] | |||
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 3.2 | July 15, 2011[76] |
|
|
| 3.2.1 | September 20, 2011 |
| |
| 3.2.2 | August 30, 2011 |
| |
| 3.2.3 |
| ||
| 3.2.4 | December 2011 |
| |
| 3.2.5 | January 2012 |
| |
| 3.2.6 | February 2012 |
| |
| Android 4.0–4.0.2 Ice Cream Sandwich (API level 14) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| The SDK for Android 4.0.1 (Ice Cream Sandwich), based on Linux kernel 3.0.1,[78] was publicly released on October 19, 2011.[79] Google's Gabe Cohen stated that Android 4.0 was "theoretically compatible" with any Android 2.3.x device in production at that time.[80] The source code for Android 4.0 became available on November 14, 2011.[81] Ice Cream Sandwich was the last version to officially support Adobe Systems' Flash player.[82] The update introduced numerous new features:[83][84][85] | |||
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 4.0 | October 18, 2011[83] |
|
 Android 4.0 on the Samsung Galaxy Nexus |
| 4.0.1 | October 21, 2011 |
| |
| 4.0.2 | November 28, 2011 |
| |
| Android 4.0.3–4.0.4 Ice Cream Sandwich (API level 15) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 4.0.3 | December 16, 2011[91] |
|
|
| 4.0.4 | March 29, 2012[93] |
| |
| Android 4.1–4.1.2 Jelly Bean (API level 16) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Google announced Android 4.1 (Jelly Bean) at the Google I/O conference on June 27, 2012. Based on Linux kernel 3.0.31, Jelly Bean was an incremental update with the primary aim of improving the functionality and performance of the user interface. The performance improvement involved "Project Butter", which uses touch anticipation, triple buffering, extended vsync timing and a fixed frame rate of 60 fps to create a fluid and "buttery-smooth" UI.[95] Android 4.1 Jelly Bean was released to the Android Open Source Project on July 9, 2012,[96] and the Nexus 7 tablet, the first device to run Jelly Bean, was released on July 13, 2012. | |||
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 4.1 | July 9, 2012 |
|
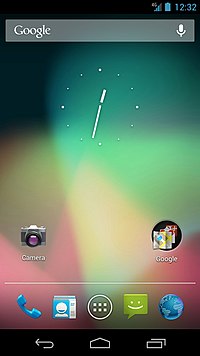 Android 4.1 on the Samsung Galaxy Nexus |
| 4.1.1 | July 11, 2012[100] |
| |
| 4.1.2 | October 9, 2012[101] | ||
| Android 4.2–4.2.2 Jelly Bean (API level 17) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Google was expected to announce Jelly Bean 4.2 at an event in New York City on October 29, 2012, but the event was cancelled due to Hurricane Sandy.[104] Instead of rescheduling the live event, Google announced the new version with a press release, under the slogan "A new flavor of Jelly Bean". Jelly Bean 4.2 was based on Linux kernel 3.4.0, and debuted on Google's Nexus 4 and Nexus 10, which were released on November 13, 2012.[105][106] | |||
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 4.2 | November 13, 2012[107] |
|
File:Nexus 4 - Android 4.2.pngAndroid 4.2 on the Nexus 4 |
| 4.2.1 | November 27, 2012[112] | ||
| 4.2.2 | February 11, 2013[114] |
| |
| Android 4.3–4.3.1 Jelly Bean (API level 18) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Google released Jelly Bean 4.3 under the slogan "An even sweeter Jelly Bean" on July 24, 2013, during an event in San Francisco called "Breakfast with Sundar Pichai". Most Nexus devices received the update within a week, although the second-generation Nexus 7 tablet was the first device to officially ship with it.[116] A minor bugfix update was released on August 22, 2013.[117] | |||
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 4.3 | July 24, 2013[118] |
|
File:Android 4.3 on Nexus 7 (2013).jpg Android 4.3 on the second-generation Nexus 7 |
| 4.3.1 | October 3, 2013[127] |
| |
| Android 4.4–4.4.4 KitKat (API level 19) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Google announced Android 4.4 KitKat on September 3, 2013. Although initially under the "Key Lime Pie" ("KLP") codename, the name was changed because "very few people actually know the taste of a key lime pie."[129] Some technology bloggers also expected the "Key Lime Pie" release to be Android 5.[130] KitKat debuted on Google's Nexus 5 on October 31, 2013, and was optimized to run on a greater range of devices than earlier Android versions, having 512 MB of RAM as a recommended minimum; those improvements were known as "Project Svelte" internally at Google.[131] The required minimum amount of RAM available to Android is 340 MB, and all devices with less than 512 MB of RAM must report themselves as "low RAM" devices.[132] | |||
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 4.4 | October 31, 2013[133][134] |
|
File:Nexus 4 - Android 4.4.png Android 4.4 on the Nexus 4 |
| 4.4.1 | December 5, 2013[146] |
| |
| 4.4.2 | December 9, 2013[149] | ||
| 4.4.3 | June 2, 2014[151] | ||
| 4.4.4 | June 19, 2014[154] |
| |
| Android 4.4W–4.4W.2 KitKat, with wearable extensions (API level 20) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 4.4W[156] | June 25, 2014[157] |
|
|
| 4.4W.1 | September 6, 2014[158] |
| |
| 4.4W.2 | October 21, 2014[159] |
| |
| Android 5.0–5.0.2 Lollipop (API level 21) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Android 5.0 "Lollipop" was unveiled under the codename "Android L" on June 25, 2014, during Google I/O. It became available as official over-the-air (OTA) updates on November 12, 2014, for select devices that run distributions of Android serviced by Google, including Nexus and Google Play edition devices. Its source code was made available on November 3, 2014.[160][161]
Lollipop features a redesigned user interface built around a responsive design language referred to as "material design". Other changes include improvements to the notifications, which can be accessed from the lockscreen and displayed within applications as top-of-the-screen banners. Furthermore, Google made internal changes to the platform, with the Android Runtime (ART) officially replacing Dalvik for improved application performance, and with changes intended to improve and optimize battery usage, known internally as Project Volta.[162][163][164][165] | |||
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 5.0[166] | November 12, 2014[167] |
|
File:Android 5.0-en.png Android 5.0 on the Nexus 5 |
| 5.0.1 | December 2, 2014[181] |
| |
| 5.0.2 | December 19, 2014[182] | ||
| Android 5.1–5.1.1 Lollipop (API level 22) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 5.1 | March 9, 2015[184] |
|
|
| 5.1.1 | April 21, 2015[187] |
| |
| Android 6.0–6.0.1 Marshmallow (API level 23) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Android 6.0 "Marshmallow" was unveiled under the codename "Android M" during Google I/O on May 28, 2015, for the Nexus 5 and Nexus 6 phones, Nexus 9 tablet, and Nexus Player set-top box, under the build number MPZ44Q.[189] The third developer preview (MPA44G) was released on August 17, 2015 for the Nexus 5, Nexus 6, Nexus 9 and Nexus Player devices,[190] and was updated to MPA44I that brought fixes related to Android for Work profiles.[191] | |||
| Version | Release date | Features | Image(s) |
| 6.0 | October 5, 2015[192] |
|
File:Android 6.0-en.png Android 6.0 on the Nexus 5 |
| 6.0.1 | December 2015 | ||
Hardware requirements
The main hardware platform for Android is the ARM architecture (ARMv7 and ARMv8-A architectures), with x86[d] and MIPS[e] architectures also officially supported in later versions of Android. Since Android 5.0 "Lollipop", 64-bit variants of all platforms are supported in addition to the 32-bit variants.[209] Unofficial Android-x86 project used to provide support for the x86 and MIPS architectures ahead of the official support.[210][211] Since 2012, Android devices with Intel processors began to appear, including phones[212] and tablets. While gaining support for 64-bit platforms, Android was first made to run on 64-bit x86 and then on ARM64.[citation needed]
Requirements for the minimum amount of RAM for devices running Android 5.1 range from 512 MB of RAM for normal-density screens, to about 1.8 GB for high-density screens.[213] The recommendation for Android 4.4 is to have at least 512 MB of RAM,[214] while for "low RAM" devices 340 MB is the required minimum amount that does not include memory dedicated to various hardware components such as the baseband processor.[132] Android 4.4 requires a 32-bit ARMv7, MIPS or x86 architecture processor (latter two through unofficial ports),[210][215] together with an OpenGL ES 2.0 compatible graphics processing unit (GPU).[216] Android supports OpenGL ES 1.1, 2.0, 3.0 and 3.1. Some applications may explicitly require a certain version of the OpenGL ES, and suitable GPU hardware is required to run such applications.[216]
Android used to require an autofocus camera, which was relaxed to a fixed-focus camera[217] if present at all, since the camera was dropped as a requirement entirely (except for smartphones) when Android started to be used on set-top boxes.
See also
Notes
- ^ Honeycomb is the first version to support tablets, but it can be used only on tablets and the full source code has not been released. All later versions of Android support both tablets and smartphones.
- ^ The 2.3.6 update had the side-effect of impairing the Wi-Fi hotspot functionality of many Canadian Nexus S phones. Google acknowledged this problem and fixed it in late September.[63][64]
- ^ For Canadian consumers, 4.0.2 reportedly created a bug on the Galaxy Nexus that crashed the application market when users attempted to view details of any Android application. It also inadvertently reduced the NFC capabilities of the Nexus phone.[89][90]
- ^ Lowest supported x86 generation is the P6 microarchitecture, also called i686.[207]
- ^ Supported is revision 1 of MIPS32[208] and revision 6 for 64-bit MIPS64[207]
References
- ^ "Android Developers: Dashboards". developer.android.com. February 1, 2016. Retrieved February 8, 2016.
- ^ Elgin, Ben (August 17, 2005). "Google Buys Android for Its Mobile Arsenal". Bloomberg Businessweek. Bloomberg. Archived from the original on February 24, 2011. Retrieved February 20, 2012.
- ^ "A History of Pre-Cupcake Android Codenames". Android Police. September 17, 2012. Retrieved October 20, 2013.
- ^ "Dianne Hackborn". Google+. September 1, 2012. Retrieved April 8, 2013.
- ^ "Dan Morrill". Google+. January 2, 2013. Retrieved January 5, 2013.
- ^ Breeze, Mez. "The designer behind the logo". TheNextWeb.com. TNW. Retrieved August 14, 2013.
- ^ "Google Launches Android, an Open Mobile Platform". Google Operating System. November 5, 2007.
- ^ "Live Google's gPhone Open handset alliance conference call" (transcript). Gizmodo. November 5, 2007. Retrieved February 8, 2013.
- ^ "Google releases Android SDK". Macworld. November 12, 2007. Retrieved February 8, 2013.
- ^ "Android's 5th Birthday Celebration: European Best-of-Best Hackathon Series". Devfest.info. October 2012. Retrieved January 5, 2013.
- ^ a b "SDK Archives". developer.android.com. Retrieved March 7, 2015.
- ^ "Android 0.5, Milestone 3—the first public build - The history of Android". Ars Technica. June 16, 2014. Retrieved March 7, 2015.
- ^ "Android: the first week". Android Developers Blog. November 16, 2007. Retrieved January 24, 2013.
- ^ "Life can be tough; here are a few SDK improvements to make it a little easier". Android Developers Blog. December 14, 2007. Retrieved January 24, 2013.
- ^ "Android SDK m5-rc14 now available". Android Developers Blog. February 13, 2008. Retrieved January 24, 2013.
- ^ "Announcing a beta release of the Android SDK". Android Developers Blog. August 18, 2008. Retrieved January 24, 2013.
- ^ "Android 0.9, Beta—hey, this looks familiar! - The history of Android". Ars Technica. June 16, 2014. Retrieved March 11, 2015.
- ^ "Announcing the Android 1.0 SDK, release 1". Android Developers Blog. September 23, 2008. Retrieved January 24, 2013.
- ^ "Android 1.0—introducing Google Apps and actual hardware - The history of Android". Ars Technica. June 16, 2014. Retrieved March 11, 2015.
- ^ Morrill, Dan (September 23, 2008). "Announcing the Android 1.0 SDK, release 1". Android Developers Blog. Retrieved January 12, 2011.
- ^ "T-Mobile Unveils the T-Mobile G1 – the First Phone Powered by Android". T-Mobile. Retrieved October 15, 2013.
- ^ a b Topolsky, Joshua (October 16, 2008). "T-Mobile G1 review, part 2: software and wrap-up". Engadget. Retrieved June 28, 2013.
- ^ a b c d e "Release features – Android 1.0". Google. 2008. Retrieved February 7, 2013.
- ^ a b c Segan, Sascha (October 16, 2008). "T-Mobile G1 (Google Android Phone)". PC Magazine. Retrieved February 6, 2013.
- ^ LaCouvee, Darcy (October 17, 2008). "Folders on the Android desktop, and how to rename them". Android Authority. Retrieved June 28, 2013.
- ^ "Status Bar Notifications". Android Developers. May 24, 2012. Retrieved June 1, 2012.
- ^ "What is Android?". TechPluto.com. September 18, 2008. Retrieved June 28, 2013.
- ^ "Android Platform Overview". Android.com. Retrieved September 15, 2012.
- ^ "Android 1.1 Version Notes". Android Developers. February 2009. Retrieved January 12, 2011.
- ^ a b Ducrohet, Xavier (April 27, 2009). "Android 1.5 is here!". Android Developers Blog. Archived from the original on September 25, 2009. Retrieved September 3, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Rob, Jackson (April 30, 2009). "CONFIRMED: Official Cupcake Update Underway for T-Mobile G1 USA & UK!". Phandroid. Retrieved September 3, 2009.
- ^ "Android 1.5 Platform Highlights". Android Developers. April 2009. Retrieved September 3, 2009.
- ^ "App Widgets". Android Developers. 2012. Retrieved October 23, 2012.
- ^ a b "Android 1.6 Platform Highlights". Android Developers. September 2009. Archived from the original on September 27, 2009. Retrieved October 1, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Ducrohet, Xavier (September 15, 2009). "Android 1.6 SDK is here". Android Developers Blog. Archived from the original on September 25, 2009. Retrieved October 1, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Ryan, Paul (October 1, 2009). "Google releases Android 1.6; Palm unleashes WebOS 1.2". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on October 2, 2009. Retrieved October 1, 2009.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Android 2.0, Release 1". Android Developers. Archived from the original on October 28, 2009. Retrieved October 27, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Android 2.0 Platform Highlights". Android Developers. Archived from the original on October 29, 2009. Retrieved October 27, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Android 2.0 API Changes Summary". Archived from the original on January 24, 2010. Retrieved March 6, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Android 2.0.1, Release 1 SDK". Android Developers. Archived from the original on January 15, 2010. Retrieved January 17, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Android 2.1, Release 1". Android Developers. Archived from the original on January 15, 2010. Retrieved January 17, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Ducrohet, Xavier (May 20, 2010). "Android 2.2 and developers goodies". Android Developers Blog. Google. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
- ^ a b "Unofficially Confirmed Froyo Features, Post-Day-1 Of Google I/O". Android Police. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
- ^ "Nexus One Is Running Android 2.2 Froyo. How Fast Is It Compared To 2.1? Oh, Only About 450% Faster". Android Police. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
- ^ Sorrel, Charlie (May 13, 2010). "Android 2.2 'Froyo' Features USB, Wi-Fi Tethering". Wired. Retrieved February 14, 2013.
- ^ "Browser support for file upload field is coming in Froyo". code.google.com. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
- ^ Stone, Brad (April 27, 2010). "Google's Andy Rubin on Everything Android". New York Times. Archived from the original on April 30, 2010. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Supporting Multiple Screens: Range of screens supported". Android Developers. Retrieved February 8, 2013.
- ^ Hollister, Sean (January 22, 2011). "Nexus One gets tiny update to Android 2.2.2, fixes SMS routing issues". Engadget. Retrieved November 17, 2011.
- ^ "Android 2.2.3 source tag". Google. Retrieved September 2, 2013.
- ^ a b "Android 2.3 Platform Highlights". Android Developers Blog. December 6, 2010. Archived from the original on December 10, 2010. Retrieved December 7, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Ducrohet, Xavier (December 6, 2010). "Android 2.3 Platform and Updated SDK Tools". Android Developers Blog. Archived from the original on December 27, 2010. Retrieved December 7, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Ts'o, Theodore (December 12, 2010). "Android will be using ext4 starting with Gingerbread". Linux Foundation. Archived from the original on May 28, 2011. Retrieved June 11, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Tim Bray (December 19, 2010). "Saving Data Safely". Android Developers Blog. Retrieved June 11, 2011.
- ^ "Android 2.3.3 Platform". Android Developers. 2011. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ "Android 2.3.4 source tag". Google. Retrieved September 2, 2013.
- ^ "Video Chat on Your Android Phone". Google Mobile Blog. April 28, 2011. Retrieved April 18, 2013.
- ^ "Open Accessory Library 2.3.4". Android Developers. Retrieved August 3, 2012.
- ^ Sarkar, Abhijoy (October 14, 2013). "Is it Java that weakened Android's SSL security?". Muktware. Retrieved November 2, 2013.
- ^ "Why Android SSL was downgraded from AES256-SHA to RC4-MD5 in late 2010". op-co.de. October 15, 2013. Retrieved November 2, 2013.
- ^ Arghire, Ionut. "Android 2.3.5 Arrives on Galaxy S in the UK". Softpedia.com. Retrieved December 1, 2011.
- ^ Stephen Schenck (September 2, 2011). "Nexus S Ushers-In Android 2.3.6, But Does It Fix Or Cause Bugs?". pocketnow. Retrieved August 4, 2014.
- ^ Ali Waqas (September 28, 2011). "Android 2.3.6 Gingerbread Update For Nexus S Available (Wi-Fi And Tethering Fix)". Addictive Tips. Retrieved December 20, 2011.
- ^ Anton D. Nagy (September 27, 2011). "Google Samsung Nexus S Gets Android 2.3.6 Update". PocketNow. Retrieved December 20, 2011.
- ^ a b "Android 3.0 Platform Highlights". Android Developers. Archived from the original on February 16, 2011. Retrieved February 23, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Rubin, Andy (January 5, 2011). "A Sneak Peek of Android 3.0, Honeycomb". Google Mobile Blog. Archived from the original on January 8, 2011. Retrieved January 5, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Xavier Ducrohet (February 22, 2011). "Final Android 3.0 Platform and Updated SDK Tools". Android Developers Blog. Archived from the original on March 5, 2011. Retrieved February 23, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Mithun Chandrasekhar (February 2, 2011). "Google's Android Event Analysis". AnandTech. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
I confirmed this with Google; Honeycomb, at least in the current form, will not be coming to non-tablet devices.
- ^ Nilay Patel (January 26, 2011). "Motorola Atrix 4G and Xoom tablet launching at the end of February, Droid Bionic and LTE Xoom in Q2". Engadget. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- ^ a b Ho, Joshua. "Examining MicroSD changes in Android 4.4". Anandtech. Retrieved March 28, 2014.
- ^ Cody Toombs (February 17, 2014). "External Blues: Google Has Brought Big Changes To SD Cards In KitKat, And Even Samsung Is Implementing Them". Android Police. Retrieved February 20, 2014.
- ^ Ducrohet, Xavier (May 10, 2011). "Android 3.1 Platform, New SDK tools". Android Developers Blog. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved May 10, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Android Supported Media Formats". Android Developers. Retrieved March 30, 2012.
- ^ "Issue 1461 – Android – FLAC file support enhancement request". Code.google.com. Retrieved August 5, 2011.
- ^ "Google TV goes Android 3.2, next up Ice Cream Sandwich". GigaOM. February 2, 2012. Retrieved February 6, 2013.
- ^ Ducrohet, Xavier (July 15, 2011). "Android 3.2 Platform and Updated SDK tools". Android Developers Blog. Retrieved July 16, 2011.
- ^ "Supporting Multiple Screens: Declaring Tablet Layouts for Android 3.2". Android Developers. 2012. Retrieved February 18, 2013.
- ^ Maroger (October 19, 2011). "Ice Cream Sandwich Runs on Linux Kernel 3.0.1". Fine Oils. Blogspot. Retrieved July 24, 2013.
- ^ Rey, Francis (October 19, 2011). "Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich SDK Now Available". Social Barrel. Retrieved July 24, 2013.
- ^ Stevens, Tim (October 19, 2011). "Google confirms Nexus S will get Ice Cream Sandwich – for real this time (Gingerbread devices, too)". Engadget. Retrieved July 24, 2013.
- ^ Messina, Vincent (November 15, 2011). "Ice Cream Sandwich source code released, custom ROMs inevitable". AndroidGuys. Retrieved July 24, 2013.
- ^ "Today Is The Last Day To Get Flash For Android". WebProNews. August 14, 2012. Retrieved February 7, 2013.
- ^ a b Molen, Brad (October 19, 2011). "Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich now official, includes revamped design, enhancements galore". Engadget. Retrieved October 19, 2011.
- ^ German, Kent (October 18, 2011). "Ice Cream Sandwich adds tons of new features". CNET. Retrieved July 24, 2013.
- ^ Velazco, Chris (October 18, 2011). "A Quick Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich Feature Rundown". Tech Crunch. Retrieved July 24, 2013.
- ^ Fitzpatrick, Jason. "What Exactly Happens When You Swipe An Android App From the Recent Apps List?". How-To Geek. Retrieved September 19, 2014.
- ^ Kennemer, Quentyn (October 19, 2011). "Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich has Hardware Acceleration". Phandroid. Retrieved October 19, 2011.
- ^ "Wi-Fi Direct". Android Developers. Retrieved July 27, 2013.
- ^ "Verizon's 4G LTE Galaxy Nexus Gets Pictured, Receives Android 4.0.2 Update". DroidLife. November 28, 2011. Retrieved December 8, 2011.
- ^ "Within 2 Hours of Activation, Your Galaxy Nexus Will Receive an Update". DroidLife. December 15, 2011. Retrieved December 15, 2011.
- ^ "Android 4.0.3 Platform and Updated SDK tools". Android Developers Blog. December 16, 2011. Retrieved January 4, 2012.
- ^ "Android 4.0.3 announced, bringing 'variety of optimizations and bug fixes' to phones and tablets". Engadget. December 16, 2011. Retrieved December 17, 2011.
- ^ "Google announces Android 4.0.4". The Inquirer. March 29, 2012. Retrieved March 31, 2012.
- ^ Google announces 4.0.4 on Google+. March 28, 2012. Retrieved March 31, 2012.
- ^ a b c d "Android 4.1 for Developers". Android Developers. Retrieved February 9, 2013.
- ^ Queru, Jean-Baptiste. "Android 4.1 in AOSP". Retrieved July 12, 2012.
- ^ "Confirmed: Android 4.1 uses different layouts for different tablet sizes". ComputerWorld. Retrieved July 8, 2012.
- ^ "Issue 3461: Implement Gapless Playback of consecutive audio files". code.google.com. Retrieved November 12, 2012.
- ^ "Android 4.1 finally adds gapless music playback to stock music apps". Pocketables.com. June 29, 2012. Retrieved June 30, 2012.
- ^ "Android 4.1.1 Nexus 7 Update". GSMArena.com. July 11, 2012. Retrieved February 26, 2013.
- ^ "Android 4.1.2 rolling out for Nexus 7". The Verge. October 9, 2012. Retrieved October 9, 2012.
- ^ "Android 4.1.2 brings homescreen rotation to devices". GigaOM. October 9, 2012. Retrieved October 9, 2012.
- ^ "New Feature In Android 4.1.2: Expanding/Collapsing Notifications With One Finger (Video)". Android Police. October 9, 2012. Retrieved October 9, 2012.
- ^ "Monday's Google event in NYC canceled due to Hurricane Sandy". Android Central. October 27, 2012. Retrieved February 19, 2014.
- ^ "Android 4.2 Jelly Bean lands on Nexus 7". Know Your Mobile. November 14, 2012.
- ^ "Google Releases Nexus 4, Nexus 10 and Android 4.2". IGN. November 13, 2012. Retrieved November 16, 2012.
- ^ "Android 4.2 adds gestue typing, wireless TV display, multiple user support on tablets, and more". The Verge. October 29, 2012. Retrieved October 29, 2012.
- ^ "Android 4.2 Jelly Bean brings all-new photography powers". TechRadar.com. October 29, 2012. Retrieved November 12, 2012.
- ^ a b Brian Klug. "AnandTech - The Next Version of Android - Some of What's Coming". Retrieved October 28, 2014.
- ^ "Jelly Bean". Android developer portal. Retrieved July 2, 2014.
- ^ "Exclusive Android 4.2 Alpha Teardown, Part 2: SELinux, VPN Lockdown, And Premium SMS Confirmation". Android Police. October 17, 2012. Retrieved November 12, 2012.
- ^ "(Changelog) What's New In Android 4.2.1 (JOP40D)". Android Police. November 27, 2012. Retrieved November 27, 2012.
- ^ "Sorry, Santa – Google Cancels December In Android 4.2". Android Police. November 17, 2012. Retrieved November 27, 2012.
- ^ "Breaking: Android 4.2.2 (Build JDQ39) Update Rolling Out To GSM Galaxy Nexus, Nexus 7, Nexus 10". Android Police. February 11, 2013. Retrieved February 12, 2013.
- ^ "Android 4.2.2 brings Bluetooth audio fixes to Nexus phones and tablets". Ars Technica. February 12, 2013. Retrieved February 12, 2013.
- ^ "Google Announces Android 4.3, Update Rolling Out Today". Tom's Hardware. July 24, 2013. Retrieved July 25, 2013.
- ^ "Android Open Source Project now has latest 4.3 fixes for most Nexus hardware". Engadget. August 22, 2013. Retrieved August 22, 2013.
- ^ "Android 4.3 announced, rolling out to Nexus devices today". The Verge. July 24, 2013. Retrieved July 24, 2013.
- ^ a b c d e "Introducing Android 4.3, a sweeter Jelly Bean". Official Android Blog. July 24, 2013. Retrieved July 30, 2013.
- ^ "Android 4.3 supports TRIM, improves performance on Nexus devices". Engadget. July 30, 2013. Retrieved July 30, 2013.
- ^ "Another Android 4.3 Change: Photo Spheres Look A Lot Better Now". Android Police. July 25, 2013. Retrieved July 28, 2013.
- ^ "Android 4.3 And Updated Camera UI Spotted On A Nexus 4 At Thailand Mobile Expo". Android Police. May 24, 2013. Retrieved July 30, 2013.
- ^ "App Ops: Android 4.3's Hidden App Permission Manager, Control Permissions For Individual Apps!". Android Police. July 25, 2013. Retrieved July 30, 2013.
- ^ "Android 4.3 source code reveals support for 4K resolution". Engadget. July 26, 2013. Retrieved July 30, 2013.
- ^ "An In-Depth Look At The Big (And Small) Additions To Android Jelly Bean 4.3". Android Police. July 24, 2013. Retrieved July 25, 2013.
- ^ Jaymar Cabebe (July 25, 2013). "Google Android 4.3 Jelly Bean Release Date, Price and Specs - CNET". CNET. CBS Interactive.
- ^ "Suddenly, A Wild Android 4.3.1 Appears – LTE Nexus 7 Receiving Android 4.3.1 OTA (JLS36I)". Android Police. October 3, 2013. Retrieved October 4, 2013.
- ^ "Factory Image And Binaries Are Now Available For The Nexus 7 LTE Android 4.3.1 Update (JLS36I)". Android Police. October 8, 2013. Retrieved October 9, 2013.
- ^ Kelion, Leo (September 3, 2013). "Android KitKat announced". BBC News. Retrieved September 3, 2013.
- ^ "Android 5.0 Key Lime Pie release date, news and rumors". TechRadar. July 2, 2013. Retrieved July 22, 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f Molen, Brad (November 5, 2013). "Engadget review the Nexus 5". Engadget. Retrieved November 11, 2013.
- ^ a b "7.6.1". Android Compatibility Definition Document (PDF) (4.4 ed.). Google. November 27, 2013. p. 33.
- ^ "Android for all and the new Nexus 5 ". Google Official Blog. October 31, 2013. Retrieved November 1, 2013.
- ^ "Android KitKat". Android Developers Portal. Retrieved November 1, 2013.
- ^ Bonn, Dieter (October 31, 2013). "Google's Nexus 5 with KitKat available today, starting at $349: hands-on impressions". The Verge. Retrieved November 1, 2013.
- ^ David Ruddock (October 31, 2013). "KitKat Feature Spotlight: Apps Can Now Go Truly Full-Screen, Hide The Navigation Bar". androidpolice.com. Retrieved November 3, 2013.
- ^ "Android menu button now on by default on all device with KitKat". PhoneArena.com. December 9, 2013. Retrieved February 9, 2014.
- ^ "Getting Your SMS Apps Ready for KitKat". Android Developers Blog. Retrieved October 14, 2013.
- ^ "Android 4.4 brings support for low-power audio playback". PhoneArena.com. October 31, 2013. Retrieved February 25, 2014.
- ^ Jason Cipriani (November 5, 2013). "How to record your screen on Android 4.4 KitKat". CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved January 4, 2014.
- ^ "Android Developers: ART and Dalvik". source.android.com. March 9, 2015. Retrieved March 19, 2015.
- ^ David Ruddock (October 31, 2013). "KitKat Feature Spotlight: Android Finally Supports Bluetooth MAP, Will Make Bluetooth Integration With Your Car Suck A Lot Less". Android Police. Retrieved November 2, 2013.
- ^ "Android Issue 61975: Undo removal of access to BATTERY_STATS permission for apps". Code.google.com. November 2013. Retrieved January 29, 2014.
- ^ "Android Issue 61834: 4.4 KitKat reception/Wifi indicators no longer show data rx/tx during operation". Code.google.com. November 2013. Retrieved February 20, 2014.
- ^ "Android Issue 62378: KitKat WebView text wrap no longer works". code.google.com. Retrieved October 28, 2014.
- ^ Official Nexus Google+ page (December 5, 2013). "Android 4.4.1 Released to Nexus 5". Google Plus. Retrieved December 5, 2013.
{{cite web}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ Christopher Trout (December 5, 2013). "Android update focuses on Nexus 5 camera improvements". Engadget. Retrieved December 5, 2013.
- ^ David Pierce (December 5, 2013). "Fixing the Nexus 5: with a new version of Android, Google tackles the camera". The Verge. Retrieved December 6, 2013.
- ^ Artem Russakovskii (December 9, 2013). "Android 4.4.2 (KOT49H) Is Already Rolling Out To All Nexus Devices – Here Are The OTA ZIP Links For Manual Updating". Android Police. Retrieved December 9, 2013.
- ^ Peter Eckersley (December 12, 2013). "Google Removes Vital Privacy Feature From Android, Claiming Its Release Was Accidental". Electronic Frontier Foundation. Retrieved December 14, 2013.
- ^ Ron Amadeo (June 2, 2014). "Google releases Android 4.4.3 to Nexus devices". Ars Technica. Retrieved June 2, 2014.
- ^ Kellex (June 2, 2014). "Fresh New Dialer Arrives in Android 4.4.3". Droid Life. Retrieved June 2, 2014.
- ^ Android Developers (June 3, 2014). "Android 4.4.3 aka KitKat MR2 is rolling out - Google+". Android Developers (Google+). Retrieved June 4, 2014.
- ^ Kellex (June 19, 2014). "Whoa: Android 4.4.4 Factory Images Posted as Build KTU84P". Droid Life. Retrieved June 19, 2014.
- ^ Ryan Whitwam (June 19, 2014). "Google Rolling Out Android 4.4.4 Update (KTU84P) With A Security Fix, Factory Images/Binaries Up For Nexus Devices". androidpolice.com. Retrieved June 25, 2014.
- ^ Rob, Triggs. "Google uploads part of the Android Wear source code to AOSP". Android Authority. Retrieved July 22, 2014.
- ^ Andrew Grush (September 6, 2014). "Android Wear platform fully unveiled at I/O 2014". Android Authority. Retrieved January 25, 2015.
- ^ Michael Crider (September 6, 2014). "Samsung Gear Live Updated To Android Wear 4.4W.1 Build KGW42N: Here's What's New". Android Police. Retrieved January 25, 2015.
- ^ Rita El Khoury (October 21, 2014). "Android Wear 4.4W.2 Build KNX01Q Starts Rolling Out For The LG G Watch, Brings Offline Music And GPS Support (Though You Can't Use The Latter)". Android Police. Retrieved January 25, 2015.
- ^ "From Android L to Google Fit: All the new products and features from Google I/O". PC World. June 25, 2014. Retrieved June 26, 2014.
- ^ "Updated Android Lollipop Developer Preview image coming to Nexus devices in a couple of days". PhoneArena.com. October 15, 2014. Retrieved October 16, 2014.
- ^ "Google's new 'Material Design' UI coming to Android, Chrome OS and the web". Engadget. June 25, 2014. Retrieved June 26, 2014.
- ^ "We just played with Android's L Developer Preview". Engadget. AOL. Retrieved June 26, 2014.
- ^ "Google Reveals Details About Android L at Google IO". Anandtech. Retrieved June 26, 2014.
- ^ Andrei Frumusanu (July 1, 2014). "A Closer Look at Android RunTime (ART) in Android L". AnandTech. Retrieved July 5, 2014.
- ^ a b "Android 5.0 APIs". Android.com. Retrieved October 28, 2014.
- ^ "Android: Be together. Not the same". Official Google Blog. October 15, 2014. Retrieved October 17, 2014.
- ^ Ben Cheng; Bill Buzbee (May 2010). "A JIT Compiler for Android's Dalvik VM" (PDF). android-app-developer.co.uk. Google. pp. 5–14. Retrieved March 19, 2015.
- ^ "Exploring Android L: Lockscreen widgets also bite the dust". Pocketables.com. June 2014. Retrieved January 25, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e "Android 5.0 Lollipop's new features". India Times. November 27, 2014. Retrieved December 23, 2014.
- ^ "Lollipop brings proper multi-user accounts to your phone". Android Central. Retrieved January 25, 2015.
- ^ Cody Toombs (November 4, 2014). "Android 5.0 Makes SD Cards Great Again, Extends API To Allow Full Directory Access, Automatic MediaStore, And Improves Security". Android Police. Retrieved November 29, 2014.
- ^ Michael Crider (November 27, 2014). "Root Explorer 3.3 Update Adds SD Card Write Capability Without Root In Lollipop". Android Police. Retrieved November 29, 2014.
- ^ "Lollipop stops Chromium bugs from endangering Android". ZDNet. October 24, 2014. Retrieved October 28, 2014.
- ^ "Android - 5.0 Lollipop". Android.com. November 3, 2014. Retrieved November 28, 2014.
- ^ Jason Cipriani (November 3, 2014). "Set up 'Priority' mode on Android 5.0 Lollipop". CNET. Retrieved December 23, 2014.
- ^ "Smart lock screen security options in Android 5.0 Lollipop".
- ^ "Android 5.0 Emoji Changelog".
- ^ a b Saturday, Oct 25, 2014 at 5:22 pm EDT (October 25, 2014). "Accessibility features in Android 5.0 Lollipop". Android Central. Retrieved January 30, 2016.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Block-Based OTAs | Android Open Source Project". Source.android.com. Retrieved January 30, 2016.
- ^ Liam Spradlin (December 2, 2014). "Android 5.0.1 (LRX22C) Hitting AOSP Now (Update: Factory Images Too)". Android Police. Retrieved December 3, 2014.
- ^ "Factory Images for Nexus - Android". Google.
- ^ Stephen Schenck (December 22, 2014). "What's actually new in Android 5.0.2?". PocketNow.com. Retrieved January 6, 2015.
- ^ David Nield. "10 Things You Can Do in Android 5.1 That You Couldn't Before". Field Guide. Gawker Media.
- ^ a b "Google confirms Android 5.1 is rolling out today, will support multi-SIM devices and HD calls". VentureBeat. Retrieved April 24, 2015.
- ^ "Android 5.1 reinstates Silent Mode, but there's a catch". AndroidPIT. Retrieved March 27, 2015.
- ^ a b "Android 5.1.1 (LMY47V) officially uploaded to AOSP and here's the full changelog, Nexus Player factory images also available". Retrieved May 1, 2015.
- ^ Jennings, Jack (June 26, 2015). "Google Open Source Code for Wi-Fi Calling". XDA. Retrieved November 2, 2015.
- ^ "Google's Android M preview build will run on the Nexus 5, 6, 9, and Player [Updated]". Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved May 28, 2015.
- ^ "Downloads Android Developers". August 17, 2015.
- ^ "Support and Release Notes | Android Developers". developer.android.com. Retrieved August 22, 2015.
- ^ "Get ready for the sweet taste of Android 6.0 Marshmallow". Android Developers. Retrieved October 6, 2015.
- ^ "Now on Tap".
- ^ "Android Doze".
- ^ "Android vertical app drawer".
- ^ "Android 6.0 APIs - Android Developers".
- ^ "Handling App Links". developer.android.com.
- ^ "App Linking in Android 6.0". developer.android.com.
- ^ "Use Android 6.0's Hidden System UI Tuner to Customize Your Quick Settings and Status Bar".
- ^ "Android 6.0 APIs - Android Developers".
- ^ "Android 6.0 APIs - Android Developers".
- ^ "Android 6.0 APIs - Android Developers".
- ^ "MIDI - Android Open Source Project".
- ^ "How to Unlock the Hidden Multi-Window Mode in Android 6.0 Marshmallow".
- ^ "Enable Multi-Window mode in Android 6.0 Marshmallow with a bit of tinkering".
- ^ "Android 6.0.1 Emoji Changelog".
- ^ a b "The syntax of the Android.mk build file". developer.android.com. Retrieved June 14, 2015.
- ^ Shah, Agam (March 23, 2015). "Imagination floats sub-$100 MIPS tablet running Firefox OS". PC World. IDG News Service. Retrieved June 5, 2015.
- ^ "Android Lollipop". developer.android.com. Retrieved November 24, 2014.
It's supported on ARM, x86, and MIPS architectures and is fully 64-bit compatible.
- ^ a b Shah, Agam (December 1, 2011). "Google's Android 4.0 ported to x86 processors". Computerworld. International Data Group. Retrieved February 20, 2012.
- ^ "Android on Intel Architecture". 01.org. July 11, 2013. Retrieved February 9, 2014.
- ^ Warman, Matt (June 7, 2012). "Orange San Diego Intel Android mobile phone review". The Daily Telegraph. Telegraph Media Group Limited. Retrieved June 19, 2013.
- ^ http://static.googleusercontent.com/media/source.android.com/en//compatibility/android-cdd.pdf
- ^ "Android KitKat". Android Developers Portal. android.com. Retrieved November 16, 2013.
- ^ "Android on Intel Architecture". 01.org. July 11, 2013. Retrieved February 9, 2014.
- ^ a b "Android Developers: Graphics". android.com. Retrieved November 15, 2013.
- ^ "Android Developers: Android Compatibility". android.com. Retrieved November 16, 2013.
External links
- Official Android website
- Android API Levels via Android Developer
- Android: A visual history, The Verge, by Chris Ziegler
- The history of Android, Ars Technica, by Ron Amadeo
- Website with Android version distribution historical charts
- A Brief History of Android Version From Cupcake To Lollipop
- Android versions comparison
- Google Android: List of CVE security vulnerabilities
