Dumaguete
Dumaguete | |
|---|---|
| City of Dumaguete | |
 Dumaguete City Hall | |
| Nickname: The City of Gentle People | |
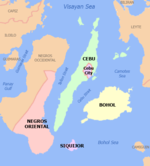
 Map of Negros Oriental with Dumaguete highlighted | |
Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 9°18′37″N 123°18′29″E / 9.31028°N 123.30806°E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Negros Island Region |
| Province | Negros Oriental |
| District | 2nd district of Negros Oriental |
| Cityhood | November 24, 1948 |
| Barangays | 30 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlungsod |
| • Mayor | Felipe Antonio “Ipe” B. Remollo |
| • Vice Mayor | Franklin D. Esmeña Jr. |
| • Electorate | 91,931 voters (2022) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 33.62 km2 (12.98 sq mi) |
| Population (2020 census)[3] | |
| • Total | 134,103 |
| • Density | 4,000/km2 (10,000/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Dumagueteño (masculine) Dumagueteña (feminine) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 6200 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)35 |
| Income class | 3rd city income class |
| Revenue (₱) | ₱ 988.7 million (2020) |
| Native languages | Cebuano Magahat Tagalog |
| Website | www |
Dumaguete, officially the City of Dumaguete, (Cebuano: Dakbayan sa Dumaguete; Filipino: Lungsod ng Dumaguete), or simply as Dumaguete City, is a 3rd class component city in the province of Negros Oriental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 134,103 people.[3]
It is the capital and most populous city of the province of Negros Oriental. The city is nicknamed The City of Gentle People.[4]
Dumaguete is referred to as a university city because of the presence of four universities and a number of other colleges where students of the province converge to enroll for tertiary education. The city is also a popular educational destination for students of surrounding provinces and cities in Visayas and Mindanao. The city is best known for Silliman University, the country's first Protestant university and the first American university in Asia.[5][6] There are also 18 public elementary schools and 8 public high schools. The city's student population is estimated at 45,000.[4]
Dumaguete attracts a considerable number of foreign tourists, particularly Europeans, because of easy access from Cebu City in Central Visayas, the availability of beach resorts and dive sites, the attraction of dolphin and whale watching in nearby Bais City. Dumaguete is listed 5th in Forbes Magazine's "7 Best Places to Retire Around the World".[7] The Philippine Retirement Authority a government agency under the Department of Tourism has named the city as the Best Place to Retire in the Philippines for 2018.
The power source of the city comes from the geothermal power plant in Palinpinon, Valencia. The city has redundant fiber optic lines and is a focal point for telecommunications. It is the landing point for fiber optic cables linking it to the whole Visayas, Manila (the capital of the nation) and cities south of Luzon, as well as to other cities north of Mindanao. Scholars have been pushing for the city's inclusion in the tentative list of the Philippines for future UNESCO World Heritage Site nomination.[8]
Etymology
"Dumaguete" was coined from the Cebuano word dagit, which means "to snatch". The word dumaguet, meaning "to swoop", was coined because of frequent raids by Moro pirates on this coastal community and its power to attract and keep visitors, both local and foreign. In 1572, Diego López Povedano indicated the place as Dananguet, but cartographer Pedro Murillo Velarde in 1734 already used present name of Dumaguete for the settlement.[9]
Geography and Climate

Dumaguete has a land area of 3,362 hectares (8,310 acres), situated on the plains of the southeastern coast of the large island of Negros, near the mouth of the Banica River. Of the province's 19 municipalities/towns and 6 cities, Dumaguete is the smallest in terms of land area. It is bounded on the north by the town of Sibulan, on the south by the town of Bacong and on the west by the town of Valencia.
As a coastal city, it is bounded on the east by the Bohol Sea and the Tañon Strait, serving as a natural border of southeastern Negros Island Region to the neighboring Central Visayas. The city's topography is generally flat from two to six kilometers from the shoreline. It slopes gently upwards to the adjoining municipality of Valencia. The highest ground elevation is located at the boundary of the municipality of Valencia, about one hundred meters above mean sea level. About 93% of the land have slopes of less than 3%. The remaining areas have 3% to 5% slope.
Climate
Dumaguete has two seasons, namely; the dry and the wet seasons. The wet season covers the period from June to November, and the dry season starts from December to May, the hottest being April and May. The average maximum temperature is 34.3 °C and the average minimum temperature is 22.9 °C for the past years. The relative humidity of the locality for the past years was 78¾% with the month of December registering the highest.
| Climate data for Dumaguete (1981–2010, extremes 1910–2012) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 33.7 (92.7) |
34.2 (93.6) |
34.2 (93.6) |
36.8 (98.2) |
36.2 (97.2) |
37.4 (99.3) |
36.6 (97.9) |
36.7 (98.1) |
37.0 (98.6) |
36.1 (97.0) |
34.7 (94.5) |
34.2 (93.6) |
37.4 (99.3) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 29.0 (84.2) |
29.2 (84.6) |
30.0 (86.0) |
31.0 (87.8) |
31.7 (89.1) |
31.6 (88.9) |
31.3 (88.3) |
31.7 (89.1) |
31.5 (88.7) |
31.0 (87.8) |
30.5 (86.9) |
29.7 (85.5) |
30.7 (87.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.8 (80.2) |
26.8 (80.2) |
27.3 (81.1) |
28.1 (82.6) |
28.6 (83.5) |
28.2 (82.8) |
27.8 (82.0) |
27.9 (82.2) |
27.8 (82.0) |
27.7 (81.9) |
27.7 (81.9) |
27.2 (81.0) |
27.7 (81.9) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 24.5 (76.1) |
24.3 (75.7) |
24.6 (76.3) |
25.2 (77.4) |
25.4 (77.7) |
24.9 (76.8) |
24.3 (75.7) |
24.2 (75.6) |
24.2 (75.6) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.8 (76.6) |
24.8 (76.6) |
24.6 (76.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 19.3 (66.7) |
19.8 (67.6) |
19.6 (67.3) |
18.9 (66.0) |
20.7 (69.3) |
20.7 (69.3) |
19.8 (67.6) |
20.5 (68.9) |
18.0 (64.4) |
20.8 (69.4) |
20.4 (68.7) |
19.8 (67.6) |
18.0 (64.4) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 82.0 (3.23) |
61.4 (2.42) |
46.3 (1.82) |
53.7 (2.11) |
81.8 (3.22) |
129.7 (5.11) |
122.7 (4.83) |
110.6 (4.35) |
127.3 (5.01) |
156.7 (6.17) |
138.7 (5.46) |
107.3 (4.22) |
1,218.4 (47.97) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 13 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 10 | 14 | 16 | 13 | 15 | 16 | 14 | 15 | 150 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 83 | 82 | 81 | 78 | 78 | 79 | 80 | 80 | 81 | 82 | 81 | 82 | 81 |
| Source: PAGASA[10][11] | |||||||||||||
Barangays
Dumaguete is politically subdivided into 30 barangays, all classified as urban. The eight barangays in the city's downtown area are known primarily by number. The smallest barangay is Barangay 4 with an area of only 5.11 hectares, while the biggest barangay is Barangay Banilad with 362.71 hectares.
- Bagacay
- Bajumpandan
- Balugo
- Banilad
- Bantayan
- Barangay 1 (Tinago)
- Barangay 2 (Upper Lukewright)
- Barangay 3 (Business District)
- Barangay 4 (Rizal Boulevard)
- Barangay 5 (Silliman Area)
- Barangay 6 (Cambagroy)
- Barangay 7 (Mangga)
- Barangay 8 (Cervantes Extension)
- Batinguel
- Buñao
- Cadawinonan
- Calindagan
- Camanjac
- Candau-ay
- Cantil-e
- Daro
- Junob
- Looc
- Mangnao-Canal
- Motong
- Piapi
- Pulantubig
- Tabuc-tubig
- Taclobo
- Talay
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1903 | 14,894 | — |
| 1918 | 16,336 | +0.62% |
| 1939 | 22,236 | +1.48% |
| 1948 | 24,838 | +1.24% |
| 1960 | 35,282 | +2.97% |
| 1970 | 52,000 | +3.95% |
| 1975 | 52,765 | +0.29% |
| 1980 | 63,411 | +3.74% |
| 1990 | 80,262 | +2.39% |
| 1995 | 92,637 | +2.72% |
| 2000 | 102,265 | +2.14% |
| 2007 | 116,392 | +1.80% |
| 2010 | 120,883 | +1.39% |
| 2015 | 131,377 | +1.60% |
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[12][13][14][15] | ||
As of the census in 2015, there are 131,377 people and 21,582 households residing in the city (as of 2010). The city has the least poverty incidence among urban centers in Visayas, according to the 2009 Small Area Estimates (SAE) of Poverty done by the National Statistical Coordination Board (NSCB). It has an average daylight population of 400,000 people. Dumaguete is the most populous city in Negros Oriental, comprising 9.05% of the province's total population. Its total voting population is 91,931 voters (2022).
Education

Dumaguete has earned the distinction of being known as the "center of learning in the South," or a university city due to the presence of universities that have made their mark nationally and abroad. The city is a melting pot of students, professionals, artists, scholars and the literati coming from different parts of the country and the world.
Silliman University is the dominant institution of higher learning in Dumaguete, providing the city with a distinct university town atmosphere. It is the first Protestant university in the country and the first American university in Asia. The 610,000 m² campus is adjacent to and intermixed with the city's downtown district.[17] Some of its buildings have likewise been recognized as landmarks. These buildings include the Silliman Hall, Hibbard Hall, Katipunan Hall, the Luce Auditorium, and the Silliman Main Library (considered as one of the biggest libraries in the Philippines).[4][18][19][20]
Other universities within the urban parameters of the city are: Foundation University (1949), a private non-sectarian university, its Main Campus where the site of a very popular Sofia Soller Sinco Hall dubbed as White House of Dumaguete is located at Meciano Road offers tertiary education programs while North Campus along Locsin Street is the home of Foundation Preparatory Academy for basic education programs. The Negros Oriental State University (NORSU) which was founded in 1907, has its two main campuses in the city, the Main Campus 1 is beside the Provincial Capitol building while Main Campus 2 is located in barangay Bajumpandan. It is the only state university in Negros Oriental, the biggest among the four universities in the city in terms of student population and is very popular among students from different towns and cities of the province and some other parts of the country. St. Paul University Dumaguete (1904) is the first Saint Paul educational institution to be established in the Philippines by the Sisters of Saint Paul of Chartres (SPC) from France, second oldest Catholic university of Central Visayas and considered as premier Catholic university of Dumaguete City. SPUD is best known for its core academic courses like Nursing, Teacher Education, Business and Accountancy.
Economy
Tourism, the academe, the retail industries, BPO and technology-related activities are the major sources of income for the city. BPOs and IT firms, as well as retailing, are the fastest rising industries.
Hotels and tourism
Data from the Department of Tourism show that Dumaguete and Negros Oriental are among the top ten most visited tourist destinations in the country.[21] Tourists visit popular sites such as: the historic Rizal Boulevard aligned with some hotels, coffee shops, fine-dining restaurants and bars including the latest dining commercial complex, Paseo Perdices is the preferred location of Max's Restaurant, Yellow Cab Pizza and among others; Silliman Hall-home of University's Anthropology Museum; St. Catherine of Alexandria Cathedral being the oldest stone church of the island of Negros and ecclesiastical seat of the bishop of Roman Catholic Diocese of Dumaguete and Campanario de Dumaguete which is considered as one of the oldest heritage landmarks of Negros Island and Central Visayas. Dumaguete serves as the main gateway to Negros Oriental.
The city comes alive every September by celebrating its Sandurot Festival, which means “fellowship and reaching out” is a commemoration of Dumaguete’s rich history dating back from the pre-Hispanic period when people of different foreign cultures converged and created a varied community that is Dumaguete City today. Through the course of history and to the present time, the people of Dumaguete have always been known to welcome strangers from different shores and countries, and to live with them in complete peace and understanding. The celebration started with the Paghimamat, a re-enactment of how people from different cultures and races came to the shores of Dumaguete, bringing gifts of rich cultures. Pasigarbo followed, gracing the City streets with dancing to drumbeats and other instruments participated by different barangays and schools in Dumaguete. The streetdancing ended at Quezon Park after which the participants prepared for the grand Pasundayag, a display of dances portraying different stories of the Dumaguete tradition.
Meanwhile, Buglasan Festival also known as Festival of all festivals is celebrated annually in the province of Negros Oriental every October since 2002. The festival is a ten-day event held in the city of Dumaguete, a movable provincial fiesta, participated in by the Province's six cities and 19 municipalities. Though this is a province-wide event (sponsored by the provincial government), the activities are mostly centered in the province's capital, Dumaguete City. Majority of activities are held in the Provincial Capitol and Ninoy Aquino's Freedom Park with booths and local products either on display or for sale, it is also spread to other venues such as Sidlakan Negros Village at Brgy. Piapi and city's Rizal Boulevard. Showdowns and streetdancing activities happen every 3rd Friday of the month of October.
Business process outsourcing
Dumaguete's outsourcing industry has a range of businesses, such as call centers, publishing, medical transcription, animation, editing, and architectural outsourcing. Dumaguete City has over 20 IT and BPO locators, and has been described as a hub for Business Process Outsourcing and Information Technology.[22][23]
Retail
Major malls and shopping centers in Dumaguete include the following:
- 1. Cang's, Inc. Shopping Complex (North National Highway, Brgy. Daro)
- 2. CityMall Dumaguete (North National Highway, Brgy. Daro)
- 3. Lee Super Plaza[24] (Perdices St.)
- 4. Robinsons Townville (Perdices St.)
- 5. LP Hypermart (Jose Romero Road, Brgy. Bagacay)
- 6. Robinsons Place Dumaguete [the first full-service mall in the city, located in Brgy. Calindagan, about 2 km (1.2 mi) from the city center heading to the south]
- 7. Ever Mall (Perdices St.)
The upcoming Festival Mall Dumaguete at Escaño Beach, Piapi (North Boulevard) will be one of the major components of Filinvest's township project called Marina Town Dumaguete.
Banking
As of June 2017 (data from PDIC), deposits in the city's banks reached a total of 34.7 billion pesos. Most of the major Philippine banks, as well as the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (the central bank), maintain branches in Dumaguete.
- 1. BDO Colon St.
- 2. BDO Robinsons Place
- 3. BDO Silliman Campus
- 4. BDO CityMall
- 5. Chinabank
- 6. BPI Perdices St.
- 7. BPI San Jose St.
- 8. BPI North Road
- 9. BPI Family Savings
- 10. BPI Direct Banko
- 11. PNB Veterans Ave.
- 12. PNB Locsin St.
- 13. PNB Calindagan
- 14. RCBC
- 15. RCBC Savings
- 16. Unionbank
- 17. City Savings Bank
- 18. PBCOM
- 19. Robinsons Bank
- 20. First Consolidated Bank
- 21. Rural Bank of Rizal
- 22. Wealthbank
- 23. 1st Valley Bank
- 24. SG Bank
- 25. Dumaguete Rural Bank
- 26. Rural Bank of Bacong
- 27. Rural Bank of Santa Catalina
- 28. Rural Bank of Tanjay
- 29. Katipunan Bank
- 30. Banco Dipolog
- 31. Asia United Bank
- 32. PS Bank
- 33. Metrobank Veterans Ave.
- 34. Metrobank Locsin St.
- 35. Metrobank Capitol
- 36. Bank of Commerce
- 37. PR Savings Bank
- 38. Rizal Bank
- 39. First Agro-Industrial Bank
- 40. Dumaguete City Development Bank
- 41. EastWest Bank
- 42. Security Bank
- 43. Mactan Bank
- 44. Philtrust Bank
- 45. Maybank
- 46. Landbank
- 47. Development Bank of the Philippines
- 48. Veterans Bank
- 49. Cooperative Bank of Negros Oriental
- 50. Philippine Business Bank
- 51. Producers Savings Bank
- 52. UCPB
In addition, One Network Bank (BDO's rural bank subsidiary) and BPI's 4th branch are set to open in 2018.
Health care and services
Dumaguete has three major tertiary hospitals, namely the Holy Child Hospital, Negros Oriental Provincial Hospital, and the Silliman Medical Center which is currently associated with St. Luke's Medical Center in Metro Manila[25] and considered one of the best hospitals outside Metro Manila and Metro Cebu. Under proposal is a medical resort with a 100-bed tertiary hospital, and which will cater primarily to the retirement market from North American, European and East Asian countries. Also being constructed is ACE Dumaguete Doctors Hospital, an eight storeys, 200-bed hospital near the downtown area. Dumaguete City is one of the five areas identified by the Philippine government as retirement hubs.[citation needed]
Transportation
Air
Sibulan Airport (IATA: DGT, ICAO: RPVD), also known as Dumaguete Airport or Dumaguete-Sibulan Airport, is the city's domestic airport located in neighboring Sibulan town in the north. It provides daily flights to and from Manila and Cebu City through Cebu Pacific, Cebgo and PAL Express while Cebgo is servicing both Mindanao important urban centers, thrice weekly flights to Davao City and Cagayan de Oro City.[26] However, a new airport is being planned to be built in Bacong, a town bordering Dumaguete in the south[27] The proposal for the transfer and upgrading of this airport to international standards has already been approved and should be completed before 2025. An initial PHP 500 million budget has already been released for initial study and procurement of free lands.[28]
Sea
Dumaguete, as a major port city is a jump-off point for passengers/tourists who are going to other Visayas and Mindanao areas. There are daily ferry connections to the islands of Cebu, Bohol, Siquijor and Mindanao operated by Archipelago Philippine Ferries Corporation (Fast Cat), Montenegro Lines, Ocean Jet Shipping, Cokaliong and other companies. Dumaguete is an access city for passengers/tourists going to Cebu which is dubbed as economic hub of the Visayas. There are smaller ports north of the city where short and frequent ferry connections are available to that island as an alternative. Dumaguete is a port of call for travelers to Manila, Dapitan and Zamboanga City by ship serviced by 2GO Travel.
Land
The main form of public transport in Dumaguete is the motorized tricycle. The Dumaguete version of the motorized tricycle can fit up to 6-8 passengers. For transport to destinations outside the city limit, there are jeepney and buses travelling set routes. Meanwhile, Vallacar Transit Corporation, the company that operates Ceres buses recently constructed a 2-storey terminal building in Dumaguete just beside the newly erected commercial center, the Marketplace.[citation needed]
Notable people
Sister cities
Dumaguete has the following sister cities:
Local
International
 Yeongdong County of North Chungcheong, Republic of Korea
Yeongdong County of North Chungcheong, Republic of Korea Alameda of California, United States
Alameda of California, United States
Gallery
-
Silliman Avenue
-
Hibbard Hall of Silliman University
-
St. Catherine of Alexandria Cathedral
-
Dumaguete Belfry with grotto
-
Provincial Capitol of Negros Oriental
-
Skyline of the Port of Dumaguete
-
Bandera Building
-
Dumaguete Public Market
See also
References
- ^ City of Dumaguete | (DILG)
- ^ "Province:". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- ^ a b Census of Population (2020). "Region VII (Central Visayas)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ^ a b c "Dumaguete City, the City of Gentle People". Department of Tourism. Retrieved 2010-11-04.
- ^ "CSF program up in Dumaguete" Archived 2009-07-19 at the Wayback Machine. Manila Bulletin. By Atty. Ignacio Bunye. Posted July 5, 2009. Accessed October 14, 2009.
- ^ "Heritage Diary of Negros Oriental". Inquirer.net. By: Dexter Matilla. Posted July 14, 2008. Accessed October 15, 2009.
- ^ Dumaguete among 7 best places to retire, according to Forbes Magazine. GMA Network. November 15, 2014.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2010-09-26. Retrieved 2010-08-12.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) NegrosHub.com - Dumaguete City - ^ experiencephilippines.org
- ^ "Dumaguete City, Negros Oriental Climatological Normal Values". Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration. Archived from the original on 13 October 2018. Retrieved 13 October 2018.
- ^ "Dumaguete City, Negros Oriental Climatological Extremes". Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration. Archived from the original on 13 October 2018. Retrieved 13 October 2018.
- ^ Census of Population (2015). "Region VII (Central Visayas)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region VII (Central Visayas)" (PDF). Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. National Statistics Office. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^ Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region VII (Central Visayas)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. National Statistics Office.
- ^ "Province of". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- ^ "Dumaguete, Negros Oriental". Philippine Airlines. Retrieved 2010-09-01.
- ^ UP is No.1 based on PRC exams Archived February 7, 2012, at the Wayback Machine. UP Newsletter, Vol. XXVIII, No. 09. September 01, 2007. Accessed May 26, 2009.
- ^ Philippine Travel Center: Negros Oriental. Accessed September 1, 2009.
- ^ Negros Chronicle. Where to go in Negros Oriental Archived 2016-05-27 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed September 1, 2009.
- ^ WOWPhilippines: Things to do and see in Negros Oriental. Accessed September 1, 2009.
- ^ Top Tourist Destinations in the Philippines Archived September 9, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Baguio, Dumaguete now in top 10 BPO Next Wave Cities
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2015-04-02. Retrieved 2015-03-29.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Lee Plaza Shopping". Lee Plaza Shopping. Retrieved 2017-02-16.
- ^ "St. Luke's inks MOA with Silliman Medical Center". Philstar.com. Retrieved 2010-04-28.
- ^ "CEB adds 2nd daily frequency to Manila-Dumaguete " Archived June 18, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. Cebu Pacific. Retrieved 2010-11-04.
- ^ To a new site in bacong town Solon wants to relocate airport from Dumaguete
- ^ Master Plan for Philippine Airports