IRAK1
Appearance
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the IRAK1 gene.[5][6]
Function
This gene encodes the interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1, one of two putative serine/threonine kinases that become associated with the interleukin-1 receptor (IL1R) upon stimulation. This gene is partially responsible for IL1-induced upregulation of the transcription factor NF-kappa B. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[7]
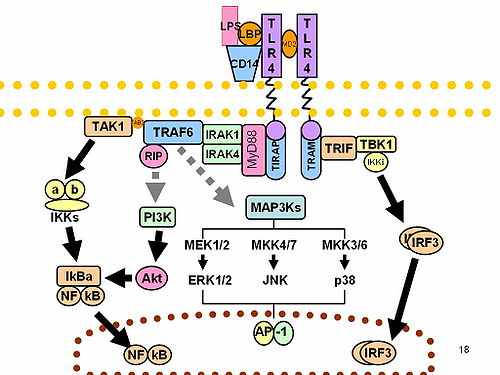
Interactions
IRAK1 has been shown to interact with:
Clinical significance
IRAK1 signaling is involved in rheumatoid arthritis.[27]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000184216 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000031392 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Muzio M, Ni J, Feng P, Dixit VM (November 1997). "IRAK (Pelle) family member IRAK-2 and MyD88 as proximal mediators of IL-1 signaling". Science. 278 (5343): 1612–5. doi:10.1126/science.278.5343.1612. PMID 9374458.
- ^ Cao Z, Henzel WJ, Gao X (February 1996). "IRAK: a kinase associated with the interleukin-1 receptor". Science. 271 (5252): 1128–31. doi:10.1126/science.271.5252.1128. PMID 8599092.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: IRAK1 interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1".
- ^ a b c d Windheim M, Stafford M, Peggie M, Cohen P (March 2008). "Interleukin-1 (IL-1) induces the Lys63-linked polyubiquitination of IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 to facilitate NEMO binding and the activation of IkappaBalpha kinase". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 28 (5): 1783–91. doi:10.1128/MCB.02380-06. PMC 2258775. PMID 18180283.
- ^ a b Vig E, Green M, Liu Y, Yu KY, Kwon HJ, Tian J, Goebl MG, Harrington MA (March 2001). "SIMPL is a tumor necrosis factor-specific regulator of nuclear factor-kappaB activity". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (11): 7859–66. doi:10.1074/jbc.M010399200. PMID 11096118.
- ^ a b Conze DB, Wu CJ, Thomas JA, Landstrom A, Ashwell JD (May 2008). "Lys63-linked polyubiquitination of IRAK-1 is required for interleukin-1 receptor- and toll-like receptor-mediated NF-kappaB activation". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 28 (10): 3538–47. doi:10.1128/MCB.02098-07. PMC 2423148. PMID 18347055.
- ^ Chen BC, Wu WT, Ho FM, Lin WW (July 2002). "Inhibition of interleukin-1beta -induced NF-kappa B activation by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase occurs through Akt activation associated with interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase phosphorylation and uncoupling of MyD88". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (27): 24169–79. doi:10.1074/jbc.M106014200. PMID 11976320.
- ^ a b Wesche H, Gao X, Li X, Kirschning CJ, Stark GR, Cao Z (July 1999). "IRAK-M is a novel member of the Pelle/interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) family". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (27): 19403–10. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.27.19403. PMID 10383454.
- ^ a b Li S, Strelow A, Fontana EJ, Wesche H (April 2002). "IRAK-4: a novel member of the IRAK family with the properties of an IRAK-kinase". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 99 (8): 5567–72. doi:10.1073/pnas.082100399. PMC 122810. PMID 11960013.
- ^ Fitzgerald KA, Palsson-McDermott EM, Bowie AG, Jefferies CA, Mansell AS, Brady G, Brint E, Dunne A, Gray P, Harte MT, McMurray D, Smith DE, Sims JE, Bird TA, O'Neill LA (September 2001). "Mal (MyD88-adapter-like) is required for Toll-like receptor-4 signal transduction". Nature. 413 (6851): 78–83. doi:10.1038/35092578. PMID 11544529.
- ^ a b c Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "IRAK1 Gene - GeneCards | IRAK1 Protein | IRAK1 Antibody". www.genecards.org.
- ^ Muzio, M. (1997). "IRAK (Pelle) Family Member IRAK-2 and MyD88 as Proximal Mediators of IL-1 Signaling". Science. 278 (5343): 1612–1615. doi:10.1126/science.278.5343.1612. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 9374458.
- ^ Qian Y, Commane M, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Matsumoto K, Li X (November 2001). "IRAK-mediated translocation of TRAF6 and TAB2 in the interleukin-1-induced activation of NFkappa B". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (45): 41661–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M102262200. PMID 11518704.
- ^ Cao Z, Xiong J, Takeuchi M, Kurama T, Goeddel DV (October 1996). "TRAF6 is a signal transducer for interleukin-1". Nature. 383 (6599): 443–6. doi:10.1038/383443a0. PMID 8837778.
- ^ Takatsuna H, Kato H, Gohda J, Akiyama T, Moriya A, Okamoto Y, Yamagata Y, Otsuka M, Umezawa K, Semba K, Inoue J (April 2003). "Identification of TIFA as an adapter protein that links tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) to interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor-associated kinase-1 (IRAK-1) in IL-1 receptor signaling". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (14): 12144–50. doi:10.1074/jbc.M300720200. PMID 12566447.
- ^ Ling L, Goeddel DV (August 2000). "T6BP, a TRAF6-interacting protein involved in IL-1 signaling". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 97 (17): 9567–72. doi:10.1073/pnas.170279097. PMC 16905. PMID 10920205.
- ^ Takaesu G, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Kishida S, Li X, Stark GR, Matsumoto K (April 2001). "Interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor-associated kinase leads to activation of TAK1 by inducing TAB2 translocation in the IL-1 signaling pathway". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 21 (7): 2475–84. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.7.2475-2484.2001. PMC 86880. PMID 11259596.
- ^ Chen F, Du Y, Zhang Z, Chen G, Zhang M, Shu HB, Zhai Z, Chen D (April 2008). "Syntenin negatively regulates TRAF6-mediated IL-1R/TLR4 signaling". Cellular Signalling. 20 (4): 666–74. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.12.002. PMID 18234474.
- ^ Newton K, Matsumoto ML, Wertz IE, Kirkpatrick DS, Lill JR, Tan J, Dugger D, Gordon N, Sidhu SS, Fellouse FA, Komuves L, French DM, Ferrando RE, Lam C, Compaan D, Yu C, Bosanac I, Hymowitz SG, Kelley RF, Dixit VM (August 2008). "Ubiquitin chain editing revealed by polyubiquitin linkage-specific antibodies". Cell. 134 (4): 668–78. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.039. PMID 18724939.
- ^ Xiao H, Qian W, Staschke K, Qian Y, Cui G, Deng L, Ehsani M, Wang X, Qian YW, Chen ZJ, Gilmour R, Jiang Z, Li X (May 2008). "Pellino 3b negatively regulates interleukin-1-induced TAK1-dependent NF kappaB activation". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 283 (21): 14654–64. doi:10.1074/jbc.M706931200. PMC 2386918. PMID 18326498.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Burns K, Clatworthy J, Martin L, Martinon F, Plumpton C, Maschera B, Lewis A, Ray K, Tschopp J, Volpe F (June 2000). "Tollip, a new component of the IL-1RI pathway, links IRAK to the IL-1 receptor". Nature Cell Biology. 2 (6): 346–51. doi:10.1038/35014038. PMID 10854325.
- ^ He X, Jing Z, Cheng G (2014). "MicroRNAs: new regulators of Toll-like receptor signalling pathways". BioMed Research International. 2014: 1–14. doi:10.1155/2014/945169. PMC 3977468. PMID 24772440.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Reference, Genetics Home. "IRAK1 gene". Genetics Home Reference.
Further reading
- Auron PE (1999). "The interleukin 1 receptor: ligand interactions and signal transduction". Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews. 9 (3–4): 221–37. doi:10.1016/S1359-6101(98)00018-5. PMID 9918122.
- Cao Z, Xiong J, Takeuchi M, Kurama T, Goeddel DV (October 1996). "TRAF6 is a signal transducer for interleukin-1". Nature. 383 (6599): 443–6. doi:10.1038/383443a0. PMID 8837778.
- Brenner V, Nyakatura G, Rosenthal A, Platzer M (August 1997). "Genomic organization of two novel genes on human Xq28: compact head to head arrangement of IDH gamma and TRAP delta is conserved in rat and mouse". Genomics. 44 (1): 8–14. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4822. PMID 9286695.
- Huang J, Gao X, Li S, Cao Z (November 1997). "Recruitment of IRAK to the interleukin 1 receptor complex requires interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 94 (24): 12829–32. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.24.12829. PMC 24223. PMID 9371760.
- Muzio M, Natoli G, Saccani S, Levrero M, Mantovani A (June 1998). "The human toll signaling pathway: divergence of nuclear factor kappaB and JNK/SAPK activation upstream of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6)". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 187 (12): 2097–101. doi:10.1084/jem.187.12.2097. PMC 2212359. PMID 9625770.
- Maschera B, Ray K, Burns K, Volpe F (April 1999). "Overexpression of an enzymically inactive interleukin-1-receptor-associated kinase activates nuclear factor-kappaB". The Biochemical Journal. 339 (2): 227–31. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3390227. PMC 1220149. PMID 10191251.
- Wesche H, Gao X, Li X, Kirschning CJ, Stark GR, Cao Z (July 1999). "IRAK-M is a novel member of the Pelle/interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) family". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (27): 19403–10. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.27.19403. PMID 10383454.
- Yang RB, Mark MR, Gurney AL, Godowski PJ (July 1999). "Signaling events induced by lipopolysaccharide-activated toll-like receptor 2". Journal of Immunology. 163 (2): 639–43. PMID 10395652.
- Thomas JA, Allen JL, Tsen M, Dubnicoff T, Danao J, Liao XC, Cao Z, Wasserman SA (July 1999). "Impaired cytokine signaling in mice lacking the IL-1 receptor-associated kinase". Journal of Immunology. 163 (2): 978–84. PMID 10395695.
- Reichwald K, Thiesen J, Wiehe T, Weitzel J, Poustka WA, Rosenthal A, Platzer M, Strätling WH, Kioschis P (March 2000). "Comparative sequence analysis of the MECP2-locus in human and mouse reveals new transcribed regions". Mammalian Genome. 11 (3): 182–90. doi:10.1007/s003350010035. PMID 10723722.
- Burns K, Clatworthy J, Martin L, Martinon F, Plumpton C, Maschera B, Lewis A, Ray K, Tschopp J, Volpe F (June 2000). "Tollip, a new component of the IL-1RI pathway, links IRAK to the IL-1 receptor". Nature Cell Biology. 2 (6): 346–51. doi:10.1038/35014038. PMID 10854325.
- Böl G, Kreuzer OJ, Brigelius-Flohé R (July 2000). "Translocation of the interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1 (IRAK-1) into the nucleus". FEBS Letters. 477 (1–2): 73–8. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01759-2. PMID 10899313.
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (November 2000). "DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination". Genome Research. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948. PMID 11076863.
- Vig E, Green M, Liu Y, Yu KY, Kwon HJ, Tian J, Goebl MG, Harrington MA (March 2001). "SIMPL is a tumor necrosis factor-specific regulator of nuclear factor-kappaB activity". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (11): 7859–66. doi:10.1074/jbc.M010399200. PMID 11096118.
- Li X, Commane M, Jiang Z, Stark GR (April 2001). "IL-1-induced NFkappa B and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation diverge at IL-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK)". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 98 (8): 4461–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.071054198. PMC 31857. PMID 11287640.
- Jensen LE, Whitehead AS (August 2001). "IRAK1b, a novel alternative splice variant of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK), mediates interleukin-1 signaling and has prolonged stability". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (31): 29037–44. doi:10.1074/jbc.M103815200. PMID 11397809.
- Qian Y, Commane M, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Matsumoto K, Li X (November 2001). "IRAK-mediated translocation of TRAF6 and TAB2 in the interleukin-1-induced activation of NFkappa B". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (45): 41661–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M102262200. PMID 11518704.