Ukraine
Ukraine Україна | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: [Shche ne vmerla Ukraina] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) "Ukraine has Not Yet Died" | |
| Location of Ukraine (green) in Europe (dark grey) (disputed territory in light green) Location of Ukraine (green) (disputed territory in light green)in Europe (dark grey) | |
| Capital and largest city | |
| Official languages | Ukrainian |
| Recognised regional languages | |
| Ethnic groups (2001[2]) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Ukrainian |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic |
| Oleksandr Turchynov | |
| Arseniy Yatsenyuk | |
| Oleksandr Turchynov | |
| Legislature | Verkhovna Rada |
| Formation | |
| 882 | |
| 1199 | |
| 17 August 1649 | |
| 7 November 1917 | |
| 1 November 1918 | |
| 10 March 1919 | |
| 8 October 1938 | |
| 15 November 1939 | |
| 30 June 1941 | |
| 24 August 1991a | |
| 21 February 2014 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 603,628 <span[convert: unknown unit] (46th) |
• Water (%) | 7 |
| Population | |
• 2013 estimate | 44,573,205 (including Crimea and Sevastopol)/ 42,227,200 (excluding Crimea and Sevastopol)[3] (29th) |
• 2001 census | 48,457,102[2] |
• Density | 73.8/km2 (191.1/sq mi) (115th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2013 estimate |
• Total | $337.360 billion[4] |
• Per capita | $7,422[4] |
| GDP (nominal) | 2013 estimate |
• Total | $175.527 billion[4] |
• Per capita | $3,862[4] |
| Gini (2010) | 25.6[5] low |
| HDI (2012) | high (78th) |
| Currency | Ukrainian hryvnia (UAH) |
| Time zone | UTC+2[7] (Eastern European Time) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (Eastern European Summer Time) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +380 |
| ISO 3166 code | UA |
| Internet TLD | |
| |
Ukraine (/juːˈkreɪn/ ⓘ; Ukrainian: Україна, transliterated: [Ukrayina] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help), [ukrɑˈjinɑ]) is a country in Eastern Europe.[8] It has an area of 603,628 km2 (233,062 sq mi), making it the largest country entirely within Europe.[9][10][11] Ukraine borders Russia to the east and northeast, Belarus to the northwest, Poland, Slovakia and Hungary to the west, Romania and Moldova to the southwest, and the Black Sea and Sea of Azov to the south and southeast, respectively.
The territory of Ukraine has been inhabited for at least 44,000 years,[12] with the country being a candidate site for the domestication of the horse[13][14][15] and for the origins of the Indo-European language family.
In the Middle Ages, the area became a key center of East Slavic culture, as epitomized by the powerful state of Kievan Rus'. Following its fragmentation in the 13th century, Ukraine was contested, ruled and divided by a variety of powers. A Cossack republic emerged and prospered during the 17th and 18th centuries, but Ukraine remained otherwise divided until its consolidation into a Soviet republic in the 20th century, becoming an independent state only in 1991.
Ukraine has long been a global breadbasket because of its extensive, fertile farmlands. As of 2011, it was the world's third-largest grain exporter with that year's harvest being much larger than average.[16] Ukraine is one of the ten most attractive agricultural land acquisition regions.[17] Additionally, the country has a well-developed manufacturing sector, particularly in aerospace and industrial equipment.
Ukraine is a unitary republic under a semi-presidential system with separate powers: legislative, executive, and judicial branches. Its capital and largest city is Kiev. Since the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Ukraine continues to maintain the second-largest military in Europe, after that of Russia, when reserves and paramilitary personnel are taken into account.[18]
The country (including Crimea) is home to 45.4 million people,[3][19] 77.8% of whom are Ukrainians and with sizable minorities of Russians (17%), Belarusians, Tatars and Romanians. Ukrainian is the official language of Ukraine; its alphabet is Cyrillic. Russian is also widely spoken. The dominant religion in the country is Eastern Orthodox Christianity, which has strongly influenced Ukrainian architecture, literature and music.
There are different hypotheses as to the etymology of the name Ukraine. According to the older and most widespread hypothesis, it means "borderland",[20] while more recently some linguistic studies claim a different meaning: "homeland" or "region, country".[21] "The Ukraine" was once the usual form in English[22] but since the Declaration of Independence of Ukraine, "the Ukraine" has become much less common in the English-speaking world and style-guides largely recommend not using the definite article.[23][24] However, other sources do recommend the article.[25]
History
Early history
Human settlement in Ukraine and its vicinity dates back to 32,000 BC, with evidence of the Gravettian culture in the Crimean Mountains.[26][27] By 4,500 BC, the Neolithic Cucuteni-Trypillian Culture flourished in a wide area that included parts of modern Ukraine including Trypillia and the entire Dnieper-Dniester region. During the Iron Age, the land was inhabited by Cimmerians, Scythians, and Sarmatians.[28] Between 700 BC and 200 BC it was part of the Scythian Kingdom, or Scythia.
Later, colonies of Ancient Greece, Ancient Rome and the Byzantine Empire, such as Tyras, Olbia and Hermonassa, were founded, beginning in the 6th century BC, on the northeastern shore of the Black Sea, and thrived well into the 6th century AD. The Goths stayed in the area but came under the sway of the Huns from the 370s AD. In the 7th century AD, the territory of eastern Ukraine was the centre of Old Great Bulgaria. At the end of the century, the majority of Bulgar tribes migrated in different directions, and the Khazars took over much of the land.
Golden Age of Kiev

Kievan Rus' was founded by the Rus' people, Varangians who first settled around Ladoga and Novgorod, then gradually moved southward eventually reaching Kiev about 880. Kievan Rus' included the western part of modern Ukraine, Belarus, with larger part of it situated on the territory of modern Russia. According to the Primary Chronicle the Rus' elite initially consisted of Varangians from Scandinavia.
During the 10th and 11th centuries, it became the largest and most powerful state in Europe.[29] In the following centuries, it laid the foundation for the national identity of Ukrainians and Russians.[30] Kiev, the capital of modern Ukraine, became the most important city of the Rus'.
The Varangians later assimilated into the local Slavic population and became part of the first Rus' dynasty, the Rurik Dynasty.[30] Kievan Rus' was composed of several principalities ruled by the interrelated Rurikid knyazes ("princes"). The seat of Kiev, the most prestigious and influential of all principalities, became the subject of many rivalries among Rurikids as the most valuable prize in their quest for power.
The Golden Age of Kievan Rus' began with the reign of Vladimir the Great (980–1015), who turned Rus' toward Byzantine Christianity. During the reign of his son, Yaroslav the Wise (1019–1054), Kievan Rus' reached the zenith of its cultural development and military power.[30] This was followed by the state's increasing fragmentation as the relative importance of regional powers rose again. After a final resurgence under the rule of Vladimir II Monomakh (1113–1125) and his son Mstislav (1125–1132), Kievan Rus' finally disintegrated into separate principalities following Mstislav's death.
In the 11th and 12th centuries, constant incursions by nomadic Turkic tribes, such as the Pechenegs and the Kipchaks, caused a massive migration of Slavic populations to the safer, heavily forested regions of the north.[31] The 13th century Mongol invasion devastated Kievan Rus'. Kiev was totally destroyed in 1240.[32] On today's Ukrainian territory, the state of Kievan Rus' was succeeded by the principalities of Halych and Volodymyr-Volynskyi, which were merged into the state of Galicia-Volhynia.
Danylo Romanovych (Daniel I of Galicia or Danylo Halytskyi) son of Roman Mstyslavych, re-united all of south-western Rus', including Volhynia, Galicia and Rus' ancient capital of Kiev. Danylo was crowned by the papal archbishop in Dorohychyn 1253 as the first King of all Rus'. Under Danylo's reign, the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia was one of the most powerful states in east central Europe.[33]
Foreign domination
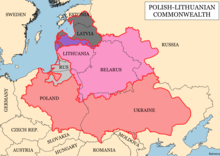
In the mid-14th century, upon the death of Bolesław Jerzy II of Mazovia, king Casimir III of Poland initiated campaigns (1340–1366) to take Galicia-Volhynia. Meanwhile the heartland of Rus', including Kiev, became the territory of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, ruled by Gediminas and his successors, after the Battle on the Irpen' River. Following the 1386 Union of Krewo, a dynastic union between Poland and Lithuania, much of what became northern Ukraine was ruled by the increasingly Slavicised local Lithuanian nobles as part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and by 1392 the so-called Galicia–Volhynia Wars ended. Polish colonisers of depopulated lands in northern and central Ukraine founded or refounded many towns. In 1430 Podolia was incorporated under the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland as Podolian Voivodeship. In 1441, in the southern Ukraine, especially Crimea and surrounding steppes, Genghisid prince Haci I Giray founded the Crimean Khanate.
In 1569 the Union of Lublin established the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and a considerable part of Ukrainian territory was transferred from the Grand Duchy of Lithuania to the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, becoming Polish territory de jure. Under the demographic, cultural and political pressure of Polonisation begun already in late 14th century, many landed gentry of Polish Ruthenia (another name for the land of Rus) converted to Catholicism and became indistinguishable from the Polish nobility.[34] Deprived of native protectors among Rus nobility, the commoners (peasants and townspeople) began turning for protection to the emerging Zaporozhian Cossacks, who by the 17th century became devoutly Orthodox. The Cossacks did not shy from taking up arms against those they perceived as enemies, including the Polish state and its local representatives.[35]

The Crimean Khanate was one of the strongest powers in Eastern Europe until the 18th century; at one point it even succeeded, under the Crimean khan Devlet I Giray, in capturing and devastating Moscow.[36] The population of the borderlands suffered annual Tatar invasions and tens of thousands of soldiers were required to protect the southern boundaries. From the beginning of the 16th century until the end of 17th century, the Crimean Tatar raiding bands made almost annual forays into agricultural Slavic lands in search of captives for sale as slaves,[37] exporting about 2 million slaves from Russia and Ukraine over the period 1500–1700.[38] According to Orest Subtelny, "from 1450 to 1586, eighty-six Tatar raids were recorded, and from 1600 to 1647, seventy."[39] In 1688, Tatars captured a record number of 60,000 Ukrainians.[40] The Tatar raids took a heavy toll, discouraging settlement in more southerly regions where the soil was better and the growing season was longer. Muscovy, Poland-Lithuania, Moldavia and Wallachia were all subjected to extensive slave raiding. The last remnant of the Crimean Khanate was finally conquered by the Russian Empire in 1783.[41] The Taurida Governorate was formed to govern this territory.
In the mid-17th century, a Cossack military quasi-state, the Zaporozhian Host, was formed by Dnieper Cossacks and by Ruthenian peasants who had fled Polish serfdom.[42] Poland exercised little real control over this population, but found the Cossacks to be a useful opposing force to the Turks and Tatars,[43] and at times the two were allies in military campaigns.[44] However the continued harsh enserfment of peasantry by Polish nobility and especially the suppression of the Orthodox Church alienated the Cossacks.[43]
The Cossacks sought representation in the Polish Sejm, recognition of Orthodox traditions, and the gradual expansion of the Cossack Registry. These were rejected by the Polish nobility, who dominated the Sejm.


In 1648, Bohdan Khmelnytsky and Petro Doroshenko led the largest of the Cossack uprisings against the Commonwealth and the Polish king John II Casimir.[45]

The Ruin
In 1657–1686 came "The Ruin", a devastating 30-year war amongst Russia, Poland, Turks and Cossacks for control of Ukraine, which occurred at about the same time as the Deluge of Poland. For three years, Khmelnytsky's armies controlled present-day western and central Ukraine, but, deserted by his Tatar allies, he suffered a crushing defeat at Berestechko, and turned to the Russian tsar for help.

In 1654, Khmelnytsky signed the Treaty of Pereyaslav, forming a military and political alliance with Russia that acknowledged loyalty to the tsar. The wars escalated in intensity with hundreds of thousands of deaths. Defeat came in 1686 as the "Eternal Peace" between Russia and Poland gave Kiev and the Cossack lands east of the Dnieper over to Russian rule and the Ukrainian lands west of the Dnieper to Poland.
In 1709, Cossack Hetman Ivan Mazepa (1639–1709) sided with Sweden against Russia in the Great Northern War (1700–1721). Mazepa, a member of the Cossack nobility, received an excellent education abroad and proved to be a brilliant political and military leader enjoying good relations with the Romanov dynasty. After Peter the Great became tsar, Mazepa as hetman gave him more than twenty years of loyal military and diplomatic service and was well rewarded.

Eventually Peter recognized that to consolidate and modernize Russia's political and economic power it was necessary to do away with the hetmanate and Ukrainian and Cossack aspirations to autonomy. Mazepa accepted Polish invitations to join the Poles and Swedes against Russia. The move was disastrous for the hetmanate, Ukrainian autonomy, and Mazepa. He died in exile after fleeing from the Battle of Poltava (1709), where the Swedes and their Cossack allies suffered a catastrophic defeat at the hands of Peter's Russian forces.
The hetmanate was abolished in 1764; the Zaporizhska Sich abolished in 1775, as Russia centralised control over its lands. As part of the partitioning of Poland in 1772, 1793 and 1795, the Ukrainian lands west of the Dnieper were divided between Russia and Austria. From 1737 to 1834, expansion into the northern Black Sea littoral and the eastern Danube valley was a cornerstone of Russian foreign policy.
Lithuanians and Poles controlled vast estates in Ukraine, and were a law unto themselves. Judicial rulings from Cracow were routinely flouted, while peasants were heavily taxed and practically tied to the land as serfs. Occasionally the landowners battled each other using armies of Ukrainian peasants. The Poles and Lithuanians were Roman Catholics and tried with some success to convert the Orthodox lesser nobility. In 1596, they set up the "Greek-Catholic" or Uniate Church, under the authority of the Pope but using Eastern rituals; it dominates western Ukraine to this day. Tensions between the Uniates and the Orthodox were never resolved, and the religious differentiation left the Ukrainian Orthodox peasants leaderless, as they were reluctant to follow the Ukrainian nobles.[46]
Cossacks led an uprising, called Koliivshchyna, starting in the Ukrainian borderlands of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1768. Ethnicity was one root cause of this revolt, which included Ukrainian violence that killed tens of thousands of Poles and Jews. Religious warfare also broke out between Ukrainian groups. Increasing conflict between Uniate and Orthodox parishes along the newly reinforced Polish-Russian border on the Dnepr River in the time of Catherine II set the stage for the uprising. As Uniate religious practices had become more Latinized, Orthodoxy in this region drew even closer into dependence on the Russian Orthodox Church. Confessional tensions also reflected opposing Polish and Russian political allegiances.[47]
After the Russians annexed the Crimean Khanate in 1783, the region called New Russia was settled by Ukrainian and Russian migrants.[48] Despite the promises of Ukrainian autonomy given by the Treaty of Pereyaslav, the Ukrainian elite and the Cossacks never received the freedoms and the autonomy they were expecting from Imperial Russia. However, within the Empire, Ukrainians rose to the highest Russian state and church offices. [a] At a later period, tsarists established a policy of Russification of Ukrainian lands, suppressing the use of the Ukrainian language in print, and in public.[49]
19th century, World War I and revolution

In the 19th century, Ukraine was a rural area largely ignored by Russia and Austria. With growing urbanization and modernization, and a cultural trend toward romantic nationalism, a Ukrainian intelligentsia committed to national rebirth and social justice emerged. The serf-turned-national-poet Taras Shevchenko (1814–1861) and the political theorist Mykhailo Drahomanov (1841–1895) led the growing nationalist movement.
After Ukraine and Crimea became aligned with the Russian Empire in the Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774), significant German immigration occurred after it was encouraged by Catherine the Great and her immediate successors. Immigration was encouraged into Ukraine and especially the Crimea by Catherine in her proclamation of open migration to the Russian Empire. Immigration was encouraged for Germans and other Europeans to thin the previously dominant Turk population and encourage more complete use of farmland.

Beginning in the 19th century, there was a continuous migration from Ukraine to settle the distant areas of the Russian Empire. According to the 1897 census, there were 223,000 ethnic Ukrainians in Siberia and 102,000 in Central Asia.[50] An additional 1.6 million emigrated to the east in the ten years after the opening of the Trans-Siberian Railway in 1906.[51]
Nationalist and socialist parties developed in the late 19th century. Austrian Galicia, which enjoyed substantial political freedom under the relatively lenient rule of the Habsburgs, became the center of the nationalist movement.
Ukrainians entered World War I on the side of both the Central Powers, under Austria, and the Triple Entente, under Russia. 3.5 million Ukrainians fought with the Imperial Russian Army, while 250,000 fought for the Austro-Hungarian Army.[53] During the war, Austro-Hungarian authorities established the Ukrainian Legion to fight against the Russian Empire. This legion was the foundation of the Ukrainian Galician Army that fought against the Bolsheviks and Poles in the post-World War I period (1919–23). Those suspected of Russophile sentiments in Austria were treated harshly. Up to 5,000 supporters of the Russian Empire from Galicia were detained and placed in Austrian internment camps in Talerhof, Styria and in a fortress at Terezín (now in the Czech Republic).[54]
World War I brought about the end of the Russian and Austrian empires. The Russian Revolution of 1917 ended the Russia empire, led to the founding of the Soviet Union under the Bolsheviks, and subsequent civil war in Russia. A Ukrainian national movement for self-determination reemerged, with heavy Communist and Socialist influence. During 1917–20, several separate Ukrainian states briefly emerged: the Ukrainian People's Republic, the Hetmanate, the Directorate and the pro-Bolshevik Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic (or Soviet Ukraine) successively established territories in the former Russian Empire; while the West Ukrainian People's Republic and the Hutsul Republic emerged briefly in the former Austro-Hungarian territory. This led to civil war, and an anarchist movement called the Black Army led by Nestor Makhno, developed in Southern Ukraine during that war.[55]
However, Poland defeated Western Ukraine in the Polish-Ukrainian War, but failed against the Bolsheviks in an offensive against Kiev. According to the Peace of Riga concluded between the Soviets and Poland, western Ukraine was officially incorporated into Poland, which in turn recognised the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic in March 1919. With establishment of the Soviet power in Ukraine, the country lost half of its territory: the eastern Galicia was given to Poland, Pripyat marshes region – to Belarus, half of Sloboda Ukraine and northern fringes of Severia were passed to Russia, while on the left bank of Dniester River was created Moldavian autonomy. Eventually, Ukraine became a founding member of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics or the Soviet Union in December 1922.[56]
Western Ukraine, Carpathian Ruthenia and Bukovina
The war in Ukraine continued for another two years; by 1921, however, most of Ukraine had been taken over by the Soviet Union, while Galicia and Volhynia (West Ukraine) were incorporated into independent Poland. Bukovina was annexed by Romania and Carpathian Ruthenia, with mediation of the United States, was admitted to the Czechoslovakian Republic as an autonomy.
A powerful underground Ukrainian nationalist movement arose in Poland in the 1920s and 1930s due to Polish national policies in Western Ukraine, which was led by the Ukrainian Military Organization and the Organisation of Ukrainian Nationalists (OUN). The movement attracted a militant following among students. Hostilities between state authorities and the popular movement led to a substantial number of fatalities. The autonomy which had been promised Eastern Galicia (West Ukraine) was never implemented. A number of Ukrainian parties, the Ukrainian Catholic Church, an active press, and a business sector existed in Poland. Economic conditions improved in the 1920s, but the region suffered from the Great Depression in the 1930s.
Inter-war Soviet Ukraine

The civil war that eventually brought the Soviet government to power devastated Ukraine. It left over 1.5 million people dead and hundreds of thousands homeless. In addition, Soviet Ukraine had to face the famine of 1921.[57] Seeing an exhausted Ukraine, the Soviet government remained very flexible during the 1920s.[58] Thus, under the aegis of the Ukrainization policy pursued by the national Communist leadership of Mykola Skrypnyk, Soviet leadership encouraged a national renaissance in literature and the arts. The Ukrainian culture and language enjoyed a revival, as Ukrainisation became a local implementation of the Soviet-wide policy of Korenisation (literally indigenisation) policy.[56] The Bolsheviks were also committed to introducing universal health care, education and social-security benefits, as well as the right to work and housing.[59] Women's rights were greatly increased through new laws designed to wipe away centuries-old inequalities.[60] Most of these policies were sharply reversed by the early 1930s after Joseph Stalin gradually consolidated power to become the de facto communist party leader.

The communists gave a privileged position to manual labour[citation needed], the largest class in the cities, where Russians dominated. The typical worker was more attached to class identity than to ethnicity[citation needed]. Although there were incidents of ethnic friction among workers (in addition to Ukrainians and Russians there were many Poles, Germans, Jews and others in the Ukrainian workforce), industrial laborers had already adopted Russian culture and language to a great extent[citation needed]. Few workers whose ethnicity was Ukrainian were attracted to campaigns of Ukrainianisation or de-Russification, but remained loyal members of the Soviet working class[citation needed]. There was allegedly little antagonism between workers identifying themselves as Ukrainian or Russian[citation needed].
Starting from the late 1920s, Ukraine was involved in the Soviet industrialisation and the republic's industrial output quadrupled during the 1930s.[56]
The industrialisation had a heavy cost for the peasantry, demographically a backbone of the Ukrainian nation. To satisfy the state's need for increased food supplies and to finance industrialisation, Stalin instituted a programme of collectivisation of agriculture as the state combined the peasants' lands and animals into collective farms and enforced the policies by the regular troops and secret police.[56] Those who resisted were arrested and deported and the increased production quotas were placed on the peasantry. The collectivisation had a devastating effect on agricultural productivity. As the members of the collective farms were not allowed to receive any grain until sometimes unrealistic quotas were met, starvation in the Soviet Union became more common. In 1932–33, millions starved to death in a famine known as Holodomor or "Great Famine".[c] Scholars are divided as to whether this famine fits the definition of genocide, but the Ukrainian parliament and other countries recognise it as such.[c]

The famine claimed up to 10 million Ukrainian lives as peasants' food stocks were forcibly removed by the Soviet government by the NKVD secret police.[61] Some explanations for the causes for the excess deaths in rural areas of Ukraine, southern Russia and Kazakhstan during the Soviet famine of 1932–33 have been given by dividing the causes into three groups: objective non-policy-related factors, like the drought of 1931 and poor weather in 1932; inadvertent result of policies with other objectives, like rapid industrialisation, socialisation of livestock and neglected crop rotation patterns; and deaths caused intentionally by a starvation policy. The Communist leadership perceived famine not as a humanitarian catastrophe but as a means of class struggle and used starvation as a punishment tool to force peasants into collective farms.[62] It was largely the same groups of individuals who were responsible for the mass killing operations during the civil war, collectivisation, and the Great Terror. These groups were associated with Efim Georgievich Evdokimov (1891–1939) and operated in Ukraine during the civil war, in the North Caucasus in the 1920s, and in the Secret Operational Division within General State Political Administration (OGPU) in 1929–31. Evdokimov transferred into Communist Party administration in 1934, when he became Party secretary for North Caucasus Krai. But he appears to have continued advising Joseph Stalin and Nikolai Yezhov on security matters, and the latter relied on Evdokimov's former colleagues to carry out the mass killing operations that are known as the Great Terror in 1937–38.[63]
On 13 January 2010, Kiev Appellate Court posthumously found Stalin, Kaganovich and other Soviet Communist Party functionaries guilty of genocide against Ukrainians during the Holodomor famine.[64]
With Joseph Stalin's change of course in the late 1920s, however, Moscow's toleration of Ukrainian national identity came to an end. Systematic state terror of the 1930s destroyed Ukraine's writers, artists and intellectuals; the Communist Party of Ukraine was purged of its "nationalist deviationists". Two waves of Stalinist political repression and persecution in the Soviet Union (1929–34 and 1936–38) resulted in the killing of some 681,692 people; this included four-fifths of the Ukrainian cultural elite and three-quarters of all the Red Army's higher-ranking officers.[56][b]
World War II

Following the Invasion of Poland in September 1939, German and Soviet troops divided the territory of Poland. Thus, Eastern Galicia and Volhynia with their Ukrainian population became reunited with the rest of Ukraine. The unification that Ukraine achieved for the first time in its history was a decisive event in the history of the nation.[65][66]
In 1940, Romania ceded Bessarabia and northern Bukovina in response to Soviet demands. The Ukrainian SSR incorporated northern and southern districts of Bessarabia, northern Bukovina, and the Hertsa region. But it ceded the western part of the Moldavian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic to the newly created Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic. All these territorial gains were internationally recognised by the Paris peace treaties of 1947.

German armies invaded the Soviet Union on 22 June 1941, thereby initiating four straight years of incessant total war. The Axis allies initially advanced against desperate but unsuccessful efforts of the Red Army. In the encirclement battle of Kiev, the city was acclaimed as a "Hero City", because the resistance by the Red Army and by the local population was fierce. More than 600,000 Soviet soldiers (or one-quarter of the Soviet Western Front) were killed or taken captive there.[67][68]
Although the majority of Ukrainians fought alongside the Red Army and Soviet resistance,[69] some elements of the Ukrainian nationalist underground created an anti-Soviet nationalist formation in Galicia, the Ukrainian Insurgent Army (1942). At times it allied with the Nazi forces, it also carried out the massacres of ethnic Poles,[70] and, after the war, continued to fight the USSR. Using guerrilla war tactics, the insurgents targeted for assassination and terror those who they perceived as representing, or cooperating at any level with, the Soviet state.[71][72]
At the same time, the Ukrainian Liberation Army, another nationalist movement, fought alongside the Nazis.
In total, the number of ethnic Ukrainians who fought in the ranks of the Soviet Army is estimated from 4.5 million[69] to 7 million.[73][dead link][d] The pro-Soviet partisan guerrilla resistance in Ukraine is estimated to number at 47,800 from the start of occupation to 500,000 at its peak in 1944; with about 50% being ethnic Ukrainians.[74] Generally, the Ukrainian Insurgent Army's figures are not very reliable, with figures ranging anywhere from 15,000 to as many as 100,000 fighters.[75][76]
Most of the Ukrainian SSR was organised within the Reichskommissariat Ukraine, with the intention of exploiting its resources and eventual German settlement. Initially, some western Ukrainians, who had only joined the Soviet Union in 1939 under pressure, hailed the Germans as liberators. But brutal German rule in the occupied territories eventually turned its supporters against them. Nazi administrators of conquered Soviet territories made little attempt to exploit the dissatisfaction of Ukraine with Stalinist political and economic policies.[77] Instead, the Nazis preserved the collective-farm system, systematically carried out genocidal policies against Jews, deported men to work in forced labour camps in Germany, and began a systematic depopulation of Ukraine (along with Poland) to prepare it for German colonisation.[77] They blockaded the transport of food on the Kiev River.[78]
The vast majority of the fighting in World War II took place on the Eastern Front.[79] It has been estimated that 93% of all German casualties took place on the Eastern Front.[80] The total losses inflicted upon the Ukrainian population during the war are estimated between 5 and 8 million,[81][82] including estimated one and a half million Jews killed by the Einsatzgruppen,[83] sometimes with the help of local collaborators. Of the estimated 8.7 million Soviet troops who fell in battle against the Nazis,[84][85][86] 1.4 million were ethnic Ukrainians.[84][86][d][e] Victory Day is celebrated as one of ten Ukrainian national holidays.[87]
Post-World War II

The republic was heavily damaged by the war, and it required significant efforts to recover. More than 700 cities and towns and 28,000 villages were destroyed.[88] The situation was worsened by a famine in 1946–47, which was caused by a drought and the wartime destruction of infrastructure. The death toll of this famine varies, with even the lowest estimate in the tens of thousands.[89][90][91]
In 1945, the Ukrainian SSR became one of the founding members of the United Nations organization.[92] The first Soviet computer, MESM, was built at the Kiev Institute of Electrotechnology and became operational in 1950.[93]
Post-war ethnic cleansing occurred in the newly expanded Soviet Union. As of 1 January 1953, Ukrainians were second only to Russians among adult "special deportees", comprising 20% of the total.[94] In addition, over 450,000 ethnic Germans from Ukraine and more than 200,000 Crimean Tatars were victims of forced deportations.[94]
Following the death of Stalin in 1953, Nikita Khrushchev became the new leader of the USSR. Having served as First Secretary of the Communist Party of Ukrainian SSR in 1938–49, Khrushchev was intimately familiar with the republic; after taking power union-wide, he began to emphasize the friendship between the Ukrainian and Russian nations. In 1954, the 300th anniversary of the Treaty of Pereyaslav was widely celebrated. Crimea was transferred from the Russian SFSR to the Ukrainian SSR.[95]

By 1950, the republic had fully surpassed pre-war levels of industry and production.[96] During the 1946–1950 five-year plan, nearly 20% of the Soviet budget was invested in Soviet Ukraine, a 5% increase from prewar plans. As a result, the Ukrainian workforce rose 33.2% from 1940 to 1955 while industrial output grew 2.2 times in that same period.
Soviet Ukraine soon became a European leader in industrial production,[97] and an important centre of the Soviet arms industry and high-tech research. Such an important role resulted in a major influence of the local elite. Many members of the Soviet leadership came from Ukraine, most notably Leonid Brezhnev. He later ousted Khrushchev and became the Soviet leader from 1964 to 1982. Many prominent Soviet sports players, scientists, and artists came from Ukraine.
On 26 April 1986, a reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant exploded, resulting in the Chernobyl disaster, the worst nuclear reactor accident in history.[98] This was the only accident to receive the highest possible rating of 7 by the International Nuclear Event Scale, indicating a "major accident", until the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in March 2011.[99] At the time of the accident, 7 million people lived in the contaminated territories, including 2.2 million in Ukraine.[100]
After the accident, the new city of Slavutych was built outside the exclusion zone to house and support the employees of the plant, which was decommissioned in 2000. A report prepared by the International Atomic Energy Agency and World Health Organization attributed 56 direct deaths to the accident and estimated that there may have been 4,000 extra cancer deaths.[101]
Independence

On 16 July 1990, the new parliament adopted the Declaration of State Sovereignty of Ukraine.[102] The declaration established the principles of the self-determination of the Ukrainian nation, its democracy, political and economic independence, and the priority of Ukrainian law on the Ukrainian territory over Soviet law. A month earlier, a similar declaration was adopted by the parliament of the Russian SFSR. This started a period of confrontation between the central Soviet, and new republican authorities. In August 1991, a conservative faction among the Communist leaders of the Soviet Union attempted a coup to remove Mikhail Gorbachev and to restore the Communist party's power. After the attempt failed, on 24 August 1991 the Ukrainian parliament adopted the Act of Independence in which the parliament declared Ukraine as an independent democratic state.[103]
A referendum and the first presidential elections took place on 1 December 1991. That day, more than 90% of the electorate expressed their support for the Act of Independence, and they elected the chairman of the parliament, Leonid Kravchuk to serve as the first President of the country. At the meeting in Brest, Belarus on 8 December, followed by the Alma Ata meeting on 21 December, the leaders of Belarus, Russia, and Ukraine, formally dissolved the Soviet Union and formed the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS).[104]

Although the idea of an independent Ukrainian nation had previously not existed in the 20th century in the minds of international policy makers,[105] Ukraine was initially viewed as a republic with favorable economic conditions in comparison to the other regions of the Soviet Union.[106] However, the country experienced deeper economic slowdown than some of the other former Soviet Republics. During the recession, Ukraine lost 60% of its GDP from 1991 to 1999,[107][108] and suffered five-digit inflation rates.[109] Dissatisfied with the economic conditions, as well as the amounts of crime and corruption in Ukraine, Ukrainians protested and organised strikes.[110]
The Ukrainian economy stabilized by the end of the 1990s. A new currency, the hryvnia, was introduced in 1996. Since 2000, the country has enjoyed steady real economic growth averaging about seven percent annually.[111][112] A new Constitution of Ukraine was adopted under second President Leonid Kuchma in 1996, which turned Ukraine into a semi-presidential republic and established a stable political system. Kuchma was, however, criticised by opponents for corruption, electoral fraud, discouraging free speech and concentrating too much power in his office.[113] He also repeatedly transferred public property into the hands of loyal oligarchs.[citation needed]
Orange Revolution

In 2004, Viktor Yanukovych, then Prime Minister, was declared the winner of the presidential elections, which had been largely rigged, as the Supreme Court of Ukraine later ruled.[114] The results caused a public outcry in support of the opposition candidate, Viktor Yushchenko, who challenged the outcome of the elections. This resulted in the peaceful Orange Revolution, bringing Viktor Yushchenko and Yulia Tymoshenko to power, while casting Viktor Yanukovych in opposition.[115] Activists of the Orange Revolution were funded and trained in tactics of political organisation and nonviolent resistance by a coalition of Western pollsters and professional consultants who were partly funded by a range of Western government and non-government agencies but received most of their funding from domestic sources.[nb 1][116] According to The Guardian, the foreign donors included the U.S. State Department and USAID along with the National Democratic Institute for International Affairs, the International Republican Institute, the NGO Freedom House and George Soros's Open Society Institute.[117] The National Endowment for Democracy, a foundation supported by the U.S. government, has supported non-governmental democracy-building efforts in Ukraine since 1988.[118] Writings on nonviolent struggle by Gene Sharp contributed in forming the strategic basis of the student campaigns.[119]
Yanukovych returned to a position of power in 2006, when he became Prime Minister in the Alliance of National Unity,[120] until snap elections in September 2007 made Tymoshenko Prime Minister again.[121] Amid the 2008–09 Ukrainian financial crisis the Ukrainian economy plunged by 15%.[122] Disputes with Russia over debts for natural gas briefly stopped all gas supplies to Ukraine in 2006 and again in 2009, leading to gas shortages in several other European countries.[123][124] Viktor Yanukovych was elected President in 2010 with 48% of votes.[125]
Euromaidan and 2014 revolution
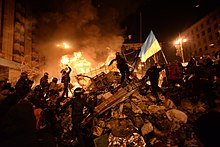
The Euromaidan (Ukrainian: Євромайдан, literally "Eurosquare") protests started in November 2013 after the president, Viktor Yanukovych, began shying away from an association agreement that had been in the works with the European Union and instead chose to establish closer ties with Russia.[126][127] Some Ukrainians took to the streets to show their support for closer ties with Europe. Over time, Euromaidan came to describe a wave of demonstrations and civil unrest in Ukraine, the scope of which evolved to include calls for the resignation of President Yanukovych and his government.[128] Violence escalated after 16 January 2014 when the government accepted Bondarenko-Oliynyk laws, also known as Anti-Protest Laws. Anti-government demonstrators occupied buildings in the centre of Kiev, including the Justice Ministry building, and riots left 98 dead and thousands injured from 18–20 February.[129][130] Owing to violent protests on 22 February 2014, Members of Parliament found the president unable to fulfill his duties and exercised "constitutional powers" to set an election for 25 May to select his replacement.[131]
Russian intervention in Ukraine

In the wake of the collapse of the Yanukovych government and the resultant 2014 Ukrainian revolution in February 2014, a secession crisis began on Ukraine's Crimean Peninsula which had a significant number of Russophone people. On 1 March 2014, exiled Ukrainian President Viktor Yanukovych requested that Russia use military forces "to establish legitimacy, peace, law and order, stability and defending the people of Ukraine".[132] On the same day, Putin requested and received authorization from the Russian Parliament to deploy Russian troops to Ukraine and took control of the Crimean Peninsula by the next day.[133][134][135][136]
On 6 March 2014, the Crimean Parliament voted to "enter into the Russian Federation with the rights of a subject of the Russian Federation" and later held a referendum asking the people of these regions whether they wanted to join Russia as a federal subject, or if they wanted to restore the 1992 Crimean constitution and Crimea's status as a part of Ukraine.[137] Though passed with an overwhelming majority, the vote was not monitored by outside parties and the results are internationally contested.[138][139][140] Crimea and Sevastopol formally declared independence as the Republic of Crimea and requested that they be admitted as constituents of the Russian Federation.[141] On 18 March 2014, Russia and Crimea signed a treaty of accession of the Republic of Crimea and Sevastopol in the Russian Federation, though the United Nations General Assembly voted in favor of a non-binding statement to oppose Russian annexation of the peninsula.[142]
Meanwhile, unrest began in the Eastern and Southern regions of Ukraine. In several cities in the Donetsk and Lugansk regions armed men, declaring themselves as local militia, seized government buildings, police and special police stations in several cities of the regions. Talks in Geneva between the EU, Russia, Ukraine and USA yielded a Joint Diplomatic Statement referred to as the 2014 Geneva Pact[143] in which the parties requested that all unlawful militias lay down the arms and vacate seized government buildings, and also establish a political dialogue that could lead to more autonomy for Ukraine's regions.
On May 11, 2014, the Donetsk and Lugansk regions held an independence referendum. The majority of the population in both regions voted for a split from Kiev, and the regions are set to have another referendum on May 18 on joining the Russian Federation.[144]
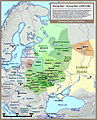
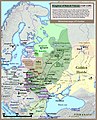
Historical maps of Ukraine
The Ukrainian state has occupied a number of territories since its initial foundation. Most of these territories have been located within Eastern Europe, however, as depicted in the maps in the gallery below, has also at times extended well into Eurasia and South-Eastern Europe. At times there has also been a distinct lack of a Ukrainian state, as its territories were on a number of occasions, annexed by its more powerful neighbours.
-
Territory of Slavic peoples (6th century).
-
Historical map of Kievan Rus' and territory of Ukraine: last 20 years of the state (1220–1240).
-
The Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia or Kingdom of Halych-Volynia (1245–1349).
-
Historical map of Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Rus' and Samogitia until 1434.
-
Proposed Polish–Lithuanian–Ruthenian Commonwealth or Commonwealth of Three Nations (1658).
-
Historical map of Ukrainian Cossack Hetmanate and territory of Zaporozhian Cossacks under rule of Russian Empire (1751).
Geography
At 603,628 square kilometres (233,062 sq mi) and with a coastline of 2,782 kilometres (1,729 mi), Ukraine is the world's 46th-largest country (after the Central African Republic, before Madagascar). It is the largest wholly European country and the second largest country in Europe (after the European part of Russia, before metropolitan France).[i][29] It lies between latitudes 44° and 53° N, and longitudes 22° and 41° E.
The Ukrainian landscape consists mostly of fertile plains (or steppes) and plateaus, crossed by rivers such as the Dnieper ([Dnipro] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)), Seversky Donets, Dniester and the Southern Buh as they flow south into the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. To the southwest, the delta of the Danube forms the border with Romania. Its various regions have diverse geographic features ranging from the highlands to the lowlands. The country's only mountains are the Carpathian Mountains in the west, of which the highest is the Hora Hoverla at 2,061 metres (6,762 ft), and the Crimean Mountains on Crimea, in the extreme south along the coast.[146] However Ukraine also has a number of highland regions such as the Volyn-Podillia Upland (in the west) and the Near-Dnipro Upland (on the right bank of Dnieper); to the east there are the south-western spurs of the Central Russian Uplands over which runs the border with Russia. Near the Sea of Azov can be found the Donets Ridge and the Near Azov Upland. The snow melt from the mountains feeds the rivers, and natural changes in altitude form a sudden drop in elevation and create many opportunities to form waterfalls.
Significant natural resources in Ukraine include iron ore, coal, manganese, natural gas, oil, salt, sulphur, graphite, titanium, magnesium, kaolin, nickel, mercury, timber and an abundance of arable land. Despite this, the country faces a number of major environmental issues such as inadequate supplies of potable water; air and water pollution and deforestation, as well as radiation contamination in the north-east from the 1986 accident at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant. Recycling toxic household waste is still in its infancy in Ukraine.[147]
Biodiversity
Ukraine is home to a very wide range of animals, fungi, micro-organisms and plants.
Animals
Ukraine is divided into two main zoological areas. One of these areas, in the west of the country, is made up of the borderlands of Europe, where there are species typical of mixed forests, the other is located in eastern Ukraine, where steppe-dwelling species thrive. In the forested areas of the country it is not uncommon to find lynxes, wolves, wild boar and martens, as well as many other similar species; this is especially true of the Carpathian Mountains, where a large number of predatory mammals make their home, as well as a contingent of brown bears. Around Ukraine's lakes and rivers beavers, otters and mink make their home, whilst within, carp, bream and catfish are the most commonly found species of fish. In the central and eastern parts of the country, rodents such as hamsters and gophers are found in large numbers.
Fungi
More than 6,600 species of fungi (including lichen-forming species) have been recorded from Ukraine,[148][149] but this number is far from complete. The true total number of fungal species occurring in Ukraine, including species not yet recorded, is likely to be far higher, given the generally accepted estimate that only about 7% of all fungi worldwide have so far been discovered.[150] Although the amount of available information is still very small, a first effort has been made to estimate the number of fungal species endemic to Ukraine, and 2217 such species have been tentatively identified.[151]
Climate
Ukraine has a mostly temperate continental climate, although the southern coast has a humid subtropical climate.[152] Precipitation is disproportionately distributed; it is highest in the west and north and lowest in the east and southeast. Western Ukraine receives around 1,200 millimetres (47.2 in) of precipitation annually, while Crimea receives around 400 millimetres (15.7 in). Winters vary from cool along the Black Sea to cold farther inland. Average annual temperatures range from 5.5–7 °C (41.9–44.6 °F) in the north, to 11–13 °C (51.8–55.4 °F) in the south.[153]
Politics

Ukraine is a republic under a mixed semi-parliamentary semi-presidential system with separate legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
The Constitution of Ukraine
With the proclamation of its independence on 24 August 1991, and adoption of a constitution on 28 June 1996, Ukraine became a semi-presidential republic. However, in 2004, deputies introduced changes to the Constitution, which tipped the balance of power in favour of a parliamentary system. From 2004 to 2010, the legitimacy of the 2004 Constitutional amendments had official sanction, both with the Constitutional Court of Ukraine, and most major political parties.[158] Despite this, on 30 September 2010 the Constitutional Court ruled that the amendments were null and void, forcing a return to the terms of the 1996 Constitution and again making Ukraine's political system more presidential in character.
The ruling on the 2004 Constitutional amendments became a major topic of political discourse. Much of the concern was due to the fact that neither the Constitution of 1996 nor the Constitution of 2004 provided the ability to "undo the Constitution", as the decision of the Constitutional Court would have it, even though the 2004 constitution arguably has an exhaustive list of possible procedures for constitutional amendments (articles 154–159). In any case, the current Constitution could be modified by a vote in Parliament.[158][159][160]
On 21 February 2014 an agreement between President Viktor Yanukovych and opposition leaders saw the country return to the 2004 Constitution. The historic agreement, brokered by the European Union, followed protests that began in late November 2013 and culminated in a week of violent clashes in which scores of protesters were killed. In addition to returning the country to the 2004 Constitution, the deal provided for the formation of a coalition government, the calling of early elections, and the release of former Prime Minister Yulia Tymoshenko from prison.[161] A day after the agreement was reached the Ukraine parliament dismissed Yanukovych and installed its speaker Oleksandr Turchynov as interim president[162] and Arseniy Yatsenyuk as the Prime Minister of Ukraine.[163]
The president, parliament and government
The President is elected by popular vote for a five-year term and is the formal head of state.[164] Ukraine's legislative branch includes the 450-seat unicameral parliament, the Verkhovna Rada.[165] The parliament is primarily responsible for the formation of the executive branch and the Cabinet of Ministers, headed by the Prime Minister.[166] However, the President still retains the authority to nominate the Ministers of the Foreign Affairs and of Defence for parliamentary approval, as well as the power to appoint the Prosecutor General and the head of the Security Service.

Laws, acts of the parliament and the cabinet, presidential decrees, and acts of the Crimean parliament may be abrogated by the Constitutional Court, should they be found to violate the constitution. Other normative acts are subject to judicial review. The Supreme Court is the main body in the system of courts of general jurisdiction. Local self-government is officially guaranteed. Local councils and city mayors are popularly elected and exercise control over local budgets. The heads of regional and district administrations are appointed by the President in accordance with the proposals of the Prime Minister. This system virtually requires an agreement between the President and the Prime Minister, and has in the past led to problems, such as when President Yushchenko exploited a perceived loophole by appointing so-called 'temporarily acting' officers, instead of actual governors or local leaders, thus evading the need to seek a compromise with the Prime Minister. This practice was controversial and was subject to Constitutional Court review.
Ukraine has a large number of political parties, many of which have tiny memberships and are unknown to the general public.[citation needed] Small parties often join in multi-party coalitions (electoral blocs) for the purpose of participating in parliamentary elections.
Courts and law enforcement
The courts enjoy legal, financial and constitutional freedom guaranteed by measures adopted in Ukrainian law in 2002. Judges are largely well protected from dismissal (except in the instance of gross misconduct). Court justices are appointed by presidential decree for an initial period of five years, after which Ukraine's Supreme Council confirms their positions for life in an attempt to insulate them from politics. Although there are still problems with the performance of the system, it is considered to have been much improved since Ukraine's independence in 1991. The Supreme Court is regarded as being an independent and impartial body, and has on several occasions ruled against the Ukrainian government. The World Justice Project ranks Ukraine 66 out of 99 countries surveyed in its annual Rule of Law Index.[167]

Prosecutors in Ukraine have greater powers than in most European countries, and according to the European Commission for Democracy through Law 'the role and functions of the Prosecutor's Office is not in accordance with Council of Europe standards".[168] In addition to this, from 2005 until 2008 the criminal judicial system maintained an average 99.5% conviction rate and this number grew to 99.83% in 2012,[169] equal to the conviction rate of the Soviet Union, with[170] suspects often being incarcerated for long periods before trial.[171] On 24 March 2010, President Yanukovych formed an expert group to make recommendations how to "clean up the current mess and adopt a law on court organization".[171] One day after setting this commission Yanukovych stated "We can no longer disgrace our country with such a court system."[171] Judicial and penal institutions play a fundamental role in protecting citizens and safeguarding the common good. The criminal judicial system and the prison system of Ukraine remain quite punitive. In contemporary Ukraine prison ministry of chaplains does not exist de jure.

Since 1 January 2010 it has been permissible to hold court proceedings in Russian by mutual consent of the parties. Citizens unable to speak Ukrainian or Russian may use their native language or the services of a translator.[172] Previously all court proceedings had to be held in Ukrainian, the nation's only language with any truly official administrative status.
Law enforcement agencies in Ukraine are typically organised under the authority of the Ministry of Internal Affairs. They consist primarily of the national police force (Мiлiцiя) and various specialised units and agencies such as the State Border Guard and the Coast Guard services. In recent years the law enforcement agencies, particularly the police, have faced criticism for their heavy handling of the 2004 Orange Revolution, this criticism stems from the use by the Kuchma government's contemplated use of Berkut special operations units and internal troops in a plan to put an end to demonstrations on Kiev's Maidan Nezalezhnosti. The actions of the government saw many thousands of police officers mobilised and stationed throughout the capital, primarily to dissuade protesters from challenging the state's authority but also to provide a quick reaction force in case of need; most officers were armed and another 10,000 were held in reserve nearby.[173] Bloodshed was only avoided when Lt. Gen. Sergei Popkov heeded his colleagues' calls to withdraw.
The Ministry of Internal Affairs is also responsible for the maintenance of the State Security Service; Ukraine's domestic intelligence agency, which has on occasion been accused of acting like a secret police force serving to protect the country's political elite from media criticism. On the other hand however, it is widely accepted that members of the service provided vital information about government plans to the leaders of the Orange Revolution to prevent the collapse of the movement.
Foreign relations

In 1999–2001, Ukraine served as a non-permanent member of the UN Security Council. Historically, Soviet Ukraine joined the United Nations in 1945 as one of the original members following a Western compromise with the Soviet Union, which had asked for seats for all 15 of its union republics. Ukraine has consistently supported peaceful, negotiated settlements to disputes. It has participated in the quadripartite talks on the conflict in Moldova and promoted a peaceful resolution to conflict in the post-Soviet state of Georgia. Ukraine also has made a substantial contribution to UN peacekeeping operations since 1992.

Ukraine currently considers Euro-Atlantic integration its primary foreign policy objective, but in practice balances its relationship with the European Union and the United States with strong ties to Russia. The European Union's Partnership and Cooperation Agreement (PCA) with Ukraine went into force on 1 March 1998. The European Union (EU) has encouraged Ukraine to implement the PCA fully before discussions begin on an association agreement. The EU Common Strategy toward Ukraine, issued at the EU Summit in December 1999 in Helsinki, recognizes Ukraine's long-term aspirations but does not discuss association. On 31 January 1992, Ukraine joined the then-Conference on Security and Cooperation in Europe (now the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE), and on 10 March 1992, it became a member of the North Atlantic Cooperation Council. Ukraine also has a close relationship with NATO and had previously declared interest in eventual membership; however, this was removed from the government's foreign policy agenda upon election of Viktor Yanukovych to the presidency, in 2010. It is the most active member of the Partnership for Peace (PfP). All major political parties in Ukraine support full eventual integration into the European Union. The Association Agreement with the EU was expected to be signed into effect by the end of 2011, but the process has been suspended as of 2012 due to recent political developments.[174]
Ukraine maintains peaceful and constructive relations with all its neighbours; it had enjoyed especially close ties with Russia and Poland, although relations with the former were complicated by energy dependence and payment arrears. However, following the events of March 2014, Ukraine now disputes sovereignty over the Crimean Peninsula with Russia.
Ukraine is included in the European Union's European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP) which aims at bringing the EU and its neighbours closer.
Administrative divisions
The system of Ukrainian subdivisions reflects the country's status as a unitary state (as stated in the country's constitution) with unified legal and administrative regimes for each unit.
Ukraine is subdivided into twenty-four oblasts (provinces) and one autonomous republic ([avtonomna respublika] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)), Crimea. Additionally, the cities of Kiev, the capital, and Sevastopol, both have a special legal status. The 24 oblasts and Crimea are subdivided into 490 [raions] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) (districts), or second-level administrative units. The average area of a Ukrainian raion is 1,200 square kilometres (460 sq mi); the average population of a raion is 52,000 people.[175]
Urban areas (cities) can either be subordinated to the state (as in the case of Kiev and Sevastopol), the oblast or [raion] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) administrations, depending on their population and socio-economic importance. Lower administrative units include urban-type settlements, which are similar to rural communities, but are more urbanized, including industrial enterprises, educational facilities and transport connections, and villages.
Following 2014 Crimean crisis Crimea and Sevastopol became de facto administrated by the Russian Federation, which claims them as Republic of Crimea and federal city of Sevastopol. Internationally they are still recognised as parts of Ukraine.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
Armed forces
After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Ukraine inherited a 780,000-man military force on its territory, equipped with the third-largest nuclear weapons arsenal in the world.[176][177] In May 1992, Ukraine signed the Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (START) in which the country agreed to give up all nuclear weapons to Russia for disposal and to join the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty as a non-nuclear weapon state. Ukraine ratified the treaty in 1994, and by 1996 the country became free of nuclear weapons.[176]
Ukraine took consistent steps toward reduction of conventional weapons. It signed the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe, which called for reduction of tanks, artillery, and armoured vehicles (army forces were reduced to 300,000). The country plans to convert the current conscript-based military into a professional volunteer military.[178]
Ukraine has been playing an increasingly larger role in peacekeeping operations. On Friday 3 January 2014, the Ukrainian frigate Hetman Sagaidachniy joined the European Union’s counter piracy Operation Atalanta and will be part of the EU Naval Force off the coast of Somalia for two months.[179] Ukrainian troops are deployed in Kosovo as part of the Ukrainian-Polish Battalion.[180] A Ukrainian unit was deployed in Lebanon, as part of UN Interim Force enforcing the mandated ceasefire agreement. There was also a maintenance and training battalion deployed in Sierra Leone. In 2003–05, a Ukrainian unit was deployed as part of the Multinational force in Iraq under Polish command. The total Ukrainian armed forces deployment around the world is 562 servicemen.[181]
Military units of other states participate in multinational military exercises with Ukrainian forces in Ukraine regularly, including U.S. military forces.[182]
Following independence, Ukraine declared itself a neutral state.[183] The country has had a limited military partnership with Russia, other CIS countries and a partnership with NATO since 1994. In the 2000s, the government was leaning towards NATO, and a deeper cooperation with the alliance was set by the NATO-Ukraine Action Plan signed in 2002. It was later agreed that the question of joining NATO should be answered by a national referendum at some point in the future.[178] Recently deposed President Viktor Yanukovych considered the current level of co-operation between Ukraine and NATO sufficient,[184] and was against Ukraine joining NATO.[185] During the 2008 Bucharest summit, NATO declared that Ukraine will become a member of NATO, whenever it wants and when it would correspond to the criteria for the accession.[184]
Economy

In Soviet times, the economy of Ukraine was the second largest in the Soviet Union, being an important industrial and agricultural component of the country's planned economy.[29] With the dissolution of the Soviet system, the country moved from a planned economy to a market economy. The transition process was difficult for the majority of the population which plunged into poverty.[186] Ukraine's economy contracted severely following the years after the Soviet dissolution. Day-to-day life for the average person living in Ukraine was a struggle. A significant number of citizens in rural Ukraine survived by growing their own food, often working two or more jobs and buying the basic necessities through the barter economy.[187]

In 1991, the government liberalised most prices to combat widespread product shortages, and was successful in overcoming the problem. At the same time, the government continued to subsidise state-run industries and agriculture by uncovered monetary emission. The loose monetary policies of the early 1990s pushed inflation to hyperinflationary levels. For the year 1993, Ukraine holds the world record for inflation in one calendar year.[188] Those living on fixed incomes suffered the most.[56] Prices stabilised only after the introduction of new currency, the hryvnia, in 1996.

The country was also slow in implementing structural reforms. Following independence, the government formed a legal framework for privatisation. However, widespread resistance to reforms within the government and from a significant part of the population soon stalled the reform efforts. A large number of state-owned enterprises were exempt from the privatisation process.
In the meantime, by 1999, the GDP had fallen to less than 40% of the 1991 level.[189] It recovered considerably in the following years, but as at 2014 had yet to reach the historical maximum.[190] In the early 2000s, the economy showed strong export-based growth of 5 to 10%, with industrial production growing more than 10% per year.[191] Ukraine was hit by the economic crisis of 2008 and in November 2008, the IMF approved a stand-by loan of $16.5 billion for the country.[192]
Ukraine's 2010 GDP (PPP), as calculated by the CIA, is ranked 38th in the world and estimated at $305.2 billion.[29] Its GDP per capita in 2010 according to the CIA was $6,700 (in PPP terms), ranked 107th in the world.[29] Nominal GDP (in U.S. dollars, calculated at market exchange rate) was $136 billion, ranked 53rd in the world.[29] By July 2008 the average nominal salary in Ukraine reached 1,930 hryvnias per month.[193] Despite remaining lower than in neighbouring central European countries, the salary income growth in 2008 stood at 36.8%[194] According to the UNDP in 2003 4.9% of the Ukrainian population lived under 2 US dollars a day[195] and 19.5% of the population lived below the national poverty line that same year.[196] According to the World Bank in 2010 only 0.1% of population lived under 2 US dollar a day.[197]

Ukraine produces nearly all types of transportation vehicles and spacecraft. Antonov airplanes and KrAZ trucks are exported to many countries. The majority of Ukrainian exports are marketed to the European Union and CIS.[198] Since independence, Ukraine has maintained its own space agency, the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU). Ukraine became an active participant in scientific space exploration and remote sensing missions. Between 1991 and 2007, Ukraine has launched six self made satellites and 101 launch vehicles, and continues to design spacecraft.[199][200][201]

The country imports most energy supplies, especially oil and natural gas and to a large extent depends on Russia as its energy supplier. While 25% of the natural gas in Ukraine comes from internal sources, about 35% comes from Russia and the remaining 40% from Central Asia through transit routes that Russia controls. At the same time, 85% of the Russian gas is delivered to Western Europe through Ukraine.[202]
The World Bank classifies Ukraine as a middle-income state.[203] Significant issues include underdeveloped infrastructure and transportation, corruption and bureaucracy. The public will to fight against corrupt officials and business elites culminated in a strong wave of public demonstrations against the Victor Yanukovych’s regime in November 2013.[204] In 2007 the Ukrainian stock market recorded the second highest growth in the world of 130 percent.[205] According to the CIA, in 2006 the market capitalization of the Ukrainian stock market was $111.8 billion.[29]
Growing sectors of the Ukrainian economy include the information technology (IT) market, which topped all other Central and Eastern European countries in 2007, growing some 40 percent.[206] Ukraine ranks fourth in the world in number of certified IT professionals after the United States, India and Russia.[207]
Corporations

Ukraine has a very large heavy-industry base and is one of the largest refiners of metallurgical products in Eastern Europe.[208] However, the country is also well known for its production of high-technological goods and transport products, such as Antonov aircraft and various private and commercial vehicles.[209] The country's largest and most competitive firms are components of the PFTS index, traded on the PFTS Ukraine Stock Exchange.
Well-known Ukrainian brands include Naftogaz Ukrainy, AvtoZAZ, PrivatBank, Roshen, Yuzhmash, Nemiroff, Motor Sich, Khortytsa, Kyivstar and Aerosvit.[210]
Ukraine is regarded as a developing economy with high potential for future success, though such a development is thought likely only with new all-encompassing economic and legal reforms.[211] Although Foreign Direct Investment in Ukraine has remained relatively strong ever since recession of the early 1990s, the country has had trouble maintaining stable economic growth. Issues relating to current corporate governance in Ukraine are primarily linked to the large scale monopolisation of traditional heavy industries by wealthy individuals such as Rinat Akhmetov, the enduring failure to broaden the nation's economic base and a lack of effective legal protection for investors and their products.[212] Despite all this, Ukraine's economy is still expected to grow by around 3.5% in 2010.[213]
Transport

Most of the Ukrainian road system has not been upgraded since the Soviet era, and is now outdated. In total, Ukrainian paved roads stretch for 164,732 kilometres (102,360 mi).[29] The network of major routes, marked with the letter 'M' for 'International' (Ukrainian: Міжнародний), extends nationwide and connects all the major cities of Ukraine as well as providing cross-border routes to the country's neighbours. Currently there are only two true motorway standard highways in Ukraine; a 175 kilometres (109 miles) stretch of motorway from Kharkiv to Dnipropetrovsk and a section of the M03 which extends 18 km (11 mi) from Kiev to Boryspil, where the city's international airport is located.[citation needed]

Rail transport in Ukraine plays the role of connecting all major urban areas, port facilities and industrial centres with neighbouring countries. The heaviest concentration of railway track is located in the Donbas region of Ukraine. Although the amount of freight transported by rail fell by 7.4% in 1995 in comparison with 1994, Ukraine is still one of the world's highest rail users.[214] The total amount of railroad track in Ukraine extends for 22,473 kilometres (13,964 mi), of which 9,250 kilometres (5,750 mi) is electrified.[29] Currently the state has a monopoly on the provision of passenger rail transport, and all trains, other than those with cooperation of other foreign companies on international routes, are operated by its company 'Ukrzaliznytsia'.
The aviation section in Ukraine is developing very quickly, having recently established a visa-free programme for EU nationals and citizens of a number of other Western nations,[215] the nation's aviation sector is handling a significantly increased number of travellers. Additionally, the granting of the Euro 2012 football tournament to Poland and Ukraine as joint hosts prompted the government to invest huge amounts of money into transport infrastructure, and in particular airports.[216]
Kiev Boryspil is the county's largest international airport; it has a total of three main passenger terminals and is the base for both of Ukraine's national airlines. Other large airports in the country include those in Kharkiv, Lviv and Donetsk (all of which have recently constructed, modern terminals and aviation facilities), whilst those in Dnipropetrovsk and Odessa have plans for terminal upgrades in the near future. Ukraine has a number of airlines, the largest of which are the nation's flag carriers, Aerosvit and UIA. Antonov Airlines, a subsidiary of the Antonov Aerospace Design Bureau is the only operator of the world's largest fixed wing aircraft, the An-225.
International maritime travel is mainly provided through the Port of Odessa, from where ferries sail regularly to Istanbul, Varna and Haifa. The largest ferry company presently operating these routes is Ukrferry.[217]
Energy
In 2014, Ukraine was ranked number 19 on the Emerging Market Energy Security Growth Prosperity Index, published by the think tank Bisignis Institute, which ranks emerging market countries using government corruption, GDP growth and oil reserve information.[218]
Fuel resources
Ukraine produces and processes its own natural gas and petroleum. However, the majority of these commodities are imported (and transited), mostly from Russia. Natural gas is heavily utilised not only in energy production but also by steel and chemical industries of the country, as well as by the district heating sector. In 2012, Shell started exploration drilling for shale gas in Ukraine—a project aimed at the nation's total gas supply independence.
Ukraine has sufficient coal reserves and increases its use in electricity generation.
Power generation
Ukraine has been a net energy exporting country, for example in 2011, 3.3% of electricity produced were exported,[219] but also one of Europe's largest energy consumers.[220] As of 2011, 47.6% of total electricity generation was from nuclear power[219] The largest nuclear power plant in Europe, the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant, is located in Ukraine. Most of the nuclear fuel has been coming from Russia. In 2008 Westinghouse Electric Company won a five-year contract selling nuclear fuel to three Ukrainian reactors starting in 2011.[221] Following Euromaidan then President Viktor Yanukovich introduced a ban on Rosatom nuclear fuel shipments to Europe via Ukraine, which was in effect from 28 January until 6 March 2014.[222] After the Russian annexation of Crimea in April 2014, the National Nuclear Energy Generating Company of Ukraine Energoatom and Westinghouse extended the contract for fuel deliveries through 2020.[223]
Coal- and gas-fired thermal power stations and hydroelectricity are the second and third largest kinds of power generation in the country.[citation needed]
Renewable energy use
The share of renewables within the total energy mix is still very small, but is growing fast. Total installed capacity of renewable energy installations more than doubled in 2011 and as of 2012 stands at 397 MW.[224] In 2011 several large solar power stations were opened in Ukraine, among them Europe's largest solar park in Perovo, (Crimea).[225] Ukrainian State Agency for Energy Efficiency and Conservation forecasts that combined installed capacity of wind and solar power plants in Ukraine could increase by another 600 MW in 2012.[226] According to Macquarie Research, by 2016 Ukraine will construct and commission new solar power stations with a total capacity of 1.8 GW, almost equivalent to the capacity of two nuclear reactors.[227]
The Economic Bank for Reconstruction and Development estimates that Ukraine has great renewable energy potential: the technical potential for wind energy is estimated at 40 TWh/year, small hydropower stations at 8.3 TWh/year, biomass at 120 TWh/year, and solar energy at 50 TWh/year.[228] In 2011, Ukraine's Energy Ministry predicted that the installed capacity of generation from alternative and renewable energy sources would increase to 9% (about 6 GW) of the total electricity production in the country.[229]
Internet
Ukraine has a large and steadily growing Internet sector, mostly uninfluenced by the global financial crisis; rapid growth is forecast for at least two more years.[230] Internet penetration – 45% and 19.9 million users in December 2012.[231] Ukraine ranks 8th among the world's TOP-10 countries with the fastest Internet access speed.[232]
Tourism

Ukraine occupies 8th place in Europe by the number of tourists visiting, according to the World Tourism Organisation rankings,[233] due to its numerous tourist attractions: mountain ranges suitable for skiing, hiking and fishing: the Black Sea coastline as a popular summer destination; nature reserves of different ecosytems; churches, castle ruins and other architectural and park landmarks; various outdoor activity points. Kiev, Lviv, Odessa, Kamyanets-Podilskyi and Yalta are Ukraine's principal tourist centers each offering many historical landmarks as well as formidable hospitality infrastructure.
The Seven Wonders of Ukraine and Seven Natural Wonders of Ukraine are the selection of the most important landmarks of Ukraine, chosen by the general public through an internet-based vote.
Demographics

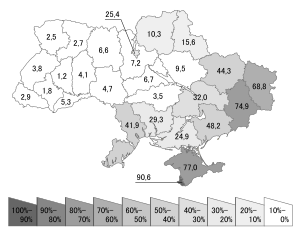
According to the Ukrainian Census of 2001, Ukrainians make up 77.8% of the population. Other significant groups have identified themselves as belonging to the nationality of Russians (17.3%), Belarusians (0.6%), Moldovans (0.5%), Crimean Tatars (0.5%), Bulgarians (0.4%), Hungarians (0.3%), Romanians (0.3%), Poles (0.3%), Jews (0.2%), Armenians (0.2%), Greeks (0.2%) and Tatars (0.2%).[2] The industrial regions in the east and southeast are the most heavily populated, and about 67.2% of the population lives in urban areas.[234][235]
Population decline
Ukraine has been losing population since the 1990s because of its high death rate and a low birth rate. The population is shrinking by over 150,000 a year. The birth rate has recovered in recent years from a low level around 2000, and is now comparable to the European average. It would need to increase by another 50% or so to stabilize the population and offset the high mortality rate.
In 2007, the country's population was declining at the fourth fastest rate in the world.[236]
Life expectancy is falling. The nation suffers a high mortality rate from environmental pollution, poor diets, widespread smoking, extensive alcoholism and deteriorating medical care.[237][238]
In the years 2008 to 2010, more than 1.5 million children were born in Ukraine, compared to fewer than 1.2 million during 1999–2001 during the worst of the demographic crisis. In 2008 Ukraine posted record-breaking birth rates since its 1991 independence. Infant mortality rates have also dropped from 10.4 deaths to 8.3 per 1,000 children under one year of age. This is lower than in 153 countries of the world.[239]
Fertility and natalist policies

The current birth rate in Ukraine, as of 2010, is 10.8 births/1,000 population, and the death rate is 15.2 deaths/1,000 population (see demographic tables)
The phenomenon of lowest-low fertility, defined as total fertility below 1.3, is emerging throughout Europe and is attributed by many to postponement of the initiation of childbearing. Ukraine, where total fertility (a very low 1.1 in 2001), was one of the world's lowest, shows that there is more than one pathway to lowest-low fertility. Although Ukraine has undergone immense political and economic transformations during 1991–2004, it has maintained a young age at first birth and nearly universal childbearing. Analysis of official national statistics and the Ukrainian Reproductive Health Survey show that fertility declined to very low levels without a transition to a later pattern of childbearing. Findings from focus group interviews suggest explanations of the early fertility pattern. These findings include the persistence of traditional norms for childbearing and the roles of men and women, concerns about medical complications and infertility at a later age, and the link between early fertility and early marriage.[242]
To help mitigate the declining population, the government continues to increase child support payments. Thus it provides one-time payments of 12,250 Hryvnias for the first child, 25,000 Hryvnias for the second and 50,000 Hryvnias for the third and fourth, along with monthly payments of 154 Hryvnias per child.[194][243] The demographic trend is showing signs of improvement, as the birth rate has been steadily growing since 2001.[244] Net population growth over the first nine months of 2007 was registered in five provinces of the country (out of 24), and population shrinkage was showing signs of stabilising nationwide. In 2007 the highest birth rates were in the western oblasts.[245] In 2008, Ukraine emerged from lowest-low fertility, and the upward trend has continued since, except for a slight dip in 2010 due to the economic crisis of 2009 (see demographic tables).
Urbanisation
In total, Ukraine has 457 cities, 176 of them are labelled oblast-class, 279 smaller [raion] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)-class cities, and two special legal status cities. These are followed by 886 urban-type settlements and 28,552 villages.[175] Template:Largest cities of Ukraine
Language
According to the constitution, the state language of Ukraine is Ukrainian.[246] Russian is widely spoken, especially in eastern and southern Ukraine.[246] According to the 2001 census, 67.5 percent of the population declared Ukrainian as their native language and 29.6 percent declared Russian.[247] Most native Ukrainian speakers know Russian as a second language.[246] Russian was the de facto official language of the Soviet Union but both Russian and Ukrainian were official languages in the Soviet Union[248] and in the schools of the Ukrainian SSR learning Ukrainian was mandatory.[246] Effective in August 2012, a new law on regional languages entitles any local language spoken by at least a 10% minority be declared official within that area.[249] Russian was within weeks declared as a regional language in several southern and eastern oblasts (provinces) and cities.[250] Russian can now be used in these cities'/oblasts' administrative office work and documents.[251][252] On 23 February 2014, following the 2014 Ukrainian revolution, the Ukrainian Parliament voted to repeal the law on regional languages, making Ukrainian the sole state language at all levels; however, this vote was vetoed by acting President Turchynov on March 2.[253][254]
Ukrainian is mainly spoken in western and central Ukraine.[246] In western Ukraine, Ukrainian is also the dominant language in cities (such as Lviv). In central Ukraine, Ukrainian and Russian are both equally used in cities, with Russian being more common in Kiev,[f] while Ukrainian is the dominant language in rural communities. In eastern and southern Ukraine, Russian is primarily used in cities, and Ukrainian is used in rural areas. These details result in a significant difference across different survey results, as even a small restating of a question switches responses of a significant group of people.[f]
For a large part of the Soviet era, the number of Ukrainian speakers declined from generation to generation, and by the mid-1980s, the usage of the Ukrainian language in public life had decreased significantly.[255] Following independence, the government of Ukraine began restoring the image and usage of Ukrainian language through a policy of Ukrainisation.[256] Today, all foreign films and TV programs, including Russian ones, are subtitled or dubbed in Ukrainian.[failed verification]
According to the Constitution of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea, Ukrainian is the only state language of the republic. However, the republic's constitution specifically recognises Russian as the language of the majority of its population and guarantees its usage 'in all spheres of public life'. Similarly, the Crimean Tatar language (the language of 12 percent of population of Crimea)[257] is guaranteed a special state protection as well as the 'languages of other ethnicities'. Russian speakers constitute an overwhelming majority of the Crimean population (77 percent), with Crimean Tatar speakers 11.4 percent and Ukrainian speakers comprising just 10.1 percent.[258] But in everyday life the majority of Crimean Tatars and Ukrainians in Crimea use Russian.[259]
Religion


Estimates compiled by the independent Razumkov Centre in a nationwide survey in 2006 found that 75.2 percent of the respondents believe in God and 22 percent said they did not believe in God. 37.4 percent said that they attended church on regular basis.[261]

Among Ukrainians who are affiliated with an organised religion, the most common religion in Ukraine is Orthodox Christianity, currently split between three Church bodies: the Ukrainian Orthodox Church – Kiev Patriarchate, the Ukrainian Orthodox Church autonomous church body under the Patriarch of Moscow, and the Ukrainian Autocephalous Orthodox Church.[262]
A distant second by the number of the followers is the Eastern Rite Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church, which practices a similar liturgical and spiritual tradition as Eastern Orthodoxy, but is in communion with the Holy See of the Roman Catholic Church and recognises the primacy of the Pope as head of the Church.[263]
Additionally, there are 863 Latin Rite Catholic communities, and 474 clergy members serving some one million Latin Rite Catholics in Ukraine.[262] The group forms some 2.19 percent of the population and consists mainly of ethnic Poles and Hungarians, who live predominantly in the western regions of the country.
Protestant Christians form around 2.19 percent of the population. Protestant numbers have grown greatly since Ukrainian independence. The Evangelical Baptist Union of Ukraine is the largest group, with more than 150,000 members and about 3,000 clergy. The second largest Protestant church is the Ukrainian Church of Evangelical faith (Pentecostals) with 110,000 members and over 1,500 local churches and over 2,000 clergy, but there also exist other Pentecostal groups and unions and together all Pentecostals are over 300,000, with over 3,000 local churches. Also there are many Pentecostal high education schools such as the Lviv Theological Seminary and the Kiev Bible Institute. Other groups include Calvinists, Jehovah's Witnesses, Lutherans, Methodists and Seventh-day Adventists. The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormon) are also present.[262]
There are an estimated 500,000 Muslims in Ukraine and about 300,000 of them are Crimean Tatars.[264] There are 487 registered Muslim communities, 368 of them on Crimea. In addition, some 50,000 Muslims live in Kiev; mostly foreign-born.[265]
The Jewish population is a tiny fraction of what it was before World War II. (In Tsarist times, Ukraine had been part of the Pale of Settlement, to which Jews were largely restricted in the Russian Empire.) The largest Jewish communities in 1926 were in Odessa, 154,000 or 36.5% of the total population; and Kiev, 140,500 or 27.3%.[266] The 2001 census indicated that there are 103,600 Jews in Ukraine, although community leaders claimed that the population could be as large as 300,000. There are no statistics on what share of the Ukrainian Jews are observant, but Orthodox Judaism has the strongest presence in Ukraine. Smaller Reform and Conservative Jewish (Masorti) communities exist as well.[262]
One 2006 survey put the number of non-religious in Ukraine at approximately 62.5% of the population.[261]
Famines and migration
The famines of the 1930s, followed by the devastation of World War II, comprised a demographic disaster. Life expectancy at birth fell to a level as low as ten years for females and seven for males in 1933 and plateaued around 25 for females and 15 for males in the period 1941–44.[267] According to The Oxford companion to World War II, "Over 7 million inhabitants of Ukraine, more than one-sixth of the pre-war population, were killed during the Second World War."[268]
Significant migration took place in the first years of Ukrainian independence. More than one million people moved into Ukraine in 1991–92, mostly from the other former Soviet republics. In total, between 1991 and 2004, 2.2 million immigrated to Ukraine (among them, 2 million came from the other former Soviet Union states), and 2.5 million emigrated from Ukraine (among them, 1.9 million moved to other former Soviet Union republics).[269] Currently, immigrants constitute an estimated 14.7% of the total population, or 6.9 million people; this is the fourth largest figure in the world.[270] In 2006, there were an estimated 1.2 million Canadians of Ukrainian ancestry,[271] giving Canada the world's third-largest Ukrainian population behind Ukraine itself and Russia. There are also large Ukrainian immigrant communities in the United States, Australia, Brazil and Argentina.
Health

The Ukrainian Red Cross Society was established in April, 1918 in Kyiv as an independent humanitarian society of the Ukrainian People's Republic. Its immediate tasks were to help refugees and prisoners of war, care of handicapped people, orphaned children, fighting famine and epidemics, support and organize sick quarters, hospitals and public canteens. At present, society involves more than 6.3 million of supporters and activists. Its Visiting Nurses Service has 3200 qualified nurses. The organization takes part in more than 40 humanitarian programmes all over Ukraine, which are mostly funded by public donation and corporate partnerships. By its own estimations, the Society annually provides services to more than 105 000 of lonely elderly people, about 23 000 of people disabled during the Second World War and handicapped workers, more than 25 000 of war veterans, and more than 8 000 of adults handicapped since childhood. The assistance for orphaned and disabled children is also rendered.
Ukraine's healthcare system is state subsidised and freely available to all Ukrainian citizens and registered residents. However, it is not compulsory to be treated in a state-run hospital as a number of private medical complexes do exist nationwide.[272] The public sector employs most healthcare professionals, with those working for private medical centres typically also retaining their state employment as they are mandated to provide care at public health facilities on a regular basis.
All the country's medical service providers and hospitals are subordinate to the Ministry of Health, which provides oversight and scrutiny of general medical practice as well as being responsible for the day-to-day administration of the healthcare system. Despite this standards of hygiene and patient-care have fallen.[273]

Hospitals in Ukraine are organised along the same lines as most European nations, according to the regional administrative structure; resultantly most towns have their own hospital (Міська Лікарня) and many also have district hospitals (Районна Лікарня). Larger and more specialised medical complexes tend only to be found in major cities, with some even more specialised units located only in the capital, Kiev. However, all oblasts have their own network of general hospitals which are able to deal with almost all medical problems and are typically equipped with major trauma centres; such hospitals are called 'regional hospitals' (Обласна Лікарня).
Ukraine currently faces a number of major public health issues, and is considered to be in a demographic crisis due to its high death rate and low birth rate (the current Ukrainian birth rate is 11 births/1,000 population, and the death rate is 16.3 deaths/1,000 population). A factor contributing to the high death rate is a high mortality rate among working-age males from preventable causes such as alcohol poisoning and smoking.[238] In 2008, the country's population was one of the fastest declining in the world at −5% growth.[236][274] The UN warned that Ukraine's population could fall by as much as 10 million by 2050 if trends did not improve.[275] In addition, obesity, systemic high blood pressure and the HIV endemic are all major challenges facing the Ukrainian healthcare system.
As of March 2009 the Ukrainian government to reforming the health care system, by the creation of a national network of family doctors and improvements in the medical emergency services.[276] former Prime Minister Yulia Tymoshenko put forward (in November 2009) an idea to start introducing a public healthcare system based on health insurance in the spring of 2010.[277]
Education

According to the Ukrainian constitution, access to free education is granted to all citizens. Complete general secondary education is compulsory in the state schools which constitute the overwhelming majority. Free higher education in state and communal educational establishments is provided on a competitive basis.[278] There is also a small number of accredited private secondary and higher education institutions.
Because of the Soviet Union's emphasis on total access of education for all citizens, which continues today, the literacy rate is an estimated 99.4%.[29] Since 2005, an eleven-year school programme has been replaced with a twelve-year one: primary education takes four years to complete (starting at age six), middle education (secondary) takes five years to complete; upper secondary then takes three years.[279] In the 12th grade, students take Government tests, which are also referred to as school-leaving exams. These tests are later used for university admissions.
The first higher education institutions (HEIs) emerged in Ukraine during the late 16th and early 17th centuries. The first Ukrainian higher education institution was the Ostrozka School, or Ostrozkiy Greek-Slavic-Latin Collegium, similar to Western European higher education institutions of the time. Established in 1576 in the town of Ostrog, the Collegium was the first higher education institution in the Eastern Slavic territories. The oldest university was the Kyiv Mohyla Academy, first established in 1632 and in 1694 officially recognised by the government of Imperial Russia as a higher education institution. Among the oldest is also the Lviv University, founded in 1661. More higher education institutions were set up in the 19th century, beginning with universities in Kharkiv (1805), Kiev (1834), Odessa (1865) and Chernivtsi (1875) and a number of professional higher education institutions, e.g.: Nizhyn Historical and Philological Institute (originally established as the Gymnasium of Higher Sciences in 1805), a Veterinary Institute (1873) and a Technological Institute (1885) in Kharkiv, a Polytechnic Institute in Kiev (1898) and a Higher Mining School (1899) in Katerynoslav. Rapid growth followed in the Soviet period. By 1988 a number of higher education institutions increased to 146 with over 850,000 students.[280] Most HEIs established after 1990 are those owned by private organisations.

The Ukrainian higher education system comprises higher educational establishments, scientific and methodological facilities under national, municipal and self-governing bodies in charge of education.[281] The organisation of higher education in Ukraine is built up in accordance with the structure of education of the world's higher developed countries, as is defined by UNESCO and the UN.[282] Ukraine has more than 800 higher education institutions and in 2010 the number of graduates reached 654,700 people.[283]
Nowadays higher education is either state funded or private. Students that study at state expense receive a standard scholarship if their average marks at the end-of-term exams and differentiated test is at least 4 (see the 5-point grade system below); this rule may be different in some universities. In the case of all grades being the highest (5), the scholarship is increased by 25%. For most students the level of government subsidy is not sufficient to cover their basic living expenses. Most universities provide subsidised housing for out-of-city students. Also, it is common for libraries to supply required books for all registered students. There are two degrees conferred by Ukrainian universities: the Bachelor's Degree (4 years) and the Master's Degree (5–6th year). These degrees are introduced in accordance with the Bologna process, in which Ukraine is taking part. Historically, Specialist's Degree (usually 5 years) is still also granted; it was the only degree awarded by universities in the Soviet times.
Regional differences

Ukrainian is the dominant language in Western Ukraine and in Central Ukraine, while Russian is the dominant language in the cities of Eastern Ukraine and Southern Ukraine. In the Ukrainian SSR schools, learning Russian was mandatory; currently in modern Ukraine, schools with Ukrainian as the language of instruction offer classes in Russian and in the other minority languages.[246][284][285][286]
The average view(s) of the inhabitants of Eastern Ukraine and Southern Ukraine on the Russian language, on Soviet Union and Ukrainian nationalism tends to be the exact opposite of the views of Western Ukrainians; while the views on these subjects of the people of Central Ukraine tends not to be so extreme as in Western Ukraine, Eastern Ukraine and Southern Ukraine.[285][287][288][289] There are not only clear regional differences on questions of identity but historical cleavages remain evident at the level of individual social identification. Attitudes toward the most important political issue, relations with Russia, differed strongly between Lviv, identifying more with Ukrainian nationalism and the Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church and Donetsk, predominantly Russian orientated and favourable to the Soviet era, while in central and southern Ukraine, as well as Kiev, such divisions were less important and there was less antipathy toward people from other regions (a poll by the Research & Branding Group held March 2010 showed that the attitude of the citizens of Donetsk to the citizens of Lviv was 79% positive and that the attitude of the citizens of Lviv to the citizens of Donetsk was 88% positive[290]). However, all were united by an overarching Ukrainian identity based on shared economic difficulties, showing that other attitudes are determined more by culture and politics than by demographic differences.[290][291] Surveys of regional identities in Ukraine have shown that the feeling of belonging to a "Soviet identity" is strongest in the Donbas (about 40%) and the Crimea (about 30%).[292]
During elections voters of Western and Central Ukrainian oblasts (provinces) vote mostly for parties (Our Ukraine, Batkivshchyna)[293][294] and presidential candidates (Viktor Yuschenko, Yulia Tymoshenko) with a pro-Western and state reform platform, while voters in Southern and Eastern oblasts vote for parties (CPU, Party of Regions) and presidential candidates (Viktor Yanukovych) with a pro-Russian and status quo platform.[295][296][297][298] However, this geographical division is decreasing.[299][300][301]
Culture

Ukrainian customs are heavily influenced by Christianity, the dominant religion in the country.[262] Gender roles also tend to be more traditional, and grandparents play a greater role in bringing up children, than in the West.[302] The culture of Ukraine has also been influenced by its eastern and western neighbours, reflected in its architecture, music and art.

The Communist era had quite a strong effect on the art and writing of Ukraine.[303] In 1932, Stalin made socialist realism state policy in the Soviet Union when he promulgated the decree "On the Reconstruction of Literary and Art Organisations". This greatly stifled creativity. During the 1980s glasnost (openness) was introduced and Soviet artists and writers again became free to express themselves as they wanted.[304]
The tradition of the Easter egg, known as pysanky, has long roots in Ukraine. These eggs were drawn on with wax to create a pattern; then, the dye was applied to give the eggs their pleasant colours, the dye did not affect the previously wax-coated parts of the egg. After the entire egg was dyed, the wax was removed leaving only the colourful pattern. This tradition is thousands of years old, and precedes the arrival of Christianity to Ukraine.[305] In the city of Kolomyia near the foothills of the Carpathian Mountains in 2000 was built the museum of Pysanka which won a nomination as the monument of modern Ukraine in 2007, part of the Seven Wonders of Ukraine action.
Literature
The history of Ukrainian literature dates back to the 11th century, following the Christianisation of the Kievan Rus'.[306] The writings of the time were mainly liturgical and were written in Old Church Slavonic. Historical accounts of the time were referred to as chronicles, the most significant of which was the Primary Chronicle.[307][g] Literary activity faced a sudden decline during the Mongol invasion of Rus'.[306]
Ukrainian literature again began to develop in the 14th century, and was advanced significantly in the 16th century with the introduction of print and with the beginning of the Cossack era, under both Russian and Polish dominance.[306] The Cossacks established an independent society and popularized a new kind of epic poems, which marked a high point of Ukrainian oral literature.[307] These advances were then set back in the 17th and early 18th centuries, when publishing in the Ukrainian language was outlawed and prohibited. Nonetheless, by the late 18th century modern literary Ukrainian finally emerged.[306]
| Ivan Kotlyarevsky (1769–1838) |
Taras Shevchenko (1814–1861) |
Ivan Franko (1856–1916) |
Mykhailo Kotsiubynsky (1864–1913) |
Lesya Ukrainka (1871–1913) |
|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|
The 19th century initiated a vernacular period in Ukraine, led by Ivan Kotliarevsky's work [Eneyida] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help), the first publication written in modern Ukrainian. By the 1830s, Ukrainian romanticism began to develop, and the nation's most renowned cultural figure, romanticist poet-painter Taras Shevchenko emerged. Where Ivan Kotliarevsky is considered to be the father of literature in the Ukrainian vernacular; Shevchenko is the father of a national revival.[308]
Then, in 1863, use of the Ukrainian language in print was effectively prohibited by the Russian Empire.[49] This severely curtailed literary activity in the area, and Ukrainian writers were forced to either publish their works in Russian or release them in Austrian controlled Galicia. The ban was never officially lifted, but it became obsolete after the revolution and the Bolsheviks' coming to power.[307]
Ukrainian literature continued to flourish in the early Soviet years, when nearly all literary trends were approved. These policies faced a steep decline in the 1930s, when Stalin implemented his policy of socialist realism. The doctrine did not necessarily repress the Ukrainian language, but it required writers to follow a certain style in their works. Literary activities continued to be somewhat limited under the Communist Party, and it was not until Ukraine gained its independence in 1991 when writers were free to express themselves as they wished.[306]
Architecture





Ukrainian architecture is a term that describes the motifs and styles that are found in structures built in modern Ukraine, and by Ukrainians worldwide. These include initial roots which were established in the Eastern Slavic state of Kievan Rus'. After the 12th century, the distinct architectural history continued in the principalities of Galicia-Volhynia. During the epoch of the Zaporozhian Cossacks, a new style unique to Ukraine was developed under the western influences of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. After the union with the Tsardom of Russia, architecture in Ukraine began to develop in different directions, with many structures in the larger eastern, Russian-ruled area built in the styles of Russian architecture of that period, whilst the western Galicia was developed under Austro-Hungarian architectural influences, in both cases producing fine examples. Ukrainian national motifs would finally be used during the period of the Soviet Union and in modern independent Ukraine.
The great churches of the Rus', built after the adoption of Christianity in 988, were the first examples of monumental architecture in the East Slavic lands. The architectural style of the Kievan state, which quickly established itself, was strongly influenced by the Byzantine. Early Eastern Orthodox churches were mainly made of wood, with the simplest form of church becoming known as a cell church. Major cathedrals often featured scores of small domes, which led some art historians to take this as an indication of the appearance of pre-Christian pagan Slavic temples.
Several examples of these churches survive to this day; however, during the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries, many were externally rebuilt in the Ukrainian Baroque style (see below). Examples include the grand St. Sophia of Kiev – the year 1017 is the earliest record of foundation laid, Church of the Saviour at Berestove – built from 1113 to 1125 and St. Cyril's Church, circa 12th-century. All can still be found in the Ukrainian capital. Several buildings were reconstructed during the late-19th century, including the Assumption Cathedral in Volodymyr-Volynskyi, built in 1160 and reconstructed in 1896–1900, the Paraskevi church in Chernihiv, built in 1201 with reconstruction done in the late 1940s, and the Golden gates in Kiev, built in 1037 and reconstructed in 1982. The latter's reconstruction was criticised by some art and architecture historians as a revivalist fantasy. Unfortunately little secular or vernacular architecture of Kievan Rus' has survived.
As Ukraine became increasingly integrated into the Russian Empire, Russian architects had the opportunity to realise their projects in the picturesque landscape that many Ukrainian cities and regions offered. St. Andrew's Church of Kiev (1747–1754), built by Bartolomeo Rastrelli, is a notable example of Baroque architecture, and its location on top of the Kievan mountain made it a recognisable monument of the city. An equally notable contribution of Rasetrelli was the Mariyinsky Palace, which was built to be a summer residence to Russian Empress Elizabeth. During the reign of the last Hetman of Ukraine, Kirill Razumovsky, many of the Cossack Hetmanate's towns such as Hlukhiv, Baturyn and Koselets had grandiose projects built by Andrey Kvasov. Russia, winning successive wars over the Ottoman Empire and its vassal Crimean Khanate, eventually annexed the whole south of Ukraine and Crimea. Renamed New Russia, these lands were to be colonised, and new cities such as the Nikolayev, Odessa, Kherson and Sevastopol were founded. These would contain notable examples of Imperial Russian architecture.
In 1934, the capital of Soviet Ukraine moved from Kharkiv to Kiev. During the preceding years, the city was seen as only a regional centre, and hence received little attention. All of that was to change, but at a great price. By this point, the first examples of Stalinist architecture were already showing, and, in light of the official policy, a new city was to be built on top of the old one. This meant that much-admired examples such as the St. Michael's Golden-Domed Monastery were destroyed. Even the St. Sophia Cathedral was under threat. Also, the Second World War contributed to the wreckage. After the war, a new project for the reconstruction of central Kiev was unveiled. This transformed the Khreshchatyk avenue into one of the most notable examples of Stalinism in Architecture. However, by 1955, the new politics of architecture once again promptly stopped the project from fully being realised.
The task for modern Ukrainian architecture is diverse application of modern aesthetics, the search for an architect's own artistic style and inclusion of the existing historico-cultural environment. An example of modern Ukrainian architecture is the reconstruction and renewal of the Maidan Nezalezhnosti in central Kiev, despite the limit set by narrow space within the plaza, the engineers were able to blend together the uneven landscape and also use underground space to set a new shopping centre.
A major project, which may take up most of the 21st century, is the construction of the Kiev City-Centre on the Rybalskyi Peninsula, which, when finished, will include a dense skyscraper park amid the picturesque landscape of the Dnieper.[309]
Music

Music is a major part of Ukrainian culture, with a long history and many influences. From traditional folk music, to classical and modern rock, Ukraine has produced a long list of internationally recognised musical talent including Tchaikovsky[citation needed], Okean Elzy and Ruslana. Elements from traditional Ukrainian folk music made their way into Western music and even into modern jazz.
Ukraine found itself at the crossroads of Asia and Europe and this is reflected within the music in a perplexing mix of exotic melismatic singing with chordal harmony which does not always easily fit the rules of traditional Western European harmony. The most striking general characteristic of authentic ethnic Ukrainian folk music is the wide use of minor modes or keys which incorporate augmented 2nd intervals. This is an indication that the major-minor system developed in Western European music did not become as entrenched or as sophisticated in Ukraine. However, during the Baroque period, music was an important discipline for those that had received a higher education in Ukraine. It had a place of considerable importance in the curriculum of the Kyiv-Mohyla Academy. Much of the nobility was well versed in music with many Ukrainian Cossack leaders such as (Mazepa, Paliy, Holovatyj, Sirko) being accomplished players of the kobza, bandura or torban.
In the course of the 18th century in the Russian Empire court musicians were typically trained at the music academy in Hlukhiv, and largely came from Ukraine. Notable performers of the era include Tymofiy Bilohradsky who later studied lute under Sylvius Leopold Weiss in Dresden, his daughter Yelyzaveta who was a famous operatic soprano, and Oleksiy Rozumovsky, a court bandurist and the morganatic husband of Empress Elizabeth. The first dedicated musical academy was set up in Hlukhiv, Ukraine in 1738 and students were taught to sing, play violin and bandura from manuscripts. As a result many of the earliest composers and performers within the Russian empire were ethnically Ukrainian, having been born or educated in Hlukhiv, or had been closely associated with this music school. See: Dmytro Bortniansky, Maksym Berezovsky and Artemiy Vedel.

Ukrainian classical music falls into three distinct categories defined by whether the composer was of Ukrainian ethnicity living in Ukraine, a composer of non-Ukrainian ethnicity who was born or at some time was a citizen of Ukraine, or an ethnic Ukrainian living outside of Ukraine within the Ukrainian diaspora. The music of these three groups differs considerably, as do the audiences for whom they cater.

The first category is closely tied with the Ukrainian national school of music spearheaded by Mykola Lysenko. It includes such composers as Kyrylo Stetsenko, Mykola Leontovych, Levko Revutsky, Borys Lyatoshynsky and Mykola Vilinsky. Most of their music contains Ukrainian folk figures and are composed to Ukrainian texts. On the other hand, the second category is of particular importance and international visibility, because of the large percentage of ethnic minorities in urban Ukraine. This category includes such composers as Franz Xavier Mozart, Isaak Dunayevsky, Rheinhold Gliere, Yuliy Meitus and Sergei Prokofiev, performers Volodymyr Horovyts, David Oistrakh, Sviatoslav Richter and Isaac Stern. The music of these composers rarely contains Ukrainian folk motives and more often is written to the texts of Russian or Polish poets. Whilst the third category includes a number of prominent individuals who are often not part of the mainstream Ukrainian culture but who have made a significant impact on music in Ukraine, while living outside of its borders. These include historic individuals such as: Bortniansky, Berezovsky, Vedel and Tuptalo and Titov. It also contains "Soviet" composers such as Mykola Roslavets and Isaak Dunayevsky who were born in Ukraine but who moved to other cultural centres within the Soviet Union. In North America there is Mykola Fomenko, Yuriy Oliynyk, Zinoviy Lavryshyn and Wasyl Sydorenko.
Since the mid-1960s, Western-influenced pop music, in its various forms, that has been growing in popularity in Ukraine. One of the most important and truly original musicians to come out of Ukraine in recent years is the ultra avant-garde folk singer and harmonium player Mariana Sadovska. Ukrainian pop and folk music arose with the international popularity of groups like Vopli Vidoplyasova, Viy and Okean Elzy.
Cinema
Ukraine has had an influence on the history of the cinema. Ukrainian directors Alexander Dovzhenko, often cited as one of the most important early Soviet filmmakers, as well as being a pioneer of Soviet montage theory, Dovzhenko Film Studios, and Sergei Parajanov, Armenian film director and artist who made significant contributions to Ukrainian, Armenian and Georgian cinema. He invented his own cinematic style, Ukrainian poetic cinema, which was totally out of step with the guiding principles of socialist realism.

Other important directors including Kira Muratova, Larisa Shepitko, Sergei Bondarchuk, Leonid Bykov, Yuri Ilyenko, Leonid Osyka, Ihor Podolchak with his Delirium and Maryna Vroda. Many Ukrainian actors have achieved international fame and critical success, including: Vera Kholodnaya, Bohdan Stupka, Milla Jovovich, Olga Kurylenko, Renata Litvinova, Mila Kunis.
Despite a history of important and successful productions, the industry has often been characterised by a debate about its identity and the level of Russian and European influence. Ukrainian producers are active in international co-productions and Ukrainian actors, directors and crew feature regularly in Russian (Soviet in past) films. Also successful films have been based on Ukrainian people, stories or events, including Battleship Potemkin, Man with a Movie Camera, Everything Is Illuminated. The highest-grossing film ever is Avatar with £5.2 million in 2009.
Ukrainian State Film Agency owns National Oleksandr Dovzhenko Film Centre, film copying laboratory and archive, takes part in hosting of the Odessa International Film Festival, and Molodist is the only one FIAPF accredited International Film Festival held in Ukraine; competition program is devoted to student, first short and first full feature films from all over the world. Held annually in October.
Media
Ukrayinska Pravda[310] founded by Georgiy Gongadze in April, 2000 (the day of the Ukrainian constitutional referendum). Published mainly in Ukrainian with selected articles published in or translated to Russian and English, the newspaper is tailored towards the general readership with some particular emphasis placed on the hot issues of the politics of Ukraine. The Ukrainian government has at times reportedly exerted pressure on the publication to restrict access to freedom of information. Freedom of the press in Ukraine is considered to be among the freest of the post-Soviet states other than the Baltic states. Freedom House classifies the Internet in Ukraine as "free" and the press as "partly free". Press freedom has significantly improved since the Orange Revolution of 2004. However, in 2010 Freedom House perceived "negative trends in Ukraine".
Kyiv dominates the media sector in Ukraine: the Kyiv Post is Ukraine's leading English-language newspaper. National newspapers Den, Mirror Weekly, tabloids, such as The Ukrainian Week or Focus (Russian), and television and radio are largely based there, although Lviv is also a significant national media centre. The National News Agency of Ukraine, Ukrinform was founded here in 1918. The Ukraine publishing sector, including books, directories and databases, journals, magazines and business media, newspapers and news agencies, has a combined turnover. Sanoma publishing Ukrainian editions of such magazines as Esquire, Harpers Bazaar and National Geographic Magazine. BBC Ukrainian started its broadcasts in 1992.
Ukrainians listen to radio programming, such as Radio Ukraine or Radio Liberty, largely commercial, on average just over two-and-a-half hours a day.
The first official broadcast took place in Kiev on 1 February 1939, television in Ukraine was introduced in 1951. The most watched television channels in Ukraine are commercial Inter and 1+1. Network covers 99.7 percent of Ukraine's territory (according the channel's own information). Inter is among the top-rated networks in Ukraine, competing with such as 1+1 media, StarLightMedia Group, which operates 6 TV channels, 5 Kanal and TVi. Ukraine's First National publicly television corporation works closely and provides broadcasting for Euronews and Hromadske.TV, an Internet television station in Ukraine that started to operate on 22 November 2013. Aside from web portals and search engines, the most popular websites are Vk, YouTube, Wikipedia, Facebook, Livejournal, EX.UA and Odnoklassniki.[310]
Weaving and embroidery

Artisan textile arts play an important role in Ukrainian culture,[311] especially in Ukrainian wedding traditions. Ukrainian embroidery, weaving and lace-making are used in traditional folk dress and in traditional celebrations. Ukrainian embroidery varies depending on the region of origin[312] and the designs have a long history of motifs, compositions, choice of colours and types of stitches.[313] Use of color is very important and has roots in Ukrainian folklore. Embroidery motifs found in different parts of Ukraine are preserved in the Rushnyk Museum in Pereiaslav-Khmelnytskyi.
National dress is woven and highly decorated. Weaving with handmade looms is still practised in the village of Krupove, situated in Rivne Oblast. The village is the birthplace of two famous personalities in the scene of national crafts fabrication. Nina Myhailivna[314] and Uliana Petrivna[315] with international recognition. To preserve this traditional knowledge the village is planning to open a local weaving centre, a museum and weaving school.
Sport

Ukraine greatly benefited from the Soviet emphasis on physical education. Such policies left Ukraine with hundreds of stadia, swimming pools, gymnasia and many other athletic facilities.[316] The most popular sport is football. The top professional league is the Vyscha Liha ("premier league"). The two most successful teams in the Vyscha Liha are rivals FC Dynamo Kyiv and FC Shakhtar Donetsk. Although Shakhtar is the reigning champion of the Vyscha Liha, Dynamo Kyiv has been much more successful historically, winning two UEFA Cup Winners' Cups, one UEFA Super Cup, a record 13 USSR Championships and a record 12 Ukrainian Championships; while Shakhtar only won six Ukrainian championships and one and last UEFA Cup.[317] Ukraine co-hosted UEFA Euro 2012 alongside Poland.

Sergey Bubka held the record in the Pole vault from 1993 to 2014; with great strength, speed and gymnastic abilities, he was voted the world's best athlete on several occasions.[318][319]
Many Ukrainians also played for the Soviet national football team, most notably Ihor Belanov and Oleh Blokhin, winners of the prestigious Golden Ball Award for the best football player of the year. This award was only presented to one Ukrainian after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Andriy Shevchenko, the current captain of Ukraine. The national team made its debut in the 2006 FIFA World Cup, and reached the quarterfinals before losing to eventual champions, Italy. Ukrainians also fared well in boxing, where the brothers Vitali and Wladimir Klitschko have held world heavyweight championships.
Basketball is becoming popular in Ukraine over the past years as well. In 2011, Ukraine was granted a right to organize EuroBasket 2015, two years later Ukraine national basketball team finished 6th in EuroBasket 2013 and qualified to FIBA World Cup for the first time in its history. Euroleague participant Budivelnyk Kyiv is the strongest professional basketball club in Ukraine.
Ukraine made its Olympic debut at the 1994 Winter Olympics. So far, Ukraine has been much more successful in Summer Olympics (115 medals in five appearances) than in the Winter Olympics (five medals in four appearances). Ukraine is currently ranked 35th by number of gold medals won in the All-time Olympic Games medal count, with every country above it, except for Russia, having more appearances.[citation needed]
Cuisine


The traditional Ukrainian diet includes chicken, pork, beef, fish and mushrooms. Ukrainians also tend to eat a lot of potatoes, grains, fresh and pickled vegetables. Popular traditional dishes include [varenyky] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) (boiled dumplings with mushrooms, potatoes, sauerkraut, cottage cheese or cherries), borsch (soup made of beets, cabbage and mushrooms or meat), [holubtsy] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) (stuffed cabbage rolls filled with rice, carrots and meat) and pierogi (dumplings filled with boiled potatoes and cheese or meat). Ukrainian specialties also include Chicken Kiev and Kiev Cake. Ukrainians drink stewed fruit, juices, milk, buttermilk (they make cottage cheese from this), mineral water, tea and coffee, beer, wine and horilka.[320]
See also
- General Secretariat of Ukraine
- West Ukrainian People's Republic
- Ukraine after the Russian Revolution
- Green Ukraine - projected Ukrainian country in the Russian Far East.
- History of the Jews in Ukraine
- Ukrainian karbovanets - the first official Ukrainian currency
- Belarusian People's Republic
- People's Republic
- Universal (act)
- Orange Revolution
- 2014 Ukrainian revolution
- 2014 Russian military intervention in Ukraine
- 2014 Crimean crisis
- Category:Ukraine-related lists
- Outline of Ukraine
- Template:Wikipedia books link
Notes
a.^ Among the Ukrainians that rose to the highest offices in the Russian Empire were Aleksey Razumovsky, Alexander Bezborodko and Ivan Paskevich. Among the Ukrainians who greatly influenced the Russian Orthodox Church in this period were Stephen Yavorsky, Feofan Prokopovich and Dimitry of Rostov.
b.^ See the Great Purge article for details.
c.1 2 Estimates on the number of deaths vary. Official Soviet data is not available because the Soviet government denied the existence of the famine. See the Holodomor article for details. Sources differ on interpreting various statements from different branches of different governments as to whether they amount to the official recognition of the Famine as Genocide by the country. For example, after the statement issued by the Latvian Sejm on 13 March 2008, the total number of countries is given as 19 (according to Ukrainian BBC: "Латвія визнала Голодомор ґеноцидом"), 16 (according to Korrespondent, Russian edition: "После продолжительных дебатов Сейм Латвии признал Голодомор геноцидом украинцев"), "more than 10" (according to Korrespondent, Ukrainian edition: "Латвія визнала Голодомор 1932–33 рр. геноцидом українців") Retrieved 27 January 2008.
d.1 2 These figures are likely to be much higher, as they do not include Ukrainians from nations or Ukrainian Jews, but instead only ethnic Ukrainians, from the Ukrainian SSR.
e.^ This figure excludes POW deaths.
f.1 2 3 According to the official 2001 census data (by nationality;[321] by language[322]) about 75 percent of Kiev's population responded 'Ukrainian' to the native language (ridna mova) census question, and roughly 25 percent responded 'Russian'. On the other hand, when the question 'What language do you use in everyday life?' was asked in the 2003 sociological survey, the Kievans' answers were distributed as follows: 'mostly Russian': 52 percent, 'both Russian and Ukrainian in equal measure': 32 percent, 'mostly Ukrainian': 14 percent, 'exclusively Ukrainian': 4.3 percent.
"What language is spoken in Ukraine?". Welcome to Ukraine. February 2003. Retrieved 11 July 2008.
g.^ Such writings were also the base for Russian and Belarusian literature.
h.^ Without the city of Inhulets.
i.^ Russia and Kazakhstan are the first and second largest but both these figures include European and Asian territories. Russia is the only country possessing European territories larger than Ukraine.
References
- ^ Pavol Demes and Joerg Forbrig estimate in 2006 that only US$130,000 out of a total of US$1.56 million in Pora came from donors outside Ukraine.[116]
- ^ "Law of Ukraine "On Principles of State Language Policy" (Current version — Revision from 01.02.2014)". Document 5029-17, Article 7: Regional or minority languages Ukraine, Paragraph 2. Zakon2.rada.gov.ua. 1 February 2014. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- ^ a b c "Population by ethnic nationality, 1 January, year". ukrcensus.gov.ua. Ukrainian Office of Statistics. Archived from the original on 23 March 2008. Retrieved 17 April 2010.[dead link]
- ^ a b "People and Society: Ukraine". CIA World Factbook. Retrieved 21 February 2014.
- ^ a b c d "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". World Economic Outlook Database. International Monetary Fund. October 2013. Retrieved 20 October 2013.
- ^ "Gini index". World Bank. Retrieved 26 March 2013.
- ^ "2013 Human Development Report Statistics" (PDF). Human Development Report 2013. United Nations Development Programme. 14 March 2013. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
- ^ "Рішення Ради: Україна 30 жовтня перейде на зимовий час " Події " Україна " Кореспондент". Ua.korrespondent.net. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ "The World Factbook – Ukraine". Central Intelligence Agency. 7 January 2014. Retrieved 23 January 2014.
- ^ Chin, Richard (2011). Global Clinical Trials. Elsevier. p. 345. ISBN 0-12-381537-1.
- ^ Evans, Chandler (2008). Future of Google Earth. BookSurge. p. 174. ISBN 1-4196-8903-7.
- ^ "Basic facts about Ukraine". Ukrainian consul in NY. Retrieved 10 November 2010.
- ^ Gray, Richard (18 December 2011). "Neanderthals built homes with mammoth bones". Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ Matossian Shaping World History p. 43
- ^ "What We Theorize – When and Where Did Domestication Occur". International Museum of the Horse. Retrieved 12 December 2010.[dead link]
- ^ "Horsey-aeology, Binary Black Holes, Tracking Red Tides, Fish Re-evolution, Walk Like a Man, Fact or Fiction". Quirks and Quarks Podcast with Bob Macdonald. CBC Radio. 7 March 2009. Retrieved 18 September 2010.
- ^ "Ukraine becomes world's third biggest grain exporter in 2011 – minister" (Press release). Black Sea Grain. 20 January 2012. Retrieved 31 December 2013.
- ^ "World Trade Report 2013". World Trade Organisation. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- ^ IISS 2010, pp. 195–197
- ^ country Economy 2014 demographics
- ^ Stay informed today and every day (5 February 2014). "Linguistic divides: Johnson: Is there a single Ukraine?". Economist.com. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ Походження українців, росіян, білорусів та їхніх мов Template:Uk icon
- ^ "Ukraine – Definition and More from the Free Merriam-Webster Dictionary". Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary. Retrieved 4 May 2012.
- ^ Why Ukraine Isn't 'The Ukraine,' And Why That Matters Now, Business Insider (9 December 2013)
- ^ The "the" is gone, The Ukrainian Weekly (8 December 1991)
- ^ Ukraine or the Ukraine: Why do some country names have 'the'?, BBC News (7 June 2012)
- ^ Prat, Sandrine; Péan, Stéphane C.; Crépin, Laurent; Drucker, Dorothée G.; Puaud, Simon J.; Valladas, Hélène; Lázničková-Galetová, Martina; van der Plicht, Johannes; Yanevich, Alexander (17 June 2011). "The Oldest Anatomically Modern Humans from Far Southeast Europe: Direct Dating, Culture and Behavior". plosone. Retrieved 21 June 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ^ Carpenter, Jennifer (20 June 2011). "Early human fossils unearthed in Ukraine". BBC. Retrieved 21 June 2011.
- ^ "Scythian". Encyclopædia Britannica (fee required). Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 12 September 2007.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Ukraine". CIA World Factbook. 13 December 2007. Retrieved 24 December 2007.
- ^ a b c "Kievan Rus". The Columbia Encyclopedia (6 ed.). 2001–2007. Archived from the original on 22 July 2008. Retrieved 8 January 2014.[dead link]
- ^ Klyuchevsky, Vasily (1987). The course of the Russian history. v.1: "Myslʹ. ISBN 5-244-00072-1.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ "The Destruction of Kiev". University of Toronto's Research Repository. Retrieved 3 January 2008.
- ^ "Daniel Romanovich".Encyclopædia Britannica. 2007. Britannica Concise Encyclopedia. 23 August 2007
- ^ Subtelny, pp. 92–93
- ^ "Poland". Encyclopædia Britannica (fee required). Archived from the original on 11 October 2007. Retrieved 12 September 2007.
- ^ Brian Glyn Williams (2013). "The Sultan's Raiders: The Military Role of the Crimean Tatars in the Ottoman Empire" (PDF). The Jamestown Foundation. p. 16.
- ^ Halil Inalcik. "Servile Labour in the Ottoman Empire" in A. Ascher, B. K. Kiraly, and T. Halasi-Kun (eds), The Mutual Effects of the Islamic and Judeo-Christian Worlds: The East European Pattern, Brooklyn College, 1979, pp. 25–43.
- ^ Darjusz Kołodziejczyk, as reported by Mikhail Kizilov (2007). "Slaves, Money Lenders, and Prisoner Guards: The Jews and the Trade in Slaves and Captives in the Crimean Khanate". The Journal of Jewish Studies. p. 2.
- ^ Subtelny, Orest (1988). "Ukraine: a history.". p 106
- ^ Junius P. Rodriguez (1997). "The Historical encyclopedia of world slavery". ABC-CLIO. p. 659. ISBN 0-87436-885-5
- ^ Mikhail Kizilov. "Slave Trade in the Early Modern Crimea From the Perspective of Christian, Muslim, and Jewish Sources". Oxford University.
- ^ Krupnytsky B. and Zhukovsky A. "Zaporizhia, The". Encyclopedia of Ukraine. Retrieved 16 December 2007.
- ^ a b "Ukraine – The Cossacks". Encyclopædia Britannica (fee required). Archived from the original on 11 October 2007. Retrieved 12 September 2007.
- ^ "The Crimean Tatars and their Russian-Captive Slaves" (PDF). Eizo Matsuki, Mediterranean Studies Group at Hitotsubashi University.
- ^ Subtelny, pp. 123–124
- ^ Reid (2000) p 27–30
- ^ Barbara Skinner, "Borderlands of Faith: Reconsidering the Origins of a Ukrainian Tragedy." Slavic Review 2005 64(1): 88–116. Fulltext: in Jstor
- ^ Ukraine under direct imperial Russian rule. Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ a b Remy, Johannes (March–June 2007). "The Valuev Circular and Censorship of Ukrainian Publications in the Russian Empire (1863–1876): Intention and Practice". Canadian Slavonic Papers / Revue Canadienne des Slavistes. 47. Canadian Association of Slavists: 87–110.
- ^ Rainer Münz, Rainer Ohliger (2003). "Diasporas and ethnic migrants: German, Israel, and post-Soviet successor ". Routledge. p. 164. ISBN 0-7146-5232-6
- ^ Subtelny, Orest (2000). "Ukraine: a history.". University of Toronto Press. p. 262. ISBN 0-8020-8390-0
- ^ "31 серпня 1919 року. Як галичани з денікінцями Київ звільняли(31 August 1919. How Galicians and Denikians liberated Kiev" (in Ukrainian). Ukrayinska Pravda.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Subtelny, Orest (2000). Ukraine: A History. University of Toronto Press. pp. 340–344. ISBN 0-8020-8390-0.
- ^ Horbal, Bogdan. "Talerhof". The world academy of Rusyn culture. Retrieved 20 January 2008.
- ^ Cipko, Serge. "Makhno, Nestor". Encyclopedia of Ukraine. Retrieved 17 January 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f "Interwar Soviet Ukraine". Encyclopædia Britannica (fee required). Retrieved 12 September 2007.
- ^ Famine, Encyclopedia of Ukraine
- ^ Subtelny, p. 380
- ^ Communism. Archived from the original on 1 November 2009. Retrieved 5 July 2008.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ Cliff, pp. 138–39
- ^ "Ukraine remembers famine horror". BBC News. 24 November 2007.
- ^ Michael Ellman, "The Role of Leadership Perceptions and of Intent in the Soviet Famine of 1931–1934." Europe-Asia Studies 2005 57(6): 823–841. ISSN 0966-8136 Fulltext in Ebsco
- ^ Stephen G. Wheatcroft, "Agency and Terror: Evdokimov and Mass Killing in Stalin's Great Terror." Australian Journal of Politics and History 2007 53(1): 20–43. ISSN 0004-9522 Fulltext in Ebsco; Robert Conquest, The Harvest of Sorrow: Soviet collectivization and the terror-famine (1986). Mark B. Tauger, "The 1932 Harvest and the Famine of 1933" Slavic Review, Vol. 50, No. 1 (Spring, 1991), pp. 70–89, notes the harvest was unusually poor. online in JSTOR; R. W. Davies, M. B. Tauger, S. G. Wheatcroft, "Stalin, Grain Stocks and the Famine of 1932–1933," Slavic Review, Vol. 54, No. 3 (Autumn, 1995), pp. 642–657 [1]; online in JSTOR]; Michael Ellman. "Stalin and the Soviet famine of 1932–33 Revisited", Europe-Asia Studies, Volume 59, Issue 4 June 2007, pages 663–93.
- ^ Yushchenko Praises Guilty Verdict Against Soviet Leaders For Famine, Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty (14 January 2010)
- ^ Wilson, p. 17
- ^ Subtelny, p. 487
- ^ Roberts, p. 102
- ^ Boshyk, p. 89
- ^ a b "World wars". Encyclopedia of Ukraine. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ Timothy Snyder. A fascist hero in democratic Kiev. NewYork Reviev of Books. 24 February 2010
- ^ Piotrowski pp. 352–54
- ^ Weiner pp. 127–237
- ^ "Losses of the Ukrainian Nation, p. 2". Peremoga.gov.ua (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 15 May 2005. Retrieved 16 December 2007.
- ^ Subtelny, p. 476
- ^ Magocsi, p. 635
- ^ "Ukrainian Insurgent Army". Encyclopedia of Ukraine. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ a b "Ukraine – World War II and its aftermath". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 28 December 2007.
- ^ Karel Cornelis Berkhoff. Harvest of despair: life and death in Ukraine under Nazi rule, Harvard University Press: April 2004. p. 164
- ^ Weinberg, p. 264
- ^ Rozhnov, Konstantin, "Who won World War II?", BBC. Citing Russian historian Valentin Falin. Retrieved 5 July 2008.
- ^ "Losses of the Ukrainian Nation, p. 1". Peremoga.gov.ua (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 25 October 2007. Retrieved 16 December 2007.[dead link]
- ^ Kulchytsky, Stalislav, "Demographic losses in Ukrainian in the twentieth century", Zerkalo Nedeli, 2–8 October 2004. Available online in Russian[dead link] and in Ukrainian[dead link]. Retrieved 27 January 2008.
- ^ Smale, Alison (27 January 2014). "Shedding Light on a Vast Toll of Jews Killed Away From the Death Camps". The New York Times.
- ^ a b "Losses of the Ukrainian Nation, p. 7". Peremoga.gov.ua (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 15 May 2005. Retrieved 16 December 2007.[dead link]
- ^ Overy, p. 518
- ^ a b Кривошеев Г. Ф., Россия и СССР в войнах XX века: потери вооруженных сил. Статистическое исследование (Krivosheev G. F., Russia and the USSR in the wars of the 20th century: losses of the Armed Forces. A Statistical Study) Template:Ru icon
- ^ "Holidays". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Ukraine. Retrieved 24 August 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "Ukraine: World War II and its aftermath". Encyclopædia Britannica (fee required). Archived from the original on 29 September 2007. Retrieved 12 September 2007.
- ^ Кульчинский [Kulchytsky], Станислав [Stanislav] (2–8 October 2004), "Демографические потери Украины в XX веке", Зеркало Недели [The Mirror of the Week] (in Russian), RU: [Demoscope]
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ "Демографические потери Украины в XX веке" (in Russian). Зеркало Недели. Archived from the original on 21 July 2006. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ "Демографічні втрати України в хх столітті" (in Ukrainian). Зеркало Недели. Archived from the original on 13 March 2007. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ "Activities of the Member States – Ukraine". United Nations. Retrieved 17 January 2011.
- ^ Reliable Software Technologies – Ada-Europe '99: 1999 Ada-Europe International Conference on Reliable Software Technologies, Springer Science+Business Media, 1999, ISBN 3-540-66093-3 (p. 181)
Science in Russia and the Soviet Union: A Short History by Loren R. Graham, Cambridge University Press, 1994, ISBN 0-521-28789-8 (p. 256) - ^ a b Malynovska, Olena (14 June 2006). "Migration and migration policy in Ukraine".
- ^ "The Transfer of Crimea to Ukraine". International Committee for Crimea. July 2005. Retrieved 25 March 2007.
- ^ "Ukraine – The last years of Stalin's rule". Encyclopædia Britannica (fee required). Archived from the original on 15 January 2008. Retrieved 28 December 2007.
- ^ Magocsi, p. 644
- ^ Remy, Johannes (1996). "'Sombre anniversary' of worst nuclear disaster in history – Chernobyl: 10th anniversary". UN Chronicle. Find articles. Retrieved 16 December 2007.
- ^ "'Fukushima, Chernobyl and the Nuclear Event Scale'".
- ^ "Geographical location and extent of radioactive contamination". Chernobyl.info. Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation. Archived from the original on 30 June 2007. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ "IAEA Report". In Focus: Chernobyl. Retrieved 31 May 2008.
- ^ "Declaration of State Sovereignty of Ukraine". Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine. 16 July 1990. Retrieved 12 September 2007.
- ^ "Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine Resolution On Declaration of Independence of Ukraine". Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine. 24 August 1991. Retrieved 12 September 2007.
- ^ "Soviet Leaders Recall 'Inevitable' Breakup Of Soviet Union". RadioFreeEurope. 8 December 2006. Retrieved 12 September 2007.
- ^ The International Politics of Eurasia: The Influence of National Identity v. 2 by Roman Szforluk, M.E. Sharpe, 2004, ISBN 1-56324-355-5/ISBN 978-1-56324-355-4, pp. 118–119
- ^ Shen, p. 41
- ^ "Ukrainian GDP (PPP)". World Economic Outlook Database, October 2007. International Monetary Fund (IMF). Retrieved 10 March 2008.
- ^ "Can Ukraine Avert a Financial Meltdown?". World Bank. June 1998. Retrieved 16 December 2007.[dead link]
- ^ Figliuoli, Lorenzo; Lissovolik, Bogdan (31 August 2002). "The IMF and Ukraine: What Really Happened". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 16 December 2007.
- ^ Aslund, Anders; Aslund, Anders (Autumn 1995). "Eurasia Letter: Ukraine's Turnaround". Foreign Policy. 100 (100). JSTOR: 125–143. doi:10.2307/1149308. JSTOR 1149308.
- ^ "Macroeconomic Indicators". National Bank of Ukraine. Archived from the original on 21 October 2007.
- ^ "Ukraine. Country profile" (PDF). World Bank. Retrieved 16 December 2007.[dead link]
- ^ Wines, Michael (1 April 2002). "Leader's Party Seems to Slip In Ukraine". The New York Times. Retrieved 24 December 2007.
- ^ "The Supreme Court findings" (in Ukrainian). Supreme Court of Ukraine. 3 December 2004. Retrieved 7 July 2008.
- ^ "Ukraine-Independent Ukraine". Encyclopædia Britannica (fee required). Archived from the original on 15 January 2008. Retrieved 14 January 2008.
- ^ a b The Colour Revolutions in the Former Soviet Republics: Ukraine by Nathaniel Copsey, Routledge Contemporary Russia and Eastern Europe Series (page 30-44)
- ^ US campaign behind the turmoil in Kiev, The Guardian (26 November 2004)
- ^ Diuk, Nadia. "In Ukraine, Homegrown Freedom." Washington Post, 4 December 2004. URL Retrieved 12 September 2006
- ^ Russia, the US, “the Others” and the “101 Things to Do to Win a (Colour)Revolution”: Reflections on Georgia and Ukraine by Abel Polese, Routledge (26 October 2011)
- ^ Ukraine comeback kid in new deal, BBC News (4 August 2006)
- ^ Tymoshenko picked for Ukraine PM, BBC News (18 December 2007)
- ^ Roman Olearchyk (31 July 2013). "Lacklustre GDP data push Ukraine towards fresh IMF bailout". Financial Times. Kiev. Retrieved 3 March 2014.
- ^ Russia shuts off gas to Ukraine, BBC News (1 January 2009)
- ^ Q&A: Russia-Ukraine gas row, BBC News (20 January 2009)
- ^ Ukraine election: Yanukovych urges Tymoshenko to quit, BBC News (10 February 2010)
- ^ Stand-off in Ukraine over EU agreement, BBC News (17 December 2013)
- ^ Kiev protesters gather, EU dangles aid promise, Reuters (12 December 2013)
- ^ Kiev protesters gather, EU and Putin joust, Reuters (12 December 2013)
- ^ Shaun Walker in Kiev and agencies (27 January 2014). "Ukraine threatens state of emergency after protesters occupy justice ministry". Theguardian.com. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ Krasnolutska, Daryna. "Ukraine clashes resume in Kiev as foreign mediation urged". Businessweek.com. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ Keating, Dave (25 February 2014). "Ukraine sets date for presidential election". Europeanvoice.com. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ Reuters (3 March 2014). "Ousted Ukrainian President Asked For Russian Troops, Envoy Says". NBC News. Retrieved 21 March 2014.
{{cite news}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ "Putin to deploy Russian troops in Ukraine". BBC News. 1 March 2014. Retrieved 1 March 2014.
- ^ Radyuhin, Vladimir (1 March 2014). "Russian Parliament approves use of army in Ukraine". The Hindu. Chennai, India.
- ^ Walker, Shaun (4 March 2014). "Russian takeover of Crimea will not descend into war, says Vladimir Putin". The Guardian. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
- ^ Yoon, Sangwon; Krasnolutska, Daryna; Choursina, Kateryna (4 March 2014). "Russia Stays in Ukraine as Putin Channels Yanukovych Request". Bloomberg News. Retrieved 5 March 2104.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "BBC News - Ukraine crisis: Crimea parliament asks to join Russia". Bbc.com. 6 March 2014. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ OSCE Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (11 March 2014). "Chair says Crimean referendum in its current form is illegal and calls for alternative ways to address the Crimean issue". OSCE. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Report on the human rights situation in Ukraine". Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights. 15 April 2014.
- ^ Jacobs, Harrison (11 April 2014). "The UN's Scathing Crimea Report Suggests Russia May Have Rigged Secession Vote". Business Insider.
- ^ 16 March 2014, David Herszenhornmarch, The New York Times, "Crimea Votes to Secede From Ukraine as Russian Troops Keep Watch."
- ^ "Backing Ukraine’s territorial integrity, UN Assembly declares Crimea referendum invalid". UN News Centre. 27 March 2014. Retrieved 28 March 2014.
- ^ Text of Joint Diplomatic Statement on Ukraine, April 17, 2014, The New York Times, retrieved 30 April 2014
- ^ Will Vernon (1 January 1970). "BBC News - Ukraine rebels hold referendums in Donetsk and Luhansk". Bbc.com. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Города и области Украины – Гора Ай-Петри [Cities and regions of Ukraine – Mount Ai-Petri]". Ukrainian.su. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- ^ "Ukraine – Relief". Encyclopædia Britannica (fee required). Archived from the original on 15 January 2008. Retrieved 27 December 2007.
- ^ Environment suffers from lack of recycling, Kyiv Post (9 December 2011)
- ^ D.W. Minter and Dudka, I.O. "Fungi of Ukraine – a preliminary checklist". CAB International, 1996
- ^ "Cybertruffle's Robigalia – Observations of fungi and their associated organisms". cybertruffle.org.uk. Retrieved 13 July 2011.
- ^ Kirk, P.M., Cannon, P.F., Minter, D.W. and Stalpers, J. "Dictionary of the Fungi". Edn 10. CABI, 2008
- ^ "Fungi of Ukraine – potential endemics". cybertruffle.org.uk. Retrieved 13 July 2011.
- ^ Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. (2006). "World Map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated" (PDF). Meteorol. Z. 15 (3): 259–263. doi:10.1127/0941-2948/2006/0130. Retrieved 15 February 2007.
- ^ "Ukraine – Climate". Encyclopædia Britannica (fee required). Archived from the original on 15 January 2008. Retrieved 27 December 2007.
- ^ Understanding Ukrainian Politics:Power, Politics, And Institutional Design by Paul D'Anieri, M.E. Sharpe, 2006, ISBN 978-0-7656-1811-5 (p. 63)
- ^ EU endorses Ukraine election result, euobserver (8 February 2010)
- ^ International observers say Ukrainian election was free and fair, Washington Post (9 February 2010)
- ^ European Parliament president greets Ukraine on conducting free and fair presidential election, Kyiv Post (9 February 2010)
- ^ a b Віталій Портников. "Vitaly Portnykov. "Comment on the Constitutional Court of Ukraine on elimination of political reform in 2004 for Radio Liberty asked Nicholas Onischuk, former Justice Minister ... February 25, 2008 the Constitutional Court came to the conclusion that this bill can not be subject to constitutional control, but now we see that the Constitutional Court concluded that it can". 01.10.2010". Radiosvoboda.org. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ "Address Tymoshenko to the people: "October 1, 2010 – marks the end of Ukraine's democracy and beginning of dictatorship". This morning the Constitutional Court of Ukraine, defying all logic of constitutional law, arbitrarily announced a new constitutional order in Ukraine. The court illegally appropriated the rights held by the people and Verkhovna Rada. Oct 01, 2010". Tymoshenko.ua. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ Sergey Grabovsky. "Judicial absurd or Kotlyarevsky laughs again" ... It turns out that "stability of the constitutional order" – it will not change his voter or even parliament, and the decision of 18 judges. 01.10.2010.[clarification needed]
- ^ "President Yanukovych and Ukraine opposition sign early poll deal". Europe Sun. 19 February 2014.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Ukraine: Speaker Oleksandr Turchynov named interim president". BBC News. 19 February 2014.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Who exactly is governing Ukraine?". The Guardian. 4 March 2014.
- ^ "General Articles about Ukraine". Government Portal. Retrieved 24 December 2007.
- ^ "Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine". Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine Official Web-site. Retrieved 24 December 2007.
- ^ "Constitution of Ukraine". Wikisource. Retrieved 24 December 2007.
- ^ WJP Rule of Law Index Rankings
- ^ Prosecutors fail to solve biggest criminal cases, Kyiv Post (25 March 2010)
- ^ Template:Uk icon Українські суди майже не виносять виправдувальних вироків Ukrainian courts almost can not stand the acquittals, Ukrayinska Pravda (8 March 2013)
- ^ Moskal: 'Rotten to the core', Kyiv Post (25 March 2010)
- ^ a b c Jackpot, Kyiv Post, 25 March 2010
- ^ "Constitutional Court rules Russian, other languages can be used in Ukrainian courts". Kyiv Post. 15 December 2011.
Template:Uk icon "З подачі "Регіонів" Рада дозволила російську у судах". Ukrayinska Pravda. 23 June 2009.
Template:Uk icon "ЗМІ: Російська мова стала офіційною в українських судах[dead link]". Novynar. 29 July 2010.
Template:Uk icon "Російська мова стала офіційною в українських судах". forUm. 29 July 2010. - ^ C. J. Chivers, BACK CHANNELS: A Crackdown Averted; How Top Spies in Ukraine Changed the Nation's Path, The New York Times, 17 January 2005.
- ^ "Teixeira: Ukraine's EU integration suspended, association agreement unlikely to be signed". Interfax. 31 August 2012. Retrieved 6 September 2012.
- ^ a b "Regions of Ukraine and their divisions". Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine Official Web-site (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 24 December 2007.
- ^ a b "The history of the Armed Forces of Ukraine". Ministry of Defence of Ukraine. Retrieved 5 July 2008.
- ^ "Ukraine Special Weapons". GlobalSecurity.org. Retrieved 24 December 2007.
- ^ a b "White Book 2006" (PDF). Ministry of Defense of Ukraine. Retrieved 24 December 2007.
- ^ "Ukrainian Navy Warship Hetman Sagaidachniy Joins EU Naval Force Counter Piracy Operation Atalanta". Eunavfor.eu. 6 January 2014. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- ^ "Multinational Peacekeeping Forces in Kosovo, KFOR". Ministry of Defense of Ukraine. Retrieved 24 December 2007.
- ^ "Peacekeeping". Ministry of Defense of Ukraine. Retrieved 2 May 2008.
- ^ "Parliament approves admission of military units of foreign states to Ukraine for exercises". Kyiv Post. 18 May 2010[dead link]
- ^ "Declaration of State Sovereignty of Ukraine". Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine Official Web-site. Retrieved 24 December 2007.
- ^ a b NATO confirms readiness for Ukraine's joining organization, Kyiv Post (13 April 2010)
- ^ "Yanukovich vows to keep Ukraine out of NATO". Reuters. 7 January 2010.
- ^ "Child poverty soars in eastern Europe". BBC News. 11 October 2000. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- ^ "Independent Ukraine". Encyclopædia Britannica (fee required). Retrieved 12 September 2007.
- ^ Skolotiany, Yuriy (8 September 2006). "The past and the future of Ukrainian national currency". Zerkalo nedeli. Archived from the original on 25 June 2008. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ "CIA World Factbook – Ukraine. 2002 edition". CIA. Retrieved 5 July 2008.
- ^ "Ukraine – gdp". Index Mundi. Retrieved 15 July 2012.
- ^ "CIA World Factbook – Ukraine. 2004 edition". CIA. Retrieved 5 July 2008.
- ^ "Head of IMF's Resident Representative Office in Ukraine to change his job". Interfax-Ukraine. Retrieved 17 December 2008.
- ^ "Average Wage Income in 2008 by Region". State Statistics Committee of Ukraine. Retrieved 5 July 2008.
- ^ a b "Bohdan Danylyshyn at the Economic ministry". Economic Ministry. Retrieved 1 February 2008.
- ^ Human and income poverty: developing countries / Population living below $2 a day (%)[dead link], Human Development Report 2007/08, UNDP. Retrieved 3 February 2008
- ^ Data Human and income poverty: developing countries / Population living below the national poverty line (%)[dead link], Human Development Report 2007/08, UNDP. Retrieved 3 February 2008
- ^ Poverty headcount ratio at $2 a day (PPP) (% of population), World Bank/indicator
- ^ "Structure export and import, 2006". State Statistics Committee of Ukraine. Retrieved 5 July 2008.
- ^ "Statistics of Launches of Ukrainian LV". National Space Agency of Ukraine. Retrieved 24 December 2007.
- ^ "Missile defence, NATO: Ukraine's tough call". Business Ukraine. Archived from the original on 25 March 2008. Retrieved 5 July 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "Ukraine Special Weapons". The Nuclear Information Project. Retrieved 5 July 2008.
- ^ Pirani, Simon (June 2007). "Ukraine's Gas Sector" (PDF). Oxford Institute for Energy Studies. p. 36. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ "What are Middle-Income Countries?". The World Bank Group. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ "Business Corruption in Ukraine". Business Anti-Corruption Portal. Retrieved 25 March 2014.
- ^ Pogarska, Olga. "Ukraine macroeconomic situation – February 2008". UNIAN news agency. Retrieved 29 February 2008.
- ^ Ballmer, Steve (20 May 2008). "Microsoft CEO Steve Ballmer Visits Ukraine". Microsoft. Retrieved 28 July 2008.
- ^ Template:Uk icon Україна – четверта в світі за кількістю ІТ-фахівців Ukraine in fourth place in the world in the number of IT professionals, UNIAN (27 March 2013)
- ^ "Industry of Ukraine". Usndt.com.ua. Retrieved 30 December 2010.[dead link]
- ^ "Ilyushin Finance to buy 10 An-158 planes from Ukraine's Antonov". RIA Novosti. 20 July 2010. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ "Brand "Ukraine" will be reloaded in 2012". Ukraineanalysis.wordpress.com. 1 May 2008. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- ^ "waghid1neu" (PDF). Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ "U.S. embassy: Ukraine could again be put on list of copyright violators". Kyiv Post. Interfax-Ukraine. 10 November 2010. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ "Ukraine's economic growth to resume in 2010, unemployment to be high". Kyiv Post. 17 December 2009. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ "Transportation in Ukraine". U.S. Government Printing Office. Retrieved 22 December 2007.
- ^ "Consulate General of Ukraine". Ukrconsul.org. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ "Kharkiv airport gets new terminal on". UEFA. 28 August 2010. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ "Судоходная компания Укрферри. Морские паромные перевозки на Черном Море между Украиной, Грузией, Турцией и Болгарией". Ukrferry.com. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ "Bisignis Institute releases new country profiles for Azerbaijan and Ukraine" (Press release). Bisignis Institute. 6 January 2014. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ a b Інформаційна довідка про основні показники розвитку галузей паливно-енергетичного комплексу України за грудень та 2011 рікTemplate:Uk icon
- ^ "Ukraine". Energy Information Administration (EIA). US government. Archived from the original on 27 March 2008. Retrieved 22 December 2007.[dead link]
- ^ "Westinghouse Wins Contract to Provide Fuel Supplies to Ukraine" (press release). 30 March 2008. Westinghouse Electric. Retrieved 15 April 2014.
- ^ "Russia says restarts nuclear fuel transit to Europe via Ukraine". Reuters. 8 March 2014. Retrieved 15 April 2014.
- ^ "Westinghouse and Ukraine's Energoatom Extend Long-term Nuclear Fuel Contract". 11 April 2014. Westinghouse. Retrieved 15 April 2014.
- ^ "Відновлювана енергетика України стрімко зростає, але досі має мізерну частку | Зелена Хвиля". Ecoclubua.com. 29 July 2012. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- ^ Roca, Marc (29 December 2011). "Europe's Biggest Solar Park Completed With Russian Bank Debt". Bloomberg.[dead link]
- ^ "Ukraine could boost alternative energy capacity by 600 MW in 2012". SteelGuru. 1 February 2012. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ Katya Gorchinskaya (12 June 1997). "Small business bearing the brunt of corruption". Kyiv Post. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- ^ Rachkevych, Mark (2 February 2012). "Ukraine only starting to harness potential of renewable energy". Kyiv Post. Archived from the original on 9 May 2012. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ "9% of electricity will be received from renewable sources in 2030". Ukrinform.ua. 27 March 2012. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- ^ Ukraine's Internet growth rates will stabilize in 2 or 3 years Template:Uk icon
- ^ Template:Uk icon Половина населення України має доступ в інтернет Template:Uk icon
- ^ "Pando Networks Releases Global Internet Speed Study". Pandonetworks.com. 22 September 2011. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- ^ UNWTO World Tourism Barometer, volume 6[dead link], UNWTO (June 2008)
- ^ "Ukraine – Statistics". United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF). Retrieved 7 January 2008.
- ^ "Total population, as of September 1, 2009. Average annual populations January–August 2009". State Statistics Committee of Ukraine. 2009. Retrieved 16 October 2009.
- ^ a b "Field Listing – Population growth rate". CIA World Factbook. Retrieved 5 July 2008.
- ^ Hanna H. Starostenko, "Economic and Ecological Factors of Transformations in Demographic Process in Ukraine", Uktraine Magazine No. 2, 1998.
- ^ a b "What Went Wrong with Foreign Advice in Ukraine?". The World Bank Group. Retrieved 16 January 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "Infant mortality rate, Ukraine". Cia.gov. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- ^ State Statistics Committee of Ukraine Retrieved 18 September 2009
- ^ Demoscope Retrieved 18 September 2009
- ^ Perelli-Harris, Brienna (2005). "The Path to Lowest-low Fertility in Ukraine". Population Studies. 59 (1): 55–70. doi:10.1080/0032472052000332700. JSTOR 30040436. PMID 15764134.
- ^ "President meets with business bosses". Press office of President Victor Yushchenko. Archived from the original on 14 December 2007. Retrieved 1 February 2008.[dead link]
- ^ Template:Uk icon The demographic situation in Ukraine in January–September 2009[dead link], State Statistics Committee of Ukraine
- ^ "Ukraine's birth rate shows first positive signs in decade". Ukrainian Independent Information Agency (UNIAN). 5 October 2007. Retrieved 3 July 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f Serhy Yekelchyk Ukraine: Birth of a Modern Nation, Oxford University Press (2007), ISBN 978-0-19-530546-3
- ^ "Linguistic composition of the population". All-Ukrainian population census, 2001. Archived from the original on 5 January 2008. Retrieved 27 January 2008.[dead link]
- ^ Language Policy in the Soviet Union by L.A. Grenoble. Books.google.com. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- ^ "Yanukovych signs language bill into law". Kyivpost.com. 8 August 2012. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- ^ "Russian spreads like wildfires in dry Ukrainian forest". Kyivpost.com. 23 August 2012. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- ^ Romanian becomes regional language in Bila Tserkva in Zakarpattia region, Kyiv Post (24 September 2012)
- ^ Schwirtz, Michael (5 July 2012). "Ukraine". The New York Times.
- ^ Traynor, Ian (24 February 2014). "Western nations scramble to contain fallout from Ukraine crisis". The Guardian.
- ^ Kramer, Andrew (2 March 2014). "Ukraine Turns to Its Oligarchs for Political Help". New York Times. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- ^ Shamshur, p. 159–168
- ^ "Світова преса про вибори в Україні-2004 (Ukrainian Elections-2004 as mirrored in the World Press)". Архіви України (National Archives of Ukraine). Retrieved 7 January 2008.
- ^ Template:Wayback[dead link], 2001 Ukrainian Census. Retrieved 27 January 2008.
- ^ Template:Wayback[dead link], 2001 Ukrainian Census. Retrieved 27 January 2008.
- ^ For a more comprehensive account of language politics in Crimea, see Natalya Belitser, "The Constitutional Process in the Autonomous Republic of Crimea in the Context of Interethnic Relations and Conflict Settlement," International Committee for Crimea. Retrieved 12 August 2007.
- ^ "Kiev Saint Sophia Cathedral". United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO). UN. Retrieved 8 July 2008.
- ^ a b "Опитування: Віруючим якої церкви, конфесії Ви себе вважаєте?" (in Ukrainian). UA: Razumkov Centre. 2006. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e "State Department of Ukraine on Religious". 2003 Statistical report. Archived from the original on 4 December 2004. Retrieved 27 January 2008.
- ^ "Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church (UGCC)". Archived from the original on 26 February 2008. Retrieved 27 January 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "2012 Report on International Religious Freedom – Ukraine". United States Department of State. 20 May 2013. Retrieved 19 November 2013.
- ^ "2007 Report on International Religious Freedom – Ukraine". United States Department of State. 2007. Retrieved 19 November 2013.
- ^ "Jews", Encyclopedia of Ukraine
- ^ Vallin, Jacques; Meslé, France; Adamets, Serguei; Pyrozhkov, Serhii (2002). "A New Estimate of Ukrainian Population Losses During the Crises of the 1930s and 1940s". Population Studies. 56 (3): 249–264. doi:10.1080/00324720215934. JSTOR 3092980.
- ^ Ian Dear, Michael Richard Daniell Foot (2001). The Oxford companion to World War II. Oxford University Press. p. 909. ISBN 0-19-860446-7
- ^ Malynovska, Olena (January 2006). "Caught Between East and West, Ukraine Struggles with Its Migration Policy". National Institute for International Security Problems, Kiev. Retrieved 3 July 2008.
- ^ "International migration 2006". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Retrieved 5 July 2008.
- ^ "Ethnic origins, 2006 counts, for Canada, provinces and territories – 20% sample data". Statistics Canada.
- ^ "Medical Care in Ukraine. Health system, hospitals and clinics". BestOfUkraine.com. 1 May 2010. Retrieved 30 December 2010.[dead link]
- ^ Ukraine. "Health in Ukraine. Healthcare system of Ukraine". Europe-cities.com. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ "State Statistics Committee of Ukraine". Ukrstat.gov.ua. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- ^ "World Population Prospects: The 2012 Revision". United Nations. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ National network of family doctors to be established by 2010, says health minister, Interfax-Ukraine (30 March 2009)
- ^ Ukraine to start introducing insurance-based healthcare system in spring of 2010, Kyiv Post (24 November 2009)
- ^ Constitution of Ukraine, Chapter 2, Article 53. Adopted at the Fifth Session of the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine on 28 June 1996
- ^ "General secondary education". Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine. Archived from the original on 16 October 2007. Retrieved 23 December 2007.
- ^ "Higher education in Ukraine; Monographs on higher education; 2006" (PDF). Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ "System of Higher Education of Ukraine". Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine. Archived from the original on 17 December 2007. Retrieved 23 December 2007.
- ^ "System of the Education of Ukraine". Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine. Archived from the original on 12 December 2007. Retrieved 23 December 2007.
- ^ "Educational system in Ukraine". Outsourcing-ukraine.org. 14 October 2011. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- ^ The Educational System of Ukraine, Nordic Recognition Network, 2009
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b The language question, the results of recent research in 2012, UA: Rating, 25 May 2012
- ^ "Poll: Ukrainian language prevails at home", Ukrinform, UA, 7 September 2011
- ^ Snyder, Timothy D (21 September 2010), "Who's Afraid of Ukrainian History?", The New York Review of Books
- ^ "Poll: Over half of Ukrainians against granting official status to Russian language". Kyiv Post. 27 December 2012. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ Ставлення населення України до постаті Йосипа Сталіна (in Ukrainian), Kyiv International Institute of Sociology, 1 March 2013
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ a b "Ukraine. West-East: Unity in Diversity". Research & Branding Group. March 2010. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ Malanchuk, Oksana (2005), "Social Identification Versus Regionalism in Contemporary Ukraine", Nationalities Papers, 33 (3), Informa World: 345–68, ISSN 0090-5992
- ^ Kuzio, Taras (23 August 2011), Soviet conspiracy theories and political culture in Ukraine: Understanding Viktor Yanukovych and the Party of Region (PDF)
- ^ Вибори народних депутатів України 2012 (in Ukrainian), Центральна виборча комісія України [Central Election Commission of Ukraine
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ CEC substitues Tymoshenko, Lutsenko in voting papers, For UA, 30 August 2012.
- ^ Backes, Uwe; Moreau, Patrick (2008), Communist and Post-Communist Parties in Europe, Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht, p. 396, ISBN 978-3-525-36912-8
- ^ Ukraine right-wing politics: is the genie out of the bottle?, openDemocracy.net, 3 January 2011
- ^ Kuzio, Taras (17 October 2012), Eight Reasons Why Ukraine's Party of Regions Will Win the 2012 Elections, The Jamestown Foundation
- ^ Kuzio, Taras (5 October 2007), UKRAINE: Yushchenko needs Tymoshenko as ally again (PDF), Oxford Analytica
- ^ "Election winner lacks strong voter mandate". Kyiv Post. 11 February 2010.
- ^ "Ukraine's Party of Regions: A pyrrhic victory". EurActiv.com. 16 November 2012.
- ^ "Ukraine vote ushers in new constellation of power". Deutsche Welle. 30 October 2012.
- ^ "Cultural differences". Ukraine's Culture. Retrieved 27 January 2008.
- ^ "Interwar Soviet Ukraine". Encyclopædia Britannica (fee required). Retrieved 12 September 2007.
In all, some four-fifths of the Ukrainian cultural elite was repressed or perished in the course of the 1930s
- ^ "Gorbachev, Mikhail". Encyclopædia Britannica (fee required). Archived from the original on 22 June 2008. Retrieved 30 July 2008.
Under his new policy of glasnost ("openness"), a major cultural thaw took place: freedoms of expression and of information were significantly expanded; the press and broadcasting were allowed unprecedented candour in their reportage and criticism; and the country's legacy of Stalinist totalitarian rule was eventually completely repudiated by the government
- ^ "Pysanky – Ukrainian Easter Eggs". University of North Carolina. Retrieved 28 July 2008.
- ^ a b c d e "Ukraine – Cultual Life – The Arts – Literature". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ a b c Ukraine – Literature. Archived from the original on 6 April 2008. Retrieved 3 July 2008.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ Struk, Danylo Husar. "Literature". Encyclopedia of Ukraine. Retrieved 17 January 2008.
- ^ "Project of reconstruction of the Rybalskyi Peninsula". archunion.com.ua (in Russian). 7 December 2005. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ a b "Top Sites in Ukraine". Alexa. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Ukrainian folk dress. Traditional clothes of Ukraine". Ua-travelling.com. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ "Podvyzhnytsi narodnoho mystetstva", Kyiv 2003 and 2005, by Yevheniya Shudra, Welcome to Ukraine Magazine
- ^ "Traditional Ukrainian Embroidery". Ukrainian Museum-Archives. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ "Рівненська обласна державна адміністрація – Обласний центр народної творчості". Rv.gov.ua. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ "ПІСНІ ТА ВИШИВКИ УЛЯНИ КОТ – Мистецька сторінка". Storinka-m.kiev.ua. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ "Ukraine – Sports and recreation". Encyclopædia Britannica (fee required). Archived from the original on 15 January 2008. Retrieved 12 January 2008.
- ^ Trophies of Dynamo[dead link] – Official website of Dynamo Kyiv Template:Uk icon. Retrieved 23 June 2008.
- ^ International Olympic Committee. "Mr. Sergey BUBKA". Official website of the Olympic Movement. Retrieved 27 May 2010.
... voted world's best athlete on several occasions.
- ^ "Track and Field Athlete of the Year". Trackandfieldnews.com. Retrieved 30 January 2011.[dead link]
- ^ Stechishin, Savella. "Traditional Foods". Encyclopedia of Ukraine. Retrieved 10 August 2007.
- ^ "About number and composition population of Kyiv city by All-Ukrainian population census'2001 data". State Statistics Committee of Ukraine. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ "About number and composition population of Kyiv on the results of Census 2001" (in Ukrainian). State Statistics Committee of Ukraine. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
Print sources
Reference books
- Encyclopedia of Ukraine (University of Toronto Press, 1984–93) 5 vol; partial online version, from Canadian Institute of Ukrainian Studies
- Ukraine: A Concise Encyclopedia Vol.1 ed by Volodymyr E. KubijovyC; University of Toronto Press. 1963; 1188pp
- Dalton, Meredith. Ukraine (Culture Shock! A Survival Guide to Customs & Etiquette) (2001)
- Evans, Andrew. Ukraine (2nd ed 2007) The Bradt Travel Guide online excerpts and search at Amazon.com
- Johnstone, Sarah. Ukraine (Lonely Planet Travel Guides) (2005)
Recent (since 1991)
- Aslund, Anders, and Michael McFaul.Revolution in Orange: The Origins of Ukraine's Democratic Breakthrough (2006)
- Birch, Sarah. Elections and Democratization in Ukraine Macmillan, 2000 online edition
- Edwards Mike: "Ukraine – Running on empty" National Geographic Magazine March 1993
- Kuzio, Taras: Contemporary Ukraine: Dynamics of Post-Soviet Transformation, M.E. Sharpe, 1998, ISBN 0-7656-0224-5
- Kuzio, Taras. Ukraine: State and Nation Building Routledge, 1998 online edition
- Shamshur O. V., Ishevskaya T. I., Multilingual education as a factor of inter-ethnic relations: the case of the Ukraine, in Language Education for Intercultural Communication, By D. E. Ager, George Muskens, Sue Wright, Multilingual Matters, 1993, ISBN 1-85359-204-8
- Shen, Raphael (1996). Ukraine's Economic Reform: Obstacles, Errors, Lessons. Praeger/Greenwood. ISBN 0-275-95240-1.
- Whitmore, Sarah. State Building in Ukraine: The Ukrainian Parliament, 1990–2003 Routledge, 2004 online edition
- Wilson, Andrew, Ukraine's Orange Revolution (2005)
- Wilson, Andrew, The Ukrainians: Unexpected Nation, 2nd ed. 2002; online excerpts at Amazon
- Wilson, Andrew, Ukrainian Nationalism in the 1990s: A Minority Faith, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-57457-9
- Zon, Hans van. The Political Economy of Independent Ukraine. 2000 online edition
History
- Bilinsky, Yaroslav The Second Soviet Republic: The Ukraine after World War II (Rutgers UP, 1964) online
- Hrushevsky, Michael. A History of Ukraine (1986)
- Katchanovski Ivan; Kohut, Zenon E.; Nebesio, Bohdan Y.; and Yurkevich, Myroslav. Historical Dictionary of Ukraine. Second Edition. Scarecrow Press, 2013. 968 pp.
- Kononenko, Konstantyn. Ukraine and Russia: A History of the Economic Relations between Ukraine and Russia, 1654–1917 (Marquette University Press 1958) online
- Luckyj, George S. Towards an Intellectual History of Ukraine: An Anthology of Ukrainian Thought from 1710 to 1995. (1996)
- Magocsi, Paul Robert, A History of Ukraine. University of Toronto Press, 1996 ISBN 0-8020-7820-6
- Reid, Anna. Borderland: A Journey Through the History of Ukraine (2003) online edition
- Subtelny, Orest. Ukraine: A History, 1st edition. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 1988. ISBN 0-8020-8390-0.
- Yekelchyk, Serhy. Ukraine: Birth of a Modern Nation (Oxford University Press 2007) online
World War II
- Boshyk, Yuri (1986). Ukraine During World War II: History and Its Aftermath. Canadian Institute of Ukrainian Studies. ISBN 0-920862-37-3.
- Berkhoff, Karel C. Harvest of Despair: Life and Death in Ukraine Under Nazi Rule. Harvard U. Press, 2004. 448 pp.
- Cliff, Tony (1984). Class Struggle and Women's Liberation. Bookmarks. ISBN 0-906224-12-8.
- Gross, Jan T. Revolution from Abroad: The Soviet Conquest of Poland's Western Ukraine and Western Belorussia (1988).
- Lower, Wendy. Nazi Empire-Building and the Holocaust in Ukraine. U. of North Carolina Press, 2005. 307 pp.
- Piotrowski Tadeusz, Poland's Holocaust: Ethnic Strife, Collaboration with Occupying Forces and Genocide in the Second Republic, 1918–1947, McFarland & Company, 1998, ISBN 0-7864-0371-3
- Redlich, Shimon. Together and Apart in Brzezany: Poles, Jews, and Ukrainians, 1919–1945. Indiana U. Press, 2002. 202 pp.
- Zabarko, Boris, ed. Holocaust In The Ukraine, Mitchell Vallentine & Co, 2005. 394 pp.
External links
- "Ukraine". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Ukraine Corruption Profile from the Business Anti-Corruption Portal
- Website Ukraine-CityGuide
- Ukraine information from the United States Department of State
- Portals to the World from the United States Library of Congress
- Ukraine at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Ukraine at Curlie
- Ukraine from the BBC News
 Wikimedia Atlas of Ukraine
Wikimedia Atlas of Ukraine Geographic data related to Ukraine at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Ukraine at OpenStreetMap Ukraine travel guide from Wikivoyage
Ukraine travel guide from Wikivoyage- Key Development Forecasts for Ukraine from International Futures
- Encyclopedia of Ukraine
- EU Neighbourhood Info Centre: Ukraine
- EU Neighbourhood Library
- Government
- The President of Ukraine
- Government Portal of Ukraine
- The Parliament of Ukraine
- Ukrainian art. Most famous modern painters
- Trade
Template:Link GA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA