Android Auto: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{reflist}} |
{{reflist}} |
||
23 http://www.shadowswork.com/2019/09/05/android-auto-cars/ |
|||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
Revision as of 10:52, 7 September 2019
 | |
| Original author(s) | Google,2.0W.M |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | |
| Initial release | March 19, 2015 |
| Operating system | Android 5.0+ |
| Type | Telematics |
| License | Proprietary |
| Website | android |
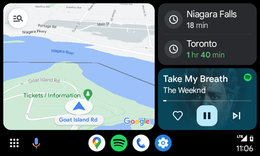
Android Auto is a mobile app developed by Google to mirror features from an Android device, such as a smartphone, to a car's compatible in-dash information and entertainment head unit.
Once an Android device is paired with the head unit, the system mirrors qualified apps from the device to the vehicle's display, with a simple, driver-friendly user interface. Supported apps include GPS mapping/navigation, music playback, SMS, telephone, and web search. The system supports both touchscreen and button-controlled head unit displays, although hands-free operation through voice commands is encouraged to minimize driving distraction.
Android Auto is part of the Open Automotive Alliance that was announced on June 25, 2014, and is a joint effort between 28 automobile manufacturers, with Nvidia as tech supplier. It is available in 36 countries.
Functionality

The most common way Android Auto is deployed is via an Android mobile device running the Android Auto app, acting as a master to a vehicle's dashboard head unit that supports this functionality.[1] Once the user's Android device is connected to the vehicle, the head unit will serve as an external display for the Android device, presenting supported software in a car-specific user interface provided by the Android Auto app.[1][2] In Android Auto's first iterations, the device was required to be connected via USB to the car.[3]
Alternatively, in November 2016, Google added the option to run Android Auto as a regular app on an Android device, i.e., not tethered to a car's head unit, which allows it to be used on Android-powered head units, or simply on a personal phone or tablet in the vehicle.[4] In addition, on January 1, 2018, it was announced that JVCKenwood would be exhibiting wireless Android Auto-enabled head units at CES 2018, which would be capable of operating without the need for a wired connection.[5]

Availability
As of May 2019, Android Auto is available in 36 countries.[6] The availability of apps on the system varies.
History
- June 25, 2014: Android Auto debuted at Google I/O 2014
- March 19, 2015: Android Auto was released[7]
- November 2016: Google added the option to run Android Auto as a regular app on an Android device[8]
- July 2019: Android Auto received its first major UI rework, which among other changes, brought an app drawer to Android Auto for the first time. Google also announced that the app's ability of being used on a phone would be discontinued in favor of Google Assistant's drive mode.[9]
App support
An Android Auto SDK has been released, allowing third parties to modify their apps to work with Android Auto;[2] initially, only APIs for music and messaging apps would be available,[10][11] but it is expected that through Android Auto, the mobile device will have access to several of the automobile's sensors and inputs, such as GPS and high-quality GPS antennas, steering-wheel mounted buttons, the sound system, directional speakers, directional microphones, wheel speed, compass, mobile antennas, etc. Also, there is partial access to car data, a feature still under development.[12]
At CES 2018, Google confirmed that the Google Assistant would be coming to Android Auto later in the year.[13]
Currently supported apps include Google Maps and Waze, popular music players such as Google Play Music, YouTube Music, Amazon Music, Apple Music and Spotify; and messaging apps, including WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, Google Hangouts, Skype and Telegram.
Head unit support
In May 2015, Hyundai became the first manufacturer to offer Android Auto support, making it available first in the 2015 Hyundai Sonata.[14] Automobile manufacturers that will offer Android Auto support in their cars include Abarth, Acura, Alfa Romeo, Audi, Bentley, Buick, Cadillac, Chevrolet, Chrysler, Dodge, Fiat, Ford, GMC, Genesis, Holden[15], Honda, Hyundai, Infiniti, Jaguar Land Rover, Jeep, Kia, Lamborghini, Lexus, Lincoln, Mahindra and Mahindra, Maserati, Mazda, Mercedes-Benz, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Opel, Peugeot, RAM, Renault, SEAT, Škoda, SsangYong, Subaru, Suzuki, Tata Motors Cars, Toyota, Volkswagen and Volvo.[16]
Additionally, aftermarket car-audio systems supporting Android Auto add the technology into host vehicles, including Pioneer,[17] Kenwood,[18] Panasonic,[19] and Sony.[20][21]
Criticism
In May 2019, Italy filed an antitrust complaint targeting Android Auto, citing that a Google policy of only allowing third-party media and messaging apps on the platform prevented Enel from offering an app for locating vehicle charging stations.[22]
See also
References
- ^ a b Devine, Richard (June 26, 2014). "What you need to know about Android Auto". Android Central. Retrieved June 27, 2014.
- ^ a b Goodwin, Antuan (June 25, 2014). "Google's new Android Auto is like Google Now for your car". CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved June 26, 2014.
- ^ Gorman, Michael (June 25, 2014). "Google gives us a simulated ride with Android Auto". Engadget. AOL Inc. Retrieved June 26, 2014.
- ^ "Android Auto: now available in every car". Official Google Blog. 2016-11-07. Archived from the original on 2016-11-07.
- ^ "JVCKENWOOD will have a pair of wireless Android Auto-capable head units on display at CES". WCCFTech. 2018-01-01.
- ^ "FAQ". Android. Retrieved 23 January 2019.
- ^ Welch, Chris. "Google's launch of Android Auto starts today with Pioneer head units". The Verge. Retrieved 19 August 2019.
- ^ "Android Auto: now available in every car". Official Google Blog. 2016-11-07. Archived from the original on 2016-11-07.
- ^ "The new Android Auto officially starts rolling out today, and it's mostly an improvement". 2019-07-30.
- ^ Moynihan, Tim (June 25, 2014). "Google Announces Android Auto, Its Answer to Apple's CarPlay". Wired. Condé Nast. Retrieved June 26, 2014.
- ^ "Autoradio GPS". Archived from the original on March 17, 2016. Retrieved March 17, 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Brenner, Andy (June 27, 2014). "Google I/O 2014 - Android Auto: Developers, Start Your Engines!". YouTube. Google. Retrieved July 5, 2014.
- ^ Reigh, Brian (8 January 2018). "Google Assistant will soon live inside your car". Android Authority. Retrieved 10 January 2018.
- ^ "Android Auto: The First Great In-Car Infotainment System". WIRED. Retrieved 2017-11-10.
- ^ "Android Auto for Holden". Android. Retrieved 2019-02-26.
- ^ https://www.android.com/auto/
- ^ "Pioneer-Android-Auto". Retrieved 28 August 2015.
- ^ "Kenwood-Android-Auto". Retrieved January 4, 2016.
- ^ "Android Auto for Panasonic". Android. Retrieved 2016-11-17.
- ^ "Android Auto for Sony". Retrieved 2017-07-25.
- ^ Kim Bussing, Anton Galang (27 June 2019). "The 8 Best Car Stereo Systems of 2019". Lifewire. Retrieved 11 August 2019.
- ^ O'Kane, Sean (2019-05-17). "Italy opens antitrust probe into Google because of a rejected Android Auto app". The Verge. Retrieved 2019-05-18.
23 http://www.shadowswork.com/2019/09/05/android-auto-cars/
External links
- Official website
- Android Auto app at the Play Store
- Apps for Android Auto at the Play Store
