25I-NBOMe: Difference between revisions
Updating {{drugbox}} (no changed fields - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref', 'CAS_number_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or [[use... |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
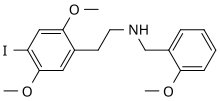
'''25I-NBOMe''' ('''NBOMe-2C-I''', '''BOM-CI''', '''Cimbi-5 |
'''25I-NBOMe''' ('''NBOMe-2C-I''', '''BOM-CI''', '''Cimbi-5''') is a derivative of the [[phenethylamine]] [[psychedelic|hallucinogen]] [[2C-I]], discovered in 2003 by Ralf Heim at the [[Free University of Berlin]],<ref>[http://www.diss.fu-berlin.de/diss/receive/FUDISS_thesis_000000001221 Ralf Heim PhD. Synthese und Pharmakologie potenter 5-HT2A-Rezeptoragonisten mit N-2-Methoxybenzyl-Partialstruktur. Entwicklung eines neuen Struktur-Wirkungskonzepts. (German)]</ref> and subsequently investigated in more detail by a team at [[Purdue University]] led by [[David Nichols]].<ref>[http://proquest.umi.com/pqdlink?Ver=1&Exp=01-23-2014&FMT=7&DID=1417800971&RQT=309&attempt=1&cfc=1 Michael Robert Braden PhD. Towards a biophysical understanding of hallucinogen action. Purdue University 2007.]</ref> |
||
25I-NBOMe acts as a highly [[potency (pharmacology)|potent]] [[agonist]] for the [[human]] [[5-HT2A receptor|5-HT<sub>2A</sub>]] [[Receptor (biochemistry)|receptor]],<ref>{{Cite doi|10.1007/s00259-010-1686-8}}</ref><ref name="pmid21088982">{{cite journal |author=Silva ME, Heim R, Strasser A, Elz S, Dove S |title=Theoretical studies on the interaction of partial agonists with the 5-HT(2A) receptor |journal=Journal of Computer-aided Molecular Design |volume=25 |issue=1 |pages=51–66 |year=2011 |month=January |pmid=21088982 |doi=10.1007/s10822-010-9400-2 |url=}}</ref> with a [[Dissociation constant|K<sub>i</sub>]] of 0.044 nM, making it some sixteen times the potency of 2C-I itself, and a [[isotopic labelling|radiolabelled]] form of 25I-NBOMe can be used for mapping the distribution of 5-HT<sub>2A</sub> receptors in the brain.<ref name="pmid18468904">{{cite journal |author=Nichols DE, Frescas SP, Chemel BR, Rehder KS, Zhong D, Lewin AH |title=High Specific Activity Tritium-Labeled N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenethylamine (INBMeO): A High Affinity 5-HT2A Receptor-Selective Agonist Radioligand |journal=Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry |volume=16 |issue=11 |pages=6116–23 |year=2008 |month=June |pmid=18468904 |pmc=2719953 |doi=10.1016/j.bmc.2008.04.050 |url=}}</ref><ref>{{Cite doi|10.2967/jnumed.109.074021}}</ref> ''[[In vitro]]'' tests showed this compound acted as an agonist but animal studies have not been reported. While the ''N''-benzyl derivatives of 2C-I were significantly increased in potency compared to 2C-I, the ''N''-benzyl derivatives of [[2,5-Dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine|DOI]] were inactive.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Braden | first1 = MR | last2 = Parrish | first2 = JC | last3 = Naylor | first3 = JC | last4 = Nichols | first4 = DE | title = Molecular interaction of serotonin 5-HT2A receptor residues Phe339(6.51) and Phe340(6.52) with superpotent N-benzyl phenethylamine agonists | journal = Molecular pharmacology | volume = 70 | issue = 6 | pages = 1956–64 | year = 2006 | pmid = 17000863 | doi = 10.1124/mol.106.028720 }}</ref> |
25I-NBOMe acts as a highly [[potency (pharmacology)|potent]] [[agonist]] for the [[human]] [[5-HT2A receptor|5-HT<sub>2A</sub>]] [[Receptor (biochemistry)|receptor]],<ref>{{Cite doi|10.1007/s00259-010-1686-8}}</ref><ref name="pmid21088982">{{cite journal |author=Silva ME, Heim R, Strasser A, Elz S, Dove S |title=Theoretical studies on the interaction of partial agonists with the 5-HT(2A) receptor |journal=Journal of Computer-aided Molecular Design |volume=25 |issue=1 |pages=51–66 |year=2011 |month=January |pmid=21088982 |doi=10.1007/s10822-010-9400-2 |url=}}</ref> with a [[Dissociation constant|K<sub>i</sub>]] of 0.044 nM, making it some sixteen times the potency of 2C-I itself, and a [[isotopic labelling|radiolabelled]] form of 25I-NBOMe can be used for mapping the distribution of 5-HT<sub>2A</sub> receptors in the brain.<ref name="pmid18468904">{{cite journal |author=Nichols DE, Frescas SP, Chemel BR, Rehder KS, Zhong D, Lewin AH |title=High Specific Activity Tritium-Labeled N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenethylamine (INBMeO): A High Affinity 5-HT2A Receptor-Selective Agonist Radioligand |journal=Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry |volume=16 |issue=11 |pages=6116–23 |year=2008 |month=June |pmid=18468904 |pmc=2719953 |doi=10.1016/j.bmc.2008.04.050 |url=}}</ref><ref>{{Cite doi|10.2967/jnumed.109.074021}}</ref> ''[[In vitro]]'' tests showed this compound acted as an agonist but animal studies have not been reported. While the ''N''-benzyl derivatives of 2C-I were significantly increased in potency compared to 2C-I, the ''N''-benzyl derivatives of [[2,5-Dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine|DOI]] were inactive.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Braden | first1 = MR | last2 = Parrish | first2 = JC | last3 = Naylor | first3 = JC | last4 = Nichols | first4 = DE | title = Molecular interaction of serotonin 5-HT2A receptor residues Phe339(6.51) and Phe340(6.52) with superpotent N-benzyl phenethylamine agonists | journal = Molecular pharmacology | volume = 70 | issue = 6 | pages = 1956–64 | year = 2006 | pmid = 17000863 | doi = 10.1124/mol.106.028720 }}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 23:38, 4 February 2012
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H22INO3 |
| Molar mass | 427.277 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
25I-NBOMe (NBOMe-2C-I, BOM-CI, Cimbi-5) is a derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-I, discovered in 2003 by Ralf Heim at the Free University of Berlin,[1] and subsequently investigated in more detail by a team at Purdue University led by David Nichols.[2]
25I-NBOMe acts as a highly potent agonist for the human 5-HT2A receptor,[3][4] with a Ki of 0.044 nM, making it some sixteen times the potency of 2C-I itself, and a radiolabelled form of 25I-NBOMe can be used for mapping the distribution of 5-HT2A receptors in the brain.[5][6] In vitro tests showed this compound acted as an agonist but animal studies have not been reported. While the N-benzyl derivatives of 2C-I were significantly increased in potency compared to 2C-I, the N-benzyl derivatives of DOI were inactive.[7]
Anecdotal reports from human users suggest 25I-NBOMe to be an active hallucinogen at a dose of as little as 500 mcg, making it a similar potency to other phenethylamine derived hallucinogens such as bromo-dragonfly.[citation needed]
See also
- 2CBCB-NBOMe (NBOMe-TCB-2)
- 2CBFly-NBOMe (NBOMe-2CB-Fly)
- 25C-NBOMe (NBOMe-2CC)
- 25B-NBOMe (NBOMe-2CB)
- 25I-NBMD (NBMD-2CI)
- 25I-NBOH (NBOH-2CI)
- 25I-NBF (NBF-2CI)
- 5-MeO-NBpBrT
References
- ^ Ralf Heim PhD. Synthese und Pharmakologie potenter 5-HT2A-Rezeptoragonisten mit N-2-Methoxybenzyl-Partialstruktur. Entwicklung eines neuen Struktur-Wirkungskonzepts. (German)
- ^ Michael Robert Braden PhD. Towards a biophysical understanding of hallucinogen action. Purdue University 2007.
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1007/s00259-010-1686-8, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1007/s00259-010-1686-8instead. - ^ Silva ME, Heim R, Strasser A, Elz S, Dove S (2011). "Theoretical studies on the interaction of partial agonists with the 5-HT(2A) receptor". Journal of Computer-aided Molecular Design. 25 (1): 51–66. doi:10.1007/s10822-010-9400-2. PMID 21088982.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Nichols DE, Frescas SP, Chemel BR, Rehder KS, Zhong D, Lewin AH (2008). "High Specific Activity Tritium-Labeled N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenethylamine (INBMeO): A High Affinity 5-HT2A Receptor-Selective Agonist Radioligand". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 16 (11): 6116–23. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2008.04.050. PMC 2719953. PMID 18468904.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.2967/jnumed.109.074021, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.2967/jnumed.109.074021instead. - ^ Braden, MR; Parrish, JC; Naylor, JC; Nichols, DE (2006). "Molecular interaction of serotonin 5-HT2A receptor residues Phe339(6.51) and Phe340(6.52) with superpotent N-benzyl phenethylamine agonists". Molecular pharmacology. 70 (6): 1956–64. doi:10.1124/mol.106.028720. PMID 17000863.
