25-NB
The 25-NB (25x-NBx) series, sometimes alternatively referred to as the NBOMe compounds, is a family of serotonergic psychedelics.[1] They are substituted phenethylamines and were derived from the 2C family.[1] They act as selective agonists of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor.[2][3][4][5][6][7][8] The 25-NB family is unique relative to other classes of psychedelics in that they are, generally speaking, extremely potent and relatively selective for the 5-HT2A receptor.[1] Use of NBOMe series drugs has caused many deaths and hospitalisations since the drugs popularisation in the 2010s. This is primarily due to their high overdose potential and sellers passing off the compounds in the series as LSD.[9]
Chemical structure
The 25-NB compounds are mostly N-benzylphenethylamines,[1][10] though in some cases the phenyl ring of the N-benzyl group is replaced by other heterocycles such as thiophene, pyridine, furan, tetrahydrofuran, benzodioxole or naphthalene, among others.[11][12]
Generally speaking, they have methoxy groups at the 2 and 5 positions of the phenyl ring, a substitution such as a halogen or alkyl group at the 4 position of the phenyl ring, and a methoxy or other substitution (e.g., hydroxyl, fluoro) at the 2 position of the N-benzyl ring.[1] More rarely, other substitution patterns may be present [13][14] (see e.g. NBOMe-mescaline, 25G-NBOMe, 2CBFly-NBOMe, 25C-NB3OMe). They differ from the 2C series by the presence of the N-benzyl moiety.[1]
Rarely an alpha-methyl group is present making them N-benzyl amphetamines rather than N-benzyl phenethylamines, but this greatly reduces potency and activity. However in some cases where a side chain methyl group is cyclised back to the ring (e.g. in 2CBCB-NBOMe) or links the two alpha positions (e.g. in DMBMPP), this can improve selectivity for the 5-HT2A receptor subtype.[15]
List of 25-NB derivatives

This list includes notable compounds representative of most of the structural variations that have been explored in this series, but is by no means exhaustive. Many derivatives invented for scientific study into the structure-activity relationships of 5-HT2 receptor agonists have never appeared as designer drugs, while conversely some derivatives that have appeared as designer drugs are structurally novel and of unknown pharmacological activity (e.g. C30-NBOMe, 5-APB-NBOMe).
| Chemical structure | Common name | Chemical name | CAS number | R | R1 | Cyc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
25B-NB | N-benzyl-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 155639-26-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | phenyl |

|
25C-NB | N-benzyl-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391487-65-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | phenyl |

|
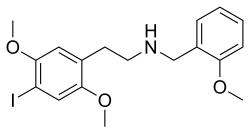
25I-NB | N-benzyl-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 919797-18-5 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | phenyl |
|
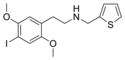
25I-NMeTh | N-[(thiophen-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391499-03-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | thiophen-2-yl |

|
25B-NMePyr | N-[(pyridin-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391499-21-0 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | pyridin-2-yl |

|
25I-NMeFur | N-[(furan-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391498-93-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | furan-2-yl |

|
25I-NMeTHF | N-[(tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | tetrahydrofuran-2-yl | |

|
25B-NBF | N-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1539266-17-5 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2-fluorophenyl |

|
25B-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1335331-46-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25B-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1026511-90-9 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
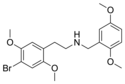
25B-NB23DM | N-(2,3-dimethoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391493-68-7 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2,3-dimethoxyphenyl |
|
25B-NB25DM | N-(2,5-dimethoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2,5-dimethoxyphenyl | |

|
25B-NMe7BF | N-[(benzofuran-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391492-46-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | benzofuran-7-yl |

|
25B-NMe7DHBF | N-[(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391492-40-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl |

|
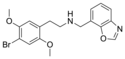
25B-NMe7BT | N-[(benzothiophen-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391492-59-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | benzothiophen-7-yl |
|
25B-NMe7Box | N-[(benzoxazol-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391498-73-9 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | benzoxazol-7-yl |

|
25B-NMe7Ind | N-[(indol-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391498-28-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | indol-7-yl |
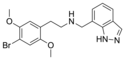
|
25B-NMe7Indz | N-[(indazol-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391498-43-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | indazol-7-yl |

|
25B-NMe7Bim | N-[(benzimidazol-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391498-62-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | benzimidazol-7-yl |

|
FECIMBI-36 | N-[(2-fluoroethoxy)benzyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2-(2-fluoroethoxy)phenyl | |
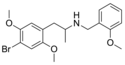
|
DOB-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminopropane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | methyl | 2-methoxyphenyl | |

|
25C-NB3OMe | N-(3-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1566571-34-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 3-methoxyphenyl |
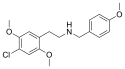
|
25C-NB4OMe | N-(4-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1566571-35-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 4-methoxyphenyl |
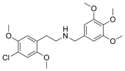
|
C30-NBOMe | N-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1445574-98-0 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl |

|
25C-NBF | N-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1539266-21-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-fluorophenyl |
|
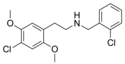
25C-NBCl | N-(2-chlorobenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-chlorophenyl | |

|
25C-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391488-16-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25C-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1227608-02-7 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25C-NBOEt | N-(2-ethoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-ethoxyphenyl | |
|
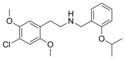
25C-NBOiPr | N-(2-isopropoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2-isopropoxyphenyl | |

|
25F-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-fluorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1373917-84-0 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-fluoro | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
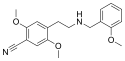
25CN-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-cyanophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1539266-32-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-cyano | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |
|
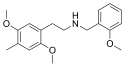
25CN-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-cyanophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-16-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-cyano | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |
|
25D-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-02-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methyl | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25D-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391488-44-0 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methyl | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25E-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-ethylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-14-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-ethyl | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25E-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-ethylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391489-79-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-ethyl | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |
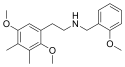
|
25G-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-65-7 | 2,5-dimethoxy-3,4-dimethyl | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25H-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1566571-52-5 | 2,5-dimethoxy | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25I-NB34MD | N-(3,4-methylenedioxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391497-81-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl |

|
25I-NB3OMe | N-(3-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1566571-40-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 3-methoxyphenyl |
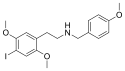
|
25I-NB4OMe | N-(4-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1566571-41-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 4-methoxyphenyl |
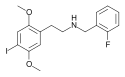
|
25I-NBF | N-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 919797-21-0 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-fluorophenyl |
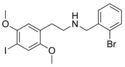
|
25I-NBBr | N-(2-bromobenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1648649-98-2 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-bromophenyl |
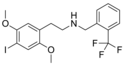
|
25I-NBTFM | N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl | |

|
25I-NBMD | N-(2,3-methylenedioxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 919797-25-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2,3-methylenedioxyphenyl |

|
25B-NBMD | N-(2,3-methylenedioxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-19-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo | H | 2,3-methylenedioxyphenyl |

|
25C-NBMD | N-(2,3-methylenedioxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1373879-26-5 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro | H | 2,3-methylenedioxyphenyl |
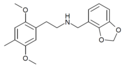
|
25D-NBMD | N-(2,3-methylenedioxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391488-97-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methyl | H | 2,3-methylenedioxyphenyl |

|
25I-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 919797-20-9 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |
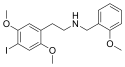
|
25I-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 919797-19-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
DOI-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | methyl | 2-methoxyphenyl | |

|
25I-NBMeOH | N-[2-(hydroxymethyl)benzyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391494-71-5 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl |

|
25I-NBAm | N-[2-(carbamoyl)benzyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391494-85-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2-(carbamoyl)phenyl |
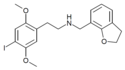
|
25I-NMe7DHBF | N-[(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl | |

|
25I-N2Nap1OH | N-[(1-hydroxynaphthalen-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 1-hydroxynaphthalen-2-yl | |

|
25I-N3MT2M | N-[(3-methoxythiophen-2-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-66-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 3-methoxythiophen-2-yl |

|
25I-N4MT3M | N-[(4-methoxythiophen-3-yl)methyl]-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-73-7 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo | H | 4-methoxythiophen-3-yl |
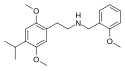
|
25iP-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-isopropylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391487-83-4 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-isopropyl | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25N-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-03-3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitro | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |
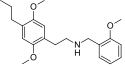
|
25P-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-propylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391489-07-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-propyl | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25P-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-propylphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1391490-34-8 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-propyl | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
25TFM-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1027161-33-6 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(trifluoromethyl) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25T-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(methylthio)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1539266-47-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(methylthio) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25T2-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(ethylthio)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1539266-51-7 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(ethylthio) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25T4-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(isopropylthio)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1354632-17-9 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(isopropylthio) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25T7-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(propylthio)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1539266-55-1 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(propylthio) | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
25T7-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-(propylthio)phenyl]-2-aminoethane | 1354632-41-9 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(propylthio) | H | 2-hydroxyphenyl |

|
NBOMe-mescaline | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 1354632-01-1 | 3,4,5-trimethoxy | H | 2-methoxyphenyl |

|
NBOMe-escaline | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(3,5-dimethoxy-4-ethoxyphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 3,5-dimethoxy-4-ethoxy | H | 2-methoxyphenyl | |

|
MDPEA-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-2-aminoethane | 3,4-methylenedioxy | H | 2-methoxyphenyl | |
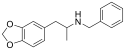
|
MDBZ | N-benzyl-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-2-aminopropane | 65033-29-6 | 3,4-methylenedioxy | methyl | phenyl |
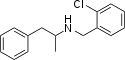
|
Clobenzorex | N-(2-chlorobenzyl)-1-phenyl-2-aminopropane | 13364-32-4 | H | methyl | 2-chlorophenyl |

|
4-EA-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(4-ethylphenyl)-2-aminopropane | 4-ethyl | methyl | 2-methoxyphenyl | |
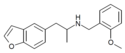
|
5-APB-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(benzofuran-5-yl)-2-aminopropane | benzofuran-5-yl instead of phenyl | methyl | 2-methoxyphenyl |
Similar compounds with related structures are also known including;
| Chemical structure | Common name | Chemical name | CAS number |
|---|---|---|---|

|
25B-N1POMe | N-[1-(2-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]-2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenethylamine | 1335331-49-1 (R) 1335331-51-5 (S) |

|
2C-B-AN [16] | 2-phenyl-2-[2-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)ethylamino]acetonitrile | |

|
2CBCB-NBOMe | N-[(3-bromo-2,5-dimethoxy-bicyclo[4,2,0]octa-1,3,5-trien-7-yl)methyl]-1-(2-methoxyphenyl)methanamine | 1354634-09-5 |
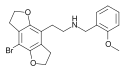
|
2CBFly-NBOMe | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-1-(8-bromo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[1,2-b:4,5-b’]difuran-4-yl)-2-aminoethane | 1335331-42-4 |
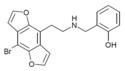
|
2C-B-DRAGONFLY-NBOH | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-1-(8-bromobenzo[1,2-b:4,5-b’]difuran-4-yl)-2-aminoethane | 1335331-45-7 |

|
2C-B-FLY-NB2EtO5Cl [17] | N-(2-ethoxy-5-chlorobenzyl)-1-(8-bromo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[1,2-b:4,5-b’]difuran-4-yl)-2-aminoethane | |
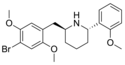
|
DMBMPP | (S,S)-2-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromobenzyl)-6-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperidine | 1391499-52-7 |
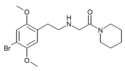
|
25B-NAcPip | 2-{[2-(4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]amino}-1-(piperidin-1-yl)ethanone | |

|
ZDCM-04 | 1,3-dimethyl-7-{2-[1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)propan-2-ylamino]ethyl}purine-2,6-dione | |
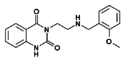
|
RH-34 | 3-[2-(2-methoxybenzylamino)ethyl]-1H-quinazoline-2,4-dione | 1028307-48-3 |
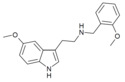
|
5MT-NBOMe [18] | N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-5-methoxytryptamine | 1335331-37-7 |

|
5MT-NB3OMe | N-(3-methoxybenzyl)-5-methoxytryptamine | 1648553-42-7 |
Legality
United Kingdom
A large number of substances in the 25-NB class are Class A drugs in the United Kingdom as a result of the N-benzylphenethylamine catch-all clause in the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971[19] or are otherwise covered by the Psychoactive Substances Act 2016.[20]
See also
External links
References
- ^ a b c d e f Halberstadt AL (2017). "Pharmacology and Toxicology of N-Benzylphenethylamine ("NBOMe") Hallucinogens". Curr Top Behav Neurosci. Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. 32: 283–311. doi:10.1007/7854_2016_64. ISBN 978-3-319-52442-9. PMID 28097528.
- ^ Pertz, HH; Rheineck, A; Elz, S (1999-01-01). "N-Benzylated derivatives of the hallucinogenic drugs mescaline and escaline as partial agonists at rat vascular 5-HT2A receptors". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 359: R29. Archived from the original on September 25, 2015.
- ^ Heim R (February 28, 2010). "Synthese und Pharmakologie potenter 5-HT2A-Rezeptoragonisten mit N-2-Methoxybenzyl-Partialstruktur. Entwicklung eines neuen Struktur-Wirkungskonzepts" (in German). diss.fu-berlin.de. Retrieved 2013-05-10.
- ^ Silva M (2009). Theoretical study of the interaction of agonists with the 5-HT2A receptor (Ph.D. thesis). Universität Regensburg.
- ^ Hansen M (2011). Design and Synthesis of Selective Serotonin Receptor Agonists for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of the Brain (Ph.D. thesis). University of Copenhagen.
- ^ Silva ME, Heim R, Strasser A, Elz S, Dove S (January 2011). "Theoretical studies on the interaction of partial agonists with the 5-HT(2A) receptor". Journal of Computer-aided Molecular Design. 25 (1): 51–66. Bibcode:2011JCAMD..25...51S. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.688.2670. doi:10.1007/s10822-010-9400-2. PMID 21088982. S2CID 3103050.
- ^ Rickli, Anna; Luethi, Dino; Reinisch, Julian; Buchy, Danièle; Hoener, Marius C.; Liechti, Matthias E. (2015). "Receptor interaction profiles of novel N-2-methoxybenzyl (NBOMe) derivatives of 2,5-dimethoxy-substituted phenethylamines (2C drugs)" (PDF). Neuropharmacology. 99: 546–553. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.08.034. PMID 26318099. S2CID 10382311.
- ^ Hansen M, Phonekeo K, Paine JS, Leth-Petersen S, Begtrup M, Bräuner-Osborne H, Kristensen JL (March 2014). "Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of N-benzyl phenethylamines as 5-HT2A/2C agonists". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 5 (3): 243–9. doi:10.1021/cn400216u. PMC 3963123. PMID 24397362.
- ^ Lipow, Matthew; Kaleem, Syed; Espiridion, Eduardo (2022-03-30). "NBOMe Toxicity and Fatalities: A Review of the Literature". Transformative Medicine (T-Med). 1 (1): 12–18. doi:10.54299/tmed/msot8578. ISSN 2831-8978.
- ^ Poulie, Christian B. M.; Jensen, Anders A.; Halberstadt, Adam L.; Kristensen, Jesper L. (2019). "DARK Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: NBOMes". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 11 (23): 3860–3869. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00528. PMID 31657895. S2CID 204952449.
- ^ Michael Robert Braden (2007). "Towards a biophysical understanding of hallucinogen action". Dissertation: 1–176.
- ^ Nichols, David E. (2012). "Structure-activity relationships of serotonin 5-HT2A agonists". Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Membrane Transport and Signaling. 1 (5): 559–579. doi:10.1002/wmts.42.
- ^ Leth-Petersen, Sebastian; Petersen, Ida N.; Jensen, Anders A.; Bundgaard, Christoffer; Bæk, Mathias; Kehler, Jan; Kristensen, Jesper L. (2016). "5-HT2A/5-HT2C Receptor Pharmacology and Intrinsic Clearance of N-Benzylphenethylamines Modified at the Primary Site of Metabolism". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 7 (11): 1614–1619. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.6b00265. PMID 27564969.
- ^ Prabhakaran, Jaya; Solingapuram Sai, Kiran Kumar; Zanderigo, Francesca; Rubin-Falcone, Harry; Jorgensen, Matthew J.; Kaplan, Jay R.; Tooke, Katharine I.; Mintz, Akiva; Mann, J. John; Kumar, J.S. Dileep (2017). "In vivo evaluation of [ 18 F]FECIMBI-36, an agonist 5-HT 2A/2C receptor PET radioligand in nonhuman primate". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 27 (1): 21–23. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.11.043. PMC 5348621. PMID 27889455.
- ^ Juncosa JI, Hansen M, Bonner LA, Cueva JP, Maglathlin R, McCorvy JD, Marona-Lewicka D, Lill MA, Nichols DE (January 2013). "Extensive rigid analogue design maps the binding conformation of potent N-benzylphenethylamine 5-HT2A serotonin receptor agonist ligands". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 4 (1): 96–109. doi:10.1021/cn3000668. PMC 3547484. PMID 23336049.
- ^ Daniel Trachsel, David Lehmann and Christoph Enzensperger. Phenethylamine Von der Struktur zur Funktion, p 843. Nachtschatten Verlag AG, 2013. ISBN 978-3-03788-700-4
- ^ Richter, Lilian H. J.; Menges, Julia; Wagmann, Lea; Brandt, Simon D.; Stratford, Alexander; Westphal, Folker; Flockerzi, Veit; Meyer, Markus R. (2020). "In vitro toxicokinetics and analytical toxicology of three novel NBOMe derivatives: Phase I and II metabolism, plasma protein binding, and detectability in standard urine screening approaches studied by means of hyphenated mass spectrometry" (PDF). Forensic Toxicology. 38: 141–159. doi:10.1007/s11419-019-00498-7. S2CID 202879918.
- ^ Nichols, David E.; Sassano, M. Flori; Halberstadt, Adam L.; Klein, Landon M.; Brandt, Simon D.; Elliott, Simon P.; Fiedler, Wolfgang J. (2015). "N-Benzyl-5-methoxytryptamines as Potent Serotonin 5-HT2Receptor Family Agonists and Comparison with a Series of Phenethylamine Analogues". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 6 (7): 1165–1175. doi:10.1021/cn500292d. PMC 4505863. PMID 25547199.
- ^ "The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (Ketamine etc.) (Amendment) Order 2014". www.legislation.gov.uk.
- ^ "Psychoactive Substances Act 2016". www.legislation.gov.uk.
