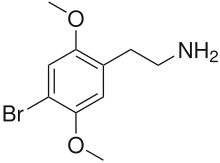
2C-B
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral, insufflation, vaporization, rectal |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Onset of action | 1 minute–75 minutes depending on route of administration |
| Elimination half-life | 2.48 ± 3.20 h[1] |
| Duration of action | 4–12 hours depending on route of administration |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.088 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H14BrNO2 |
| Molar mass | 260.131 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
2C-B or 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenethylamine is a psychedelic drug of the 2C family. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin in 1974. In Shulgin's book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 12–24 mg. 2C-B is sold as a white powder sometimes pressed in tablets or gel caps and is also referred to by a number of other names.[2] The drug is usually taken orally, but can also be snorted (insufflated) or vaporized.
History
2C-B was synthesized from 2,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde by Alexander Shulgin in 1974. It first saw use among the psychiatric community as an aid during therapy. It was considered one of the best drugs for this purpose because of its short duration, relative absence of side effects, and comparably mild nature.[3] Shortly after becoming popular in the medical community, it became popular recreationally. 2C-B was first sold commercially as an aphrodisiac[4] under the trade name "Erox", which was manufactured by the German pharmaceutical company Drittewelle.[5] For several years, it was available as tablets in Dutch smart shops under the name "Nexus".
Patterns of use
2C-B first became popularized in the United States as a short-lived legal substitute for the street drug Ecstasy when MDMA became illegal in 1985.[6] Many 2C-B users are young adults who attend raves.[2] Though 2C-B is still used in the rave subculture, commonly mistaken for and/or sold as Ecstasy, its intentional use has become more common in the 2000s.[7] Since 2013, 2C-B has emerged as the drug of choice for club drug users in Colombia.[6]
Street prices range between $10 and $30 per tablet in the United States in 2011 when purchased in small quantities.[2] Larger retail purchases cost between $200 and $500 per gram. Wholesale purchases of 2C-B can lower the price ($100 to $300 per gram in 2001[needs update]).[4]
Toxicity and dosage
The September 1998 Journal of Analytical Toxicology reported that very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of 2C-B. The relationship between its use and death are unknown.[4] The common oral recreational dose is around 15–25 mg,[8] at which visual and auditory effects are experienced. Severe adverse reactions are extremely rare, but use of 2C-B has been linked to significant brain injury in one case where the dosage was unknown, and the purity of the chemical was not verified.[9]
| Oral | Insufflated | |
|---|---|---|
| ED50 | 10 mg | 4–6 mg |
| Moderate | 15–25 mg | 5–9 mg |
| Strong | 26–35 mg | 10–20 mg |
| Extremely Intense | >35 mg | >20 mg |
| Duration | 4–8 hours | 2–4 hours |
The lethal dosage is unknown. It was reported in PiHKAL, by Alexander Shulgin, that a psychologist had accidentally taken a 100 mg dose orally without apparent harm.[10]
When sold as "Ecstasy", tablets containing 2C-B often contain about 5 mg of the drug, an amount which produces stimulatory effects that mimic the effects of MDMA; in contrast, tablets marketed as 2C-B have larger quantities of the drug (10–20 mg) which cause hallucinogenic effects.[11] Street purity of 2C-B, when tested, has been found to be relatively high.[12] Researchers in Spain found that 2C-B samples in the country doubled between 2006 and 2009, switched from primarily powder form to tablets, and exhibited "low falsification rates".[13] An analysis of street samples in the Netherlands found impurities "in small percentages"; only one of the impurities, the N-acetyl derivative of 2C-B, could be identified, and comprised 1.3% of the sample. The authors suggested that this compound was a by-product of 2C-B synthesis.[11]
Effects

Little or no academic research has been conducted on the effects of 2C-B in humans. The information available is largely anecdotal and limited. Effects are often described as being more easily managed than other psychedelics;[14] it is often compared to a mixture of a serotonergic psychedelic and MDMA.[13] At 5–10 mg, experiments with young chickens have shown it to produce effects similar to a low dosage of amphetamines.[15]
The anecdotal effects of 2C-B that have been reported by users on online discussion forums include:[3][16][17]
- At low doses the experience may shift in intensity from engaging to mild/undetectable. Experienced users report the ability to take control of the effects and switch from engaged to sober at will
- The hallucinations have a tendency to decrease and then increase in intensity, giving the users a sense of “waves” or even glowing. These are popularly described as “clichéd ’70s visuals” or objects taking on "water color" like textures
- While the effects of the drug often render users unable to concentrate deeply on anything in particular, some can become engrossed in an activity such as watching a movie or playing a video game, distracting themselves from the visual and auditory effects of the drug
- Excessive giggling or smiling is common, as is a tendency for deeper “belly laughs”
- Some users say that the effects are more intense when listening to music and report that they can see sounds and noises
- Some users experience a decrease in visual acuity, although others report sharper vision
- Increased awareness of one’s body; attention may be brought to perceived "imperfections" or internal body processes.
The following effects are highly dose-dependent.
- Open eye visuals (OEVs), such as cartoon-like distortions and red or green halos around objects. Closed eye visuals (CEVs) are more common than OEVs.
- Affects and alters ability to communicate, engage in deep thought, or maintain attention span.
- Some users report experiencing frightening or fearful effects during the experience. Users describe feeling frigid or cold on reaching a plateau, while others feel wrapped in comfortable blankets/ultimate pleasure.
- Coordination may be affected, some users lose balance or have perceptual distinction problems.
- Onset time of 2C-B is highly dose dependent, but usually from 45 to 75 minutes. Taken on a full stomach, the onset time is increased to two hours or more.
- Before it was scheduled, 2C-B was sold in small doses as an aphrodisiac (see History). Some users report aphrodisiac effects at lower doses.[10][16]
Side effects
- Some users report mild "jitters" (body tremors), shuddering breath, and/or mild muscle spasms after insufflating 2C-B. Whether or not these effects are enjoyable depends on the user
- Mild to intense diarrhea, gas, nausea, and general gastrointestinal discomfort
- Severe headaches after coming down from large doses have been reported. However, many users report a lack of "comedown" or "crash", instead noting a gradual return to sobriety
- At doses over 30–40 mg the user may experience frightening hallucinations, as well as tachycardia, hypertension, and hyperthermia[18]
- 2C-B HCl is very painful to insufflate. Anecdotal evidence suggests that 2C-B HBr, the hydrobromide salt with greater water solubility, is less irritating to the mucous membranes lining the nose but slightly less potent when compared dose-for-dose with the HCl salt.[19]
Duration
When orally consumed, 2C-B has a much longer delay before the onset of effects than when it is insufflated. Oral ingestion generally takes roughly 45–75 minutes for the effects to be felt, plateau lasts 2–4 hours, and coming down lasts 1–2 hours. Rectal administration ("boofing") onset varies from 5–20 minutes. Insufflated onset takes 1–10 minutes for effects to be felt. The duration can last from 4 to 12 hours depending on route of administration, dose, and other factors.[3]
With insufflation, the effects are more abrupt and intense but have a significantly shorter duration, while oral usage results in a milder, longer experience. When insufflated, the onset happens very rapidly, usually reaching the peak at about 20–40 minutes and plateauing for 2–3 hours. 2C-B is also considered one of the most painful drugs to insufflate, with users reporting intense nasal burning[14] lasting as long as 30 minutes.[20][unreliable source?] The sudden intensity of the experience combined with the pain can often start the experience with a negative imprint and nausea is also increased with insufflation, compounding the issue.
Pharmacology
Unlike most hallucinogens, 2C-B has been shown to be a low efficacy serotonin 5-HT2A receptor partial agonist or even full antagonist.[21][22] This suggests that the 5-HT2C receptor is primarily responsible for mediating the effects experienced by users of 2C-B, although functional antagonism of 5-HT2A or activation of the 5-HT2A-coupled phospholipase D pathway may also play a role.[21] The rank order of 5-HT2A receptor antagonist potency for this family of drugs is 2C-I > 2C-B > 2C-D > 2C-H.[22]
Research suggests that 2C-B increases dopamine levels in the brains of rats, which may contribute to its psychoactivity.[23]
Metabolism
2C-B has been shown to be metabolized by liver hepatocytes, resulting in deamination and demethylation that produces several products. Oxidative deamination results in the 2-(4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-ethanol (BDMPE) and 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenylacetic acid (BDMPAA) metabolites. Additionally, 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxybenzoic acid (BDMBA) can also be produced by oxidative deamination. Further metabolism of BDMPE and BDMPAA may occur by demethylation. Alternatively, the later metabolites can be generated by demethylation of 2C-B followed by oxidative deamination.[18]
There is species differentiation in the metabolism of 2C-B. Mice hepatocytes produce 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxy-phenol (BDMP), a previously unknown metabolite. Meanwhile, human, monkey and rabbit hepatocytes produce 2-(4-bromo-2-hydroxy-5-methoxyphenyl)-ethanol (B-2-HMPE), but dog, rat and mouse hepatocytes do not.[18] 2C-B also reduces aggressive responses in drugged rats.[24]
Analogues and derivatives
Analogues and derivatives of 2C-B:
25-N:
- 25B-NB
- 25B-NB23DM
- 25B-NB25DM
- 25B-NB3OMe
- 25B-NB4OMe
- 25B-NBF
- 25B-NBMD
- 25B-NBOH
- 25B-NBOMe (NBOMe-2CB)
- 2C-B-FLY
- 2CBFly-NBOMe (NBOMe-2CB-Fly)
- DOB-FLY
- DOB-2-DRAGONFLY-5-BUTTERFLY
Other:
- BOB
- BOH-2C-B, β-Hydroxy-2C-B, βOH-2CB[27][28]
- BMB
- 2C-B-5-hemifly
- 2C-B-aminorex (2C-B-AR)
- 2C-B-AN
- 2C-B-BZP
- 2C-B-FLY-NB2EtO5Cl
- 2C-B-PP
- 2CB-Ind
- βk-2C-B (beta-keto 2C-B)
- N-Ethyl-2C-B
- TCB-2 (2C-BCB)
A variety of N-substituted derivatives of 2C-B have been tested, including N-methyl-2CB, N,N-dimethyl-2CB, N-ethyl-2CB and N-benzyl-2CB. Most simple alkyl derivatives were considerably less potent than 2C-B, with N-ethyl-2CB for instance having a 40 times lower affinity for the 5-HT2A receptor. The N-benzyl derivative however was found to have higher binding affinity than 2C-B itself, with N-(4-bromobenzyl)-2CB binding even more tightly.[29] This initial research did not include functional assays of activity, but later led to the development of potent substituted N-benzyl derivatives such as 25B-NBOMe,[30] and 25B-NBOH.
Entheogenic use
2C-B is used as entheogen by the Sangoma, Nyanga, and Amagqirha people over their traditional plants; they refer to the chemical as Ubulawu Nomathotholo, which roughly translates to "Medicine of the Singing Ancestors".[31][32][33]
Drug prohibition laws
United Nations
The UN Commission on Narcotic Drugs added 2C-B to Schedule II of the Convention on Psychotropic Substances in March 2001.[34]
2C-B was mislabelled "2 C-B" in the Green List 26th edition, 2015.[35] However, this was corrected in Green List 27th edition, 2016.[36]
2C-B is a scheduled drug in most jurisdictions.[37] The following is a partial list of territories where the substance has been scheduled.
Countries
Argentina
2C-B is controlled under the List 1, as well as similar substances like 2C-I or 2C-T-2.[38]
Australia
2C-B is controlled in Australia and on the list of substances subject to import and export controls (Appendix B). It was placed on Schedule One of the Drugs Misuse and Trafficking Act when it first came to notice in 1994, when in a showcase legal battle chemist R. Simpson was charged with manufacturing the substance in Sydney. Alexander Shulgin came to Australia to testify on behalf of the defense, to no avail.
2C-B is not specifically listed in the Australia Poisons Standard (October 2015), however similar drugs such as 2C-T-2 and 2C-I are making 2C-B fall under the Australian analogue act.[39]
Brazil
In Brazil, 2C-B is a controlled substance making production, distribution, and possession illegal.
Belgium
In Belgium, 2C-B is a controlled substance making production, distribution, and possession illegal.
Canada
In Canada, 2C-B is classified under Controlled Drugs and Substances Act as Schedule III as "4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxybenzeneethanamine and any salt, isomer or salt of isomer thereof".[40]
2C-B has been rescheduled (Schedule III), in a new amendment, taking effect on October 31, 2016. This is to include the other 2C-x analogues.[41]
Chile
In August 2007, 2C-B (4-bromo-2,5-dimetoxifenetilamina), along with many other psychologically active substances,[42] was added to Ley 20.000, known as the Ley de Drogas.
Czech Republic
Possession of more than 200 mg of 2C-B is punishable with a two years jail sentence.[43]
Denmark
In Denmark, 2C-B is listed as a category B drug.[44]
Estonia
In Estonia, 2C-B is classified as Schedule I.
Germany
In Germany, 2C-B is controlled in the Betäubungsmittelgesetz (BtMG) Anlage I as "Bromdimethoxyphenethylamin" (BDMPEA).
Italy
2C-B is schedule I (tabella I).[45]
Japan
In Japan, 2C-B was scheduled in 1998. It was previously marketed as "Performax".
Netherlands
In the Netherlands, 2C-B was scheduled on July 9, 1997.
In the Netherlands, 2C-B became a list I substance of the Opium Law despite no health incidents occurring. Following the ban, other phenethylamines were sold in place of 2C-B until the Netherlands became the first country in the world to ban 2C-I, 2C-T-2 and 2C-T-7 alongside 2C-B.
Norway
In Norway, 2C-B was classified as Schedule II on March 22, 2004, listed as 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine.[46]
Poland
2C-B is schedule I (I-P group) in Poland.
Russia
Banned as a narcotic drug with a criminal penalty for possession of at least 10 mg.[47]
Spain
In Spain, 2C-B was added to Category 2 prohibited substances in 2002.
Sweden
2C-B is currently classified as Schedule I in Sweden.
2C-B was first classified as "health hazard" under the act Lagen om förbud mot vissa hälsofarliga varor (translated: Act on the Prohibition of Certain Goods Dangerous to Health) as of April 1, 1999, under SFS 1999:58[48] that made it illegal to sell or possess. Then it became schedule I as of June 1, 2002, publicated in LVFS 2002:4[49] but mislabeled "2-CB" in the document. However, this was corrected in a new document, LVFS 2009:22[50] effective December 9, 2009.
Switzerland
In Switzerland, 2C-B is listed in Anhang D of the DetMV and is illegal to possess.[51]
UK
All drugs in the 2C family are Class A under the Misuse of Drugs Act which means they are illegal to produce, supply or possess. Possession carries a maximum sentence of seven years imprisonment while supply is punishable by life imprisonment and an unlimited fine.[52]
United States
In the United States, 2C-B is classified as CSA Schedule I Section (d) Subsection (3) 4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine.
In the United States, a notice of proposed rulemaking published on December 20, 1994, in the Federal Register and after a review of relevant data, the Deputy Administrator of the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) proposed to place 4-bromo-2,5-DMPEA into Schedule I, making 2C-B illegal in the United States.[53] This became permanent law on July 2, 1995.[citation needed]
References
- ^ Papaseit E, Farré M, Pérez-Mañá C, Torrens M, Ventura M, Pujadas M, de la Torre R, González D (2018). "Acute Pharmacological Effects of 2C-B in Humans: An Observational Study". Frontiers in Pharmacology. 9: 206. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00206. PMC 5859368. PMID 29593537.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b c "2C-B Street Names" (PDF). February 1, 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 16, 2012. Retrieved 2012-09-28.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c "Erowid 2C-B Vault: Effects". Erowid. Retrieved 2013-09-25.
- ^ a b c "2C-B (Nexus) Reappears on the Club Drug Scene" (PDF). National Drug Intelligence Center. Department of Justice. May 2001. Retrieved 11 February 2013.
- ^ "Drittewelle 2C-B Packaging". Erowid.org. 2002. Retrieved 25 September 2013.
- ^ a b Pachico, Elyssa (1 November 2012). "'2CB Now Drug of Choice for Colombia Elite'". InSight Crime. Retrieved 11 February 2013.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Gahlinger, Paul (2004). Illegal Drugs: A Complete Guide to Their History, Chemistry, Use and Abuse. Penguin. pp. 343–344. ISBN 9780452285057.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ "Erowid 2C-B Vault : Dose/Dosage".
- ^ Ambrose JB, Bennett HD, Lee HS, Josephson SA (May 2010). "Cerebral vasculopathy after 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine ingestion". The Neurologist. 16 (3): 199–202. doi:10.1097/NRL.0b013e3181a3cb53. PMID 20445431.
- ^ a b "Shulgin, A (1991) PIHKAL". Erowid.org. Retrieved May 15, 2012.
- ^ a b de Boer D, Gijzels MJ, Bosman IJ, Maes RA (1999). "More data about the new psychoactive drug 2C-B". Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 23 (3): 227–8. doi:10.1093/jat/23.3.227. PMID 10369336.
- ^ Cole MD, Lea C, Oxley N (October 2002). "4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine (2C-B): a review of the public domain literature". Science & Justice. 42 (4): 223–4. doi:10.1016/S1355-0306(02)71832-7. PMID 12632938.[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b Caudevilla-Gálligo F, Riba J, Ventura M, González D, Farré M, Barbanoj MJ, Bouso JC (July 2012). "4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine (2C-B): presence in the recreational drug market in Spain, pattern of use and subjective effects". Journal of Psychopharmacology. 26 (7): 1026–35. doi:10.1177/0269881111431752. PMID 22234927.
- ^ a b "Erowid 2C-B Vault: Basics". Erowid. 2011-02-20. Retrieved 2013-09-25.
- ^ Bronson ME, Jiang W, DeRuiter J, Clark CR (1995). "A behavioral comparison of Nexus, cathinone, BDB, and MDA". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 51 (2–3): 473–5. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(95)00013-M. PMID 7667371.
- ^ a b "Drugscope: 2C-B". Drugscope. Jan 2004. Archived from the original on 2013-09-28. Retrieved 2013-09-25.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "2C-B - Dancesafe.org". Dancesafe. Retrieved 2013-09-25.
- ^ a b c Carmo H, Hengstler JG, de Boer D, Ringel M, Remião F, Carvalho F, Fernandes E, dos Reys LA, Oesch F, de Lourdes Bastos M (January 2005). "Metabolic pathways of 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine (2C-B): analysis of phase I metabolism with hepatocytes of six species including human". Toxicology. 206 (1): 75–89. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2004.07.004. PMID 15590110.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ^ "Erowid 2C-B Vault : FAQ v1.0". erowid.org.
- ^ Cole, Krystle. "Neurosoup: 2C-B". Neurosoup.com. Retrieved 2013-10-17.
- ^ a b Moya PR, Berg KA, Gutiérrez-Hernandez MA, Sáez-Briones P, Reyes-Parada M, Cassels BK, Clarke WP (June 2007). "Functional selectivity of hallucinogenic phenethylamine and phenylisopropylamine derivatives at human 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)2A and 5-HT2C receptors". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 321 (3): 1054–61. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.117507. PMID 17337633.
- ^ a b Villalobos CA, Bull P, Sáez P, Cassels BK, Huidobro-Toro JP (April 2004). "4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine (2C-B) and structurally related phenylethylamines are potent 5-HT2A receptor antagonists in Xenopus laevis oocytes". British Journal of Pharmacology. 141 (7): 1167–74. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0705722. PMC 1574890. PMID 15006903.
- ^ Páleníček T, Fujáková M, Brunovský M, Horáček J, Gorman I, Balíková M, Rambousek L, Syslová K, Kačer P, Zach P, Bubeníková-Valešová V, Tylš F, Kubešová A, Puskarčíková J, Höschl C (January 2013). "Behavioral, neurochemical and pharmaco-EEG profiles of the psychedelic drug 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine (2C-B) in rats". Psychopharmacology. 225 (1): 75–93. doi:10.1007/s00213-012-2797-7. PMID 22842791.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ^ Muehlenkamp F, Lucion A, Vogel WH (April 1995). "Effects of selective serotonergic agonists on aggressive behavior in rats". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 50 (4): 671–4. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(95)00351-7. PMID 7617717.
- ^ "Explore N-(2C-B)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ^ "Explore N-(2C-FLY)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ^ Glennon, Richard A.; Bondarev, Mikhail L.; Khorana, Nantaka; Young, Richard; May, Jesse A.; Hellberg, Mark R.; McLaughlin, Marsha A.; Sharif, Najam A. (November 2004). "β-Oxygenated Analogues of the 5-HT2ASerotonin Receptor Agonist 1-(4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminopropane". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 47 (24): 6034–6041. doi:10.1021/jm040082s. ISSN 0022-2623. PMID 15537358.
- ^ Beta-hydroxyphenylalkylamines and their use for treating glaucoma
- ^ Glennon RA, Dukat M, el-Bermawy M, Law H, De los Angeles J, Teitler M, King A, Herrick-Davis K (June 1994). "Influence of amine substituents on 5-HT2A versus 5-HT2C binding of phenylalkyl- and indolylalkylamines". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 37 (13): 1929–35. doi:10.1021/jm00039a004. PMID 8027974.
- ^ Heim, Ralf (March 19, 2004). Synthese und Pharmakologie potenter 5-HT2A-Rezeptoragonisten mit N-2-Methoxybenzyl-Partialstruktur: Entwicklung eines neuen Struktur-Wirkungskonzepts [Synthesis and pharmacology of potent 5-HT2A receptor agonists which have a partial N-2-methoxybenzyl structure: Development of a new structure-activity concept] (Thesis) (in German). Free University of Berlin. Retrieved August 1, 2014.
{{cite thesis}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ "2CB chosen over traditional entheogen's by South African healers". Tacethno.com. 2008-03-27. Retrieved May 15, 2012.
- ^ The Nexus Factor - An Introduction to 2C-B Erowid
- ^ Ubulawu Nomathotholo Pack Photo by Erowid. © 2002 Erowid.org
- ^ "List of psychotropic substances under international control" (PDF). Green List (23rd ed.). International Narcotics Control Board. August 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 March 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "List of Psychotropic Substances under International Control" (PDF). Green List (26th ed.). International Narcotics Control Board. 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 October 2017.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "List of Psychotropic Substances under International Control" (PDF). Green List (27th ed.). International Narcotics Control Board. 2016. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-04-21. Retrieved 2017-04-20.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Erowid 2C-B page".
- ^ "Last Argentina Controlled Drugs List" (PDF). Retrieved May 15, 2012.
- ^ Poisons Standard October 2015 https://www.comlaw.gov.au/Details/F2015L01534
- ^ "CDSA Schedule II".
- ^ "Regulations Amending the Food and Drug Regulations (Part J — 2C-phenethylamines)". Canada Gazette. Government of Canada, Public Works and Government Services Canada, Public Services and Procurement Canada, Integrated Services Branch, Canada.
- ^ "APRUEBA REGLAMENTO DE LA LEY Nº 20.000 QUE SANCIONA EL TRÁFICO ILÍCITO DE ESTUPEFACIENTES Y SUSTANCIAS SICOTRÓPICAS Y SUSTITUYE LA LEY Nº 19.366" (PDF).
- ^ "Erowid Psychoactive Vaults : Drug Laws : Czech Republic". www.erowid.org.
- ^ "Bekendtgørelse om euforiserende stoffer" (in Danish). 2008-07-01. Retrieved 2013-10-01.
- ^ "Italy Drug Schedule (Tabella I)". Archived from the original on 2011-06-27.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Norway Drug Schedule".
- ^ "Постановление Правительства РФ от 01.10.2012 N 1002 "Об утверждении значительного, крупного и особо крупного размеров наркотических средств и психотропных веществ, а также значительного, крупного и особо крупного размеров для растений, содержащих наркотические средства или психотропные вещества, либо их частей, содержащих наркотические средства или психотропные вещества, для целей статей 228, 228.1, 229 и 229.1 Уголовного кодекса Российской Федерации" (с изменениями и дополнениями)". base.garant.ru.
- ^ "Förordning (1999:58) om förbud mot vissa hälsofarliga varo" (in Swedish). 1999-02-25. Retrieved 2013-10-01.
- ^ "Föreskrifter om ändring i Läkemedelsverkets föreskrifter (LVFS 1997:12) om förteckningar över narkotika: LVFS 2002:4" (PDF) (in Swedish).
- ^ "Föreskrifter om ändring i Läkemedelsverkets föreskrifter (LVFS 1997:12) om förteckningar över narkotika: LVFS 2009:22" (PDF) (in Swedish).
- ^ "Verzeichnis aller betäubungsmittelhaltigen Stoffe" [Directory of all narcotics-containing substances]. Swissmedic (in German). Swiss Agency for Therapeutic Products. 2011-08-18. p. 2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-15. Retrieved 2013-11-30.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "BBC - Advice - 2CB". BBC. Retrieved 2013-10-01.
- ^ "Schedules of Controlled Substances; Proposed Placement of 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine into Schedule I" (PDF). Federal Register. 59 (243): 65521. 20 December 1994. Retrieved 2013-09-26.
External links
- 2C-B Entry in PiHKAL
- 2C-B Entry in PiHKAL • info
- Erowid 2C-B vault—includes reports from users of 2C-B, as well as scientific and government reports
- 2C-B Dosage chart
