Urokinase receptor
The Urokinase receptor, also known as uPA receptor or uPAR or CD87 (Cluster of Differentiation 87), is a multidomain glycoprotein tethered to the cell membrane with a glycosylphosphotidylinositol (GPI) anchor. uPAR was originally identified as a saturable binding site for urokinase on the cell surface.
Molecular characteristics
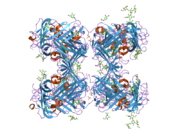
uPAR consists of three different domains of the three-finger protein domain family, which also includes domains found in lymphocyte antigen 6 and in snake venom toxins of the three-finger toxin family, such as alpha-neurotoxins.[5] All three three-finger domains are necessary for high affinity binding of the primary ligand, urokinase. It has been possible to express uPAR recombinantly in CHO-cells and S2 cells from Drosophila melanogaster. 4 out of 5 of the possible glycosylation sites are used in vivo giving the protein a molecular weight of 50-60 kDA. Recently the structure of uPAR was solved by X-ray crystallography in complex with a peptide antagonist[6] and with its native ligand, urokinase.[7]
Besides the primary ligand urokinase, uPAR interacts with several other proteins, among others: vitronectin, the uPAR associated protein (uPARAP) and the integrin family of membrane proteins.
Physiological significance
uPAR is a part of the plasminogen activation system, which in the healthy body is involved in tissue reorganization events such as mammary gland involution and wound healing. In order to be able to reorganize tissue, the old tissue must be able to be degraded. An important mechanism in this degradation is the proteolysis cascade initiated by the plasminogen activation system. uPAR binds urokinase and thus restricts plasminogen activation to the immediate vicinity of the cell membrane. Thus uPAR seems to be an important player in the regulation of this process.
When uPA is bound to the receptor, there is cleavage between the GPI-anchor and the uPAR, releasing suPAR.[8]
Clinical significance
Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) has been found to be a biomarker of inflammation.[9] Elevated suPAR is seen in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, liver failure, heart failure, cardiovascular disease, and rheumatoid arthritis.[9] Smokers have significantly higher suPAR compared to non-smokers.[9]
Urokinase receptors have been found to be highly expressed on senescent cells, leading researchers to use chimeric antigen receptor T cells to eliminate senescent cells in mice.[10]
The components of the plasminogen activation system have been found to be highly expressed in many malignant tumors, indicating that tumors are able to hijack the system, and use it in metastasis. Thus inhibitors of the various components of the plasminogen activation system have been sought as possible anticancer drugs.[11]
uPAR has been involved in various other non-proteolytical processes related to cancer, such as cell migration, cell cycle regulation, and cell adhesion.
Interactions
Urokinase receptor has been shown to interact with LRP1.[12]
See also
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000011422 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000046223 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Kessler, Pascal; Marchot, Pascale; Silva, Marcela; Servent, Denis (August 2017). "The three-finger toxin fold: a multifunctional structural scaffold able to modulate cholinergic functions". Journal of Neurochemistry. 142: 7–18. doi:10.1111/jnc.13975. PMID 28326549.
- ^ Llinas P, Le Du MH, Gårdsvoll H, Danø K, Ploug M, Gilquin B, Stura EA, Ménez A (May 2005). "Crystal structure of the human urokinase plasminogen activator receptor bound to an antagonist peptide". The EMBO Journal. 24 (9): 1655–63. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600635. PMC 1142576. PMID 15861141.
- ^ Huai Q, Mazar AP, Kuo A, Parry GC, Shaw DE, Callahan J, Li Y, Yuan C, Bian C, Chen L, Furie B, Furie BC, Cines DB, Huang M (February 2006). "Structure of human urokinase plasminogen activator in complex with its receptor". Science. 311 (5761): 656–9. doi:10.1126/science.1121143. PMID 16456079.
- ^ Thunø M, Macho B, Eugen-Olsen J (2009). "suPAR: the molecular crystal ball". Disease Markers. 27 (3): 157–72. doi:10.1155/2009/504294. PMC 3835059. PMID 19893210.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b c Desmedt S, Desmedt V, Delanghe JR, Speeckaert R, Speeckaert MM (2017). "The Intriguing Role of Soluble Urokinase Receptor in Inflammatory Diseases". Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences. 54 (2): 117–133. doi:10.1080/10408363.2016.1269310. PMID 28084848.
- ^ Wagner V, Gil J (2020). "T Cells Engineered to Target Senescence". Nature (journal). 583 (7814): 37–38. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-01759-x. PMID 32601490.
- ^ Josip Madunić (2018). "The Urokinase Plasminogen Activator System in Human Cancers: An Overview of Its Prognostic and Predictive Role". Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 118 (12): 2020–2036. doi:10.1055/s-0038-1675399. PMID 30419600.
- ^ Czekay RP, Kuemmel TA, Orlando RA, Farquhar MG (May 2001). "Direct binding of occupied urokinase receptor (uPAR) to LDL receptor-related protein is required for endocytosis of uPAR and regulation of cell surface urokinase activity". Molecular Biology of the Cell. 12 (5): 1467–79. doi:10.1091/mbc.12.5.1467. PMC 34598. PMID 11359936.
Further reading
- Ploug M (2003). "Structure-function relationships in the interaction between the urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its receptor". Current Pharmaceutical Design. 9 (19): 1499–528. doi:10.2174/1381612033454630. PMID 12871065.
- Kjøller L (January 2002). "The urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton and cell motility". Biological Chemistry. 383 (1): 5–19. doi:10.1515/BC.2002.002. PMID 11928822.
- Chavakis T, Kanse SM, May AE, Preissner KT (April 2002). "Haemostatic factors occupy new territory: the role of the urokinase receptor system and kininogen in inflammation". Biochemical Society Transactions. 30 (2): 168–73. doi:10.1042/BST0300168. PMID 12023845.
- Ploug M, Gårdsvoll H, Jørgensen TJ, Lønborg Hansen L, Danø K (April 2002). "Structural analysis of the interaction between urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its receptor: a potential target for anti-invasive cancer therapy". Biochemical Society Transactions. 30 (2): 177–83. doi:10.1042/BST0300177. PMID 12023847.
- Alfano M, Sidenius N, Blasi F, Poli G (November 2003). "The role of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA)/uPA receptor in HIV-1 infection". Journal of Leukocyte Biology. 74 (5): 750–6. doi:10.1189/jlb.0403176. PMID 12960238.
- Alfano D, Franco P, Vocca I, Gambi N, Pisa V, Mancini A, Caputi M, Carriero MV, Iaccarino I, Stoppelli MP (February 2005). "The urokinase plasminogen activator and its receptor: role in cell growth and apoptosis". Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 93 (2): 205–11. doi:10.1160/TH04-09-0592. PMID 15711734.
External links
- PLAUR+protein,+human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: Q03405 (Human Urokinase plasminogen activator surface receptor) at the PDBe-KB.