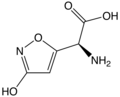
Ibotenic acid
This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 74.112.4.185 (talk) at 19:08, 30 December 2010 (Undid revision 405027113 by 98.204.74.45 (talk)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(S)-2-amino-2- (3-hydroxyisoxazol-5-yl) acetic acid
| |||
| Other names
Ibotenic acid
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider |
| ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.151.170 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H6N2O4 | |||
| Molar mass | 158.11 g/mol | ||
| Melting point | 151-152° (anhydrous); 144-146° (monohydrate) | ||
| Solubility in Methanol | Soluble | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Ibotenic acid is a chemical compound that is naturally occurring in the mushrooms Amanita muscaria and Amanita pantherina, among others. Ibotenic acid is a powerful neurotoxin that is used as a "brain-lesioning agent" [1] [2] and has shown to be highly neurotoxic when injected directly into the brains of mice and rats.[3]
In 1960s, ibotenic acid was originally isolated from Amanita ibotengutake in Japan. A. ibotengutake is very like to A. pantherina.
Psychopharmacology

When ibotenic acid is ingested, a small portion is decarboxylated into muscimol. Ibotenic acid evokes entheogenic effects in human beings at doses in range of 50-100 mg.[4] Peak intoxication is reached approximately 2-3 hours after oral ingestion,[5] consisting of one or all of the following; visual distortions/hallucinations, loss of equilibrium, muscle twitching (commonly mislabeled as convulsions), and altered sensory perception. These effects generally last for 6-8 hours, varying with dose.[6]
Use in Research
Ibotenic acid is used as a brain-lesioning agent in the research environment. When injected intracranially, ibotenic acid causes the development of excitotoxic lesions of the brain. This method of experimental brain lesioning may be preferable in certain circumstances because, while it destroys neuron bodies in a particular area, tracts that cross through the target nucleus are not damaged.[7]
Role in shamanic rituals
Ibotenic acid (coupled with other substances such as muscimol, found in Amanita muscaria and Amanita pantherina) is a common factor in shamanic rituals, used as a sacrament. Muscimol is excreted unchanged in the urine in relatively large amounts, and there are stories of shamans "reusing" urine for intoxication purposes, or the rest of the tribe making use of the shaman's urine.[8]
See also
References
- ^ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10435405
- ^ http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v311/n5985/abs/311458a0.html
- ^ Erowid -- Amanitas
- ^ Chilton 1975; Theobald et al. 1968
- ^ Chilton 1975
- ^ Chilton 1975; Ott 1976a
- ^ Erowid Psychoactive Amanitas Vault : Pharmacology of Amanita Muscaria
- ^ Erowid Psychoactive Amanitas Vault : Traditional Uses
Poisonous Amanita mushrooms | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subgenus Amanita |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subgenus Amanitina |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Psychedelics (5-HT2A agonists) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dissociatives (NMDAR antagonists) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deliriants (mAChR antagonists) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionotropic |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabotropic |
| ||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bacterial toxins |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mycotoxins |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Plant toxins |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Invertebrate toxins |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vertebrate toxins |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Animal toxins | |
|---|---|
| Bacterial | |
| Cyanotoxins | |
| Plant toxins | |
| Mycotoxins | |
| Pesticides | |
| Nerve agents | |
| Bicyclic phosphates | |
| Cholinergic neurotoxins | |
| Other | |
- Articles using duplicate arguments in template calls
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without EBI source
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chembox image size set
- Articles with short description
- Short description is different from Wikidata