Budapest
Budapest[9] (Hungarian: [ˈbudɒpɛʃt] ; names in other languages) is the capital and the largest city of Hungary,[10] and one of the largest cities[11] in the European Union. It is the country's principal political, cultural, commercial, industrial, and transportation centre,[12] sometimes described as the primate city of Hungary.[13] According to the census, in 2011 Budapest had 1.74 million inhabitants,[14] down from its 1989 peak of 2.1 million[15] due to suburbanisation.[16] The Budapest Metropolitan Area is home to 3.3 million people.[17][18] The city covers an area of 525 square kilometres (203 sq mi).[19] Budapest became a single city occupying both banks of the river Danube with the unification of Buda and Óbuda on the west bank, with Pest on the east bank on 17 November 1873.[19][20]
The history of Budapest began with Aquincum, originally a Celtic settlement[21][22] that became the Roman capital of Lower Pannonia.[21] Hungarians arrived in the territory[23] in the 9th century. Their first settlement was pillaged by the Mongols in 1241–42.[24] The re-established town became one of the centres of Renaissance humanist culture[25] by the 15th century.[26] Following the Battle of Mohács and nearly 150 years of Ottoman rule,[27] the region entered a new age of prosperity in the 18th and 19th centuries, and Budapest became a global city after its unification in 1873.[28] It also became the second capital of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, a great power that dissolved in 1918, following World War I. Budapest was the focal point of the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, the Hungarian Republic of Councils in 1919, the Battle of Budapest in 1945, and the Revolution of 1956.
Cited as one of the most beautiful cities in Europe,[10][29][30] Budapest's extensive World Heritage Site includes the banks of the Danube, the Buda Castle Quarter, Andrássy Avenue, Heroes' Square and the Millennium Underground Railway, the second-oldest metro line in the world.[29][31] It has around 80 geothermal springs,[32] the world's largest thermal water cave system,[33] second largest synagogue, and third largest Parliament building. The city attracts about 4.4 million tourists a year, making it the 25th most popular city in the world, and the 6th in Europe, according to Euromonitor.[34]
Considered a financial hub in Central Europe,[35] the city ranked third on Mastercard's Emerging Markets Index,[36] and ranked as the most liveable Central or Eastern European city on EIU's quality of life index.[37][38] It is also ranked as "the world's second best city" by Condé Nast Traveler,[39] and "Europe's 7th most idyllic place to live" by Forbes.[40] It is the highest ranked Central/Eastern European city on Innovation Cities' Top 100 index.[41][42]
Budapest is home to the headquarters of the European Institute of Innovation and Technology (EIT),[43] the European Police College (CEPOL)[44] and the first foreign office of the China Investment Promotion Agency (CIPA).[45] Eighteen universities are situated in Budapest, including the Central European University, Eötvös Loránd University and the Budapest University of Technology and Economics.
Etymology
"Budapest" is the combination of the city names Buda and Pest, which were (together with Óbuda) united into a single city in 1873.[46] One of the first documented occurrences of the combined name "Buda-Pest" was in 1831 in the book "Világ" ("World" / "Light"), written by Count István Széchenyi.[47]
The origins of the names Buda and Pest are obscure. According to chronicles from the Middle Ages, the name Buda comes from the name of its founder, Bleda (Buda), brother of the Hunnic ruler Attila. The theory that "Buda" was named after a person is also supported by modern scholars.[48] An alternative explanation suggests that Buda derives from the Slavic word вода, voda ("water"), a translation of the Latin name Aquincum, which was the main Roman settlement in the region.[49]
There are also several theories about the origin of the name Pest. One of the theories[50] states that the word "Pest" comes from the Roman times, since there was a fortress ("Contra-Aquincum") in this region that was referred to as "Pession" ("Πέσσιον", iii.7.§ 2) by Ptolemaios.[51] According to another theory, Pest originates from the Slavic word for cave (most closely related to Bulgarian and Macedonian: пещера, peștera), or oven (Template:Lang-bg, peșt), in reference either to a cave where fires burned or to a local limekiln.[52]
History
Early history

The first settlement on the territory of Budapest was built by Celts[21] before 1 AD. It was later occupied by the Romans. The Roman settlement – Aquincum – became the main city of Pannonia Inferior in 106 AD.[21] At first it was a military settlement, and gradually the city rose around it, making it the focal point of the city's commercial life. Today this area corresponds to the Óbuda district within Budapest.[53] The Romans constructed roads, amphitheaters, baths and houses with heated floors in this fortified military camp.[54] The Roman city of Aquincum is the best-conserved of the Roman sites in Hungary. The archaeological site was turned into a museum with inside and open-air sections.[citation needed]
Hungarians led by Árpád settled in the territory at the end of the 9th century,[23][55] and a century later officially founded the Kingdom of Hungary.[23] Research places the probable residence of the Árpáds as an early place of central power near what became Budapest.[56] The Tatar invasion in the 13th century quickly proved that it is difficult to mount a defence on a plain.[19][23] King Béla IV of Hungary therefore ordered the construction of reinforced stone walls around the towns[23] and set his own royal palace[24] on the top of the protecting hills of Buda. In 1361[24] it became the capital of Hungary.[19]
The cultural role of Buda was particularly significant during the reign of King Matthias Corvinus. The Italian Renaissance had a great influence on the city. His library, the Bibliotheca Corviniana, was Europe's greatest collection of historical chronicles and philosophic and scientific works in the 15th century, and second only in size to the Vatican Library.[19] After the foundation of the first Hungarian university in Pécs in 1367 (University of Pécs), the second one was established in Óbuda in 1395 (University of Óbuda).[57] The first Hungarian book was printed in Buda in 1473.[58] Buda had about 5,000 inhabitants around 1500.[59]

The Ottomans pillaged Buda in 1526, besieged it in 1529, and finally occupied it in 1541.[60] The Turkish occupation lasted for more than 140 years.[19] The Turks constructed many fine bathing facilities within the city.[23] Some of the baths that the Turks erected during their occupation period are still in use 500 years later (Rudas Baths and Király Baths). Under Ottoman rule many Christians became Muslim. By 1547 the number of Christians was down to about a thousand, and by 1647 it had fallen to only about seventy.[59] The unoccupied western part of the country became part of the Habsburg Empire as Royal Hungary.
In 1686, two years after the unsuccessful siege of Buda, a renewed campaign was started to enter the Hungarian capital. This time, the Holy League's army was twice as large, containing over 74,000 men, including German, Croat, Dutch, Hungarian, English, Spanish, Czech, Italian, French, Burgundian, Danish and Swedish soldiers, along with other Europeans as volunteers, artillerymen, and officers. The Christian forces reconquered Buda, and in the next few years, all of the former Hungarian lands, except areas near Timișoara (Temesvár), were taken from the Turks. In the 1699 Treaty of Karlowitz these territorial changes were officially recognised, and in 1718 the entire Kingdom of Hungary was removed from Ottoman rule.


Contemporary history after Unification
The 19th century was dominated by the Hungarian struggle for independence[19] and modernisation. The national insurrection against the Habsburgs began in the Hungarian capital in 1848 and was defeated one and a half years later, with the help of the Russian Empire. 1867 was the year of Reconciliation that brought about the birth of Austria-Hungary. This made Budapest the twin capital of a dual monarchy. It was this compromise which opened the second great phase of development in the history of Budapest, lasting until World War I. In 1849 the Chain Bridge linking Buda with Pest was opened as the first permanent bridge across the Danube[61] and in 1873 Buda and Pest were officially merged with the third part, Óbuda (Ancient Buda), thus creating the new metropolis of Budapest. The dynamic Pest grew into the country's administrative, political, economic, trade and cultural hub. Ethnic Hungarians overtook Germans in the second half of the 19th century due to mass migration from the overpopulated rural Transdanubia and Great Hungarian Plain. Between 1851 and 1910 the proportion of Hungarians increased from 35.6% to 85.9%, Hungarian became the dominant language, and German was crowded out. The proportion of Jews peaked in 1900 with 23.6%.[62][63][64] Due to the prosperity and the large Jewish community of the city at the start of the 20th century, Budapest was often called the "Jewish Mecca"[65] or "Judapest".[66][67] In 1918, Austria-Hungary lost the war and collapsed; Hungary declared itself an independent republic (Republic of Hungary). In 1920 the Treaty of Trianon partitioned the country, and as a result, Hungary lost over two-thirds of its territory, and about two-thirds of its inhabitants, including 3.3 million out of 15 million ethnic Hungarians.[68][69]
In 1944, about one year before the end of World War II, Budapest was partly destroyed by British and American air raids (first attack 4 April 1944,[70][71][72]). From 24 December 1944 to 13 February 1945, the city was besieged during the Battle of Budapest. Budapest suffered major damage caused by the attacking Soviet and Romanian troops and the defending German and Hungarian troops. More than 38,000 civilians lost their lives during the conflict. All bridges were destroyed by the Germans. The stone lions that have decorated the Chain Bridge since 1852 survived the devastation of the war.[citation needed]
Between 20% and 40% of Greater Budapest's 250,000 Jewish inhabitants died through Nazi and Arrow Cross Party, during the Germany occupation of Hungary, from 1944 to early 1945.[73]
Swiss diplomat Carl Lutz rescued tens of thousands of Jews by issuing Swiss protection papers and designating numerous buildings, including the now famous Glass House (Üvegház) at Vadász Street 29, to be Swiss protected territory. About 3,000 Hungarian Jews found refuge at the Glass House and in a neighboring building. Swedish diplomat Raoul Wallenberg managed to save the lives of tens of thousands of Jews in Budapest by giving them Swedish protection papers and taking them under his consular protection.[74] Wallenberg was abducted by the Russians on 17 January 1945 and never regained freedom. Some other diplomats also abandoned diplomatic protocol and rescued Jews. There are two monuments for Wallenberg and one for Carl Lutz in Budapest.
Following the liberation of Hungary from Nazi Germany by the Red Army, Soviet military occupation ensued, which ended only in 1991. The Soviets exerted significant influence on Hungarian political affairs. In 1949, Hungary was declared a communist People's Republic (People's Republic of Hungary). The new Communist government considered the buildings like the Buda Castle symbols of the former regime, and during the 1950s the palace was gutted and all the interiors were destroyed (also see Stalin era). On 23 October 1956 citizens held a large peaceful demonstration in Budapest demanding democratic reform. The demonstrators went to the Budapest radio station and demanded to publish their demands. The regime ordered troops to shoot into the crowd. Hungarian soldiers gave rifles to the demonstrators who were now able to capture the building. This initiated the Hungarian Revolution of 1956. The demonstrators demanded to appoint Imre Nagy to be Prime Minister of Hungary. To their surprise, the central committee of the "Hungarian Working People's Party" did so that same evening. This uprising was an anti-Soviet revolt that lasted from 23 October until 11 November. After Nagy had declared that Hungary was to leave the Warsaw Pact and become neutral, Soviet tanks and troops entered the country to crush the revolt. Fighting continued until mid November, leaving more than 3000 dead. A monument was erected at the fiftieth anniversary of the revolt in 2006, at the edge of the City Park. Its shape is a wedge with a 56 angle degree made in rusted iron that gradually becomes shiny, ending in an intersection to symbolize Hungarian forces that temporarily eradicated the Communist leadership.[citation needed]
From the 1960s to the late 1980s Hungary was often satirically referred to as "the happiest barrack" within the Eastern bloc, and much of the wartime damage to the city was finally repaired. Work on Erzsébet Bridge, the last to be rebuilt, was finished in 1964. In the early 1970s, Budapest Metro's East-West M2 line was first opened, followed by the M3 line in 1976. In 1987, Buda Castle and the banks of the Danube were included in the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites. Andrássy Avenue (including the Millennium Underground Railway, Hősök tere, and Városliget) was added to the UNESCO list in 2002. In the 1980s, the city's population reached 2.1 million. In recent times a significant decrease in population occurred mainly due to a massive movement to the neighbouring agglomeration in Pest county, i.e., suburbanisation.[citation needed]
In the last decades of the 20th century the political changes of 1989–90 (Fall of the Iron Curtain) concealed changes in civil society and along the streets of Budapest. The monuments of the dictatorship were removed from public places, into Memento Park. In the first 20 years of the new democracy, the development of the city was managed by its mayor, Gábor Demszky.[citation needed]
-
The tomb of the Turkish dervish Gül Baba in Budapest
-
Andrássy Avenue (1875)
-
Zeppelin above Budapest in 1931
Geography
Topography

Budapest, strategically placed at the centre of the Carpathian Basin, lies on an ancient route linking the hills of Transdanubia with the Great Plain. By road it is 216 kilometres (134 mi) south-east of Vienna, 545 kilometres (339 mi) south of Warsaw, 1,565 kilometres (972 mi) south-west of Moscow, 1,122 kilometres (697 mi) north of Athens, 788 kilometres (490 mi) north-east of Milan, and 443 kilometres (275 mi) south-east of Prague.[75]
The 525 square kilometres (203 sq mi) area of Budapest lies in Central Hungary, surrounded by settlements of the agglomeration in Pest county. The capital extends 25 and 29 km (16 and 18 mi) in the north-south, east-west direction respectively. The Danube enters the city from the north; later it encircles two islands, Óbuda Island and Margaret Island.[19] The third island Csepel Island is the largest of the Budapest Danube islands, however only its northernmost tip is within city limits. The river that separates the two parts of the city is 230 m (755 ft) wide at its narrowest point in Budapest. Pest lies on the flat terrain of the Great Plain while Buda is rather hilly.[19]
The wide Danube was always fordable at this point because of a small number of islands in the middle of the river. The city has marked topographical contrasts: Buda is built on the higher river terraces and hills of the western side, while the considerably larger Pest spreads out on a flat and featureless sand plain on the river’s opposite bank.[76] Pest's terrain rises with a slight eastward gradient, so the easternmost parts of the city lie at the same altitude as Buda's smallest hills, notably Gellért Hill and Castle Hill.[citation needed]
The Buda hills consist mainly of limestone and dolomite, the water created speleothems, the most famous ones being the Pálvölgyi cave (total length 7200 m) and the Szemlőhegyi cave (total length 2200 m). The hills were formed in the Triassic Period. The highest point of the hills and of Budapest is János hill, at 527 metres (1,729 ft) above sea level. The lowest point is the line of the Danube which is 96 metres (315 ft) Above mean sea level|above sea level. Budapest is also rich in green areas. Of the 525 square kilometres (203 sq mi) occupied by the city, 83 square kilometres (32 sq mi) is green area, park and forest.[77] The forests of Buda hills are environmentally protected.[citation needed]
The city's importance in terms of traffic is very central, because all major European roads and European railway lines lead to Budapest.[78] The Danube was and is still an important water-way and this region in the centre of the Carpathian Basin lies at the cross-roads of trade routes.[79] Budapest is the only capital city in the world which has thermal springs. Some 125 springs produce 70 million litres of thermal water a day, with temperatures ranging up to 58 Celsius. Some of these waters have medicinal effects due to their medically valuable mineral contents.[78]
Climate
Budapest has an oceanic climate (Cfb) using the −3 °C (26.6 °F) isotherm of the original Köppen scheme, or a humid continental climate (Köppen Dfb), using the 0 °C (32 °F) isotherm preferred by some climatologists, with relatively cold winters and warm summers.[80] Winter (November until early March) can be cold and the city receives little sunshine. Snowfall is fairly frequent in most years, and nighttime temperatures of −10 °C (14 °F) are not uncommon between mid-December and mid-February. The spring months (March and April) see variable conditions, with a rapid increase in the average temperature. The weather in late March and April is often very agreeable during the day and fresh at night. Budapest's long summer – lasting from May until mid-September – is warm or very warm. Budapest has as much summer sunshine as many Mediterranean resorts. Sudden heavy showers also occur, particularly in May and June. The autumn in Budapest (mid-September until late October) is characterised by little rain and long sunny days with moderate temperatures. Temperatures often turn abruptly colder in late October.
Mean annual precipitation in Budapest is around 23.5 inches (600 mm). On average, there are 78 days with precipitation and 1988 hours of sunshine (of a possible 4383) each year.[2][81][82]
The city lies on the boundary between Zone 6 and Zone 7 in terms of the hardiness zone.[83][84]
| Climate data for Budapest, 1971–2000 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 18.1 (64.6) |
19.7 (67.5) |
25.4 (77.7) |
30.2 (86.4) |
34.0 (93.2) |
39.5 (103.1) |
40.7 (105.3) |
39.4 (102.9) |
35.2 (95.4) |
30.8 (87.4) |
22.6 (72.7) |
19.3 (66.7) |
40.7 (105.3) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 2.9 (37.2) |
5.5 (41.9) |
10.6 (51.1) |
16.4 (61.5) |
21.9 (71.4) |
24.6 (76.3) |
26.7 (80.1) |
26.6 (79.9) |
21.6 (70.9) |
15.4 (59.7) |
7.7 (45.9) |
4.0 (39.2) |
15.3 (59.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.4 (32.7) |
2.3 (36.1) |
6.1 (43.0) |
12.0 (53.6) |
16.6 (61.9) |
19.7 (67.5) |
21.5 (70.7) |
21.2 (70.2) |
16.9 (62.4) |
11.8 (53.2) |
5.4 (41.7) |
1.8 (35.2) |
11.3 (52.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −1.6 (29.1) |
0.0 (32.0) |
3.5 (38.3) |
7.6 (45.7) |
12.1 (53.8) |
15.1 (59.2) |
16.8 (62.2) |
16.5 (61.7) |
12.8 (55.0) |
7.85 (46.13) |
2.9 (37.2) |
0.0 (32.0) |
7.8 (46.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −25.6 (−14.1) |
−23.4 (−10.1) |
−15.1 (4.8) |
−4.6 (23.7) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
3.0 (37.4) |
5.9 (42.6) |
5.0 (41.0) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
−9.5 (14.9) |
−16.4 (2.5) |
−20.8 (−5.4) |
−25.6 (−14.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 37 (1.5) |
29 (1.1) |
30 (1.2) |
42 (1.7) |
62 (2.4) |
63 (2.5) |
45 (1.8) |
49 (1.9) |
40 (1.6) |
39 (1.5) |
53 (2.1) |
43 (1.7) |
532 (20.9) |
| Average precipitation days | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 78 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 79 | 74 | 66 | 59 | 61 | 61 | 59 | 61 | 67 | 72 | 78 | 80 | 68.1 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 62 | 93 | 137 | 177 | 234 | 250 | 271 | 255 | 187 | 141 | 69 | 52 | 1,988 |
| Source: Hungarian Meteorological Service[85] | |||||||||||||
Architecture


Budapest has architecturally noteworthy buildings in a wide range of styles and from distinct time periods, from the ancient times as Roman City of Aquincum in Óbuda (District III), which dates to around 89 AD, to the most modern Palace of Arts, the contemporary arts museum and concert hall.[86][87][88]
Most buildings in Budapest are relatively low: in the early 2010s there were around 100 buildings higher than 45 metres (148 ft). The number of high-rise buildings is kept low by building legislation, which is aimed at preserving the historic cityscape and to meet the requirements of the World Heritage Site. Strong rules apply to the planning, authorisation and construction of high-rise buildings and consequently much of the inner city does not have any. But Budapest is planning to ease rules for the construction of skyscrapers and in the near future would like to build skyscrapers around the city's historic core.[89][90]
In the chronological order of architectural styles Budapest represents on the entire timeline. Start with the Roman City of Aquincum represents the ancient architecture.

The next determinative style is the Gothic architecture in Budapest. The few remaining ones can be found in the Castle District. Buildings to look for are no. 18, 20 and 22 on Országház Street, which date back to the 14th century and No. 31 Úri Street, which has a Gothic façade that dates back to the 15th century. Another building with Gothic remains is the Inner City Parish Church in Pest, built in the 12th century.[91] The most characteristic Gothic-style buildings are actually Neo-Gothic, like the most well-known Budapest landmarks, the Hungarian Parliament Building and the Matthias Church, where much of the original material was used (originally built in Romanesque style in 1015).[citation needed]
The next chapter of the human architecture is the Renaissance architecture and one of the earliest places to be influenced by the Renaissance style of architecture was Hungary and Budapest. The style appeared following the marriage of King Matthias Corvinus and Beatrice of Naples in 1476. Many Italian artists, craftsmen and masons came to Buda with the new queen. Today, many of the original renaissance buildings disappeared during the varied history of Buda, but Budapest is still rich in renaissance and neo-renaissance buildings, like the famous Hungarian State Opera House, the St. Stephen's Basilica and the Hungarian Academy of Sciences.[citation needed]
During the Turkish occupation (1541–1686), multiple mosques and baths were built in the city. These were great examples of Ottoman architecture, which was influenced by Iranian, and to a larger extent, Byzantine architecture as well as Islamic traditions. Budapest is in fact one of the few places in the world with functioning original Turkish bathhouses dating back to the 16th century, like Rudas Baths or Király Baths. Another little known fact is that Budapest is home to the northernmost holy place of Islam, the Tomb of Gül Baba, tomb of a Turkish dervish. After 1686, the Baroque architecture designated the dominant style of art in catholic countries from the 17th century to the 18th century.[citation needed]


There are many Baroque-style buildings in Budapest and one of the finest examples of original Baroque-style architecture is the Church of St. Anna in Batthyhány square. An interesting part of Budapest is the less touristy Óbuda, the main square of which also has some beautiful historic buildings with original Baroque façades. The Castle District is another place to visit where the best-known landmark Buda Royal Palace and many other buildings were built in the Baroque style.[citation needed]
The Classical architecture and Neoclassical architecture are the next in the timeline. Budapest had not one but two architects that were masters of the Classicist style. Mihály Pollack (1773–1855) and József Hild (1789–1867), built many beautiful Classicist-style buildings in the city. Some of the best examples are the Hungarian National Museum, the Lutheran Church of Budavár (both designed by Pollack) and the seat of the Hungarian president, the Sándor Palace. The most iconic Classicist-style attraction in Budapest, the most widely known Chain Bridge. A bit of maverick in architectural styles the Romanticism. Budapest's two most beautiful Romantic architecture buildings are the Great Synagogue in Dohány Street and the Vigadó Concert Hall on the Danube Promenade, both designed by architect Frigyes Feszl (1821–1884). Another noteworthy structure is the Budapest Western Railway Station, which was designed by August de Serres and built by the Eiffel Company of Paris in 1877.[citation needed]

Art Nouveau came into fashion in Budapest by the exhibitions which were held in and around 1896 and organised in connection with the Hungarian Millennium celebrations.[92] Art Nouveau in Hungary (Szecesszió in Hungarian) is a blend of several architectural styles, with a focus on Hungary's specialities. One of the leading Art Nouveau architects, Ödön Lechner (1845–1914), was inspired by Indian and Syrian architecture as well as traditional Hungarian decorative designs. One of his most beautiful buildings in Budapest is the Museum of Applied Arts. Another examples for Art Nouveau in Budapest is the Gresham Palace in front of the Chain Bridge, the Hotel Gellért, the Franz Liszt Academy of Music or Budapest Zoo and Botanical Garden.[86]
In the 21st century, Budapest faces new challenges in its architecture. The pressure towards the high-rise buildings is unequivocal among today's world cities, but preserving Budapest's unique cityscape and its very diverse architecture, along with green areas, is force Budapest to balance between them. The Contemporary architecture has wide margin in the city. Public spaces attract heavy investment by business and government also, so that the city has gained entirely new (or renovated and redesigned) squares, parks and monuments, for example the city central Kossuth Lajos square, Deák Ferenc square and Liberty Square. Budapest's current urban landscape is one of the modern and contemporary architecture. Numerous landmarks are created in the last decade in Budapest, like the National Theatre, Palace of Arts, Rákóczi Bridge, Megyeri Bridge, Budapest Airport Sky Court among others, and millions of square meters of new office buildings and apartments. But there are still large opportunities in real estate development in the city.[93][94][95]
Districts
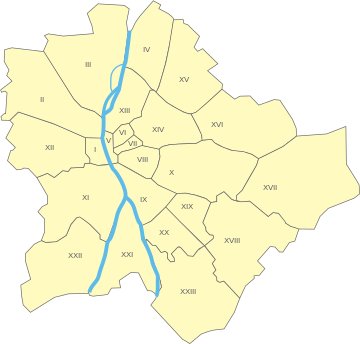
Budapest's twenty-three districts overview
| ||||
| Administration | Population | Area and Density | ||
| District | Official name | Official 2013 | Km2 | People/km2 |
| I | Várkerület | 24.528 | 3,41 | 7.233 |
| II | (no official name) | 88.011 | 36,34 | 2.426 |
| III | Óbuda-Békásmegyer | 123.889 | 39,69 | 3.117 |
| IV | Újpest | 99.050 | 18,82 | 5.227 |
| V | Belváros-Lipótváros | 27.342 | 2,59 | 10.534 |
| VI | Terézváros | 43.377 | 2,38 | 18.226 |
| VII | Erzsébetváros | 64.767 | 2,09 | 30.989 |
| VIII | Józsefváros | 85.173 | 6,85 | 11.890 |
| IX | Ferencváros | 63.697 | 12,53 | 4.859 |
| X | Kőbánya | 81.475 | 32,5 | 2.414 |
| XI | Újbuda | 145.510 | 33,47 | 4.313 |
| XII | Hegyvidék | 55.776 | 26,67 | 2.109 |
| XIII | (no official name) | 118.320 | 13,44 | 8.804 |
| XIV | Zugló | 123.786 | 18,15 | 6.820 |
| XV | (no official name) | 79.779 | 26,95 | 2.988 |
| XVI | (no official name) | 68.235 | 33,52 | 2.037 |
| XVII | Rákosmente | 78.537 | 54,83 | 1.418 |
| XVIII | Pestszentlőrinc-Pestszentimre | 94.663 | 38,61 | 2.414 |
| XIX | Kispest | 62.210 | 9,38 | 6.551 |
| XX | Pesterzsébet | 63.887 | 12,18 | 5.198 |
| XXI | Csepel | 76.976 | 25,75 | 2.963 |
| XXII | Budafok-Tétény | 51.071 | 34,25 | 1.473 |
| XXIII | Soroksár | 19.982 | 40,78 | 501 |
| 1.740.041 | 525,2 | 3.314,9 | ||
| 9.937.628 | 93.030 | 107,2 | ||
| Source: Eurostat,[96] HSCO[6] | ||||
Most of today's Budapest is the result of a late-nineteenth-century renovation, but the wide boulevards lain then only bordered and bisected much older quarters of activity created by centuries of Budapest's city evolution. Budapest's vast urban area is often described using a set of district names. These are either informal designations, reflect the names of villages that have been absorbed by sprawl, or are superseded administrative units of former boroughs.[97] Such names have remained in use through tradition, each referring to a local area with its own distinctive character, but without official boundaries.[98] Originally Budapest had 10 districts after coming into existence upon the unification of the three cities in 1873. Since 1950, Greater Budapest has been divided into 22 boroughs (and 23 since 1994). At that time there were changes both in the order of districts and in their sizes. The city now consists of 23 districts, 6 in Buda, 16 in Pest and 1 on Csepel Island between them. The city centre itself in a broader sense comprises the District V, VI, VII, VIII, IX[99] and XIII on the Pest side,[100] and the I, II, XI and XII on the Buda side of the city.[citation needed]
District I is a small area in central Buda, including the historic Buda Castle. District II is in Buda again, in the northwest, and District III stretches along in the northernmost part of Buda. To reach District IV, one must cross the Danube to find it in Pest (the eastern side), also at north. With District V, another circle begins, it is located in the absolute centre of Pest. Districts VI, VII, VIII and IX are the neighbouring areas to the east, going southwards, one after the other. District X is another, more external circle also in Pest, while one must jump to the Buda side again to find Districts XI and XII, going northwards. No more districts remaining in Buda in this circle, we must turn our steps to Pest again to find Districts XIII, XIV, XV, XVI, XVII, XVIII, XIX and XX (mostly external city parts), almost regularly in a semicircle, going southwards again. District XXI is the extension of the above route over a branch of the Danube, the northern tip of a long island south from Budapest. District XXII is still on the same route in southwest Buda, and finally District XXIII is again in southernmost Pest, irregular only because it was part of District XX until 1994.[citation needed]
Demographics
| Budapest | Hungary | European Union | |
| Total Population | 1,740,041 | 9,937,628 | 507,890,191 |
| Population change, 2004 to 2014 | +2.7%[101] | −1.6%[101] | +2.2%[102] |
| Population density | 3,314 /km2 | 107 /km2 | 116 /km2 |
| GDP per capita PPP | 52,770 $[103] | 20,455 $[104] | 33,084 $[105] |
| Bachelor's Degree or higher | 34.1%[106] | 19.0%[106] | 27.1%[107] |
| Foreign born | 7.3%[108] | 1.7%[109] | 6.3%[110] |
| Largest groups of foreign residents[111] | |
| Nationality | Population (2011) |
|---|---|
| 18,278 | |
| 6,189 | |
| 4,692 | |
| 3,124 | |
| 2,581 | |
| 2,518 | |
| 2,361 | |
| 2,252 | |
| 2,041 | |
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1784[112] | 57,100 | — |
| 1870 | 302,086 | +429.0% |
| 1880 | 402,706 | +33.3% |
| 1890 | 560,079 | +39.1% |
| 1900 | 861,434 | +53.8% |
| 1910 | 1,110,453 | +28.9% |
| 1920 | 1,232,026 | +10.9% |
| 1930 | 1,442,869 | +17.1% |
| 1940 | 1,712,791 | +18.7% |
| 1950 | 1,590,316 | −7.2% |
| 1960 | 1,804,606 | +13.5% |
| 1970 | 1,945,083 | +7.8% |
| 1980 | 2,059,226 | +5.9% |
| 1990 | 2,016,681 | −2.1% |
| 2000 | 1,777,921 | −11.8% |
| 2005 | 1,697,343 | −4.5% |
| 2010 | 1,721,556 | +1.4% |
| 2015e | 1,757,618 | +2.1% |
| Population 2001 to 2014[101] Present-territory of Budapest | ||
Budapest is the most populous city in Hungary and one of the largest cities in the European Union, with a growing number of inhabitants, estimated at 1,742,000 in 2014, whereby inward migration exceeds outward migration.[10] These trends are also seen throughout the Budapest metropolitan area, which is home to 3.3 million people.[113][114] This amounts to about 34% of Hungary's population. In 2014, the city had a population density of 3,314 people per square kilometre (8,580/sq mi), rendering it the most densely populated of all municipalities in Hungary. The population density of District VII (Elisabethtown) is 30,989/km² (80,260/sq mi), which is the highest population density figure in Hungary and one of the highest in the world[citation needed] (for comparison the density in Manhattan is 25,846/km²[115]).
Budapest is the fourth most "dynamically growing city" by population in Europe,[116] and the Euromonitor predicts a population increase of almost 10% between 2005 and 2030.[117] The European Observation Network for Territorial Development and Cohesion says Budapest's population will increase by 10% to 30% only due to migration by 2050.[118] A constant inflow of migrants in recent years has fuelled population growth in Budapest. Productivity gains and the relatively large economically active share of the population explain why household incomes have increased in Budapest to a greater extent than in other parts of Hungary. Higher incomes in Budapest are reflected in the lower share of expenditure the city’s inhabitants allocate to necessity spending such as food and non-alcoholic drinks.[113]
At the 2011 census, there were 1,729,040 people with 906,782 households living in Budapest.[119] Some 1.6 million persons from the metropolitan area may be within Budapest's boundaries during work hours, and during special events. This fluctuation of people is caused by hundreds of thousands of suburban residents who travel to the city for work, education, health care, and special events. By ethnicity there were 1,397,851 (80.8%) Hungarians, 19,530 (1.1%) Romani, 18,278 (1.0%) Germans, 6,189 (0.4%) Romanians, 4,692 (0.3%) Chinese and 2,581 (0.1%) Slovaks. 301,943 people (17.5%) did not declare their ethnicity. In Hungary people can declare more than one ethnicity, so the sum of ethnicities is higher than the total population.[108][120] The city is home to one of the largest Jewish communities in Europe.[121]
According to the same census, 1,600,585 people (92.6%) were born in Hungary, 126,036 people (7.3%) outside Hungary while the birthplace of 2,419 people (0.1%) was unknown.[108] Although only 1.7% of the population of Hungary in 2009 were foreigners, 43% of them lived in Budapest, making them 4.4% of the city's population (up from 2% in 2001).[109] Nearly two-thirds of foreigners living in Hungary were under 40 years old. The primary motivation for this age group living in Hungary was employment.[109] According to the 2011 census, 1,712,153 people (99.0%) speak Hungarian, of whom 1,692,815 people (97.9%) speak it as a first language, while 19,338 people (1.1%) speak it as a second language. Other spoken (foreign) languages were: English (536,855 speakers, 31.0%), German (266,249 speakers, 15.4%), French (56,208 speakers, 3.3%) and Russian (54,613 speakers, 3.2%).[108]
Budapest is the home to one of the most populous Christian community in Central Europe, numbered 698,521 people (40.4%) in 2011.[108] According to the 2011 census, there were 501,117 (29.0%) Roman Catholics, 146,756 (8.5%) Calvinists, 30,293 (1.8%) Lutherans, 16,192 (0.9%) Greek Catholics, 7,925 (0.5%) Jews and 3,710 (0.2%) Orthodox in Budapest. 395,964 people (22.9%) were irreligious while 585,475 people (33.9%) did not declare their religion.[108] A Hungarian Central Statistical Office report showed that also, the proportion of Romani in Budapest increased from 2% in 1990 to 4.6% in 2009.[16][122]
Economy




Budapest is a significant economic hub, classified as an Alpha- world city in the study by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network and it is the second fastest-developing urban economy in Europe as GDP per capita in the city increased by 2.4 per cent and employment by 4.7 per cent compared to the previous year in 2014.[123][124] On national level, Budapest is the primate city of Hungary regarding business and economy, accounting for 39% of the national income, the city has a gross metropolitan product more than $100 billion in 2015, making it one of the largest regional economy in the European Union.[125][126] According to the Eurostat GDP per capita in purchasing power parity is 147% of the EU average in Budapest, which means €37.632 ($52.770) per capita.[103] Budapest is also among the Top100 GDP performing cities in the world, measured by PricewaterhouseCoopers.[127] The city was named as the 52nd most important business centre in the world in the Worldwide Centres of Commerce Index, ahead of Beijing, Warsaw, Sao Paulo or Shenzhen and ranking 3rd (out of 65 cities) on MasterCard Emerging Markets Index.[36][128] The city is 48th on the UBS The most expensive and richest cities in the world list, standing before cities such as Prague, Shanghai, Kuala Lumpur or Buenos Aires.[129] In a global city competitiveness ranking by EIU, Budapest is stands before Tel Aviv, Lisbon, Moscow and Johannesburg among others.[130]
The city is a major centre for banking and finance, real estate, retailing, trade, transportation, tourism, new media as well as traditional media, advertising, legal services, accountancy, insurance, fashion and the arts in Hungary and regionally. Budapest is home not only to almost all national institutions and government agencies, but also to many domestic and international companies, in 2014 there are 395.804 companies registered in the city.[131] Most of these entities are headquartered in the Budapest's Central Business District, in the District V and District XIII. The retail market of the city (and the country) is also concentrated in the downtown, among others through the two largest shopping centre in Central and Eastern Europe, the 186,000sqm WestEnd City Center and the 180,000sqm Arena Plaza.[132][133]
Budapest has notable innovation capabilities as a technology and start-up hub, many start-ups are headquartered and begin its business in the city, for instance deserve to mention the most well-known Prezi, LogMeIn or Nav N Go. Budapest is the highest ranked Central and Eastern European city on Innovation Cities' Top 100 index.[41] A good indicator of the city's potential for innovation and research also, is that the European Institute of Innovation and Technology chose Budapest for its headquarters, along with the UN, which Regional Representation for Central Europe office is in the city, responsible for UN operations in seven countries.[134] Moreover, the global aspect of the city's research activity is shown through the establishment of the European Chinese Research Institute in the city.[135] Other important sectors include also, as natural science research, information technology and medical research, non-profit institutions, and universities. The leading business schools and universities in Budapest, the Budapest Business School, the CEU Business School and Corvinus University of Budapest offers a whole range of courses in economics, finance and management in English, French, German and Hungarian.[136] The unemployment rate is far the lowest in Budapest within Hungary, it was 2.7%, besides the many thousands of employed foreign citizens.[137]
Budapest is among the 25 most visited cities in the world, the city welcoming more than 4.4 million international visitors each year,[138] therefore the traditional and the congress tourism industry also deserve a mention, it contributes greatly to the city's economy. The capital being home to many convention centre and thousands of restaurants, bars, coffee houses and party places, besides the full assortment of hotels. In restaurant offerings can be found the highest quality Michelin-starred restaurants, like Onyx, Costes, Tanti or Borkonyha. The city ranked as the most liveable city in Central and Eastern Europe on EIU's quality of life index in 2010.[139]
Finance and corporate location
Budapest Stock Exchange, key institution of the publicly offered securities in Hungary and Central and Eastern Europe is situated in Budapest's CBD at Liberty Square. BSE also trades other securities such as government bonds and derivatives such as stock options. Large Hungarian multinational corporations headquartered in Budapest are listed on BSE, for instance the Fortune Global 500 firm MOL Group, the OTP Bank, FHB Bank, Gedeon Richter, Magyar Telekom, CIG Pannonia, Zwack Unicum and more.[140] Nowadays nearly all branches of industry can be found in Budapest, there is no particularly special industry in the city's economy, but the financial centre role of the city is strong, nearly 40 major banks are presented in the city,[141] also those like Bank of China, KDB Bank and Hanwha Bank, which is unique in the region.
Also support the financial industry of Budapest, the firms of international banks and financial service providers, such as Citigroup, Morgan Stanley, GE Capital, Deutsche Bank, Sberbank, ING Group, Allianz, KBC Group, UniCredit and MSCI among others. Another particularly strong industry in the capital city is biotechnology and pharmaceutical industry, these are also traditionally strong in Budapest, through domestic companies, as Egis, Gedeon Richter, Chinoin and through international biotechnology corporations, like Pfizer, Teva, Novartis, Sanofi, who are also has R&D and production division here. Further high-tech industries, such as software development, engineering notable as well, the Nokia, Ericcson, Bosch, Microsoft, IBM employs thousands of engineers in research and development in the city. Game design also highly represented through headquarters of domestic Digital Reality, Black Hole and studio of Crytek or Gameloft. Beyond the above, there are regional headquarters of global firms, such as Alcoa, General Motors, GE, Exxon Mobil, British Petrol, Hudson Legal, British Telecom, Flextronics, Panasonic Corp, Huawei, Knorr-Bremse, Liberty Global, Tata Consultancy, Aegon, WizzAir, TriGránit, MVM Group, Graphisoft, there is a base for Nissan CEE, Volvo, Saab, Ford, including but not limited to.[142]
Politics and government



As the capital of Hungary, Budapest is the seat of the country's national government. For the executive, the two chief officers each have their own official residences, which also serve as their offices. The President of Hungary resides at the Sándor Palace in the District I (Buda Castle District),[143] while the office of the Hungarian Prime Minister is in the Hungarian Parliament. Government ministries are all located in various parts of the city, most of them are in the District V, Leopoldtown. The National Assembly is seated in the Hungarian Parliament, which also located in the District V.[144] The President of the National Assembly, the third-highest public official in Hungary, is also seated in the largest building in the country, in the Hungarian Parliament.
Hungary's highest courts are located in Budapest. The Curia (supreme court of Hungary), the highest court in the judicial order, which reviews criminal and civil cases, is located in the District V, Leopoldtown. Under the authority of its President it has three departments: criminal, civil and administrative-labour law departments. Each department has various chambers. The Curia guarantees the uniform application of law. The decisions of the Curia on uniform jurisdiction are binding for other courts.[145] The second most important judicial authority, the National Judicial Council, is also housed in the District V, with the tasks of controlling the financial management of the judicial administration and the courts and giving an opinion on the practice of the president of the National Office for the Judiciary and the Curia deciding about the applications of judges and court leaders, among others.[146] The Constitutional Court of Hungary is one of the highest level actors independent of the politics in the country. The Constitutional Court serves as the main body for the protection of the Constitution, its tasks being the review of the constitutionality of statutes. The Constitutional Court performs its tasks independently. With its own budget and its judges being elected by Parliament it does not constitute a part of the ordinary judicial system. The constitutional court passes on the constitutionality of laws, and there is no right of appeal on these decisions.[147]
Budapest hosts the main and regional headquarters of many international organizations as well, including United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, European Institute of Innovation and Technology, European Police Academy, International Centre for Democratic Transition, Institute of International Education, International Labour Organization, International Organization for Migration, International Red Cross, Regional Environmental Center for Central and Eastern Europe, Danube Commission and even others.[148] The city is also home to more than 100 embassies and representative bodies as an international political actor.[149]
Environmental issues have a high priority among Budapest's politics. Institutions such as the Regional Environmental Center for Central and Eastern Europe, located in Budapest, are very important assets.[150] To decrease the use of cars and greenhouse gas emissions, the city has worked to improve public transportation, and nowadays the city has one of the highest mass transit usage in Europe. Budapest has one of the best public transport systems in Europe with an efficient network of buses, trolleys, trams and subway. Budapest has an above-average proportion of people commuting on public transport or walking and cycling for European cities.[151] Riding on bike paths is one of the best ways to see Budapest – there are currently about 180 kilometres (110 miles) of bicycle paths in the city, fitting into the EuroVelo system.[152]
The crime in Budapest investigated by different bodies. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime notes in their 2011 Global Study on Homicide that, according to criminal justice sources, the homicide rate in Hungary, calculated based on UN population estimates, was 1.4 in 2009, compared to Canada's rate of 1.8 that same year.[153] The homicide rate in Budapest is below the EU capital cities’ average according to WHO also.[154] However, the organised crime is associated with the city, the Institute of Defence in a UN study named Budapest as the "global epicentres" of illegal pornography, money laundering and contraband tobacco, and also the negotiation center for international crime group leaders.[155]
City governance
Current composition of the 33 seats in the General Assembly
| |||
| Fidesz – Hungarian Civic Union | 19 seats + Mayor of Budapest (60,6%) | ||
| Hungarian Socialist Party | 6 seats (15,2%) | ||
| style="background:Template:Together 2014/meta/color"| | Together 2014 | 2 seats (6,1%) | |
| Democratic Coalition | 2 seats (6,1%) | ||
| Politics Can Be Different | 1 seats (3,0%) | ||
| Jobbik | 1 seats (3,0%) | ||
| Independent | 1 seats (3,0%) | ||
Budapest has been a metropolitan municipality with a mayor-council form of government since its consolidation in 1873, but Budapest also holds a special status as a county-level government, and also special within that, as holds a capital-city territory status.[156] In Budapest, the central government is responsible for the urban planning, statutory planning, public transport, housing, waste management, municipal taxes, correctional institutions, libraries, public safety, recreational facilities, among others. The Mayor is responsible for all city services, police and fire protection, enforcement of all city and state laws within the city, and administration of public property and most public agencies. Besides, each of Budapest' twenty-three districts has its own town hall and a directly elected council and the directly elected mayor of district.[citation needed]
István Tarlós, the current Mayor was re-elected mayor for another 5-year term on the 2014 local elections, he received 49.06% of the votes.[157] He is an independent (but supported by Fidesz) who assumed the office first on 3 October 2010.[158] The composition of the 33 seats in the Budapest General Assembly after the 2014 elections is in the table. The mayor and members of General Assembly are elected to five-year terms.[citation needed]
The Budapest General Assembly is a unicameral body consisting of 33 members, which consist of the 23 mayors of the districts, 9 from the electoral lists of political parties, plus Mayor of Budapest (the Mayor is elected directly). Each term for the mayor and assembly members lasts five years.[159] Submitting the budget of Budapest is the responsibility of the Mayor and the deputy-mayor in charge of finance. The latest, 2014 budget was approved with 18 supporting votes from ruling Fidesz and 14 votes against by the opposition lawmakers.[160]
Main sights and tourism
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Criteria | Cultural: i, ii, iv |
| Reference | 400 |
| Inscription | 1987 (11th Session) |


The neo-Gothic Parliament, the biggest building in Hungary with its 268 metres (879 ft) length, containing amongst other things the Hungarian Crown Jewels. Saint Stephen's Basilica, where the Holy Right Hand of the founder of Hungary, King Saint Stephen is on display. The Hungarian cuisine and café culture: for example, Gerbeaud Café, and the Százéves, Biarritz, Fortuna, Alabárdos, Arany Szarvas, Kárpátia and the world famous Mátyás Pince Restaurants. There are Roman remains at the Aquincum Museum, and historic furniture at the Nagytétény Castle Museum, just 2 out of 223 museums in Budapest. Another historical museum is the House of Terror, hosted in the building that was the venue of the Nazi Headquarters. The Castle Hill, the River Danube embankments and the whole of Andrássy út have been officially recognized as UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
Castle Hill and the Castle District; there are three churches here, six museums, and a host of interesting buildings, streets and squares. The former Royal Palace is one of the symbols of Hungary – and has been the scene of battles and wars ever since the 13th century. Nowadays it houses two impressive museums and the National Széchenyi Library. The nearby Sándor Palace contains the offices and official residence of the President of Hungary. The seven-hundred-year-old Matthias Church is one of the jewels of Budapest, it is in neo-Gothic style, decorated with coloured shingles and elegant pinnacles. Next to it is an equestrian statue of the first king of Hungary, King Saint Stephen, and behind that is the Fisherman's Bastion, built in 1905 by the architect Frigyes Schulek, the Fishermen's Bastions owes its name to the namesake corporation that during the Middle Ages was responsible of the defence of this part of ramparts, from where opens out a panoramic view of the whole city. Statues of the Turul, the mythical guardian bird of Hungary, can be found in both the Castle District and the Twelfth District.

In Pest, arguably the most important sight is Andrássy út. This Avenue is an elegant 2.5 kilometres (2 miles) long tree-lined street that covers the distance from Deák Ferenc tér to the Heroes Square. On this Avenue overlook many important sites. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. As far as Kodály körönd and Oktogon both sides are lined with large shops and flats built close together. Between there and Heroes' Square the houses are detached and altogether grander. Under the whole runs continental Europe's oldest Underground railway, most of whose stations retain their original appearance. Heroes' Square is dominated by the Millenary Monument, with the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier in front. To the sides are the Museum of Fine Arts and the Kunsthalle Budapest, and behind City Park opens out, with Vajdahunyad Castle. One of the jewels of Andrássy út is the Hungarian State Opera House. Statue Park, a theme park with striking statues of the Communist era, is located just outside the main city and is accessible by public transport.
The Dohány Street Synagogue is the largest synagogue in Europe, and the second largest active synagogue in the world.[161] The synagogue is located in the Jewish district taking up several blocks in central Budapest bordered by Király utca, Wesselényi utca, Grand Boulevard and Bajcsy Zsilinszky road. It was built in moorish revival style in 1859 and has a capacity of 3000 people. Adjacent to it is a sculpture reproducing a weeping willow tree in steel to commemorate the Hungarian victims of the Holocaust. The city is also home to the largest medicinal bath in Europe (Széchenyi Medicinal Bath) and the third largest Parliament building in the world, once the largest in the world. Other attractions are the bridges of the capital. Seven bridges provide crossings over the Danube, and from north to south are: the Árpád Bridge (built in 1950 at the north of Margaret Island); the Margaret Bridge (built in 1901, destroyed during the war by an explosion and then rebuilt in 1948); the Chain Bridge (built in 1849, destroyed during the II World War and the rebuilt in 1949); the Elisabeth Bridge (completed in 1903 and dedicated to the murdered Queen Elisabeth, it was destroyed by the Germans during the war and rebuilt in 1964); the Liberty Bridge (opened in 1896 and rebuilt in 1989 in Art Nouveau style); the Petőfi Bridge (completed in 1937, destroyed during the war and rebuilt in 1952); the Rákóczi Bridge (completed in 1995). Most remarkable for their beauty are the Margaret bridge, the Chain bridge and the Liberty bridge. The world's largest panorama photograph was created in (and of) Budapest in 2010.[162]
Tourists visiting Budapest can receive free maps and information from the nonprofit Budapest Festival and Tourism Center at its info-points.[163] The info centers also offer the Budapest Card which allows free public transit and discounts for several museums, restaurants and other places of interest. Cards are available for 24, 48 or 72-hour durations.[164] The city is also well known for its ruin bars both day and night.[165]
Parks and gardens

Budapest has many municipal parks and most have playgrounds for children and seasonal activities like skating in the winter and boating in the summer. Access from the city center is quick and easy with the Millennium Underground. Budapest has a complex park system, with various lands operated by the Budapest City Gardening Ltd.[166] The wealth of greenspace afforded by Budapest's parks is further augmented, a network of open spaces containing forest, streams, and lakes that are set aside as natural areas which lie along not for from inner city, among others the Budapest Zoo and Botanical Garden (established in 1866) in the City Park.[167] The most notably and popular parks in Budapest are the City Park which were established in 1751 (302 acres) along with Andrássy Avenue,[168] the Margaret Island in the Danube (238 acres or 96 hectares),[169] the People's Park and the Kopaszi Dam.[170]
The Buda Hills also offer a variety of adventurous outdoor activities, along with some spectacular views. A popular place frequented by locals is Normafa, offering activities for all seasons. With a modest ski run, it is also a winter favorite for skiers and snow boarders if there is enough snowfall.
Islands


Seven islands can be found on the Danube: Shipyard Island, Margaret Island, Csepel Island, Palotai-sziget (now a peninsula), Népsziget, Háros-sziget, and Molnár-sziget. Notable islands include:
- Margaret Island is a 2.5 km (1.6 mi) long island and 0.965 square kilometres (238 acres) in area. The island mostly consists of a park and is a popular recreational area for tourists and locals alike. The island lies between bridges Margaret Bridge (south) and Árpád Bridge (north). Dance clubs, swimming pools, an aqua park, athletic and fitness centres, bicycle and running tracks can be found around the Island. During the day the island is occupied by people doing sports, or just resting. In the summer (generally on the weekends) mostly young people go to the island at night to party on its terraces, or to recreate with a bottle of alcohol on a bench or on the grass (this form of entertainment is sometimes referred to as bench-partying).
- Csepel Island (Csepel-sziget, Hungarian pronunciation: [ˈtʃɛpɛlsiɡɛt]) is the largest island of the River Danube in Hungary. It is 48 km (30 mi) long; its width is 6 to 8 km (4 to 5 mi) and its area comprises 257 km2 (99 sq mi), whereas only the northern tip is inside the city limits.
- Hajógyári-sziget ([ˈhɒjoːɟaːri siɡɛt], or Óbudai-sziget) is a man-made island located in the third district. This island hosts many activities such as: wake-boarding, jet-skiing during the day, and dance clubs during the night. This is the island where the famous Sziget Festival takes place, hosting hundreds of performances per year and now around 400,000 visitors in its last edition. Many building projects are taking place to make this island into one of the biggest entertainment centres of Europe. The plan is to build apartment buildings, hotels, casinos and a marina.
- Luppa-sziget is the smallest island of Budapest and is located in the northern region of the city.
- Rock of Ínség can be found in the river Danube under the Gellért mountain. It can be seen only during a drought period when the river level is very low.
Spas

One of the reasons the Romans first colonised the area immediately to the west of the River Danube and established their regional capital at Aquincum (now part of Óbuda, in northern Budapest) is so that they could utilise and enjoy the thermal springs. There are still ruins visible today of the enormous baths that were built during that period. The new baths that were constructed during the Turkish period (1541–1686) served both bathing and medicinal purposes, and some of these are still in use to this day. Budapest gained its reputation as a city of spas in the 1920s, following the first realisation of the economic potential of the thermal waters in drawing in visitors. Indeed, in 1934 Budapest was officially ranked as a "City of Spas". Today, the baths are mostly frequented by the older generation, as, with the exception of the "Magic Bath" and "Cinetrip" water discos, young people tend to prefer the lidos which are open in the summer. Construction of the Király Baths started in 1565, and most of the present-day building dates from the Turkish period, including most notably the fine cupola-topped pool. The Rudas Baths are centrally placed – in the narrow strip of land between Gellért Hill and the River Danube – and also an outstanding example of architecture dating from the Turkish period. The central feature is an octagonal pool over which light shines from a 10 metres (33 ft) diameter cupola, supported by eight pillars. The Gellért Baths and Hotel were built in 1918, although there had once been Turkish baths on the site, and in the Middle Ages a hospital. In 1927, the Baths were extended to include the wave pool, and the effervescent bath was added in 1934. The well-preserved Art Nouveau interior includes colourful mosaics, marble columns, stained glass windows and statues. The Lukács Baths are also in Buda and are also Turkish in origin, although they were only revived at the end of the 19th century. This was also when the spa and treatment centre were founded. There is still something of an atmosphere of fin-de-siècle about the place, and all around the inner courtyard there are marble tablets recalling the thanks of patrons who were cured there. Since the 1950s it has been regarded as a centre for intellectuals and artists.
The Széchenyi Baths are one of the largest bathing complexes in all Europe, and the only "old" medicinal baths to be found in the Pest side of the city. The indoor medicinal baths date from 1913 and the outdoor pools from 1927. There is an atmosphere of grandeur about the whole place with the bright, largest pools resembling aspects associated with Roman baths, the smaller bath tubs reminding one of the bathing culture of the Greeks, and the saunas and diving pools borrowed from traditions emanating in northern Europe. The three outdoor pools (one of which is a fun pool) are open all year, including winter. Indoors there are over ten separate pools, and a whole host of medical treatments is also available. The Szécheny Baths are built in modern Renaissance style.
Infrastructure and transportation
Airport

Budapest is served by Budapest Ferenc Liszt International Airport (BUD) (named after Franz Liszt, the notable Hungarian composer), one of the busiest airports in Central and Eastern Europe, located 16 kilometres (9.9 mi) east-southeast of the centre of Budapest, in the District XVIII. The airport offers international connections among all major European cities, and also to North America, Africa and the Middle East. As Hungary's busiest airport, handles nearly all of the country's air passenger traffic. Budapest Liszt Ferenc handled around 250 scheduled flights daily in 2013, and an ever rising number of charters. London, Brussels, Frankfurt, Munich, Paris, and Amsterdam are the busiest international connections respectively, while Toronto, Montreal, Dubai, Doha and Alicante are the most unusual in the region.[171] Today the airport serves as a base for Ryanair, Wizz Air, Budapest Aircraft Service, CityLine Hungary, Farnair Hungary and Travel Service Hungary among others. The airport is accessible via public transportation from the city centre by the Metro line 3 and then the airport bus No. 200E.[172]
As part of a strategic development plan, €561 million have spent to expanding and modernising the airport infrastructure until December 2012. Most of these improvements are already completed,[173] the postponed ones are the new cargo area and new piers for terminal 2A and 2B, but these development are on standby also, and will start immediately, when the airport traffic will reach the appropriate level. SkyCourt, the newest, state-of-the-art building between the 2A and 2B terminals with 5 levels. Passenger safety checks were moved here along with new baggage classifiers and the new Malév and SkyTeam business lounges, as well as the first MasterCard lounge in Europe.[174]
Public transportation


The Centre for Budapest Transport (BKK), the transportation authority of Budapest,[175] operates one of the largest public transportation systems in Europe, which covers the city of Budapest and 80 surrounding suburbs. Budapest's public transport system consists of four metro lines, with Line 1 (Yellow) — constructed 1896, being the second oldest in the world; 5 suburban railway lines; 33 city tram lines; 15 trolleybus lines; 264 bus lines, with 40 routes providing night bus services; 4 city boat services plus the BuBi, the smart bicycle sharing network with bikes monitored by computer and GPS. On an average weekday, BKK lines transports 3.9 million riders. In 2011, it handled a total of 1.4 billion passengers.[176] In 2014, the 65% of the passenger traffic in Budapest was by public transport and 35% by car. The aim is 80%–20% by 2030 in accordance with the strategy of BKK.
The development of complex Intelligent transportation system in the city is rapidly advancing, the application of smart traffic lights is widespread, they are GPS and computer controlled and give priority to the GPS connected public transport vehicles automatically, as well as the traffic is measured and analyzed on the roads and car drivers informed about the expected travel time and traffic by intelligent displays (EasyWay project).[177] Public transport users are immediately notified of any changes in public transport online, on smartphones and on PIDS displays, as well car drivers can keep track of changes in traffic and road management in real-time online and on smartphones through the BKK Info.[178][179] As well all vehicles can be followed online and on smartphones in real-time throughout the city with the Futár PIDS system,[180] while the continuous introducing of integrated e-ticket system will help the measurement of passenger numbers on each line and the intelligent control of service frequency.
The development of Futár, the citywide real-time passenger information system and real-time route planner is finished already and now all of the public transport vehicle is connected via satellite system. The real-time information of trams, buses and trolleybuses are available for both the operators in the control room and for all the passengers in all stops on smartphone and on city street displays.[181] The implementation of latest generation automated fare collection and e-ticket system with NFC compatibility and reusable contactless smart cards for making electronic payments in online and offline systems in Budapest is started in 2014, the project is implemented and operated by the operator of Hong Kong Octopus card jointly with one of the leading European companies of e-ticket and automated fare collection, Scheidt & Bachmann.[182] The deployment of 300 new digital contactless ticket vending machine will be finished by the end of 2014 in harmonization with the e-ticket system.[183]

The tram lines no. 4 and 6 are the busiest city tram lines in the world,[184] with one of the world's longest trams (54-metre long Siemens Combino) running at 2–3 minute intervals at peak time and 4–5 minutes off-peak. Day services are usually from 4am until 23pm-0.30am. The night service has a reputation for being excellent.[151] Hungarian State Railways operates an extensive network of commuter rail services, their importance in the suburban commuter passenger traffic is significant, but in travel within the city is limited. The organiser of public transport in Budapest is the municipal corporation Centre for Budapest Transport (Budapesti Közlekedési Központ – BKK), that is responsible for planning and organising network and services, planning and developing tariff concepts, attending to public service procurer duties, managing public service contracts, operating controlling and monitoring systems, setting and monitoring service level agreements related to public transport, attending to customer service duties, selling and monitoring tickets and passes, attending to integrated passenger information duties, unified Budapest-centric traffic control within public transport, attending to duties related to river navigation, plus the management of Budapest roads, operating taxi stations, unified control of bicycle traffic development in the capital, preparing parking strategy and developing an operational concept, preparation of road traffic management, developing an optimal traffic management system, organising and co-ordinating road reconstruction and even more, in short, everything which is related to transport in the city.[185]
Roads and railways

Budapest is the most important Hungarian road terminus, all of the major highways and railways ends within the city limits. The road system in the city is designed in a similar manner to that of Paris, with several ring roads, and avenues radiating out from the center. Ring road M0 around Budapest is nearly completed, with only one section missing on the west side due to local disputes. Currently the beltway is 80 kilometres (50 miles) in length, and once finished it will be 107 kilometres (66 mi) of highway in length.
The city is a vital traffic hub because all major European roads and European railway lines lead to Budapest.[78] The Danube was and is still today an important water-way and this region in the centre of the Carpathian Basin lies at the cross-roads of trade routes.[79] Hungarian main line railways are operated by Hungarian State Railways. There are three main railway station in Budapest, the Budapest Eastern railway station, the Budapest Western railway station and Budapest Southern railway station, operating both domestic and international rail services. Budapest is one of the main stops of the Orient Express on its Central and Eastern European route.[186] There is also a suburban rail service in and around Budapest, operated under the name HÉV.
Ports and shipping
The river Danube flows through Budapest on its way from Germany to the Black Sea. The river is easily navigable and so Budapest historically has a major commercial port at Csepel District and at New Pest District also. The Pest side is also a famous port place with international shipping ports for cargo[187] and for passenger ships.[188] In the summer months, a scheduled hydrofoil service operates on the Danube connecting the city to Vienna.
BKK (through the operator BKV) also provides public transport with boat service within the borders of the city. Four routes, marked D11-14, connect the 2 banks with Margaret Island and Hajógyári-island, from Római fürdő (Buda side, North to Óbudai island) or Árpád Bridge (Pest side) to Rákóczi Bridge, with a total of 15 stops. In addition, several companies provides sightseeing boat trips and also an amphibious vehicle (bus and boat) operates constantly.
Water quality in Budapest harbours improved dramatically in the recent years, treatment facilities processed 100% of generated sewage in 2010. Budapesters regularly kayak, canoe, jet-ski and sail on the Danube, which has continuously become a major recreational site for the city.
Other modes of transport

Special vehicles in Budapest, besides metros, include suburban rails, trams and boats. There are a couple of less common vehicles in Budapest, like the trolleybus on several lines in Pest, the Castle Hill Funicular between the Chain Bridge and Buda Castle, the cyclecar for rent in Margaret Island, the chairlift, the Budapest Cog-wheel Railway and children's railway. The latter three vehicles runs among Buda hills.
Bridges
12 road bridge and 2 train bridge connect the two banks of the river Danube (between Pest and Buda) at the city of Budapest. The first permanent bridge was Chain Bridge, nowadays the capital has 2 more historical bridges from the 19th century. Some bridges are combined use because of its tram lines.
Culture and contemporary life

The culture of Budapest is reflected by Budapest's size and variety. Most Hungarian cultural movements first emerged in the city. Budapest is an important center for music, film, theatre, dance and visual art. Artists have been drawn into the city by opportunity, as the city government funds the arts with adequate financial resources. Budapest is headquarter of the Hungarian LGBT community.
Museums and galleries

Budapest is packed with museums and galleries, and there are plenty of temporary exhibitions in the most unlikely of settings, particularly in summer. The city glories in 223 museums and galleries, which presents several memories, not only the Hungarian historical, art and science ones, but also the memories of universal and European culture and science. Here are the greatest examples among them: the Hungarian National Museum, the Hungarian National Gallery, the Museum of Fine Arts (where can see the pictures of Hungarian painters, like Victor Vasarely, Mihály Munkácsy and a great collection about Italian art, Dutch art, Spanish art and British art from before the 19th century and French art, British art, German art, Austrian art after the 19th century), the House of Terror, the Budapest Historical Museum, the Aquincum Museum, the Memento Park, Museum of Applied Arts and the contemporary arts exhibition Palace of Arts Budapest.[189] In Budapest there are currently 837 different monuments, which represent the most of the European artistic style. The classical and unique Hungarian Art Nouveau buildings are prominent.
Libraries
A lot of libraries have unique collections in Budapest, such as the National Széchenyi Library, which keeps historical relics from the age before the printing of books. The Metropolitan Szabó Ervin Library plays an important role in the general education of the capital's population. Other libraries: The Library of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Eötvös University Library, the Parliamentary Library, Library of the Hungarian Central Statistical Office and the National Library of Foreign Literature.
Opera and theatres

In Budapest there are forty theatres, seven concert halls and an opera house.[190] Outdoor festivals, concerts and lectures enrich the cultural offer of summer, which are often held in historical buildings. The largest theatre facilities are the Budapest Operetta and Musical Theatre, the József Attila Theatre, the Katona József Theatre, the Madách Theatre, the Hungarian State Opera House, the National Theatre, the Vigadó Concert Hall, Radnóti Miklós Theatre, the Comedy Theatre and the Palace of Arts, known as MUPA. The Budapest Opera Ball is an annual Hungarian society event taking place in the building of the Budapest Opera (Operaház) on the last Saturday of the carnival season, usually late February.[191]
Performing arts and festivals

Several annual festivals take place in Budapest, such as Sziget Festival, one of the largest outdoor music festival in Europe, the Budapest Spring Festival presents on concerts at several venues across the city. The Budapest Autumn Festival brings free music, dance, art, and other cultural events to the streets of the city. Budapest Wine Festival and Budapest Pálinka Festival occurs each May and gastronomy festivals focus on culinary pleasures. Budapest Pride (or Budapest Pride Film and Cultural Festival) occurs annually across the city, and usually involves a parade on the Andrássy Avenue. Other festivals include the Budapest Fringe Festival, which brings more than 500 artists in about 50 shows to produce a wide range of interesting works in alternative theatre, dance, music and comedy outside the mainstream. The LOW Festival was a multidisciplinary contemporary cultural festival held in Hungary in the cities Budapest and Pécs from February till March. The name of the festival alludes to the Low Countries, the region encompassing the Netherlands and Flanders. Budapest Jewish Summer Festival, in late August, is also one of the largest in Europe.
There are many symphony orchestras in Budapest with the Budapest Philharmonic Orchestra being preeminent orchestras. It was founded in 1853 by Ferenc Erkel and still presents regular concerts in the Hungarian State Opera House and National Theatre.
The dance tradition of the Carpathian Basin is a unique area of the European dance culture, which is also a special transition between the Balkans and Western Europe regions. The city is home to several authentic Hungarian folk dance ensembles which range from small ensembles to professional troupes. Budapest is one of the few cities in the world where a high school for folk dance learning exists.
Fashion
Budapest is home to a fashion week twice a year, where the city's fashion designers and houses present their collections and provide a meeting place for the fashion industry representatives. Budapest Fashion Week additionally a place for designers from other countries may present their collections in Budapest. Hungarian models, like Barbara Palvin, Enikő Mihalik, Diána Mészáros, Viktória Vámosi usually appearing at these events along international participants. Fashion brands like Zara, H&M, Mango, ESPRIT, Douglas AG, Lacoste, Nike and other retail fashion brands are common across the city's shopping malls and on the streets. [citation needed]
Major luxury fashion brands such as Roberto Cavalli, Dolce & Gabbana, Gucci, Versace, Ferragamo, Moschino, Prada and Hugo Boss, can be found among the city's most prestigious shopping streets, the Fashion Street, Váci Street and Andrássy Avenue in Budapest's main upscale fashion district, the Leopoldtown, District V. Budapest's newest fashion and design mall, the il Bacio di Stile, opened in 2013 and houses most major fashion houses and brands from around the world including Bottega Veneta, Giorgio Armani, Saint Laurent, Lanvin, Valentino, Oscar de la Renta.[192]
Media

Budapest is a prominent location for the Hungarian entertainment industry, with many films, television series, books, and other media set there. Budapest is the largest centre for film and television production in Hungary. In 2011, it employed more than 50,000 people and generated 63.9% of revenues of the media industry in the country.[193] Budapest is the media centre of Hungary, and the location of the main headquarters of Hungarian Television and other numerous local and national TV and radio stations, such as M1, M2, Duna TV, Duna World, RTL Klub, TV2 (Hungary), EuroNews, Comedy Central, MTV Hungary, VIVA Hungary, Viasat 3, Cool TV, Pro4 and politics and news channels such as, Hír TV, ATV, Echo TV, furthermore documentary channels such as, Discovery Channel, Discovery Science, Discovery World, National Geographic Channel, Nat Geo Wild, Spektrum, BBC Entertainment and it is less than a quarter of the channels broadcast from Budapest, for the whole picture see the Television in Hungary. In 2012, there were 7.2 million internet users in Hungary (72% of the population).[194] and there were 2.3 million subscriptions for mobile broadband,[195]
Cuisine
In the modern age, Budapest developed its own peculiar cuisine, based on products of the nearby region, as lamb, pork and vegetables special in the region. Modern Hungarian cuisine is a synthesis of ancient Asiatic components mixed with French, Germanic, Italian, and Slavic elements. The food of Hungary can be considered a melting pot of the continent, with a culinary base formed from its own, original Magyar cuisine. Considerable numbers of Saxons, Armenians, Italians, Jews and Serbs settled in the Hungarian basin and in Transylvania, also contributing with different new dishes. Elements of ancient Turkish cuisine were adopted during the Ottoman era, in the form of sweets (for example different nougats, like white nougat called törökméz, quince (birsalma), Turkish delight, Turkish coffee or rice dishes like pilaf, meat and vegetable dishes like the eggplant, used in eggplant salads and appetizers, stuffed peppers and stuffed cabbage called töltött káposzta. Hungarian cuisine was influenced by Austrian cuisine under the Austro-Hungarian Empire, dishes and methods of food preparation have often been borrowed from Austrian cuisine, and vice versa.[196]
Budapest restaurants reflect diversity, with menus carrying traditional regional cuisine, fusions of various culinary influences, or innovating in the leading edge of new techniques. Budapest' food shops also have a solid reputation for supplying quality specialised culinary products and supplies, reputations that are often built up over generations. These include many shops, such as Café Gerbeaud, one of the greatest and most traditional coffeehouses in Europe, or the Gundel restaurant and gastro shop in the City Park. Diners can also find the highest quality foods served in several Michelin-starred restaurants, like Onyx, Costes, Borkonyha or Tanti.
In fiction
The 1906 novel The Paul Street Boys, the 1937 novel Journey by Moonlight, the 1957 book The Bridge at Andau, the 1975 novel Fateless, the 1977 novel The End of a Family Story, the 1986 book Between the Woods and the Water, the 1992 novel Under the Frog, the 1987 novel The Door, the 2002 novel Prague, the 2003 book Budapeste, the 2004 novel Ballad of the Whisky Robber, the 2005 novels Parallel Stories and The Historian, the 2012 novel Budapest Noir are set, amongst others, partly or entirely in Budapest. Some of the better known feature films set in Budapest are Kontroll, The District!, Ein Lied von Liebe und Tod, Sunshine, An American Rhapsody, As You Desire Me, The Good Fairy, Hanna's War, The Journey, Ladies in Love, Mehbooba, Music Box, The Shop Around the Corner, Zoo in Budapest, Underworld, and Mission: Impossible – Ghost Protocol. The Grand Budapest Hotel (2014) is a Wes Anderson film. It was filmed in Germany and set in the fictional Republic of Zubrowka which is in the alpine mountains of Hungary.
Sports


Budapest hosted many global sport event in the past, among others the 1994 IAAF World Cross Country Championships, 1997 World Amateur Boxing Championships, 2000 World Fencing Championships, 2001 World Allround Speed Skating Championships, Bandy World Championship 2004, 2008 World Interuniversity Games, 2008 World Modern Pentathlon Championships, 2010 ITU World Championship Series, 2011 IIHF World Championship, 2013 World Fencing Championships, 2013 World Wrestling Championships, 2014 World Masters Athletics Championships and will in the future, like 2017 World Aquatics Championships, 2017 World Judo Championships, only in the last two decade. Besides these, Budapest was the home of many European-level tournaments, like 2006 European Aquatics Championships, 2010 European Aquatics Championships, 2010 UEFA Futsal Championship, 2013 European Judo Championships, 2013 European Karate Championships and will be the host of 4 matches in the UEFA Euro 2020, which will be held in the 67,889-seat new multi-purpose Puskás Ferenc Stadium, to mention a few.
In 2015 the Assembly of the Hungarian Olympic Committee and the Assembly of Budapest decided to bid for the 2024 Summer Olympics. Budapest has lost several bids to host the games, in 1916, 1920, 1936, 1944, and 1960 to Berlin, Antwerp, London, and Rome, respectively.[197][198] The Hungarian Parliament also voted to support the bid on 28 January 2016, later Budapest City Council approved list of venues and Budapest became an official candidate for the 2024 Summer Olympic Games.
Numerous Olympic, World, and European Championship winners and medalists reside in the city, which follows from Hungary's 8th place among all the nations of the world in the All-time Olympic Games medal table. Hungarians have always been avid sports people: during the history of the Summer Olympic Games, Hungarians have brought home 476 medals, of which 167 are gold. The top events in which Hungarians have excelled are fencing, swimming, water polo, canoeing, wrestling and track & field sports. Beside classic sports, recreational modern sports such as bowling, pool billiard, darts, go-carting, wakeboarding and squash are very popular in Budapest, and extreme sports are also gaining ground. Furthermore, the Budapest Marathon and Budapest Half Marathon also attract many people every year. The city's largest football stadium is named after Ferenc Puskás, recognised as the top scorer of the 20th century and for whom FIFA's Puskás Award (Ballon d'Or) was named.[199]
One of Budapest's most popular sport is football and it has many Hungarian League football club, including in the top level Nemzeti Bajnokság I league, like Ferencvárosi TC (29 Hungarian League titles), MTK Budapest FC (23 titles), Újpest FC (20 titles), Budapest Honvéd FC (13 titles), Vasas SC (6 titles), Csepel SC (4 titles), Budapesti TC (2 titles). In the 2015–16 UEFA Europa League, Hungary's most popular soccer club, Ferencvárosi TC dropped out in the second qualifying round.
The Hungarian Grand Prix in Formula One has been held at the Hungaroring just outside the city, which circuit has FIA Grade 1 license.[200] Since 1986, the race has been a round of the FIA Formula One World Championship. At the 2013 Hungarian Grand Prix, it was confirmed that Hungary will continue to host a Formula 1 race until 2021.[201] The track was completely resurfaced for the first time in early 2016, and it was announced the Grand Prix's deal was extended for a further 5 years, until 2026.[202]
Education



Budapest is home to over 35 higher education institutions. Under the Bologna Process, many offered qualifications are recognised in countries across Europe. Medicine, dentistry, pharmaceuticals, veterinary programs, and engineering are among the most popular fields for foreigners to undertake in Budapest. Most universities in Budapest offer courses in English, as well as in other languages like German, French, and Dutch, aimed specifically at foreigners. Many students from other European countries spend one or two semesters in Budapest through the Erasmus Programme.[203]
Notable people
International relations
Budapest has quite a few sister cities and many partner cities around the world.[204] Like Budapest, many of them are the most influential and largest cities of their country and region, most of them are the primate city and political, economical, cultural capital of their country. The Mayor of Budapest says the aim with improving sister city relationships is to allow and encourage a mutual exchange of information and experiences, as well as co-operation, in the areas of city management, education, culture, tourism, media and communication, trade and business development.[205]
Historic sister cities
Partnerships around the world
Some of the city's districts are also twinned to small cities or districts of other big cities, for details see the article List of districts and towns in Budapest.
Gallery
-
Heroes' Square with the Millenary Monument
-
Budai Vigadó
-
Fisherman's Bastion
-
Andrássy Avenue was recognised as a World Heritage Site
-
King Saint Stephen's sculpture in Buda Castle
-
Castle Theatre
-
Operett Theatre
-
Bálna
-
Brudern House
-
Nyugati Railway Station
See also
- Bridges of Budapest
- Budapest metropolitan area
- Fort Budapest
- List of cemeteries in Budapest
- List of films shot in Budapest
- List of historical capitals of Hungary
- List of tourist attractions in Budapest
- Music of Budapest
- Outline of Hungary
- Spas in Budapest
- Urban and Suburban Transit Association (most of its activity is centred on Budapest)
References
Bibliography
- Budapest: Eyewitness Travel Guildes. DK Travel. 2007. ISBN 978-0-7566-2435-4.
- Barber, Annabel (2004). Visible Cities Budapest: A City Guide. Somerset. ISBN 978-963-212-986-0.
- Ungvary, Krisztian (2006). The Siege of Budapest: One Hundred Days in World War II. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-11985-5.
- Molnar, Miklos (2001). A Concise History of Hungary. Cambridge Concise Histories. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-66736-4.
Notes
- ^ "The Municipality of Budapest (official)". Municipality of Budapest. 11 September 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ^ a b "Budapest". 2014 Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. 11 September 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ^ "Functional Urban Areas - Population on 1 January by age groups and sex". Eurostat. 1 April 2016. Retrieved 12 April 2016.
- ^ "Best view in Budapest from the city's highest hilltop". stay.com – Budapest. 11 September 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ^ "Population by type of settlement – annually". Hungarian Central Statistical Office. 12 April 2016. Retrieved 12 April 2016.
- ^ a b "Gazetteer of Hungary, Hungarian Central Statistical Office, 2012" (PDF). Retrieved 2 October 2013.
- ^ "Budapest City Review". Euromonitor International. December 2012. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
- ^ "Budapest – HU101 – Employment Institute". Iz.sk. Retrieved 10 June 2013.
- ^ UK: /ˌb[invalid input: 'ju:']dəˈpɛst/, /ˌbud-/, /ˈb[invalid input: 'ju:']dəpɛst/, /ˈbud-/
US: /ˈbuːdəpɛst/
Source: Wells, John C. (2008), Longman Pronunciation Dictionary (3rd ed.), Longman, ISBN 978-1-4058-8118-0 - ^ a b c Bachmann, Helena (18 March 2002). "Beauty and the Feast". Time. Retrieved 22 May 2008.
- ^ Meer, Dr Jan van der; Carvalho, Dr Luis; Berg, Professor Leo van den (28 May 2014). Cities as Engines of Sustainable Competitiveness: European Urban Policy in Practice. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. ISBN 978-1-4724-2704-5.
- ^ "Budapest". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica. 2008. Retrieved 30 January 2008.
- ^ Taşan-Kok, Tuna (2004). Budapest, Istanbul and Warsaw: Institutional and spatial change. Eburon Uitgeverij. p. 41. ISBN 978-90-5972-041-1. Retrieved 21 May 2013.
- ^ "2011 Hungarian Census" (PDF). Hungary Central Statistical Office. 27 March 2012. Retrieved 27 March 2012.[dead link]
- ^ "Interactive population pyramids of Budapest (1980–2010)". Hungary Central Statistical Office. Retrieved 10 May 2011.[dead link]
- ^ a b Zoltán, Dövényi; Zoltán, Kovács (1999). "A szuburbanizáció térbeni-társadalmi jellemzői Budapest környékén (Spatial and societal parameters of the suburbanization in Budapest)" (PDF) (in Hungarian). Földrajzi Értesítő (Geographical Report). Retrieved 21 May 2013.
- ^ History of the Budapest Commuter Association (English) Archived 2011-10-07 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Settlements of the Budapest Commuter Area (Hungarian) Archived 2011-10-07 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Török, András. "Budapest". Encarta. Archived from the original on 31 October 2009. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Molnar, A Concise History of Hungary, Chronology pp. 15.
- ^ a b c d "Aquincum". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica. 2008. Retrieved 16 March 2016.
- ^ Sugar, Peter F.; Péter Hanák; Tibor Frank (1990). "Hungary before the Hungarian Conquest". A History of Hungary. Indiana University Press. p. 3. ISBN 0-253-20867-X. Retrieved 19 May 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f "Budapest". Travel Channel. Retrieved 22 May 2008.
- ^ a b c s:1911 Encyclopædia Britannica/Budapest
- ^ Drake, Miriam A. (2003). "Eastern Europe, England and Spain". Encyclopedia of Library and Information Science. CRC Press. p. 2498. ISBN 0-8247-2080-6. Retrieved 22 May 2008.
- ^ Casmir, Fred L. (1995). "Hungarian culture in communication". Communication in Eastern Europe: The Role of History, Culture, and media in contemporary conflicts. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. p. 122. ISBN 0-8058-1625-9. Retrieved 21 May 2008.
- ^ Molnar, A Concise History of Hungary, Chronology pp. 15
- ^ Beaverstock, J. V.; R. J. Smith; P. J. Taylor (1999). "A Roster of World Cities". Loughborough University. Retrieved 22 May 2008.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b "Nomination of the banks of the Danube and the district of the Buda Castle" (PDF). International Council on Monuments and Sites. Retrieved 31 January 2008.
- ^ Lyman, Rick (3 October 2006). "Budapest Is Stealing Some of Prague's Spotlight". The New York Times. Retrieved 29 January 2008.
- ^ "World Heritage Committee Inscribes 9 New Sites on the World Heritage List". Unesco World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 31 January 2008.
- ^ "Hungary's, Budapest's and Balaton's Guide: Budapest's spas: Gellért, Király, Rác, Ru..'l'; l;lldas, Széchenyi, Lukács". Guideviaggi.net. Archived from the original on 28 September 2008. Retrieved 7 July 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Big underground thermal lake unveiled in Budapest, Hungary". Tvnz.co.nz. 19 November 2008. Archived from the original on 27 November 2009. Retrieved 7 July 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Euromonitor International's top city destinations ranking". Euromonitor. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- ^ "Doing Business: Budapest, the soul of Central Europe". International Herald Tribune. 4 August 2004. Archived from the original on 3 November 2011. Retrieved 29 January 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "New MasterCard Research Ranks 65 Cities in Emerging Markets Poised to Drive Long-Term Global Economic Growth". MasterCard. 22 October 2008. Retrieved 7 July 2009.
- ^ "Index – Külföld – Budapest a legélhetőbb európai nagyváros". Index.hu. 7 July 2008. Archived from the original on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 7 July 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Gazdaság: EIU: Budapest, London és New York között a legjobban élhető városok listáján". HVG.hu. 1 January 1970. Archived from the original on 28 September 2011. Retrieved 15 September 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Cha, Frances (16 October 2013). "The world's best city is..." CNN. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ Beckett, Edward; Olson, Parmy. "In Pictures: Europe's Most Idyllic Places To Live". Forbes. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- ^ a b "Innovation Cities Top 100 Index » Innovation Cities Index & Program – City data training events from 2THINKNOW for USA Canada America Europe Asia Mid-East Australia". Innovation-cities.com. 1 September 2010. Retrieved 15 September 2011.
- ^ "CEE City Ranking puts capitals under the spotlight | Local and regional publications". Rolandberger.at. Archived from the original on 28 September 2011. Retrieved 15 September 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "EU nations pick Budapest for technology institute". Sydney Morning Herald. 18 June 2008. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ European Union Document Nos. 2013/0812 (COD), ENFOPOL 395 CODEC 2773 PARLNAT 307
- ^ "hírek szünet nélkül: Kínai nagyfalat – Budapesten nyílik az első kínai befektetési támaszpont külföldön". Heti Világgazdaság (in Hungarian). Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ Meusburger, Peter; Jöns, Heike, eds. (2001). Transformations in Hungary: Essays in Economy and Society. Springer Verlag. ISBN 3-7908-1412-1. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ Bácskai Vera: Széchenyi tervei Pest-Buda felemelésére és szépítésére Archived 2014-10-22 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Kiss, Lajos (1978). Földrajzi nevek etimológiai szótára. Budapest: Akadémiai. pp. 131–132.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ Györffy, György (1997). Pest-Buda kialakulása: Budapest története a honfoglalástól az Árpád-kor végi székvárossá alakulásig. Budapest: Akadémiai. p. 242. ISBN 978-963-05-7338-2. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ Schütte, Gudmund (1917). Ptolemy's Maps of Northern Europe. Copenhagen: Royal Danish Geographical Society. p. 101. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- ^ Smith, William, ed. (2 March 2006). A Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. London: I.B. Tauris. ISBN 978-1-84511-001-7. Facsim. of ed. published: London: John Murray, 1872.
- ^ Adrian Room (2006). Placenames of the World. McFarland. p. 70. ISBN 978-0-7864-2248-7. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- ^ "Association of professional tour guides". Lovely Budapest. Retrieved 21 May 2013.
- ^ Sugar, Peter F. (1990). "Hungary before the Hungarian Conquest". A History of Hungary. Indiana University Press. p. 5. ISBN 978-0-253-20867-5. Retrieved 3 June 2008.
- ^ Molnar, A Concise History of Hungary, Chronology pp. 12
- ^ Molnar, A Concise History of Hungary, p. 14
- ^ Sugar, Peter F. (1990). "The Angevine State". A History of Hungary. Indiana University Press. p. 48. ISBN 978-0-253-20867-5. Retrieved 3 June 2008.
- ^ Mona, Ilona (1974). "Hungarian Music Publication 1774–1867". Studia Musicologica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae. 16 (1/4). Akadémiai Kiadó: 261–275. doi:10.2307/901850. JSTOR 901850.
- ^ a b Southeastern Europe under Ottoman rule, 1354–1804, Peter F. Sugar, page 88
- ^ UNESCO World Heritage Centre. "Budapest, including the Banks of the Danube, the Buda Castle Quarter and Andrássy Avenue". unesco.org. Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- ^ Hughes, Holly (13 August 2009). "7 Famous Briges". Frommer's 500 Places to Take Your Kids Before They Grow Up. Wiley Indianapolis Composition Services. ISBN 0-470-57760-6.
- ^ Budapest statisztikai évkönyve 1943 (Statistical Yearbook of Budapest, 1943), p. 33, Hungarian Central Statistical Office
- ^ Budapest székes főváros Statisztikai és Közigazgatási Évkönyve 1921–1924 (Statistical Yearbook of Budapest, 1921–1924), p. 38, Hungarian Central Statistical Office
- ^ Budapest statisztikai évkönyve 1944–1946 (Statistical Yearbook of Budapest, 1944–1946), p. 12, Hungarian Central Statistical Office
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica 1911, Budapest article
- ^ "History of the word (Jewish-Hungarian Cultural Site)" (in Hungarian). Judapest.org. Archived from the original on 31 May 2013. Retrieved 21 May 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Jüdische Nachrichten (28 November 2004). "Karl Pfeifer: Jüdisches Budapest (Jewish Budapest)" (in German). Buecher.hagalil.com. Retrieved 21 May 2013.
- ^ Macartney, C.A. (1937). Hungary and her successors – The Treaty of Trianon and Its Consequences 1919–1937. Oxford University Press.
- ^ Bernstein, Richard (9 August 2003). "East on the Danube: Hungary's Tragic Century". The New York Times. Retrieved 15 March 2008.
- ^ "RAF raids Budapest – second heavy attack". Sydney Morning Herald. 5 April 1944.
- ^ "RAF Follows US Raid on Budapest". Sydney Morning Herald. 5 April 1944.
- ^ "Budapest bombed by RAF". Sydney Morning Herald. 5 April 1944.
- ^ "Budapest". United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. Retrieved 18 July 2007.
- ^ "Raoul Wallenberg". Jewish Virtual Library. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ "Budapest". Google Maps. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ Péter, Laszlo (21 November 2013). "Budapest". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ "Geography of Budapest". Budapest Tourist Info. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ a b c "Geography". Budapest.com. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ a b "Geography of Budapest". Budapest Pocket Guide. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ Peel, M. C.; Finlayson, B. L.; McMahon, T. A. "World Map of Köppen-Geiger climate classification". The University of Melbourne. Retrieved 26 April 2013.
- ^ "Climate Budapest – Hungary". Climatedata.eu. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ "Sunshine & Daylight Hours in Budapest, Hungary". climatemps.com. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ "Hardiness zone – Gardenology.org – Plant Encyclopedia and Gardening wiki". Gardenology.org. Retrieved 13 October 2012.
- ^ "Europa Hardiness zone map". Backyardgardener.com. Retrieved 13 October 2012.
- ^ "Monthly Averages for Budapest, Hungary (based on data from 1970–2010)". Hungarian Meteorological Service.
- ^ a b "Budapest Architecture". visitbudapest.travel. 2013. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- ^ "The Incredible Architecture of Budapest". pbase.com. 2013. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- ^ "Exceptional Buildings Budapest". budapest.com. 2014. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- ^ "The high-rise buildings as emblematique element of luxury district, 13th District of Budapest". Prestigecity. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- ^ "The coming of skyscrapers?". euscreen.eu. 17 December 2006. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- ^ "The oldest church in Pest". visitbudapest.travel. 2011. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- ^ "Budapest Tour: Early Art Nouveau 1897–1904". budapestarchitect.com. 2011. Archived from the original on 29 May 2014. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Budapest High Street Overview 2013" (PDF). Jones Lang LaSalle. October 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 April 2015. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Emerging Trends in Real Estate, 2013 Europe" (PDF). PricewaterhouseCoopers. 2013. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- ^ "Bulls return to the European commercial real estate market (Budapest)". CBRE Group. 24 March 2014. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- ^ "Eurostat regional yearbook 2011" (PDF). Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- ^ "Neighborhoods in Brief". Frommer's Budapest. 2011. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- ^ "Budapest district by district". budapestbydistrict.com. 2011. Archived from the original on 6 May 2014. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Urbandivercities.eu, Case study Budapest and Budapest's 8th district". 2013. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- ^ Berényi, Eszter B. (2010), The transformation of historical city districts in inner city of Budapest (PhD dissertation) (PDF), Budapest, retrieved 5 May 2014
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b c "Population of Budapest and Hungary from 2001, Hungarian Statistical Office". HSCO. 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
- ^ "Eurostat, Population on 1 January (EU27 2004 to 2014)". Eurostat. 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
- ^ a b "Budapest – HU101 – Employment Institute". Iz.sk. Retrieved 10 June 2013.
- ^ "IMF World Economic Outlook (Hungary), 2014 April". IMF. 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
- ^ "IMF World Economic Outlook, 2014 April". IMF. 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
- ^ a b "Hungarian Census 2011" (PDF). Hungarian Statistical Office. 2013. p. 17, table 1.4.1. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
- ^ "The European Higher Education Area in 2012, page 104 (average of age groups ((33,2+26,5+21,5)/3))" (PDF). European Commission. 2012. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f "Népszámlálás 2011: Területi adatok – Budapest" (in Hungarian). Central Statistical Office.
Table 1.1.1.1. A népesség számának alakulása, népsűrűség, népszaporodás (Total number of population, population density, natural growth), 1.1.4.2 A népesség nyelvismeret és nemek szerint (population by spoken language), 1.1.6.1 A népesség anyanyelv, nemzetiség és nemek szerint (population by mother tongue and ethnicity), 1.1.7.1 A népesség vallás, felekezet és nemek szerint (population by religion), 2.1.2.2 A népesség születési hely, korcsoport és nemek szerint (population by place of birth)
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c "Budapest's population is increasing". Index.hu. 2010. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ^ "Population and Social conditions (31,4 million (6,3%) born outside of the EU)" (PDF). Eurostat. 2011. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
- ^ "Nemzetiségek otthona – fókuszban Pozsony és Budapest". korkep.sk/. Retrieved 22 August 2013.
- ^ Dezső Danyi-Zoltán Dávid: Az első magyarországi népszámlálás (1784–1787) / The first census in Hungary (1784–1787), Hungarian Central Statistical Office, Budapest, 1960, pp. 30
- ^ a b "Budapest City Review". Euromonitor International. December 2012. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
- ^ "Members of EMTA". European Metropolitan Transport Authorities (EMTA). August 2013. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
- ^ "Population Density", Geographic Information Systems – GIS of Interest. Accessed 17 May 2007. Archived 2007-02-10 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Cities and Green Growth, page 3" (PDF). OECD. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
- ^ "Eastern Europe in 2030: The future demographic, Population by City" (PDF). Euromonitor. March 2012. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
- ^ "IMPACT OF MIGRATION ON POPULATION CHANGE, Results from the Demographic and Migratory flows Affecting European Regions and Cities Project" (PDF). European Observation Network for Territorial Development and Cohesion. 2013. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
- ^ "The housing stock and the housing density". Hungarian Central Statistical Office. 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
- ^ Hungarian census 2011 – final data and methodology
- ^ "World Jewish Population". SimpleToRemember.com – Judaism Online. Retrieved 2 September 2012.
- ^ "Budapest's population is increasing (Növekszik Budapest népessége)". Index.hu. 2010. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ^ "BUDAPEST EUROPE'S SECOND FASTEST-DEVELOPING URBAN ECONOMY, STUDY REVEALS – The study examines the development of the world's 300 largest urban economies, ranking them according to the pace of development". Brookings Institution. 23 January 2015. Retrieved 8 March 2016.
- ^ "The World According to GaWC 2010". www.lboro.ac.uk. 13 April 2010. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ Istrate, Emilia. "Global MetroMonitor | Brookings Institution". Brookings.edu. Retrieved 10 June 2013.
- ^ "Hungary's GDP (IMF, 2016 est.) is $265.037 billion x 39% = $103,36 billion". Portfolio online financial journal. Retrieved 10 June 2013.
- ^ "ukmediacentre.pwc.com". PricewaterhouseCoopers. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Worldwide Centers of Commerce Index" (PDF). MasterCard Worldwide. 2008. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "World's most expensive cities in 2012 – Ranking". City Mayors. Retrieved 10 June 2013.
- ^ "Benchmarking global city competitiveness" (PDF). Economist Intelligence Unit. 2012. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "6.3.2.1. A regisztrált vállalkozások száma (Number of registered companies)". Ksh.hu. Retrieved 8 March 2016.
- ^ "Budapest City Report 2013" (PDF). Jones Lang LaSalle. September 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 April 2014. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Arena Plaza – Hungary". Plaza Centers. 2014. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Central Europe's regional office". United Nations. 2014. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Budapest to be CEE Region Headquarters for Chinese Research Institute". Promote CEE – Investment in the CEE Region. 18 September 2011. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Bachelor, Master and PhD study programs in foreign languages". Budapest Business School. 4 August 2011. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Budapest status of employment" (PDF). Budapest Public Employment Service Non-profit Company. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Top 100 Cities Destination Ranking – Analyst Insight from Euromonitor International". Blog.euromonitor.com. 21 January 2013. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- ^ "Gazdaság: EIU: Budapest, London és New York között a legjobban élhető városok listáján". HVG.hu. Archived from the original on 17 May 2013. Retrieved 10 June 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Global 500 – Countries: Hungary – Fortune". Money. 23 July 2012. Retrieved 10 June 2013.
- ^ "HFSA – Credit institutions' data". Pszaf.hu. Retrieved 10 June 2013.
- ^ "Regional Headquarters Central and Eastern Europe" (PDF). investinaustria.at. 23 September 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 April 2014. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "About the institution of the President of Hungary". Office of the President of the Republic. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "The Hungarian National Assembly". Office of the National Assembly. 2014. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Curia of Hungary". National Office for the Judiciary. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "The National Judicial Council". National Judicial Council. 23 March 2012. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Brief history of the Constitutional Court of Hungary". The Constitutional Court. 2014. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "International organizations in Hungary". Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Embassies in Budapest". 123embassy.com. 2014. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "TRANSITION AND ENVIRONMENT". Bedrvich Moldan. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ a b "A good place to live – Budapest" (PDF). Siemens, Studio Metropolitana Workshop for Urban Development. 8 November 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 May 2014. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Transport Budapest". WWF Global. 2014. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Hungary: Crime situation, including organized crime; police and state response including effectiveness – 1.1 Homicide". UNHCR-The UN Refugee Agency. 10 July 2012. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ Urban crime and violence: Conditions and trends (Figure 3.6). WHO. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Hungary: Crime situation, including organized crime; police and state response including effectiveness – 2. Organized Crime". UNHCR-The UN Refugee Agency. 10 July 2012. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Municipality of Budapest". Budapest Official Site. 11 May 2011. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Tarlós István harca csak most kezdődik". 13 October 2014. Retrieved 13 October 2014.
- ^ "Mayor of Budapest election results". valasztas.hu. 3 October 2010. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Five year terms in the local governments of Hungary". Website of the Hungarian government. 11 May 2011. Archived from the original on 13 May 2014. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Budapest City Council approves 2014 budget". dailynewshungary.com/. 26 February 2014. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ Kulish, Nicholas (30 December 2007). "Out of Darkness, New Life". The New York Times. Retrieved 12 March 2008.
- ^ "The largest photo on Earth – created by 360world.eu". 70 Billion Pixels Budapest. Retrieved 15 September 2011.
- ^ "Tourist Information Points". Budapest Info. Archived from the original on 22 December 2014. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Budapest Card". Budapest Info. Archived from the original on 20 September 2014. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Baker, Mark (15 August 2011). "Travel – The 'ruin pubs' of Budapest's seventh district: Food & Drink, Budapest". BBC. Retrieved 11 March 2013.
- ^ "Parks". Budapest.com. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ "Budapest Parks & Caves". visitBudapest.travel. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ "City Park". visitBudapest.travel. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ "Margaret Island". visitBudapest.travel. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ "Parks and Recreation in Budapest". Funzine. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ "Air Transat unveils its new Europe program for 2015". 15 October 2014. Archived from the original on 17 October 2014. Retrieved 15 October 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "From the Airport to the City centre by public transport" (PDF). Centre for Budapest Transport. 2014. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ^ "Budapest Airport Property development". Budapest Airport. 17 March 2014. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ^ "Budapest Airport unveils Europe's first MasterCard lounge". Future Travel Experience. 15 September 2011. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ^ "Centre for Budapest Transport in brief". Centre for Budapest Transport. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ^ "Annual Report 2011" (PDF). BKV Zrt. February 2012. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ^ "Easyway project – Digital information". BKK Zrt. 23 September 2014. Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- ^ "BKK Info online (public transport)". BKK Zrt. 28 October 2014. Retrieved 28 October 2014.
- ^ "BKK Info online (roads and road transport)". BKK Zrt. 28 October 2014. Retrieved 28 October 2014.
- ^ "BKK Futár PIDS system online". BKK Zrt. 28 October 2014. Retrieved 28 October 2014.
- ^ "BKK has launched its FUTÁR Journey Planner app for web, smartphones and tablets". BKK Zrt. 23 September 2014. Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- ^ "Budapest signed the Contract Agreement for the Automated Fare Collection system". BKK Zrt. 8 October 2014. Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- ^ "Purchase your ticket easier". BKK Zrt. 17 July 2014. Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- ^ "Putting the world's longest trams into service in Budapest". Railwaygazette.com. 1 April 2006. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ^ "Tasks & Responsibilities". Centre for Budapest Transport. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ^ "Venice Simplon-Orient-Express Destinations". Retrieved 23 September 2014.
- ^ "Budapest Freeport". danubeports.info. 6 May 2011. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ^ "Budapest cruise terminal". cruise-profi.com. 2014. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ^ "Budapest Museums & Galleries". visitbudapest.travel/. Retrieved 23 May 2014.
- ^ "Theaters&Concert Halls". budapest.com. 2014. Retrieved 23 May 2014.
- ^ "Short History of the Budapest Opera Ball". operabal.com. February 2010. Archived from the original on 23 February 2014. Retrieved 23 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "il Bacio di Stile, L'Occhio Di Stile". il Bacio di Stile. 2014. Retrieved 23 May 2014.
- ^ "Budapest: A great place for creative industry development?". Urbani izziv. February 2010. Archived from the original on 23 May 2014. Retrieved 23 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Calculated using penetration rate and population data from "Countries and Areas Ranked by Population: 2012", Population data, International Programs, U.S. Census Bureau, retrieved 26 June 2013
- ^ "Active mobile-broadband subscriptions per 100 inhabitants 2012", Dynamic Report, ITU ITC EYE, International Telecommunication Union. Retrieved on 29 June 2013.
- ^ "Food in Hungary". foodbycountry.com. Retrieved 23 May 2014.
- ^ "A MOB közgyűlése támogatja a budapesti olimpiapályázat szándéknyilatkozatának benyújtását" (in Hungarian). Hungarian Olympic Committee (MOB). 10 June 2015. Retrieved 23 June 2015.
- ^ Tenczer Gábor (23 June 2015). "A főváros szavazott: kell az olimpia" (in Hungarian). Index. Retrieved 23 June 2015.
- ^ "FIFA introduces new FIFA Puskás Award to honour the "goal of the year"" (Press release). FIFA.com. Archived from the original on 29 August 2011. Retrieved 15 September 2011.
{{cite press release}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "LIST OF FIA LICENSED CIRCUITS" (PDF). FIA. 6 February 2015. Retrieved 28 May 2015.
- ^ "Hungarian Grand Prix deal extended until 2021". GP Today. Retrieved 6 January 2015.
- ^ "Aszfaltavató a Hungaroringen" (in Hungarian). Hungaroring. 14 April 2016. Retrieved 15 April 2016.
A Magyar Nagydíj szerződését újabb öt évvel meghosszabbítottuk, ami azt jelenti, hogy a futamunknak 2026-ig helye van a Formula–1-es versenynaptárban." Translates as "We have extended the Hungarian Grand Prix's contract for a further 5 years, which means that our race has a place on the F1 calendar until 2026.
- ^ "Study in Hungary – a guide for international students in Budapest". Blog for expats & International students in Budapest, Hungary. 2016. Retrieved 2016.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Budapest – Testvérvárosok". Budapest Főváros Önkormányzatának hivatalos oldala [Official site of the Municipality of Budapest] (in Hungarian). Retrieved 14 August 2013.
{{cite web}}: Check|archiveurl=value (help); Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ "Budapest to Sign Sister City Agreement with Beijing". Archived from the original on 27 April 2014. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "NYC's Sister Cities". Sister City Program of the City of New York. 2006. Archived from the original on 29 April 2011. Retrieved 1 September 2008.
- ^ "NYC's Partner Cities". The City of New York. Archived from the original on 14 August 2013. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Sister City – Budapest". Official website of New York City. Archived from the original on 25 May 2011. Retrieved 14 May 2008.
- ^ "Budapest, Hungary". fwsistercities.org. Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- ^ "Sanghaj is Budapest testvérvárosa let". Origo.hu. Retrieved 29 August 2013.
- ^ "Sister Cities". Beijing Municipal Government. Retrieved 23 June 2009.
- ^ "Budapest To Sign Twin-City Agreement With Tehran". Hungary Today. Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- ^ "Berlin – City Partnerships". Der Regierende Bürgermeister Berlin. Archived from the original on 21 May 2013. Retrieved 17 September 2013.
- ^ "Berlin's international city relations". Berlin Mayor's Office. Archived from the original on 22 August 2008. Retrieved 1 July 2009.
- ^ http://www.frankfurt.de/sixcms/detail.php?id=317589&_ffmpar[_id_inhalt]=54766
- ^ http://www.goworldtravel.com/travel-sister-cities-budapest-prague-and-vienna/
- ^ "Lisboa – Geminações de Cidades e Vilas". Associação Nacional de Municípios Portugueses [National Association of Portuguese Municipalities] (in Portuguese). Retrieved 23 August 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ "Acordos de Geminação, de Cooperação e/ou Amizade da Cidade de Lisboa". Camara Municipal de Lisboa (in Portuguese). Retrieved 23 August 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ "Tel Aviv sister cities" (in Hebrew). Tel Aviv-Yafo Municipality. Retrieved 1 July 2009.
- ^ "Intercity and International Cooperation of the City of Zagre b". 2006–2009 City of Zagreb. Retrieved 23 June 2009.
- ^ daenet d.o.o. "Sarajevo Official Web Site : Fraternity cities". sarajevo.ba. Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- ^ "City Partnerships and Projects of cooperation". Archived from the original on 27 April 2014. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Partnerská města HMP". Portál „Zahraniční vztahy“ [Portal "Foreign Affairs"] (in Czech). 18 July 2013. Archived from the original on 25 June 2013. Retrieved 5 August 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ http://www.rotterdam.nl/BSD/Document/collegedocumenten/PIEA-Ev3s.pdf
- ^ "Cities: Sister Cities (How many?) (rates, places, America, Los Angeles) – City vs. City – City-Data Forum". city-data.com. Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- ^ "Kraków – Miasta Partnerskie". Miejska Platforma Internetowa Magiczny Kraków (in Polish). Archived from the original on 2 July 2013. Retrieved 10 August 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ Sister Cities Week in Bangkok mfa.gov.hu/kulkepviselet
- ^ Dr. Gábor Bagdy, Vice Mayor of Budapest
- ^ Daejeon.kr Daejeon.kr Archived 2013-09-05 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Vacca, Maria Luisa. "Comune di Napoli-Gemellaggi". Comune di Napoli (in Italian). Archived from the original on 22 June 2013. Retrieved 8 August 2013.
{{cite web}}:|archive-date=/|archive-url=timestamp mismatch; 22 July 2013 suggested (help); Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ Burak Sansal. "Sister Cities of Istanbul – All About Istanbul". greatistanbul.com. Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- ^ "Ankara'nın yeni kardeşi Budapeşte". Hürriyet (in Turkish). 26 February 2015. Retrieved 27 February 2015.
- ^ "Welcome to Vilnius". vilnius.com. Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- ^ "Twin cities of the City of Kosice". Magistrát mesta Košice, Tr. Retrieved 27 July 2013.
- ^ "Новини ЛМР" (in Russian). Archived from the original on 18 August 2010. Retrieved 17 June 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)
External links
- Ill-formatted IPAc-en transclusions
- Budapest
- Budapest metropolitan area
- Tourism in Hungary
- 1873 establishments in Hungary
- Capitals in Europe
- County seats in Hungary
- Landmarks in Hungary
- NUTS 3 statistical regions of the European Union
- Populated places established in 1873
- Populated places on the Danube
- Roman legions' camps in Central Europe
- Spa towns in Hungary
- World Heritage Sites in Hungary