Madrid
Madrid
[Villa de Madrid] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | |
|---|---|
 From upper left: Puerta de Alcalá, Campo del Moro Gardens and Royal Palace, City Hall, Alcalá and Gran Vía street, Prado Museum, Statue of the Bear and the Strawberry bush (madroño) in Puerta del Sol Square, Cervantes Institute Foundation Headquarter, View of Royal Palace and Almudena Cathedral. | |
| Motto(s): [«Fui sobre agua edificada, mis muros de fuego son. Esta es mi insignia y blasón»] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) ("On water I was built, my walls are made of fire. This is my ensign and escutcheon") | |
| Country | Spain |
| Autonomous community | Community of Madrid |
| Founded | 9th century[1] |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor-council |
| • Body | Ayuntamiento de Madrid |
| • Mayor | Ana Botella (PP) |
| Area | |
| • City | 605.77 km2 (233.89 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 667 m (2,188 ft) |
| Population (2013) | |
| • City | 3,236,344 |
| • Rank | 1st |
| • Density | 5,390/km2 (14,000/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 6,183,000[3] |
| • Metro | 6,489,162[2] |
| Demonym(s) | Madrilenian, Madrilene [madrileño, -ña; matritense (es)] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 28001–28080 |
| Area code | +34 (ES) + 91 (M) |
| Patron Saints | Isidore the Laborer Virgin of Almudena |
| Website | www.madrid.es |
Madrid (/məˈdrɪd/, Spanish: [maˈðɾið], locally [maˈðɾiθ]) is the capital and largest city of Spain. The population of the city is roughly 3.3 million[4] and the entire population of the Madrid metropolitan area is calculated to be around 6.5 million. It is the third-largest city in the European Union, after London and Berlin, and its metropolitan area is the third-largest in the European Union after London and Paris.[5][6][7][8] The city spans a total of 604.3 km2 (233.3 sq mi).[9]
The city is located on the Manzanares River in the centre of both the country and the Community of Madrid (which comprises the city of Madrid, its conurbation and extended suburbs and villages); this community is bordered by the autonomous communities of Castile and León and Castile-La Mancha. As the capital city of Spain, seat of government, and residence of the Spanish monarch, Madrid is also the political, economic and cultural centre of Spain.[10] The current mayor is Ana Botella from the People's Party (PP).
The Madrid urban agglomeration has the third-largest GDP[11] in the European Union and its influences in politics, education, entertainment, environment, media, fashion, science, culture, and the arts all contribute to its status as one of the world's major global cities.[12][13] Due to its economic output, high standard of living, and market size, Madrid is considered the major financial centre of Southern Europe[14][15] and the Iberian Peninsula; it hosts the head offices of the vast majority of the major Spanish companies, such as Telefónica, Iberia or Repsol. Madrid is the 17th most livable city in the world according to Monocle magazine, in its 2014 index.[16][17]
Madrid houses the headquarters of the World Tourism Organization (WTO), belonging to the United Nations Organization (UN), the SEGIB, the Organization of Ibero-American States (OEI), and the Public Interest Oversight Board (PIOB). It also hosts major international regulators of Spanish: the Standing Committee of the Association of Spanish Language Academies, headquarters of the Royal Spanish Academy (RAE), the Cervantes Institute and the Foundation of Urgent Spanish (Fundéu BBVA). Madrid organizes fairs such as FITUR,[18] ARCO,[19] SIMO TCI[20] and the Cibeles Madrid Fashion Week.[21]
While Madrid possesses a modern infrastructure, it has preserved the look and feel of many of its historic neighbourhoods and streets. Its landmarks include the Royal Palace of Madrid; the Royal Theatre with its restored 1850 Opera House; the Buen Retiro Park, founded in 1631; the 19th-century National Library building (founded in 1712) containing some of Spain's historical archives; a large number of national museums,[22] and the Golden Triangle of Art, located along the Paseo del Prado and comprising three art museums: Prado Museum, the Reina Sofía Museum, a museum of modern art, and the Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum, which completes the shortcomings of the other two museums.[23] Cibeles Palace and Fountain have become the monument symbol of the city.[24][25][26]
Madrid is home to two world-famous football clubs, Real Madrid and Atlético de Madrid. Madrid has also made multiple applications to host the Summer Olympics, which have been rejected.
History
Toponym
There are several theories regarding the origin of the name "Madrid".[citation needed] According to legend, Madrid was founded by Ocno Bianor (son of King Tyrrhenius of Tuscany and Mantua) and was named "Metragirta" or "Mantua Carpetana". Others contend that the original name of the city was "Ursaria" ("land of bears" in Latin), because of the many bears that were to be found in the nearby forests, which, together with the strawberry tree (Spanish madroño), have been the emblem of the city from the Middle Ages.[27]
The most ancient recorded name of the city "Magerit" (for *Materit or *Mageterit?) comes from the name of a fortress built on the Manzanares River in the 9th century AD, and means "Place of abundant water".[28] If the form is correct, it could be a Celtic place-name from ritu- 'ford' (Old Welsh rit, Welsh rhyd, Old Breton rit, Old Northern French roy) and a first element, that is not clearly identified *mageto derivation of magos 'field, plain' (Old Irish mag 'field', Breton ma 'place'), or matu 'bear', that could explain the Latin translation Ursalia.[29]
Nevertheless, it is now commonly believed[citation needed] that the origin of the current name of the city comes from the 2nd century BC. The Roman Empire established a settlement on the banks of the Manzanares river. The name of this first village was "Matrice" (a reference to the river that crossed the settlement). Following the invasions carried out by the Germanic Sueves and Vandals, as well as the Sarmatic Alans during the 5th century AD, the Roman Empire no longer had the military presence required to defend its territories on the Iberian Peninsula, and as a consequence, these territories were soon occupied by the Vandals, who were in turn dispelled by the Visigoths, who then ruled Hispania in the name of the Roman emperor, also taking control of "Matrice". In the 8th century, the Islamic conquest of the Iberian Peninsula saw the name changed to "Mayrit", from the Arabic term ميرا Mayra (referencing water as a 'tree' or 'giver of life') and the Ibero-Roman suffix it that means 'place'. The modern "Madrid" evolved from the Mozarabic "Matrit", which is still in the Madrilenian gentilic.[30]
Middle Ages
Although the site of modern-day Madrid has been occupied since prehistoric times,[31][32][33] and there are archeological remains of Carpetani settlement,[31] Roman villas,[34] a Visigoth basilica near the church of Santa María de la Almudena[27][35] and three Visigoth necropolises near Casa de Campo, Tetúan and Vicálvaro,[36] the first historical document about the existence of an established settlement in Madrid dates from the Muslim age. At the second half of the 9th century,[37] Emir Muhammad I of Córdoba built a fortress on a headland near the river Manzanares,[38] as one of the many fortress he ordered to be built on the border between Al-Andalus and the kingdoms of León and Castile, with the objective of protecting Toledo from the Christian invasions and also as a starting point for Muslim offensives. After the disintegration of the Caliphate of Córdoba, Madrid was integrated in the Taifa of Toledo.
With the surrender of Toledo to Alfonso VI of León and Castile, the city was conquered by Christians in 1085, and it was integrated into the kingdom of Castile as a property of the Crown.[39] Christians replaced Muslims in the occupation of the center of the city, while Muslims and Jews settled in the suburbs. The city was thriving and was given the title of Villa, whose administrative district extended from the Jarama in the east to the river Guadarrama in the west. The government of the town was vested to the neighboring of Madrid since 1346, when king Alfonso XI of Castile implements the regiment, for which only the local oligarchy was taking sides in city decisions.[40] Since 1188, Madrid won the right to be a city with representation in the courts of Castile. In 1202, King Alfonso VIII of Castile gave Madrid its first charter to regulate the municipal council,[41] which was expanded in 1222 by Ferdinand III of Castile.
The first time the Courts of Castile were joined in Madrid was in 1309 under Ferdinand IV of Castile, and later in 1329, 1339, 1391, 1393, 1419 and twice in 1435. Since the unification of the kingdoms of Spain under a common Crown, the Courts were convened in Madrid more often.
Modern Age
During the revolt of the Comuneros, led by Juan de Padilla, Madrid joined the revolt against Emperor Charles V of Germany and I of Spain, but after defeat at the Battle of Villalar, Madrid was besieged and occupied by the royal troops. However, Charles I was generous to the town and gave it the titles of Coronada (Crowned) and Imperial. When Francis I of France was captured at the battle of Pavia, he was imprisoned in Madrid. And in the village is dated the Treaty of Madrid of 1526 (later denounced by the French) that resolved their situation.[42]


In June 1561, when the town had 30,000 inhabitants, Philip II of Spain moved his court from Valladolid to Madrid, installing it in the old castle.[44] Thanks to this, the city of Madrid became the political center of the monarchy, being the capital of Spain except for a short period between 1601 to 1606 (Philip III of Spain's government), in which the Court returned to Valladolid. This fact was decisive for the evolution of the city and influenced its fate. A famous expression indicated that identity: "Sólo Madrid es corte" (Madrid is the only court) which, conceptually, is also understood backwards: "Madrid es sólo corte" (Madrid is just court).
During the reign of Philip III and Philip IV of Spain, Madrid saw a period of exceptional cultural brilliance, with the presence of geniuses such as Miguel de Cervantes, Diego Velázquez, Francisco de Quevedo and Lope de Vega.[45]

The death of Charles II of Spain resulted in the War of the Spanish succession. The city supported the claim of Philip of Anjou as Philip V. While the city was occupied in 1706 by a Portuguese army, who proclaimed king the Archduke Charles of Austria under the name of Charles III, and again in 1710, remained loyal to Philip V.
Philip V built the Royal Palace, the Royal Tapestry Factory and the main Royal Academies.[46] But the most important Bourbon was King Charles III of Spain, who was known as "the best mayor of Madrid". Charles III took upon himself the feat of transforming Madrid into a capital worthy of this category. He ordered the construction of sewers, street lighting, cemeteries outside the city, and many monuments (Puerta de Alcalá, Cibeles Fountain), and cultural institutions (El Prado Museum, Royal Botanic Gardens, Royal Observatory, etc.). Despite being known as one of the greatest benefactors of Madrid, his beginnings were not entirely peaceful, as in 1766 he had to overcome the Esquilache Riots, a traditionalist revolt instigated by the nobility and clergy against his reformist intentions, demanding the repeal of the clothing decree ordering the shortening of the layers and the prohibition of the use of hats that hide the face, with the aim of reducing crime in the city.[47]
The reign of Charles IV of Spain is not very meaningful to Madrid, except for the presence of Goya in the Court, who portrayed the popular and courtly life of the city.
From the 19th century to present day

On 27 October 1807, Charles IV and Napoleon I signed the Treaty of Fontainebleau, which allowed the passage of French troops through Spanish territory to join the Spanish troops and invade Portugal, which had refused to obey the order of international blockade against England. As this was happening, there was the Mutiny of Aranjuez (17 March 1808), by which the crown prince, Ferdinand VII, replaced his father as king. However, when Ferdinand VII returned to Madrid, the city was already occupied by Joachim-Napoléon Murat, so that both the king and his father were virtually prisoners of the French army. Napoleon, took advantage of the weakness of the Spanish Bourbons, forcing both, first the father then the son, to join him in Bayonne, where Ferdinand arrived on 20 April.
In the absence of the two kings, the situation became more and more tense in the capital. On 2 May, a crowd began to gather at the Royal Palace. The crowd saw the French soldiers pulled out of the palace to the royal family members who were still in the palace. Immediately, the crowd launched an assault on the floats. The fight lasted hours and spread throughout Madrid. Subsequent repression was brutal. In the Paseo del Prado and in the fields of La Moncloa hundreds of patriots were shot due to Murat's order against "Spanish all carrying arms". Paintings such as The Third of May 1808 by Goya reflect the repression that ended the popular uprising on 2 May.[48]
The Peninsular War against Napoleon, despite the last absolutist claims during the reign of Ferdinand VII, gave birth to a new country with a liberal and bourgeois character, open to influences coming from the rest of Europe. Madrid, the capital of Spain, experienced like no other city the changes caused by this opening and filled with theaters, cafes and newspapers. Madrid was frequently altered by revolutionary outbreaks and pronouncements, such as Vicálvaro 1854, led by General Leopoldo O'Donnell and initiating the progressive biennium. However, in the early 20th century Madrid looked more like a small town than a modern city. During the first third of the 20th century the population nearly doubled, reaching more than 950,000 inhabitants. New suburbs such as Las Ventas, Tetuán and El Carmen became the homes of the influx of workers, while Ensanche became a middle-class neighbourhood of Madrid.[49]

The Spanish Constitution of 1931 was the first legislated on the state capital, setting it explicitly in Madrid.
Madrid was one of the most heavily affected cities of Spain in the Civil War (1936–1939). The city was a stronghold of the Republicans from July 1936. Its western suburbs were the scene of an all-out battle in November 1936 and it was during the Civil War that Madrid became the first European city to be bombed by aeroplanes (Japan was the first to bomb civilians in world history, at Shanghai in 1932) specifically targeting civilians in the history of warfare. (See Siege of Madrid (1936–39)).[50]
During the economic boom in Spain from 1959 to 1973, the city experienced unprecedented, extraordinary development in terms of population and wealth, becoming the largest GDP city in Spain, and ranking third in Western Europe. The municipality was extended, annexing neighbouring council districts, to achieve the present extension of 607 km2 (234.36 sq mi). The south of Madrid became very industrialized, and there were massive migrations from rural areas of Spain into the city. Madrid's newly built north-western districts became the home of the new thriving middle class that appeared as result of the 1960s Spanish economic boom, while the south-eastern periphery became an extensive working-class settlement, which was the base for an active cultural and political reform.[50]
After the death of Franco and the democratic regime, the 1978 constitution confirmed Madrid as the capital of Spain. In 1979, the first municipal elections brought Madrid's first democratically elected mayor since the Second Republic. Madrid was the scene of some of the most important events of the time, such as the mass demonstrations of support for democracy after the foiled coup, 23-F, on 23 February 1981. The first democratic mayors belonged to the leftist parties (Enrique Tierno Galván, Juan Barranco Gallardo), turning the city after more conservative positions (Agustín Rodríguez Sahagún, José María Álvarez del Manzano, Alberto Ruiz-Gallardón and Ana Botella). Benefiting from increasing prosperity in the 1980s and 1990s, the capital city of Spain has consolidated its position as an important economic, cultural, industrial, educational, and technological centre on the European continent.[50]
Government

The City Council consists of 57 members, one of them being the Mayor, currently Ana Botella. The Mayor presides over the Council.
The Plenary of the Council is the body of political representation of the citizens in the municipal government. Some of its attributions are: fiscal matters, the election and deposition of the Mayor, the approval and modification of decrees and regulations, the approval of budgets, the agreements related to the limits and alteration of the municipal term, the services management, the participation in supramunicipal organizations, etc.[51] Nowadays, mayoral team consists of the Mayor, the Deputy Mayor and 8 Delegates; all of them form The Board of Delegates (the Municipal Executive Committee).[52]
Madrid has tended to be a stronghold of the People's Party (PP, right-wing political party), which has controlled the city's mayoralty since 1989. In the 2007 regional and local elections, the People's Party obtained 34 seats, the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE, centre-left political party) obtained 18 and United Left (IU, left political party) obtained 5.
Ana Botella has been in office since 2011, as former mayor Alberto Ruiz-Gallardón, also from the PP, left the post after the 2011 General Election to become Spain's Minister of Justice. Botella's party keeps the majority in the City Council that PP reached in the 2011 Municipal Election (31 seats out of 57), taking 49.6% of the popular vote and winning in all but two districts.
Geography
Climate

The Madrid region experiences a Mediterranean climate[53] (Köppen Csa)[54] with continental characteristics, with cool to cold winters due to its altitude of 667 m (2,188 ft) above sea level, including sporadic snowfalls and minimum temperatures often below freezing. Summers are hot with average July temperatures ranging from 32 to 33 °C (90 to 91 °F) depending on location. Summer temperatures occasionally climb over 35 °C (95 °F) during the city's heatwaves. Due to Madrid's altitude and dry climate, diurnal ranges are often significant during the summer. The highest recorded temperature was on 10 August 2012 with 40.6 °C (105.1 °F), and the lowest recorded temperature was on 16 January 1945 with −10.1 °C (13.8 °F).[55] Precipitation is concentrated in the autumn and spring. It is particularly sparse during the summer, taking the form of about two showers and/or thunderstorms a month.
| Climate data for Madrid (667m), Buen Retiro Park in the city centre (1981-2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 9.8 (49.6) |
12.0 (53.6) |
16.3 (61.3) |
18.2 (64.8) |
22.2 (72.0) |
28.2 (82.8) |
32.1 (89.8) |
31.3 (88.3) |
26.4 (79.5) |
19.4 (66.9) |
13.5 (56.3) |
10.0 (50.0) |
19.9 (67.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.3 (43.3) |
7.9 (46.2) |
11.2 (52.2) |
12.9 (55.2) |
16.7 (62.1) |
22.2 (72.0) |
25.6 (78.1) |
25.1 (77.2) |
20.9 (69.6) |
15.1 (59.2) |
9.9 (49.8) |
6.9 (44.4) |
15.0 (59.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 2.7 (36.9) |
3.7 (38.7) |
6.2 (43.2) |
7.7 (45.9) |
11.3 (52.3) |
16.1 (61.0) |
19.0 (66.2) |
18.8 (65.8) |
15.4 (59.7) |
10.7 (51.3) |
6.3 (43.3) |
3.6 (38.5) |
10.1 (50.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 33 (1.3) |
35 (1.4) |
25 (1.0) |
45 (1.8) |
51 (2.0) |
21 (0.8) |
12 (0.5) |
10 (0.4) |
22 (0.9) |
60 (2.4) |
58 (2.3) |
51 (2.0) |
421 (16.6) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1 mm) | 6 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 7 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 59 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 148 | 157 | 214 | 231 | 272 | 310 | 359 | 335 | 261 | 198 | 157 | 124 | 2,769 |
| Source: Agencia Estatal de Meteorología[56][57][58][59] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Madrid-Barajas Airport(609m), 9 km (5.59 mi) from the city's financial district (1981-2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 10.7 (51.3) |
13.0 (55.4) |
17.0 (62.6) |
18.7 (65.7) |
23.1 (73.6) |
29.5 (85.1) |
33.5 (92.3) |
32.8 (91.0) |
27.9 (82.2) |
21.0 (69.8) |
14.8 (58.6) |
10.9 (51.6) |
21.1 (70.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 5.5 (41.9) |
7.1 (44.8) |
10.2 (50.4) |
12.2 (54.0) |
16.2 (61.2) |
21.7 (71.1) |
25.2 (77.4) |
24.7 (76.5) |
20.5 (68.9) |
14.8 (58.6) |
9.4 (48.9) |
6.2 (43.2) |
14.5 (58.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 0.2 (32.4) |
1.2 (34.2) |
3.5 (38.3) |
5.7 (42.3) |
9.3 (48.7) |
13.9 (57.0) |
16.8 (62.2) |
16.5 (61.7) |
13.1 (55.6) |
8.7 (47.7) |
4.1 (39.4) |
1.4 (34.5) |
7.9 (46.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 29 (1.1) |
32 (1.3) |
22 (0.9) |
38 (1.5) |
44 (1.7) |
22 (0.9) |
9 (0.4) |
10 (0.4) |
24 (0.9) |
51 (2.0) |
49 (1.9) |
42 (1.7) |
371 (14.6) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1 mm) | 5 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 55 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 144 | 168 | 224 | 226 | 258 | 310 | 354 | 329 | 258 | 199 | 151 | 128 | 2,749 |
| Source: Agencia Estatal de Meteorología[60] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Madrid-Cuatro Vientos Airport, 8 km (4.97 mi) from the city centre (altitude: 690m, satellite view) (1981-2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 10.4 (50.7) |
12.5 (54.5) |
16.5 (61.7) |
18.3 (64.9) |
22.6 (72.7) |
28.9 (84.0) |
32.8 (91.0) |
32.2 (90.0) |
27.3 (81.1) |
20.4 (68.7) |
14.3 (57.7) |
10.7 (51.3) |
20.6 (69.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.0 (42.8) |
7.6 (45.7) |
10.8 (51.4) |
12.6 (54.7) |
16.5 (61.7) |
22.2 (72.0) |
25.6 (78.1) |
25.1 (77.2) |
21.0 (69.8) |
15.2 (59.4) |
9.8 (49.6) |
6.7 (44.1) |
14.9 (58.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 1.6 (34.9) |
2.7 (36.9) |
5.1 (41.2) |
6.8 (44.2) |
10.4 (50.7) |
15.4 (59.7) |
18.3 (64.9) |
18.1 (64.6) |
14.6 (58.3) |
9.9 (49.8) |
5.4 (41.7) |
2.7 (36.9) |
9.3 (48.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 34 (1.3) |
35 (1.4) |
25 (1.0) |
43 (1.7) |
50 (2.0) |
25 (1.0) |
12 (0.5) |
11 (0.4) |
24 (0.9) |
60 (2.4) |
57 (2.2) |
53 (2.1) |
428 (16.9) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1 mm) | 6 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 7 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 59 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 158 | 173 | 221 | 238 | 280 | 316 | 364 | 335 | 250 | 203 | 161 | 135 | 2,840 |
| Source: Agencia Estatal de Meteorología[61] | |||||||||||||
Location
Water supply
Madrid derives almost 73.5 percent of its water supply from dams and reservoirs built on the Lozoya River, such as the El Atazar Dam. This water supply is managed by Canal de Isabel II, a public entity created in 1851. It is responsible for the supply, depurating waste water and the conservation of all the Comunidad de Madrid region natural water resources.
Demographics
| Year | Municipality | Community | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1897 | 542,739 | 730,807 | 74.27 |
| 1900 | 575,675 | 773,011 | 74.47 |
| 1910 | 614,322 | 831,254 | 73.90 |
| 1920 | 823,711 | 1,048,908 | 78.53 |
| 1930 | 1,041,767 | 1,290,445 | 80.73 |
| 1940 | 1,322,835 | 1,574,134 | 84.04 |
| 1950 | 1,553,338 | 1,823,418 | 85.19 |
| 1960 | 2,177,123 | 2,510,217 | 86.73 |
| 1970 | 3,120,941 | 3,761,348 | 82.97 |
| 1981 | 3,158,818 | 4,686,895 | 67.40 |
| 1991 | 3,010,492 | 4,647,555 | 64.78 |
| 2001 | 2,938,723 | 5,423,384 | 54.19 |
| 2009 | 3,255,944 | 6,386,932 | 50.98 |
| 2010 | 3,273,049 | 6,458,684 | 50.68 |
| 2011 | 3,265,038 | 6,489,680 | 50.31 |
| Source: INE | |||
The population of Madrid generally increased from when the city became the national capital in the mid-16th century and stabilised at about 3 million from the 1970s.
From around 1970 until the mid-1990s, the city's population dropped. This phenomenon, which also affected other European cities, was caused in part by the growth of satellite suburbs at the expense of the downtown. Another reason might have been the slowdown in the rate of growth of the European economy.
The demographic boom accelerated in the late 1990s and early first decade of the 21st century due to immigration, in response to a surge in Spanish economic growth. According to census data, the population of the city grew by 271,856 between 2001 and 2005.
As the capital city of Spain, the city has attracted many immigrants from around the world. About 83.8% of the inhabitants are Spaniards, while people of other origins, including immigrants from Latin America, Europe, Asia, North Africa and West Africa, represented 16.2% of the population in 2007.
The ten largest immigrant groups include: Ecuadorian: 104,184, Romanian: 52,875, Bolivian: 44,044, Colombian: 35,971, Peruvian: 35,083, Chinese: 34,666, Moroccan: 32,498, Dominican: 19,602, Brazilian: 14,583, and Paraguayan: 14,308. There are also important communities of Filipinos, Equatorial Guineans, Bulgarians, Indians, Italians, Argentines, Senegalese and Poles.[62]
A study made by Unión de comunidades islámicas de España demonstrated that there were about 250,000 inhabitants of Muslim background living in Community of Madrid as of 2012 ( less than 4% of the total population of Madrid). The vast majority was composed of immigrants and descendants originating from Morocco and other African countries. More than 130,000 (52%) of them had Spanish nationality.[63]
Districts that host the largest number of immigrants are Usera (28.37%), Centro (26.87%), Carabanchel (22.72%) and Tetuán (21.54%). Districts that host the smallest number are Fuencarral-El Pardo (9.27%), Retiro (9.64%) and Chamartín (11.74%).
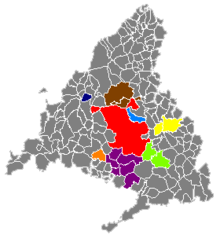
Districts
Madrid is administratively divided into 21 districts, which are further subdivided into 128 wards (barrios)
| Madrid districts. The numbers correspond with the list in the left |
- Centro: Palacio, Embajadores, Cortes, Justicia, Universidad, Sol.
- Arganzuela: Imperial, Acacias, La Chopera, Legazpi, Delicias, Palos de Moguer, Atocha.
- Retiro: Pacífico, Adelfas, Estrella, Ibiza, Jerónimos, Niño Jesús.
- Salamanca: Recoletos, Goya, Parque de las Avenidas, Fuente del Berro, Guindalera, Lista, Castellana.
- Chamartín: El Viso, Prosperidad, Ciudad Jardín, Hispanoamérica, Nueva España, Castilla.
- Tetuán: Bellas Vistas, Cuatro Caminos, Castillejos, Almenara, Valdeacederas, Berruguete.
- Chamberí: Gaztambide, Arapiles, Trafalgar, Almagro, Vallehermoso, Ríos Rosas.
- Fuencarral-El Pardo: El Pardo, Fuentelarreina, Peñagrande, Barrio del Pilar, La Paz, Valverde, Mirasierra, El Goloso.
- Moncloa-Aravaca: Casa de Campo, Argüelles, Ciudad Universitaria, Valdezarza, Valdemarín, El Plantío, Aravaca.
- Latina: Los Cármenes, Puerta del Ángel, Lucero, Aluche, Las Águilas, Campamento, Cuatro Vientos.
- Carabanchel: Comillas, Opañel, San Isidro, Vista Alegre, Puerta Bonita, Buenavista, Abrantes.
- Usera: Orcasitas, Orcasur, San Fermín, Almendrales, Moscardó, Zofío, Pradolongo.
- Puente de Vallecas: Entrevías, San Diego, Palomeras Bajas, Palomeras Sureste, Portazgo, Numancia.
- Moratalaz: Pavones, Horcajo, Marroquina, Media Legua, Fontarrón, Vinateros.
- Ciudad Lineal: Ventas, Pueblo Nuevo, Quintana, La Concepción, San Pascual, San Juan Bautista, Colina, Atalaya, Costillares.
- Hortaleza: Palomas, Valdefuentes, Canillas, Pinar del Rey, Apóstol Santiago, Piovera.
- Villaverde: San Andrés, San Cristóbal, Butarque, Los Rosales, Los Ángeles.
- Villa de Vallecas: Casco Histórico de Vallecas, Santa Eugenia.
- Vicálvaro: Casco Histórico de Vicálvaro, Ambroz.
- San Blas: Simancas, Hellín, Amposta, Arcos, Rosas, Rejas, Canillejas, Salvador.
- Barajas: Alameda de Osuna, Aeropuerto, Casco Histórico de Barajas, Timón, Corralejos.
Metropolitan area
The Madrid metropolitan area comprises the city of Madrid and forty surrounding municipalities. It has a population of slightly more than 6.271 million people[64] and covers an area of 46,097 square kilometres (17,798 sq mi). It is the largest metropolitan area in Spain and the third largest in the European Union.[5][6][7][8]
As with many metropolitan areas of similar size, two distinct zones of urbanisation can be distinguished:
- Inner ring (primera corona): Alcorcón, Leganés, Getafe, Móstoles, Fuenlabrada, Coslada, Alcobendas, Pozuelo de Alarcón, San Fernando de Henares
- Outer ring (segunda corona): Villaviciosa de Odón, Parla, Pinto, Valdemoro, Rivas-Vaciamadrid, Torrejón de Ardoz, Alcalá de Henares, San Sebastián de los Reyes, Tres Cantos, Las Rozas de Madrid, Majadahonda, Boadilla del Monte
The largest suburbs are to the South, and in general along the main routes leading out of Madrid.
Submetropolitan areas inside Madrid metropolitan area:
(km²) |
(pop.) |
(pop./km²) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Madrid – Majadahonda | 996.1 | 3,580,828 | 3,595.0 |
| Móstoles – Alcorcón | 315.1 | 430,349 | 1,365.6 |
| Fuenlabrada – Leganés – Getafe – Parla – Pinto – Valdemoro | 931.7 | 822,806 | 883.1 |
| Alcobendas | 266.4 | 205,905 | 772.9 |
| Arganda del Rey – Rivas-Vaciamadrid | 343.6 | 115,344 | 335.7 |
| Alcalá de Henares – Torrejón de Ardoz | 514.6 | 360,380 | 700.3 |
| Colmenar Viejo – Tres Cantos | 419.1 | 104,650 | 249.7 |
| Collado Villalba | 823.1 | 222,769 | 270.6 |
| Madrid metropolitan area | 4,609.7 | 5,843,031 | 1,267.6 |
Cityscape
Architecture

Very little medieval architecture is preserved in Madrid, and most of it is located inside the Almendra central. Historical documents show that the city was walled and had a castle (the Alcázar) in the same place where the Royal Palace now stands. Among the few preserved medieval buildings are the mudejar towers of San Nicolás and San Pedro el Viejo churches, the palace of Luján family (located in the Plaza de la Villa), the Gothic church of St. Jerome, part of a monastery built by the Catholic Monarchs in the 15th century, and the Bishop's Chapel.
Nor has Madrid retained many examples of Renaissance architecture, except for the Cisneros house (one of the buildings flanking the Plaza de la Villa), the Bridge of Segovia and the Convent of Las Descalzas Reales, whose austere exterior gives no idea of the magnificent art treasures inside.
When Philip II moved his court to Madrid in 1561,[65] a series of reforms began, reforms that aimed to transform the town into a capital city worthy of the name. These reforms were embodied in the Plaza Mayor, designed by Juan de Herrera (author of El Escorial) and Juan Gómez de Mora, characterized by its symmetry and austerity, as well as the new Alcázar, who would become the second most impressive royal palace of the kingdom.
Many of the historic buildings of Madrid were built during the reign of the Habsburgs. The material used was mostly brick and the humble façades contrast with the elaborate interiors. Juan Gómez de Mora built notable buildings such as Casa de la Villa, Prison of the Court, the Palace of the Councils and Royal Convent of La Encarnación. The Buen Retiro Palace was a vanished work by Alonso Carbonel, today on the grounds of the Buen Retiro Park, with beautiful rooms decorated by the best artists in times of Philip IV (Velázquez, Carducci, Zurbarán). Imperial College become an important institution run by the Jesuits, and the model dome of the church would be imitated in all Spain, thanks to the cheap materials used in its construction.

Before the arrival of the Bourbons at Madrid, the architect Pedro de Ribera was one of the most important architects in Madrid. Ribera introduced Churrigueresque architecture to Madrid, characterized by ornamental overload on their covers, as an altarpiece. The History Museum, the Cuartel del Conde-Duque, the church of Montserrat and the Bridge of Toledo are the best examples.
The arrival of the Bourbons marked a new era in the city. The burning of the Alcazar of Madrid served as an excuse for the first Bourbon, Philip V of Spain to build a palace on its foundations, a palace more in line with the French taste. Filippo Juvarra, an architect specializing in the construction of royal palaces, was chosen to design the new palace. His design was inspired by Bernini's design rejected for the Louvre Palace in Paris. Juvarra died before the work began, and the project was substantially modified by his disciple Giovainni Battista Sacchetti. Philip V tried to complete the vision of urbanization of Madrid initiated by King Philip II, which included a bridge spanning a large ravine, linking The Royal Alcázar to the southern part of town. Philip V would never see the bridge even begin and neither would several of his successors. It wasn't built until the 19th century and is called the Segovia Viaduct. Other buildings of the time were the St. Michael's Basilica and the Church of Santa Bárbara.
King Charles III of Spain was more interested in beautifying the city. He was an enlightened monarch and endeavored to convert Madrid into one of the great European capitals. He pushed forward the construction of the Prado Museum (designed by Juan de Villanueva). The building was originally intended to serve as a Natural Science Museum. Charles III was also responsible for design of the Puerta de Alcalá, the Royal Observatory (Juan de Villanueva), the Royal Botanic Gardens, the Basilica of San Francisco el Grande (Francesco Sabatini), the Casa de Correos in Puerta del Sol, the Real Casa de la Aduana (Francesco Sabatini) and the General Hospital by Sabatini (now houses the Reina Sofia Museum and Royal Conservatory of Music). The Paseo del Prado, surrounded by gardens and decorated with neoclassical statues inspired by mythological gods, is an example of urban planning. The Duke of Berwick ordered Ventura Rodríguez the construction of the Liria Palace.
Subsequently, the Peninsular War, the loss of colonies in the Americas, and the continuing coups prevented the city from developing interesting architecture (Royal Theatre,the National Library of Spain, the Palace of the Senate and the Congress). In the slums of Madrid during this time, a kind of substandard house was developed that today has a special historical charm: an example is the corralas, which currently still exist in the neighborhood of Lavapiés.

From the late 19th century until the Civil War, Madrid modernized and built new neighborhoods and monuments, both in the capital and in neighboring towns. In the mid-19th century the expansion of Madrid developed under the Plan Castro, resulting in the neighborhoods of Salamanca, Argüelles and Chamberí. Arturo Soria conceived the linear city and built the first few kilometers of the road that bears his name, which embodies the idea. Antonio Palacios build a series of eclectic buildings inspired by the Viennese Secession. Some representative examples are the Palace of Communication (Palacio de Comunicaciones), the Fine Arts Circle of Madrid (Círculo de Bellas Artes) and the Río de La Plata Bank (Instituto Cervantes). Ricardo Velázquez Bosco designed the Crystal Palace and the Palace of Velázquez in the Retiro Park. Secundino Zuazo built the Palace of Music and the Casa de las Flores. The Bank of Spain was designed by Eduardo Adaro and Severiano Sainz de la Lastra. Meanwhile, the Marquis of Cubas began the Almudena Cathedral project, which was to be a neo-Gothic church with neo-Romanesque cloister. Alberto de Palacio designed Atocha Station. The Palace of Longoria was designed by José Grases Riera in Catalan art-nouveau. Las Ventas Bullring was built in the early 20th century, as the Market of San Miguel (Cast-Iron style). Finally, Delicias Railway Station is the oldest example of this kind of infrastructure according to the model of Henri de Dion.
Also the construction of Gran Vía began in the early 20th century, with the task of freeing the old town. They used different styles that evolved over time: The Metropolis building is built in French style and the Edificio Grassy is eclectic, while Telefónica Building is art deco, with baroque ornaments. The Carrión (or Capitol) Building is expressionist, and the Palace of the Press, another example of art deco.
The Civil War severely damaged the city, including the Ciudad Universitaria (University City), which was one of the most beautiful architectural complexes of the time. Subsequently, unscrupulous mayors would destroy the old town and the Ensanche, in a city which until the war was a good example of urban planning and architecture. Numerous blocks of flats with no value were built, and some examples of Fascist architecture, such as the Spanish Air Force headquarters (inspired by El Escorial), the Nuevos Ministerios by Secundino Zuazo and the skyscrapers of Plaza de España, at the time the highest in Europe, were built.

With the advent of democracy and Spanish economic development, skyscrapers appeared in the city such as Torre Picasso, designed by Minoru Yamasaki; Torres Blancas and Torre BBVA (both by Francisco Javier Sáenz de Oiza) and in the 1990s, the Gate of Europe, architects Philip Johnson and John Burgee. Moreover, in the 1990s construction was completed of the Cathedral of the Almudena. The National Auditorium of Music is a work of 1988.
In the 21st century, Madrid faces new challenges in its architecture. An old industrial warehouse is the Interpretation Centre of New Technologies, and the CaixaForum Madrid (Herzog & de Meuron) was a former power station.
Under the government of Alberto Ruiz-Gallardón the four tallest skyscrapers in Spain were built, and together form the Cuatro Torres Business Area (CTBA). The Manzanares River is crossed by new edge bridges, and work started on the International Convention Centre (Mansilla+Tuñón), an original round building, whose works remain paralyzed by the crisis. Caja Mágica (Dominique Perrault) sport centre was also built and the Reina Sofía Museum has been expanded with the help of Jean Nouvel.
Madrid Barajas International Airport Terminal 4, designed by Antonio Lamela and Richard Rogers (winning them the 2006 Stirling Prize), and TPS Engineers, (winning them the 2006 IStructE Award for Commercial Structures) was inaugurated on 5 February 2006. Terminal 4 is one of the world's largest terminal areas, with an area of 760,000 square metres (8,180,572 square feet) in two separate terminals: a main building, T4 (470,000 square metres), and satellite building, T4S (290,000 square metres), which are separated by approximately 2.5 km (2 mi). The new terminal is meant to give passengers a stress-free start to their journey. This is managed through careful use of illumination, available by glass panes instead of walls and numerous domes in the roof which allow natural light to pass through. With the new addition, Barajas is designed to handle 70 million passengers annually.
Urban sculpture
The streets of Madrid are a veritable museum of outdoor sculpture. The Museum of Outdoor Sculpture, located in the Paseo de la Castellana, is dedicated to abstract works, among which the Sirena Varada (Strander Mermaid) by Eduardo Chillida.
Since the 18th century, the Paseo del Prado is decorated with an iconographic program with classical monumental fountains: the Fuente de la Alcachofa (Fountain of the Artichoke), the Cuatro Fuentes (Four Fountains), the Fuente de Neptuno (Fountain of Neptune), the Fuente de Apolo (Fountain of Apollo) and the Fuente de Cibeles (Fountain of Cybele, also known as Fountain of Cibeles), all designed by Ventura Rodríguez.
The equestrian sculptures are particularly important, starting chronologically with two designed in the 17th century: the statue of Philip III, in the Plaza Mayor by Giambologna, and the statue of Philip IV, in the Plaza de Oriente (undoubtedly the most important statue of Madrid, projected by Velázquez and built by Pietro Tacca with scientific advice of Galileo Galilei).
Many areas of the Buen Retiro Park (Parque del Retiro) are really sculptural scenography: among them are The Fallen Angel by Ricardo Bellver, and the Monument to Alfonso XII, designed by José Grases Riera.
In another vein are the neon advertising signs, some of which have acquired a historic range and are legally protected, such as Schweppes in Plaza de Callao or Tío Pepe in the Puerta del Sol, recently retired from its location for the restoration of the building.
-
Fountain of Neptune (Ventura Rodríguez)
-
Fountain of Cybele (Ventura Rodríguez)
-
Monument to Alfonso XII (José Grasés Riera)
-
Strander Mermaid (Eduardo Chillida)
-
Philip IV (Pietro Tacca)
-
Fuente del Ángel Caído (Ricardo Bellver)
-
Cervantes Monument at Plaza de España (Madrid)
Environment

Madrid is the European city with the highest number of trees and green surface per inhabitant and it has the second highest number of aligned trees in the world, with 248,000 units, only exceeded by Tokyo. Madrid's citizens have access to a green area within a 15-minute walk. Since 1997, green areas have increased by 16%. At present, 8.2% of Madrid's grounds are green areas, meaning that there are 16 m2 (172 sq ft) of green area per inhabitant, far exceeding the 10 m2 (108 sq ft) per inhabitant recommended by the World Health Organization.

Buen Retiro Park (Parque del Buen Retiro, or simply Parque del Retiro), formerly the grounds of the palace built for Philip IV of Spain, is Madrid's most popular park and the largest park in central Madrid. Its area is more than 1.4 km2 (0.5 sq mi) (350 acres) and it is located very close to the Puerta de Alcalá and not far from the Prado Museum. The park is entirely surrounded by the present-day city. Its lake in the middle once staged mini naval sham battles to amuse royalty; these days the more tranquil pastime of pleasure boating is popular. Inspired by London's Crystal Palace, the Palacio de Cristal can be found at the south-eastern end of the park.
In the Buen Retiro Park is also the Forest of the Departed (Bosque de los Ausentes), a memorial monument to commemorate the 191 victims of the 11 March 2004 Madrid attacks.
Atocha Railway Station (Estación de Atocha) is the city's first and most central station, and is also home to a 4,000 square metre indoor garden, with more than 500 species of plant life and ponds with turtles and goldfish in.

Casa de Campo is an enormous urban parkland to the west of the city, the largest in Spain and Madrid's main green lung. Its area is more than 1,700 hectares (6.6 sq mi). It is home to a fairground, the Madrid Zoo, an amusement park, the Parque de Atracciones of Madrid, and an outdoor municipal pool, to enjoy a bird's eye view of the park and city take a cable car trip above the tree tops. Casa de Campo's vegetation is one of its most important features. There are, in fact, three different ecosystems: oak, pine and river groves. The oak is the dominant tree species in the area and, although many of them are over 100 years old and reach a great height, they are also present in the form of chaparral and bushes. The pine-forest ecosystem boasts a large number of trees that have adapted perfectly to the light, dry conditions in the park. In addition, mushrooms often emerge after the first rains of autumn. Finally, the river groves, or riparian forests, are made up of various, mainly deciduous, species that grow in wetter areas. Examples include poplars, willows and alder trees. As regards fauna, this green space is home to approximately 133 vertebrate species.
The Royal Botanical Garden of Madrid (Real Jardín Botánico de Madrid) is an 8-hectare botanical garden located in the Plaza de Murillo, next to the Prado Museum. It was an 18th-century creation by Carlos III and it was used as a base for the plant species being collected across the globe. There is an important research facility that started life as a base to develop herbal remedies and to house the species collected from the new-world trips, today it is dedicated to maintaining Europe's ecosystem.

The Royal Palace (Palacio Real) is surrounded by three green areas. In front of the palace, are the gardens of the Plaza de Oriente; to the north, the gardens of Sabatini and to the west up to the Manzanares River, the famous Campo del Moro. Campo del Moro gardens has a surface area of 20 hectares and is a scenic garden with an unusual layout filled with foliage and an air of English romanticism. The Sabatini Gardens have a formal Neoclassic style, consisting of well-trimmed hedges, in symmetric geometrical patterns, adorned with a pool, statues and fountains, with trees also planted in a symmetrical geometric shape. Plaza de Oriente can distinguish three main plots: the Central Gardens, the Cabo Noval Gardens and the Lepanto Gardens. The Central Gardens are arranged around the central monument to Philip IV, in a grid, following the barroque model garden. They consist of seven flowerbeds, each packed with box hedges, forms of cypress, yew and magnolia of small size, and flower plantations, temporary. These are bounded on either side by rows of statues paths, popularly known as the Gothic kings, and mark the dividing line between the main body of the plaza and the Cabo Noval Gardens at north, and the Lepanto Gardens at south.

Mount of El Pardo (Monte de El Pardo) is a mediterranean forest inside the city of Madrid. It is one of the best preserved Mediterranean Forests in Europe. The European Union has designated the Monte de El Pardo as a Special Protection Area for bird-life. This meadow, which has been used as hunting grounds by the royalty given the variety of game animals that have inhabited it since the Middle Ages, is home to 120 flora species and 200 vertebrae species. Rabbits, red partridges, wild cats, stags, deer and wild boars live among ilexes, cork oaks, ash trees, black poplars, oaks, junipers and rockroses. Monte del Pardo is part of the Regional Park of the High Basin of the Manzanares, spreading out from the Guadarrama Mountains range to the centre of Madrid, and protected by strong legal regulations. Just before crossing the city, the River Manzanares forms a valley composed by sandy elements and detritus from the mountain range.

Soto de Viñuelas, also known as Mount Viñuelas, is a meadow-oak forest north of the city of Madrid and east of the Monte de El Pardo. It is a fenced property of about 3,000 hectares, which includes important ecological values, landscape and art. Soto de Viñuelas is part of the Regional Park of the High Basin of the Manzanares, a nature reserve which is recognised as a biosphere reserve by UNESCO, where it has been classified as Area B, the legal instrument that allows agricultural land use. Soto de Viñuelas has also received the statement of Special Protection Area for Birds.

El Capricho is a 14-hectare garden located in the area of Barajas district. It dates back to 1784. The art of landscaping in El Capricho is displayed in three different styles of classical gardenscapes: the "parterre" or French garden, English landscaping and the Italian giardino.
Madrid Río (Madrid River) is a linear park that runs along the bank of the Manzanares River, in the middle of Madrid. It is an area of parkland 10 kilometres (6 miles) long and covers 649 hectares in six districts: Moncloa-Aravaca, Centro, Arganzuela, Latina, Carabanchel and Usera. It is a large area of environmental, sporting, leisure and cultural interest. Madrid Río provides a link with other green spaces in the city such as Casa de Campo and the Linear Park of the Manzanares River. The main landscaped area in Madrid Río is the Arganzuela Park, covering 23 hectares where pedestrian and cycling routes cover the whole park. The Madrid Río cycling network covers some 30 km (19 mi) and is linked to other bike routes. To the north, Madrid Rio connects to the Senda Real, the Green Ring for Cyclists and the E 7 (GR 10) trail, which goes as far as the Sierra de Guadarrama mountain range. To the south, Madrid Río provides access to the Enrique Tierno Galván Park and the Linear Park of the Manzanares River, an extensive green zone running parallel to the river as far as Getafe. As well as the cycle routes there are 42 km (26 mi) of paths for walkers and runners. In the Salón de Pinos, a 6-kilometre long tree-lined promenade, there are circuits for aerobic and anaerobic exercise, while near the Puente de Praga bridge there is a tennis court and seven tennis courts.
The theme park Faunia is a natural history museum and zoo combined, aimed at being fun and educational for children. It comprises eight eco-systems from tropical rain forests to polar regions, and contains over 1,500 animals, some of which roam freely within.
Economy
Middle Ages to 20th century



During the end of the Middle Ages, Madrid experienced astronomic growth as a consequence of its establishment as the new capital of the Spanish Empire. As Spain (like many other European countries) continued to centralize royal authority, this meant that Madrid took on greater importance as a center of administration for the Spanish Kingdom. It evolved to become an important nucleus of artisanal activity that eventually experienced industrial revolution during the 19th century. The city made even greater strides at expansion during the 20th century, especially after the Spanish Civil War, reaching levels of industrialization found in other European capital cities. The economy of the city was then centred on diverse manufacturing industries such as those related to motor vehicles, aircraft, chemicals, electronic devices, pharmaceuticals, processed food, printed materials, and leather goods.[66]
1992 to present
Madrid is a major centre for international business and commerce. It is one of Europe's largest financial centres and the largest in Spain.

During the period from 1992 to 2006, Madrid experienced very significant growth in its service sector. The most notable of these services are those geared towards companies, followed by transport and communications, property and financial services. These four groups generate 51% of gross value added for Madrid's economy and 62% of gross value added for the services sector. The importance of the Barajas Airport to the city's economy is substantial. The construction of housing and public works, such as the ringroads and train network, constituted a major pillar of the economy up to 2006.
As Spain has become decentralized politically, Madrid has taken on a smaller administrative profile as compared to the rest of the Spanish state. Even so, the Community of Madrid (centred upon the city of Madrid) experienced the highest growth of all the Spanish regions between 2004 to 2006. Its growth rate was higher than for the country as a whole by 1.4% during the period 2000–2006, and that of the Eurozone by 13%.[67]
By 2005 Madrid had become the 23rd richest city in the world and third richest in Europe in terms of absolute GDP; the economic output for the year 2005 was of $201.5 billion, behind the considerably larger cities of Paris ($460 billion) and London ($452 billion) and ahead of Moscow and Barcelona.[68] Additionally in terms of GDP per capita, Madrid, in specific the Madrid region is the richest in Spain and one of the richest in Europe. At 133.9% of the European average of €25,800 (€34,572/$48,313) Madrid is ahead of all the other 8 Spanish regions above 100%.[69]
Madrid is a global financial leader, rising to the top five Centres of Commerce in Europe. Madrid continues its upward trajectory as a key European city, rising from its 2007 spot at number 16 to number 11 globally and from number 6 to the number 5 spot in Europe. Madrid's stable GDP, exchange rate and strong bond market, coupled with a high standard of living, place this city in the company of Europe's most prominent cities: London, Paris, Frankfurt and Amsterdam.[70]
Madrid is one of the cities in the Iberian Peninsula that attracts most foreign investment and job seekers. The average monthly salary in Madrid during 2007 was €2540, clearly above the Spanish average of €2085.[71] In terms of net earnings, Madrid places second in Spain; Madrid is 30th in the world, at 78.6%.[72]
Art and culture
Museums and art centres

Madrid is considered one of the top European destinations concerning art museums. Best known is the Golden Triangle of Art, located along the Paseo del Prado and comprising three museums. The most famous one is the Prado Museum, known for such highlights as Diego Velázquez's Las Meninas and Francisco de Goya's La maja vestida and La maja desnuda. The other two museums are the Thyssen Bornemisza Museum, established from a mixed private collection, and the Reina Sofía Museum, where Pablo Picasso's Guernica hangs, returned to Spain from New York after more than two decades.
The Prado Museum (Museo del Prado) is a museum and art gallery that features one of the world's finest collections of European art, from the 12th century to the early 19th century, based on the former Spanish Royal Collection. The collection currently comprises around 7,600 paintings, 1,000 sculptures, 4,800 prints and 8,200 drawings, in addition to a large number of works of art and historic documents. El Prado is one of the most visited museums in the world, and it is considered to be among the greatest museums of art. It has the best collection of artworks by Goya, Velázquez, El Greco, Rubens, Titian, Hieronymus Bosch, José de Ribera and Patinir; and works by Rogier van der Weyden, Raphael Sanzio, Tintoretto, Veronese, Caravaggio, Van Dyck, Albrecht Dürer, Claude Lorrain, Murillo and Zurbarán, among others. Among the most famous paintings in this museum are 'Las Meninas,' ‘The immaculate Conception,’ and ‘The judgement of Paris.'

The Reina Sofía Museum, in full Reina Sofía National Art Museum (Museo Nacional Centro de Arte Reina Sofía, abbreviated as MNCARS), is the Spain's national museum of 20th-century art. The museum is mainly dedicated to Spanish art. Highlights of the museum include excellent collections of Spain's greatest 20th-century masters, Pablo Picasso, Salvador Dalí, Joan Miró, Juan Gris and Julio González. Certainly the most famous masterpiece in the museum is Picasso's painting Guernica. The Reina Sofía also hosts a free-access library specializing in art, with a collection of over 100,000 books, over 3,500 sound recordings and almost 1,000 videos.[73]

The Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum (Museo Thyssen-Bornemisza) is an art museum that fills the historical gaps in its counterparts' collections: in the Prado's case this includes Italian primitives and works from the English, Dutch and German schools, while in the case of the Reina Sofía the Thyssen-Bornemisza collection, once the second largest private collection in the world after the British Royal Collection,[74] includes Impressionists, Expressionists, and European and American paintings from the second half of the 20th century, with over 1,600 paintings.[75]
The Royal Academy of Fine Arts of San Fernando (Real Academia de Bellas Artes de San Fernando) currently functions as a museum and gallery that houses a fine art collection of paintings from the 15th to 20th centuries: Giovanni Bellini, Correggio, Rubens, Zurbarán, Murillo, Goya, Juan Gris, Pablo Serrano. The academy is also the headquarters of the Madrid Academy of Art. Francisco Goya was once one of the academy's directors, and, its alumni include Pablo Picasso, Salvador Dalí, Antonio López García, Juan Luna, and Fernando Botero.[76][77]

The Royal Palace of Madrid (Palacio Real de Madrid) is the official residence of Juan Carlos I of Spain, but he uses it only for official acts. It is a baroque palace full of artworks and is one of the largest European Royal Palaces, characterized by its luxurious rooms and its rich collections of armors and weapons, pharmaceuticals, silverware, watches, paintings, tapestries and the most comprehensive collection of Stradivarius in the world[78]
The National Archaeological Museum (Museo Arqueológico Nacional) collection includes, among others, Pre-historic, Celtic, Iberian, Greek and Roman antiquities and medieval (Visigothic, Muslim and Christian) objects. Highlights include a replica of the Altamira cave (the first cave in which prehistoric cave paintings were discovered), Lady of Elx (an enigmatic polychrome stone bust), Lady of Baza (a famous example of Iberian sculpture), Biche of Balazote (an Iberian sculpture) and Treasure of Guarrazar (a treasure that represents the best surviving group of Early Medieval Christian votive offerings and the high point of Visigothic goldsmith's work).[79]
The Museum of the Americas (Museo de América) is a National museum that holds artistic, archaeological and ethnographic collections from the whole American continent, ranging from the Paleolithic period to the present day. The permanent exhibit is divided into five major thematical areas: an awareness of America, the reality of America, society, religion and communication.[80]

The National Museum of Natural Sciences (Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales) is the National Museum of Natural History of Spain. The research departments of the museum are: Biodiversity and Evolutionary Biology, Evolutionary Ecology, Paleobiology, Vulcanology and Geology.[81]
The Naval Museum (Museo Naval) is managed by the Ministry of Defence. The Museum's mission is to acquire, preserve, investigate, report and display for study, education and contemplation, parts, sets and collections of historical, artistic, scientific and technical related to naval activity in order to disseminate the story sea of Spain; to help illustrate, highlight and preserve their traditions and promote national maritime awareness.[82]

The Convent of Las Descalzas Reales (Monasterio de las Descalzas Reales) resides in the former palace of King Charles I of Spain and Isabella of Portugal. Their daughter, Joan of Austria, founded this convent of nuns of the Poor Clare order in 1559. Throughout the remainder of the 16th century and into the 17th century, the convent attracted young widowed or spinster noblewomen. Each woman brought with her a dowry. The riches quickly piled up, and the convent became one of the richest convents in all of Europe. It has many works of Renaissance and Baroque art, including a recumbent Christ by Gaspar Becerra, a staircase whose paintings were painted by unknown author (perhaps Velázquez) and they are considered of the masterpieces of Spanish illusionist painting, and Brussels tapestries inspired by paintings of Rubens.[83]
The Museum of Lázaro Galdiano (Museo de Lázaro Galdiano) houses an encyclopedic collection specializing in decorative arts.
Apart from paintings and sculptures it displays 10th-century Byzantine enamel; Arab and Byzantine ivory chests; Hellenistic, Roman, medieval, renaissance, baroque and romantic jewelry; Pisanello and Pompeo Leoni medals; Spanish and Italian ceramics; Italian and Arab clothes and an collection of weapons including the sword of Pope Innocent VIII.[84]
The National Museum of Decorative Arts (Museo Nacional de Artes Decorativas) is one of the oldest museums in the city. It illustrates the evolution of the called "minor arts" (furniture, ceramics and glass, textile, etc.). Its 60 rooms expones 15,000 objects, of the approximate 40,000 which it has.[85]
The National Museum of Romanticism (Museo Nacional de Romanticismo) contains a large collection of artefacts and art, focusing on daily life and customs of the 19th century, with special attention to the aesthetics about Romanticism.[86]
The Cerralbo Museum (Museo Cerralbo) houses a private collection of ancient works of art, artifacts and other antiquities collected by Enrique de Aguilera y Gamboa, XVII Cerralbo Marquis.[87]
The National Museum of Anthropology (Museo Nacional de Antropología) provides an overview of the different cultures in the world, with objects and human remains from around the world, highlighting a Guanche mummy of the island of Tenerife.[88]
The Sorolla Museum (Museo Sorolla) is located in the building in which the Valencian Impressionist painter had his home and workshop. The collection includes, in addition to numerous works of Joaquín Sorolla, a large number of objects that possessed the artist, including sculptures by Auguste Rodin.[89]

CaixaForum Madrid is a post-modern art gallery in the centre of Madrid. It is sponsored by the Catalan-Balearic bank La Caixa and located next to the Salón del Prado. Although the CaixaForum is a modern building, it also exhibits retrospectives of artists from earlier time periods and has evolved into one of the most-visited museums in Madrid. It was constructed by the Swiss architects Herzog & de Meuron from 2001 to 2007, which combined an old, unused, industrial building and hollowed it out at the base and inside and placed on top further floors which are encased with rusted steel. Next to it is an art installation of green plants growing on the wall of the neighbouring house by French botanist Patrick Blanc. The red of the top floors with the green of the wall next to it form a contrast. The green is in reflection of the neighbouring Royal Botanical Gardens.[90]
Major cultural centres organize parallel cultural events and they are housed in unique buildings:

Centrocentro is an exhibition space in Cibeles Palace, formerly the Palace of Communications and now the City Hall. Two social areas have been set up and offer catalogues and publications about current exhibitions and cultural events along the Art Walk. Near these social areas are two large street maps showing the 59 institutions, monuments and buildings of special interest that make the Art Walk such a diverse experience.
The Fine Arts Circle (Círculo de Bellas Artes), built by Antonio Palacios, is one of Madrid's oldest arts centres and one of the most important private cultural centres in Europe. It is a multidisciplinary centre with activities ranging from visual art to literature, from science and philosophy to film and the performing arts. Nowadays it hosts exhibitions, shows, film screenings, conferences and workshops; its radio and magazine Minerva play an important part in the country's cultural life.
Matadero Madrid, literally "Madrid Abattoir", is a complex situated by the river Manzanares and their buildings shape an architectural ensemble devoted to performance arts, which is managed and programmed by the Teatro Español. Matadero is a flexible area that allows the autonomous operation of these three interconnected spaces: a theatre café, which accommodates small-scale shows, a large stage, for all sorts of genres and the most experimental options, and a third building for dressing rooms and areas for training, debate, analysis and rehearsing new productions.
Conde Duque cultural centre has expanded the amount of space dedicated to culture and art. The new installations now accommodate a theatre, an exhibition hall and an auditorium with a programme running all year long.
Other art galleries and museums in Madrid include:
-
Lady of Elche (National Archaeological Museum)
-
Museum of the Americas
-
National Museum of Natural Sciences
-
Museum of Madrid History
Landmarks

In the year 2006 Madrid was the fourth most visited city in Europe and the first of Spain, with almost seven million tourists.[94] It is also the seat of the World Tourism Organization and the International Tourism Fair – FITUR.
Most of the tourist attractions of Madrid are in the old town and the Ensanche, corresponding with the districts of Centro, Salamanca, Chamberí, Retiro and Arganzuela. The nerve centre of the city is the Puerta del Sol, starting point for the numbering of all city streets and all the country's highways.
The Calle de Alcalá or Alcalá Street leads from the Puerta del Sol from the NE of the city. From the street you get from Plaza de Cibeles. Subsequently the street reaches the "Plaza de la Independencia", which includes the Puerta de Alcalá and an entrance to the Buen Retiro Park.
The Calle Mayor leads to Plaza Mayor continuing for the so-called Madrid de los Austrias, in reference to the Dynasty of Habsburg - finally reaching Calle de Bailén, near the Cathedral of the Almudena and the church of San Francisco el Grande.
The Calle del Arenal comes to Royal Theatre in Plaza de la Ópera, continuing through Plaza de Oriente, where the Royal Palace is it. From there the Calle Bailen leads to Plaza de España and the Temple of Debod, an Egyptian temple moved stone by stone to Spain in gratitude for their help in the construction of the Aswan Dam. Also in this square is the start of Gran Vía street.
Churches



Madrid has a considerable number of Catholic churches, some of them are among the most important Spanish religious artworks.
The oldest church that survives today is San Nicolás de los Servitas, whose oldest item is the bell tower (12th century), in Mudéjar style. The next oldest temple is San Pedro el Real, with its high brick tower.
St. Jerome Church is a gothic church next to El Prado Museum. The Catholic Monarchs ordered its construction in the 15th century, as part of a vanished monastery. The monastery's cloister is preserved. It has recently been renovated by Rafael Moneo, with the goal to house the neoclassical collection of El Prado Museum, and also sculptures by Leone Leoni and Pompeo Leoni.
The Bishop Chapel is a gothic chapel which was built in the 16th century by order of the Bishop of Plasencia, Gutierre de Vargas. It was originally built to house the remains of Saint Isidore Laborer (Madrid's patron saint), but it was used as the Vargas family mausoleum. Inside are the altairpiece and the tombs of the Vargas family, which were the work of Francisco Giralte, a disciple of Alonso Berruguete. They are considered masterpieces of Spanish Renaissance sculpture.

St. Isidore Church was built between 1620 and 1664 by order of Empress Maria of Austria, daughter of Charles V of Germany and I of Spain, to become part of a school run by the Jesuits which still exists today. Its dome is the first example of a dome drawing on a wooden frame covered with plaster, which, given its lightness makes it easy to support the walls. It was the cathedral of Madrid between 1885 and 1993, which is the time it took to build the Almudena. The artwork inside were mostly burned during the Spanish Civil War, but it retained the tomb that holds the incorrupt body of Saint Isidore Laborer and the urn containing the ashes of his wife Maria Torribia.
Royal Convent of La Encarnación is an Augustinian Recollect convent. The institution, which belonged ladies of the nobility, was founded by Queen Margaret of Austria, wife of Philip III of Spain, in the early 17th century. Due to the frescoes and sculptures which houses is one of the most prominent temples in the city. The building's architect was Fray Alberto de la Madre de Dios, who built it between 1611 and 1616. The façade responds to an inspiring Herrerian style, with great austerity, and it was imitated by other Spanish churches. The church's interior is a sumptuous work by the great Baroque architect Ventura Rodriguez.
In the church are preserved shrines containing the blood of St. Januarius and St. Pantaleon, the second (according to tradition) liquefies every year on the saint's day on 27 July.
San Antonio de los Alemanes (St. Anthony Church) is a pretty 17th-century church which was originally part of a Portuguese hospital. Subsequently it was donated to the Germans living in the city.
The interior of the church has been recently restored. It has some beautiful frescoes painted by Luca Giordano, Francisco Carreño and Francisco Rizi. The frescoes represent some kings of Spain, Hungary, France, Germany and Bohemia. They all sit looking at the paintings in the vault, which represent the life of Saint Anthony of Padua.
Royal Chapel of St. Anthony of La Florida is sometimes named the "Goya's Sistine Chapel". The chapel was built on orders of King Charles IV of Spain, who also commissioned the frescoes by Goya. These were completed over a six-month period in 1798. The frescoes portray miracles by Saint Anthony of Padua, including one which occurred in Lisbon, but which the painter has relocated to Madrid. On every 13 June, the chapel becomes the site of a lively pilgrimage in which young unwed women come to pray to St. Anthony and to ask for a partner.
San Francisco el Grande Basilica was built in neoclassical style in the second half of the 18th century by Francesco Sabatini. It has the fifth largest diameter dome to Christianity. (33 meters in diameter: it's smaller than the dome of the Rome's Pantheon (43.4meters), St. Peter's Basilica (42.4 meters), the Florence Cathedral (42 meters)and the Rotunda of Mosta (37.2 meters) in Malta, but it's larger than St. Paul's Cathedral (30.8 meters) in London and Hagia Sophia (31.8 meters) in Istanbul).
The church is dedicated to St. Francis of Assisi, who according to legend was established in Madrid during his pilgrimage to Santiago de Compostela. Its sumptuous interior features many artworks, including paintings by Goya and Zurbarán.
The Cathedral of Santa María la Real de la Almudena is the episcopal seat of the Archdiocese of Madrid. It is a temple of 102 meters long and 73 high, built during the 19th and 20th centuries in a mixture of different styles: neoclassical exterior, neo-Gothic interior and neo-Romanesque crypt and neo-Byzantine apse's paints.
The cathedral was built in the same place which was built the Moorish citadel (Al-Mudayna) in Madrid. It was consecrated by Pope John Paul II on his fourth trip to Spain on 15 June 1993, thus being the only Spanish cathedral dedicated by a pope.
Literature

Madrid has been one of the great centers of Spanish literature. Some of the best writers of the Spanish Golden Century were born in Madrid, including: Marta Salto (professor at the Universadad Complutense), Lope de Vega (Fuenteovejuna, The Dog in the Manger, The Knight of Olmedo), who reformed the Spanish theater, a work continued by Calderon de la Barca (Life is a Dream), Francisco de Quevedo, Spanish nobleman and writer famous for his satires, which criticized the Spanish society of his time, and author of ´El Buscón. And finally, Tirso de Molina, who created the famous character Don Juan. Cervantes and Góngora also lived in the city, although they were not born there. The homes of Lope de Vega, Quevedo, Gongora and Cervantes are still preserved, and they are all in the Barrio de las Letras (District of Letters).
Other writers born in Madrid in later centuries have been Leandro Fernandez de Moratín, Mariano José de Larra, Jose de Echegaray (Nobel Prize in Literature), Ramón Gómez de la Serna, Dámaso Alonso, Enrique Jardiel Poncela and Pedro Salinas.
The "Barrio de las Letras" (District of Letters) owes its name to the intense literary activity developed over the 16th and 17th centuries. Some of the most prominent writers of the Spanish Golden Age settled here, as Lope de Vega, Quevedo or Góngora, and the theatres of Cruz and Príncipe, two of the major comedy theaters of that time. At 87 Calle de Atocha, one of the roads that limit the neighborhood, was the printing house of Juan Cuesta, where the first edition of the first part of Don Quixote (1604) was published, one of the greatest works of Spanish literature. Most of the literary routes are articulated along the Barrio de las Letras, where you can find scenes from novels of the Siglo de Oro and more recent works like "Bohemian Lights".
Madrid is home to the Royal Academy of Spanish Language, an internationally-important cultural institution dedicated to language planning by enacting legislation aimed at promoting linguistic unity within the Hispanic states; this ensures a common linguistic standard, in accordance with its founding statutes "to ensure that the changes undergone [by the language] [...] not break the essential unity that keeps all the Hispanic".[95]
Madrid is also home to another international cultural institution, the Instituto Cervantes, whose task is the promotion and teaching of the Spanish language as well as the dissemination of the culture of Spain and Latin America.
The National Library of Spain is the largest major public library in Spain. The library's collection consists of more than 26,000,000 items, including 15,000,000 books and other printed materials, 30,000 manuscripts, 143,000 newspapers and serials, 4,500,000 graphic materials, 510,000 music scores, 500,000 maps, 600,000 sound recording, 90,000 audiovisuals, 90,000 electronic documents, more than 500,000 microforms, etc.[96]
-
Commemorative plaque of the 1st edition of Don Quixote
-
Plaza de Santa Ana, Barrio de las Letras
Nightlife
This section needs additional citations for verification. (September 2014) |
The nightlife in Madrid is one of the city's main attractions. Tapas bars, cocktail bars, clubs, jazz lounges, live music venues, flamenco theatres, and establishments of all kinds cater to all. Every night, venues pertaining to the Live Music Venues Association La Noche en Vivo host a wide range of live music shows. Everything from acclaimed to up-and-coming artists, singer-songwriters to rock bands, jazz concerts or electronic music sessions to showcase music at its best.
Nightlife and young cultural awakening flourished after the death of Franco, especially during the 80s while Madrid's mayor Enrique Tierno Galván (PSOE) was in office. At this time, the cultural movement called La Movida flourished, and it initially gathered around Plaza del Dos de Mayo. Nowadays, the Malasaña area is known for its alternative scene.
Some of the most popular night destinations include the neighbourhoods of Bilbao, Tribunal, Atocha, Alonso Martínez or Moncloa, together with the Puerta del Sol area (including Ópera and Gran Vía, both adjacent to the popular square) and Huertas (Barrio de las Letras), destinations which are also filled with tourists day and night. The district of Chueca has also become a hot spot in the Madrilenian nightlife, especially for the gay population. Chueca is popularly known as the gay quarter, comparable to The Castro district in San Francisco.
What is also popular is the practice of meeting in parks or streets with friends and drinking alcohol together (this is called botellón, from botella, 'bottle'), but in recent years, drinking in the street is punished with a fine of €600.
Usually in Madrid people do not go out until later in the evening and do not return home until early in the morning. A typical evening out could start after 12:00 AM and end at 6:30 AM.
Bohemian culture
The city has venues for performing alternative art and expressive art. They are mostly located in the centre of the city, including in Ópera, Antón Martín, Chueca and Malasaña. There are also several festivals in Madrid, including the Festival of Alternative Art, the Festival of the Alternative Scene.[97][98][99][100]
The neighbourhood of Malasaña, as well as Antón Martín and Lavapiés, hosts several bohemian cafés/galleries. These cafés are typified with period or retro furniture or furniture found on the street, a colourful, nontraditional atmosphere inside, and usually art displayed each month by a new artist, often for sale. Cafés include the retro café Lolina and bohemian cafés La Ida, La Paca and Café de la Luz in Malasaña, La Piola in Huertas and Café Olmo and Aguardiente in Lavapiés.
In the neighbourhood of Lavapiés, there are also "hidden houses", which are illegal bars or abandoned spaces where concerts, poetry readings and[101][102][103] the famous Spanish botellón (a street party or gathering that is now illegal but rarely stopped).
Classical music and opera

The Auditorio Nacional de Música [104] is the main venue for classical music concerts in Madrid. It is home to the Spanish National Orchestra, the Chamartín Symphony Orchestra[105] and the venue for the symphonic concerts of the Community of Madrid Orchestra and the Madrid Symphony Orchestra. It is also the principal venue for orchestras on tour playing in Madrid.
The Teatro Real is the main opera house in Madrid, located just in front of the Royal Palace, and its resident orchestra is the Madrid Symphony Orchestra.[106] The theatre stages around seventeen opera titles (both own productions and co-productions with other major European opera houses) per year, as well as two or three major ballets and several recitals.
The Teatro de la Zarzuela is mainly devoted to Zarzuela (the Spanish traditional musical theatre genre), as well as operetta and recitals.[107][108] The resident orchestra of the theatre is the Community of Madrid Orchestra.
The Teatro Monumental is the concert venue of the RTVE Symphony Orchestra.[109]
Other concert venues for classical music are the Fundación Joan March and the Auditorio 400, devoted to contemporary music.
Local festivities
- 2 May, Fiesta de la Communidad (Madrid's Community Day).
- 15 May, San Isidro Labrador (Madrid's patron saint).
- 13 June, San Antonio de la Florida (Moncloa neighbourhood's patron saint).
- 16–25 July, Virgen del Carmen festivities (Vallecas neighbourhood's patron saint).
- 6–14 August, Virgen de la Paloma festivities (Madrid's popular patron saint).
- 7 August, San Cayetano (Cascorro neighbourhood's patron saint).
- 10 August, San Lorenzo (Lavapiés neighbourhood's patron saint).
- 9 November, Feast of the Virgin of Almudena (Madrid's patron saint).
Sport

Madrid is home to La Liga football club giants Real Madrid, who play their home games at the Santiago Bernabéu. Their supporters are referred to as Madridistas or Merengues (Meringues). Real Madrid is one of the most prestigious football clubs of the world (FIFA selected Real Madrid the best team of the 20th century), having won a record 10 European Cups.
Their successful hometown rivals, Atlético Madrid, are also well-supported in the city. The club has recently won two UEFA Europa League titles and the 2012-13 Copa del Rey, beating their crosstown rivals Real 1-2 at the Santiago Bernabéu in the final, and winning a new league title in 2014. Historically, Atletico has won 10 league titles and 10 Copa del Rey titles. The players (and supporters) are referred to as Colchoneros (The Mattressers), in reference to the team's red and white jersey colours, which were determined by mattress material being the cheapest at the time of the club's formation. Atletico play at the Estadio Vicente Calderon.
In 1982, Madrid hosted the FIFA World Cup Final. Madrid is one of only four cities in Europe to contain two UEFA 5-star stadia: Real Madrid's Santiago Bernabéu and Atlético Madrid's Vicente Calderón. Rayo Vallecano and Getafe CF are two further teams from the Madrid area currently playing in La Liga.

Some of Spain's top footballers are Madrilenians (born in Madrid), including Real Madrid former player Emilio Butragueño (and co-teammate of La Quinta del Buitre, "The Vulture's Cohort"), Fernando Torres and Real Madrid veterans Raúl, and Iker Casillas.
Madrid boasts a prominent place in Spanish basketball, with two clubs in the country's top-level Liga ACB. Real Madrid's basketball section has won 30 Spanish League championships, 22 Spanish Cup championships, 8 Euroleague Championships, 4 Saporta Cups, 4 Intercontinental Cups and have won 2 Triple Crowns. Madrid's other professional basketball club is Estudiantes that have won 3 Spanish Cup championships.
The city serves as the final stage of the Vuelta a España cycling event.
| Club | League | Sport | Venue | Established | Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real Madrid C.F. | La Liga | Football | Santiago Bernabéu | 1902 | 85,454 |
| Atlético Madrid | La Liga | Football | Vicente Calderón | 1903 | 54,851 |
| Rayo Vallecano | La Liga | Football | Estadio de Vallecas | 1924 | 15,500 |
| Real Madrid Castilla | Segunda División B | Football | Alfredo di Stéfano | 1930 | 6,000 |
| Real Madrid Baloncesto | ACB | Basketball | Palacio de Deportes de Madrid | 1932 | 16,000 |
| CB Estudiantes | ACB | Basketball | Palacio de Deportes de Madrid | 1948 | 16,000 |
| BM Atlético Madrid | ASOBAL | Handball | Palacio Vistalegre | 2011 | 15,000 |
Bullfighting

Madrid hosts the largest plaza de toros (bullring) in Spain, Las Ventas, established in 1929. Las Ventas is considered by many to be the world centre of bullfighting and has a seating capacity of almost 25,000. Madrid's bullfighting season begins in March and ends in October. Bullfights are held every day during the festivities of San Isidro (Madrid's patron saint) from mid May to early June, and every Sunday, and public holiday, the rest of the season. The style of the plaza is Neo-Mudéjar. Las Ventas also hosts music concerts and other events outside of the bullfighting season.
Olympic Games Bids
The history of Madrid's bid to host the Olympic Games dates back to December 29, 1965 when the Spanish government presented a joint bid Madrid-Barcelona to the International Olympic Committee (IOC) to host the 20th edition of the Games in 1972. The Spanish candidature was however ruled out in the IOC session held in Rome on 26 April 1966, where Munich was finally elected.
Many years later, Madrid's council presented a bid to host the 2012 Summer Olympics. The candidate city logo was designed by Javier Mariscal, a Spanish artist who also designed the mascot for the Barcelona 1992 Olympic Games.[110] On May 18, 2004 the IOC selected in Lausanne (Switzerland) the five official candidate cities for the organization of the Olympic Games of 2012: Madrid, Paris, London, New York and Moscow. On July 6, 2005, the IOC announced the result of the election of the city that would host the 2012 Olympics: the choice was London, and the city of Madrid finished third. Later, an IOC member told reporters he made a mistake when marking his vote, so Madrid was eliminated in the penultimate voting.[111]
During the selection process for the 2012 Summer Olympics, there was among Madrid citizens a minority social movement of opposition to the nomination, which was accused of favoring real estate speculation and increase the already high indebtedness of the council.
The Spanish Olympic Committee renewed on May 30, 2007 the Madrid bid for the 2016 Summer Olympics. On June 4, 2008 Madrid was shortlisted as one of the candidates to host 2016 Games, along with Chicago, Tokyo and Rio de Janeiro. The project presented was based on the prior application with improvements, which allowed him to be the second city with the highest rating, slightly behind Tokyo. Finally, on October 2, 2009 the city of Rio de Janeiro won the election, despite having initially a general technical assessment below that of the other three cities.
Madrid resubmitted an application to host the games in 2020. The IOC selected Madrid as candidate city on May 23, 2012.[112] On September 7, 2013 the candidate cities were Madrid, Istanbul and Tokyo. On the first ballot Madrid and Istanbul yielded the same votes after Tokyo. In the runoff vote, Madrid was eliminated[113] and in the final vote, Tokyo won by a large amount of votes.
Following Madrid's failure to secure the 2020 Olympics, it was confirmed that Madrid would not be bidding for the 2024 Summer Olympics.[114]
Education
State Education in Spain is free, and compulsory from 6 to 16 years. The current education system is called LOE (Ley Orgánica de Educación).[115]
Universities
Madrid is home to a large number of public and private universities. Some of them are among the oldest in the world, and many of them are the most prestigious universities in Spain.

The Complutense University of Madrid (Universidad Complutense de Madrid) is the largest university in Spain and one of the oldest universities in the world. It has 10,000 staff members and a student population of 117,000. Nearly all academic staff are Spanish. It is located on two campuses, in the university quarter Ciudad Universitaria at Moncloa in Madrid, and in Somosaguas.[116] The Complutense University of Madrid was founded in Alcalá de Henares, old Complutum, by Cardinal Cisneros in 1499. Nevertherless, its real origin dates back to 1293, when King Sancho IV of Castile built the General Schools of Alcalá, which would give rise to Cisnero's Complutense University. During the course of 1509–1510 five schools were already operative: Artes y Filosofía (Arts and Philosophy), Teología (Theology), Derecho Canónico (Canonical Laws), Letras (Liberal Arts) and Medicina (Medicine). In 1836, during the reign of Isabel II, the University was moved to Madrid, where it took the name of Central University and was located at San Bernardo Street. Subsequently, in 1927, a new university area was planned to be built in the district of Moncloa-Aravaca, in lands handed over by the King Alfonso XIII to this purpose. The Spanish Civil War turned the Ciudad Universitaria into a war zone, causing the destruction of several schools in the area, as well as the loss of part of its rich scientific, artistic and bibliographic heritage. In 1970 the Government reformed the High Education, and the Central University became the Complutense University of Madrid. It was then when the new campus at Somosaguas was created to house the new School of Social Sciences. The old Alcalá campus was reopened as the independent UAH, University of Alcalá, in 1977. Complutense also serves to the population of students who select Madrid as their residency during their study abroad period. Students from the United States for example, might go to Madrid on a program like API (Academic Programs International) and study at Complutense for an intense immersion into the Spanish Language. The beautiful setting of the campus allows students living temporarily in Madrid to have access to all of the city's public features including Retiro Park, El Prado Museum, and much more. After studying at the University, students return home with a fluent sense of Spanish as well as culture and diversity.[117]

The Technical University of Madrid (Universidad Politécnica de Madrid), is the top technical university in Spain. It is the result of the merge of different Technical Schools of Engineering.
The Autonomous University of Madrid (Universidad Autónoma de Madrid) was instituted under the leadership of the famous physicist, Nicolás Cabrera. The Autonomous University is widely recognised for its research strengths in theoretical physics. Known simply as La Autónoma in Madrid, its main site is the Cantoblanco Campus, situated 10 miles (16 km) to the northeast of the capital (M-607) and close to the municipal areas of Madrid, namely Alcobendas, San Sebastián de los Reyes, Tres Cantos and Colmenar Viejo. Located on the main site are the Rectorate building and the Faculties of Science, Philosophy and Fine Arts, Law, Economic Science and Business Studies, Psychology, Higher School of Computing Science and Engineering, and the Faculty of Teacher Training and Education. La Autónoma is considered the institution to study Law in Spain, even is ranked in first place over private and public universities such as Comillas Pontifical University or Charles III University.[118] The Medical School is sited outside the main site and beside the Hospital Universitario La Paz.[119]
The Charles III University of Madrid (Universidad Carlos III de Madrid), whose philosophy is to create responsible free-thinking people with a sensitivity to social problems and an involvement in the concept of progress based on freedom, justice and tolerance. The undergraduate degrees in Business Administration, Economics is ranked first among those offered by public and private universities in Spain,[118] and its Master and PhD programs also rank top in the country.[120] The Department of Economics[121] is among the 50 best worldwide, and in the top 10 in Econometrics.[122]
Some other prestigious universities include University of Alcalá (Universidad de Alcalá), rebuilt at Alcalá de Henares in 1975; and the Comillas Pontifical University (Universidad Pontificia Comillas), involved in a number of academic exchange programmes, work practice schemes and international projects with over 200 Higher Education Institutions in Europe, Latin America, North America and Asia.
Other universities in Madrid, some of them private, are: Rey Juan Carlos University (public), Alfonso X University, Antonio de Nebrija University, Camilo José Cela University, Francisco de Vitoria University, European University of Madrid, Pontifical University of Salamanca–Madrid Campus, Saint Louis University Madrid Campus and San Pablo CEU University (all of them private).
Madrid is also home to the Queen Sofía College of Music (Escuela Superior de Música Reina Sofía), the Madrid Royal Conservatory (Real Conservatorio Superior de Música de Madrid)
Business schools
IE Business School (formerly Instituto de Empresa) has its main campus on the border of the Chamartín and Salamanca districts of Madrid. IE Business School recently ranked #1 in WSJ's 2009 rankings for Best MBA Programs under 2 years. It scored ahead of usual stalwarts, INSEAD and IMD, giving it top billing among International MBA programs. Although based in Barcelona, both IESE Business School and ESADE Business School also have Madrid campuses. These three schools are the top-ranked business schools in Spain, consistently rank among the top 20 business schools globally, and offer MBA programs (in English or Spanish) as well as other business degrees. Other Madrid business schools and universities that have MBA programs include:
- EAE Business School (in English and Spanish).
- Charles III University of Madrid through the Centro de Ampliación de Estudios (in English or Spanish).
- Comillas Pontifical University (in Spanish only).
- Technical University of Madrid (in Spanish only).
Transport
Madrid is served by highly developed communication infrastructures, making the Spanish capital the leading logistics hub for both Spain and all of southern Europe. It also boasts a network of motorways, encompassing both ring roads and radial roads, and provides the backbone for Spain's railway network, thereby providing effective connections with not only other parts of the region, but also the rest of Spain and Europe as a whole. Madrid ranks alongside Tokyo and Paris as one of the world's three largest high-speed railway hubs. Madrid is also home to the Madrid-Barajas airport, Spain's flagship airport and one of the largest in the world.
Air

Madrid–Barajas Airport (Aeropuerto de Madrid-Barajas) is Spain's busiest airport, and is the main hub of Iberia Airlines. It consequently serves as the main gateway to the Iberian peninsula from Europe, America and the rest of the world. Current passenger volumes range upwards of 49.8 million passengers per year, making it the country's largest and busiest airport, and in 2009 it was the world's 11th busiest airport[123] and Europe's fifth busiest airport. Given annual increases close to 10%, a new fourth terminal has been constructed. It has significantly reduced delays and doubled the capacity of the airport to more than 70 million passengers per year. Two additional runways have also been constructed, making Barajas a fully operational four-runway airport.
The airport located within the city limits of Madrid, at 9 km (5.6 mi) from the city's financial district and 13 km (8.1 mi) northeast of the Puerta del Sol, Madrid's historic centre. The airport name derives from the adjacent district of Barajas, which has its own metro station on the same rail line serving the airport.
The Minister of Transport of the Community of Madrid, Manuel Lamela, announced in 2007 that the city will also be served by two new airports which are expected to be fully operative in 2016, the first of which will be located in Campo Real, it will be initially be used for cargo flights, and also as hub for low-cost carriers, and the second one, expected to be built between the two municipalities of El Álamo and Navalcarnero, which will only take over the routes operating in Cuatro Vientos Airport (Aeropuerto de Cuatro Vientos).
The closed Ciudad Real Central Airport was intended to be the second airport for the city, linked to it by high speed rail.
National rail

Spain's railway system, the Red Nacional de Ferrocarriles Españoles (RENFE) operates the vast majority of Spain's railways. Cercanías Madrid is the commuter rail service that serves Madrid and its metropolitan area. It is operated by Cercanías Renfe, the commuter rail division of Renfe. The total length spans 339.1 kilometres (210.7 miles). Main rail terminals are Atocha in the south and Chamartín in the north.
The most important project in the next decade is the Spanish high-speed rail network, Alta Velocidad Española AVE. Currently, an ambitious plan includes the construction of a 7,000-kilometre (4,300 mi) network, centred on Madrid. The overall goal is to have all important provincial cities be no more than 4 hours away from Madrid, and no more than 6 hours away from Barcelona. As of 2008, AVE high-speed trains link Atocha station to Seville, Málaga, Córdoba, Ciudad Real and Toledo in the south and to Cuenca, Albacete, Valencia, Zaragoza, Lleida, Tarragona and Barcelona in the east. AVE trains also arrive from Valladolid in the north.
Metro

Serving a population of some five million, the Madrid Metro (Metro de Madrid) is one of the most extensive and fastest-growing metro networks in the world.[124] With the addition of a loop serving suburbs to Madrid's south-west "Metrosur", it is now the second largest metro system in Western Europe, second only to London's Underground. In 2007 Madrid's metro system was expanded and it currently runs over 283 kilometres (176 mi) of line. The region of Madrid is also served by an extensive commuter rail network of 370 kilometres (230 mi) called Cercanías.
The system is the sixth longest metro in the world after London, New York, Moscow, Seoul and Shanghai, though Madrid is approximately the fiftieth most populous metropolitan area in the world. Its fast growth in the last 20 years has also put it among the fastest growing networks in the world, on par with the Shanghai Metro and the Beijing Subway. Unlike normal Spanish road and rail traffic, Madrid Metro trains use left-hand running on some lines due to historical reasons.
Buses
This railway network is ably supported by an ever-expanding network of city buses. The overall length of the bus network of Madrid's Municipal Transport Corporation (Empresa Municipal de Transportes, or EMT) at yearclose 2013, when 426 million passengers were transported, stood at 3,690 km (2,293 mi), marking a 31% increase over the last eight years. These routes are serviced by a growing fleet of over 3,000 vehicles, while the network as a whole is undergoing a continuous improvement process with a view to attaining the utmost standards of speed, quality and sustainability. The buses in Madrid are the only public transport system available 24hours as the metro network closes down during night hours. The night buses, also known as “Buhos” (Owls), are running from 11.45pm to 6.00am.[125] The heavy traffic in Madrid can in some cases make the city buses a fairly slow form of transportation but the city of Madrid has more than 90 km of special bus and taxi lines to help solve this issue.[126]
Roads

Madrid is the most important hub of Spain's motorway network and is surrounded by four orbital motorways: M30, M40, M45 and M50. M30 circles the central districts and is the inner ring motorway of Madrid. Significant portions of M30 runs underground and its urban motorway tunnels have sections of more than 6 km (3.73 mi) in length and 3 to 6 lanes in each direction, between the south entry of the Avenida de Portugal tunnel and the north exit of the M-30 south by-pass there are close to 10 km (6.21 mi) of continuous tunnels. M40 is a ring motorway which borders Madrid at a mean distance of 10.07 kilometres (6.26 mi) and it has a total length of 63.3 km (39.33 mi). M45 is a partial ring around the city serving the metropolitan area of Madrid. It was built to help alleviate the congestion of the M40 from the southern to the north-eastern, runs between the M40 and the M50 where the two ring motorways are more separated. M50 is the outer of the Madrid orbital motorways and has a total length of 85 km (52.82 mi). It services mainly the metropolitan area at a mean distance of 13.5 km (8.39 mi).
The most important radial autovías of Madrid are:
| Signal | Denomination | Itinerary |
|---|---|---|
| A-1 | Autovía del Norte | Madrid – Aranda de Duero – Burgos – Miranda de Ebro – Vitoria – San Sebastián |
| A-2 | Autovía del Nordeste | Madrid – Guadalajara – Zaragoza – Lérida – Barcelona |
| A-3 | Autovía del Este | Madrid – Valencia |
| A-4 | Autovía del Sur | Madrid – Córdoba – Sevilla – Jerez – Cádiz |
| A-5 | Autovía del Suroeste | Madrid – Talavera de la Reina – Navalmoral de la Mata – Mérida – Badajoz – Portugal |
| A-6 | Autovía del Noroeste | Madrid – Medina del Campo – Benavente – Astorga – Ponferrada – Lugo – A Coruña |
| A-42 | Autovía de Toledo | Madrid – Illescas – Toledo |
Radial tolled autopistas (named R-n instead of A-n) form a new system of accesses to the capital that merges with their autovía counterparts far from Madrid. The main advantage to these roads is that they allow true fast travel from the first kilometer.
| Signal | Denomination | Itinerary |
|---|---|---|
| R-2 |
Autopista Radial 2 | Madrid (M-40)—M-50—Guadalajara (A-2) |
| R-3 |
Autopista Radial 3 | Madrid (M-30)—Arganda del Rey (A-3) |
| R-4 |
Autopista Radial 4 | Madrid (M-50)—Aranjuez—Ocaña (A-4/A-40/AP-36) |
| R-5 |
Autopista Radial 5 | Madrid (M-40)—Navalcarnero (A-5) |
| M-12 |
Eje aeropuerto | Madrid (M-40)—M-11—Airport terminal 4—A-1 |
International relations
Twin towns and sister cities
List of Madrid's twin towns, sister cities and partner cities:[127]
Notable people
Other historic buildings
-
Plaza de la Villa
-
Bridge of Toledo
-
Spanish Ministry of Agriculture
-
Delicias Train Station
-
San Manuel & San Benito church
-
Palacio de la Prensa
-
Carrión Building
-
Spanish Air Force Headquarters
-
Edificio Girasol
-
Torres Blancas
Honours
- Madrid Dome on Oscar II Coast in Graham Land, Antarctica is named after the city.[134]
See also
- C40 Cities Climate Leadership Group
- Madrid capital
- Madrid Conference of 1991
- Mayor of Madrid
- List of tallest buildings in Madrid
- OPENCities
References
- ^ "History of Madrid". Madrid Traveller. Retrieved 27 August 2014.
- ^ Population by sex and age groups - Eurostat, 2012
- ^ World Urban Areas - Demographia, March 2013
- ^ INE.es Instituto Nacional de Estadística (National Statistics Institute)
- ^ a b "World Urban Areas: Population & Density" (PDF). Demographia. Retrieved 10 August 2008.
- ^ a b Eurostat, UrbanAudit.org. Retrieved 12 March 2009. Data for 2004.
- ^ a b Brinkoff, Thomas "Principal Agglomerations of the World". Retrieved 12 March 2009. Data for 1 January 2009.
- ^ a b United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, World Urbanization Prospects (2007 revision), (United Nations, 2008), Table A.12. Data for 2007.
- ^ "Member of the Governing Council. Delegate for Economy, Employment and Citizen Involvement" (PDF). p. 6. Retrieved 3 September 2012.
- ^ "Madrid". Indiana.edu. 10 July 2006.[dead link]
- ^ "Global city GDP rankings 2008–2025". Pricewaterhouse Coopers. Retrieved 20 November 2009.
- ^ Globalization and World Cities (GaWC) Study Group and Network, Loughborough University. "The World According to GaWC 2010".
- ^ "Global Power City Index 2009" (PDF). Retrieved 14 April 2011.
- ^ "Worldwide Centers of Commerce Index" (PDF). Retrieved 3 September 2012.
- ^ "Global Power City Index" (PDF). Retrieved 3 September 2012.
- ^ "Monocle's World's Most Liveable Cities Index 2009". Monocle.com. 10 June 2009. Retrieved 18 October 2010.[dead link]
- ^ "Top 20 liveable cities – 10 Madrid". Monocle.com. Retrieved 18 October 2010.[dead link]
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ "Arte Contemporaneo en España - ARCOmadrid". Ifema.es. Retrieved 9 November 2012.
- ^ [2] SIMO TCI
- ^ [3]Cibeles Madrid Fashion Week
- ^ "Arquitectura. Edificios de los Museos Estatales". Mcu.es. 25 January 2012. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
- ^ "Geography of Madrid". Easy expat. 11 August 2006.
- ^ "Plaza de Cibeles | Spain.info in english". Spain.info. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
- ^ "Madrid's Palacio de Cibeles Renovated Into Jaw-Dropping CentroCentro Cultural Center | Inhabitat – Sustainable Design Innovation, Eco Architecture, Green Building". Inhabitat. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
- ^ "Cibeles Fountain – Tourism in Madrid". Turismomadrid.es. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
- ^ a b "El Madrid Medieval (Medieval Madrid). Includes Pre-historic, Roman and medieval up to the Catholic Monarchs". History of Madrid. (in Spanish). José Manuel Castellanos. Retrieved 28 October 2007.
- ^ "Madrid History – Museums – Suggested Itineraries Madrid". Indigoguide.com. Retrieved 3 February 2010.
- ^ Xavier Delamarre, Dictionnaire de la langue gauloise, éditions errance 2003. p. 258.
- ^ "El origen del nombre". JLL & JRP. 16 August 2006.
- ^ a b "Los primeros madrileños llegaron hace 500.000 años. Los descubrimientos de la M-30".
- ^ "La prehistoria de Madrid". Retrieved 13 March 2007.
- ^ Ocupaciones achelenses en el valle del Jarama (Arganda, Madrid);Santonja, Manuel; López Martínez, Nieves y Pérez-González, Alfredo;1980;Diputación provincial de Madrid;ISBN 84-500-3554-6
- ^ "Las villas romanas de Madrid. Madrid en época romana" (PDF).
- ^ El Madrid antiguo en época romana;Fernández Palacios, Fernando;Estudios de Prehistoria y Arqueología Madrileñas;Number 13; year 2004
- ^ "824 tumbas visigodas en Vicalvaro".
- ^ "Madrid Islámico". Nova.es. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
- ^ It was recorded in the 15th century by the Arab geographer al-Himyari, who his book "The Perfurmed Garden book about the news of the countrie"s (Kitab al Rawd to mi'tar) describes: "Madrid, remarkable city of Al-Andalus, which was built by Amir Muhammad ibn Abd ar-Rahman..."
- ^ "Ayuntamiento de Madrid – Alfonso VI en Madrid" (in Spanish). Madrid.es. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "E L M A D R I D M E D I E V A L = José Manuel Castellanos Oñate". Elmadridmedieval.jmcastellanos.com. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
- ^ "Ayuntamiento de Madrid – El Siglo XIII" (in Spanish). Madrid.es. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ Esarte, Pedro (2001). Navarra, 1512–1530. Pamplona: Pamiela. ISBN 84-7681-340-6.
- ^ This and other 16th- and 17th-century views of Madrid (from Frederic de Witt and Pedro Texeira)can be seen at this website
- ^ "Ayuntamiento de Madrid – Madrid capital" (in Spanish). Madrid.es. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Ayuntamiento de Madrid – El Madrid del Siglo de Oro" (in Spanish). Madrid.es. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ [4] Royal Academies
- ^ "Ayuntamiento de Madrid – Madrid bajo el signo del reformismo ilustrado" (in Spanish). Madrid.es. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Ayuntamiento de Madrid – Madrid y la Guerra de la Independencia" (in Spanish). Madrid.es. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Ayuntamiento de Madrid - El Madrid liberal" (in Spanish). Madrid.es. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- ^ a b c "Madrid, de territorio fronterizo a región metropolitana. Madrid, from being the "frontier" to become a Metropole". History of Madrid. (in Spanish). Luis Enrique Otero Carvajal (Profesor Titular de Historia Contemporánea. Universidad Complutense. Madrid). Retrieved 28 October 2007.
- ^ "Pleno de Madrid (Spanish Only)" (in Spanish). Munimadrid.es. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
- ^ "Local Government Organization (Spanish Only)" (in Spanish). Munimadrid.es. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
- ^ "Tipos de clima" (in Spanish).
- ^ J. Klausen, MeteoSwiss, Switzerland. "GAWSIS 2.2". Gaw.empa.ch. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Extreme Values (annual), Madrid. AEMet.
- ^ "Guía resumida del clima en España (1981-2010)". AEMet. November 2011. Retrieved 17 November 2011.
- ^ "Extreme Values (Jan–Apr), Madrid". AEMet.
- ^ "Extreme Values (May–Aug), Madrid". AEMet.
- ^ "Extreme Values (Sep–Dec), Madrid". AEMet.
- ^ "Guía resumida del clima en España (1981-2010)". AEMet. November 2011. Retrieved 17 November 2011.
- ^ "Guía resumida del clima en España (1981-2010)". AEMet.
- ^ "Foreign Population in the city of madrid. A study by the Dirección General de Estadística of the municipality of Madrid" (PDF). Retrieved 27 August 2014.
- ^ "Explotación estadística del censo de ciudadanos musulmanes en España referido a fecha 31/12/2012" (PDF). UNIÓN DE COMUNIDADES ISLÁMICAS DE ESPAÑA: 6–9. 2012.
- ^ "Eurostat - Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". Epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu. 2 April 2012. Retrieved 9 November 2012.
- ^ Royal Palace of Madrid
- ^ "Overview: Economy of Madrid". EasyExpat. 16 August 2006.
- ^ "Madrid Economy" (PDF). Empresa Municipal Promoción de Madrid. Retrieved 15 August 2008.
- ^ "City Mayors reviews the richest cities in the world in 2005". Citymayors.com. 11 March 2007. Retrieved 8 July 2009.
- ^ Colpisa. "Ocho regiones españolas superan ya el PIB medio de la Unión Europea. La Verdad". Laverdad.es. Retrieved 8 July 2009.
- ^ "The world's best financial cities". City Mayors.
- ^ "El salario medio bruto se acerca a 2.000 euros en el segundo trimestre del año". elmundo.es. 29 September 2007. Retrieved 8 July 2009.
- ^ "World's richest cities in 2008". City Mayors. Retrieved 8 July 2009.
- ^ "Museo Reina Sofía (MNCARS), official english webpage". Museoreinasofia.es. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- ^ Kandell, Jonathan (28 April 2002). "Baron Thyssen-Bornemisza, Industrialist Who Built Fabled Art Collection, Dies at 81". The New York Times. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
- ^ "Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum, official english webpage".
- ^ "The Real Academia de Bellas Artes de San Fernando Museum, Madrid". Gomadrid.com. Retrieved 14 April 2011.
- ^ title=Fernando Botero
- ^ .http://www.patrimonionacional.es/Home/Palacios-Reales/Palacio-Real-de-Madrid.aspx
- ^ Ignacio Sánchez Ramírez – info @ visionados. com. "Museo Arqueológico Nacional | Inicio". Man.mcu.es. Retrieved 1 June 2011.
- ^ "Museo de América". Museodeamerica.mcu.es. Retrieved 1 June 2011.
- ^ "Portada". MNCN. 27 May 2011. Retrieved 2 June 2011.
- ^ "INICIO MUSEO NAVAL MADRID - Museo Naval - Armada Española - Ministerio de Defensa - Gobierno de España" (in Spanish). Armada.mde.es. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- ^ "Patrimonio Nacional – Monasterio de las Descalzas Reales". Patrimonionacional.es. Retrieved 14 April 2011.
- ^ "Fundación Lázaro Galdiano museum website". Flg.es. Retrieved 14 April 2011.
- ^ "Museo de Artes Decorativas". Mnartesdecorativas.mcu.es. Retrieved 1 June 2011.
- ^ "Museo del Romanticismo". Museoromanticismo.mcu.es. Retrieved 1 June 2011.
- ^ "Museo Cerralbo". Museo Cerralbo. Retrieved 1 June 2011.
- ^ "Museo Nacional de Antropología". Mnantropologia.mcu.es. Retrieved 1 June 2011.
- ^ "Museo Sorolla". Museo Sorolla. Retrieved 1 June 2011.
- ^ "Caixaforum Madrid | Nuestros centros | Obra Social "la Caixa"". Obrasocial.lacaixa.es. 15 January 1974. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- ^ "de Madrid" (in Spanish). Museo del Aire. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- ^ "Patrimonio Nacional - Real Sitio de El Pardo". Patrimonionacional.es. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- ^ "Museo del Ferrocarril de Madrid Delicias - Fundación de los Ferrrocarriles Españoles". Museodelferrocarril.org. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- ^ "Madrid es la cuarta ciudad europea más visitada. Datos del Consejero delegado de Economía y Participación Ciudadana, Miguel Ángel Villanueva". Madridiario.es. 30 January 2007. Retrieved 11 May 2013.
- ^ "Real Decreto 1109/1993, de 9 de julio, por el que se aprueba los Estatutos de la Real Academia Española". Noticias.juridicas.com. 21 January 2011. Retrieved 14 April 2011.
- ^ National Library website
- ^ MSO.net - http://www.mso.net. "Things to do in Madrid – Popular sightseeing activities & things to do in Madrid". Directline-citybreaks.co.uk. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
{{cite web}}: External link in|author= - ^ "11 Festival Escena Contemporánea". Escenacontemporanea.com. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- ^ "Festival Alternativo de las Artes Escénicas, Madrid, Spain – Things to Do Reviews". NileGuide.com. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- ^ El Mundo. "El Mundo – Art Madrid ¿Alternativo o complementario a ARCO?". elmundo.es. Retrieved 27 August 2014.
- ^ "Madrid's Bohemian Best: Exploring Lavapiés – La Castiza". En.momondo.com. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- ^ "Madrid Neighbourhoods: Lavapiés... Going out, eating, drinking, and bohemian cool! – Notes from Madrid – Tapas bars, restaurants, shopping, and nightlife in Madrid". Notesfrommadrid.com. 15 November 2007. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- ^ "El Rastro & Lavapiés". Whatmadrid.com. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- ^ "Auditorio Nacional de Música". Time Out. Retrieved 19 August 2009.
- ^ "Orquesta Sinfónica Chamartín-Historia (in Spanish)". Orquesta Sinfónica Chamartín. 20 February 2008. Retrieved 28 August 2008.
- ^ "Teatro Real (Timeout Madrid)". Retrieved 31 January 2009.
- ^ History of the Teatro de la Zarzuela
- ^ "''Teatro de la Zarzuela – Timeout Madrid''". Timeout.com. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
- ^ "La Orquesta Sinfónica (in Spanish)". RTVE. Retrieved 27 August 2014.
- ^ "Javier Mariscal - Drawing Life". Egodesign.ca.
- ^ "'Voting error' gave London Games". BBC Sport.
- ^ IOC selects three cities as Candidates for the 2020 Olympic Games
- ^ "Madrid knocked out in first round of voting for 2020 Olympics"
- ^ "Madrid should not seek to host 2024 Games, says Mayor"
- ^ "Sistema Educativo LOE by the Spanish Ministry of Education(Spanish Only)" (in Spanish). Mec.es. Archived from the original on 12 April 2008. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
- ^ "Universidad Complutense". Missouri-St. Louis University. 10 July 2006.
- ^ "Complutense University of Madrid". UCM.
- ^ a b ""El Mundo" ''50 Carreras 2008''". Elmundo.es. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- ^ "Universidad Autónoma". Universidad Autónoma de Madrid. 10 July 2006.
- ^ ""El Mundo" ''250 Masters 2007''". Aula2.elmundo.es. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- ^ "Department of Economics, U. Carlos III de Madrid". Eco.uc3m.es. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- ^ http://www.econphd.net/rankings.htm
- ^ "ACI Passenger Traffic Data – 2009". Airports.org. 5 August 2010. Retrieved 27 August 2014.
- ^ "Madrid Metro". Robert Schwandl. 17 August 2006.
- ^ "Public Transportation in Madrid". .madrid-university.es.
- ^ "Bus lines in Madrid". ecomovilidad.net.
- ^ "Mapa Mundi de las ciudades hermanadas". Ayuntamiento de Madrid.
- ^ "Berlin - City Partnerships". Der Regierende Bürgermeister Berlin. Archived from the original on 21 May 2013. Retrieved 17 September 2013.
- ^ "Bordeaux - Rayonnement européen et mondial". Mairie de Bordeaux (in French). Archived from the original on 7 February 2013. Retrieved 29 July 2013.
- ^ "Bordeaux-Atlas français de la coopération décentralisée et des autres actions extérieures". Délégation pour l’Action Extérieure des Collectivités Territoriales (Ministère des Affaires étrangères) (in French). Archived from the original on 7 February 2013. Retrieved 29 July 2013.
- ^ "Lisboa - Geminações de Cidades e Vilas". Associação Nacional de Municípios Portugueses [National Association of Portuguese Municipalities] (in Portuguese). Retrieved 23 August 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ "Acordos de Geminação, de Cooperação e/ou Amizade da Cidade de Lisboa". Camara Municipal de Lisboa (in Portuguese). Retrieved 23 August 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ "NYC's Partner Cities". The City of New York. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ^ Madrid Dome. SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer.
External links
- Official website of Madrid
- Official website of Madrid on tourism and business
- Official website of Madrid in the Spain's national tourism portal
- Official website of Madrid–Barajas International Airport
- Official website of Metro Madrid
- WikiSatellite view of Madrid at WikiMapia