Incheon International Airport: Difference between revisions
Transphasic (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Rescuing 2 sources and tagging 0 as dead. #IABot (v1.3beta4) |
||
| Line 99: | Line 99: | ||
==Statistics== |
==Statistics== |
||
Located {{convert|48|km|mi|abbr=on}} west of [[Seoul]], the capital and the largest city of [[South Korea]], Incheon International Airport is the main hub for [[Korean Air]], [[Asiana Airlines]], [[Jeju Air]], and [[Polar Air Cargo]]. The airport serves as a hub for international civilian air transportation and cargo traffic in East Asia. Incheon International Airport is also currently Asia's eighth busiest airport in terms of passengers, the world's [[World's busiest airports by cargo traffic|fourth busiest airport]] by cargo traffic, and the world's [[World's busiest airports by international passenger traffic|eighth busiest airport]] in terms of international passengers in 2014. In that year, 40,785,953 international passengers used the airport.<ref>{{cite web|url= |
Located {{convert|48|km|mi|abbr=on}} west of [[Seoul]], the capital and the largest city of [[South Korea]], Incheon International Airport is the main hub for [[Korean Air]], [[Asiana Airlines]], [[Jeju Air]], and [[Polar Air Cargo]]. The airport serves as a hub for international civilian air transportation and cargo traffic in East Asia. Incheon International Airport is also currently Asia's eighth busiest airport in terms of passengers, the world's [[World's busiest airports by cargo traffic|fourth busiest airport]] by cargo traffic, and the world's [[World's busiest airports by international passenger traffic|eighth busiest airport]] in terms of international passengers in 2014. In that year, 40,785,953 international passengers used the airport.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.aci.aero/aci/aci/file/Press%20Releases/2011/PR_01082011_2010_WATR.pdf |title=ACI releases World Airport Traffic Report 2010 |date=1 August 2011 |format=[[Portable Document Format|PDF]] |accessdate=29 April 2013 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20120324122400/http://www.aci.aero/aci/aci/file/Press%20Releases/2011/PR_01082011_2010_WATR.pdf |archivedate=24 March 2012 |df=dmy-all }}</ref> |
||
The airport opened for business in early 2001 to replace the older Gimpo International Airport, which now serves mostly domestic destinations plus shuttle flights to alternate airports in [[China]], [[Japan]], and [[Taiwan]]. |
The airport opened for business in early 2001 to replace the older Gimpo International Airport, which now serves mostly domestic destinations plus shuttle flights to alternate airports in [[China]], [[Japan]], and [[Taiwan]]. |
||
| Line 692: | Line 692: | ||
*Named by Global Traveler (GT) as the Best Airport in the World for the second straight year in January 2008.<ref name="autogenerated1"/> |
*Named by Global Traveler (GT) as the Best Airport in the World for the second straight year in January 2008.<ref name="autogenerated1"/> |
||
*Named World's Best Airport for 2009, in the World Airport Survey results published by Skytrax. {{cn|date=January 2017}} |
*Named World's Best Airport for 2009, in the World Airport Survey results published by Skytrax. {{cn|date=January 2017}} |
||
* In 2012 it was ranked the best airport in the world by Skytrax.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.worldairportawards.com/Awards_2012/Airport2012.htm |title=Incheon International Airport is named the World's Best Airport in 2012 by airline travelers |publisher=Worldairportawards.com |date= |accessdate=2013-07-29}}</ref> |
* In 2012 it was ranked the best airport in the world by Skytrax.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.worldairportawards.com/Awards_2012/Airport2012.htm |title=Incheon International Airport is named the World's Best Airport in 2012 by airline travelers |publisher=Worldairportawards.com |date= |accessdate=2013-07-29 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20130803061329/http://www.worldairportawards.com/Awards_2012/Airport2012.htm |archivedate=3 August 2013 |df=dmy-all }}</ref> |
||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" |
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" |
||
Revision as of 02:49, 10 April 2017
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2016) |
Incheon International Airport | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Aerial view of Terminal 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||||||
| Owner | South Korean government | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operator | Incheon International Airport Corporation | ||||||||||||||||||
| Serves | Seoul Metro Area | ||||||||||||||||||
| Location | Jung District, Incheon, South Korea | ||||||||||||||||||
| Hub for | |||||||||||||||||||
| Focus city for | |||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 7 m / 23 ft | ||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 37°27′48″N 126°26′24″E / 37.46333°N 126.44000°E | ||||||||||||||||||
| Website | www.airport.kr | ||||||||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Helipads | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2016) | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Statistics from IIAC[1] | |||||||||||||||||||
| Incheon International Airport | |
| Hangul | 인천국제공항 |
|---|---|
| Revised Romanization | Incheon gukje gonghang |
Incheon International Airport (IIA) (IATA: ICN, ICAO: RKSI) (sometimes referred to as Seoul–Incheon International Airport) is the largest airport in South Korea, the primary airport serving the Seoul Capital Area, and one of the largest and busiest airports in the world. Since 2005, it has been rated the best airport worldwide by Airports Council International every year.[2] It is also rated as the world's cleanest airport and the world's best international transit airport by Skytrax.[3]
The airport has a golf course, spa, private sleeping rooms, an ice skating rink, a casino, indoor gardens, and a Museum of Korean Culture. Airport authorities claim that average departure and arrival takes 19 minutes and 12 minutes respectively, as compared to worldwide average of 60 minutes and 45 minutes respectively, ranking it among of the fastest airports in the world for customs processing.[4] Its duty-free shopping mall has been rated the world's best for three years in a row in 2013 by Business Traveller.[5] Incheon International Airport also claims that it has only a 0.0001% baggage mishandling rate.[6]
The airport opened for business in early 2001 to replace the older Gimpo International Airport, which now serves mostly domestic destinations and shuttle flights to several East Asian metropolitan areas including Tokyo, Osaka, Beijing, Shanghai, and Taipei.
Incheon International Airport is located west of Incheon's city center, on an artificially created piece of land between Yeongjong and Yongyu islands. The two islands were originally separated by shallow sea. That area between the two islands was reclaimed for the construction project, effectively connecting the once separate Yeongjong and Yongyu islands. The reclaimed area as well as the two islands are all part of Jung-gu, an administrative district of Incheon.
The airport holds a record of being ranked the Best Airport Worldwide for 11 consecutive years by the Airports Council International (ACI)'s Airport Service Quality Award from 2005 to 2016, and has also been rated the world's best among airports of its size (25–40 million passengers) and region (Asia-Pacific) since 2012 due to the institution's decision to discontinue the Best Airport Worldwide category. [citation needed]
Seoul Incheon International Airport's terminal has 76 boarding gates altogether, with 44 in the main terminal and 30 in Concourse A.
History

After the Seoul Olympics of 1988, international air traffic to Korea increased. In the 1990s, it became apparent that Gimpo International Airport could not cope with the increase in air traffic. To reduce the load on Gimpo International Airport, the government decided to build a new airport.
The new airport was originally planned to be located in Cheongju, 124 km far from Seoul, but due to its distance, it was opposed by Seoul and Gyeonggi citizens. [citation needed] Hwaseong was the other choice, but it was also rejected due to similar reasons. Finally the area chosen was Incheon. [when?]
In November 1992, the construction of the Incheon airport began on reclaimed land between Yeongjong Island and Youngyu Island, and took eight years to finish, with an additional six months for testing. Completion was initially scheduled for 1997 but delayed due to the economic crisis. [citation needed] Finally, the airport was officially opened in March 2001.
On 15 November 2006, the Airbus A380 landed at the airport as part of the first leg of its certification trip. [citation needed] Tests on the runways, taxiways, and ramps showed that the airport could handle the aircraft.
To further upgrade service, Incheon and major Korean logistics firm Hanjin Corporation (parent company of the Korean Flag Carrier, Korean Air) agreed on January 10, 2008 to build Yeongjong Medical Centre, which was completed in 2012. This hospital is currently serving nearby residents and some of Korea's annual 30,000 medical tourists.[7]
Statistics
Located 48 km (30 mi) west of Seoul, the capital and the largest city of South Korea, Incheon International Airport is the main hub for Korean Air, Asiana Airlines, Jeju Air, and Polar Air Cargo. The airport serves as a hub for international civilian air transportation and cargo traffic in East Asia. Incheon International Airport is also currently Asia's eighth busiest airport in terms of passengers, the world's fourth busiest airport by cargo traffic, and the world's eighth busiest airport in terms of international passengers in 2014. In that year, 40,785,953 international passengers used the airport.[8]
The airport opened for business in early 2001 to replace the older Gimpo International Airport, which now serves mostly domestic destinations plus shuttle flights to alternate airports in China, Japan, and Taiwan.

Construction stages

The airport was originally planned to be built in three phases, incrementally increasing airport capacity as the demand grew. This was changed, however, to four phases after the airport was opened.
Phase 1
In Phase 1, the airport had a capacity of 30 million passengers annually, and a cargo capacity of 1.7 million metric tonnes annually. In this phase, a passenger terminal with a floor space of 496,000 square metres (5,340,000 sq ft), two parallel runways, a control tower, an administrative building, a transportation centre (the Integrated Transportation Centre, designed by Terry Farrell and Partners and Samoo Architects & Engineers), and integrated operations centre, three cargo terminals, international business centre, and a government office building were constructed.
Phase 2
Phase 2 construction began in 2002, and was originally expected to be completed in December 2008. However, in an attempt to have the airport ready for the 2008 Beijing Olympics, which took place in August 2008, the schedule was modified, and Phase 2 construction was completed on 20 June 2008. During this construction phase, a third parallel 4,000 metres (13,000 ft) long runway and a 13-hectare cargo terminal area were added. A 16.5 hectare concourse connected to the main passenger building via two parallel 870 metres (2,850 ft) long underground passageways was added, with a Mitsubishi Crystal Mover shuttle train APM shuttling passengers between the concourse and the main terminal.[9]
Many long distance foreign carriers were moved to the new concourse, with Korean Air and Asiana Airlines continuing to use the existing terminal.
Phase 3
Plans to invest ₩4 trillion by 2017 to expand Incheon International Airport. The South Korean government plans to add a second passenger terminal in the northern field of the airport, and expand its existing cargo terminal and other infrastructure. The terminals will be connected with each other by the underground "Starline" train, which currently links the first terminal and the concourse. Upon completion, Incheon International Airport will be able to handle 62 million passengers and 5.8 million tonnes of cargo a year, up from the current capacity of 44 million passengers and 4.5 million tonnes. Construction began in 2011 with completion targeted for 2017. Plans for Incheon's expansion also include adding more aprons to park planes and extending a railway line to the city centre of Seoul about 70 kilometres (43 mi) away from the airport. The airport also signed an agreement to build a resort called "Inspire" which includes 6 star hotels,theme parks,and a casino.[10]
Phase 4
Estimated to be completed in 2020, this is the final and the ultimate construction stage. Upon completion, the airport will have two passenger terminals, four satellite concourses, 128 gates, and five parallel runways (one exclusively for cargo flights). It will be able to handle 100 million passengers and 7 million metric tonnes of cargo annually, with further possible expansions. The airport is projected to be transformed into one of the ten busiest airports in the world by 2020.
Terminals
This section needs additional citations for verification. (February 2013) |
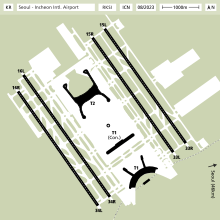
Main Terminal (To be renamed Terminal 1)
The main passenger terminal (measuring 594,000 square metres) is the largest airport terminal in area in South Korea. The passenger terminal was designed by Curtis W. Fentress, FAIA, RIBA of Fentress Architects. It is 1,060 metres (3,480 ft) long, 149 metres (489 ft) wide, and 33 metres (108 ft) high. Its construction cost was 1.3816 trillion South Korean Won.[citation needed] The terminal has 44 boarding ports (all of which can accommodate the new Airbus A380), 50 customs inspection ports, 2 biological quarantine counters, 6 stationary and 14 portable passenger quarantine counters, 120 arrival passport inspection counters, 8 arrival security ports, 28 departure security ports, 252 check in counters, and 120 departure passport inspection counters. In 2015, an automatic check-in counter lane was introduced, where people travelling via Korean Air, Asiana Airlines and China Southern Airlines can use. Instead of having airport staff at the counter, there is a machine where travelers input their flight information, scan their passports, receive their flight tickets and lastly, load the luggage onto the conveyor. This system was planned to be introduced in Terminal 2, but in May 2015 Incheon Airport used one of the counter islands for the unmanned luggage handling system.[11]
Concourse
The passenger concourse was completed at the end of May 2008, and all foreign airlines use this terminal as of 10 June 2008. [citation needed] It is connected to the Main Terminal by two parallel 870-metre (2,850 ft) long underground passageways equipped with IATs (Intra Airport Transit). It has 30 gates and six lounges [citation needed](Asiana Airlines/Star Alliance, Singapore Airlines/Star Alliance, Cathay Pacific/Oneworld, Japan Airlines/Oneworld, Korean Air/SkyTeam, and China Eastern Airlines/SkyTeam).
Terminal 2 (Opening in October 2017)
A new passenger terminal will be opened in October 2017. Korean Air, KLM, Delta Air Lines and Air France will be relocated to the future Terminal 2. [12]
Airlines and destinations






Passenger
Cargo


Traffic and statistics
Incheon airport is eighth busiest internationally.
Top Destinations
The top seven domestic destinations are shown below:
| Rank | Airport | Passengers | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Busan | 353,268 | ||
| 2 | Daegu | 119,099 | ||
| 3 | Jeju | 88,371 | ||
| Source: KAC Airport statics | ||||
Annual Traffic
| Years | Passengers | Aircraft
Operations |
Cargo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 14,542,290 | 86,807 | 1,186,015 | |
| 2002 | 20,924,171 | 126,094 | 1,705,928 | |
| 2003 | 19,789,874 | 130,185 | 1,843,055 | |
| 2004 | 24,084,072 | 149,776 | 2,133,444 | |
| 2005 | 26,051,466 | 160,843 | 2,150,139 | |
| 2006 | 28,191,116 | 182,007 | 2,336,571 | |
| 2007 | 31,227,897 | 211,404 | 2,555,580 | |
| 2008 | 29,973,522 | 211,102 | 2,423,717 | |
| 2009 | 28,549,770 | 198,918 | 2,313,002 | |
| 2010 | 33,478,925 | 214,835 | 2,684,499 | |
| 2011 | 35,062,366 | 229,580 | 2,539,222 | |
| 2012 | 38,970,864 | 254,037 | 2,456,724 | |
| 2013 | 41,482,828 | 271,224 | 2,464,385 | |
| 2014 | 45,512,099 | 290,043 | 2,557,681 | |
| 2015 | 49,281,220 | 305,446 | 2,595,677 | |
| 2016 | 57,765,397 | 339,673 | 2,714,341 | |
| Source: IIAC Airport Statistics[1] | ||||
Top carriers
In 2015, the twelve carriers with the largest percentage of passengers flying into, out of, or through Incheon are as follows:
| Rank | Carrier | Domestic Passengers |
International Passengers |
Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Korean Air | 471,664 | 14,990,026 | 15,461,690 | 31.37% |
| 2 | Asiana Airlines | 79,016 | 11,363,072 | 11,442,088 | 23.22% |
| 3 | Jeju Air | 1,761 | 2,170,003 | 2,171,764 | 4.41% |
| 4 | Jin Air | 2,502 | 1,787,196 | 1,789,698 | 3.63% |
| 5 | China Southern Airlines | - | 1,590,590 | 1,590,590 | 3.23% |
| 6 | China Eastern Airlines | - | 1,501,667 | 1,501,667 | 3.05% |
| 7 | Cathay Pacific | - | 1,038,164 | 1,038,164 | 2.11% |
| 8 | Air China | - | 1,024,053 | 1,024,053 | 2.08% |
| 9 | Thai Airways International | - | 851,225 | 851,225 | 1.73% |
| 10 | Eastar Jet | 3,130 | 833,571 | 836,701 | 1.70% |
| 11 | Tway Airlines | 1,540 | 782,022 | 783,562 | 1.59% |
| 12 | Philippine Airlines | - | 669,116 | 669,116 | 1.36% |
Accolades
Incheon International airport has been the recipient of a number of awards since its opening, including:
- Best Airport Worldwide at the first Airport Service Quality Awards in 2007.[18]
- Won the GT Tested Award for Best Airport in the World in January 2007.[19]
- Named by Global Traveler (GT) as the Best Airport in the World for the second straight year in January 2008.[7]
- Named World's Best Airport for 2009, in the World Airport Survey results published by Skytrax. [citation needed]
- In 2012 it was ranked the best airport in the world by Skytrax.[20]
| Year | Award | Category | Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | Airport Service Quality Awards by Airports Council International |
Best Airport Worldwide | Won | [21] |
| Best Airport in Asia-Pacific | Won | |||
| Best Airport by Size (25–40 million passengers) | Won | |||
| 2010 | Best Airport Worldwide | Won | [22] | |
| 2011 | Won | [23] |
Accidents and Incidents
On 16 June 2011, Asiana Airlines Flight 324 operated by Airbus A321-200 HL7763 between Chengdu Shuangliu International Airport, China and Incheon International Airport was fired upon by two soldiers of the Republic of Korea Marine Corps as it came in to land at Incheon. A total of 99 rounds were discharged at the aircraft, which was out of range and made a safe landing without sustaining any damage. The soldiers had misidentified the aircraft as belonging to the North Korean military, and were acting on orders that gave them permission to engage without reference to senior officers, following the Bombardment of Yeonpyeong in November 2010.[24]
Ground Transport

Public transport
Bus
Airport buses are called limousine buses. Standard limousine buses travel to Gimpo Airport & Songjeong Station.
Intercity buses connect with other towns and cities in Korea.
The Korea City Air Terminal in Gangnam is linked with the airport through limousine buses.

Rail
The Incheon International Airport Railroad airport express (or AREX, and styled as A'REX) station is located in the Transport Centre, adjacent to the main terminal building. It provides service to Gimpo International Airport and Seoul. Many of the stations along the AREX line provide connections to the Incheon Subway and Seoul Metropolitan Subway.
Seoul station city airport has check-in and immigration facilities before arrival at the airport.
The Korea Train eXpress (KTX) operates at the same station as AREX. However, it uses a different platform. It operates 20 times per day from Incheon airport. It operates twelve times on the Gyeonbu line, twice on the Gyeonjeon line, four times on the Honam line, and twice on the Jeolla line.
The maglev opened in February 2016. The first phase is 6.1 km long, spread over six stations, taking riders from the airport toward the south-west of the island where a water park is located. Phase 2 will be 9.7 km long, extending the line to the north-west of the island. Phase 3 will add 37.4 km, transforming the line into a circle. [citation needed]

Ferry
A ferry service connects Yeongjong-do to the mainland. However, the dock is located a considerable distance from the airport. An alternative means of transport must be sought upon arriving at the island to be able to get to the airport.[25]
Car
The airport provides a short term parking lot for 4,000 cars and a long term parking lot for 6,000 cars. Shuttle services connect the long term parking lot to the passenger terminal and the cargo terminal. Car rental is located near the long term parking lot. A link to the mainland is provided by the toll Yeongjong Bridge and an expressway. A second expressway on the Incheon Bridge connects the island with central Incheon.
See also
- Transportation in South Korea
- List of Korea-related topics
- List of airports in South Korea
- Busiest airports in South Korea by passenger traffic
References
- ^ a b "Airport Statistics". Retrieved 15 February 2017.
- ^ The Korea Herald. "Incheon Airport tops service quality for 9th year". Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- ^ "The World's Best Airports for Transit Passengers". Retrieved 7 May 2016.
- ^ "Incheon International named Best Airport Worldwide 7 years in a row". Rus Tourism News. 21 February 2012. Retrieved 4 July 2013.
- ^ "인천공항 면세점, 3년연속 '세계 최고 면세점 선정' - Chosunbiz - 프리미엄 경제 파워". Biz.chosun.com. 1 January 2013. Retrieved 4 July 2013.
- ^ "25 Reasons Incheon International Airport is the Best Airport in the World". Seulistic. 12 July 2012. Retrieved 29 April 2013.
- ^ a b [1]
- ^ "ACI releases World Airport Traffic Report 2010" (PDF). 1 August 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 March 2012. Retrieved 29 April 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Incheon Airport to Open New Concourse". Koreatimes.co.kr. 29 May 2008. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ^ "Incheon Airport to Have New Terminal by 2017". Korea Herald. 29 June 2009. Retrieved 29 June 2009.
- ^ Future Travel Experience. "Incheon Airport launches new self-service bag drop system". Future Travel Experience. Retrieved 7 May 2016.
- ^ 구정모. "인천공항, 2018년 제2여객터미널에 대한항공 배치". 연합뉴스. Retrieved 7 May 2016.
- ^ a b c "Aeroméxico announces new flights to Seoul, Korea" (in Spanish). EnElAire. January 2017. Retrieved 19 January 2017.
- ^ http://news.delta.com/delta-korean-air-strengthen-partnership-new-flights-seoul
- ^ "Korean Air conectará Seúl y Barcelona con un vuelo directo en abril de 2017". Europa Press. Retrieved 23 November 2016. (spanish)
- ^ "United ends Tokyo – Seoul route in Oct 2017". routesonline. Retrieved 5 April 2017.
- ^ "항공통계". 항공통계; Cannot access direct link. Retrieved 4 June 2016.
- ^ [2] Archived 16 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Premium Travelers Name Incheon International Top Airport Global Traveler Readers have Chosen the Airport as the Best in the World". PR Web Website. 21 January 2007. Retrieved 27 January 2006.
- ^ "Incheon International Airport is named the World's Best Airport in 2012 by airline travelers". Worldairportawards.com. Archived from the original on 3 August 2013. Retrieved 29 July 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "ACI Airport Service Quality Awards 2009, Asia Pacific airports sweep top places in worldwide awards" Airports Council International. 16 February 2010. Retrieved 2012-04-13
- ^ "ASQ Award for winners for 2010". Airports Council International. Retrieved 13 April 2012.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "World's best airports announced -- Asia dominates". CNN Go. 15 February 2012. Retrieved 12 April 2012.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ Hradecky, Simon. "Incident: Asiana A321 near Seoul on Jun 17th 2011, aircraft under fire". The Aviation Herald. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- ^ "Transport in Yeongjongdo & Muuido - Lonely Planet Travel Information". lonelyplanet.com. Lonely Planet. Retrieved 1 October 2014.

