Qingdao
Qingdao
青岛市 | |
|---|---|
 Clockwise from top left: Qingdao skyline, St. Michael's Cathedral, Qingdao harbour by night, a temple at the base of Mount Lao, and May Fourth Square | |
 Location of Qingdao City (yellow) in Shandong province | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Shandong |
| Municipal seat | Shinan District |
| Government | |
| • CPC Secretary | Li Qun |
| • Mayor | Zhang Xinqi (张新起) |
| Area | |
| • Sub-provincial city | 11,067 km2 (4,273 sq mi) |
| • Land | 11,067 km2 (4,273 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 3,239 km2 (1,251 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 5,019 km2 (1,938 sq mi) |
| Population (2014) | |
| • Sub-provincial city | 9,046,200 |
| • Density | 820/km2 (2,100/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 6,188,100 |
| • Urban density | 1,900/km2 (4,900/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 266000 |
| Area code | 532 |
| GDP | ¥ 940.00 billion (2015) |
| GDP per capita | ¥ 102,519 (2015) |
| License Plate Prefix | 鲁B & 鲁U |
| Coastline | 862.64 km (536.02 mi) (inclusive of offshore islands) 730.64 km (454.00 mi) (exclusive of islands) |
| Major Nationalities | Han: 99.86% |
| County-level divisions | 10 |
| Website | www.qingdao.gov.cn |
| Qingdao | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 "Qingdao" in Simplified (top) and Traditional (bottom) Chinese characters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 青岛 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 青島 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal | Tsingtao Tsingtau (1898–1922) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "Green island" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| German name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| German | Tsingtau | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Qingdao ([tɕʰíŋtàʊ]; Chinese: 青岛; also spelt Tsingtao) is a city in eastern Shandong Province on the east coast of China as well as one of the largest cities in Shandong province. Administered at the sub-provincial level,[1] Qingdao has jurisdiction over seven districts and five county-level cities. As of 2014[update] Qingdao had a population of 9,046,200 with an urban population of 6,188,100.[2] Lying across the Shandong Peninsula and looking out to the Yellow Sea, it borders Yantai to the northeast, Weifang to the west and Rizhao to the southwest. Qīng (青) in Chinese means "green" or "lush", while dǎo (岛) means "island".
Qingdao is a major seaport, naval base, and industrial centre. The world's longest sea bridge, the Jiaozhou Bay Bridge, links the main urban area of Qingdao with Huangdao district, straddling the Jiaozhou Bay sea areas.[3] It is also the site of the Tsingtao Brewery, the second largest brewery in China.[4]
In 2016, Qingdao ranks 79th in the Global Financial Centres Index published by the Z/Yen Group and Qatar Financial Centre Authority, the other Chinese cities on the list being Hong Kong, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Beijing and Dalian.[5] In 2007, Qingdao was named as among China's top ten cities by the Chinese Cities Brand Value Report, which was released at the 2007 Beijing Summit of China Cities Forum.[6] In 2009, Qingdao was named China's most livable city by the Chinese Institute of City Competitiveness.[7][8]
Other names
- Jiāo'ào: (胶澳): former name during the Qing dynasty.
- Qindao: (琴岛, lit. "Stringed Instrument Isle"): additional modern name for the area, refers according to locals to the shape of the coastline.
- Tsingtao: Postal romanization
- Tsingtau: German name during the concession period, written in German romanization of Chinese (Lessing-Othmer).
- Jiaozhou: a historical name which refers to the Jiaozhou Bay.
- Kiaochow, Kiauchau, Kiautschou: romanizations of Jiaozhou.
History
Ancient times
Human settlement in the area dates back 6,000 years. The Dongyi nationality, one of the important origins of the Chinese nation, lived here and created the Dawenkou, Longshan and Dongyeshi cultures. In the Eastern Zhou Dynasty (770BC~256BC), the town of Jimo was established, which was then the second largest one in the Shandong region. The area in which Qingdao is located today was named Jiao'ao (胶澳) when it was administered by the Qing Dynasty on 14 June 1891.
German colonial period and Japanese occupations



In 1891, the Qing government decided to make coastal Tsingtao (Jiao'ao) a defense base against naval attack and began to improve Qingdao's existing fortifications. German naval officials observed and reported on this Chinese activity during a formal survey of Jiaozhou Bay in May 1897. Subsequently, German troops seized and occupied the fortification.[9] China conceded the area to Germany the following year, and the Kiautschou Bay concession, as it became known, existed from 1898 to 1914 (Li 2005, p. 81). With an area of 552 square kilometres (136,000 acres; 213 sq mi), it was located in the imperial province of Shandong (alternately romanized as Shantung or Shan-tung) on the southern coast of the Shandong Peninsula in northern China. Jiaozhou was romanized as Kiaochow, Kiauchau or Kiao-Chau in English and Kiautschou in German. Qingdao was its administrative center. "The so-called Marktstrasse (Market street) was nothing more than the old main street of the Chinese village of Tsingtao, and the buildings lining it were the former homes of fishermen and farmers. Having sold their property, they resettled their homes and fields in the villages further east."[10] Upon gaining control of the area, the Germans outfitted the impoverished fishing village of "Tsingtao" (Qingdao) with wide streets, solid housing areas, government buildings, electrification throughout, a sewer system and a safe drinking water supply, a rarity in large parts of Asia at that time and later.[11] The area had the highest school density and the highest per capita student enrollment in all of China, with primary, secondary and vocational schools funded by the Imperial German treasury and Protestant and Roman Catholic missions.[11] Commercial interests established the Germania Brewery in 1903, which later became the world-famous Tsingtao Brewery.[12] German influence extended to other areas of Shandong Province, including the establishment of diverse commercial enterprises.
Identified by the German authorities as a strategically important port, Qingdao was administered by the Imperial Department of the Navy (Reichsmarineamt) rather than the Imperial Colonial Office (Reichskolonialamt). The navy based their Far East Squadron there, allowing the ships to conduct operations throughout the Pacific. Beginning January 1898 the marines of III. Seebataillon were based at Tsingtao. Construction of the Jiaoji Railway began on September 23, 1899, and was completed in 1904.[13]
Siege of Tsingtao
10 sen (1914)
Before the outbreak of World War I, ships of the German naval forces under Admiral Count von Spee were located at central Pacific colonies on routine missions. The fleet then rendezvoused in the Marianas to plan a transit to Germany rather than be trapped in the Pacific by Allied fleets.[14]
After a minor British naval attack on the German colony in 1914, Japan occupied the city and the surrounding province during the Siege of Tsingtao after Japan's declaration of war on Germany in accordance with the Anglo-Japanese Alliance.[15] China protested Japan's violation of her neutrality but did not interfere in the operations.[16] The decision of the Paris Peace Conference not to restore Chinese rule over Qingdao after the war triggered the May Fourth Movement.[17]
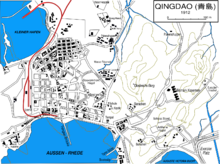
The city reverted to Chinese rule in December, 1922, under control of the Republic of China. However, Japan maintained its economic dominance of the railway and the province as a whole.[18] The city became a direct-controlled municipality of the ROC Government in July 1929.
Japan re-occupied Qingdao in 1938 with its plans of territorial expansion into China's coast. On June 2, 1949, shortly before the founding of the People’s Republic of China on October 1, 1949 the city was taken by Chairman Mao Zedong and his troops.
Qingdao city planning and development
1891–1914
The development of Tsingtao urban space during Germany-occupied period (1891–1914) originated from the port area. Large scale urban construction began in 1898 with the relocation of Chinese dwellers along the coast.[19] With the completion of such series of projects as wharves, Tsingtao-Jinan Railway Line,[20] Tsingtao Railway Station and locomotive works, a city was starting to take shape. The area had the highest schools density and highest per capita student enrollment in all of China, with primary, secondary and vocational schools funded by the Berlin treasury and Protestant and Roman Catholic missions.[21] In the year of 1910, the Germans drew up for the second time the city planning of Tsingtao (Warner 2001, p. 33). As a result, the former urban area was extended for four times highlighted by the emphasis on the development of commerce and trade. Sun Yat-sen visited the Tsingtau area and stated in 1912, “... I am impressed. The city is a true model for China’s future.”[22]
1914–1922
The development of Tsingtao urban space during the first Japan-occupation period (1914–1922). In 1914, Tsingtao was taken over by Japanese and served as a base for the exploitation of natural resources of Shandong and northern China. With the development of industry and commerce, a “New City District” was established to furnish the Japanese colonists with commercial sections and living quarters, which suggested a striking contrast to the shabby houses in the local Chinese zones(Li 2007, p. 133). In the meantime, a number of schools, hospitals and public buildings were constructed, followed by urban streets and intercity highways as well. The urban spatial layout continued to expand northward along the eastern bay area.
1922–1938
The development of Tsingtao urban space during the ROC-ruled period (1922–1938). This period saw the substantial progress of the urban development of Tsingtao. The government engaged itself in mass construction that gave birth to villa districts at the beach and bank groups in CBD. Plenty of public buildings and facilities for the purpose of entertainment and sports were completed. By the year of 1937, the urban population numbered 385,000(Lu 2001, p. 327). Tsingtao consequently distinguished itself as a prominent holiday resort and summer retreat.
1938–1945
The development of Tsingtao urban space during the second Japan-occupied period (1938–1945). Japan staged a comeback to Tsingtao in 1938 and started to strive for the construction of the Greater Tsingtao in the following June. Accordingly, they worked out the City Planning of the Greater Tsingtao and the City Planning of the Mother Town (Tsingtao City Proper), even though they had not had the opportunity to realize them respectively. The period in question did not witness much urban progress except for the logical construction of No. 6 Wharf, some Japanese residences and a small number of roads and streets(Lu 2001, p. 339).
Post–World War II
After World War II the KMT allowed Qingdao to serve as the headquarters of the Western Pacific Fleet of the US Navy in 1945. On 2 June 1949, the CCP-led Red Army entered Qingdao and the city and province have been under PRC control since that time.
Since the 1984 inauguration of China's open-door policy to foreign trade and investment, western Qingdao developed quickly as a port city. It is now the headquarters of the Chinese navy's northern fleet. An early example of the open-door policy occurred on 5 November 1984, when three United States Naval vessels visited Qingdao. This was the first US port call in more than 37 years to China. USS Rentz, USS Reeves, and USS Oldendorf and their crews were officially hosted by the Chinese People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN).
Northern Qingdao, particularly Shibei, Licang, and Chengyang districts, are now major manufacturing centers. The city has recently experienced a strong growth period, with a new central business district created to the east of the older business district. Outside of the center of the city, there is a large industrial zone, which includes chemical processing, rubber and heavy manufacturing, in addition to a growing high-tech area. Numerous local and national service companies, rather than manufacturers, are based in the city's southern district; this, as well as local wind patterns, allows Qingdao to enjoy clean, clear air year round.
Administrative divisions
The sub-provincial city of Qingdao has 4 core districts (区 qu):Shinan, Shibei, Licang, Laoshan as the center city of Qingdao, 2 suburban districts and 4 county-level cities (市 shi):
| Subdivision | Chinese (Simplified) | Pinyin Romanization | Admin. Code[23] |
Land Area (km2) |
Urbanization Rate (%) |
Permanent Resident Population ('000s, 2010) |
Population Density (1/km2) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Districts | ||||||||
| Shinan District (city seat) | 市南区 | Shìnán Qū | 370202 | 30.01 | 100 | 544.8 | 18153.95 | |
| Shibei District | 市北区 | Shìběi Qū | 370203 | 63.18 | 100 | 1020.7 | 16155.43 | |
| Huangdao District (Xihai'an New Area) |
黄岛区 (西海岸新区) |
Huángdǎo Qū (Xīhǎi'àn Xīnqū) |
370211 | 2220.10 | 80 | 1392.6 | 627.27 | |
| Laoshan District | 崂山区 | Láoshān Qū | 370212 | 389.34 | 80 | 379.5 | 974.73 | |
| Licang District | 李沧区 | Lǐcāng Qū | 370213 | 95.52 | 100 | 512.4 | 5364.32 | |
| Chengyang District | 城阳区 | Chéngyáng Qū | 370214 | 553.20 | 80 | 737.2 | 1332.61 | |
| Jimo District | 即墨区 | Jímò Qū | 370282 | 1727 | 58.1 | 1177.2 | 681.64 | |
| County-level cities | ||||||||
| Jiaozhou | 胶州市 | Jiāozhōu Shì | 370281 | 1210 | 68.0 | 843.1 | 696.78 | |
| Pingdu | 平度市 | Píngdù Shì | 370283 | 3166 | 52.8 | 1357.4 | 428.74 | |
| Laixi | 莱西市 | Láixī Shì | 370285 | 1522 | 58.1 | 750.2 | 492.90 | |
Geographically, there are four city proper districts of Qingdao. Shinan is viewed as the old downtown, located in the south of Qingdao city proper, while Shibei is located in the center of the city designated as the new downtown, Licang located further up the peninsula in the outskirts of the city, and Laoshan is located at the eastern urban Qingdao.
Geography and climate
| Qingdao | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Qingdao is located on the south facing coast of the Shandong Peninsula (Template:Lang-de). It borders three prefecture-level cities, namely Yantai to the northeast, Weifang to the west, and Rizhao to the southwest. The city's total jurisdiction area occupies 10,654 square kilometres (4,114 sq mi), and stretches in latitude from 35° 35' to 37° 09' N and in longitude from 119° 30' to 121° 00' E. The populated sections of the city are relatively flat while mountains spur up within city limits and nearby. The highest elevation in the city is 1,133 metres (3,717 ft) above sea level. Of the total area of Qingdao, 15.5% is highland, while the foothill, plain and lowland areas constitute 25.1%, 37.8% and 21.7%. The city has a 730.64 kilometres (454.00 mi) coastline. Five significant rivers that flow for more than 50 kilometres (31 mi) can be found in the region.
Qingdao has a temperate, four-season, monsoon-influenced[25] climate that lies in the transition between the humid subtropical (Köppen Cwa) and humid continental (Köppen Dwa) regimes, but favouring the former. Winter is cool to cold and windy, but generally dry, with a January average of −0.5 °C (31.1 °F). Summer is generally hot and humid, but very hot days are rare, with an August average of 25.3 °C (77.5 °F). Due to its proximity to the coast and being on a peninsula, it experiences a one-month delayed spring compared to most inland areas of China,[25] and the annual diurnal temperature variation is only 6.3 °C (11.3 °F). Conversely, autumn is milder than inland areas in Shandong. The water temperature peaks at about 25 °C (77 °F) in late August, with swimming possible two months on either side. The annual mean temperature is 12.6 °C (54.7 °F). Extremes since 1951 have ranged from −15.5 °C (4 °F) on 16 January 1958 to 38.9 °C (102 °F) on 15 July 2002.[26]
During the summer months, the beaches of Qingdao are afflicted by massive algal blooms. The decomposing algae release large amounts of hydrogen sulfide gas, which gives off the odour of rotten eggs. The blooms of sea lettuce, which are partially caused by seaweed farming in Jiangsu Province, led local officials to declare a "large-scale algae disaster" in 2013.[27]
| Climate data for Qingdao | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 12.9 (55.2) |
19.6 (67.3) |
21.5 (70.7) |
25.2 (77.4) |
34.2 (93.6) |
34.4 (93.9) |
37.4 (99.3) |
34.3 (93.7) |
33.2 (91.8) |
28.4 (83.1) |
22.1 (71.8) |
16.2 (61.2) |
37.4 (99.3) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 2.8 (37.0) |
4.6 (40.3) |
9.0 (48.2) |
15.0 (59.0) |
20.3 (68.5) |
23.7 (74.7) |
27.1 (80.8) |
28.4 (83.1) |
25.3 (77.5) |
19.8 (67.6) |
12.3 (54.1) |
5.7 (42.3) |
16.2 (61.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −0.5 (31.1) |
0.9 (33.6) |
5.1 (41.2) |
10.9 (51.6) |
16.2 (61.2) |
20.3 (68.5) |
24.2 (75.6) |
25.3 (77.5) |
21.7 (71.1) |
16.2 (61.2) |
8.9 (48.0) |
2.4 (36.3) |
12.6 (54.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −3.3 (26.1) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
2.3 (36.1) |
7.9 (46.2) |
13.2 (55.8) |
17.8 (64.0) |
22.2 (72.0) |
23.0 (73.4) |
18.9 (66.0) |
13.1 (55.6) |
5.9 (42.6) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
9.9 (49.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −14.3 (6.3) |
−12.1 (10.2) |
−6.2 (20.8) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
6.1 (43.0) |
12.0 (53.6) |
13.6 (56.5) |
16.3 (61.3) |
10.1 (50.2) |
1.9 (35.4) |
−7.2 (19.0) |
−11.3 (11.7) |
−14.3 (6.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 11.3 (0.44) |
12.1 (0.48) |
21.4 (0.84) |
34.6 (1.36) |
54.9 (2.16) |
84.0 (3.31) |
142.1 (5.59) |
151.1 (5.95) |
62.7 (2.47) |
48.2 (1.90) |
27.9 (1.10) |
11.8 (0.46) |
662.1 (26.06) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 3.1 | 3.7 | 4.7 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 9.4 | 12.4 | 10.2 | 6.5 | 6.1 | 4.7 | 3.4 | 78.4 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 186.0 | 180.8 | 220.1 | 222.0 | 244.9 | 219.0 | 182.9 | 223.2 | 219.0 | 220.1 | 189.0 | 182.9 | 2,489.9 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 60 | 59 | 60 | 56 | 56 | 50 | 41 | 53 | 59 | 63 | 61 | 61 | 57 |
| Source: China Weather (1971–2000),[28] Hong Kong Observatory (sun only, 1961–1990)[24] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1913[29] | 58,000 | — |
| 1953 | 916,846 | +1480.8% |
| 1964 | 1,383,433 | +50.9% |
| 1982 | 4,227,594 | +205.6% |
| 1990 | 6,663,989 | +57.6% |
| 2000 | 7,494,194 | +12.5% |
| 2010 | 8,715,100 | +16.3% |
| Population size may be affected by changes on administrative divisions. | ||
By the end of 2006, Qingdao was estimated to be the home of about 8 million inhabitants, of which around 3 million reside in the Qingdao urban area. Another estimated 5 million live in other cities under Qingdao's jurisdiction. The annual birth rate is calculated around 76,507, with a birth rate of 10.15 per year per thousand, and a death rate of 6.32, both calculated on an annual basis. Living standards are among the highest of leading Chinese cities due to the strong export economy and relatively high family wages.
Qingdao is home to 38 Chinese ethnic minorities, which account for 0.14% of the city's total population.
There is a large Korean community in Qingdao. By 2009, there are approximately 100,000 Koreans working, studying and living in Qingdao, which makes Qingdao the second in terms of Korean population in China, following Beijing which has about 200,000 Koreans.[30]
Economy

An important region in Eastern China, Shandong Province has seen substantial change in its economic landscape in recent years. Much of this development has been concentrated in Qingdao.[31] Qingdao has seen rapid development. With an annual growth rate of 18.9 percent in 2006, the city's GDP reached 42.3 billion, ranking first in Shandong Province and tenth out of China's top 20 cities.[31] GDP per capita comprised ¥52,895 (US$7,616) in 2008. The GDP has grown steadily at an average pace of 16% annually. In 2006, Qingdao was ranked one of six "golden cities" by the World Bank, out of 120 Chinese cities assessed on factors including investment climate and government effectiveness.[31]
Internationally, Qingdao is perhaps best known for its Tsingtao Brewery, founded by a German-British joint venture in 1903 that produces Tsingtao beer, the best-known Chinese export beer. It is also home to Haier, a large white goods manufacturer, and Hisense, a major electronics company. In 2002 guitar manufacturers Epiphone opened a factory in Qingdao.[32]
In 1984 the Chinese government named a district of Qingdao a Special Economic and Technology Development Zone (SETDZ). Along with this district, the entire city had gone through amazing development of secondary and tertiary industries. As an important trading port in the province, Qingdao flourishes with foreign investment and international trade. South Korea and Japan in particular made extensive investment in the city. Approximately 80,000 South Korean citizens reside there. Construction proceeds at a relatively fast pace in Qingdao.
In terms of primary industry, Qingdao has an estimated 50,000 acres (200 km2) of arable land. Qingdao has a zigzagging pattern coastline, and thus possesses an invaluable stock of fish, shrimp, and other sea resources.
Qingdao is also home to a variety of mineral resources. Up to thirty different kinds have been mined.
Qingdao's wind power electricity generation performs at among the highest levels in the region.[citation needed]
Industrial zones
- Qingdao Special Economic & Technological Development Area
- Qingdao Free Trade Zone
- Qingdao High-tech Industrial Zone
- Qingdao University Industrial Zone
Transport
Road
The total lengths of operational highways[clarification needed] is 14,326 km (8,902 mi), including 700 km (430 mi) Expressways. At the present,[when?] the traffic mileage is more than 6.02 billion km (3.74 billion mi) per year. [citation needed] There are a total of 1,145 km (711 mi) of roads in the Qingdao area, with nearly 500 km (310 mi) of expressways. These National Trunk Highway System (NTHS) Expressways begin or pass through in Qingdao.[33] Expressways that begin in Qingdao are in Bold:
- G15 Shenhai Expressway (Shenyang, Liaoning-Haikou, Hainan)
- G18 Rongwu Expressway (Rongcheng, Shandong-Wuhai, Inner Mongolia)
- G20 Qingyin Expressway (Qingdao-Yinchuan, Ningxia)
Spur Route: G2011 Qingxin Expressway (Qingdao-Xinhe, Pingdu, Shandong)
- G22 Qinglan Expressway (Qingdao-Lanzhou, Gansu)
These provincial expressways begin in or pass through Qingdao. Expressways that begin in Qingdao are in Bold:
- S16 Rongwei Expressway (Rongcheng-Weifang)
- S19 Longqing Expressway (Longkou-Qingdao)
- S21 Xinwei Expressway (Xinhe-Weifang)
- S24 Weiqing Expressway (Weihai-Qingdao)
Other than Expressways, there are also National Highways that pass through or begin in Qingdao. National Highways that begin in Qingdao are in bold:
In June 30, 2011, the longest bridge over water opened in Qingdao. The bridge, Haiwan Bridge, is 26.4 miles (42.5 km) long and connects Qingdao to an offshore island, Huangdao. It would easily cross the English Channel and is almost three miles (4.8 km) longer than the previous record-holder, the Lake Pontchartrain Causeway in the American state of Louisiana. Haiwan Bridge is supported by more than 5,000 pillars and costs about 10 billion yuan which is about 1.5 billion dollars. The bridge was designed by the Shandong Gausu Group and the construction lasted for four years. Haiwan Bridge cut the commute between the city of Qingdao and the sprawling suburb of Huangdao by 30 minutes. At least 10,000 workers toiled in two teams around the clock to build the bridge, which was constructed from opposite ends.[34] On the same day, the Jiaozhou Bay Tunnel opened.The tunnel brought much convenience to people by supporting public buses and making transport between the two areas more convenient.
Marine
The Orient Ferry connects Qingdao with Shimonoseki, Japan. There are two ferry lines connecting Qingdao with South Korea. The New Golden Bridge II operates between Qingdao and Incheon, and the Blue Sea Ferry operates between Qingdao and Gunsan.[35]
Qingdao hosts one of the world's busiest seaports. Cooperative relations have been established with 450 ports in 130 countries worldwide. In 2003, the annual cargo handling capacity exceeded 100 million tons for the first time. The number of containers reached 3.41 million twenty-foot equivalent units (TEU) of cargoes.[36] By 2011, the port had become the world’s sixth-busiest by Total Cargo Volume, having handled 372 million tonnes of cargo in that year. It is the 8th in the world in terms of TEUs (Twenty Foot Equivalent Units).[37]
Aviation
The Qingdao Liuting International Airport, 23 km (14 mi) away from city centre, is served by 13 domestic and international airlines, operating 94 routes, 12 of which are international and regional. In 2011, Qingdao Liuting International Airport was the 16th busiest airport in the People's Republic of China with 11,716,361 passengers. A new civil aviation airport with much larger capacities will be built in Jiaozhou District.[38]
Intercity rail

Qingdao's railway development was picked up during the late 1990s. It is at the beginning of the Jiaoji Railway. Qingdao's city proper has some major railway stations, Qingdao Station, Sifang Station,[39] Cangkou Station, Great-Seaport Station, etc.
D and G series High speed trains travel on the Jiaoji High Speed Railway and reach speeds of 200 km/h (120 mph) on the Jinan-Qingdao Section.[40] Services go to Beijing, Shanghai, Hefei, Jinan and Tianjin.[41]
Domestic rail lines connect Qingdao with many cities in China including Beijing, Lanzhou, Chengdu, Xi'an, Zhengzhou, Jinan and Jining.
Public transport
Qingdao's public traffic owns 5283 large and medium-sized buses, CNG buses as of 2012[update].There are also 136 trolleybuses as of 2012[update]. There are 260 bus routes and 3 trolleybus routes as of 2012[update]. [citation needed] All of these buses and trolleybuses can be accessed using the Qingdao Public Traffic IC Card (Qin dao Card 琴岛卡), which uses radio frequencies so the card does not have to physically touch the scanner. Non air-conditioned busses cost 1 yuan, The volume of road passenger transport approaches 0.8 billion per year. [citation needed] The Public Transport Brand of 'Ri-Xin Bus (日新巴士)' is also known in China.
There are a number of taxi companies in Qingdao including Yiqing Company, Zhongqing Company, Jiaoyun Company and, Huaqing Company.
Subway
After getting the approval from the State Council, the government announced on 18 August 2009 that Qingdao is ready to spend more than 29 billion yuan ($4.2 billion) before 2016 on its subway construction. Construction of 54.7 km (34.0 mi) of subway line will be completed before 2016 with a total investment of 29.2 billion yuan ($4.3 billion). Metro Line 3 is the first line in function and opened on 16 December 2015. In the long term, the city plans to build eight subway lines in downtown and some suburban districts, which account for 231.5 km (143.8 mi) in future.[42]
Military
Qingdao is headquarters of the North Sea Fleet of the People's Liberation Army Navy.
Culture
Architecture

There is a large number of German-style buildings in Qingdao city centre, remarkable considering the German colonial period only lasted 16 years (1898–1914). The unique combination of German and Chinese architecture in the city centre, combined with German demographic roots and a large Korean expatriate population, gives Qingdao a distinct atmosphere. An old saying described Qingdao as a city of "red tiles green trees, blue sky and blue sea." This saying indeed gives a picture of birdview of Qingdao. A larger number of areas in former foreign styles are well preserved. Although the new city area is under large-scale reconstruction, the old city area (especially the western part of Shinan District) still retains many traditional buildings.


Celebrities
- Ma Jian (马建)
- Xiao Hong (萧红)
- Xiao Jun (萧军)
- Duanmu Hongliang (端木蕻良)
- Sun Li (孙犁)
- Li Zhaoxing (李肇星)
- Victoria Song (宋茜, f(x))
- Huang Xiao Ming
- Huang Bo (黄勃)
Other notable people include:
- Gao Fenghan (高凤翰)
- Toshiro Mifune (was born in Qingdao)
- Li Cunxin (李存信)
- Huang Xiaoming (黄晓明)
- Chen Hao (陈好)
- Xia Yu (夏雨)
- Fan Bingbing (范冰冰)
- Wang Dong (Chinese Footballer)
Movies shot in Qingdao
- The Great Wall (长城)2016
- Underdog Fight (硬汉)2008
- Underdog Fight II (硬汉 II)2013
- Ocean Paradise (海洋天堂)2010
- Beauty Remains (美人依旧)2005
Language
During the city's colonial days, German was the official language and rigorously taught and promoted. Since the demise of Germany's colonial empire during World War I, the German language is virtually dead here and left little impact on the local languages. A local accent known as Qingdao dialect (青岛话, pinyin qingdao hua) distinguishes the residents of the city from those of the surrounding Shandong province. Due to the efforts by the city government to promote standard Mandarin, most educated people can speak that dialect in addition to their native dialect. With reform policies and English teaching, some young citizens have been taught English and many can converse with English-speaking foreigners. Business and traffic signs in English are becoming more and more common.
Cuisine
Seafood is a typical delicacy of the coastal city, divided into two categories: "Great Seafood" including sea cucumbers, abalones, shark's fin, prawns, crabs, conch, and some big fish, and "Little Seafood" comprising squid, shrimps, octopus, oysters, razor clams, clams, periwinkles, yellow croakers, etc. Generally, fresh seafood is served in every hotel.
The distinctive cuisine of the area is Lu Cai, the Shandong regional style.
Festivals

The Qingdao International Horticultural Exposition 2014 is the biggest international fair that has been held in the history of the city. Other important festivities include:
- Qingdao International Beer Festival(青岛国际啤酒节) in August/September, held annually since 1991
- China International Afforestation Fair, since 2003
- APEC SMEs Technology Conference and Fair
- China Qingdao Fishing Competition(中国青岛钓鱼比赛)
- Qingdao Bar-Culture Festival(中国酒吧文化节)
- China International Exposition of electronic home appliances (中国电子产品博览会)
- China Qingdao Ocean Festival (中国青岛海洋节)
- China International Maritime Exhibition (中国国际海事展)
- Qingdao International Fashion Week (青岛国际时装周)
- China International Fishery Fair
- China Qingdao International Hot Air Balloon Festival
- Qingdao International Beach Festival (青岛国际海滩节日)
Media
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (October 2012) |

Qingdao previously had a large German community and a German garrison, so three German newspapers operated in Qingdao.[43] German papers included Deutsch-Asiatische Warte (T: 泰東古今鑑, S: 泰东古今鉴, P: Tàidōng Gǔjīn Jiàn;[44] weekly newspaper published until 1906, included Die Welt des Ostens, Altes und Neues aus Asiens drei Kaiserreichen, a cultural supplement),[43] the Tsingtauer Neueste Nachrichten and the Kiautschou Post (a daily paper published from 1908 to 1912, referring to the Kiautschou (Jiaozhou) Bay concession). German publishing in Qingdao ended after World War I and the beginning of the Japanese administration.[44]
A 1912 publication of the United States Department of Commerce, Bureau of Foreign and Domestic Commerce said that the Tageblatt für Nordchina of Tianjin was read in Qingdao, and that major newspapers from Shanghai were also read in Qingdao.[45]
Tourism
Qingdao attracts many tourists due to its seaside setting and temperate weather. Parks, beaches, sculptures and unique German and modern architecture line the shore. The central tourist information, the Qingdao Information Centre for International Visitors, is located on Middle Hong Kong Road (香港中路).
Qingdao's major attractions include:
Western Shinan district
- Zhan Qiao (Pier, 栈桥)
- Little Qingdao Isle (小青岛)
- Tian Hou Temple (天后宫), Qingdao Folk Museum
- Ba Da Guan (Eight Great Passes, 八大关), the older area of town with some surviving German and Japanese architecture.
- Lu Xun Park, named after Lu Xun (鲁迅), modern Chinese writer and critic, who lived and taught in the 1930s.
- Zhongshan Park, named after the style name 'Zhongshan' of Sun Yat-sen (孙文,字中山), a famous modern Chinese politician.
- Xiao Yu Shan (Little Fish Hill, 小鱼山)
- Qingdao Botanical Garden
- Qingdao Zoological Garden
- The twin-spired St. Michael's Cathedral (Kathedrale St. Michael) (天主教堂), one piece of the famous Neo-romanesque architecture in Qingdao, designed by German architect Alfred Fräbel, completed in 1934.
- Huashi Villa (花石楼), a mansion originally built for a Russian aristocrat
- Qingdao Aquarium
- Jiaozhou Governor's Hall (提督府), office building of former German governors (Gouverneurspalast) and former municipal government
- Former German Governor's Mansion (Gouverneursvilla)
- Xinhao Hill (信号山)
- Astronomical Observatory Hill (观象山)
- Tuan Dao Shan (Dumpling Peninsula Hill, 团岛山)
- Underground World of Chinese Mythology, life-size figures and groups depicting scenes from the Chinese mythology.
- Qingdao Hill Fort ruins
- Qingdao Naval Museum
- The Evangelical Church (Evangelisch Kirche) (基督教堂)
- Qingdao Bathing Beaches, there are 6 well-known beaches with complete facilities.
- Qingdao Aofan sailing base (奥帆基地)
Eastern Shinan district
- May Fourth Square (Mai vierten Platz), Coastal plaza with the Wind of May sculpture
- Music Square, famous for the Sail of Music
- Qingdao Seaside Sightseeing Path
- Qingdao International Beer town, the primary site of the annual Qingdao International Beer Festival.
- Tsingtao Brewery (Tsingtao-Brauerei), originally founded by Germans and the most exported beer from China.
- Qingdao Sculpture Museum
- Qingdao Etsong Natural Grass Ski Field
- Zhanshan Temple (Dschanschan Tempel), Qingdao's oldest Buddhist temple.
Laoshan district (崂山区)
- Lao Shan (Mount Lao, Lauschan, 崂山), 40 km (25 mi) east of Qingdao, the most famous Taoist mountain with Taoist retreat – Great Purity Palace (太清宫).
- Jufeng (Huge Peak, 巨峰)
- Nine Waters & Eighteen Pools (九水十八潭)
- Kang Cheng Shuyuan (Kang Cheng Study House, 康成书院)
- Yangkou (仰口)
- Yakou (垭口)
Other districts of Qingdao
- Langya Observation Resort (瑯琊台度假区), located in the previous Qi State, Jiaonan City.
- Great Wall of Qi
- Chanzhi Reservoir, located 10 km (6 mi) to the north of Laixi City, on the middle and upperreaches of the Dagu River.
- Sanlihe Garden, Jiaozhou City
- Jiaozhou Governor's Hall (Gouverneurspalast), former seat of the present and previous two governments.
Education
Post-secondary educational institutions

Qingdao is home to a large number of higher education institutions. Ocean University of China, formerly called Ocean University of Qingdao, is the most important university of maritime sciences in China. In addition, the Qingdao University, the Qingdao University of Science and Technology as well as the Qingdao Technological University have also been integral parts of higher education in Qingdao for decades. Other institutions include:
- China University of Petroleum, completed its relocation from Dongying to Qingdao in 2012
- Shandong University of Science and Technology, main campus is based in Qingdao since 2003
- Qingdao Agricultural University, main campus is based in Qingdao since 2007
- Qingdao Technical College
- Qingdao Binhai University, located at Huangdao.
Shandong University was located in Qingdao from 1909 to 1936. A new branch campus of the university is under construction in Jimo.
International schools
- Korean International School of Qingdao
- Qingdao MTI International School
- Qingdao Amerasia International School
- Qingdao No.1 International School
- Qingdao Oxford International College
- Yew Chung International School of Qingdao
Sports
Qingdao has long been a hub of professional sports in The People's Republic of China.
Stadiums
- Guoxin Gymnasium (Qingdao city sports center)
- Hongcheng Stadium
- Qingdao Tiantai Stadium
- Yizhong Sports Center
Olympic Games
Along with Beijing's hosting of the 2008 Summer Olympics, Qingdao was the host city for the Olympic Sailing competitions which took place along the shoreline by the city. These events were hosted at the Qingdao International Sailing Centre and held in Fushan Bay, near the city's central business district. A hotel and an international broadcasting centre were built.
Football
Qingdao Jonoon F.C. (previously named Qingdao Hainiu Football Club) was founded in 1993. It is one of the founding members of the second-division of Chinese professional football league. They got the championship in their first season in 1994 and were promoted to the Chinese Jia-A League. In 1995, they finished 11th (out of a total 12 teams) and were relegated from the top league. Only one year later, after finishing as runner-up in the second-division, they returned to the top league. They have been part of Chinese Super League from its inauguration in 2004.
Motorsport
The IZOD IndyCar Series has signed a contract with the Qingdao city council to hold an IndyCar race in Qingdao in 2012. The race was supposed to take place on a 6.23 km (3.87 mi) street circuit[46] but it has been cancelled.[47]
Surfing
Qingdao is one of the few cities in northern China where surfing is possible. The best surfing season is during the typhoon season (June–October). The south oriented beaches of Qingdao are the most appropriate to receive swells. Shinan and Laoshan districts are reported to have the best wave and wind orientation.
See also
References
- Gottschall, Terrell D. By Order of the Kaiser: Otto von Diederichs and the Rise of the Imperial German Navy 1865–1902. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. 2003. ISBN 1-55750-309-5
- Schultz-Naumann, Joachim. Unter Kaisers Flagge: Deutschlands Schutzgebiete im Pazifik und in China einst und heute [Under the Kaiser’s Flag, Germany’s Protectorates in the Pacific and in China then and today]. Munich: Universitas Verlag. 1985.
- Miscellaneous series, Issues 7–11. United States Department of Commerce, Bureau of Foreign and Domestic Commerce, 1912.
- Walravens, Hartmut. "German Influence on the Press in China". In: Newspapers in International Librarianship: Papers Presented by the Newspaper Section at IFLA General Conferences. Walter de Gruyter, January 1, 2003. ISBN 3110962799, ISBN 9783110962796.
- Also available at (Archive) the website of the Queens Library – This version does not include the footnotes visible in the Walter de Gruyter version.
- Also available in Walravens, Hartmut and Edmund King. Newspapers in international librarianship: papers presented by the newspapers section at IFLA General Conferences. K.G. Saur, 2003. ISBN 3598218370, 9783598218378.
Notes
- ^ "中央机构编制委员会印发《关于副省级市若干问题的意见》的通知. 中编发[1995]5号". 豆丁网. 19 February 1995. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
- ^ "3-4各市人口数和总户数(2014年)-tjsql.com". www.tjsql.com. Retrieved 6 March 2016.
- ^ A bridge too far? China unveils world's longest sea bridge which is five miles FURTHER than the Dover-Calais crossing | Mail Online. Dailymail.co.uk. Retrieved on 2011-08-28.
- ^ "China Beer" (PDF). Retrieved 13 June 2013.
- ^ "The Global Financial Centres Index 19". Long Finance. March 2016.
- ^ "China's Top 10 Most Livable Cities". hnloudi.gov.cn. Hunan Loudi Official Government. 28 March 2012. Retrieved 18 June 2014.
- ^ "List of 10 Most Livable Cities in China Issued". 9 July 2009. Retrieved 18 December 2010.
- ^ 蔺丽瑶 (27 July 2011). "Top 10 livable cities in China 2011". China.org.cn. Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- ^ Gottschall, Terrell (2003). By Order of the Kaiser, Otto von Diederichs and the Rise of the Imperial German Navy 1865–1902. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. p. 146. ISBN 978-1-55750-309-1.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Matzat, Wilhelm (May 2003). "Landmann Gottfried 1860–1926 Uhrmacher, Optiker, Bierbrauer". tsingtau.org (in German). Wilhelm Matzat. Retrieved 9 June 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Schultz-Naumann, Joachim (1985). Unter Kaisers Flagge: Deutschlands Schutzgebiete im Pazifik und in China einst und heute (in German). Universitas. p. 183. ISBN 978-3-8004-1094-1.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|month=(help); Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ Matzat, Wilhelm (May 2003). "Germania Brauerei und ihre Angestellten 1903–1914". tsingtau.org (in German). Wilhelm Matzat. Retrieved 9 June 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ 斯, 李. "1904年06月01日 胶济铁路通车". www.todayonhistory.com. Retrieved 1 September 2014.
- ^ see German East Asia Squadron, Battle of Coronel and Battle of the Falkland Islands for fleet engagements
- ^ Duffy, Michael (22 August 2009). "Primary Documents – Count Okuma on the Japanese Capture of Tsingtao, 15 August 1914". firstworldwar.com. Retrieved 28 July 2014.
- ^ "Germans lose possessions in China". The Independent. 16 November 1914. Retrieved 24 July 2012.
- ^ A. Whitney Griswold, The Far Eastern Policy of the United States (1938) pp 239–68
- ^ Griswold, The Far Eastern Policy of the United States (1938) pp 326–28
- ^ Toyokichi Iyenaga (26 October 1914). "What is Kiaochou worth?". The Independent. Retrieved 24 July 2012.
- ^ Schultz-Naumann, p. 182
- ^ Schultz-Naumann, Joachim (1985). Unter Kaisers Flagge: Deutschlands Schutzgebiete im Pazifik und in China einst und heute (in German). Universitas. p. 183. ISBN 978-3-8004-1094-1.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|trans_title=and|month=(help) - ^ Schultz-Naumann, p. 184
- ^ 2016年统计用区划代码和城乡划分代码:青岛市 (in Simplified Chinese). National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. 2016. Retrieved 1 February 2018.
统计用区划代码 名称 370201000000 市辖区 370202000000 市南区 370203000000 市北区 370211000000 黄岛区 370212000000 崂山区 370213000000 李沧区 370214000000 城阳区 370281000000 胶州市 370282000000 即墨市 370283000000 平度市 370285000000 莱西市
- ^ a b "Climatological Normals of Qingdao". Hong Kong Observatory. Retrieved 10 April 2010.
- ^ a b 自然地理 (in Chinese). Qingdao: Shinan District Information Office.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ http://cdc.cma.gov.cn/dataSetLogger.do?changeFlag=dataLogger
- ^ Jacobs, Andrew (5 July 2013). "Huge Algae Bloom Afflicts Coastal Chinese City". The New York Times.
- ^ 青岛城市介绍 (in Chinese). Weather.com.cn. June 2011. Retrieved 1 June 2011.
- ^ Annette S. Biener: Das deutsche Pachtgebiet Tsingtau in der Provinz Schantung, 1897–1914. Institutioneller Wandel durch Kolonialisierung (Studien und Quellen zur Geschichte Schantungs und Tsingtaus. Bd. 6). Matzat, Bonn 2001, ISBN 3-924603-05-7.
- ^ "韩国旅客位居北京入境外国人之首". 8 October 2009. Retrieved 1 December 2009.
- ^ a b c "Qingdao Shinan District Investment Environment Study 2007", Report, KPMG Huazhen, 2007, retrieved 10 June 2010
- ^ "Gibson Qingdao Factory – All Epiphone... All The Time!". Epiphone.com. Retrieved 24 February 2012.
- ^ 中国公路信息服务网-公路地图 (in Chinese). 中国公路信息服务网. Retrieved 12 January 2013.
- ^ Eimer, David (8 January 2011). "China builds world's longest bridge". London: The Telegraph. Retrieved 23 March 2013.
- ^ Ferries Korea-China. Seat61.com. Retrieved on 2012-11-12.
- ^ Qingdao port sees upsurge in cargo handling capacity. People's Daily. Retrieved on 2012-11-12.
- ^ http://www.aapa-ports.org/Industry/content.cfm?ItemNumber=900#Statistics
- ^ "New Qingdao Airport Location Confirmed". World Civil Aviation Net. 29 September 2013.
- ^ Until August 2008, travelers not from Qingdao are often confused as railway tickets to Qingdao are listed as destined for "Sifang". These trains are headed to Qingdao's Sifang district. The destination's name will revert to "Qingdao" once renovations to the larger Qingdao Railway Station is complete.
- ^ 杨传忠 (17 October 2012). 济青高铁建设近年无望 济青1小时生活圈得等等. 齐鲁晚报 (in Chinese).
济南铁路局胶济客专公司一位负责人说,胶济客专的客运正线长362.5公里,设计速度最高250公里/小时,现在行车时速为200公里.
{{cite news}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ 列车时刻 (in Chinese). 青岛火车站. Retrieved 12 January 2013.
- ^ "$4.3 billion budget to boost Qingdao subway construction". 19 August 2008.
- ^ a b Walravens, p. 90.
- ^ a b Walravens, p. 91.
- ^ United States Bureau of Foreign and Domestic Commerce, p. 188. "Tageblatt für Nord China, a German paper published in Tientsin, and the leading papers published in Shanghai are also largely read in Tsingtau."
- ^ IndyCar (10 November 2011). "INDYCAR: Series Confirms China Race". SPEED Channel. Fox Sports. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ "IndyCar scheduled August race in China has been canceled". Washington Posts. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) [dead link]












