Visa policy of mainland China


Visitors to the People's Republic of China must obtain a visa from one of the Chinese diplomatic missions unless they come from one of the visa exempt countries. The two Special Administrative Regions – Hong Kong and Macau – maintain their own independent border control policy and thus have their own visa requirements.[1]
A Chinese visa is issued by the Chinese diplomatic missions to a foreign passport holder, which authorizes him to enter and depart or transit through China.[2] Due to the separate border control policies, ordinary Chinese visas are not valid for entry to Hong Kong or Macau, so travelers must apply for Chinese visas for Hong Kong or Chinese visas for Macau should they require a visa for travelling to these regions.
The government of the People's Republic of China allows citizens of some countries (see below) to travel to Mainland China for tourism or business purposes for up to 15 or 30 days without having to obtain a visa. Most foreign passport holders travelling to China, however, are required to hold a visa due to the lack of visa-free travel agreements. In order to boost tourism, some ports of entry of China allow certain nationals to visit specified regions within 72 or 144 hours if they are in transit to a third country (see "Visa-free transit" below). In 2014 the PRC government announced its intention to sign mutual visa facilitation and visa-free agreements with as many countries as possible.[3] Since then, a number of such agreements were concluded with some countries.
All non-Chinese travelers as well as Hong Kong and Macau permanent residents who stays in Mainland China for more than 24 hours must register with local Public Security Bureaus (PSBs). When staying in a hotel, the registration is usually done as a part of check-in process. When staying in a private home, the visitor must physically report to the PSB within 24 hours of arrival for cities or 72 hours for rural areas. All visa-free passengers, including those in transit who stays for more than 24 hours, must adhere to the rule, as failure to comply can result in a fine or detention for up to 15 days.[4]
Eligible nationalities for visa-free entry

Travelers who are nationals of the following nations are not required to obtain a visa prior to travel to China as long as their trip lasts no more than the visa waiver limit listed below.
Visa-free for ordinary passports
90 days
30 days15 days |
Nationals of Brunei, Japan and Singapore can apply for a visa at the local Public Security Bureaus if their stay exceeds 15 days.[1]
Visa-free for Passport for Public Affairs or its equivalents
The list includes countries which had signed visa-free agreements with China for holders of passports for public affairs or ordinary passports endorsed for public affairs. Exceptions are listed below.[1]
1 - Visa free only for holders of "E-series" normal passports.
2 - Visa free for both "Passport For Public Affairs" or "Passport For Official Trip".
3 - Visa free only for normal passports with a sticker stating "For Business Purposes Only".
4 - Visa free only if the passport for public affairs has a sheet attached on the visa page showing in red capitals "AB" and an additional validity date.
Visa-free for diplomatic, official, and/or service passports

Holders of passports issued by the following countries are allowed to enter and remain in China for up to 30 days (unless otherwise noted).[16]
D — diplomatic passports
O — official passports
S — service passports
Sp — special passports
LP — laissez-passers
1 - 90 days in 180 days, for EU countries not otherwise indicated
2 - 90 days
3 - 60 days
4 - only when accompanying a Minister of the Irish government on an official visit
Merchant Seamen
All Merchant Seamen who benefits from a visa waiver must travel on duty, hold a Port Visa Notification, Letter of Employment or Letter of Guarantee issued by a Chinese shipping company, Seaman Book, onward tickets and all documents required for their next destination if they are arriving by air in order to board a ship, or arriving by ship and proceeding to the airport .
Merchant Seamen from the 9 visa-free countries can enter China without a visa if they satisfy the conditions listed above.
Merchant Seamen from the following countries can also enter China without a visa if they satisfy the conditions listed above. When utilizing the visa-free scheme, they must enter via the following ports of entry:[1]
For nationals of ![]() Ukraine:
Ukraine:
- Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport
- Shanghai Pudong International Airport
- Xiamen Gaoqi International Airport
- Beijing Capital International Airport
- Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport
- Nanjing Lukou International Airport
- Tianjin Binhai International Airport
For nationals of ![]() Poland:
Poland:
- Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport
- Shanghai Pudong International Airport
- Xiamen Gaoqi International Airport
- Beijing Capital International Airport
- Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport
- Tianjin Binhai International Airport
For nationals of ![]() Lithuania and
Lithuania and ![]() Russia:
Russia:
- Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport
- Shanghai Pudong International Airport
- Beijing Capital International Airport
- Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport
In addition, nationals of ![]() Russia who holds an identity certificate for suite stewards on international trains can enter visa-free.
Russia who holds an identity certificate for suite stewards on international trains can enter visa-free.
APEC Business Travel Card
Holdes of passports issued by the following countries who possess an APEC Business Travel Card (ABTC) which states on the reverse that it is valid for travel to China can enter visa-free.[1]
ABTCs are issued to nationals of:[17]
ABTCs are also issued to permanent residents of ![]() Hong Kong, however permanent residents with Chinese nationality are required to use their Home Return Permits instead. Only holders of foreign passports can use the card to enter Mainland China.
Hong Kong, however permanent residents with Chinese nationality are required to use their Home Return Permits instead. Only holders of foreign passports can use the card to enter Mainland China.
Although ![]() Republic of China (Taiwan) is a member of this program, its nationals are also not allowed to use ABTC to enter Mainland China, instead they are required to use Taiwan Compatriot Permits.
Republic of China (Taiwan) is a member of this program, its nationals are also not allowed to use ABTC to enter Mainland China, instead they are required to use Taiwan Compatriot Permits.
Entry procedures for residents of Hong Kong SAR, Macau SAR, and nationals of Republic of China (Taiwan)
Although Hong Kong SAR and Macau SAR are constituents of China, they have their own immigration policies which are different from the Mainland China, and individual border controls that separate the territories from Mainland. The Chinese government, however, does not consider Chinese nationals with resident status of Hong Kong and Macau travelling to China as international travelers, and hence their respective passports cannot be used when entering China. Therefore, permanent and non-permanent residents of Hong Kong SAR and Macau SAR who are Chinese nationals should apply for a Mainland Travel Permit for Hong Kong and Macao Residents, an ID card like travel document, in order to enter Mainland China, regardless of whether arriving from Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan or from overseas. This permit is valid for 10 years, and can only be applied through the China Travel Service in Hong Kong and Macau. Holder of this permit can enter Mainland China with any purpose of entry and can remain in Mainland China indefinitely, although their employment rules and social benefits are different from Chinese nationals with hukou.
The government of People's Republic of China (PRC) also does not recognize Republic of China (Taiwan) (ROC), and consider all territories of Taiwan as part of its own. Hence, travelling between Taiwan and Mainland China are not considered by PRC government as international travel. As a result, ROC passports are not accepted for entry and transit through Mainland China, and ROC nationals with residence in Taiwan ("residence" is defined as the eligibility of holding a Taiwanese National ID Card) are required to apply for a Mainland Travel Permit for Taiwan Residents when visiting Mainland China. The Permit is valid for 5 years and allows the holder to remain in Mainland China for up to 5 years as well as unlimited visit to Mainland China. A 30-day stay for each visit to Hong Kong and Macau is also permitted with the permit. A single-entry travel permit can also be obtained from some ports of entry of Mainland China on arrival.[18] Holder of this permit can also take up employment in Mainland China and can enjoy social benefits in certain municipalities like Shanghai, which are only offered to local residents.[19]
The Home Return Permit can only be applied through China Travel Service (CTS) in Hong Kong and Macau, and the Mainland Travel Permit for Taiwan Residents can be applied in Taiwan through travel agencies in Taiwan, or through CTS in Hong Kong and Macau.
PRC nationals residing in Hong Kong and Macau, as well as all ROC nationals (including those without right of residence in Taiwan), can apply for a passport-like Chinese Travel Document through the Chinese foreign missions if they are residing outside the Greater China region. The travel document is valid for up to two years. Those who also have multiple citizenship with other countries, however, are not eligible to apply for the travel document, and they must use their non-SAR or ROC passports (along with appropriate visas) to travel to Mainland China, or they can apply for Home Return Permits or Taiwan Compatriot Permits if they are physically in Hong Kong, Macau or Taiwan and they are eligible to do so.
| Nationality | Residency | Travel with... | Validity | Number of entries | Duration of stay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mainland Travel Permit for Hong Kong and Macao Residents (Home Return Permit)[20] | 10 years (for adults over 18), 5 years (for minors) | Multiple | Unlimited stay | ||
| Mainland Travel Permit for Taiwan Residents (Taiwan Compatriot Permit)[18] | 5 years | Multiple | Up to 5 years | ||
| 3 months | Single | 3 months | |||
| None (or other countries) | Chinese Travel Document | 2 years (maximum) | Multiple | Up to 2 years |
Other visa-free arrangements
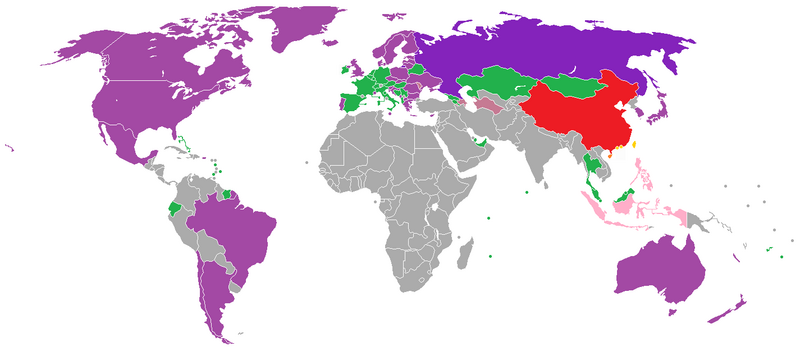
Tour groups
Citizens of following countries may visit China without a visa for up to 30 days if traveling as part of a tour group that is accompanied by a representative of a tour operator registered in both countries:[1]
Crew members
Citizens of following countries may visit China without a visa if they are travelling as part of the airline crew:[1]
1 - only when travelling on duty with Emirates Airlines.
In addition, visa is not required for crew members of airlines that have an agreement with the Chinese government exempting crew members.
Visa-free transit
24-hour transit
Visas are not required for any travelers who:
- arrives and departs from an international airport (except for Fuzhou Changle International Airport and Yanji Chaoyangchuan Airport, where all passengers in transit are required to hold a visa);
- holds confirmed air ticket receipts to a third-country final destination outside Mainland China with assigned seats, and
- departs Mainland China within 24 hours (if transiting through Urumqi Diwopu International Airport, passengers are permitted to stay in transit for a maximum of 2 hours, afterwards they need to either continue to other domestic transit points and depart China in the next 22 hours, or depart from Urumqi immediately in the 2-hour period on an international flight).[21][1]
The 24-hour transit rule allows multiple stops within Mainland China, as long as the traveler has a flight segment leaving Mainland China in 24 hours, so it's possible to enter through a port of entry in China, take multiple segments of domestic flights within China, and depart from a different port of entry in under 24 hours. Contrary to the transit rules of other countries, all travelers in transit are required to go through immigration even if they do not intend to leave the airport, except for passengers arriving and departing from Beijing Capital International Airport where they can proceed directly to the sterile transit area without immigration checks.
Leaving the transit area is allowed even for passengers who only have one transit point within Mainland China, however they must also depart China within 24 hours.[1]
Nationals of ![]() Canada and
Canada and ![]() United States cannot use the multiple-stop transit within China if transiting through Tianjin Binhai International Airport, Weihai Dashuibo Airport, Wuhan Tianhe International Airport, Xi'an Xianyang International Airport or Zhengzhou Xinzheng International Airport.[1]
United States cannot use the multiple-stop transit within China if transiting through Tianjin Binhai International Airport, Weihai Dashuibo Airport, Wuhan Tianhe International Airport, Xi'an Xianyang International Airport or Zhengzhou Xinzheng International Airport.[1]
This rule applies to most nationalities, except for nationals of ![]() Republic of China (Taiwan) who cannot transit solely with their ROC passports and are required to hold either the Mainland Travel Permit for Taiwan Residents or the Chinese Travel Document even if they don't leave the airport or the transit area; British National (Overseas) travelling on a BN(O) passport (a Home Return Permit or a visa is required depending on holder's ethnicity); and holders of Hong Kong Document of Identity for Visa Purposes or Macau SAR Travel Permit (also require Home Return Permits or visas).[18]
Republic of China (Taiwan) who cannot transit solely with their ROC passports and are required to hold either the Mainland Travel Permit for Taiwan Residents or the Chinese Travel Document even if they don't leave the airport or the transit area; British National (Overseas) travelling on a BN(O) passport (a Home Return Permit or a visa is required depending on holder's ethnicity); and holders of Hong Kong Document of Identity for Visa Purposes or Macau SAR Travel Permit (also require Home Return Permits or visas).[18]
Nationals of these countries require a visa to transit through Urumqi:[1]
In addition, nationals of ![]() Syria are not eligible for visa-free transit if transiting through Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport.[1]
Syria are not eligible for visa-free transit if transiting through Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport.[1]
72-hour stay / 144-hour stay
Holders of passports issued by the following 49 countries do not need a visa for a 72-hour or a 144-hour[22][23] stay (duration of stay starts from 12:01 AM of the next day of arrival) if they are transiting through the following ports of entry, provided that they:
- enter through a port of entry listed below;
- hold valid passports and visas for the destination countries (if required); and
- hold ticket receipts with confirmed seats departing in 72 or 144 hours, which shows that their first destination (including stopovers) outside China is a third country.
Hong Kong and Macau are considered as third countries for transit purposes.
Travelers utilizing this scheme are only authorized to visit certain municipalities or provinces listed below, cannot leave the municipalities or provinces and must depart from the same port of entry, except for travelers who enters through ports of entry marked with # below, in which they can also depart from any port of entry marked with #.[24][25][26] In December 2014, the authorities proposed to extend the allowed stay to 96 hours and to allow all visitors when they transfer via Beijing regardless of nationality.[27] Starting from 30 January 2016, any travelers who enter through any ports of entry marked with # in the list below can stay in the permitted areas for up to 144 hours.[22]
Eligible countries
|
1 - for holders of diplomatic or official passports.
2 - for British citizens only.
Eligible ports of entry
Region-specific visa regulations
The Chinese government has implemented visa waiver schemes for foreign nationals travelling to particular areas of Mainland China.[42]
Dalian Transit Visa on Arrival for Merchant Seamen
Merchant Seamen can obtain a 7-day visa on arrival at Dalian Zhoushuizi International Airport for a fee of US$168 if they satisfy the following requirements:[1]
- They are nationals of a country which has diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China
- They have a ticket to a third country
- They are not nationals of the following countries:
Visa-Free Group Tour to Pearl River Delta
All visitors to Hong Kong and/or Macao are able to visit the surrounding Pearl River Delta visa-free as long as the following conditions are met:[43]
- The visitor is a national of a country which has diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China
- The visitor is visiting the Pearl River Delta as part of a tour group organised by a Hong Kong or Macao based travel agency
- The stay is for six days or less (21 days for citizens of
 Germany,
Germany,  Russia and
Russia and  South Korea)
South Korea) - The visitor stays only within the cities of Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Zhuhai, Foshan, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Jiangmen, Zhaoqing, Huizhou and Shantou.
Special Economic Zone Visa on Arrival
Visitors from most countries may obtain an entry visa when travelling to and staying solely in the three Special Economic Zones: Shenzhen, Zhuhai and Xiamen.[44] Visitors can only travel within these cities and cannot proceed further into other parts of Mainland China. Visa for Shenzhen is valid for 5 days, and visa for Xiamen and Zhuhai is valid for 3 days. The visa can only be obtained only upon arrival at Luohu Port, Huanggang Port Control Point, Fuyong Ferry Terminal or Shekou Passenger Terminal for Shenzhen;[45] Gongbei Port of Entry, Hengqin Port or Jiuzhou Port for Zhuhai;[46] and Xiamen Gaoqi International Airport for Xiamen.[47] Visa fees are charged on a reciprocal basis ranging from ¥168 to ¥420.
Nationals of the following countries are ineligible for the SEZ visa for Shenzhen:[48]
Hainan Province
Group Tour Visa Waiver
Nationals of the following countries can visit Hainan Island without a visa for no more than 15 days if they are visiting as part of a tour group organised by a travel agency approved by National Tourism Administration and based in Hainan with a party of 5 or more people unless otherwise stated:[49][1]
1 - Nationals of these countries can stay for up to 21 days with a tour group of a minimum of 2 people.
2 - for British citizens only.
Visa on Arrival
Citizens of the following countries can obtain a visa on arrival at a cost of ¥200 for a maximum stay of 15 days if holding two passport photos and arriving from Haikou Meilan International Airport or Sanya Phoenix International Airport:[1]
1 - for British citizens only.
Border area
- Citizens of
 Russia that are residents of Amur Oblast may visit Heihe without a visa for a day.[50]
Russia that are residents of Amur Oblast may visit Heihe without a visa for a day.[50] - Citizens of
 Russia may visit Suifenhe without a visa for up to 15 days if travelling with at least one companion.[51]
Russia may visit Suifenhe without a visa for up to 15 days if travelling with at least one companion.[51] - Citizens of
 Kazakhstan can visit Jeminay County (East Kazakhstan Region residents) and Tacheng in Xinjiang without a visa for three days.[52][53]
Kazakhstan can visit Jeminay County (East Kazakhstan Region residents) and Tacheng in Xinjiang without a visa for three days.[52][53]
Visa for Hong Kong residents who are not Chinese nationals
Non-visa-exempt nationals who are residents of Hong Kong require a visa to visit the Mainland. Hong Kong Permanent Residents may apply for a 3-year multiple entry visa. Hong Kong non-Permanent Residents can apply for a 1-year multiple entry visa. In most cases the length of stay for each individual trip is one 30 days. For non-Chinese Nationals, currently it is not possible to apply for a resident visa for Mainland China based on the applicant's status as a Hong Kong Permanent Resident.
Visa-on-arrival for emergency purposes
Visitors who would normally require a visa are able to obtain a visa on arrival at the following airports if they satisfy the following requirements:[1]
- have genuine emergencies which prevent them from applying a visa in advance;
- hold an invitation letter issued by a sponsor or Chinese authorities;
- have made arrangements with the immigration authorities at the arriving airport; and,
- have a government-approved sponsor to meet them at the airport.
Visas can be issued at the following airports:[1]
For a maximum stay of 3 months
For a maximum stay of 1 month
- Chengdu Shuangliu International Airport
- Fuzhou Changle International Airport
- Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport
- Shanghai Pudong International Airport
- Xiamen Gaoqi International Airport
No additional restrictions on stay
- Chongqing Jiangbei International Airport
- Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport
- Guilin Liangjiang International Airport
- Haikou Meilan International Airport
- Kunming Changshui International Airport
- Qingdao Liuting International Airport
- Sanya Phoenix International Airport
- Shenzhen Bao'an International Airport
- Weihai Dashuibo Airport
- Wuhan Tianhe International Airport[54]
- Xi'an Xianyang International Airport
- Yantai Laishan International Airport
The service is not applicable to the following nationals:
In addition to those listed above, nationals of the following countries are not eligible for visa-on-arrival service at Beijing:
Nationals of the following countries, in addition to those listed above, are not eligible for visa-on-arrival at Chengdu, Fuzhou, Shanghai (Pudong and Hongqiao), and Xiamen:
Nationals of ![]() Republic of China (Taiwan) are not eligible for visa on arrival since the PRC government refuse to recognize their passports, but they can obtain a single-entry Taiwan Compatriot Permit on arrival at some airports if they have never held a long-term Taiwan Compatriot Permit.[1] Residents of
Republic of China (Taiwan) are not eligible for visa on arrival since the PRC government refuse to recognize their passports, but they can obtain a single-entry Taiwan Compatriot Permit on arrival at some airports if they have never held a long-term Taiwan Compatriot Permit.[1] Residents of ![]() Hong Kong and
Hong Kong and ![]() Macau are not eligible since they are Chinese nationals and should use their Home Return Permits. Stateless persons and refugees are also not eligible for this service.
Macau are not eligible since they are Chinese nationals and should use their Home Return Permits. Stateless persons and refugees are also not eligible for this service.
Visa facilitation agreements
China has concluded visa facilitation agreements on a reciprocal basis with the following countries:
Overview
| Nationality | Validity of visa | Types of visas affected | Fee |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 years | L, M, Q2, S2 | US$140 | |
| 5 years | X1 | ||
| Up to 9 years and 11 months | L, M, Q2, S2 | CA$100 | |
| 2 years 5 or 10 years (for eligible persons) |
L, M, Q2, S2 | £85 | |
| Unchanged | F, L, M, Q2 | Gratis | |
| 10 years | L, M | TBA |
United States
Since November 2014, China agreed to issue L Tourist visas, M Business visas, Q2 Family Visit visas, and S2 Short-term Private Visit visas to citizens of ![]() United States with a validity for a maximum of 10 years; while validity of X1 Long-term Study visa is elongated to five years. The duration of stay is 60 days per entry for L and M visas, 90 days for S2 visas, and 120 days for Q2 visas. Visa applicants can enjoy a 180-day duration of stay when applying for Q2 visas if they have "special needs". The application fee for a Chinese visa is US$140.[55][56]
United States with a validity for a maximum of 10 years; while validity of X1 Long-term Study visa is elongated to five years. The duration of stay is 60 days per entry for L and M visas, 90 days for S2 visas, and 120 days for Q2 visas. Visa applicants can enjoy a 180-day duration of stay when applying for Q2 visas if they have "special needs". The application fee for a Chinese visa is US$140.[55][56]
Canada
Starting from March 2015, China announced that multiple-entry L, M, Q2, and S2 visas with the validity for up to nine years and 11 months (not exceeding the life of the passport) would be issued to citizens of ![]() Canada.[57] The duration of stay is 60 days per entry for L and M visas, 90 days for S2 visas, and 120 days for Q2 visas. Visa applicants who are of Chinese descent can enjoy a 180-day duration of stay when applying for Q2 visas. The application fee is CA$100.[58]
Canada.[57] The duration of stay is 60 days per entry for L and M visas, 90 days for S2 visas, and 120 days for Q2 visas. Visa applicants who are of Chinese descent can enjoy a 180-day duration of stay when applying for Q2 visas. The application fee is CA$100.[58]
United Kingdom
In January 2016, Chinese authorities announced that 2-year, multiple-entry L, M, Q2, S2 visas are to be issued to citizens and nationals of ![]() United Kingdom, and the application fee is £85. In addition, Chinese foreign missions can issue visas with 5 or 10 years of validity for "eligible" British citizens and nationals.[59]
United Kingdom, and the application fee is £85. In addition, Chinese foreign missions can issue visas with 5 or 10 years of validity for "eligible" British citizens and nationals.[59]
Chile
Arrangements were made between Chinese and Chilean governments regarding visa fees. Starting from July 2015, Citizens of ![]() Chile can have their visa fees waived when applying for F, L, M, and Q2 visas.[60]
Chile can have their visa fees waived when applying for F, L, M, and Q2 visas.[60]
Argentina
Another agreement, signed by Argentine and Chinese governments, claimed to have "facilitates application procedures" for Argentine citizens applying for Chinese visas, In reality, the procedures, processing times and validity have remain unchanged for Argentine, since the agreement in fact only facilitated the lengthy visa application procedures for Chinese nationals.[61]
Israel
China and Israel's visa facilitation agreements, signed on 29 March 2016, provide citizens of ![]() Israel access to 10-year L and M visas. The details are not yet announced.[62][63]
Israel access to 10-year L and M visas. The details are not yet announced.[62][63]
Overview of Chinese visas
Visa application procedures

Nationals who are not visa exempt are required to apply for a Chinese visa prior to entry into China. When applying for a visa, the applicant can choose to apply either through a travel agency or directly to the Chinese diplomatic missions.
In the latter case, the local diplomatic mission may outsource the handling of application to a Chinese Visa Application Service Centre (Visa Centre), or a Chinese Visa Application Service Facility (CVASF). The Visa Centre is "a commercial service organization registered in accordance with local laws and regulations and recognized by a Chinese Embassy or Consulate-General to handle the daily routine work of processing ordinary visa applications".[64] The CVASF is similar organization but is run exclusively by VFS Global.[65] Visa applicants, whose resident countries host Visa Centres or CVASFs, are required to submit their applications to these organizations instead of the Chinese embassies or consulates.
As of April 2016, the following 19 countries host Visa Centres:[66]
In addition, CVASFs are available in the following countries:[67]
In countries without Visa Centres or CVASFs, visa application requires submitting the passport and required documents directly to the embassy or consulate.
Nationals of the following countries must hold a visa issued in their home country. If visa is issued in a third country, a residence visa or working permit from that country is also required. [1]
1 - for holders of normal passports only.
Types of Chinese Visas
There are four main types of Chinese visa: diplomatic visa, courtesy visa, service visa and ordinary visa. Ordinary visas are further divided into 12 sub-types or 16 categories.[68] The sub-type codes of ordinary visas derive from the first letter of the names in Pinyin.[69][70]
| Code | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| C | Crew Visa (乘务签证) |
Issued to foreign crew members of means of international transportation, including aircraft, trains and ships, or motor vehicle drivers engaged in cross-border transport activities, or to the accompanying family members[Note 1] of the crew members of the above-mentioned ships. |
| D | Permanent Residence Visa (定居签证) |
Issued to those who intend to reside in China permanently. Chinese government has started to implement new permanent residence policy for foreigners to attract and introduce technical talents and experts since August 2014.[71] |
| F | Visit Visa (访问签证) |
Issued to those who intend to go to China for exchanges, visits, study tours and other activities. |
| G | Transit Visa (过境签证) |
Issued to those who intend to transit through China. |
| J1 | Long-term Journalist Visa (常驻记者签证) |
Issued to resident foreign journalists of foreign news organizations stationed in China. The intended duration of stay in China exceeds 180 days. |
| J2 | Short-term Journalist Visa (临时记者签证) |
Issued to foreign journalists who intend to go to China for short-term news coverage. The intended duration of stay in China is no more than 180 days. |
| L | Tourist Visa (旅游签证) |
Issued to those who intend to go to China as a tourist. |
| M | Business Visa (商贸签证) |
Issued to those who intend to go to China for commercial and trade activities. |
| Q1 | Family Reunion Visa (家庭团聚签证) |
Issued to those who are family members[Note 1] of Chinese citizens or of foreigners with Chinese permanent residence and intend to go to China for family reunion, or to those who intend to go to China for the purpose of foster care. The intended duration of stay in China exceeds 180 days. |
| Q2 | Family Visit Visa (探亲签证) |
Issued to those who intend to visit their relatives who are Chinese citizens residing in China or foreigners with permanent residence in China. The intended duration of stay in China is no more than 180 days. |
| R | Talent Visa (人才签证) |
Issued to those who are high-level talents or whose skills are urgently needed in China. |
| S1 | Long-term Private Visit Visa (长期私人事务签证) |
Issued to those who intend to go to China to visit the foreigners working or studying in China to whom they are spouses, parents, sons or daughters under the age of 18 or parents-in-law, or to those who intend to go to China for other private affairs. The intended duration of stay in China exceeds 180 days. |
| S2 | Short-term Private Visit Visa (短期私人事务签证) |
Issued to those who intend to visit their family members[Note 1] who are foreigners working or studying in China, or to those who intend to go to China for other private matters. The intended duration of stay in China is no more than 180 days. |
| X1 | Long-term Study Visa (长期学习签证) |
Issued to those who intend to study in China for a period of more than 180 days. |
| X2 | Short-term Study Visa (短期学习签证) |
Issued to those who intend to study in China for a period of no more than 180 days. |
| Z | Working Visa (工作签证) |
Issued to those who intend to work in China. |
Validity, Number of Entries and Duration of Each Stay of Chinese Visas
- The "Enter Before" date is the expiration date of the visa. The visa can be used for entry into China from the date of issue until the "Enter Before" date indicated on the visa. If a visa has unused entries, the bearer can enter China before 00:00 Beijing Time on the expiration date.[68]
- "Entries" refers to the number of times permitted to enter China during the validity of the visa. A visa becomes invalid if there are no entries left, or if there are entries left but the visa has expired. If a visa becomes invalid, its bearer must apply for a new visa before entering China. Traveling with an invalid visa will result in refusal of entry.[68]
- "Duration of Each Stay" refers to the maximum number of days the visa bearer is permitted to remain in China for each visit. The duration of stay is calculated from (and includes) the date of entry into China.[68]
A non-Chinese national who overstays the period of his or her authorized stay in China without applying for an extension is subject to fines and other penalties for violation of the Law of the People's Republic of China on Control of the Entry and Exit of Aliens and its Detailed Rules for Implementation. If a visa bearer needs to stay in China longer than the duration of stay allowed on the visa, approval must be obtained from county-level PSBs before the duration of stay expires. Approval of an extension of stay may not be granted, in which case the bearer must depart China immediately. Chinese diplomatic missions are not authorized to extend a visa.[68]
Holders of D, Q1, J1, S1, X1 and Z visas must apply for a residence permit at the local PSB within 30 days of entry into China, unless the "Duration of Each Stay" on the visa is marked as 30 days. Members of foreign diplomatic or consular missions in China must also apply for a residence permit at the Ministry of Foreign Affairs or local Foreign Affairs Offices (FSOs) within 30 days of entry into China.[68]
Region-specific visa restrictions
Tibet Autonomous Region
Non-Chinese passport holders entering Tibet must have a Tibet Travel Permit (TTP), issued by the Tibet Tourism Bureau. Although any travel between Tibet and other party of Mainland China is considered domestic travel with no immigration checks (unlike Hong Kong and Macau), the TTP will be checked for all non-Chinese when going on board any buses, trains or airlines that are bound for the TAR.
The only way to obtain a TTP is to arrange a tour operated by a Tibet-based travel agent which at least includes hotels and transportation. Visitors are also not permitted to travel by public buses across Tibet and are only allowed to travel by private transportation as organised in the tour. Moreover, if entering Tibet from Nepal, one must also join a group tour and be only allowed on a group visa. The TTP has to be handed in to the tour guide upon arrival at the airport or train station, and the tour guide will keep the permit until the traveler leaves the TAR.
The TTP is also required by citizens of Republic of China (Taiwan) holding a Taiwan Compatriot Permit, but it is not required for Chinese nationals residing in Hong Kong or Macau with a Home Return Permit or any person with a Chinese Resident Identity Card.[72]
See also
Notes
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s "Visa Information - China". Timatic. IATA. Retrieved 17 December 2013.
- ^ Exit-Entry Administration Law, article 15.
- ^ [1]
- ^ 境外人员临时住宿登记
- ^ 中华人民共和国政府和圣马力诺共和国政府关于互免签证的协定
- ^ 中华人民共和国和外交部. "中国和巴哈马关于互免签证的协定将于2014年2月12日生效". 中国领事服务网. Retrieved 2014-03-29.
- ^ 京华时报. "中斐互免签证今日生效 持护照入境可停留30日". 网易新闻. Retrieved 2015-03-13.
- ^ Visa-free travel to Europe, China for Grenadians
- ^ 中华人民共和国和外交部. "中国政府和毛里求斯政府关于互免签证的协定即将生效". 中国领事服务网. Retrieved 2014-03-29.
- ^ 中华人民共和国和外交部. "中国政府和塞舌尔政府关于互免签证的协定即将生效". 中国领事服务网. Retrieved 2014-03-29.
- ^ a b 中华人民共和国外交部. "持普通护照短期来华的新加坡公民、文莱公民自二00三年七月一日起实行免办签证待遇". 中国领事服务网. Retrieved 2014-03-29.
- ^ "关于对短期来华日本公民实行免签的通知". 中国驻福冈总领事馆. Retrieved 2014-03-29.
- ^ 中华人民共和国和外交部. "自2008年7月1日起新加坡公民来华需事先办妥签证". 中国领事服务网. Retrieved 2014-03-29.
- ^ 中华人民共和国和外交部. "自2008年9月19日起恢复对持普通护照新加坡公民短期来华免签安排". 中国领事服务网. Retrieved 2014-03-29.
- ^ Eng, Dennis (22 September 2008). "Mainland visa restrictions on foreigners in HK to be lifted". South China Morning Post.
- ^ "''Mutual visa-free agreement between China and Foreign Countries''" (PDF). Retrieved 2016-03-02.
- ^ ABTC Summary
- ^ a b c https://www.timaticweb.com/cgi-bin/tim_website_client.cgi?SpecData=1&VISA=&page=visa&NA=TW&AR=00&PASSTYPES=PASS&DE=CN&user=KLMB2C&subuser=KLMB2C
- ^ http://www.spcsc.sh.cn/shrdgzw/node4/node22/node36/n116/u1ai116934.html 上海市台湾同胞投资权益保护规定
- ^ https://www.timaticweb.com/cgi-bin/tim_website_client.cgi?SpecData=1&VISA=&page=visa&NA=HK&AR=00&PASSTYPES=PASS&DE=CN&user=KLMB2C&subuser=KLMB2C
- ^ "Information about Visas not required". fmprc.gov.cn. Embassy of the People's Republic of China in the Republic of Indonesia. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Ministry of Public Security. "中华人民共和国公安部公告".
- ^ China's Yangtze River Delta Now Offers 144-hour Visa-free Entry
- ^ 关于将塞尔维亚等6国列入72小时过境免签政策国家名单的通知
- ^ [2]
- ^ Answers to Frequently Asked Questions Concerning 72-hour Transit Visa Exemption for Foreign Nationals Measure at Airports of Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou and Chengdu
- ^ Beijing Plans to Attract International Tourists with Extended Visa Policy
- ^ a b c d e 中华人民共和国公安部出入境管理局. "北京、上海、广州、成都机场实行外国人72小时过境免签政策及常遇问题解答".
- ^ Changsha to offer 72-hour visa-free entry
- ^ a b c 中华人民共和国公安部出入境管理局. "重庆、沈阳、大连机场实施外国人72小时过境免签政策".
- ^ 桂林生活网. "桂林72小时过境免签7月28日起实施 边检做详细说明".
- ^ 新华网. "杭州:航空口岸72小时过境免签".
- ^ Harbin offers 72-hour visa-free entry
- ^ "Harbin Will Offer Transit without Visa 72 Hours for Foreign Visitors".
- ^ 云南网. "72小时过境免签政策 方便国外旅客游昆明". 新华网云南频道.
- ^ "Nanjing now Offering Transit without Visa 72 Hours for Foreign Visitors".
- ^ iQTV-Qingdao News. "青岛国际机场口岸对51个国家的公民实施72小时过境免签政策".
- ^ 北方网. "6月8日起天津将实施外国人72小时过境免签政策".
- ^ 中国民用航空中南地区管理局. "武汉天河机场口岸即将实施72小时过境免签". 中国民用航空中南地区管理局.
- ^ 西安市外事侨务办公室. "西安实行"72小时过境免签"".
- ^ 厦门网. "51个国家的外国人过境厦门 即可免签停留72小时".
- ^ "北京、上海、广州机场实行外国人72小时过境免签政策及常遇问题解答". Bureau of Exit and Entry Administration of the Ministry of Public Security. 2013-08-07. Retrieved 2013-08-29.
- ^ "Visa-free Entry into Mainland China". Embassy of the People's Republic of China in Australia. Retrieved August 2014.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ http://www.mps.gov.cn/n16/n1555903/n1555963/n1556053/n1640330/3880657.html
- ^ http://www.sz.gov.cn/cn/bmtx/200609/t20060915_104724.htm
- ^ http://www.zhuhai.gov.cn/xxgk/xwzx/zhyw/201512/t20151222_8870721.html
- ^ "Shenzhen Visa". About.com. Retrieved November 2013.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ http://www.travelchinaguide.com/embassy/visa/service.htm Visa on Arrival (Issued at Entry Ports)
- ^ "常见问题". 海南旅游咨询网.
- ^ Where Amur connects Russia and China
- ^ 新华网. "Sino-Russian border city to offer visa-free stays".
- ^ 3-day visa-free stay for Kazakhstanis in Chinese Tacheng
- ^ Kazakhstan citizens enjoy 72-hour visa-free services at Jeminay Port
- ^ "武汉航空口岸取得落地签证权". Retrieved 2011-12-08.
- ^ http://www.chinanews.com/gn/2014/11-12/6767333.shtml 中国实施对美新签证措施 4类签证可获10年有效期
- ^ 2015 American Business in China White Paper. Beijing, China: The American Chamber of Commerce in China. 2015. p. 132.
- ^ http://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/national/china-agrees-to-provide-10-year-visas-to-canadians/article23353672/ China agrees to provide 10-year visas to Canadians
- ^ https://www.visaforchina.org/YTO_ZH/generalinformation/news/276343.shtml 关于中国-加拿大十年多次签证的互惠安排
- ^ http://www.chinese-embassy.org.uk/eng/visa/notice/t1330627.htm Chinese Embassy and Consulates in the UK to Issue Two-year Multi-entry Visas to British Nationals
- ^ http://cs.mfa.gov.cn/gyls/lsgz/fwxx/t1275440.shtml 中国和智利便利人员往来互惠安排即将生效
- ^ 关于转发中阿便利双方旅游人员签证协定的通知
- ^ 中国以色列互发十年签证
- ^ Israel and China to sign 10-year multiple entry visa deal
- ^ About the Visa Centre
- ^ Apply for VISA to China In Kenya
- ^ Visa Centres
- ^ VFS Global
- ^ a b c d e f "Introduction to Chinese Visa". Chinese Embassy in the USA.
- ^ 申请办理中华人民共和国签证须知
- ^ "About Chinese Visa". Chinese Embassy in the USA.
- ^ 中国新闻网. "中国正式发布实施"绿卡"制度 以吸纳外籍人才". 新浪新闻.
- ^ Tibet Tourism Bureau Permit


