BZIP domain: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
The '''Basic Leucine Zipper Domain''' ('''bZIP domain''') is found in many [[DNA]] binding eukaryotic proteins. One part of the domain contains a region that mediates sequence specific DNA binding properties and the [[leucine zipper]] that is required for the dimerization of two DNA binding regions. The DNA binding region comprises a number of basic aminoacids such as [[arginine]] and [[lysine]]. Proteins containig this domain are [[transcription factors]]. |
The '''Basic Leucine Zipper Domain''' ('''bZIP domain''') is found in many [[DNA]] binding eukaryotic proteins. One part of the domain contains a region that mediates sequence specific DNA binding properties and the [[leucine zipper]] that is required for the dimerization of two DNA binding regions. The DNA binding region comprises a number of basic aminoacids such as [[arginine]] and [[lysine]]. Proteins containig this domain are [[transcription factors]]. |
||
==bZIP transcription factors== |
|||
bZIP transcription factors are found in all organisms. A recent evolutionary study revealed that 4 bZIP genes were encoded in the last recent common ancestor of all plants <ref name="pmid18698409 ">. |
|||
bZIP transcription factors are found in all organisms. A recent evolutionary study revealed that 4 bZIP genes were encoded by the genome of the [[most recent common ancestor]] of all plants <ref name="pmid18698409 ">{{cite journal |author=Corrêa LGG, Riaño-Pachón DM, Schrago CG, dos Santos RV, Mueller-Roeber B, Vincentz M. |title=The role of bZIP transcription factors in green plant evolution: adaptive features emerging from four founder genes |journal=PLos ONE |volume=3 |issue=8 |pages=e2944 |year=2008 |pmid=18698409 |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0002944}}</ref>. |
|||
==bZIP domain containing proteins== |
==bZIP domain containing proteins== |
||
*AP-1 [[fos]]/[[Jun (protein)|jun]] heterodimer that forms a [[transcription factor]] |
*AP-1 [[fos]]/[[Jun (protein)|jun]] heterodimer that forms a [[transcription factor]] |
||
*[[Jun-B]] transcription factor |
*[[Jun-B]] transcription factor |
||
| Line 57: | Line 61: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
*[http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/smart/do_annotation.pl?DOMAIN=BRLZ bZIP domain entry in the SMART database] |
*[http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/smart/do_annotation.pl?DOMAIN=BRLZ bZIP domain entry in the SMART database] |
||
*[http://plntfdb.bio.uni-potsdam.de/v2.0/fam_mem.php?family_id=bZIP Plant bZIP transcription factors] |
|||
== References == |
== References == |
||
Revision as of 05:57, 18 August 2008
It has been suggested that this article be merged with Leucine zipper. (Discuss) Proposed since December 2007. |
| bZIP transcription factor | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
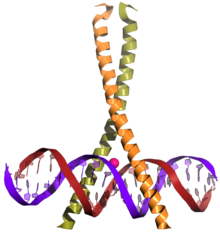 CREB (top) is a transcription factor capable of binding DNA via the bZIP domain (bottom) and regulating gene expression. | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | bZIP_1 | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF00170 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR011616 | ||||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00036 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1ysa / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
The Basic Leucine Zipper Domain (bZIP domain) is found in many DNA binding eukaryotic proteins. One part of the domain contains a region that mediates sequence specific DNA binding properties and the leucine zipper that is required for the dimerization of two DNA binding regions. The DNA binding region comprises a number of basic aminoacids such as arginine and lysine. Proteins containig this domain are transcription factors.
bZIP transcription factors
bZIP transcription factors are found in all organisms. A recent evolutionary study revealed that 4 bZIP genes were encoded by the genome of the most recent common ancestor of all plants [1].
bZIP domain containing proteins
- AP-1 fos/jun heterodimer that forms a transcription factor
- Jun-B transcription factor
- CREB cAMP response element transcription factor
- OPAQUE2 (O2) transcription factor of the 22-kD zein gene that encodes a class of storage proteins in the endosperm of maize (Zea Mays) kernels
Human proteins containing this domain
ATF1; ATF2; ATF4; ATF5; ATF6; ATF7; BACH1; BACH2; BATF; BATF2; CREB1; CREB3; CREB3L1; CREB3L2; CREB3L3; CREB3L4; CREB5; CREBL1; CREM; E4BP4; FOSL1; FOSL2; JUN; JUNB; JUND; NFE2; NFE2L2; NFE2L3; SNFT; CREM
External links
References
- ^ Corrêa LGG, Riaño-Pachón DM, Schrago CG, dos Santos RV, Mueller-Roeber B, Vincentz M. (2008). "The role of bZIP transcription factors in green plant evolution: adaptive features emerging from four founder genes". PLos ONE. 3 (8): e2944. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002944. PMID 18698409.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
