Hyderabad: Difference between revisions
Dwaipayanc (talk | contribs) →Nizam period: copy-edit; taking out some details (may be too much detail for this early part of history in this summarized article); adding a general sentence on modernization of the city |
|||
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
===Nizam period=== |
===Nizam period=== |
||
{{See also|Nizam of Hyderabad}} |
{{See also|Nizam of Hyderabad}} |
||
The sixth of Aurangzeb's successors, [[Farrukhsiyar]] appointed [[Asaf Jah I]] as the Viceroy of the Deccan in 1712, with the title of "[[Nizam|Nizam-ul-Mulk]]" (Regulator of the Realm) ''Fateh Jung''. In 1724, [[Asaf Jah I]] gained autonomy by defeating a rival official to establish control over the Deccan Suba and named it "[[Hyderabad State|Hyderabad Deccan]]", thus starting the dynasty which came to be known as the Asaf Jahi dynasty. The rulers retained the title "Nizam ul-Mulk", and were referred to as Asif Jahi Nizams, or Nizams of Hyderabad.<ref name="Richards"/><ref name="columbia&TOI"/> |
The sixth of Aurangzeb's successors, [[Farrukhsiyar]] appointed [[Asaf Jah I]] as the Viceroy of the Deccan in 1712, with the title of "[[Nizam|Nizam-ul-Mulk]]" (Regulator of the Realm) ''Fateh Jung''. In 1724, [[Asaf Jah I]] gained autonomy by defeating a rival official to establish control over the Deccan Suba and named it "[[Hyderabad State|Hyderabad Deccan]]", thus starting the dynasty which came to be known as the Asaf Jahi dynasty. The rulers retained the title "Nizam ul-Mulk", and were referred to as Asif Jahi Nizams, or Nizams of Hyderabad.<ref name="Richards"/><ref name="columbia&TOI"/> Following the death of Asaf Jah I in 1748, there was political unrest due to the feud on ascension to the throne among the sons of Asaf Jah I, aided by the opportunistic neighbouring states and colonial foreign forces. The reign of [[Ali Khan Asaf Jah II|Asif Jah II]] brought an end to the political instability. The Nizam signed the treaty of [[Masulipatnam]] in 1768 with the [[East India Company]]; through this treaty the Nizam surrendered the coastal region to the East India Company, in return the East India Company would have to pay a fixed annual rent to the Nizam.<ref name="Reg Sal Geo">{{cite book|title=Nizam-British relations, 1724–1857|publisher=Concept Publishing| pages=130–150|isbn=81-7022-195-1|last=Regani|first=Sarojini|year=1988}} |
||
* {{cite book|title=A comprehensive history of medieval India|publisher=[[Dorling Kindersley]]|page=346|isbn=978-81-317-3202-1|last=Farooqui|first=Salma Ahmed|year=2011}} |
* {{cite book|title=A comprehensive history of medieval India|publisher=[[Dorling Kindersley]]|page=346|isbn=978-81-317-3202-1|last=Farooqui|first=Salma Ahmed|year=2011}} |
||
* {{cite book|title=An historical sketch of the native states of India in subsidiary alliance with the British government|publisher=Asian Education Services|pages=280–292|isbn=978-81-206-1971-5|last=Malleson|first= George Bruce|year=2005}} |
* {{cite book|title=An historical sketch of the native states of India in subsidiary alliance with the British government|publisher=Asian Education Services|pages=280–292|isbn=978-81-206-1971-5|last=Malleson|first= George Bruce|year=2005}} |
||
* {{cite book|title=The annals of Indian administration, Volume 14| publisher=BiblioBazaar|page=467|isbn=978-1-145-42314-5|last=Townsend|first=Meredith|year=2010}}</ref> In 1769, Hyderabad city became the formal capital of the |
* {{cite book|title=The annals of Indian administration, Volume 14| publisher=BiblioBazaar|page=467|isbn=978-1-145-42314-5|last=Townsend|first=Meredith|year=2010}}</ref> In 1769, Hyderabad city became the formal capital of the Nizams.<ref name="Richards"/><ref name="columbia&TOI"/> Due to regular threats from the neighboring rulers of [[Hyder Ali|Mysore]], [[Baji Rao I|Maratha]] and Basalath Jung (Asaf Jah II's elder brother supported by [[Marquis de Bussy-Castelnau|De Bussy]]), the Nizam signed a [[subsidiary alliance]] with the East India Company in 1798, allowing [[British Indian Army|British troops]] to stationed at [[Bolaram]] (modern [[Secunderabad]]) to protect the borders of the Hyderabad State, for which the Nizams had to pay an annual maintenance to the British.<ref name="Reg Sal Geo"/> Starting from the late nineteenth century, establishment of railways, transport services, under ground drainage, running water, [[Hussain Sagar Thermal Power Station|electricity]], [[Begumpet Airport|airport]], universities and industries marked the transformation of the city to a modern one. The Nizams ruled the Hyderabad state from the city until 17 September 1948, a year after India's independence from the [[British Raj]].<ref name="Richards"/><ref name="columbia&TOI"/> |
||
===Post-independence=== |
===Post-independence=== |
||
Revision as of 01:07, 31 July 2012
Hyderabad | |
|---|---|
metropolitan city | |
| Top:Golconda Fort, 2nd left:Charminar, 2nd right:Skyline in Hyderabad, 3rd left;Qutb Shahi Tombs, 3rd right:Andhra Pradesh Legislature, Bottom:View of Hussain Sagar Lake and Buddha Statue. Top:Golconda Fort, 2nd left:Charminar, 2nd right:Skyline in Hyderabad, 3rd left;Qutb Shahi Tombs, 3rd right:Andhra Pradesh Legislature, Bottom:View of Hussain Sagar Lake and Buddha Statue. | |
| Nickname: City of Pearls | |
| Country | India |
| State | Andhra Pradesh |
| Region | Deccan |
| Districts | Hyderabad, Rangareddy and Medak |
| Founded | 1591 AD |
| Government | |
| • Body | GHMC, HMDA |
| • Mayor | Mohammad Majid Hussain |
| • City Police Commissioner | Anurag Sharma |
| • Members of Parliament | Asaduddin Owaisi, Anjan Kumar Yadav, Sarve Satyanarayana |
| Area | |
| • metropolitan city | 650 km2 (250 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 536 m (1,759 ft) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • metropolitan city | 6,809,970 |
| • Rank | 4th |
| • Density | 18,480/km2 (47,900/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 7,749,334 |
| Languages | |
| • Official | Telugu and Urdu |
| Time zone | UTC+5:30 (IST) |
| PIN | 500 xxx, 501 xxx, 502 xxx, 508 xxx, 509 xxx |
| Telephone code | 91–40, 8413, 8414, 8415, 8417, 8418, 8453, 8455 |
| Vehicle registration | AP 09, 10, 11, 12, 13, 22, 23, 24, 28 & 29 |
| Coastline | 0 kilometres (0 mi) |
| Planning agency | GHMC, HMDA |
| Climate | Aw (Köppen) |
| Precipitation | 603 millimetres (23.7 in) |
| Avg. annual temperature | 26.0 °C (78.8 °F) |
| Avg. summer temperature | 32 °C (90 °F) |
| Avg. winter temperature | 20.2 °C (68.4 °F) |
| Website | www |
Hyderabad (/ˈhaɪdərəbæd/ ) is the capital of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located on the banks of the Musi River in the Deccan Plateau in southern India. The city has an area of 650 square kilometres (250 sq mi) with a population of 6.8 million, and the metropolitan area contains 7.7 million residents, making it the fourth most populous city and the sixth most populous urban agglomeration in the country. As of 2011, the city had per capita annual income of Indian rupee (₹) 44,300. The city was expanded in 2007 to form the Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation. As a growing metropolitan city in a developing country, Hyderabad confronts substantial urban pollution, traffic congestion, overpopulation and other logistic and socio-economic problems.
Hyderabad was established in 1591 CE by Muhammad Quli Qutb Shah and fell under the rule of the Qutb Shahi dynasty until 1687 when Mughal emperor Aurangzeb conquered the sultanate, and the city became part of the Deccan province of the Mughal empire. In 1724 Asif Jah I, a Mughal viceroy, declared his sovereignty and formed the Asif Jahi dynasty, also known as the Nizams of Hyderabad. The Nizams ruled the princely state of Hyderabad for more than two centuries, under subsidiary alliance with the British Raj. The city remained the princely state's capital from 1769 to 1948—when the Nizam signed an Instrument of Accession with the Indian Union following the Operation Polo. The city became capital of Andhra Pradesh following the 1956 State Reorganisation Act. Since 1969, Hyderabad has been a major center of the Telangana movement, which demands a separate state for the Telangana region of Andhra Pradesh.
Situated at the crossroads of North and South India, Hyderabad is noted for its unique culture. As the former capital of the largest and richest Princely state of India and with the patronage from Nizams, Hyderabad established local traditions in art, literature, architecture and cuisine. The city is a tourist destination and has many places of interest, including the Chowmahalla Palace, Charminar and Golconda fort. Hyderabad is home to several museums, bazaars, galleries, libraries, sporting and other cultural institutions. The Telugu film industry, known as "Tollywood" is based in the city. The city was a global center of the diamond and pearl trade, for which it is known as "City of Pearls", Hyderabad has emerged as a hub for the information technology, pharmaceuticals and biotechnology industries, alongside traditional and service industries since the 1990s. Hyderabad's 13 universities and business schools form a major centre for higher education and research.
History
Etymology
The etymology of Hyderabad is the subject of many myths and apocryphal accounts. One myth postulates that Muhammad Quli Qutb Shah, the founder of Hyderabad, named the city Bhaganagar after Bhagmathi, a local nautch (dancer) girl with whom he fell in love. He married Bhagmathi who converted to Islam and adopted the title Hyder Mahal. The city was renamed in her honour to "Hyderabad", literally meaning "Hyder's abode".[2] Andrew Petersen, a scholar of Islamic architecture, states that the city was originally called Baghnagar which means "the city of gardens".[3] Yet another theory says Hyderabad was named to honour the Caliph Ali Ibn Abi Talib, who was also known as Hyder.[4]
Early and medieval history
Archaeologists have unearthed Iron Age sites near the city that could date back to 500 BCE.[5] The region comprising modern Hyderabad and its surrounding was known as Golkonda (English: The Shepherd's Hill),[6] which was ruled by the Chalukya dynasty from 731 CE to 966 CE.[7] Following the dissolution of the Chalukya dynasty into four empires in the 11th century, Golkonda came under the control of the Kakatiya dynasty (1000–1310).[8] The Kakatiya dynasty's headquarters was at Warangal, located 148 kilometres (92 mi) northeast of modern Hyderabad.[9]

When Sultan Alauddin Khilji of Delhi Sultanate took over Warangal, Hyderabad region came under the Khilji dynasty (1310–1321). Alauddin Khilji carried with him to Delhi the Koh-i-Noor diamond, which was mined from the Kollur Mines in Golkonda.[10] Soon the Delhi sultanate was occupied by Muhammad bin Tughluq, bringing Warangal under rule of the Tughlaq dynasty until 1347. Ala-ud-Din Bahman Shah, a governor of Muhammad bin Tughluq, revolted against the sultanate and established the Bahmani Sultanate in the Deccan with Gulbarga (200 kilometres (124 mi) west of Hyderabad) as its capital. The Bahmani kings ruled the region until 1518, becoming the first independent Muslim rulers of the Deccan.[9]
In 1518, Sultan Quli, a governor of Golkonda, revolted against the Bahmani Sultanate and established the Qutb Shahi dynasty.[9] Muhammad Quli Qutb Shah, the fifth sultan of the Qutb Shahi dynasty, established Hyderabad on the banks of the Musi River in 1591;[11] the city was established to avoid water shortage experienced at Golkonda, the capital of the Sultanate.[12] He constructed the Charminar, Purana pul and Mecca Masjid in the city.[13] On 21 September 1687, the Golkonda Sultanate came under the rule of Mughal emperor Aurangzeb after a year-long siege of the Golkonda fort.[14][15] The annexed area was renamed as "Deccan Suba" (Deccan province), and during this period of Mughal rule, the capital was shifted from Golkonda to Aurangabad (about 550 kilometres (342 mi) northwest of Hyderabad).[14][16]

Nizam period
The sixth of Aurangzeb's successors, Farrukhsiyar appointed Asaf Jah I as the Viceroy of the Deccan in 1712, with the title of "Nizam-ul-Mulk" (Regulator of the Realm) Fateh Jung. In 1724, Asaf Jah I gained autonomy by defeating a rival official to establish control over the Deccan Suba and named it "Hyderabad Deccan", thus starting the dynasty which came to be known as the Asaf Jahi dynasty. The rulers retained the title "Nizam ul-Mulk", and were referred to as Asif Jahi Nizams, or Nizams of Hyderabad.[14][16] Following the death of Asaf Jah I in 1748, there was political unrest due to the feud on ascension to the throne among the sons of Asaf Jah I, aided by the opportunistic neighbouring states and colonial foreign forces. The reign of Asif Jah II brought an end to the political instability. The Nizam signed the treaty of Masulipatnam in 1768 with the East India Company; through this treaty the Nizam surrendered the coastal region to the East India Company, in return the East India Company would have to pay a fixed annual rent to the Nizam.[17] In 1769, Hyderabad city became the formal capital of the Nizams.[14][16] Due to regular threats from the neighboring rulers of Mysore, Maratha and Basalath Jung (Asaf Jah II's elder brother supported by De Bussy), the Nizam signed a subsidiary alliance with the East India Company in 1798, allowing British troops to stationed at Bolaram (modern Secunderabad) to protect the borders of the Hyderabad State, for which the Nizams had to pay an annual maintenance to the British.[17] Starting from the late nineteenth century, establishment of railways, transport services, under ground drainage, running water, electricity, airport, universities and industries marked the transformation of the city to a modern one. The Nizams ruled the Hyderabad state from the city until 17 September 1948, a year after India's independence from the British Raj.[14][16]
Post-independence

Following independence of India from the British Empire in 1947, the Asaf Jahi Nizam declared his intention to remain independent.[17] In 1948, the Hyderabad State Congress began agitating against the Nizam VII, with the support of Indian National Congress and the Communist Party of India. On 17 September 1948, the Indian Army took control of Hyderabad state through Operation Polo and the Nizam VII joined Indian Union by signing the "Instrument of Accession", which made him the Rajpramukh ("Princely Governor") of Hyderabad State.[16][18] A peasant uprising or Telangana uprising was a communist-led peasant rebellion against the feudal lords of the Telangana region and later against the princely state of Hyderabad between 1946 and 1951.[19] The Constitution of India, which became effective on 26 January 1950, made Hyderabad State one of the part B states of India and Hyderabad city continued to be its capital. In 1955, B. R. Ambedkar, the then chairman of the Drafting Committee of the Indian Constitution, expressed in his report that the city should be designated as the second capital of India, due to its strategic central location in the country and available amenities.[20]
Since 1956, the Rashtrapati Nilayam located in Hyderabad is the second official residence and business office of the President of India.[21] On 1 November 1956, the states of India were reorganised on linguistic basis. Hyderabad state was split on linguistic basis to become the parts of three newly carved states. Nine Telugu and Urdu speaking districts of Hyderabad state, collectively known as Telangana region, were merged with Telugu-speaking Andhra State to create the state of Andhra Pradesh, with Hyderabad city as its capital.[22] There have been several movements to invalidate the merger of Telangana and Andhra, major ones occurring in 1969, 1972 and 2010 onwards. The Telangana movement gained momentum over decades becoming a widespread political demand of creating a new state from the Telangana region of Andhra Pradesh.[23] As of 2011, the movement continues with Hyderabad being a major centre of strikes and agitations.[24] In 2007, terrorist outfits carried out a series of bomb blasts in the city in May and August, leading to temporary communal tension and riot.
Geography

Topography
Hyderabad is located in the north-western part of Andhra Pradesh and lies on the banks of the Musi River in the northern part of the Deccan plateau in Southern India.[1][25] The city is spread over an area of 650 km2 (250 sq mi), making it one of the largest metros in India.[1] The predominant topography of the city is sloping rocky terrain of grey and pink granites. Some locations with higher altitude are scattered throughout, giving rise to the appearance of several small hillocks. Hyderabad has an average altitude of 1,778 feet (542 m) above mean sea level (MSL), and the highest point in the city is Banjara Hills at 2,206 feet (672 m).[25][26] As of 1996, the city houses 140 lakes and 834 water tanks of below the size of 10 hectares.[27] The lakes in the city are often referred to as sagar which means sea. The Hussain Sagar lake, built in 1562, is located in the city central. The Osman Sagar and Himayat Sagar are two artificial lakes created as a result of dams on the Musi River.[25][28]
Neighbourhood and landmarks
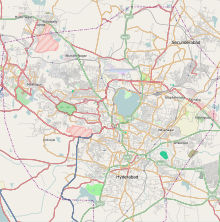
The historic city established by Muhammad Quli Qutb Shah on the southern banks of the Musi River exists as the "Old City", while the "New City" encompasses the urbanized area on the northern banks. The old and new cities are connected by many bridges that cross the river, of which "Purana pul" is the oldest.[29] Hyderabad is twined with neighboring Secunderabad, and the cities are separated through the Hussain Sagar lake. Both the cities come under the ambit of a single municipal unit of Greater Hyderabad.[1][25]
The central Hyderabad, bisected by the Musi River, is the nucleus of the city. The south of the river houses the historical and tourism sites such as the Charminar, Mecca Masjid, Salar Jung Museum, Nizam's museum, the Falaknuma Palace, the traditional retail corridor comprising the Laad Bazaar, Pearls Market and Madina circle. The north of the river houses hospitals, colleges, and major railway stations and business areas such as Begum Bazaar, Koti, Abids, Sultan Bazaar and Moazzam Jahi Market along with administrative and recreational establishments such as Reserve Bank of India, Andhra Pradesh Secretariat, Hyderabad Mint, Andhra Pradesh Legislature Assembly, Public Garden, Nizam Club, Ravindra Bharathi, state museum, Birla Temple and Birla Planetarium.[30][31][32]
Towards the north of central Hyderabad lies the Hussain Sagar Lake, along with Tank Bund Road, Rani Gunj and Secunderabad Railway Station.[30] Majority of the city's parks and recreation centers are located here—Sanjeevaiah Park, Indira Park, Lumbini Park, NTR Gardens, Buddha statue and Tankbund Park.[33] Upscale residential areas such as Banjara Hills, Jubilee Hills, Begumpet and Khairatabad are located on the northwest part of the city. The northern end houses industrial areas such as Sanathnagar, Moosapet, Balanagar, Pathan Cheru and Chanda Nagar. The northeast end is filled with residential colonies.[30][31][32] The southwest and west parts of the city have grown rapidly since 1990s, and are home to information technology and bio-pharmaceutical companies along with landmarks such as Hyderabad Airport, Osman sagar, Himayath sagar and KBR National Park. On the eastern part of the city lies the defence research centers and the Ramoji Film City.
Climate
Hyderabad has a combination of a tropical wet and dry climate (Köppen Aw) that borders on a hot semi-arid climate (Köppen BSh).[34] The annual mean temperature is 26 °C (78.8 °F); monthly mean temperatures are 21–32 °C (70–90 °F).[35] Summers (March–June) are hot and humid, with average highs in the mid 30s Celsius;[36] maximum temperatures often exceed 40 °C (104 °F) between April and June.[35] Winter lasts for only about two-and-a-half months, with the lowest temperature dipping occasionally to 10 °C (50 °F) in December and January.[35] May is the hottest month, with daily temperatures ranging from 26–38.8 °C (79–102 °F); January, the coldest month, has temperatures varying from 14.7–28.6 °C (58–83 °F).[36] Temperatures in the evenings and mornings are generally cooler because of the city's moderate elevation.
Rains brought by the south-west summer monsoon lash Hyderabad between June and September,[37] supplying it with most of its annual rainfall of 812.5 mm (32 in).[36] The highest monthly rainfall total, 181.5 mm (7 in), occurs in September.[36] The city receives 2,731 hours of sunshine per year, with maximum daily sunlight exposure occurring in February. The heaviest rainfall recorded in a 24-hour period is 241.5 millimetres on 24 August 2000. The maximum (day) temperature ever recorded was 45.5 °C (114 °F) on 2 June 1966, while the minimum recorded temperature was 8 °C (46 °F) on 8 January 1946.[37][38]
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Record high °C (°F) | 35.9 (96.6) |
39.1 (102.4) |
42.2 (108.0) |
43.3 (109.9) |
44.5 (112.1) |
45.5 (113.9) |
38.0 (100.4) |
37.6 (99.7) |
36.5 (97.7) |
36.7 (98.1) |
34.0 (93.2) |
35.0 (95.0) |
45.5 (113.9) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 28.6 (83.5) |
31.8 (89.2) |
35.2 (95.4) |
37.6 (99.7) |
38.8 (101.8) |
34.4 (93.9) |
30.5 (86.9) |
29.6 (85.3) |
30.1 (86.2) |
30.4 (86.7) |
28.8 (83.8) |
27.8 (82.0) |
32.0 (89.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 22.8 (73.0) |
25.4 (77.7) |
28.8 (83.8) |
31.4 (88.5) |
33.2 (91.8) |
29.7 (85.5) |
27.2 (81.0) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.8 (80.2) |
26.2 (79.2) |
24.1 (75.4) |
22.2 (72.0) |
27.0 (80.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 13.9 (57.0) |
15.5 (59.9) |
20.3 (68.5) |
24.1 (75.4) |
26.0 (78.8) |
23.9 (75.0) |
22.5 (72.5) |
22.0 (71.6) |
21.7 (71.1) |
20.0 (68.0) |
16.4 (61.5) |
13.1 (55.6) |
20.0 (67.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 6.1 (43.0) |
8.9 (48.0) |
13.2 (55.8) |
16.0 (60.8) |
16.7 (62.1) |
17.8 (64.0) |
18.6 (65.5) |
18.7 (65.7) |
17.8 (64.0) |
11.7 (53.1) |
7.4 (45.3) |
7.1 (44.8) |
6.1 (43.0) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 9.2 (0.36) |
10.2 (0.40) |
12.3 (0.48) |
27.2 (1.07) |
34.5 (1.36) |
113.8 (4.48) |
162.0 (6.38) |
203.9 (8.03) |
148.5 (5.85) |
113.9 (4.48) |
19.1 (0.75) |
5.0 (0.20) |
859.6 (33.84) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.3 mm) | 1.1 | 1 | 1.4 | 3.7 | 4.2 | 10.9 | 15.4 | 16.3 | 12.3 | 7.6 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 76.9 |
| Average rainy days | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 6.8 | 9.5 | 11.3 | 8.4 | 5.6 | 1.3 | 0.3 | 49.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) (at 17:30 IST) | 41 | 33 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 52 | 65 | 70 | 67 | 59 | 49 | 44 | 48 |
| Average dew point °C (°F) | 12 (54) |
12 (54) |
13 (55) |
15 (59) |
15 (59) |
19 (66) |
20 (68) |
20 (68) |
20 (68) |
17 (63) |
15 (59) |
13 (55) |
16 (61) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 272.8 | 265.6 | 272.8 | 276.0 | 279.0 | 180.0 | 136.4 | 133.3 | 162.0 | 226.3 | 243.0 | 251.1 | 2,698.3 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 8.8 | 9.4 | 8.8 | 9.2 | 9.0 | 6.0 | 4.4 | 4.3 | 5.4 | 7.3 | 8.1 | 8.1 | 7.4 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 9 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 11 |
| Source 1: India Meteorological Department (sun 1971–2000)[39][40][41] Time and Date (dewpoints, 2005-2015)[42][43] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Tokyo Climate Center (mean temperatures 1991–2020)[44] Weather Atlas[45] | |||||||||||||
Administration

Local government
The Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation (GHMC) is in charge of the civic administration of Hyderabad city. It was formed in April 2007 by merging Municipal Corporation of Hyderabad (MCH) with 12 municipalities of two neighbouring districts. The GHMC covers an area of 650 km2 (250 sq mi), that is spread over three districts—Hyderabad, Ranga Reddy and Medak. The 150 municipal wards that constitute GHMC are grouped into eighteen circles and five zones. Each ward is headed by a corporator, elected by popular vote. The corporators elect the Mayor who is the titular head of GHMC. The executive powers of the GHMC lies with the Municipal Commissioner appointed by the Government of Andhra Pradesh. In 2009 municipal election, the Indian National Congress and Majlis Ittehadul Muslimeen alliance formed the majority.[46]
The Secunderabad Cantonment Board (SCB) is a civic administration agency overseeing an area of 40.1 km2 (15.5 sq mi)[47]: 5 that houses several military camps.[48]: 2 The campus of the Osmania University is administered independently by its management.[47]: 6 The Hyderabad Metropolitan Development Authority (HMDA) was formed in 2008 as an umbrella authority by merging multiple local development bodies. The jurisdiction of HMDA extends to 54 mandals located in five districts with a total area of 7,100 km2 (2,700 sq mi).[49] It manages the development activities of the area including the administration of the Hyderabad Metropolitan Water Supply and Sewerage Board (HMWSSB), the Andhra Pradesh Transmission Corporation and the Andhra Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation (APSRTC).[47]: 13
The Hyderabad City Police is responsible for the enforcement of law and order. Hyderabad police commissionerate jurisdiction is divided into five police zones, each headed by a deputy commissioner.[50] The Hyderabad Traffic Police is headed by a deputy commissioner who is answerable to the Hyderabad city police commissioner.[51] The area under the jurisdiction of Hyderabad City Police is smaller than the GHMC area, thus the suburbs of the city falls under the jurisdiction of Cyberabad Police Commissionerate. As of 2012, The "Greater Hyderabad Police Commissionerate" is a proposed plan of Andhra Pradesh Government which would be formed by merging Hyderabad and Cyberabad Police Commissionerates.[52]
Hyderabad houses the offices of the local governing bodies, along with the Andhra Pradesh Legislature Assembly, the Andhra Pradesh Secretariat, and the Andhra Pradesh High Court. Under the jurisdiction of High Court comes the lower city civil court and the Metropolitan Criminal Court.[53] Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation area contains 24 state Legislative Assembly constituencies which come under five Lok Sabha (the lower house of the Parliament of India) constituencies.[54]
Utility services
In Hyderabad, electricity, water and sewerage services were first commissioned in 1925.[55] The Hyderabad Metropolitan Water Supply and Sewerage Board (HMWSSB) regulates rainwater harvesting, water and sewerage services.[49] The HMWSSB sources water supply from multiple dams located in the suburbs of the city.[56] In 2005 the HMWSSB started operating 150 kilometres (93 mi)-long water supply piple-line from Nagarjuna Sagar Dam to meet the increasing consumption requirement.[56] The electricity is regulated through Andhra Pradesh Central Power Distribution Company.[49] Fire fighting services are provided by the Andhra Pradesh Fire Services department, as of March 2012, the department have 13 fire stations in Hyderabad.[57] The Indian Postal Service is the major service provider in the city with five head post offices and multiple sub-post offices; many private courier services also operate in the city.[25] In 1999, the AP state government launched e-Seva (electronic service) services for multiple utility agency's bill payment from one platform.[58]
Pollution control
Hyderabad produces around 4,500 metric tonnes of solid waste everyday, which is transported from three collection units located in Imlibun, Yousufguda and Lower Tank Bund to the garbage dumping site of Jawaharnagar.[59] The "Integrated Solid Waste Management" project was started in 2010 by GHMC to manage the waste disposal in the city.[60] The Andhra Pradesh Pollution Control Board (APPCB) is the regulatory and screening authority of pollution in Hyderabad. The rapid rate of urbanisation with increased economic activities had encouraged migration and industries in Hyderabad, these changes led to an increase of air pollution, industrial waste, noise pollution and water pollution.[61] As of 2006, contribution of different sources to air pollution were as follows—20–50% from vehicle, 40–70% combining vehicle discharge with road dust, 10–30% from industrial discharges and 3–10% from household garbage burning.[62] The estimated deaths from particulate matter are about 1700–3000 persons every year in Hyderabad.[63] The ground water in Hyderabad has total water hardness up to 1000 ppm.[64] The region's ground water levels are shrinking, and dams are facing water shortage due to burgeoning population and consequent increased demand of water.[56][65] Inadequately treated effluents from industrial treatment plants are polluting the drinking water sources of the city.[66] APPCB and local authorities have designed and implemented multiple actions to control pollution in the city.[63]
Healthcare

The Andhra Pradesh Vaidya Vidhana Parishad, a department of the state government, administers the healthcare in Hyderabad.[67] The medical services are provided by hospitals and clinics run by the government, corporate and charity organizations.[68] As of 2010–11, the city houses 50 government hospitals,[69] 300 corporate and charity hospitals, 194 nursing homes (smaller privately run acute inpatient care providers); together these facilities provide the city with approximately 12,000 hospital beds, which is less than 50% of required 25000 hospital beds.[68][70] For every 10,000 people in the city, there are 17.6 hospital beds,[71] 9 doctors (specialist), 14 nurses and 6 physicians (general consultants).[70] In addition the city houses about 4,000 individual clinics,[72] and 500 medical diagnostic centers.[68] The majority of residents prefer treatment at private facilities and only 28% of residents uses government facilities, due to distant locations, poor quality of patient care and extreme waiting time.[73]: 60–61 As of 2012, 15 international corporate chains had acquired spaces to develop super specialty hospitals in the city.[72] Overall, the healthcare services in Hyderabad are standardized and affordable, as compared to many other cities in India.[74] The Government of Andhra Pradesh also supports and provides traditional health facility of Unani, Homeopathy and Ayurvedic medical treatment system for both outpatient and inpatient.[75]
According to the 2005 National Family Health Survey, 24% of Hyderabad households were covered under government health schemes or health insurance, which is the highest covered proportion in India among the surveyed cities.[73]: 4 The total fertility rate in the city is 1.8,[73]: 95 and 66% of the married women used contraceptives.[73] Only 61% of the children had been provided with all basic vaccines which is second least among the surveyed cities.[73]: 98 The infant mortality rate was 35 per 1,000 live births, and the mortality rate for children under five was 41 per 1,000 live births.[73]: 97 According to the survey, about one third of women and one fourth of men are overweight and obese, about 49% of children below 5 years are anemic and up to 20% children are underweight.[73]: 44, 55–56 More than 2% of women and 3% of men suffer from diabetes in Hyderabad.[73]: 57
Demographics
Template:India census population
Hyderabad, covering an area of 650 square kilometres (250 sq mi),[76] has a population of 6,809,970, making it the fourth most populous city in India.[77] There are 3,500,802 male and 3,309,168 female citizens. The area under the municipality increased from 170 square kilometres (66 sq mi) to 650 square kilometres (250 sq mi) in 2007 when the Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation was created.[78] As a consequence, the total population leaped from 3,637,483 in 2001 census to 6,809,970 in 2011 census, an increase of over 87%. Migrants from rest of India constitute 24% of the city population.[48]: 2 The sex ratio is 945 female per 1000 males,[79] higher than the national average of 926 per 1000.[80] Among children aged 0–6 years, 373,794 are boys and 352,022 are girls, leading to the ratio of 942 girls per 1000 boys.[79] The city's population density is 18,480/km2 (47,900/sq mi),[81] and literacy rate 82.96% (male 85.96% and female 79.79%), higher than the national average of 74.04%.[82] The Hyderabad Urban Agglomeration has a population of 7,749,334, the sixth most populous urban agglomeration in the country.[77]
Ethnic groups, Language and Religion
Residents of Hyderabad are called Hyderabadi. Telugu people comprise the majority of Hyderabad's population, followed by Marathi and Arab communities. The minority communities of Hyderabad are Kannada (including Nawayathi), Marwari, Bengali, Tamil, Malayali, Gujarati, Punjabi and Uttar Pradeshi. Among the foreign-origin communities Yemeni Arabs forms the majority, while African Arabs, Armenian, Abyssinians, Iranian, Pathan and Turkish ethnicity are also present. The foreign-origin population declined since Hyderabad State became a part of the Indian Union.[83]
Telugu and Urdu are the first and second official languages of Hyderabad,[84] while English is also used particularly among white-collar workers.[85] Telugu in Hyderabad has a varied dialect called the Telangana dialect,[86] and the Urdu spoken in the city is called Deccani Urdu.[87] A significant population of the city speaks different languages such as Hindi, Marathi, Bengali, Kannada and Tamil.[83]
In Hyderabad, the Hindus form a majority of the population, and Muslims have large presence across the city and are predominant in and around the Old City. The other religious communities are Christian, Sikh, Jain, Buddhist and Parsi. Iconic temples, mosques and churches are housed in the city.[88] According to 2001 census, (before Greater Hyderabad was formed), the Hyderabad city's religious make up included Hindus (55%), Muslims (42%), Christians (2%), Sikhs (0.5%), Buddhists (0.3%), and Jains (0.2%).[89]
Slums
According to 2012 report submitted to the World Bank by GHMC, Hyderabad has 1,476 slums, with a total population of 1.7 million; among those 66% live in 985 slums located in the core of the city and the remaining 34% live in 491 slums located in the city's suburbs.[90] Among the slum-dwellers, 22% of the households migrated from different parts of India and 63% of the households had been staying in the slums for over 10 years.[48]: 55 The literacy rate in the slums is 60–80% and the female literacy rate is 52–73%. One third of the city's slums have basic service connections, and 90% slums have water supply lines. There are 405 government schools, 267 government aided schools, 175 private schools and 528 community halls across the slums of Hyderabad.[91]: 70 According to a survey conducted in 2008 by the Centre for Good Governance, 87.6% of the slum household are nuclear families, 18% households are very poor with an income of ₹20,000 (US$240) per annum, 73% of the household live below poverty line (a standard poverty line recognized by the AP Government is ₹24,000 (US$290) per annum), 27% chief wage earner's (CWE) are casual labour and 38% of the CWE are illiterate. About 3.72% of the slum children of age group 5–14 years do not go to school and 3.17% of slum children work as child labour—among those 64% are boys and 36% are girls; the largest employer of child labour are street shops and construction sites. Among working children, 35% are engaged in hazardous jobs.[48]: 59
Economy

Hyderabad is the largest contributor to the Andhra Pradesh state's GDP, state tax and other revenues.[92] As of 2011, the per capita annual income of Hyderabad was ₹44,300 (US$530).[93] As of 2006, the largest employers in the city are the Governments of Andhra Pradesh (113,098) and Governments of India (85,155) employees.[94] The World Bank Group ranked the city as the second best Indian city for doing business in 2009.[95] In 2010, the economic analysis group GaWC ranked Hyderabad in its third tier (Gamma+ World City) of cities by importance.[96] Hyderabad and its suburbs house the highest number of special economic zones among India cities.[93]
Hyderabad is known as the "City of Pearls", due to the presence of pearls trading industry—until the 18th century the city was the only global trade center of large diamonds.[15][97] Many traditional and historical bazaars are located in the city.[98][99] The Laad Bazaar and nearby markets have shops that sell pearls, diamonds and other traditional ware and cultural antiques.[98] The commercial market structure of Hyderabad is defined into 4 sectors—The Central Business Districts (CBD), the sub-central business centers, the neighborhood business centers and local business centers.[100] According to a survey in 2007, the retail industry in Hyderabad had been growing along with traditional markets.[101] and several central business districts are spread across the city.[102]
During Nizam's rule in the 1930s industrialization was started, which was helped by expansion of railways, connecting the city with major ports of the country.[103][104] From 1950s to 1970s, several Indian public enterprises were established in the city,[105] such as Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL), National Mineral Development Corporation (NMDC), Bharat Electronics (BE), Indian Drugs and Pharmaceuticals Limited (IDPL), Electronics Corporation of India Limited (ECIL), Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), Andhra Bank (AB) and State Bank of Hyderabad (SBH). This changed the economic pattern of the city from a traditional manufacturing base to a cosmopolitan industrial service sector.[31] Since 1990s, the growth of information technology (IT), IT-enabled services (ITES), insurance and financial institution, had expanded the service sector on large scale, these economic activities boosted ancillary sectors of trade and commerce, transport, storage, communication, real-estate and retail.[104] The service industry remains dominant in the city with 90% of the employed workforce engaged in the sector.[106] According to a survey, as of 2005, 77% of males and 19% of females are employed in the city.[107]

Hyderabad emerged as a pharmaceutical and biotechnology hub and is known as "India's pharmaceutical capital" and "Genome Valley of India".[108] It is among the global centers of information technology for which it is known as Cyberabad (Cyber City).[109][110] During 2008–09, Hyderabad's IT exports reached US$ 4.7 billion,[111] and 22% of the NASSCOM's total membership is from the city.[93] The development of a township with technological infrastructure called HITEC City prompted multinational companies to establish their operations in Hyderabad.[109] The city is home to more than 1300 IT firms, including global conglomerates such as Microsoft (the largest R&D campus outside the US), Google, IBM, Yahoo!, Dell, Facebook,[48]: 3 [112] and major Indian firms including Mahindra Satyam, Infosys, TCS, Genpact and Wipro.[48]: 3
As in the rest of India, Hyderabad has a large informal economy that employees 30% of the labor force.[91]: 71 According to a survey conducted in 2006 and 2009, Hyderabad has 50,000 street vendors, which are growing periodically.[113] Among the street vendors, 84% are males and 16% female, and 80% of the vendors have stationary shops. Personal savings are the source of finance for 92% of the total street vendors, where as 8% of the vendors borrow loans from money lenders.[114] the vendors earning varies from minimum ₹50 (60¢ US) to ₹800 (US$9.60) per day.[113] The other unorganized economical sectors include dairy, poultry farming, brick kiln jobs, casual labors, domestic helps and others. The people involved in the informal sector constitute a major portion of urban poor as these units have a low labor income.[91]: 71
Transport

In Hyderabad, public transport such as buses, auto rickshaws and multi modal railways are the most frequently used transport by the residents.[115] The composition of vehicles in Hyderabad are—75% two-wheelers, 14% cars, 1% taxis, 4% goods vehicles, 2% buses (including 3,800 RTC buses[116]) and 4% other vehicles (including 71,000 auto rickshaws[115]).[47]: 28 In some parts of the city cycle rickshaws are used as a means of public transport for smaller distances.[47]: 32 As of 2001, two-wheeler and cars are involved in 50% of road accidents, public transport buses and trucks in 10% and auto-rickshaws are involved in 15% of the road accidents. Among these, 12% are fatal accident and 88% are injurious (including 40% of total accidents that occurs due to non availability of pedestrian facilities[47]: 32 ).[115] As of 2010, the maximum speed limits assigned for individual vehicles within city limits are 50 km/h (31 mph) for two-wheelers and cars, 35 km/h (22 mph) for auto-rickshaw and 40 km/h (25 mph) for light commercial vehicle and transport buses.[117]
Three National Highways (NH) pass through the city—NH-7, NH-9 and NH-202.[118] Five state highways—SH-1, SH-2, SH-4, SH-5 and SH-6 begin passes from Hyderabad.[47]: 1 Multiple development projects in the city have made traffic congestion a common issue.[119] Like many other Indian metropolitan cities, Hyderabad also faces parking problems, particularly in the city center. In Hyderabad the roads occupy 6% of the total city area.[47]: 3 The HMDA developed multiple projects such as Inner Ring Road, Outer Ring Road, interchanges, overpasses and underpasses to ease the traffic congestion. As of 2008, Hyderabad Elevated Expressway is the longest flyover bridge in India.[120]

The bus service, governed by Andhra Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation (APSRTC), is the most frequently used means of public transport within the city.[121] According to the Guinness World Records (2005), APSRTC operates the world's largest fleet of buses, estimated to carry 13 million passengers a day.[122] Mahatma Gandhi Bus Station, located at center of the city, is the main bus station.[123] Parallel to APSRTC under the sponsorship of the Setwin, minibuses are available.[124] Hired modes of transport include taxi and the widely used auto rickshaws.[125]
The Secunderabad Railway Station is the headquarters of the South Central Railway zone of the Indian Railways and the largest railway station in Hyderabad. Other major railway stations are Hyderabad Deccan Station, Kachiguda Railway Station and Begumpet Railway Station.[126] Hyderabad's light rail transportation system, known as the MultiModal Transport System (MMTS), is used by over 150,000 passengers daily, as of 2010.[127] Hyderabad Metro, the city's under-construction rapid transit system, is scheduled to operate three lines by 2014.[128] The Rajiv Gandhi International Airport (RGIA) (IATA: HYD, ICAO: VOHS) was inaugurated in 2008, replacing the previous Begumpet Airport.[129] As of 2010, the Airports Council International (ACI), an autonomous body representing world airports, had judged RGIA as the world's best airport in the category of serving 5–15 million passengers, and world's fifth best airport for Airport service quality.[130]
Culture

Distinct linguistic and cultural traditions of North and South India meet and mingle in Hyderabad, and the combination of Hindu and Muslim traditions is notable in the city.[131] Telugu and Urdu are the most commonly spoken languages among the residents.[132] The traditional Hyderabadi garb is Sherwani and Kurta–Paijama for men,[133] Khara Dupatta and Salwar kameez for women. [134][135] Burqa and Hijab are commonly worn by the Muslim women in public.[136] Most of the youth wear western clothing.[137] Festivals celebrated in Hyderabad include the Ganesh Chaturthi, Diwali, Bonalu, Eid ul-Fitr and Eid al-Adha.
Literature
Hyderabad received royal patronage for arts, literature and architecture from its former rulers; this attracted men of letters and arts from different parts of the world to get settled in the city. Such multi-ethnic settlements popularised cultural events such as mushairas.[138] The Qutb Shahi reign patronised the growth of Deccani Urdu literature—the Deccani Masnavi and Diwan (collection of poems) composed during this period are among the earliest available manuscripts in Urdu language.[139] Nizam's reign saw many reforms in literary work, and introduction of Urdu as a language of court, administration and education.[140] In 1824, a collection of Urdu Ghazals named Gulzar-e-Mahlaqa, penned by Mah Laqa Bai—the first female poet in Urdu—was published from Hyderabad.[141] The Hyderabad Literary Festival, held since 2010, is an annual event which showcases the city's literary and cultural aspects.[142] Organisations engaged in research and development of literary works are Sahitya Akademi, Urdu Academy, Telugu Academy, National Council for Promotion of Urdu Language, The Comparative Literature Association of India and Andhra Saraswata Parishad. The State Central Library, Hyderabad, established in 1891, is the largest public library of Andhra Pradesh.[143] The other major libraries are the Sri Krishna Devaraya Andhra Bhasha Nilayam, the British Library and the Sundarayya Vignana Kendram.[144]
Music, performing arts and films
In princely Hyderabad, the nobles had a tradition of courtesan dance and poetry, which led to the development of certain styles of court music and dance. Taramati of the early 16th century and Mah Laqa Bai (18th century) are two courtesans who popularised Kathak dance. Besides western and Indian popular music genres such as the filmi music, the residents of Hyderabad play city-based Marfa Music especially during weddings, festivals and other celebratory events.[145] The state government organizes Golconda Music and Dance Festival, Taramati Music Festival, and Premavathi Dance Festival.[141][146] Though not noted for theatre and drama,[147] the state government took efforts to promote the art of theatre with multiple programmes and festivals in Hyderabad.[148] The Ravindra Bharati, Shilpakala Vedika and Lalithakala Thoranam are auditoria for theatre and performing arts in the city. The Hyderabad International Convention Centre (HICC), also known as HITEX, has become well known venue address internationally.[149] Numaish is a popular annual exhibition of local and national products.[150]
The city is home to the Telugu film industry, popularly known as "Tollywood";[151] it is the second largest film industry in India in terms of number of films produced, after Bollywood.[152] Since 2005, films in local Hyderabadi dialect have gained popularity.[153] The city hosts the annual International Children Film Festival and the Hyderabad International Film Festival.[154] In 2005, the Guinness World Records declared the Ramoji Film City as the world's largest film studio.[155]
Art and handicraft

The Golconda and the Hyderabad styles are two branches of the Deccani school of painting.[156] The Golconda style that originated in 16th century during Qutb Shahi sultans is an insightful native style with the blend of foreign techniques, sharing similarity with neighbouring Vijayanagara paintings. Significant use of luminous gold and white colours is generally found in Golconda style.[157] The Hyderabad style of painting originated in the early 17th century. Highly influenced by the Mughal painting, this style makes use of bright colors, and mostly depicts regional landscape, culture, costumes and jewellery.[156] A fine art metal handicraft of the region known as Bidri ware was popularised in Hyderabad in the 18th century. The Bidri ware is an Geographical Indication (GI) awarded craft of India.[158][159] The Kalamkari, a fine art of handicraft producing hand-painted or block-printed cotton textile is popular in the city.[160] Museums in Hyderabad include the AP State Archaeology Museum, the Salar Jung Museum (housing "the world's largest one-man-collection"), the Nizam Museum, the City Museum and the Birla Science Museum which contains a planetarium.[161]
Architecture
A distinct Indo-Islamic architecture style enriched with regional influences is reflected in the buildings of the city.[3][162] The Qutb Shahi architecture of the 15th century is manifest in colossal arches found in Golconda fort, Charminar, Mecca Masjid and Charkaman—the chief ingredients used in these constructions are granite and lime mortar. Later, from 17th century Asif Jahi architecture emerged. Osman Ali Khan, the Nizam VII, is called as the maker of modern Hyderabad. The buildings constructed during his reign are impressive and represent a rich variety of architecture.[158] Structures such as the Osmania University, Osmania General Hospital and High Court are designed and constructed in the styles of medieval and the Mughal architecture. The Nizams applied the European styles in some of the constructions such as Falaknuma and King Kothi Palaces.[163] Other historical sites include the Chowmahalla Palace, the Purani Haveli, and the Andhra Pradesh Legislature.[158][164] In 2012, The government of India declared Hyderabad as the first "Best heritage city of India".[165]

Cuisine
Hyderabadi cuisine is prominent since the Nizams.[166] The cuisine comprises repertoire of spices, rice, wheat and meat dishes.[167] The Hyderabadi Biryani and Hyderabadi Haleem, with a blend of Mughlai and Arabic cuisine,[168] have become iconic dishes of India.[169] Hyderabadi cuisine is highly influenced by Mughals and partially by French,[166] Arabic, Turkish and Irani food along with the influence of native Telugu and Marathwada cuisines where rice, wheat, spices and meat are widely used to great effect bringing in a unique taste to the Hyderabadi dishes.[135][168] Other popular native dishes include Nahari, Kulche, Chakna, Baghara baingan and in desserts Qubani ka meetha, Double ka meetha and Kaddu Ki Kheer (a sweet porridge made with sweet gourd).[135][170] Cuisines popular among expatriates and other residents are South Indian, Italian, Mexican, Chinese and Continental.[170][171] Coffee bars and pubs are also frequented by the youth in the city.[172]
Media
Among the early newspapers in Hyderabad was The Deccan Times established in the 1780s.[173] The major Telugu dailies published in Hyderabad are Eenadu, Sakshi and Andhra Jyothy; the major English dailies are The Times of India, The Hindu and The Deccan Chronicle[174] and the major Urdu dailies include The Siasat Daily, The Munsif Daily and Etemaad. Multiple coffee table magazines, professional magazines and research journals are regularly published from Hyderabad.[175] In 1919 the British cantonment of Secunderabad established the communication station in the Hyderabad State and in 1924. Deccan Radio was the first general broadcasting radio station of Hyderabad to go on air on 3 February 1935.[176] In 2000, radio stations were permitted to broadcast in FM.[177] Notable FM radio channels in the city include All India Radio (AIR), Radio Mirchi, Radio City and Big FM.[178]
Television relay in Hyderabad was started in 1974, with the launch of Doordarshan (DD), the government of India's public service broadcaster.[179] DD transmit two free-to-air terrestrial television channels and one satellite channel from Hyderabad. The private satellite channels were started in July 1992, with the launch of Star TV.[180] Satellite TV channels are accessible via cable subscription, direct-broadcast satellite services or internet-based television.[177][181] In Hyderabad, the first dial-up Internet access was started in the early 1990s, which was limited to software development companies.[182] In 1995 public dial-up internet service was started and in 1998 private internet access service was initiated.[183]
Education

Schools in Hyderabad are affiliated to either CBSE, SSC[184] or ICSE, run by government or private aid (local governing bodies, individuals, missionaries or other agencies). An estimated two thirds of students study at private schools.[185] The medium of instruction include English, Hindi, Urdu[186] and Telugu. Schools in Hyderabad follow the "10+2+3" plan. After completing their secondary education, students typically enroll in schools or junior colleges that have a higher secondary facility. They usually choose a focus on liberal arts, business, or science. Admissions to professional colleges in Hyderbad is through Engineering Agricultural and Medical Common Entrance Test (EAMCET). Majority of the colleges are affiliated with either Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University or Osmania University.[187]
As of 2012, there are 13 universities located in Hyderabad, of which two are private universities, two deemed universities, six state universities and three central universities. The central universities in the city are the University of Hyderabad,[188] Maulana Azad National Urdu University and English and Foreign Languages University.[189] The Osmania University established in 1918 is the earliest university in Hyderabad. As of 2012, it is the second most popular destination in India for international students.[190] The Dr. B. R. Ambedkar Open University, established in 1982, is the first distance learning open university in India.[191]

Notable business and management schools in Hyderabad are the Indian School of Business (ISB),[192] and the Institute of Chartered Financial Analysts of India (ICFAI).[193] Institutes of national importance based in city include the Institute of Public Enterprise (IPE), the Administrative Staff College of India (ASCI), and the Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel National Police Academy (SVP-NPA). Hyderabad is home to five major medical schools—Osmania Medical College (established in 1846), Gandhi Medical College, Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences, Deccan College of Medical Sciences, Shadan Institute Of Medical Sciences,[194] and many affiliated teaching hospitals. The Government Nizamia Tibbi College, established in 1810, is a unani medicine college.[195] The city is also a major centre for biomedical, biotechnology and pharmaceutical studies and research;[196] the National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER) is located here.[197] The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) and the Acharya N. G. Ranga Agricultural University are notable agricultural engineering institutes. The city is home to many of India's premier technical and engineering schools, including the International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad (IIIT-H), the Indian Institute Of Technology (IIT-H), and the Birla Institute of Technology & Science (BITS). The premier professional fashion designing institutions in the city are Raffles Millennium International, NIFT Hyderabad and Wigan and Leigh College.
Sports

Cricket and football (soccer) are the most popular sports in Hyderabad.[198] The city has hosted national and international sports events such as the 2002 National Games of India, the 2003 Afro-Asian Games, the 2004 Hyderabad Open, the 2007 Military World Games, the 2009 BWF World Championships and IBSF World Snooker Championship (2009). The Lal Bahadur Shastri Stadium and the Rajiv Gandhi International Cricket Stadium host cricket matches;[199] the latter serves as a home ground of Hyderabad Cricket Association. Hyderabad has been the venue of multiple international cricket matches, including matches in 1987, 1996 and 2011 Cricket World Cups. The Swarnandhra Pradesh Sports Complex is a venue for field hockey, and the G.M.C. Balayogi Stadium at Gachibowli is a athletics and football venue.[200]
The Hyderabad cricket team represents the city in the Ranji Trophy, a first-class cricket tournament between India's states and cities. The Deccan Chargers, a franchise in the Indian Premier League (IPL), won the 2009 Indian Premier League held in South Africa.[201] The city houses many elite clubs formed by the Nizams and British, such as the Secunderabad Club, the Nizam Club and the Hyderabad Race Club known for its horse racing,[202] especially the annual Deccan derby.[203] The Andhra Pradesh Motor Sports Club organises popular events like the Deccan 1/4 Mile Drag, TSD Rallies and 4x4 Off road.[204] The Hyderabad Golf Club is a eighteen-hole golf course.[205] Notable sports persons of international stature from Hyderabad include cricketers Ghulam Ahmed, M. L. Jaisimha, Mohammed Azharuddin, V. V. S. Laxman, Venkatapathy Raju, Shivlal Yadav, Arshad Ayub, Noel David, football players Syed Abdul Rahim, Syed Nayeemuddin, Shabbir Ali,[206] tennis player Sania Mirza,[207] badminton players S. M. Arif, Pullela Gopichand, Saina Nehwal, Jwala Gutta, Chetan Anand, hockey players Syed Mohammad Hadi, Mukesh Kumar and bodybuilder Mir Mohtesham Ali Khan.
Sister Cities
| City | Geographical location | Nation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brisbane | Queensland | [208] | |
| Ipswich | Queensland | [208] | |
| Dubai | Dubai | [209] | |
| Miyoshi | Hiroshima | [210] | |
| Riverside | California | [211] | |
| Indianapolis | Indiana | [212] | |
| San Diego | California | [213] |
See also
References
- ^ a b c d "Greater Hyderabad municipal corporation". Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation (GHMC). Retrieved 17 August 2011.
- ^ McCann, Michael W. (1994). Rights at work: pay equity reform and the politics of legal mobilization. University of Chicago Press. p. 6. ISBN 0-226-55571-2.
- Reddy, Gayatri (2005). With respect to sex: negotiating hijra identity in south India. University of Chicago Press. p. 6. ISBN 0-226-70755-5.
- Kakar, Sudhir (1996). The colors of violence: cultural identities, religion, and conflict. University of Chicago Press. p. 23. ISBN 0-226-42284-4.
- ^ a b Petersen, Andrew (1996). Dictionary of Islamic architecture. Routledge. p. 112. ISBN 0-415-06084-2.
- ^ Prasad, Rajendra (1984). The Asif Jahs of Hyderabad: their rise and decline. Vikas. p. 46. ISBN 978-0-7069-1965-3.
- ^ "Hyderabad's history could date back to 500 BC". GHMC. 10 September 2008. Retrieved 10 September 2008.
- ^ Ramachandran, Priya (4 February 2012). "Golconda fort: Hyderabad's time machine". The Siasat Daily. Retrieved 8 February 2012.
- ^ Reddy, V.Ramakrishna (1987). Economic history of Hyderabad state: Warangal suba, 1911–1950. Gian Publishing House. p. 2. ISBN 978-81-212-0099-8.
- ^ Sastri, Kallidaikurichi Aiyah Nilakanta (1976). A history of south India from prehistoric times to the fall of Vijayanagar. Oxford University Press. p. 192. ISBN 0-19-560686-8.
- ^ a b c Sardar, Marika (2007). Golconda through time: a mirror of the evolving Deccan. ProQuest. pp. 20–41. ISBN 0-549-10119-5.
- Jaisi, Sidq (2004). The nocturnal court: life of a prince of Hyderabad. Oxford University Press. pp. 29–30. ISBN 978-0-19-566605-2.
- ^ Ghose, Archana Khare (29 February 2012). "Heritage Golconda diamond up for auction at Sotheby's". The Times of India. Retrieved 1 March 2012.
- ^ Olson, James Stuart; Shadle, Robert (1996). Historical dictionary of the British empire. Greenwood Press. p. 544. ISBN 978-0-313-27917-1.
- ^ Aleem, Shamim; Aleem, M. Aabdul, eds. (1984). Developments in administration under H.E.H. the Nizam VII. Osmania University Press. p. 243. Retrieved 15 June 2012.
- ^ Bansal, Sunita Pant (2005). Encyclopedia of India. Smriti Books. p. 61. ISBN 978-81-87967-71-2.
- ^ a b c d e Richards, J. F. (1975). "The Hyderabad Karnatik, 1687–1707". Modern Asian Studies. Cambridge University Press: 241–260. doi:10.1017/S0026749X00004996. Retrieved 20 April 2012.
- ^ a b Hansen, Waldemar (1972). The Peacock throne:the drama of Mogul India. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 168 and 471. ISBN 81-208-0225-X.
- ^ a b c d e Ikram, S.M. (1964). "A century of political decline:1707–1803". In Embree, Ainslie T (ed.). Muslim civilization in India. Columbia University. ISBN 978-0-231-02580-5.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help)- Rao, Sushil (11 December 2009). "Testing time again for the pearl of Deccan". The Times of India. Retrieved 22 April 2012.
- ^ a b c Regani, Sarojini (1988). Nizam-British relations, 1724–1857. Concept Publishing. pp. 130–150. ISBN 81-7022-195-1.
- Farooqui, Salma Ahmed (2011). A comprehensive history of medieval India. Dorling Kindersley. p. 346. ISBN 978-81-317-3202-1.
- Malleson, George Bruce (2005). An historical sketch of the native states of India in subsidiary alliance with the British government. Asian Education Services. pp. 280–292. ISBN 978-81-206-1971-5.
- Townsend, Meredith (2010). The annals of Indian administration, Volume 14. BiblioBazaar. p. 467. ISBN 978-1-145-42314-5.
- ^ Venkateshwarlu, K (17 September 2004). "Momentous day for lovers of freedom, democracy". The Hindu. Retrieved 23 May 2012.
- ^ Sathees, P.V.; Pimbert, Michel; The DDS Community Media Trust (2008). Affirming life and diversity. Pragati Offset. pp. 1–10. ISBN 978-1-84369-674-2.
- ^ "Ambedkar for Hyderabad as second capital of India". Ambedkar organization. 1955. Retrieved 17 May 2010.
- ^ "Rashtrapati bhavan:presidential retreats". presidentofindia.nic. Retrieved 26 May 2012.
- Vohra, J.N. (8 July 2007). "Palaces of the president". The Tribune. Retrieved 26 May 2012.
- ^ Falzon, Mark-Anthony (2009). Multi-sited ethnography: theory, praxis and locality in contemporary research. Ashgate Publishing. pp. 165–166. ISBN 978-0-7546-9144-0.
- ^ "How Telangana movement has sparked political turf war in Andhra". Rediff.com. 5 October 2011. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- ^ "Pro-Telangana AP govt employees threaten agitation". The Economic Times. 10 February 2012. Retrieved 18 February 2012.
- ^ a b c d e "Physical Feature" (PDF). AP Government. 2002. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- ^ "Hyderabad geography". JNTU. Retrieved 4 May 2012.
- ^ Singh, Sreoshi (2010). "Water security in peri-urban south Asia" (PDF). South Asia Consortium for Interdisciplinary Water Resources Studies. Retrieved 18 May 2012.
- ^ "Water sources and water supply" (PDF). rainwaterharvesting.org. 2005. p. 2. Retrieved 20 January 2012.
- ^ "Puranapul 'rented' out to vendors by extortionist". The Deccan Chronicle. 24 June 2011. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
- ^ a b c Alam, Shah Manzoor; Reddy, A. Geeta; Markandey, Kalpana (2011). Urban growth theories and settlement systems of India. Concept Publishing. pp. 79–99. ISBN 978-81-8069-739-5.
- ^ a b c Rao, Nirmala (2007). Cities in transition. Routledge. pp. 117–140. ISBN 0-203-39115-2.
- ^ a b Gopi, K.N (1978). Process of urban fringe development:a model. Concept Publishing. pp. 13–17. ISBN 978-81-7022-017-6.
- Nath, Viswambhar; Aggarwal, Surinder.K (2007). Urbanization, urban development, and metropolitan cities in India. Concept Publishing. pp. 375–380. ISBN 81-8069-412-7.
- Alam, Shah Manzoor; khan, Fatima Ali (1987). Poverty in metropolitan cities. Concept Publishing. pp. 139–157.
- ^ Kodarkar, Mohan. "Implementing the ecosystem approach to preserve the ecological integrity of urban lakes: the case of lake Hussain sagar, Hyderabad, India" (PDF). Ecosystem approach for conservation of lake Hussainsagar. International Lake Environment Committee Foundation. p. 3. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
- "Hussain sagar stink is not a bother". The Times of India. 2 February 2004. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
- ^ Climate and food security. International Rice Research Institute. 1987. p. 348. ISBN 978-971-10-4210-3.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)- Norman, Michael John Thornley; Pearson, C.J; Searle, P.G.E (1995). The ecology of tropical food crops. Cambridge University Press. pp. 249–251. ISBN 978-0-521-41062-5.
- ^ a b c "Weatherbase entry for Hyderabad". Canty and Associates LLC. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- ^ a b c d "Hyderabad". India Meteorological Department. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- ^ a b Yimene, Ababu Minda (2004). An African Indian community in Hyderabad. Cuvillier Verlag. pp. 5–6. ISBN 978-3-86537-206-2.
- ^ "Historical weather for Hyderabad, India". Weatherbase. Retrieved 3 October 2008.
- ^ "Station: Hyderabad (A) Climatological Table 1981–2010" (PDF). Climatological Normals 1981–2010. India Meteorological Department. January 2015. pp. 331–332. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2020. Retrieved 13 February 2020.
- ^ "Extremes of Temperature & Rainfall for Indian Stations (Up to 2012)" (PDF). India Meteorological Department. December 2016. p. M9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2020. Retrieved 13 February 2020.
- ^ "Table 3 Monthly mean duration of Sun Shine (hours) at different locations in India" (PDF). Daily Normals of Global & Diffuse Radiation (1971–2000). India Meteorological Department. December 2016. p. M-3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2020. Retrieved 13 February 2020.
- ^ "Climate & Weather Averages in Hyderabad, Telangana, India". Time and Date. Retrieved 18 July 2022.
- ^ "Climatological Tables 1991-2020" (PDF). India Meteorological Department. p. 21. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 January 2023. Retrieved 1 January 2023.
- ^ "Normals Data: Hyderabad Airport - India Latitude: 17.45°N Longitude: 78.47°E Height: 530 (m)". Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved 29 February 2020.
- ^ "Climate and monthly weather forecast Hyderabad, India". Weather Atlas. Retrieved 13 June 2022.
- ^ "Karthika not in a hurry to hand over mayor baton to MIM". The Times of India. 23 October 2011. Retrieved 25 October 2011.
- "Greater Hyderabad municipal corporation" (PDF). GHMC. Retrieved 25 October 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Exploring urban growth management in three developing country cities" (PDF). World Bank. 2007. Retrieved 20 May 2012.
- ^ a b c d e f "Survey of child labour in slums of Hyderabad: final report" (PDF). Center for Good Governance, Hyderabad. 17 December 2008. Retrieved 16 May 2012.
- ^ a b c "Welcome to HMDA". Hyderabad Metropolitan Development Authority. Retrieved 7 October 2011.
- ^ "About us". Hyderabad City Police. Retrieved 24 January 2009.
- ^ Buddi, Mahesh (27 January 2012). "Why compulsory helmet rule not being implemented in city". The Times of India. Retrieved 18 April 2012.
- ^ "Hyderabad & Cyberabad police commissionerates to be merged". NDTV. 14 March 2012. Retrieved 18 April 2012.
- ^ "Heritage buildings". Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage. 2005. Retrieved 9 October 2011.
- ^ "24 assembly constituencies under GHMC". GHMC. 2011. Retrieved 9 October 2011.
- "6 city, 2 RR dist MLAs may hitch on to Jagan". The Times of India. 14 January 2011. Retrieved 9 October 2011.
- ^ Muhammad, Mahmood Bin (1999). A policeman ponders: memories and melodies of a varied life. A.P.H.Publishing. p. 19. ISBN 978-81-7648-026-0.
- "Modern period". Government of Andhra Pradesh. 2002. Retrieved 10 October 2011.
- ^ a b c "If Singur, Manjira dry up, there's Krishna". The Times of India. 11 February 2005. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- ^ "Fire stations inadequate". CNN-IBN. 26 March 2012. Retrieved 18 April 2012.
- ^ "About eSeva". Government of Andhra Pradesh. 2011. Retrieved 4 May 2012.
- ^ "Twin festivals pile more garbage load on GHMC". The Hindu. 3 September 2011. Retrieved 18 April 2012.
- ^ "Waste management project gets nod". The Times of India. 18 January 2010. Retrieved 17 April 2012.
- ^ Guttikunda, Sarath (March 2008). "Co-benefits analysis of air pollution and GHG emissions for Hyderabad,India" (PDF). Integrated Environmental Strategies Program. Retrieved 18 April 2012.
- ^ Gurjar, Bhola R.; Molina, Luisa T.; Ojha, Chandra S.P., eds. (2010). Air pollution:health and environmental impacts. Taylor and Francis. p. 90. ISBN 978-1-4398-0963-1.
- ^ a b "50 research scholars to study pollution". CNN-IBN. 3 January 2012. Retrieved 18 April 2012.
- "Be a pal and stop polluting". The Deccan Chronicle. 26 October 2011. Retrieved 18 April 2012.
- Anjaneyulu, Y.; Jayakumar, I.; Hima Bindu, V.; Sagareswar, G.; Mukunda Rao, P.V.; Rambabu, N.; Ramani, K.V. (2005). "Use of multi-objective air pollution monitoring sites and online air pollution monitoring system for total health risk assessment in Hyderabad, India". International journal of environmental research and public health. 2 (2): 343–354. Retrieved 18 April 2012.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)
- ^ "Ground water in city unfit for use". The Deccan Chronicle. 30 August 2011. Retrieved 18 April 2012.
- ^ "City stares at water scarcity". The Times of India. 13 January 2012. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- ^ Chunduri, Mridula (29 November 2003). "Manjira faces pollution threat". The Times of India. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- ^ Kennedy, Loraine; Duggal, Ravi; Lama-Rewal, Stephanie Tawa (2009). "7: Assessing urban governance through the prism of healthcare services in Delhi, Hyderabad and Mumbai". In Ruet, Joel; Lama-Rewal, Stephanie Tawa (eds.). Governing India's metropolises: case studies of four cities. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-55148-9.
- ^ a b c Bhargava, Gopal K.; Bhatt, S.C. (2006). Land and people of Indian states and union territories.(2 Andhra Pradesh). Kalpaz Publication. p. 312. ISBN 81-7835-358-X.
- ^ "Government hospitals". GHMC. 2011. Retrieved 9 May 2012.
- ^ a b "Hyderabad hospital report". Northbridge Capital. 2010. p. 8. Retrieved 10 May 2012.
- ^ As of 2011 census city population is (6809970) and available hospital beds are (12000) which gives the derived rate
- ^ a b Gopal, M.Sai (18 January 2012). "Healthcare sector takes a leap in city". The Hindu. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Gupta, Kamla; Arnold, Fred; Lhungdim, H. (2009). "Health and living conditions in eight Indian cities" (PDF). National Family Health Survey (NFHS-3), India, 2005–06. International Institute for Population Sciences. Retrieved 13 June 2012. Cite error: The named reference "NFHS-3" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ "Bed strength of hospitals under DME". Government of Andhra Pradesh. 2002. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ "Ayush department". Government of Andhra Pradesh. Retrieved 9 May 2012.
- ^ Mahesh, Koride (20 December 2009). "Expansion of city on cards". The Times of India. Retrieved 18 April 2012.
- ^ a b "Urban agglomerations/cities having population 1 lakh and above" (PDF). Government of India. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- "Hyderabad district records highest literacy rate". The Siasat Daily. 1 April 2011. Retrieved 6 April 2011.
- ^ "GHMC allowed to have development control". The Hindu. 26 June 2007. Retrieved 25 April 2012.
- ^ a b "Hyderabad (greater Hyderabad) city". Census of India, 2011. 2012. Retrieved 16 April 2012.
- ^ "Urban sex ratio below national mark". The Times of India. 21 September 2011. Retrieved 16 April 2012.
- ^ "Sex ratio goes up in state". The Times of India. 1 April 2011. Retrieved 16 April 2011.
- ^ Henry, Nikhila (23 May 2011). "AP slips further in national literacy ratings". The Times of India. Retrieved 18 February 2012.
- ^ a b Krank, Sabrina (2007). "Cultural, spatial and socio-economic fragmentation in the Indian megacity Hyderabad" (PDF). Irmgard Coninx Foundation. Retrieved 17 April 2012.
- Freitag, Ulrike; Clarence-Smith, W.G (1997). Hadhrami traders, scholars, and statesmen in the Indian ocean, 1750s–1960s. Brill Publishers. pp. 77–81. ISBN 90-04-10771-1.
- Ifthekhar, J.S. (10 June 2012). "Hyderabad appeal endures". The Hindu. Retrieved 10 June 2012.
- ^ "Name doesnt sound as well in other languages!". CNN-IBN. 17 November 2011. Retrieved 6 June 2012.
- ^ "MCH plans citizens' charter in Telugu, Urdu". The Times of India. 1 May 2002. Retrieved 25 October 2011.
- ^ Rao, P.V.L.N. (23 September 2003). "Espousing Telangana's cause". The Hindu. Retrieved 9 October 2011.
- ^ "National level Urdu meet to celebrate I-day". The Times of India. 15 August 2001. Retrieved 19 August 2011.
- ^ Khan, Masood Ali (16–31 August 2004). "Muslim population in AP". The Milli Gazette. Retrieved 23 May 2012.
- Chillibreeze ePublishing Team (2007). Hyderabad: an expat survival guide. Chillibreeze. p. 21. ISBN 978-81-904055-5-3.
- Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1080/19472498.2011.577568, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1080/19472498.2011.577568instead.
- ^ "Census GIS household". Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India. Retrieved 17 April 2012.
- ^ "World bank team visits Hyderabad slums". The Times of India. 12 June 2012. Retrieved 12 June 2012.
- ^ a b c "Basic services to the urban poor" (PDF). City development plan. GHMC. Retrieved 17 April 2012.
- ^ "India's 25 most competitive cities". Rediff.com. 10 December 2010. Retrieved 10 December 2010.
- Jafri, Syed Amin (20 February 2012). "Civic infra bodies get a raw deal in budget". The Times of India. Retrieved 18 April 2012.
- ^ a b c Sivaramakrishnan, K.C. (12 July 2011). "Heat on Hyderabad". The Times of India. Retrieved 19 April 2012.
- ^ "Employee census 2006". Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Andhra Pradesh Government. 2006. Retrieved 17 May 2010.
- "Census of central government employees" (PDF). Ministry of Labour, Government of India. 2003. Retrieved 17 May 2010.
- ^ "Ease of doing business in Hyderabad – India (2009)". World Bank Group. Retrieved 8 February 2011.
- ^ "The world according to GaWC 2010". Loughborough University. 2011. Retrieved 26 December 2011.
- ^ de Bruyn, Pippa; Bain, Keith; Allardice, David; Joshi, Shonar (2010). Frommer's India. Wiley Publishing. p. 403. ISBN 978-0-470-55610-8.
- "Hyderabad in NYT 2011 list of must see places". The Times of India. 26 January 2011. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- ^ a b Kumar, Abhijit Dev (22 February 2008). "Laad bazaar traders cry foul". The Hindu. Retrieved 22 February 2008.
- Abram, David; Edwards, Nick; Ford, Mike (1982). The rough guide to south India. The Penguin Group. p. 553. ISBN 1-84353-103-8.
- ^ Venkateshwarlu, K. (10 March 2004). "Glory of the gates". The Hindu. Retrieved 11 October 2011.
- ^ Scott, Peter (2009). Geography and retailing. Rutgers University Press. pp. 137–138. ISBN 978-0-202-30946-0.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ "Hyderabad, Chennai & Bangalore witness high rental growth: retail survey". the Hindu Business Line. 16 November 2001. Retrieved 16 November 2007.
- ^ Bharadwaj-Chand, Swati (6 May 2012). "Despite Telangana heat, city's information technology cup brimming over: report". The Times of India. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- Mathew, Dennis Marcus (23 July 2005). "Will the real central hub stand up?". The Hindu. Retrieved 11 October 2011.
- ^ "Other Albion CX19". Albion CX19 restoration project. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- ^ a b Economy, population and urban sprawl (PDF). Urban population, development and environment dynamics in developing countries. 13 June 2007. pp. 7–19. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- ^ Bharadwaj Chand, Swati (14 November 2011). "Brand Hyderabad loss of gloss?". The Times of India. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- ^ "Country briefing:India–economy". Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 1 September 2010. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- ^ "Employment-unemployment situation in million plus cities of India" (PDF). Delhi Government. 2005: 15. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Hyderabad: India's genome valley". Rediff.com. 30 November 2004. Retrieved 13 June 2011.
- "Hyderabad is a hot destination for Walsh". The Daily Telegraph. 25 January 2009. Retrieved 18 October 2011.
- "Job market booming overseas for many American companies". Huffington Post. 28 December 2010. Retrieved 6 October 2011.
- ^ a b Roy, Ananya; Aihwa, Ong (2011). Worlding cities: Asian experiments and the art of being global. John Wiley & Sons. p. 253. ISBN 978-1-4051-9277-4.
- ^ "An Amazon shot for city". The Times of India. 13 October 2011. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- Chary, Manish Telikicherla (2009). India:nation on the move. iUniverse.com. pp. 247–248. ISBN 978-1-4401-1636-0-.
- ^ "Brand Hyderabad, takes a hit in Indian unrest". The Daily Telegraph. 5 January 2010. Retrieved 18 October 2011.
- ^ "Tour Google India". CNN. 23 October 2007. Retrieved 5 October 2011.
- "The top five cities". Business Today (business magazine). 27 August 2011. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- "Our office locations". Microsoft. 2011. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- ^ a b Wipper, Marlis; Dittrich, christoph (2007). "Urban street food vendors in the food provisioning system of Hyderabad" (PDF). Analysis and action for sustainable development of Hyderabad. Humboldt University of Berlin. pp. 9–25. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- ^ Bhowmik, Sharit K.; Saha, Debdulal (2012). "Street vending in ten cities in India" (PDF). Tata Institute of Social Sciences. pp. 10–25. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- ^ a b c "Executive summary of detailed project report" (PDF). Government of Andhra Pradesh. Retrieved 18 May 2012.
- ^ "AC buses are RTC's, white elephants". Asian Age. 20 May 2012. Retrieved 20 May 2012.
- ^ "Speed limits fixed for vehicles on city roads". The Hindu. 10 January 2010. Retrieved 25 May 2012.
- ^ "NH wise details of NH in respect of stretches entrusted to NHA" (PDF). National Highways Authority of India. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- "NH wise details of NH in respect of stretches entrusted to NHA". National Highways Authority of India. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- ^ "Pipeline repair leads to traffic jam". The Hindu. 5 March 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
- "Hi-Tec flyover ready for inauguration tomorrow". The Times of India. 1 October 2010. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
- ^ Maitreyi, M.L.Melly (23 January 2008). "Expressway behind schedule". The Hindu. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- ^ "APSRTC". 31 July 2011. Retrieved 4 September 2011.
- ^ A major frota de onibus. Guinness World Records. 2005. p. 143. ISBN 85-00-01522-5.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ "Chaos reigns supreme at MGBS". The Hindu. 22 October 2011. Retrieved 23 October 2011.
- ^ "SETWIN buses back on roads". The Hindu. 4 September 2006. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
- ^ "Move to replace auto-rickshaws with taxis in Hyderabad in four years". The Hindu. 12 October 2007. Retrieved 5 September 2011.
- ^ "History". Indian Railways. Retrieved 23 May 2012.
- ^ "Will railway budget give impetus to MMTS-II". The Hindu. 23 February 2010. Retrieved 23 February 2010.
- ^ "L&T set to bag Rs 12,132-cr Hyderabad metro rail project". Business Line. 14 July 2011. Retrieved 14 July 2010.
- ^ Kurmanath, K.V. (3 March 2010). "A hub beginning to take roots". Business Line. Retrieved 9 May 2012.
- ^ "Delhi, Hyderabad airports among top in the world". The Times of India. 16 February 2011. Retrieved 16 February 2011.
- "Hyderabad airport adjudged amongst top five in world". The Hindu. 17 February 2010. Retrieved 17 February 2010.
- ^ Hyderabad: an expat survival guide. Chillibreeze. 2007. p. 9. ISBN 978-81-904055-5-3.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)- Mohammed, Syed (24 July 2011). "Hyderabad through the eyes of a voyager". The Times of India. Retrieved 27 December 2011.
- ^ "Languages". Government of Andhra Pradesh. 2011. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ Rajamani, Radhika (21 March 2002). "Clothes make-over for men". The Hindu. Retrieved 22 April 2012.
- ^ "Changing trends in city's culture". The Times of India. 8 July 2012. Retrieved 8 July 2012.
- ^ a b c Leonard, Karen Isaksen (2007). Locating home: India's Hyderabadis abroad. Stanford University Press. pp. 14 and 248–255. ISBN 978-0-8047-5442-2.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ Baseerat, Bushra (28 December 2010). "Burqa sale on the rise in old city". The Times of India. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ "Efforts should be made to preserve traditional wear". The Hindu. 23 March 2009. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ "Anjuman Muhibban-e-Urdu to hold international mushaira". The Siasat Daily. 13 April 2012. Retrieved 13 April 2012.
- ^ Hussain Khan, Masud (1996). Mohammad Quli Qutb Shah. Sahitya Akademi. pp. 50–77. ISBN 81-260-0233-6.
- ^ Datta, Amaresh (2005). Encyclopaedia of Indian literature: Devraj to Jyoti, Volume 2. Sahitya Akademi. pp. 1260, 1746–1748. ISBN 81-260-1194-7.
- ^ a b Tharu, Susie J.; Lalita, K. (1991). Women writing in India volume 1, 600 BC to the early twentieth century. The Feminist Press. pp. 120–122. ISBN 1-55861-027-8. Retrieved 23 June 2012.
- ^ "Celebrating creativity". Hyderabad Literary Festival 2012. 2012. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ Singh, T. Lalith (6 August 2005). "State central library to sport a grand look again". The Hindu. Retrieved 13 April 2012.
- ^ "The original Urdu research center (URC)". Digital South Asia Library. 29 September 2009. Retrieved 29 April 2012.
- "The Urdu research centre, Hyderabad:a souvenir" (PDF). Sundarayya Vignana Kendram. 10 June 2004. Retrieved 29 April 2012.
- ^ Kumar, Abhijit Dev (23 October 2008). "It's "teen maar" for marriages, festivals". The Hindu. Retrieved 17 June 2012.
- ^ "Doorway to culture in the name of Taramati". The Times of India. 28 December 2003. Retrieved 23 June 2012.
- Vora, Shivani (13 May 2012). "36 hours in Hyderabad, India". The New York Times. Retrieved 23 June 2012.
- ^ Kumar, S. Sandeep (19 January 2009). "Theatre is catching up in Hyderabad". The Hindu. Retrieved 23 June 2012.
- ^ Srihari, Gudipoodi (15 April 2011). "Verse drama feast". The Hindu. Retrieved 23 June 2012.
- ^ "Rs 300 cr convention centre ready for inauguration in Hyderabad". Rediff.com. 28 December 2005. Retrieved 13 April 2012.
- ^ "Exhibition named 'Numaish' at last". The Siasat Daily. 20 December 2009. Retrieved 17 June 2012.
- ^ "Tollywood loses top slot". The Times of India. 22 August 2011. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ Krishnamoorthy, Suresh (23 March 2011). "Telugu film industry MoU with Motion pictures association of America". The Hindu. Retrieved 25 March 2012.
- ^ Kavirayani, Suresh (1 May 2011). "New breed of Hyderabadi stars". The Times of India. Retrieved 13 April 2012.
- ^ "17th international children's film fest starts in Hyderabad". CNN IBN. 26 December 2011. Retrieved 13 April 2012.
- K., Sangeetha Devi (15 March 2007). "Fuelled by passion". The Hindu. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ Largest film studio. Guinness World Records. 2012. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ a b "Miniature painting". Centre for Cultural Resources and Training. Retrieved 9 June 2012.
- ^ Zebrowski, Mark (1983). Deccani painting. University of California Press. pp. 40–285. ISBN 0-85667-153-3.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)- James, Ralph; Lefèvre, L (2010). National exhibition of works of art, at Leeds, 1868: official catalogue. The Executive Committee. pp. 301–313. ISBN 978-1-165-04393-4.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- James, Ralph; Lefèvre, L (2010). National exhibition of works of art, at Leeds, 1868: official catalogue. The Executive Committee. pp. 301–313. ISBN 978-1-165-04393-4.
- ^ a b c Bloom, Jonathan; Blair, Sheila (2009). The grove encyclopedia of Islamic art and architecture, volume 2. Oxford University Press. pp. 179 and 286. ISBN 978-0-19-530991-1.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ "Proving their mettle in metal craft". The Times of India. 2 January 2012. Retrieved 13 April 2012.
- ^ Mohammed, Syed (20 January 2012). "Kalamkari losing Islamic thread". The Times of India. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- Imperial Gazetteer of India, Provincial Series (1991). Hyderabad state. Atlantic Publishers. p. 42. Retrieved 8 June 2012.
- ^ "Partnership with the Salar Jung museum, Hyderabad". World collections programme. British Museum. Retrieved 13 April 2012.
- "Muffakham Jah opens City museum". The Hindu. 12 March 2012. Retrieved 13 April 2012.
- Menon, Aparna (16 May 2011). "Here's a treasure trove". The Hindu. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ Burton-Page, John; Michell (208). Indian Islamic architecture:forms and typologies, sites and monuments. Brill Publishers. pp. 146–148. ISBN 978-90-04-16339-3.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ Michell, George (1987). The new Cambridge history of India, volumes 1–7. Cambridge University Press. pp. 218–219. ISBN 0-521-56321-6.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)- "Jubilee hall a masterpiece of Asaf Jahi architecture". The Siasat Daily. 31 December 2011. Retrieved 12 April 2012.
- ^ "UNESCO Asia-Pacific heritage awards for culture heritage conservation". UNESCO. 2010. Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- ^ "Heritage award for Hyderabad raises many eyebrows". The Times of India. 2 March 2012. Retrieved 20 March 2012.
- ^ a b Sen, Colleen Taylor (2004). Food culture in India. Greenwood Puplication. p. 90. ISBN 0-313-32487-5.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ Hahne, Elsa (2008). You are where you eat: stories and recipes from the neighborhoods of new orleans. University Press of Mississippi. pp. 47–49. ISBN 978-1-57806-941-5.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ a b Kapoor, Sanjeev (2008). Royal Hyderabadi cooking. Popular Prakashan. p. 3. ISBN 978-81-7991-373-4.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ "Hyderabadi haleem now close to being patented". NDTV. 2 September 2010. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- Roy, Amrita (10 September 2010). "The original 'slow food' staple: a GI tag for the iconic Hyderabadi dish is reason to raise a toast". Mint (newspaper). Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- "Andhra Pradesh / Hyderabad news: legendary biryani now turns 'single'". The Hindu. 18 August 2005. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ a b "A plateful of culture". The Hindu. 25 November 2010. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- "Times food guide 2012 reaches Hyderabad". The Times of India. 24 February 2012. Retrieved 25 April 2012.
- ^ Dundoo, Sangeetha Devi (29 March 2012). "It's kiwi fruit, pitted olives for the global Hyderabadi". The Hindu. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ Morrison, Ann M. (21 January 2007). "Hyderabad, India". The New York Times. Retrieved 12 April 2012.
- Sengupta, Sudipta (9 February 2011). "Aap katar mein hai". The Times of India. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ Masood Ali, Khan (1995). The history of Urdu press: a case study of Hyderabad. Classical Publishing. p. 27. ISBN 81-7054-221-7.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ "Step-press". Rediff.com. 15 November 1997. Retrieved 15 November 1997.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Magazine publishers of India". Publishers Global. p. 1. Retrieved 13 May 2012.
- ^ "The long and interesting story of all India Radio, Hyderabad – part 1". ontheshortwaves.com. 15 August 2010. Retrieved 20 January 2012.
- ^ a b "South Asia: India". Central Intelligence Agency. 12 April 2012. Retrieved 22 May 2012.
- ^ "Radio stations in Andhra Pradesh, India". asiawaves.net. Retrieved 18 September 2011.
- ^ "Kendra's origin". Doordarshan Kendra Hyderabad. 2008. Retrieved 7 October 2011.
- ^ Manchanda, Usha (1998). "Invasion from the skies: the impact of foreign television in India" (PDF). Australian studies in journalism. 7: 146. Retrieved 22 April 2012.
- ^ "Consolidated list of channels allowed to be carried by cable operators/ multi system operators/ DTH licensees in India" (PDF). Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (India). Retrieved 13 May 2012.
- ^ Fortner, Robert.S; Fackler, P. Mark (2011). The handbook of global communication and media ethics. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-4051-8812-8.
- ^ "Information and communication technologies throughout the world" (PDF). UNESCO. 1998. p. 210. Retrieved 26 May 2012.
- ^ "SSC results: girls score higher percentage". The Hindu. 22 May 2011. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- ^ Bajaj, Vikas; Yardley, Jim (30 December 2011). "Many of India's poor turn to private schools". The New York Times. Retrieved 10 June 2012.
- ^ "Centre extends 40-cr aid to Urdu schools". The Times of India. 27 February 2002. Retrieved 9 July 2011.
- ^ "Vice chancellor's speech about Osmania university". Osmania University. Retrieved 15 November 2007.
- ^ "Annual report 2005–2006" (PDF). University Grants Commission (India). pp. 195–217. Retrieved 20 January 2012.
- ^ "Central universities". Ministry of Human Resource Development, Government of India. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
- ^ Reddy, T. Karnakar (30 March 2012). "OU to hike fee for foreign students". CNN-IBN. Retrieved 2 May 2012.
- ^ Reddy, R. Ravikanth (22 August 2005). "Distance no bar". The Hindu. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- ^ "ISB ranked at 12 among global B schools". The Hindu. 26 January 2010. Retrieved 17 May 2010.
- ^ "India's top B-Schools: Looking beyond IIMs". Rediff.com. Retrieved 27 January 2011.
- ^ "List of colleges teaching MBBS". Medical Council of India. 2010. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- ^ "Unani". Health, Medical and Family Welfare Department, Government of Andhra Pradesh. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- ^ "Another research body to come up in Hyderabad". The Hindu. 25 January 2009. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- Iype, George (30 November 2004). "Hyderabad: India's Genome Valley". Rediff.com. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- ^ "A fillip to pharma sector". The Hindu. 21 September 2009. Retrieved 3 January 2011.
- ^ Kapadia, Novy (2001). "Triumphs and disaster: the story of Indian football, 1889–2000" (PDF). Soccer and Society. 2 (2): 19. Retrieved 3 April 2012.
- ^ "Stadiums in India". World Stadium. Retrieved 22 August 2011.
- ^ "Synthetic track at GMC Balayogi stadium will be protected:SAAP". The Hindu. 15 December 2005. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- "Balayogi athletic stadium". World Stadiums. Retrieved 7 October 2011.
- ^ "Last in 2008, toppers this year: Deccan script IPL fairytale". The Indian Express. 24 May 2009. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- ^ "Race course slows traffic in Malakpet". The Times of India. 5 March 2004. Retrieved 5 March 2004.
- ^ "Starsky claims The Hindu Deccan Derby". The Hindu. 3 October 2001. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- ^ "Excitement unlimited at drag race". The Hindu. 14 December 2009. Retrieved 14 December 2009.
- ^ "Hyderabad". WORLD GOLF. Retrieved 6 September 2011.
- ^ Sen Gupta, Abhijit (7 November 2002). "Remembering unsung heroes". The Hindu. Retrieved 25 October 2011.
- ^ Thottam, Jyoti (15 April 2010). "India's celebrity wedding nearly derailed by scandal". Time (magazine). Retrieved 14 September 2011.
- ^ a b "Hyderabad". Brisbane City Council. 2 November 2011. Retrieved 7 June 2012.
- ^ "Dubai's sister cities". dubaicityguide.com. Retrieved 22 August 2011.
- ^ "GHMC praised for its efforts in keeping the city green". The Times of India. 10 August 2010. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- ^ "Riverside's sister cities". City of Riverside. 2009. Retrieved 5 August 2009.
- ^ "GHMC inks sister city pact with Indianapolis". The Hindu. 29 April 2010. Retrieved 7 June 2012.
- ^ Mahesh, Koride (17 October 2011). "GHMC sister city pacts a farce!". The Times of India. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
Further reading
History
- Austin, Ian (1992). City of legends:the story of Hyderabad. Penguin Books. ISBN 0-670-84724-0.
- Law, John (2011). Modern Hyderabad (Deccan 1914). Newman Press. ISBN 978-1-4067-3816-2.
- Krishnan, Usha R (2002). Jewels of the Nizam. India Book House. ISBN 978-81-7508-306-6.
- Khalidi, Omar (1999). Romance of the Golconda diamonds. Mapin Publishing. ISBN 978-1-890206-10-9.
- Scott, Allan N.; Weld, Charles Richard (1862). Sketches in India: [photographic pictures] taken at Hyderabad and Secunderabad, in the Madras presidency. The University of Michigan. ISBN 978-1-144-61614-2.
Administration
- Kate, P.V. (1987). Marathwada Under the Nizams, 1724–1948. Mittal Publications. ISBN 81-7099-017-3.
- Lynton, Harriet Ronken; Rajan, Mohini (1974). The Days of the beloved. University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-02442-7.
- Pernau, Margrit (2000). The passing of patrimonialism: politics and political culture in Hyderabad,(1911–1948). Manohar Publication. ISBN 81-7304-362-0.
- Jayaram, R (1988). Administrative system under the Nizams. Ultra Publications. ISBN 81-900998-4-1.
Culture
- Leonard, Karen Isaksen (2007). Locating home: India's Hyderabadis abroad. Stanford University Press. ISBN 0-8047-5442-X.
- Yimene, Ababu Minda (2004). An African Indian community in Hyderabad: Siddi identity, its maintenance and change. Cuvillier Verlag. ISBN 3-86537-206-6.
- Ahmad, Akbar S. (1985). "Muslim society in South India: the case of Hyderabad". Journal of Muslim Minority Affairs. 6 (2). Routledge: 317–331. doi:10.1080/13602008508715945.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Zebrowski, Mark (1983). Deccani painting. University of California Press. ISBN 0-85667-153-3.
- Naidu, Ratna (1990). Old Cities, New Predicament : A Study Of Hyderabad. SAGE Publications. ISBN 81-7036-202-4.
Architecture
- Bilgrami, Syed Ali Asgar (1927). Landmarks of the Deccan. Asian Educational Services. ISBN 81-206-0543-8.
Modern Hyderabad
- Khalidi, Omar (1988). Hyderabad after the fall. South Asia Books. ISBN 978-0-930811-02-0.
- Kobayashi-Hillary, Mark (2005). Outsourcing to India: the offshore advantage. Commonwealth Business council. ISBN 978-3-540-23943-7.
External links
- Use dmy dates from May 2012
- Hyderabad, India
- Cities and towns in Hyderabad district, India
- Indian capital cities
- Metropolitan cities in India
- Populated places established in 1591
- High-technology business districts
- South Central Railway Zone
- Divisions of Indian Railways
- Historic districts
- Former national capitals
- Capitals of former nations
- Afro-Asian Games
- South Asia
- Multiculturalism
- Sociology of culture
- Railway junction stations in India
